VMware vCenter Orchestrator - 4.0.4, vCenter Orchestrator - 4.0.2, vCenter Orchestrator - 4.0.1, vCenter Orchestrator - 4.0.3, vCenter Orchestrator - 4.0 User Manual
Page 1

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and
Configuration Guide
vCenter Orchestrator 4.0.1
This document supports the version of each product listed and
supports all subsequent versions until the document is replaced
by a new edition. To check for more recent editions of this
document, see http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
EN-000227-03
Page 2

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware Web site at:
http://www.vmware.com/support/
The VMware Web site also provides the latest product updates.
If you have comments about this documentation, submit your feedback to:
docfeedback@vmware.com
Copyright © 2008–2010 VMware, Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and
intellectual property laws. VMware products are covered by one or more patents listed at
http://www.vmware.com/go/patents.
VMware is a registered trademark or trademark of VMware, Inc. in the United States and/or other jurisdictions. All other marks
and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies.
VMware, Inc.
3401 Hillview Ave.
Palo Alto, CA 94304
www.vmware.com
2 VMware, Inc.
Page 3

Contents
Updated Information 5
About This Book 7
Introduction to VMware vCenter Orchestrator 9
1
Key Features of the Orchestrator Platform 9
Orchestrator User Roles and Related Tasks 10
Orchestrator Architecture 11
Orchestrator System Requirements 13
2
Hardware Requirements for Orchestrator 13
Operating Systems Supported by Orchestrator 13
Supported Directory Services 14
Browsers Supported by Orchestrator 14
Orchestrator Database Requirements 14
Level of Internationalization (i18n) Support 14
Orchestrator Components Setup Guidelines 17
3
vCenter Server Setup 17
Directory Services Setup 17
Orchestrator Database Setup 18
Enable Support for MySQL Databases on Windows 18
MySQL Database Parameters 19
Orchestrator Configuration Maximums 19
VMware, Inc.
Installing Orchestrator 21
4
Install vCenter Server and Orchestrator 21
Install Orchestrator Standalone 23
Upgrade Orchestrator with vCenter Server 25
5
Upgrade Orchestrator Standalone 27
6
Upgrading Orchestrator Applications After Upgrading vCenter Server 29
7
Uninstall Orchestrator 31
8
Configuring Orchestrator 33
9
Start the Orchestrator Configuration Service 34
Log In to the Orchestrator Configuration Interface 34
3
Page 4

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
Change the Default Password 35
Revert to the Default Password for Orchestrator Configuration 35
Configure the Network Connection 36
Orchestrator Network Ports 36
Change the Default Configuration Ports on the Orchestrator Client Side 38
Import the vCenter SSL Certificate 39
Configuring LDAP Settings 39
Generate the LDAP Connection URL 40
Import the LDAP Server SSL Certificate 41
Specify the Browsing Credentials 42
Define the LDAP Lookup Paths 43
Define the LDAP Search Options 44
Common Active Directory LDAP Errors 44
Password Encryption and Hashing Mechanism 45
Configure the Database Connection 45
Database Connection Parameters 46
Identify the SQL Server Authentication Type 47
Server Certificate 47
Import a Server Certificate 47
Create a Self-Signed Server Certificate 48
Obtain a Server Certificate Signed by a Certificate Authority 48
Export a Server Certificate 49
Change a Self-Signed Server Certificate 49
Configure the Default Plug-Ins 50
Define the Default SMTP Connection 51
Configure the SSH Plug-In 51
Configure the vCenter 4.0 Plug-In 52
Remove a Plug-In 53
Access Rights to Orchestrator Server 54
Import the vCenter Server License 54
Start the Orchestrator Server 55
Activate the Service Watchdog Utility 55
Unwanted Server Restarts 56
Export the Orchestrator Configuration 56
Orchestrator Configuration Files 57
Import the Orchestrator Configuration 58
Configure the Maximum Number of Events and Runs 58
Install an Application 59
Start a Published Web View 59
Change the Web View SSL Certificate 60
Define the Server Log Level 60
Where to Go From Here 63
10
Index 65
4 VMware, Inc.
Page 5
Updated Information
This vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide is updated with each release of the product or
when necessary.
This table provides the update history of the vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide.
Revision Description
EN-000227-03
EN-000227-02
EN-000227-01
n
Added a user role in “Orchestrator User Roles and Related Tasks,” on page 10.
n
Updated Step 1 in “Log In to the Orchestrator Configuration Interface,” on page 34.
n
Added reference to VMware Technical Publications glossary in “About This Book,” on page 7.
n
Updated “Install vCenter Server and Orchestrator,” on page 21.
n
Added information about supported directory service types in “Directory Services Setup,” on
page 17.
n
Corrected the note in Step 7 in “Generate the LDAP Connection URL,” on page 40.
n
Corrected the instructions in Step 3 and Step 4 in “Define the LDAP Lookup Paths,” on page 43.
n
Added a prerequisite in “Configure the Database Connection,” on page 45.
n
Added a prerequisite in “Start the Orchestrator Server,” on page 55.
n
Added a new topic, Chapter 10, “Where to Go From Here,” on page 63.
n
Added a procedure about restoring the default administrative password in “Revert to the Default
Password for Orchestrator Configuration,” on page 35.
n
Added instructions about changing the communication ports on the Orchestrator client side in “Change
the Default Configuration Ports on the Orchestrator Client Side,” on page 38.
n
Added information about using SSL with LDAP in “Import the LDAP Server SSL Certificate,” on
page 41.
n
Added instructions about deleting a plug-in in “Remove a Plug-In,” on page 53.
n
Added instructions about changing the SSL certificate for Web views in “Change the Web View SSL
Certificate,” on page 60.
VMware, Inc. 5
Page 6

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
Revision Description
EN-000227-00 Updates for the release of Orchestrator 4.0.1:
n
Added information about the supported versions of directory service types in “Supported Directory
Services,” on page 14.
n
Added information about internationalization support in “Level of Internationalization (i18n)
Support,” on page 14.
n
Added instructions about installing Orchestrator with the vCenter Server installer in “Install vCenter
Server and Orchestrator,” on page 21.
n
Added details about the location of the vCenterOrchestrator.exe file in “Install Orchestrator
Standalone,” on page 23.
n
Added information about upgrading Orchestrator in Chapter 6, “Upgrade Orchestrator Standalone,”
on page 27 and Chapter 5, “Upgrade Orchestrator with vCenter Server,” on page 25.
n
Added new topics about configuring the Orchestrator components in Chapter 3, “Orchestrator
Components Setup Guidelines,” on page 17.
n
Added information about the supported configuration maximums for Orchestrator in “Orchestrator
Configuration Maximums,” on page 19.
n
Removed information about enabling support for Oracle on Windows, because Orchestrator now
includes the Oracle database driver.
n
Added port numbers to the list in “Orchestrator Network Ports,” on page 36.
n
Added information and an example about using Global Catalog with Active Directory in “Generate the
LDAP Connection URL,” on page 40.
n
Added information about customizing the LDAP search queries in “Define the LDAP Search
Options,” on page 44.
n
Added a list of the most common LDAP authentication errors in “Common Active Directory LDAP
Errors,” on page 44.
n
Added instructions about using Windows authentication in “Configure the Database Connection,” on
page 45.
n
Added a prerequisite for using an Oracle database in an internationalized environment in “Configure
the Database Connection,” on page 45.
n
Added instructions about identifying the SQL Server authentication type in “Identify the SQL Server
Authentication Type,” on page 47.
n
Added instructions about importing a server certificate in “Import a Server Certificate,” on page 47.
n
Added instructions about enabling the Orchestrator service watchdog in “Activate the Service
Watchdog Utility,” on page 55.
n
Added troubleshooting information in “Unwanted Server Restarts,” on page 56.
n
Added instructions about changing the SSL certificate used for Web views in “Change the Web View
SSL Certificate,” on page 60.
n
Added information about uninstalling Orchestrator in Chapter 8, “Uninstall Orchestrator,” on
page 31.
EN-000192-01
n
Removed OpenLDAP from the list of supported directory services in “Supported Directory
Services,” on page 14.
n
Added information about unsupported database types and full partition warning in “Orchestrator
Database Setup,” on page 18.
n
Added a note about an unsupported directory service type in Step 3 in “Generate the LDAP Connection
URL,” on page 40.
n
Added information about the methods Orchestrator uses to store passwords in “Password Encryption
and Hashing Mechanism,” on page 45.
n
Added instructions about how to remove a self-signed server certificate in “Change a Self-Signed Server
Certificate,” on page 49.
EN-000192-00 Initial release of Orchestrator 4.0.
6 VMware, Inc.
Page 7

About This Book
The VMware vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide provides information and instructions
about installing, upgrading and configuring VMware® vCenter Orchestrator.
Intended Audience
This book is intended for advanced vCenter administrators and experienced system administrators who are
familiar with virtual machine technology and datacenter operations.
VMWare Technical Publications Glossary
VMware Technical Publications provides a glossary of terms that might be unfamiliar to you. For definitions
of terms as they are used in VMware technical documentation, go to
http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
Document Feedback
VMware welcomes your suggestions for improving our documentation. If you have comments, send your
feedback to docfeedback@vmware.com.
Technical Support and Education Resources
The following technical support resources are available to you. To access the current version of this book and
other books, go to http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
Online and Telephone
Support
Support Offerings
VMware Professional
Services
VMware, Inc. 7
To use online support to submit technical support requests, view your product
and contract information, and register your products, go to
http://www.vmware.com/support.
Customers with appropriate support contracts should use telephone support
for the fastest response on priority 1 issues. Go to
http://www.vmware.com/support/phone_support.html.
To find out how VMware support offerings can help meet your business needs,
go to http://www.vmware.com/support/services.
VMware Education Services courses offer extensive hands-on labs, case study
examples, and course materials designed to be used as on-the-job reference
tools. Courses are available onsite, in the classroom, and live online. For onsite
pilot programs and implementation best practices, VMware Consulting
Page 8

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
Services provides offerings to help you assess, plan, build, and manage your
virtual environment. To access information about education classes,
certification programs, and consulting services, go to
http://www.vmware.com/services.
8 VMware, Inc.
Page 9

Introduction to VMware vCenter
Orchestrator 1
VMware vCenter Orchestrator is a development and process-automation platform that provides a library of
extensible workflows to allow you to create and run automated, configurable processes to manage the VMware
vCenter infrastructure as well as other VMware and third-party technologies.
Orchestrator exposes every operation in the vCenter Server API, allowing you to integrate all of these
operations into your automated processes. Orchestrator also allows you to integrate with other management
and administration solutions through its open plug-in architecture.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Key Features of the Orchestrator Platform,” on page 9
n
“Orchestrator User Roles and Related Tasks,” on page 10
n
“Orchestrator Architecture,” on page 11
Key Features of the Orchestrator Platform
Orchestrator is composed of three distinct layers: an orchestration platform that provides the common features
required for an orchestration tool, a plug-in architecture to integrate control of subsystems, and a library of
workflows. Orchestrator is an open platform that can be extended with new plug-ins and libraries, and can be
integrated into larger architectures through a SOAP API.
The following list presents the key Orchestrator features.
Persistence
Central management
Check-pointing
Versioning
VMware, Inc. 9
Production grade external databases are used to store relevant information,
such as processes, workflow states, and configuration information.
Orchestrator provides a central way to manage your processes. The application
server-based platform, with full version history, allows you to have scripts and
process-related primitives in one place. This way, you can avoid scripts without
versioning and proper change control spread on your servers.
Every step of a workflow is saved in the database, which allows you to restart
the server without losing state and context. This feature is especially useful for
long-running processes.
All Orchestrator Platform objects have an associated version history. This
feature allows basic change management when distributing processes to
different project stages or locations.
Page 10

