Page 1

Perspective
Copyright © 2011 Triton Imaging Inc.
Page 2

Triton Imaging Inc.
Engineering Office
2121 41st Avenue, Suite 211
Capitola, CA 95010
USA
831-722-7373
831-475-8446
sales@tritonimaginginc.com
support@tritonimaginginc.com
© 2010 TRITON
This user guide is provided as a means to understand features in TRITON’s software. The user interface
presented in this guide is subject to change to accommodate software upgrades and revisions. While every
precaution has been taken to eliminate errors in this guide, TRITON assumes no responsibility for errors in this
document.
Users of this document are required to have a valid license and dongle for Perspective in order to activate the
software. TRITON hereby grants licensees of TRITON’s software the right to reproduce this document for
internal use only.
i | P a g e February 2011
Page 3
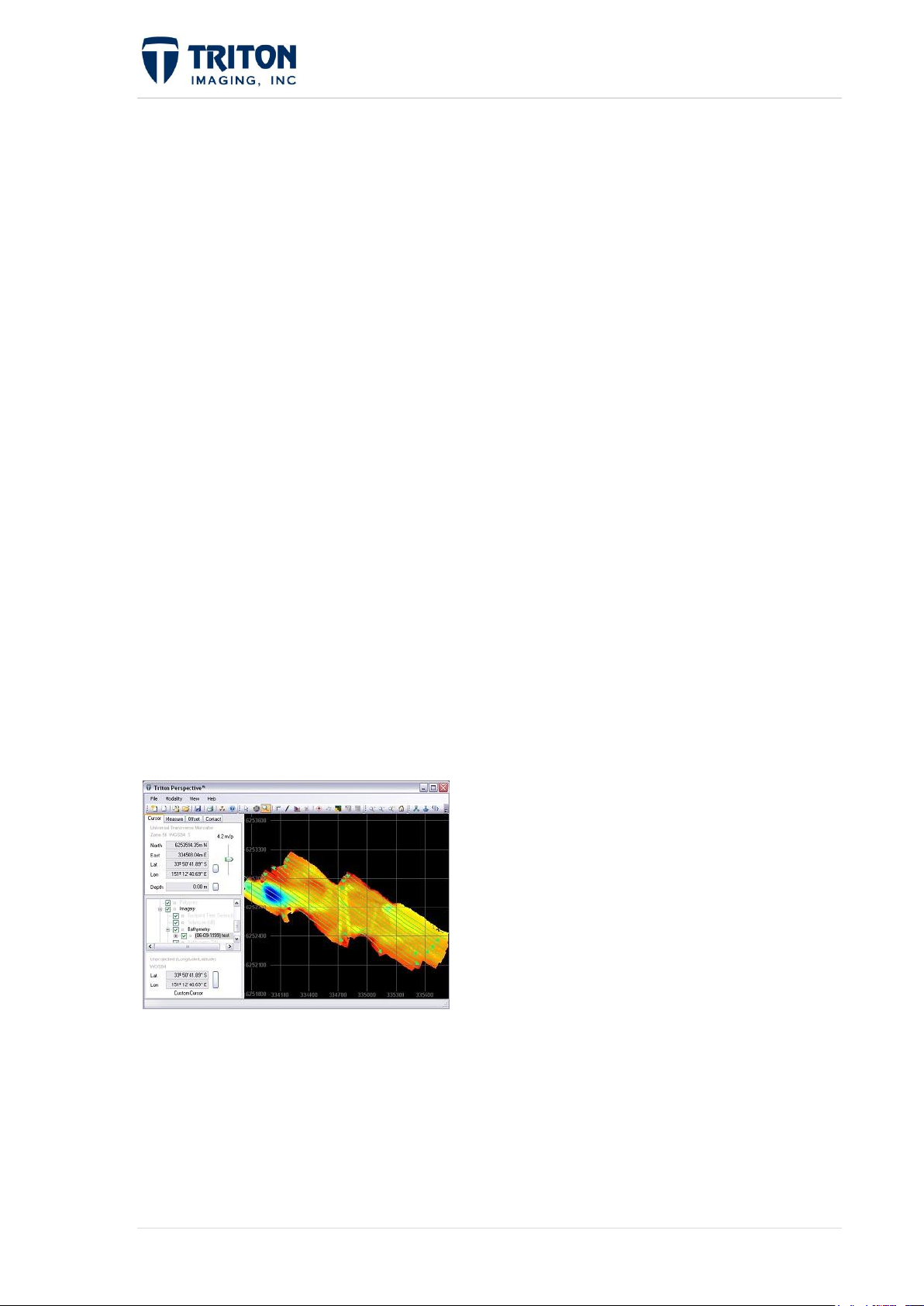
Welcome to Triton Perspective!
Triton Perspective™ is a new product line from Triton Imaging that takes advantage of the
latest in software technologies including: multi-core parallel processing, indexed cache files,
workflow wizards, XML project files, multi-resolution tiling, and dB-based rendering to
develop products that are fast, accurate, efficient, easy to use, and that provide the tools
necessary for a broad range of real-world marine applications.
Perspective Map™, a GIS-based mapping package, forms the foundation of Perspective by
integrating the Triton BathyOne™, MosaicOne™, TargetOne™, and SeaClass™ software
modules into a cohesive suite capable of processing, fusing, and displaying sidescan and
multibeam data. Each module is controlled from the Perspective Map environment via
common, embedded user-interface, tools, and displays. Perspective Map displays the output
from these modules as multi-layer, co-registered survey tracks, sidescan sonar images,
bathymetry DTMs, target icons and images, and seabed classification areas and boundaries.
These seafloor image data can be easily combined with other available geo-coded data such
as S-57 electronic nautical charts, coastline maps, and satellite or other GeoTIFF imagery as
required. Output of individual and fused data products in standard formats for processing by
third-party applications is supported.
BathyOne™ will process raw multibeam data
and combine it with vessel position, pitch, roll,
heave, and heading; tides; sound velocity; draft;
and other data to produce accurate corrected
bathymetry grid files. Total Propagated Error
(TPE) of the gridded data is calculated and made
available for review and display. Gridded results
are displayed as layers in Perspective Map along
with other survey data such as coastline vector maps, electronic charts, sidescan mosaics, etc.
A variety of display options are provided for bathymetry layers, including profiling, colorcoding gridded data by depth, relief shading, and transparency adjustment. With these tools,
comparing recently collected bathymetry with other sensor data and historical data sets is a
simple and intuitive process.
ii | P a g e February 2011
Page 4

MosaicOne™ makes the production of high quality
geo-registered sidescan mosaics a simple process.
Mosaic images of sidescan or multibeam backscatter
data are created by simply dragging and dropping raw
XTF data files into the Perspective Map multi-layer
map view. Processing options such as nadir delete,
far range clipping, and single-channel select, coupled
with a comprehensive set of navigation processing
tools, result in superior quality mosaics suited to specific application needs and collection
regimes. MosaicOne images are displayed in Perspective in correct registration with other
survey data such as shaded or color-coded bathymetry, electronic nautical charts, coastline
vector data, survey tracks, target icons, annotation, seabed classifications, etc. Data fusion is
facilitated by adjusting the transparency of mosaic images allowing visual comparison of
sidescan features with underlying data elements. Fine adjustments to line position are easily
made with the new Move Line feature and high-resolution waterfall displays of sidescan data
direct from source XTF files cab be invoked with point and click at any position on the
mosaic.
TargetOne™ is a collection of target
processing tools that enable the acquisition and
analysis of objects seen in the sidescan data.
Targets are acquired with point and click on a
sidescan mosaic displayed in Perspective Map
or from the raw sidescan data viewed in
Perspective's embedded waterfall viewer. The
TargetOne module displays target images and
provides for a variety of image manipulation
and measurement tools to facilitate object recognition and classification. Target positions are
recorded as icons displayed on the mosaic with easy access to any target by clicking on an
icon of interest. Object measurement tools are provided that exploit sonar parameters.
Output of target information is in standard XML format to support processing by other
applications.
iii | P a g e February 2011
Page 5
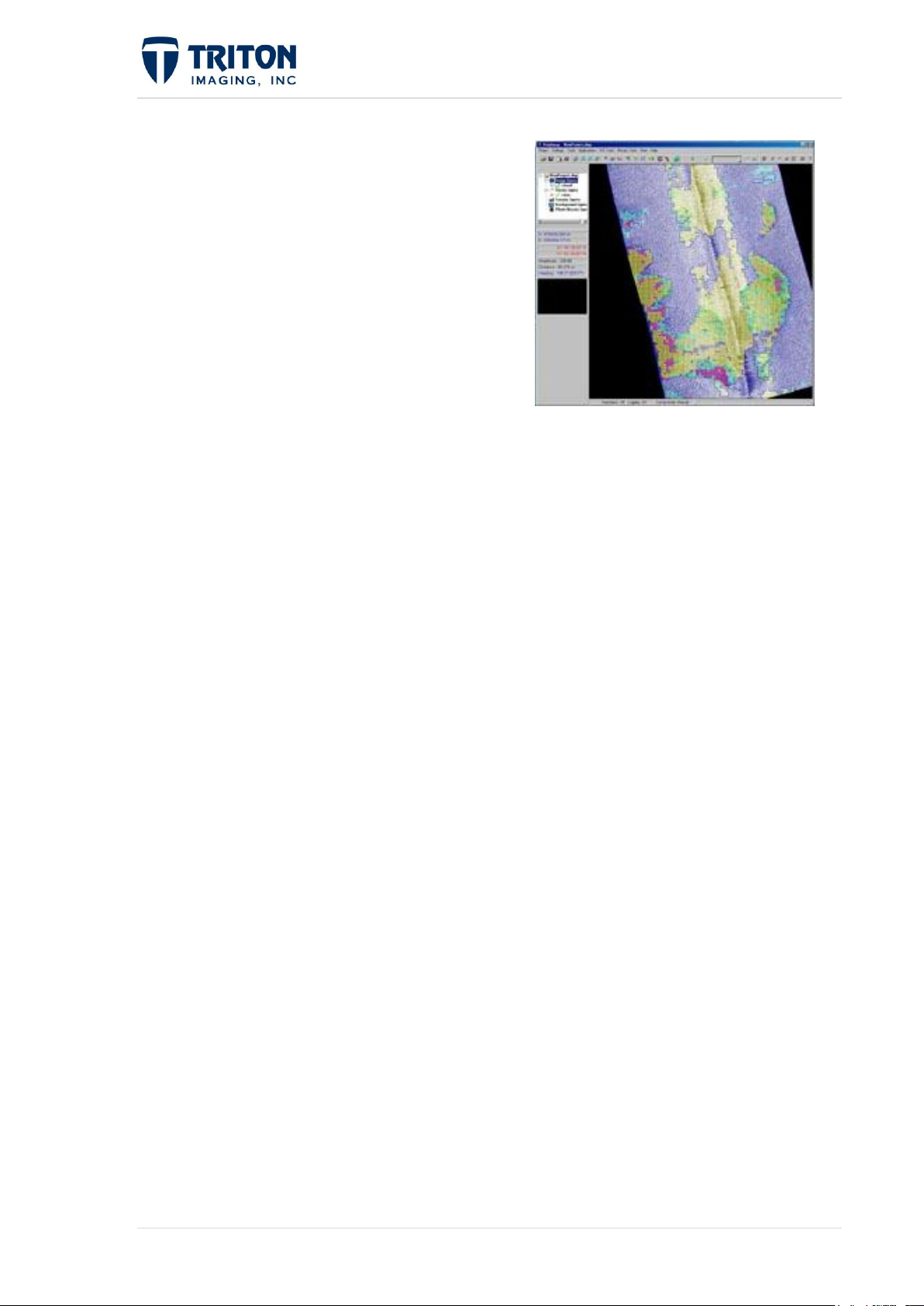
SeaClass™ is an advanced seabed
segmentation/classification module that
automatically characterizes bottom types based
on statistical properties of sidescan mosaics or
multibeam backscatter imagery. SeaClass is
based on a multi-layer perceptron supervised
neural network. The classification procedure
consists of two stages: a learning stage and a
classification stage. Training is accomplished
by the operator selecting areas in the mosaic of differing bottom type (e.g. sand, rock,
mud, etc.). Training of the classifier neural network then proceeds thru an automated
statistical analysis of the selected samples and a characterization of each type. The
following classification stage is a completely automated process where the entire mosaic
image is segmented into the different classes. Results of the classification are displayed
overlain on the mosaic image with each area colored or optionally with vector/line
boundaries around each area. Output from SeaClass can be the DXF boundary vectors or
a GeoTIFF mosaic image with the displayed color-coded areas.
iv | P a g e February 2011
Page 6

TABLE OF CONTENTS
PERSPECTIVE ................................................................................................................................................... 1
TRITON IMAGING INC.
WELCOME TO TRITON PERSPECTIVE! .............................................................................................................. II
TABLE OF CONTENTS ....................................................................................................................................... V
1: SOFTWARE INTERFACE ............................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 MAIN WINDOW OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................ 1
1.1.1 Main Window Layout ........................................................................................................................... 1
1.1.2 Main Window Menus ........................................................................................................................... 2
1.1.3 Main Window Toolbars ........................................................................................................................ 4
1.2 INFORMATION DISPLAYS ..................................................................................................................................... 6
1.2.1 Cursor Tab ............................................................................................................................................ 6
1.2.2 Measure Tab ........................................................................................................................................ 6
1.2.3 Offset Tab ............................................................................................................................................. 7
1.2.4 Contact Tab .......................................................................................................................................... 7
1.3 FILE TREE ........................................................................................................................................................ 8
1.3.1 Map Root Layer .................................................................................................................................... 8
1.3.2 The Annotation Tree............................................................................................................................. 9
1.3.3 SeaClass Tree...................................................................................................................................... 12
1.3.4 Contacts Tree ..................................................................................................................................... 15
1.3.5 Vectors Tree ....................................................................................................................................... 16
1.3.6 Navigation Tree .................................................................................................................................. 17
1.3.7 Imagery Tree ...................................................................................................................................... 20
1.3.8 Background File Tree .......................................................................................................................... 26
1.4 CUSTOM CURSOR ........................................................................................................................................... 30
1.5 MAP VIEW .................................................................................................................................................... 32
1.5.1 Moving Around the Map View ........................................................................................................... 32
1.5.2 Cursor Modes ..................................................................................................................................... 35
1.5.2.4 Zoom Mode ..................................................................................................................................... 37
............................................................................................................................ I
2: DATA MANAGEMENT ................................................................................................................................ 40
2.1 IMPORTING .................................................................................................................................................... 40
2.1.1 Import Methods ................................................................................................................................. 40
2.1.2 Import Data Types .............................................................................................................................. 41
2.2 DATABASE REFRESH ........................................................................................................................................ 44
2.3 EXPORT METHODS .......................................................................................................................................... 45
2.3.1 Map View Export ................................................................................................................................ 46
2.3.2 Imagery GeoTiff Export ...................................................................................................................... 47
2.3.3 Imagery Batch GeoTiff Export ............................................................................................................ 48
2.3.4 KML File Export .................................................................................................................................. 49
2.3.5 XYZ File Export .................................................................................................................................... 51
2.3.6 SeaClass Export .................................................................................................................................. 52
2.3.7 Printing ............................................................................................................................................... 54
2.4 PROJECT OPTIONS ........................................................................................................................................... 54
2.4.1 New Project ........................................................................................................................................ 54
2.4.2 Open Project ....................................................................................................................................... 55
2.4.3 Save Project ........................................................................................................................................ 56
2.4.4 Projected Cursor ................................................................................................................................. 57
2.4.5 Log Window ....................................................................................................................................... 57
v | P a g e February 2011
Page 7

2.4.6 Page Setup ......................................................................................................................................... 58
2.4.7 Quit Project ........................................................................................................................................ 59
3: PROGRAM SETTINGS ................................................................................................................................. 60
3.1 SETTINGS OVERVIEW ....................................................................................................................................... 60
3.2 GENERAL SETTINGS ......................................................................................................................................... 60
3.3 PEN SETTINGS ................................................................................................................................................ 62
3.4 ENC SETTINGS ............................................................................................................................................... 62
3.5 PROJECTION SETTINGS ..................................................................................................................................... 63
3.5.1 Import Projection Settings.................................................................................................................. 64
3.5.2 Export Projection ................................................................................................................................ 66
3.5.3 Custom Projection .............................................................................................................................. 68
3.5.4 Custom Datum ................................................................................................................................... 71
3.6 CONTACT SETTINGS ......................................................................................................................................... 74
3.7 DATABASE SETTINGS ........................................................................................................................................ 75
4: NAVIGATION ............................................................................................................................................. 76
4.1 NAVIGATION TYPES ......................................................................................................................................... 76
4.2 IMPORT NAVIGATION DATA .............................................................................................................................. 77
4.3 NAVIGATION PROCESSING WORKFLOWS ............................................................................................................. 79
4.4 NAVIGATION BOXCAR SETTINGS ......................................................................................................................... 80
4.5 PROCESS NAVIGATION ..................................................................................................................................... 82
5: BATHYONE ................................................................................................................................................. 83
5.1 BATHYONE MODULE ....................................................................................................................................... 83
5.2 CREATE DTM ................................................................................................................................................ 84
5.2.1 Bathymetry Processing Wizard .......................................................................................................... 84
5.2.2 BathyOne Wizard Overview ............................................................................................................... 85
5.2.3 Choose/Create Bathy Layer ................................................................................................................ 86
5.2.4 Select Input Lines ................................................................................................................................ 87
5.2.5 Gridding of Soundings ........................................................................................................................ 88
5.2.6 Ancillary Options ................................................................................................................................ 89
5.2.7 Raw Processing .................................................................................................................................. 92
5.2.8 Beam Suppression .............................................................................................................................. 95
5.2.9 SVP Processing ................................................................................................................................... 97
5.2.10 Tide/Squat Processing .................................................................................................................... 100
5.3 REBUILD USING ............................................................................................................................................ 101
5.4 EDIT GSF USING ........................................................................................................................................... 103
5.5 RE-MERGE DTM .......................................................................................................................................... 105
5.6 ADD LINES ................................................................................................................................................... 105
5.7 RESET DATE ................................................................................................................................................. 106
5.8 RENAME ..................................................................................................................................................... 107
5.9 VISUALIZATION OPTIONS ................................................................................................................................ 108
5.9.1 Color Settings ................................................................................................................................... 108
5.9.2 Bathy Histogram .............................................................................................................................. 110
5.9.3 Relief Shading ................................................................................................................................... 113
5.9.4 Swath Viewer ................................................................................................................................... 116
5.10 INTERPRETATION OPTIONS ............................................................................................................................ 118
5.10.1 Bathy Profile ................................................................................................................................... 118
5.10.2 Bathy A-B ....................................................................................................................................... 120
5.10.3 Bathy Change Detection................................................................................................................. 123
5.10.4 Bathy Blink Comparator ................................................................................................................. 123
5.10.5 Bathy Statistics ............................................................................................................................... 125
6: MOSAICONE ............................................................................................................................................. 126
6.1 MOSAICONE MODULE ................................................................................................................................... 126
6.2 CREATE MOSAIC ........................................................................................................................................... 128
vi | P a g e February 2011
Page 8

