Page 1

Trimble® S6 Total Station
Demonstration Guide
Version 1.00
Revision A
Part Number 022543-106
January 2005
Page 2

Contact Information
Trimble Geomatics and Engineering Division
5475 Kellenburger Road
Dayton, Ohio 45424-1099
USA
800-538-7800 (toll free in USA)
+1-937-233-8921 Phone
+1-937-233-9004 Fax
www.trimble.com
Copyright and Trademarks
© 2005, Trimble Navigation Limited. All rights reserved.
Trimble, the Globe & Triangle logo, Autolock, Geodimeter,
and Tracklight are tra demarks of Trimble Navig ation Li mited,
registered in the United States Patent and Trademark Office
and in other countries. MultiTrack, SurePoint, Trimble
Geomatics Office, Trimble Survey Controller and MagDrive
are trademarks of Trimble Na vigation Limited. Surve y Pro is a
trademark of Tripod Data Systems Inc., a wholly owned
subsidiary of Trimble Navigation Limited. The Bluetooth
word mark and logos are owned by the Bluetooth SIG, Inc.
and any use of such marks by Trimble Navigation Limited is
under license. Microsoft, ActiveSync, and W indo ws are either
registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation
in the United States and/or other countries. All other
trademarks are the property of their respectiv e owners.
Release Notice
This is the January 2005 release (Revision A) of the Trimble
S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide,
part number 022543-106. It applies to version 1.00 of the
Trimble S6 Total Station.
Page 3

1.1 Contents
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
The training data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Preparing for the demonstration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Selecting a Site. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Overview Session: Features of the Trimble S6 Total Station. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Hardware features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Operating features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
MagDrive servo technology. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
MultiTrack technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Robotic connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Field Sessions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Session 1: Basic station setup, and topographic measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Session 2: Advanced station setup, and automated rounds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Session 3: Staking out points and lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Session 4: Advanced topographic measurements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Session 5: Stakeout roads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Session 6: COGO and other features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide 3
Page 4

