Page 1

Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway
User Guide
Home Installation Configuration Help
Login Status Internet LAN Wireless Security Device Appendix
Wireless communication settings
These are the options available in the Wireless menu:
Setup
Client List
AP Mode
第 1 頁,共 5 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Advanced Settings
Setup
The following page allows you to enable the wireless capability, hide the access point by not
broadcasting the network name, and set the wireless network name (SSID).
Option Description
Allow wireless
connections
Broadcast
network name
A checkbox that enables or disables the wireless LAN
interface. The default is to enable wireless
communications.
If you do not want the access point to be automatically
detected by a wireless client, clear this checkbox. If you
do this, the client cannot discover the access point. You
can still set up the connection by specifying the network
name (below), then entering this name in the wireless
client utility.
Enter a name for your wireless network here. SSID stands
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX06.125\wui_...
Page 2
第 2 頁,共 5 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
for Service Set Identifier. This name must be between 1
Network name
(SSID)
MAC address
and 32 characters long. The default name is USR9108.
All wireless clients must either detect the gateway or be
configured with the correct SSID to access the Internet.
Displays the gateway's wireless MAC address. (You may
need this address if you're using WDS or multiple
gateways.) Click Apply to save changes.
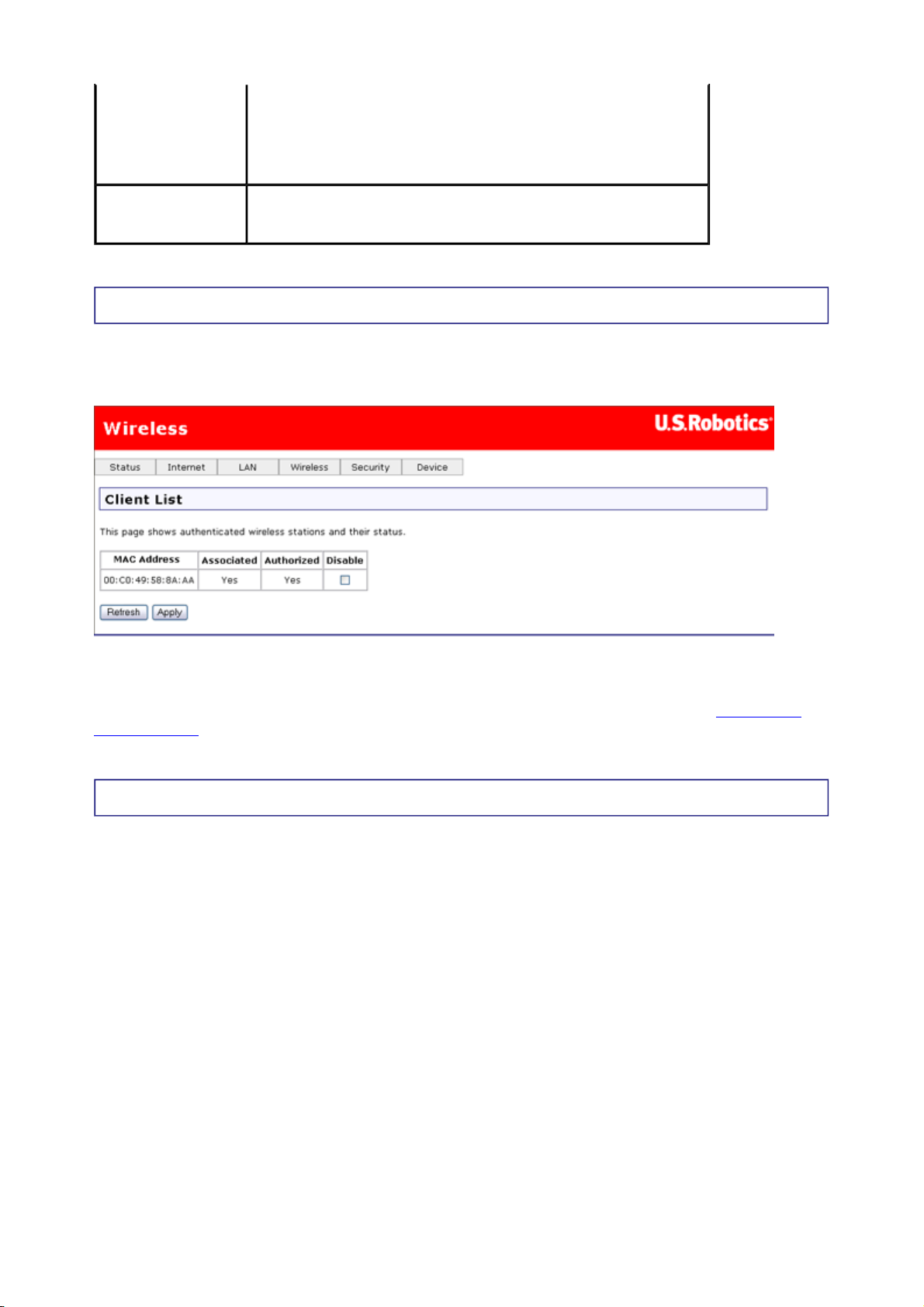
Client List
This page displays all of the wireless clients associated with or connected to your wireless
gateway. A wireless client is a machine with a wireless adapter.
If you check or uncheck any of the Disable checkboxes, click Apply to save your changes. If
you discover an unauthorized wireless user connecting to your gateway, you can use the
Disable checkbox to remove it. This also adds the unauthorized system to the MAC filter
disallow list. Click Refresh to update the list to the most current status.
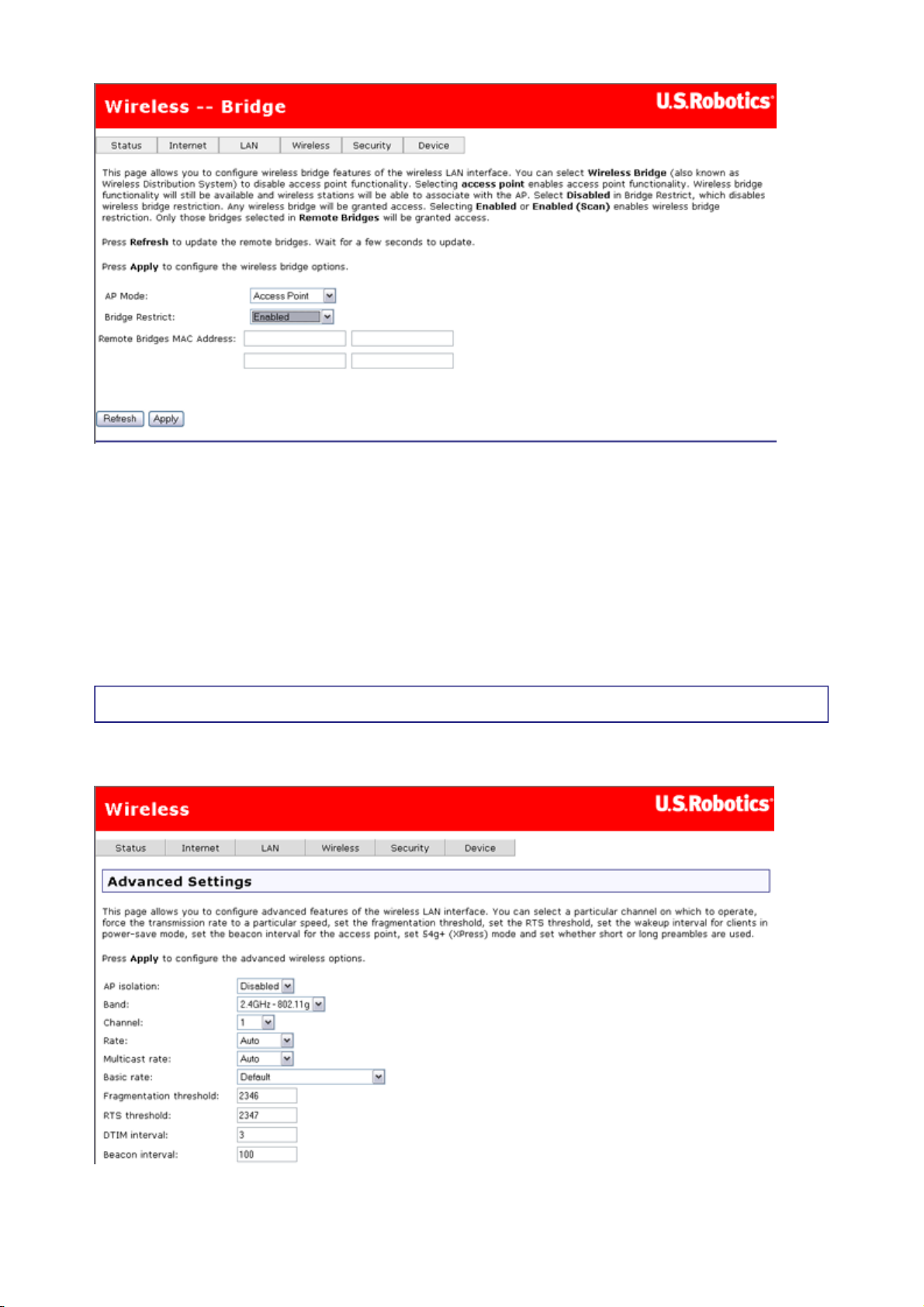
AP Mode
In this page, you can set up your gateway as either an access point (which connects wireless
machines to the Internet) or a bridge (which only exchanges data with another wireless
bridge). With an access point, wireless clients use infrastructure mode to communicate with
the gateway. In bridge mode, the gateway uses the Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
protocol to wirelessly communicate with the other wireless bridges.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX06.125\wui_...
Page 3
第 3 頁,共 5 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
If you want to set up a bridge, one or both of the devices must know the other's WLAN MAC
address. Bridge Restrict can have one of these values:
Enabled — restricts the gateway to communicating with bridges, and you enter the
WLAN MAC addresses of the other bridge(s) listed under Remote Bridges MAC
Address.
Disabled — does not restrict the gateway to communicating with bridges. It can also
communicate with wireless clients.
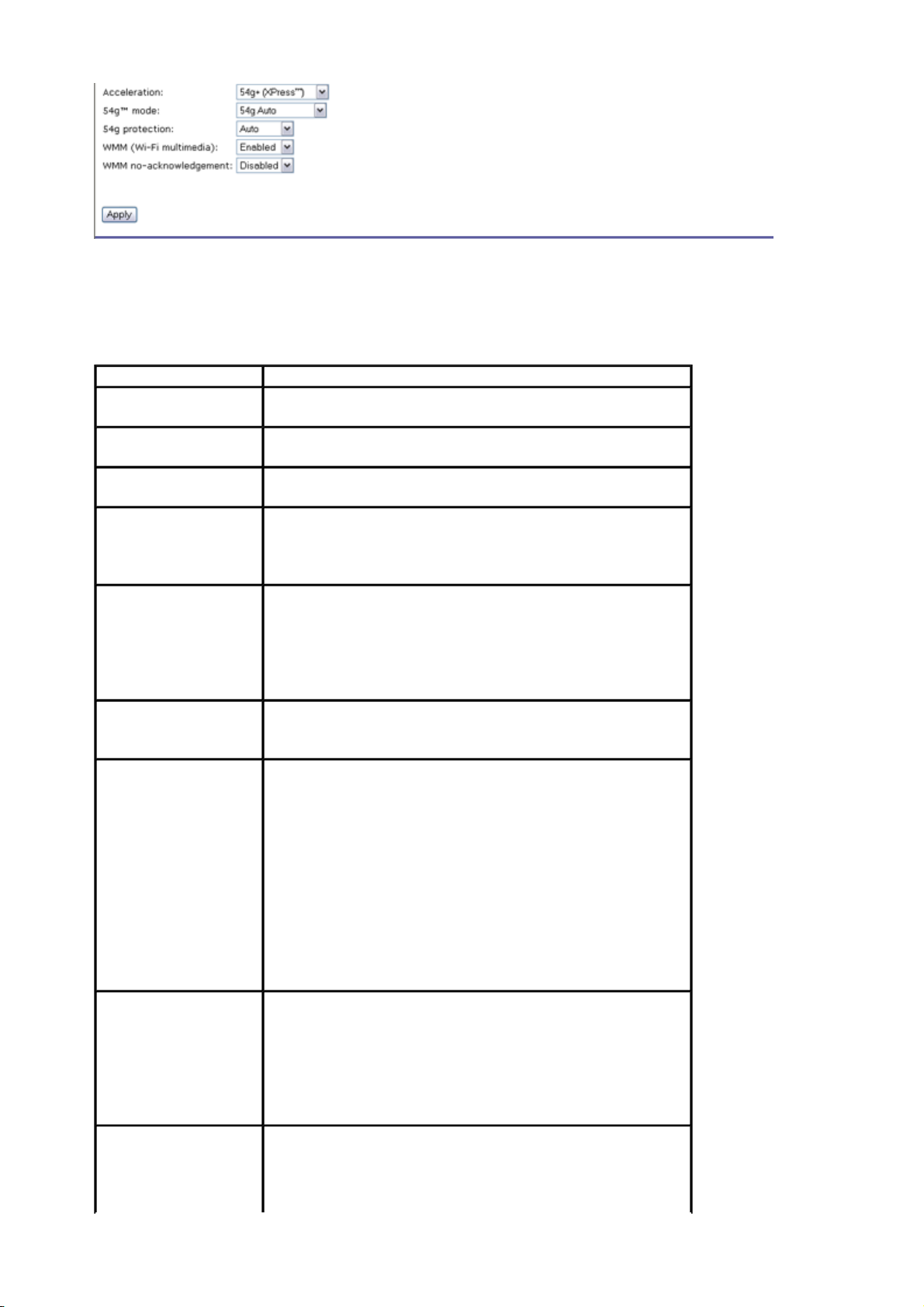
Advanced Settings
This page is where you specify a number of advanced settings for wireless communications.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX06.125\wui_...
Page 4
第 4 頁,共 5 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Note: After making any changes, click Apply to save.
Warning: The settings shown above are default settings. Changes made to these items can
cause wireless communication problems.
Field Description
AP isolation
Band
Channel
Rate
Multicast rate
Basic rate
Fragmentation
threshold
Enable this item if you do not want your wireless
machines to be able to communicate with each other.
This is the range of frequencies the gateway will use
to communicate with your wireless devices.
Drop-down menu that allows selection of specific
channel.
This drop-down list lets you specify the wireless
communication rate, which can be Auto (uses the
highest rate when possible, or else a lower rate) or a
fixed rate between 1 and 54 Mbps.
This drop-down list lets you specify the wireless
communication rate for multicast packets, which are
sent to more than one destination at a time. The
value can be Auto (uses the highest rate when
possible, or else a lower rate) or a fixed rate between
1 and 54 Mbps.
You have the option of supporting all rates listed in
Rate above or using the 1-, 2-Mbps rates, which
support only older 802.11b implementations.
A threshold, specified in bytes, that determines
whether packets will be fragmented and at what size.
On an 802.11 connection, packets that are larger the
fragmentation threshold are split into smaller units
suitable for the circuit size. Packets smaller than the
specified fragmentation threshold value are not
fragmented.
RTS threshold
Enter a value between 256 and 2346. If you
experience a high packet error rate, try to increase
this value slightly. Setting the fragmentation
threshold too low may result in poor performance.
This is number of bytes in the packet size beyond
which the gateway invokes its RTS/CTS (request to
send, clear to send) mechanism. Packets larger than
this threshold trigger the RTS/CTS mechanism, while
the gateway transmits smaller packets without using
RTS/CTS. The default setting of 2347, which is the
maximum, disables the RTS threshold mechanism.
A delivery traffic indication message (DTIM), also
known as a beacon, is a countdown informing
wireless clients of the next window for listening to
broadcast and multicast messages. When the
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX06.125\wui_...
Page 5
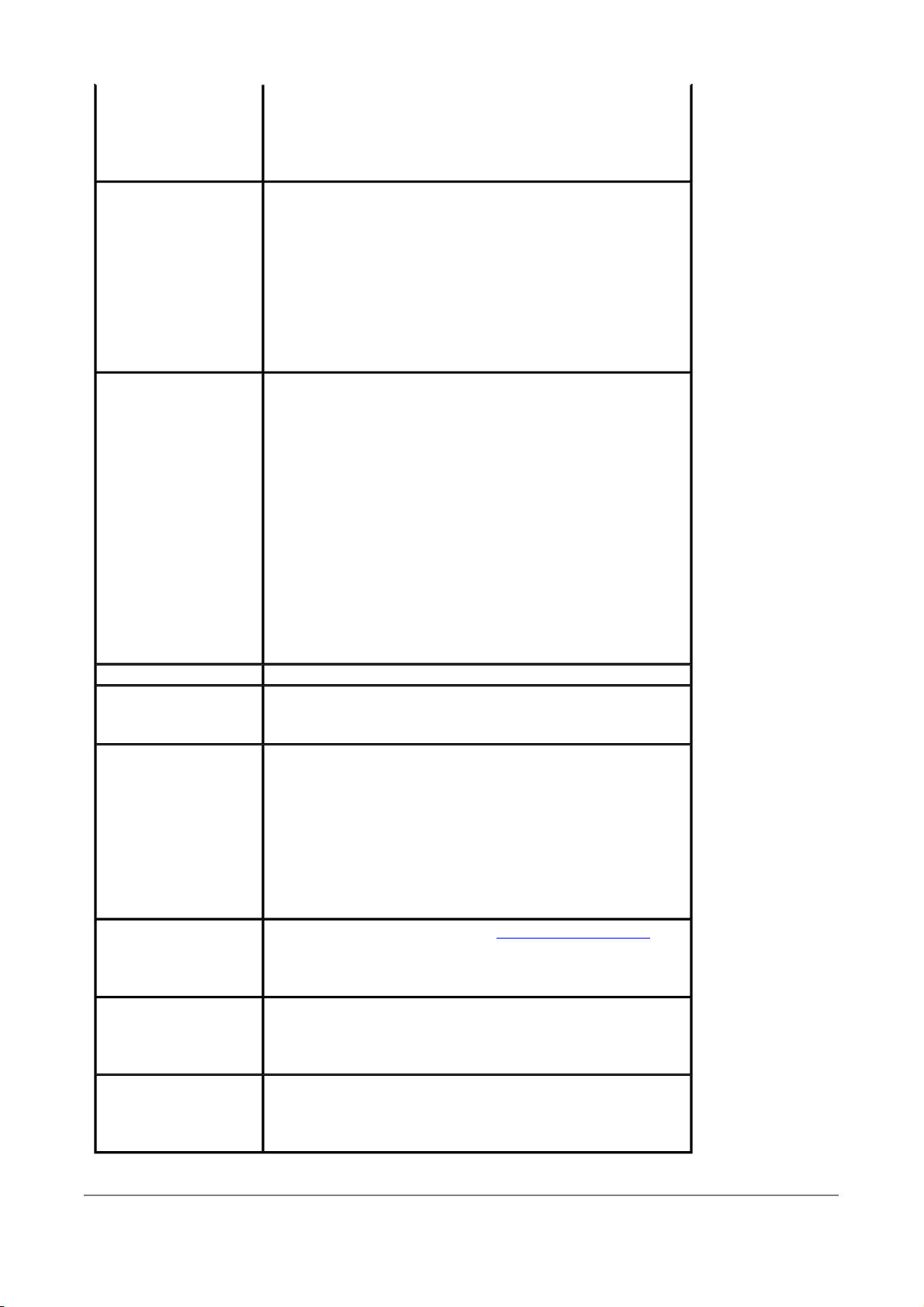
DTIM interval
g
g
g
Beacon interval
第 5 頁,共 5 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
gateway has broadcast or multicast messages for its
clients, it sends its next DTIM message with this DTIM
interval value. The clients hear the beacons and
awaken as needed to receive the broadcast and
multicast messages.
The amount of time (in milliseconds) between beacon
transmissions, each of which identifies the presence
of an access point. By default, wireless clients
passively scan all radio channels, listening for
beacons coming from access points. Before a client
enters power-save mode, it needs the beacon interval
to determine when to wake up for the next beacon
(and learn whether the access point has any
messages for it). You can enter any value between 1
and 65535, but the recommended range is 1 - 1000.
MAXg is a feature in which two U.S. Robotics MAXg
devices can communicate with each other at twice the
normal rate.
+ is a technology that achieves higher throughput
54
with frame-bursting. With 54g+ enabled, aggregate
throughput (the sum of the individual throughput of
Acceleration
MAC address This is the gateway's WLAN MAC address.
54g mode
54g protection
WMM (Wi-Fi
multimedia)
WMM noacknowledgement
Preamble
each network client) improves by up to 25% in
802.11g-only networks, and up to 75% in mixed
networks containing both 802.11g and 802.11b
equipment.
In this item, you can select either None, 54g+
(Xpress?, or MAXg (125 Mbps). If you are in
Bridge mode, MAXg (125 Mbps) is not supported.
Set this 54g+ mode to 54g Auto for the widest
compatibility, or to 54g Performance for the fastest
performance with 54g-certified equipment.
The 802.11g standards provide a protection method
so 802.11g and 802.11b devices can co-exist in the
same network without “speaking” at the same time.
Do not disable 54g protection if there is a possibility
that a 802.11b device will use your wireless network.
In Auto mode, the wireless devices use RTS/CTS to
improve 802.11g performance in mixed
802.11g/802.11b networks. Turn protection off to
maximize 802.11g throu
This item enables or disables Quality of Service
(QoS) processing of multimedia packets. In QoS,
some types of packets are
others.
No-acknowledgement refers to the acknowledge
policy used at the MAC level. Enabling noacknowledge can result in more efficient throughput
but high error rates.
A preamble is a signal that synchronizes the timing
between two or more wireless devices, allowing all
wireless systems to recognise the start of
transmission.
hput under most conditions.
iven a higher priority than
© 2004-2005 U.S. Robotics Corporation.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX06.125\wui_...
Page 6
Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway
User Guide
Home Installation Configuration Help
Login Status Internet LAN Wireless Security Device Appendix
Security settings
These are the options available in the Security menu:
Wireless Security
MAC Filter
Device Login
第 1 頁,共 10 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Internet Access Control
IP Filtering - Outbound Filters
IP Filtering - Inbound Filters
Virtual Servers
Port Triggering
DMZ Host
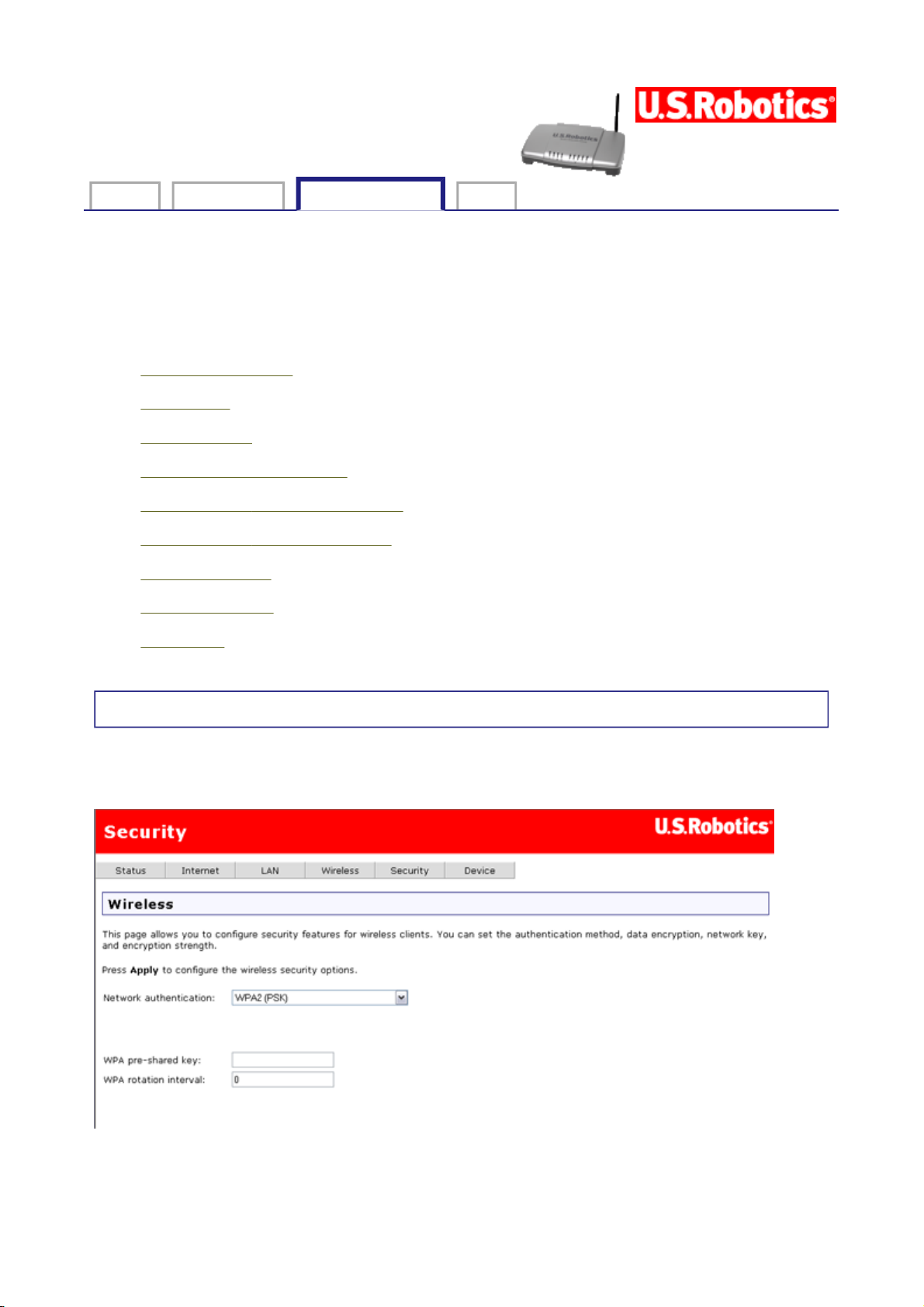
Wireless security
The wireless security page allows you to configure the security features of your wireless
network.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX25.500\wui_...
Page 7

