Page 1

Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect Devices
NovoConnect is a wireless presentation and collaboration system designed to support highly
interactive and collaborative meetings or classroom learning activities. Meeting participants,
instructors, teachers and students can interact and share digital content via their PCs, tablets,
Chromebooks and smartphones — a true BYOD device. These include the NovoCast, NovoPro,
and NovoEnterprise. For simplicity’s sake, the diagrams and examples shown are for the NovoPro
device.
To fully take advantage of NovoConnect’s capabilities, it should be properly deployed in a school
or a corporate network. Some aspects should be carefully considered and planned, for example,
Wi-Fi interference and channel selection, intranet firewall, Bonjour protocol support across
different subnets/VLANs, Quality of Service and device management. In this whitepaper, we are
going to illustrate these points one by one to facilitate a successful NovoConnect deployment in
your network.
1. Network Connection
NovoConnect has three network connection types, Ethernet, Wi-Fi Client, and Wi-Fi Hotspot.
A) Ethernet – NovoConnect can be plugged into your Ethernet via its RJ45 port. Namely,
you can connect NovoConnect to your organization’s backbone network. It is
recommended to use an Ethernet connection (when possible) since it gives you better
robustness and higher performance.
B) Wi-Fi – NovoConnect’s built-in 802.11ac Wi-Fi operates at dual bands (2.4/5GHz).
With its 2T2R antenna, it can achieve a maximum bandwidth of 300Mbps1 (NovoCast
currently only support 2.4GHz and has a 1T1R antenna). This high-performance Wi-Fi
module can operate in two modes.
a) Client Mode – NovoConnect can be connected to your organization’s Wi-Fi
