Page 1

Model IP-2002
Radio Control Console
Technical Manual
P.N. 804004 REV A
July 27, 2004
Page 2

Remote Control Console I
Page 3

Table of Contents
1 INTRODUCTION ...............................................................................................................................................1
2 HARDWARE OVERVIEW ...............................................................................................................................1
2.1 MAIN PROCESSOR PCB ..................................................................................................................................1
2.2 KEYPAD PCB AND DISPLAY...........................................................................................................................1
3 CONTROLS AND INDICATORS.....................................................................................................................2
3.1 FRONT PANEL.................................................................................................................................................2
3.1.1 Common Controls and Indicators .........................................................................................................2
3.1.1.1 VU Meter: .......................................................................................................................................................... 2
3.1.1.2 Program 1-4: ...................................................................................................................................................... 3
3.1.1.3 DTMF Keypad:.................................................................................................................................................. 3
3.1.1.4 Supervisory button: ............................................................................................................................................ 3
3.1.1.5 Menu button:...................................................................................................................................................... 3
3.1.1.5.1 Cross Patch.................................................................................................................................................. 3
3.1.1.6 Channel UP/DOWN buttons (C▲& C▼): ........................................................................................................ 3
3.1.1.7 Scan button: ....................................................................................................................................................... 3
3.1.1.8 Channel button:.................................................................................................................................................. 3
3.1.1.9 Group UP/DOWN buttons (G▲& G▼):........................................................................................................... 4
3.1.1.10 Function Buttons F1-F4:................................................................................................................................ 4
3.1.1.11 Line Buttons LN1-LN2: ................................................................................................................................ 4
3.1.1.12 Volume Control:............................................................................................................................................ 4
3.1.1.13 Monitor:......................................................................................................................................................... 4
3.1.1.14 Intercom (IC):................................................................................................................................................ 4
3.1.1.15 Panel PTT Pushbutton: .................................................................................................................................. 4
3.1.1.16 Transmit LED:............................................................................................................................................... 4
3.2 REAR PANEL CONNECTIONS ........................................................................................................................... 4
3.2.1 Rear Panel Ports ...................................................................................................................................5
4 OPERATION.......................................................................................................................................................5
4.1 RADIO LINES ..................................................................................................................................................5
4.1.1 Selecting: ...............................................................................................................................................5
4.1.2 Changing Function Tones: ....................................................................................................................5
4.1.3 Muting Unselected Lines: ...................................................................................................................... 5
4.1.4 Releasing a Line: ................................................................................................................................... 6
4.1.5 Supervisory Control Button:..................................................................................................................6
4.1.6 TX ALL Function (No button): ..............................................................................................................6
4.1.7 Intercom to parallel console:.................................................................................................................6
4.1.8 Answering a Phone call.........................................................................................................................6
4.1.9 Placing a call.........................................................................................................................................6
4.1.10 Putting a Phone line On-Hold ............................................................................................................... 6
4.1.11 Muting a phone Line: ............................................................................................................................6
4.1.12 Sending a Hook-Flash ...........................................................................................................................6
4.1.13 Releasing a Phone Line:........................................................................................................................6
4.1.14 General Display Indications: ................................................................................................................6
5 PROGRAMMING............................................................................................................................................... 7
5.1 ENTERING THE SETUP MODE ..........................................................................................................................7
5.2 SETTING THE SYSTEM CLOCK......................................................................................................................... 7
5.3 SETTING THE PIN NUMBER............................................................................................................................. 7
5.4 SETTING THE BASIC IP INFORMATION .............................................................................................................8
5.5 ENTERING IP-2002 WEB SETUP .....................................................................................................................9
5.5.1 Orange Crossover Cable ....................................................................................................................... 9
5.6 BASIC ETHERNET SETUP...............................................................................................................................10
5.6.1 Use DHCP Server: ..............................................................................................................................10
5.6.2 Unit IP Address: ..................................................................................................................................10
5.6.3 Subnet Mask: .......................................................................................................................................11
5.6.4 Gateway Address:................................................................................................................................11
Page 4

II Vega’s IP-2002
DNS Addresses 1-2:.............................................................................................................................11
5.6.5
5.6.6 SNTP Address:..................................................................................................................................... 11
5.6.7 SNTP Update Interval: ........................................................................................................................11
5.6.8 SNTP Local Time Offset: ..................................................................................................................... 11
5.6.9 Packet Delay Before Playback: ...........................................................................................................11
5.6.10 QOS Bits:.............................................................................................................................................11
5.6.11 Local IP Addresses:............................................................................................................................. 12
5.7 MULTICAST SETUP .......................................................................................................................................12
5.7.1 Enable via Ethernet:............................................................................................................................12
5.7.2 Channel Name: .................................................................................................................................... 12
5.7.3 Multicast Address: ...............................................................................................................................12
5.7.4 RX and TX Ports:................................................................................................................................. 12
5.7.5 Channel Hops:.....................................................................................................................................12
5.8 ANI DIRECTORY SETUP ...............................................................................................................................13
5.9 PER LINE SETUP PARAMETERS .....................................................................................................................13
5.9.1 Line Enabled: ......................................................................................................................................14
5.9.2 Duplex Enable: .................................................................................................................................... 14
5.9.3 Crosspatch Open Time: ....................................................................................................................... 14
5.9.4 Select Call String:................................................................................................................................ 14
5.9.5 Select Call Open Time:........................................................................................................................14
5.9.6 Disable Mute: ......................................................................................................................................14
5.9.7 Min Mute Level:...................................................................................................................................14
5.9.8 TX Enabled:.........................................................................................................................................14
5.9.9 Network Phone Enable:.......................................................................................................................14
5.9.10 Local Phone Line: ...............................................................................................................................14
5.9.11 F-Tone 1-100 Enable: .........................................................................................................................14
5.9.12 Ftone1-100 Alphanumeric:..................................................................................................................14
5.9.13 RX Block:.............................................................................................................................................14
5.9.14 TX Block: ............................................................................................................................................. 15
5.9.15 Pairs/Wildcard: ...................................................................................................................................15
5.10 GENERAL GAIN SETUP..................................................................................................................................15
5.11 GLOBAL SYSTEM SETUP 1 ............................................................................................................................16
5.11.1 Supervisor Enable: ..............................................................................................................................16
5.11.2 Supervisor Timeout: ............................................................................................................................16
5.11.3 TX Delay:.............................................................................................................................................16
5.11.4 Auto Monitor Enable:..........................................................................................................................16
5.11.5 CRP Timeout: ......................................................................................................................................16
5.11.6 Console Name: ....................................................................................................................................17
5.11.7 CRP Delay:.......................................................................................................................................... 17
5.11.8 Mute UNSEL w/ PTT:..........................................................................................................................17
5.11.9 Line Tape Output Mix:.........................................................................................................................17
5.11.10 Line Tape with Volume:................................................................................................................... 17
5.11.11 Handset or Headset RX routing: .....................................................................................................17
5.11.12 Summed RX to Handset or Headset: ...............................................................................................17
5.11.13 Network Phone Ring Type:..............................................................................................................17
5.11.14 Panel PTT Default Mic:...................................................................................................................17
5.11.15 DTMF Keypad Enable:....................................................................................................................17
5.11.16 DTMF Flywheel: .............................................................................................................................17
5.11.17 DTMF On Time: ..............................................................................................................................18
5.11.18 DTMF Off Time:..............................................................................................................................18
5.11.19 DTMF Level: ...................................................................................................................................18
5.11.20 DTMF Sidetone: ..............................................................................................................................18
5.11.21 DTMF Sidetone Level:.....................................................................................................................18
GLOBAL SYSTEM SETUP 2 ........................................................................................................................................18
5.11.22 Alert Tone Buttons Setup:................................................................................................................18
5.12 CLONE FROM OTHER CONSOLE ....................................................................................................................19
5.13 PIN CHANGE ................................................................................................................................................19
5.14 SAVE TO EEPROM ......................................................................................................................................20
Page 5

Remote Control Console III
REPROGRAMMING THE IP-2002 SOFTWARE .................................................................................................20
5.15
6 SCHEMATICS, PARTS PLACEMENTS, AND BILLS OF MATERIAL..................................................21
6.1 MAIN PROCESSOR PCB ................................................................................................................................21
6.2 KEYPAD PCB ...............................................................................................................................................22
6.3 IP-2002 ASSY DRAWING ............................................................................................................................23
7 WARRANTY, SERVICE, REPAIR AND COMMENTS..............................................................................24
8 SPECIFICATIONS ...........................................................................................................................................25
Table of Figures
Figure 1 Front Panel Diagram .........................................................................................................................2
Figure 2 Menu Button Functions.....................................................................................................................3
Figure 3Cross Patch Menu ..............................................................................................................................3
Figure 4 Rear Panel Diagram ..........................................................................................................................5
Figure 5 Initial Programming Screen ..............................................................................................................7
Figure 6 Clock Setup Screen ...........................................................................................................................7
Figure 7 PIN Setup Screen ..............................................................................................................................7
Figure 8 PIN setup Sub-menu screens............................................................................................................8
Figure 9 Main IP setup screen .........................................................................................................................8
Figure 10 IP Setup Sub-menu screens.............................................................................................................8
Figure 11 IP-2002 Login Screen .....................................................................................................................9
Figure 12 Basic Ethernet Setup Screen .........................................................................................................10
Figure 13 Multicast Setup Screen..................................................................................................................12
Figure 14 ANI Directory Setup Page ............................................................................................................13
Figure 15 Per Line Setup Page ......................................................................................................................13
Figure 16 General Gain Setup Page ..............................................................................................................15
Figure 17 Global System Setup Page 1 .........................................................................................................16
Figure 18 Global System Setup 2..................................................................................................................18
Figure 19 Console Clone Page ......................................................................................................................19
Figure 20 PIN Change Page ..........................................................................................................................19
Figure 21 Save To EEPROM Page................................................................................................................20
Page 6

