Vishay IRFR9220, IRFU9220, SiHFR9220, SiHFU9220 Data Sheet
www.vishay.com
S
G
D
P-Channel MOSFET
DPAK
(TO-252)
IPAK
(TO-251)
G
D
S
S
D
G
D
IRFR9220, IRFU9220, SiHFR9220, SiHFU9220
Vishay Siliconix
Power MOSFET
PRODUCT SUMMARY
VDS (V) - 200
R
()V
DS(on)
Q
(Max.) (nC) 20
g
Q
(nC) 3.3
gs
Q
(nC) 11
gd
Configuration Single
= - 10 V 1.5
GS
FEATURES
• Dynamic dV/dt Rating
• Repetitive Avalanche Rated
• Surface Mount (IRFR9220, SiHFR9220)
• Straight Lead (IRFUFU9220, SiHFU9220)
• Available in Tape and Reel
•P-Channel
• Fast Switching
• Material categorization: For definitions of compliance
please see www.vishay.com/doc?99912
DESCRIPTION
Third power MOSFETs technology is the key to Vishay
advanced line of Power MOSFET transistors. The efficient
geometry and unique processing of the Power MOSFETs
design achieve very low on-state resistance combined with
high transconductance and extreme device ruggedness.
The DPAK is designed for surface mounting using vapor
phase, infrared, or wave soldering techniques. The straight
lead version (IRFU, SiHFU series) is for through-hole
mounting applications. Power dissipation levels up to 1.5 W
are possible in typical surface mount applications.
ORDERING INFORMATION
Package DPAK (TO-252) DPAK (TO-252) DPAK (TO-252) DPAK (TO-252) IPAK (TO-251)
Lead (Pb)-free and
Halogen-free
Lead (Pb)-free
SiHFR9220-GE3 SiHFR9220TRL-GE3
IRFR9220PbF IRFR9220TRLPbF
SiHFR9220-E3 SiHFR9220TL-E3
a
SiHFR9220TRR-GE3aSiHFR9220TR-GE3aSiHFU9220-GE3
a
IRFR9220TRRPbF
a
SiHFR9220TR-E3
a
IRFR9220TRPbF
a
SiHFR9220T-E3
a
a
IRFU9220PbF
SiHFU9220-E3
Note
a. See device orientation.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (TC = 25 °C, unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER SYMBOL LIMIT UNIT
Drain-Source Voltage V
Gate-Source Voltage V
T
= 25 °C
Continuous Drain Current V
Pulsed Drain Current
a
at - 10 V
GS
C
= 100 °C - 2.3
C
DS
± 20
GS
I
D
IDM - 14
Linear Derating Factor 0.33
Linear Derating Factor (PCB Mount)
Single Pulse Avalanche Energy
Repetitive Avalanche Current
Repetitive Avalanche Energy
Maximum Power Dissipation T
Maximum Power Dissipation (PCB Mount)
Peak Diode Recovery dV/dt
Operating Junction and Storage Temperature Range T
Soldering Recommendations (Peak Temperature)
Notes
a. Repetitive rating; pulse width limited by maximum junction temperature (see fig. 11).
b. V
= - 50 V, Starting TJ = 25 °C, L = 35 mH, Rg = 25 , IAS = - 3.6 A (see fig. 12).
DD
c. I
- 3.9 A, dI/dt 95 A/μs, VDD VDS, TJ 150 °C.
SD
d. 1.6 mm from case.
e. When mounted on 1" square PCB (FR-4 or G-10 material).
S13-0166-Rev. E, 04-Feb-13
e
b
a
a
= 25 °C
e
c
d
C
TA = 25 °C 2.5
for 10 s 260
E
AS
I
AR
E
AR
P
D
dV/dt - 5.0 V/ns
, T
J
stg
1
For technical questions, contact: hvm@vishay.com
THIS DOCUMENT IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. THE PRODUCTS DESCRIBED HEREIN AND THIS DOCUMENT
ARE SUBJECT TO SPECIFIC DISCLAIMERS, SET FORTH AT www.vishay.com/doc?91000
- 200
- 3.6
0.020
310 mJ
- 3.6 A
4.2 mJ
42
- 55 to + 150
Document Number: 91283
V
AT
W/°C
W
°C
IRFR9220, IRFU9220, SiHFR9220, SiHFU9220
D
G
S
D
G
www.vishay.com
THERMAL RESISTANCE RATINGS
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Maximum Junction-to-Ambient R
Maximum Junction-to-Ambient
(PCB Mount)
a
Maximum Junction-to-Case (Drain) R
thJA
R
thJA
thJC
- - 110
--50
--3.0
Note
a. When mounted on 1" square PCB (FR-4 or G-10 material).
