Page 1
DSO
USERMANUAL
PCSU1000
Page 2

PC Oscilloscope PCSU1000I
Table of Contents
Part I
Part II
Foreword
Contents
................................................................................................................................... 21 Safety Instructions
................................................................................................................................... 32 1GS/s oversampling mode
................................................................................................................................... 33 Controls
................................................................................................................................... 54 Connection
................................................................................................................................... 65 Troubleshooting
................................................................................................................................... 66 Waveform Parameters Display
................................................................................................................................... 97 Add comment text in the signal screen
Menu Options
................................................................................................................................... 91 File Menu
................................................................................................................................... 102 Edit Menu
................................................................................................................................... 103 Options Menu
................................................................................................................................... 124 View Menu
................................................................................................................................... 145 Spectral Density
................................................................................................................................... 166 Math Menu
................................................................................................................................... 167 Help Menu
0
2
9
Part III
Data Transfer
................................................................................................................................... 161 Data acquisition to other applications
................................................................................................................................... 202 Data acquisition to Microsoft Excel
16
Index 0
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 3

1 Contents
Operation Instructions for Velleman PC Oscilloscope
PCSU1000
·
DIGITAL STORAGE PC OSCILLOSCOPE
·
FFT SPECTRUM ANALYZER
Safety Instructions
1GS/s sampling mode
Controls
Connection
Waveform Parameters Display
Troubleshooting
Adding comment text in the signal screen
Menu Options
Spectral Density marker
Data acquisition to other applications
Data acquisition to Microsoft Excel
SAFETY and WARNINGS
Important safety information, see user manual.
Before making measurements and for safety reasons, it is important to know some information about
the measured unit.
Safe devices are:
·
Battery operated equipment
·
Equipment supplied via a transformer or adapter.
Do not measure:
·
Equipment directly connected to mains.
·
Equipment that contains components that are directly connected to mains (dimmers…).
·
If
necessary to
measur
e
above mentioned equipment, use an isolation transformer.
Please remember that the ground
s
of both channels are interconnected and connected to the
PC ground !
Contents 2
1.1 Safety Instructions
!
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 4

PC Oscilloscope PCSU10003
·
The 1GS/s sampling rate is in use on blue 0.2us/div, 0.1us/div, 0.05us/div and 0.02us/div
ranges.
·
Triggering must be ON to get stable waveform images.
·
This mode is useable only for repetitive signals.
·
This operation mode is called "Random Interleaved Sampling" (RIS) method, sometimes also
called "Equivalwent Time Sampling" (ET) mode or "Random Repetitive Sampling". In this
sampling mode the oscilloscope uses successive triggering occurrences to gather the data to
construct a picture of a repetitive signal.
Spectrum analyzer mode
FREQ. RANGE
Sets the frequency range of the display. It is necessary to slide the screen using
X-POSITION in
order to see the full range.
LOG/LIN
To display the frequency on a linear or logarithmic scale.
ZOOM x1, x2, x4, x8
In order to expand the screen X1, X2, X4 or X8
Oscilloscope mode
VOLTS/DIV
Selected value indicates the peak-to-peak voltage required to produce a peak-to-peak deflection of
one major division on the screen
Big Screen
Displays large waveform screen with separate button bar. Use
Normal Screen
button to return
normal mode.
Note: Big screen is available only in Oscilloscope and Spectrum Analyzer modes.
Coupling
AC
: the input signal is capacitive coupled to the input amplifier/attenuator. Only the AC components
are measured.
GND
: the input signal is broken and the input amplifier/attenuator is connected to earth. Use this
position for selecting a reference point on the display.
DC
: the input signal is directly connected to the input amplifier/attenuator. Both AC and DC voltage
are measured.
Probe x1/x10
Use these buttons to adapt the readouts according to the x1/x10-probe setting.
CH1 On, CH2 On
Buttons turn the display of the trace ON or OFF. To get the cursor measurements of CH2 voltage
values switch CH1 off.
1.2 1GS/s oversampling mode
1.3 Controls
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 5
Contents 4
Autoset
Automatic setup for the Volts/div, Time/div, and Trigger level to produce a stable waveform of usable
size. The trigger will be set on if the wave aplitude on the screen is more then 0.5 divisions.
The signal should be repetitive for proper autoset function: Amplitude 5mV to 100V; frequency above
50Hz; duty cycle greater than 10%.
Persist
When this button is down the scope captures many acquisitions of a signal to the screen. Record
points accumulate until you release the button.
When this button is down the scope captures many acquisitions of a signal to the screen. Record
points accumulate until you release the button.
Using Persistence option you can easily analyze worst-case signal variations, such as jitter or noise.
The Persist option can also be used to locate errors in digital signals. Using this option you can
capture erroneous events even if they only occur once. Persist option makes it easy to compare
known and unknown circuits. Click "Single" button to capture multiple waveforms on the same screen.
Persist option lets you see the range over which a signal varies
Use the Persist option to get solid XY patterns in the XY Plot mode
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 6