Page 7

VOIP Desktop Console 1
1 Introduction
The IP-2002 is a unique multi-channel full-featured self-contained desktop radio control console. It will control
two lines and is an Ethernet only console; you can use the Vega IP223 adapter panel enabling you to connect
between the console and your base station via an Ethernet connection. The IP223 accommodates Ethernet
connections for controlling two radios.
The IP-2002 sports a VF display, which provides channel alpha/numeric indication, clock and audio-level meter
with a modern membrane keypad. These features allow for a more flexible dispatch environment in which the
console may be installed. The dispatcher can easily operate the console while sitting or standing.
The IP-2002 will accommodate a desk microphone, along with a handset (or headset) as indicated on the side of the
IP-2002 console. When a PTT occurs from either of the two microphones, the other will mute so as not to pick-up
unnecessary ambient noise during transmission. When the handset is taken off hook and a line is Selected, the
receive audio from that line is transferred to the earpiece. The IP-2002 also has a front panel microphone, which can
be used when the handset/headset is on-hook.
The IP-2002 is a Digital Signal Processor (DSP) based design, allowing easy field programmability using a
computer with installed WEB browser. Unlike other manufacturers’ equipment, no additional software is required
to configure the IP-2002 console. Modifications and enhancements can generally be made via a software change
only. If the user determines they require a special feature enhancement, please contact the Vega Sales Department
for cost and feasibility.
2 Hardware Overview
The IP-2002 is a multi-line; multi-mode console designed specifically for medium level system requirements. All
functions are housed in a single modern looking console and consist of the following sub-assemblies: Main
Processing Board and Keypad/Display Board.
2.1 Main Processor PCB
The Main Processor board contains two distinct sections, the Ethernet front end and the Signal processing circuitry.
The Ethernet front end consists of an ARM processor with an Ethernet MAC, connected to the Physical Interface IC
and Transformer. Around the ARM processor are various peripheral devices, including FLASH and SRAM. This
section controls all the Ethernet processing, such as the FTP server; web page and packet transfer for the IP-2002.
The Signal processing section, featuring the TMS320C5510, is used to do all the audio. The DSP also controls all
the keypad and device I/O, as well as, the LED and display drivers.
2.2 Keypad PCB and Display
The Keypad board is interfaced to the main board via a 40-pin IDC ribbon cable. The board contains the circuitry
to decode the keypad matrix, and interface the DSP to the display. The display is mounted to the chassis cover with
four screws and connected to Keypad PCB with a 14-pin IDC ribbon cable.
Page 8
2 Vega’s IP-2002
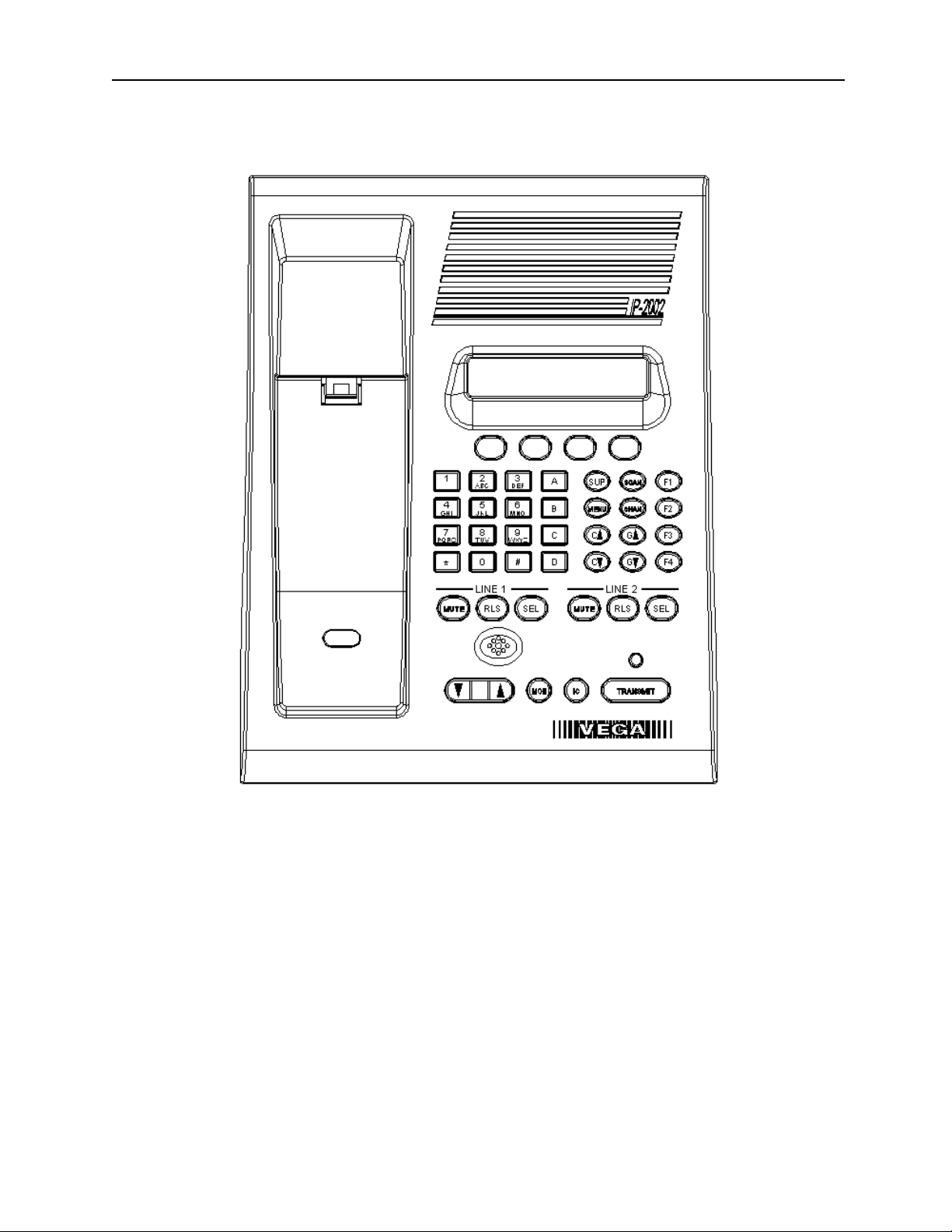
3 Controls and Indicators
Figure 1 Front Panel Diagram
3.1 Front Panel
Figure 1 shows a view of the Front panel. The Front panel contains the user I/O. It features a Volume control,
intercom and monitor functions, panel PTT with indicator, built in panel microphone, per line Select, Release and
Mute functions, DTMF keypad, Supervisory, Scan, Menu and Channel which are used with the F1-F4 Function
Tone selection. The IP-2002 is programmed from the front panel using the four gray soft keys located below the
Vacuum Florescent LCD display. The display provides channel/numeric indication, clock and audio-level meter.
3.1.1 Common Controls and Indicators
3.1.1.1 VU Meter:
Displays Selected receive and Microphone audio bus levels. This meter is shown on the top line of the display and
utilizes the first 12 display elements from the upper left.
Page 9

VOIP Desktop Console 3
3.1.1.2 Program 1-4:
Are used as “soft” programming buttons when in the tech mode. These buttons will have different functions
depending on the action required. The bottom line of the display will show their respective functions.
3.1.1.3 DTMF Keypad:
The DTMF keypad is used for transmitting DTMF digits, selecting frequencies and entering alphanumeric strings
for various features.
3.1.1.4 Supervisory button:
The SUP button allows one console operator to disable any other console. The Red LED is on during supervisory
and blinking when being supervised. Note, this is an IP based Supervisor mechanism. No wiring is required.
3.1.1.5 Menu button:
The Menu button will allow access to the following other features: Paging1, Instant Recall Recorder1 and
CrossPatch.
M a i n M e n u
PAGE IRR EXITXP
Figure 2 Menu Button Functions
3.1.1.5.1 Cross Patch
Menu button used to set the single available cross patch between line 1 and 2. Pressing XP at the main menu
will enable the cross patch. Once in the XP Menu, the available functions are Block and PTT.
X P M e n u
BLK PTT EXIT
Figure 3 Cross Patch Menu
The BLK button is used to block a receive channel that may need disabled. The PTT button is used to PTT on
the cross patch. The EXIT button will exit this setup menu and disable the cross patch.
3.1.1.6 Channel UP/DOWN buttons (C▲& C▼):
Used to change selected line F-tone frequency UP or DOWN.
3.1.1.7 Scan button:
Used to turn the radios receive Scan feature on/off if available.
3.1.1.8 Channel button:
Used to change selected line F-tone frequency via the DTMF keypad. Pressing the CHAN button then two DTMF
keys (0-9) changes the channel directly. Note the general sequence: CHAN,0,1 = F1; CHAN,0,2 = F2; …CHAN,9,9
= F99.
1
Not implemented on Software Version 1.0
Page 10