network via its built-in Wi-Fi module.
b) Hotspot Mode – NovoConnect can creates its own Wi-Fi network, allowing
users to connect their mobile devices to this ad hoc network.
The following table summarizes their feature differences and typical usage.
1
300Mbps is the maximum value while the actual bandwidth may vary depending on operating environment.
V1.0 Page 1 of 18
Page 2
Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
Ethernet/Wi-Fi Client
Mode
Wi-Fi Hotspot Mode
Number of Users Allowed 64 (8 for NovoCast) 8
Internet/Intranet Access Yes By default no, but can
enable this feature by
enabling LAN-Wi-Fi
Hotspot routing)
Typical Usage Pre-configured for School or
Corporation
Quick setup for smallgroup meetings
It is worth mentioning that Ethernet and Wi-Fi connections can coexist on NovoConnect devices.
Namely, you can configure NovoConnect devices in Ethernet and Wi-Fi Client mode, or in
Ethernet and Wi-Fi Hotspot mode.
1.1. Ethernet
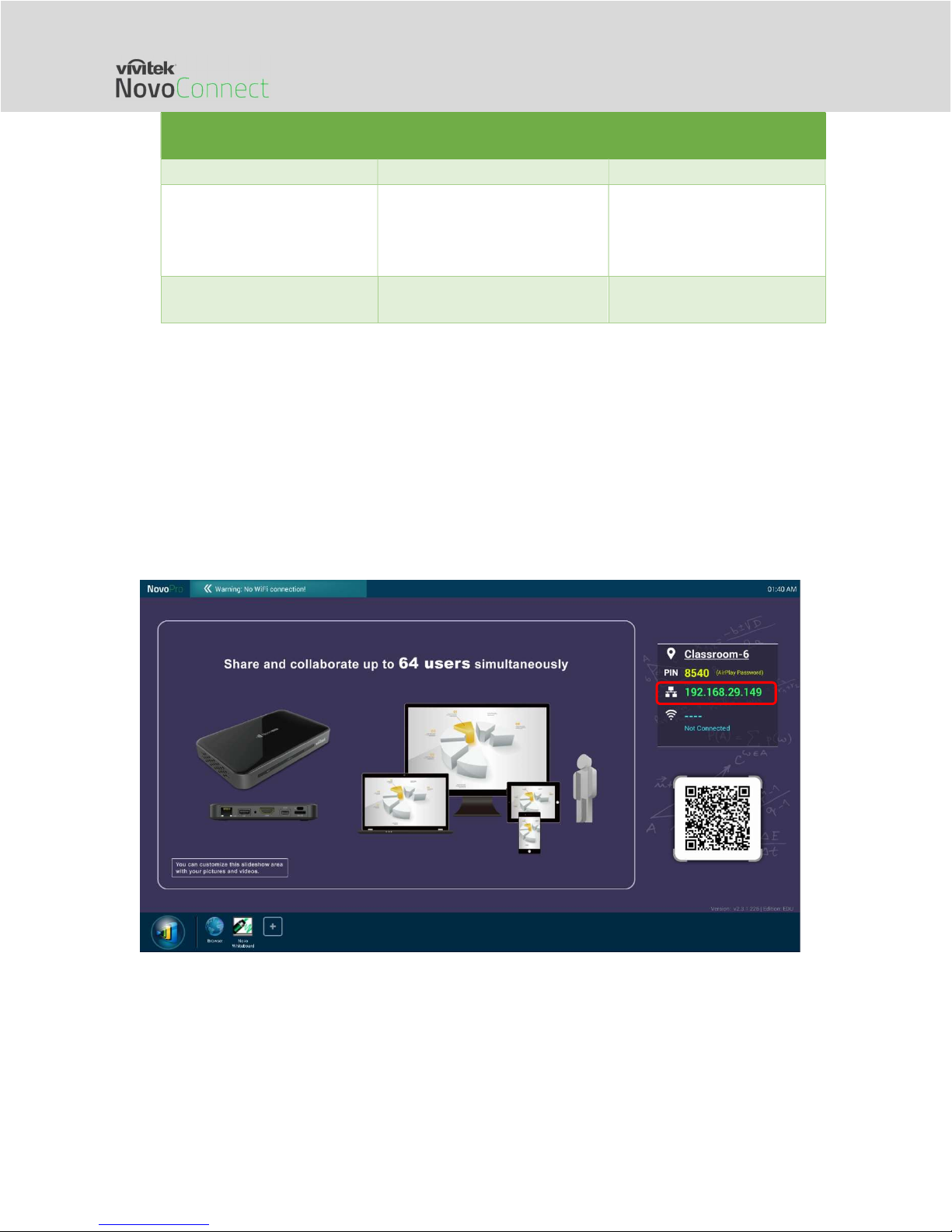
The following homescreen shows the NovoConnect device is in Ethernet mode, where its
Ethernet IP Address is highlighted in red.
When connecting to a wired network, NovoConnect devices support both DHCP and Static IP
connection types.
DHCP: NovoConnect device obtains its IP address from the DHCP server on the network.
Static IP: NovoConnect device is assigned a fixed IP address manually.
V1.0 Page 2 of 18
Page 3
Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
1 2
“DHCP” is the default connection type. However, “Static IP” might be more preferable as it makes
remote management much easier.
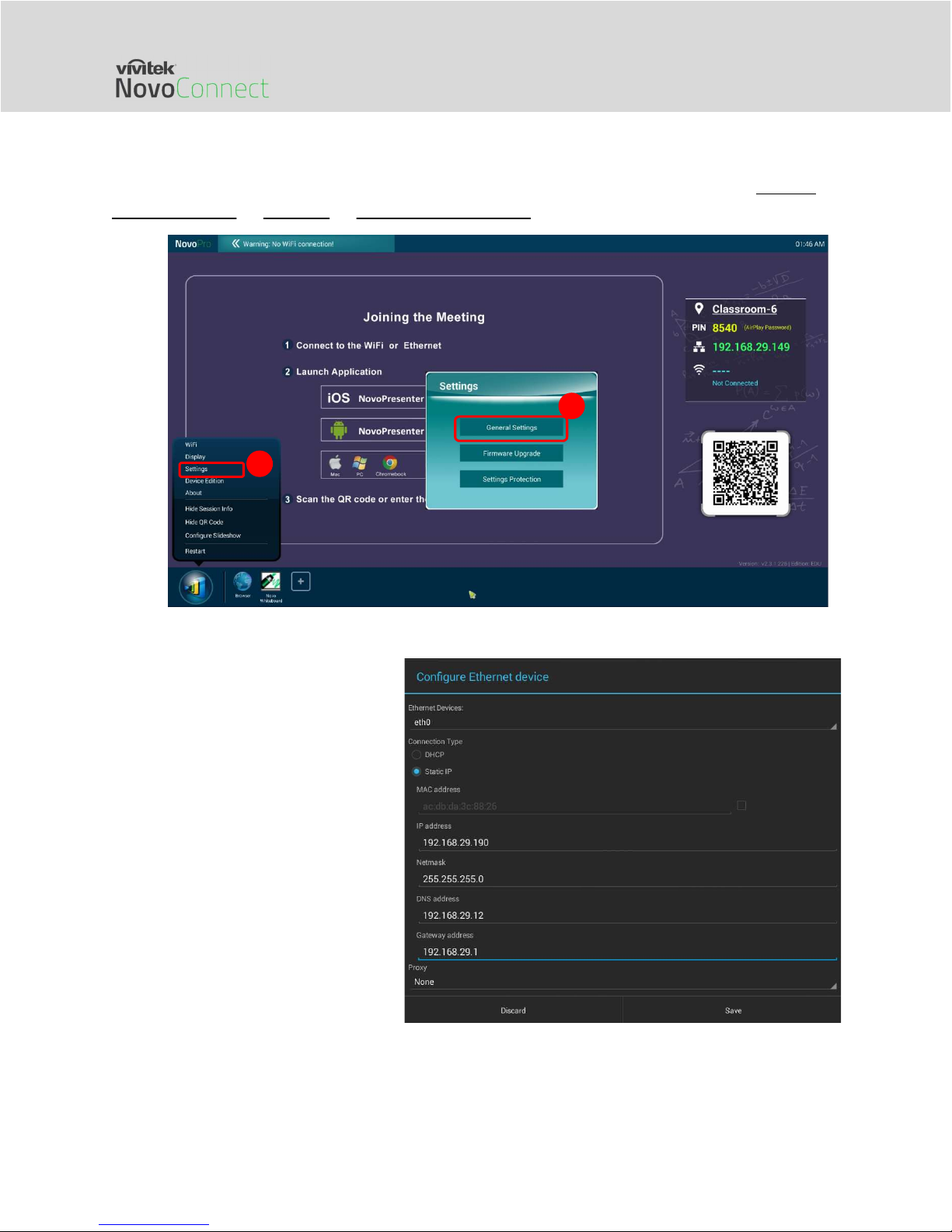
The following diagram illustrates how to select one of these two connection types. (Settings
General Settings Ethernet Ethernet Configuration).
