

Product name: Network Camera (IP61x2)
Release Date: 2006/04/04
Manual Revision: 1.10
Web site: www.vivotek.com
Email: technical@vivotek.com
sales@vivotek.com
Made in Taiwan. ©Copyright 2000-2006. All rights reserved
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532

Before You Use This Product
The use of surveillance devices may be prohibited in your country by law. The
Network Camera is not only a high-performance web-ready camera but also can be
part of a flexible surveillance system. It is the user’s responsibility to ensure that the
operation of such devices is legal before installing this unit for its intended use.
It is important to first verify that all contents received are complete according to the
list in the "Package Contents" chapter. Take notice of the warnings in “Quick
Installation Guide” before the Network Camera is installed, then ca refully read and
follow the instructions in the “Install ation” chapter to avoid damages due to faulty
assembly and installation. This also ensures the product is used properly as intended.
The Network Camera is a network device and its use should be straightforward for
those who have basic network knowledge. The “Troubleshooting” chapter in the
Appendix provides remedies to the most common errors in set up and configuration.
You should consult this chapter first if you run into a system error.
The Network Camera is designed for various applications including video sharing,
general security/surveillance, etc. The “How to Use” chapter suggests ways to best
utilize the Network Camera and ensure proper operations. For the creative and
professional develope rs, the "URL Commands of the Network Camer a" chapter serves
to be a helpful reference to customize existing homepages or integrating with the
current web server.
For paragraphs preceded by the reader should use caution to understand
completely the warnings. Ignoring the warnings may result in serious hazards or
injuries.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532

Package Contents
IP61x2
Power adapter
Camera stand
Software CD
Quick installation guide
Warranty card
Wrench
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532

Table of Contents
Before You Use This Product....................................................................2
Package Contents ....................................................................................3
Table of Contents..........................................................................................1
Installation..............................................................................................4
Hardware Installation ........................................................................... 4
To install in Ethernet..................................................................5
Software Installation ............................................................................6
Initial Access to the Network Camera.................................................... 10
Installing Plug-in .......................................................................... 10
Check Network Settings ................................................................ 11
Add Password to Prevent Unauthorized Access.................................. 11
How to Use ............................................................................................12
Authentication................................................................................... 12
Primary User’s Capabilities .................................................................. 13
Main Screen with Camera View....................................................... 13
The Configuration: .................................................................. 14
The camera view..................................................................... 14
Client Settings ............................................................................. 15
Administrator’s Capabilities ................................................................. 17
Fine-tuning for Best Performance.................................................... 17
For Best Real-time Video Images............................................... 18
Only Quality Images Will Do ..................................................... 18
Somewhere Between Real-time and Clear Images ....................... 19
Select for Motion JPEG............................................................. 19
Opening Accounts for New Users .................................................... 20
Protect Network Camera by Passwords....................................... 20
More Flexible Options for Viewers.............................................. 21
Build a Multimedia Web Attraction Site............................................. 21
Demo on Multiple Sites – Mid-scale Service................................. 21
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532

Product Demo for E-business – Large-scale Service ..................... 21
If the web space has FTP service............................................... 22
If the web space has no FTP service .......................................... 23
Build a Security Application............................................................ 25
Send Snapshots When Motion is Detected .................................. 26
Definitions in Configuration ................................................................. 28
System Parameters............................................................................ 30
User Group Administration .................................................................. 31
Edit User..................................................................................... 33
Network Settings ............................................................................... 34
General....................................................................................... 34
HTTP .......................................................................................... 35
Streaming ................................................................................... 35
DDNS & UPnP.................................................................................... 37
Mail & FTP......................................................................................... 39
SMTP.......................................................................................... 39
FTP ............................................................................................ 39
Video Codec Parameters ..................................................................... 42
Image Settings ............................................................................ 44
CCD Settings ............................................................................... 45
Audio ............................................................................................... 46
Motion Detection................................................................................ 48
Application Setup............................................................................... 50
Weekly Schedule.......................................................................... 50
Event Operation ........................................................................... 50
Sequential Operation .................................................................... 51
Naming rule of snapshot file........................................................... 52
Viewing System Log ........................................................................... 54
Viewing System Parameters ................................................................ 54
Factory Default.................................................................................. 54
Appendix ...............................................................................................55
A. Troubleshooting ............................................................................. 55
C. URL commands of Network Camera .................................................. 59
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532

Overview..................................................................................... 59
Style convention........................................................................... 59
General CGI URL syntax and parameters ......................................... 60
Get server parameter values.......................................................... 60
Set server parameter values .......................................................... 62
Available parameters on the server ................................................. 63
Application page CGI command ...................................................... 74
Drive the digital output ................................................................. 77
Query status of the digital input ..................................................... 78
Query status of the digital output.................................................... 79
Capture single snapshot ................................................................ 80
Account management......................................................................... 80
System logs................................................................................. 82
Configuration file.......................................................................... 82
System Information...................................................................... 83
D. Technical Specifications................................................................... 85
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC).................................................6
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532
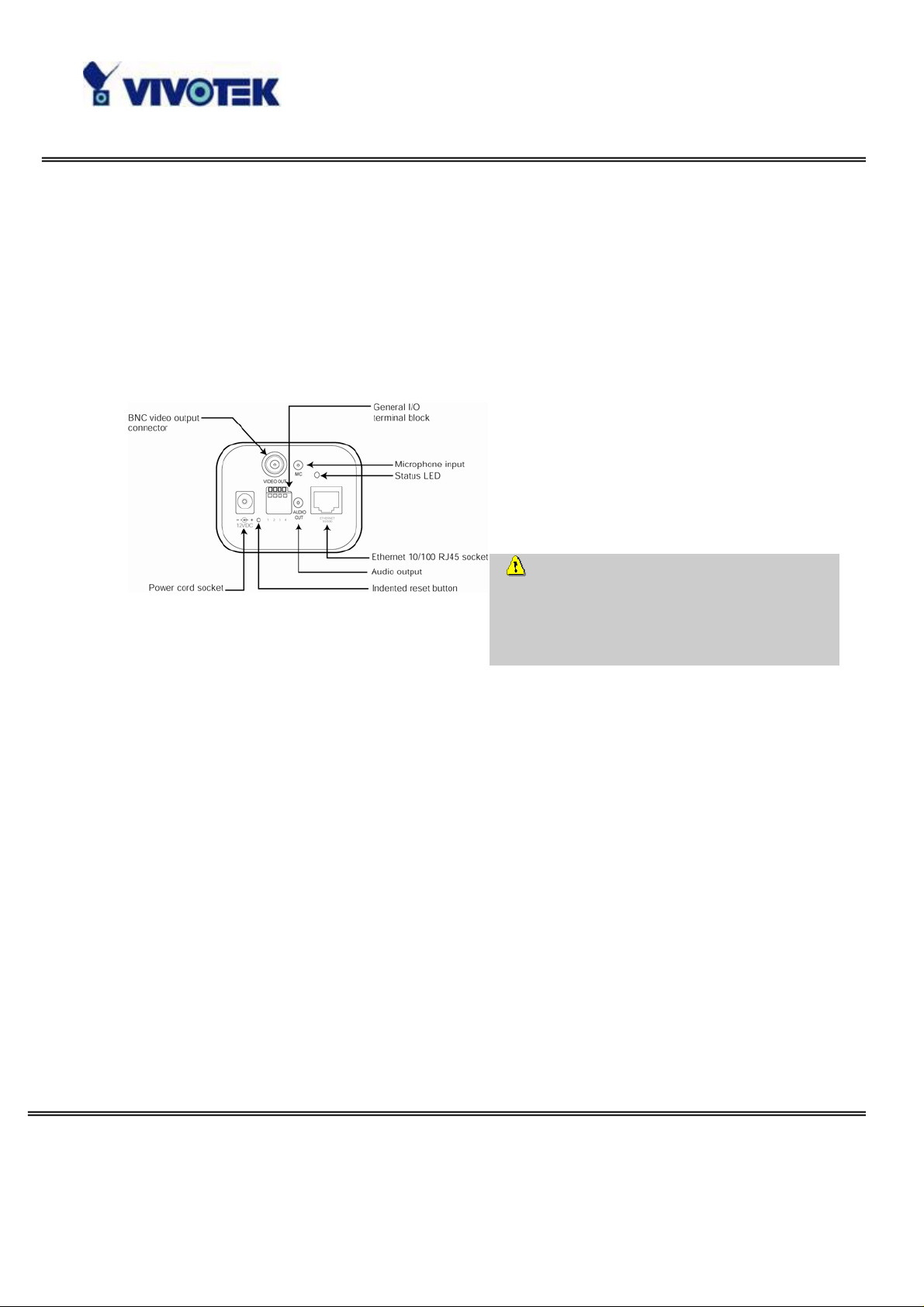
Installation
Hardware Installation
Please verify that your product
package contains all the accessories
listed in the foregoing Package
Contents. Depending on the user’s
application, an Ethernet cable may be
needed. The Ethernet cable should
meet the specs of UTP Category 5 and
not exceed 100 meters in length.
Connect the power adapter jack to
the Network Camera before plugging in
to the power socket. This will reduce
the risk of accidental electric shock.
Upon powering up, the device runs through a self-test procedure and the front LEDs
will blink between green and red for a few times. If self-test passes, the LEDs will shut
off and the Network Camera will be on stand-by and ready for software installation. If
self-test fails the red LED will blink several times. Refer to Appendix A for
troubleshooting.
The Network Camera will first detect Ethernet. If it does not connect to Ethernet, the
Network Camera will try WLAN. During the searching and connecting process to the
wireless access point or station, the LED of the Network Camera will keep red. Until
the Network Camera is connected to the other wireless device, the LED will become
green and flash. Operating in either network mode, the green L ED will flash every
second as heartbeat to indicate alive.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532