4 Vega’s IP-2002
3.1.1.9 Group UP/DOWN buttons (G▲& G▼):
Used to change selected line Group selection UP or DOWN, Trunking feature.
3.1.1.10 Function Buttons F1-F4:
When a function button is pressed, function packet burst is sent out. When a function is selected it will light to
indicate which function is chosen, a function shall remain selected until the operator changes the setting.
3.1.1.11 Line Buttons LN1-LN2:
Three buttons are available for each Line, SELect, RLS (Release) and Mute.
SELect button: When the SEL buttons is pressed that line enters the Select mode
Select LED: The Red LED under each LNx SEL Button indicates if the line is selected for transmit audio.
RLS button: The RLS button is used to release a selected line.
RLS LED: The blinking Red LED under each LNx RLS Button indicates receive audio activity on that line. A
solid LED indicates that TX block is occurring.
Mute button: The Mute button is used if RX audio from that line is not to be monitored in the speaker.
Mute LED: The steady Red LED under each LNx Mute Button indicates if the line is muted from receive audio
monitoring. A blinking LED indicates that RX block is occurring.
3.1.1.12 Volume Control:
Adjusts the receive speaker audio and handset earpiece level of the receive inputs of the line interfaces. A minimum
volume level can be set in tech-mode, so that the console operator cannot turn the speaker volume to zero. When
adjusting the level up or down, the display shows the selected level on a relative scale. If the handset is off hook,
HSVOL is displayed and the handset ear volume is adjusted. Otherwise, SPKR is displayed and the speaker volume
is adjusted.
Select and Unselect audio levels per line can also be set from the front panel by pressing and holding Line 1 or 2
SEL or RLS buttons and adjusting the normal volume control.
3.1.1.13 Monitor:
When the Monitor button is pressed a Monitor packet burst is sent out on the selected line. An LED indication
lights while the key is pressed.
3.1.1.14 Intercom (IC):
When the Intercom button is pressed and held down the IP-2002 shall transmit audio packets marked as Intercom.
Intercom is considered a Non-PTT based audio stream.
3.1.1.15 Panel PTT Pushbutton:
When pressed, audio from the Panel PTT Default microphone will be sent to all Selected lines. See Global System
Setup 1 5.11.14 for programming this option.
3.1.1.16 Transmit LED:
This LED lights when any PTT source is depressed keying up the console.
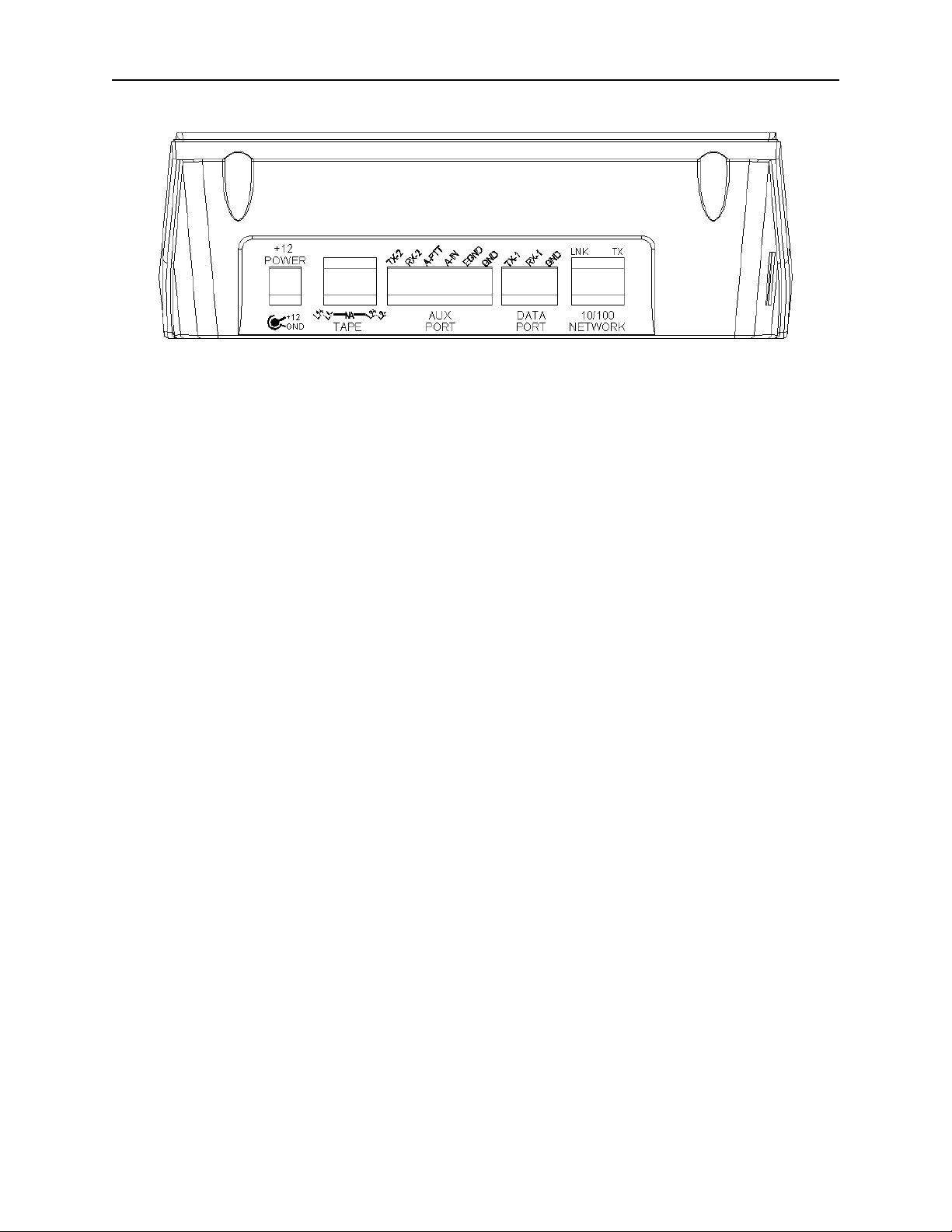
3.2 Rear Panel Connections
Figure 4 shows drawing of the rear panel of the IP-2002. Each of the ports shown is discussed in detail in the
following section.
Page 11
VOIP Desktop Console 5
Figure 4 Rear Panel Diagram
3.2.1 Rear Panel Ports
Power Jack: The left most jack on the IP-2002 is the Power Jack. The power supply that is included with the unit
plugs in to this location. It is a standard 2.5mm center positive plug and requires at least 12V to operate correctly.
Tape Port: This RJ-45 has Line 1 and Line 2 Tape recorder outputs. Line 1 on Pins 1,2. Line 2 on Pins 7,8. Both
are 600 ohm transformer coupled outputs.
Auxiliary Port:
TX-2 and RX-2: Pins 1 and 2 provide a secondary RS-232 port.
Auxiliary PTT: Pin 3 provides and alternate or auxiliary PTT input mechanism.
Auxiliary Audio Input: Pin 4 is an audio input used as the audio source when Aux PTT is pressed.
Earth Ground: Provides an Earth ground connection. Use is advised.
Data port:
TX-1 and RX-1: Pins 1 and 2 provide the primary RS-232 port for the unit. There are programming and diagnostic
capabilities available when using this port. Under normal circumstances, this port is not used. No cable is provided,
only the connector.
Ethernet Port: Standard RJ-45 Ethernet interface. Link and TX LED’s are built into the connector.
4 Operation
4.1 Radio Lines
4.1.1 Selecting:
When the desired line Select pushbutton is momentarily pressed, the receive audio from this Selected line is placed
on the speaker and the previously Selected line is disengaged. The currently Selected line name (programmable) is
displayed on the screen and the line Select indicator is illuminated.
The receive audio from the selected line will be heard on the consoles speaker and can be adjusted by the selected
master volume control. If the handset or headset is enabled and taken off hook, the receive audio is transferred to
the earpiece, see 5.11.11.
4.1.2 Changing Function Tones:
The function tone keys are used to select a function tone for a specific line. This function tone will be remembered
per line. If a group PTT is sent, the function packet that corresponds to each line will be sent on that line. If the
Function button is pressed independently, a Function packet is sent. These keys are backlit with a single RED LED.
4.1.3 Muting Unselected Lines:
Both lines can be Muted, when unselected, by pressing the MUTE key for that line. If the line is selected it cannot
be muted. A brief line volume ON/OFF display occurs when the button is pressed.
Page 12

6 Vega’s IP-2002
4.1.4 Releasing a Line:
To release a radio line, simply press the RLS pushbutton for that line.
4.1.5 Supervisory Control Button:
The SUP Button is used to disable all units on a particular line, by pressing the SUP Button, the Button will light
and disable all connected paralleled consoles. On the consoles that are being supervised, the SUP Button will blink,
if they have selected a line that the supervisor has selected
4.1.6 TX ALL Function (No button):
There is no specific button for the TX ALL function. This function is completed as follows: Press the Line 1 select
button and hold, then press Line 2 select button. This will select both lines to complete the TX ALL function. No
order for this press and hold sequence is required.
4.1.7 Intercom to parallel console:
To intercom to a parallel console simply select a shared line and press INTERCOM.
4.1.8 Answering a Phone call
To select a ringing phone line (audible and select LED blinking) simply press the desired lines Select pushbutton.
The phone line will go off-hook and the receive audio is then routed to the earpiece of the handset or headset
depending on which one you are currently using. Any selected radio line audio, is now routed into the speaker. If
you were speaking on another selected phone line it will automatically be put on hold.
4.1.9 Placing a call
To place a call, simply select a phone line and dial the number on the DTMF pad. The number dialed will be
displayed.
DTMF keypad digits
0-9 = Allows direct entry of a three digit number specifying a particular phone number.
4.1.10 Putting a Phone line On-Hold
To put a line on hold simply press the select button after the call is initiated, the select button LED will blink and
phone line audio will be routed to the speaker. To talk on a phone line that is already On-hold simply press the
select button again.
4.1.11 Muting a phone Line:
Receive audio from phone lines On-hold are played out the speaker, undesired receiver audio may be muted by
pressing that lines MUTE button. The orange LED under the MUTE pushbutton will also illuminate to indicate a
muted condition.
4.1.12 Sending a Hook-Flash
To cause a hook flash (needed sometimes to transfer calls) simply press and release the RLS button.
4.1.13 Releasing a Phone Line:
To release a phone line, simply press the RLS pushbutton and hold for 1 second then release.
4.1.14 General Display Indications:
The IP-2002 will display Receive, Transmit(TX1,TX2) and Intercom(EI1,EI2) events, per line. They will appear as
text on the lower right corner of the display. Receive audio will be indicated by the RLS LED flashing. The selected
line will show VU indication for receive audio as well.
Page 13
VOIP Desktop Console 7
5 Programming
5.1 Entering the Setup Mode
Setup of the IP-2002 is almost entirely done using a web browser. The first step required during setup is to assign
the IP and Mask addresses to the IP-2002. This is done through the front panel. To enter the front panel setup
mode, press and hold Line 1 MUTE, and G▲, then press DTMF *. The front panel display will appear like Figure
5. From the front panel of the IP-2002, the internal clock, Ethernet parameters, and security PIN can be set.
P r o g r a m m i n g M o d e:
C L K IP PIN EXIT
Figure 5 Initial Programming Screen
5.2 Setting the System Clock
Pressing PROG1 from the top-level setup menu will open the screen to set the internal Real Time Clock. Figure 6
shows the screen for the clock setup. PROG1 selects the Edit option that allows setting of the actual minutes and
hours. PROG2 sets AM or PM., PROG3 selects 12 or 24-hour mode, PROG4 (back) returns to the previous setup
screen in Figure 5.
C l o c k 1 2 : 0 0 A M
12 hr
E d i t A/P 12/24 back
Figure 6 Clock Setup Screen
5.3 Setting the PIN number
The Pin number is used to prevent unauthorized modification of operation parameters. When a PIN number is set,
the IP-2002 will prompt for it before allowing entry into the setup mode. The web-based setup for the IP-2002 also
has provision for a user password; it is the same four-digit value as the PIN number entered from this menu option.
From Figure 5, selecting PROG3 (PIN) from the main menu will cause the IP-2002 to prompt for the new PIN
number twice. If both are entered identically, the new PIN number will take affect. Figure 8 shows the two
available sub-menu screen in the PIN setup.
P I N S e t u p [ -- -- -- -- ] :
N e w C l r back
Figure 7 PIN Setup Screen
Page 14