PC Oscilloscope PCSU10005
TIME/DIV
Selects the time setting for the beam to sweep one major division on the screen
By selecting different TIME/DIV settings it is possible to
zoom
the frozen waveform on the screen.
TRIGGER On/Off
Selects free run mode or trigged mode.
TRIGGER Level
Selects the signal level at which the sweep is triggered.
Triggering reference mark is displayed with the horizontal line on the left side of the screen.
TRIGGER Channel
Selects the trigger source signal (Ch1, Ch2 or Ext)
TRIGGER Edge
Selects the triggering slope:
Arrow up: Trigger occurs when triggering signal crosses trigger level in a positive going direction.
Arrow down: Trigger occurs when triggering signal crosses trigger level in a negative going direction.
>|<
Resets the triggering x-position reference point. Triggering reference mark is displayed with the
vertical line on the bottom of the screen.
RUN
Selects recurrent display update mode (RUN). Pressing the button again freezes the display.
SINGLE
When button is depressed and the trigger level is reached, refreshment of the display takes place
only once.
X-POSITION SCROLLBAR
(Below the waveform display)
Positions the trace horizontally on the screen. Triggering reference point is displayed with the vertical
line on the bottom of the screen.
S/L
Button selects linear (L) or sine(x)/x (S) interpolation. Linear interpolation connects the data points
with straight lines. Sine(x)/x interpolation uses curves to connect the data points. This smoothed
interpolation gives better waveform display at highest sine frequencies. Linear interpolation is better
for step signals. The S/L selection effects only at TIME/DIV settings 0.2 and 0.1us.
Note: Sine interpolation can result in incorrect top-top signal displaying, at frequencies above 5MHz.
1GS/s
This 1GS/s sampling rate is in use on 0.2us/div, 0.1us/div, 0.05us/div and 0.02us/div ranges.
CH1 + CH2
CH1 - CH2
XY Plot
INV. CH2
This button appears only in math mode. Toggles between math mode and normal mode.
Tip: Use Wheel Mouse's scroll wheel to fine adjust the triggering level and traces' y-position.
Connect the oscilloscope unit to the
USB
port.
For Circuit Analyzer (Bode Plotter) option connect function generator PCG10 or K8016 to
LPT1
,
LPT2
or
LPT3
.
To select the LPT port address for the function generator click
Hardware Setup
on
Options
menu or
select it from
Pc-Lab2000
startup screen.
1.4 Connection
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 7

1.5 Troubleshooting
Spectrum analyzer doesn't work
.
·
No arithmetic coprocessor in the computer.
No signal on the oscilloscope display
·
No communication with the computer (check that the cable is connected to the USB port)
·
If USB cable is connected, close the program. Disconnect and reconnect the USB cable and run
the Pc-Lab2000 program again.
·
RUN button is not ON.
·
The channel concerned is OFF.
·
TIME/DIV switch is in the wrong setting.
·
TRIGGER is ON, set TRIGGER OFF
·
The unit input selection is at GND.
·
Y position is wrongly adjusted.
·
Input amplitude is too large, adjust VOLTS/DIV setting.
If the above tips have no effect, then test on a different computer or different USB port.
Note. Close the program before disconnecting the USB cable.
Waveform Parameters Display
When the menu option "Waveform Parameters" of the View menu is selected the software
automatically calculates various voltage and time parameters of a signal, such as DC mean,
amplitude, rise time etc.
These parameters are displayed in a separate window. Use the check boxes in the window to select
the parameters you which to be displayed.
You may select the parameters to display for frozen waveform as well.
You may even re-open saved waveform data file to perform these measurements.
Please Note:
Do not change the scope settings when the re-opened waveform parameters are to be
read.
The green labeled parameters (High, Low, Amplitude, Rise time and Fall time) are mainly intended for
pulse shaped waveform measurements only.
For proper waveform measurement the signal levels must be appropriate. Signal levels too small will
result in noisy and inaccurate measurements. Signal levels too large will result in clipping and yield
incorrect results.
Error indication:
?? Indicates that clipping has occurred.
??? Indicates that there are too few or too many wave cycles in the waveform data or the signal
amplitude is too low. Also too noisy signal and variable frequency signal causes this
indication.
Contents 6
1.6 Waveform Parameters Display
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 8

