Page 1

UHF FM Transceiver
VX-5500U
Service Manual
©2003 VERTEX STANDARD CO., LTD. EC034U90A
POWER
VERTEX STANDARD CO., LTD.
4-8-8 Nakameguro, Meguro-Ku, Tokyo 153-8644, Japan
VERTEX STANDARD
US Headquarters
10900 Walker Street, Cypress, CA 90630, U.S.A.
YAESU EUROPE B.V.
P.O. Box 75525, 1118 ZN Schiphol, The Netherlands
YAESU UK LTD.
Unit 12, Sun Valley Business Park, Winnall Close
Winchester, Hampshire, SO23 0LB, U.K.
VERTEX STANDARD HK LTD.
Unit 5, 20/F., Seaview Centre, 139-141 Hoi Bun Road,
Kwun Tong, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Introduction
This manual provides technical information necessary for servicing the VX-5500U UHF FM Transceiver.
Servicing this equipment requires expertise in handling surface-mount chip components. Attempts by non-qualified
persons to service this equipment may result in permanent damage not covered by the warranty, and may be illegal in
some countries.
Two PCB layout diagrams are provided for each double-sided circuit board in the Transceiver. Each side of is referred
to by the type of the majority of components installed on that side (“leaded” or “chip-only”). In most cases one side has
only chip components, and the other has either a mixture of both chip and leaded components (trimmers, coils, electrolytic
capacitors, ICs, etc.), or leaded components only.
While we believe the technical information in this manual to be correct, VERTEX STANDARD assumes no liability
for damage that may occur as a result of typographical or other errors that may be present. Your cooperation in pointing
out any inconsistencies in the technical information would be appreciated.
Contents
Operating Manual Reprint......................... 1-1
Cloning ....................................................................
2-1
Specifications ................................................ 2-2
Exploded View & Miscellaneous Parts ... 3-1
Block Diagram .............................................. 3-2
Interconnection Diagram............................ 3-4
Circuit Description ..................................... 4-1
Alignment ...................................................... 5-1
Board Unit (
MAIN Unit........................................................... 6A-1
DISPLAY Unit ...................................................... 6B-1
KEY Unit ............................................................... 6C-1
VR Unit................................................................. 6D-1
MIC CONN Unit................................................. 6D-2
Optional Board Unit (
F2D-8 2-Tone Decode Unit ................................ 7A-1
VTP-50 VX-Trunk Unit ....................................... 7B-1
FVP-25 Encryption / DTMF Pager Unit ........... 7C-1
F5D-14 5-Tone Unit ............................................ 7D-1
FIF-7A Connection Unit ..................................... 7E-1
Schematics, Layouts & Parts
Schematics, Layouts & Parts
)
)
1
Page 2
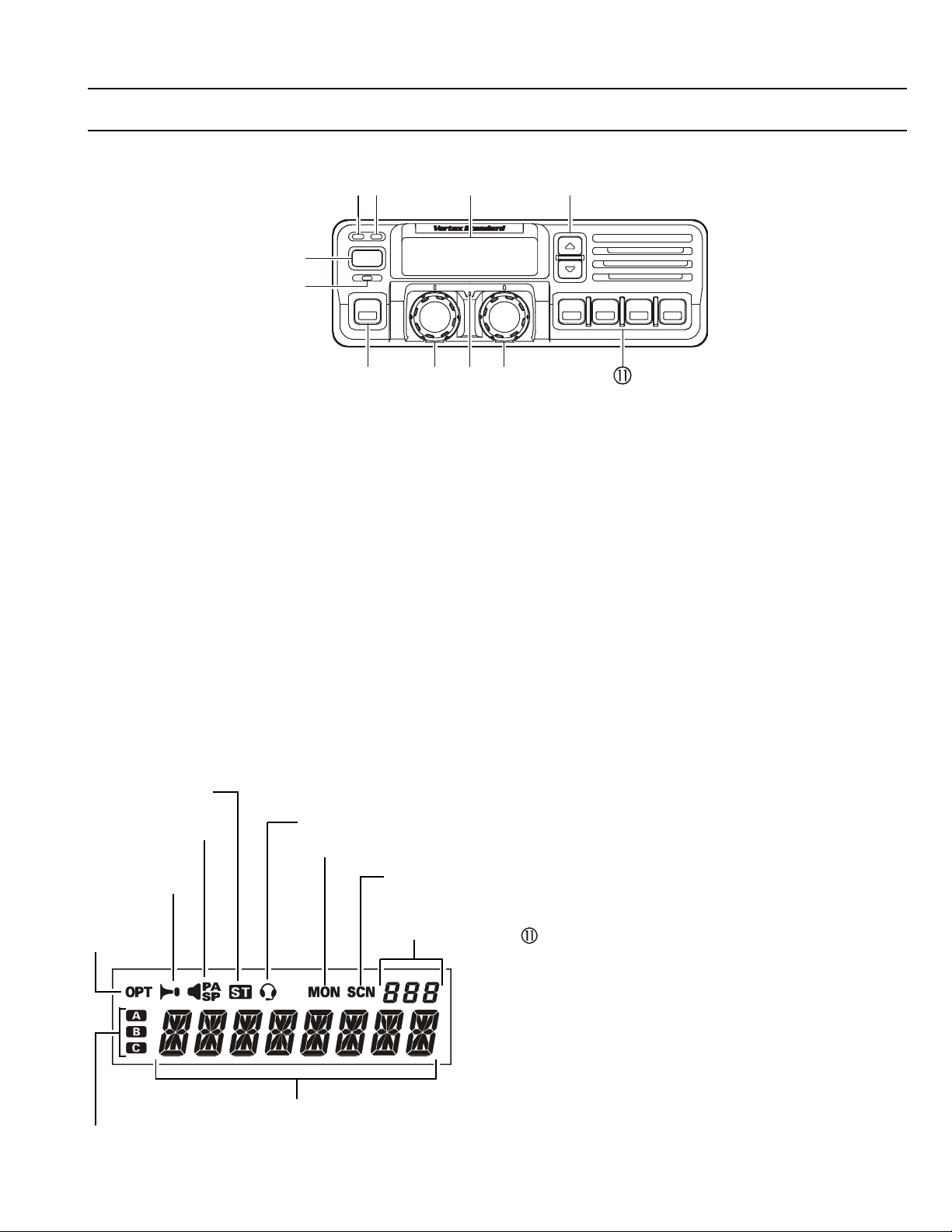
Front Panel
Operating Manual Reprint
CONTROLS & CONNECTORS
POWER
POWER Button
Press the button to turn the transceiver ON and
OFF.
TX Indicator
This lamp glows red when the radio is transmit-
ting.
BUSY Indicator
This lamp glows green when the channel is busy.
Liquid Crystal Display
The display include an 8-character alpha-numeric
section showing channel and group names, sta-
tus and identity information, and error messages.
Additional indicators on the display show prior-
ity channel assignments and scan include / ex-
clude selection.
This channel on
“S
ELECTABLE TONE” List
This channel on “PUBLIC
ADDRESS” or “SPEAKER”
List
This channel on
“H
ORN ALERT” List
This channel
on “O
PTION”
List
This channel on “I
Receiver Monitor
NTERCOM” List
This channel on
“S
Channel Group
CAN” List
Number
/ Button
Pressing these buttons changes the current group
(and displayed group number or name). Holding
this button for more than 1/2 second causes the
function to repeat.
SQC Indicator
This lamp glows orange when incorrect position
at the setting of CE49.
Programmable Function Button (PF button)
This button can be set up for special applications,
such as high/low power selection, monitor, dimmer, talk-around, and call alert function, as determined by your network requirements and programmed by your VERTEX STANDARD dealer.
VOLUME Knob
This knob sets the volume of the receiver.
EMERGENCY Microphone
The emergency microphone is located behind this
small slit. When the emergency feature is activated, this Microphone is enabled.
CHANNEL Selector Knob
This knob select the operating channel.
Programmable Function Button (PF button)
This button can be set up for special applications,
such as high/low power selection, monitor, dimmer, talk-around, and call alert function, as determined by your network requirements and programmed by your VERTEX STANDARD dealer.
8 Character Alpha-numeric Display
This channel on “AUX A/B/C” List
1-1
Page 3

Operating Manual Reprint
CONTROLS & CONNECTORS
Side Panel
Microphone Jack (It is on both sides.)
Connect the microphone plug to this jack.
Microphone Jack
REAR (Heatsink)
Antenna Socket
The 50-ohm coaxial feedline to the antenna must
be connected here, using a type-M (PL-259) plug.
External Speaker Jack
An external loudspeaker may be connected to this
2-contact, 3.5-mm mini-phone jack.
Caution: Do not connect this line to ground, and be
certain that the speaker has adequate capability to handle the audio output from the
VX-5500.
13.8-V DC Power Connector
The supplied DC power cable must be connected
to this 4-pin connector. Use only the supplied
fused cable, extended if necessary, for power connection.
DSUB 25-Pin Accessory Connector
External TX audio line input, PTT (Push To Talk),
Squelch, and external RX audio line output signal may be obtained from this connector for use
with accessories such as data transmission/reception modems, ets.
1-2
Page 4

Operating Manual Reprint
BASIC OPERATION OF THE TRANSCEIVER
Important! - Before turning on the radio the first time,
confirm that the power connections have been made correctly and that a proper antenna is connected to the antenna jack.
Switching Power ON/OFF
Push the POWER switch turn on the radio. The
display will become illuminated. The radio will
start up on the last channel used prior to shut-
down during the previous operating session.
Turn the CHANNEL selector knob to choose the
desired operating channel. A channel name will
appear on the display. If you want to select the
operating channel from a different Memory Chan-
nel Group, press the UP () or DOWN () but-
ton to select the Memory Channel Group you
want before selecting the operating channel.
Setting the Volume
Turn the VOLUME knob clockwise to increase the
volume, and counterclockwise to decrease it. If
no signal is present, press and hold in the MON
button more than 1/2 seconds; background noise
will now be heard, and you may use this to set
the VOLUME knob for the desired audio level.
Press and hold the MON button more than 1/2 sec-
onds to quiet the noise and resume normal (quiet)
monitoring.
Transmitting
To transmit, wait until the “BUSY” indicator is
off (the channel is not in use), and press the PTT
(Push-To-Talk) switch on the side of the microphone (the “TX” indicator will appear or the “TX”
indicator will glow red). While holding in the PTT
switch, speak across the face of the microphone
in a clear, normal voice level, and then release the
PTT switch to receive.
Selecting Groups and Channels
H Press the UP () or DOWN () button (repeat-
edly, if necessary) to select a different group of
channels.
H Turn the CHANNEL selector knob to select a
different channel within the current group.
Automatic Time-Out Timer
If the selected channel has been programmed for
automatic time-out, you must limit the length of
each transmission. While transmitting, a beep will
sound five seconds before time-out. Another beep
will sound just before the deadline; the “TX” indicator will disappear and transmission will cease
soon thereafter. To resume transmitting, you must
release the PTT and wait for the “penalty timer”
to expire (if you press the PTT before this timer
expires, the timer restarts, and you will have to
wait another “penalty” period.)
1-3
Page 5

Operating Manual Reprint
ADVANCED OPERATION
Programmable Function Button (PF button)
The VX-5500 includes the seven Programmable
Function Buttons (PF button). The PF button
functions can be customized, via programming
by your VERTEX STANDARD dealer, to meet
your communications/network requirements.
Some features may require the purchase and installation of optional internal accessories. The
possible PF button programming features are il-
POWER
Functions
None
SCAN (SCN)
Dual Watch
Call/Reset
Talk-Around (TA)
Alpha Numeric (A/N)
DIMMER (DIM)
Emergency (EMG)
Horn Alert (HA)
Home Channel (HOM)
Intercom (IC)
Low Power (LOW)
GRP UP
GRP DWN
CH UP
CH DWN
AUX A
AUX B
AUX C
Public Address (PA)
Monitor (MON)
RCL
Selectable Tone (ST)
SP*
Squelch Level (SQL)
Compander
Encryption** (OPT)
* requires RMK-4000 ** requires Encryption Unit
<1.5 sec
>1.5 sec
Programmable Function Button (PF button)
<1.5 sec
>1.5 sec
<1.5 sec
lustrated at the below, and their functions are explained on next page.
For further details, contact your VERTEX STANDARD dealer. For future reference, check the box
next to each function that has been assigned to
the PF button on your particular radio, and keep
it handy.
>1.5 sec
<1.5 sec
>1.5 sec
<1.5 sec
>1.5 sec
<1.5 sec
>1.5 sec
<1.5 sec
>1.5 sec
1-4
Page 6

Operating Manual Reprint
ADVANCED OPERATION
Channel Scan
The Scanning feature is used to monitor multiple
signals programmed into the transceiver. While
scanning, the transceiver will check each channel
for the presence of a signal, and will stop on a
channel if a signal is present.
To activate scanning:
H Press the assigned PF button of the “Scan” mo-
mentarily to activate scanning.
H The scanner will search the channels, looking
for active ones; it will pause each time it finds
a channel on which someone is speaking.
To stop scanning
H Press the assigned PF button of the “Scan”.
H Operation will revert to the channel to which
the CHANNEL selector knob is set.
Note:Your dealer may have programmed your
radio to stay on one of the following channels if you press the PTT switch during scanning pause:
Current channel (“Talk Back”)
Ì
“Last Busy” channel
Ì
“Priority” channel
Ì
“Home” channel
Ì
Scan Start” channel
Ì
Dual Watch
The Dual Watch feature is similar to the Scan fea-
ture, except that only two channels are monitored:
Ì The current operating channel; and
Ì The “Priority” channel.
To activate Dual Watch:
H Press the assigned PF button of the “Dual
Watch”.
H The scanner will search the two channels; it
will pause each time it finds a channel on which
someone is speaking.
H Press the assigned PF button of the “Dual
Watch”.
H Operation will revert to the channel to which
the CHANNEL selector knob is set.
ARTS (Auto Range Transpond System)
This system is designed to inform you when you
and another ARTS-equipped station are within
communication range.
During ARTS operation, your radio automatically
transmits for about 1 second every 25 (or 55) seconds (the interval is programmed by Dealer) in
an attempt to Shake hands with the other station.
If you move out of range for more than one minutes, your radio senses that no signal has been
received, a ringing beeper will sound. If you subsequently move back into range, as soon as the
other station transmits, your beeper will sound.
The PF Button Function
The PF (Programmable Function) button can be
programmed by the dealer to provide two of the
other functions described below.
To activate the primary Accessory function, press
the PF button momentarily. To access the secondary Accessory function (which may include the
Alarm), press and hold the PF button for 1.5 seconds or longer.
Call/Reset
When this feature is programmed and a selective
call has been received, momentarily press the assigned PF button of the “Call/Reset” to reset the
flashing indicator and mute the receiver, otherwise press the assigned PF button of the “Call/
Reset” to sent your radio’s identification code
(ANI) to the dispatcher.
Talk-Around
The feature causes the assigned PF button of the
“Talk-Around” to select simplex operation on
semi-duplex channels: the transmit frequency
becomes the same as the receive frequency (regardless of any programmed offset for the channel).
Note:This feature has no effect on simplex channels.
After pressing the button, “-TAKARD-” is displayed
on the LCD.
Alpha Numeric
Press the assigned PF button of the “Alpha Numeric” to switch the display between the Group/
Channel number, and the Group/Channel name
(alphanumeric). A tone will sound each time you
switch between numerical and alphanumerical
display.
1-5
Page 7

Operating Manual Reprint
ADVANCED OPERATION
DIM
Press the assigned PF button of the “DIM” to adjust the brightness of the display and key
backright.
EMG (Emergency)
Press the assigned PF button of the “EMG” to
initiate an emergency call (requires ANI board).
When an emergency call is made, not tone is emitted and the display does not change. To end the
emergency call, turn the transceiver power OFF.
HA (Horn Alert)
Press the assigned PF button of the “HA” to turn
the Horn Alert function ON or OFF. If you receive
a call from the base station with 2Tone or DTMF
signaling, horn alert will activate.
When you turn Horn Alert ON, a tone will sound
and “
” appears on the display.
Home (Home Channel)
Press the assigned PF button of the “Home” to
select the pre-programmed Home Channel. Press
it again to return to the previous channel. If used
while scanning, pressing this key a second time
will change to the revert channel.
IC (Intercom)
This feature requires dual head configuration.
Press the assigned PF button of the “IC” to turn
the intercom feature ON or OFF. While ON, you
can press the PTT switch to communicate to another control head operator without transmitting
over the air. When you press this key, a tone
sounds and “
tercom can be used even while scanning and receiving a call.
” appears on the display. The in-
Low Power
Press the assigned PF button of the “Low Power”
to set the radio's transmitter to the “Low Power”
mode.
Press this key again to return to “High Power”
operation when in difficult terrain.
GRP UP/DWN
Press the assigned PF button of the “GRP UP” or
“GRP DWN” to select a different group of channels.
CH UP/DWN
Press the assigned PF button of the “CH UP” or
“CH DWN” to select a different channel within
the current group.
AUX A/B/C
Press the assigned PF button of the “AUX A”,
“AUX B”, or “AUX C” to turn the output port (respectively).
PA (Public Address)
Press the assigned PF button of the “PA” to use
the transceiver as a PA amplifier. When you enable this function, a tone sounds and “
pears on the display. The public address can be
used even while scanning and receiving a call.
MONI (Monitor)
Press the assigned PF button of the “MONI” momentarily to cancel CTCSS and DCS signaling
squelch; the “MON” icon appears on the display.
Press and hold this key for 1/2 seconds to hear
background noise (unmute the audio); the MON
icon blinks on the display.
RCL (Channel Recall)
During scan, you can press the assigned PF button of the “RCL” to select the last called channel.
ST (Selectable Tone)
Press the assigned PF button of the “Selectable
Tone”, then rotate the CHANNEL selector knob
to select a 2-Tone.
SP
Press the assigned PF button of the “SP” to switch
“Front panel”, “Front panel & Body” and “Body”
speaker. When “Body” is selected, a tone sounds
and the “
can use this function while scanning and receiving a call. However, all audio will be emitted from
the PA speaker.
” icon appears on the display. You
SQL (Squelch Level)
You can manually adjust the squelch level using
this function:
1. Press the assigned PF button of the “SQL”. A
tone sounds and SQL appears on the display
with the current squelch level.
2. Rotate the CHANNEL selector knob to select
the desired level.
3. Press the this key. A tone sounds and the display returns to the normal channel.
” ap-
1-6
Page 8

ADVANCED OPERATION
COMP (Compander)
Press the PF button assigned to the “COMP”
function to turn the “Compander” IC ON or OFF.
This IC contains two variable gain circuits configured for compressing and expanding the dynamic range of the radio's transmitted audio signal.
When you enable this function, the signal-to-noise
radio can be improved by reducing the transmitted audio dynamic range.
Encryption (Option)
When the Voice Scrambler feature is enabled,
pressing the assigned PF button of the “Encryp-
tion” toggles the Scrambler on and off.
1-7
Page 9

