Page 1
Information sheet
Display Defects
1. Introduction
This information sheet gives more information on how to recognize display defects and determine whether a
display conforms to quality standards.
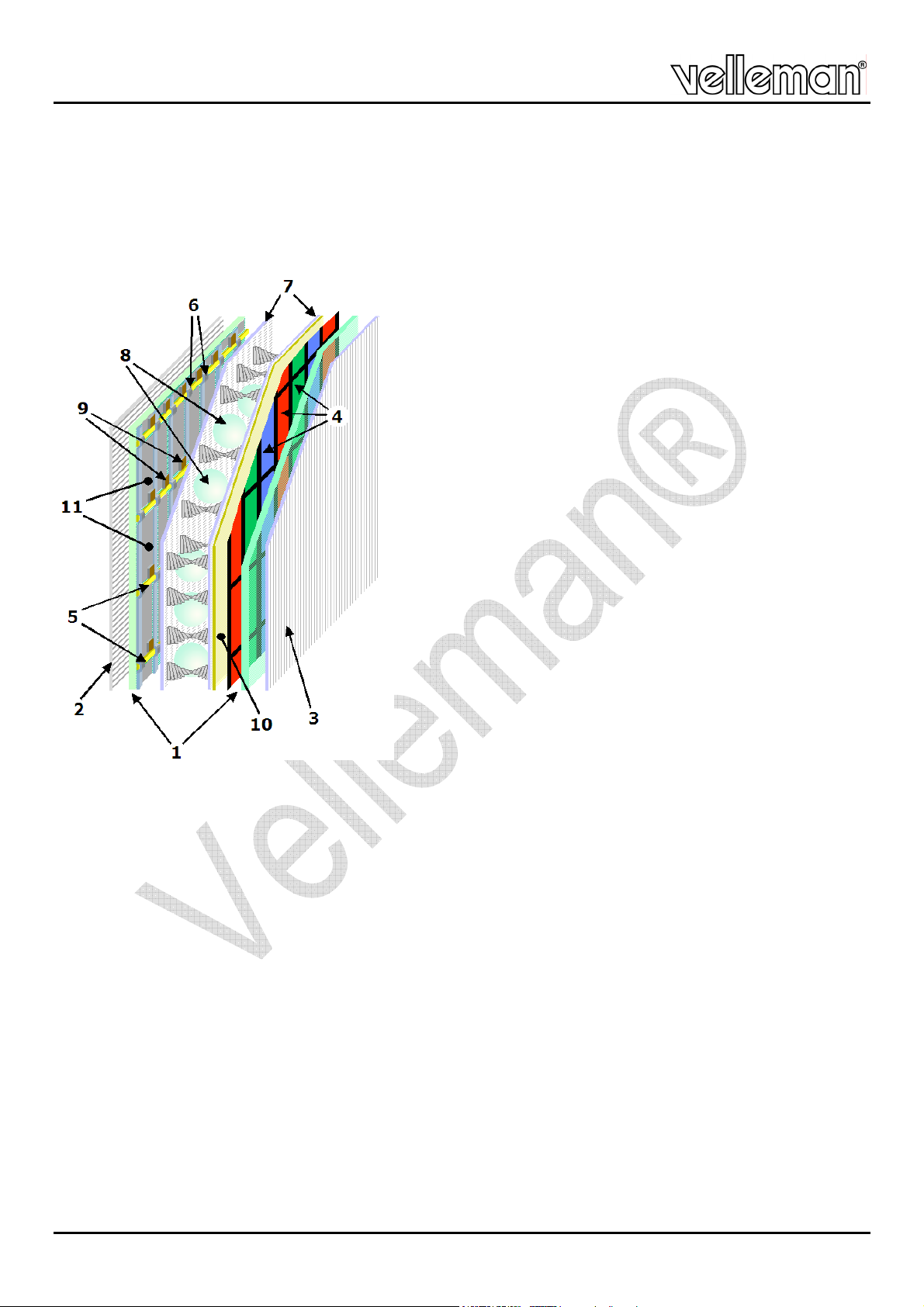
A TFT LCD monitor consists of multiple layers (see figure below).