8 Vega’s IP-2002
C l e a r P I N ?
YES NO
N e w P I N :
Cancel
Figure 8 PIN setup Sub-menu screens
5.4 Setting the basic IP information
As was mentioned before, all other parameters are setup by using a browser such as Netscape or Internet Explorer.
Before connecting to the console with the browser, an IP address and Mask that is compatible with the users
existing network must be set. Figure 9 shows the screen selected when PROG2 (IP) is pressed from the main setup
screen. See your network administrator to determine the proper values. Figure 10 shows the dotted quad editing
screens for the IP and Mask.
I P S e t u p :
I P Mask back
Figure 9 Main IP setup screen
I P : 1 7 2 . 1 9 . 1 0 0 . 1 2 3
Clr < back>
Mask : 1 7 2 . 1 9 . 1 0 0 . 1 2 3
Clr < back>
Figure 10 IP Setup Sub-menu screens
The following keys are used to enter the IP and Mask dotted quad once PROG1 (IP) or PROG2 (Mask) is pressed.
DTMF 0-9: The DTMF digits allow entry of the specific numbers.
DTMF A: DTMF * or “A” is the decimal point used in dotted quad.
PROG4: The “back” key is pressed when the dotted quad has been entered.
PROG1: The “Clr” function clears the current entered value and starts over.
PROG2: The < “backspace” function deletes the last entered number.
PROG3: The > “forward space” function steps past the next number if necessary.
Page 15
VOIP Desktop Console 9
Once these values have been set, the unit must be reset for them to take affect. It is now possible to connect to
the IP-2002 with a computer and web browser.
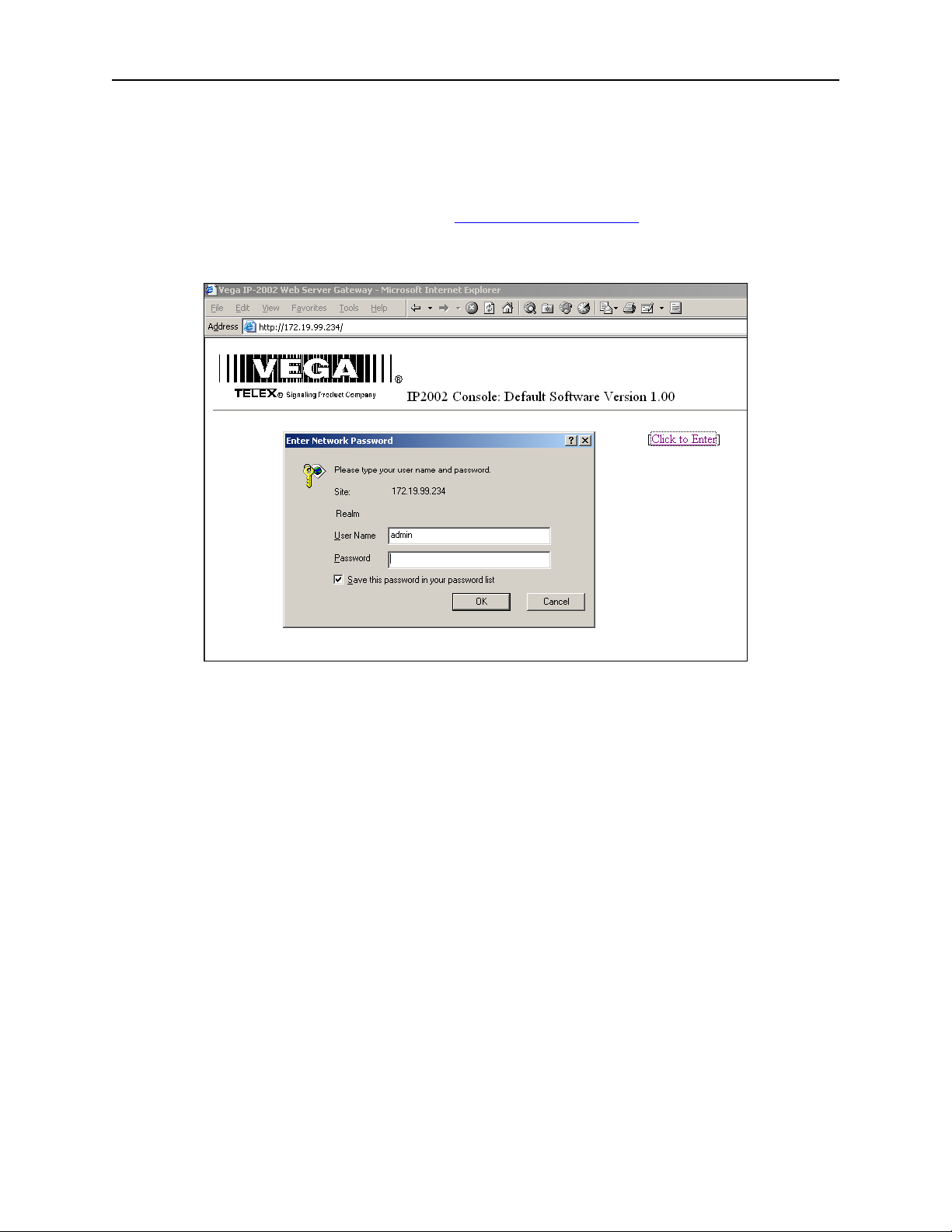
5.5 Entering IP-2002 Web Setup
To begin setup of the IP-2002 console, the user must know the base IP address that was entered from the front
panel. The address then entered into the browser is http://XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
values for the assigned IP address. Upon pressing return in the browser the opening screen should appear as shown
in Figure 11.
, where the XXX’s refer to the
Figure 11 IP-2002 Login Screen
Clicking on the hyperlink [Click to Enter] will open a dialog box requesting user authentication. There is only one
user name defined. It is “admin”. If it is the first time the console as been started and no PIN number has been
entered, no password will be required. If a PIN has been set, enter it into the password field. Once the username
and password has been successfully entered, the opening web page for Basic Ethernet Setup will be displayed.
5.5.1 Orange Crossover Cable
An orange crossover cable provides for direct PC to IP-2002 programming through the Ethernet port. This cable
should not be used for a direct IP-2002 to Ethernet port connection.
Page 16
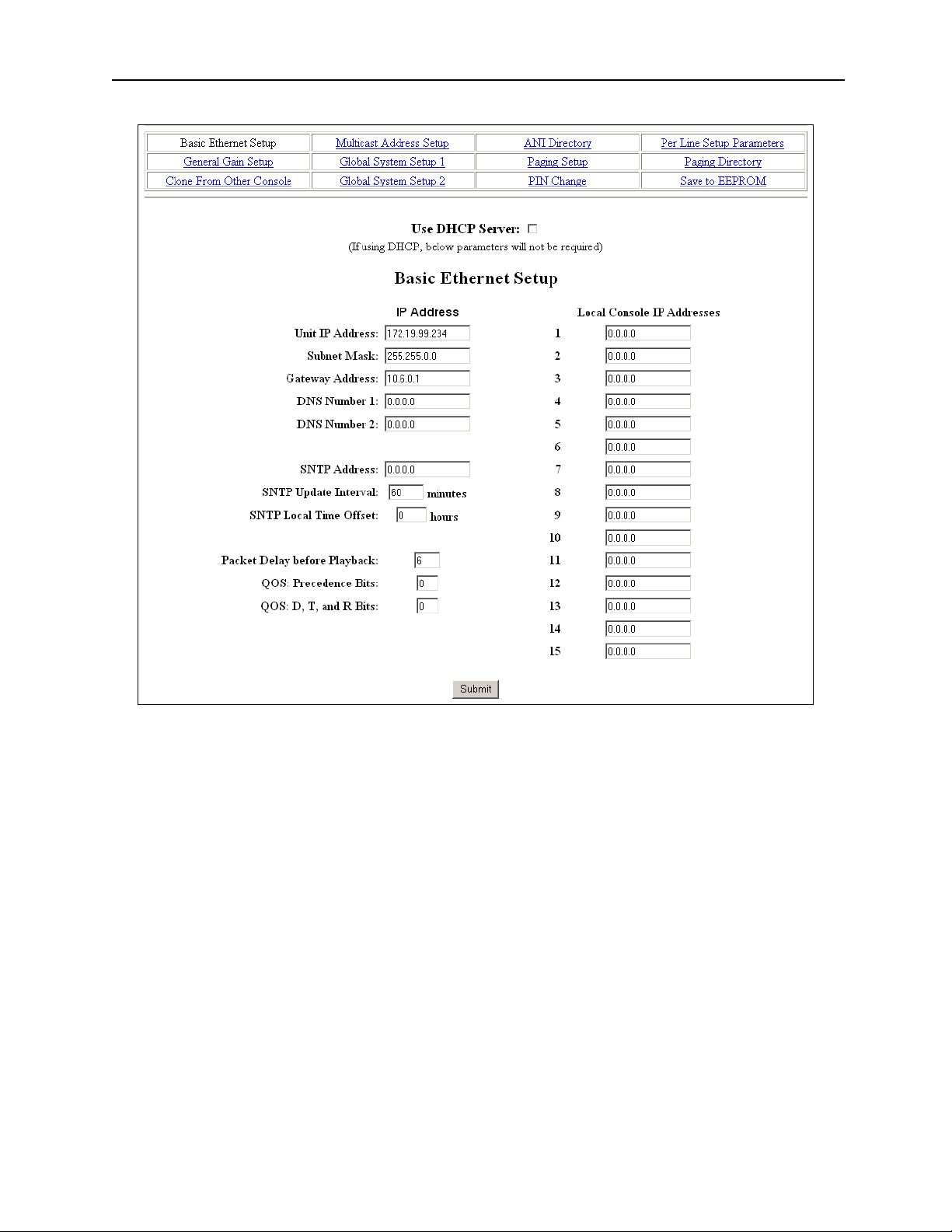
10 Vega’s IP-2002
5.6 Basic Ethernet Setup
Figure 12 Basic Ethernet Setup Screen
The Basic Ethernet Setup Page is the default startup page when entering the setup mode, see Figure 12. Across the
top of the page is a table 4x3 cells in dimension. Each of these text strings is a link to a different setup page.
Clicking the mouse pointer on any of these will immediately load the page clicked on. Moving from one page to the
next does not automatically save any data that has been entered. To make changes to a page and save it to memory
requires that the “Submit” button at the bottom of each page be pressed. Submit has the effect of sending the
contents of the web page back to the IP-2002 for storage.
The fields of the Basic Ethernet Setup page are as follows:
5.6.1 Use DHCP Server:
The DHCP server check box is generally left unchecked. DHCP is the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. It
allows the IP-2002 to require all of the information for operation on the network bypassing its manual entry. Vega
does not recommend operating with DHCP on. It can cause the Base IP address to change unexpectedly making
changing setup of software more difficult. It can be useful for initial setup efforts in determining some of the other
parameters.
5.6.2 Unit IP Address:
The Unit IP Address is the base address assigned to the IP-2002. It must be unique on the Network. It identifies the
console for such operations as setup and software upgrades.
Page 17