Operating Manual Reprint
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES
MH-25
MH-53
MH-53
MH-53
CE49 Programming Software
CT-70 Radio Programming Cable (Requires VPL-1)
CT-71 Radio to PC Programming Cable
CT-72 Radio to Radio Programming Cable
CT-93 Cable for RMK-4000 (33 ft,10 m)
CT-81 Cable for RMK-4000 (20 ft, 6 m)
CT-82 Cable for RMK-4000 (8 ft, 2.5 m)
CT-83 Cable for RMK-4000 (2 ft, 0.6 m)
CNT-6000 Control Head
RF DECK RF Deck w/MMB-75 (for Dual Band Installations)
RMK-4000SH Remote Kit (for Single Transceiver)
RMK-4000DH Remote Kit (for Dual-Head Installations)
RMK-4000DB Remote Kit (for Dual Band Installations)
RMK-4000DBH Remote Kit (for Dual Band plus Dual Head Installations)
F2D-8 2-Tone Decode Unit (Requires FIF-7A)
F5D-14 5-Tone ENC-DEC Unit (Requires FIF-7A)
VTP-50 VX-Trunk Unit (Requires FIF-7A)
FVP-25 Band inversion scrambler/DTMF paging Unit (Requires FIF-7A)
FVP-35 Encryption Unit (Rolling code voice scrambler; Requires FIF-7A)
MDC1200 Digital ANI encoder Unit (Requires FIF-7A)
FP-1023 External 23A Power Supply
MLS-100 Mobile Loud speaker (12 W Peak Power)
MMB-75 Mobile Mounting Bracket
MMB-76 Locking Mobile Mounting Bracket
FIF-7A Inter face Board (for F2D-8, F5D-14, VTP-50, FVP-25)
CN-6 Inter face Board (for Accessories)
LF-1 Line Filter
B7A
C7A
A7A
B7A
Microphone
Heavy Duty Microphone
Heavy Duty Microphone w/Noise Canceler
Heavy Duty DTMF Microphone w/Noise Canceler
1-8
Page 10

DSUB 25-PIN ACCESSORY CONNECTOR
Pin 1: RSSI [Analog Output]
A DC voltage proportional to the strength of the
signal currently being received (Receiver Signal
Strength Indicator) is provided on this pin. This
low impedance output is generated by the receiver
IF sub-system and buffered by an internal opamp. Typical voltages are graphed as follows:
Operating Manual Reprint
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
DSUB25 output level (V)
0
1259 398 125 398 12.5 4 1.25 0.4 0.125 0.04
SSG Input Level (uV)
Pin 2, 3, 4, 5 & 6: SELECT, DSUB 03, DSUB 04, DSUB
05 & DSUB 06
[Digital Input Port]
These input port features can be programmed via
the CE49 programmer. The same item can not be
chosen twice.
To select the “Input port” page, (Common «
DSUB-25 « Input port).
Pin 2
Pin 4
Pin 6
Pin 3
Pin 5
DSUB 25-Pin Numbering
None
MON This feature is the same as pressing and
holding in the Monitor key.
DIMMERLCD illumination dimmer “on.”
Hook Activates the Hook1 feature.
SCAN Activates the scanner.
G-SCAN Activates the Group scanner.
RPT INH Disables the repeater feature during
Multi Deck operation.
EMG Activates the Emergency feature.
Home Switches to the Home Channel.
CH SW0 Memory channel recall
(Channel Switch Table bit 0)
CH SW1 Memory channel recall
(Channel Switch Table bit 1)
CH SW2 Memory channel recall
(Channel Switch Table bit 2)
CH SW3 Memory channel recall
(Channel Switch Table bit 3)
Example
If you assign “CH SW0” and “CH SW1” to the
Universal Input Port, you can recall Channels 1~3
as shown below.
Channel CH SW0 CH SW1
11 0
20 1
31 1
LOGIC level (+5V / 0V) input (Low active).
High Impedance input.
1-9
Page 11

Operating Manual Reprint
DSUB 25-PIN ACCESSORY CONNECTOR
Similarly, if you assign “CH SW0,” “CH SW1,”
and “CH SW2” to the Universal Input Port, you
can recall Channels 1~7 as shown below:
Channel CH SW0 CH SW1 CH SW2
11 0 0
20 1 0
31 1 0
40 0 1
51 0 1
60 1 1
71 1 1
If you need to recall all memory channels (15 CH)
from the External Controller via the Uni-versal
Input Port, you should assign the “All Channel
Recall” Command (CH SW 0 ~ CH SW 3) to the
Universal Input Port.
In this case:
Channel CH SW0 CH SW1 CH SW2 CH SW3
11 0 0 0
20 1 0 0
31 1 0 0
40 0 1 0
51 0 1 0
60 1 1 0
71 1 1 0
80 0 0 1
91 0 0 1
10 0 1 0 1
11 1 1 0 1
12 0 0 1 1
13 1 0 1 1
14 0 1 1 1
15 1 1 1 1
The Memory Channel is determined via the CE49
Programmer. (Common « DSUB-25pin connector « Channel switch Table).
DSUB 25-Pin
PI NS 2, 3 , 4, 6
Sample Circuit
Pin 7: E
[GND]
Ground for all logic levels and power supply return.
Pin 8: A KEY OUT [Universal Output Port]
Open collector output. Output voltage 0 ~ 5 V,
Max. sink current 30 mA.
The possible programming features (use CE49)
are illustrated below.
A PORT/B PORT/C PORT/D PORT/E PORT/
None
Refer to the “Pins 20, 21, & 22” section for details.
Pin 9: TXD
[Digital Output for Alignment software]
Connect to the RS232C cable (requires FIF-8 and
CT-88)
Pin 10: RXD
[Digital Input for Alignment software]
Connect to the RS232C cable (requires FIF-8 and
CT-88)
Pin 11: EXT PTT
Shorting this port to ground causes the transceiver
to be placed in the Transmit mode, while opening the connection to this port returns the transceiver to the Receive mode.
1-10
Pin 12: MIC MUTE
MIC mute on: Level High (5V)
MIC mute off: Open
LOGIC level (+5V / 0V) output.
When the PTT/EXT PTT switch is pressed, this
pin switches to “open.”
Page 12

Operating Manual Reprint
DSUB 25-PIN ACCESSORY CONNECTOR
Pin 13: TXDI [Digital Input for DATA Communications]
H TX Hi-speed Data Input Type (jumper JP2005).
Input level 800 mV/600 Ohms, Max.input 1.2V
H Tx Low-speed Data input Type (Jumper
JP2006). Input level 40 mV/600-Ohms
If the Jumper setting is “Low-speed Data” (JP2006
jumpered), this port is usable in the AUDIO
(300~3000 Hz) range.
If the jumper setting is “HI-speed Data” (JP2005
jumpered), this port is usable for 9600 bps DATA
communications, because the filter and limiter are
not engaged in the Audio line.
Pin 14: DC OUT
[13.4 V/5 V DC Output]
H Switched 13.8V output for supplying power to
an accessory (jumper JP2008).
H Switched and regulated DC 5.0V output for
supplying power to an accessory (jumper
JP2007).
Maximum output current is 200 mA
Pin 15: IGN
[Ignition Sense feature]
The VX-5500 may automatically be switched to
the STAND-BY mode when the vehicle's igni-tion
key is turned on.
Maximum current is 20 mA.
This feature is only enabled on transceivers configured for Dual Deck operation.
Pin 17: RX DO [Digital Output for DATA Communications]
H RX Hi-speed Data Output Type (jumper
JP2003). output level 600 mV/10k Ohms
H RX Low-speed Data Output Type (jumper
JP2004). output level 200 mV/600 Ohms
If the Jumper setting is “Low-speed Data” (JP2004
jumpered), this port is usable in the AUDIO
(300~3000 Hz) range.
If the jumper setting is “HI-speed Data” (JP2003
jumpered), this port is usable for 9600 bps DATA
communications, because the filter and limiter are
not engaged in the Audio line.
Pin 18: E
[GND]
Ground for all logic levels and power supply return.
Pins 19, 20, 21, & 22: DSUB 19, DSUB 20, DSUB 21
and DSUB 22
[Universal Output Port]
LOGIC level (+5V / 0V) output.
The logic output appears at these pins when the
front panel's PF key is turned on.
The possible programming features (use CE49)
are illustrated below.
If the HA feature is assigned to these ports, a current amplifier must be connected between the
Horn circuit and the port.
Pin 16: NC
Ignition 13.8V
[NO connection]
DSUB 25-Pin
None/A PORT/B PORT/C PORT/D PORT/E
PORT/HA PORT
Pin 23: EXT SQL
[Squelch Signal Output]
Open collector output. Max. sink current 10 mA.
A Signal is present (Squelch is open): Level High
No Signal is present (Squelch is closed): Open
When you connect the solder jumper on JP2002,
this port changes to PULL UP (5 V) output.
This status can be changed by CE49 programmer.
Pin 24: SP MUTE
[Speaker Mute Output]
Open collector output.
External Speaker mute on: Level High
External Speaker mute off: Open
Pin 25: E
[GND]
Chassis ground.
1-11
Page 13

Operating Manual Reprint
Note:
1-12
Page 14

Cloning
The VX-5500 includes a convenient “Clone” feature,
which allows the programming data from one transceiver to be transferred to another VX-5500. Here is
the procedure for Cloning one radio's data to another.
Note: When a cloning isn't made, you correct the following part using "CE49."
When a "Radio to Radio Clone" which is in the
"Miscellaneous" menu is "Disabled," change this
menu to "Enabled."
1. Turn both transceivers off.
2. Remove the plastic cap and its two mounting
screws from the Microphone jack on the transceiver. Do this for both transceivers.
3. Connect the optional CT-72 cloning cable between the Microphone jacks of the two transceivers.
4. On the Destination transceiver, press and hold
the PF Button (just below the POWER Button)
while turning the transceiver on.
5. Now, on the source transceiver, press and hold
the
Button while turning the transceiver
on.Data will now be transferred to the Destination transceiver from the source transceiver.
6. If there is a problem during the cloning process,
sound an error beep from source the transceiver.
Check your cable connections and battery voltage, and try again.
7. If cloning is a successful, turn the Destination
transceiver off. Now turn the source transceiver
off.
8. Disconnect the CT-72. Replace the plastic cap
and its two mounting screws.
9. You can then turn the transceivers back on, and
begin normal operation.
Optional Cloning Cable
CT-72
POWERPOWER
Destination source
DealerProgramming of VTP-50 and F5D-14
These procedures are designed to be used by the installing technician after the VTP-50 and F5D-14 has
been installed in the transceiver. To program a VX-5500's VTP-50 and F5D-14 board, you will need the
CT-71 programming interface cable, the CE-26 Programming diskette, and an IBM PC/AT or PS/2compatible type computer.
To enter the Programming mode, use the following procedure:
1. Turn the transceiver off.
2. Turn on the transceiver while holding in the
PF Button (just below the
Button).
POWER
2-1
Page 15

Specifications
GENERAL
Number of Channels: 250 channels
Frequency Range: 450 - 490 MHz
Channel Spacing: 5 / 10 / 12.5 / 15/ 20 / 25 / 50 kHz
Power Supply Voltage: 13.8V DC ±15 %
Current Consumption: Standby: 500 mA
Receive: 2.5 A
Transmit: 15 A (High)
Ambient Temperature Range: –22°F to +140°F (–30°C to +60°C)
Frequency Stability: Better than ±2.5 ppm
RF Input-Output Impedance: 50 Ohms
Audio Output Impedance: 4 Ohms
Dimensions: 7" (w) x 2.4" (H)x 7.7" (D) (178 x 60 x 195 mm)
Weight (Approx.): 4.9 lbs. (2.2 kg)
RECEIVER (Measurements made per EIA standard TIA/EIA-603)
Circuit Type: Double-conversion Super-heterodyne
Sensitivity(EIA 12 dB SINAD): 0.25 µV
Adjacent Channel Selectivity: 85/75 dB
Intermodulation: 80/75 dB
Spurious and Image Rejection: 90 dB
Audio Output: 12 W @ 4 Ohms w/5 % THD
TRANSMITTER (Measurements made per EIA standard TIA/EIA-603)
Power Output: 45 (Low:25 W)
Modulation: 16K0F3E, 11K0F3E
Max Deviation: 5.0/2.5 kHz
Conducted Spurious Emissions: 70 dB Below Carrier
FM Hum & Noise: 50/45 dB
Audio Distortion (@ 1 kHz): < 5 %
Measurements per EIA standards unless noted above.
Specifications subject to change without notice or obligation.
2-2
Page 16

Screw List
REF. VXSTD P/N Description Qty.
1 U20306007 BINDING HEAD SCREW M3x6B 4
2 U20306002 BINDING HEAD SCREW M3x6NI 6
3 U24308002 TAPTITE SCREW M3x8NI 9
4 U23206001 TAPTITE SCREW M2.6x6 14
5 U20308002 BINDING HEAD SCREW M3x8NI 2
6 U24208001 TAPTITE SCREW M2.6x8 1
7 U20305007 BINDING HEAD SCREW M3x5B 2
8 U32450007 FLAT HEAD SCREW M2.6x5B 2
9 U31306007 OVAL HEAD SCREW M3x6B 2
10 S5000182 SCREW JFS-4S-B1MW 2
Accessories
Description VXSTD P/N Qty.
BLADE FUSE ATC 15A Q0000075 2
DC CABLE 02P 15AX2 T9021015 1
KNOB CAP RA0254100 5
NAME PLATE RA0254700 1
RA0253000
LCD HOLDER
VR Unit
VR3601*
RA0254000
RUBBER KNOB (PWR)
RA0254200
RUBBER PACKING
RA0251900
PANEL ASSY
Supplide is VR3601*
DISPLAY Unit
RA0252800
DIFFUSER SHEET
G6090140
LCD
RA0262600
HOLDER
MAIN Unit
RA0262400
PACKING SHEET
MIC CONN Unit
RA0252700
REFLECTOR SHEET
KEY Unit
R0145680
FITTING (x4 pcs)
M4090133
SPEAKER
P1090654
CONNECTOR
(W/ *A)
MIC CONN Unit
RA0254800
RA0252300
LIGHT GUIDE
RA0252900
RUBBER CONNECTOR
CONTACT ASSY (Both Side)
Exploded View & Miscellaneous Parts
RA0254900
CASE
RA0262700
PACKING SHEET
Q6000114
TERMINAL STRIP
*A
RA0215000
EXT CAP
RA0251500
CHASSIS
RA020830A
DOUBLE FACE (Both Side)
RA0215400
SHEET
S6000395
COVER P-25P(23)
T9206926
WIRE ASSY
RA0262300
HOLDER PLATE
RA0262500
PACKING SHEET
S6000396
RUBBER GROMMET TM-96-17
P1090984
CONNECTOR
RA02543A0
KNOB
RA0254300
KNOB
R6054387B
SPECIAL NUT
RA0253900
RUBBER KNOB (CH)
RA0275500
RUBBER KNOB ASSY
Non-designated parts are available only as part of a
designated assembly.
3-1
Page 17

Block Diagram
3-2
Page 18

Block Diagram
3-3
Page 19

Interconnection Diagram
3-4
Page 20

Circuit Description
Reception and transmission are switched by "RX"
and "TX" lines from the microprocessor unit (MPU).
The receiver uses double-conversion super-heterodyne circuitry, with a 43.95MHz 1st IF and 450 kHz
2nd IF. The 1st LO, produced by a PLL synthesizer,
yields the 43.95MHz 1st IF.
The 2nd LO uses a 43.5 MHz (43.95 MHz-450 kHz)
signal generated by a crystal oscillator. The 2nd mixer and other circuits use a custom IC to convert and
amplify the 2nd IF, and detect FM to obtain demodulated signals. During transmit, the PLL synthesizer oscillates at the desired frequency directly, for
amplification to obtain RF power output. During
transmit, voice modulation and CTCSS (or DCS)
modulation are applied to this synthesizer. Transceiver functions, such as Tx/Rx control, PLL synthesizer settings, and channel programming, are controlled using the MPU.
Receiver
Incoming RF signals from the antenna connector
are delivered to the MAIN Unit, and pass through a
low-pass filter (LPF) antenna switching network
consisting of coils L1008, L1004, L1022 and L1003,
capacitors C1338, C1337, C1336, C1335, and C1325,
and antenna switching diodes D1047, D1048 and
D1049 for delivery to the receiver front end.
Signals within the frequency range of the transceiver are then passed through a varactor-tuned
band-pass filter consisting of L1007, L1020 before RF
amplification by Q1018 (2SC3357).
The amplified RF is then band-pass filtered again
by varactor-tuned resonators L1009, L1011 to ensure
pure in-band input to 1st mixer Q1188, Q1189, Q1190,
Q1191 (2SK520 x 4).
Buffered output from the VCO Unit is amplified
by Q1032 (2SC5107), Q1192 (2SC3357) and lowpass filtered by L1041 / L1045/ L1060 and C1153 /
C1154 / C1343 / C1174 / C1089, to provide a pure 1st
local signal between 406.05 and 446.05 MHz to the
1st mixer.
The 43.95MHz 1st mixer product then passes
through dual monolithic crystal filters XF1001 and
XF1002 (12 kHz BW)/ XF1003 and XF1004 (7kHz BW)
and is amplified by Q1041 (2SC4215Y) and delivered to the input of the FM IF subsystem IC Q1034
(TA31136FN).
This IC contains the 2nd mixer, 2nd local oscillator, limiter amplifier, FM detector, noise amplifier,
and squelch gates.
The 2nd LO in the IF-IC is produced from crystal
OSC X1001 (14.500MHz), and the 1st IF is converted
to 450kHz by the 2nd mixer and stripped of unwanted components by ceramic filter CF1001 or CF1002.
After passing through a limiter amplifier, the signal
is demodulated by the FM detector.
Demodulated receive audio from the IF-IC is
amplified by Q2019 (CXA1846N). After volume adjustment by the AF power amplifier Q2018
(TDA7240AV), the audio signal is passed to the optional headphone jack or 4 W loudspeaker.
PLL synthesizer
The 1st LO maintains stability from the PLL synthesizer by using a 14.500 MHz reference signal from
crystal OSC X1001. PLL synthesizer IC Q1033
(SA7025DK) consists of a prescaler, reference
counter, swallow counter, programmable counter,
a serial data input port to set these counters based
on the external data, a phase comparator, and charge
pump. The PLL-IC divides the 14.500 MHz reference signal by 725 using the reference counter (20.0
kHz comparison frequency). The phase detector
comparison frequency to be eight times the channel
spacing (2.5kHz). The VCO output is divided by the
prescaler, swallow counter and programmable
counter. These two signals are compared by the
phase comparator and input to the charge pump. A
voltage proportional to their phase difference is delivered to the low-pass filter circuit, then fed back to
the VCO as a voltage with phase error, controlling
and stabilizing the oscillating frequency. This synthesizer also operates as a modulator during transmit.
The RX-VCO is comprised of Q1019 (2SK508) and
D1011, D1018 (1SV282 x 2), and oscillates between
406.050 MHz and 446.050 MHz according to the programmed receiving frequency. And the TX-VCO is
comprised of Q1020 (2SC4226-R24) and D1014,
D1015, D1020 (1SV284 x 3) and oscillates between
134.000MHz and 174.000MHz according to the programmed transmit frequency. The VCO output passes through buffer amplifier Q1026 (2SC5107), and
a portion is fed to the buffer amplifier Q1029
(2SC5107) of the PLL IC, and at the same time amplified by Q1032 (2SC5107) to obtain stable output.
The VCO DC supply is regulated by Q1006
(2SC4154E). Synthesizer output is fed to the 1st
mixer by diode switch D1021 (1SS321) during receive, and to drive amplifier Q1031 (2SC3356) /
Q1025 (2SC3357) for transmit.
4-1
Page 21