To set up “Static IP” properly, you
need to have the following
information, as shown in the diagram
on the right.
An unallocated IP address;
Netmask;
DNS address;
Gateway address.
V1.0 Page 3 of 18
Page 4
Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
1
2
1.2. Wi-Fi Client Mode
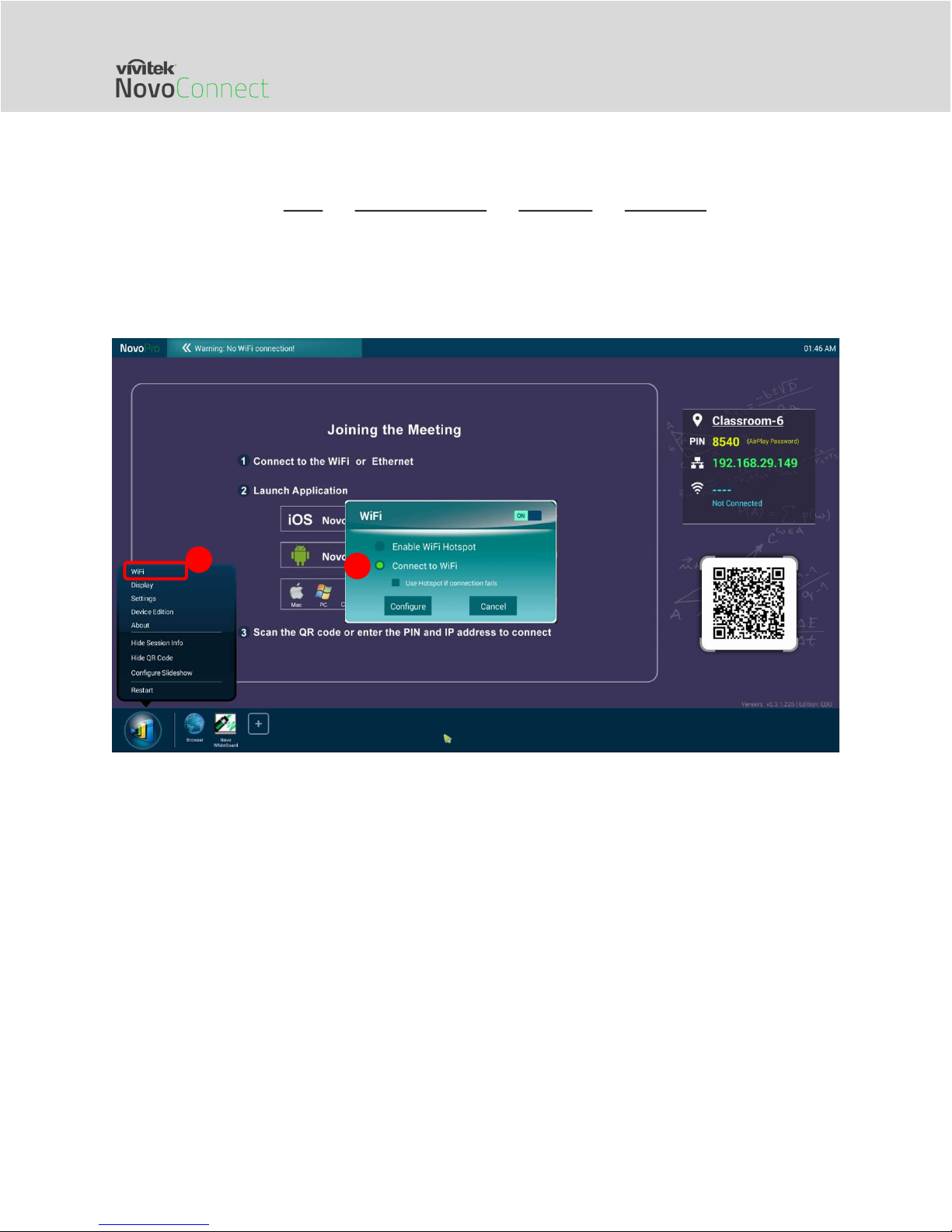
In this mode, the NovoConnect device functions as a client to join an existing Wi-Fi network. As
illustrated in the following diagram, to set up the Wi-Fi connection, on the NovoConnect device
homescreen, click on Wi-Fi Connect to Wi-Fi Configure Wi-Fi (ON). Then select the
desired Wi-Fi SSID (the name associated with the Wi-Fi network) and enter the proper credentials
when necessary.