6.2.1 Sidescan Processing Wizard ............................................................................................................. 128
6.2.2 MosaicOne Wizard Overview ........................................................................................................... 129
6.2.3 Choose/Create Mosaic Layer............................................................................................................ 129
6.2.4 Choose Mosaic Settings ................................................................................................................... 130
6.2.5 Select/Order Input Lines ................................................................................................................... 132
6.2.6 Choose Line Settings......................................................................................................................... 133
6.3 RE-MERGE MOSAIC ...................................................................................................................................... 135
6.4 ADD LINES ................................................................................................................................................... 135
6.5 FORCE REGENERATION ................................................................................................................................... 136
6.6 MOVE LINE .................................................................................................................................................. 137
6.7 REMOVE LINE ............................................................................................................................................... 138
6.8 VISUALIZATION OPTIONS ................................................................................................................................ 139
6.8.1 Color Settings ................................................................................................................................... 139
6.8.2 Mosaic Histogram ............................................................................................................................ 140
6.9 WATERFALL VIEWER ...................................................................................................................................... 142
6.9.1 Waterfall Module ............................................................................................................................. 142
6.9.2 Waterfall Layout .............................................................................................................................. 144
6.9.3 Waterfall Menu Options .................................................................................................................. 145
6.9.4 Waterfall Toolbars ........................................................................................................................... 147
6.9.5 Waterfall Information Displays ........................................................................................................ 147
6.9.6 File Playback Options ....................................................................................................................... 148
6.9.7 Waterfall Map – Link ........................................................................................................................ 150
6.10 WATERFALL TOOLS ..................................................................................................................................... 151
6.10.1 Bottom Tracking ............................................................................................................................. 151
6.10.2 Slant Range Corrections ................................................................................................................. 155
6.10.3 Speed Corrections........................................................................................................................... 156
6.10.4 Waterfall Histogram ...................................................................................................................... 156
6.10.5 Waterfall LUT ................................................................................................................................. 158
6.10.6 Waterfall TVG................................................................................................................................. 159
6.10.7 Waterfall Targets ........................................................................................................................... 162
6.11 INTERPRETATION OPTIONS ............................................................................................................................ 163
6.11.1 Sidescan Blink Comparator ............................................................................................................ 163
6.11.2 Sidescan Statistics .......................................................................................................................... 164
6.11.3 Sidescan Mosaic Targets ................................................................................................................ 165
6.11.4 Sidescan Classification ................................................................................................................... 166
7: TARGETONE ............................................................................................................................................. 166
7.1 TARGETONE MODULE ................................................................................................................................... 166
7.2 TARGET SELECTION........................................................................................................................................ 167
7.2.1 Waterfall Targets ............................................................................................................................. 167
7.2.2 Map View Targets ............................................................................................................................ 167
7.3 TARGETONE APPLICATION .............................................................................................................................. 168
7.3.1 TargetOne Layout ............................................................................................................................ 168
7.3.2 TargetOne Menu Options ................................................................................................................. 169
7.3.3 TargetOne Toolbars ......................................................................................................................... 172
7.4 TARGETONE WINDOW................................................................................................................................... 174
7.4.1 TargetOne Window Regions ............................................................................................................ 174
8: SEACLASS ................................................................................................................................................. 175
8.1 SEACLASS MODULE ....................................................................................................................................... 175
8.2 CREATE TRAINING SET ................................................................................................................................... 175
8.3 BOTTOM CLASSIFICATION ............................................................................................................................... 180
8.4 NEURAL NET TRAINING .................................................................................................................................. 182
8.5 EDIT CLASSIFICATION ..................................................................................................................................... 184
8.6 QUICK CLASSIFICATION .................................................................................................................................. 186
vii | P a g e February 2011
Page 9
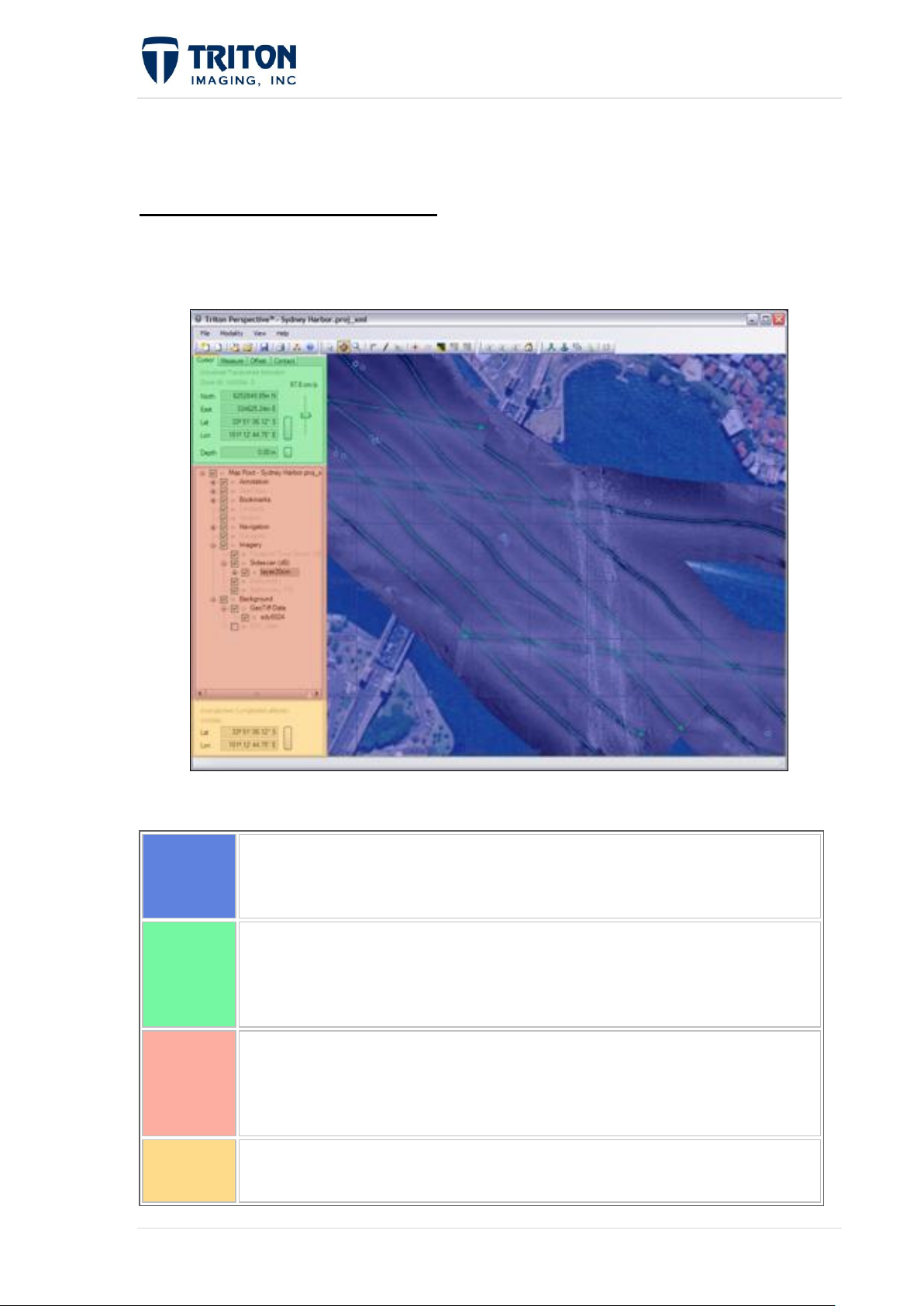
Map View
The map displays all loaded layers. It renders a composite view of all the
data according to the settings of each layer.
Information Tabs
This is a four tab window that displays information based on the current
modality. The tabs include cursor position information, measurement
results, moved line offsets and contact/target information.
File Tree
The Tree View displays all layers loaded into Perspective. Each layer type
has its own right-click menu for changing specific settings. Data in the Tree
View is rendered in the map by compositing the data from bottom to top.
Custom Cursor
This allows the user to display cursor locations using a custom projection.
1: Software Interface
1.1 Main Window Overview
1.1.1 Main Window Layout
Main Window Layout
1 | P a g e February 2011
Page 10

New Project
Create a new Perspective Project
Open Project
Open an existing Project (*.proj_xml)
Save Project
Save your current project (*.proj_xml)
Save Project As
Save project with new name (*.proj_xml)
Import
Primary import menu for recognized types. Can also be
accessed through standard windows drag and drop.
Export
Export Geo TIFF and KML files
Page Setup
Page setup for printing
Print
Print the current project
Quit
Quit Perspective
Select
Map Selection mode
Measure
Map Measure mode
Pan
Map Pan mode
Zoom
Map Zoom mode
Contact Generation
TargetOne or XML Contact Mode
SB Interpretation
Sub-bottom Interpretation mode (not implemented yet)
Classification Training
SeaClass Classification mode
Quick Classification
Quick Classification mode
Edit Classification
Edit Classification mode
Annotation
Annotation mode
Bathy Profile
Bathymetry Profiling mode
Bathy Edit
3D Area Editor mode (not implemented yet)
1.1.2 Main Window Menus
File Menu
Modality Menu
2 | P a g e February 2011
Page 11

A – B
A – B mode
Digitize Lines and
Polygons
Digitization mode (not yet implemented)
Display Depth-Scale
Display Depth-Scale mode
Toolbar
Turn toolbar visibility on/off
Zoom In
Zoom in on map
Zoom Out
Zoom out on map
Zoom 1:1
Zoom to 1 meter/pixel
Zoom Home
Zoom to the extents of your survey area or saved home location
Save As Home
Save current viewport as Home
Add Viewport
Add current viewport to Region node in the file tree
Globe
Turn on ENC Globe rendering
Settings Info
Show settings dialog box
Custom Cursor
Change projection for custom cursor
Log Window
Show the log window
Contents
Show help table of contents
Licensing
Show licensing dialog box
Sales
Show sales dialog box
About
Show about dialog box
Check for Updates
Check for Perspective version updates (via web connection)
View Menu
Help Menu
3 | P a g e February 2011
Page 12
Create a new Perspective project
Open Perspective project
Import raw data files
Import data from folder
Save current projection
Print
Application settings
Help
Mosaic Wizard
BathyPro Wizard
Line Merge
Spot Histogram
Refresh from database
1.1.3 Main Window Toolbars
Main Toolbar
Utility Toolbar
4 | P a g e February 2011
Page 13
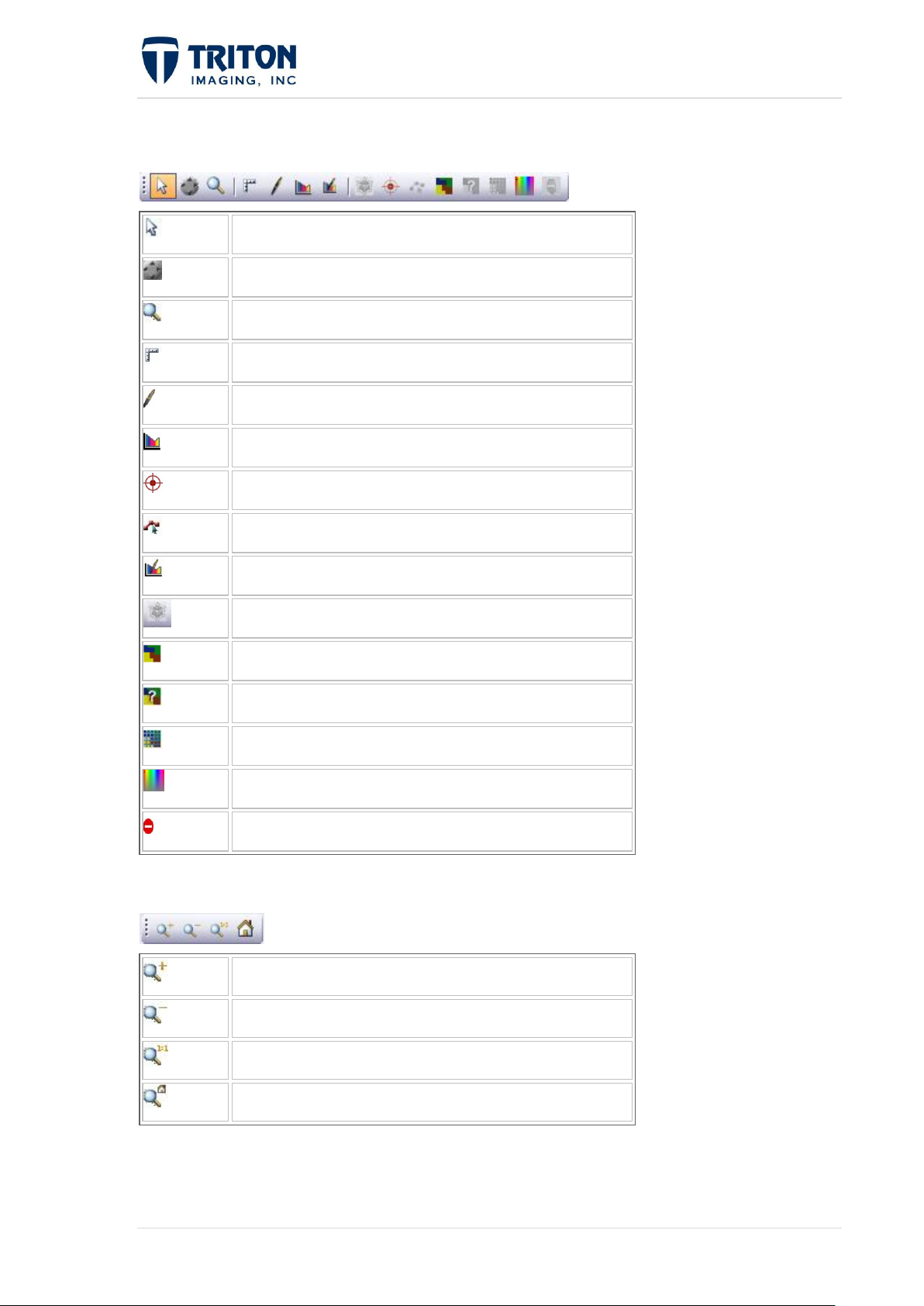
Select Mode
Pan Mode
Zoom Mode
Measure mode
Draw Mode
Bathy Profile Mode
Contact Mode
Sub-bottom interpretation
Bathy Area Edit mode - not yet implemented
Digitize Lines and Polygons - not yet implemented
Classification training mode
Quick classification mode
Edit classification mode
Display Depth Scale
A-B
Zoom in
Zoom out
Zoom 1 to 1
Zoom Home
Modality Toolbar
Zoom Toolbar
5 | P a g e February 2011
Page 14
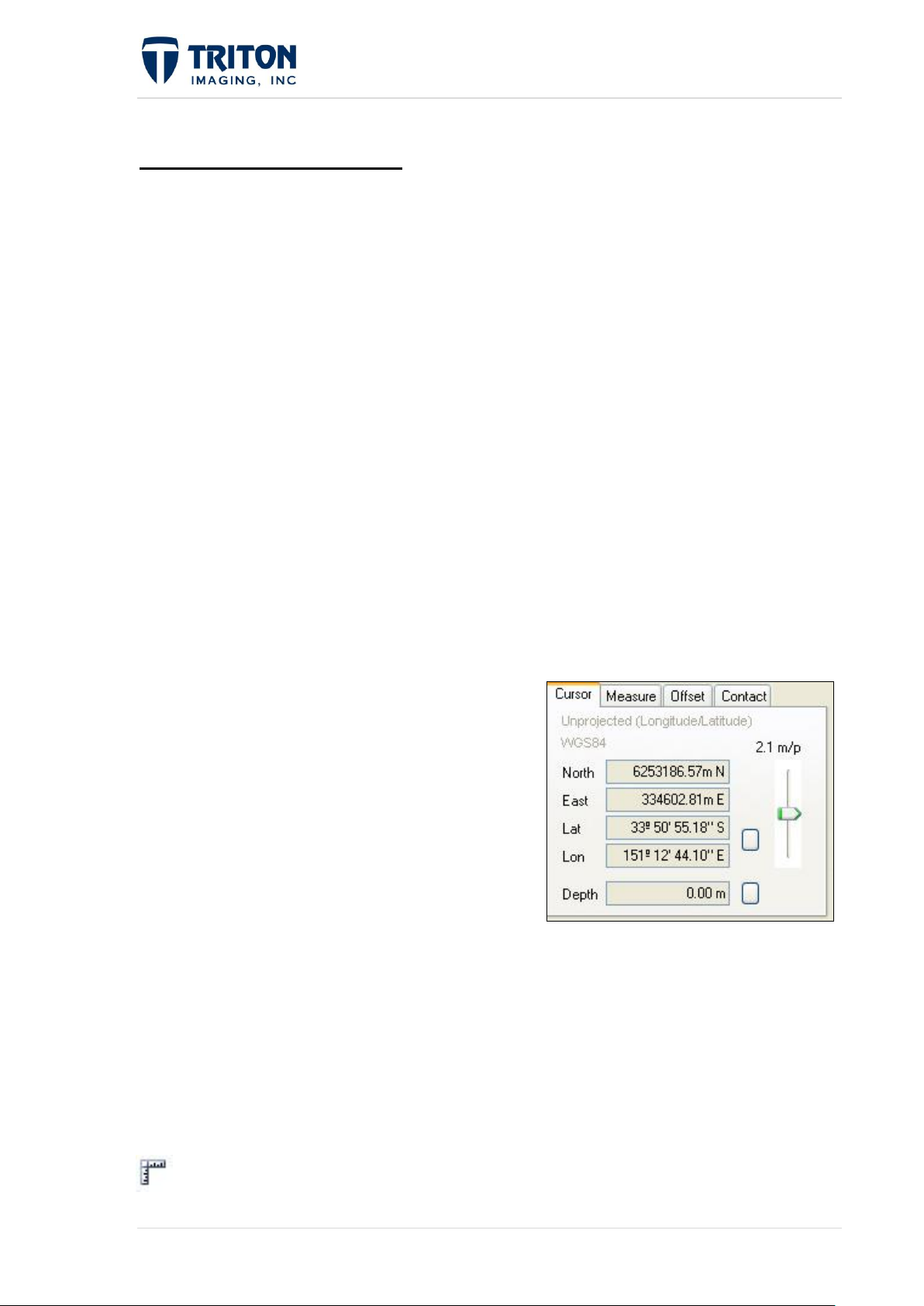
1.2 Information Displays
Perspective Map has four tab-controlled information displays in the upper left corner of the
software window, located to the left of the Map View and above the File Tree.
Cursor Tab: This the default display, which shows the cursor position and the map.
Measure Tab: Shows the results of measurements made in the map view.
Offset Tab: Shows the amount a sidescan line has been moved for feature alignment.
Contact Tab: Indicates the target capture size and next target number.
Custom Cursor: In addition to the 4 tabs of information, there is another cursor information
display below the File Tree for setting a custom cursor position display.
For Custom Cursor Tab details go to Section 1.4.
1.2.1 Cursor Tab
The cursor display is where position values can be viewed dynamically as the cursor is
moved across the Map View.
The current project projection is displayed in gray at
the top of this tab.
North and East, Lat and Lon display the current
cursor position in the Map View. It is updated as the
cursor moves.
The button beside 'Lat' and 'Lon' is used to change
the format of latitude and longitude from 'degrees
minutes decimal seconds' to 'degrees decimal
minutes' to 'decimal degrees'.
The button beside 'Depth' is used to change the depth value from meters to feet.
The slider button is used to change the Map View resolution from meter/pixel to cm/pixel.
Acts like a zoom.
1.2.2 Measure Tab
Selecting the 'Measure' toolbar button in Perspective map will switch the information
6 | P a g e February 2011
Page 15