Circuit Description
Transmitter
Voice audio from the microphone is delivered via
the MIC (Jack) Unit to the MAIN Unit, after passing
through amplifier Q3039/Q2041 (NJM2902V), preemphasis, limiter (IDC instantaneous deviation control), and LPF Q2001 (NJM2902V), is adjusted for
optimum deviation level and delivered to the next
stage.
Voice input from the microphone and CTCSS are
FM-modulated to the VCO of the synthesizer, while
DCS audio is modulated by the reference frequency
oscillator of the synthesizer.
Synthesizer output, after passing through diode
switch D1025 (1SS321), is amplified by driver Q1031
(2SC3356) / Q1025 (2SC3357) and power module
Q1017 (RA45H4552M) to obtain full RF output. The
RF energy then passes through antenna switch
D1047 / D1048 and a low-pass filter circuit and finally to the antenna connector.
RF output power from the final amplifier is sampled by CM coupler and is rectified by D1037, D1038
(HSM88AS x 2). The resulting DC is fed through
Automatic Power Controller Q1007 (NJM2902V) to
transmitter RF amplifier and thus the power output.
Generation of spurious products by the transmitter is minimized by the fundamental carrier frequency being equal to the final transmitting frequency,
modulated directly in the transmit VCO. Additional harmonic suppression is provided by a low-pass
filter consisting of L1008 L1004, L1002, L1001 and
C1338, C1336, C1337, C1335, C1334, C1333 and
C1332, resulting in more than 60 dB of harmonic suppression prior to delivery to the RF energy to the
antenna.
DCS Demodulator
DCS signals are demodulated on the MAIN-
UNIT, and are applied to low-pass filter Q2040
(NJM2902V), as well as the limiter comparator
Q2003.
CTCSS encoder/decoder
The CTCSS code is generation and encoding by
MPU IC Q2025 (MB90F583B).
Demodulation and detection of the CTCSS tones
are carried out by IC Q2017 (MX165C).
MPU
Operation is controlled by 16-bit MPU IC Q2025
(MB90F583B). The system clock uses a 16.000 MHz
crystal for a time base. IC Q2035 (RN5VL35AA) resets the MPU when the power is on, and monitors
the voltage of the regulated 5V power supply line.
EEPROM
The EEPROM retains TX and RX data for all memory channels and CTCSS data, DCS data, prescaler
dividing, and REF oscillator data (internal/external).
4-2
Page 22

Alignment
The VX-5500 has been carefully aligned at the
factory for the specified performance across the frequency range specified for each version.
Realignment should therefore not be necessary
except in the event of a component failure, or when
altering the transceiver version. If a sudden problem occurs during normal operation, it is likely due
to component failure; realignment should not be
done until after the faulty component has been replaced. All component replacement and service
should be performed only by an authorized
VERTEX STANDARD representative, or the warranty policy may be voided. Therefore, if a fault is suspected, contact the dealer from whom the transceiver
was purchased for instructions regarding repair.
Authorized VERTEX STANDARD service technicians realign all circuits and make complete performance checks to ensure compliance with factory
specifications after replacing any faulty components.
Those who do undertake any of the following alignments are cautioned to proceed at their own risk.
Problems caused by unauthorized attempts at realignment are not covered by the warranty policy.
Also, VERTEX STANDARD must reserve the right
to change circuits and alignment procedures in the
interest of improved performance, without notifying owners.
Under no circumstances should any alignment
be attempted unless the normal function and operation of the transceiver are clearly understood, the
cause of the malfunction has been clearly pinpointed and any faulty components replaced, and the
need for realignment determined to be absolutely
necessary.
Required Test Equipment
The following test equipment (and thorough familiarity with its correct use) is necessary for complete realignment. Correction of problems caused
by misalignment resulting from use of improper test
equipment is not covered under the warranty policy.
While most steps do not require all of the equipment listed, the interactions of some adjustments
may require that more complex adjustments be performed afterwards. Do not attempt to perform only
a single step unless it is clearly isolated electrically
from all other steps. Have all test equipment ready
before beginning, and follow all of the steps in a section in the order presented.
Ì RF signal generator: calibrated output level at
1000 MHz
Ì Deviation Meter (linear detector)
Ì AF Millivoltmeter
Ì SINAD Meter
Ì Inline Wattmeter with 5% accuracy at 1000 MHz
Ì Regulated DC Power Supply: adjustable from 10
to 17 VDC, 15A
Ì 50-ohm non-reactive Dummy Load: 100 W at 1000
MHz
Ì Frequency Counter: <0.1 ppm accuracy at 1000
MHz
Ì AF Signal Generator
Ì DC Voltmeter: high impedance
Ì RF Sampling Coupler (attenuation pad)
Ì AF Dummy Load: 4 ohms, 20W
Ì Oscilloscope
Ì Spectrum Analyzer
Ì IBM PC-compatible computer w/VERTEX
STADARD CT-71 programming cable and CE49
channel programming editor.
Alignment Preparation & Precautions
A dummy load and inline wattmeter must be connected to the main antenna jack in all procedures
that call for transmission, except where specified
otherwise. Correct alignment is not possible with an
antenna. After completing one step, read the following step to determine whether the same test equipment will be required. If not, remove the test equipment (except dummy load and wattmeter, if connected) before proceeding.
Correct alignment requires that the ambient temperature be the same as that of the transceiver and
test equipment, and that this temperature be held
constant between 68° and 86°F (20° ~ 30°C). When
the transceiver is brought into the shop from hot or
cold air it should be allowed some time for thermal
equalization with the environment before alignment.
If possible, alignments should be made with oscillator shields and circuit boards firmly affixed in place.
Also, the test equipment must be thoroughly
warmed up before beginning.
5-1
Page 23

Alignment
Before beginning, connect the transceiver and PC
using the CT-71 programming cable, and download
the EEPROM data from the transceiver to the computer.
Store this data in a disk file so that it can be saved
and retrieved later. Using the table below, program
the channel, CTCSS, and DCS alignment settings for
your transceiver version. Upload this file to the
transceiver.
Note:Signal levels in dB referred to in this proce-
dure are based on 0 dBµ = 0.5 µV (closed circuit).
Caution:Do not connect the audio output line to
ground, and be certain that the speaker has
adequate capability to handle the audio
output from the radio.
Because of the bridge audio amplifier circuit used in the radio, it is necessary to construct and use a simple audio load test
adapter as shown in the schematic diagram
below, when conducting receiver alignment steps.
3.5 PLUG
2-ohm
10W
2-ohm
10W
(4-ohm Dummy Load)
AF Test Adapter Schematic
470uF
Attenuate d
Tes t Ou tp ut( 1/ 2)
GND
Alignment Channel Frequencies
Channel
CH1 450.01 MHz
CH2 470.01 MHz None None Wide
CH3 489.99 MHz
CH4 450.01 MHz
CH5 470.01 MHz None None Narrow
CH6 489.99 MHz
CH7 470.01 MHz 151.4 Hz None Wide
CH8 470.01 MHz None 023 Wide
CH9 470.01 MHz 151.4 Hz None Narrow
CH10 470.01 MHz None 023 Narrow
Frequency CTCSS DCS
(simplex) Encode Encode
Narrow/Wide
PLL & Transmitter
Set up the test equipment as shown for transmit-
ter alignment.
Maintain the supply voltage at 13.8 V DC for all
steps.
RF Signal
Generator
Inline Wattmeter
Deviation Meter
Frequency
Counter
RF Sampling
Coupler
CT-71 connection
Cable
PC
COM port
Transceiver
Power Supply
13.8V DC
PLL VCV
Ì Connect the positive lead of the DC voltmeter to
test point TP1008 (VCV) on the Main Unit, as indicated in the figure, and connect the negative
lead to chassis ground.
Ì Set the transceiver to the high band edge fre-
quency channel (CH3 or CH6), then key the transmitter, and adjust L1026 on the Main Unit for 4.35
V ±0.05 V on the voltmeter.
Ì Adjust L1023 on the Main Unit for 4.3 V ±0.1 V
on the voltmeter.
Ì Next select to the low edge frequency channel
(CH1 or CH4) and confirm the VCV is more than
1.0 V on the voltmeter.
Ì Key the transmitter, and confirm the VCV is more
than 0.8 V on the voltmeter.
PLL Reference Frequency
With the wattmeter, dummy load and frequency
counter connected to the antenna jack, and select
band center frequency channel (CH2 or CH5), key
the transmitter and adjust VR1001 on the Main Unit,
if necessary, so the counter frequency is within 100
Hz of the channel center frequency for the transceiver version.
5-2
Page 24

Alignment
Transmitter Output Power
The following transmitter parameters can be adjusted from the computer by utilizing the Alignment
Software. Refer to the onboard help of the Alignment Software Manual for details.
Ì Select the band center frequency channel (CH2
or CH5), and select the “high” power output level.
Key the transmitter and adjust “TX PWR Hi“ for a
power output of 45 Watts (± 1.0 W) as indicated
on the wattmeter.
Ì Stay on the band center frequency channel (CH2
or CH5), and select the “low” power output level.
Key the transmitter and adjust “TX PWR L3“ for
a power level of 25 Watts (± 0.5 W) as indicated
on the wattmeter.
Transmitter Deviation
The following modulation parameters can be adjusted from the computer by utilizing the Alignment
Software. Refer to the onboard help of the Alignment Software Manual for details.
Microphone Audio Modulation Level
Ì Select the band center frequency channel (CH2),
and select the “low” power output level.
Ì Adjust the AF generator for 50mV (–30dBm) out-
put at 1 kHz, as applied to the microphone jack.
Ì Key the transmitter and adjust “MAX Dev (wide)“
for maximum deviation of 4.3 kHz ± 0.1 kHz as
indicated on the deviation meter.
Ì Select the band center frequency channel (CH5),
and select the “low” power output level.
Ì Adjustdjust the AF generator for 50mV (–30dBm)
output at 1 kHz, as applied to the microphone
jack.
TP1008L1023L1026 VR1001
5-3
Page 25

Alignment
Ì Key the transmitter and adjust “MAX Dev (Nar-
row)“ for maximum deviation of 2.2 kHz ± 0.2 kHz
as indicated on the deviation meter.
CTCSS Modulation Level
Ì Select the “low” power output level.
Ì Select the band center frequency channel (CH7),
with 151.4 Hz CTCSS encode, and reduce the AF
generator injection to zero.
Ì Key the transmitter and adjust “CTCSS Dev (wide)“
for CTCSS deviation of 0.75 kHz ± 0.1 kHz as indicated on the deviation meter.
Ì Select the band center frequency channel (CH9),
with 151.4 Hz CTCSS encode, and reduce the AF
generator injection to zero.
Ì Key the transmitter and adjust “CTCSS Dev (Nar-
row)“ for CTCSS deviation of 0.35 kHz ± 0.1 kHz
as indicated on the deviation meter.
DCS Modulation Level
Ì Select the “low” power output level.
Ì Select the band center frequency channel (CH8),
with 023 DCS code, and reduce the AF generator
injection to zero.
Ì Key the transmitter and adjust “DCS Dev (wide)“
for DCS deviation of 0.75 kHz ± 0.1 kHz as indicated on the deviation meter.
Ì Select the band center frequency channel (CH10),
with 023 DCS code, and reduce the AF generator
injection to zero.
Ì Key the transmitter and adjust “DCS Dev (Nar-
row)“ for CTCSS deviation of 0.35 kHz ± 0.1 kHz
as indicated on the deviation meter.
Receiver
The sensitivity parameters can be adjusted from
the computer by utilizing the Alignment Software.
Refer to the onboard help of the Alignment Software
Manual for details.
Ì Set up the test equipment as shown for receiver
alignment, and install the audio test adapter.
50-Ohm
Dummy Load
Inline
Watt meter
Deviation
Meter
Frequency
Counter
RF Sampling
Coupler
CT-71
Connection
Cable
AC Volt
Meter
Ì With the transceiver set to the band center fre-
quency channel (CH2), and with the RF signal
generator tuned to the same frequency, set the
generator for ±3.0 kHz deviation with 1 kHz tone
modulation, and set the output level for –5.0 dBµ
at the antenna jack.
Ì Adjust “Rx TUNE“ the receiver front-end tuning
for optimum SINAD, reducing signal generator
output level as necessary for proper meter de-
flection.
Ì After the previous step, the final signal genera-
tor level should be less than –5.0 dBµ for 12dB
SINAD.
RF Signal
Generator
Power Supply
13.8V DC
13.6
Transceiver
AF Generator
SINAD
Meter
AF Test
Adapter
5-4
Page 26

Alignment
Squelch Threshold
The squelch parameters can also be adjusted from
the computer by utilizing the Alignment Software.
Refer to the onboard help of the Alignment Software
Manual for details.
Tight SQL RSSI LEVEL (Wide)
Ì Select the band center frequency channel (CH2),
and with the RF signal generator turned to the
same frequency, set the generator for ±3.0 kHz
deviation with 1 kHz tone modulation, and set
the output level for 3.0 dBµ at the antenna jack.
Threshold NSQ LEVEL (Wide)
Ì Select the band center frequency channel (CH2),
and with the RF signal generator turned to the
same frequency, set the generator for ±3.0 kHz
deviation with 1 kHz tone modulation, and set
the output level for –8.0 dBµ at the antenna jack.
Tight SQL NSQ LEVEL (Wide)
Ì Select the band center frequency channel (CH2),
and with the RF signal generator turned to the
same frequency, set the generator for ±3.0 kHz
deviation with 1 kHz tone modulation, and set
the output level for 0 dBµ at the antenna jack.
Tight SQL RSSI LEVEL (Narrow)
Ì Select the band center frequency channel (CH5),
and with the RF signal generator turned to the
same frequency, set the generator for ±1.5 kHz
deviation with 1 kHz tone modulation, and set
the output level for 3.0 dBµ at the antenna jack.
Threshold NSQ LEVEL (Narrow)
Ì Select the band center frequency channel (CH5),
and with the RF signal generator turned to the
same frequency, set the generator for ±1.5 kHz
deviation with 1 kHz tone modulation, and set
the output level for –8.0 dBµ at the antenna jack.
Tight SQL NSQ LEVEL (Narrow)
Ì Select the band center frequency channel (CH5),
and with the RF signal generator turned to the
same frequency, set the generator for ±1.5 kHz
deviation with 1 kHz tone modulation, and set
the output level for 0 dBµ at the antenna jack.
Ì Adjust the squelch threshold level “Tight SQL
NSQ(Narrow)“ such that the squelch just open at
this signal input level (the BUSY LED will turn
on).
5-5
Page 27

Alignment
Note:
5-6
Page 28

Circuit Diagram
Circuit Diagram
MAIN Unit
MAIN Unit
(13.8V)
3.6V
(1.3V)
(13.7V)
(13.1V)
5.9V
(8.9V)
1.5V
3.6V (1.3V)
3.6V
2.0V
3.6V
(8.8V)
0.9V
(8.9V)
8.8V (0.0V)
4.0V
3.8V
7.0V
7.4V (7.2V)
(1.5V)
3.2V
1.5V
6.9V (6.9V)
2.0V
2.4V
(2.4V)
2.1V
1.1V
(1.1V)
4.0V (4.0V)
7.7V
2.8V
(7.7V)
Wide : (8.7V)
Narrow : (4.1V)
(4.9V)
(0.9V)
(4.8V)
(1.7V)
(5.6V)
(5.5V)
Wide : (4.1V)
Narrow : (8.7V)
(4.3V)
(4.9V)
(5.3V)
(4.4V)
(0.8V)
(4.9V)
(4.2V)
(3.2V)
(5.6V)
(4.8V)
(5.2V)
(2.2V)
(1.1V)
(0.6V)
Wide : (8.7V)
Narrow : (4.1V)
(4.8V)
Wide : (4.1V)
Narrow : (8.7V)
(3.8V)
Wide : 0V (5.0V)
Narrow : 5.0V (0V)
(3.0V)
(1.5V)
3.9V
3.9V
4.3V
4.3V
8.8V
(8.2V)
0V (5.0V)
Narrow : 5.0V (0.0V)
Wide : 0.0V (5.0V)
(2.5V)
(1.7V)
(1.3V)
(8.5V)
8.2V (8.8V)
5.0V (0V)
(1.3V)
0V (8.81V)
(2.2V)
2.4V (2.7V)
(2.1V)
4.4V (4.4V)
(8.4V)
(1.3V)
(7.0V)
(4.9V)
Narrow : (8.7V)
(2.7V)
(8.5V)
(2.1V)
XX : TX 470.1 MHz, MIC Input Level 1 kHz 3.0mV (STD Dev), High Power
(XX) : RX 470.1 MHz, RF Input Level 40dBµ emf (MOD=1.0 kHz, Dev=3.0 kHz), EXT SP OUT 10% Distn
(3.1V)
(4.8V)
Narrow : (4.0V)
Wide : (8.7V)
Narrow : (8.7V)
Wide : (4.0V)
Narrow : (0.0V)
Wide : (8.7V)
Wide : (0.0V)
Narrow : (8.7V)
Wide : (4.0V)
Narrow : (4.0V)
Wide : (8.7V)
(4.8V)
(3.2V)
(8.6V)
(2.4V)
6A-1
Page 29

MAIN Unit
4.5V
(1.0V)
Power ON : 0.3V
OFF : 13.7V
(12.4V)
(5.0V)
(4.2V)
(1.2V)
(3.2V)
4.5V
(0.2V)
(0.8V)
(2.1V)
(3.2V)
4.5V
(2.4V)
(3.9V)
(3.2V)
4.5V
(3.9V)
(3.9V)
(1.0V)
(3.9V)
(0.9V)
(3.9V)
(1.1V)
(1.1V)
(1.1V)
(1.2V)
(1.1V)
(1.1V)
(13.7V)
(6.8V)
(0V)
(3.9V)
(5.0V)
(5.0V)
Power ON: 0.0V
OFF: 13.7V
0.6V
(5.0V)
4.9V
(4.9V)
3.2V (3.2V)
3.2V
(3.2V)
3.2V
3.2V (3.2V)
(13.1V)
(4.9V)
(2.3V)
(6.2V)
(2.2V)
(2.4V)
(2.5V)
(6.1V)
(2.5V)
(0V)
(4.4V)
(4.4V)
2.2V
(4.4V)
(4.4V)
(4.5V)
(2.6V)
4.4V
3.9V
3.9V
3.9V (3.9V)
3.9V
3.8V
3.9V
3.8V
COMP ON : 5.0V
OFF : 0.0V
Q2031
1 2.5V 9 2 0.7V 10 3 2.5V 11 4 - 12 2.5V
5 - 13 2.5V
6 2.5V 14 2.5V
7 - 15 0.5V
8 2.5V 16 2.5V
6A-2
3.2V (3.2V)
3.2V
(6.2V)
(6.1V)
XX : TX 470.1 MHz, MIC Input Level 1 kHz 3.0mVrms (STD Dev), High Power
(XX) : RX 470.1 MHz, RF Input Level 40dBµ emf (MOD=1.0 kHz, Dev=3.0 kHz), EXT SP OUT 10% Distn
Page 30