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
Scripting engine
Workflow engine
Policy engine
Web 2.0 front end
The Mozilla Rhino JavaScript engine provides a way to create new building
blocks for Orchestrator Platform. The scripting engine is enhanced with basic
version control, variable type checking, name space management and
exception handling. It can be used in the following building blocks:
n
Actions
n
Workflows
n
Policies
The workflow engine allows you to capture business processes. It uses the
following objects to create a step-by-step process automation in workflows:
n
Workflows and actions that Orchestrator provides.
n
Custom building blocks created by the customer
n
Objects that plug-ins add to Orchestrator
Users, other workflows, a schedule, or a policy can start workflows.
The policy engine allows monitoring and event generation to react to changing
conditions in the Orchestrator server or plugged-in technology. Policies can
aggregate events from the platform or any of the plug-ins, which allows you
to handle changing conditions on any of the integrated technologies.
The Web 2.0 front end allows you to integrate Orchestrator functions into Webbased interfaces, using Web views. For example, you can create Web views that
add buttons to start workflows from a page in your company's Intranet. It
provides a library of user customizable components to access vCO orchestrated
objects and uses Ajax technology to dynamically update content without
reloading complete pages.
Security
Orchestrator provides the following advanced security functions:
n
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to sign and encrypt content imported and
exported between servers
n
Digital Rights Management (DRM) to control how exported content might
be viewed, edited and redistributed
n
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encrypted communications between the
desktop client and the server and HTTPS access to the Web front end.
n
Advanced access rights management to provide control over access to
processes and the objects manipulated by these processes.
Orchestrator User Roles and Related Tasks
vCenter Orchestrator provides different tools and interfaces based on the specific responsibilities of the two
global user roles: Administrators and End Users.
Administrators
This role has full access to all of the Orchestrator platform capabilities. Basic
administrative tasks include the following items:
n
Installing and configuring Orchestrator
n
Managing access rights for Orchestrator and applications
n
Importing and exporting packages
n
Enabling and disabling Web views
10 VMware, Inc.
Page 11
Orchestrator
database
vCenter
Orchestrator
Client application
vCenter
Server
browser access web service
workflow library
vCenter VI3 WMI XML SSH JDBC SMTP
3rd-party
plug-in
directory
services
workflow engine
Chapter 1 Introduction to VMware vCenter Orchestrator
n
Running workflows and scheduling tasks
n
Managing version control of imported elements
n
Creating new workflows and plug-ins
Developers
This role has full access to all of the Orchestrator platform capabilities.
Developers are granted access to the Orchestrator client interface and have the
following responsibilities:
n
n
n
End Users
Users in this role are granted access to only the Web front end. They can run
and schedule workflows and policies that you make available in a browser by
using Web views.
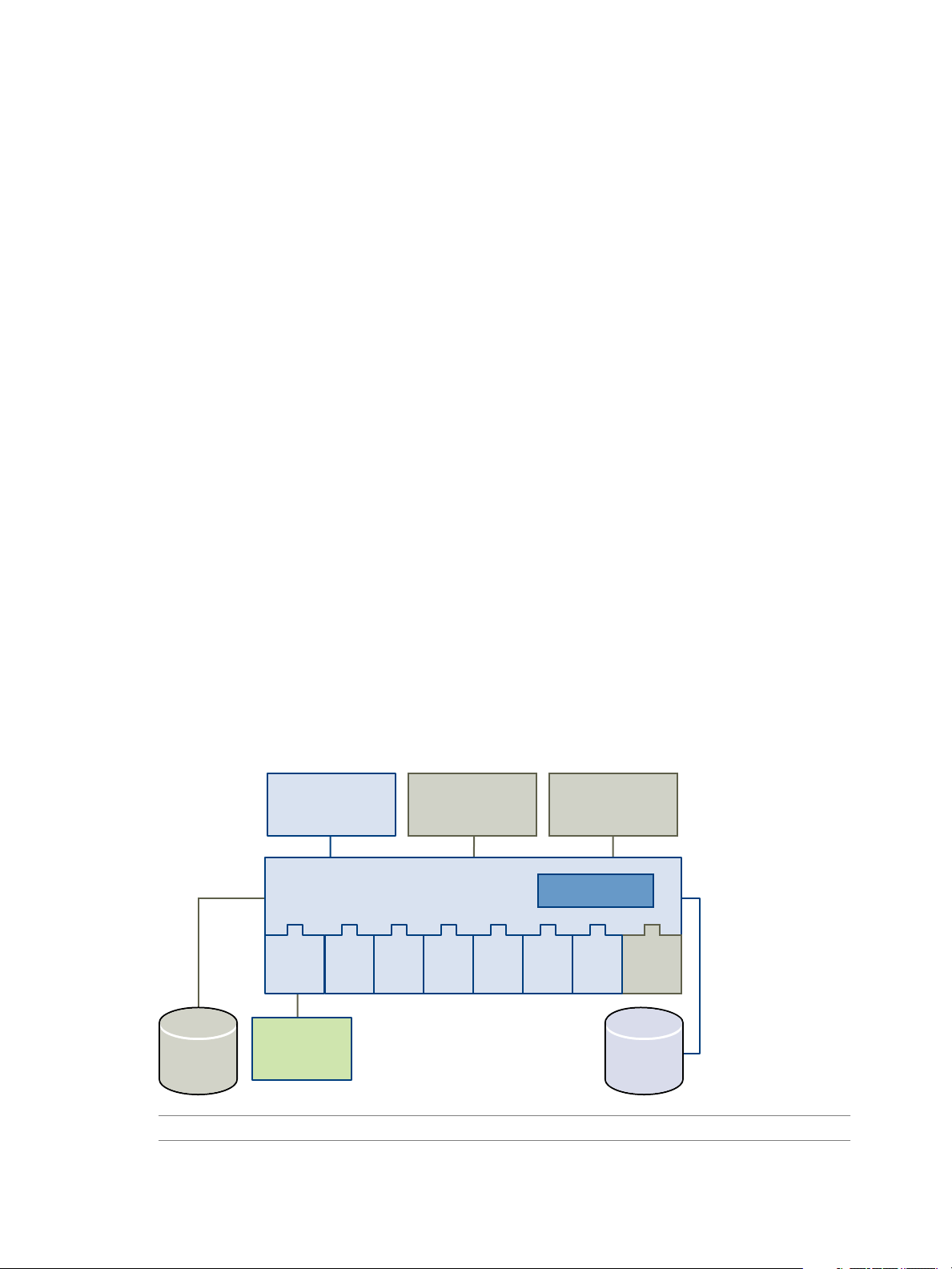
Orchestrator Architecture
Orchestrator contains a workflow library and workflow engine to allow you to create and run workflows that
automate orchestration processes. You run workflows on the objects of different technologies that Orchestrator
accesses through a series of plug-ins.
Orchestrator provides a standard set of plug-ins, including a plug-in to VMware vCenter Server, to allow you
to orchestrate tasks in the different environments that the plug-ins expose.
Orchestrator also presents an open architecture to allow you to plug in external third-party applications to the
orchestration platform. You can run workflows on the objects of the plugged-in technologies that you define
yourself. Orchestrator connects to a directory services server to manage user accounts, and to a database to
store information from the workflows that it runs. You can access Orchestrator and the workflows and objects
it exposes through the Orchestrator client interface, through a Web browser, or through Web services.
Creating applications to extend the Orchestrator platform functionality
Automating processes by customizing existing workflows and creating
new workflows and plug-ins
Customizing Web front ends for these processes, using Web 2.0
Figure 1-1 shows the architecture of Orchestrator.
Figure 1-1. VMware vCenter Orchestrator Architecture
NOTE The VMware Infrastructure 3 and Microsoft plug-ins are not installed by default.
VMware, Inc. 11
Page 12

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
12 VMware, Inc.
Page 13

Orchestrator System Requirements 2
Your system must meet the technical requirements that are necessary to install and configure VMware vCenter
Orchestrator.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Hardware Requirements for Orchestrator,” on page 13
n
“Operating Systems Supported by Orchestrator,” on page 13
n
“Supported Directory Services,” on page 14
n
“Browsers Supported by Orchestrator,” on page 14
n
“Orchestrator Database Requirements,” on page 14
n
“Level of Internationalization (i18n) Support,” on page 14
Hardware Requirements for Orchestrator
Make sure your system meets the minimum hardware requirements before you install Orchestrator.
n
2.0GHz or faster Intel or AMD x86 processor. At least two CPUs are recommended. Processor requirements
might differ if your database runs on the same hardware.
n
4GB RAM. You might need more RAM if your database runs on the same hardware.
n
2GB disk space. You might need more storage if your database runs on the same hardware.
n
A free static IP address.
Operating Systems Supported by Orchestrator
Orchestrator offers support for several operating systems.
n
Windows Server 2008 Datacenter, 64-bit
n
Windows Server 2008 Enterprise R2, 64-bit
n
Windows Server 2008 Enterprise SP1, 64-bit
n
Windows Server 2008 Standard, 64-bit
n
Windows Server 2008 Datacenter, 32-bit
n
Windows Server 2008 Enterprise, 32bit
n
Windows Server 2008 Standard, 32bit
n
Windows Server 2003 R2 SP2, 32-bit
VMware, Inc.
13
Page 14

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
n
Windows Server 2003 R2 SP2, 64-bit
n
Windows Server 2003 R2, 32-bit
Supported Directory Services
Orchestrator requires a working LDAP server on your infrastructure.
Orchestrator supports these directory service types.
n
Windows Server 2003 Active Directory
n
Windows Server 2008 Active Directory
n
Novell eDirectory Server 8.8.3
n
Sun Java Directory Server Enterprise Edition (DSEE) Version 6.3
Browsers Supported by Orchestrator
The Orchestrator user interface requires a Web browser.
You must have one of the following browsers to connect to Orchestrator.
n
Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 and 7.0
n
Mozilla Firefox 3.0.x
Orchestrator Database Requirements
Orchestrator requires you to have a database that is separate from the standard vCenter database.
NOTE Because of CPU and memory use, you should consider hosting the Orchestrator database and the
Orchestrator server on different machines from the same datacenter. Make sure at least 1GB of free disk space
is available on each machine.
The following database types are supported by Orchestrator:
n
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Enterprise Edition x64 (10.0.1600)
n
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Enterprise Edition x32 (9.0.3042)
n
Oracle 10g Enterprise Edition, Release 2 x32 (10.2.0.1.0)
Level of Internationalization (i18n) Support
Orchestrator is compliant with i18n level 1. Although Orchestrator is not localized, it can run on a non-English
operating system and handle non-English text.
Non-ASCII Character Support in Orchestrator
Table 2-1 displays the level of internationalization compliance and limitations in Orchestrator GUI data entries.
Table 2-1. Non-ASCII Character Support
Support for Non-ASCII Characters
Input and
Item
Action Yes No No No
Category Yes Yes - -
14 VMware, Inc.
Description
Field Name Field
Output
Parameters Attributes
Page 15

Chapter 2 Orchestrator System Requirements
Table 2-1. Non-ASCII Character Support (Continued)
Support for Non-ASCII Characters
Input and
Description
Item
Configuration element Yes Yes - No
Package Yes Yes - -
Policy Yes Yes - -
Policy template Yes Yes - -
Resource element Yes Yes - -
Web view Yes Yes - No
Workflow Yes Yes No No
Workflow presentation display group
and input step
Field Name Field
Yes Yes - -
Output
Parameters Attributes
CAUTION You cannot use non-ASCII characters in the filename when you export Orchestrator objects. This is
due to a third party limitation.
Non-ASCII Character Support for Oracle Databases
To store characters in the correct format in an Oracle database, set the NLS_CHARACTER_SET parameter to
AL32UTF8 before configuring the database connection and building the table structure for Orchestrator. This
setting is crucial for an internationalized environment.
VMware, Inc. 15
Page 16