SPECIFICATIONS (TJ = 25 °C, unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Static
Drain-Source Breakdown Voltage V
V
Temperature Coefficient VDS/TJ Reference to 25 °C, ID = - 1 mA - - 0.22 - V/°C
DS
Gate-Source Threshold Voltage V
Gate-Source Leakage I
Zero Gate Voltage Drain Current I
Drain-Source On-State Resistance R
Forward Transconductance g
DS
GS(th)
V
GSS
DSS
VGS = - 10 V ID = - 2.2 A
DS(on)
fs
Dynamic
Input Capacitance C
Reverse Transfer Capacitance C
Total Gate Charge Q
Gate-Drain Charge Q
Turn-On Delay Time t
Rise Time t
Turn-Off Delay Time t
Fall Time t
Internal Drain Inductance L
Internal Source Inductance L
iss
- 110 -
oss
-33-
rss
g
--3.3
gs
--11
gd
d(on)
r
d(off)
-19-
f
D
V
-7.3-
Between lead,
6 mm (0.25") from
package and center of
S
die contact
Drain-Source Body Diode Characteristics
Continuous Source-Drain Diode Current I
Pulsed Diode Forward Current
a
Body Diode Voltage V
Body Diode Reverse Recovery Time t
Body Diode Reverse Recovery Charge Q
Forward Turn-On Time t
S
I
SM
SD
rr
rr
on
MOSFET symbol
showing the
integral reverse
p - n junction diode
TJ = 25 °C, IF = - 3.9 A, dI/dt = 100 A/μs
Notes
a. Repetitive rating; pulse width limited by maximum junction temperature (see fig. 11).