Introduction – The training data
1.2 Introduction
Welcome to the Demonstration Guide for the Trimble® S6 Total Station using a
Trimble CU running the Trimble Surve y Controller™ softw are. This document provides
a complete, easy-to-use guide of how to demonstrate the benefits and capabilities of this
instrument.
The guide can be used for sales demonstrations, product introductions, or to form the
basis of a complete training course. While providing a clear and simple overview of the
complete instrument, the guide has also been structured to enable you to tailor a
demonstration to your customer’s particular area of interest. It is not expected that a
demonstration will cover all the points given in this guide. You should always identify
your customer’s needs in adv ance. This will enable you to refer to the relev ant sections of
the demonstration guide to concentrate on the key features and benefits that are relevant
for their applications and workflows.
This guide is also just that, a “guide”, which enables you to quickly get up to speed with
the Trimble S6 total station. Once you hav e this solid base, you will naturally apply your
own experience and knowledge when carrying out demonstrations.
Use this guide to describe and demonstrate:
• Key features and benefits of the instrument
• Hardware features and benefits of the instrument
• Basic operating features of the instrument
• How to perform a basic station establishment
• How to perform topographic measurements
• How to perform a resection and multiple rounds of observations
• How to use automated topographic measurement techniques
• How to stake out points
• How to stake out lines
• How to stake out roads
• Additional survey features, such as field calculations and file transfer
12.1 The training data
The training data is designed to provide one simple data set that enables the features of
the Trimble S6 total station and Trimble Survey Controller software to be effectively
demonstrated. The files that comprise the training data include:
• Survey Control.csv (CSV control coordinate file)
• Survey DTM.dtm (sample DTM)
• Demo road.job (sample template road design)
• Road XML (sample XML road design)
4 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 5
Selecting a Site – Preparing for the demonstration
• Road and Building.dxf (background map DXF file)
• Building and Services.dxf (background map DXF file)
• Vegetation.dxf (background map DXF file)
• DTM.dxf (background map DXF file)