VOIP Desktop Console 11
5.6.3 Subnet Mask:
The Subnet Mask is used by the IP Stack to determine what are local addresses and what address require use of the
gateway to be reached. See your network administrator for this value.
5.6.4 Gateway Address:
The Gateway address is the IP address for the node that is used to reach other networks. See your network
administrator for this value.
5.6.5 DNS Addresses 1-2:
The DNS Addresses, or Domain Name Service Addresses, are used to resolve word based IP addresses into dotted
quads. For example, www.espn.com
address. Currently word based addresses are not supported by the IP-2002. These addresses are stored as a place
holder for when they might be.
5.6.6 SNTP Address:
This is the IP address of the time server on the network. The time server is used as a standard clock for all devices
on the network. It can be a PC, a national atomic clock source available on the internet, or a local GPS or atomic
clock based network resource.
5.6.7 SNTP Update Interval:
This is the amount of time between queries to the time server to update the clock. Since the real time clock of the
IP-2002 is already very accurate, this value only needs to be updated at most once per hour.
requires lookup on a name server to determine the actual dotted quad IP
5.6.8 SNTP Local Time Offset:
A time server always gives its time as Greenwich Mean Time. Enter the value that corresponds to the consoles
location. See the table for a list of offset and enter the appropriate offset.
Location: Offset: Location: Offset:
Eniwetok, Kwajalien -12
-11
-10
-9
Pacific Time (US-Canada) -8
Mountain Time (US-Canada) -7
Central Time (US-Canada) -6
Eastern Time (US-Canada) -5
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
5.6.9 Packet Delay Before Playback:
The IP-2002 utilizes a 20ms UDP/IP packet to encode audio. Some buffering of these packets must occur before
playback to help absorb network jitter and delays, the typical value is 6. Larger values may be required for larger
networks, smaller values for simpler networks.
5.6.10 QOS Bits:
The QOS bits section contains two entries. The first entry, QOS Precedence, is used when Differentiated Services
QOS is active on the network. Typically this value is left at 0 for normal traffic and 5 for voice traffic. The second
entry, D, T and R bits, are used for advanced purposes. These bits are usually 0. Contact your Information Services
department for proper values for these entries.
Page 18

12 Vega’s IP-2002
5.6.11 Local IP Addresses:
Up to 15 addresses can be entered for the Local IP addresses. These addresses should correspond to the base IP
address of the other Vega VoIP consoles within the same room. This list is used for the Ethernet crosspatch
function. The IP-2002 examines the source of the audio and flags it if the source was from another console in this
list.
5.7 Multicast Setup
Figure 13 Multicast Setup Screen
Figure 13 shows the Multicast Setup Page is used to determine which ports the IP-2002 will use to communicate
various channel information on. The specific columns are discussed next:
5.7.1 Enable via Ethernet:
This checkbox is used to turn Ethernet connectivity on and off. It should always be checked if the line is to be
active. The Phone check box needs to be checked if any line within the console is defined as a phone line.
5.7.2 Channel Name:
This field allows for an alphanumeric to be assigned to a particular line.
5.7.3 Multicast Address:
The Multicast Address is used as the broadcast address for all audio traffic. This number must be between 224.0.0.2
and 239.255.255.255. All lines that are to interoperate between consoles must have the same Multicast Address.
Phone operation requires that the Multicast Address field have the static IP address of the C-6200 with PCRD’s
installed or an IP-223 with Phone Interface Box (PIB) attached, be entered into any lines assigned phone operation.
5.7.4 RX and TX Ports:
The next two columns specify the port number for each channel. This number must be unique, per channel, and be
greater than 1024. As an example, consider Line 1 in Figure 13. The RX Port is 1054 and the TX Port is 1072. All
consoles that wish to monitor receive audio for channel 1 must have their Base Multicast address set the same as
well as the same RX Port number. The same goes for TX audio. Any console on the network that wishes to
transmit must set its port number to 1072.
Phone operation requires that the Multicast Address Port field have a unique port number entered into any lines
assigned phone operation.
5.7.5 Channel Hops:
The Channel Hops value represents the number of routers the multicast audio packets will go through before being
stopped. Network design will dictate this value. If audio is not reaching a particular node on the network,
increasing this value is one option that might be tried.
Page 19

VOIP Desktop Console 13
5.8 ANI Directory Setup
Figure 14 ANI Directory Setup Page
Automatic Numerical ID numbers can be mapped to General Alphanumeric names in this page. The directory
contains 100 possible entries, 20 are displayed at a time. Currently ID’s from Kenwood (Fleetsync) and Motorola
(MDC) can be displayed. This feature works in conjunction with the IP-223.
The table must be enabled or the ANI number will be displayed before translation.
5.9 Per Line Setup Parameters
Figure 15 Per Line Setup Page
Figure 15 shows the Per Line Setup Page. Each lines setup parameters can be viewed and changed by pressing the
buttons numbered 1 or 2. Note that pressing those buttons does not save the current information on the screen. The
user must first Submit the information to be saved and then click on a button to move to the next lines information.
All of the information on this web page is specific to the line. Descriptions of the various parameters follow.
Page 20

14 Vega’s IP-2002
5.9.1 Line Enabled:
The Line Enabled checkbox at the top middle enables or disables the line. If the Line is disabled, it will not allow
selection for transmission or play received audio.
5.9.2 Duplex Enable:
Checking this box will make the line Full duplex.
5.9.3 Crosspatch Open Time:
This is the amount of time the console will continue to play audio with receiving audio above the squelch threshold.
This is also used by the Ethernet to determine how long to send audio.
5.9.4 Select Call String:
The Select Call string is used to allow a user in the field to guarantee that the dispatcher is monitoring in the
channel. The String is a sequence of DTMF digits that when received, will open the MUTE gate and allow receive
audio through to the speakers.
5.9.5 Select Call Open Time:
When the Select Call String is received, this value is the amount of time that the mute gate remains open for the
received audio. After the timer has expired, an indication continues to notify the console operator which channel
the received audio came in on. It will continue until the operator performs a PTT operation on the channel.
5.9.6 Disable Mute:
By check this box, the console will not allow the line to be muted. This forces the console operator to monitor the
line.
5.9.7 Min Mute Level:
The Mute key can be set to be an audio level reduction rather than an on/off function. By setting this entry to –20
for example, when the mute is activated for this line, the audio will be reduced by –20dB rather than all the way off.
A value of 0, has the effect of a hard mute.
5.9.8 TX Enabled:
Checking this box allows the line to be selected for TX operations. Leaving it unchecked allows the operator to still
monitor the channel.
5.9.9 Network Phone Enable:
Checking this box allows the line to be selected for phone operations.
To setup the Network Phone, the following steps need to occur.
5.9.10 Local Phone Line:
Used to select which phone line installed within the network console with phone cards you want this line assigned.
Use ANY for pool operation or select a line for dedicated operation.
5.9.11 F-Tone 1-100 Enable:
Checking this box will allow the associated Function tone to be selected. Note, in Figure 15 the [Next Tones] button
at the right of the [Line 2] button must be pressed to get to the next group of 16 frequencies.
5.9.12 Ftone1-100 Alphanumeric:
This text string will be displayed when the particular line and function tone is selected. Note, in Figure 15 the [Next
Tones] button at the right of the [Line 2] button must be pressed to get to the next group of 16 frequencies.
5.9.13 RX Block:
The RX block checkboxes allow the user to select other channels that should be RX muted during transmit on this
channel.
Page 21

VOIP Desktop Console 15
5.9.14 TX Block:
The TX Block checkboxes prevent checked boxes from being selected at the same time as this channel. The IP2002 will automatically reciprocate selections between two different lines.
5.9.15 Pairs/Wildcard:
Only function 3 and 4 are available as Pair Mode control groups. Function 1 and 2 are not allowed in a wildcard
group.
5.10 General Gain Setup
Figure 16General Gain Setup Page
The General Gain Setup Page is shown in Figure 16. The IP-2002 is based largely on software controlled variable
resistors with a resolution of 1.5dB per step. Each output is set to be at is maximum drive and may therefore need to
have its output reduced to get the proper level out/in. The General gain screen allows the operator to adjust the
levels down as required. As an example, if given the particular properties of a transmission line, it is determined
that the output level is 3dB to high, the corresponding Transmit Gain would be set to –3.0dB. The actual values
adjusted are spelled out on the web page and should be adjusted as required.
Page 22