Parts Layout
MAIN Unit
ACE
FBD G
TA31136FN
(Q1034)
MB90F583B
(Q2025)
SA7025DK
(Q1033)
1
AT24C256
(Q2036)
CXA1846N
(Q2019)
RA45H4452M
(Q1017)
TC4W53FU
(Q2004)
BU4066BF
(Q2007)
TDA7240AV
(Q2018)
2
2SC4154E (LE)
(Q1035, 1193, 2024)
2SC4226 (R24)
(Q1020)
3
4
5
2SC5107-O (MFO)
(Q1026)
RT1N241M (N2)
(Q1010, 1027, 1042,
1044, 1194, 2005,
2008, 2009, 2010,
2014, 2015, 2032,
2033, 2037, 2039)
DTC323TK (H02)
(Q2016, 2023)
2SB1132R (BA)
(Q1011, 1012)
IMH6 (H6)
(Q1014, 1028)
2SK520 (K41)
(Q1188, 1189, 1190,
1191)
2SK508 (K52)
(Q1019)
2SC3357-T2
(Q1018, 1030,
1192)
IMD3 (D3)
(Q2002, 2020)
TC4S66F (C9)
(Q2038, 2045)
Side A
MC2850 (A7)
(D2012)
MC2846 (A4)
(D2001)
6A-3
Page 31

MAIN Unit
MX165CDW
(Q2017)
2SB1201STP
(Q1005)
MM1216ENRE (1A)
(Q1004)
BU4053BCF
(Q2026)
LA8630M
(Q2031)
2SJ327Z
(Q2027)
NJM2902V
(Q1007, 2001, 2003,
2040, 2041, 2042,
2046)
IMH6 (H6)
(Q1003, 1045, 2011)
RN5RL30AA (OC)
(Q1046)
a dc fe
gb
1
2
IMZ1 (Z1)
(Q2013)
2SC4154E (LE)
(Q1006)
2SC5107-O (MFO)
(Q1029, 1032)
2SC3356 (R24)
(Q1031)
2SC4215Y (QY)
(Q1041)
2SA1602A (MF)
(Q2029)
DTB123EK (F12)
(Q2021, 2022)
2SC3357-T2
(Q1025)
RN5VL35AA (C5)
(Q2035)
IMX1 (X1)
(Q2006)
RT1N241M (N2)
(Q1015, 2030)
NJM78L05UA (8C)
(Q1038, 2028)
3
4
5
6A-4
MC2846
(D2011)
1SS321 (F9)
(D1025)
MC2850 (A7)
(D2006, 2007, 2008,
2013)
HSM88AS (C1)
(D1037, 1038)
Side B
Page 32

Parts List
MAIN Unit
REF.
C 1001 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B b2
C 1002 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B b2
C 1005 CHIP CAP. 0.0047uF 50V B GRM39B472K50PT K22174833 1- B e5
C 1006 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A D2
C 1007 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A B5
C 1008 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B f2
C 1009 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B f1
C 1010 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B f1
C 1020 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B b2
C 1022 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- B f2
C 1026 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A D2
C 1027 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A D2
C 1028 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B d2
C 1029 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d2
C 1030 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 10uF 16V RV2-16V100MB55-R K48120014 1- A B2
C 1031 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B f2
C 1032 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 25V TEMSVB21E475M-8R K78140019 1- B f2
C 1035 CHIP CAP. 68pF 50V CH GRM39CH680J50PT K22174231 1- B e5
C 1036 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 16V TESVA1C105M1-8R K78120009 1- A B5
C 1038 CHIP CAP. 6pF 50V CH GRM39CH060D50PT K22174207 1- A G3
C 1039 CHIP CAP. 3pF 50V CJ GRM39CJ030C50PT K22174204 1- A G3
C 1040 CHIP CAP. 5pF 50V CH GRM39CH050C50PT K22174206 1- A G3
C 1045 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B c2
C 1047 CHIP CAP. 0.022uF 25V B GRM39B223K25PT K22144807 1- B c2
C 1048 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c2
C 1049 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d4
C 1050 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B f2
C 1051 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- B d4
C 1052 CHIP TA.CAP. 47uF 16V TEMSVC1C476M12R K78120057 1- B f2
C 1053 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- B d4
C 1054 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d4
C 1055 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B c2
C 1056 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d2
C 1057 CHIP CAP. 7pF 50V CH GRM39CH070D50PT K22174208 1- A G3
C 1058 CHIP CAP. 5pF 50V CH GRM39CH050C50PT K22174206 1- A G3
C 1060 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 25V TEMSVC1E106M12R K78140021 1- A E2
C 1061 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c2
C 1062 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A D2
C 1063 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d5
C 1064 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM39CH040C50PT K22174205 1- A F3
C 1066 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A G3
C 1067 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a3
C 1068 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM39CH040C50PT K22174205 1- A F3
C 1070 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A E2
C 1071 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B c2
C 1072 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d2
C 1073 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c2
C 1075 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A E2
C 1078 CHIP CAP. 22pF 50V CH GRM39CH220J50PT K22174219 1- A D5
C 1079 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- A D5
C 1080 CHIP CAP. 6pF 50V CH GRM39CH060D50PT K22174207 1- A D5
C 1081 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- A D5
C 1082 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM39CH040C50PT K22174205 1- A D5
C 1083 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- B d5
C 1084 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- A D5
C 1085 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- B d5
C 1086 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- A D5
DESCRIPTION
PCB with Components CB1968001
Printed Circuit Board FR008090C 1-
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
*** MAIN UNIT ***
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-5
Page 33

MAIN Unit
REF.
C 1087 FILM CAP. 0.022uF 16V ECHU1C223JB5 K57120011 1- A E5
C 1088 FILM CAP. 0.022uF 16V ECHU1C223JB5 K57120011 1- A E5
C 1089 CHIP CAP. 5pF 50V CH GRM39CH050C50PT K22174206 1- A F4
C 1091 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- A F3
C 1094 CHIP CAP. 8pF 50V CH GRM39CH080D50PT K22174209 1- B d2
C 1099 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH GRM39CH100D50PT K22174211 1- B d2
C 1100 CHIP CAP. 9pF 50V CH GRM39CH090D50PT K22174210 1- B d2
C 1102 CHIP CAP. 8pF 50V CH GRM39CH080D50PT K22174209 1- A D5
C 1103 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B d4
C 1104 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- A D4
C 1105 CHIP CAP. 0.5pF 50V CK GRM39CK0R5C50PT K22174201 1- A D4
C 1106 CHIP CAP. 3pF 50V CJ GRM39CJ030C50PT K22174204 1- A D5
C 1107 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH GRM39CH100D50PT K22174211 1- A D4
C 1108 CHIP CAP. 6pF 50V CH GRM39CH060D50PT K22174207 1- A D4
C 1109 CHIP CAP. 1pF 50V CK GRM39CK010C50PT K22174202 1- A D4
C 1112 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- A D4
C 1116 CHIP CAP. 9pF 50V CH GRM39CH090D50PT K22174210 1- A F3
C 1117 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B b3
C 1118 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d3
C 1119 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A D3
C 1120 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 16V TESVA1C105M1-8R K78120009 1- A D3
C 1121 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d3
C 1122 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A D3
C 1123 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A D4
C 1124 CHIP CAP. 12pF 50V CH GRM39CH120J50PT K22174213 1- A D4
C 1125 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A D4
C 1126 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V CH GRM39CH471J50PT K22174249 1- A D4
C 1127 CHIP CAP. 15pF 50V CH GRM39CH150J50PT K22174215 1- B c4
C 1128 CHIP CAP. 22pF 50V CH GRM39CH220J50PT K22174219 1- B c4
C 1129 CHIP TA.CAP. 0.68uF 10V TESVSP1A684M-8R K78100025 1- A E4
C 1130 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d4
C 1131 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c4
C 1132 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A F3
C 1133 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A C2
C 1135 CHIP CAP. 9pF 50V CH GRM39CH090D50PT K22174210 1- A E2
C 1136 CHIP CAP. 5pF 50V CH GRM39CH050C50PT K22174206 1- A E3
C 1137 CHIP CAP. 6pF 50V CH GRM39CH060D50PT K22174207 1- B d3
C 1138 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d3
C 1139 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d3
C 1141 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d4
C 1142 CHIP CAP. 15pF 50V CH GRM39CH150J50PT K22174215 1- B c4
C 1143 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d3
C 1145 CHIP CAP. 9pF 50V CH GRM39CH090D50PT K22174210 1- B c4
C 1146 CHIP CAP. 9pF 50V CH GRM39CH090D50PT K22174210 1- B c4
C 1148 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- B c4
C 1149 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A C3
C 1153 CHIP CAP. 5pF 50V CH GRM39CH050C50PT K22174206 1- A E4
C 1154 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH GRM39CH100D50PT K22174211 1- A E4
C 1156 CHIP CAP. 8pF 50V CH GRM39CH080D50PT K22174209 1- A E3
C 1157 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A E3
C 1158 CHIP CAP. 8pF 50V CH GRM39CH080D50PT K22174209 1- B c3
C 1159 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c3
C 1160 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B b5
C 1161 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B c4
C 1162 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c4
C 1164 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B c4
C 1165 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B c4
C 1166 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A E5
C 1167 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A E4
C 1168 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH GRM39CH330J50PT K22174223 1- A E4
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-6
Page 34

MAIN Unit
REF.
C 1169 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A E4
C 1170 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c4
C 1171 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A E5
C 1172 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- B b5
C 1173 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B b5
C 1174 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH GRM39CH100D50PT K22174211 1- A E4
C 1175 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B b3
C 1177 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH GRM39CH100D50PT K22174211 1- A E5
C 1178 CHIP CAP. 6pF 50V CH GRM39CH060D50PT K22174207 1- A E5
C 1179 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A F5
C 1180 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B b5
C 1181 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A F5
C 1182 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B b4
C 1183 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B b4
C 1184 CHIP CAP. 120pF 50V CH GRM39CH121J50PT K22174237 1- A F5
C 1185 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A E5
C 1186 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A A5
C 1187 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 6.3V TEMSVA0J106M-8R K78080027 1- B c5
C 1188 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c5
C 1189 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH GRM39CH330J50PT K22174223 1- A G4
C 1190 CHIP CAP. 15pF 50V CH GRM39CH150J50PT K22174215 1- B a4
C 1191 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A G3
C 1192 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B c5
C 1194 CHIP CAP. 18pF 50V CH GRM39CH180J50PT K22174217 1- B a4
C 1195 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B b5
C 1196 CHIP TA.CAP. 33uF 10V TEMSVB21A336M-8R K78100047 1- B b5
C 1197 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A F5
C 1198 CHIP CAP. 82pF 50V CH GRM39CH820J50PT K22174233 1- A F5
C 1199 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A F5
C 1200 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- A F5
C 1201 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B b5
C 1202 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c5
C 1203 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 6.3V TEMSVA0J106M-8R K78080027 1- B c5
C 1204 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- B c5
C 1205 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM39CH040C50PT K22174205 1- A G3
C 1206 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH GRM39CH100D50PT K22174211 1- A E5
C 1207 CHIP CAP. 18pF 50V CH GRM39CH180J50PT K22174217 1- A F3
C 1208 CHIP CAP. 18pF 50V CH GRM39CH180J50PT K22174217 1- A E3
C 1209 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM39CH040C50PT K22174205 1- A E3
C 1210 CHIP CAP. 27pF 50V CH GRM39CH270J50PT K22174221 1- A G5
C 1211 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a5
C 1212 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a5
C 1213 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH GRM39CH330J50PT K22174223 1- B a5
C 1214 CHIP CAP. 3pF 50V CJ GRM39CJ030C50PT K22174204 1- A E3
C 1215 CHIP CAP. 39pF 50V CH GRM39CH390J50PT K22174225 1- A G5
C 1216 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A F5
C 1217 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM39CH040C50PT K22174205 1- A E3
C 1218 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM39CH040C50PT K22174205 1- A E3
C 1219 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM39CH040C50PT K22174205 1- A E3
C 1220 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM39CH040C50PT K22174205 1- A E3
C 1221 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a5
C 1222 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A E5
C 1223 CHIP CAP. 3pF 50V CJ GRM39CJ030C50PT K22174204 1- A E3
C 1226 CHIP CAP. 0.5pF 50V CK GRM39CK0R5C50PT K22174201 1- A D5
C 1227 CHIP CAP. 27pF 50V CH GRM39CH270J50PT K22174221 1- A G4
C 1228 CHIP CAP. 39pF 50V CH GRM39CH390J50PT K22174225 1- A G4
C 1233 CHIP CAP. 22pF 50V CH GRM39CH220J50PT K22174219 1- A F3
C 1234 CHIP CAP. 9pF 50V CH GRM39CH090D50PT K22174210 1- A E3
C 1235 CHIP CAP. 7pF 50V CH GRM39CH070D50PT K22174208 1- A G3
C 1236 CHIP CAP. 7pF 50V CH GRM39CH070D50PT K22174208 1- A F3
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-7
Page 35

MAIN Unit
REF.
C 1238 CHIP CAP. 7pF 50V CH GRM39CH070D50PT K22174208 1- A E3
C 1239 CHIP CAP. 7pF 50V CH GRM39CH070D50PT K22174208 1- A E3
C 1241 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a4
C 1242 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A F3
C 1244 CHIP CAP. 5pF 50V CH GRM39CH050C50PT K22174206 1- A F3
C 1245 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B b3
C 1246 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B b4
C 1247 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a3
C 1248 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A G3
C 1249 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- A G3
C 1250 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- A G4
C 1251 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A G4
C 1253 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- B b3
C 1255 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V CH GRM39CH471J50PT K22174249 1- B b2
C 1256 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V CH GRM39CH471J50PT K22174249 1- B b2
C 1257 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V CH GRM39CH471J50PT K22174249 1- B b2
C 1258 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V CH GRM39CH471J50PT K22174249 1- B b2
C 1259 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B c3
C 1260 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c3
C 1261 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH GRM39CH330J50PT K22174223 1- A G5
C 1263 CHIP CAP. 39pF 50V CH GRM39CH390J50PT K22174225 1- A G4
C 1264 CHIP CAP. 39pF 50V CH GRM39CH390J50PT K22174225 1- A G5
C 1265 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a5
C 1267 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a5
C 1268 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a4
C 1269 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a4
C 1270 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a5
C 1271 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a4
C 1272 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a5
C 1273 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B b3
C 1274 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B b3
C 1275 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c4
C 1276 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B c4
C 1278 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A F3
C 1279 CHIP CAP. 5pF 50V CH GRM39CH050C50PT K22174206 1- A F3
C 1280 CHIP CAP. 2pF 50V CK GRM39CK020C50PT K22174203 1- A E3
C 1282 CHIP CAP. 3pF 50V CJ GRM39CJ030C50PT K22174204 1- A E3
C 1283 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A E3
C 1284 CHIP CAP. 1pF 50V CK GRM39CK010C50PT K22174202 1- A F3
C 1287 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A E3
C 1288 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- B d3
C 1289 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- B d4
C 1290 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- A E4
C 1291 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- A E4
C 1292 CHIP CAP. 7pF 50V CH GRM39CH070D50PT K22174208 1- B c4
C 1293 CHIP CAP. 12pF 50V CH GRM39CH120J50PT K22174213 1- A E4
C 1294 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- B c4
C 1296 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A D2
C 1299 CHIP CAP. 7pF 50V CH GRM39CH070D50PT K22174208 1- A D4
C 1300 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A E5
C 1301 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A F5
C 1302 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B b5
C 1304 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c3
C 1305 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B b5
C 1307 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a5
C 1308 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a4
C 1309 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a5
C 1310 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a4
C 1311 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- B d4
C 1312 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c5
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-8
Page 36

MAIN Unit
REF.
C 1314 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c3
C 1315 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B a3
C 1316 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A D2
C 1317 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d2
C 1318 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B b5
C 1319 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B b5
C 1322 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A F4
C 1323 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A C3
C 1324 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A C3
C 1325 CHIP CAP. 1pF 50V CK GRM39CK010C50PT K22174202 1- B a2
C 1327 CHIP CAP. 2pF 50V CK GRM39CK020C50PT K22174203 1- B a3
C 1328 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM39CH040C50PT K22174205 1- A D5
C 1329 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A A5
C 1330 CHIP CAP. 0.0056uF 50V B GRM39B562M50PT K22174818 1- A A5
C 1331 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A G3
C 1332 FILM CAP. 2pF 500V UC232H0020D-T K33279043 1- B a2
C 1333 FILM CAP. 7pF 500V UC232H0070D-T K33279046 1- B a2
C 1334 FILM CAP. 2pF 500V UC232H0020D-T K33279043 1- B a2
C 1335 FILM CAP. 3pF 500V UC232H0030D-T K33279027 1- B a2
C 1336 FILM CAP. 5pF 500V UC232H0050D-T K33279010 1- B a1
C 1337 FILM CAP. 1pF 500V UC232H0010D-T K33279036 1- B a1
C 1338 FILM CAP. 1pF 500V UC232H0010D-T K33279036 1- B a1
C 1339 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 630V R GHM1030R102K630PT K22281801 1- B a1
C 1340 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A F2
C 1341 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B c2
C 1342 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A E4
C 1343 CHIP CAP. 2pF 50V CK GRM39CK020C50PT K22174203 1- A E4
C 1344 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 3300uF 16V RE3-16V332M 3300UF K40129065 1C 1345 CHIP CAP. 0.0056uF 50V B GRM39B562M50PT K22174818 1- A A5
C 1346 CHIP CAP. 0.0056uF 50V B GRM39B562M50PT K22174818 1- A A5
C 1347 CHIP CAP. 0.0056uF 50V B GRM39B562M50PT K22174818 1- A A5
C 1348 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 16V TESVA1C105M1-8R K78120009 1- A A5
C 1349 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a5
C 1350 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH GRM39CH330J50PT K22174223 1- A E3
C 1351 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1C 2001 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A B1
C 2002 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A B1
C 2003 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A A1
C 2004 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A B1
C 2005 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A B1
C 2006 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A B1
C 2007 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A B1
C 2008 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A B1
C 2009 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A B1
C 2010 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A A1
C 2011 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A B1
C 2012 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A B1
C 2013 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A A1
C 2014 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A A1
C 2015 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A A1
C 2016 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A A1
C 2017 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A A1
C 2018 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- B f5
C 2019 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- B f5
C 2020 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B f5
C 2021 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- B f5
C 2022 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A B5
C 2023 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- B f5
C 2024 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- B f5
C 2025 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B f5
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-9
Page 37

MAIN Unit
REF.
C 2026 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B f5
C 2027 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A B5
C 2028 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- B e5
C 2029 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B e5
C 2030 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A B5
C 2031 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B f5
C 2032 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A C4
C 2033 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- B g1
C 2034 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A A1
C 2035 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- A A2
C 2036 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A B1
C 2037 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A A1
C 2038 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A A1
C 2039 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A A1
C 2040 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V CH GRM39CH471J50PT K22174249 1- B f5
C 2041 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V CH GRM39CH471J50PT K22174249 1- B f5
C 2042 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V CH GRM39CH471J50PT K22174249 1- B g5
C 2043 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- B f5
C 2044 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V CH GRM39CH471J50PT K22174249 1- B f5
C 2045 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A B5
C 2046 CHIP CAP. 47pF 50V CH GRM39CH470J50PT K22174227 1- B f5
C 2047 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B f5
C 2051 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- B g1
C 2052 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B f4
C 2057 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B d4
C 2058 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B e4
C 2059 CHIP CAP. 0.0022uF 50V B GRM39B222K50PT K22174822 1- B e4
C 2060 CHIP CAP. 0.022uF 25V B GRM39B223K25PT K22144807 1- B e4
C 2061 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B e4
C 2062 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A C4
C 2063 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A B5
C 2064 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A B5
C 2065 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B f4
C 2066 CHIP CAP. 0.015uF 25V B GRM39B153K25PT K22144805 1- B f4
C 2067 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B e3
C 2068 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B e3
C 2069 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 16V TESVA1C105M1-8R K78120009 1- A C3
C 2070 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B e3
C 2071 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A C3
C 2072 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A C3
C 2073 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- A C4
C 2074 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- A C4
C 2075 CHIP CAP. 0.22uF 10V B GRM39B224K10PT K22104801 1- B g3
C 2078 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 100uF 16V ECEV1CA101WP K48120012 1- A A2
C 2079 CHIP CAP. 0.22uF 10V B GRM39B224K10PT K22104801 1- B g3
C 2080 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A A2
C 2081 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- A A3
C 2082 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- B g3
C 2083 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 16V TESVA1C105M1-8R K78120009 1- B e4
C 2084 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V CH GRM39CH471J50PT K22174249 1- B e4
C 2085 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B e4
C 2086 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 16V TESVA1C105M1-8R K78120009 1- A C4
C 2087 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V CH GRM39CH471J50PT K22174249 1- B e4
C 2088 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V CH GRM39CH471J50PT K22174249 1- B d4
C 2089 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B f5
C 2090 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A B5
C 2092 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B f3
C 2093 CHIP CAP. 22pF 50V CH GRM39CH220J50PT K22174219 1- A D3
C 2094 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A B4
C 2095 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A C5
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-10
Page 38