display to the 'Measure' tab to show the results of measurements made in the map view.
When using the 'Measure' tool, select a starting point on the map by left clicking on the spot
and holding the button down while the distance to measure is spanned. Once the end point is
reached, release the mouse button. The measurement results are displayed dynamically in the
'Measure' tab. Units are always in meters.
The following image shows the results of the most recent measurement:
Horiz. Dist.: the distance covered by the
measurement in the horizontal or "X" direction.
Vert. Dist.: the distance covered by the
measurement in the vertical or "Y" direction.
Distance: the direct distance along the line drawn
in Perspective Map.
1.2.3 Offset Tab
When a sidescan line is moved with the 'Move Line'
function (see topic for move line), the amount the line
was moved in order to align it with the rest of the
mosaic is stored in the cache file.
When a line is moved using the ‘Move Line’ tool, the
amount the line was moved will be displayed in the
‘Offset’ information tab as shown in the image to the
right.
For this line the total amount of displacement was
7.93m, with the horizontal (X) displacement of 3.12m and vertical (Y) displacement of
7.29m.
1.2.4 Contact Tab
Selecting the 'Contact Generation' toolbar button in
Perspective map will switch the information display
to the 'Contact' tab.
Size (in meters) indicates the size of the screen
capture to be made when a target is selected from
7 | P a g e February 2011
Page 16

the Map View.
Contact Number is the number to be assigned to the next target selected.
Also shown is the 'Contacts Color Legend' to visually distinguish between the types of
contacts displayed in the Map View.
1.3 File Tree
The file tree organizes project layers by
grouping similar items. The layers can be
toggled on or off by clicking in the box next to
the layer. A green check-mark appears next to
the items in the map root that are displayed in
the Map View. The order the items are arranged
in the map tree dictates the display order in the
Map View.
1.3.1 Map Root Layer
Layers organized under the heading of Map
Root include:
Annotation
SeaClass
Contacts
Vectors
Navigation
Imagery
Background
All layers in the File Tree can be toggled on/off by checking or un-checking the box next to
the layer. If a box is unchecked, all sub-layers will also be unchecked. Conversely, by
checking a box that is not already checked, all sub-layers will
also be checked.
The image above shows the basic File Tree structure and the
check boxes for toggling the display of that layer:
Right-clicking on ‘Map Root’ will bring up the following menu
for user-defined controls of the map root dialog.
8 | P a g e February 2011
Page 17

Selection Color: Allows the user to identify the color which the selected line will change to,
in order to identify it as being successfully selected in the map directory
Collapse to Roots: Quickly collapse the tree to the major headings. A plus sign will be
assigned in front of those headings which have additional data in their hierarchy.
Expand All: Allows the user to quickly expand all directories within the map root. A
negative sign will be assigned in front of those headings which are fully expanded.
Open Project: Allows the user to open a project from the tree diagram. This has the same
functionality as the “File > Open Project” pathway.
New Project: Allows the user to create a new project from the tree diagram. This has the
same functionality as the “File > New Project” pathway.
Info: Gives the user a “Window” on the Project File contents. The project file has the file
extension .proj xml and is an XML file. Advanced users could edit this file directly using
any XML file editor.
1.3.2 The Annotation Tree
This layer includes information that is user-defined in the Map View. The annotation layer
has three sub-layers: Regions, Grid, and User.
The Regions layer provides one-click access to different preset map zoom levels that are
commonly used for quickly navigating around the Map View.
The Grid layer provides options for changing the projection grid color and resolution settings.
Text and drawing annotations made by the user are stored in the User layer.
1.3.2.1 Regions
Regions are predefined zoom extents that
are useful for quickly moving around in
the map window.
To add a region, zoom the map window
to the area that is to be considered a
region, right click on “Regions” and
select ‘Add Viewport’ as shown below
This is will give a user dialog window to
9 | P a g e February 2011
Page 18
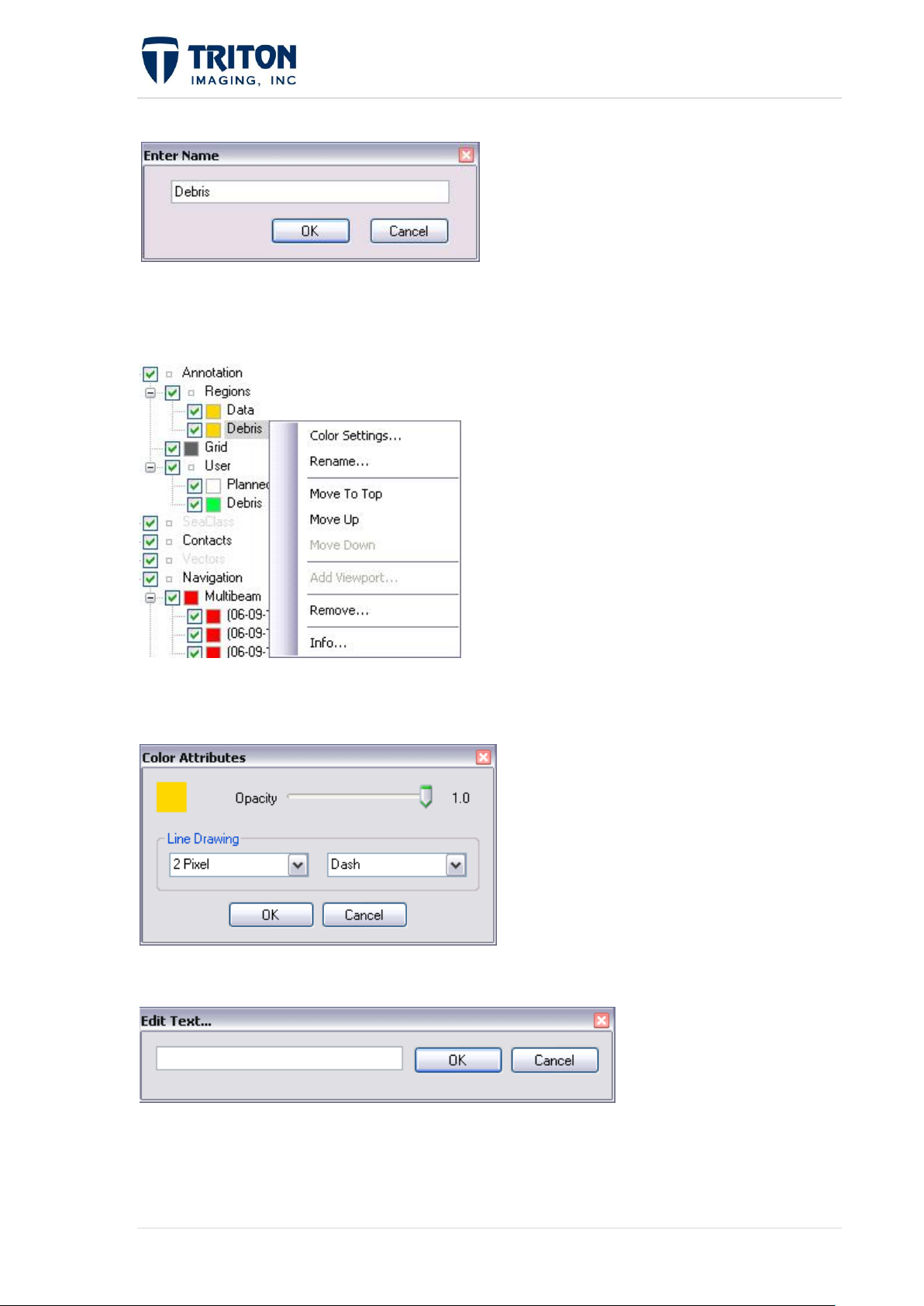
name the selected region.
A dashed outline will appear in the Map View
delineating the area as being selected. The
region name will appear as a node under the
‘Regions’ layer node.
Right-clicking on the region name gives the following options:
Color Settings: The user can change the color and characteristics of the outline, as well as
color, opacity, thickness and character of the line.
Rename: The name of the region can be changed by selecting “Rename…”
Move To Top, Move Up, Move Down: Allows the used to move the region up and down
within the region file tree node.
10 | P a g e February 2011
Page 19
Remove: The region can
be removed by selecting
“Remove…”
Info: Allows the user to
view the datum/projection
and coordinates of the
region.
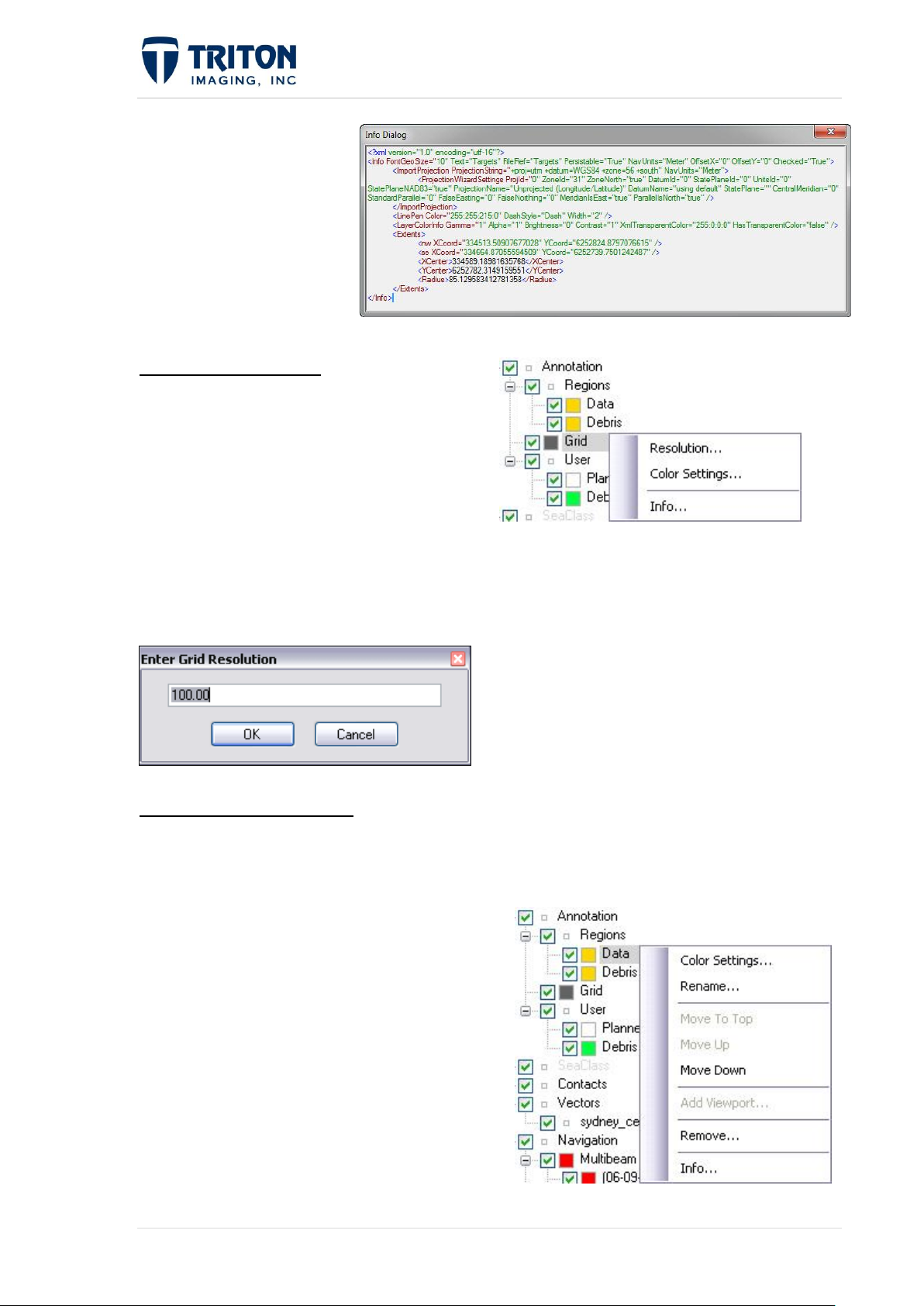
1.3.2.2 Grid Overlay
This is an overlay graph of the lines of
Easting and Northing, which are
automatically displayed in the Map View. It
can be modified in resolution and in color.
Right-clicking on the ‘Grid’ layer will give
the following options:
Resolution: Allows the user to change the resolution of the grid overlay to a user-defined
distance.
Color Settings: Allows the user to change the
color of the grid overlay.
Info: Allows the user to view the resolution,
datum/projection and coordinates of the grid.
1.3.2.3 User Annotation
Drawing tools are available under the Modality > Annotation menu or by selecting the 'Pen'
toolbar button. When annotations are created using the drawing tools, they appear in the
Annotation > User file tree menu.
The following options are available by rightclicking on the individual annotation:
Color Settings: Allows the user to change the
characteristics of the annotation
Rename: Allows the user to rename the userdefined annotation.
Move To Top: Moves the corresponding
annotation to the top of the Tree View within
11 | P a g e February 2011
Page 20
the ‘User’ heading.
Move Up: Moves the corresponding annotation above the previous annotation within the
‘User’ heading.
Move Down: Moves the corresponding annotation below the successive annotation within
the ‘User’ heading.
Remove: Allows the user to remove the annotation from the Map View and Tree View.
Info: Provides the projected position of the annotation.
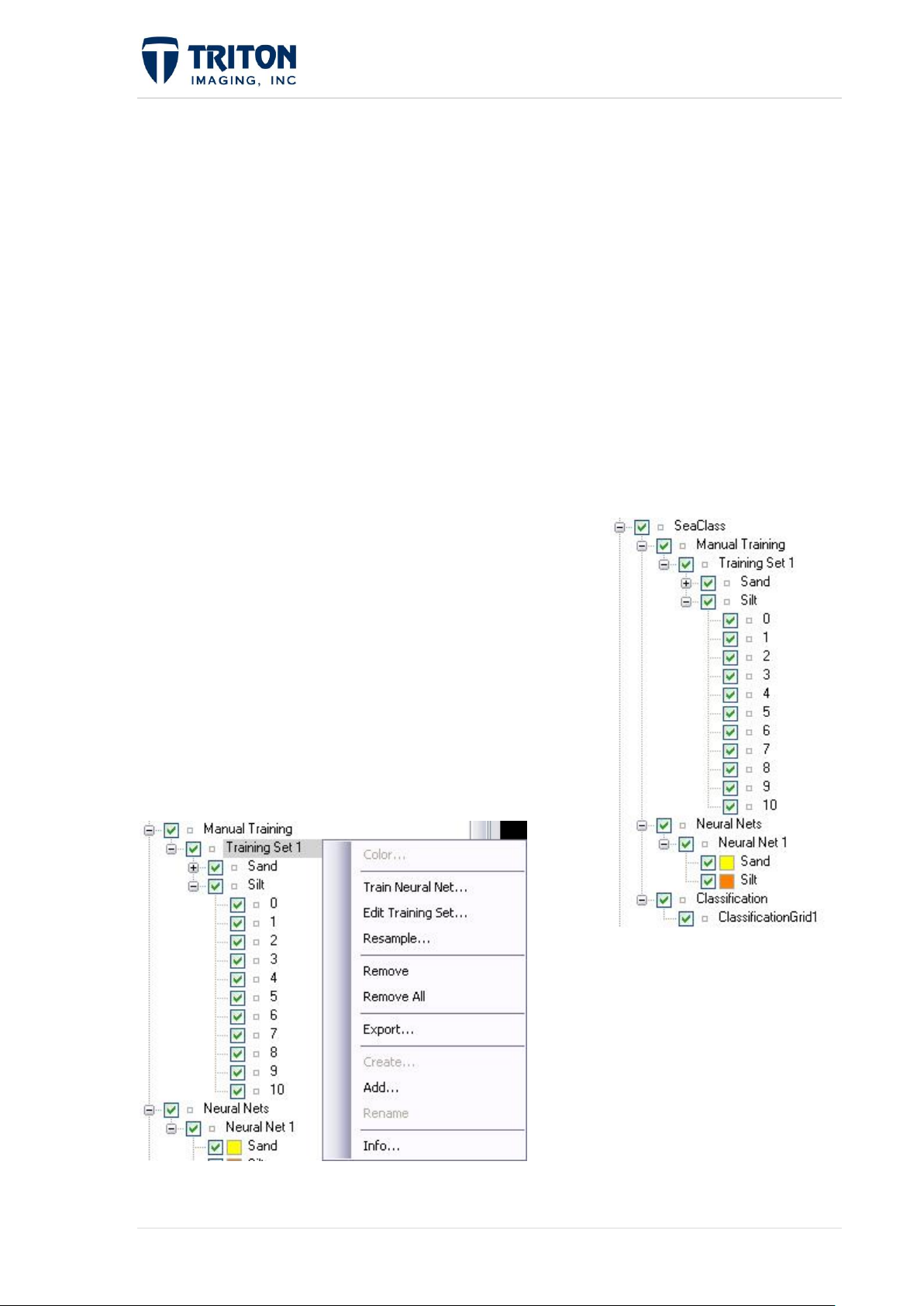
1.3.3 SeaClass Tree
The SeaClass layer contains three sub-layers as shown in the image below:
Manual Training - where training data points are stored
Neural Nets - for displaying the neural nets generated
from the training data
Classification - includes the results of the classification
process
Right-clicking on the Manual Training layer or any of its
sub-layers will give the following options:
12 | P a g e February 2011
Page 21