第 2 頁,共 10 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
There are several security methods to choose from, depending on your needs and the
capabilities of your wireless machines.
WEP open and WEP shared —WEP is an encryption scheme that is used to protect
your wireless data communications. WEP uses a combination of 64-bit keys or 128-bit
keys to provide access control to your network and encryption security for every data
transmission. To decode a data transmission, each wireless client on the network must
use an identical 64-bit or 128-bit key. WEP is an older wireless encryption method that
is not as hard to break as the more-recent WPA.
802.1x — In 802.1x (also known as RADIUS), a separate machine called an
authentication server receives a user ID and password. It grants or denies access
based on whether the ID and password match any entries in its account list. You can
optionally enable WEP encryption with this option. Because it requires a separate
machine acting as the authentication server, 802.1x is most often used in business
enviroments.
WPA with 802.1x (RADIUS) — WPA is a more recent encryption method that
addresses many of the weaknesses in WEP. Any client capable of WPA encryption
should use it instead of WEP. This option uses WPA and an authentication server.
WPA (PSK) — This is WPA encryption combined with a pre-shared key (PSK), which is
a text string known only to the gateway and authorized wireless clients. The gateway
rejects the login if the client's PSK does not match.
WPA2 with 802.1x (RADIUS) — WPA2 is a more advanced encryption method than
WPA. Because it is a more recent standard, some of your wireless devices might not be
able to use it. This option specifies WPA2 encryption and an authentication server.
WPA2 (PSK) — This option uses WPA2 with a pre-shared key.
WPA2 and WPA with 802.1x (RADIUS) — This option supports an authentication
server and WPA2/WPA encryption for devices capable of one or the other standard. The
gateway automatically detects whether a particular device can use WPA2 or WPA.
WPA2 AND WPA (PSK) — This has WPA2 or WPA encryption based on client abilities,
as well as a pre-shared key.
After making changes, click Apply to save.
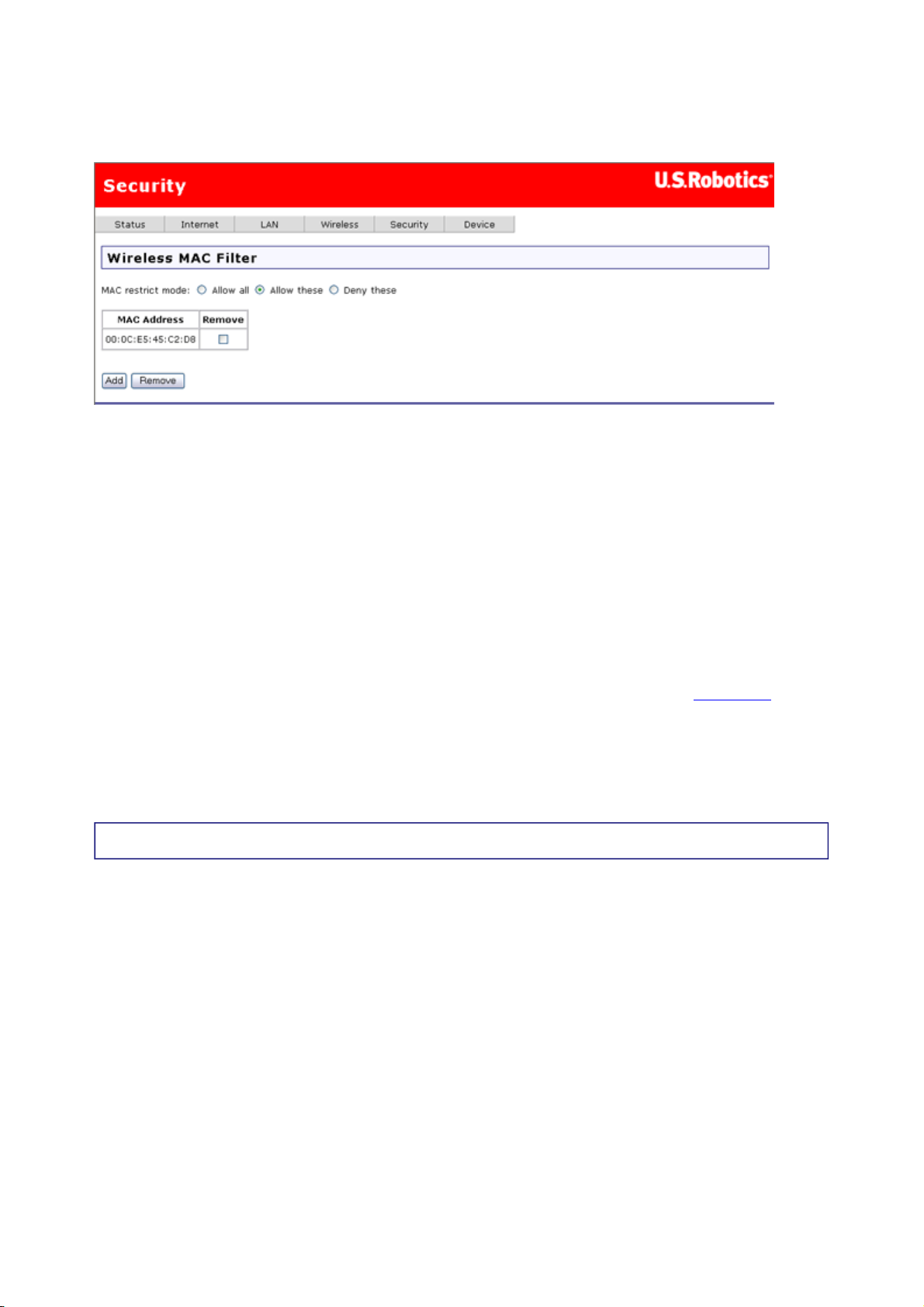
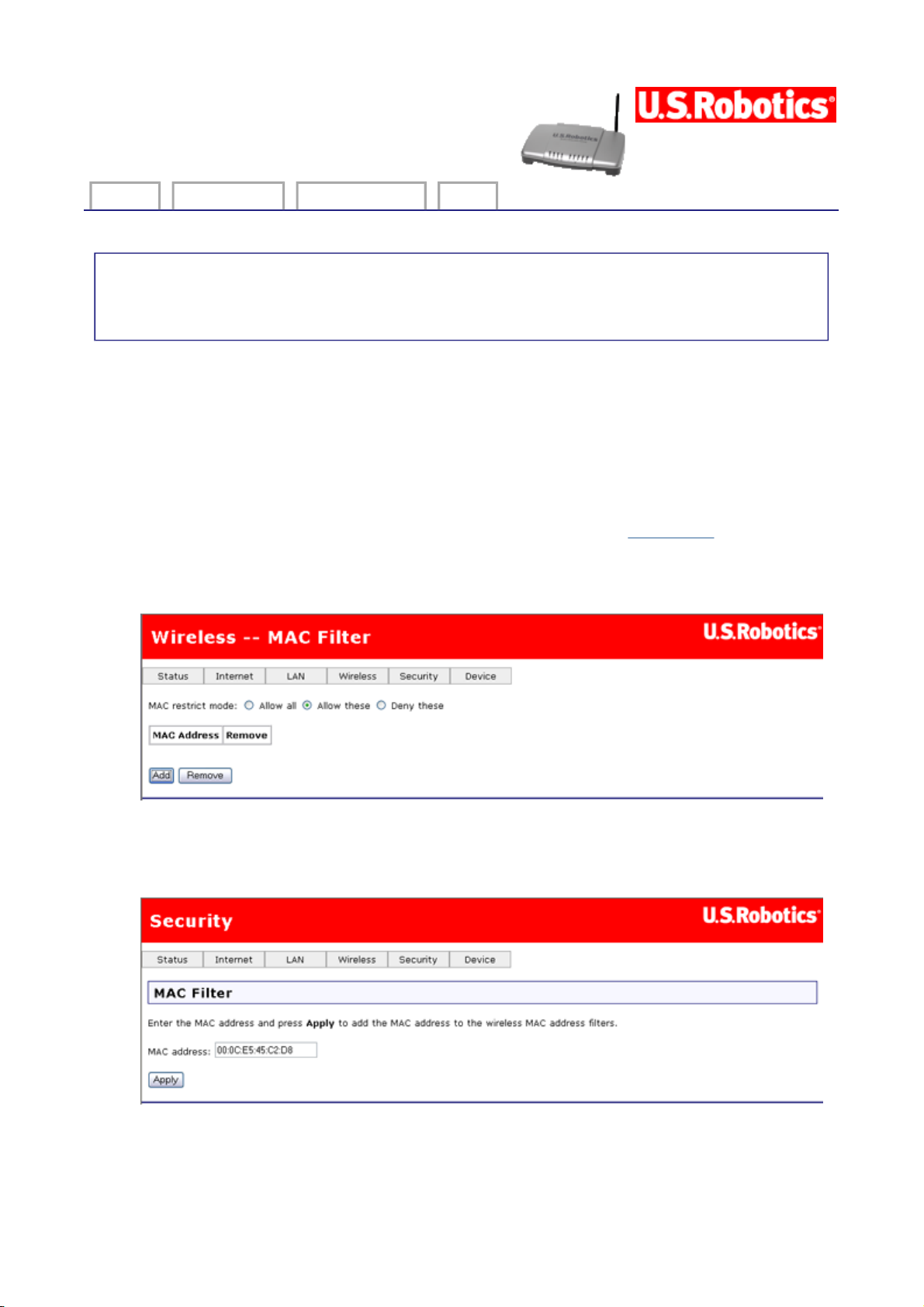
MAC Filter
All network interface cards are built with a unique 48-bit MAC address. When MAC address
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX25.500\wui_...
Page 8
第 3 頁,共 10 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
filtering is enabled, you can restrict the wireless devices that are allowed to connect to your
gateway by their respective MAC addresses. You could also grant access to any wireless
device whose MAC address is on its "allow" list.
These are the values for the MAC restrict mode:
Allow all — Allow any wireless device to access your local network, which amounts to
turning off MAC filtering.
Allow these — Let only the devices with the MAC addresses in the MAC filter list have
access to your wireless network.
Deny these — Exclude only the devices with the MAC addresses in the MAC filter list
from accessing your wireless network. Allow access to any other MAC addresses.
Below the MAC restrict mode is a table showing all MAC addresses that the restrict mode
applies to. You can add up to 60 addresses to the list. For an example of adding MAC
addresses to the list and otherwise configuring MAC filtering, please see the Tutorials
section of this User Guide.
If you wish to delete an entry from the list, select the appropriate MAC restrict mode,
select the Remove checkbox for the entry you want to delete, and click the Remove button.
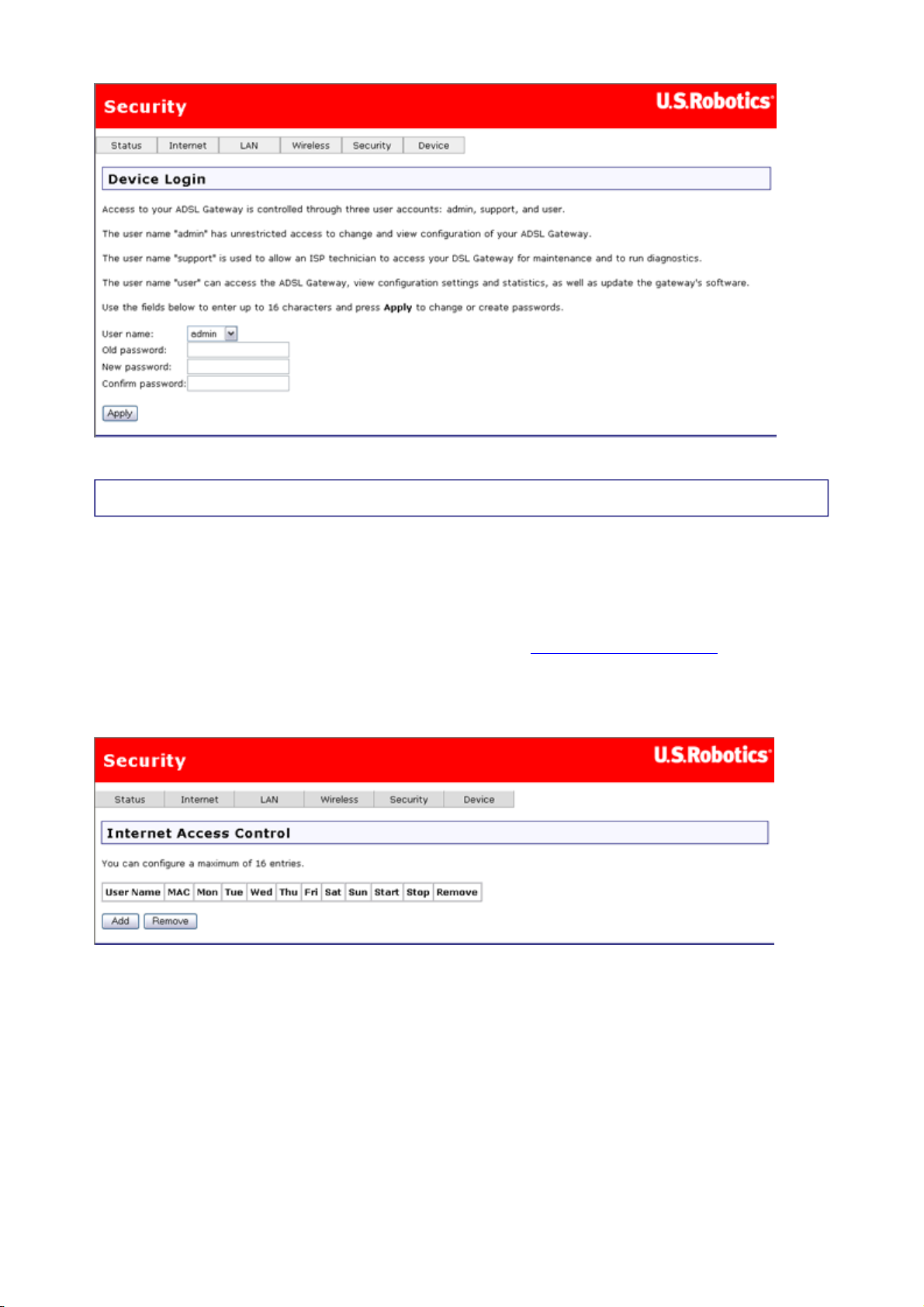
Device Login
You can use this page to change the password for the admin, support and user accounts.
(Their default passwords are admin, support, and user respectively.) Simply select an
account in the User name drop-down list, then enter the current and new passwords for the
account. Enter the new password a second time to confirm it. Then click Apply to save the
new password.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX25.500\wui_...
Page 9
第 4 頁,共 10 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
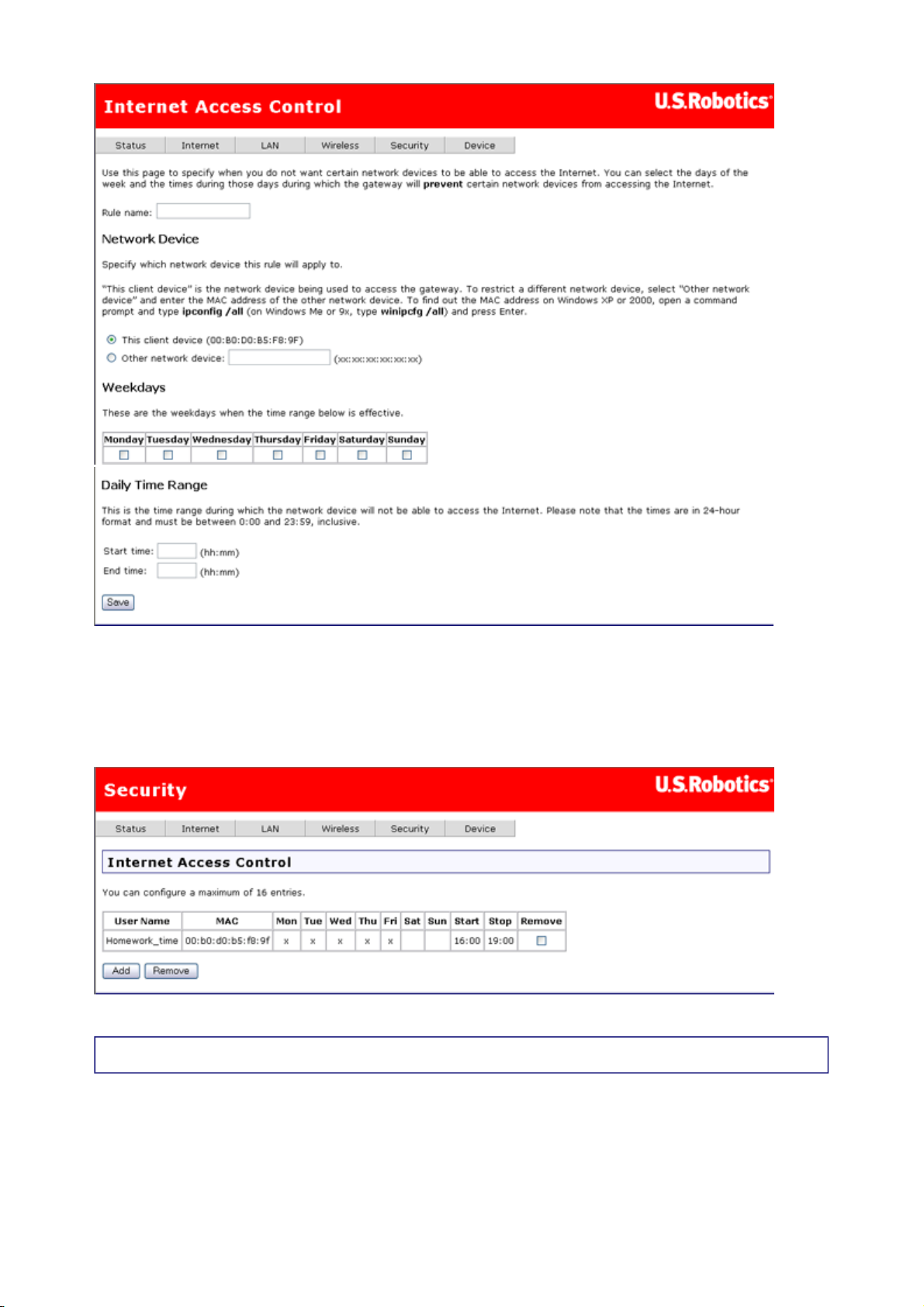
Internet Access Control
You can use the Internet Access Control page to create a parental control rule that keeps
certain network devices off the Internet for specific time periods. The rules can block access
for a defined time period on certain days of the week.
Note: If you want to use this feature, you must configure the gateway to synchronize its
time with at least one Internet time-of-day server. See Time
information.
This is the Internet Access Control page when there are no filters defined:
synchronization for more
Click Add to define an Internet access filter, and enter its settings in the following page. In
addition to the rule name, each rule you define has the MAC address of the machine to block,
the time period to block it for, and a list of days that the time-period block is enforced.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX25.500\wui_...
Page 10
第 5 頁,共 10 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Caution: If you want to set up access control for a machine other than the one you're
currently using, select Other network device and enter that device's MAC address.
After configuring the Internet access filter, click Save to save it. Here's what it might look
like if you wanted to keep children off the Internet during after-school study hours:
IP Filtering - Outbound Filters
The gateway's firewall can block internal users or applications from accessing the Internet.
There are two ways to accomplish this:
Using the TCP/UDP port numbers to block internal users or applications (a technique
called port filtering).
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX25.500\wui_...
Page 11
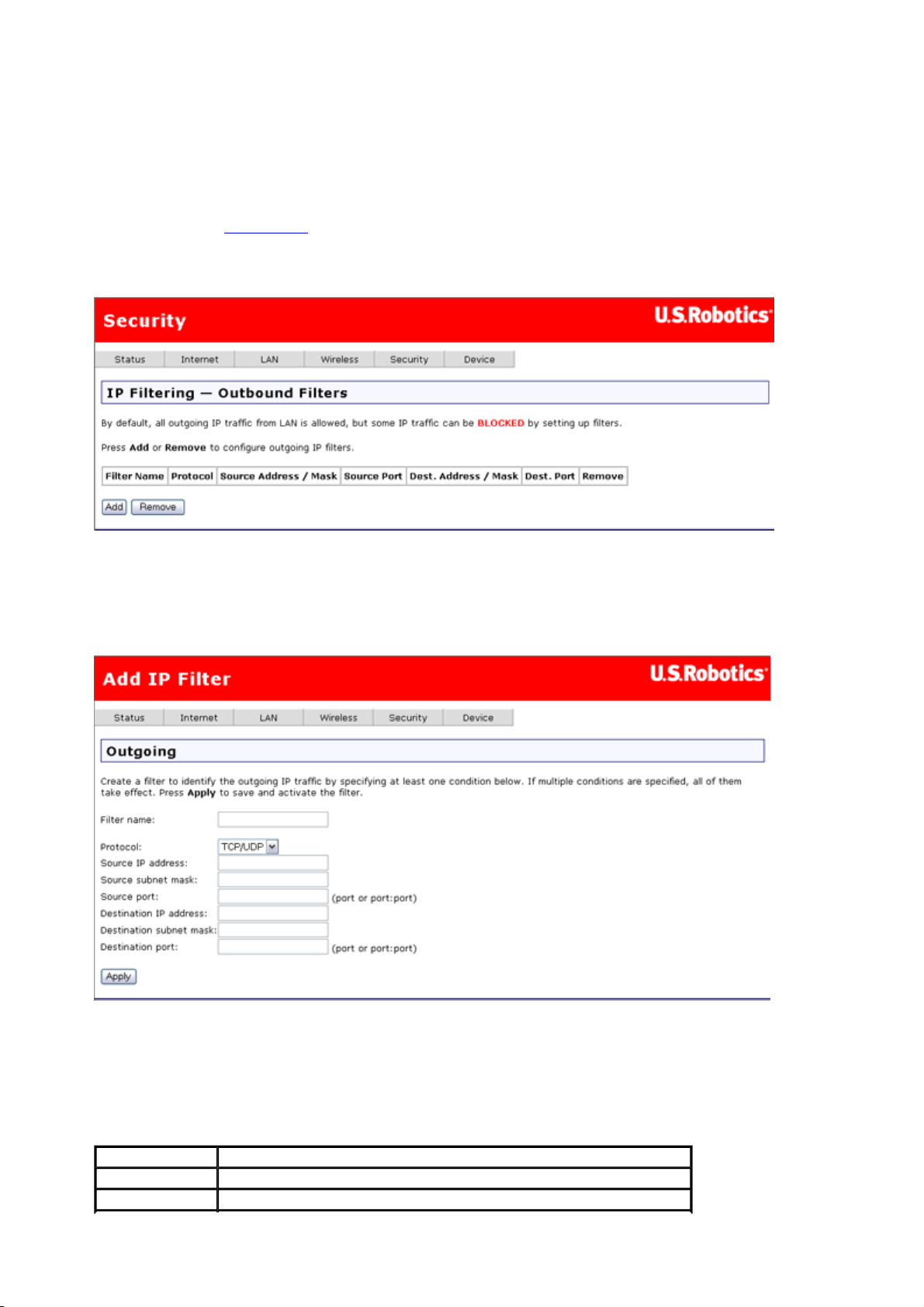
第 6 頁,共 10 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Using a combination of the source or destination port, protocol or source/destination IP
address to block a specific machine from accessing the Internet. This is also known as
address filtering. The outbound filter page allows you to block outgoing packet types
using either TCP, UDP, or a combination of both from specific ports.
For a tutorial on how to use the outbound filter page to keep a computer from accessing the
Internet, please click here
This is the outbound filtering page before adding a filter:
.
To remove an existing filter definition from the outbound filter table (the first screen shown
above), check the Remove checkbox for the filter and click the Remove button.
The following page appears after you click Add.
When you are done entering values for your filter, click Apply to save the filter.
These are the fields on the second page above (the page labeled Add IP Filter and
Outgoing), where you define a filter that specifies a set of conditions for which to block
access for one or more local machines.
Item Description
Filter name Enter a name for the filter here.
Protocol Select TCP, UDP, a combination of TPC & UDP, or ICMP.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX25.500\wui_...
Page 12
第 7 頁,共 10 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Source IP
address
Source
subnet mask
Source port
Destination
IP address
Destination
subnet mask
Destination
port
Enter the IP address that you do not want to let access the
Internet or the destination address.
Enter the subnet mask for the source IP address.
Enter the source port number, or range of ports, for which
you want to block access.
Enter the IP address you do not want the source IP address
to have access to.
Enter the subnet mask for the destination IP address.
Enter the destination port number, or range of port
numbers, you want to block access.
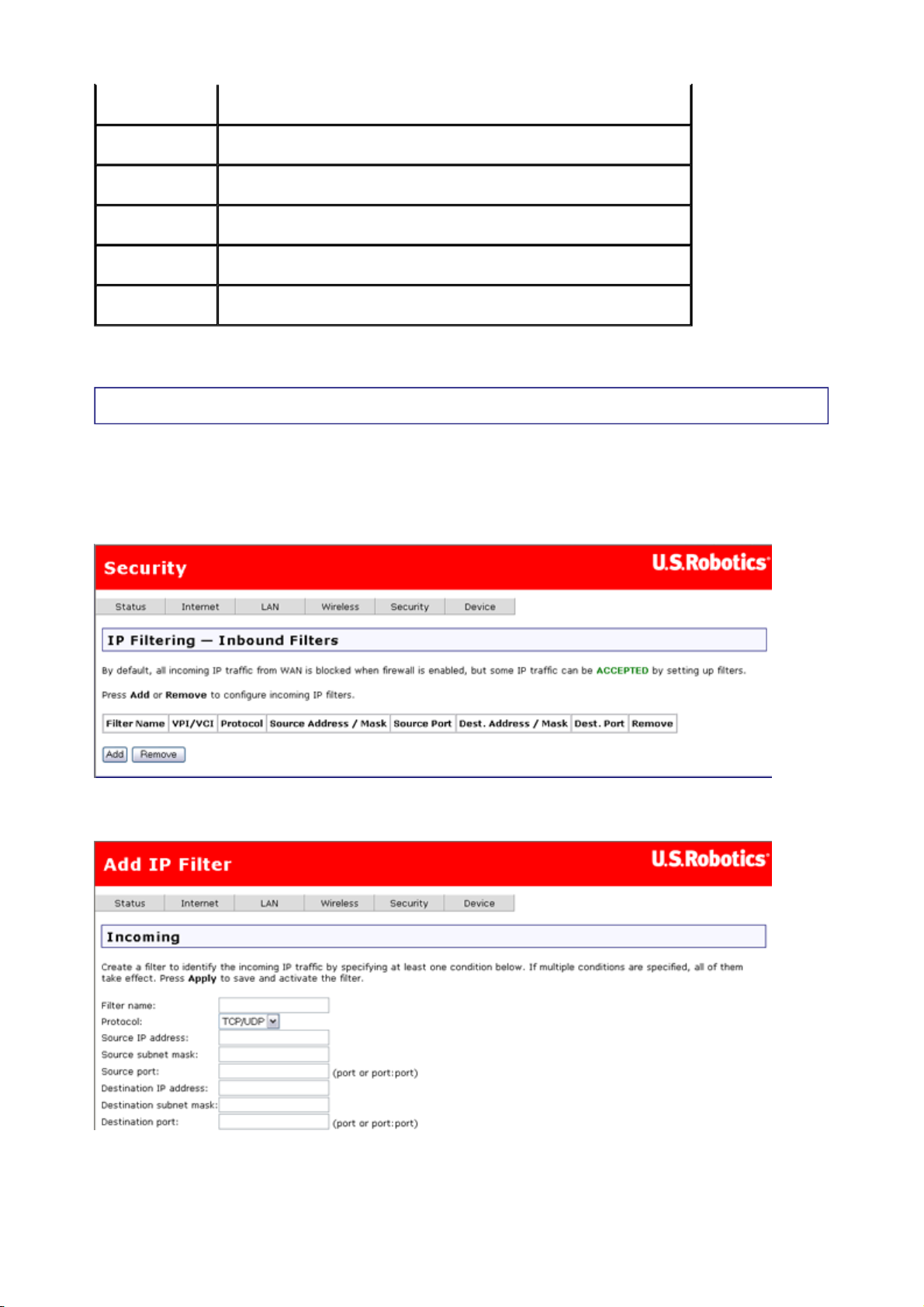
IP Filtering - Inbound Filters
This page allows incoming packets to reach their intended destinations by specifying rules for
unblocking certain incoming packets. You could use it any time you want to allow restricted
access to a machine, or you could configure unlimited access to a particular system (for
example if one of your local machines is a Web server).
Click on Add to create a new inbound filter.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX25.500\wui_...
Page 13
This table describes the fields in this Add IP Filter page:
Field Description
Filter name Enter a name for your inbound filter here.
Protocol Selects TCP, UDP, or a combination of TCP/UDP.
Source IP
address
Source
subnet mask
Source port Enter a source port number, or a range of port numbers.
Destination
IP address
Destination
subnet mask
Destination
port
Enter the external IP address you want to allow access to
your internal address that appears in the Destination IP
address field.
Enter a subnet mask for the source IP address.
Enter the internal IP address you want to provide access to.
Enter a subnet mask for the destination IP address.
Enter the destination port number, or range of port
numbers, you want to allow access (for the destination IP).
第 8 頁,共 10 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
After setting up your filter, click Apply to save it.
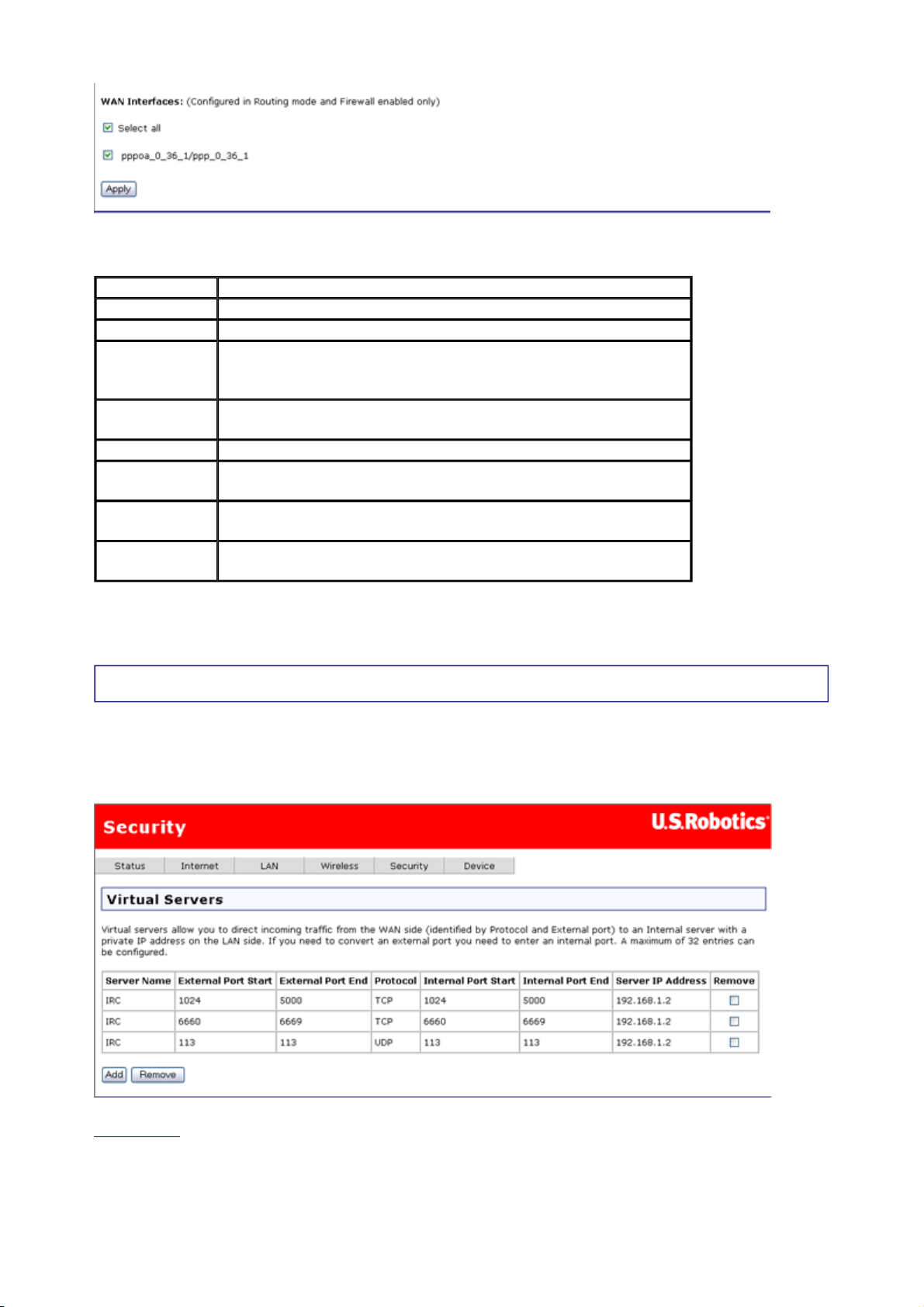
Virtual Servers
A virtual server allows you to direct incoming traffic from the Internet (identified by protocol
and external port) to an internal server with a private IP address on the LAN. If you need to
convert an external port you need to enter an internal port.
Click here
delete a virtual server, check the Remove checkbox for the appropriate line in the table and
click Remove.
to go to a tutorial showing you how to set up a virtual server. If you want to
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX25.500\wui_...
Page 14
第 9 頁,共 10 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Note: If you set up a DMZ host, all packets for addresses other than those specified in this
page go to a designated DMZ machine.
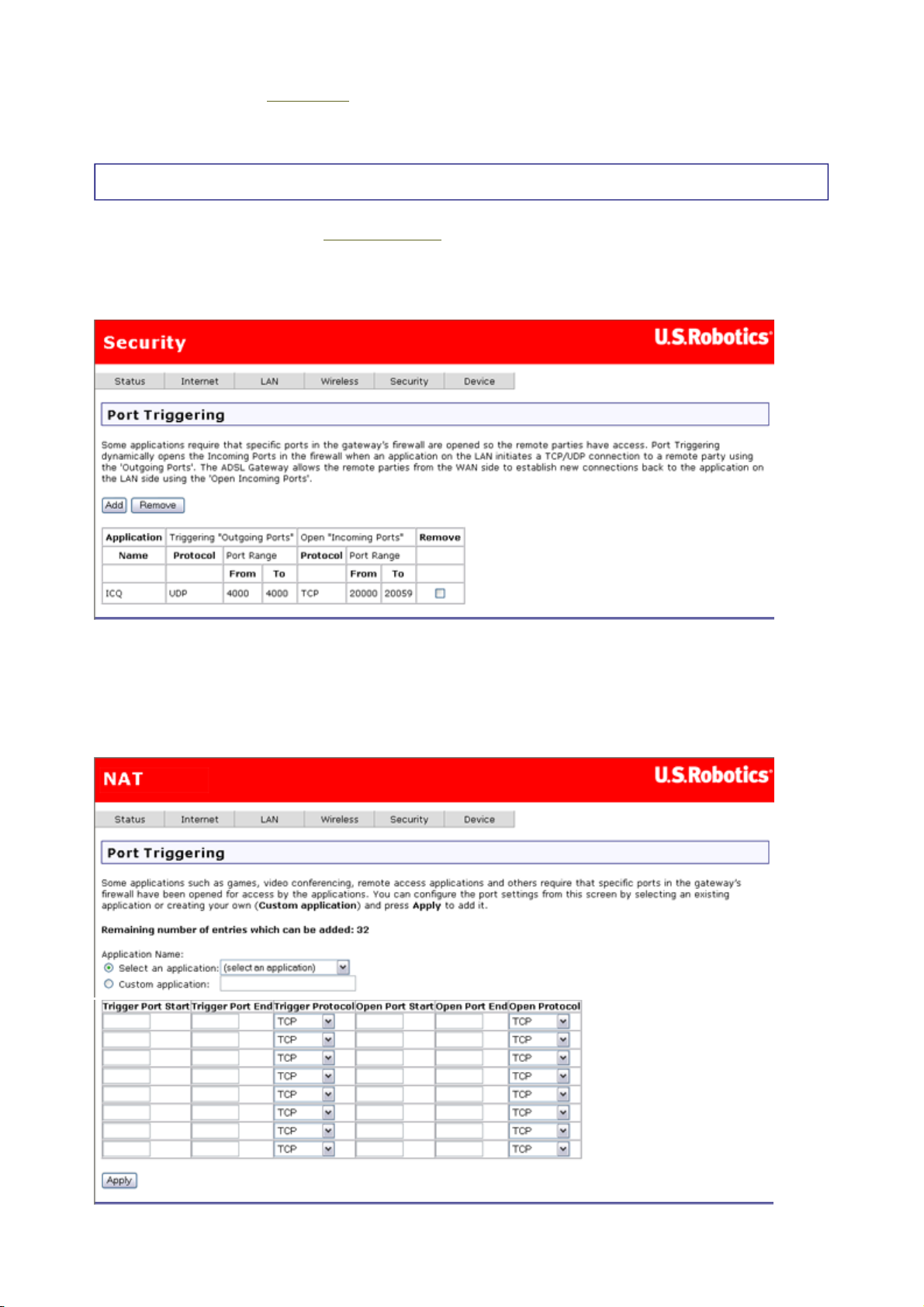
Port Triggering
Port triggering is similar to a virtual server, except that it creates a dynamic or temporary
hole in the firewall. Port triggering is more secure than a virtual server, but it does not
support simultaneous use of the same ports by multiple systems. It allows remote systems
access through the gateway's firewall.
Click Add to set up port triggering for an Internet application. In the next page (shown
below), select the application name, which fills in the settings in the table below. If the
application you want is not in the list, select Custom application and fill in the table
parameters below. (See the application's documentation to find out what the settings should
be.) Click Apply to save the port trigger.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX25.500\wui_...
Page 15