To install in Ethernet
Make sure the Ethernet is firmly connected to a switch hub. After attaching the
Ethernet cable plug in the power adapter . If the LED turns out to be steady green after
self-test, go to next paragraph “Software Installation” . If the Ethernet is not available,
the Network Camera will switch to wireless LAN mode.
The Network Camera provides a general I/O terminal block with one digital input and
one relay switch for device control. Pin 3 and Pin 4 can be connected to an external
sensor device and the state of voltage can be monitored from the initial state 'LOW'.
The relay switches Pin 1 and Pin 2 can be used to turn on or off an external device.
Consult with the dealer of the peripherals for correct installation.
1 SW_COMMON OUTPUT (open from SW_OPEN at initial state)
(close with SW_OPEN when set DO to ON)
2 SW_NOPEN OUTPUT (Max. 1A, 24VDC or 0.5A, 125VAC)
3 DI+ INPUT (Max. 50mA, 12VDC)
4 DI- INPUT (Initial state of DI is low)
The Network Camera also provides the auto iris lens connector . If the auto iris lens is
used, AES option in CCD settings must be turned OFF. And you also have to select
VIDEO drive or DC drive lens by select correct iris mode in CCD settings. The pin
assignment of the auto iris lens connector is as follows.
Video Drive DC Drive
1. Ground, Shield 1. Driver -
2. Not used 2. Driver +
3. Video signal 3. Damp +
4. Power source 4. Damp -
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532

Software Installation
In this manual, "User" refers to whoever has access to the Network Camera, and
"Administrator" refers to the person who can configure the Network Camera and
grant user access to the camera.
At the end of the hardware installation, the Administrator must place the product
software CD into the CD-ROM drive of the PC running in MS Wi ndows. An auto-run
program will pop up (If the program is not on auto-run, go to the root directory of the
software CD and click on “autorun.exe”).
Click on “Software Utility” item, after the window contains changed, click on
“Installation Wizard” to run Vivotek’s installation program.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532