• Default.fal (Feature and Attribute library file)
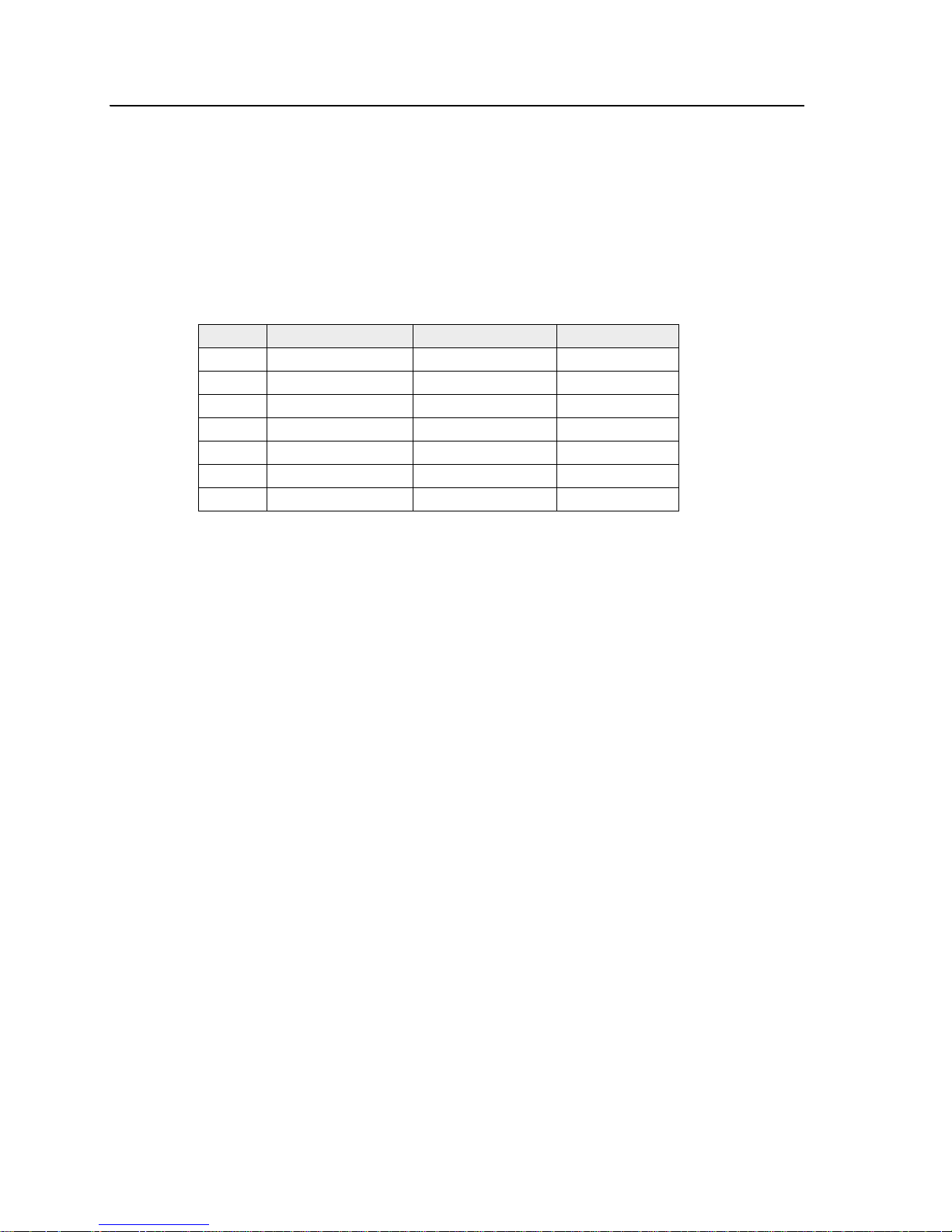
The points in the Survey Control.csv file include:
Point Northing Easting Elevation
1 1000.000 m 1000.000 m 100.000 m
100 1013.645 m 986.285 m 101.500 m
101 1041.688 m 991.026 m 104.800 m
102 1041.695 m 1002.759 m 104.700 m
103 1012.151 m 1000.463 m 101.278 m
104 1041.923 m 1014.910 m 104.450 m
105 1012.481 m 1013.975 m 100.625 m
12.2 Preparing for the demonstration
Before starting your demonstration, make sure that all your demonstration equipment is
ready and in good condition. This includes:
• Charging the batteries
• Loading data to the data collector
• Checking that the instrument is properly collimated and adjusted. Demo units
should be regularly taken to the dealer’s Service Center to keep them it good
condition.
In addition, keep in mind where you will carry out the demonstration: Try to a v oid noisy,
distracting, or dangerous locations.
1.3 Selecting a Site
When you select a site:
1. Make sure the site has at least 40 m (90 ft) of flat, open space with good visibility.
2. Place two markers in the ground to use as point 1 and point 2 from the training data.
3. Ensure that point 1 is on one edge of the open space and that point 2 is on the
opposite edge.
4. The survey area for the demonstration uses an area between point 1 and 2. See
Figure 1.1.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 5
Page 6
Overview Session: Features of the Trimble S6 To tal Station – Hardware features
Figure 1.1 Demonstration survey area
1.1 Overview Session: Features of the Trimble S6 Total Station
To demonstrate the key features and benefits of the instrument, including:
• MagDrive™ servo technology – fast and accurate integrated angle and servo
system
• SurePoint™ technology to protect accuracy
• MultiTrack™ technology to track prism targets and allow active tracking with the
Tar get ID
• Trimble DR technology to provide fast, accurate, long range measurements
• Integrated surveying to provide seamless integration with GPS and office software
These features add value:
• Applications – Basic control, topographic surveys.
• Features – Instrument and software functionality
• Benefits – Ease of use, functionality, productivity
11.1 Hardware features
Objective – To demonstrate the hardware features of the instrument.
The session should take approximately 5-10 minutes to demonstrate and should not
require the instrument to be powered on.
6 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 7