Color: Available at the class file tree level. Opens color dialog for changing the color of the
sample point icons in the map view.
Train Neural Net: Initiates the second step in the classification process using the training
set created.
More information about the Neural Net training process is presented in Section 8.4.
Edit Training Set: Allows user to make changes to training sets by adding or deleting data
points in a class (bottom type) or to add another class with new data points.
More information about the Edit Training Set process is presented in Section 8.5.
Resample: This will resample the targeted image with the updated training set after edits are
made.
Remove: Removes the selected layer from the project. This is available at the training set
layer and the class layer nodes.
Remove All: Removes all sub-layers from the current tree node.
Export: Allows users to save the SeaClass training set created. SeaClass export options are
described in Section 2.3.6.
Create: Launches the Create Training Set wizard as described in Section 8.2.
Add: Adds an existing training set to the project and Map View.
Rename: Allows users to rename an existing training set that is in the file tree.
Info: Allows the user to view XML info for the selected file.
Right-clicking on the Neural Nets layer or any of its sub-layers will give the following
options:
Move to Top: Moves the selected layer to the
first position within the “Neural Nets” heading.
Move Up: Moves the selected layer above the
previous file within the “Neural Nets” heading.
Move Down: Moves the selected layer below
the succeeding file with the “Neural Nets”
heading.
Add: Adds an existing neural net to the project and Map View.
13 | P a g e February 2011
Page 22

Remove: Removes the selected layer from the project.
Remove All: Removes all sub-layers from the current tree
node.
Rename: Allows users to rename an existing neural net that
is in the file tree.
Edit Color: Opens color dialog for changing the color of the
neural net class.
Right-clicking on the Classification layer or any of its sublayers will give the following options:
Color Settings: Opens following window for changing background color, opacity, and line
drawing settings.
Move to Top: Moves the selected layer to the first position within the “Classification”
heading.
14 | P a g e February 2011
Page 23
Move Up: Moves the selected layer above the previous file within the “Classification”
heading.
Move Down: Moves the selected layer below the succeeding file with the “Classification”
heading.
Export: This will export the classification results to an AutoCAD DXF file.
Add: Adds an existing classification grid to the project and Map View.
Remove: Removes the selected layer from the project.
Info: Allows the user to view XML info for the selected file.
Zoom to Extents: Quick zoom option to zoom to full extent of selected mosaic.
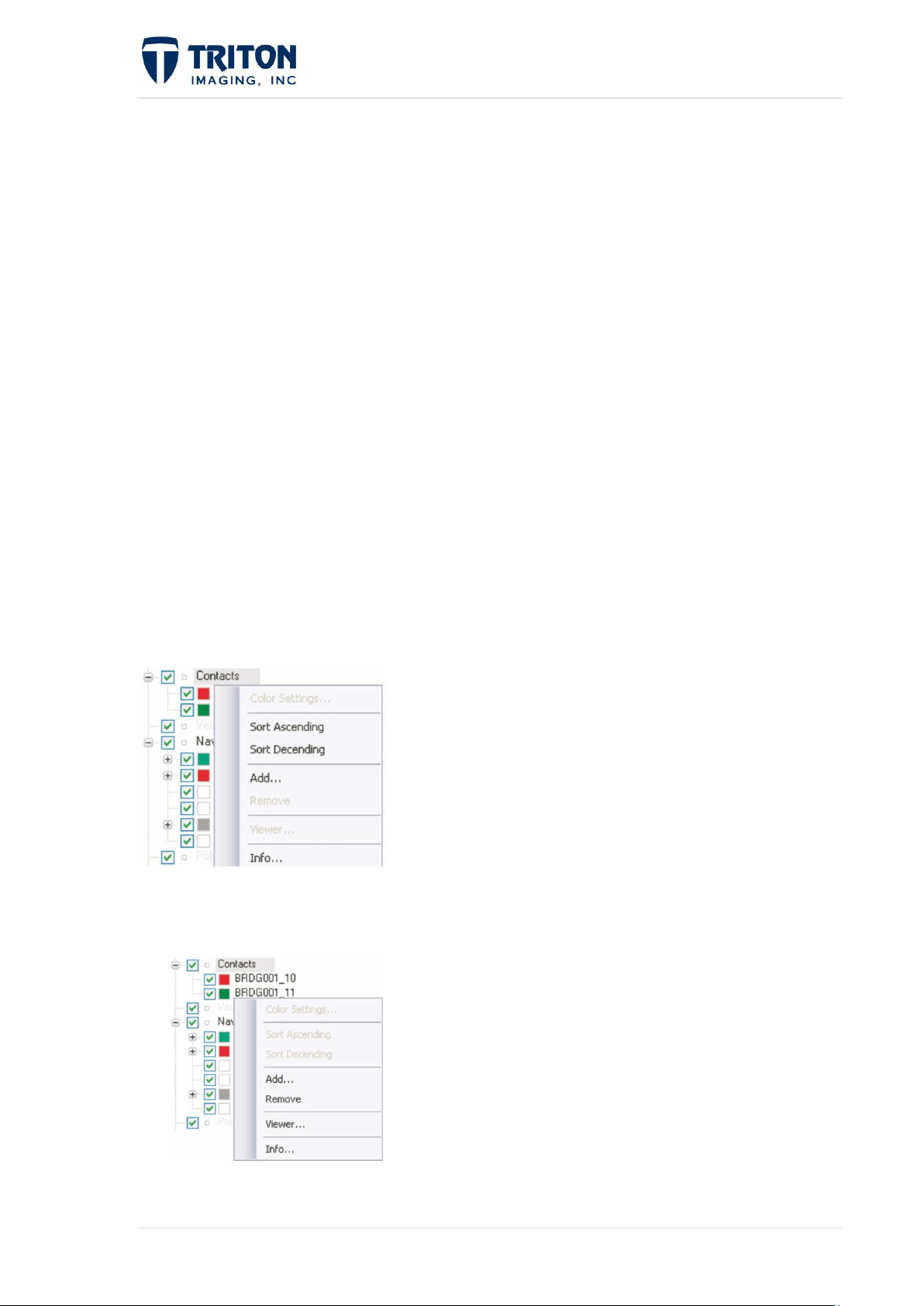
1.3.4 Contacts Tree
The Contacts layer contains the contacts and targets identified and saved with TargetOne.
Contacts classified as targets show up as a different color which can be defined by the user.
Right-clicking on the ‘Contacts’ layer will give the following options:
Sort Ascending: Sorts the ‘Contacts’ in the project by
name in ascending order in the file tree.
Sort Descending: Sorts the ‘Contacts’ in the project by
name in descending order in the file tree.
Add: Adds a saved contact to the project and Map View.
Info: Allows the user to view the file location,
datum/projection and coordinates of the contact file.
Right-clicking on the region name gives the following options:
Add: Adds a saved contact to the project and Map View.
Remove: This will remove a contact from the project.
Please note that this will not delete the contact from the
hard drive, only remove it from the project and Map View.
Viewer: Selecting this option opens the contact in
TargetOne.
Info: Allows the user to view the file location,
datum/projection and coordinates of the contact file.
15 | P a g e February 2011
Page 24
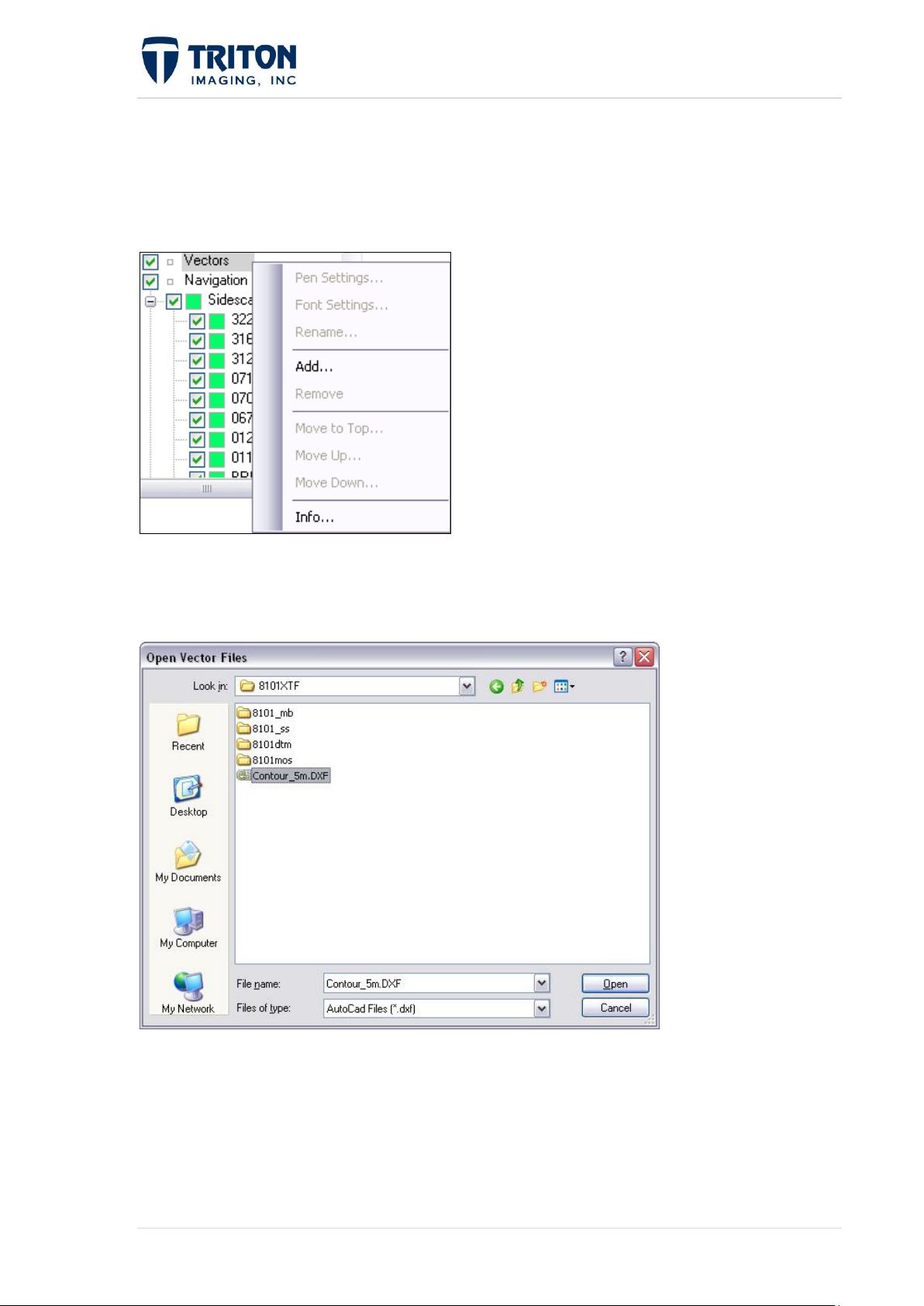
1.3.5 Vectors Tree
Vector files can be imported in DXF format (Autocad R12 DXF only). Right-clicking on
‘Vector’ will give the user the following options.
If no vector files are currently available, the user can click on ‘Add’ to insert a file. This will
open a browser window that will be searching for a file in the DXF file format.
After selecting the DXF file to be imported into the Map View, the user will define the
projection and datum for the file. Projection and Datum standards are available for selection,
or user defined projections can be set by selecting ‘Custom’.
Right-clicking on a vector file that has been imported into Perspective provides the following
16 | P a g e February 2011
Page 25
options:
Rename: Allows the user to rename the vector file in the Tree
View. This does not change the name of the file, only the
reference name within Perspective Tree View.
Remove: Allows the user to remove individual vector files
from the map tree and Map View.
Move to Top: Moves the individual vector file to the first
position within the ‘Vector’ heading.
Move Up: Moves the individual vector file above the previous file within the ‘Vector’
heading.
Move Down: Moves the individual vector file below the succeeding file with the
‘Vector’ heading.
Info: Allows the user to view the projection and file path directory of the vector file.
1.3.6 Navigation Tree
This file tree layer is where the navigation for the various files are kept and organized. The
main sources of navigation available in this heading are:
Sidescan - navigation for sidescan data imported from raw data file
Multibeam - navigation for multibeam data imported from raw data file
Singlebeam - navigation for singlebeam data imported from raw data file
Subbottom - navigation for subbottom data imported from raw data file
Vessel - vessel navigation imported from raw data file
The navigation data automatically populate these sub-tree layers depending on the type of
data present in the import file. There is an additional node in the Navigation tree called
Viewer.
When viewing the raw data of an imported file, the line name will appear under the Viewer
node. This applies to sidescan data in the waterfall window and multibeam data in the swath
viewer.
17 | P a g e February 2011
Page 26
There are no right-click options on the Navigation tree node but sub-layers have the
following options:
Reset Navigation: Allows the user to return the navigation
to its original position as interpreted from the data file.
Selecting this option from right-clicking on a mosaic file
will reset the navigation for all XTF files in the mosaic.
Right-clicking on a single XTF will only reset the
navigation for the selected file and file type.
View: This option is available on the XTF layer level and
will open a waterfall viewer for sidescan navigation and a
swath viewer for multibeam navigation.
More information on the Waterfall Viewer and Swath
Viewer can be found at Sections 5.9 and 5.9.4.
Sort Ascending: Sorts the data files by name in ascending
alphanumeric order.
Sort Descending: Sorts the data files by name in descending alphanumeric order.
Add: Allows the user to add data files.
Remove: Allows the user to remove all navigation for a particular line from the Map View.
It will remove the navigation line from the Multibeam, Sidescan and Vessel nodes.
Info: Access XML settings file for viewing the projection, file path directory of the vector
file, ping range in viewer window, and other information.
Zoom to Extents: Quick zoom option which zooms to the full extent of the navigation data
for Multibeam, Sidescan and Vessel nodes.
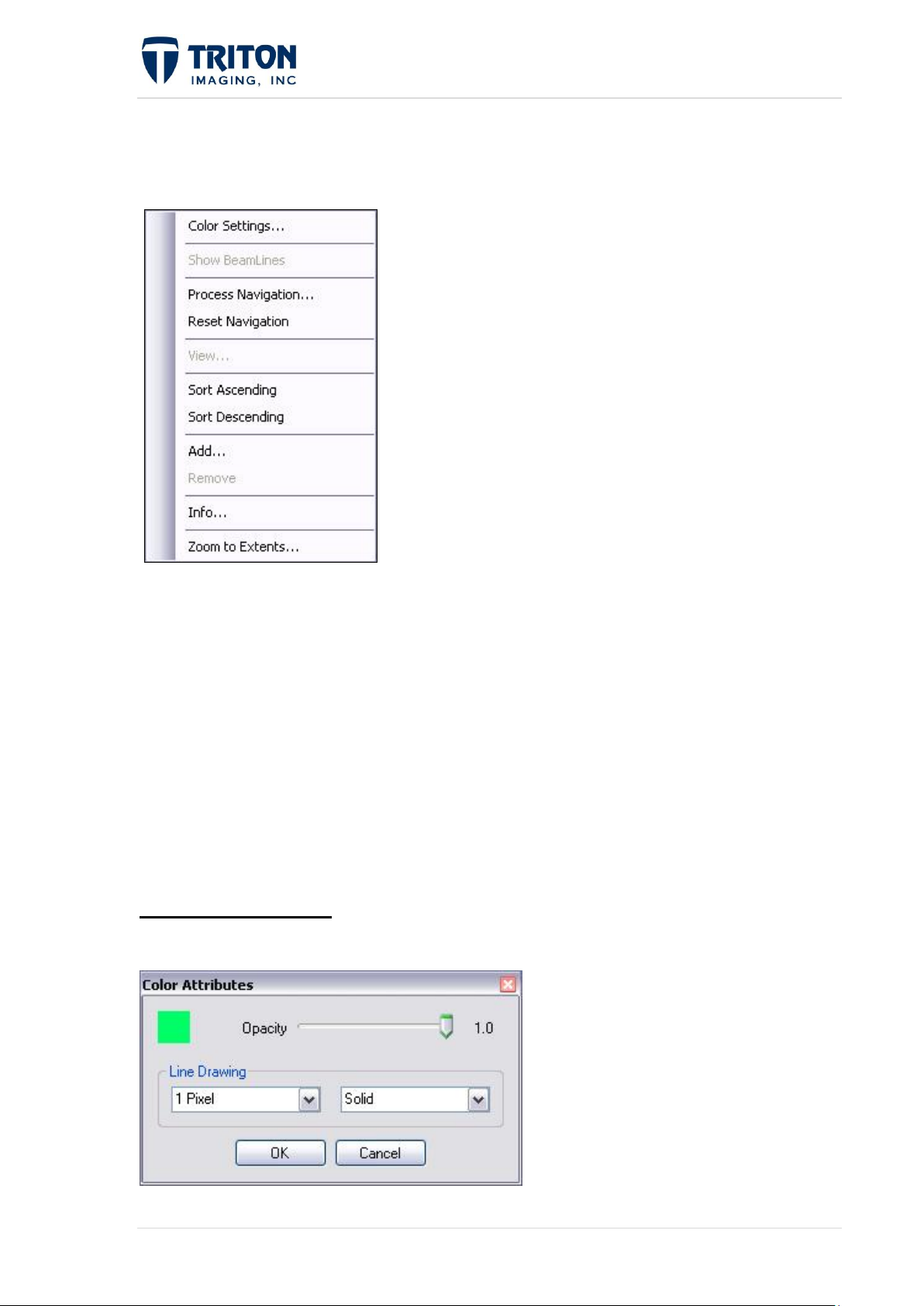
1.3.6.1 Color Settings
Selecting this will open the following window:
18 | P a g e February 2011
Page 27
Options include:
Color - click on colored box and select new color from 'Color' window
Opacity - slider bar for changing transparency level
Line Drawing - line thickness can be changed by selecting left drop-down menu, line
style can be changed be selecting the right drop-down menu. Line style options
include:
Color Settings are available for all navigation sub-layers.
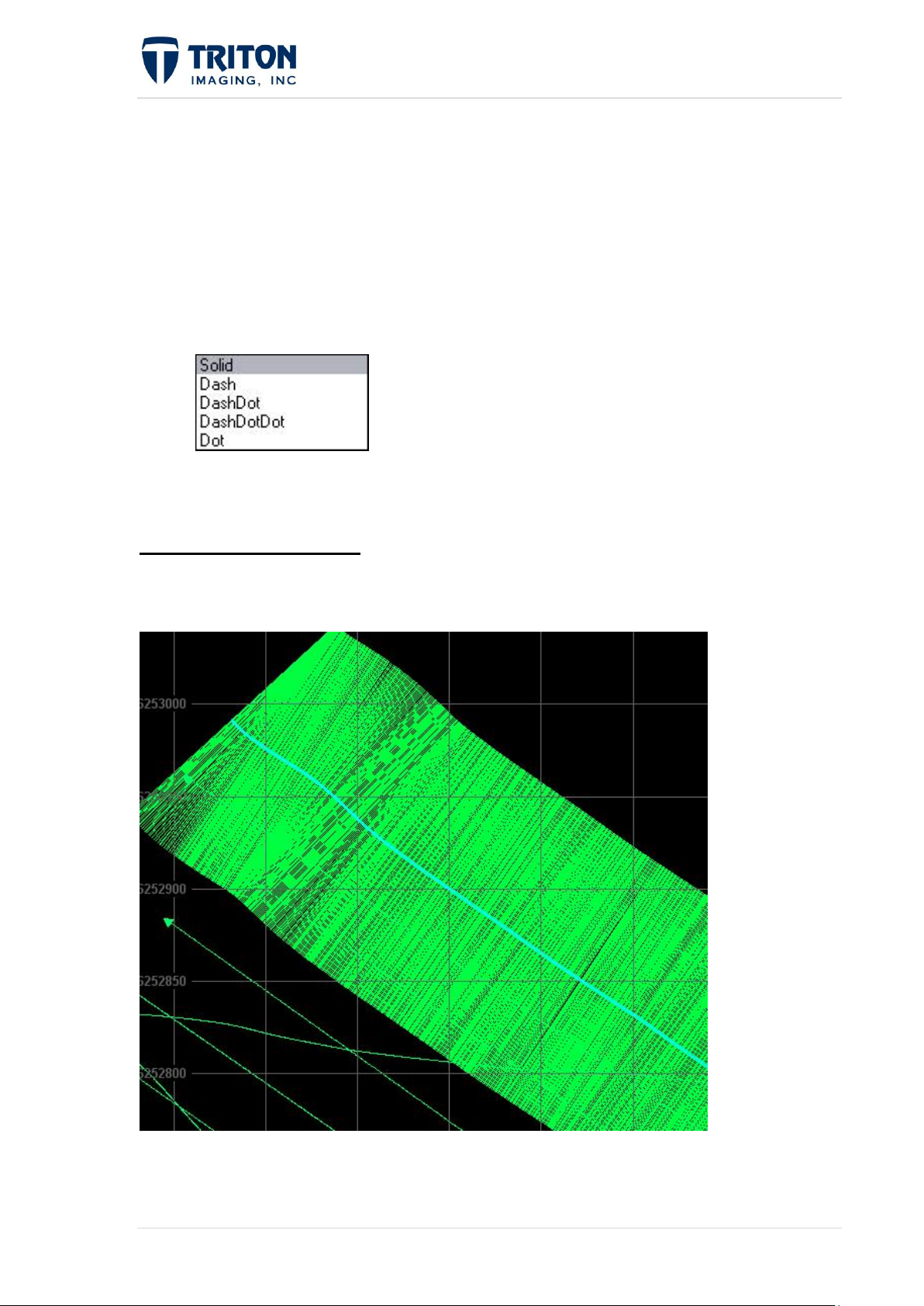
1.3.6.2 Show BeamLines
This is only available for sidescan data by right-clicking on the individual lines. By selecting
this option, the swath lines for each ping are displayed in the Map View as shown below:
The line selected is highlighted in light blue and the individual swath lines indicate the swath
coverage for that line.
19 | P a g e February 2011
Page 28
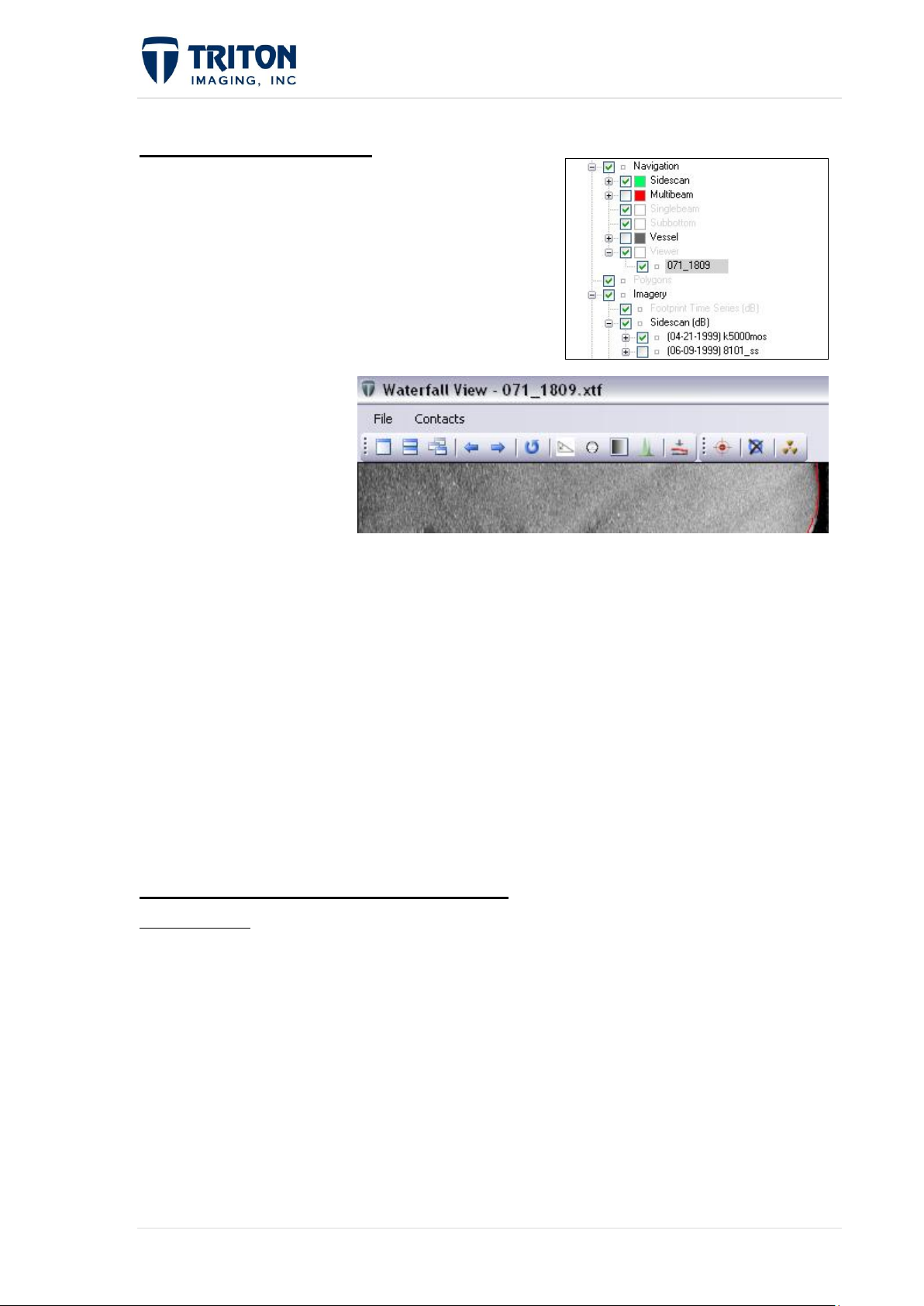
1.3.6.3 Navigation Viewer
This option is available at all tree levels in the
Navigation. When the raw data from any Navigation
tree layer is being viewed, the line name will appear
under the ‘Viewer’ node. Currently this is only
enabled for the sidescan waterfall window and the
multibeam swath viewer. The example shown below
is for a sidescan line:
As shown in the ‘Viewer’
node in the Navigation file
tree, the line being viewed
is 071-1809. This is
confirmed in the waterfall
window title bar as shown
to the right.
1.3.7 Imagery Tree
This file tree layer is where the imagery data is kept and organized. There are five types of
imagery supported:
Footprint Time Series
Sidescan
Bathymetry
Bathymetry TIN
Bathymetry TPE
1.3.7.1 Sidescan & Footprint Time Series
Sidescan Node: The sidescan imagery file tree layer is where the mosaic files that are
imported or created from raw data are managed. The following options are available by
right-clicking on the sidescan node.
Move to Top: Allows the user to move the Sidescan imagery to the top of the tree within
the Imagery node.
Move Up: Allows the user to move the Sidescan imagery to above the previous imagery
within the Imagery node.
Move Down: Allows the user to move the Sidescan imagery to below the successive
imagery within the Imagery node.
20 | P a g e February 2011
Page 29