MAIN Unit
REF.
C 2097 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 16V TESVA1C105M1-8R K78120009 1- A A3
C 2098 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B g4
C 2099 CHIP CAP. 270pF 50V B GRM39B271M50PT K22174802 1- B e5
C 2100 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B e5
C 2101 CHIP CAP. 270pF 50V B GRM39B271M50PT K22174802 1- B e5
C 2102 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B e4
C 2103 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V CH GRM39CH471J50PT K22174249 1- B d4
C 2104 CHIP CAP. 0.0047uF 50V B GRM39B472K50PT K22174833 1- B d4
C 2105 CHIP CAP. 9pF 50V CH GRM39CH090D50PT K22174210 1- A A4
C 2106 CHIP CAP. 18pF 50V CH GRM39CH180J50PT K22174217 1- A A4
C 2107 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM39CH040C50PT K22174205 1- A A4
C 2108 CHIP CAP. 820pF 50V B GRM39B821M50PT K22174808 1- A D4
C 2109 CHIP CAP. 0.0056uF 50V B GRM39B562M50PT K22174818 1- A D3
C 2110 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 16V TESVA1C105M1-8R K78120009 1- B d4
C 2111 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A D4
C 2112 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A D3
C 2113 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A D4
C 2114 CHIP CAP. 7pF 50V CH GRM39CH070D50PT K22174208 1- A C3
C 2115 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A C4
C 2116 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A C3
C 2117 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A C5
C 2118 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A C5
C 2119 CHIP CAP. 0.0015uF 50V B GRM39B152K50PT K22174827 1- A C5
C 2120 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A C5
C 2121 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A C5
C 2122 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A C5
C 2123 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 16V TESVA1C105M1-8R K78120009 1- A C5
C 2124 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH GRM39CH100D50PT K22174211 1- B e5
C 2125 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 16V B GRM39B473K16PT K22124804 1- A A3
C 2126 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A B3
C 2127 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 16V TESVA1C105M1-8R K78120009 1- A B3
C 2128 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A B2
C 2129 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B e5
C 2130 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- A C5
C 2131 CHIP CAP. 330pF 50V B GRM39B331K50PT K22174820 1- B e5
C 2132 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B d5
C 2133 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B e4
C 2134 CHIP CAP. 330pF 50V B GRM39B331K50PT K22174820 1- B e4
C 2135 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B d4
C 2136 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B f4
C 2137 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 16V TESVA1C105M1-8R K78120009 1- A C5
C 2138 CHIP CAP. 820pF 50V B GRM39B821M50PT K22174808 1- B e5
C 2139 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B e5
C 2140 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- B e5
C 2141 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B e4
C 2142 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B d5
C 2143 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B f5
C 2144 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B d4
C 2145 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B f2
C 2146 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A A5
C 2147 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B f4
C 2148 CHIP CAP. 0.0022uF 50V B GRM39B222K50PT K22174822 1- B e5
C 2149 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- B e5
C 2150 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 470uF 16V RE3-16V471M 470UF K40129066 1- A C2
C 2151 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B f2
C 2153 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B f3
C 2155 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A B4
C 2156 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B g4
C 2157 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B g4
C 2158 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B g4
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-11
Page 39

MAIN Unit
REF.
C 2159 CHIP CAP. 0.22uF 10V B GRM39B224K10PT K22104801 1- B g4
C 2160 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B g4
C 2162 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- B g4
C 2163 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B f2
C 2164 CHIP CAP. 0.22uF 10V B GRM39B224K10PT K22104801 1- B e3
C 2165 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A B3
C 2166 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A B3
C 2167 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- A B3
C 2168 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B f3
C 2169 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B f3
C 2170 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- B g4
C 2171 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B g4
C 2172 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- B f2
C 2173 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B e3
C 2174 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A A3
C 2176 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A B5
C 2177 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 16V B GRM39B473K16PT K22124804 1- A B3
C 2178 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B a1
C 2179 CHIP CAP. 0.015uF 25V B GRM39B153K25PT K22144805 1- B g5
C 2180 CHIP CAP. 0.015uF 25V B GRM39B153K25PT K22144805 1- B g4
C 2181 CHIP CAP. 0.015uF 25V B GRM39B153K25PT K22144805 1- B f5
C 2182 CHIP CAP. 0.015uF 25V B GRM39B153K25PT K22144805 1- B f4
C 2211 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A A5
C 2223 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A A4
C 2226 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B g5
C 2227 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B f2
C 2228 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- A A5
C 2230 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM39CH101J50PT K22174235 1- B f5
C 2232 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1C 2233 CHIP CAP. 0.22uF 10V B GRM39B224K10PT K22104801 1C 2251 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A C3
C 2253 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A C3
C 2255 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B e3
C 2256 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B e3
C 2257 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B e3
C 2258 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B e3
C 2259 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B e2
C 2260 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B e3
C 2261 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B e3
C 2262 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B ECUV1C103KBV K22129510 1- B e3
CD1001 CERAMIC DISC CDBC450CX24-TC H7901340 1- B b5
CF1001 CERAMIC FILTER CFWM450G H3900435 1- A F4
CF1002 CERAMIC FILTER CFWM450E H3900466 1- A F4
CO2001 CERAMIC OSC 1MHz CSBF1000J221T-TC01 H7900950 1- A C4
D 1001 DIODE RLS135 TE-11 G2070128 1- A G3
D 1003 SURGE ABSORBER P6KA18 Q9000721 1- A B2
D 1004 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- B c2
D 1005 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- B d2
D 1007 DIODE HVU350TRF G2070380 1- A G3
D 1009 DIODE HVU350TRF G2070380 1- A F3
D 1011 DIODE 1SV282(TPH3) G2070778 1- A D5
D 1014 DIODE 1SV284(TPH3) G2070622 1- A D5
D 1015 DIODE 1SV284(TPH3) G2070622 1- A D5
D 1018 DIODE 1SV282(TPH3) G2070778 1- A D5
D 1020 DIODE 1SV284(TPH3) G2070622 1- A D5
D 1023 DIODE HVU350TRF G2070380 1- A D3
D 1024 DIODE HVU350TRF G2070380 1- A D3
D 1025 DIODE 1SS321 TE85R G2070076 1- B c3
D 1027 DIODE UDZS TE-17 5.6B G2070910 1- B a5
D 1028 DIODE HSC277TRF G2070584 1- B b4
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-12
Page 40

MAIN Unit
REF.
D 1029 DIODE HSC277TRF G2070584 1- B b4
D 1031 DIODE HSC277TRF G2070584 1- A G5
D 1034 DIODE HSC277TRF G2070584 1- A G5
D 1036 DIODE DSA3A1 G2090445 1- A B1
D 1037 DIODE HSM88AS TR G2070170 1- B b2
D 1038 DIODE HSM88AS TR G2070170 1- B b2
D 1039 DIODE HSC277TRF G2070584 1- A G4
D 1040 DIODE HSC277TRF G2070584 1- A G4
D 1041 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A D2
D 1043 DIODE HSC277TRF G2070584 1- B b4
D 1044 DIODE HSC277TRF G2070584 1- B b4
D 1047 DIODE UM9957F/TR G2070562 1- B a2
D 1048 DIODE UM9957F/TR G2070562 1- B a2
D 1049 DIODE UM9957F/TR G2070562 1- B a2
D 2001 DIODE MC2846-T11-1 G2070702 1- A A3
D 2002 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- B g1
D 2003 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A B5
D 2004 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A A2
D 2005 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- B g1
D 2006 DIODE MC2850-T11-1 G2070704 1- B e4
D 2007 DIODE MC2850-T11-1 G2070704 1- B e4
D 2008 DIODE MC2850-T11-1 G2070704 1- B e4
D 2009 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- B f3
D 2010 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A B4
D 2011 DIODE MC2846-T11-1 G2070702 1- B f2
D 2012 DIODE MC2850-T11-1 G2070704 1- A B5
D 2013 DIODE MC2850-T11-1 G2070704 1- B f3
D 2014 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A C4
F 2001 CHIP FUSE 0.25A KAB-2402-251NA31 Q0000085 1- A A2
J 2001 CONNECTOR JBY-25S-1A3F P1090815 1- B f1
J 2004 CONNECTOR BM03B-SRSS-TBT P0091301 1- A A2
J 2005 CONNECTOR AXN426C530P P0091296 1- A B4
L 1001 COIL 0.015uH AS1203-15NK L0022543 1- A G2
L 1002 COIL 0.015uH AS1203-15NK L0022543 1- A G2
L 1003 COIL E2 0.28-1.0-4T-R L0022365 1- A G3
L 1004 COIL 0.022uH AS1004-22NK L0022545 1- A G2
L 1005 COIL E2 0.45-1.4-4T-L L0022391 1- A G3
L 1006 COIL E2 0.45-1.4-4T-L L0022391 1- A G3
L 1007 COIL E2 0.35-1.6-4T-L L0022456 1- A G3
L 1008 COIL 0.015uH AS1203-15NK L0022543 1- A G1
L 1009 COIL E2 0.35-1.6-4T-L L0022456 1- A E3
L 1010 M.RFC 0.082uH 5% C2012C-82NJ L1690791 1- A D5
L 1011 COIL E2 0.35-1.6-4T-L L0022456 1- A E3
L 1012 M.RFC 0.01uH HK1608 10NJ-T L1690516 1L 1013 CHIP COIL 4.7uH C2520F-4R7K L1690592 1- B a4
L 1014 CHIP COIL 0.68uH C2520C-R68J L1690554 1- A F3
L 1015 M.RFC 0.39uH 5% C2012C-R39J L1691019 1- A D5
L 1016 M.RFC 0.39uH 5% C2012C-R39J L1691019 1- A D5
L 1017 M.RFC 0.027uH HK1608 27NJ-T L1690521 1- A F3
L 1018 CHIP COIL 0.064uH LQN1A64NJ04 L1690258 1- A G4
L 1019 COIL 0.11uH AS0810-B0NK L0022542 1- A E2
L 1020 COIL E2 0.35-1.6-4T-L L0022456 1- A F3
L 1021 CHIP COIL 0.0147uH LQN1A15NJ04 L1690251 1- B d2
L 1022 COIL 0.022uH AS1004-22NK L0022545 1- A G2
L 1023 COIL E2 0.35-1.6-4T-L L0022456 1- A D5
L 1024 M.RFC 0.39uH 5% C2012C-R39J L1691019 1- A D4
L 1025 M.RFC 0.39uH 5% C2012C-R39J L1691019 1- A D4
L 1026 COIL E2 0.35-1.6-4T-L L0022456 1- A D5
L 1029 CHIP COIL 0.0147uH LQN1A15NJ04 L1690251 1- B d3
L 1031 M.RFC 0.022uH HK1608 22NJ-T L1690520 1- A D4
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-13
Page 41

MAIN Unit
REF.
L 1032 M.RFC 0.015uH HK1608 15NJ-T L1690518 1- B c4
L 1037 M.RFC 0.015uH HK1608 15NJ-T L1690518 1- B d3
L 1038 M.RFC 0.018uH LL1608-F18NK L1690362 1- B c4
L 1041 M.RFC 0.018uH HK1608 18NJ-T L1690519 1- A E4
L 1042 M.RFC 0.047uH LL1608-F47NK L1690367 1- B d3
L 1044 M.RFC 0.047uH HK1608 47NJ-T L1690524 1- B c3
L 1045 M.RFC 0.018uH HK1608 18NJ-T L1690519 1- A E4
L 1046 M.RFC 0.1uH HK1608 R10J-T L1690528 1- A F5
L 1047 M.RFC 0.56uH LK2125 R56K-T L1690316 1- A G4
L 1049 M.RFC 0.56uH LK2125 R56K-T L1690316 1- A G4
L 1050 M.RFC 0.56uH LK2125 R56K-T L1690316 1- B a5
L 1051 M.RFC 0.33uH LK1608 R33K-T L1690412 1- B b5
L 1052 M.RFC 0.56uH LK2125 R56K-T L1690316 1- B a5
L 1054 M.RFC 0.022uH HK1608 22NJ-T L1690520 1- A F3
L 1055 COIL E2 0.35-1.6-4T-L L0022456 1- A E3
L 1056 COIL E2 0.35-1.6-4T-L L0022456 1- A E3
L 1059 CHIP COIL 0.064uH LQN1A64NJ04 L1690258 1- A G4
L 1060 M.RFC 0.018uH HK1608 18NJ-T L1690519 1- A F4
L 1061 M.RFC 0.047uH HK1608 47NJ-T L1690524 1- A E4
L 1063 M.RFC 0.082uH 5% C2012C-82NJ L1690791 1- A D5
L 1064 M.RFC 0.015uH HK1608 15NJ-T L1690518 1- B b3
L 2001 M.RFC 2.2uH LK1608 2R2K-T L1690634 1- A A4
P 1001 WIRE ASSY RED 125 <7>/<7> T9318109 1Q 1003 TRANSISTOR IMH6A T108 G3070066 1- B d2
Q 1004 IC MM1216ENRE G1092432 1- B f2
Q 1005 TRANSISTOR 2SB1201S-TL G3070195 1- B f2
Q 1006 TRANSISTOR 2SC4154-T11-1E G3341548E 1- B d4
Q 1007 IC NJM2902V-TE1 G1091679 1- B d2
Q 1010 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A C5
Q 1011 TRANSISTOR 2SB1132 T100 Q G3211327Q 1- A C3
Q 1012 TRANSISTOR 2SB1132 T100 Q G3211327Q 1- A C3
Q 1014 TRANSISTOR IMH6A T108 G3070066 1- A B3
Q 1015 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- B d5
Q 1017 IC RA45H4452M-01 G1093821 1- A C1
Q 1018 TRANSISTOR 2SC3357-T2 RF G3333577F 1- A F3
Q 1019 FET 2SK508-T2B K52 G3805087B 1- A D5
Q 1020 TRANSISTOR 2SC4226-T2B R24 G3342267D 1- A D4
Q 1025 TRANSISTOR 2SC3357-T2 RF G3333577F 1- B d3
Q 1026 TRANSISTOR 2SC5107-O(TE85R) G3351077O 1- A D4
Q 1027 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A D4
Q 1028 TRANSISTOR IMH6A T108 G3070066 1- A D4
Q 1029 TRANSISTOR 2SC5107-O(TE85R) G3351077O 1- B c4
Q 1030 TRANSISTOR 2SC3357-T2 RF G3333577F 1- A G4
Q 1031 TRANSISTOR 2SC3356-T2B R24 G3333567D 1- B d3
Q 1032 TRANSISTOR 2SC5107-O(TE85R) G3351077O 1- B c4
Q 1033 IC SA7025DK G1093014 1- A E4
Q 1034 IC TA31136FN(EL) G1091605 1- A F5
Q 1035 TRANSISTOR 2SC4154-T11-1E G3341548E 1- A E5
Q 1038 IC NJM78L05UA TE1 G1091325 1- B b5
Q 1041 TRANSISTOR 2SC4215Y TE85R G3342157Y 1- B a5
Q 1042 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A F5
Q 1044 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A F5
Q 1045 TRANSISTOR IMH6A T108 G3070066 1- B b5
Q 1046 IC RN5RL30AA-TR G1091646 1- B c5
Q 1188 FET 2SK520-T2B K41 G3805207A 1- A F3
Q 1189 FET 2SK520-T2B K41 G3805207A 1- A E3
Q 1190 FET 2SK520-T2B K41 G3805207A 1- A E3
Q 1191 FET 2SK520-T2B K41 G3805207A 1- A F3
Q 1192 TRANSISTOR 2SC3357-T2 RF G3333577F 1- A E4
Q 1193 TRANSISTOR 2SC4154-T11-1E G3341548E 1- A F5
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-14
Page 42

MAIN Unit
REF.
Q 1194 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A A5
Q 2001 IC NJM2902V-TE1 G1091679 1- B e5
Q 2002 TRANSISTOR IMD3 T108 G3070053 1- A A3
Q 2003 IC NJM2902V-TE1 G1091679 1- B e4
Q 2004 IC TC4W53FU TE12L G1091675 1- A A5
Q 2005 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A B5
Q 2006 TRANSISTOR IMX1 T110 G3070024 1- B g5
Q 2007 IC BU4066BF-E2 G1092593 1- A C4
Q 2008 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A B5
Q 2009 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A A1
Q 2010 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A A1
Q 2011 TRANSISTOR IMH6A T108 G3070066 1- B e4
Q 2013 TRANSISTOR IMZ1 T108 G3070025 1- B f5
Q 2014 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A B5
Q 2015 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A C5
Q 2016 TRANSISTOR DTC323TK T146 G3070042 1- A B5
Q 2017 IC MX165CDW-TR G1092775 1- B e3
Q 2018 IC TDA7240AV G1091020 1- A A3
Q 2019 IC CXA1846N-T4 G1092690 1- A C4
Q 2020 TRANSISTOR IMD3 T108 G3070053 1- A B4
Q 2021 TRANSISTOR DTB123EK T146 G3070022 1- B f3
Q 2022 TRANSISTOR DTB123EK T146 G3070022 1- B g5
Q 2023 TRANSISTOR DTC323TK T146 G3070042 1- A A3
Q 2024 TRANSISTOR 2SC4154-T11-1E G3341548E 1- A A4
Q 2025 IC 1- A B4
Q 2026 IC BU4053BCF-E2 G1092723 1- B e5
Q 2027 FET 2SJ327-Z-E1 G4070010 1- B f2
Q 2028 IC NJM78L05UA TE1 G1091325 1- B f2
Q 2029 TRANSISTOR 2SA1602A-T11-1F G3116028F 1- B f3
Q 2030 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- B f3
Q 2031 IC LA8630M-B-TE-R G1093452 1- B g4
Q 2032 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A C5
Q 2033 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A B5
Q 2035 IC RN5VL35AA-TR G1091666 1- B e3
Q 2036 IC AT24C256-10TI-2.7 G1093887 1- A A3
Q 2037 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A B4
Q 2038 IC TC4S66F TE85R G1090893 1- A A4
Q 2039 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- A A4
Q 2040 IC NJM2902V-TE1 G1091679 1- B e5
Q 2041 IC NJM2902V-TE1 G1091679 1- B f5
Q 2042 IC NJM2902V-TE1 G1091679 1- B g5
Q 2045 IC TC4S66F TE85R G1090893 1- A A4
Q 2046 IC NJM2902V-TE1 G1091679 1- B e3
R 1002 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B d5
R 1003 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B d5
R 1004 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B g5
R 1005 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A A5
R 1006 CHIP RES. 120k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 124JATP J24185124 1- B d5
R 1007 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 683JATP J24185683 1- A C5
R 1008 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A C5
R 1010 CHIP RES. 2.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 272JATP J24185272 1- B d2
R 1011 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B d2
R 1013 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 224JATP J24185224 1- A D2
R 1014 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B f5
R 1015 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 224JATP J24185224 1- B f5
R 1016 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 683JATP J24185683 1- B e5
R 1017 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B d5
R 1018 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B d5
R 1019 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B c2
R 1020 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B d2
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
Please contact VERTEX STANDARD.
6A-15
Page 43

