
I
UBCT9 Scanner
250 Channels
12 Bands
Programmable
Trunk Tracker lll
with Close Call RF Capture
UBCT9 OM 1 12/11/07 3:52:21 PM
Precautions
Before you use this scanner, please observe the following:
WARNING!
Uniden does not represent this unit to be waterproof. To reduce the risk of re,
electrical shock, or damage to the unit, do not expose this unit to rain or moisture.
IMPORTANT!
• Changes or modications to this product not expressly approved by Uniden,
or operation of this product in any way other than as detailed by this Operating
Guide, could void your authority to operate this product.
• The screen displays used in this manual are representations of what might
appear when you use your scanner.
UBCT9 OM 1 12/11/07 3:52:22 PM
I
Contents
Introduction ............................................................................................................................................1
Front and Rear Views ............................................................................................................................2
Icon Display ...........................................................................................................................................3
Terminology ...........................................................................................................................................4
What is Scanning? ..........................................................................................................................
4
What is Searching? .........................................................................................................................
4
What is Trunk Tracking? ..................................................................................................................
4
Feature Highlights .................................................................................................................................6
Included with Your Scanner Package ....................................................................................................7
Optional Accessories .......................................................................................................................
7
Installing the UBCT9..............................................................................................................................8
For Home Use (Desktop Installation) ..............................................................................................
8
For Mobile Use (In-Car Installation) ................................................................................................
8
Typical Mounting Methods ............................................................................................................
10
Mounting the Scanner in Your Vehicle ..........................................................................................
10
Applying Power for Vehicle Installation .........................................................................................
11
Applying Power Using Standard AC Power ..................................................................................
12
Connecting an External Speaker ..................................................................................................
12
Listening Safely .............................................................................................................................
12
Connecting the Clone Cable .........................................................................................................
12
Scanning Overview..............................................................................................................................13
Turn the Scanner On .....................................................................................................................
13
How Squelch Works ......................................................................................................................
14
Setting the Squelch .......................................................................................................................
14
State Scanning ....................................................................................................................................15
Selecting the State ........................................................................................................................
15
State Scan Hold ............................................................................................................................
16
Storing State Scan Frequency ......................................................................................................
16
Skip a Frequency.
..........................................................................................................................16
Close Call RF Capture.........................................................................................................................17
Set Close Call Mode .....................................................................................................................
17
Close Call Operation .....................................................................................................................
18
Set Close Call Option ....................................................................................................................
19
Select Close Call Bands ................................................................................................................
19
Set Close Call Alert .......................................................................................................................
20
Setting of Pager screen .................................................................................................................
20
Alert Tone Volume .........................................................................................................................
20
Alert Light Adjustment ...................................................................................................................
20
Private Bank Scanning ........................................................................................................................21
Programming Frequencies into Channels .....................................................................................
21
Deleting a Stored Frequency ........................................................................................................
21
Duplicate Frequency Alert .............................................................................................................
22
Memory Lock .................................................................................................................................
22
Scanning Private Bank ..................................................................................................................
22
Hold/Resume ................................................................................................................................
23
Channel Lockout ...........................................................................................................................
23
Restoring a Locked-out Channel in Hold Mode ............................................................................
23
Restoring All Locked-out Channels ...............................................................................................
24
Priority Scan ..................................................................................................................................
24
Changing the Priority Channel ......................................................................................................
24
Service Scanning.................................................................................................................................25
Band Search ........................................................................................................................................26
Setting a Search Band .................................................................................................................
26
UBCT9 OM 1 12/11/07 3:52:22 PM
II
Search Hold Feature .....................................................................................................................27
Data Skip .......................................................................................................................................
27
Frequency Skip .............................................................................................................................
27
Storing Search Frequencies ..........................................................................................................
28
Delay .............................................................................................................................................
28
Trunk Tracking .....................................................................................................................................29
Setting the Squelch ......................................................................................................................
29
Programming Trunking Frequencies ..................................................................................................30
STEP 1: Selecting Trunking System Type ....................................................................................
30
STEP 2: Programming Trunking Frequencies ..............................................................................
31
Programming Talk Group ID/Scan Lists .......................................................................................
31
Scan Lists .....................................................................................................................................
31
Receiving Trunked Systems .........................................................................................................
33
ID Scan Mode ..............................................................................................................................
33
ID Scan Hold Feature ...................................................................................................................
34
ID Search Mode ...........................................................................................................................
34
ID Monitor Mode ...........................................................................................................................
35
ID Search Hold and Direct Entry ID in Hold Mode .......................................................................
35
Programming Scan Lists During Search ......................................................................................
35
Deleting a Stored ID .....................................................................................................................
35
ID Lockout ....................................................................................................................................
36
Review ID Lockout .......................................................................................................................
36
Restoring Locked-out ID’s ............................................................................................................
36
Setting the Delay Mode for Trunking Mode ..................................................................................
37
Trunking Frequency Conrmation ................................................................................................
37
Setting Priority in Trunking Mode .................................................................................................
37
Moving between Scan List Memories ..........................................................................................
37
Multi-Track ....................................................................................................................................
38
EDACS ® Reception ...........................................................................................................................39
EDACS
®
Tracking ........................................................................................................................39
Programming EDACS
®
System Frequencies ..............................................................................39
An EDACS
®
Trunked system ......................................................................................................40
Special EDACS
®
Features ..........................................................................................................41
EDACS
®
ID Range Search ..........................................................................................................41
EDACS
®
SCAT ............................................................................................................................41
LTR ® Reception .................................................................................................................................42
LTR
®
Tracking .............................................................................................................................42
Motorola Reception ............................................................................................................................43
Motorola Tracking .........................................................................................................................
43
Fleet Map Programming ...............................................................................................................
44
Selecting Preset Fleet Map ..........................................................................................................
44
Programming a User Fleet Map ...................................................................................................
44
Programming a Hybrid System ....................................................................................................
45
Setting the Base, Spacing Frequencies and Offset Channel for Motorola
VHF/UHF Trunked Systems ...................................................................................................
45
Toggling the Status Bit .................................................................................................................
46
Control Channel Only Mode .........................................................................................................
46
Disconnect Tone Detect Option (End Code) ................................................................................
47
Remote Interface ................................................................................................................................48
PC Control Mode ..........................................................................................................................
48
Clone Mode ..................................................................................................................................
49
Care and Maintenance .......................................................................................................................52
Troubleshooting ..................................................................................................................................53
Specications .....................................................................................................................................55
Appendix .............................................................................................................................................56
One Year Limited Warranty ................................................................................................................63
UBCT9 OM 2 12/11/07 3:52:23 PM
1
Introduction
The UBCT9 is a state-of-the-art Trunk Tracking Scanner with Bear Tracker
technology. It can store 250 frequencies such as police, re/emergency, marine,
railroad, air, amateur, and other communications into 5 banks of 50 channels for a
total of 250 channels.
Use your new scanner to monitor:
• Close Call ™ RF Capture
• Police
• Trunking for:
Motorola
Type I
Type II
Type II: (Hybrid)
EDACS
Wide band
Scat
LTR
• Business/Industrial Radio
• Utilities
• Marine Band
• Aircraft Band
• And much more...