Export to GeoTiff: Allows the user to export the imagery to a geotiff imagery file.
Batch Export to GeoTiff: Allows the user to export all sidescan mosaics in the file tree
to a geotiff imagery files.
Export KML: Allows the user to export a Google Earth KML file.
Create: Allows the user to create a new mosaic layer using any of the existing raw data
files in the project. A new layer name is specified, then the parameters for the new layer
are processed and finally the user can choose which lines to include.
Add: Allows the user to add other mosaic files to an
existing project.
Info: Access XML settings file for viewing the
projection, resolution, file path directory of the
sidescan data, plus other information.
Mosaic Node: The following options are available by
right-clicking on the individual mosaic layer under the
sidescan node.
Color Settings: Allows the user to change the color
characteristics of the sidescan layer.
Histogram: This is the graphical representation of the
imagery signal level in dB versus the occurrence of
that dB within the image.
Move to Top: Moves the selected image file to the
top of the Tree View within the Imagery > Sidescan
layer. The image file listed on top (or first) within the
Tree View will be displayed on top of all other image
files of similar type.
Move Up: Moves the selected image file above the
previous sidescan image file in the Tree View. The
image files will be displayed in the order listed within
the Tree View.
Move Down: Moves the image file below the successive sidescan imagery file. The
image files will be displayed in the order listed within the Tree View.
Mosaic Settings: Opens the Mosaic Wizard so that the user can make changes to mosaic
settings used to create the imagery. More information about the MosaicOne Wizard can
be found at section 6.2.
21 | P a g e February 2011
Page 30
Re-merge Mosaic: Applies user corrections and line changes to the mosaic.
Export GeoTiff: Exports a GeoTiff of the selected sidescan mosaic file.
Export KML: Exports a KML file of the selected sidescan mosaic file(s).
Classify: Classifies the selected sidescan mosaic file. Details on using the sediment
classification tool in Perspective are available in section 8.3.
Blink Comparator: Toggles a sidescan layer on and off at a set cycle rate to get a visual
comparison of the same location in two different sidescan layers or mapping events.
Statistics: This gives an overview of the data used to create the image. Included in the
statistics window are the following:
Allocated Coverage: This is the number of square nautical miles which the tiles used
to store the data in the DTM or MOZ file represent.
Actual Coverage: This is the number of square meters of the actual ensonified area.
Total Lines: This is the number of lines included and used in the creation of the
mosaic file
Along-Track Distance: This is the combined along-track distance of all lines included
and used in the creation of the mosaic file.
Add Lines: Allows the user to add other raw data files in the project to the mosaic.
Remove: Allows the user to remove the imagery from the Map View. Perspective will
prompt the user to confirm before removing the imagery.
Delete: This action removes the imagery file from the project and deletes the mosaic file
that was created on import. Perspective will ask for confirmation before deleting the
imagery from the disk.
Info: Access XML settings file for viewing the projection, resolution, file path directory
of the mosaic file, plus other information.
Zoom to Extents: Quick zoom option to zoom to full extent of selected mosaic.
Sidescan Data File: The following options are available by right-clicking on the individual
sidescan data files under the mosaic node.
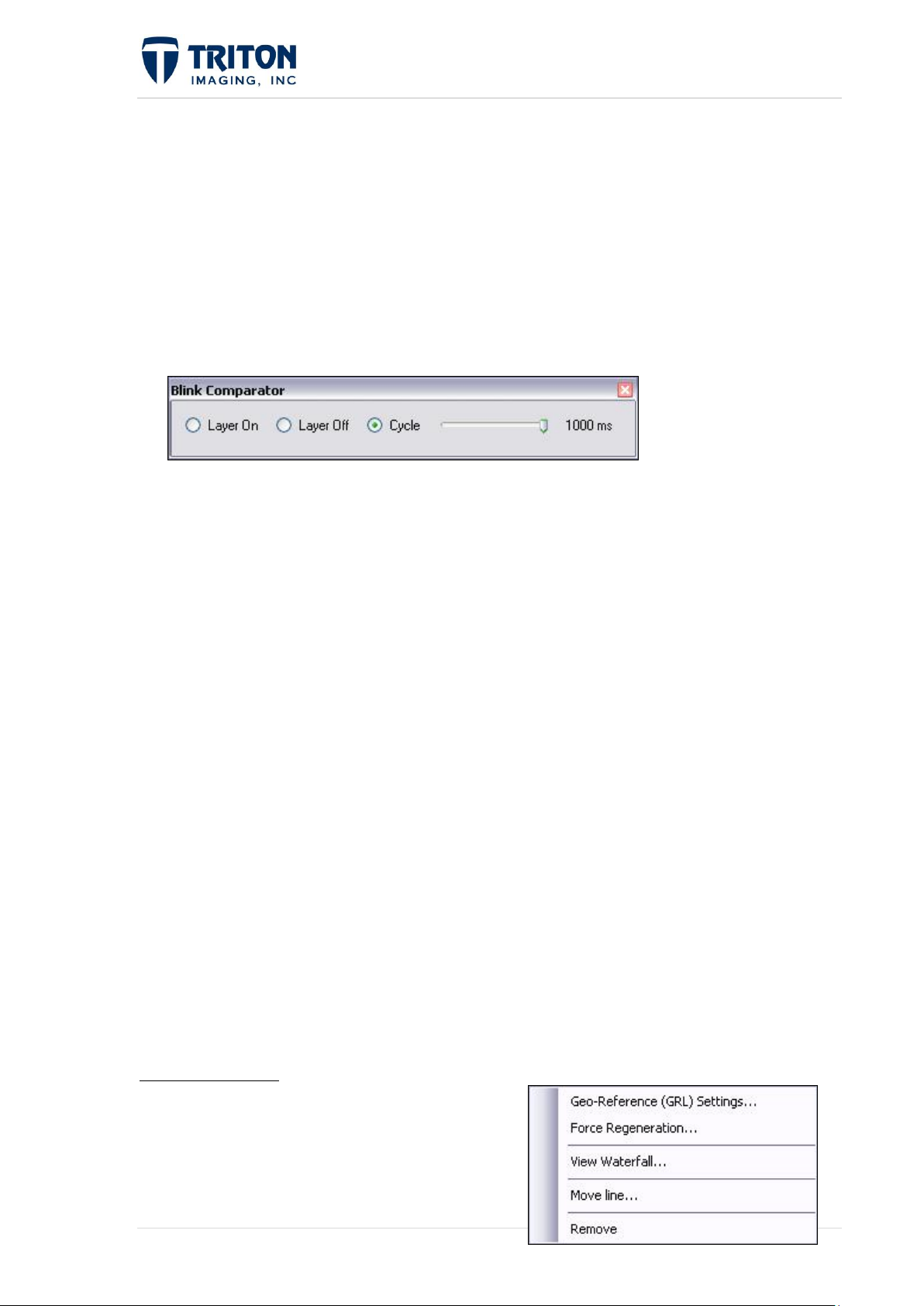
Geo-Reference (GRL) Settings: Opens the
Mosaic Wizard and allows changes to be
made to the Line Settings page.
22 | P a g e February 2011
Page 31

Force Regeneration: Rebuilds the mosaic using the current settings.
View Waterfall: This option is available on the XTF layer level and will open a
waterfall viewer.
Move Line: This option allows the user to move an individual line of sidescan data to
align features on adjacent lines in the mosaic.
Remove: Allows the user to remove the data file from the DTM. Perspective will
prompt the user to confirm before removing the selected file.
1.3.7.2 Bathymetry, TIN & TPE
The bathymetry imagery file tree layer is where the DTM files that are imported or created
from raw data are managed.
Bathymetry Node: The options shown in this image are
available by right-clicking on the Bathymetry node.
Color Settings: Allows the user to change the color
characteristics of the bathymetry imagery. Changing
the settings at this level affects the color settings for all
bathymetry layers.
Histogram: This is the graphical representation of the
imagery signal level in dB versus the occurrence of that
dB within the image. Changing the settings at this
level affects the histogram for all bathymetry layers.
Relief Shading: This tool simulates the illumination
of the sun on the bathymetry data. This is a global
setting and can only be changed at this node level.
Move to Top: Allows the user to move the
Bathymetry imagery to the top of the tree within the
Imagery node.
Move Up: Allows the user to move the Bathymetry
imagery to above the previous imagery within the
Imagery node.
Move Down: Allows the user to move the Bathymetry
imagery to below the successive imagery within the
Imagery node.
Sort by: Allows the user to sort Bathymetry layers by either Name or Date.
23 | P a g e February 2011
Page 32