You may notice that you have the choice of using “DHCP” or “Static IP” in the connection dialog,
which is exactly the same as an Ethernet connection.
Logging into a Wi-Fi Network via Captive Portal: Some Wi-Fi networks are equipped with a
captive portal, which requires users to log in via a web browser before they can access the
Internet. When a NovoConnect device is connected to this type of network, users can follow
the following steps:
A. Follow the above configuration steps to connect to the organization’s Wi-Fi network;
B. After the Wi-Fi is connected, click on “Browser” on the home screen (see the picture
below);
C. Open this web browser and you will be prompted for login credentials.
D. Enter the proper username and password, and you will be connected to the network;
E. Click “Return Back” on the homescreen to return to the NovoConnect device’s App main
interface.
V1.0 Page 4 of 18
Page 5
Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
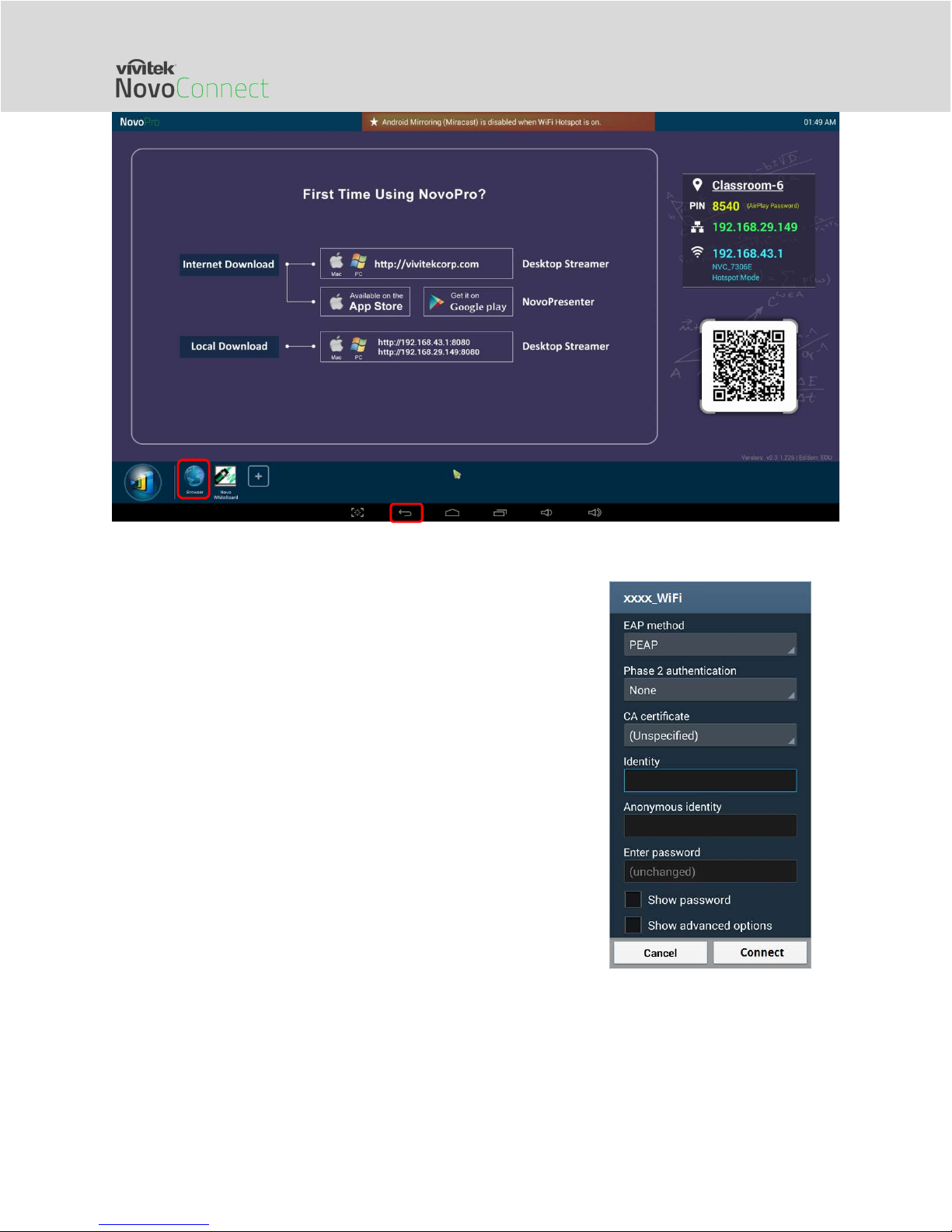
Logging into a Wi-Fi Network with 802.1x Authentication:
When you connect to a Wi-Fi network with 802.1x
authentication (for example, radius server), you will need to
enter the following fields to set up the connection properly:
Network SSID Your network
Security 802.1x Enterprise
Choose the correct settings for
o EAP method
o Phase 2 authentication
Identity Your username (such as
DOMAIN\John.Smith )
Password Your password
Click on button “Connect” to start the connection.