b. Pulse width 300 μs; duty cycle 2 %.
VGS = 0 V, ID = - 250 μA - 200 - - V
VDS = VGS, ID = - 250 μA - 2.0 - - 4.0 V
= ± 20 V - - ± 100 nA
GS
VDS = - 200 V, VGS = 0 V - - - 100
V
= - 160 V, VGS = 0 V, TJ = 125 °C - - - 500
DS
b
VDS = - 50 V, ID = - 2.2 A 1.1 - - S
VGS = 0 V,
V
= - 25 V,
DS
f = 1.0 MHz, see fig. 5
= - 3.9 A, VDS = - 160 V,
I
= - 10 V
GS
V
R
= 18 , RD = 24 , see fig. 10
g
TJ = 25 °C, IS = - 3.6 A, VGS = 0 V
D
see fig. 6 and 13
= - 100 V, ID = - 3.9 A,
DD
b
b
b
b
Intrinsic turn-on time is negligible (turn-on is dominated by LS and LD)
Vishay Siliconix
°C/W
--1.5
- 340 -
--20
-8.8-
-27-
-4.5-
-7.5-
--- 3.6
--- 14
--- 6.3V
- 150 300 ns
- 0.97 2.0 μC
μA
pFOutput Capacitance C
nC Gate-Source Charge Q
ns
nH
A
S13-0166-Rev. E, 04-Feb-13
THIS DOCUMENT IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. THE PRODUCTS DESCRIBED HEREIN AND THIS DOCUMENT
ARE SUBJECT TO SPECIFIC DISCLAIMERS, SET FORTH AT www.vishay.com/doc?91000
For technical questions, contact: hvm@vishay.com
2
Document Number: 91283
IRFR9220, IRFU9220, SiHFR9220, SiHFU9220
www.vishay.com
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (25 °C, unless otherwise noted)