16 Vega’s IP-2002
5.11 Global System Setup 1
Figure 17 Global System Setup Page 1
Figure 17 shows the Global System Setup 1 Page for all the functions that are not line specific. Each of the options
on this page are discussed in the following section.
5.11.1 Supervisor Enable:
When checked, the SUP button will be active on the console. This allows a console operator to take control of any
selected line. It will send a SUP packet such that other consoles will not be able to transmit or monitor receive
audio on the line. The SUP input is active at all times no matter the status of this checkbox.
5.11.2 Supervisor Timeout:
This variable sets a timeout for the supervisory button. Setting the value to a 0 make it a toggle on/off function.
Setting the value to a number makes it a timed supervisory.
5.11.3 TX Delay:
This value is the delay in ms for microphone audio. By setting this value to something greater than the radio system
channel acquire time, the console operator can begin speaking after the PTT is pressed and the audio will be delayed
until the system is actually able to transmit.
5.11.4 Auto Monitor Enable:
This checkbox is used with the handset/headset option. When the handset/headset is taken offhook, the monitor
packet is sent.
5.11.5 CRP Timeout:
The time in seconds allowed for inactivity before a crosspatch will be automatically dropped.
Page 23

VOIP Desktop Console 17
5.11.6 Console Name:
This field allows for an alphanumeric to be assigned to the console, will display in the WEB page header.
5.11.7 CRP Delay:
This value is the delay in ms for crosspatch audio. By setting this value to something greater than the radio system
channel acquire time, the crosspatch audio will be delayed until the system is actually able to transmit.
5.11.8 Mute UNSEL w/ PTT:
This option will mute the receive audio from any channel that is not selected during a PTT operation.
5.11.9 Line Tape Output Mix:
Each of these checkboxes determines what kind of audio is summed into the Line tape output. The Line tape output
can be any combination of select, unselect, and crosspatch audio.
5.11.10 Line Tape with Volume:
When checked, only speaker audio will be sent to the tape out, no muted lines or microphone audio is included.
5.11.11 Handset or Headset RX routing:
When a handset or headset is installed, this box should be checked so that the IP-2002 knows where to route receive
audio based on hookswitch position.
5.11.12 Summed RX to Handset or Headset:
When checked, provides both Select and Unselected RX audio to the earpiece.
5.11.13 Network Phone Ring Type:
This selects the type of annunciation (ring) the console will do with a incoming phone call. There are 8 different
rings to select from, all cadences are 1 second annunciation, 4 second ring period. Possible notes are, from lowest to
highest: A=440Hz, B=494Hz, C=523Hz, D=587Hz, E=659Hz, F=698Hz, G=784Hz, 2A=880Hz.
Setup Option Note One Note Two Note Three Note Four
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
E A E A
A E C G
F G A C
G D A D
A C E G
G E C A
G G C C
G 2A G 2A
5.11.14 Panel PTT Default Mic:
This pull down menu allows the selection of a microphone source when the front
panel PTT is pressed. Note that if the handset and/or desk microphone are installed,
they still operate normally.
Option one: The panel microphone is active when the front panel PTT is pressed.
Option two: The desk microphone is active. Option three: If the handset/headset is enabled, it will be the active
source, if off hook. Otherwise the panel microphone is active (on hook). Option four: If the handset/headset is
enabled, it will be the source, if off hook. Otherwise, the desk microphone is active (on hook).
5.11.15 DTMF Keypad Enable:
Allows the DTMF keys to be enabled or ignored.
5.11.16 DTMF Flywheel:
The DTMF flywheel sets the time in milliseconds between key presses without the unit de-keying.
Page 24

18 Vega’s IP-2002
5.11.17 DTMF On Time:
The minimum duration of DTMF digit.
5.11.18 DTMF Off Time:
The minimum time between DTMF digits.
5.11.19 DTMF Level:
The approximate absolute level of the DTMF digits for the lines.
5.11.20 DTMF Sidetone:
When checked, provides DTMF sidetone to be played on the speaker. If the handset/headset is enabled and off
hook, the sidetone is played to the earpiece.
5.11.21 DTMF Sidetone Level:
The approximate relative level of the DTMF sidetone played on the speaker. If the handset/headset is enabled and
off hook, the sidetone is played to the earpiece.
Global System Setup 2
Figure 18 Global System Setup 2
Figure 18 shows the Global System Setup 2 Page for all the remaining functions that are not line specific. Each of
the options on this page will be discussed in the following sections.
5.11.22 Alert Tone Buttons Setup:
Four Alert Tones can be generated. They can be made active or inactive. Single Tone, Pulsed Tone, and Hi-Lo
warble are all supported. The Single Tone and Pulsed Tone use the Low Freq setting only. An approximate relative
level is also supported for each Alert Tone.
To activate an Alert Tone, press the CHAN button, then press DTMF (A, B, C, D) corresponding to Alert 1-4.
Holding DTMF A-D will cause the tone sequence to sustain.
Page 25

VOIP Desktop Console 19
5.12 Clone From Other Console
Figure 19 Console Clone Page
The Clone from Other Console Page is show in Figure 19. It works similarly to the other Vega products clone
features. In this case, both consoles must be connected to the Ethernet network. Enter the dotted quad of the
console to clone from and pressing the Submit button will copy the entire configuration from the other console. The
only things not copied from the other console are the serial number, Base IP address, and Mask IP address. After
copying the values, they still must be saved to EEPROM memory for permanent storage.
5.13 PIN Change
Figure 20 PIN Change Page
The PIN change web page is used to set the “admin” password for the console and is shown in Figure 20. Enter the
four-digit number in both entry boxes and click Submit. If the two PIN’s are the same, the PIN number will be
updated in memory. To take effect, it must be saved to EEPROM memory and a reboot must occur. The PIN will
be immediately effective in the DSP setup screen mode however.
Page 26

20 Vega’s IP-2002
5.14 Save to EEPROM
Figure 21 Save To EEPROM Page
Figure 21 shows the screen for saving parameters to non-volatile memory. Three buttons are available. The first is
to Reset Parameters back to factory defaults. This will clear everything out of memory. It does not save these
values however. Clicking the Save Current Parameters button will store all parameters in memory to Non-Volatile
memory for permanent storage. It will also reset the DSP so that it may reload its configuration data in a controlled
manner. The third button is for remote reset of the IP-2002, this will allow you to a hard reset on a remote unit.
5.15 Reprogramming the IP-2002 Software
First you must obtain the latest software revision from
the Telex-Vega Website(www.vega-signaling.com). Go
to the product page and then to “Software and Manual
Downloads” page for that product.
Along with the latest firmware there will be an FTP
application for uploading the firmware to the unit. Both
the firmware and the application are available from this
page. The firmware is shown in the table with a short
revision history. The FTP application is can be retrieved
by clicking the hyperlink in the phrase “Download it
here”. When you download the FTP application what
appears is:
The ZIP file contains instructions and FtpTelex.exe, the
actual FTP application. The FtpTelex.exe file is the
program that is used to update the software, via the
Ethernet port, of the Vega VoIP products. Remember,
you must download a copy of the firmware for the
product you wish to update. In this case, the IP-2002.
Copy all files into a subdirectory. Create a shortcut to
the FtpTelex.exe program file. Run the program
FtpTelex.exe.
Enter the IP address of the IP-2002 to update. Enter the
User name and password fields into the FTP dialog box.
Select the file name to download. In this case,
IP2002rev1.bin has been chosen. Press the Download
button. The progress meter will start towards 100% as
the software is downloaded. The bottom task bar will
show the progress, while the VEGA logo paints. The
task bar will show complete and disconnect
automatically. The reboot takes approximately 30
seconds.
Page 27

VOIP Desktop Console 21
6 Schematics, Parts Placements, and Bills of Material
6.1 Main Processor PCB
Page 28

Page 29

Page 30

Page 31

Page 32

Page 33

22 Vega’s IP-2002
6.2 Keypad PCB
Page 34

770759(BNSF_RDC_Keypad)_b.sch-1 - Wed Jul 21 21:58:32 2004
Page 35

VOIP Desktop Console 23
6.3 IP-2002 ASSY Drawing
Page 36

REV
DESCRIPTION
ECO NO
DATE
APPD
1
PROTOTYPE
02/25/04
A
RELEASE - PC BOARD TO REV A
ITEM 21 QTY TO 12
ITEM 41 QTY TO 26
ITEM 42 QTY TO 119
ITEM 50 QTY TO 27
ITEM 52 DELETED
ITEM 60 CHG PART # TO 57148410
ITEM 63 QTY TO 2
ITEM 66 QTY TO 35
ITEM 72 QTY TO 2
ADDED ITEM 113
ITEM 76 DELETED
This drawing, written description or specification Is
without the written permission of TELEX.
DATE: 09/16/2003
SBC
Digitally signed by
SBC
DN: cn=SBC, c=US
Date: 2004.04.30
15:29:54 -06'00'
Signature Not
Verified
Hieu Ninh
Digitally signed by Hieu
Ninh
DN: cn=Hieu Ninh,
o=Telex, ou=Vega, c=US
Date: 2004.05.03
10:30:48 -06'00'
Signature Not
Verified
a proprietary product of TELEX, Lincoln, NE, and
shall not be released, disclosed, nor duplicated
APPROVALS: DR BY: SBC
Telex Communications INC.
Lincoln, Nebraska USA
PROD:CHK: APPD:
PART NO:
REV LEVEL:
879856
A
TITLE:
PCB ASSY, IP-2002
..\IP-2002 Hw Revision History.doc
REVISIONS
LN,BE PAGE 1 OF 6
Page 37