1.3. Wi-Fi Hotspot Mode
A newly unpacked NovoConnect device starts up in Wi-Fi Hotspot mode, where you can start
using it without any entanglement with the network setup. The default SSID for this Wi-Fi Hotspot
V1.0 Page 5 of 18
Page 6
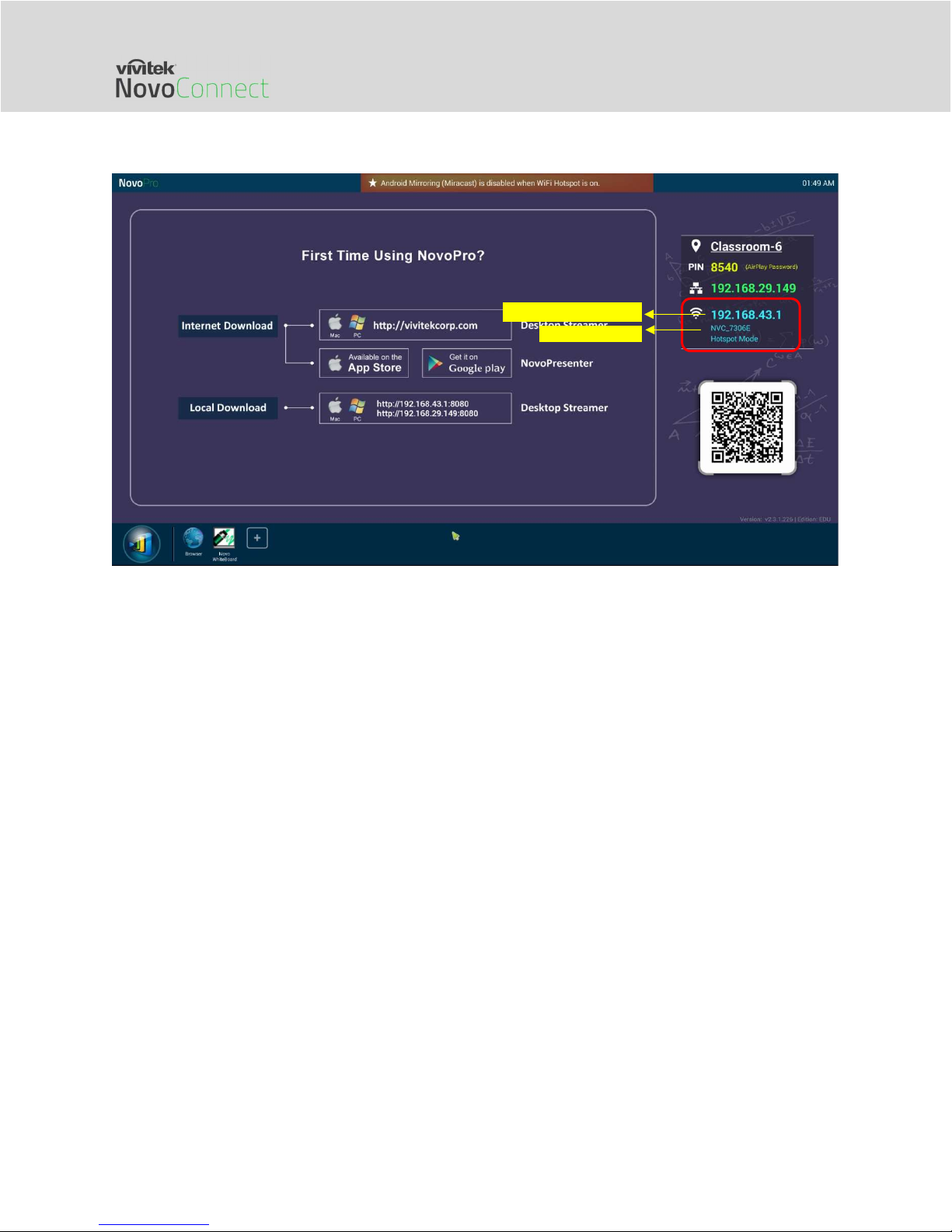
Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
Hotspot AP
SSID
is “NVC_XXXXX” (for example, “NVC_4DF8F” in the following screenshot), where “XXXXX” is a
device-generated text string.