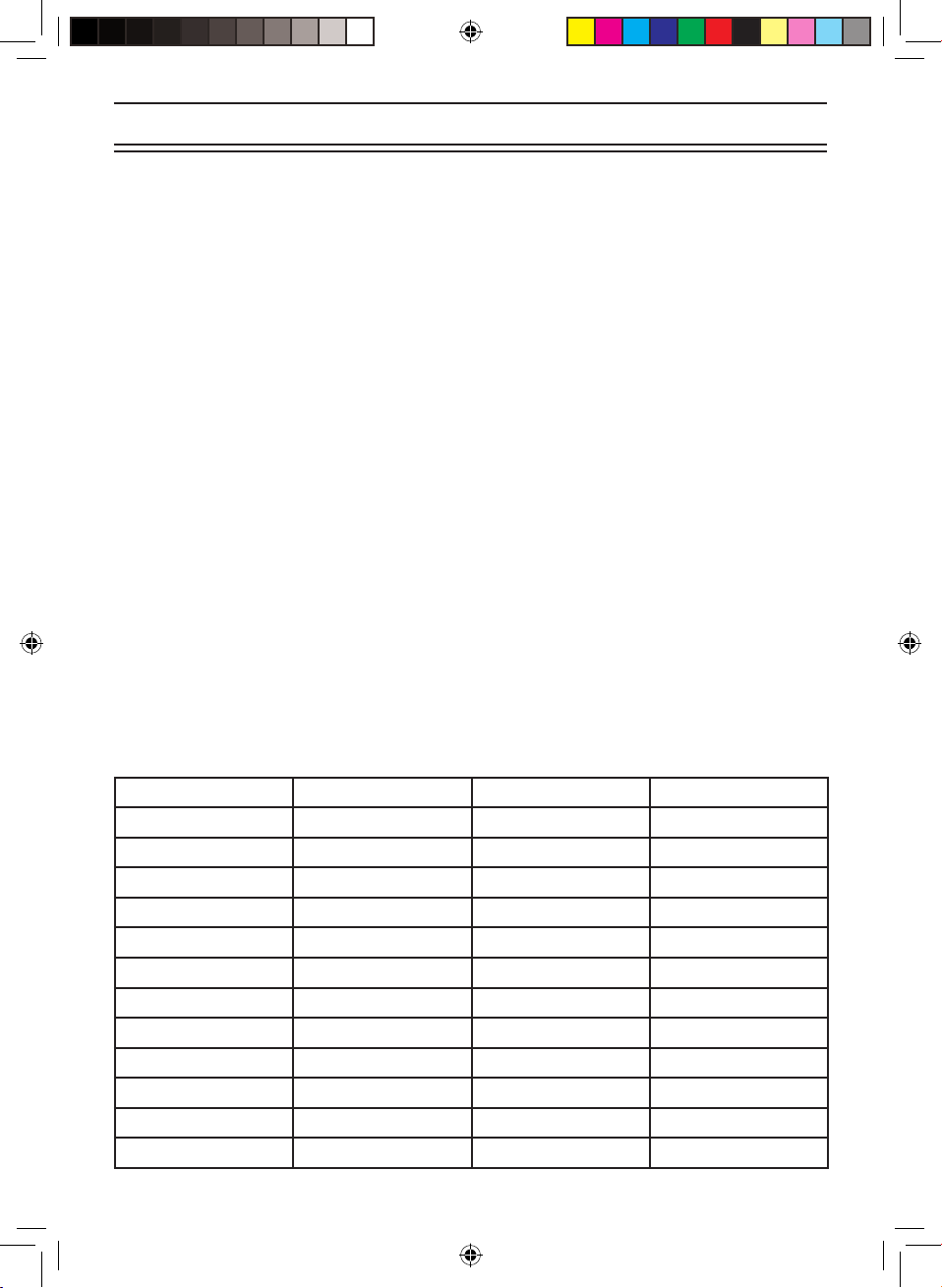
The chart below identies the scanner band numbers, the frequency range, the
modulation mode and the default step size settings.
No Range (Mhz) Mode Step
1
0025.0000 - 0027.9950
AM 5kHz
2
0028.0000 - 0069.9900
FM 10kHz
3
0070.0000 - 0087.9875
FM 12.5kHz
4
0088.0000 - 0107.9000
WFM 100kHz
5
0108.0000 - 0136.9875
AM 12.5kHz
6
0137.0000 - 0147.9950
FM 5kHz
7
0148.0000 - 0173.9875
FM 12.5kHz
8
0174.0000 - 0224.9500
WFM 50kHz
9
0225.0000 - 0399.9500
AM 50kHz
10
0400.0000 - 0512.0000
FM 6.25kHz
11
0806.0000 - 0956.0000
FM 12.5kHz
12
1240.0000 - 1300.0000
FM 12.5kHz
UBCT9 OM 1 12/11/07 3:52:23 PM
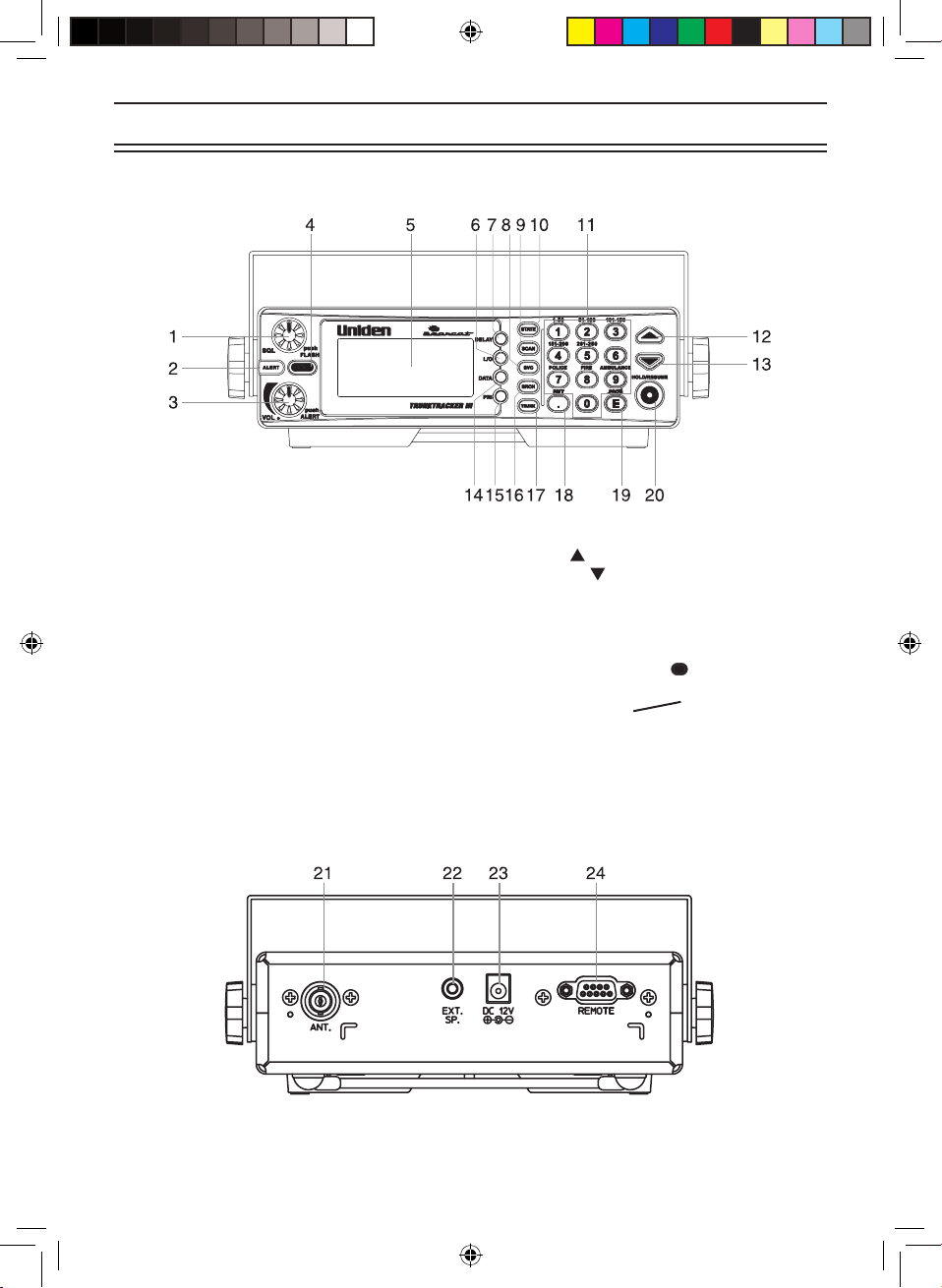
2
1. Squelch Control / Flash Brightness
Selector (SQL, FLASH)
2. Alerting Light (ALERT)
3. Volume Control / Alert Tone Selector (VOL)
4. Close Call RF Capture (C.C.)
5. Display (window)
6. Lockout Key (L/O)
7. Delay Key (DELAY)
8. Service Key (SVC)
9. State Scan or Private Scan Key (SCAN)
10. State Key (STATE)
11. Numeric Keypad
12. Up Key ( )
13. Down Key ( )
14. Data Key (DATA)
15. Priority Key (PRI)
16. Search Key (SRCH)
17. Trunk Key (TRUNK)
18. Decimal/Remote Key ( , RMT)
19. Enter / Program Enable
- Disable Key (E, PROG)