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
16 VMware, Inc.
Page 17

Orchestrator Components Setup
Guidelines 3
To enhance the availability and scalability of your Orchestrator setup, install Orchestrator on a server different
from the server on which vCenter Server runs. Separating Orchestrator from vCenter Server makes it possible
to adjust the operating system to meet the specific recommendations for each service.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“vCenter Server Setup,” on page 17
n
“Directory Services Setup,” on page 17
n
“Orchestrator Database Setup,” on page 18
n
“Orchestrator Configuration Maximums,” on page 19
vCenter Server Setup
Increasing the number of vCenter Server instances causes Orchestrator to manage more sessions. Each active
session implies activity on the corresponding vCenter and too many active sessions can cause Orchestrator to
experience timeouts when more than 10 vCenter connections occur.
NOTE Run only one vCenter Server on a virtual machine. You can run multiple vCenter instances on different
virtual machines in your Orchestrator setup if your network has sufficient bandwidth and latency. If you are
using LAN to improve the communication between Orchestrator and vCenter, a 100Mb line is mandatory.
Directory Services Setup
Orchestrator requires a connection to an LDAP server on your infrastructure.
The supported directory service types are: Active Directory, eDirectory, and Sun Java System Directory Server.
OpenLDAP is not supported and can only be used for testing and evaluation purposes.
Connect your system to the LDAP server that is physically closest to your Orchestrator server and avoid
connections to remote LDAP servers. Long response times for LDAP queries can lead to slower performance
of the whole system.
To improve the performance of the LDAP queries, keep the user and group lookup base as narrow as possible.
Try to limit the users to targeted groups that are going to need access, rather than to whole organizations with
many users who are not going to need access. Depending on the combination of database and directory service
you choose, the resources you need can vary. For recommendations, see third-party documentation.
VMware, Inc.
17
Page 18
vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
Orchestrator Database Setup
Orchestrator requires a database to store workflows and actions.
Orchestrator server supports Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server databases and provides experimental support
for MySQL and PostgreSQL. You can use MySQL and PostgreSQL for testing and evaluation purposes.
NOTE The driver for MySQL is not installed with Orchestrator. For details about enabling support for this
database type, see “Enable Support for MySQL Databases on Windows,” on page 18.
The way in which your database is set up can affect Orchestrator performance. Install the database on a virtual
machine other than the one on which Orchestrator is installed. This method avoids the JVM and DB server
having to share CPU, RAM, and IOs.
Storing your database plug-ins in a database separate from the one that Orchestrator uses allows more
modularity when upgrading the system. A dedicated database instance allows you to perform upgrades and
maintenance without impacting other products.
The location of the database is important because almost every activity on the Orchestrator server triggers
operations on the database. To avoid latency in the database connection, connect to the database server that is
closest to your Orchestrator server and that is on the network with the highest bandwidth.
The size of the Orchestrator database varies depending on the setup and how workflow tokens are handled.
Allow for approximately 50K per vCenter Server object and 4KB per workflow run.
CAUTION Make sure that at least 1GB of free disk space is available
n
on the virtual machine where the database is installed
n
on the virtual machine where the Orchestrator server is installed
Insufficient disk storage space might result in unwanted behavior of the Orchestrator server and client.
Enable Support for MySQL Databases on Windows
To use a MySQL database, you must download the driver and copy it to the appropriate locations. The
Orchestrator installer does not install drivers for MySQL databases.
Procedure
1 Download the latest MySQL driver from http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/j/.
2 Extract the downloaded archive.
3 In the extracted folder, locate the mysql-connector-java-
subminor version.
x.x.x
.jar file, where x.x.x is the current
18 VMware, Inc.
Page 19

Chapter 3 Orchestrator Components Setup Guidelines
4 To make the driver available to VMware vCenter Orchestrator server and VMware vCenter Orchestrator
configuration interface, copy mysql-connector-java-
n
VMware vCenter Orchestrator configuration interface:
x.x.x
.jar to the following locations:
install_directory
n
VMware vCenter Orchestrator server:
install_directory
\VMware\Orchestrator\configuration\jetty\lib\ext\
\VMware\Orchestrator\app-server\server\vmo\lib\
5 Restart the Orchestrator servers.
a Right-click My Computer on your desktop and select Manage.
b In the Computer Management dialog box, expand Services and Applications and select Services.
c In the right pane, right-click and select VMware vCenter Orchestrator Configuration > Restart.
d In the right pane, right-click and select VMware vCenter Orchestrator Server > Restart.
You installed the MySQL database driver.
MySQL Database Parameters
When you use a MySQL database, the database server must be configured with the parameter
max_allowed_packet set to 16M.
Procedure
1 Open the C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server
2 In section [mysql], add the line: max_allowed_packet = 16M.
Orchestrator Configuration Maximums
X.X
\my.ini file for editing.
When you configure Orchestrator, make sure you stay at or below the supported maximums.
Table 3-1 contains information about the tested and recommended configuration maximums for Orchestrator.
Table 3-1. Orchestrator Configuration Maximums
Item Maximum
Connected vCenter Server systems 10
Connected ESX/ESXi servers 100
Connected virtual machines 3000
Concurrent running workflows 150
VMware, Inc. 19
Page 20

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
20 VMware, Inc.
Page 21

Installing Orchestrator 4
Orchestrator consists of a server component and a client component. You can install the Orchestrator
components on the machine where vCenter Server is installed or on a separate machine. To improve
performance, install the Orchestrator server component on a separate machine.
To install Orchestrator, you must be either a local Administrator or a domain user that is a member of the
Administrators group. To run and use Orchestrator, you must use a local system account for the machine on
which Orchestrator is installed.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Install vCenter Server and Orchestrator,” on page 21
n
“Install Orchestrator Standalone,” on page 23
Install vCenter Server and Orchestrator
When you install VMware vCenter Server, Orchestrator is silently installed on your system as an additional
component.
NOTE To install the vCenter Server on a drive other than C:, verify that the C:\WINDOWS\Installer folder is
large enough to install the Microsoft Windows Installer .msi file. If the folder is not large enough, your
vCenter Server installation might fail.
VMware, Inc.
For a list of required ports, see the ESX and vCenter Server Installation Guide.
Prerequisites
See vCenter Server installation prerequisites in the ESX and vCenter Server Installation Guide.
Procedure
1 Download the vCenter Server installation package from the VMware Web site.
Option Description
Use ISO image
Use ZIP archive
The filename is VMware-VIMSetup-xx-4.
major and minor version, xx is the two-character language code, and yyyy is
the build number.
The filename is VMware-VIMSetup-xx-4.
major and minor version, xx is the two-character language code, and yyyy is
the build number.
a.b-yyyy
a.b-yyyy
.iso, where a and b are
.zip, where a and b are
2 Extract the files from the archive and in the C:\
autorun.exe file.
install_directory
\ directory, double-click the
3 When the vCenter Server Installer appears, click vCenter Server.
21
Page 22

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
4 Select a language for the installer and click OK.
5 When the Welcome page appears, click Next.
6 Select I agree to the terms in the license agreement and click Next.
7 Type your user name, organization, and vCenter Server license key, and click Next.
8 Select the type of database to use.
Option Action
To use the bundled database
To use an existing database
A dialog box might appear, warning you that the DSN points to an older version of a repository that must
be upgraded. If you click Yes, the installer upgrades the database schema, making the database irreversibly
incompatible with previous VirtualCenter versions.
Click Install SQL Server 2005 Express instance (for small-scale
deployments).
This database is suitable for deployments of up to 5 hosts and 50 virtual
machines.
Click Use an existing supported database and select your database from the
list. Type the user name and password for the DSN and click Next.
If your database is a local SQL Server database using Windows NT
authentication, leave the user name and password fields blank.
If you specify a remote SQL Server database that uses Windows NT
authentication, the database user and the logged-in user on the
vCenter Server machine must be the same.
9 Enter the administrator name and password that you use when you log in to the system on which you are
installing vCenter Server and click Next.
10 Select Use SYSTEM Account and click Next.
11 Select the account type.
If you want to use Windows authentication for SQL Server, specify an account that is an administrator on
the local machine. As a best practice, type the account name as DomainName\Username. Type the account
password, retype the password, and click Next.
12 Either accept the default destination folders or click Change to select another location, and click Next.
The installation path cannot have commas (,) or periods (.).
13 Select Create a standalone VMware vCenter Server instance or Join Group and click Next.
Join a Linked Mode group to enable the vSphere Client to view, search, and manage data across multiple
vCenter Server systems.
This option does not appear if you are upgrading the VirtualCenter database schema. If it does not appear,
you can join a Linked Mode group after the installation is complete.
14 (Optional) If you join a group, enter the fully qualified domain name and LDAP port number of any remote
vCenter Server system and click Next.
In some cases, you can enter the IP address instead of the fully qualified domain name. To help ensure
connectivity, the best practice is to use the fully qualified domain name. For IPv6, unless both the local
and the remote machine are in IPv6 mode, you must enter the fully qualified domain name of the remote
machine instead of the IPv6 address. If the local machine has an IPv4 address and the remote machine has
an IPv6 address, the local machine must support IPv4 and IPv6 mixed mode. The domain name server
must be able to resolve both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses if your environment has both addressing types in a
single Linked Mode group.
15 Enter the port numbers to use or accept the default port numbers and click Next.
16 Select the vCenter Server configuration that best describes your setup and click Next.
22 VMware, Inc.
Page 23

17 Click Install.
Installation might take several minutes. Multiple progress bars appear during the installation of the
selected components.
18 When the installation finishes, click Finish.
You completed the installation of vCenter Server. The Orchestrator client and server components are installed
on your system.
What to do next
Start the VMware vCenter Orchestrator Configuration service and log in to the Orchestrator configuration
interface. Configure Orchestrator using an IPv4 operating system. Orchestrator does not support IPv6
operating systems.
For the detailed procedures, see
1 “Start the Orchestrator Configuration Service,” on page 34
2 “Log In to the Orchestrator Configuration Interface,” on page 34
3 Chapter 9, “Configuring Orchestrator,” on page 33
Install Orchestrator Standalone
Chapter 4 Installing Orchestrator
If you install VMware vCenter Server, Orchestrator is already installed on your system. To make Orchestrator
available to use, you must only configure it or import a backed up configuration. For production environments
and to enhance the scalability of your Orchestrator setup, install Orchestrator on a dedicated Microsoft
Windows server.
Prerequisites
Verify that your hardware meets the Orchestrator system requirements. See “Hardware Requirements for
Orchestrator,” on page 13.
Procedure
1 Download the vCenter Server installation package from the VMware Web site.
Option Description
Use ISO image
Use ZIP archive
The filename is VMware-VIMSetup-xx-4.
major and minor version, xx is the two-character language code, and yyyy is
the build number.
The filename is VMware-VIMSetup-xx-4.
major and minor version, xx is the two-character language code, and yyyy is
the build number.
a.b-yyyy
a.b-yyyy
.iso, where a and b are
.zip, where a and b are
2 Extract the files from the archive and browse to the
VIMSetup_image
\vpx\vCO\ folder.
3 Double-click the vCenterOrchestrator.exe file and click Next.
4 Select I accept the terms of the License Agreement and click Next.
VMware, Inc. 23
Page 24

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
5 Select the Orchestrator installation directory.
CAUTION You cannot install Orchestrator in a directory whose name contains non-ASCII characters. If
you are operating in a locale that features non-ASCII characters, you must install Orchestrator in the
default location. This is because of a third-party limitation.
Option Action
Accept the default location
Select a different location
6 Select the type of installation and click Next.
Option Description
Client
Server
Client-Server
7 Specify the location for the Orchestrator shortcuts and click Next.
Click Next to accept the default installation directory C:\Program
Files\VMware\Orchestrator.
Browse for a different installation directory and click Next.
Installs the Orchestrator client application, which allows you to create and
edit workflows.
Installs the Orchestrator platform.
Installs the Orchestrator client and server.
CAUTION The name of the shortcuts directory must not contain non-ASCII characters. This is because of
a third-party limitation.
8 Click Install to complete the installation process.
9 Click Done to close the installer.
What to do next
Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface, change the default password, and start configuring
Orchestrator. For the detailed procedures, see
n
“Log In to the Orchestrator Configuration Interface,” on page 34
n
“Change the Default Password,” on page 35
24 VMware, Inc.
Page 25

Upgrade Orchestrator with vCenter
Server 5
If you installed Orchestrator with the vCenter installer, you can upgrade to the latest version of Orchestrator
by upgrading your vCenter Server. The vCenter Server installer detects the previous version and the
installation path.
Prerequisites
n
Back up your vCenter environment.
n
Make sure the vCenter Server upgrade prerequisites and database upgrade prerequisites are met.
See the vSphere Upgrade Guide for details.
Procedure
1 Stop the VMware vCenter Orchestrator Server and the VMware VirtualCenter Server services.
a Right-click My Computer on your desktop and select Manage.
b In the Computer Management dialog box, expand Services and Applications and select Services.
c In the right pane, right-click and select VMware vCenter Orchestrator Server > Stop.
d In the right pane, right-click and select VMware VirtualCenter Server > Stop.
2 Download the vCenter Server installation package from the VMware Web site.
Option Description
Use ISO image
Use ZIP archive
3 Extract the files from the archive and in the C:\
autorun.exe file.
4 When the vCenter Server Installer appears, click vCenter Server.
5 Select a language for the installer and click OK.
6 When the Welcome page appears, click Next.
The Welcome page informs you that an earlier version of vCenter is detected and will be upgraded.
7 Select I agree to the terms in the license agreement and click Next.
8 Type your vCenter Server license key and clickNext.
The filename is VMware-VIMSetup-xx-4.
major and minor version, xx is the two-character language code, and yyyy is
the build number.
The filename is VMware-VIMSetup-xx-4.
major and minor version, xx is the two-character language code, and yyyy is
the build number.
install_directory
\ directory, double-click the
a.b-yyyy
a.b-yyyy
.iso, where a and b are
.zip, where a and b are
VMware, Inc.
25
Page 26