Overview Session: Features of the Trimble S6 Total Station – Hardware features
1. Begin with an introduction to the hardware features of the instrument. See
Figure 1.2 and Figu re 1.3.
Ergonomic offset handle
Coarse sight
Focus motion
servo knob
Eye-piece
Coarse sight
Control unit attachment
Figure 1.2 Trimble S6 total station face 1 position
Instrument
height mark
Vertical motion
servo knob
On/Off key and
Trigger key
Horizontal motion
servo knob
Bottom instrument
height mark
Communication (COM) connector
Power (PWR) connector
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 7
Page 8

Overview Session: Features of the Trimble S6 To tal Station – Hardware features
Coaxial optics for
angle and distance
measurements,
tracker, and
pointing laser
Antenna connector
Optics for Tracklight
Optical plummet
Figure 1.3 Trimble S6 total station face 2 position
Internal battery
Face 2 display
Face 2 keyboard
8 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 9
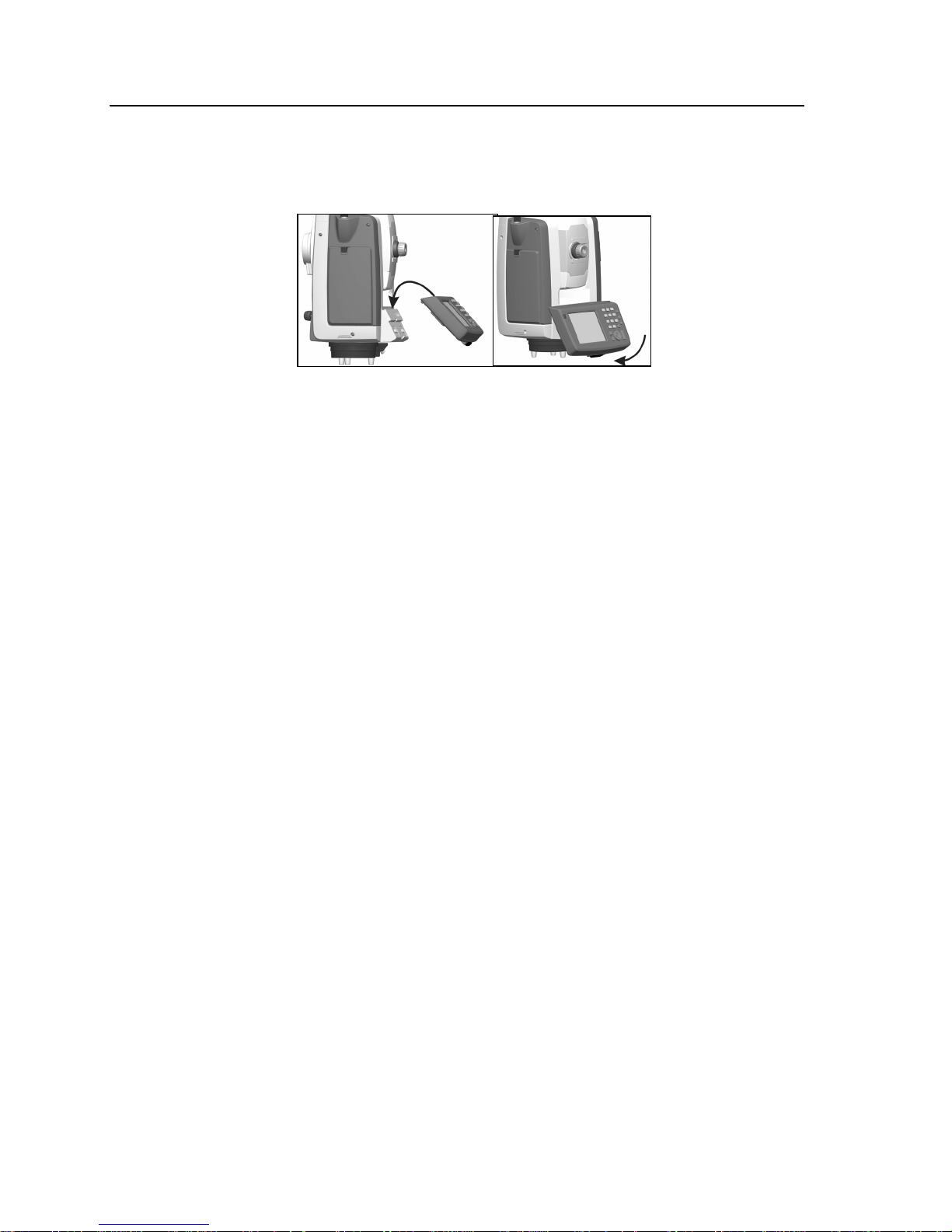
Overview Session: Features of the Trimble S6 Total Station – Hardware features
2. Turn the instrument to the face 1 position:
a. Describe the Trimble CU and demonstrate how it attaches to the
instrument. See Figure 1.4 .
Figure 1.4 The Trimble CU
b. Describe how the Trimble CU and embedded software helps provide
Integrated Surveying—seamless integration between conventional, GPS,
and office software.
3. Turn the instrument to the servo control side:
a. Identify the horizontal and vertical servo controls. Describe the MagDrive
servo technology, an integrated servo and angle system where the servo
drive operates like the drive of a magnetically levitated (maglev) train and
is integrated with the angle sensor to provide exceptional speed and
accuracy compared to conventional techniques.
b. Identify the location of the servo focus control and describe the improved
ergonomics. Describe that for steep angles or when using a 90 degree
eyepiece you can still focus the instrument.
c. Describe the Trigger key and the function that it performs, for example,
On/Off and Enter in field software.
d. Describe the instrument height marks at the trunnion axis and the bottom
notch. The field software allows heights to be entered to either mark.
Describe how measuring to the bottom notch provides a more accurate
instrument height measurement. See Figure 1.5.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 9
Page 10

Overview Session: Features of the Trimble S6 To tal Station – Hardware features
.
Figure 1.5 Instrument height marks
e. Identify the two external ports in the instrument base for external power
and communications.
4. Turn the instrument to the face 2 position:
Highlight the fully coaxial telescope including the optics, EDM, A utoloc k® technol ogy, and
the laser pointer.
Highlight the “Optics by Carl Zeiss” on the telescope as a sign of the quality of the lenses
used.
a. Identify the Tracklight® below the telescope.
b. Describe the face 2 display.
c. Describe the purpose of the face 2 buttons (Change face, Scroll, and
Enter).
d. Demonstrate the internal optical plummet and explain that it provides a
higher accuracy for instrument centering with the ability to rotate the
plummet around the ground mark.
e. Demonstrate the ergonomic offset handle and how this features makes it
easier to observe steep or vertical measurements without obstruction.
5. Turn the instrument to the battery side:
a. Demonstrate how to replace the battery. See Figure 1.6.
10 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 11