20. Hold/Resume Key (HOLD/RESUME)
Front and Rear Views
21. Antenna Connector (ANT.)
22. External Speaker Jack (EXT. SP.)
23. DC Power Jack (DC 12V)
24. Remote Control Terminal (REMOTE)
UBCT9
UBCT9 OM 2 12/11/07 3:52:25 PM
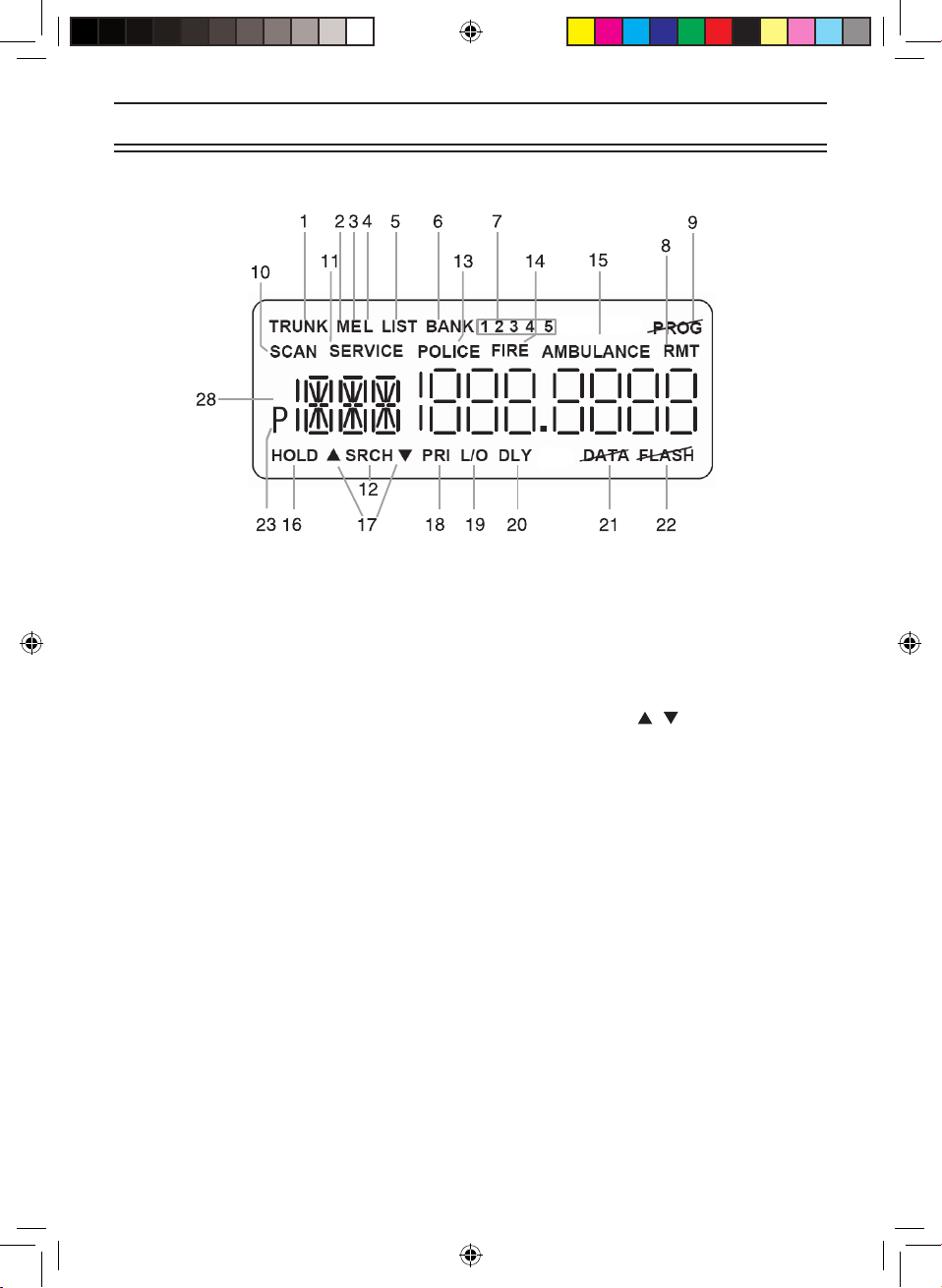
3
1. Trunk Tracking Mode (TRUNK)
2. Motorola trunking channel (M)
3. EDACS trunking channel (E)
4. LTR trunking channel (L)
5. Scan list (LIST)
6. Scan bank (BANK)
7. Bank’s number and ID’s list
number (1 2 3 4 5)
8. Remote control mode (RMT)
9. Programming is locked (PROG)
10. State scanning and Private scanning
mode (SCAN)
11. Service scanning mode (SERVICE)
12. Band searching mode (SRCH)
13. POLICE Bank included with State
scanning (POLICE)
14. FIRE Bank included with State
scanning (FIRE)
15. AMBULANCE Bank included with
State scanning (AMBULANCE)
16. Scanning or the searching is on hold (HOLD)
17. Search direction ( , )
18. Priority function option (PRI)
19. Lockout channel and talk group (L/O)
20. Delay option (DLY)
21. DATA Skip option (DATA)
22. Warning Light disabled (FLASH)
23. Priority channel and talk group (P)
Icon Display
UBCT9 OM 3 12/11/07 3:52:26 PM
4
Terminology
What is Scanning?
Unlike standard AM or FM radio stations, most two-way communications do not
transmit continuously. The UBCT9 scans the Frequencies you have programmed
into the Scanner’s channels until it nds an active frequency.
Scanning stops on an active frequency and remains on that channel as long as
the transmission continues. When the transmission ends, the scanning cycle
resumes until another transmission is received.
What is Searching?
The UBCT9 can search each of its 12 bands to nd active frequencies. This is
different from scanning because you are searching for frequencies that have
not been programmed into your Scanner’s channels. The scanner automatically
chooses between two speeds while searching. During search mode the scanner
will search 100 frequencies per second for bands with 12.5 kHz steps and during
Turbo SEARCH mode the scanner can achieve up to 300 frequencies per second
for bands with 5 kHz steps.
What is Trunk Tracking?
Conventional scanning is a simple concept. You enter a radio frequency in your
scanner’s memory which is used by someone you want to monitor. For example,
the police in your area may broadcast on 467.850 MHz, the re department on
161.250 MHz, etc.
So when your scanner stops on a frequency, you usually know who it is, and more
importantly, you can stop on a channel and listen to an entire conversation.
As the demand for public communications has increased, many public radio
users don’t have enough frequencies to meet their needs, and this has created
a serious problem. Trunking radio systems have been implemented to solve this
problem.
In a trunked radio system the frequencies are shared among the police and re
departments and a computer systematically assigns available frequencies when
they are needed for communications.
UBCT9 OM 4 12/11/07 3:52:26 PM
5
Sharing of the available public service frequencies, or trunking, allows cities,
counties, or other agencies to accommodate hundreds of users with relatively
few frequencies. Following a conversation on a trunked system using a scanner
is difcult, if not impossible. Because when there’s a short break during the
conversation you’re monitoring, it’s possible that the talk group will be assigned
to a completely different frequency in the trunked system. This type of scanning is
difcult and frustrating.
TrunkTracker Technology changes this! Not only does your new UBCT9 scan
channels like a conventional scanner, it actually follows the users of a trunked
radio system. Once you know a talk groups ID, you won’t miss any of the action.
If you’re a new scanner enthusiast, you may want to read the rst part of this
manual and use your scanner in conventional mode before you begin trunk
tracking. Understanding scanning fundamentals and its terminology will make
trunk tracking much easier.
UBCT9 OM 5 12/11/07 3:52:26 PM

6
Feature Highlights
• Pre-programmed frequencies specic to each
• Pre-programmed Trunked frequencies
• Close Cal ™ RF Capture Technology
You can set the scanner so it detects and provides information about nearby
radio transmissions.
• Pre-programmed Service Scanning by the following service banks;
- Police
- Rail Roads
- Aircraft (except Aeronautic radio Navigation (108-117.9875MHz)
- Marine Band
- UHF CB Radio
- AM CB Radio
• Trunk Tracking – Follow VHF High Band UHF 800MHz trunked public safety and
public service systems just as if conventional two-way communications were used.
• Multi-Track
– Track more than one trunking system at a time.
Scan conventional and trunked systems at the same time.
• 250 Channels – Program one frequency into each channel. You must have at least
one channel programmed to use the Scan mode.
• 12 Bands – Includes 12 bands, with aircraft and 800 MHz.
• 5 Banks– 5 banks with 50 channels each are useful for storing similar frequencies to
maintain faster scanning cycles or for storing all the frequencies of a trunked system.
• 25 MHz-1300 MHz– Indicates the range of frequencies that can be searched within the
bands of your scanner.
Note: The frequency coverage is not continuous.
• 5 Priority Channels– You can assign one priority channel in each bank. Assigning a
priority channel allows you to track activity on your most important channel(s) while
monitoring other channels for transmissions.
You can also assign trunking priority talkgroups.
• Data Skip – Allows your scanner to skip unwanted data transmissions and
reduces birdies.
• Direct Channel Access – Go directly to any channel without entering
programming mode.
• Turbo Search– Increases the search speed to 300 steps per second. This applies only
to transmission bands with 5 kHz steps.
• PC Programmable – Allows you to easily program all frequencies and Trunking Talk
Groups into your UBCT9 through the Uniden UBCT9-SS programming software
running on your PC.