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
9 Enter the database password that corresponds to the username and DSN that the installer displays and
click Next.
You can omit the database username and password if the DSN is using Windows NT authentication.
If you specify a remote SQL Server database that uses Windows NT authentication, the database user and
the logged-in user on the vCenter Server machine must be the same.
10 Select Yes, I want to upgrade my vCenter Server database to upgrade the vCenter Server database schema.
If the database schema is current, this dialog does not appear.
11 Click I have taken a backup of the existing vCenter Server database and SSL certificates and click
Next.
12 Specify the account for the vCenter Service to run in.
n
Click Next to use the SYSTEM account. You cannot use the SYSTEM account if you are using Windows
authentication for SQL Server.
n
Deselect Use SYSTEM Account, accept the default Administrator account name and password, and
click Next.
n
Deselect Use SYSTEM Account and enter a different Administrator account name and password.
13 Enter the port numbers to use or accept the default port numbers and click Next.
14 Click Install.
15 When the installation finishes, click Finish.
You upgraded vCenter Server and the Orchestrator client and server components. The existing Orchestrator
configuration is preserved.
What to do next
Start the vCO configuration service and log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface. On the Database tab,
update the database. Reimport the vCenter SSL certificate and start the Orchestrator Server.
For the detailed procedures, see
n
“Start the Orchestrator Configuration Service,” on page 34
n
“Log In to the Orchestrator Configuration Interface,” on page 34
n
“Import the vCenter SSL Certificate,” on page 39
n
“Start the Orchestrator Server,” on page 55
26 VMware, Inc.
Page 27

Upgrade Orchestrator Standalone 6
To upgrade an installation of Orchestrator on a Microsoft Windows server different from the server on which
vCenter Server runs, run the latest version of the Orchestrator standalone installer.
Prerequisites
n
Create a backup of the Orchestrator database.
n
Export the Orchestrator configuration to a local file.
n
Export your custom workflows and packages.
n
Stop the VMware vCenter Orchestrator Server.
Procedure
1 Download the vCenter Server installation package from the VMware Web site.
Option Description
Use ISO image
Use ZIP archive
2 Extract the files from the archive and browse to the
The filename is VMware-VIMSetup-xx-4.
major and minor version, xx is the two-character language code, and yyyy is
the build number.
The filename is VMware-VIMSetup-xx-4.
major and minor version, xx is the two-character language code, and yyyy is
the build number.
VIMSetup_image
a.b-yyyy
a.b-yyyy
\vpx\vCO\ folder.
.iso, where a and b are
.zip, where a and b are
VMware, Inc.
3 Double-click the vCenterOrchestrator.exe file and click Next.
4 Select I accept the terms of the License Agreement and click Next.
5 When the installer detects an earlier version of Orchestrator, decide to continue or quit the update
procedure.
Option Description
Continue with update
Quit
Click this button if you exported the Orchestrator configuration and backed
up your custom workflows and packages.
Click this button to cancel the upgrade procedure and create backups.
6 When the installer detects the installation directory, click Next.
You cannot change the installation directory when upgrading Orchestrator. To change this parameter,
you must perform a clean installation.
27
Page 28

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
7 Select the type of installation that matches your existing installation type and click Next.
Option Description
Client
Server
Client-Server
For example, if you have installed the Orchestrator client, select Client and upgrade your Orchestrator
server separately.
The versions of the Orchestrator client and server versions must be the same.
8 Specify the location for the Orchestrator shortcuts and click Next.
CAUTION The name of the shortcuts directory must not contain non-ASCII characters. This is because of
a third-party limitation.
9 Click Install to complete the installation process.
10 Click Done to close the installer.
You upgraded to the latest version of Orchestrator. The existing Orchestrator configuration is preserved.
Installs the Orchestrator client application, which allows you to create and
edit workflows.
Installs the Orchestrator platform.
Installs the Orchestrator client and server.
What to do next
Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface and on the Database tab, update the database. Reimport the
vCenter SSL certificate and start the Orchestrator Server.
For the detailed procedures, see
n
“Import the vCenter SSL Certificate,” on page 39
n
“Start the Orchestrator Server,” on page 55
28 VMware, Inc.
Page 29

Upgrading Orchestrator Applications
After Upgrading vCenter Server 7
You must refactor any legacy Orchestrator applications that you wrote for use with VMware Infrastructure
3.5 so that they run with vCenter Server 4.0 and above. Orchestrator provides workflows to help you refactor
the applications to the new version.
For detailed information about refactoring applications, see the VMware vCenter Orchestrator Developer's
Guide.
VMware, Inc. 29
Page 30

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
30 VMware, Inc.
Page 31

Uninstall Orchestrator 8
You can remove the Orchestrator client and server components from your system by using the Windows Add
or Remove Programs Utility from the Control Panel.
Prerequisites
Save the Orchestrator system settings to a local file. For details, see “Export the Orchestrator Configuration,”
on page 56.
Procedure
1 From the Windows Start menu, select Settings > Control Panel > Add or Remove Programs.
2 Select vCenter Orchestrator and click Remove.
3 Click Uninstall in the Uninstall vCenter Orchestrator dialog.
A message confirming that all items were successfully removed appears.
4 Click Done to close the uninstaller.
Orchestrator is uninstalled from your system.
VMware, Inc.
31
Page 32

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
32 VMware, Inc.
Page 33

Configuring Orchestrator 9
VMware vCenter Orchestrator Web Configuration is installed silently with VMware vCenter Server. This is
the tool you use to configure the components that are related to the Orchestrator engine, such as network,
database, server certificate, and so on. The correct configuration of these components ensures the proper
functioning of Lifecycle Manager or any other applications running on the Orchestrator platform.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Start the Orchestrator Configuration Service,” on page 34
n
“Log In to the Orchestrator Configuration Interface,” on page 34
n
“Change the Default Password,” on page 35
n
“Revert to the Default Password for Orchestrator Configuration,” on page 35
n
“Configure the Network Connection,” on page 36
n
“Change the Default Configuration Ports on the Orchestrator Client Side,” on page 38
n
“Import the vCenter SSL Certificate,” on page 39
n
“Configuring LDAP Settings,” on page 39
n
“Password Encryption and Hashing Mechanism,” on page 45
VMware, Inc.
n
“Configure the Database Connection,” on page 45
n
“Server Certificate,” on page 47
n
“Configure the Default Plug-Ins,” on page 50
n
“Access Rights to Orchestrator Server,” on page 54
n
“Import the vCenter Server License,” on page 54
n
“Start the Orchestrator Server,” on page 55
n
“Export the Orchestrator Configuration,” on page 56
n
“Import the Orchestrator Configuration,” on page 58
n
“Configure the Maximum Number of Events and Runs,” on page 58
n
“Install an Application,” on page 59
n
“Start a Published Web View,” on page 59
n
“Change the Web View SSL Certificate,” on page 60
n
“Define the Server Log Level,” on page 60
33
Page 34

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
Start the Orchestrator Configuration Service
The VMware vCenter Orchestrator Configuration service startup type is set to Manual by default. You must
start it manually before you try to access the Orchestrator configuration interface and after you reboot.
If you installed Orchestrator standalone, the Orchestrator Configuration service is already started.
Procedure
1 Right-click My Computer on your desktop and select Manage.
2 In the Computer Management dialog box, expand Services and Applications and select Services.
3 Locate VMware vCenter Orchestrator Configuration on the list and check its status.
4 If the status is not set, right-click VMware vCenter Orchestrator Configuration and select Start.
The Orchestrator Configuration service is now running and Orchestrator configuration interface is available
for use.
What to do next
You can log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface and start the process of configuring Orchestrator.
Log In to the Orchestrator Configuration Interface
To start the configuration process, you must access the Orchestrator configuration interface.
Prerequisites
The VMware vCenter Orchestrator Configuration service must be running.
CAUTION To avoid potential exploitation of the administrative credentials, change the nonsecure password
when you first access the configuration interface. Retaining the default password might cause serious security
issues in a production environment and is a common cause of data breach.
Procedure
1 Select Start > Programs > VMware > vCenter Orchestrator Web Configuration.
You cannot view the Orchestrator configuration shortcut if you are logged in to the Orchestrator server
machine as a different user than the user who installed Orchestrator. To access the configuration interface,
go to
install_directory
You can also access the Orchestrator configuration interface by entering the following URL address in a
Web browser:
http://
orchestrator_server_DNS_name_or_IP_address
8282 is the default HTTP access port reserved for the Web UI of Orchestrator configuration. To enable
HTTPS connection through port 8283, you must configure Jetty to use SSL. See Jetty Documentation,
Configuring SSL.
\Orchestrator\configuration and double-click the VMOConfiguration shortcut.
:8282
2 Log in with the default credentials.
n
User name: vmware.
You cannot change the vmware default user name.
n
Password: vmware
You can change the password after you log in for the first time.
34 VMware, Inc.
Page 35

When you log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface for the first time, you see the installation path, the
Orchestrator version, and the server status in the Information tab. The status indicators of all tabs on the left
display red triangles, indicating that the components are not configured.
What to do next
Select a tab and follow the links in the inspector on the right, entering the necessary information until a green
circle appears on the selected tab. The green circle indicates that your configuration changes are correct and
that all dependencies are met.
Change the Default Password
You must change the default password to avoid potential security issues.
Prerequisites
The VMware vCenter Orchestrator Configuration service must be running.
CAUTION To avoid potential exploitation of the administrative credentials, change the nonsecure password
when you first access the configuration interface. Retaining the default password might cause serious security
issues in a production environment and is a common cause of data breach.
Procedure
Chapter 9 Configuring Orchestrator
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 On the General tab, click Change Password.
3 In the Current password text box, enter vmware.
4 In the New password text box, enter the new password.
5 Reenter the new password to confirm it.
6 Click Apply changes.
Revert to the Default Password for Orchestrator Configuration
If the default password for the Orchestrator configuration interface is changed, you cannot retrieve it because
Orchestrator uses encryption to encode passwords. You can revert to the default password vmware if the
current password is not known.
Procedure
1 Navigate to the following folder on the Orchestrator server system.
Option Action
If you installed Orchestrator with the
vCenter Server installer
If you installed the standalone
version of Orchestrator
2 Open the password.properties file in a text editor.
Go to
install_directory
uration\jetty\etc.
Go to
install_directory
tc.
\VMware\Infrastructure\Orchestrator\config
\VMware\Orchestrator\configuration\jetty\e
3 Delete the content of the file.
4 Add the following line to the password.properties file.
vmware=92963abd36c896b93a36b8e296ff3387
VMware, Inc. 35
Page 36

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
5 Save the password.properties file.
6 Restart the Orchestrator Configuration service.
You can log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface with the default credentials.
n
User name: vmware
n
Password: vmware
Configure the Network Connection
When you install Orchestrator, the IP address for your server is set as not set. To change this, you must configure
the network settings used by Orchestrator.
Prerequisites
System administrators must make sure that the network provides a fixed IP, which is obtained by using a
properly configured DHCP server (using reservations) or by setting a static IP. The Orchestrator server requires
that this IP address remain constant while it is running.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click Network.
3 From the IP address drop-down menu, select the network interface to which to bind the Orchestrator
server.
Orchestrator discovers the IP address of the machine on which the server is installed.
When an interface is selected, the corresponding DNS name appears. If no network name is found, the IP
address appears in the DNS name text box. Use this IP address to log in to the Orchestrator client interface.
4 Set up the communication ports.
For more information about default ports, see “Orchestrator Network Ports,” on page 36.
5 Click Apply changes.
What to do next
Click SSL Certificate to load the vCenter SSL certificate in Orchestrator.
Orchestrator Network Ports
Orchestrator uses specific ports that allow communication with the other systems. Some of the communication
ports you must set are a subset of the standard ports that JBoss uses. The ports are set with a default value, but
you can change these values at any time. When you make the changes, make sure that all ports are free on your
host and, if necessary, open these ports on required firewalls.
Default Configuration Ports
Table 9-1 lists the default ports that Orchestrator needs to provide the Orchestrator service. You must configure
your firewall to allow incoming TCP connections.
NOTE Other ports might be required if you are using custom plug-ins.
36 VMware, Inc.
Page 37