第 10 頁,共 10 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Note: A port trigger is available to a single active session. It cannot simultaneously support
same-port triggers to multiple clients.
DMZ Host
The de-militarized zone (DMZ) option is for forwarding IP packets from the Internet that are
not meant for any of the applications configured in the virtual server
are forwarded to a designated DMZ host computer. While a virtual server can only forward
(redirect) a limited number of services (ports), DMZ hosting allows all the services (ports)
running on the DMZ host to be accessible externally.
This is the DMZ Host page.
table. These packets
To configure the DMZ, simply enter the IP address of the computer that will function as the
DMZ host. Click Apply to save the DMZ address. To deactivate the DMZ feature, clear DMZ
host IP address and click Apply.
© 2004-2005 U.S. Robotics Corporation.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX25.500\wui_...
Page 16
Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway
User Guide
Home Installation Configuration Help
Login Status Internet LAN Wireless Security Device Appendix
Device settings
These are the options available in the Device menu:
Time
Print Server
Back Up Settings
第 1 頁,共 8 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Restore Settings
Restart
Upgrade
Restore Defaults
Diagnostics
SNMP
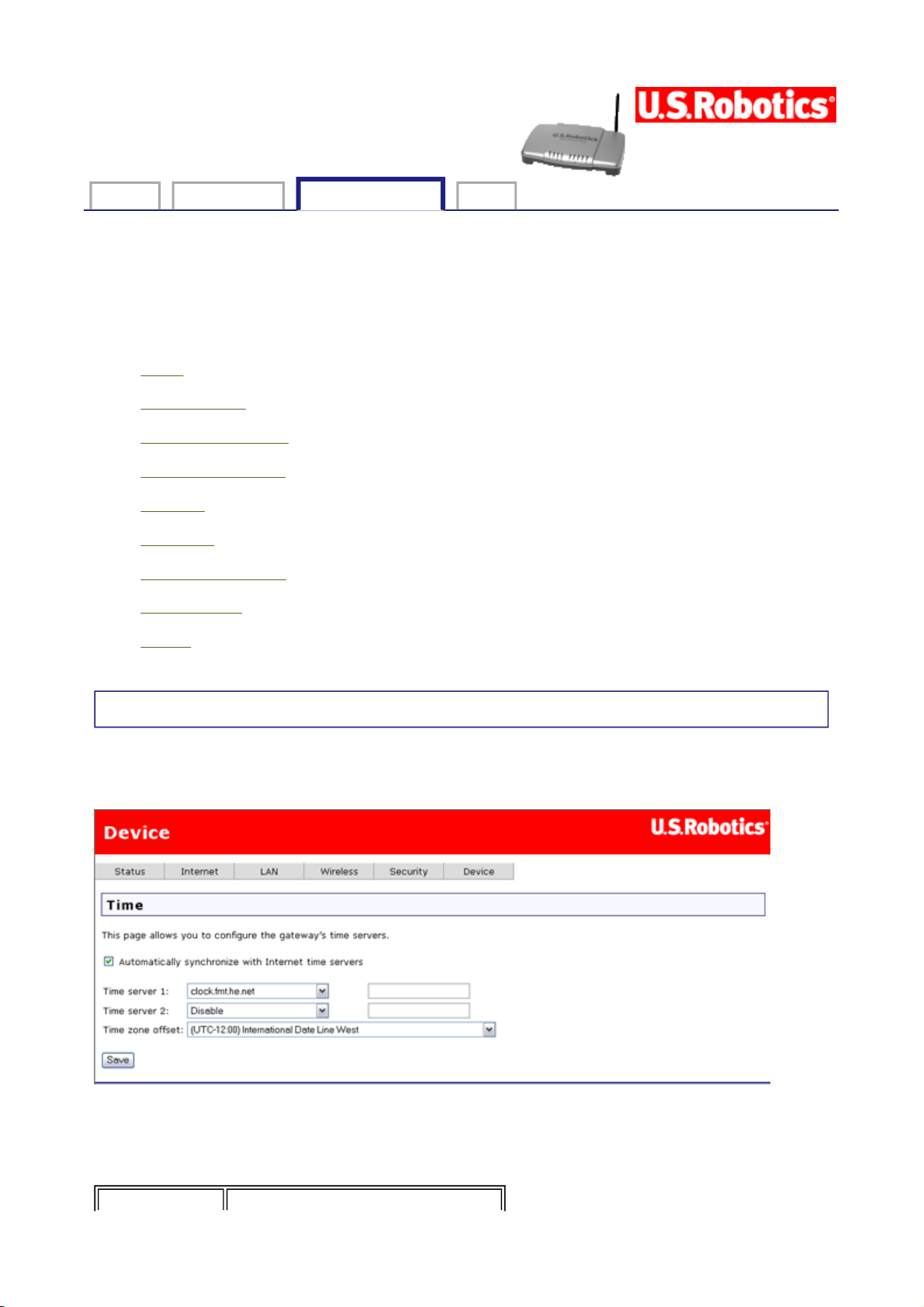
Time
The gateway can synchronize its internal clock with time servers on the Internet. In this
page, you can configure how it does this.
To synchronize with the Internet time server(s), specify one or two servers by either
selecting them from a list or entering their IP addresses. Then select your time zone in the
Time zone offset and click Save.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX08.296\wui_...
Page 17