Upon Installation Wizard’s start up, a searching box will pop up. This program
searches for Vivotek’s product on the same LAN:
After searching, Vivotek Video Servers or
Network Cameras will be located by the
Installation Wizard. There may be several
entries shown in the window. The
Administrator may differentiate the
Network Cameras with the serial number.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532
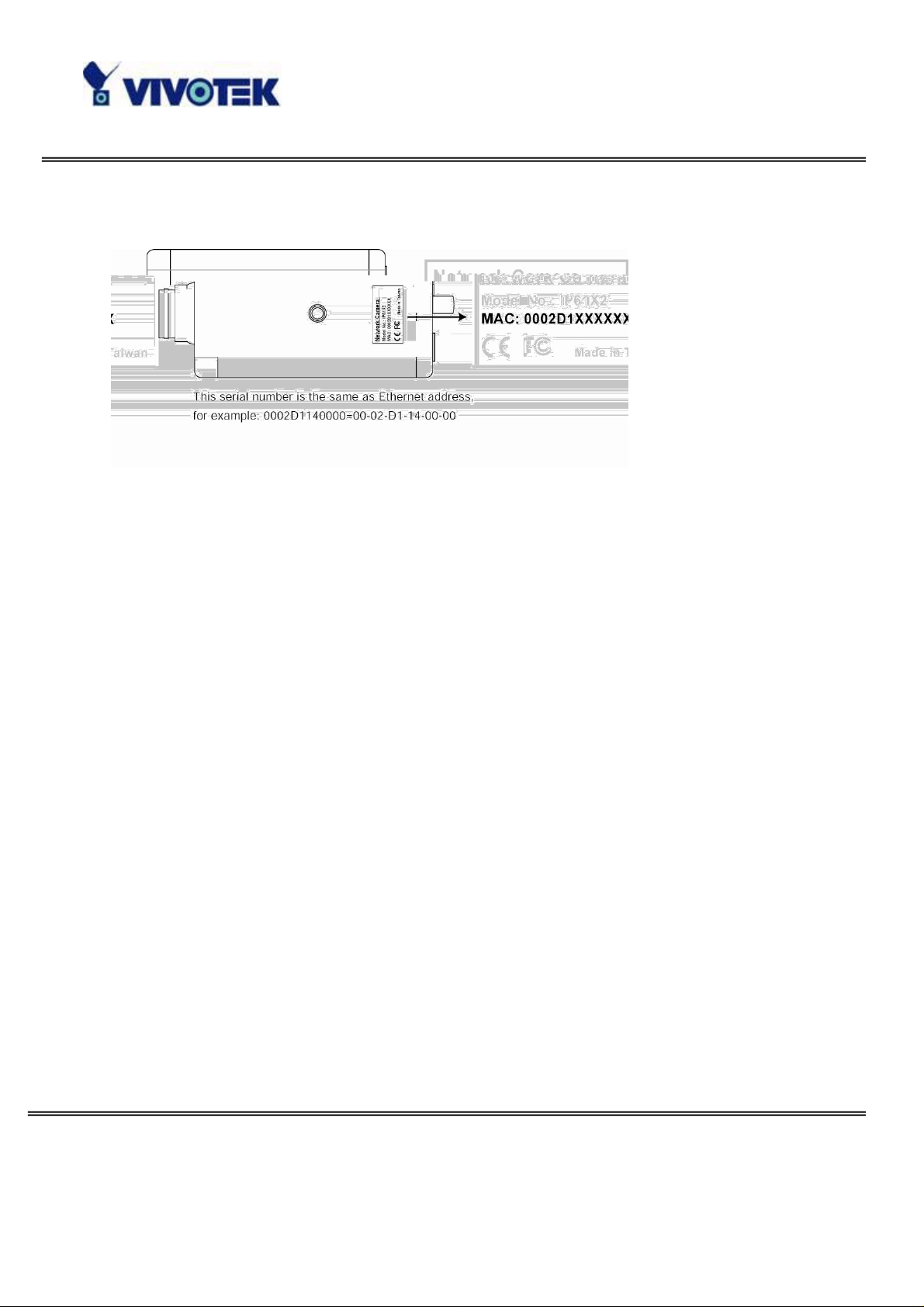
For the series number in the “Serial Number” field, please check the label on th e
bottom of the camera.
The IP addresses shown in the "Current IP Address" field reflect those on the local
network. They may be from the DHCP server. If there is no DHCP server, the
camera will try to find a free IP address (this takes from 15 second to 3 minutes,
depending on the LAN status). The method of finding IP address is seeking from
192.168.0.99, to 192.168.0.254. If any o f the address in side thi s range is free, the
Network Camera will be assigned to this IP address, and its subnet mask would be
255.255.255.0. If none of the addresses is free, the Network Camera will try the
range from 192.168.0.2 to 192.168.0.98. After an IP address is assigned to the
camera, the “Activity” status LED blinks.
The Vivotek’s new UPnP function will always assign an IP address for the Network
Camera. The Administrator can click on button “Link to selected device” to connect
the I.E. to the camera.
If the camera is not on the IP installer list, click on the “Search” button to search for
the camera on the LAN.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532
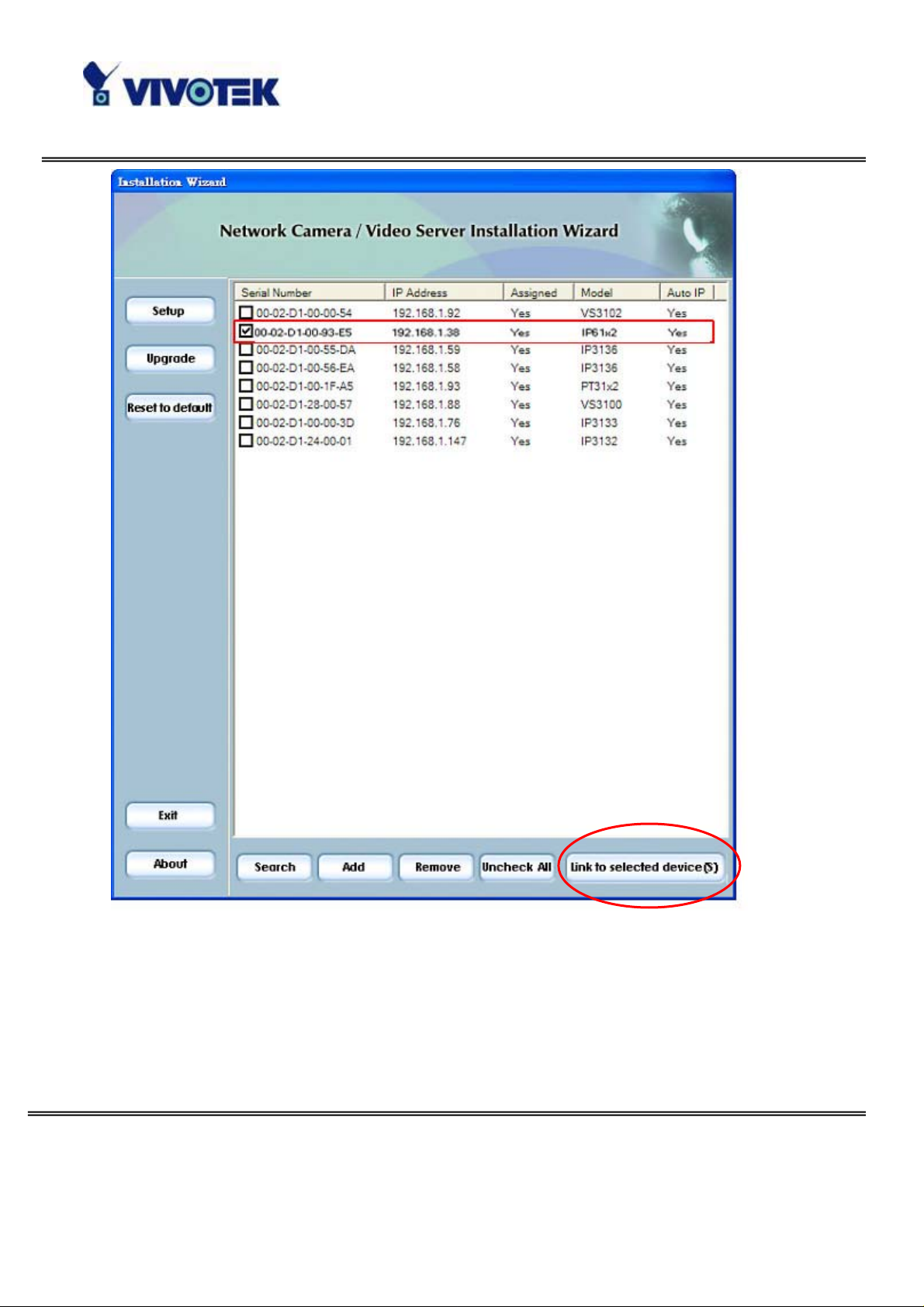
For more detailed usage of the Installation Wizard, please refer to the user’s manual
of the Installation Wizard.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532
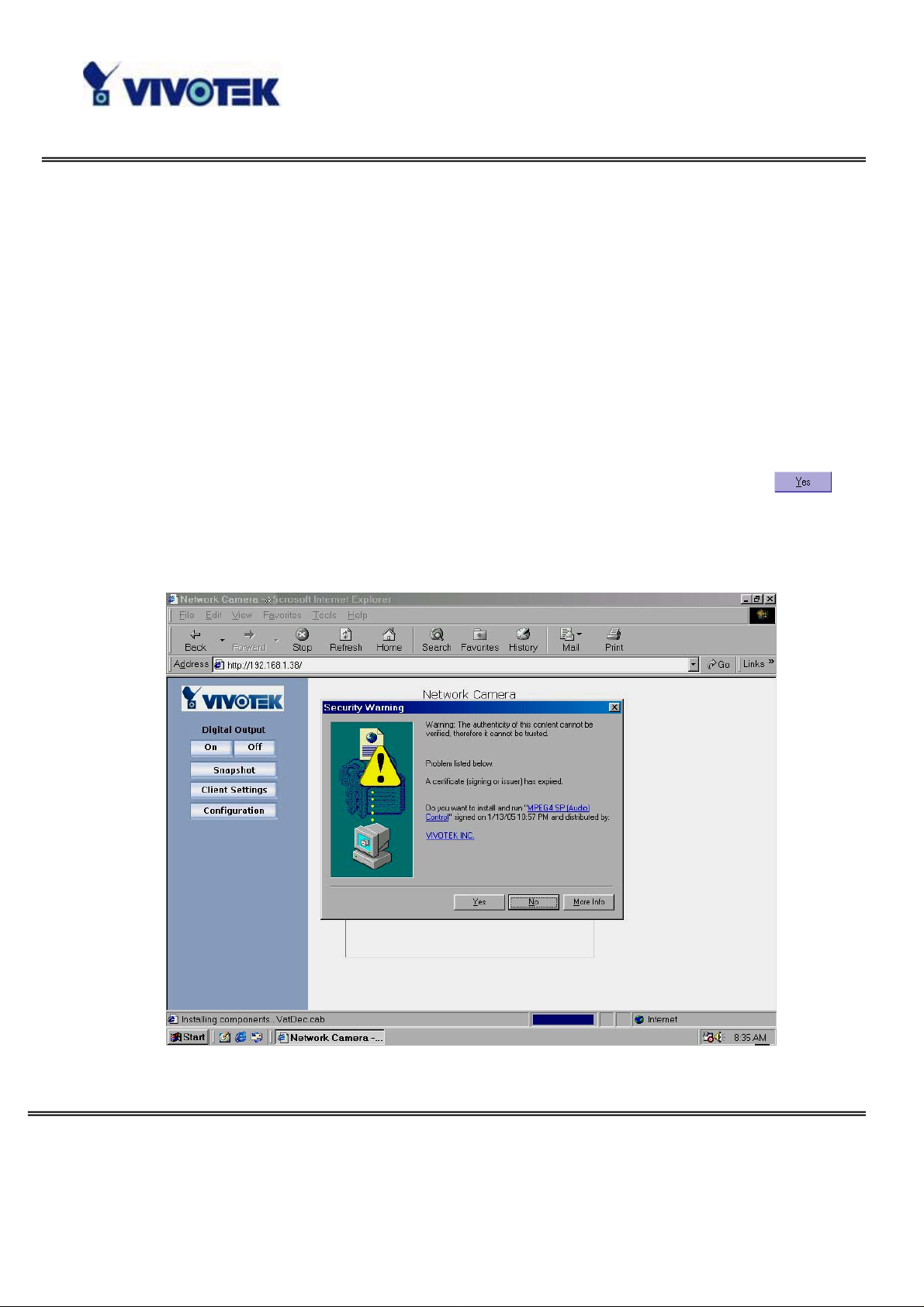
Initial Access to the Network Camera
Installing Plug-in
For the initial access to the Network Camera in Windows, the web browser may
prompt for permission to install a new plug-in for the Network Camera after a period
of time of downloading. Permission request depends on the Internet security settings
of the user’s PC or notebook. If the highest security level is set, the computer may
prohibit any installation and execution attempt. This plug-in has been registered for
certificate and is used to displ ay the video in the brows er. Users may click on
to proceed. If the web browser does not allow the user to continue to install, check
the Internet security option and lower the security levels or contact your IT or
networking supervisor for help.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532