Table 9-1. VMware vCenter Orchestrator Default Configuration Ports
Port Number Protocol Source Target Description
Chapter 9 Configuring Orchestrator
Lookup port 8230 TCP vCO Client vCO Server The main port to communicate with the Orchestrator
Command port 8240 TCP vCO Client vCO Server The application communication port (RMI container
Messaging port 8250 TCP vCO Client vCO Server The Java messaging port used to dispatch events. It is
Data port 8244 TCP vCO Client vCO Server The port used to access all Orchestrator data models,
HTTP server
port
HTTPS server
port
Web
configuration
HTTP access
port
Web
configuration
HTTPS access
port
8280 TCP end-user
Web browser
8281 TCP end-user
Web browser
8282 TCP end-user
Web browser
8283 TCP end-user
Web browser
vCO Server The port used by the Orchestrator Server to connect to
vCO Server The SSL secured HTTP protocol used to connect to the
vCO
Configuration
vCO
Configuration
server (JNDI port). All other ports communicate with
the Orchestrator smart client through this port. It is
part of the Jboss Application server infrastructure.
port) used to load remotely. It is part of the Jboss
Application server infrastructure.
part of the Jboss Application server infrastructure.
such as workflows and policies. It is part of the Jboss
Application server infrastructure.
the Web frontend through HTTP.
Web frontend and to communicate with the vCenter
API.
The access port for the Web UI of Orchestrator
configuration.
The SSL access port for the Web UI of Orchestrator
configuration.
NOTE To enable the HTTPS connection, configure
Jetty to use SSL. See Jetty Documentation, Configuring
SSL.
External Communication Ports
Table 9-2 lists the ports to which Orchestrator connects to communicate with external services. You must allow
your firewall to allow outgoing connections.
Table 9-2. VMware vCenter Orchestrator External Communication Ports
Port Number Protocol Source Target Description
LDAP 389 TCP vCO Server LDAP Server The look up port of your LDAP Authentication server.
LDAP using
SSL
LDAP using
Global Catalog
PostgreSQL 5432 TCP vCO Server PostgreSQL
SQL Server 1433 TCP vCO Server Microsoft SQL
Oracle 1521 TCP vCO Server Oracle DB
MySQL 3306 TCP vCO Server MySQL Server The port used to communicate with the MySQL Server
636 TCP vCO Server LDAP Server The look up port of your secure LDAP Authentication
server.
3268 TCP vCO Server Global Catalog
Server
Server
Server
Server
The port to which Microsoft Global Catalog server
queries are directed.
The port used to communicate with the PostgreSQL
Server that is configured as the Orchestrator database.
The port used to communicate with the Microsoft SQL
Server that is configured as the Orchestrator database.
The port used to communicate with the Oracle
Database Server that is configured as the Orchestrator
database.
that is configured as the Orchestrator database.
VMware, Inc. 37
Page 38

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
Table 9-2. VMware vCenter Orchestrator External Communication Ports (Continued)
Port Number Protocol Source Target Description
SMTP Server
port
vCenter API
port
25 TCP vCO Server SMTP Server The port used for email notifications.
443 TCP vCO Server vCenter Server The vCenter API communication port used by
Orchestrator to obtain virtual infrastructure and
virtual machine information from orchestrated
vCenter Server(s).
Internal JBoss Ports
Table 9-3 lists the internal JBoss Server ports. These ports do not need to be added to the firewall exceptions.
Table 9-3. Internal JBoss Server Ports
Port Number Description
3455 RMI server registry invoker
3873 EJB3/AOP remoting connector
4445 JBoss pooled invoker
4446 Remoting server service connector
8083 Dynamic class/resource loader
Change the Default Configuration Ports on the Orchestrator Client Side
When you change the default network ports in the Orchestrator configuration interface, your changes are
applied only on the Orchestrator server side. To connect to the server with the client, you must change the
configuration of all Orchestrator client instances or connect to the server by using your Orchestrator server
DNS name or IP address followed by the new Lookup port number.
The main port to communicate with the Orchestrator server is the Lookup port. The Orchestrator client
discovers all other ports through this port. If you change the default lookup port value in the Orchestrator
configuration interface after you install the Orchestrator client instances, you can add a vmo.properties
configuration file for each Orchestrator client instance and define the new Lookup port by adding the
ch.dunes.net.jboss-server.port system property.
Prerequisites
Log in to the server where the vCenter Orchestrator Client application is installed.
Procedure
1 Navigate to the apps folder on the Orchestrator client system.
Option Action
If you installed Orchestrator with the
vCenter Server installer
If you installed the standalone
version of Orchestrator
Go to
install_directory
Go to
install_directory
\VMware\Infrastructure\Orchestrator\apps.
\VMware\Orchestrator\apps.
2 Create a file that contains the lookup port value.
ch.dunes.net.jboss-server.port=
new_lookup_port_number
38 VMware, Inc.
Page 39

3 Save the file as vmo.properties.
4 Repeat the procedure for every Orchestrator client instance.
You can log in to the Orchestrator client without adding the lookup port number to the Orchestrator server
DNS name or IP address.
Import the vCenter SSL Certificate
The Orchestrator configuration interface uses a secure connection to communicate with vCenter. You can
import the required SSL certificate from a URL or file.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click Network.
3 In the right pane, click the SSL Certificate tab.
4 Load the vCenter SSL certificate in Orchestrator from a URL address or file.
Option Description
Import from URL
Import from file
5 Click Import.
Enter URL of the vCenter server:
https://
Obtain the server certificate file. Usual locations are:
n
C:\Documents and
Settings\AllUsers\ApplicationData\VMware\VMware
VirtualCenter\SSL\rui.crt
n
/etc/vmware/ssl/rui.crt
Chapter 9 Configuring Orchestrator
your_vcenter_server_IP_address
A message confirming that the import is successful appears.
6 Repeat the steps for each vCenter server.
7 Click Startup Options.
8 Click Restart the vCO configuration server to restart the Orchestrator Configuration service after adding
a new SSL certificate.
The imported certificate appears in the Imported SSL certificates list. On the Network tab, the red triangle
changes to a green circle to indicate that the component is now configured correctly.
What to do next
Each time you want to specify the use of an SSL connection, you must return to the SSL Certificate tab on the
Network tab and import the corresponding vCenter SSL certificate.
Configuring LDAP Settings
Orchestrator requires a connection to a working LDAP server on your infrastructure.
1 Generate the LDAP Connection URL on page 40
The LDAP service provider uses a URL address to configure the connection to the directory server. To
generate the LDAP connection URL, you must specify the LDAP host, port, and root.
2 Import the LDAP Server SSL Certificate on page 41
If your LDAP server uses SSL, you can import the SSL certificate file to the Orchestrator configuration
interface and activate secure connection between Orchestrator and LDAP.
VMware, Inc. 39
Page 40

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
3 Specify the Browsing Credentials on page 42
Orchestrator must read your LDAP structure to inherit its properties. You can specify the credentials
that Orchestrator uses to connect to an LDAP server.
4 Define the LDAP Lookup Paths on page 43
You can define the users and groups lookup information.
5 Define the LDAP Search Options on page 44
You can customize the LDAP search queries and make searching in LDAP more effective.
6 Common Active Directory LDAP Errors on page 44
When you encounter the LDAP:error code 49 error message and experience problems connecting to your
LDAP authentication server, you can check which LDAP function is causing the problem.
Generate the LDAP Connection URL
The LDAP service provider uses a URL address to configure the connection to the directory server. To generate
the LDAP connection URL, you must specify the LDAP host, port, and root.
The supported directory service types are: Active Directory, eDirectory, and Sun Java System Directory Server.
OpenLDAP is not supported and can only be used for testing and evaluation purposes.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click LDAP.
3 From the LDAP client drop-down menu, select the directory server type that you are using as the LDAP
server.
NOTE If you change the LDAP server or type after you set permissions on Orchestrator objects (such as
access rights on workflows or actions), you must reset these permissions.
If you change the LDAP settings after configuring custom applications that capture and store user
information, the LDAP authentication records created in the database become invalid when used against
the new LDAP database.
4 (Optional) If you use Sun Java System Directory Server you must set objectClass to
groupOfUniqueNames when you add users, create groups, or assign group memberships. The User ID
(uid) attribute is mandatory for every user that can log in to Orchestrator.
Use Java System Directory Service Control Center from Sun Microsystems to set objectClass to
groupOfUniqueNames. When creating a new group, select Entry Type > Static Group >
groupOfUniqueNames in Java System Directory Service Control Center.
5 In the Primary LDAP host text box, type the IP address or the DNS name of the host on which your primary
LDAP service runs.
This is the first host on which the Orchestrator configuration interface verifies user credentials.
6 (Optional) In the Secondary LDAP host text box, type the IP address or the DNS name of the host on
which your secondary LDAP service runs.
If the primary LDAP host becomes unavailable, Orchestrator verifies user credentials on the secondary
host.
40 VMware, Inc.
Page 41

Chapter 9 Configuring Orchestrator
7 In the Port text box, type the value for the look up port of your LDAP server.
NOTE Orchestrator supports Active Directory hierarchical domains structure. If your Domain Controller
is configured to use Global Catalog, you must use port 3268. You cannot use the default port 389 to connect
to the Global Catalog server.
8 In the Root text box, type the root element of your LDAP service.
If your domain name is company.org, your root LDAP is dc=company,dc=org.
This is the node used to browse your service directory after typing the appropriate credentials. For large
service directories, specifying a node in the tree narrows the search and improves performance. For
example, rather than searching in the entire directory, you can specify
ou=employees,dc=company,dc=org. This displays all the users in the Employees group.
9 (Optional) Select the Use SSL check box to activate encrypted certification for the connection between
Orchestrator and LDAP.
If your LDAP uses SSL, you must first import the SSL certificate and restart the Orchestrator Configuration
service. See “Import the LDAP Server SSL Certificate,” on page 41.
10 (Optional) Select the Use Global Catalog check box to allow LDAP referrals when the LDAP client is
Active Directory.
The LDAP server look up port number changes to 3268. Orchestrator follows the LDAP referrals to find
users and groups in a subdomain that is part of the Active Directory tree to which Orchestrator is
connected. You can add permissions on any groups that can be accessed from your Global Catalog.
Example: Example Values and Resulting LDAP Connection URL Addresses
n
LDAP host: DomainController
n
Port: 389
n
Root: ou=employees,dc=company,dc=org
Connection URL: ldap://DomainController:389/ou=employees,dc=company,dc=org
n
LDAP host using Global Catalog: 10.23.90.130
n
Port: 3268
n
Root: dc=company,dc=org
Connection URL: ldap://10.23.90.130:3268/dc=company,dc=org
What to do next
Assign credentials to Orchestrator to ensure its access to the LDAP server. See “Specify the Browsing
Credentials,” on page 42.
Import the LDAP Server SSL Certificate
If your LDAP server uses SSL, you can import the SSL certificate file to the Orchestrator configuration interface
and activate secure connection between Orchestrator and LDAP.
SSL capabilities are not installed as part of Microsoft Active Directory, eDirectory, and Sun Java Directory
Server, and require more configuration. For instructions about configuring your LDAP server for SSL access,
see third-party documentation.
VMware, Inc. 41
Page 42

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
Prerequisites
n
Verify that SSL access is enabled on the LDAP server.
n
Obtain a self-signed server certificate or a certificate that is signed by a Certificate Authority.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click Network.
3 In the right pane, click the SSL Certificate tab.
4 Browse to select a certificate file to import.
5 Click Import.
A message confirming that the import is successful appears.
6 Click Startup Options.
7 Click Restart the vCO configuration server to restart the Orchestrator Configuration service after adding
a new SSL certificate.
The imported certificate appears in the Imported SSL certificates list. You activated secure connection between
Orchestrator and your LDAP server.
What to do next
You must enable SSL on the LDAP tab in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
Specify the Browsing Credentials
Orchestrator must read your LDAP structure to inherit its properties. You can specify the credentials that
Orchestrator uses to connect to an LDAP server.
Prerequisites
You must have a working LDAP service on your infrastructure and have generated the LDAP connection URL.
Procedure
1 In the LDAP tab of the Orchestrator configuration interface, enter a valid user name (LDAP string) in the
User name text box for a user on your LDAP who has browsing permissions.
The possible formats in which you can specify the user name in Active Directory are as follows:
n
Bare user name format, for example user.
n
Distinguished name format: cn=user,ou=employees,dc=company,dc=org.
Use this format with OpenLDAP, Sun, and eDirectory. No spaces between the comma and the next
identifier.
n
Principle name format: user@company.org.
n
NetBEUI format: COMPANY\user.
2 In the Password text box, enter the valid password for the user name you entered in Step 1.
Orchestrator uses these credentials to connect to the LDAP server.
What to do next
Define the LDAP containers for Orchestrator to look up users and groups.
42 VMware, Inc.
Page 43