UBCT9 OM 6 12/11/07 3:52:26 PM
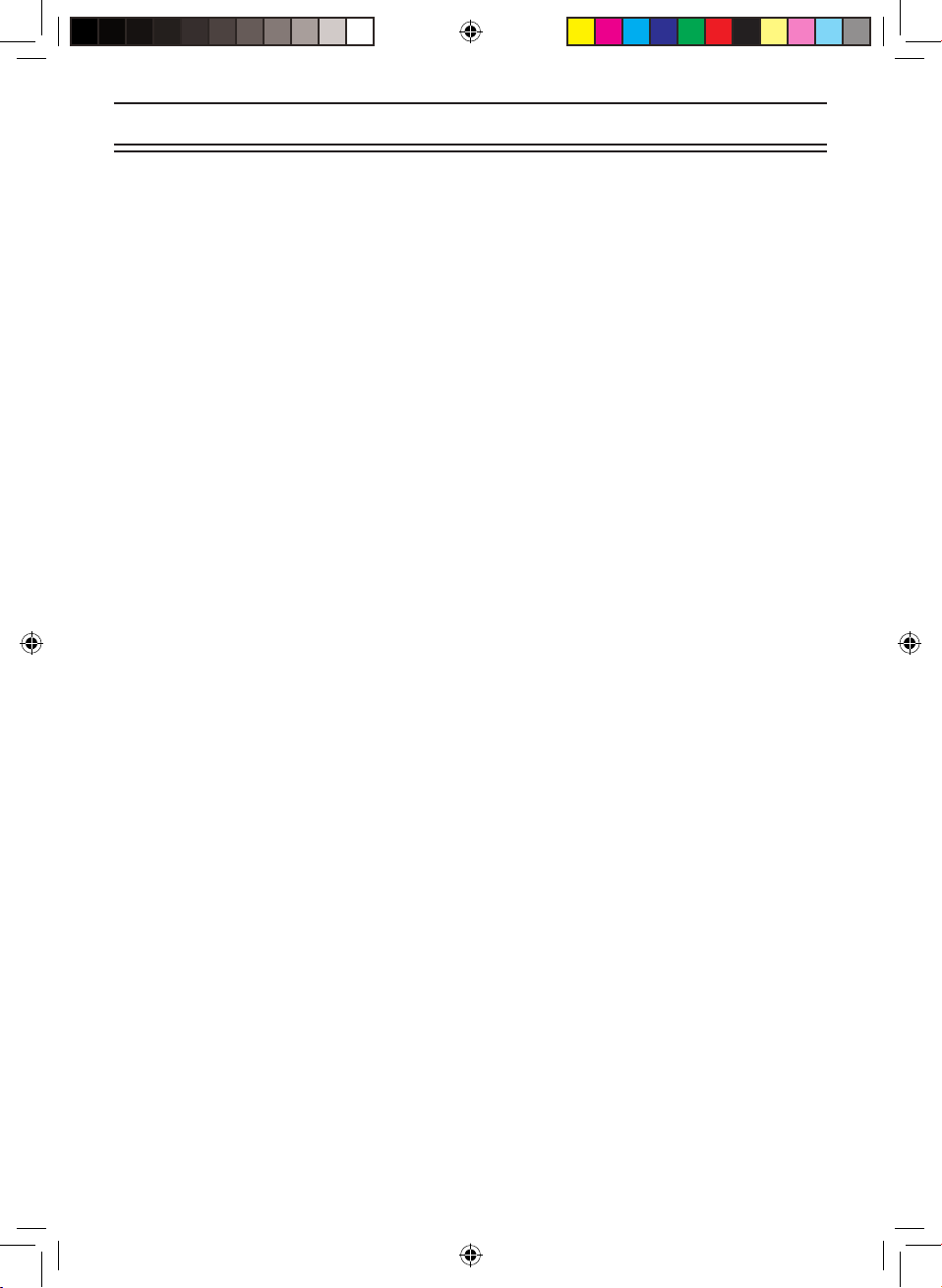
7
Included with Your Scanner Package
• UBCT9 Scanner
• AC Adapter
• DC Power Cord
• Cigarette Lighter Adapter Plug
• Telescopic Antenna
• Window Mount Antenna
• Operating Guide
• UBCT9 SS Programming Software CD
• Australian Scanner Frequencies CD
• Other Printed Materials
• Mobile Mounting Bracket
If any of these items are missing or damaged, immediately contact your place of purchase.
Optional Accessories
The following optional accessories for your UBCT9 are available from your local Uniden
Retailer.
Motorola Antenna Adapter - Use only if your antenna has a Motorola-type plug.
UBCT9 OM 7 12/11/07 3:52:27 PM
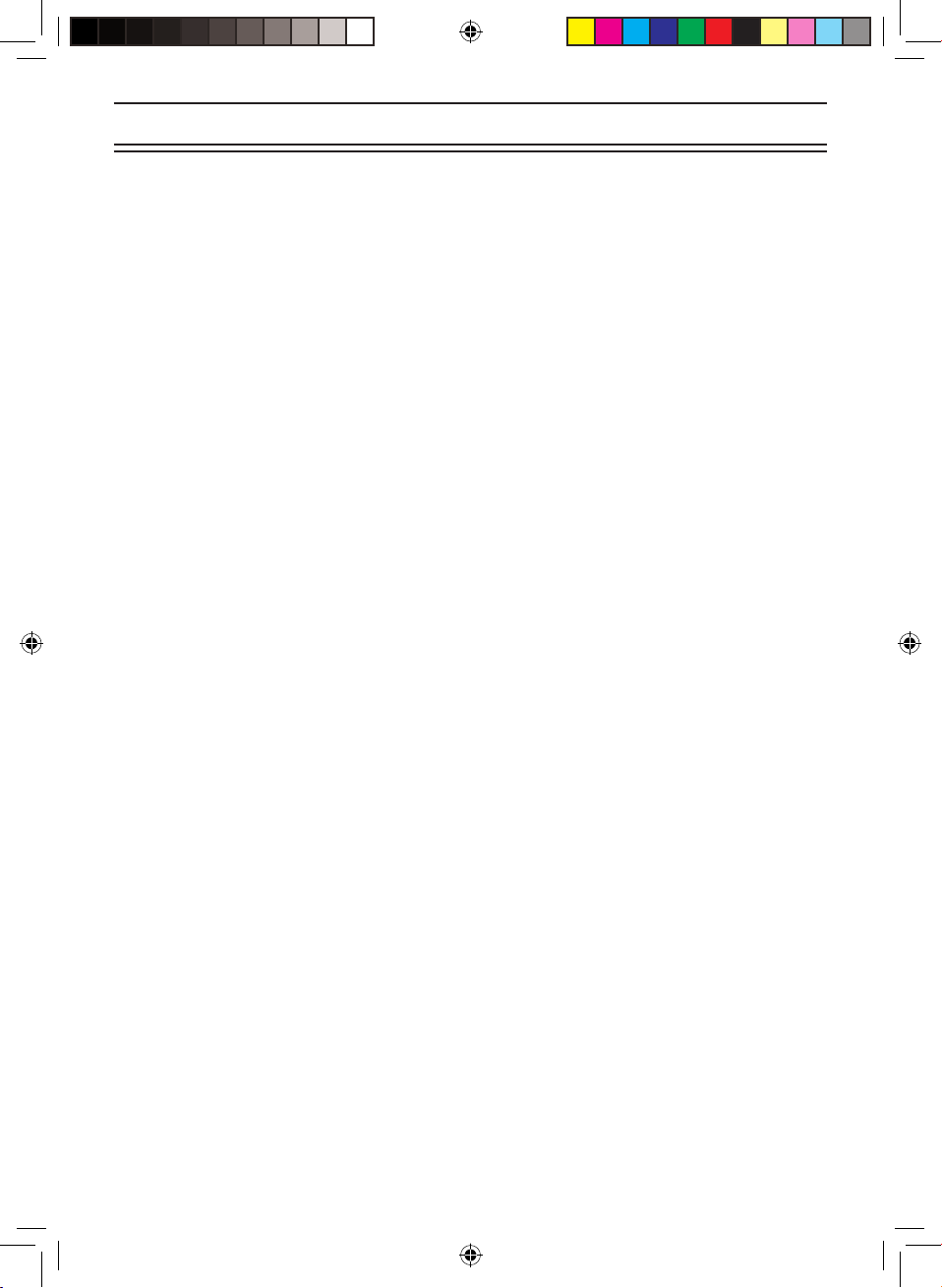
8
Installing the UBCT9
For Home Use (Desktop Installation)
1. Insert the DC plug end of the AC Adapter into the DC 12V jack on the rear panel.
2. Plug the AC Adapter into a standard 240V AC wall outlet.
3. Plug the Telescoping Antenna into the ANT connector.
Extend the antenna to its full height. For frequencies higher than 406 MHz, shortening
the antenna may improve the reception.