Check Network Settings
The Network Camera can be connected either before or immediately after software
installation onto the Local Area Network. The Administrator should complete the
network settings on the configuration page, including the correct subnet mask and IP
address of gateway and DNS. Ask your network administrator or Internet service
provider for the detail information. By default the Network Camera requires the
Administrator to run installation every time it reboots. If the network settings are to
remain unchanged, disable the Install option. Refer to “Network settings” on the
System Configuration page for details. If any setting is entered incorrectly and cannot
proceed to setting up the Network Camera, restore the factory settings following the
steps in the “Troubleshooting” chapter of the Appendix.
Add Password to Prevent Unauthorized Access
The default Administrator’s password is blank and the Network Camera initially will
not ask for any password. The Administrator should immediately implement a new
password as a matter of prudent security practice. Once the Administrator’s
password is saved, the Network Camera will ask for the user’s name and password
before each access. The Administrator can set up a maximum of twenty (20) user
accounts. Each user can access the Network Camera except to perform system
configuration. Some critical functions are exclusive for the Administrator, such as
system configuration, user administration, and software upgrades. The user name for
the Administrator is permanently assigned as “root” . Once the password is changed,
the browser will display an authentication window to ask for the new password. Once
the password is set, there is no provision to recover the Administrator’s
password. The only option is to restore to the original factory default
settings.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532
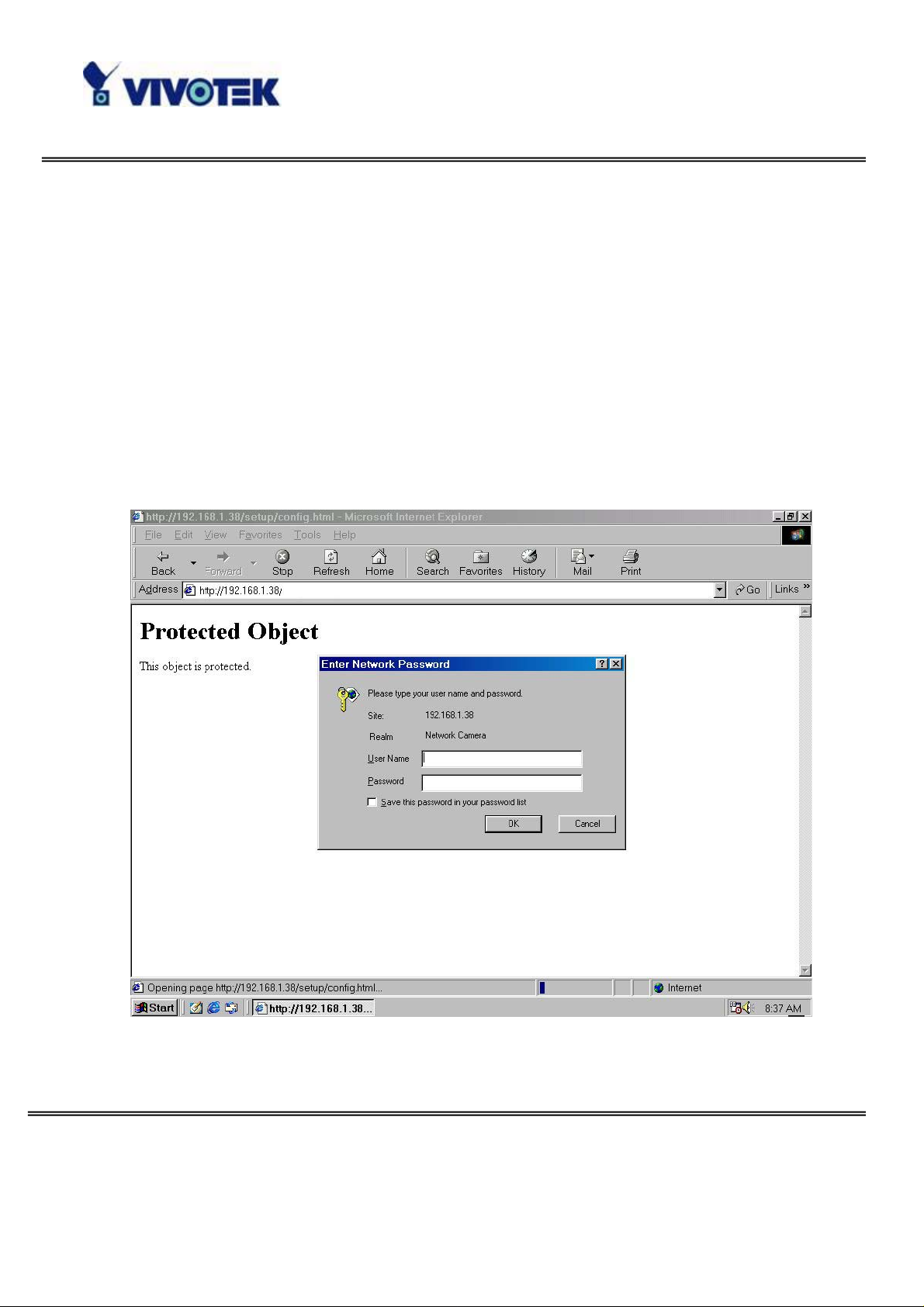
How to Use
Authentication
After opening the web browser and typing in the URL of the Network Camera, a
dialogue window pops up to request a username and password.
The foreground is the login window and the background shows the message if
authentication fails. The user may check the option box to save the password for
future convenience.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532
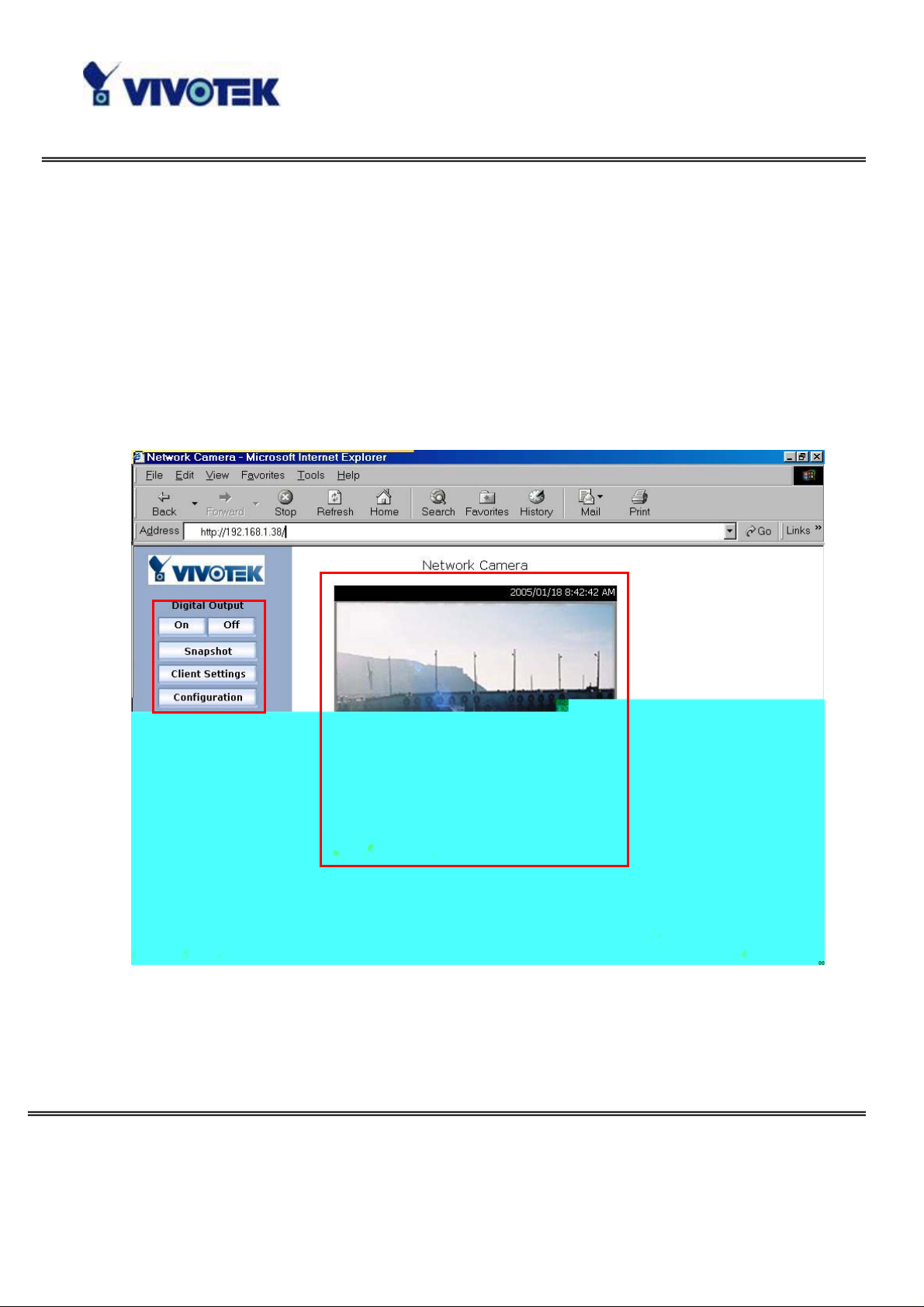
Primary User’s Capabilities
Main Screen with Camera View
The main page layout has two parts:
Configuration functions: The camera can be configured using these user
interfaces.
Camera View: What the camera sees.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532
The Configuration:
“Digital Output”
Clicking on the “On” or “Off” b utton turns the digital output to either on or off
status.
“Snapshot”
Clicking on the “Snapshot” can get a JPEG format image of the current camera view
in another window.
“Client Settings”
Clicking on this button links you to the client setting page, please check the
following session for more details.
“Configuration” Only the Administrator can access camera configurations.
The camera view
The information bar at the top of the camera view shows the assigned caption and
the current date/time. The information bar at the bottom of the camera view shows
the current streaming mode and audio transmission mode. You can push/toggle
the talk button to talk to the remote server . The volume of speaker and microphone
can also be adjusted.
Digital zoom
Talk button
Speaker volume
Microphone volume
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532
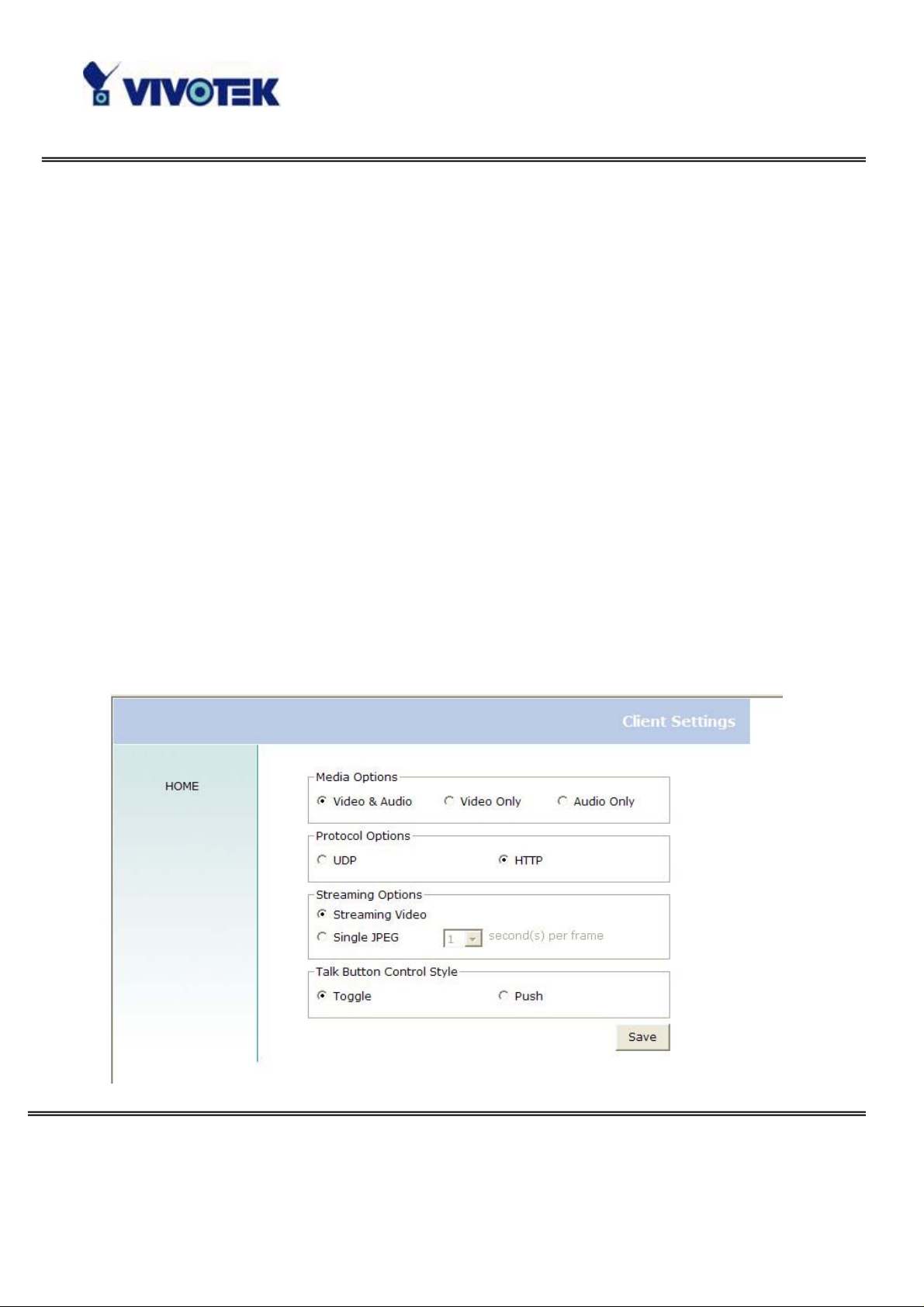
Client Settings
There are four settings for the client side.
Media Options - For the User to determine whether to receive video, audio or
both.
Protocol Options – Which allows choosing on connection protocol between client
and server. There are two protocol choices to optimize your usage – UDP and HTTP.
The UDP protocol allows for more real-time au dio and video streams. However , some
packets may be lost due to network burst traffic and images may be obscured.
The HTTP protocol must be selected if the network is protected by a firewall which
allows only HTTP Port (80) to be opened. If there is no restriction, UDP protocol is
recommended. Generally speaking, the client’s choice will be in the order of UDP →
HTTP. After the Network Camera is connected successfully, “Protocol Options” will
indicate the selected protocol. The selected protocol will be recorded in the user's PC
and will be used for the next connection. If the network environment is changed, or
the user wants to let the web browser to detect again, manually select the UDP
protocol and save, then return to HOME to connect to the Network Camera.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532