Chapter 9 Configuring Orchestrator
Define the LDAP Lookup Paths
You can define the users and groups lookup information.
Two global roles are identified in Orchestrator: Developers and Administrators. The users in the Developers
role have editing privileges on all elements. The users in the Administrators role have unrestricted privileges.
Administrators can manage permissions, or discharge administration duties on a selected set of elements to
any other group or user. These two groups must be contained in the Group lookup base.
Prerequisites
You must have a working LDAP service on your infrastructure.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click LDAP.
3 Define the User lookup base.
This is the LDAP container (the top level domain name or organizational unit) where Orchestrator searches
for potential users.
a Click Search and type the top-level domain name or organizational unit.
Searching for company returns dc=company,dc=org and other common names containing the search
term. If you type dc=company,dc=org as a search term, no results are found.
b Click the LDAP connection string for the discovered branch to insert it in the User lookup base text
box.
If no matches are found, check your LDAP connection string in the main LDAP page.
NOTE You can connect to the Global Catalog Server through port 3268. It issues LDAP referrals which
Orchestrator follows to find the account or group in a subdomain.
4 Define the Group lookup base.
This is the LDAP container where Orchestrator looks up groups.
a Click Search and type the top-level domain name or organizational unit.
b Click the LDAP string for the discovered branch to insert it in the Group lookup base text box.
5 Define the vCO Admin group.
This must be an LDAP group (like Domain Users) to which you grant administrative privileges for
Orchestrator.
a Click Search and type the top-level group name.
b Click the LDAP string for the discovered branch to insert it in the vCO Admin group text box.
IMPORTANT In eDirectory installations, only the eDirectory administrator can see users or user groups that
have administration rights. If you are using an eDirectory LDAP server, and you log into Orchestrator as
a member of the vCO Admin group but you are not the eDirectory administrator, you can create users or
user groups with administration rights, but you cannot see those users using their own rights and
permissions. This issue does not apply to other LDAP servers.
6 Click the Test Login tab and type credentials for a user to test whether they can access the Orchestrator
smart client.
After a successful login, the system checks if the user is in the Orchestrator Administrator group.
VMware, Inc. 43
Page 44

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
What to do next
Define the LDAP search options and apply your changes.
Define the LDAP Search Options
You can customize the LDAP search queries and make searching in LDAP more effective.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click LDAP.
3 In the Request timeout text box, enter a value in milliseconds.
This value determines the period during which the Orchestrator server sends a query to the service
directory, the directory searches, and sends a reply. If the timeout period elapses, modify this value to
check whether the timeout occurs in the Orchestrator server.
4 (Optional) For all links to be followed before the search operation is performed, select the Dereference
links check box.
Sun Java System Directory Server does not support reference links. If you are using it, you must select the
Dereference links check box.
5 (Optional) To filter the attributes that the search returns, select the Filter attributes check box.
Selecting this check box makes searching in LDAP faster. However, you might need to use some extra
LDAP attributes for automation later.
6 (Optional) Select the Ignore referrals check box to disable referral handling.
When you select the check box, the system does not display any referrals.
7 In the Host reachable timeout text box, enter a value in milliseconds.
This value determines the timeout period for the test checking the status of the destination host.
8 Click Apply changes.
On the LDAP tab, the red triangle changes to a green circle to indicate that the component is now configured
correctly.
What to do next
Proceed with the database configuration.
Common Active Directory LDAP Errors
When you encounter the LDAP:error code 49 error message and experience problems connecting to your LDAP
authentication server, you can check which LDAP function is causing the problem.
Table 9-4. Common Active Directory Authentication Errors
Error Description
525 The user is not found.
52e The user credentials are not valid.
530 The user is not allowed to log in at this time.
531 The user is not allowed to log in to this workstation.
532 The password has expired.
533 This user account has been disabled.
44 VMware, Inc.
Page 45

Table 9-4. Common Active Directory Authentication Errors (Continued)
Error Description
701 This user account has expired.
773 The user must reset their password.
775 The user account has been locked.
Password Encryption and Hashing Mechanism
Orchestrator utilizes PBE with MD5 and DES encryption mechanism to encode the stored passwords used to
connect to the database, LDAP, and Orchestrator servers.
Table 9-5. Encryption and Hashing Algorithms in Orchestrator
Algorithm Description
Password Based Encryption (part of Java 2 SDK 1.4) Generates an encryption key from a password. PBE stores
and checks the hash value of the password. For more
information, see the Java Cryptography Extension Reference
Guide on java.sun.com.
Message Digest 5 algorithm Generates a 128-bit cryptographic message digest value,
usually expressed as a 32 digit hexadecimal number.
Data Encryption Standard Applies a 56-bit key to each 64-bit block of data.
Chapter 9 Configuring Orchestrator
Configure the Database Connection
To establish a connection to the Orchestrator database, you must configure the database connection parameters.
Prerequisites
Set up a new database to use with the Orchestrator server. See “Orchestrator Database Setup,” on page 18.
If you are using an SQL Server database, verify that the SQL Server Browser service is running.
To store characters in the correct format in an Oracle database, set the NLS_CHARACTER_SET parameter to
AL32UTF8 before configuring the database connection and building the table structure for Orchestrator. This
setting is crucial for an internationalized environment.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click Database.
3 From the Select the database type drop-down menu, select the type of database for Orchestrator server
to use.
NOTE Orchestrator supports Oracle and SQL Server databases and provides experimental support for
MySQL and PostgreSQL. You can use MySQL and PostgreSQL for testing and evaluation purposes.
4 Specify the database connection parameters.
For a list of connection parameters, see “Database Connection Parameters,” on page 46.
If the specified parameters are correct, a message states that the connection to the database is successful.
NOTE Although Orchestrator has established a connection to the database, the database configuration is
not yet complete. You must install or update the database.
VMware, Inc. 45
Page 46

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
5 To build or update the table structure for Orchestrator, install or update the database.
Option Description
Install the database
Update the database
After the database is populated, you can reset the database access rights to db_dataread and
db_datawrite.
6 Click Apply changes.
NOTE If you change the Orchestrator database after configuring and installing the default plug-ins, click
the Troubleshooting tab and force plug-in reinstallation by clicking the Reset current version link. This
operation deletes the
server\server\vmo\plugins\_VSOPluginInstallationVersion.xml file, which holds the version of the
install_directory
plug-ins already installed, and forces plug-in reinstallation.
The database configuration is successfully updated. On the Database tab, the red triangle changes to a green
circle to indicate that the component is now configured correctly.
Database Connection Parameters
Configures a new database.
Uses the database from your previous Orchestrator installation.
\app-
To establish a connection to the database, you must specify the database connection parameters. Depending
on the type of database you are connecting to, the required information may vary.
Table 9-6 lists the connection parameters that you must specify.
Table 9-6. Database Connection Parameters
Connection Parameter Description
User name The user name that Orchestrator uses to connect and operate the selected database. The name
you select must be a valid user on the target database with db_owner rights.
Password The valid password for the user name you entered.
Database host IP address or
DNS name
Port The database server port that allows communication to your database.
Database name The full unique name of your database. The database name is specified by the
Instance name The name of the database instance that can be identified by the INSTANCE_NAME parameter
Domain (SQL Server only) To use Windows authentication, enter the Windows domain, for example company.org.
Use Windows
authentication mode (SQL
Server only)
The database server IP address or DNS name.
SERVICE_NAMES parameter in the initialization parameter file.
NOTE PostgreSQL JDBC driver does not support non-ASCII characters in the database name.
in the database initialization parameter file.
To use SQL authentication, leave this text box blank.
Select to send NTLMv2 responses when using Windows authentication.
46 VMware, Inc.
Page 47

Identify the SQL Server Authentication Type
You can identify whether SQL Server is using Windows NT or SQL Server authentication.
Procedure
1 Open the SQL Server Management Studio.
2 Click the Properties tab.
3 Check the connection type.
Server Certificate
The server certificate is a form of digital identification that is used with HTTPS to authenticate Web
applications. Issued for a particular server and containing information about the server’s public key, the
certificate allows you to sign all elements created in Orchestrator and guarantee authenticity. When the client
receives an element from your server (typically this is a package), they verify your identity and decide whether
to trust your signature.
1 Import a Server Certificate on page 47
You can import a server certificate and use it with Orchestrator.
Chapter 9 Configuring Orchestrator
2 Create a Self-Signed Server Certificate on page 48
Installing Orchestrator requires that you create a self-signed certificate. You can create a self-signed
certificate to guarantee encrypted communication and a signature for your packages. However, the
recipient cannot be sure that the self-signed package you are sending is in fact a package issued by your
server and not a third party claiming to be you.
3 Obtain a Server Certificate Signed by a Certificate Authority on page 48
To provide recipients with an acceptable level of trust that the package was created by your server,
certificates are typically signed by a Certificate Authority (CA). Certificate Authorities guarantee that
you are who you claim to be, and as a token of their verification, they sign your certificate with their
own.
4 Export a Server Certificate on page 49
The server certificate private key is stored in the vmo_keystore table of the Orchestrator database. In case
you lose or delete this key, or if you bind the Orchestrator server to a different database, the content of
the exported packages signed with this certificate will become unavailable. To ensure that packages are
decrypted on import, you must save this key to a local file.
5 Change a Self-Signed Server Certificate on page 49
If you want to sign your packages with a server certificate different from the one you used for the initial
Orchestrator configuration, you need to export all your packages and reinstall the Orchestrator server.
Import a Server Certificate
You can import a server certificate and use it with Orchestrator.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click Server Certificate.
3 Click Import certificate database.
VMware, Inc. 47
Page 48

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
4 Browse to select the certificate file to import.
5 Enter the password used to decrypt the content of the imported keystore database.
The details about the imported server certificate appear in the Server Certificate window.
Create a Self-Signed Server Certificate
Installing Orchestrator requires that you create a self-signed certificate. You can create a self-signed certificate
to guarantee encrypted communication and a signature for your packages. However, the recipient cannot be
sure that the self-signed package you are sending is in fact a package issued by your server and not a third
party claiming to be you.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click Server Certificate.
3 Click Create certificate database and self-signed server certificate.
4 Enter the relevant information.
5 From the drop-down menu, select a country.
6 Click Create.
Orchestrator generates a server certificate that is unique to your environment. The details about the certificate
public key appear in the Server Certificate window. The certificate private key is stored in the vmo_keystore
table of the Orchestrator database.
What to do next
For disaster recovery purposes, you can save the certificate private key to a local file.
Obtain a Server Certificate Signed by a Certificate Authority
To provide recipients with an acceptable level of trust that the package was created by your server, certificates
are typically signed by a Certificate Authority (CA). Certificate Authorities guarantee that you are who you
claim to be, and as a token of their verification, they sign your certificate with their own.
Prerequisites
Create a self-signed server certificate or import an existing server certificate.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click Server Certificate.
3 Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
a Click Export certificate signing request.
b Save the VSOcertificate.csr file in your file system when prompted.
4 Send the CSR file to a Certificate Authority, such as Verisign or Thawte.
Procedures might vary from one CA to another, but they all require a valid proof of your identity.
CA returns a Certificate Signing Request that you must import. This is an exact copy of your actual
certificate and the CA signature.
5 Click Import certificate signing request signed by GA and select the file sent by your CA.
48 VMware, Inc.
Page 49

Chapter 9 Configuring Orchestrator
Orchestrator uses the server certificate to
n
Sign all packages before they are exported by attaching your certificate’s public key to each one.
n
Display a user prompt on importing a package that contains elements signed by untrusted certificates.
What to do next
You can import this certificate on other servers.
Export a Server Certificate
The server certificate private key is stored in the vmo_keystore table of the Orchestrator database. In case you
lose or delete this key, or if you bind the Orchestrator server to a different database, the content of the exported
packages signed with this certificate will become unavailable. To ensure that packages are decrypted on import,
you must save this key to a local file.
Prerequisites
You must have created or imported a server certificate.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click Server Certificate.
3 Click Export certificate database.
4 Enter a password to encrypt the content of the exported keystore database.
You must enter this password again when importing the file.
5 Click Export.
6 Save the vmo-server.vmokeystore file when prompted.
Change a Self-Signed Server Certificate
If you want to sign your packages with a server certificate different from the one you used for the initial
Orchestrator configuration, you need to export all your packages and reinstall the Orchestrator server.
Procedure
1 Export all your packages.
a Click the Packages view in the Orchestrator client.
b Right-click the package to export and select Export package.
c Browse to select a location in which to save the package and click Open.
d Leave the View content, Re-Packageable, and Edit element options selected.
CAUTION Do not sign the package with your current certificate. You must not encrypt the package.
When you delete the certificate database, the private key will be lost and the content of the exported
package will become unavailable.
e (Optional) Deselect the Export version history check box if you do not want to export the version
history.
f Click Save.
2 (Optional) Export the Orchestrator configuration.
3 Uninstall the Orchestrator server.
VMware, Inc. 49
Page 50