4. Use the desktop stand for a better viewing and operating angle.
Helpful Hints
• If strong interference or electrical noise is received, relocate the scanner or its antenna
away from the source.
• If you are operating the scanner in a fringe area or need to improve reception, use an
optional antenna designed for multi-band coverage. (You can purchase this type of
antenna at a local electronics store.)
• If the optional antenna has no cable, use 50-70 ohm coaxial cable for lead-in. A mating
plug may be necessary for the optional antennas.
For Mobile Use (In-Car Installation)
Installation for Temporary Use:
A Cigarette Lighter Power Cord is provided for easy, temporary installation.
Warning: Do not use the cigarette lighter power cord in a positive ground vehicle.
Plug one end of the Cigarette Lighter Power Cord into the cigarette lighter jack and the
other end into the DC 12V jack on the back of the scanner.
Connecting the Antenna Plug
Connect the mobile antenna plug into the ANT connector on the rear panel. (For more
information on antenna installation, please refer to the instruction guide that came with
your antenna.)
The UBCT9 can be mounted using the supplied mounting bracket.
1. Select an ideal location in your vehicle to mount the UBCT9. Avoid a location that could
interfere with your driving. In a passenger car, the ideal location is underneath the
dashboard on the passenger side.
2. Use the supplied mounting bracket as a template for marking the location of the
mounting screws. Note: If there are screws already holding the dashboard, you can use
the same screw holes to mount the bracket.
UBCT9 OM 8 12/11/07 3:52:27 PM

9
3. Drill the necessary holes and secure the mounting bracket in place using the screws
provided.
4. Mount the radio to the bracket only after the wiring has been connected to the rear
panel.
Connecting the Power Cord
Note: If you are not experienced in connecting accessories to the vehicle fuse box, please
see your automotive dealer for advice on proper installation.
Installation for everyday use:
1. Check the vehicle battery connections to determine which battery terminal (positive or
negative) is grounded to the engine block or chassis. Most of today’s vehicles use a
negative ground. If your vehicle has a negative ground, follow Steps 2 and 3.
Otherwise, skip to the note following Step 3.
2. Connect the RED wire of the DC power cord to the accessory contact in your vehicle’s
+12V DC fuse box.
3. Connect the BLACK wire of the DC power cord to the negative side of the vehicle
(usually the chassis).
Note: In vehicles with a positive ground, the RED wire connects to the chassis and the
BLACK wire connects to the accessory contact in the fuse box.
4. Insert the DC plug into the DC 12V jack on the back of the scanner.
UBCT9 OM 9 12/11/07 3:52:27 PM
10
Typical Mounting Methods
The UBCT9 can be conveniently mounted on a table, bulkhead, overhead, or any other
desired location with the supplied mounting bracket (refer to gure below for typical
mounting methods).
Caution: Make sure there are no hidden electrical wires or other items behind the
desired location before proceeding. Check that free access for mounting and
cabling is available.
• Table top mount • Bulkhead mount • Overhead mount
Mounting the Scanner in Your Vehicle
Before you mount the scanner, make sure you have all the necessary materials. Then
conrm that the scanner ts your vehicle’s mounting area. This unit requires a mounting
area of 50.8mm high by 176.5mm wide by 153.6mm deep.
Caution: Be sure to avoid obstructions behind the mounting surface.
Follow these steps to mount the scanner in your vehicle.
1. Choose a mounting location, then use the supplied
mounting bracket as a template to mark the positions
for the mounting screw holes.
2. In the marked positions, drill holes slightly smaller
than the supplied screws.
3. Attach the mounting bracket to the mounting location
using the supplied screws and lock washers.
4. Attach the scanner to the mounting bracket using the
supplied mounting knobs.
5. Connect the antenna’s cable to the ANT. connector
on the rear of the scanner.
Note: If the antenna cable’s connector does not t in
the ANT connector, you might also need a
Motorola-to BNC antenna plug adapter
(available at a local electronics store).
UBCT9 OM 10 12/11/07 3:52:53 PM
11
Applying Power for Vehicle Installation
You can power your scanner using the supplied DC cigarette lighter power cord or an DC
power cord.
DC power Installation
To power the scanner from a vehicle’s 12V power source (such as a cigarette-lighter
socket), you need a cigarette-lighter adapter.
To connect an DC cigarette-lighter power cable, insert its barrel plug into the DC 12V
jack on the rear of the scanner, then plug the power cable into your vehicle’s
cigarette lighter socket.
Note : If you use a cigarette-lighter power cable and your vehicle’s engine is running,
you might hear electrical noise from the engine while scanning. This is normal.
Caution: DC 12 V Jack can use a power source that supplies 12V DC at least
500 mA. You must use a power source that supplies 12V DC and delivers at
least 500 mA. Your standard 12V car battery should be sufcient. The cord
connector’s center tip must be set to positive and its plug must t the scanner’s
DC 12V jack. The supplied DC power cord meets these specications. Using a
power cord that does not meet these specications could damage the scanner
or the adapter.
• Always connect the adapter or DC power cord to the scanner before you connect it to
the power source. When you nish, disconnect the adapter or DC power cord from the
power source before you disconnect it from the scanner.
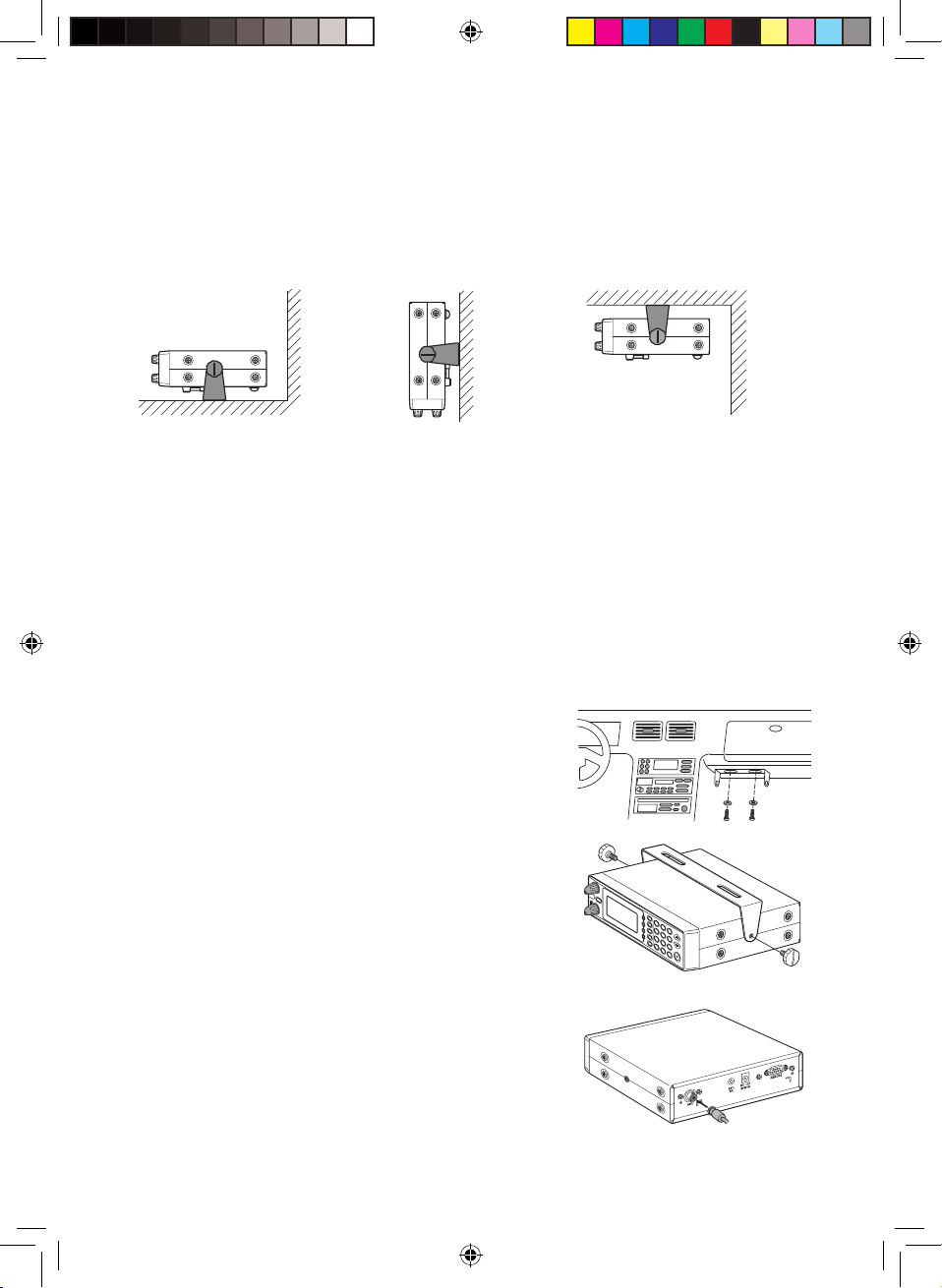
• For added safety and to protect your scanner,
disconnect the cable from your vehicle battery’s
negative (-) terminal before you begin.