1
1
BATT
3V COIN LEADED
724023
B1
C1 C3 C18 C19 C94 C95 C119 C123 C124 C131
3
4
CAP
6PF 0603 50V +/- 5%
102879805T
C13 C62 C121 C137
4
2
CAP
22PF 0603
723482121T
C151 C152
5
3
CAP
CAP TANT 1uF 25V 3216
102877053T
C153 C206 C375
6
1
CAP
0805 0.047UF 25V +/-10%
102881185T
C175
7
8
CAP
0.018uF 0805 25V +/-10%
102881126T
C185 C204 C219 C220 C222 C224 C230 C232
8
8
CAP
3.3UF TANT 10V B(3528)
102877021T
C186 C205 C214 C221 C223 C225 C231 C233
C23 C24 C25 C26 C27 C28 C31 C32 C33 C34 C35
C36 C37 C44 C45 C48 C49 C50 C51 C52 C53 C58
C63 C64 C65 C66 C67 C70 C78 C79 C80 C83 C84
10
11
1
CAP
1000U,ELECTROLYTIC,LEADED
51821526
C369
12
2
CAP TANT
4.7UF 3216 TANT
102877067T
C38 C39
13
2
CAP
330PF 0603 50V +/-5%
723482136T
C47 C57
C72 C73 C179 C180 C187 C202 C210 C278 C279
19
1
CAP
1000PF 500V 1206
723538T
C88203
LED
RED SMT 0805
760532
D1 D2 D8
D3 D5 D15 D16 D17 D18 D19 D20 D21 D22 D23
22
1
LED
GREEN SMT 0805
7605321
D4
This drawing, written description or specification Is
a proprietary product of TELEX, Lincoln, NE, and
without the written permission of TELEX.
DATE: 02/25/2004
shall not be released, disclosed, nor duplicated
APPROVALS: DR BY: SBC
Telex Communications INC.
Lincoln, Nebraska USA
PROD:CHK: APPD:
PART NO:
REV LEVEL:
879856
A
TITLE:
ITEM
2
9
PCB ASSY, IP-2002
TYPE DESCRIPTION PART NO. DESIGNATOR
QTY
NEW
C154 C157 C158 C162 C181 C207 C212 C213
C282 C284 C287 C298 C304 C307 C309 C355
27 CAP 10uf 16vTANT 3528 B 102877065T
93 CAP 0.1UF 0603 723489101T
C362
C2 C4 C9 C10 C11 C12 C16 C17 C20 C21 C22
C87 C89 C92 C93 C96 C97 C98 C99 C100 C101
C102 C103 C104 C105 C106 C107 C108 C109
C110 C111 C112 C113 C114 C115 C116 C117
C118 C120 C122 C127 C128 C136 C155 C156
C160 C167 C182 C196 C197 C198 C199 C200
C208 C211 C280 C311 C354 C371 C373
14
15
16
17
18
21
27 CAP .001UF 0603 50V +/-10% 102881717T
17 CAP 0.01UF 0603 25V +80/-20% 723489100T
37 CAP 0805 1UF 10V +/-10% 102881875T
15 CAP 220PF 0603 50V +/-5% 723482134T
28 CAP 0603 47PF 723482126T
12 DIODE DIODE MMBD914 SOT-23 58711000
C5 C6 C14 C56 C59 C71 C90 C126 C130 C132
C133 C134 C150 C176 C177 C178 C188 C189
C190 C215 C302 C320 C322 C340 C341 C342
C349
C40 C41 C42 C43 C46 C61 C91 C129 C201 C281
C283 C285 C288 C303 C306 C308 C310
C7 C8 C15 C29 C30 C74 C85 C125 C149 C159
C174 C183 C184 C191 C192 C193 C194 C195
C203 C242 C243 C264 C266 C267 C268 C270
C272 C286 C290 C294 C296 C297 C305 C321
C324 C326 C330
C293 C295 C328 C329 C334 C335
C54 C55 C81 C82 C86 C135 C138 C139 C140
C141 C142 C143 C144 C145 C146 C147 C148
C161 C163 C164 C165 C166 C168 C169 C170
C171 C172 C173
D6
LN,BE Page 2 of 6
Page 38

This drawing, written description or specification Is
a proprietary product of TELEX, Lincoln, NE, and
without the written permission of TELEX.
DATE: 02/25/2004
23
1
DIODE
8 AMP MBRD835L
760513
D48242
FUSE
7101051
F10 F44
FB15 FB16 FB17 FB46
FB19 FB20 FB21 FB25 FB30 FB31 FB51
FB44
J1 J2 (DO NOT PLACE FOR PRODUCTION)
J11
J15
J21
J24
J27
J3
J35
J36
J5
J7
J8
TRANSISTOR
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Q7 Q8 Q9 Q10 Q11 Q12 Q13
R1 R2 R6 R15 R17 R18 R30 R32 R33 R34 R37
R38 R41 R44 R46 R61 R73 R74 R77 R78 R79 R80
R81 R83 R84 R85 R86 R88 R89 R90 R91 R93 R94
R102 R104 R114 R115
R12 R69
R13 R70 R71 R75
R141 R57
R142 R144
R143 R147
R23 R24 R25 R26 R150 R181 R196 R371 R372
shall not be released, disclosed, nor duplicated
APPROVALS: DR BY: SBC
Telex Communications INC.
Lincoln, Nebraska USA
PROD:CHK: APPD:
PART NO:
REV LEVEL:
879856
A
TITLE:
ITEM
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
PCB ASSY, IP-2002
TYPE DESCRIPTION PART NO. DESIGNATOR
QTY
NEW
SMT FUSE WITH HOLDER 1.5A SLO BLO
FB1 FB2 FB3 FB4 FB5 FB6 FB7 FB8 FB9 FB10
FB11 FB12 FB13 FB14 FB18 FB22 FB23 FB24
FB26 FB27 FB28 FB29 FB32 FB33 FB34 FB35
FB36 FB37 FB38 FB39 FB40 FB41 FB42 FB43
FB45 FB47 FB48 FB49 FB50 FB53 FB54 FB57
50 FERRITE 0805 FERRITE BEAD 723511T
4 FERRITE FERRITE BEAD 56-13-051659T
7 RES 0 OHM 0805 5% 102506000T
1 FERRITE COMMON MODE FB 724039T
1 CONN EMULATOR HEADER 640125
1 CONN RJ-8 LOW PROFILE 640134
1 CONN HEADER 3 PIN SMT 640124
1 CONN RT ANGLE 4 PIN HANDSET JACK 640123
1 CONN RT ANGLE 6 PIN 59946000
1 CONN SHIELDED RJ-45 ETHERNET w/ LEDs 640157
1 CONN 3 PIN RT ANG CONNECTOR 2862050
1 CONN DC PWR JACK, PCB, D 2.5MM, 16PJ032 59697000
1 CONN 6 PIN RT ANGLE TERMINAL CONNECTOR 2862056
1 CONN 20 PIN SHROUDED HEADER SMT 650387
1 CONN 40 PIN SHROUDED HEADER SMT 650388
1 CONN 2 PIN LOCKING HEADER 2861922
26
MMBT3904 SOT-23 54671200T
FB58 FB92 FB93 FB94 FB95 FB96 FB97 FB98
Q14 Q15 Q16 Q17 Q18 Q19 Q20 Q21 Q22 Q23
Q24 Q25 Q31 Q26
119 RES 10K 0603 5% 723488103T
43
44
45
46
47
48
4 RES 75 OHM 0603 1% 723481084T
2 RES 53.6K 0805 1% 102515370T
4 RES 30.1K 0603 5% 723481346T
2 RES 301 1% 0603 723481146T
2 RES 604 OHMS 0603 1% 723481175T
2 RES 2.7K 0603 5% 723488272T
49
12 RES 2.4K 0603 723488242T
LN,BE Page 3 of 6
R100 R101 R103 R105 R106 R107 R109 R111
R118 R119 R125 R126 R127 R131 R132 R133
R135 R138 R148 R149 R151 R152 R153 R154
R155 R168 R169 R170 R171 R172 R173 R176
R178 R184 R187 R199 R203 R205 R212 R214
R219 R222 R224 R225 R226 R229 R230 R231
R234 R235 R236 R242 R243 R245 R247 R248
R250 R251 R252 R254 R255 R258 R265 R268
R271 R272 R275 R277 R281 R284 R299 R302
R304 R305 R306 R307 R308 R309 R310 R311
R312 R314 R317 R318 R60 R123
R373 R388 R389
Page 39