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
4 Delete the Orchestrator database, or create a backup if you want to keep old data.
The database you bind Orchestrator to must not contain records in the vmo_keystore table.
5 Reinstall the Orchestrator server.
6 (Optional) Import your Orchestrator configuration.
7 Create a new self-signed certificate or import one.
8 Reimport your packages.
a Click the Packages view in the Orchestrator client.
b From the drop-down menu, select Import package.
c Browse to select the package to import and click Open.
d Click Import or Import and trust provider.
e Click Import checked elements.
The server certificate change is effective at the next package export.
Configure the Default Plug-Ins
To deploy the set of default plug-ins when the Orchestrator server starts, the system must authenticate against
the LDAP server. You can specify the administrative credentials that Orchestrator uses with plug-ins, and
enable as well as disable plug-ins on the Plug-ins tab.
If you change the Orchestrator database after configuring and installing the default plug-ins, you must click
the Reset current version link in the Troubleshooting tab. This operation deletes the
server\server\vmo\plugins\_VSOPluginInstallationVersion.xml file, which holds the version of the plug-ins
install_directory
\app-
already installed, and forces plug-in reinstallation.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click Plug-ins.
3 Type the credentials for a user who is a member of the Orchestrator Administration group that you
specified on the LDAP tab.
When the Orchestrator server starts, the system uses these credentials to set up the plug-ins. The system
checks the enabled plug-ins and performs any necessary internal installations such as package import,
policy run, script launch, and so on.
4 (Optional) Install a new plug-in.
a Click the magnifying glass icon.
b Select the file to install.
c Click Open.
d Click Upload and install.
The allowed file extensions are .vmoapp and .dar. A .vmoapp file can contain a collection of several .dar
files and can be installed as an application, while a .dar file contains all the resources associated with one
plug-in.
The installed plug-in file is stored in the
install_directory
\app-server\server\vmo\plugins folder.
NOTE If you add a .dar file directly to the file system, you must click Reload plug-ins to update the plug-
ins available to the Orchestrator configuration interface.
50 VMware, Inc.
Page 51

Chapter 9 Configuring Orchestrator
5 (Optional) To disable a plug-in, deselect the check box next to it.
This action does not remove the plug-in file.
6 Click Apply changes.
On the Plug-ins tab, the red triangle changes to a green circle to indicate that the component is now configured
correctly. The first time the server boots, it installs the selected plug-ins.
What to do next
You can now configure the settings for Mail, SSH, and vCenter 4.0 plug-ins.
Define the Default SMTP Connection
The Mail plug-in is installed with Orchestrator Server and is used for email notifications. The only option
available for this plug-in is to use default values for new mail messages. You can set the default email account.
Avoid load balancers when configuring mail in Orchestrator. You will get SMTP_HOST_UNREACHABLE.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click Mail.
3 Select the Define default values check box and fill in the required text boxes.
Text box Description
SMTP host
SMTP port
User name
Password
From name and address
Enter the IP address or domain name of your SMTP server.
Enter a port number to match your SMTP configuration.
The default SMTP port is 25.
Enter a valid email account.
This is the email account Orchestrator uses to send emails.
Enter the password associated with the user name.
Enter the sender information to appear in all emails sent by Orchestrator.
4 Click Apply changes.
Configure the SSH Plug-In
You can set up the SSH plug-in to ensure encrypted connections.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click SSH.
3 Click New connection.
4 In the Host name text box, enter the host to access with SSH through Orchestrator.
NOTE The username and password are not required because Orchestrator uses the credentials of the
currently logged-in user to run SSH commands. You must reproduce the accounts you want to work on
SSH on target hosts from the LDAP server.
VMware, Inc. 51
Page 52

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
5 Click Apply changes.
The host is added to the list of SSH connections.
6 (Optional) Configure an entry path on the server.
a Click New root folder.
b Enter the new path and click Apply changes.
The SSH host is available in the Inventory view of the Orchestrator smart client.
Configure the vCenter 4.0 Plug-In
Orchestrator uses the vCenter Web Service API to control vCenter. You can set all the parameters to enable
Orchestrator to connect to your vCenter Sever instances.
Prerequisites
Import the SSL certificates for each vCenter Server instance you define. For more information, see “Import the
vCenter SSL Certificate,” on page 39.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click vCenter 4.0.
3 Click New vCenter host.
4 From the Available drop-down menu, select Enabled.
5 In the Host text box, type the IP address or the DNS name of the vCenter Server host.
6 In the Port text box, leave the default value, 443.
7 (Optional) Select the Secure channel check box to establish a secure connection to your vCenter Server
host.
8 In the Path text box, use the default value, /sdk.
This is the location of the SDK that you use to connect to your vCenter Server instance.
9 In the User name and Password text boxes, type the credentials for Orchestrator to use to establish the
connection to the vCenter Server host.
The user that you select must be a valid user with administrative privileges on your vCenter Server,
preferably at the top of the vCenter Server tree structure. Orchestrator uses these credentials to monitor
the vCenter Web service (typically to operate Orchestrator system workflows). All other requests inherit
the credentials of the user who triggers an action.
10 Specify the method you use to manage user access on the vCenter Server host.
Option Action
Share a unique session
Session per user
Select this option to allow Orchestrator to create only one connection to
vCenter Server. Enter the credentials of a user who is a vCenter Server
administrator.
Select this option if your vCenter Server is in an Active Directory domain.
Make sure that the user has the necessary permissions to perform the
required operations.
CAUTION Each user who logs in Orchestrator creates a new session to vCenter
Server. This can rapidly strain CPU, memory and bandwidth.
52 VMware, Inc.
Page 53

Chapter 9 Configuring Orchestrator
11 Click Apply changes.
The URL to the newly configured vCenter Server host is added to the list of defined hosts.
12 Repeat Step 3 through Step 11 for each vCenter Server instance.
What to do next
If you did not restart the Orchestrator Configuration service after importing the vCenter SSL Certificate, select
Startup Options > Restart the vCO configuration server.
Remove a Plug-In
You can disable an Orchestrator plug-in from the Plug-ins tab, but this action does not remove the plug-in file
from the Orchestrator server file system. To remove the plug-in file, you must log in to the machine on which
the Orchestrator server is installed and remove the plug-in file manually.
Prerequisites
Log in to the machine on which the Orchestrator server is installed.
Procedure
1 Navigate to the Orchestrator installation folder on the Orchestrator server system.
Option Action
If you installed Orchestrator with the
vCenter Server installer
If you installed the standalone
version of Orchestrator
Go to
install_directory
server\server\vmo\plugins.
Go to
install_directory
server\server\vmo\plugins.
\VMware\Infrastructure\Orchestrator\app-
\VMware\Orchestrator\app-
2 Delete the .dar archive that contains the plug-in to remove.
3 Restart the Orchestrator Configuration service.
The plug-in is removed from the Orchestrator configuration interface.
4 Log in to the Orchestrator client.
5 In the Orchestrator client, click the Packages view.
6 Right-click the package to delete and select Delete element with content.
NOTE Orchestrator elements that are locked in the read-only state, for example workflows in the standard
library, are not deleted.
You removed all custom workflows and actions, policies, Web views, configurations, settings, and resources
that the plug-in contains.
VMware, Inc. 53
Page 54

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
Access Rights to Orchestrator Server
The type of vCenter Server license you apply in the Orchestrator configuration interface determines whether
you get read-only or full access to the Orchestrator server capabilities.
Table 9-7. Orchestrator Server Modes
vCenter License Edition vCenter Orchestrator Mode Description
Standard Server You are granted full read and write
Foundation Player You are granted read privileges on all
Essentials Player You are granted read privileges on all
Evaluation Server You are granted full read and write
privileges to all Orchestrator elements.
You can run and edit workflows.
Orchestrator elements. You can run
workflows but you cannot edit them.
Orchestrator elements. You can run
workflows but you cannot edit them.
privileges to all Orchestrator elements.
You can run and edit workflows.
NOTE All predefined workflows are locked as read-only by design. To edit a standard workflow, you must
duplicate the workflow and make changes to the duplicated workflow.
Import the vCenter Server License
To finish the configuration of the Orchestrator server, you must import the vCenter Server license. The set of
plug-ins delivered with Orchestrator do not require a license. If you add a plug-in that requires a license, you
must import it.
To access the vCenter Server license, you can log in the VMware Web site with the credentials that were used
to order the license.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click Licenses.
3 In the Serial number text box, type your vCenter Server license key.
The serial number is a string of five hyphen-separated groups of five alphanumeric characters each.
4 Click Apply changes and verify that the license is installed.
To view details, click the name of the imported license.
5 Start the Orchestrator server.
The Orchestrator server is now configured correctly.
54 VMware, Inc.
Page 55

Start the Orchestrator Server
You can install the Orchestrator server as a service on the Startup Options tab. When you do this, you can
start, stop, and restart the service from the Configuration interface. This process is reversible as you can always
use the Uninstall vCO server from service option.
Prerequisites
n
If you installed Orchestrator silently with vCenter Server, verify that your system has at least 4GB of RAM
and that the database is running on a dedicated server. The Orchestrator server might not start if your
system does not meet this requirement.
n
If you installed Orchestrator standalone, verify that your system has at least 2GB of RAM. The Orchestrator
server might not start if your system does not meet this requirement.
n
All of the status indicators must display a green circle. You cannot start the Orchestrator server if any of
the components is not configured properly.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click Startup Options.
Chapter 9 Configuring Orchestrator
3 Click Install vCO server as service.
The Orchestrator server is installed as a Windows service.
4 Click Start service.
The Orchestrator server status appears as Service is starting. The first boot can take around 5-10
minutes because it is building the database tables.
A message states that the service is started successfully. The Orchestrator server status appears at the bottom
of each configuration tab and is one of the following:
n
Running
n
Not available
n
Stopped
To see the Orchestrator server status, update the page by clicking the Refresh link.
What to do next
You can save and export the Orchestrator configuration file so that it can be imported later if needed. See
“Export the Orchestrator Configuration,” on page 56.
Activate the Service Watchdog Utility
Orchestrator provides a watchdog utility that checks for the activity of the Orchestrator server service. The
utility pings the Orchestrator server service periodically, and restarts it if a certain timeout period is exceeded.
By default, the timeout period is set to zero (0), which means that the watchdog utility is deactivated.
You can activate the service watchdog utility by setting the timeout period for the service's response to the
ping from the utility. You can set the timeout period for the response from the Orchestrator server service in
the wrapper.conf configuration file. The wrapper.conf file defines the wrapping of the Orchestrator server in
the host system.
Prerequisites
The Orchestrator server must be running as a Windows service.
VMware, Inc. 55
Page 56

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
Procedure
1 Navigate to the wrapper.conf wrapper configuration file.
The wrapper configuration file is in the following location:
install_directory
2 Open the wrapper.conf file in an editor.
3 Locate the -wrapper.ping.timeout parameter in the wrapper.conf file, or add it to the file if it does not
exist.
4 Set the number of seconds to allow between a ping from the watchdog utility and the response from the
service.
The default timeout is 0 seconds, which means that the utility is deactivated.
For example, you can increase the timeout period to 30 seconds by setting the parameter as -
wrapper.ping.timeout=30.
5 Save and close the wrapper.conf file.
6 In the Orchestrator configuration interface, select Startup Options > Restart Service to restart the
Orchestrator server.
You activated the Orchestrator watchdog utility by setting the timeout parameter.
/app-server/bin/wrapper.conf
Unwanted Server Restarts
You might experience unwanted server restarts if you have activated the service watchdog utility.
Problem
In certain circumstances, if the response time exceeds the watchdog timeout period, the watchdog utility can
falsely detect a JVM error, which causes a server restart.
Cause
The problem occurs when the Orchestrator server is running with a heavy load, for example if you have
connected Orchestrator to many vCenter Server instances that are running many virtual machines, or if the
server is performing swapping.
Solution
If you experience this behavior, extend the watchdog timeout period by increasing the timeout parameter in
the wrapper.conf configuration file. If the problem still persists, deactivate the watchdog utility by setting the
timeout parameter back to zero (0).
Export the Orchestrator Configuration
Orchestrator Configuration provides a mechanism to export your system settings to a local file. This mechanism
allows you to take a snapshot of your system configuration at any moment and import this configuration into
a new Orchestrator instance.
VMware recommends that you export and save your configuration settings on a regular basis, especially when
making modifications, performing maintenance, or upgrading the system.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 On the General tab, click Export Configuration.
56 VMware, Inc.
Page 57