Streaming Options – For users to select the video streaming types. Select
“Streaming Video” options, the video connection will keep alive to enable you to see
smooth video, while “Single JPEG” options will let you see the video in JPEG format
by client periodic updat e the JPEG image from serv er according to the “Frame rate”
settings.
Talk Button Control Style – For the User to determine whether to “click once and
talk” or “push to talk”.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532
Administrator’s Capabilities
Fine-tuning for Best Performance
There are a few choices the Administrator is allowed to maximize the capabilities of
the Network Camera. Best performance generally equates to the fastest image
refresh rate with the best video quality, and at the lowest network bandwidth as
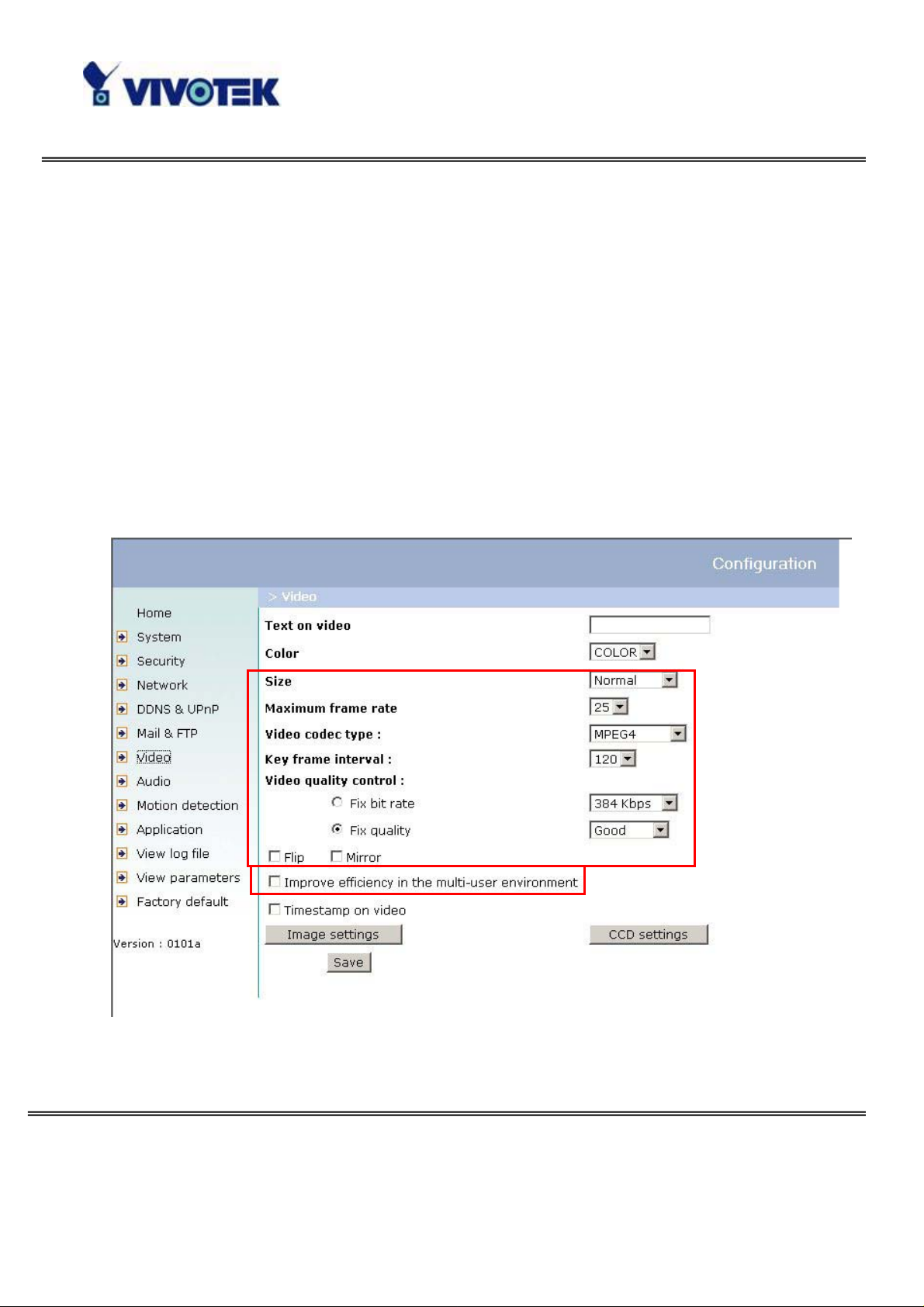
possible. The six factors, “Size”, “Maximum frame rate”, “ Video codec type”, “Key
frame interval”, “Fix bit rate” , and “Fix quality” on the Video Configuration page, are
correlative to allow for achieving the best performance possible.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532