Item Description
Automatically
synchronize...
Time server 1
Time server 2
Time zone
offset
Enable this field if you want the
gateway to automatically
synchronise its internal time.
Select a primary time server for
the gateway to query. To use a
server that is not in the list, enter
its IP address in the box to the
right.
You can optionally specify a
second time server to query.
Select your time zone here — the
number of hours you are offset
from Greenwich mean time.
Print Server
第 2 頁,共 8 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
A USB printer can be connected to the gateway and used as a network printer if you are
using an operating system that supports printing to an Internet Printing Protocol (IPP)-based
printer. Windows XP and 2000 have built-in support for this function, but other Windows
users will need to download either a Microsoft patch for their version of Windows or a thirdparty application. Refer to the documentation for your version of Windows for more
information. Other operating systems will need to either already support IPP-based printing
or download a third party application for their operating system.
Start by enabling the print server and entering the printer name, make and model. Then click
Save.
Now perform the following steps to install and set up the printer:
1. Connect the printer to the gateway. Plug the square end of a USB cable into the USB
port on your printer. Plug the thin rectangular end of the USB cable into the USB port
on the gateway. Connect the power supply to your printer and turn your printer on.
2. Set up your printer. Launch a Web browser. Go to the Web user interface by opening
the http://192.168.1.1 address (if you have changed this address, use the new
address).
3. Perform the following steps to set up your printer. You will need to do this on every
computer that is connected to your network that you want to be able to access the
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX08.296\wui_...
Page 18