Hotspot AP IP address
One can also configure Hotspot’s RF channel and its routing behavior with LAN. As shown in
the figure below,
You can change the RF channel to avoid unnecessary radio interference, as explained in
Section 1.4.
“Enabling LAN-Wi-Fi-Hotspot routing” gives you the option to either keep LAN and Wi-Fi
Hotspot completely isolated, or, allow Wi-Fi Hotspot to piggyback to the LAN for
Internet access.
V1.0 Page 6 of 18
Page 7

Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
1
2
In addition, you can rename the Wi-Fi Hotspot SSID and change its security settings (security
protocol and its password.) To do so, click on Settings General Settings More Tethering
& portable hotspot. Then the following “Set up Wi-Fi hotspot” window pops up to allow you to
make the necessary changes.
1.4. Wi-Fi Network Optimization
One of the most common issues users run into when using a NovoConnect device is a loss of
connection, which is likely caused by an unstable Wi-Fi connection. Maintaining a stable Wi-Fi
connection is always a challenge due to the plain fact that it is wireless, subject to noise
interference and the physical environment. To keep a good connection, you should follow some
generic Wi-Fi setup guidelines, such as
V1.0 Page 7 of 18
Page 8

Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
1) Do not place a NovoConnect device next to electric noise sources, such as an electric fan
or power supplies. Especially when you attach a NovoConnect device next to a projector
or an LCD monitor, you need to keep an eye on these potential “pollution” sources.
2) Make sure you do not place a NovoConnect device behind metal frames/bars, etc. Metal
will greatly degrade Wi-Fi signal strength.
3) NovoConnect device’s hotspot mode supports devices within 30 meters (100 feet). If
you have an external router, it is recommended to use the NovoConnect device’s Wi-Fi
client mode instead of hotspot mode.
4) Try using 5GHz band as it is more robust than 2.4GHz band.
5) Lastly, you might want to check how crowded the Wi-Fi spectrum is. Two popular Apps
can give you a very good view of the Wi-Fi spectrum.
“Wi-Fi Analyzer” on Android devices;
“InSSIDer” tool on Windows OS.
If too many Wi-Fi Access Points occupy the same RF channel, it can lead to sluggish
performance, and, disconnection if it becomes severe. The following example is a
screenshot from the “Wi-Fi Analyzer” App. As you can see, Wi-Fi channel 6 is heavily
utilized. You may want to change one or some of them to other less-crowded channels.
1.5. Dual-network Configuration
NovoConnect devices can even be set up to support dual networks:
Ethernet & Wi-Fi client mode: connect to your organization’s existing wired network and
wireless network simultaneously. This function is extremely useful for organizations with
“guest” wireless networks set up for external visitors.
Ethernet & Wi-Fi hotspot mode: connect to your organization’s wired network and run
as a Wi-Fi hotspot simultaneously. If needed, “LAN-Wi-Fi-Hotspot routing” function can
V1.0 Page 8 of 18
Page 9

Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
be enabled to allow all devices connecting to its hotspot Wi-Fi to have internet/intranet
access (via the wired Ethernet connection). You may find this configuration suitable for
meeting rooms.
Ethernet & Wi-Fi client mode
In this case, the NovoConnect device’s RJ45 port is connected to a wired EMPLOYEE network for
employees to securely access it; at the same time, the NovoConnect device’s Wi-Fi is connected
to a GUEST network to allow visitors to access it. The following graph describes such a network
setup scenario.
By doing so, the GUEST and EMPLOYEE networks are kept separate, while at the same time, the
NovoConnect device is available to both guest users and employees.
Notes on Network Security: Within a NovoConnect device, the Wi-Fi section is completely
separated from the Ethernet section, namely, there is NO network routing between these two
sections. Therefore, users connecting to the Wi-Fi section will not be able to access any resource
on the Ethernet at all, and vice versa. In short, security is not compromised in this configuration.
Ethernet & Wi-Fi hotspot mode
In this case, the NovoConnect device’s RJ45 port is connected to a wired network connecting to
the internet/intranet; at the same time, the NovoConnect device is also running in Wi-Fi hotspot
mode allowing PCs and tablets to connect to it wirelessly. The following graph describes such a
network setup scenario.
V1.0 Page 9 of 18
Page 10

Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
As described in Section 1.3, you can enable the routing between LAN and Wi-Fi Hotspot. Once
you enable this routing feature, devices on the Wi-Fi Hotspot side will be able to access intranet
or Internet resources via the LAN connection.
Notes on Network Security: before you enable this routing feature,
1) You may consult your organization’s IT administrators to avoid compromising your
network security.
2) Wi-Fi Hotspot by default is an open network. It is strongly recommended that you change
it to a secure Wi-Fi network.