Follow these steps to connect the DC power cord.
1. Connect the power cord’s black wire to a chassis ground, such as a metal screw
attached to a metal part of the vehicle’s frame. Be sure that the screw is not insulated
from the frame by a plastic part.
2. Connect the power cord’s red wire (with in-line fuse) to a source
of voltage that turns on and off with the ignition switch, such as
a spare accessory terminal in your vehicle’s fuse box.
3. Insert the power cord’s barrel plug into the DC 12V jack on
the rear of the scanner.
4. Reconnect the cable to the vehicle battery’s negative (-)
terminal.
UBCT9 OM 11 12/11/07 3:52:54 PM
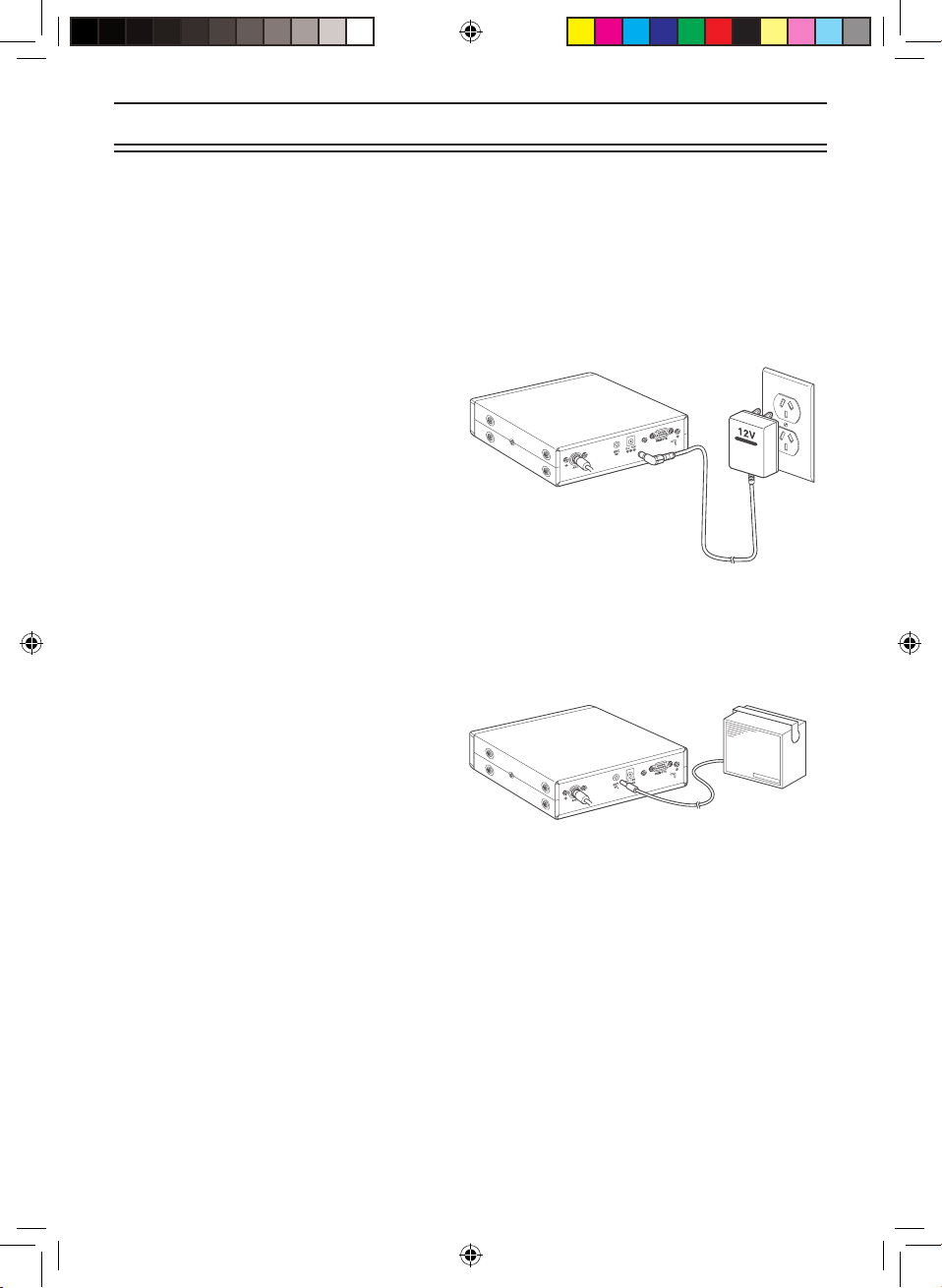
12
Applying Power Using Standard AC Power
To power the scanner from an AC outlet, use the provided AC adapter with a 5.5 mm outer
diameter/2.1mm inner diameter tip.
Caution: You must use a Class 2 power source that supplies 12V DC and delivers at
least 500 mA. The cord connector’s center tip must be set to positive
and its plug must t the scanner’s DC 12V jack. Using an adapter that does not
meet these specications could damage the scanner or the adapter.
• Always connect the AC adapter to the scanner before you connect it to AC power.
When you nish, disconnect the adapter from the AC power before you disconnect it
from the scanner.
1. Insert the adapter’s barrel plug into the
DC 12V jack on the rear of the scanner.
2. Plug the adapter into a standard AC outlet.
Use only the AC adapter supplied with
your scanner.
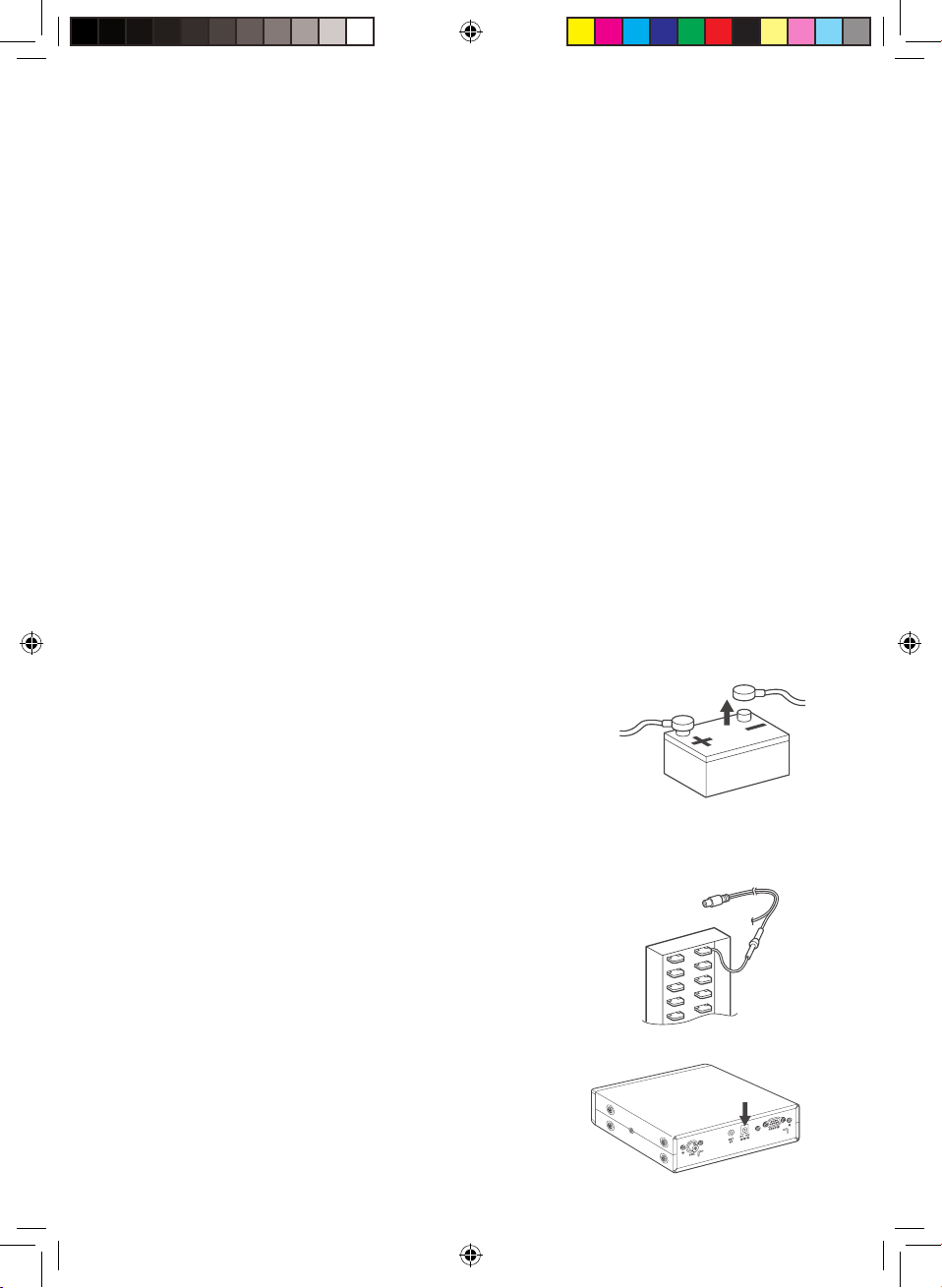
Connecting an External Speaker
In a noisy area, an external speaker (available at a local electronics store) positioned in the
right place might provide more comfortable listening.