第 3 頁,共 8 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
printer. For non-Windows operating systems: Adapt this to follow the printer
installation process for your operating system.
1. Windows XP users: Click Windows Start and then Printers and Faxes. Windows
2000, Me, and 98 users: Click Windows Start, Settings, and then Printers.
2. Click Add Printer and the Add Printer Wizard launches. Click Next.
3. Select Network printer and click Next.
4. Select Connect to a printer on the Internet... Under Printer location, enter
the following.
http://192.168.1.1:1631/printers/printer_name
If you have changed the gateway's IP address, replace 192.168.1.1 with the
changed address. For the printer_name part, use the name you entered in
Printer name on the Print Server page shown above. This name is casesensitive, and it must exactly match the Printer name on the Print Server
page.
5. You will be prompted to choose the brand and model of your printer. You can
either select them from the list or click Have Disk, then insert the CD-ROM that
came with your printer, and navigate to your CD-ROM drive to locate the drivers.
When you are finished, click Next.
6. When prompted, select Yes or No to set this printer as your default printer. If
prompted, you can print a test page.
7. You will be shown the information regarding your printer. Click Finish to
complete the setup process.
4. To verify the printer connection, print a page from this computer. If this prints
correctly, your printer setup is complete. If not, make sure the printer is turned on and
that the USB cable is firmly connected to both the printer and to the gateway. If the
page still does not print correctly, repeat the setup procedure and make sure you enter
all the correct information.
Back Up Settings
To save your gateway configuration settings, click Back Up and specify a file location on
your hard drive.
Note: If you are using Internet Explorer 5.5 or earlier, the WUI will display the settings on
the screen rather than save them to a file. We suggest that you upgrade your browser or
install a different browser.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX08.296\wui_...
Page 19