Export to GeoTiff: Allows the user to export the imagery to a geotiff imagery file.
Batch Export to GeoTiff: Allows the user to export all bathymetry DTMs in the file tree
to geotiff imagery files.
Export KML: Allows the user to export a Google Earth KML file.
Create: Allows the user to create a new DTM layer using any of the existing raw data
files in the project. A new layer name is specified, then the parameters for the new layer
are processed and finally the user can choose which lines to include.
Add: Allows the user to add other mosaic files to an existing project.
Info: Access XML settings file for viewing the projection, resolution, file path directory
of the bathymetry data, and other information.
DTM Node: The options shown in the image to the right are available by right-clicking on
the individual ‘DTM’ layer under the Bathymetry node.
Color Settings: Allows the user to change the color characteristics of the bathymetry
layer.
Histogram: This is the graphical representation of the imagery signal level in dB versus
the occurrence of that dB within the image.
Move to Top: Moves the selected image file to the top of the Tree View within the
Imagery > Bathymetry layer. The image file listed on top (or first) within the Tree View
will be display on top of all other image files of similar type.
Move Up: Moves the selected image file above the previous bathymetry image file in the
Tree View. The image files will be displayed in the order listed within the Tree View.
Move Down: Moves the image file below the successive bathymetry imagery file. The
image files will be displayed in the order listed within the Tree View.
Sort by: Allows the user to sort Bathymetry layers by either Name or Date.
Rebuild Using: Upon selecting this option, the user is asked if they want to use the GSF
flags already present in the GSF. The Bathy Wizard then opens to allow the user to make
changes to bathymetry settings used to create the imagery and apply any edits/flags made
to the GSF file.
For more information about the Rebuild Using tool, visit Section 5.3.
Edit GSF Using: Upon selecting this option, the Bathy Wizard opens so that the user
can apply any edits/flags made to the GSF file.
For more information about the Edit GSF tool, visit Section 5.4.
24 | P a g e February 2011
Page 33

Re-merge DTM: Applies user corrections and line changes to the DTM.
For more information about the Re-Merge DTM tool, visit Section 5.5.
Batch Export to GeoTiff: Allows the user to export all bathymetry DTMs in the file tree
to GeoTiff imagery files.
Export KML: Exports a KML file of the selected bathymetry DTM file(s).
Export XYZ: Allows the user to export the selected bathymetry DTM in the file tree to
an ASCII XYZ file.
A-B: Subtracts co-registered DTMs to look for changes to bathymetry. This algorithm
does a direct pixel to pixel comparison at each grid node.
For more information about the Bathy A-B tool, visit Section 5.10.2.
Blink Comparator: Toggles a sidescan layer on and off at a set cycle rate to get a visual
comparison of the same location in two different sidescan layers or mapping events.
Change Detection: Subtracts co-registered DTMs to look for changes to bathymetry.
This algorithm differs slightly from the A-B algorithm in that it also includes a statistical
neighborhood approach to account for mis-registration between layers. Operating the
Change Detection tool is the same as the A-B tool.
Statistics: This gives an overview of the data used to create the image. Included in the
statistics window are the following:
Allocated Coverage: This is the number of square nautical miles which the tiles used
to store the data in the DTM file represent.
Actual Coverage: This is the number of square meters of the actual ensonified area.
Total Lines: This is the number of lines included and used in the creation of the
mosaic file
Along-Track Distance: This is the combined along-track distance of all lines included
and used in the creation of the mosaic file.
Add Lines: Allows the user to add other raw data files in the project to the DTM.
25 | P a g e February 2011
Page 34

Remove: Allows the user to remove the imagery from the Map View. Perspective will
prompt the user to confirm before removing the imagery.
Reset Date: Provides the ability to change the date of the DTM file.
Delete: This action removes the imagery file from the project and deletes the DTM file
that was created on import. Perspective will ask for confirmation before deleting the
imagery from the disk.
Info: Access XML settings file for viewing the projection, resolution, file path directory
of the DTM file, and other information.
Zoom to Extents: Quick zoom option which zooms to the full extent of the selected
DTM.
Bathy Data File: The following options are available by right-clicking on the individual
bathymetry data files under the ‘DTM’ node.
Remove: Allows the user to remove the data file from
the DTM. Perspective will prompt the user to confirm
before removing the selected file.
View Swath: This option is available on the XTF layer level and will open a swath
viewer to view the multi-beam data by swath.
View GSF History: This option is available on the XTF layer level and will indicate
what processing steps have been performed on the GSF file.
1.3.8 Background File Tree
This is where the background data is stored and organized within the Tree View.
There are two types of files that are used for background images:
1. GeoTiff
2. ENC Charts
1.3.8.1 Background GeoTiff Data
To bring a background GeoTiff into the project, you can either right-click on the layer node in
the file tree:
Background > GeoTiff Data
26 | P a g e February 2011
Page 35

or the window menu option:
File > Import > GeoTIFF File.
Both options will open a file browser to locate a GeoTiff.
Once selected the projection for the image will need to be defined if this was not previously
set in the Projections Tab for the Application Settings or for a previous background import.
Perspective will remember your import projection after the first image is imported so the user
will not need to repeat the projection wizard for every background file.
GeoTiff Data Node Options: By right-clicking on the GeoTiff Data node, the following
options exist:
Color Settings: Allows the user to change the color
characteristics of the GeoTiff layer.
Add: Allows the user to add other GeoTiff files to an existing
project.
Info: Access XML settings file for viewing the projection,
resolution, file path directory of the background data, and other
information.
Zoom to Extents: Quick zoom option which zooms to the full
27 | P a g e February 2011
Page 36

extent of selected GeoTiff.
GeoTiff Options: Right-click on the imported GeoTiff, for the following options:
Color Settings: Allows the user to change the color characteristics of the GeoTiff layer.
Projection: Allows the user to change the GeoTiff projection.
Tag Info: Displays the GeoTiff world file information as shown below:
Remove: Removes the selected GeoTiff file from the project.
Info: Access the XML settings file for viewing the projection, resolution, file path
directory of the background data, and other information.
Zoom to Extents: Quick zoom option which zooms to the full extent of selected
GeoTiff.
1.3.8.2 Background ENC Charts
To bring a background S57 ENC (Electronic Nautical Chart) into the project, you can either
right-click on the Layer node in the file tree and select ‘Add’
Background > ENC Data or the window menu option File > Import > ENC (S57) File.
Both options will open the ENC Search
window.
Pressing the Import button will open a file
browser to locate a S57 .000 or .7cb file.
28 | P a g e February 2011
Page 37

Once selected, the ENC will be imported into Perspective. It will then be displayed in the
Map View and added to the Background > ENC Data layer in the File Tree.
ENC Data Node Options: By right-clicking on the ENC Data node, the following options
exist:
Add: Allows the user to add other S57 ENC files to an existing project.
29 | P a g e February 2011
Page 38

Info: Access XML settings file for viewing information about the ENCs in the node.
ENC Options: Right-click on the imported ENC, for the following option:
Info: Access XML settings file for viewing information about the ENC.
Display settings for ENC data files can be found in Program Settings in Section 3.4.
1.4 Custom Cursor
In addition to the 'Cursor' tab which displays the cursor position in both projected and unprojected coordinates, the cursor position can be displayed in another coordinate system in
the Custom Cursor display located below the File Tree.
The elongated button beside 'Lat' and 'Lon' is used to change the format to either a preset or a
custom format. Clicking this button starts the ‘Select Custom Projection’ wizard as shown
below.
30 | P a g e February 2011
Page 39

In this example we set the ‘Custom Cursor’ to a Transverse Mercator projection. To enter a
custom projection, select the 'Custom' button in the window to launch the 'Custom Projection
Tool'.
For Custom Projection details go to Section 3.5.3.
The projection parameters can be entered here.
31 | P a g e February 2011
Page 40

Select the datum here or the 'Custom' button to setup a custom datum.
For Custom Datum details go to Section 3.5.4.
1.5 Map View
1.5.1 Moving Around the Map View
There are two methods for navigating the Map View. These are:
1. Zoom Tools
2. Pan Tool
Zoom - There are several available zoom options including:
Zoom Mode
Zoom In
Zoom Out
Zoom 1:1
Zoom Home
32 | P a g e February 2011
Page 41

Zoom to Region
Zoom to Extents
Pan - This mode allows the user to move around the screen by dragging the map.
1.5.1.1 Zoom Mode
Selecting the zoom toolbar button
puts the cursor in Zoom Mode.
This allows the user to select an area to
zoom into by left-clicking or rightclicking on any point on the map and
holding the button down while defining
an area to zoom into.
1.5.1.2 Zoom In
This will zoom in one level and is accessed by the following options
ToolBar Icon
View menu option
Keyboard 'Page Down' or '+' key
1.5.1.3 Zoom Out
This will zoom out one level and is accessed by the following options
ToolBar Icon
View menu option
Keyboard 'Page Up' or '-' key
1.5.1.4 Zoom 1:1
This will zoom such that 1 meter is equivalent to 1 pixel on the computer screen and is
accessed by the following options
33 | P a g e February 2011
Page 42

ToolBar Icon
View menu option
Keyboard 'End' key
1.5.1.5 Zoom Home
This will zoom to Home which by default is the full extent of the data but can be manually
set to any zoom with the 'Save As Home' option in the View menu. Zoom Home is accessed
by the following options
ToolBar Icon
View menu option
Keyboard 'Home' key
1.5.1.6 Zoom to Region
This option is only available by selecting the desired Region in the Annotation file tree as
shown in the example below:
By clicking on 'Region 0' in the file tree, the Map View will automatically zoom to that
region (shown as a yellow dashed box in image).
34 | P a g e February 2011
Page 43

1.5.1.7 Zoom to Extents
This option is available by right-clicking on select nodes within the File Tree. Selecting this
will zoom the Map View to the full extent of the chosen data.
1.5.1.8 Pan Mode
This mode allows for moving around the data at a particular zoom level by dragging the
screen with the cursor.
Select the pan/zoom icon and then left-click and drag the screen with the button
depressed.
When the mouse button is released, the view will redraw at the new location. Pan mode is
discussed more in section 1.5.2.3.
To exit this mode, another mode button must be selected, such as the Select mode button
1.5.2 Cursor Modes
There are several cursor modes available through the toolbar buttons and menu options.
These are:
1. Select Mode
2. Measure Mode
3. Pan Mode
4. Zoom Mode
5. Contact Generation / Targeting Mode
6. Classification Modes
Classification Training
Edit Classification
Quick Classification
7. Annotation Mode
8. Bathymetry Profiling Mode
9. A-B Mode
35 | P a g e February 2011
Page 44

10. Depth Scale Mode
The cursor modes are described in detail in the following sections.
1.5.2.1 Select Mode
This option is available when the pointer toolbar button is selected. It is the default mode
and is used for selecting items in the map view.
1.5.2.2 Measure Mode
Selecting the 'Measure' toolbar button in Perspective map will switch the cursor to the
Measure mode for making measurements of features seen in the Map View.
When using the 'Measure' tool, select a starting point on the map by left clicking on the spot
and hold the button down while the distance to measure is spanned. Once the end point is
reached, release the mouse button.
The following window shows how the measured line appears in the map window with the
distance annotated on the line. Also shown are the results of the measurements in the
Measure information tab. For Measure Tab details go to Section: 1.2.2.
36 | P a g e February 2011
Page 45

1.5.2.3 Pan Mode
This mode allows the user to center the screen over a particular object for using the ‘ZoomIn’ and ‘Zoom-Out’ options, and also is good for following a pipeline or route while zoomed
in where the full extent of the feature following does not fit entirely in the display.
Select the pan icon and then click and drag the screen with the button depressed.
1.5.2.4 Zoom Mode
Selecting the zoom toolbar button puts the cursor in Zoom Mode.
This allows the user to select an area to zoom into by left-clicking or right-clicking on any
point on the map and holding the button down while defining an area to zoom to.
When the mouse button is released, the map will zoom into the selected area. To zoom back
out, use the toolbar buttons for zooming out or returning to the home zoom.
The image below is an example of the selection process:
When the mouse button is released the screen will redraw to the selected extents.
37 | P a g e February 2011
Page 46

Ellipse: Dimensions are determined by clicking and dragging to the desired size
Rectangle: Dimensions are determined by clicking and dragging to the desired size
Triangle: Dimensions are determined by clicking and dragging to the desired size
Polygon: Dimensions are determined by clicking and dragging to the desired size
Fixed size Ellipse: Dimensions of the annotation are entered by the user prior to
insertion of the character on the map.
Fixed size Rectangle: Dimensions of the annotation are entered by the user prior to
insertion of the character on the map.
Text: A text box used to mark and describe features on the map.
Common Annotation Tools
1.5.2.5 User Annotation Mode
Drawing tools are available under the Modality > Annotation
menu or by selecting the 'Pen' toolbar button. When selected, an
annotations window will appear as shown below:
All user annotations placed in the Map View from this dialog
will appear as items under the Annotation > User heading in the
file tree. Various shapes and text options are available.
Options include:
After selecting an annotation mode, the user may preselect the annotations attributes from
this same dialog.
38 | P a g e February 2011
Page 47

The color, opacity, thickness and character of the annotation line are defined by
clicking on the paint palette.
The color of the icon is the current color selected for the annotation and will
remain the default color until changed in this attribute box.
The font attributes of text annotation are selected by clicking on the letter icon.
The symbols can be hollow or filled by clicking on the corresponding icon.
Object attributes can be set at the time of creation, or later by right-clicking on the layer in
the file tree structure.
Annotations can be turned on and off from the map display from the file tree. More
information about annotation options from the file tree is presented in Section 1.3.2.3.
1.5.2.6 Bathymetry Profiling
Selecting the 'Bathy Profile' toolbar button in Perspective map will switch the cursor to
the Profile mode for evaluating features seen in the Map View.
Select a starting point on the map by left clicking on the spot and holding the button down
while the profile line is spanned. Once the end point is reached, release the mouse button.
The Bathy Profile tool is described in detail in the BathyOne section of this user manual.
1.5.2.7 Contact Generation
Selecting the 'Contact Generation' option in the Modality menu or selecting the toolbar
button in Perspective map will switch the cursor to the Contact Generation mode for marking
locations of interest seen in the Map View. Selecting this toolbar will automatically launch
TargetOne for analyzing and saving the selected target.
1.5.2.8 Classification
Bottom types can be classified in MosaicOne using the built-in classification module called
SeaClass. The classification process is described in detail in Section 8.3.
1.5.2.9 A-B Mode
Selecting the 'A-B' toolbar button in Perspective Map or the 'A-B' option in the 'Modality'
menu will switch the cursor to the A-B mode for determining differences in DTM layers seen
in the Map View.
39 | P a g e February 2011
Page 48

Select a starting point on the map by left clicking on the spot and holding the button down
while the area to be used for the A-B calculation is defined. A box will be drawn in the
screen defining the area and when done, release the mouse button to start the calculation. The
'A-B' tool is described in detail in the BathyOne part of the Help guide in Section 5.10.2.
1.5.2.10 Display Depth Scale Mode
This option is available when there is a DTM layer in the project. To display the depth scale,
first select a DTM layer from the file tree by clicking on it once.
The depth scale is then launched by either selecting the 'Display Depth-Scale'
option in the Modality menu or by clicking on the toolbar button shown below
This will open the following depth scale window shown to the right which can
be moved around in the window or placed anywhere on your desktop.
2: Data Management
2.1 Importing
2.1.1 Import Methods
The toolbar offers three methods to bring data into Perspective.
This will open a window browser to import selected raw data files into the project as
shown in the image below:
40 | P a g e February 2011
Page 49

This button will import all compatible data file in a selected
folder. (NOT YET IMPLEMENTED)
This button will use the database search function to remove all data in a project and
load only the data that lies within a selected time range or a defined geographic area.
Currently the only raw survey data format supported by Perspective is the Triton XTF data
format. However, there are several existing Triton file format converters to allow importing
of additional data types.
In addition to raw data files, Perspective can import a variety of data types including Triton
mosaic and DTM files, GeoTiffs, XYZ files, GSF files, AutoCAD DXF files, and a few
various others. Data types supported and methods for importing each data type are described
in the following sections.
2.1.2 Import Data Types
All data types can be imported from the Import option in the File menu or directly from the
File Tree by selecting ‘Add’ from the right click menu:
SeaClass layers
Contacts
Vectors
Navigation layers
41 | P a g e February 2011
Page 50

Imagery layers
Background layers
The Import option found in the File menu allows the ability to import all compatible data
types into Perspective. The options available are shown in the menu window below:
Raw Data File: Selecting this option from the
File>Import menu will open a window browser for
selecting compatible raw data files for import into the
project. Currently XTF is the only raw data file type
supported. Selecting raw data for import will
automatically launch the processing wizard for sidescan
and/or bathymetry depending on the contents of the
imported file.
Mosaic File: Selecting this option will allow users to
import mosaic files previously generated in Perspective.
ENC (S57) File: Allows users to import S57 charts for
background project imagery.
GeoTIFF File: This option imports selected GeoTiff
files into the project for use as background imagery.
Contact File: Allows the user to import contacts or
target files generated with TargetOne.
TritonMap File: Mosaic files created with TritonMap can be imported using this option.
Vector File: Supported AutoCAD DXF files can be imported with this option.
Neural Net: This option allows users to import a neural net created in Triton’s SeaClass
module for sediment classification.
Classification File: Sediment classification results can be imported using this option.
Symbol: Selecting the 'Symbol' option found in the File > Import menu will open the
following window:
42 | P a g e February 2011
Page 51

This window allows the user to set the name, category, size and transparent color of the
symbol. To load a symbol into this window, select the 'Load' button which will open the
file browser below to select the symbol file. Navigate to a compatible file type and select
'Open'. This will automatically insert the symbol image into the Symbol Importer
window. Selecting ‘OK’ will load the symbol into the project.
ASCII XYZ Grid File: Selecting an ASCII XYZ file to import will launch the XYZ Grid
Parsing window as shown below:
Options and displays include:
Data Field: The data in the XYZ file is shown in the box at the top of the window.
43 | P a g e February 2011
Page 52