For Best Real-time Video Images
To achieve good real-time visual effect, the network bandwidth should be large
enough to allow a transmission rate of greater than 20 image fr ames per second. If
the broadband network is over 1 Mbps, set the “Fix bit rate” to 1000Kbps or
1200Kbps, or set “Fix quality” at the highest quality. The maximum frame r ate is 25
fps in a 50Hz system and 30 fps in a 60Hz system. If your network bandwidth is more
than 384Kbps, you can fix the bit rate according to your bandwidth and set the
maximum frame rate to 25 fps or 30 fps. If you are shooting fast-moving images, you
may want to slow the maximum frame rate down to 20 fps in order to lower the rate
of data transmission. This allows for better video quality and the human eyes cannot
readily detect the differences between those of 20, 25, or 30 frames per second. If
your network bandwidth is below 384 Kbps, set the “Fix bit rate” according to your
bandwidth and try to get the best performance by fine-tuning with the “ Maximum
frame rate”. In a slo w network, greater frame rate results in blur images. Another
work-around is to choose “Half” in the “Size” option for better images, or “Halfx2” for
a larger image view. Video quality performance will vary somewhat due to the
number of users viewing on the network; even when the parameters have initially
been finely tuned. Performance will also suffer due to poor connectivity because of
the network’s burst constraint.
In multi-user environment, the user who has poor network performance will receive
only the key frame in MPEG4 format. T ry to reduce the key frame interval can improve
the frame rate for poor network performance, but the penalty is the increasing of
network traffic. If the server is running on the Internet, select the “improve efficiency
in the multi-user environment” will improve the efficiency in the multi-user
environment.
Only Quality Images Will Do
T o have the best video quality , you should set “Fix quality” at “Detailed” or “Excellent”
and adjust the “Maximum frame rate” to match your network’s bandwidth. If your
network is slow and you receive “broken” pictures, go to the HTTP protocol in
“Connection type” and choose a more appropriate mode of transmission. The images
may suffer a time delay due to a slower connection.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532