PC Oscilloscope PCSU10007
Voltage parameters
DC Mean
The arithmetic mean of the entire waveform data.
Max
The signal's positive peak voltage.
(Difference between zero and highest value.)
Min
The signal's negative peak voltage.
(Difference between zero and lowest value.)
Peak-to-Peak
The signal's peak-to-peak voltage.
(Difference between highest and lowest value.)
High
The statistical maximum level recorded for all the cycles in the signal.
Low
The statistical minimum level recorded for all the cycles in the signal.
Amplitude
The voltage difference between the High and Low of the signal.
AC RMS
The true RMS value of the AC component of the signal is calculated and converted to voltage.
AC dBV
The measured signal (AC only) is converted to dBV (0dB= 1V).
AC dBm
The measured signal (AC only) is converted to dBm (0dB= 0.775V).
AC+DC RMS
The true RMS value of the wave (AC+DC) is calculated and converted to voltage.
AC+DC dBV
The measured signal (AC+DC) is converted to dBV (0dB= 1V).
AC+DC dBm
The measured signal (AC+DC) is converted to dBm (0dB= 0.775V).
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 9

Contents 8
Time parameters
Duty Cycle
The ratio (expressed as a percentage) of the average positive pulse width to the average period of the
signal. The time intervals are determined at middle reference level.
Duty Cycle = (Positive Pulse Width)/Period x 100%
Positive Width
Average positive pulse width in the waveform.
The time intervals are determined at middle reference level.
The middle reference is the middle point between the high and low levels.
Negative Width
Average negative pulse width in the waveform.
The time intervals are determined at middle reference level.
Rise Time
Time for a signal's rising edge to go from the low reference level to the high reference level.
The low reference level is 10% and high reference level is 90% of the pulse amplitude.
Fall Time
Time for a signal's falling edge to go from the high reference level to the low reference level.
The low reference level is 10% and high reference level is 90% of the pulse amplitude.
Period
The time interval between two consecutive crossings on the same slope of the signal at the middle
reference level.
Frequency
The inverse of the Period of the signal.
Phase
Phase angle in degrees between CH1 and CH2.
For phase measurement the frequency of CH1 must be equal to the frequency of CH2.
Phase measurement is time consuming process. In slow PCs this reduces the display update rate.
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 10

PC Oscilloscope PCSU10009
For explanation and documentation, each measurement can be supplied with a comment text.
This text will be saved together with the waveform data to the disk file.
To enter the text:
1.
Right mouse click into the screen.
2.
Text box will open, to write your comment.
3.
Click
Add Text on Screen
or
Remove
to remove previously inserted text.
4.
Right click on the screen to position your text.
5.
Click
Close
.
To make the text transparent with the background, check
Transparent text.
The text will have the same color as the vertical time/frequency markers.
File Menu
Edit Menu
Options Menu
View Menu
Math Menu
Help Menu
Note:
Default subdirectory (folder)
\DATA
for image and data files is created when the program is
run the first time.
Open Image
Opens an image file and displays it on the screen.
Open DSO Data
Opens and displays the waveform data saved in text format using the
Save DSO Data
option.
Save Image
Saves the image to a file in Windows Bitmap (*.BMP) format.
Save DSO Data
Saves the waveform data in text format. All captured data (4096 points/channel) is saved.
Save FFT Data
Saves the FFT data in text format. Only the portion of the data displayed on the screen is saved
(250 points).
Save Settings
Saves the Oscilloscope, Spectrum Analyzer and Transient Recorder settings to a file. Also
Function Generator settings (frequency, amplitude, offset and duty cycle) are stored to the file.
Recall Settings
Loads a previously-stored settings file to the oscilloscope.
1.7 Add comment text in the signal screen
2 Menu Options
2.1 File Menu
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 11

Print
Prints the image in color.
You can edit the image caption.
Print Setup
Selects a printer and sets printer options before printing. The available options depend on the
printer you select.
Exit
Terminates the program.
Calibrate & Exit
Makes the oscilloscope calibration, saves the calibration values to the WinDSO.INI file and
terminates the program. This option should be used when the new oscilloscope has been on for
about 1h.
This option performs following operations:
1.
The fine adjustment of the trace Y-position (offset) on different Volt/Div and Time/Div scales.
2.
Sets the trace labels (on the left side of the screen) to correspond the trace GND level.
3.
Sets the triggering level mark to correspond the triggering level.
2.2 Edit Menu
Copy
Copies the image to the Windows' clipboard.
Paste
Pastes the image residing in Windows' clipboard to the screen.
FFT Window
Set the window function used to taper the original signal before calculating the FFT.
.
Spectrum analyzer supports six different FFT windows
1.
Rectangular
2.
Bartlett
3.
Hamming
4.
Hanning
5.
Blackman
6.
Flat top
The Hamming window is set as default at the startup
Background information
It is common practice to taper the original signal before calculating the FFT (Fast Fourier
Transformation). This reduces any discontinuities at the edges of the signal. This is done by
multiplying the signal with a suitable window function. By choosing a tapered window it is possible to
achieve a good compromise between main lobe width and sidelobe levels of a spectral line. The
undesirable spectral leakage can be reduced using a tapered window, at the expense of some
broadening around individual spectral lines. Many different windows have been designed for this
purpose.
The choice of a suitable one depends on the nature of the signal or data, and on the type of
information to be extracted from its spectrum. In general, a good FFT window has a narrow main
spectral lobe to prevent local spreading of the spectrum, and low sidelobe levels to reduce 'distant'
spectral leakage. In some cases it may be best to leave the data alone -- in effect, to use a
rectangular window. For example, if a signal has close spaced components of roughly the same
amplitude, the rectangular window will probably offer the best chance of resolving them. Conversely,
Menu Options 10
2.3 Options Menu
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 12