Line: If there was a header, the box next to ‘Line’ is for entering the number of
lines to skip for the header, before the data begins.
Delimiters: This is where the data delimiters are defined. In the example above
the data is separated by spaces and therefore the ‘Space’ box is checked.
Parsed Field: Displays data elements available for mapping to predefined field
types.
Field: Predefined field types to assign data to.
Format: Set the units or format of the data value assigned to this field.
Attribute: Can attribute the defined field as a header or as a data value.
Update: The user must select this after the parsed field has been applied to a field
and the format has been selected to complete the decoding process for that data
type.
Decoded Data Element: Displays the results of data to field mapping.
Decoded Header Element: Displays the results of header to field mapping
For this example, the first data column is for Easting, the second is for Northing, and the
third is for depth. The parsing window shown on the previous page was captured after
the data had been mapped to the appropriate fields with the decoded data elements
indicating which Field and Format was applied to each element.
Select ‘OK’ when finished. This will launch the BathyOne Wizard to create a bathymetry
layer.
ASCII Singlebeam File: This will import singlebeam data from an XYZ or TXT file.
Selecting this option will launch the Singlebeam ASCII Parsing window (identical to the
XYZ Grid Parsing window).
Bathy DTM File: Selecting this option will allow users to import DTM files previously
generated in Perspective.
GSF File: This option allows users to import GSF files into Perspective. Selecting GSF File
import will automatically launch the BathyOne Wizard to create a bathymetry layer.
2.2 Database Refresh
An alternative method for importing mosaic and DTM files created from Perspective is to use
the Database Refresh toolbar button shown below:
44 | P a g e February 2011
Page 53

The database refresh tool gives the user the option to import files into the project, based on
either time or location. It is important to note that instead of just being an import tool, the
database refresh tool also removes layers from your project that do not meet the search
criteria.
Database settings need to be defined prior to using this toolbar button to setup the data
directory and to setup the query parameters.
To use this tool, zoom into a region of interest in Perspective Map and select the Database
Refresh toolbar button. This will open the following window:
The search parameters shown were copied from the Database settings tab, but can be changed
here for quick access to the search parameters.
Using the parameters shown above, selecting ‘OK’ will clear the project window and load the
mosaic and DTM files (all layers selected) in the project folder that intersect the viewport and
was collected since May 1, 2009.
Selecting the checkbox in the lower left corner will not open this window upon selecting the
Database Refresh toolbar button and instead will use the search criteria entered in the
Database settings tab.
2.3 Export Methods
There are a few options for exporting data from Perspective Map. Export file types include:
GeoTiff file
45 | P a g e February 2011
Page 54

KML file
XYZ file
Layers visible in the Map View can be exported as a GeoTiff by using the Composite
GeoTiff export menu option. Right-clicking on the File Tree layers offers additional export
options
Printing the Map View is similar to selecting Composite GeoTiff Export from the File menu
but also includes annotations and allows the user to save the map View as a PDF (with Adobe
Acrobat) or send the map View to a printer for a hard copy of the project.
Export options are discussed in detail in the following sections.
2.3.1 Map View Export
Exporting the Map View to a GeoTiff will create a geo-referenced TIFF that includes all the
layers selected in the File Tree.
Selecting 'File > Export > Composite GeoTiff' will open the following window:
Options available in this window include:
Resolution: Sets the output file resolution in meters/pixel. The size of the output file
in pixels will show next to Dimensions, just below the resolution.
46 | P a g e February 2011
Page 55

Tiles/Export: The slider bar below the Dimensions is for indicating the number of
tiles to break up the export image in order to reduce the individual file size of the
output. The image above shows the output divided into 16 tiles with resulting
dimensions of each tile being 1097 x 992 pixels.
Selection Tree: Allows the user to select or deselect additional imagery to be
included in the export.
Selecting the Export button will open the following window for saving the file:
2.3.2 Imagery GeoTiff Export
Sidescan and bathymetry data can be exported from an existing project from the File Tree to
a geo-referenced TIFF file. For sidescan data, the GeoTiff Exporter is launched from either
the sidescan root node or the individual sidescan layer. Individual GeoTiff files for
bathymetry are only exported from right-clicking on the Bathymetry root layer node.
All options launch the same export wizard. For sidescan exports, only sidescan data is
available for inclusion in the export. For bathymetry exports, only bathymetry data is
available for inclusion in the export as shown in the image on the following page:
47 | P a g e February 2011
Page 56

Options available in this window include:
Resolution: Sets the output file resolution in meters/pixel. The size of the output file
in pixels will show next to Dimensions, just below the resolution.
Tiles/Export: The slider bar below Dimensions is for indicating the number of tiles to
break up the export image, in order to reduce the individual file size of the output.
The image above shows the output in only 1 tile with resulting dimensions of each tile
being 4096 x 3703 pixels.
Selection Tree: Allows the user to select or deselect imagery for the export.
Selecting the Export button will open the ‘Save GeoTIFF’ browser window for selecting a
location and file name for the export.
2.3.3 Imagery Batch GeoTiff Export
Sidescan and bathymetry data can be exported from an existing project from the File Tree.
For sidescan data, the Batch GeoTiff Export window is launched from the sidescan
root node only.
For bathymetry, the Batch Export GeoTiff is available from right-clicking on either
the Bathymetry root layer node or on an individual DTM as shown:
48 | P a g e February 2011
Page 57

There are no settings to change in this window and default export options are automatically
applied. To complete the export, select the green 'Play' button in the upper left corner of the
window. The files are exported to the default project folder and the results are shown in the
output window as seen in the image below:
2.3.4 KML File Export
Sidescan and bathymetry data can be exported from an existing project from the File Tree to
a Google Earth KML file. For sidescan and bathymetry data, the ‘KML Exporter’ is
launched from either the sidescan/bathymetry root node or the individual mosaic/DTM layer.
49 | P a g e February 2011
Page 58

All options launch the same export wizard. For bathymetry exports, only bathymetry data is
available for inclusion in the export. For sidescan exports, only sidescan data is available to
be included in the export as shown below:
Options available in this window include:
Resolution: Sets the output file resolution in meters/pixel. The size of the output file
in pixels will show next to Dimensions, just below the resolution.
Range: Sets the default zoom range above the Earth for opening the file with Google
Earth.
Tiles/Export: The slider bar below Dimensions is for indicating the number of tiles to
break up the export image, in order to reduce the individual file size of the output.
The image above shows the output in 48 tiles with resulting dimensions of each tile
being 256 x 231 pixels.
Checkbox: Automatically launch Google Earth and insert the exported KML file for
viewing at the distance above ground specified above.
Selection Tree: Allows the user to select or deselect imagery for the export.
Selecting the Export button will open the ‘Save KML’ browser window for selecting a
location and file name for the export.
If the checkbox was selected, then Google Earth will automatically launch and open the
exported file. Please note that Google Earth needs to be installed on your computer for the
auto-launch feature to work.
50 | P a g e February 2011
Page 59

2.3.5 XYZ File Export
Bathymetry data can be exported from an existing project from the File Tree to a text .xyz
file. This can only be launched from right-clicking the bathymetry ‘DTM’ layer.
This will launch the Export XYZ wizard shown below:
Options available in this window include:
Resolution: Sets the output file resolution in meters/pixel. The cell size can be set to
maintain a 1:1 aspect or the X and Y size can be set individually.
Projection: Allows the user to set the export projection. Information on the
Projection Wizard and Projection Settings can be found in Section 3.5.
Selecting the ‘Save’ button will open the following window for saving the file:
51 | P a g e February 2011
Page 60

2.3.6 SeaClass Export
Results from the classification process can be exported through the following methods:
1. Composite Export: This will export all layers turned on in the file tree including the
SeaClass results as a composite GeoTiff file.
2. Manual Training Export: This exports the training sets to an XML file and is launched
by right-clicking on the Training Set file tree layer and selecting Export as shown below:
This opens the file save dialog window shown below:
52 | P a g e February 2011
Page 61

3. Classification Export: This exports the classification grid to an AutoCAD DXF file
which is launched by right-clicking on the classification grid tree layer and selecting
Export as shown below:
This opens the file save dialog window shown below:
53 | P a g e February 2011
Page 62

2.3.7 Printing
In order to print the Map View to a PDF file (you will need Adobe Acrobat for this) or to a
printer, select ‘Print’ from the File menu. This will open a standard Windows printing
window as shown below:
Select ‘Print’ to output the Map View to the chosen printer.
2.4 Project Options
2.4.1 New Project
To create a new project, select the ‘New Project’ option from the File menu as shown below:
Selecting this will open a new project. If an existing
project is open and not already saved, the user will be
asked to save the project.
54 | P a g e February 2011
Page 63

2.4.2 Open Project
To open an existing project, select the ‘Open Project’ option from the File menu as shown
below:
Selecting this will open the following window:
55 | P a g e February 2011
Page 64

2.4.3 Save Project
To save an existing project, select the ‘Save Project’ option from the File menu as shown
below left:
To save a new project select the ‘Save Project As’ option from the File menu as shown above
right.
Selecting this will open the following window:
56 | P a g e February 2011
Page 65

2.4.4 Projected Cursor
The Project Cursor option is available from the View menu as shown below:
-
Selecting this will add the ‘Custom Cursor’ display to the main
window as shown to the right.
The Custom Cursor is discussed in detail in Section 1.4.
2.4.5 Log Window
To log the project activities, select the ‘Log
Window’ option in the View menu as shown
right:
Selecting this will open a new window with a
record of the activities since the project was
opened. Additional actions will automatically
record in this window to document workflow
steps.
An example of the Log Window is shown left:
57 | P a g e February 2011
Page 66

2.4.6 Page Setup
Page Setup options are available from the File menu as shown below:
Selecting this will open the Page Setup window as shown below:
58 | P a g e February 2011
Page 67

2.4.7 Quit Project
When finished working on a project, the project can be closed by selecting ‘Quit’ from the
File menu as shown below:
Selecting this will prompt the user with the following dialog box:
59 | P a g e February 2011
Page 68

3: Program Settings
3.1 Settings Overview
Application settings can be accessed
through the toolbar button or by
selecting Settings Info from the View menu
as shown below:
There are up to six tabs available in the
Program Settings window, two of which
require additional licensing.
General
Pen
ENC (requires S57 license/dongle)
Projection
Contact
Database (requires additional database license)
3.2 General Settings
Scratch Path: This is the directory
where temporary Perspective files are
kept. Select the button to the right of the
file path to change to a new scratch
location.
Optimize GeoTiffs: This will speed
up viewing large GeoTiffs by
indexing a copy of the file in the
scratch folder, than accessing it from
the scratch folder. This indexing
allows Perspective to only load part
of the GeoTiff when needed rather
than the whole GeoTiff file.
Number of Cores: This is where the
user tells Perspective how many (if any)
of the cores the host computer is utilizing. This helps to optimize Perspective processing.
60 | P a g e February 2011
Page 69

Options:
Ask before removing layers: This allows the user to turn on or off the message, "Are you
sure you want to remove...", that pops up when "Remove" is selected in the File Tree.
Show Mosaic Tiles: This lets the user see the tiles that the mosaic is divided into.
Load Zoom Out: Selecting this option will automatically zoom to the full extent of an
imported layer.
Relative Paths: Allows the project to be relocated to a new hard drive without losing
track of the relative file paths of imported files.
Hide Mouse Over ToolTips: Hides the display of the cursor when over pop-up tooltips.
Auto Update: Checking this box will allow Perspective to look for any updates to the
Perspective software on the Triton Imaging Inc. website each time Perspective is opened.
Auto Save: Perspective will automatically save the project every user defined interval while
it’s running.
Cache Options:
Force Cache Rebuild: When a survey file is opened in Perspective it is cached or
"indexed" and an .xtf_idx file is created. This allows Perspective to access an XTF file in
a non-linear fashion which significantly speeds up the processing once the .xtf_idx file is
created. The first time a survey file is read, the xtf_idx file is created and it takes a little
longer to load the file, once the idx file is created “Forcing a cache rebuild” forces this
xtf_idx file to be recreated.
Use Ensemble X/Y (SEG-Y): Some SEG-Y have the data "stacked" and the navigation
stored in a different place, checking this box identifies the file as this type.
Suppress Warnings: These are warnings that come from indexing a file when building
the cache. For example "10 pings had no navigation". If you do not want to have these
warning pop up then click the box to "suppress warnings".
Sync Views:
For a data file that contains bathymetry and sidescan data, the ‘Sync View’ option allows the
user to sync the playback of the waterfall viewer and swath viewer by ping number.
Reset Factory Settings:
This will reset the Program Settings to the default factory settings.
61 | P a g e February 2011
Page 70

3.3 Pen Settings
Intersection: Allows the user to
change the color Perspective assigns to
sub bottom intersections.
Background: Allows the user to
change the color of the Map View
background.
Profile Font: Allows the user to
change the color of the profile font in
SB-I (not yet implemented).
Zoom Tool: Allows the user to change
the color of the zoom box.
Measure Tool: Allows the user to
change the color of the measuring line
used by the measure tool.
3.4 ENC Settings
The way that ENC charts are displayed
in Perspective can be controlled from
the ENC tab on the Settings dialog.
Note that this tab will only appear if
you have an S-57 license and
corresponding dongle plugged in.
Paths: These file paths need to be set
in order to access the ENC data.
Color Scheme: There are four options
to select from for changing the ENC
palette.
Lookup Table: This setting controls
of the amount of items that are included
in the display of the ENC. The
simplified option yields an ENC with
fewer items and less clutter.
The ‘Advanced’ button will invoke the
62 | P a g e February 2011
Page 71

Advanced ENC Settings window.
From this window, the attributes that
are included in the display of the
ENC can be selected and the
parameters associated with each
attribute can be specified (in meters).
The Color Intensity slider allows the
adjustment of the brightness of the
ENC in the Map Display to be
adjusted.
3.5 Projection Settings
These are the five separate projection settings available in the Projections tab.
XTF Import Projection
GeoTiff Import Projection
ASCII XYZ Projection
Contact Save Projection
Export Projection
63 | P a g e February 2011
Page 72

There are also two check boxes in the Projections tab, related to import and export
projections.
Auto set Export Projection to UTM/WGS84: As specified, this requires that the input files
are in latitude and longitude coordinates. Checking this box will export the data in the same
projection as displayed in the Map View.
Ask to use current import projection: This will prompt the user during the file import process
and ask whether to use the current projection. If the current projection is not satisfactory, an
import projection wizard will launch.
3.5.1 Import Projection Settings
The import projection wizard is identical for the XTF, GeoTiff, XYZ, and Contact projection
settings.
The default import projection is un-projected latitude and longitude in WGS84. When the
first file is loaded into a new project, the import projection wizard will launch and the
projection can be set at that time.
Alternatively, the user can preset the import projection using the Program Settings option
described below.
Selecting 'Change' under any of the top four options in the Projections tab of the Program
Settings will launch the import projection wizard shown below:
On this page, select the projection to use. If a custom projection is needed, select the
64 | P a g e February 2011
Page 73

‘Custom’ button. For Custom Projection details, see Section: 3.5.3.
Press the ‘Next’ button to select additional projection information. For this example the
correct UTM zone, hemisphere, and units need to be specified.
Select the datum to use. If a custom datum is needed, select the ‘Custom’ button. For
Custom Datum details, see Section: 3.5.4.
Select Finish when done.
65 | P a g e February 2011
Page 74

3.5.2 Export Projection
The export projection wizard is basically identical to the import projection wizard except for
the name in the title bar.
The default projection for exporting files is un-projected latitude and longitude in WGS84. If
the 'Auto set Export Projection to UTM/WGS84' box is checked, Perspective will
automatically assign a UTM zone based on WGS84 coordinates.
Selecting 'Change' under Export Projection in the Projections tab of the Program Settings will
launch the following projection wizard:
On this page, select the projection to use. If a custom projection is needed, select the
‘Custom’ button.
Press the ‘Next’ button to select additional projection information. For this example the
correct UTM zone, hemisphere, and units need to be specified.
66 | P a g e February 2011
Page 75

Select the datum to use. If a custom datum is needed, select the ‘Custom’ button.
Select ‘Finish’ when done.
67 | P a g e February 2011
Page 76

3.5.3 Custom Projection
To define a custom projection, select 'Custom' from the Select Projection page of the import
or export projection wizards as shown below:
This will open the following window:
Select ‘Create’ to start the Projection Definition window.
68 | P a g e February 2011
Page 77

Enter the appropriate information for the projection to be defined.
Below is an example with random test data:
To generate the information in the lower left window, select the ‘Generate String’ button.
Select ‘Done’ once the projection string has been generated.
This returns the user to the original window, with the projection string generated in the
previous window now entered automatically in the Projection String box.
69 | P a g e February 2011
Page 78

Enter a name to save the projection to and select ‘OK’.
This returns the user to the Select Projection window. Choose the new projection just created
from the projection list and select ‘Finish’ or ‘Finish and Save’ to keep the custom projection
for future projects.
70 | P a g e February 2011
Page 79

3.5.4 Custom Datum
To define a custom datum, select 'Custom' from the Choose Datum page of the import or
export projection wizards as shown below:
This will open the following window:
71 | P a g e February 2011
Page 80

Select an existing ellipsoid or choose custom from the list as shown below:
Enter the appropriate information for the projection to be defined and a ‘Save As’ name and
select ‘OK’ when done.
The Choose Datum window now has the custom datum listed at the bottom.
72 | P a g e February 2011
Page 81

Select the new datum just created from the projection list and select ‘Finish’ or ‘Finish and
Save’ to keep the custom datum for future projects.
Selecting ‘Finish and Save’ will open the following window to save the datum:
Enter a name for the datum and select ‘OK’.
73 | P a g e February 2011
Page 82

3.6 Contact Settings
Size (meters): This is where the user selects the size of the contact to be saved, in meters.
Bookmarks: The user can select whether or not to show bookmarks in the Waterfall view.
Targeting Paths: It is recommended that the user choose the same directory paths for
Perspective and TargetOne. If both programs use the same directory paths, contacts that are
saved in TargetOne will automatically be displayed in Perspective.
Temporary: The user can select where to have TargetOne keep contacts until they are saved.
Saved: The user can select
where to have TargetOne
save contacts once they have
been temporarily saved in
TargetOne. Note that this
needs to be different from
temp directory.
Note that the temporary and
saved file paths must be
different.
Contact Usage: The contact
generated from Perspective
can either be sent to
TargetOne or to an XML
file. Contacts sent to
TargetOne will have the
Triton Imaging Inc .CON file
format.
A contact generated as XML
contains the parameters
required to queue external programs to areas of interest within the mosaic. Included in the
XML structure is a link to a geo-referenced TIFF file (.tif + .tfw) that is the snapshot from the
Perspective Mosaic.
XML contacts can contain links to other types of imagery such as AUV mounted optical
cameras.
Threshold:
Use Target One setting: Set the default display threshold using the TargetOne settings.
Calculate from data: Set the display threshold by calculating the value from the data file.
74 | P a g e February 2011
Page 83