Plug the speaker cable’s 1/8 inch (3.5 mm)
plug into your scanner’s EXT. SP jack.
Note: Connecting an external speaker
disconnects the scanner’s
internal speaker.
Listening Safely
• Do not use the earphone. The volume is not adjustable for the Warning Alert and
damage to your hearing could occur.
Connecting the Clone Cable
You can transfer the programmed data to and from another UBCT9 scanner using
a RS232C Straight Cable (9 pin to 9 pin) (not supplied). Connect the cable between
each scanner’s REMOTE jacks. See “Clone Mode” on page 49. You can also upload
or download the programmed data to or from a PC using the UBCT9-SS programming
software included with the UBCT9.
UBCT9 OM 12 12/11/07 3:52:55 PM
13
CC
Scanning Overview
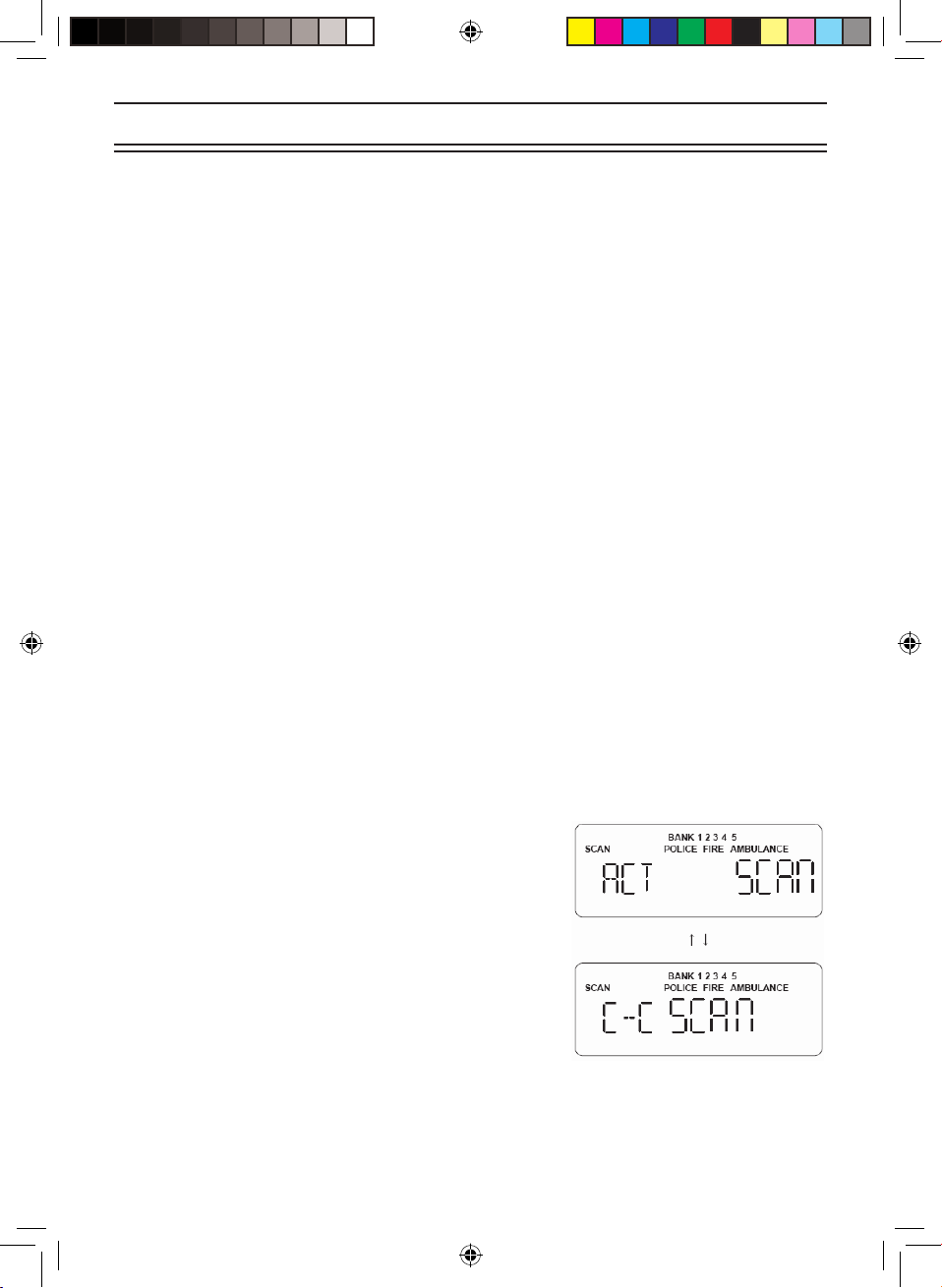
You can scan in one of ve ways:
1. Close Call RF Capture When you activate Close Call your scanner will detect nearby
strong radio frequencies. You may run Close Call in the background of any of the four
options below or on its own.
2. Service Scanning Press SVC to select one of the six services to nd an active
frequency. Police, Railroad and AM CB service frequencies are valid for Australia only.
Aircraft, Marine and UHF CB service frequencies are valid for both Australia and
New Zealand.
3. Band Search Band Search Select a frequency band to search. The Search function is
different from scanning. It searches for any active frequency step by step within the
lower and upper limits of the band. When an active frequency is found, the scanner
will stop and stay on that frequency as long as that transmission lasts. If that frequency
is interesting to you, press HOLD/RESUME to hold the frequency on the display. Then
program it into the private bank you want to store. If you do not want to program that
frequency, press HOLD/RESUME or just wait until the transmission ends. The search
resumes automatically 2 seconds after the last transmission and looks for more active
frequencies.
4. Private Scanning If you have programmed frequencies into this bank, press SCAN,
then 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or to scan only those that you have programmed in this bank.
5. State Scanning You can select Police, Fire and Ambulance frequencies which are
pre-programmed on a Australian state by state (including New Zealand) basis.
Note: Before you can scan the Private Bank, you must program frequencies into the
channels. To program frequencies, see “Programming Frequencies into
Channels” on page 21.
When scanning stops on an active frequency, it remains on that
channel as long as the transmission continues. When the
transmission ends, the scanner will remain on the same
channel for 2 more seconds, waiting for a responding
transmission. If there is no responding transmission within 2
seconds, the scanning cycle resumes.