Overview Session: Features of the Trimble S6 Total Station – Operating features
Figure 1.6 The internal battery
b. Describe the internal battery and its specifications.
c. Describe the battery self-test.
Figure 1.7 Battery self-test panel
d. Describe the internal 2.4 GHz robotic radio (if available).
10.1 Operating features
Objective – To describe the basic operating features of the instrument.
This session should take approximately 10 minutes to demonstrate. Use this session to
introduce and describe:
• Ergonomics
• Speed, accuracy, and quietness of the MagDrive servo technology
Button
Power gauge
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 11
Page 12

Overview Session: Features of the Trimble S6 Total Station – Operating features
1. Attach the Trimble CU and connect to the instrument:
a. To switch on the instrument, press on the Trimble CU. The
instrument performs self-diagnostic tests to ensure that all its comp onents
are operating correctly.
b. Start the Trimble Survey Controller software. The software automatically
connects to the instrument and the Electronic level dialog appears:
c. Position and level the instrument and then tap C. Make sure that you
are still over the setup point.
d. When prompted by the Corrections dialog, enter appropriate atmospheric
values and then tap C.
The Survey Controller Basic dialog that appears shows the current
instrument readings. The large, clear display of information is ideal for
demonstrating the instrument features:
Note – You cannot store measurements in Survey Controller Basic mode.
2. Demonstrate how to aim and measure to a prism:
a. Turn the instrument using the servo controls.
Highlight the speed and quietness of the MagDrive servo technology.
12 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 13

Overview Session: Features of the Trimble S6 Total Station – MagDrive servo technology
b. Aim at a target using the servo controls and the servo focus.
Highlight the improved ergonomics.
c. Measure a distance to a prism.
Highlight the status bar and status line information that appears during the measurement.
3. Demonstrate Trimble functions and how to turn the instrument:
a. Select the Trimble key to display the Trimble functions form.
Highlight the ease with which the customer can gain access to the various instrument
controls. Tap and hold a button to access additional controls:
b. If the customer is a GDM CU user, explain that they can enter a program
number while the Trimble functions form is displayed to access programs
in the Trimble Survey Controller software, for example, tap + 23 to
access stakeout points.
c. Tap
Change Face to demonstrate the speed of the servo system.
Highlight the speed and accuracy.
d. Tap the face 2 button to turn the instrument back to the face 1 position.
e. Tap the Trimble key to display the Trimble functions form. Tap
Turn to and then select a method of HA VA. Enter a horizontal angle and
then tap
ã.
Highlight the speed and accuracy of the turn.
f. Select the softkey to demonstrate turning a right angle.
10.1 MagDrive servo technology
Objective – To demonstrate the following key features:
• MagDrive servo technology
• SurePoint technology
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 13
Page 14

Overview Session: Features of the Trimble S6 Total Station – MagDrive servo technology
This session should take approximately 10-15 minutes to demonstrate. Ensure that the
instrument is in good adjustment before starting the demonstration.
1. Describe the following MagDrive servo techn ology:
– integrated servo and angle system
– servo drive operates like a magnetically levitated (maglev) train and is
integrated with the angle sensor
– exceptional performance with high speed movement and accurate angles
2. Demonstrate SurePoint technology, which the instrument uses to hold the aimed
angles during windy conditions or when lightly tapped:
a. Allow the customer to aim at a target and then tap the instrument or
Trimble CU keys.
Highlight that the angles remain the same and that the instrument is still aimed at the
correct location.
3. Demonstrate the improved compensation features:
a. Explain that most instruments compensate for mislevelment by correcting
the horizontal and vertical angles, for example, when a tripod leg subsid es.
The instrument compensates both the angles and aiming for up to 6’ of
mislevelment.
b. Turn on the laser pointer and aim at a nearby point. If you are outdoors,
aim at a distant point.
c. Make a note of the current horizontal and vertical angle.
d. Watch the laser point, or cross hairs, while turning one of the tribrach foot
screws to create a mislevelment error.
e. The laser point, or cross hair, will be re-aimed at the original location
using the compensation values and MagDrive servo technology.
This ensures that the instrument aiming and horizontal and vertical angles are both
compensated to remove mislevelment errors and improve measurement accuracy.
4. Demonstrate the improved steep angle features that can be used in conjunction with
the optional 90 degree eyepiece:
a. Explain that in all instruments, the horizontal angle changes slightly as the
instrument is turned vertically.
With the Trimble S6 total station, the MagDrive servo technology uses the
compensation and error information to automatically adjust the horizontal
angle and position to the correct straight line value when the ve rtical
control knob is turned.
b. Aim to the base of a straight vertical building, tower, or tree, close to the
instrument.
c. Make a note of the current horizontal angle.
14 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 15