PC Oscilloscope PCSU100011
if the amplitudes are very different, a window with low sidelobes will reduce leakage around the large
component, and should make the small one easier to detect.
Comparison of the window functions
Window type
Window characteristics
Applications
Rectangular
Narrow mainlobe
Slow rolloff rate
Broadband random (white noise)
Closely spaced sine-wave signals
Bartlett
Narrow mainlobe
Fast rolloff rate
Hamming
Good spectral resolution
Narrow mainlobe
Closely spaced sine-wave signals
Hanning
High maximum sidelobe level
Good frequency resolution
Reduced leakage
Fast rolloff rate
Narrowband random signals
Sine wave or combination
of sine-wave signals
Blackman
Wide mainlobe
Fast rolloff rate
Flat top
Good amplitude accuracy
Wide mainlobe
Poor frequency resolution
More spectral leakage
Sine wave with need
for amplitude accuracy
FFT Options
Maximum
Maximum value of each frequency is displayed in Run mode.
This option can be used for recording signal levels as a function of frequency (Bode plot). You can
use spreadsheet to display the frequency response curve including the frequency labels. On
File
menu, click
Save FFT Data
to export the data to the spreadsheet.
RMS Average
Use this averaging mode to reduce signal fluctuations.
RMS averaging provides an excellent estimate of the true signal and noise levels of the input signal.
Vector Average
Use this averaging mode to reduce random or uncorrelated noise in the synchronous signal you want
to display.
Vector averaging requires a trigger - set
Trigger ON
.
The signal of interest must be both periodic and phase synchronous with the trigger.
Vector averaging reduces the noise floor for random signals since they are not phase coherent from
time record to time record.
If not trigged, the signal will not add in phase and instead will cancel randomly.
Hardware setup
Select the LPT port where the hardware is connected.
Operation mode
1.
Oscilloscope connected to
USB
port.
2.
Demo mode. (No hardware needed).
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 13

Menu Options 12
Select the LPT port address where the Function Generator PCG10 or K8016 is connected
378,
278 or 3BC
You'll find the address from Windows' Device Manager:
1.
Click "System" icon in Control Panel and then the Device Manager tab.
2.
Click the plus sign next to the "Ports".
3.
Double-click "Printer Port (LPTx)".
4.
Click the Resources tab to see the Input/Output address.
Select the LPT port communication speed for
the Function Generator
Normal
This can be used in most cases.
Slow
Select this option if the waveform of the function generator is corrupte
Colors
Select the display colors.
Select the color for various items on the waveform display.
To change the color of an item, click the corresponding button. This will open a dialog in which you
can select the new color.
Full color selection is possible only if True Color (24 bit) palette is used.
There are restrictions in the color combinations with other palettes.
Click
Bright Screen
or
Black Screen
button to resets all colors to the
Default settings
.
Trigger Options
Noise Reject
Select this option to get stable triggering on noisy signals.
This option works only in the Run mode and only in the Real-time Sampling mode.
RMS value
Displays AC RMS value of the signal
When this option is selected the true RMS AC value of the signal is displayed on the screen.
·
If CH1 is
on
the RMS value of CH1 is shown
·
If CH1 is
off
the RMS value of CH2 is shown
dBm Value
Displays AC dBm value of the signal
Sample Rate
Displays the sampling rate on the top of the screen.
When this option is selected the dBm value of the signal's AC component is displayed on the screen.
·
If CH1 is
on
the dBm value of CH1 is shown
·
If CH1 is
off
the dBm value of CH2 is shown
The dBm value displayed on the screen:
0 dBm = 1 milliwatt at 600 ohms ( 0.775 Vrms)
2.4 View Menu
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 14