第 4 頁,共 8 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Restore Settings
This option lets you restore device settings previously saved in a backup operation. To
update your ADSL Gateway configuration settings, follow the steps provided on the screen.
Restart
In this page, you can restart the gateway. This takes about two minutes.
Upgrade
The upgrade page allows you to update the firmware in the gateway.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX08.296\wui_...
Page 20

第 5 頁,共 8 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
You can either check the U.S. Robotics Web site for newer firmware (by clicking Check for
Update), or you might receive new firmware from your Internet Service Provider. With the
new firmware file on your computer's hard drive, click Browse to locate the file and Update
to perform the upgrade. The process takes about two minutes to complete. You will see a
status bar like the following. Do not turn off the gateway or unplug any cables while it
performs the upgrade.
Restore Defaults
You can return the gateway to its original factory-installed settings in one of two ways:
By using a thin tool, such as a paper clip, to press the Reset button on the back of the
gateway for at least five seconds (see the red box below)
Or you can click the Restore Defaults option in the Device menu.
You should only need this option if the gateway is not functioning or you wish to reprogram
completely. The troubleshooting
the gateway is already configured to the default values.
WARNING: You will lose all your custom configuration settings if you use this
procedure may ask you to do this. For many settings,
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX08.296\wui_...
Page 21

第 6 頁,共 8 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
option. You may want to back up the settings first.
The process takes about two minutes to complete. You will see a status bar like the
following. Do not turn off the gateway or unplug any cables until it finishes.
After resetting to the default settings, the Quick
you will need to repeat the configuration process, as you did when you first installed the
gateway. You can also run EasyConfigurator, as described in the gateway's installation guide.
Setup procedure automatically starts, and
Diagnostics
When you open this page, the gateway automatically performs a series of self-diagnostic test
and displays the results once completed:
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX08.296\wui_...
Page 22

第 7 頁,共 8 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Be sure to read the help text closely. If the gateway fails some of the tests, you may not be
experiencing a real problem.
If you want more information on a particular test or find out what to do if a test fails, click on
the Help link next to its PASS/FAIL indicator.
The help text tells you what it means when the gateway passes or fails the test, and gives
troubleshooting tips to use if the test failed.
SNMP
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol that helps you monitor and
manage the local network of systems connected to your gateway. In SNMP, a device called
an SNMP agent collects statistics about network performance, then sends the statistical data
to another machine for storage and analysis. In this page, you can configure the gateway as
an SNMP agent.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX08.296\wui_...
Page 23

Item Description
Read
community
Set
community
System name Optional SNMP system name.
System
location
System
contact
Trap
manager IP
This is the SNMP community name/password
to read SNMP values.
The SNMP community name/password to set
SNMP values.
Optional SNMP location.
Optional SNMP system contact.
IP address of SNMP hosting trap manager,
where SNMP messages will be sent.
第 8 頁,共 8 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Note: To use this feature, you need to enable SNMP on the LAN or WAN. Click here
the page where you can do this.
© 2004-2005 U.S. Robotics Corporation.
to see
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX08.296\wui_...
Page 24

第 1 頁,共 3 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway
User Guide
Home Installation Configuration Help
Login Status Internet LAN Wireless Security Device Appendix
Network Address and Port Translation (NAPT)
Network Address and Port Translation (NAPT) allows a single device, such as a gateway, to
be an agent between the Internet (or "public network") and a local (or "private") network.
This means that only a single unique IP address represents an entire group of devices to the
outside world.
Implementing dynamic NAPT automatically creates a firewall between your internal network
and the Internet. NAPT only allows connections that originate inside the internal network.
Essentially, this means that a computer on an external network cannot connect to your
computer unless your computer has initiated the contact. Nobody from the outside can latch
onto your IP address and use it to connect to a port on your computer.
Under NAPT, all internal network computers are inaccessible from the outside. However, if
you need to use public services such as Web, FTP, or e-mail servers from your private
network, you can set up a virtual server to permit secured access. In this method, a
connection with the outside is redirected to a host (the virtual server) running the services
on the private network. (IP forwarding is another term for this.)
The Virtual Servers
settings.
setup page allows you to add, remove, and save virtual server
Passing Applications Through NAPT
Port Forwarding When Hosting Services Behind NAPT
Protocol Type Port
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX77.890\appe...
Page 25

FTP ( File Transfer Protocol) TCP 21
HTTP (Web Server) TCP 80
DNS (Domain Name Server) TCP UDP 53
Telnet- Remote connection TCP 23
SMPT (Outgoing mail) TCP 25
POP3 (Incoming mail) TCP 110
NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) TCP 119
PCAnyWhere UDP TCP 5631-5632
TALK UDP 517-518
Net2Phone ** TCP UDP 2000
HTTPS (secure Web server) TCP 443
VNS (remote display system) TCP 5900-5909 5800-5809
TFTP UDP TCP 69
SSH (secure remote login) ** TCP 22
** Net2Phone and SSH have not been tested yet
第 2 頁,共 3 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Port Forwarding When Hosting Games Behind NAPT
Game Type Port
Age of Empires II TCP UDP 2300:2400 2300:2400
Star Craft TCP 4000
Half Life Team
Fortress
Diablo II TCP 6112 4000
Quake II UDP
Quake III UDP
Return to Castle
Wolfenstein
Unreal Tournament UDP 7777
TCP UDP 27015 27015
27950 27960 27910 27952
27000 26000 27951
27950 27960 27910 27952
27000 26000 27951
UDP
27950 27952 27953 27960
27961 27962 27963 27965
Port Triggering for Playing Games Behind NAPT
Game
Return to
Castle
Wolfenstein
Star Craft 4000-4000 TCP/UDP 4000-4000 TCP/UDP
Outgoing Port
Range
27950-27965 UDP 27950-27965 UDP
Protocol Incoming Port Range Protocol
Applications that Do Not Require Configuration Behind NAPT
The following applications, when run behind NAPT, do require any gateway user
configuration.
Protocol (see note 1) Type Port
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX77.890\appe...
Page 26

第 3 頁,共 3 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) TCP 21
TFTP UDP TCP 69
TALK UDP 517-518
H.323 TCP 1720
IRC TCP 6667
SNMP UDP 161-162
PPTP TCP 1723
Windows Media Player (see note 2) UDP 7000-7007
DirectX Game (see note 3) UDP 2300-2400
AOL Instant Messenger (see note 4) TCP 5190
MSN Messenger (see note 4) TCP 1863
Notes:
1. All protocols mentioned above are for clients running behind the NAPT. If a hosting
server is needed, use port forwarding instead.
2. Windows Media Player uses TCP port 1755 from the player to connect to the server,
and uses UDP ports 7000-7007 to perform the actual data streaming.
3. DirectX uses TCP port 47624 from the client behind NAPT to connect to the peer, and it
expects the peer to use the UDP ports 2300-2400 thereafter.
4. The AOL and MSN Messenger Proxy Server are required for user-user direct connection
during file and image transfer.
Applications Behind NAPT Requiring Application Configuration
Change ICQ
The following steps provide a workaround to problems you might have when using ICQ's file
transfer, Send/Start ICQ chat and PC2PC phone. The problem is that some of these
applications set the Web browser to use a proxy server to listen to incoming connection
requests.
1. In your Web browser, go to the user connection preferences and enable Using proxy.
Set the type to SOCKS 4.
2. Disconnect and reconnect.
3. Set the type back to Not using proxy and change settings to use the ports you
specify. You should now be able to make a functioning connection. Be sure to
disconnect/reconnect after you make every change.
4. From the gateway, use virtual
range chosen in the previous step to your local machine.
© 2004-2005 U.S. Robotics Corporation.
servers (port forwarding) to forward the TCP port
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX77.890\appe...
Page 27

第 1 頁,共 1 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway
User Guide
Home Installation Configuration Help
Tutorials Troubleshooting Support Glossary
Tutorials
Below you will find some examples of common situations you might encounter and how you
could use the gateway to accomplish your goals.
I want to secure my wireless network and prevent unauthorized wireless devices from
accessing it.
I want to prevent a machine from accessing the Internet.
I want to use an application over the Internet (a game, instant messaging, etc.).
I want to give higher priority to some types of traffic.
I want to configure dynamic DNS.
© 2004-2005 U.S. Robotics Corporation.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX41.125\tutor...
Page 28
第 1 頁,共 2 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway
User Guide
Home Installation Configuration Help
Tutorial: I want to secure my wireless network and
prevent unauthorized wireless devices from accessing
it.
To do this, you need to enable MAC address filtering. When this is enabled, the only systems
allowed to associate and pass data wirelessly will be computers or access points whose MAC
addresses are in a list of addresses that you program into the gateway.
In this example we have gathered the computer's MAC address, which typically appears on
the wireless card (example: 00:0C:E5:45:C2:D8). In this example, that is the only system
that should be allowed to access the network:
1. Launch the gateway's Web interface if it is not already open. (Click here
how.)
2. Go to the MAC Filter option in the Security menu.
3. Select Allow these and click Add.
4. Enter the computer's MAC address.
to find out
5. Click Apply.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX11.141\tutor...
Page 29

Congratulations. You are finished. You may close the gateway's Web page.
第 2 頁,共 2 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Return to tutorial page
© 2004-2005 U.S. Robotics Corporation.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX11.141\tutor...
Page 30

第 1 頁,共 2 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway
User Guide
Home Installation Configuration Help
Tutorial: I want to prevent a machine from accessing
the Internet.
You need to use the gateway's outbound filtering feature. To demonstrate outbound filtering,
we will show steps to configure for the following scenario:
A company has two computers connected to the U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway.
An office worker uses one of the computers while the business owner uses the other. The
owner wants to keep the office worker from using the Internet. The owner has a computer
that has an assigned IP address of 192.168.1.2 by the gateway. The office worker's machine
has been assigned an IP address of 192.168.1.3.
1. Launch the gateway's Web User Interface if it is not already open (click here
out how).
2. Go to the Security menu and select IP Filtering - Outbound Filters.
3. Click Add.
4. In the following page, pick a name for your new filter and enter the IP address in
Source IP Address.
to find
5. When you click Apply, the new filter appears in this page.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX02.218\tutor...
Page 31

第 2 頁,共 2 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Congratulations! The outgoing address filter is complete. The computer with the IP address
entered in Address Filter will not be able to access the gateway's Internet port.
Return to tutorial page
© 2004-2005 U.S. Robotics Corporation.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX02.218\tutor...
Page 32

第 1 頁,共 3 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway
User Guide
Home Installation Configuration Help
Tutorial: I want to use an application over the
Internet (a game, instant messaging, etc.).
There are a number of applications now in which your computer needs to go onto the
Internet, but your gateway's firewall might block access. This procedure shows you how to
configure the gateway to work with these applications.
Note: For additional information on opening the firewall for other applications, refer to the
Appendix
section of this User Guide.
1. Select Virtual Servers from the Security menu. This page appears.
These are the fields on this page:
Field Description
Select a
service
In this item, choose the Internet application you want to
enable. The Web user interface automatically fills in values
in the table below.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX05.609\tutor...
Page 33

第 2 頁,共 3 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
If the service you want to enable is not in the service list,
Custom server
Server IP
address
External port
(start/end)
Protocol
Internal port
(start/end)
2. In Server IP address, enter the IP address of the machine that will run the Internet
application.
3. In the Select a service list, look for and select the name of the service or application
you want to use. If it is in the list, the settings fill in automatically:
enter its name here. You will need to enter the remaining
parameters as described in the service's documentation.
The IP address of your computer, which will function as a
server.
Allows the entry of an individual external port or range of
ports.
Allows the selection of a transport protocol (UDP, TCP, or
both).
Allows the entry of an individual internal port or range of
ports.
Note: If your service does not appear in the list, look in its documentation to find out
what settings to enter.
4. When you click Apply, the settings move to the previous page.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX05.609\tutor...
Page 34

Congratulations. You are now ready to run your Internet application.
第 3 頁,共 3 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Return to tutorial page
© 2004-2005 U.S. Robotics Corporation.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX05.609\tutor...
Page 35

第 1 頁,共 3 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway
User Guide
Home Installation Configuration Help
Tutorial: I want to give higher priority to some types
of traffic.
The gateway's quality of service (QoS) feature is executed in its IP software. It classifies
traffic according to the classification rules. Each rule may contain a combination of the
following conditions: protocol (TCP/UDP/ICMP), source IP address/subnet mask, destination
IP address/subnet mask, source port (one or range), destination port (one or range). The
result of matching a classification rule is to produce a priority (high, medium, low) and a type
of service (normal service, minimum cost, maximum reliability, maximum throughput,
minimum delay).
Example: Suppose your company hosts an Internet radio station. Lately, the quality of the
radio stream has not been very good since many people at the company are browsing the
Internet and using up the company's bandwidth. A good solution would be to set high priority
for the radio broadcast, and low priority on Web traffic. Here is how you could do it.
1. Access the gateway's Web user interface (WUI) by opening an Internet browser and
entering http://192.168.1.1
NOTE: If the browser does not open successfully, please go to the Troubleshooting
section.
2. Enter your user name and password. The default user name is admin, as is the default
password. Click OK or press ENTER. The WUI then opens.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX08.359\tutor...
Page 36

3. In the LAN menu, select Quality of Service.
4. The Quality of Service page appears:
第 2 頁,共 3 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
5. Click Add.
6. The first QoS entry will be for the HTTP Web traffic. In the page shown below, type the
name of the service in the field labeled Traffic class name. Next, set the Priority, IP
precedence, and IP type of service. In this example we are setting the priority to
Low because we are trying to improve the quality of the radio stream by limiting Web
traffic. Lastly, type in the Source port and Destination port. It should look like this
when you're done:
Click Apply to continue.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX08.359\tutor...
Page 37

第 3 頁,共 3 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
7. Click Add to select another network traffic class for Internet radio. Type the name of
the service in the Traffic class name field. Next, set the Priority, IP precedence,
and IP type of service. In this example, we are setting the priority to High and the
IP type of service to Maximize Reliability, since we are trying to improve the quality
of the radio stream. Lastly, type in the Source port and Destination port numbers
and click Apply.
8. This shows how we have configured QoS for maximum radio stream quality.
Return to tutorial page
© 2004-2005 U.S. Robotics Corporation.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX08.359\tutor...
Page 38

第 1 頁,共 2 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway
User Guide
Home Installation Configuration Help
Tutorial: I want to configure dynamic DNS.
Follow this procedure.
1. In the Web user interface, go to the Internet menu and select Dynamic DNS.
2. The Dynamic DNS page opens:
Click Add.
3. In the Dynamic DNS page, select a DNS provider. You can register at
www.dyndns.org
for no charge.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX11.734\tutor...
Page 39