MAIN Unit
REF.
R 1021 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 223JATP J24185223 1- B c2
R 1022 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 223JATP J24185223 1- B c2
R 1023 CHIP RES. 27k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 273JATP J24185273 1- B c2
R 1024 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 470JATP J24185470 1- A D2
R 1025 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B d4
R 1027 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A D5
R 1028 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B c2
R 1029 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B c2
R 1030 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B c2
R 1031 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 683JATP J24185683 1- B d2
R 1032 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A G3
R 1033 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 224JATP J24185224 1- B c2
R 1035 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A C3
R 1037 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A C3
R 1038 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B d5
R 1039 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A G3
R 1040 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 332JATP J24185332 1- A F3
R 1041 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A E3
R 1042 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A F3
R 1043 CHIP RES. 18 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 180J J24205180 1- B d2
R 1046 CHIP RES. 270 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 271J J24205271 1- B d2
R 1047 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 224JATP J24185224 1- A D5
R 1048 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 331JATP J24185331 1- A D5
R 1049 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A D5
R 1050 CHIP RES. 27k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 273JATP J24185273 1- A D5
R 1051 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 334JATP J24185334 1- A D5
R 1052 CHIP RES. 56k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 563JATP J24185563 1- B d5
R 1053 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B d5
R 1054 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B d5
R 1056 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A E5
R 1057 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A E5
R 1058 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A F3
R 1062 CHIP RES. 10 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 100JATP J24185100 1- A F3
R 1063 CHIP RES. 150 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 151J J24205151 1- A F2
R 1065 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 332JATP J24185332 1- A F3
R 1066 CHIP RES. 270 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 271J J24205271 1- B d2
R 1069 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 101JATP J24185101 1- A D4
R 1070 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 153JATP J24185153 1- A D4
R 1071 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 183JATP J24185183 1- A D5
R 1072 CHIP RES. 180 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 181JATP J24185181 1- A D4
R 1073 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A E5
R 1074 CHIP RES. 680 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 681JATP J24185681 1- A D4
R 1078 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A E5
R 1081 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A E5
R 1082 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A E3
R 1083 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A E3
R 1084 CHIP RES. 47 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 470J J24205470 1- A D3
R 1085 CHIP RES. 39 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 390J J24205390 1- A D3
R 1086 CHIP RES. 56 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 560JATP J24185560 1- A D3
R 1087 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 101JATP J24185101 1- A D4
R 1088 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A D4
R 1089 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A D4
R 1090 CHIP RES. 15 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 150JATP J24185150 1- B c4
R 1091 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 221JATP J24185221 1- A D4
R 1092 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A D4
R 1093 CHIP RES. 180k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 184JATP J24185184 1- B c4
R 1094 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A E4
R 1095 CHIP RES. 270 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 271JATP J24185271 1- A E4
R 1097 CHIP RES. 10 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 100JATP J24185100 1- B b3
R 1100 CHIP RES. 10 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 100JATP J24185100 1- A G3
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-16
Page 44

MAIN Unit
REF.
R 1101 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A G4
R 1102 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B d3
R 1103 CHIP RES. 47 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 470J J24205470 1- A D3
R 1104 CHIP RES. 15 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 150JATP J24185150 1- B c4
R 1105 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 470JATP J24185470 1- B c4
R 1106 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 101JATP J24185101 1- B d3
R 1107 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B c4
R 1108 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 221JATP J24185221 1- B c4
R 1109 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B c4
R 1110 CHIP RES. 22 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 220JATP J24185220 1- B c4
R 1112 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 470JATP J24185470 1- A G4
R 1113 CHIP RES. 47 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 470J J24205470 1- B a4
R 1114 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 331JATP J24185331 1- A G4
R 1115 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 101JATP J24185101 1- B c3
R 1116 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- B b5
R 1117 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A E4
R 1118 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A E4
R 1119 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A E4
R 1120 CHIP RES. 22 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 220JATP J24185220 1- B c4
R 1123 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A F4
R 1128 CHIP RES. 270 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 271JATP J24185271 1- B b5
R 1130 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- B b4
R 1131 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- B b4
R 1132 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- B b4
R 1133 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- B b4
R 1134 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B c4
R 1135 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 332JATP J24185332 1- B c4
R 1136 CHIP RES. 56 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 560JATP J24185560 1- B c3
R 1138 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A E5
R 1139 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A F5
R 1140 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A E5
R 1141 CHIP RES. 120k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 124JATP J24185124 1- A E5
R 1142 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A F5
R 1145 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 470JATP J24185470 1- B b5
R 1147 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A G4
R 1148 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A G4
R 1149 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B a4
R 1150 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B b5
R 1153 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A G4
R 1154 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B b5
R 1155 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A F5
R 1156 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- B b5
R 1157 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A F5
R 1159 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A E5
R 1161 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B b5
R 1165 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A G5
R 1166 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B b5
R 1167 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B a5
R 1168 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 224JATP J24185224 1- B a5
R 1169 CHIP RES. 820 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 821JATP J24185821 1- B a5
R 1170 CHIP RES. 560 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 561JATP J24185561 1- B a5
R 1171 CHIP RES. 27 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 270JATP J24185270 1- B a5
R 1172 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A G5
R 1173 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A F5
R 1174 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A F5
R 1176 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A F5
R 1180 CHIP RES. 100 1/2W 5% RMC1/2 101JCTP J24275101 1- B b2
R 1181 CHIP RES. 100 1/2W 5% RMC1/2 101JCTP J24275101 1- B b2
R 1184 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B b2
R 1185 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B b2
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-17
Page 45

MAIN Unit
REF.
R 1186 CHIP RES. 1.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 182JATP J24185182 1- B b2
R 1187 CHIP RES. 1.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 182JATP J24185182 1- B b2
R 1190 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 221JATP J24185221 1- B d3
R 1191 CHIP RES. 15 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 150JATP J24185150 1- B d3
R 1288 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 224JATP J24185224 1- A E5
R 1289 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 221JATP J24185221 1- B c3
R 1290 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 101JATP J24185101 1- B d4
R 1291 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 332JATP J24185332 1- B c4
R 1292 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 332JATP J24185332 1- B c4
R 1293 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 470JATP J24185470 1- B c4
R 1294 CHIP RES. 150 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 151J J24205151 1- B c4
R 1295 CHIP RES. 150 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 151J J24205151 1- B c4
R 1297 CHIP RES. 100 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 101J J24205101 1- B d3
R 1298 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B d3
R 1299 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B d3
R 1300 CHIP RES. 47 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 470J J24205470 1- A D3
R 1301 CHIP RES. 820 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 821J J24205821 1- B d3
R 1302 CHIP RES. 680 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 681JATP J24185681 1- A D2
R 1303 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A D3
R 1304 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A F5
R 1305 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A F5
R 1306 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A C3
R 1307 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A C3
R 1308 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A E5
R 1309 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B c5
R 1310 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B d3
R 1311 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B d2
R 1312 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B c2
R 1313 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A A5
R 1314 CHIP RES. 8.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 822JATP J24185822 1- A A5
R 1315 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A A5
R 1316 CHIP RES. 56 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 560JATP J24185560 1- B c4
R 1318 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A F3
R 1320 CHIP RES. 150 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 151J J24205151 1- A F2
R 1321 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A E4
R 1322 CHIP RES. 3.9k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 392JATP J24185392 1- A E4
R 1323 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A E5
R 1324 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 224JATP J24185224 1- A A5
R 1325 CHIP RES. 82 1 W 5% RMC1 820JTE J24305820 1- B c2
R 1326 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B a1
R 1327 CHIP RES. 39 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 390J J24205390 1- A D3
R 1328 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A A5
R 1329 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A A5
R 1330 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A A5
R 2001 CHIP RES. 470 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 471JATP J24185471 1- B f1
R 2002 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A A3
R 2003 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A B4
R 2004 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B f4
R 2005 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 331JATP J24185331 1- A A3
R 2006 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 331JATP J24185331 1- B g1
R 2007 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B f1
R 2008 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B f1
R 2009 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B f1
R 2010 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B g1
R 2011 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B g1
R 2012 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B g1
R 2013 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B g1
R 2014 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B g1
R 2015 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B f1
R 2016 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A B5
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-18
Page 46

MAIN Unit
REF.
R 2017 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 331JATP J24185331 1- B f5
R 2018 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 331JATP J24185331 1- B f5
R 2019 CHIP RES. 560 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 561JATP J24185561 1- B f5
R 2020 CHIP RES. 120k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 124JATP J24185124 1- B f5
R 2021 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A B5
R 2022 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B f5
R 2023 CHIP RES. 680 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 681JATP J24185681 1- A B5
R 2024 CHIP RES. 470 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 471JATP J24185471 1- B f5
R 2025 CHIP RES. 680 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 681JATP J24185681 1- B f5
R 2026 CHIP RES. 150k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 154JATP J24185154 1- B f5
R 2027 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B f4
R 2028 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A A3
R 2029 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B g1
R 2030 CHIP RES. 680 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 681JATP J24185681 1- B g1
R 2031 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B g1
R 2032 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B f1
R 2033 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B f1
R 2034 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B g1
R 2035 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B g1
R 2037 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B g1
R 2039 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B g1
R 2040 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B g1
R 2041 CHIP RES. 5.6k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 562JATP J24185562 1- B f4
R 2042 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B f5
R 2043 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B f4
R 2044 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B f1
R 2045 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B f5
R 2046 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A B5
R 2047 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B g5
R 2048 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 223JATP J24185223 1- A B5
R 2049 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B g5
R 2050 CHIP RES. 120k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 124JATP J24185124 1- B f5
R 2051 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B g5
R 2052 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B g5
R 2053 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A B5
R 2054 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 223JATP J24185223 1- A B5
R 2055 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B f5
R 2056 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A B5
R 2057 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A B5
R 2058 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B e5
R 2059 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B f4
R 2060 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B f5
R 2061 CHIP RES. 270k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 274JATP J24185274 1- B f5
R 2062 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B f4
R 2063 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B f4
R 2064 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B f4
R 2065 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A C4
R 2066 CHIP RES. 680 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 681JATP J24185681 1- A C3
R 2067 CHIP RES. 470 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 471JATP J24185471 1- A C4
R 2068 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e4
R 2069 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e4
R 2070 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B f5
R 2071 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B f5
R 2072 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B f5
R 2073 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B f5
R 2074 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A C4
R 2075 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A B5
R 2076 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e4
R 2077 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B d4
R 2079 CHIP RES. 470 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 471JATP J24185471 1- B d4
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-19
Page 47

MAIN Unit
REF.
R 2080 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B d4
R 2081 CHIP RES. 270k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 274JATP J24185274 1- B e4
R 2082 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 105JATP J24185105 1- B e4
R 2083 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B e4
R 2084 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 105JATP J24185105 1- B e4
R 2085 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B e4
R 2086 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B e4
R 2087 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A B5
R 2088 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 105JATP J24185105 1- A B5
R 2089 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B f4
R 2092 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 332JATP J24185332 1- B e3
R 2093 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e3
R 2094 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 470JATP J24185470 1- A C3
R 2095 CHIP RES. 0.33 1W 10% RMC1 R33KATE J24309001 1- A A2
R 2096 CHIP RES. 2.2 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 2R2JATP J24185229 1- B g2
R 2097 CHIP RES. 2.2 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 2R2JATP J24185229 1- B g3
R 2098 CHIP RES. 0.33 1W 10% RMC1 R33KATE J24309001 1- A A2
R 2099 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B e4
R 2100 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e4
R 2101 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e4
R 2103 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 153JATP J24185153 1- A C4
R 2104 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- A C4
R 2105 CHIP RES. 150k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 154JATP J24185154 1- B e4
R 2106 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B e4
R 2107 CHIP RES. 180 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 181JATP J24185181 1- B e4
R 2108 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B e4
R 2110 CHIP RES. 150k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 154JATP J24185154 1- B d4
R 2111 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B f4
R 2112 CHIP RES. 39k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 393JATP J24185393 1- B f4
R 2113 CHIP RES. 680k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 684JATP J24185684 1- B f5
R 2114 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 183JATP J24185183 1- A B5
R 2115 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A B4
R 2116 CHIP RES. 3.9k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 392JATP J24185392 1- B e3
R 2117 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e3
R 2118 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 334JATP J24185334 1- B e3
R 2119 CHIP RES. 2.2M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 225JATP J24185225 1- B e3
R 2120 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A D3
R 2121 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A C4
R 2122 CHIP RES. 1.5M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 155JATP J24185155 1- A C3
R 2123 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A C3
R 2124 CHIP RES. 39k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 393JATP J24185393 1- A B4
R 2125 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 183JATP J24185183 1- A B4
R 2126 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 223JATP J24185223 1- A B4
R 2127 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A B4
R 2128 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A B4
R 2131 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 474JATP J24185474 1- A A3
R 2132 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 224JATP J24185224 1- A A3
R 2133 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 223JATP J24185223 1- A A3
R 2134 CHIP RES. 2.2M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 225JATP J24185225 1- A A3
R 2136 CHIP RES. 39k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 393JATP J24185393 1- A C4
R 2137 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 334JATP J24185334 1- B e5
R 2138 CHIP RES. 2.2M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 225JATP J24185225 1- B e5
R 2139 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 474JATP J24185474 1- B e5
R 2140 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 105JATP J24185105 1- A A4
R 2141 CHIP RES. 2.2M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 225JATP J24185225 1- B e4
R 2142 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 224JATP J24185224 1- B e5
R 2143 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 474JATP J24185474 1- B e4
R 2144 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B d4
R 2145 CHIP RES. 180 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 181JATP J24185181 1- B d4
R 2146 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A A4
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-20
Page 48

MAIN Unit
REF.
R 2147 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B f3
R 2148 CHIP RES. 680k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 684JATP J24185684 1- A D4
R 2149 CHIP RES. 180k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 184JATP J24185184 1- A D3
R 2150 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A D3
R 2151 CHIP RES. 6.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 682JATP J24185682 1- A D3
R 2152 CHIP RES. 180k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 184JATP J24185184 1- A C3
R 2153 CHIP RES. 82k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 823JATP J24185823 1- A C5
R 2154 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A C5
R 2155 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 153JATP J24185153 1- A C5
R 2156 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- A C5
R 2157 CHIP RES. 820k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 824JATP J24185824 1- A C5
R 2158 CHIP RES. 1.2M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 125JATP J24185125 1- B e5
R 2159 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 153JATP J24185153 1- A C5
R 2160 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B e5
R 2161 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 153JATP J24185153 1- B e5
R 2162 CHIP RES. 2.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 272JATP J24185272 1- A A3
R 2163 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A B3
R 2164 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A B3
R 2165 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A A3
R 2166 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A A3
R 2167 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 334JATP J24185334 1- B e5
R 2168 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 334JATP J24185334 1- B d5
R 2169 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 105JATP J24185105 1- B d5
R 2170 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 334JATP J24185334 1- B d5
R 2171 CHIP RES. 5.6k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 562JATP J24185562 1- A C4
R 2172 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 334JATP J24185334 1- B e4
R 2173 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 105JATP J24185105 1- B d4
R 2174 CHIP RES. 180k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 184JATP J24185184 1- B d4
R 2175 CHIP RES. 180k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 184JATP J24185184 1- B d4
R 2176 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 153JATP J24185153 1- A A4
R 2177 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B g4
R 2178 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B g4
R 2179 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A A4
R 2180 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B f4
R 2181 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B f4
R 2182 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B f4
R 2183 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A C5
R 2185 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B e5
R 2186 CHIP RES. 120k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 124JATP J24185124 1- B e5
R 2187 CHIP RES. 120k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 124JATP J24185124 1- B e5
R 2188 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 334JATP J24185334 1- B d5
R 2189 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B f2
R 2190 CHIP RES. 180k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 184JATP J24185184 1- B d4
R 2191 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B f2
R 2192 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A A3
R 2193 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A A3
R 2194 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e5
R 2195 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B e5
R 2196 CHIP RES. 120k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 124JATP J24185124 1- B e5
R 2197 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A C5
R 2198 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A C5
R 2199 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A C5
R 2200 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 153JATP J24185153 1- B f2
R 2201 CHIP RES. 10 1/4W 5% RMC1/4 100JATP J24245100 1- B e2
R 2202 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 224JATP J24185224 1- B f2
R 2203 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 153JATP J24185153 1- B f2
R 2204 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B f3
R 2205 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B f3
R 2206 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B f3
R 2207 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B f3
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-21
Page 49

MAIN Unit
REF.
R 2208 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B f3
R 2209 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B f4
R 2210 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A B5
R 2212 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A C5
R 2214 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B g4
R 2215 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 333JATP J24185333 1- B g4
R 2216 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B f3
R 2217 CHIP RES. 180k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 184JATP J24185184 1- B e3
R 2218 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 333JATP J24185333 1- B f3
R 2219 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 331JATP J24185331 1- B f1
R 2220 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A B3
R 2221 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e3
R 2222 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A B3
R 2224 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A B3
R 2225 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A A3
R 2226 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A B5
R 2227 CHIP RES. 150k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 154JATP J24185154 1- A B5
R 2228 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B f5
R 2229 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 105JATP J24185105 1- A C4
R 2230 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A A4
R 2231 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A A4
R 2232 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B g5
R 2233 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- B g4
R 2234 CHIP RES. 120k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 124JATP J24185124 1- A A4
R 2235 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B f5
R 2236 CHIP RES. 27k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 273JATP J24185273 1- B f4
R 2252 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A C4
R 2255 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B f1
R 2259 CHIP RES. 27k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 273JATP J24185273 1- B f4
R 2266 CHIP RES. 6.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 682JATP J24185682 1- B g4
R 2267 CHIP RES. 6.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 682JATP J24185682 1- B f4
R 2270 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 183JATP J24185183 1- A A5
R 2271 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 183JATP J24185183 1- A A5
R 2273 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A A5
R 2274 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A A5
R 2277 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B f4
R 2278 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B f4
R 2280 CHIP RES. 56k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 563JATP J24185563 1- B e3
R 2281 CHIP RES. 56k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 563JATP J24185563 1- B e3
R 2282 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e3
R 2283 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B e3
R 2284 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 683JATP J24185683 1- B e3
R 2285 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 183JATP J24185183 1- A C3
R 2286 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 183JATP J24185183 1- A C3
R 2287 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 333JATP J24185333 1- B e3
R 2288 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B e3
R 2289 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e3
R 2290 CHIP RES. 270k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 274JATP J24185274 1- B e3
R 2291 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e3
R 2292 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e3
R 2293 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e3
T 1001 COIL WIDE-TRANS. 950812004 L0022479 1- A E3
T 1002 COIL WIDE-TRANS. 950812004 L0022479 1- A F4
T 1003 COIL WIDE-TRANS. 950812004 L0022479 1- A F3
T 1004 COIL WIDE-TRANS. 990812213 L0022619 1- A G3
TH1001 THERMISTOR TBPS1R104K475H5Q G9090069 1- B a1
VR1001 POT. 10k EVN-5ESX50B14 J51811103 1- A E5
X 1001 XTAL OSC TTS12V 14.5MHZ H9500630 1- A E5
X 2001 XTAL 92SMX(A) 16MHz 16.000MHZ H0103252 1- A A4
XF1001 XTAL FILTER HDD5205 43.95M H1102365 1- A G4
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-22
Page 50