Vishay Siliconix
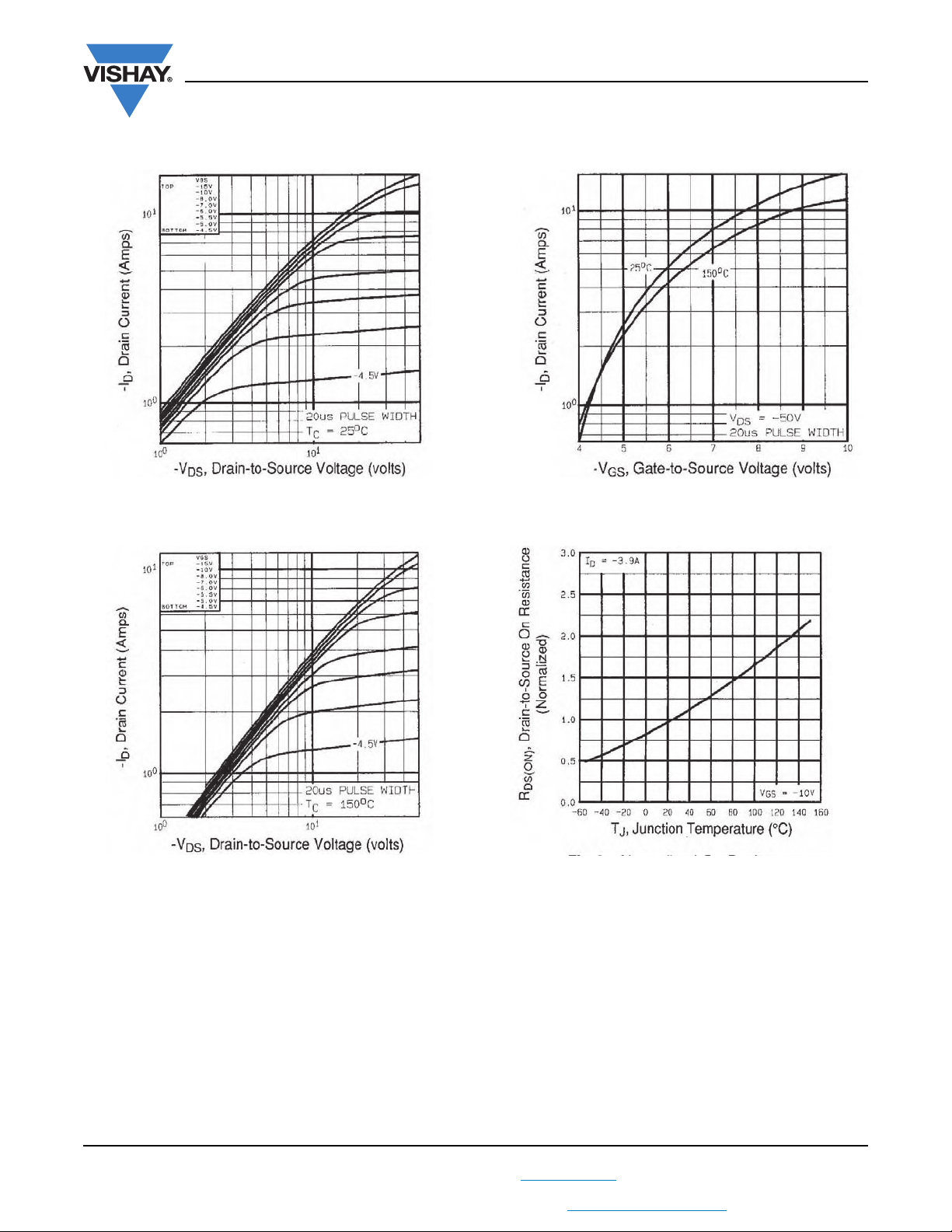
Fig. 1 - Typical Output Characteristics, TC = 25 °C
Fig. 2 - Typical Output Characteristics, T
= 150 °C
C
Fig. 3 - Typical Transfer Characteristics
Fig. 4 - Normalized On-Resistance vs. Temperature
S13-0166-Rev. E, 04-Feb-13
For technical questions, contact: hvm@vishay.com
THIS DOCUMENT IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. THE PRODUCTS DESCRIBED HEREIN AND THIS DOCUMENT
ARE SUBJECT TO SPECIFIC DISCLAIMERS, SET FORTH AT www.vishay.com/doc?91000
3
Document Number: 91283
www.vishay.com
IRFR9220, IRFU9220, SiHFR9220, SiHFU9220
Vishay Siliconix
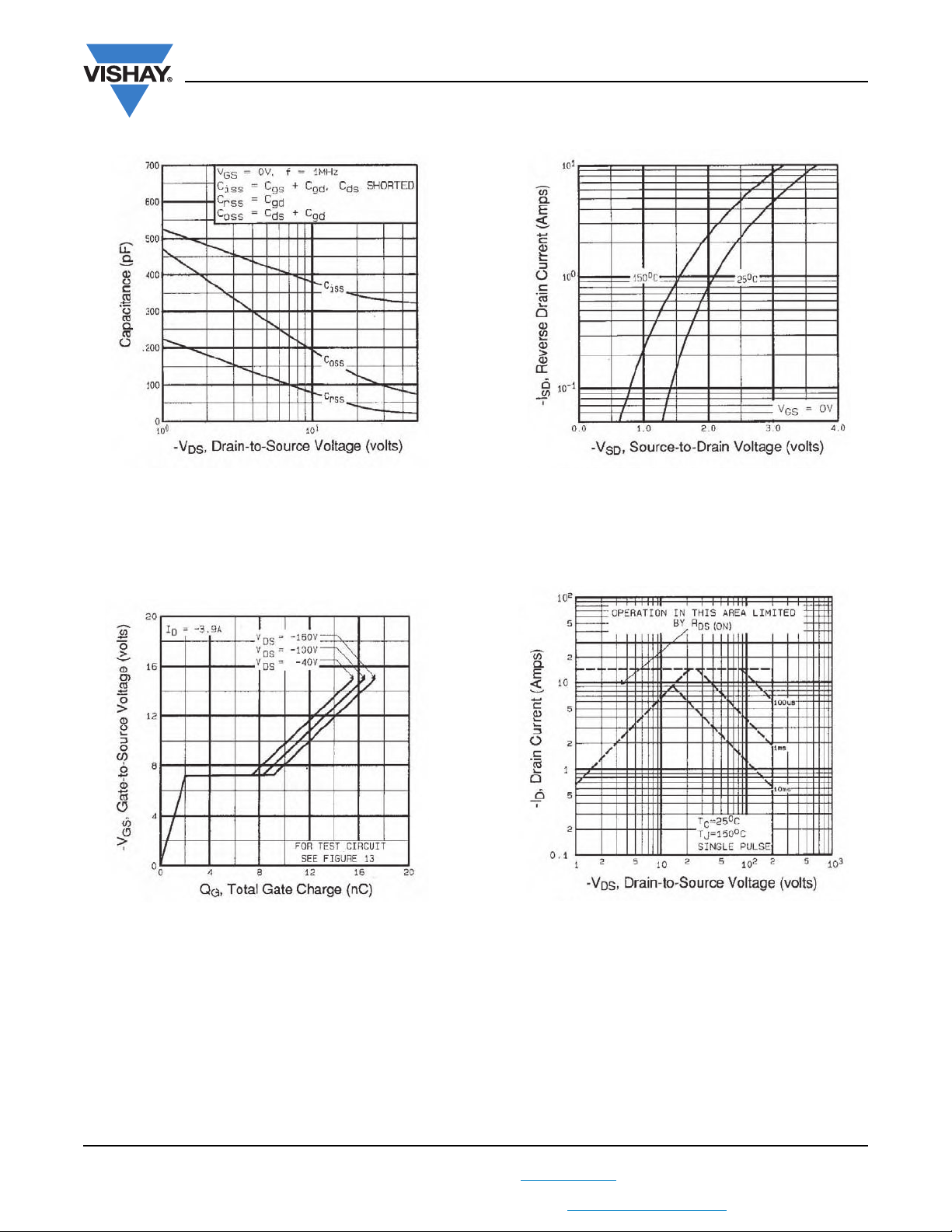
Fig. 5 - Typical Capacitance vs. Drain-to-Source Voltage
Fig. 6 - Typical Gate Charge vs. Gate-to-Source Voltage
Fig. 7 - Typical Source-Drain Diode Forward Voltage
Fig. 8 - Maximum Safe Operating Area
S13-0166-Rev. E, 04-Feb-13
For technical questions, contact: hvm@vishay.com
THIS DOCUMENT IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. THE PRODUCTS DESCRIBED HEREIN AND THIS DOCUMENT
ARE SUBJECT TO SPECIFIC DISCLAIMERS, SET FORTH AT www.vishay.com/doc?91000
4
Document Number: 91283
 Loading...
Loading...