Somewhere Between Real-time and Clear Images
If you have a broadband network, set “Fix quality” at ”Normal” or better, rather than
setting “Fix bit rate” . Y ou can also fix the bandwidth according to your actual network
speed and adjust the frame rate. Start from 30 fps down for best results but not
below 15 fps. If the image qualities are not improved, select a lower bandwidth
setting.
Select for Motion JPEG
The Network Camera is a camera with dual video codec, they’re MPEG4 and MJ PEG.
If MJPEG is selected, the camera will transmit video data in JPEG format. Therefore,
it requires higher bandwidth to view smooth video. General speaking, each normal
sized JPEG image would be 3k~12k bytes, depending on the selected vid eo quality
and contents. Together with the frame rate selected, the administrator can control
the bandwidth of each connection.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532
Opening Accounts for New Users
1
2
3
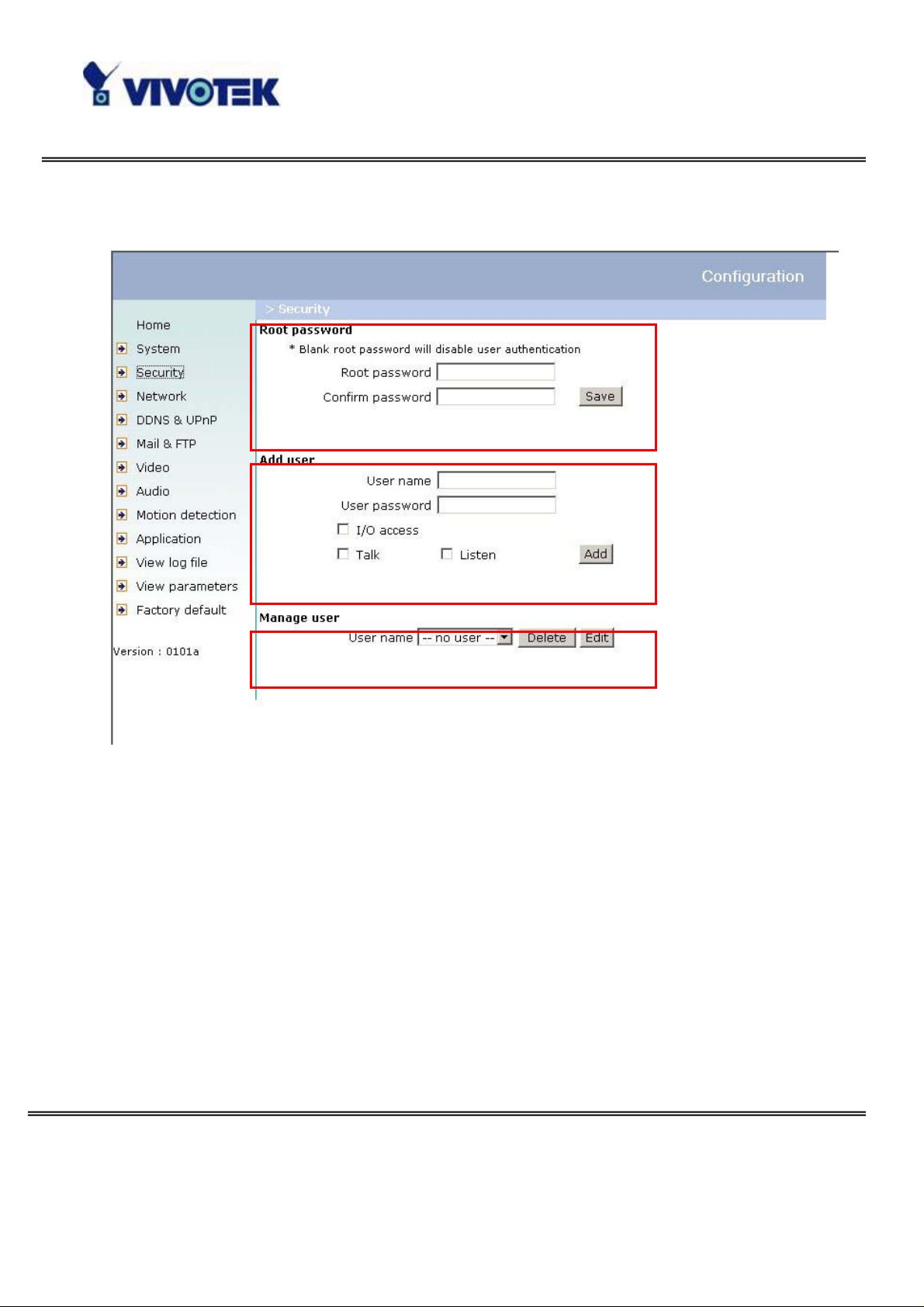
Protect Network Camera by Passwords
The Network Camera is shipped without any password by default. That means
everyone can access the Network Camera including the configuration as long as the
IP address is known. It is necessary to assign a password if the Network Camera is
intended to be accessed by others. T ype a new word twice in the first field to enable
protection. This password is used to identify the administrator. Then add an account
with user name and password for your friends in the second field. The Network
Camera can provide twenty accounts for your valuable customers or friends. Each
account identifies the access right rather than the real visitor. That allows multiple
visitors share the same account of different level. Each accou nt has four kinds of
privileges, which can be set individually . The “I/O access” privilege permits t he user
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532