MAIN Unit
REF.
XF1002 XTAL FILTER HDD5205 43.95M H1102365 1- A G5
XF1003 XTAL FILTER HDD5204 43.95M H1102366 1- A G4
XF1004 XTAL FILTER HDD5204 43.95M H1102366 1- A G4
DESCRIPTION
SHIELD CASE (A) RA0073900 1SHIELD CASE RA0414900 1SHIELD CASE VCO RA0208100 1LEAF SPRING R0140031 1-
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6A-23
Page 51

MAIN Unit
Note:
6A-24
Page 52

Circuit Diagram
DISPLAY Unit
6B-1
Page 53

DISPLAY Unit
Note:
6B-2
Page 54

Parts Layout
DISPLAY Unit
A CB ED
F
1
2
S-93C46AMFN-TB
(Q3012)
2SB1132Q (BA)
(Q3031)
DTC323TK (H02)
(Q3003)
NJM78L05UA (8C)
(Q3021)
MC2848 (A6)
(D3008)
DAP202U (P)
(D3006)
MC2850 (A7)
(D3018, 3019)
3
Side A
6B-3
Page 55

DISPLAY Unit
Parts Layout
ba dc f
e
g
1
2
HD64F3642AH
(Q3014)
LC75823W
(Q3001)
NJM2902V
(Q3039)
2SB1132Q (BA)
(Q3028, 3029)
DTC323TK (H02)
(Q3008, 3009)
TC4S66F (C9)
(Q3043)
IMD3 (D3)
(Q3013)
IMH6 (H6)
(Q3015, 3033)
IMZ1 (Z1)
(Q3004, 3011, 3040)
IMX1 (X1)
(Q3010, 3038)
2SA1602A (MF)
(Q3017, 3401)
2SC4154E (LE)
(Q3019)
UMW1 (W1)
(Q3030)
RT1N241M (N2)
(Q3005, 3020, 3022,
3025, 3026, 3027)
RN5VL35AA (C5)
(Q3016)
1SS226 (C3)
(D3005)
3
Side B
6B-4
Page 56

Parts List
DISPLAY Unit
REF.
C 3001 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B c1
C 3002 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B c1
C 3003 CHIP CAP. 680pF 50V B GRM39B681M50PT K22174807 1- B c1
C 3004 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V B ECUV1H471KBV K22179610 1- B b1
C 3005 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V B ECUV1H471KBV K22179610 1- B a1
C 3006 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- A A3
C 3009 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V B ECUV1H471KBV K22179610 1- B a1
C 3010 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V B ECUV1H471KBV K22179610 1- B b1
C 3011 CHIP CAP. 0.47uF 10V BJ LMK107BJ474KA-T K22104803 1- B d3
C 3012 CHIP CAP. 1uF 10V F GRM39F105Z10PT K22105001 1- B c3
C 3013 CHIP CAP. 1uF 10V F GRM39F105Z10PT K22105001 1- B c3
C 3014 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V CH GRM39CH221J50PT K22174243 1- B d3
C 3015 CHIP TA.CAP. 2.2uF 6.3V TESVA0J225M1-8R K78080009 1- B d3
C 3016 CHIP TA.CAP. 33uF 4V TEMSVA0G336M-8R K78060036 1- B d3
C 3017 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B d3
C 3018 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V B ECUV1H471KBV K22179610 1- B b1
C 3019 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V B ECUV1H471KBV K22179610 1- B a1
C 3020 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH GRM39CH100D50PT K22174211 1- B d2
C 3021 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 16V TMCSA1C105MTR K78120023 1- B c2
C 3022 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A F2
C 3023 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM39CH040C50PT K22174205 1- B a2
C 3024 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- A F2
C 3025 CHIP CAP. 18pF 50V CH GRM39CH180J50PT K22174217 1- B b2
C 3026 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A F2
C 3027 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B d2
C 3028 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM39CH040C50PT K22174205 1- B b2
C 3029 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50V B GRM39B103M50PT K22174823 1- B d3
C 3030 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- B d2
C 3031 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B e3
C 3032 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- B e2
C 3034 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B f1
C 3036 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A F2
C 3037 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50V B GRM39B103M50PT K22174823 1- A E1
C 3038 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- A D3
C 3039 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B e2
C 3040 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A B2
C 3042 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A F1
C 3043 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- A D3
C 3045 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 100uF 16V ECEV1CA101WP K48120012 1- B e2
C 3047 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH GRM39CH330J50PT K22174223 1- B a2
C 3049 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH GRM39CH330J50PT K22174223 1- B a3
C 3050 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50V B GRM39B103M50PT K22174823 1- A A2
C 3051 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B f2
C 3053 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 100uF 16V ECEV1CA101WP K48120012 1- B f2
C 3055 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50V B GRM39B103M50PT K22174823 1- B f2
C 3056 CHIP CAP. 0.47uF 10V BJ LMK107BJ474KA-T K22104803 1- A D3
C 3058 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50V B GRM39B103M50PT K22174823 1- B f2
C 3059 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- A C3
C 3060 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50V B GRM39B103M50PT K22174823 1- B a1
C 3062 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B d2
C 3063 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V B ECUV1H471KBV K22179610 1- B b1
C 3064 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V B ECUV1H471KBV K22179610 1- B b1
C 3065 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B e3
C 3069 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 100uF 16V ECEV1CA101WP K48120012 1- B e1
C 3070 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 100uF 16V ECEV1CA101WP K48120012 1- B e1
C 3071 CHIP CAP. 0.022uF 25V B GRM39B223K25PT K22144807 1- A G1
C 3074 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B d1
DESCRIPTION
PCB with Components CB1971001
Printed Circuit Board FR004690D 1-
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
*** DISPLAY UNIT ***
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6B-5
Page 57

DISPLAY Unit
REF.
C 3075 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEMSVA1A106M-8R K78100028 1- B d2
C 3076 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B f2
C 3079 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 25V TEMSVA1E105M-8R K78140013 1D 3005 DIODE 1SS226 TE85R G2070003 1- B d3
D 3006 DIODE DAP202U T106 G2070160 1- A F2
D 3008 DIODE MC2848-T11-1 G2070694 1- A B2
D 3010 LED TLOU1008(T04) G2070796 1- A F1
D 3011 LED TLOU262 G2090763 1- A A1
D 3012 LED TLOU1008(T04) G2070796 1- A F1
D 3013 LED TLOU262 G2090763 1- A A1
D 3015 LED GL3HS44 G2090675 1- A A2
D 3016 LED GL3PR8 G2090433 1- A A1
D 3017 LED GL3KG8 G2090432 1- A A1
D 3018 DIODE MC2850-T11-1 G2070704 1- A A2
D 3019 DIODE MC2850-T11-1 G2070704 1- A F1
D 3020 DIODE BAS316 G2070716 1- B a1
D 3021 DIODE BAS316 G2070716 1- B b1
D 3022 DIODE BAS316 G2070716 1- B a1
D 3023 DIODE BAS316 G2070716 1- B b1
DS3002 LCD MS-6403 G6090140 1- A D1
J 3001 CONNECTOR 9210B-1-08Z696-T P0091300 1- A F3
J 3005 CONNECTOR 9210B-1-08Z707-T P0091304 1- A C2
J 3007 CONNECTOR SB20-15WS P0091093 1- B f2
J 3008 CONNECTOR BM14B-SRSS-TBT P0091302 1- B a1
J 3009 CONNECTOR BM14B-SRSS-TBT P0091302 1- B f2
L 3001 M.RFC 2.2uH LK1608 2R2K-T L1690634 1- B b2
Q 3001 IC LC75823W G1092941 1- B d1
Q 3003 TRANSISTOR DTC323TK T146 G3070042 1- A D3
Q 3004 TRANSISTOR IMZ1 T108 G3070025 1- B a1
Q 3005 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- B a1
Q 3008 TRANSISTOR DTC323TK T146 G3070042 1- B d3
Q 3009 TRANSISTOR DTC323TK T146 G3070042 1- B c3
Q 3010 TRANSISTOR IMX1 T110 G3070024 1- B a1
Q 3011 TRANSISTOR IMZ1 T108 G3070025 1- B a1
Q 3012 IC S-93C46AMFN-TB G1093147 1- A F2
Q 3013 TRANSISTOR IMD3 T108 G3070053 1- B b1
Q 3014 IC 1- B b2
Q 3015 TRANSISTOR IMH6A T108 G3070066 1- B d2
Q 3016 IC RN5VL35AA-TR G1091666 1- B e3
Q 3017 TRANSISTOR 2SA1602A-T11-1F G3116028F 1- B f2
Q 3019 TRANSISTOR 2SC4154-T11-1E G3341548E 1- B b2
Q 3020 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- B e2
Q 3021 IC NJM78L05UA TE1 G1091325 1- A B2
Q 3022 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- B b2
Q 3025 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- B b1
Q 3026 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- B e2
Q 3027 TRANSISTOR RT1N241M-T11-1 G3070249 1- B f3
Q 3028 TRANSISTOR 2SB1132 T100 Q G3211327Q 1- B e1
Q 3029 TRANSISTOR 2SB1132 T100 Q G3211327Q 1- B a3
Q 3030 TRANSISTOR UMW1 TR G3070078 1- B a2
Q 3031 TRANSISTOR 2SB1132 T100 Q G3211327Q 1- A B2
Q 3033 TRANSISTOR IMH6A T108 G3070066 1- B f2
Q 3038 TRANSISTOR IMX1 T110 G3070024 1- B d3
Q 3039 IC NJM2902V-TE1 G1091679 1- B c2
Q 3040 TRANSISTOR IMZ1 T108 G3070025 1- B b1
Q 3043 IC TC4S66F TE85R G1090893 1- B a1
R 3002 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B c1
R 3004 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B d3
R 3006 CHIP RES. 56k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 563JATP J24185563 1- A A2
R 3007 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A D3
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6B-6
Please contact VERTEX STANDARD.
Page 58

DISPLAY Unit
REF.
R 3008 CHIP RES. 27k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 273JATP J24185273 1- B d3
R 3017 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B d3
R 3018 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B b1
R 3019 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B b1
R 3020 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B b1
R 3021 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B a1
R 3022 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B a1
R 3023 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B a1
R 3024 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 331JATP J24185331 1- B e1
R 3025 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B a1
R 3026 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B c2
R 3027 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B b3
R 3030 CHIP RES. 680 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 681JATP J24185681 1- A A3
R 3031 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B d3
R 3033 CHIP RES. 1.5M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 155JATP J24185155 1- B d3
R 3034 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 221JATP J24185221 1- B d3
R 3035 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B a1
R 3036 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B a1
R 3037 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B a1
R 3038 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B b2
R 3039 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B b1
R 3040 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B b1
R 3041 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B b1
R 3042 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B a1
R 3043 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 153JATP J24185153 1- B d3
R 3044 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B d3
R 3045 CHIP RES. 39k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 393JATP J24185393 1- B d3
R 3046 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 223JATP J24185223 1- B c3
R 3047 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B d3
R 3049 CHIP RES. 2.2M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 225JATP J24185225 1- B c2
R 3051 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B d2
R 3052 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 221JATP J24185221 1- B d2
R 3053 CHIP RES. 1.2M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 125JATP J24185125 1- B d3
R 3054 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B b1
R 3055 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B b1
R 3056 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B a1
R 3057 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B a1
R 3058 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B b1
R 3059 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B b1
R 3060 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 334JATP J24185334 1- B c3
R 3061 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B d2
R 3062 CHIP RES. 1.2M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 125JATP J24185125 1- B d2
R 3063 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B c3
R 3064 CHIP RES. 1.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 122JATP J24185122 1- B a1
R 3065 CHIP RES. 2.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 272JATP J24185272 1- B a1
R 3066 CHIP RES. 5.6k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 562JATP J24185562 1- B a1
R 3067 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- B a1
R 3068 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B a2
R 3069 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B a2
R 3070 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 105JATP J24185105 1- A F3
R 3071 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B d2
R 3072 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B d2
R 3073 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B d2
R 3074 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A F2
R 3075 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e2
R 3076 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B d2
R 3077 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B e2
R 3078 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B f1
R 3079 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 153JATP J24185153 1- A A2
R 3080 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 224JATP J24185224 1- B f2
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6B-7
Page 59

DISPLAY Unit
REF.
R 3081 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- A A2
R 3082 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 334JATP J24185334 1- A F1
R 3083 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 683JATP J24185683 1- A F1
R 3084 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 333JATP J24185333 1- A F1
R 3085 CHIP RES. 27k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 273JATP J24185273 1- B b1
R 3086 CHIP RES. 56k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 563JATP J24185563 1- B b1
R 3087 CHIP RES. 120k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 124JATP J24185124 1- B b1
R 3088 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 224JATP J24185224 1- B b1
R 3089 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 153JATP J24185153 1- B b2
R 3090 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A A2
R 3092 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A F2
R 3093 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A E1
R 3095 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B e2
R 3096 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- A C3
R 3097 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A D3
R 3099 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B e2
R 3103 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B b2
R 3104 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 153JATP J24185153 1- A F1
R 3105 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- A F1
R 3106 CHIP RES. 6.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 682JATP J24185682 1- A F1
R 3107 CHIP RES. 8.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 822JATP J24185822 1- A F1
R 3108 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e2
R 3109 CHIP RES. 15 1/2W 5% RMC1/2 150JCTP J24275150 1- A B2
R 3110 CHIP RES. 560 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 561JATP J24185561 1- B d2
R 3111 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B e2
R 3112 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A F2
R 3113 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 333JATP J24185333 1- B a2
R 3114 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B a2
R 3115 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B a2
R 3116 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B a2
R 3117 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B a2
R 3118 CHIP RES. 6.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 682JATP J24185682 1- B a2
R 3119 CHIP RES. 180 1/4W 5% RMC1/4 181JATP J24245181 1- B f1
R 3120 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B a2
R 3121 CHIP RES. 6.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 682JATP J24185682 1- B a2
R 3122 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B a2
R 3123 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B a3
R 3124 CHIP RES. 470 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 471JATP J24185471 1- B f1
R 3125 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 331JATP J24185331 1- B f1
R 3126 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 101JATP J24185101 1- B f1
R 3127 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B e1
R 3128 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A A2
R 3129 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B e2
R 3135 CHIP RES. 8.2 1W 5% RMC1 8R2JTE J24305829 1- B e1
R 3136 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 331JATP J24185331 1- A A2
R 3137 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 331JATP J24185331 1- A F2
R 3142 CHIP RES. 56k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 563JATP J24185563 1- B a2
R 3143 CHIP RES. 680 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 681JATP J24185681 1- A C3
R 3144 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A C3
R 3145 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B e2
R 3146 CHIP RES. 220 1/4W 5% RMC1/4 221JATP J24245221 1- A B2
R 3147 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A A1
R 3150 CHIP RES. 470 1/4W 5% RMC1/4 471JATP J24245471 1- B f1
R 3152 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B b1
R 3153 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B b1
R 3154 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B b1
R 3155 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B b1
R 3156 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- B c1
R 3157 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B b1
R 3158 CHIP RES. 180k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 184JATP J24185184 1- B e2
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6B-8
Page 60

DISPLAY Unit
REF.
R 3159 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B d2
R 3160 CHIP RES. 4.7 1W 5% RMC1 4R7JTE J24305479 1- B g2
R 3161 CHIP RES. 4.7 1W 5% RMC1 4R7JTE J24305479 1- B f2
R 3162 CHIP RES. 2.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 272JATP J24185272 1- B d3
R 3164 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B d2
R 3166 CHIP RES. 1 1/10W 5% RMC1/10T 1R0J J24205010 1- A G1
R 3167 CARBON FILM RES. 10k 1/6W 5% RD16PJ103 10K J01225103 1R 3168 CHIP RES. 8.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 822JATP J24185822 1S 3007 TACT SWITCH SKQDAB N5090058 1- A A1
S 3008 TACT SWITCH SKQDAB N5090058 1- A F1
S 3009 TACT SWITCH SKQDAB N5090058 1- A F1
X 3001 XTAL 92SMX(A) 16MHz 16.000MHZ H0103252 1- B a3
DESCRIPTION
LIGHT GUIDE RA0252300 1REFLECTOR SHEET RA0252700 1DIFFUSER SHEET RA0252800 1RUBBER CONNECTOR RA0252900 1LCD HOLDER RA0253000 1LED SPACER LH-5-6 S6000239 1LIGHT SHEET RA0276500 1-
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6B-9
Page 61

DISPLAY Unit
Note:
6B-10
Page 62

Circuit Diagram
KEY Unit
3.18V
3.87V
4.19V
1.96V
1.92V
4.34V
3.9V
4.46V
3.82V
5.8V
4.53V
7.71V
4.95V
4.61V
4.62V
2SA1602A (MF)
(Q3401)
Parts Layout
Side A
Side B
6C-1
Page 63

KEY Unit
Note:
6C-2
Page 64

Parts List
KEY Unit
REF.
C 3402 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B e1
D 3401 LED TLOU1008(T04) G2070796 1- A A1
D 3402 LED TLOU1008(T04) G2070796 1- A H1
D 3403 LED TLOU1008(T04) G2070796 1- A H1
D 3404 LED TLOU1008(T04) G2070796 1- A G1
D 3405 LED TLOU1008(T04) G2070796 1- A F1
J 3401 CONNECTOR 9110S-08 P1091014 1- B c1
MC3401 MIC. ELEMENT EM-140 M3290032 1- A D1
Q 3401 TRANSISTOR 2SA1602A-T11-1F G3116028F 1- B c1
R 3401 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 334JATP J24185334 1- B g1
R 3402 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 683JATP J24185683 1- B h1
R 3403 CHIP RES. 180 1/4W 5% RMC1/4 181JATP J24245181 1- B c1
R 3404 CHIP RES. 470 1/4W 5% RMC1/4 471JATP J24245471 1- B a1
R 3405 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 333JATP J24185333 1- B c1
R 3406 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 153JATP J24185153 1- B b1
R 3407 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- B b1
R 3408 CHIP RES. 6.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 682JATP J24185682 1- B a1
R 3409 CHIP RES. 6.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 682JATP J24185682 1- B c1
R 3410 CHIP RES. 8.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 822JATP J24185822 1- B c1
R 3411 CHIP RES. 8.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 822JATP J24185822 1- B a1
R 3412 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B a1
R 3413 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 333JATP J24185333 1- B c1
R 3414 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- B c1
R 3420 CHIP RES. 220 1/4W 5% RMC1/4 221JATP J24245221 1- B a1
R 3421 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B a1
S 3401 TACT SWITCH SKQDAB N5090058 1- A A1
S 3402 TACT SWITCH SKQDAB N5090058 1- A F1
S 3403 TACT SWITCH SKQDAB N5090058 1- A G1
S 3404 TACT SWITCH SKQDAB N5090058 1- A H1
S 3405 TACT SWITCH SKQDAB N5090058 1- A H1
DESCRIPTION
PCB with Components CB1972001
Printed Circuit Board FR006070D 1-
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
*** KEY UNIT ***
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6C-3
Page 65