2. Port Numbers and Intranet Firewall
NovoConnect devices are TCP/IP-network-based devices, and the communications between a
NovoConnect device and its client devices (e.g. laptops, tablets, etc.) are achieved through
several TCP and UDP ports. The following table summarizes all the port numbers being used by
NovoConnect devices.
V1.0 Page 10 of 18
Page 11

Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
Port
Number
80 TCP IN Port for local Desktop Streamer application download page
443 TCP OUT Port for device firmware upgrade or streaming YouTube video
8080
8443
20121 TCP IN Port to transfer commands and status reports between the
20122 TCP
20123 TCP IN Port to transfer screen image
20124 UDP
20125 TCP
20126 TCP
20127 TCP IN Port to transfer AV-streaming’s video data
Type
TCP IN Port for local Desktop Streamer application download page
Inbound (IN)/
Outbound (OUT)
IN
IN Port to send discovery message (so that the NovoConnect unit
IN
IN
Description
(need Internet access)
NovoConnect unit and users’ devices
(For example, laptops/tablets use this port to establish
“connection” to the NovoConnect unit.)
Port to enable “Remote Mouse” functionality
can be discoverable by laptops/tablets.)
Port to transfer preview image
Port to transfer AV-streaming’s command data
20128 TCP
20129 TCP IN Port to transfer Voting/Polling data
20130 TCP IN Port for video streaming service
20131 TCP
20140 TCP IN Port for mouse streaming
20141 UDP
20142 UDP OUT Port for device reporting to Remote Manager
20161 TCP IN Port for cross annotation
20162 TCP OUT Port for device home screen configuration
20192 TCP OUT Port for device home screen configuration
20193 TCP OUT Port for device firmware upgrade (used by Remote Manager)
IN
IN
IN
Port to transfer AV-streaming’s audio data
Port for file transfer service
Port for device management
To enable successful operations of a NovoConnect device, these ports should not be blocked by
your network’s firewall.
V1.0 Page 11 of 18
Page 12

Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
For NovoEnterprise, a screen-mirror application called NT LiveReceiver is available. This feature
displays content from a NovoTouch running the NT LiveScreen application. In order for this
feature to work properly, the following ports need to be open.
20200 TCP IN Port for connection on RTSP over multicast
20202 UDP OUT Port for video streaming on RTSP over multicast
20203 UDP OUT Port for video/RTCP on RTSP over multicast
20206 UDP OUT Port for audio streaming on RTSP over multicast
20207 UDP OUT Port for audio/RTCP on RTSP over multicast
20300 TCP IN/OUT Port for connection and streaming for Novo/TCP (NT LiveScreen)
3. Enabling AirPlay Mirroring Across Subnets/VLANs
NovoConnect devices supports Apple’s AirPlay, which is the native screen mirroring mechanism
for iPads, iPhones, and Mac computers. AirPlay mirroring relies on Bonjour service, which is
Apple’s implementation of “zero config” networking. Bonjour enables automatic discovery of
services on the network. However, this discovery service cannot pass through either network
subnets or VLANs. As a result, iPad devices sitting on one subnet or VLAN cannot discover the
mirroring service from a NovoConnect device sitting on another subnet or VLAN.
To make AirPlay mirroring workable across subnets/VLANs, a Bonjour proxy has to be added so
that it can take the service announcements on one subnet and announce them on the other
subnets. Bonjour service discovery uses multicast DNS (mDNS), similar to DNS.
An mDNS proxy will have multiple network interfaces, each of which connects to one
subnet/VLAN where AirPlay mirroring clients or servers reside. It does not relay traffic
between subnets/VLANs. Instead, it merely provides a lookup mechanism.
An mDNS proxy can be deployed in an existing network without changing the network
architecture. It does not change security zoning, nor create a bottleneck for network
traffic. It is a simple way to facilitate AirPlay mirroring in a business or education network.
Open-source software Avahi is such an mDNS proxy. For more information on how to setup the
Avahi service, please refer to the application note “Enabling iOS Mirroring in a Multiple-subnet
Environment” available on NovoPro’s webpage (http://novopro.vivitekusa.com).
V1.0 Page 12 of 18
Page 13

Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
4. Quality of Service
Bandwidth requirement for a smooth user experience with NovoConnect devices is summarized
in the following table.
Display
Resolution
720p
720p
1080p
1080p
Streaming
Mode
Presentation
Mode
Video Playback
Mode
Presentation
Mode
Video Playback
Mode
Static page
Ave: 150kbps
Max: 200kbps
Ave: 320kbps
Max: 500kbps
Ave: 200kbps
Max: 300kbps
Ave: 350kbps
Max: 500kbps
Animation
page
Ave: 550kbps
Max: 800kbps
Ave: 1.2mbps
Max: 1.5mbps
Ave: 1.4mbps
Max: 1.7mbps
Ave: 1.8mbps
Max: 2.2mbps
High Action
movie
Ave: 2.8mbps
Max: 4.5mbps
Ave: 5.5mbps
Max: 7.5mbps
Ave: 6.1mbps
Max: 7.7mbps
Ave: 5.8mbps
Max: 7.2mbps
4-to-1
Projection
Ave: 12mbps
Max: 16mbps
Ave: 12mbps
Max: 16mbps
Ave: 12mbps
Max: 16mbps
Ave: 12mbps
Max: 16mbps
In general, 2mbps is good for “Presentation” mode while 4~8mbps is sufficient for “Video
Playback” mode.