PC Oscilloscope PCSU100013
Waveform Parameters
Software automatically calculates various voltage and time parameters of a signal, such as DC
mean, amplitude, rise time etc.
These parameters are displayed in a separate window. Use the check boxes in the window to
select the parameters you which to be displayed.
Markers
Displays Markers on the screen.
Bright Grid
Brightens the signal grid on the screen.
Dot Join
On
: The dots of the acquired waveform data are connected by lines.
Off
: Only the dots of the acquired waveform data are displayed.
Markers in ocilloscope mode
·
Two horizontal markers for measuring voltage. The voltage difference and the absolute voltage
values (in parentheses) are displayed.
·
Two vertical markers for measuring time and frequency
Note: The voltage markers give preference to channel CH1 if both channels are being used.
Markers in spectrum analyzer mode
·
Marker function for absolute and relative voltage measurement is provided.
·
The absolute voltage level in
dBV
or the voltage difference in
decibels
(dB) can be measured.
·
Noise level can be measured using the
Spectral Density
marker.
·
One vertical marker is provided for the frequency measurement.
Moving the markers
1.
Place the mouse pointer over a dashed marker line.
2.
Press and hold the left mouse button. The markerline turns solid.
3.
Drag the marker to the appropriate position
dB
The term
dB
or
decibel
is a relative unit of measurement used to describe power or voltage
difference.
Equation to calculate a dB value based on the ratio of two voltages V2 and V1 is:
dBV
dBV = The dB value is obtained with respect to 1Volt. The dBV is an absolute unit of voltage. It
expresses voltages as a ratio relative to 1 volt.
Equation to calculate a dBV value of a voltage V is:
Equation to calculate voltage V from dBV value is:
14
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 15

dBm
A unit of measurement of signal level in an electrical circuit, expressed in decibels referenced to 1
milliwatt.
In a circuit with an impedance of 600 ohms, 0 dBm gives an equivalent voltage level of 0.775 Vrms.
The dBm value displayed on the screen:
0 dBm = 1 milliwatt at 600 ohms ( 0.775 Vrms)
2.5 Spectral Density
The Spectral Density marker may be used when measuring the density of random or noise signals
since it properly takes into account the frequency bin width and the FFT window function used by the
spectrum analyzer when measuring noise-like signals.
The
Spectral Density
marker readout is automatically normalized to 1 Hz.
The displayed unit is:
Note:
The Spectral Density marker should not be used to measure discrete frequency components as
it will provide misleading level readings.
The
Spectral Density
is simply the magnitude of the spectrum normalized to a 1 Hz bandwidth. This
measurement approximates what the spectrum would look like if each frequency component were
really a 1 Hz wide piece of the spectrum at each frequency bin.
When measuring broadband signals such as noise with a spectrum analyzer, the amplitude of the
spectrum changes with the frequency span. This is because the FFT bin width changes and the
frequency bins have a different noise bandwidth.
The
Spectral Density
marker normalizes all measurements to a 1 Hz bandwidth and the noise
spectrum becomes independent of the frequency span. This allows measurements with different
spans to be compared.
If the noise is Gaussian in nature, then the amount of noise amplitude in other bandwidths may be
approximated by scaling the
Spectral Density
measurement by the square root of the noise
bandwidth.
Example:
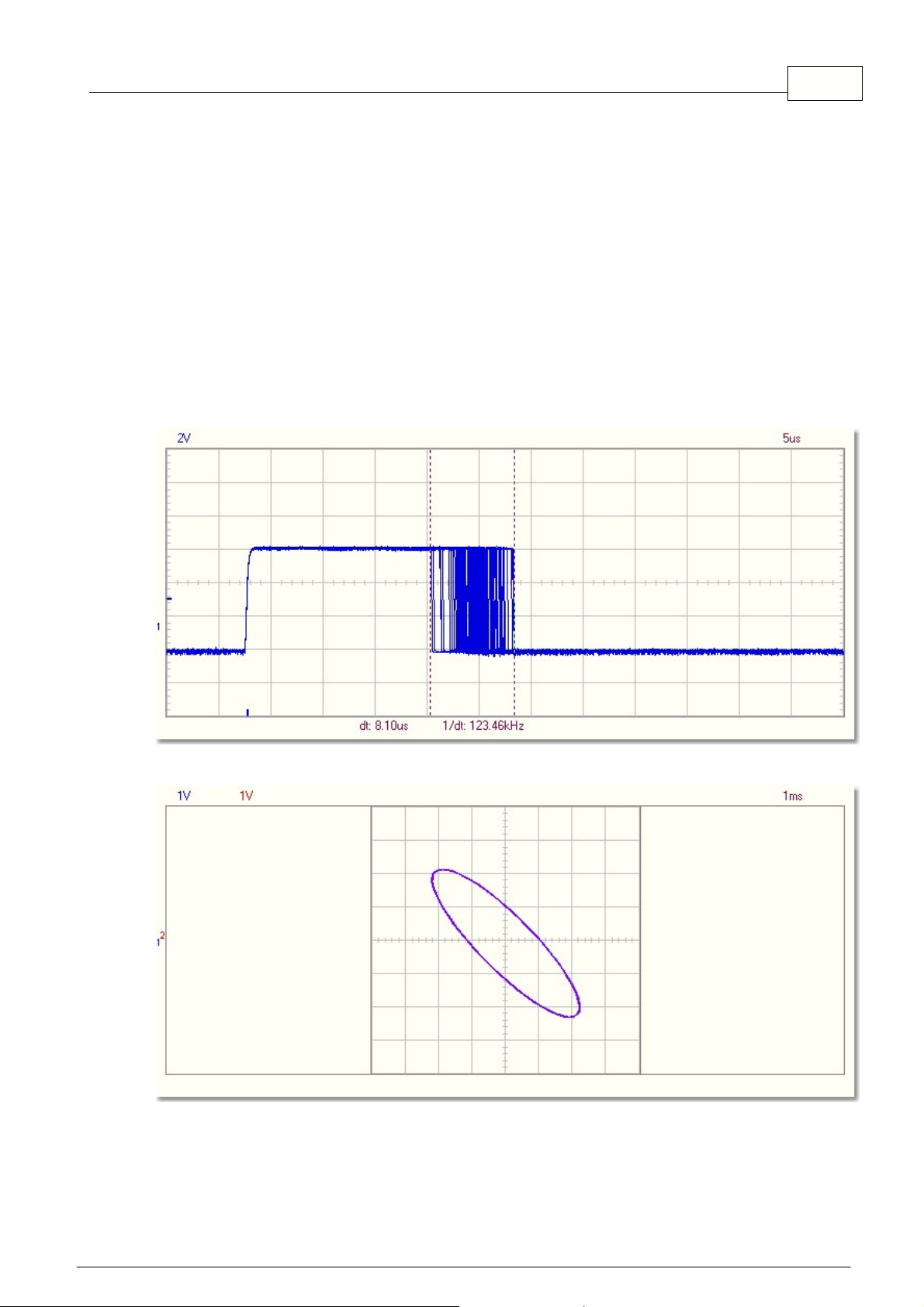
This image shows a band limited noise signal on an oscilloscope screen.
Spectrum analyzer can be used to measure the spectral density of this noise signal.
In the spectrum analyzer select the following menu options:
·
Options / FFT Options / RMS Average
Menu Options 14
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 16