This drawing, written description or specification Is
a proprietary product of TELEX, Lincoln, NE, and
without the written permission of TELEX.
DATE: 02/25/2004
R19 R20 R21 R22 R64 R65 R66 R67 R68 R92 R95
R197
R262
R263
R27 R162 R175
R29 R39 R42 R47 R260 R261 R266 R269 R279
R3 R4 R11 R50 R129 R139 R140 R166 R256
R313
R316
R333
R35 R163 R164
R36 R40 R45 R145 R259 R264 R267 R270 R280
R98 R122
R49
R51
R5 R16 R43 R53 R54
R55 R56 R130
R58 R59 R8 R9
R63
R72
R76 R110
R82
R87 R96 R97 R116 R117 R120 R121 R128 R180
S1
T1 T2
T3
U1
U12
U13
U14 U36 U38 U39 U40 U44 U51 U79
MT48LC4M16A2-75 4Mx16 SDRAM
U16 U17
U18 U33-34 U42 U48 U50
U19
U2 U43 U83
shall not be released, disclosed, nor duplicated
APPROVALS: DR BY: SBC
Telex Communications INC.
Lincoln, Nebraska USA
PROD:CHK: APPD:
PART NO:
REV LEVEL:
879856
A
TITLE:
ITEM
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
PCB ASSY, IP-2002
TYPE DESCRIPTION PART NO. DESIGNATOR
QTY
NEW
R157 R158 R159 R160 R161 R182 R183 R186
27 RES 47 OHMS 0402 5% 102514470T
1 RES 1.5K 0603 5% 723488152T
1 RES 5.62K 0603 1% 723481272T
1 RES 47.5K 0603 1% 723481365T
3 RES 15 OHM 0603 5% 723488150T
10 RES 562 0603 1% 723481172T
10 RES 0 OHM 0603 723488000T
1 RES 0603 1MEG 1% 723488105T
1 RES 1.21K 0603 1% 723481208T
1 POT 100K VERT. ADJ. T/H LINEAR 57148410
3 RES 68.1K 0603 1% 723481380T
10 RES 267K 0603 1% 723481441T
2 RES 10 OHMS 0603 1% 723481000T
1 RES 22.1K 0603 1% 723481333T
1 RES 0805 6.98k 1% 102515281T
35 RES 1K 0603 1% 723481200T
5 RES 0 OHMS 0603 DNP
3 RES 220 0603 5% 723488221T
4 RES 470 OHMS 0603 723488471
1 RES 4.7K 0603 723488472
1 RES 9.31K 0603 1% 723481293T
2 RES 33.2k 0603 1% 723481350T
1 RES 2.2M 0805 5% 102506225T
11 RES 0603 OPTIONAL OPTIONAL
1 SWITCH SMT TACT SWITCH 700182
2 XFMR 600:600 42TL016 7302831
1 XFMR PE-68515L 10/100 ETHERNET XFMR 730154
1 IC NET+50 ARM CPU, QFP208 760342
1 TC7S86FU SSOP5-P-0.65A single XOR gate 760343
1 IC AM29LV800BB-90EC 512Kx16 FLASH 7603445PS
8 IC NE5532AD8 SO8 760268
2 IC
760501
6 IC SN74LV245APW 511495005
1 74HC00 QUAD NAND 17-03-051986
3 IC LM1086CS-3.3V REG, SMT 511155000
R188 R189 R190 R191 R192 R193 R194 R218
R282
R257
R283
R52 R112 R113 R146 R174 R177 R179 R185
R198 R201 R202 R204 R213 R215 R221 R246
R249 R253 R273 R276 R278 R301 R303 R315
R14 R28 R31 R7 R99 R108 R134 R136 R137 R10
R62
R195 R274
LN,BE Page 4 of 6
Page 40

This drawing, written description or specification Is
a proprietary product of TELEX, Lincoln, NE, and
without the written permission of TELEX.
DATE: 02/25/2004
U20
U23
U24
U25
U26
U27
FOR U31
U31
U35
U37
U4
U41 U46 U47
U49
U5 U9 U10 U11 U15
U6
U67 U69
U7 U21
U8 U22
Y1
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
REFERENCE
shall not be released, disclosed, nor duplicated
APPROVALS: DR BY: SBC
Telex Communications INC.
Lincoln, Nebraska USA
PROD:CHK: APPD:
PART NO:
REV LEVEL:
879856
A
TITLE:
ITEM
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
PCB ASSY, IP-2002
TYPE DESCRIPTION PART NO. DESIGNATOR
QTY
NEW
1 MAX3232CSE S016 760349
1 Single INV gate TC7SZ04FU 760350
1 TC7SZ125FU 760500
1 IC 256Kx16BIT SRAM 71V416S10Y 760516
1 IC ADJ REGULATOR, SMT 760250
1 IC DS1302 SO8 760266
1 IC SOCKET SOCKET 44 PIN PLCC 539030044
1 IC ALTERA EPM7032AELC44-10 76026719PS
1 IC PT78ST105S REG,5V SWITCHED 7605141
1 IC 2W AUDIO AMP 760307
1 IC TMS320C5510 760502
3 SN74LV541APW TSSOP-20 760601
1 PHY Intel LXT791ALC 760533
5 IC SN74LVC245APWR TSSOP-20 760543
1 IC Single OR gate TC7S32FU 760503
2 IC TLV320AIC22CPT DUAL CHANNEL CODEC 760511
2 IC Single AND gate TC7S08FU 760504
2 IC TPS70102PWP Dual adj LDO 760505
1 XTAL 44.2368MHz 3.3V OSC 780191
1 OSC MC405-32768K 780181
1 OSC 3.3V OSC. 40.000MHZ 780188
1 XTAL 25.000MHZ SMT 780189
1 OSC 3.3V OSC 32.768MHZ 780186
1 PCB PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD 750696
A/R PASTE SOLDER PASTE BE738
0
1 RES 0603 274 OHMS 1% 723481142T R48
SCHEMATIC 770885
LN,BE Page 5 of 6
Page 41

Page 42

V
A
A
This drawing, written description or specification Is
a proprietary product of TELEX, Lincoln, NE, and
shall not be released, disclosed, nor duplicated
without the written permission of TELEX.
APPROVALS: DR BY: SBC
DATE: 01/24/02
TITLE:
RE
1
RELEASED
PART NO:
REV LEVEL:
DATE:01/24/02
Telex Communications INC.
Lincoln, Nebraska USA
APPD BY:PBH
DATE: 08/08/2002
PROD:CHKD BY:SBC
PCB ASSY, C-2002 KEYPAD BOARD
REVISIONS
DESCRIPTION ECO NO DATE
01/24/02
08/08/02
879573
A
PPD
SBC
PBH
LN,BE PAGE 1 OF 4
Page 43

7
This drawing, written description or specification Is
a proprietary product of TELEX, Lincoln, NE, and
shall not be released, disclosed, nor duplicated
without the written permission of TELEX.
APPROVALS: DR BY: SBC
DATE: 01/24/02
TITLE:
DATE:01/24/02
PCB ASSY, C-2002 KEYPAD BOARD
Telex Communications INC.
Lincoln, Nebraska USA
APPD BY: PBH
DATE: 08/08/2002
TYPE DESCRIPTION PART NO. DESIGNATOR
ITEM
QTY
NEW
1 21 LED 1206 SMT LED RED 760317
2 1 CONN SMT,PCB MOUNT,40 PIN HEADER 6401321
3 1 PANELMIC ELECTRET MIC 249024
4 X 1 PCB PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD 750598
5 X 0 REFERENCE SCHEMATIC 770759
6 A/R PASTE SOLDERPASTE BE738
PART NO:
879573
PROD:CHKD BY:SBC
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10 D11
D12 D13 D14 D15 D16 D17 D18 D19 D20
D21
J1
J2
REV LEVEL:
A
LN,BE Page 2 of 4
Page 44

Page 45

Page 46

Page 47

Page 48

24 Vega’s IP-2002
7 Warranty, Service, Repair and Comments
Important! Be sure the exact return address and a description of the problem or work to be done are
enclosed with your equipment.
Warranty (Limited)
All Telex Manufactured Vega signaling products are guaranteed against malfunction due to defects in
materials and workmanship for three years, beginning at the date of original purchase. If such a malfunction
occurs, the product will be repaired or replaced (at our option) without charge during the three-year period,
if delivered to the Telex factory. Warranty does not extend to damage due to improper repairs, finish or
appearance items, or malfunction due to abuse or operation under other than the specified conditions, nor
does it extend to incidental or consequential damages. Some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of
incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitation may not apply to you. This warranty gives the
customer specific legal rights, and there may be other rights which vary from state to state.
Factory Service Center
TELEX Communications, Inc.
Vega Signaling Products
8601 East Cornhusker Highway, Lincoln, Nebraska, 68507
Phone: (402) 465-7026 / (800) 752-7560 Fax: (402) 467-3279
E-mail: vega@telex.com, Web: www.vega-signaling.com
Claims
No liability will be accepted for damages directly or indirectly arising from the use of our materials or from any
other causes. Our liability shall be expressly limited to replacement or repair of defective materials.
Suggestions or Comments
We’d appreciate your input. Please send us your suggestions or comments concerning this manual, by fax (402-467-
3279) or e-mail them to
Visit our web site at www.vega-signaling.com
: vega@telex.com
Page 49

VOIP Desktop Console 25
8 Specifications
Front panel controls
• Select and Mute status for each line
• 100 Function tone selection
• Mute button
• MONITOR
• INTERCOM
• PTT button
• 16 digit DTMF keypad
• Select and Unselect volume controls
• Supervisory control
• Line Activity Monitor LED for each line
• Two Simultaneous Microphones
• Handset/Headset and Desk microphone
• Panel Microphone
Features
Simplex or full duplex per line
Programmable squelch control per line
Four Alert tone cadence
2 line VF Display with 4 hotkeys
Crossmute per line (Ethernet)
TX Microphone notch filter
2
Instant Recall Recorder (IRR)
CrossPatch
2
Paging
Web Page Configurable
FTP Firmware Upgrades
Specifications
Distortion: 3% maximum at full compression.
Hum and Noise: 50 dB below operating levels.
Speaker (One): 3 in, 8 ohm, heavy-duty.
Amplifier Power: 2 W maximum at 3% THD into an 8 ohm load or
equivalent
Handset Earpiece Level: Adjustable level independent of speaker volume
controls.
Audio Frequency Response: +
transmit tone notch frequency.
Select All (simulcast): Selection of all lines.
Time mute: temporarily mutes “Unselected” audio.
Microphone Connection: Handset and Headset 4-wire; Deskmic 6-wire
Operating Temperature Range: 0 to +50 degree C.
Power Requirements: 117 Vac, 60Hz, 22W, or 12Vdc at 1A maximum
Dimensions: 3 in. H X 10 in. D X 8 in. W (desktop)
1.5 dB, 300 to 3000 Hz, except at the
Special features
♦ Automatic initial level settings
♦ Radio Scan Control
♦ Channel and Group control
♦ MDC ANI Display (w/IP-223)
♦ FLEETSYNC ANI Display (w/IP-223)
♦ Clock and VU meter
♦ Summed audio recorder output
♦ Phone Line Control.
2
Not available on software version 1.0
Page 50

26 Vega’s IP-2002
Note: Specifications are subject to change with out notice.
Page 51

TELEX Communications, Inc.
Vega Signaling Products
8601 East Cornhusker Highway, Lincoln, Nebraska, 68507
Phone: (402) 465-7026 / (800) 752-7560 Fax: (402) 467-3279
E-mail: vega@telex.com, Web: www.vega-signaling.com
 Loading...
Loading...