1 glass substrates
2 horizontal polarizer
3 vertical polarizer
4 RGB colour mask
5 horizontal control wires
6 vertical control wires
7 polymer layers
8 spacers
9 Thin Film Transistors (TFT)
10 front electrode
11 rear electrode
Display defects can be caused by contamination that entered between layers either during production or
during use, short-circuits between control wires that either keep a pixel or one colour of a pixel dark or
bright, faulty control wires that keep a whole line of pixels turned on or off, scratches on polarizer or glass
substrate caused by mistreatment, dents …
A monitor contains millions of pixels (e.g. MONSCA6: 1280x1040=1,331,200), making it technical nearly
impossible to produce a display without pixel defects. Therefore certain standards were created describing
the number, size, location… of above mentioned defects that are acceptable (allowed) in a TFT LCD display.
For some industries (e.g. aviation) these standards are much more stringent than for others.
2. Definitions
Bright dot defect
Pixels or sub-pixels that appear bright and are visible through a 5% ND (Neutral Density) filter
when a black pattern is displayed. Note that the ND filter must be held parallel to the surface at
a distance of 2.5 to 3 cm.
BM (black matrix) defect
White points on a display that is switched off.
Dark/bright spot
Points on the display that appear dark or bright, usually due to contaminations. These spots do
not change in size or intensity when adjusting the contrast.
Dark/bright lines
Lines on the display that appear dark or bright, usually due to contaminations.
Dark dot defect
Pixels or sub-pixels that appear dark when an RGB coloured pattern is displayed.
Velleman® 1/3 Last update: 25/05/2010
Page 2
Information sheet
Line defect
A complete line of pixels, horizontally, vertically or diagonally, that appear bright or dark.
Mura
Brightness of the display is not uniform over the whole display area.
Pixel
Smallest addressable screen element. For colour TFT displays, these are made up of 3 separate