3 (Optional) Enter a password to protect the configuration file.
Use the same password when you import the configuration.
4 Click Export.
5 Click Save when prompted.
Chapter 9 Configuring Orchestrator
You can use the vmo_config_
dateReference
.vmoconfig file to clone or to restore the system.
What to do next
For a list of exported configuration settings, see “Orchestrator Configuration Files,” on page 57.
Orchestrator Configuration Files
When you export the system configuration, a vmo_config_
contains all the Orchestrator configuration files.
NOTE Some of the configuration files that are created during the export are empty. For example, the server
file is empty because the startup options for the Orchestrator server are individual for each machine where the
Orchestrator server is installed. These empty files must be reconfigured, even when a working configuration
was previously imported.
Table 9-8 contains a list of the settings that are not saved during configuration export.
Table 9-8. Settings Not Saved During Configuration Export
File Description
certificate Certificates are not exported. Most certificates are stored in
licenses Licenses are not exported. They are stored in the Orchestrator
server The server configuration is reset to Unknown. You must
dateReference
the Orchestrator database. However, the vCenter Server
certificate is not stored in the database. You must store it in
a separate location, or import it again when you import an
Orchestrator configuration.
database.
install the Orchestrator server as a Windows service again.
.vmoconfig file is created locally. It
Table 9-9 contains a list of the settings that are saved during configuration export.
Table 9-9. Settings Saved During Configuration Export
File Description
general The maximum number of completed events and workflows
recorded, and the Web view development and configuration.
network The IP binding address and the TCP ports used by the
different elements of the Orchestrator server.
database The database configuration.
ldap The LDAP server configuration.
log The log settings information.
plug-ins The list of disabled plug-ins and the account name.
mail plug-in The SMTP host, SMTP port, user name, password, sender's
name, sender's address.
vCenter 4.0 plug-in The vCenter 4.0 plug-in configuration.
VMware, Inc. 57
Page 58

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
Import the Orchestrator Configuration
You can restore the previously exported system configuration if a system failure occurs or when you reinstall
Orchestrator.
Procedure
1 Install a new Orchestrator instance on a new server.
2 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
3 On the General tab, click Import Configuration.
4 (Optional) Enter the protective password you used when exporting the configuration.
5 Browse to select the .vmoconfig file you exported from your previous installation.
6 Click Import.
A message states that the configuration is successfully imported. The new system replicates the old
configuration completely.
Configure the Maximum Number of Events and Runs
You can define the maximum number of events stored in the database and the maximum number of workflow
runs.
Each event corresponds to a change in the state of a workflow or policy and is stored in the database. When
the maximum number of events set for a workflow or policy is reached, the database deletes the oldest event
to store the new event.
Each time you run a workflow, a workflow token is created in the database. This token contains all parameters
related to the running of the workflow. For example, if you run the Test workflow three times, three workflow
tokens are created. The three tokens appear in the Orchestrator client above the Test workflow.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 On the General tab, click Advanced Configuration.
3 Fill in the Max number of events text box.
To track every change in your infrastructure, enter 0 (zero=infinite). This means that the server never rolls
over, but it might become unavailable. Database administrators must periodically clean the server and
archive events.
4 Fill in the Max number of runs text box.
After you reach the maximum number of runs, the rollover process starts. If you do not want the rollover
process to start, enter 0 in this text box. If you enter 0, your database continues to extend.
5 (Optional) To set the default login credentials, fill in the User name for automatic Web login and Password
for automatic Web login text boxes.
This feature allows you to generate URLs that enable you to run, answer, schedule, or monitor a workflow
without having to enter your credentials. Use your default operator credentials for these text boxes.
6 Fill in the Web view directory text box.
This is the root folder from which development Web views are loaded. Files for each Web view must be
in a separate subfolder, and the name of this subfolder must be the same as the URL folder defined in the
client.
58 VMware, Inc.
Page 59

7 (Optional) To put the server in Web view development mode, select the Enable Web view
development check box.
In this mode, all elements in the Web view are loaded from the specified Web view directory and not from
the Web view content itself.
8 Click Apply changes.
Install an Application
An application is a set of plug-ins and packages. Because a Orchestrator installation contains only a few predefined plug-ins, you must install applications frequently to extend basic functions.
Prerequisites
Obtain the .vmoapp file containing the application.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 On the General tab, click Install Application.
3 Browse to select the .vmoapp file to install.
4 Click Install.
Chapter 9 Configuring Orchestrator
What to do next
Every time you install an application, a validation is made on the server configuration. In most cases, you must
perform additional configuration steps.
Start a Published Web View
You can use Web views to build the user front-end. Web views might vary from a simple page displaying basic
information to complex Web 2.0 applications. Orchestrator provides a demonstration Web view called
WebOperator, which you can use to review how Web views work. You can access Web views through the
Orchestrator configuration interface.
Prerequisites
Make sure that the Orchestrator server is started.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 On the General tab, click Web views.
The links to your published Web views appear. You can follow them to open a Web view in a new browser
window.
VMware, Inc. 59
Page 60

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
Change the Web View SSL Certificate
Orchestrator provides an SSL certificate that controls user access to Web views. You can configure Orchestrator
to use a different SSL certificate to control access to Web views. For example, if your company security policy
requires you to use their SSL certificates.
Procedure
1 Create an SSL certificate by running the keytool Java utility at the command prompt.
keytool -genkey -alias mySslCertificate -keyalg RSA
The keytool utility generates a file called .keystore by using the information and password that you
provide when you run the command.
2 Open the following Orchestrator application server configuration file in an editor.
Option Action
If you installed the standalone
version of Orchestrator
If the vCenter Server installed
Orchestrator
3 Find the following entry at line 44 in the server.xml file.
Go to
install_directory
server\server\vmo\deploy\jboss-deploy-tomcat\jbosswebtomcat55.sar\server.xml.
Go to
install_directory
server\server\vmo\deploy\jboss-deploy-tomcat\jbosswebtomcat55.sar\server.xml.
\VMware\Orchestrator\app-
\VMware\Infrastructure\Orchestrator\app-
<!-- Define a SSL HTTP/1.1 Connector on port ${ch.dunes.https-server.port} -->
<Connector address="${jboss.bind.address}" protocol="HTTP/1.1" SSLEnabled="true"
clientAuth="false" emptySessionPath="true"
keystoreFile="${java.home}/lib/security/jssecacerts"
keystorePass="dunesdunes"
maxHttpHeaderSize="8192" maxThreads="100"
port="${ch.dunes.https-server.port}" scheme="https" secure="true"
sslProtocol="TLS" strategy="ms" />
4 Change the keystoreFile and keystorePass attributes to refer to the .keystore file and the password you
created when you ran the keytool utility.
keystoreFile="/PathToKeystore/.keystore"
keystorePass="NewKeystorePassword"
5 Save the server.xml file and restart the Orchestrator server.
You changed the SSL certificate that the Orchestrator server uses to control access to Web views.
Define the Server Log Level
In the Orchestrator configuration interface, you can set the level of server log that you require. The default
server log level is INFO. Changing the log level affects any new messages that the server writes to the server
log and the number of active connections to the database.
CAUTION Only set the log level to DEBUG or ALL to debug a problem. Do not use this setting in a production
environment because it can seriously impair performance.
60 VMware, Inc.
Page 61

Chapter 9 Configuring Orchestrator
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click Log.
3 Select an option from the Log level drop-down menu.
Option Description
FATAL
ERROR
WARN
INFO
DEBUG
ALL
OFF
Only fatal errors are written to the log file.
Errors and fatal errors are written to the log file.
Warnings, errors, and fatal errors are written to the log file.
Information, warnings, errors, and fatal errors are written to the log file.
Debug information, information messages, warnings, errors, and fatal errors
are written to the log file.
Events are not filtered. All events are written to the log file.
No entries are written to the log file and no log updates are made.
NOTE The log contains messages of the selected level and all higher levels. If you select the INFO level, all
INFO messages and higher-level messages (INFO, WARN, ERROR, and FATAL) are written to the log file.
4 Click Apply changes.
5 (Optional) Click the Generate log report link to export the log files.
This operation creates a ZIP archive of all log files.
The new log level is applied to any new messages that the server generates, without restarting the server. The
logs are stored in
install_directory
\app-server\server\vmo\log\.
VMware, Inc. 61
Page 62

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
62 VMware, Inc.
Page 63

Where to Go From Here 10
When you have installed and configured vCenter Orchestrator, you can use Orchestrator to automate
frequently repeated processes related to the management of the virtual environment.
n
Log in to the Orchestrator client, run, and schedule workflows on the vCenter Server inventory objects.
n
Publish the weboperator Web view and provide browser access to Orchestrator functions to users and
user groups.
n
Set up the user permissions on Orchestrator objects.
n
Modify the standard Orchestrator workflows and write your own actions and workflows to automate
operations in vCenter Server.
n
Develop plug-ins, Web services, and Web views to extend the Orchestrator platform.
For information about features and instructions about using and maintaining Orchestrator, see the vCenter
Orchestrator Administration Guide.
For guidance with advanced development tasks and extending the Orchestrator platform, see the vCenter
Orchestrator Developer's Guide.
VMware, Inc.
63
Page 64

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
64 VMware, Inc.
Page 65

Index
A
availability 17
C
certificate database 49
changing the Orchestrator Lookup port 38
check-pointing 9
configuration
config files 57
database connection 45, 46
default plug-ins 50
export configuration settings 56
import configuration settings 58
LDAP settings 43
network connection 36
configuration maximums 19
D
database
connection parameters 45, 46
installation 18
MySQL 18
Oracle 18
PostgreSQL 18
server size 18
setup 18
SQL Server 18
default password 35
default ports
command port 36
data port 36
HTTP port 36
HTTPS port 36
JBoss server ports 36
LDAP port 36
LDAP with Global Catalog 36
LDAP with SSL 36
lookup port 36
messaging port 36
Oracle port 36
PostgreSQL port 36
SMTP port 36
SQL Server port 36
vCenter API port 36
Web configuration HTTP access port 36
Web configuration HTTPS access port 36
dereference links 44
DES 45
E
encryption 45
events 58
F
feedback 7
filter attributes 44
H
hashing 45
I
i18n support 14
ignore referrals 44
installing Orchestrator
vCenter Orchestrator server installer 23
vCenter Server installer 21
internationalization 14
IPv4 21
IPv6 21
L
LDAP
browsing credentials 42
connection URL 40
lookup paths 43
SSL certificate 41
LDAP errors
525 44
52e 44
530 44
531 44
532 44
533 44
701 44
773 44
775 44
license
importing vCenter Server license 54
Orchestrator server access rights 54
load balancing 51
VMware, Inc.
65
Page 66

vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide
login 34
M
MD5 45
MySQL
installing MySQL driver 18
parameters 19
N
non-ASCII characters 14, 23, 45
O
Orchestrator architecture 11
Orchestrator overview 9
P
password 35
PBE 45
persistence 9
plug-ins
installing an application 59
Mail plug-in 51
removing a plug-in 53
SSH plug-in 51
vCenter plug-in 52
policy engine 9
R
refactoring 29
runs 58
LDAP server 17
vCenter Server 17
SMTP connection 51
SQL authentication type 47
SSL certificate 39
support 7
system requirements
directory services 14
hardware 13
operating systems 13
supported browsers 14
supported databases 14
T
timeouts 44
U
uninstalling 31
updated information 5
upgrading 29
upgrading Orchestrator 21
upgrading Orchestrator standalone 27
upgrading vCenter server to upgrade
Orchestrator 25
user roles 10
V
versioning 9
VMware vCenter Orchestrator Server, installing
as Windows service 55
S
scalability 17
scripting engine 9
security 9
server certificate
CA-signed 47, 48
exporting 48, 49
importing 47
removing 49
self-signed 47, 48
server log
exporting 60
log level 60
service watchdog utility
timeout parameter 55
troubleshooting server restarts 56
services
starting 34, 55
VMware vCenter Orchestrator
Configuration 34
VMware vCenter Orchestrator Server 55
setup guidelines
directory services 17
W
watchdog utility 55
Web view
displaying Web views 59
starting Web views 59
Web views, change SSL certificate 60
what to do next 63
workflow engine 9
66 VMware, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...