第 2 頁,共 2 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
4. In the rest of the Dynamic DNS page, enter the settings given to you by the provider.
Click Add when you're done.
Return to tutorial page
© 2004-2005 U.S. Robotics Corporation.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX11.734\tutor...
Page 40

第 1 頁,共 5 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway
User Guide
Home Installation Configuration Help
Tutorials Troubleshooting Support Glossary
Troubleshooting
To help diagnose a problem, first use the following troubleshooting checklist.
1. Confirm that you are using the AC power adapter that came with your gateway and
that it is connected to the gateway and to an active wall outlet. Make sure the Power
switch is switched to the on position. The LED should be lighted.
2. Confirm that you have securely connected the telephone cable to the telephone wall
jack and to the gateway. The LED should be lighted if you have ordered and
correctly configured DSL.
3. If you are using a wired connection from the computer to the gateway, confirm that
you have secured the Ethernet cable(s) to the computer’s network interface card and
to the Ethernet port(s) on the gateway (labelled 1, 2, 3, or 4). The corresponding
LED should be lighted on the front of the gateway.
For more information on the LEDs, see the Status LEDs
section earler in this document.
Opening the Web user interface
The Web user interface will be your main tool for configuring, troubleshooting and monitoring
the gateway. Follow this procedure to access it.
1. Start a Web browser.
2. Open the page http://192.168.1.1 (If you’ve modified the gateway’s LAN IP address,
you must use the new one.)
3. A login window should appear:
The default user name and password are already filled in. Click OK.
4. The Web user interface opens with a status page.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX16.109\troub...
Page 41

第 2 頁,共 5 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
If you cannot access the Internet...
A number of devices have to work together for your computer to access the Internet.
NOTE: For completeness, the following drawing shows both wired and wireless connections
between your computer and your U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway. You’ll
normally use only one type of connection on each computer.
A. Your computer connects to your Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway via a wireless or wired
connection.
B. The gateway connects to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) via ADSL over the phone
network.
The first step in solving the problem is to diagnose the cause. There are a number of places
where the connection from your computer to the Internet might fail.
Windows users: You can check your connections automatically with the included utility
program.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX16.109\troub...
Page 42

第 3 頁,共 5 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
1. Use Windows Explorer to navigate to the Troubleshooting folder on your U.S.
Robotics installation CD-ROM (for example, D:\Troubleshooting, if your CD drive is
labeled D:).
2. Double-click on Troubleshoot_Connection.
This utility program tests your connections and, if there is a problem, tells you where it is.
Step 1: Can your computer connect to your Wireless MAXg
ADSL Gateway?
Open a Web browser to the gateway’s address: http://192.168.1.1 (Please note that if
you’ve modified the gateway’s LAN IP address, you must use the new one.)
If the gateway’s Web user interface appears, go to Step
need to be restarted:
1. With a thin tool such as a paper clip, briefly press the Reset button on the back of the
gateway.
2. Wait one or two minutes as the gateway restarts.
If you use a wired connection:
If you use a cable connection between your computer and the gateway, ensure that one end
of the Ethernet cable is connected to your computer’s LAN port and the other end is
connected to one of the Ethernet ports on the gateway. Also check that the corresponding
LED is lighted.
In the unlikely event that your computer is using a static IP address, either re-configure your
computer to use a dynamic IP address or ensure that its static IP address is in the same
network as the ADSL gateway. (That means that the IP address has the format 192.168.1.x
where x can be any number between 2 and 254, inclusive.)
Now, please restart your computer. It will attempt to connect to the gateway. Proceed to
Step 2
If you use a wireless connection:
.
3. Otherwise, the gateway may
1. Ensure that your computer is close enough to your gateway to receive a wireless signal
and that there is nothing interfering with the signal, such as a microwave oven or a
concrete wall.
If your gateway broadcasts its network name, you can use your computer’s wireless
utility to scan for it. (This is typically called a “site survey.”) If the utility cannot detect
the gateway, it may be a signal problem.
2. Ensure that the computer’s wireless utility is using the correct network name and
security settings for your gateway.
Settings such as network name, security method (WPA, WEP, etc.), and security keys
must all match. So if your gateway is using WPA encryption, each wireless card or
adapter must support WPA encryption. If you are using a wireless PC card, PCI
adapter, or USB adapter that does not support WPA encryption, you will not be able to
connect to the gateway unless you use WEP encryption instead. Please click here
information on changing the security settings.
for
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX16.109\troub...
Page 43

第 4 頁,共 5 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
3. If you have enabled MAC filtering on the gateway, is this computer permitted to
connect to your gateway?
Please note that MAC filtering refers to specific wireless adapters. If you use MAC
filtering and have added a new wireless adapter to the network, you must add the MAC
address of the new wireless adapter to the gateway.
NOTE: If you need to modify the ADSL gateway’s settings, you’ll need a computer with a
wired connection to the gateway in order to access it.
If these steps fail to establish a wireless connection, please try a wired connection between
your computer and your gateway. Connect the yellow Ethernet cable to your computer’s LAN
port and to a LAN port on the gateway. Then ensure that the corresponding LAN port LED is
lighted. Then please restart your computer.
Step 2: Is your Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway responding?
Open your Web browser to the gateway’s address: http://192.168.1.1
NOTE: If you can open the gateway’s Web user interface with a wired connection but not
with a wireless connection, the problem is with the wireless connection. Please see the
documentation for your wireless adapter.
If the gateway’s Web user interface appears, please go to Step 3
If the gateway’s Web user interface doesn’t appear, the gateway may need to be restored to
the default factory settings. (Please note that you will lose all of your gateway’s custom
settings and will need to set it up again as if you were installing it for the first time. If you’ve
made a backup of the settings, you will be able to restore them. Please click
information.)
1. With a thin tool, such as a paper clip, press the Reset button on the back of the
gateway for at least five seconds.
2. Wait about one or two minutes as the gateway restarts.
3. Please restart your computer so that it will connect to the gateway.
4. Try to access the gateway’s Web address at http://192.168.1.1
If the gateway's Web user interface still does not appear, the firmware and/or default factory
settings may have been corrupted. To find out, follow these steps:
.
here for more
1. Press and hold down the Reset button on the back of the gateway for more than 30
seconds.
2. Assign a static IP address to your computer, in the same subnet as your gateway's
management IP address. (For example, the default management IP address for your
gateway is 192.168.1.1. The computer IP address can be 192.168.1.5, subnet mask
255.255.255.0, and gateway IP address 192.168.1.1.)
3. Open a browser and try to open the http://192.168.1.1 address again. If anything
opens, follow the on-screen instructions to re-load the firmware. You will need to get a
new firmware file from your Internet Service Provider or from the www.usr.com Web
site.
4. Close the Web browser and return your computer to a dynamic IP address.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX16.109\troub...
Page 44

第 5 頁,共 5 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
If the gateway’s Web user interface still does not appear, the gateway may have failed.
Please contact U.S. Robotics Customer Support. See the contact information
section of this guide.
in the Help
If the gateway’s Web user interface appears, please continue to Step 3
.
Step 3: Can your Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway connect to the
Internet?
If you have a connection between your computer and your gateway, it’s likely that the
gateway is not connected to the Internet.
1. Close your Web browser and run EasyConfigurator.
Windows users:
Press Start, then select Programs and U.S. Robotics EasyConfigurator.
Macintosh and Linux users:
Double-click the EasyConfigurator icon on the desktop.
2. Click Status at the top of the page, and check the value of the Status field.
Sample image of a gateway connected to the Internet:
Sample image of a gateway not connected to the Internet:
If the status is CONNECTED or CONNECTED TO THE INTERNET but you still cannot
access the Internet, please contact your ISP for assistance.
Otherwise, you need to configure your ADSL connection. Please click Configuration at
the top of the EasyConfigurator window and go here
configure your ADSL connection.
© 2004-2005 U.S. Robotics Corporation.
for information on how to
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX16.109\troub...
Page 45
第 1 頁,共 2 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway
User Guide
Home Installation Configuration Help
Tutorials Troubleshooting Support Glossary
Technical Support
For current product support and contact information, go to the U.S. Robotics Web site
at: http://www.usr.com/support
experience have been addressed in the site's FAQ and troubleshooting pages for your
specific product.
If you can't connect to the Internet, contact your ISP for assistance.
Many of the most common difficulties users
If your ISP is unable to help you and you still cannot connect to the Internet, contact
the U.S. Robotics Technical Support department. You can submit your technical
question using an online form at http://www.usr.com/emailsupport or you can
call the Technical Support department.
Country Voice Online Support Hours
United
States
Canada (888) 216-2850 http://www.usr.com/emailsupport
Country Telephone Online Hours
Austria
Belgium
(Flemish)
(French)
(888) 216-2850 http://www.usr.com/emailsupport
07110 900
116
+32 (0) 7
023 3545
(Flemish)
+32 (0) 7
023 3546
(French)
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/de
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/ea
9:00 A.M. - 5:00
P.M., Monday Friday Central
9:00 A.M. - 5:00
P.M., Monday Friday Central
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
Denmark
Finland
France
Germany
+45 70 10
4030
+358
981710015
+33 082
507 0693
0180 567
1548
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/uk
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/ea
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/fr
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/de
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
10:00 - 18:00
Monday - Friday
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX22.406\supp...
Page 46

第 2 頁,共 2 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Hungary
Ireland
Italy
Luxembourg
Middle
East/Africa
Netherlands
Norway
Poland --- http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/pl
Portugal
Russia
0180 567
1548
1890-252130
+848 80
9903
+352 342
080 8318
+44 870
844 4546
0900 202
5857
+47 23 50
0097
+351 (0)
21 415
4034
8-800200200-1
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/hu
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/uk
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/it
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/bn
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/me
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/ea
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/ea
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/pt
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/ru
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
9:00 - 18:00
Monday - Friday
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
10:00 - 18:00
Monday - Friday
Spain
Switzerland
Sweden
United
Kingdom
© 2004-2005 U.S. Robotics Corporation.
902 117
964
0848 840
200
+46 (0) 77
128 1020
0870 844
4546
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/es
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/de
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/ea
http://www.usr.com/emailsupport/uk
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
9:00 - 17:00
Monday - Friday
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX22.406\supp...
Page 47

第 1 頁,共 9 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway
User Guide
Home Installation Configuration Help
Tutorials Troubleshooting Support Glossary
Glossary
A | B | C | D | E | F | GH | IJKL | M | NO | P | QR | S | TU | V | WXYZ
A
ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) - Transports information to and from
customers and networks. ADSL employs different upstream and downstream data rates. The
“asymmetric” name refers to these differing rates.
AH (Authentication Header) – RFC2402 defines AH. AH provides integrity and
authentication through the shared key hashing algorithms (HMAC-MD5, HMAC-SHA1). AH
provides authentication for as much of the IP header as possible. AH also authenticates
upper level protocol data.
AM (Amplitude Modulation) Modulation method used by modems, radio, and DSL
equipment. The signal modulates or alters the amplitude or intensity of the carrier. In regular
AM, the carrier is a sinewave. The amplitude of the modulated carrier changes in proportion
to signal amplitude. AM creates two identical sidebands on either side of the carrier. These
sidebands contain the signal data. Either sideband can be attenuated or suppressed without
harming the signal data. With an equivalent signal, AM tends to require less bandwidth than
FM does. AM's disadvantage is that it's more subject to impulse noise and static than FM is.
Application Level Gateway (ALG) - Some applications embed IP addresses within the IP
payload. The U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway supports several ALGs, each
addressing a special application. The ALG replaces the private IP Address embedded within a
particular application payload.
ATM(Asynchronous Transfer Mode) - Protocol that packs digital information into 53-byte
cells. The cells switch throughout a network over virtual circuits.
Average Cell Rate - Maximum sustainable or average rate (cells/second) for sending cells
to the network. Average Cell Rate specifies bandwidth utilization. This value must always be
less than or equal to Peak Cell Rate.
B
Bandwidth - Amount of data that can be transmitted over a given time period.
BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) - Data messages exchanged across switches in an
extended LAN with a spanning tree protocol topology. BPDU packets assure that data arrives
at the intended destination. These packets contain information on addresses, costs, ports,
and priorities. Network loop detection involves exchanging BPDU messages across bridges.
Loop deletion entails placing redundant switch ports in a backup (blocked) state and shutting
down selected bridge interfaces.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX57.500\gloss...
Page 48

第 2 頁,共 9 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Bridge – A device that connects two LAN segments together. These LAN segments may be
of similar or dissimilar types, such as Ethernet and Token Ring. Inserting a bridge into a
network segments the network. The bridge improves performance by keeping traffic
contained within bridge segments.
Bridge Loop - Path that links one network segment to another. The spanning tree protocol
avoids bridge loops.
Bridge Priority - Determines which bridge becomes the root bridge.
Burst Size (Cells) - Maximum number of cells that the user can send at peak rate in a
burst. We measure burst size from within a sustainable rate.
C
CAP (Carrierless Amplitude and Phase Modulation) Modulation method used by
modems and DSL equipment. Based on QAM. Signals modulate two wideband signals using
passband modulation. CAP permits two to nine bits per frequency cycle.
Carrier wave - Periodic waveform. A carrier may be modulated or unmodulated. It may also
be continuous or switched. Typically, modems modulate the carrier wave with a data signal.
Modulation represents the data signal by impressing a variation on some characteristic of the
carrier wave. For instance, a circuit may represent the signal as a proportional shift in carrier
amplitude, frequency, or phase. Demodulation (detection) eliminates the carrier wave and
reproduces the signal. The carrier frequency must be significantly greater than the signal
frequency. A modem may simultaneously apply more than one signal and more than one
modulation method to the same carrier. The modulation method may suppress the carrier
before transmission. In that case, the receiver must reinsert the carrier before demodulation
can occur.
CBR (Constant Bit Rate) - Service type that supports real-time applications with a fixed
bandwidth. These applications, such as a video stream, produce data at regular intervals.
The user can specify how much bandwidth that he wishes to reserve.
CDVT (Cells) - Parameter that constrains the number of cells that the user can send to the
network at the maximum line rate.
Cycle - One half of a periodic wave. For instance, a sinewave includes one positive and one
negative cycle.
D
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - Protocol for automatic TCP/IP
configurations. DHCP provides static and dynamic address allocation and management.
DHCP Relay - Suppose that a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server resides on
a different LAN than the node broadcasting for DHCP service. Then the DHCP broadcast
request must be forwarded across the gateway/WAN to a subnet where a DHCP server
resides. To assure receipt of an IP address that corresponds to this subnet, the gateway
must use a DHCP relay. The gateway needs to know the IP address of the DHCP server. With
this address, the gateway can direct the request to the appropriate DHCP server.
DMT (Discrete Multitone) - Most common DSL modulation method. DMT creates 256
channels across the usable frequency spectrum. Each channel measures 4.3125KHz wide.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX57.500\gloss...
Page 49