colour elements: red, green and blue. Varying the intensity of these 3 colours (or dots) can
create pixels of any desired colour.
Polarizer dent
White spots on the display that become visible on a darker background. Their size remains the
same when adjusting the display settings.
Polarizer scratch
Lines on the display that are visible against a darker background. These lines always have the
same length.
Sub-pixel (dot)
One colour element of a pixel.
3. Defects
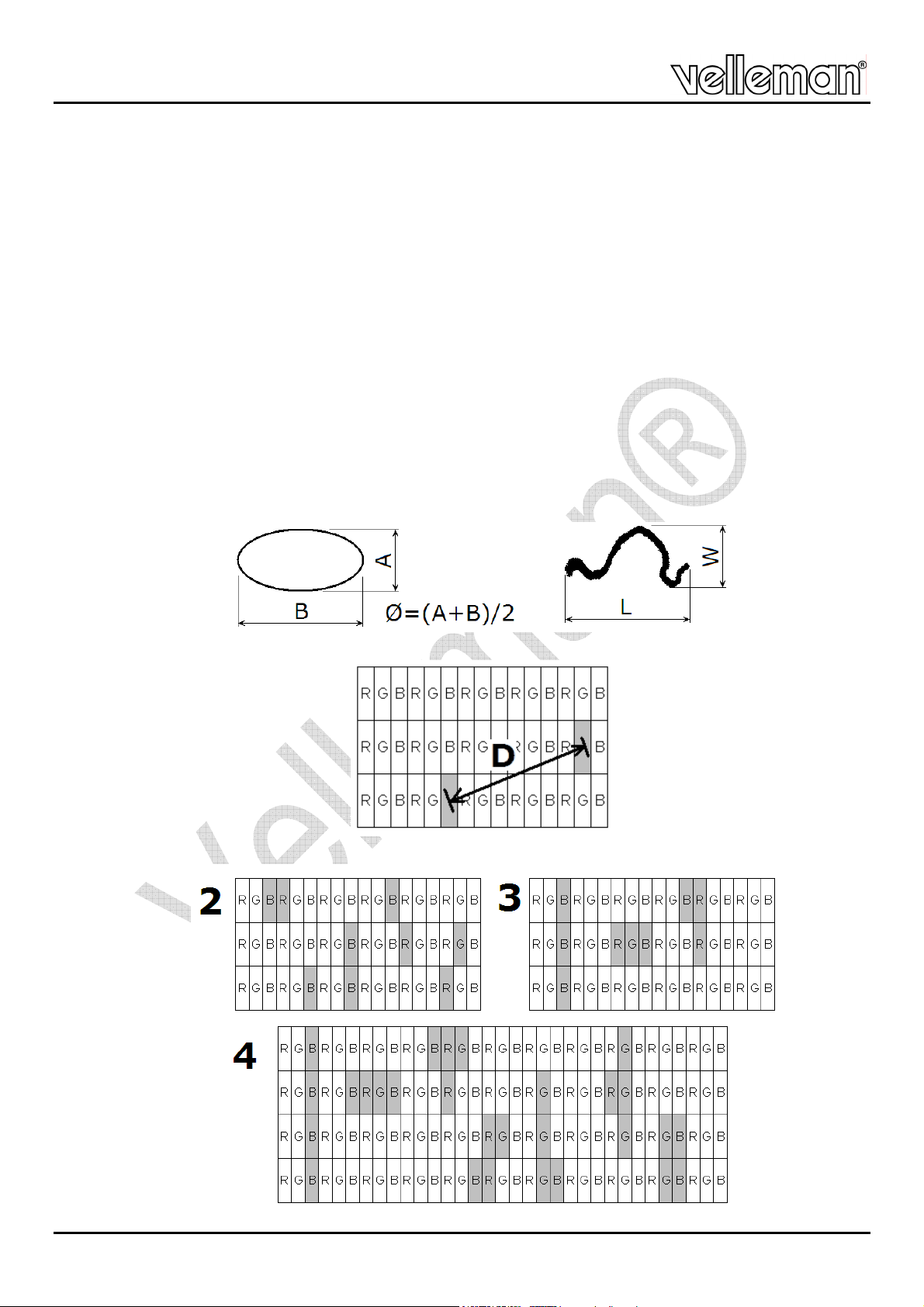
A defect can be shaped either round or elongated.
A round defect is defined by its average diameter, which equals the sum of max. height and
maximum width divided by 2.
An elongated defect is defined by its length and width.
The distance D between two defective dots is measured as indicated below:
Adjacent dots are defined as follows (examples):
Velleman® 2/3 Last update: 25/05/2010
Page 3

Information sheet
4. Procedure
Inspection conditions
• Viewing distance is approximately 35 ~ 40 cm (for
inspecting adjacent dots and distance between defect
dots, this distance is much closer)
• Viewing angle is normal to the LCD panel (max. 10°
deviation)
• Ambient temperature is 25 ± 5°C
• Ambient humidity is 60 ± 5% RH
• Ambient illuminance is between 300 ~ 500 Lux.
• Input signal timing should be typical value.
A eye position
B LCD panel
Inspection criteria
Refer to the definitions in §2.
N = number of defects.
visual
defect
electrical
defect
defect type limit
scratch
round 0.3mm ≤ Ø ≤ 1.0mm N ≤ 5
linear
defect
polarizer 0.3mm ≤ Ø ≤ 1.0mm N ≤ 5
total allowed N ≤ 10
bright* N ≤ 6
single dot
adjacent dots 2** ≤ 3 pairs
3** ≤ 2 sets
4** ≤ 1 sets
distance between 2 bright dots ≥ 10mm
dark N ≤ 6
total allowed N ≤ 9
0.03mm ≤ W ≤ 0.1mm
L ≤ 10mm
W ≤ 1.0mm
L ≤ 3.0mm
N ≤ 4
N ≤ 5
line defects N = 0 (not allowed!)
*: visible through a 5% ND (Neutral Density) filter
**: adjacent dots also add to the single dot counter
Note: other defects that may occur e.g. mura are subject to user interpretation and should be
evaluated individually.
Velleman® 3/3 Last update: 25/05/2010
 Loading...
Loading...