to access DI/DO of the server. The “Talk” privilege permits the user to send speech
to the Network Camera. The “Listen” privilege permits the user to listen sounds from
the server. You may edit or delete some users from the third field.
More Flexible Options for Viewers
If you want to have a guest account for viewers only, you just need to add a user
without password and disable all the privileges. Share the account to your friends to
access your camera.
Build a Multimedia Web Attraction Site
Demo on Multiple Sites – Mid-scale Service
The Network Camera can allow ten visitors on-line simultaneously. After Installation,
focus the Network Camera on any object you wish to share, and tell the visitors to
type in the web browser address. Caution: You may want to maintain your visitor’s list
in the security configuration page to block out unexpected visitors.
Product Demo for E-business – Large-scale Service
If the number of visitors has exceeded the limit, the Network Camera can allow the
"overload" view ers to see the snapsh ots in JPEG mode, o n the homepage. Thes e are
still images and will be refreshed periodically and automatically.
1. Click on “Client Settings” on the homepage,
2. Select “Single JPEG” in “Streaming Options”,
3. Set the snapshot interval to refresh the still image automatically. The longer the
snapshot interval, the better the snapshot mode works for multiple viewers.
If you want to expand to allow in more viewers, the host server should be able to
handle large network traffic, which must handle the picture refreshing from the
Network Camera.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532
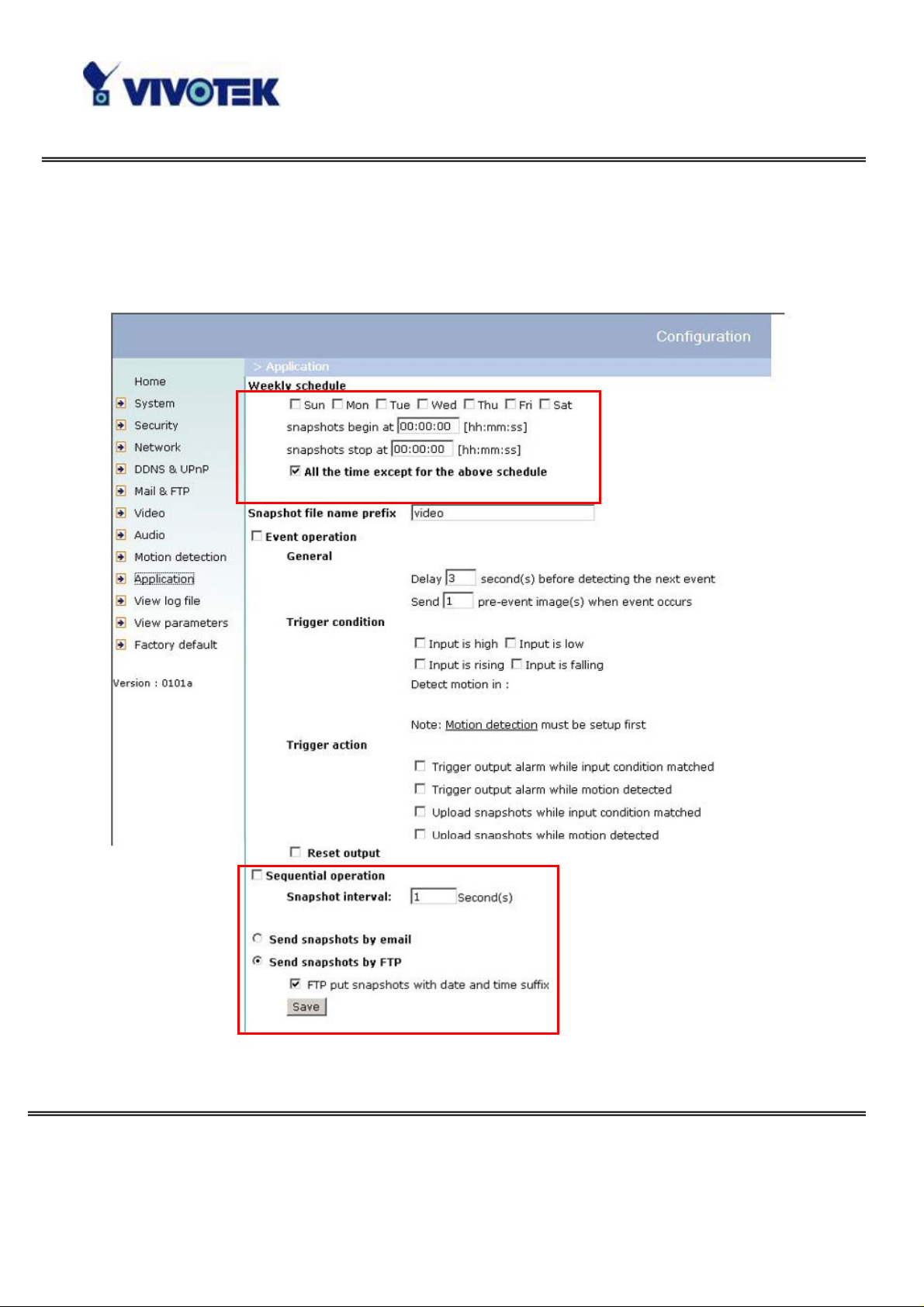
If the web space has FTP service
Set the Network Camera up as an FTP client to upload the pictures. The access to the
Network Camera will be independent of the number of viewers and the picture quality
will remain constant.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532

1. Click on “Configuration” on the homepage,
2. Click on “Mail & FTP” in the left column,
3. Fill in the FTP related settings including server, server port, user name and
password, as well as the upload path if it is specified by the web space,
4. Click on “Save”,
5. Click on “Application” in the left column,
6. Select the day or days of the week in “Weekly schedule” you want to upload the
pictures,
7. Select “Sequential operation” and set the interval,
8. Unselect “FTP put snapshots with date and time suffix” as the upload method and
click on “Save”,
9. The image file uploaded to the web space is named “video.jpg” . Check if the file is
successfully uploaded to the correct folder,
10. Prepare a homepage with the embedded image reference to the image file
uploaded via FTP in advance.
If the web space has no FTP service
An auto-refresh homepage can be used to periodically poll the newest image from the
Network Camera. It is most efficient if using a free web space provider as the FTP
service may be limiting.
1. Prepare an auto-refresh homepage as the following example. The URL of image is
http://“IP address of the Network Camera”/cgi-bin/video.jpg. Modify the IP address
according to your Network Camera. Define the refresh interval according to your
network bandwidth for best result. If the refresh rate is too fast and there is a large
number of visitors, this may overload the Network Camera and slows the response.
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532
Example of an auto-refresh web page:
<html>
<head>
<title>Example - auto refresh</title>
</head>
<body>
<p align=left>
<font size="7" face="Comic Sans MS" color="#FF0000">
MiniAVServer Demo
</font>
</p>
<p align=left>
<!-- Begin of scripts to auto refresh the image. Change the IP address in the
image URL and refreshrate if necessary. //-->
<script language=javascript>
var image="http://192.168.0.203/cgi-bin/video.jpg"; //IMAGE URL
var refreshrate=5; //SECONDS BETWEEN REFRESH
var imgwidth=352; //IMAGE WIDTH
var imgheight=240; //IMAGE HEIGHT
function refresh(){
document.images["pic"].src=image+"?"+new Date();
setTimeout('refresh()', refreshrate*1000);}
document.write('<img src="'+image+'" height="'+imgheight+'"
width="'+imgwidth+'" name="pic">');
if(document.images)window.onload=refresh;
</script>
<!-- End of scripts to auto refresh the image. //-->
</p>
</body>
</html>
www.vivotek.com
T: 886-2-82455282
F: 886-2-82455532
 Loading...
Loading...