第 3 頁,共 9 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Dividing the spectrum into channels allows DMT to function well in spite of nearby AM radio
transmitters. The DMT modulator and demodulator is the FFT (Fast Fourier Transform)
algorithm. Inside each channel, the modulation technique is QAM. Within each channel, the
number of bits per symbol may be independently selected. Independent selection allows a
DMT modem to be rate adaptive. Both G.DMT and G.Lite use DMT.
DNS (Domain Naming System) - Mechanism used in the Internet for translating names of
host computers into IP addresses.
DNS Relay - DNS requests that the gateway forwards from a LAN node to a known DNS
server. The gateway uses a DNS relay when the gateway functions as a NAPT (Network
Address Port Translation) device. The requests arrive at a DNS server over the WAN link. To
function as a NAPT, the gateway requires DNS relay settings.
DSLAM (Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer) - Network device that receives
signals from multiple customer Digital Subscriber Line connections. DSLAM places signals on
high speed lines with multiplexing techniques for the fastest phone line technology available.
E
ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) – ESP provides confidentiality. Optionally, ESP also
provides integrity, authentication, anti-replay service, and limited traffic flow confidentiality.
Options selected at the time of Security Association establishment determine provided
services. For confidentiality, shared ESP supports shared key encryption algorithms, such as
DES and Triple DES.
F
Filter - Operating parameter used in LAN bridges and gateways. When set, the filter causes
bridges and gateways to block transfer of packets between LANs. The term "filter" also
applies to a hardware device, such as a microfilter. When installed, this device reduces
interference between DSL signals and telephone signals.
Forward Delay Time - Timeout value employed by all bridges in the bridged LAN. The root
sets the forward delay value.
FM (Frequency Modulation) Modulation method used by modems, radio, and DSL
equipment. The signal modulates or alters the frequency or pitch of the carrier. In regular
FM, the carrier is a sinewave. The frequency of the modulated carrier changes in proportion
to signal amplitude. FM creates an infinite number of sidebands. These sidebands contain the
signal data. With an equivalent signal, FM tends to require more bandwidth than AM does.
FM's advantage is that it's less subject to impulse noise and static than AM is.
Frame - Variable length information unit that contains packets. Also refers to a transmission
frame, a fixed-length unit that carries bits across a physical link. A transmission frame is a
framed transport component. DSL technologies use frames. Also refers to a frame of video,
one image in a video sequence
G
Gateway - Entrance to and exit from a communications network.
G.DMT - The ADSL standard approved by the International Telecommunications Union (ITU).
G.DMT indicates full-rate ADSL, which provides standards for higher speed ADSL than G.Lite.
G.DMT provides maximum data rates of 8 Mbps downstream from the subscriber and 1.5
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX57.500\gloss...
Page 50

第 4 頁,共 9 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Mbps upstream from the subscriber.
G.lite - Standard way to install Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line service. Over regular
phone lines, G.Lite makes possible Internet connections to home and business computers at
up to 1.5 Mbps. Officially known as G.992.2.
H
Hello Time - Time interval between generations of configuration BPDUs. The root bridge
generates configuration BPDUs.
I-J-K
ICMP - (Internet Control Message Protocol) - A TCP/IP protocol for sending error and
control messages. For example, a gateway uses ICMP to notify the sender that the gateway's
destination node is unavailable. A ping utility sends ICMP echo requests to verify the
existence of an IP address.
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) - Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
(IANA) uses three blocks of IP address space, namely 10.0.0.0/8 (class-A) 172.16.0.0/ 12
(class-B), and 192.168.0.0/16 (class-C) for private internets.
Interface Name - Gateway interface that will be configured.
IP (Internet Protocol) - Protocol that allows a packet of information to travel through
many networks and LANs.
IP Address - IP addresses deliver packets of data across a network. These addresses
differentiate the source and destination IP address and keep them constant. When a gateway
port detects a packet, the gateway checks the routing table. The port attempts to match the
network number of the destination IP address with its routing table entry. If the port finds a
match, it forwards the packet to the destination network. With no match, the port forwards
the packet to a gateway defined as the default gateway.
L
LAN (Local Area Network) - Network base covering a local geographic area. A LAN
connects computers in the same building or area.
Link Cost - Cost associated with the interface. Based on this cost, the bridge decides which
link to forward data over.
M
MAC Address (Local Area Network) - Unique serial number burned into Ethernet
adapters. Distinguishes the network card from others.
Max Age Time Timeout value that all bridged LAN bridges use. The root bridge sets the Max
Age value.
MAC Filter (Local Area Network) - Method of allowing or rejecting WAN access for specific
machines.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX57.500\gloss...
Page 51

第 5 頁,共 9 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Microfilter - Device that separates the ADSL data signal from the telephone signal so that
the ADSL data signal does not interfere with the telephone device.
Modulation - Varying elements of electrical carrier waves in a manner that represents signal
data. Demodulation restores the signal data. A modulated signal requires more bandwidth
and an unmodulated signal does. The bandwidth increase results from the creation of
sidebands during modulation. The sidebands contain the signal. AM creates two, identical
sidebands on either side of the carrier. FM creates an infinite number of sidebands.
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) - Parameter that limits the size of packets that
transmit on an interface. Not all interfaces support the MTU parameter. Some interfaces, like
Ethernet, have range restrictions (80 - 1500).
N-O
NAP (Network Access Point) - Public network exchange facility where ISPs connect while
peering. NAP connections determine how the Internet routes traffic.
Network Address Port Translation (NAPT) - Network Address Port Translation (NAPT)
translates multiple private IP addresses and their LAN side TCP/UDP ports, into a single
public IP address on the WAN side and its TCP/UDP ports. This is necessary as private IP
addresses are not valid nor routable in the public network.
Many homes and small offices have multiple PCs or network devices. Using private IP
addresses and NAPT in the U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway, multiple LAN devices
can access remote networks or the internet with just one public IP address assigned by their
ADSL service provider.
When configuring the gateway for PPPoE or PPPoA operating mode, NAPT is always
automatically enabled. For MER or IPoA operating mode, there is an option available to
enable or disable the NAPT.
For any IP packet sent to the WAN, the NAPT function replaces the source private IP address
in the IP header with the public IP address of the WAN interface, and replaces the TCP/UDP
source port number with a unique port number. Vice versa, it translates the destination
public IP address and the destination port number within the IP packet received from the
WAN interface back to the originating PC's private IP address and it's original TCP/UDP port
number.
Next Hop IP - IP address or Gateway used to arrive at the destination address.
NRT-VBR (Non Real Time-Variable Bit Rate) - Service type that supports applications
that have no constraints on delay and delay variation, but still have variable-rate and burst
traffic characteristics.
P
PAM (Pulse Amplitude Modulation) Modulation method used by modems and DSL
equipment. The signal modulates or alters the amplitude or intensity of the carrier. In regular
AM, the carrier is a sinewave. In PAM, the carrier is a periodic series of DC pulses.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX57.500\gloss...
Page 52

第 6 頁,共 9 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) - Digital modulation method for transmitting analog data.
PCM signals are binary. These signals can represent any analog data with only two states,
logic 0 and logic 1.
PDM (Pulse Duration Modulation) Modulation method. Signal modulates or alters the
duty cycle of the pulse. In PDM, the carrier is a pulse stream. Also called PWM (Pulse Width
Modulation).
Peak Cell Rate - Maximum rate (Cells/second) for sending cells to the network.
Phase - Position of a periodic waveform.
PM (Phase Modulation) Modulation method used by modems, radio, and DSL equipment.
The signal modulates or alters the phase or position of carrier waves. In regular PM, the
carrier is a sinewave. The phase of the modulated carrier changes in proportion to signal
amplitude.
Port Priority - Parameter that determines which port becomes the root bridge port.
POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) - Basic voice service available in residences
throughout the United States.
PP (Point-to-Point Protocol) – Communication protocol for dialing up the Internet over a
serial link. Such serial links include a POTS and an ISDN line. PPP establishes the session
between the user's computer and the ISP. PPP uses the Link Control Protocol (LCP), which
also handles authentication (PAP, CHAP, etc.), compression, and encryption.
PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) Modulation method used by modems and DSL
equipment. The signal modulates or alters the location of a pulse in the carrier. The carrier is
a stream of pulses.
PPPoA (Point-to-Point Over ATM) – Dial-up Internet connections typically use PPP
protocol. PPPoA is a method for running PPP protocol over ATM. PPPoA… ·
· offers service providers similar billing and access control with a presence in dial-up services.
· provides session authentication using Password Authentication Protocol (PAP).
· provides session authentication using Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP).
· achieves session accounting and conservation of bandwidth by closing down unused
sessions.
· allows the IAD/Gateway and ISP link to easily negotiate network parameters.
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Over Ethernet) – Dial-up Internet connections typically use PPP
protocol. PPPoE is a method for running PPP protocol over Ethernet. PPPoE… ·
· offers service providers similar billing and access control with a presence in dial-up services.
· provides a low-cost solution to multiple host maintenance at the customer premises.
· provides session authentication using Password Authentication Protocol (PAP).
· provides session authentication using Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP).
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX57.500\gloss...
Page 53

第 7 頁,共 9 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
· achieves session accounting and conservation of bandwidth by closing down unused
sessions.
· allows the IAD/gateway and ISP link to easily negotiate network parameters.
PVC (Permanent Virtual Circuit) - Virtual connection between two fixed endpoints on the
network. Frame relay and ATM networking term.
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) Modulation method. Signal modulates or alters the duty
cycle of the pulse. In PWM, the carrier is a pulse stream. Also called PDM (Pulse Duration
Modulation).
Q
QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) Modulation method used by modems and DSL
equipment. Combines two amplitude-modulated (AM) signals into a single channel. The
modem inserts the signals 90 degrees (one-quarter cycle) out of phase with each other.
Engineers call this 90-degree phase shift "quadrature." QAM modulates both carrier phase
and amplitude. Doubles effective bandwidth.
R
RAM (Random Access Memory) - Primary memory in a computer. The computer can
overwrite this type of memory with new data. The "random access" part of RAM derives from
the way RAM stores data: The computer can locate any bit of information in RAM in an equal
amount of time. This fact applies regardless of where the bit resides.
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) - Routing protocol and part of the TCP/IP suite. RIP
determines a route based on the smallest hop count between source and destination. RIP
determines the smallest hop count by communicating with other gateways within the
network. Only use RIP if the target gateway also utilizes RIP.
RJ-11 - Six-conductor modular telephone jack wired for up to four wires. The most common
telephone jack in the world is the RJ-11. This connects telephone instruments, modems, and
fax machines to a female RJ-11 jack. The female jack often mounts to the wall or floor.
RJ-45 - Eight-conductor modular telephone jack. Used for 10BaseT, ISDN and other data
connections.
Router - Device that forwards data packets between local area networks (LANs) or wide area
networks (WANs). Referring to routing tables and routing protocols, routers read the network
address in each transmitted packet. Routers then decide where to send the packet. A router
bases this decision on the best route. When a router port detects a packet, the router checks
the routing table. The port attempts to match the network number of the destination IP
address with its routing table entry. If the port finds a match, it forwards the packet to the
destination network. With no match, the port forwards the packet to a router defined as the
default gateway.
RT-VBR (Real Time-Variable Bit Rate) - Service type that supports time-sensitive
applications such as voice. Varies the rate at which cells arrive.
S
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX57.500\gloss...
Page 54

第 8 頁,共 9 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
Sideband - Band of frequencies adjacent to the carrier. Modulation of the carrier creates
sidebands. The sidebands contain the signal data, but consume bandwidth beyond what the
carrier needs. In some cases, circuitry may suppress duplicate sidebands without harming
the signal data. For instance, AM becomes single sideband when circuits delete one of two
identical AM sidebands. Some single sideband equipment also suppresses the carrier
frequency. The carrier must then be restored at the receiver before the signal can be
demodulated, that is, recovered.
Spanning Tree-Bridging - Particular algorithm or formula. Transparent bridges use the
spanning tree algorithm to dynamically determine the best source-to-destination path. This
algorithm avoids bridge loops (multiple paths that link one segment to another) within a
network. The algorithm determines all redundant paths and makes only one of them active.
The spanning tree protocol (STP) is part of IEEE standard 802.1.
Splitter - DSL device that accommodates analog telephones, plus digital data access over
the Internet. With a splitter, analog voice signals transmit at baseband frequencies. These
combine with passband data transmission through a low-pass filter.
Static routes - Permanent routes that the gateway stores. The gateway uses these routes
when determining where to forward IP packets that it receives.
Subnet Mask - Portion of a network. Distinguished from other portions by the use of a mask
or subnet number. Subnet masks split one network into a set of mini networks or subnets.
Subnetting helps to reduce traffic on each subnet. Subnetting also makes the network more
manageable. Each subnet functions as if it were an independent network.
SVC (Switched Virtual Circuit) - Virtual connection between two variable endpoints on the
network. The switch makes at the beginning of the call, and breaks at the end of the call. A
frame relay and ATM networking term.
T
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) - Set of protocols designed
to link dissimilar computers that use various networks and LANs.
Topology - Geometric physical or electrical configuration that describes a local
communication network. The most common distribution system topologies are the bus, ring,
and star.
U
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) - A protocol within the TCP/IP protocol suite. When
reliable delivery is unnecessary, communications may use UDP instead of TCP.
UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate) - Best effort service that does not require tightly constrained
delay and delay variation. UBR provides no specific quality of service or guaranteed
throughput.
UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) - With UPnP enabled in the U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg
ADSL Gateway, all UPnP aware applications running in the LAN-devices with UPnP (such as
Windows XP) can pass through the NAPT. The ADSL gateway will perform DNS relay function
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX57.500\gloss...
Page 55

第 9 頁,共 9 頁U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg ADSL Gateway User Guide
only if NAPT is enabled.
USB (Universal Serial Bus) - External bus standard that supports data transfer rates of 12
Mbps.
V
VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier) - Address of a virtual circuit. An integer that ranges from
0 to 65,535. The integer identifies a virtual channel that cells may traverse.
VPI (Virtual Path Identifier) - Address of a virtual path to a connection on an ATM
network. An integer that ranges from 0 to 4,095.
W
WAN (Wide Area Network) - Network base that covers a large geographic area.
WINS (Windows Internet Name Service) - Service that transposes Windows networking
names into addresses usable for routing purposes.
© 2004-2005 U.S. Robotics Corporation.
2005/7/4file://C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\ivonne\Local%20Settings\Temp\Rar$EX57.500\gloss...
 Loading...
Loading...