Wi-Fi: NovoConnect devices have a high-performance Wi-Fi module (802.11ac with 2T2R).
So typically, a NovoConnect device is not the bottleneck in terms of network traffic. It is
recommended that your wireless network at least support 802.11g.
Ethernet: With its higher bandwidth and better robustness, Ethernet provides the best
performance. Use it whenever possible.
Note: Even if there is not enough bandwidth, NovoConnect’s software can still work properly
(while it might skip frames every now and then).
5. Managing Multiple NovoConnect Devices Remotely
Remote manager is a stand-alone Windows/Mac application that enables administrators to
manage multiple NovoConnect devices from a single computer, making it ideal for corporations,
schools or other large institutions.
V1.0 Page 13 of 18
Page 14

Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
The software allows users to
Add devices manually or via auto discovery;
Group devices;
Manage device settings;
Configure home-screen slideshow;
Upgrade firmware;
Configure moderator credentials;
Please refer to the section 4.3 “Remote Manager” of the “NovoPro User Manual” available on
NovoPro’s webpage (http://novopro.vivitekusa.com) for details.
5.1. Adding NovoConnect devices via Auto Discovery
Before remotely managing a NovoConnect device, it has to be added into the device list of Remote
Manager. This can be done manually or via auto discovery. Especially for organizations that deploy a
great deal of NovoConnect devices, adding a device via auto discovery can save a lot of effort. This
function allows IT staff to create and install a custom configuration file to automatically configure
NovoConnect’s settings via a microSD card.
Use the Remote Manager tool to generate a “NovoAutoConfig.xml” configuration file
1. Please download and install the latest version of Remote Manager software on the computer used
for remotely managing all NovoConnect devices in your organization.
2. Launch Remote Manager, and choose “Device Discovery” and then click “Generate AutoConfig
File …”, as illustrated in the figure below.
V1.0 Page 14 of 18
Page 15

Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
3. Select the appropriate NovoConnect Device that you would like to set up and whether or not
Password Protection has been enabled then click next.
4. The following window will appear and you need to work with your organization’s IT staff to obtain
the appropriate values for each item, and click on “Save…” to save file “NovoAutoConfig.xml” to a
microSD card.
V1.0 Page 15 of 18
Page 16

Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
5. The following table describes each setting in details.
Key Value (example) Explanation
edition* CORP or EDU
Time Zone*
Wi-Fi-ssid (example_Wi-Fi) Wi-Fi network SSID name
Wi-Fi-password (example_Wi-Fi_password) Wi-Fi network password
settings-password (example_settings_password) Password used in Settings Protection
Screen Cast Configuration* (Enabled or Disabled) Enable or Disable Airplay and Google Cast
PIN Required* (Enabled or Disabled) Enable or Disable PIN Requirement
V1.0 Page 16 of 18
Current Time Zone in
designated Region
Edition value. It has to be either CORP or EDU.
Refer to Section 1.4 for more details about
these two editions.
Page 17

Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
remote-manager-ip-address* (0.0.0.0)
remote-manager-port-number* 20142
report-time-interval* 15
IP address of the computer Remote Manager
runs on
The port number used by Remote Manager to
listen to device reporting. 20142 is the default
port number. You may need to change it to
match your Remote Manager’s setting.
The time interval (in seconds) for a
NovoConnect device to report its existence to
Remote Manager.
Note:
(1) Settings marked with “*” are supported in NovoConnect software release V2.2 and above.
(2) Regarding “remote-manager-port-number”, you can change this port number of your
Remote Manager via menu “Preference”, as illustrated in the figure below.
6. An example of a NovoAutoConfig.xml file is as follows:
Apply the customized NovoConnect settings to a NovoConnect device:
V1.0 Page 17 of 18
Page 18

Network Deployment Guide for NovoConnect
1. Insert the microSD card with NovoAutoConfig.xml file to a NovoConnect device, and then the
following pop-up will appear on the home screen of the NovoConnect device. There is a 30-second
timeout window so you can verify the parameters are set with the proper values. Then the device
will be configured with those new settings automatically.
2. After the new settings take effect, the NovoConnect device will automatically report its existence to
the Remote Manager. You can click on “Device Discovery” and then “Discover Devices” to bring up a
discovery dialog window where you will be able to view live NovoConnect devices and add them to
the device list of the Remote Manager.
Thank you for choosing NovoConnect products as your collaboration solution.
V1.0 Page 18 of 18
 Loading...
Loading...