PC Oscilloscope PCSU100015
·
View / Markers (FFT) f & Spectral Density dBV/sqrt(Hz)
This image shows the spectrum of the band limited noise signal.
The analysis of noise in the frequency domain shows the distribution of the noise amplitude as a
function of frequency.
Using the
Spectral Density
marker and the Frequency marker, the voltage spectral density (V
SdBV
)
and the noise bandwidth (B
N
) can be read from the spectrum analyzer display.
First convert the voltage spectral density to
.
This can be accomplished using the following calculation:
This is the magnitude of the spectrum normalized to a 1 Hz bandwidth.
You may calculate the noise voltage over any bandwidth by multiplying this value by the square root of
the bandwidth.
Assuming a 6 kHz bandwidth, the total output noise voltage is:
(See the V
rms
value of the oscilloscope waveform image of this noise signal.)
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 17

2.6 Math Menu
The result of mathematical operation of channel 1 and 2 is displayed.
One of the following functions can be selected:
·
Ch1 + Ch2
·
Ch1 - Ch2
·
XY Plot
·
Invert Ch2
XY Plot:
Ch1 data is displayed on Y axis
Ch2 data is displayed on X axis
A button is provided to toggle between Math mode and Normal mode.
Contents
Displays this help file
Installing Windows NT4 driver
Gives instructions for the Windows NT4, Windows 2000 and Windows XP users
About
Displays information of the program version
Data acquisition to other applications
Data acquisition to Microsoft Excel
Pc-Lab2000 software package includes a DLL
(Dynamic Link Library)
DSOLink.DLL,
installed to
Windows'
SYSTEM32
folder.
This DLL allows you to write custom applications in Excel, Visual Basic, Delphi or any other 32-bit
Windows application development tool that supports calls to a DLL.
The DLL gives you direct access to real-time data and settings information from the oscilloscope.
The complete example programs are located on the VELSOFT CD. Those may be used as a starting
point how to construct your customized application programs.
Note
: Before running the following example programs: The oscilloscope software must be running and
Run
or
Single
button pressed and trace displayed on the oscilloscope screen.
2.7 Help Menu
Menu Options 16
3 Data Transfer
3.1 Data acquisition to other applications
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 18