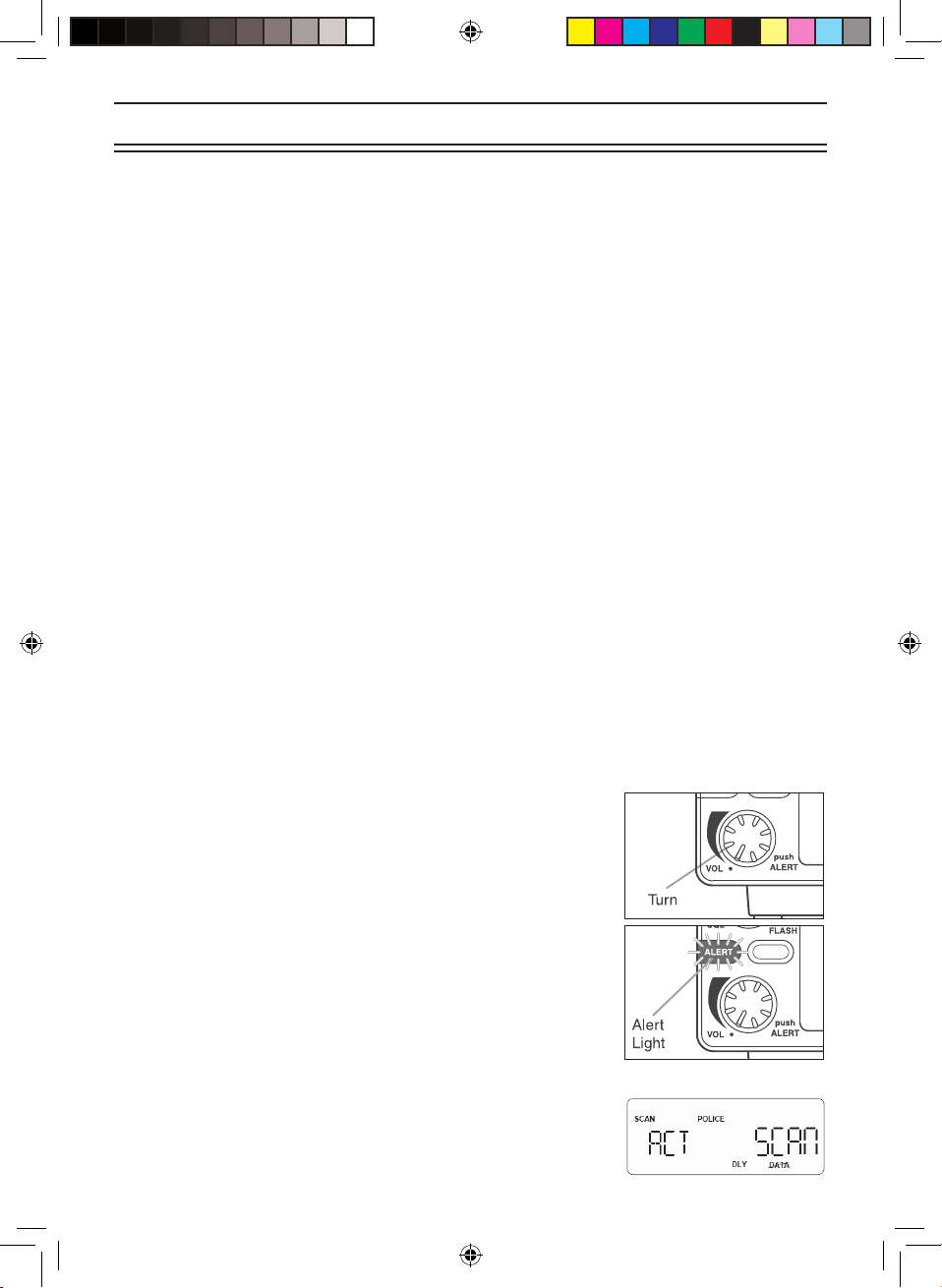
Turn the Scanner On
1. Turn the VOL knob clockwise.
The scanner is turned on: the Alert Light ashes and the Alert
Tone beeps loudly.
Note: The Alert Tone depends on the currently setting selected
(see page 20).
2. While the alert tone sounds the display shows ‘UBCT9’.
When this stops the last setting mode selected before starts.
UBCT9 OM 13 12/11/07 3:53:31 PM

14
How Squelch Works
Think of “SQUELCH” as a gate. If the gate is too low (squelch
too low), everything (all noise as well as signals) gets through.
If the gate is set too high (squelch too high), nothing gets
through.
If the gate is set just right (squelch set properly), just the
desired signals get through.
Setting the Squelch
1. To set the squelch, press HOLD/RESUME to stop
scanning.
2. Turn SQL fully counterclockwise until hiss heard.
This lowers the “squelch gate,” allowing all signals and
noise to get through.
3. Turn SQL fully clockwise just until hiss stops.
This raises the “squelch gate,” allowing only strong signals
to get through.
467.8500
UBCT9 OM 14 12/11/07 3:53:32 PM

15
State Scanning
Press POLICE, FIRE or AMBULANCE and the
scanner scans through police, re or
Ambulance Frequencies and “SCAN” scrolls from
right to left in the display.
When in the State Scan mode, press STATE and
the menu of states will appear.
Press POLICE.
The scanner will scan through Factory
Programmed Police Frequencies and ”POLICE”
appears in the display.
Press FIRE.
The scanner will scan through Factory
Programmed Fire Frequencies and ”FIRE”
appears in the display.
Press AMBULANCE. The scanner will scan
through Factory Programmed Ambulance
Frequencies, ”AMBULANCE” appears in the
display.
When the scanner nds a signal, scanning stops, the state code and the frequency
displays.
When the transmission ends, the two seconds delay feature (if you set on) holds the
scanner in that frequency for a response. If there is no response, scanning resumes. (See
Delay page 28).
Selecting the State
1. While State scanning, press STATE. The menu of
states will appear (See State Code Order Appendix:
page 56).
2. Press STATE and hold to scroll.
3. To step forward through the states (A-W), press
STATE
and, within 3 seconds, press repeatedly.
4. To step backward through the states (W-A), press
STATE
and, within 3 seconds, press repeatedly.
UBCT9 OM 15 12/11/07 3:53:33 PM

16
5. To scroll repeatedly, press and hold or and
STATE.
After 3 seconds, the scanner will begin to scan
through the Police frequencies (Police only).
6. If you want to start scanning immediately, press
HOLD/RESUME.
State Scan Hold
1. When scanning stops on a desired frequency, press
HOLD/RESUME to hold at that frequency as long
as you like.
While ”HOLD” appears in this mode, you can
use or to move up or down the frequency steps.
During Hold mode, you can see all frequencies
sequentially. It does not depend on your selected
bank.
Pressing and holding the keys for 1 sec, speeds up
frequency change.
If present frequency is locked out, then ”L/O” appears
on LCD.
2. To resume scanning, press HOLD/RESUME.
Storing State Scan Frequencies
You can quickly store any frequency you nd during scan.
1. During scan, press HOLD/RESUME to store.
You can press or to move up or down 1 frequency step.
2. If you have found the frequency you want to store, press E.
- Or When the scanner stops on the frequency you want to store, press E.
3. Select the private bank where you want to store the frequency, the smallest empty
channel number and “000.0000” ashes on and off over the frequency you want to
store. Press E (if the frequency you want to store exists already in a bank, you will hear
an error tone and the other channel displays. Press E again to store the frequency in
both channels).
Skip a frequency
To skip a frequency, press L/O. You can program up to 100 skip frequencies.
You can skip the frequencies in the scanning sequence.
If you change the state code, skipped frequencies are cancelled as soon as scanning
starts. If you change the State, skip frequencies are all clear.
UBCT9 OM 16 12/11/07 3:53:34 PM
17
Close Call RF Capture ™
Your scanner’s Close Call feature lets you set the scanner so it detects then displays the
frequency of a nearby strong radio transmission. Close Call RF capture works great for
nding frequencies at venues such as malls and sporting events. You can set the
scanner so Close Call detection works “in the background” while you are scanning other
frequencies, turn off normal scanning while Close Call is working, or turn off the Close Call
feature and use the scanner normally. You can set the scanner so it alerts you when the
Close Call feature detects a frequency. You can also set the frequency band where you
want the scanner to look for transmissions.
Unlike searching, which requires the scanner to tune to a frequency to check for a
transmission, Close Call RF capture directly detects the presence of a strong, nearby
signal and instantly tunes to the source’s frequency.
Notes:
Close Call RF capture works well for locating the source of strong local transmissions such
as mobile and handheld two-way radios in areas with no other strong transmission
sources. However, if you are in an area with many transmission sources (such as pager
radio transmitters, multi-use radio towers, trafc control devices, etc.), Close Call RF
capture might not nd the transmission you are searching for, or it might nd a transmission
other than the one you are searching for.
Close Call RF capture cannot detect satellite dishes or any transmitter with a frequency
above or below the frequency ranges listed in Select Close Call Bands on Page 19.
Close Call works better with some types of transmissions than others. It might not correctly
display frequency information for transmitters using a highly directive antenna (such as an
amateur radio beam antenna), if there are many transmitters operating at the same time in
the same area, or if the transmitter is a broadcast television station.
Every 2 seconds, the scanner checks for frequencies in the range you specied in “Set
Close Call Option” on page 19 and interrupts the audio when it checks for a Close call
Transmission in that range.
Set Close Call Mode
These settings affect when Close Call actually operates.
When Close Call is on with another mode, every 2
seconds the scanner will switch the lter settings to
the ones set by the Close Call Bands option.
• Close Call: On Close Call is on at all times, for all modes.
• Close Call: Off Close Call is turned off for all modes.
• Close Call: Only Close Call is only available.
These modes can also be toggled by pressing C.C.
When Close Call is set to On, Close Call LED is On.
When Close Call is set to only mode, Close Call LED will
ash.
When Close Call is set to off, Close Call LED is Off.
When Close Call is on, “C-C” will be displayed every a
few seconds.
UBCT9 OM 17 12/11/07 3:53:35 PM
 Loading...
Loading...