KEY Unit
Note:
6C-4
Page 66

Circuit Diagram
Parts Layout
VR Unit
R3606
S3601
J3601
VR3601
R3607
R3605
C3601
C3603
C3602
C3605
R3604
R3602
R3603
C3604
R3601
C3606
Side A Side B
Parts List
REF.
C 3601 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50V B GRM39B103M50PT K22174823 1- B a1
C 3602 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50V B GRM39B103M50PT K22174823 1- B a1
C 3603 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50V B GRM39B103M50PT K22174823 1- B b1
C 3604 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50V B GRM39B103M50PT K22174823 1- B b1
C 3605 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50V B GRM39B103M50PT K22174823 1- B a1
C 3606 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50V B GRM39B103M50PT K22174823 1- B b1
J 3601 CONNECTOR 9110S-08L P1091104 1- A A1
R 3601 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B b1
R 3602 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B b1
R 3603 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B b1
R 3604 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B b1
R 3605 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B a1
R 3606 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B b1
R 3607 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B a1
S 3601 ROTARY SWITCH SRZW0L N0190177 1- A A1
VR3601 POT. RK09L1120 L=15 10KC J60800258 1- A C1
DESCRIPTION
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.SIDE.
*** VR UNIT ***
PCB with Components CB1973001
Printed Circuit Board FR006080C 1-
LAY ADR.
6D-1
Page 67

MIC CONN Unit
Circuit Diagram
Parts Layout
Side A Side B
Parts List
REF.
J 3901 CONNECTOR 14FE-ST-VK-N P1091103 1- A
J 3902 CONNECTOR BM14B-SRSS-TBT P0091302 1- B
DESCRIPTION
PCB with Components CB1969001
Printed Circuit Board FR006090C 1-
VALUE WV TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
*** MIC CONN UNIT ***
LOT.SIDE.
LAY ADR.
6D-2
Page 68

F2D-8 2-Tone Decode Unit
Circuit Diagram
Parts Layout
TC7S04FU (E5)
(Q1003)
TA75S01F (SA)
(Q1004)
HD64F3334YTF16
(Q1001)
DTC124TU (05)
(Q1005)
Side BSide A
7A-1
Page 69

F2D-8 2-Tone Decode Unit
Parts List
DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.REF. LOT. SIDE LAY ADR
*** F2D-8 ***
Printed Circuit Board FR002530C 1C 1001 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 6.3V TEMSVA0J475M-8R K78080017 1- A
C 1002 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A
C 1003 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25V B GRM39B103K25PT K22144803 1- A
C 1007 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A
C 1007 CHIP CAP. 0.0015uF 50V B GRM39B152M50PT K22174811 6- A
C 1007 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50V B GRM39B103M50PT K22174823 18- A
C 1008 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A
C 1009 CHIP CAP. 0.0018uF 50V B GRM39B182M50PT K22174812 1- A
C 1010 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A
C 1011 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A
C 1012 CHIP CAP. 47pF 50V CH GRM39CH470J50PT K22174227 1- A
C 1013 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A
C 1014 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A
D 1001 DIODE DA221 TL G2070178 1- A
D 1002 DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 G2070470 1- A
J 1001 CONNECTOR AXK5S40035P P1091012 1- A
Q 1001 IC HD64F3334YTF16 R0226 G1092873 1- A
Q 1003 IC TC7S04FU TE85R G1091530 1- A
Q 1004 IC TA75S01F TE85R G1091593 1- A
Q 1005 TRANSISTOR DTC124TU T106 G3070065 1- A
R 1001 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A
R 1002 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A
R 1003 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A
R 1004 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A
R 1005 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A
R 1006 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A
R 1007 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A
R 1008 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 105JATP J24185105 1- A
R 1009 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A
R 1009 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 6- A
R 1010 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A
R 1015 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 183JATP J24185183 1- A
R 1016 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A
R 1016 CHIP RES. 27k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 273JATP J24185273 6- A
R 1017 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A
BLIND SHEET RA0109300 1-
7A-2
Page 70

VTP-50 VX-Trunk Unit
Circuit Diagram
Parts Layout
NJM2904V
(Q1001)
Side A
MC68HSC705C8A502
(Q1002)
TA75S01F (SA)
(Q1003)
Side B
BR93LC56FV
(Q1004)
7B-1
Page 71

VTP-50 VX-Trunk Unit
Parts List
DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.REF. LOT. SIDE LAY ADR
*** VTP-50 ***
Printed Circuit Board FR002540C 1C 1002 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A
C 1003 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25V B GRM39B103M25PT K22144802 1- A
C 1003 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25V B GRM39B103K25PT K22144803 9- A
C 1004 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A
C 1004 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25V B GRM39B103K25PT K22144803 9- A
C 1005 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25V B GRM39B103M25PT K22144802 1- A
C 1005 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25V B GRM39B103K25PT K22144803 9- A
C 1006 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH GRM39CH100C50PT K22174248 1- A
C 1007 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH GRM39CH100C50PT K22174248 1- A
C 1008 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A
C 1009 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 6.3V TEMSVA0J475M-8R K78080017 1- A
C 1010 CHIP CAP. 0.0018uF 50V B GRM39B182M50PT K22174812 1- A
C 1011 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A
C 1012 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A
C 1013 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A
C 1014 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A
D 1001 DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 G2070470 1- A
J 1001 CONNECTOR AXK5S40035P P1091012 1- A
Q 1001 IC NJM2904V-TE1 G1091677 1- A
Q 1002 IC
Q 1002 IC
Q 1003 IC TA75S01F TE85R G1091593 1- A
Q 1004 IC BR93LC56FV-E2 G1092787 1- A
R 1001 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A
R 1002 CHIP RES. 680k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 684JATP J24185684 1- A
R 1003 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A
R 1004 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 474JATP J24185474 1- A
R 1005 CHIP RES. 120k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 124JATP J24185124 1- A
R 1006 CHIP RES. 680k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 684JATP J24185684 1- A
R 1007 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 334JATP J24185334 1- A
R 1008 CHIP RES. 150k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 154JATP J24185154 1- A
R 1009 CHIP RES. 82k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 823JATP J24185823 1- A
R 1010 CHIP RES. 39k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 393JATP J24185393 1- A
R 1011 CHIP RES. 20k 1/16W 1% RMC1/16 203FTP J24183203 1- A
R 1012 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A
R 1013 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A
R 1014 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 105JATP J24185105 1- A
R 1015 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A
R 1016 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A
R 1017 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A
R 1018 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A
R 1019 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A
R 1020 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A
R 1021 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 222JATP J24185222 1- A
R 1022 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- A
R 1023 CHIP RES. 560k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 564JATP J24185564 1- A
R 1024 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 183JATP J24185183 1- A
R 1025 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 683JATP J24185683 1- A
R 1026 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 474JATP J24185474 1- A
R 1027 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 683JATP J24185683 1- A
R 1028 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 333JATP J24185333 1- A
X 1001 XTAL SX-1315 3.579545MHz 3.579545MHZ H0103185 1- A
BLIND SHEET RA0109300 1-
MC68HSC705C8A502-6030 130
MC68HSC705C8A502-6030 131
G1092917 1- A
G1093326 6- A
7B-2
Page 72

Circuit Diagram
FVP-25 Encryption / DTMF Pager Unit
Parts Layout
M64026FP
(Q1001)
Side A
LC73881
(Q1002)
DTC144EU (26)
(Q1003)
Side B
7C-1
Page 73

FVP-25 Encryption / DTMF Pager Unit
Parts List
DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.REF. LOT. SIDE LAY ADR
*** FVP-25 ***
Printed Circuit Board FR005010F 1C 1001 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A B1
C 1002 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25V B GRM39B103M25PT K22144802 1- A B1
C 1003 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH GRM39CH100D50PT K22174211 1- A A1
C 1004 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH GRM39CH100D50PT K22174211 1- A A1
C 1005 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A A1
C 1007 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A A1
C 1007 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25V B GRM39B103M25PT K22144802 32- A A1
C 1008 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A A2
C 1009 CHIP CAP. 68pF 50V CH GRM39CH680J50PT K22174231 1- A A1
C 1010 CHIP CAP. 390pF 50V CH GRM39CH391J50PT K22174255 1- A A1
C 1011 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A A2
C 1012 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 6.3V TEMSVA0J475M-8R K78080017 1- A A2
C 1013 CHIP CAP. 0.022uF 25V B GRM39B223K25PT K22144807 1- A A1
C 1014 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- A A1
D 1001 DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 G2070470 1- A B1
D 1002 DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 G2070470 1- A B1
J 1001 CONNECTOR AXK5S40035P P1091012 1- A A2
Q 1001 IC M64026FP-650C G1092754 1- A A1
Q 1002 IC LC73881M-TLM G1092755 1- A B1
Q 1003 TRANSISTOR DTC144EU T106 G3070041 1- A B1
R 1001 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A A1
R 1002 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 105JATP J24185105 1- A A1
R 1003 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 223JATP J24185223 1- A A1
R 1004 CHIP RES. 680k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 684JATP J24185684 1- A A1
R 1006 CHIP RES. 150k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 154JATP J24185154 1- A A1
R 1007 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- A B1
R 1008 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A A1
R 1008 CARBON FILM RES. 22k 1/8W 5% RD18TJ223 22K J01215223 14- A A1
R 1008 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 223JATP J24185223 17- A A1
X 1001 XTAL SX-1315 3.6263MHz 3.6263MHZ H0103183 1- A A1
X 1002 XTAL SX-1315 4.194304MHz 4.194304MHZ H0103184 1- A B1
BLIND SHEET RA0109300 1-
7C-2
Page 74

Circuit Diagram
F5D-14 5-Tone Unit
Parts Layout
TK71650SC (L50)
(Q1001)
DTC114TE (04)
(Q1002)
Side A
PIC17LC44-08/PQ
(Q1003)
2SC4617 (BR)
(Q1004)
MD09
(Q1005)
Side B
BR93LC66FV
(Q1006)
7D-1
Page 75

F5D-14 5-Tone Unit
Parts List
DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.REF. LOT. SIDE LAY ADR
*** F5D-14 ***
Printed Circuit Board FR006510B 1Printed Circuit Board FR006510D 3-
C 1001 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM36B104K10PT K22108802 1- A
C 1002 CHIP CAP. 0.0018uF 50V B GRM36B182K50PT K22178812 1- A
C 1003 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM36B102K50PT K22178809 1- A
C 1005 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A
C 1006 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A
C 1007 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM36B104K10PT K22108802 1- A
C 1008 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 6.3V EEJK0JS106R K78080079 1- A
C 1008 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 6.3V ECST0JZ106R K78080078 8- A
C 1009 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A
C 1010 CHIP CAP. 0.0027uF 50V B GRM36B272K50PT K22178814 1- A
C 1011 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM36B104K10PT K22108802 1- A
C 1012 CHIP CAP. 18pF 50V CH GRM36CH180J50PT K22178218 1- A
C 1013 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A
C 1014 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM36B104K10PT K22108802 1- A
C 1015 CHIP CAP. 18pF 50V CH GRM36CH180J50PT K22178218 1- A
C 1016 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM36B104K10PT K22108802 1- A
C 1017 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A
C 1018 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM36B102K50PT K22178809 1- A
C 1019 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 6.3V TMCP0J105MTR K78080071 1- A
C 1020 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM36CH101J50PT K22178236 1- A
C 1021 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM36CH101J50PT K22178236 1- A
D 1001 DIODE MA2S111-(TX) G2070614 1- A
J 1001 CONNECTOR AXK5S40035P P1091012 1- A
L 1001 M.RFC 22uH ELJ-FC220K L1690201 1- A
Q 1001 IC TK71650SCL G1093136 1- A
Q 1002 TRANSISTOR DTC114TE TL G3070225 1- A
Q 1003 IC PIC17LC44-08/PQ S8100917 1- A
Q 1004 TRANSISTOR 2SC4617 TL R G3346178R 1- A
Q 1005 IC MD09 G1093276 1- A
Q 1006 IC BR93LC66FV-E2 G1092853 1- A
R 1001 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 183JTH J24189040 1- A
R 1002 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- A
R 1003 CHIP RES. 82k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 823JTH J24189048 1- A
R 1004 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- A
R 1005 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1- A
R 1006 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 105JTH J24189061 1- A
R 1007 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A
R 1008 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A
R 1009 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A
R 1010 CHIP RES. 5.6k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 562JTH J24189034 1- A
R 1011 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A
R 1012 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A
R 1013 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A
R 1014 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 333JTH J24189043 1- A
R 1015 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A
R 1016 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A
R 1017 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A
R 1018 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A
R 1019 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- A
R 1020 CHIP RES. 82k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 823JTH J24189048 1- A
R 1021 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 153JTH J24189039 1- A
R 1022 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A
R 1023 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A
X 1001 XTAL 94SMX 8MHz 8.000MHZ H0103248 1- A
BLIND SHEET RA0109300 1-
7D-2
Page 76

Circuit Diagram
FIF-7A Connection Unit
Parts Layout
NJM2902V
(Q1001)
TC7WT125FU
(Q1008, 1011,
1012)
TK71635SCL (L35)
(Q1003)
Side BSide A
TC7S04FU (E5)
(Q1004)
7E-1
Page 77

FIF-7A Connection Unit
Parts List
REF.
C 1001 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B
C 1002 CHIP CAP. 68pF 50V CH GRM39CH680J50PT K22174231 1- B
C 1003 CHIP CAP. 27pF 50V CH GRM39CH270J50PT K22174221 1- B
C 1004 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B
C 1005 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 1- B
C 1006 CHIP CAP. 680pF 50V B GRM39B681M50PT K22174807 1- B
C 1007 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM39CH040C50PT K22174205 1- B
C 1008 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A
C 1009 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- A
C 1010 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B
C 1011 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TEMSVA1C475M-8R K78120031 1- B
C 1012 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B
C 1013 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- B
C 1014 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50V B GRM39B103M50PT K22174823 1- B
C 1015 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH GRM39CH100D50PT K22174211 1- A
C 1016 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH GRM39CH100D50PT K22174211 1- A
C 1017 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A
C 1018 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A
C 1019 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 3- A
C 1020 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A
C 1021 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A
C 1023 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 3- B
C 1024 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 3- A
C 1025 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM39B102K50PT K22174821 1- A
C 1028 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM39B104K16PT K22124805 3- A
D 1001 DIODE BAS316 G2070716 1- A
D 1002 DIODE BAS316 G2070716 1- A
D 1003 DIODE BAS316 G2070716 1- A
D 1004 DIODE BAS316 G2070716 1- A
D 1005 DIODE BAS316 G2070716 1- A
D 1006 DIODE BAS316 G2070716 1- A
D 1007 DIODE BAS316 G2070716 1- B
D 1008 DIODE BAS316 G2070716 3- A
D 1009 DIODE BAS316 G2070716 3- B
D 1015 DIODE GMA01U-BT G2060023 3 A
D 1015 DIODE GMA01U-BT G2060023 4 A
D 1015 DIODE BAS316 G2070716 5- A
J 1001 CONNECTOR AXN326C038P P1091080 1- B
J 1002 CONNECTOR AXK6S40535P P0091209 1- A
Q 1001 IC NJM2902V-TE1 G1091679 1- B
Q 1002 IC UPD22100GS-T2 G1092495 3 A
Q 1002 IC UPD22100GS-T2 G1092495 FIF-7A 4- A
Q 1003 IC TK71635SCL G1093135 1- B
Q 1004 IC TC7S04FU TE85R G1091530 1- A
Q 1008 IC TC7WT125FU(TAPE) G1093520 1- B
Q 1011 IC TC7WT125FU(TAPE) G1093520 1- B
Q 1012 IC TC7WT125FU(TAPE) G1093520 1- B
Q 1013 IC LC73881M-TLM G1092755 3 B
Q 1013 IC LC73881M-TLM G1092755 FIF-7A 4- B
R 1001 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B
R 1002 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 104JATP J24185104 1- B
R 1003 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 333JATP J24185333 1- B
R 1005 CHIP RES. 180k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 184JATP J24185184 1- B
R 1006 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 224JATP J24185224 1- B
DESCRIPTION
Printed Circuit Board FR007860A 1Printed Circuit Board FR007860B 4-
VALUE V/W TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
*** FIF-7A ***
LOT.
SIDE LAY ADR
7E-2
Page 78

FIF-7A Connection Unit
REF.
R 1007 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B
R 1008 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B
R 1009 CHIP RES. 150k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 154JATP J24185154 1- B
R 1011 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B
R 1012 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B
R 1013 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B
R 1014 CHIP RES. 1.5M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 155JATP J24185155 1- B
R 1015 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- B
R 1017 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B
R 1018 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 470JATP J24185470 1- A
R 1019 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 183JATP J24185183 1- A
R 1020 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 153JATP J24185153 1- A
R 1022 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 223JATP J24185223 1- B
R 1023 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- B
R 1024 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A
R 1026 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 105JATP J24185105 1- B
R 1028 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1- A
R 1029 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 470JATP J24185470 1- A
R 1033 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 332JATP J24185332 1- A
R 1034 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 332JATP J24185332 1- A
R 1035 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 332JATP J24185332 1- A
R 1037 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 332JATP J24185332 1- A
R 1038 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 332JATP J24185332 1- A
R 1047 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 332JATP J24185332 1- B
R 1049 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 123JATP J24185123 1- B
R 1050 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A
R 1051 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A
R 1052 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A
R 1053 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A
R 1054 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A
R 1059 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- A
R 1060 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A
R 1061 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 332JATP J24185332 1- B
R 1061 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 223JATP J24185223 3- B
R 1062 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 1- B
R 1062 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 3- B
R 1063 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 103JATP J24185103 1- A
R 1064 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 224JATP J24185224 3- A
R 1065 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 1- B
R 1066 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 472JATP J24185472 1- A
R 1067 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 3- B
R 1068 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 3- B
R 1069 CARBON FILM RES. 1k 1/6W 5% RD16TPJ102 1K J07225102 3 A
R 1069 CARBON FILM RES. 1k 1/6W 5% RD16TPJ102 1K J07225102 4 A
R 1069 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 102JATP J24185102 5- A
R 1070 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 473JATP J24185473 3- A
R 1071 CHIP RES. 150 1/2W 5% RMC1/2 151JCTP J24275151 5- B
X 1001 XTAL SX-1319 3.6864MHz 3.6864MHZ H0103214 1- A
X 1002 XTAL SX-1315 4.194304MHz 4.194304MHZ H0103184 3 B
X 1002 XTAL SX-1315 4.194304MHz 4.194304MHZ H0103184 FIF-7A 4- B
DESCRIPTION
AS.POLY BAG 100X100 V3002001 1TAPTITE SCREW M2.6X6 U24206001 1POLY BAG 70X100 V3000028 1POLY BAG 70X100 V3000028 4SPONGE RUBBER RA0356400 1-
VALUE V/W TOL. VXSTD P/NMFR’S DESIG VERS.
LOT.
SIDE
7E-3
Page 79

FIF-7A Connection Unit
Note:
7E-4
Page 80

Copyright © 2003
VERTEX STANDARD CO., LTD.
All rights reserved
No portion of this manual
may be reproduced
without the ermission of
VERTEX STANDARD CO., LTD.
EC034U90A
 Loading...
Loading...