PC Oscilloscope PCSU100017
Description of the procedures of the DSOLink.DLL
ReadCh1
ReadCh2
Syntax
PROCEDURE ReadCh1(Buffer: Pointer);
PROCEDURE ReadCh2(Buffer: Pointer);
Parameter
Buffer
: A pointer to the data array of 5000 long integers where the data
will be read.
Description
Read all the data and the settings of channel 1 or channel 2 of the PCSU1000.
As a return the following data is put to the buffer:
[0] : Sample rate in Hz
[1] : Full scale voltage in mV
[2] : Ground level in A/D converter counts. The value may be beyond the 0...255 range if GND level
is adjusted beyond the waveform display area.
[3...4098] : The acquired data in A/D converter counts (0...255), from PCSU1000.
The triggering point of the PCSU1000 is at the data location [1027].
Running the DSOLink in Delphi
Check the
\PC-Lab2000 tools\PCSU1000 - PCS500 - PCS100 - K8031\Data transfer
DSOLink_DLL\DSOLink_Demo_VB\
folder on the Velleman CD to locate the demo files.
This folder contains a ready to run
DSOLink_Demo.EXE
program and its source code.
You may copy the files to any folder and use Delphi to examine, edit and compile the files.
Example
(in Delphi)
var
data:
array
[0..
5000] of
longint;
procedure
ReadCh1(Buffer: Pointer);
stdcall
;
external
'DSOLink.dll'
;
procedure
TForm1.Button1Click(Sender: TObject);
var
i: longint;
p:pointer;
begin
p:= @data[
0]; ReadCh1(p);
memo1.clear;
memo1.lines.add(
'Sample rate [Hz]'
+chr(
9
)+inttostr(data[
0
]));
memo1.lines.add(
'Full scale [mV]'
+chr(
9
)+inttostr(data[
1
]));
memo1.lines.add(
'GND level [counts]'
+chr(
9
)+inttostr(data[
2
]));
memo1.lines.add(
''
);
begin
for
i:=0 to 20
do
memo1.lines.add(
'Data ('
+inttostr(i)+
')'
+chr(
9
)+chr(
9
)+inttostr(data[i+
3
]));
end;end
;
Running the DSOLink in Visual Basic
Make sure that the file
DSOLink.DLL
is copied to Windows'
SYSTEM32
folder.
Check the
\PC-Lab2000 tools\PCSU1000 - PCS500 - PCS100 - K8031\Data transfer
DSOLink_DLL\DSOLink_Demo_VB\
folder on the VELSOFT CD to locate the demo files.
This folder contains a ready to run
DSOLink_Demo.EXE
program and its source code.
You may copy the files to any folder and use Visual Basic to examine, edit and compile the files.
Example
(in Visual Basic)
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 19

Data Transfer 18
Option
Explicit
Dim
DataBuffer(0
To
5000)
As Long
Private
Declare
Sub
ReadCh1
Lib
"DSOLink.dll " (Buffer
As Long)'This reads the settingsd and 4096 bytes of data from CH1 to the data buffer.
'The first 21 values are displayed.
Private
Sub Read
_CH1_Click(Index
As Integer
)
Dim
i As
Long
List1.Clear
ReadCh1 DataBuffer(0)
List1.AddItem "Sample rate [Hz]" + Chr(9) + Str(DataBuffer(0))
List1.AddItem "Full scale [mV]" + Chr(9) + Str(DataBuffer(1))
List1.AddItem "GND level [counts]" + Chr(9) + Str(DataBuffer(2))
List1.AddItem ""
For
i = 0
To
20
List1.AddItem "Data(" + Str(i) + ")" + Chr(9) + Chr(9) + Str(DataBuffer(i + 3))
Next
End Sub
Running the DSOLink in Borland C++ Builder
The following files are available in the
\PC-Lab2000 tools\PCSU1000 - PCS500 - PCS100 -
K8031\Data transfer DSOLink_DLL\DSOLink_Demo_BCB\
folder on the VELSOFT CD for
development with Borland C++Builder:
DSOLink.dll
the dynamically linked library
DSOLink.h
the C/C++ header file for function prototypes
DSOLink.lib
the import library
DSOLink_demo.cpp
demo source
1.
Create a new project in Borland C++ Builder.
2.
Add the import library to your project using
Project | Add to Project
menu option.
3.
Add a
#include
statement in the main unit that includes
DSOLink.H
.
4.
Finally, add code that calls the DLL functions.
DSOLink.h
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// DSOLink.h
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern
"C" {/* Assume C declarations for C++ */
#endif
#define FUNCTION
__declspec
(dllimport)
FUNCTION
__stdcall
ReadCh1(
int
* ptr);
FUNCTION
__stdcall
ReadCh2(
int
* ptr);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Example
(in Borland C++Builder)
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// DSOLink_demo.cpp
#include <vcl.h>
#pragma hdrstop
#include
"DSOLink.h"
#include
"DSOLink_demo.h"
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#pragma package(smart_init)
#pragma resource
"*.dfm"
TForm1 *Form1;
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
__fastcall
TForm1::TForm1(TComponent* Owner)
: TForm(Owner)
{}//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void __fastcall
TForm1::Button1Click(TObject *Sender)
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 20