Current Contact Number: Indicates the contact number that will be given to the next
contact generated.
3.7 Database Settings
On: Check this box to turn on the auto-load database option.
Database Path: Sets the file path to the project database folder.
Date Selection Options:
Recent: The user can select the number of days back from the current date by using the Days
Back number list.
Since Date: The user can select a range of time using the Start Date field to enter a start date
and using the current date for the End date.
Range: The user can select a range of time using the ‘Start Date’ field to enter a start date
and the ‘End Date’ field for the end date.
Always ask before
search: This check box
will prompt the user for a
date option when selecting
‘Refresh to View’.
Use Refined Database
Query when Viewport is
less than: User enters a
value for using the refined
database query for small
Viewports.
This is useful for reducing
the data that is nearby but
not in the map view from
loading into the project by
reducing the size of the
layers’ bounding box.
75 | P a g e February 2011
Page 84

4: Navigation
4.1 Navigation Types
Navigation embedded in raw data files is extracted upon import of the data file and sorted
into 5 main categories.
The main types of navigation in Perspective are:
Sidescan - navigation for sidescan data imported from raw data files
Multibeam - navigation for multibeam data imported from raw data files
Singlebeam - navigation for singlebeam data imported from raw data files
Subbottom - navigation for subbottom data imported from raw data files
Vessel - vessel navigation imported from raw data files
If multiple data types are available in one raw data file, importing that one data file can
populate multiple navigation data fields in the file tree. If for example the data file comes
from a Reson 8101 which collects both sidescan and multibeam data simultaneously,
importing one raw data file will populate the Sidescan navigation node, the Multibeam
navigation node and the Vessel navigation node as shown in the image below:
Note that importing one data file, BRDG001 in this example, populated the multibeam,
sidescan and vessel layer nodes in the navigation file tree. Each navigation type has its own
color so they can be distinguished in the map view. These are kept separate since the user
may wish to process the navigation differently for sidescan data than for multibeam.
76 | P a g e February 2011
Page 85

4.2 Import Navigation Data
Navigation data that Perspective works with comes embedded in raw survey data files and do
not exist as stand-alone files. Currently, the only raw survey data format supported by
Perspective is the XTF format and the navigation data must be stored within the XTF file for
Perspective to read and process it.
Navigation data extracted from the raw data files are automatically separated and sorted into
the navigation data types available in the navigation file tree section. The navigation File
Tree structure has several options for changing the way the navigation lines appear in the
Map View and several ways to change processing and zoom options.
For Navigation Tree details, see Section: 1.3.6.
In addition to importing raw data files from the methods described in the Import Methods
section, navigation data can be added directly from the File Tree by right-clicking on any of
the navigation layer nodes and selecting 'Add'. An example is shown below:
Selecting this option will bring in all the data from the selected raw file, including the
navigation data, and launch the processing wizard.
Selecting a navigation line in the File Tree will also highlight that navigation line in the Map
View display as a thicker light blue line as shown on the next page:
77 | P a g e February 2011
Page 86

The image above shows two multibeam navigation lines, the thicker blue line is currently
selected in the navigation file tree layer and the red line is currently not selected.
When importing raw data files into Perspective, the import/processing wizard automatically
launches. While the wizard does give the option to process the navigation for the data type
being imported, multiple stages of navigation processing cannot be accomplished before the
wizard completes the mosaic or DTM creation using the partially processed navigation data.
If there is reason to believe that the navigation data needs cleanup (poor satellite coverage,
ROV/AUV tracking, etc.), then it is best to skip the creation of the mosaics or DTMs at this
stage and process the navigation completely first.
Navigation processing is an important step to obtaining clean results and some thought
should go into what parameters to use and what level of processing is necessary for the
collected data. For example, hull or pole mounted systems tend to have a cleaner position
signal and require less processing than towed sonar or ROV/AUV surveys.
Presented in the next section are a couple possible workflows a user could follow for
processing their navigation data.
78 | P a g e February 2011
Page 87

4.3 Navigation Processing Workflows
For surveys with hull-mounted equipment and good position control, very little processing is
needed of the navigation data. One pass is generally enough to remove small spikes in the
navigation data. This can be accomplished using the import/processing wizard, which only
allows one pass at the navigation processing. However, for towed sonar or data collected
from ROVs or AUVs generally more processing is needed to create imagery which
accurately reflects the true vessel position at the time of the ping transmission and reception.
Currently there are two primary workflows for processing navigation data.
1. Process on import: Upon importing raw survey data files, the processing wizards
each have a button for setting the navigation processing settings. These settings are
made and then applied when the data is being processed for creating mosaics or
DTMs.
These settings are only applied once to the raw navigation data. Towed sidescan
often needs repeatable navigation smoothing and is not adequately processed with this
method.
Navigation processing boxcar settings are described in detail in the next section of
this manual, Section 4.4.
2. Process from File Tree: Upon import of the raw survey data, the processing wizards
are skipped and only the navigation lines are imported. Then the navigation can be
processed using the Process Navigation window, which allows for multiple passes
over the navigation data. This is often necessary for towed sonar or data collected
from ROVs or AUVs.
To repeat the navigation processing, first setup the Boxcar filter to use either 'Ship' or
'Sensor' as the source navigation. Click 'Start' in the Process Navigation window to
initiate the processing. When complete, return to the Boxcar Settings and change the
navigation source to 'Smoothed'. This is a critical step, otherwise the processing will
continue to use the same raw source navigation.
Details of the Process Navigation window are presented in Section 4.5
79 | P a g e February 2011
Page 88

4.4 Navigation Boxcar Settings
Selecting the Filter Setup button in the Process Navigation window opens the following
Boxcar Settings window for setting processing parameters:
General:
- Window - sets boxcar window size
- Source - sets source navigation
Sensor - Uses the position found in the XTF sensor navigation
Ship - Uses the position found in the XTF ship navigation
Smoothed - Uses the smoothed position already in the cache file, (uses the previously
smoothed navigation from the last processing)
80 | P a g e February 2011
Page 89

Heading:
- Compute CMG - Check the box to compute a heading from the Course Made Good
(navigation)
- Bias - Apply a single bias to the computed CMG heading
- Change Cutoff - Cutoff value for CMG calculation (in degrees)
Layback:
- Source
None - Do not apply a layback
Computed - Computes a layback using the values found in the XTF file for Cable Out,
Towfish Depth, Towpoint Height, and Towpoint offset from the navigation antenna
Manual - Enter a fixed layback value (in meters)
- Tow Point Offsets - Applies the user-defined values in crossbeam direction.
- Time Delay - Static time delay (in seconds)
Offsets:
- Applies user - Defined value in X, Y relative to position.
+X equals Starboard, -X equals Port
Speed:
- Filter Speed - Turns the option on
Min - Enter the minimum expected speed
Max - Enter the maximum expected speed
Change Cutoff - Cutoff value for speed filter (in knots)
Compute:
Never - Use the speed from the XTF file
Always - Ignore existing speed and re-compute
When Zero - Only computes speed if the value in the file is zero
Mag Heading Deviation:
- On - Turns the option on
- 0, 90, 180, 270: Enter the corrected heading for each of cardinal compass points. The
mosaic engine will generate a smoothed correction curve interpolating between these values.
81 | P a g e February 2011
Page 90

4.5 Process Navigation
For processing navigation from the File Tree, select the ‘Process Navigation’ option available
by right-clicking on any tree level in the Navigation layer. Selecting this will launch the
Process Navigation window shown below:
Options include:
Filter Setup - See 'Boxcar Settings' in the previous section of this manual.
Auto Update Cache - Writes the processed navigation into the cache file, important
for repeat processing.
Check Intersections - Checks navigation at line intersections.
Start - Click after Boxcar Settings have been made to initiate processing. This can be
clicked as many times as the user wants to repeat the navigation processing. Please
note that to process the results from the previous navigation processing step the
navigation source must be changed to 'Smoothed'. This will use the processed
navigation in the cache file as the source allowing for multiple steps of processing.
Cancel Processing - Cancels the current processing step, does not remove saved
processed navigation from the cache file.
Save and Exit - Saves processing to cache file if not already done with the auto update
option, then exits processing wizard.
82 | P a g e February 2011
Page 91

5: BathyOne
5.1 BathyOne Module
BathyOne is an add-on to Perspective Map which allows users to create digital terrain models
of their raw bathymetry data and includes tools for viewing and interpolating the gridded
data. Options available in the BathyOne module are presented below; details of their options
and settings are described later in this chapter.
Grid Options
Create DTM: BathyOne provides a few methods for the creation of digital terrain models
(DTM's).
Rebuild Using: Upon selecting this option, the user is asked if they want to use the GSF flags
already present in the GSF. The BathyOne Wizard then opens to allow the user to
make changes to bathymetry settings used to create the imagery and apply any
edits/flags made to the GSF file.
Edit GSF Using: This option is only available if a GSF File was imported without a
corresponding raw data file using the 'Import/GSF File' option. Selecting this option
will launch a limited version of the BathyOne Wizard to allow the user to change
some of the processing parameters set during the GSF import process.
Swath Editor: Not yet implemented.
Re-merge DTM: Will re-create the DTM based on any changes to the processing parameters
or edits to the data made since the DTM was created.
Add Lines: Allows the user to add other raw data files in the project to the DTM.
Reset Date: Provides the ability to change the date of the DTM file.
Rename: Allows the user to rename the DTM name in the project. This will not rename the
file on the disc and only changes the display name in the Perspective Map project.
Visualization Options
Color Settings: Allows the user to change the color characteristics of the bathymetry layer.
Histogram: This is the graphical representation of the imagery signal level in dB versus the
occurrence of that dB within the image.
Relief Shading: This tool simulates the illumination of the sun on the bathymetry data. This
is a global setting and can only be changed at this node level.
View Swath: This tool allows the user to see the swath data from an individual data file.
83 | P a g e February 2011
Page 92

Interpretation Options
Bathy Profile: Selecting the 'Bathy Profile' option from the toolbar button or Modality menu
in Perspective Map will switch the cursor to the Profile mode for evaluating features
seen in the Map View.
A-B: Subtracts co-registered DTMs to look for changes to bathymetry. This algorithm does
a direct pixel to pixel comparison at each grid node.
Change Detection: Subtracts co-registered DTMs to look for changes to bathymetry. This
algorithm differs slightly from the A-B algorithm in that it also includes a statistical
neighborhood approach to account for mis-registration between layers. Operating the
Change Detection tool is basically the same as the A-B tool.
Blink Comparator: Visual comparison of two overlapping layers is made easy with this tool.
The 'Blink Comparator' allows the user to quickly turn on/off a layer or can be set to
cycle a layer on/off to help identify differences in the layers.
Statistics: This gives an overview of the data used to create the image including coverage
and line statistics.
5.2 Create DTM
5.2.1 Bathymetry Processing Wizard
Bathymetry data can be processed in Perspective Map using the BathyOne Wizard.
Presented below are a few ways to launch the bathymetry processing wizard.
During the raw data import process, the navigation data loads into the project first. If the raw
data files contain bathymetry data then the BathyOne Wizard will automatically launch and
the bathymetry data can be processed as part of the import process.
However if the navigation data needs repeat processing, the BathyOne Wizard can be
canceled during the import process and re-launched after the navigation data is properly
processed.
For more information regarding Navigation Processing Workflows, visit Section 4.3.
There are two methods to launch the BathyOne Wizard manually from within Perspective
Map, from the File Tree and using the toolbar button.
1. To launch the wizard from the File Tree, right-click on the Imagery/Bathymetry node and
select 'Create' as shown below:
84 | P a g e February 2011
Page 93

2. The processing wizard also can be launch by selecting the 'Create DTM' toolbar button:
Whether the processing wizard is automatically or manually launched as described above, the
same options are available. Processing steps in the BathyOne Wizard are presented in the
next Section.
5.2.2 BathyOne Wizard Overview
There are several steps the BathyOne Wizard guides the user through. Brief descriptions of
each step are presented below and details of their settings and options are in the following
sections.
Choose/Create Bathy Layer - options to create a new DTM file or append to an existing
file.
Select Input Lines - Choose which data files to process for the DTM.
Ancillary Options - Vessel geometry settings and GSF/HTF options.
Gridding of Soundings - Grid settings including resolution, encoding options, fill and
smoothing options, and the option to constrain the DTM to the map extent.
Raw Processing - Includes POS, navigation and TPE processing, and options for
transducer selection and attitude correction thresholds.
Beam Suppression - Several options for beam suppression with a separate tab for attitude
suppressions.
SVP Processing - Includes options for selecting and applying sound velocity profile data.
Tide/Squat Processing - Includes options for selecting and applying tides and vessel
squat.
85 | P a g e February 2011
Page 94

5.2.3 Choose/Create Bathy Layer
The first step of the BathyOne wizard is to create a new bathy layer or select an existing
bathy layer to append to as shown in the image below:
If a bathy layer already existed in the project, it will appear in the upper window under
'Existing Layers'. The user can either select the existing layer if present, or choose to create a
new bathy layer by selecting the 'Create' button.
Note that there are two types of bathy layers that can be created, a DTM or a TPE.
DTM: This stands for 'digital terrain model' and is the default bathy layer format used
for gridding the depth values from the processing results.
TPE: This stands for 'total propagated error' and is used for a visual representation of the
possible errors in the data results.
Before moving to the next step of the BathyOne processing wizard, either an existing layer
must be selected or a new layer created for the processing results. If the user selects 'Create',
to generate a new bathy layer, the following window will appear to name the layer and to
select the output directory:
86 | P a g e February 2011
Page 95

Note that the '.tmap_dtm' file extension will automatically be appended to the entered file
name.
When finished, select 'Save'. This will create the new bathy layer and will automatically
advance to the next processing step.
5.2.4 Select Input Lines
This page gives the user the option to select which lines to include in the bathy processing.
All lines loaded in the project that contain bathymetry data will be included in this list as
shown below:
87 | P a g e February 2011
Page 96

The user can select individual lines by clicking on the check box to the right of the line name,
or the user may choose 'Select All' or 'Deselect All'. If a line is deselected, it will not be
included in the DTM that is being created. Using the 'Add Lines' tool, it is possible to append
the DTM with the lines not included at a later time.
When finished selecting the lines to include in the processing, click the 'Next' button to
advance to the next processing step.
5.2.5 Gridding of Soundings
This page of the processing wizard as shown below gives the user the option to set output
resolution, encoding options, fill and smoothing options, and the option to constrain the DTM
to the map extent.
Resolution:
Enter the resolution of the DTM in meters per grid cell.
Note that the resolution chosen should be something appropriate with regard to the water
depth, number of beams, etc. This is also the "bin" size into which the raw bathy soundings
will be gridded. The resolution sets the grid cell size and therefore the smaller the number,
the larger the DTM file size of the final DTM file and the longer will be the processing time.
88 | P a g e February 2011
Page 97

Encoding:
Choose from the following options using the drop-down list:
Last: The last value to fall in the bin being processed.
Max: The deepest value to fall in the bin being processed.
Min: The shallowest value to fall in the bin being processed.
First: The first value to fall in the bin being processed.
Average: The average of all the values that fall in the bin.
Constrain to map view:
Only process the data that falls inside the current map window. This can be useful for quick
previews of grid results or for generating small grid files that are quick to work with.
Depth limit:
Choose the correct range for the data. If the data falls both deeper and shallower than 2000m
choose > 2000m.
Fill Filter:
Turn this on to fill gaps between data points, the two settings allow either a Median or
Inverse Distance filter to be used to compute the value of the depth being created. Also the
size (number of bins) East-West and North-South that will be used.
Smooth Filter:
A low-pass filter that can be applied to the DTM. The variables are similar to the Fill Filter.
Use this filter with care, useful data can easily be removed!
Hit 'Next' to continue to the Ancillary Options dialog.
5.2.6 Ancillary Options
This page of the processing wizard as shown below gives the user the option to indicate the
vessel geometry, whether to include FTS (footprint time series) data in the GSF file, and
whether to choose to generate an HTF file as well.
89 | P a g e February 2011
Page 98

Vessel Geometry: There are two options for vessel geometry. Generally vessel geometry is
stored in the raw data file header and can be read directly from the XTF file. By default the
'Use vessel geometry from XTF header' option is checked, and this information will be used
for data processing. Unchecking this option allows you to either 'Load' an existing geometry
file or 'Create' to generate a different vessel geometry (.GEO) file.
Selecting 'Load' will open a window for selecting an existing .geo_xml file.
Selecting 'Create' will open a window to enter vessel geometry information and save a new
.geo_xml file as shown on the next page:
90 | P a g e February 2011
Page 99

Note that there is a drop-down list for 'Heave Ref.' with the following options depending on
the source of the data and where in the XTF file the information is stored:
When finished, select 'OK'. This will open a window for entering the name of the vessel
geometry file and selecting an output directory.
GSF: Include FTS when available.
All data is written internally to a standard GSF (Generic Sensor Format) file. FTS (Footprint
Time Series) data is beam imagery from within each beam footprint, sometimes called
'Snippets'. If the data contains this information then leaving the box checked will generate
both a DTM and imagery from the FTS data in the GSF file.
91 | P a g e February 2011
Page 100

This type of data requires a great deal of processing and the size of the XTF files can be very
large. Unless there is a requirement for snippet imagery the box should be unchecked.
HTF: Generate HTF
Check this box and hit 'Settings' to save an HTF file. Available settings are shown in the
window below:
Enter the requested information and select 'OK' when finished.
Hit 'Next' to continue to the Raw Processing dialog.
5.2.7 Raw Processing
This page of the processing wizard as shown below includes POS, navigation and TPE
processing, plus options for transducer selection and attitude correction thresholds.
92 | P a g e February 2011
 Loading...
Loading...