PC Oscilloscope PCSU100019
{
int
data[
5000
];
ReadCh1(data);
Memo1->Clear();
Memo1->Lines->Add(
"Sample rate [Hz]: "
+IntToStr(data[
0
]));
Memo1->Lines->Add(
"Full scale [mV]: "
+IntToStr(data[
1
]));
Memo1->Lines->Add(
"GND level [counts]: "
+IntToStr(data[
2
]));
Memo1->Lines->Add(
""
);
for (int
i =
0
; i <
20
; i++)
{
Memo1->Lines->Add(
"Data "
+IntToStr(i)+
char(9
)+IntToStr(data[i+
3
]));
}
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note:
If the import library is not compatible to your Borland C++ version, you can create an import
library by running IMPLIB on the DLL.
IMPLIB works like this:
IMPLIB (destination lib name) (source dll)
For example,
IMPLIB DSOLink.lib DSOLink.dll
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 21

3.2 Data acquisition to Microsoft Excel
Pc-Lab2000 software package includes a DLL
(Dynamic Link Library)
DSOLink.DLL,
installed to
Windows'
SYSTEM32
folder.
This DLL allows you to write custom applications in Excel, Visual Basic, Delphi or any other 32-bit
Windows application development tool that supports calls to a DLL.
Transferring Waveform Data to an Excel Spreadsheet
The example Excel macro shows you how to collect data directly into the spreadsheet from the
Velleman PC oscilloscopes without the need for other software.
1.
Open
Microsoft Excel
and start a new workbook document.
2.
Select the
View / Toolbars
Menu and Select
Forms.
·
The Forms toolbar appears.
3.
Create a
Button
·
In the Forms toolbar click on the "Button" button: the mouse-pointer will become a small
cross.
·
On Excel worksheet, use the mouse to draw a rectangle to mark where you want your
button to appear.
·
When you release the mouse after drawing the rectangle the "Assign Macro" dialog-box
will appear.
4.
Type Macro name:
ReadAll
and click
New
button.
·
Microsoft Visual Basic edit window will open. A subroutine called
ReadAll
has been
created.
5.
Substitute the default text:
Sub
ReadAll()
End Sub
with the following text in the edit window:
(Use Copy and Paste.)
Option
Explicit
Dim
DataBuffer1(0
To
5000)
As Long
Dim
DataBuffer2(0
To
5000)
As Long
Private
Declare
Sub
ReadCh1
Lib
"DSOLink.dll " (Buffer
As Long
)
Private
Declare
Sub
ReadCh2
Lib
"DSOLink.dll " (Buffer
As Long
)
Data Transfer 20
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 22

PC Oscilloscope PCSU100021
Sub
ReadAll()
Dim
i As
Long
ReadCh1 DataBuffer1(0)
ReadCh2 DataBuffer2(0)
With
ActiveSheet
For
i = 0
To
99
.Cells(i + 1, 2) = DataBuffer1(i)
.Cells(i + 1, 3) = DataBuffer2(i)
Next
i End With
End Sub
6.
Press
Alt+F11
to return to Excel.
7.
Type following texts to column
A
:
Sample rate [Hz]
Full scale [mV]
GND level [counts]
Data 0
Data 1
Data 2
...
8.
Start oscilloscope program for PCSU1000, PCS500, PCS100 or K8031 and click
Run
or
Single
button.
9.
Click the button on the Excel worksheet. The created macro will execute and the data
described in column
A
will appear to the worksheet columns
B
and
C
.·Rows 4...4099 contain the acquired data in A/D converter counts (0...255) for PCSU1000
and PCS500.
·
Rows 4...4083 contain the acquired data in A/D converter counts (0...255) for PCS100 and
K8031.
·
The triggering point of PCSU1000 and PCS500 is on row 1030 and of PCS100 and K8031
on row 4.
© 2005 ... Velleman
Page 23

Data Transfer 22
The three first rows contain the scope settings and the rest of the rows contain the raw
oscilloscope data in A/D converter counts (0...255).
Using the
Sample rate
,
Full scale
and
GND level
values it is possible to reconstruct the
waveform data into engineering units (e.g. Volts and seconds) for further analysis.
© 2005 ... Velleman
 Loading...
Loading...