Overview Session: Features of the Trimble S6 Total Station – MultiTrack technology
d. Turn the vertical control knob to turn the instrument upward.
Note that the horizontal angle remains the same and that a perfect vertical
line can be extended by simply turning the vertical control knob.
5. Demonstrate extending a horizontal line:
a. Explain that the traditional way of setting out a horizontal straight line in a
direction exactly opposite to a given horizontal direction is to transit the
telescope 180° by just turning the vertical control knob. For an accurate
result, this technique requires a perfectly adjusted axis without horizontal
collimation errors.
The Trimble S6 total station uses the compensator and error information
with MagDrive servo technology to remove this limitation.
b. Aim to a point approximately 30 meters from the instrument and then turn
the vertical control knob to transit the telescope 180°.
c. Make a note of the current horizontal angle and mark a point
approximately 30 meters from the instrument.
d. Check the direction established b y turning a horizontal angle between the
two points.
The angle should be 180° degrees, which proves that an accurate
horizontal straight line direction was established by simply transiting the
telescope using the vertical control knob.
10.1 MultiTrack technology
Objective – To demonstrate the following key features:
• Autolock technology
•Target ID
This session should take approximately 10 minutes to demonstrate:
1. Describe that Autolock technology in the Trimble S6 total station can lock and track
prism or passive targets:
– The active LED of the Trimble 5600 has been integrated into the
instrument, which allows the instrument to track a larger v ariety of passive
targets without the need for a powered rod.
This improvement means that the Autolock performance now matches that
of the Trimble 5600 instrument.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 15
Page 16

Over view Session: Features of the Trimble S6 Total Sta tion – MultiTrack technology
2. Demonstrate the performance of automatically locking to a prism:
a. Select T rimble functions and then tap
Autolock. By default the instrument
snaps onto a target when it is within the field of view. This can be
configured in the Autolock settings.
b. Aim at a prism. Once the prism is within the field of view the instrument
automatically locks onto the target.
Highlight the status bar and status line information that is displayed to indicate the
instrument states.
c. Move the prism around to highlight the tracking capabilities, both in clear
visibility and around obstacles.
d. Loose lock and then select search to highlight the speed of regaining lock.
3. Describe that Target ID is available to provide quick and reliable target acquisition:
– Target ID uses an active Target ID unit at the rod to ensure that the correct
target is always locked and tracked.
– Target ID allows multiple targets with different IDs to be used on the one
site without fear of measuring to the wrong target.
4. Demonstrate the performance of Target ID:
a. Place two prisms on the site. For example one as the backsight and one on
the rod with the Target ID.
b. Turn on the Target ID.
c. Set the Target ID to an appropriate value (1-8).
d. Set the Target ID in the Trimble Survey Controller software to match the
Target ID unit. To do this, tap the Target icon and then select the target
height or prism constant values:
e. Select Trimble functions and then tap
æ.
The instrument finds the Target ID and then locks and tracks the prism.
16 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 17

Overview Session: Features of the Trimble S6 Total Station – Robotic connection
10.1 Robotic connection
If the radio channels are correctly configured, a robotic connection can be established
without having to attach the CU to the instrument.
Turn on the instrument using the trigger key and then proceed to Step 2 below. If
necessary, use the face 2 display to level the instrument and to configure the radio.
To prepare the instrument for robotics:
1. From the main menu, select Instrument / Radio settings to configure the radio. Tap
C to accept the configuration.
2. Select T rimble functions and then tap
Start Robotics.
3. Select Autocentered for the Trimble Survey Controller software to perform a search
centered around the instrument’s current horizontal and vertical angle.
4. Tap
k to suspend the Trimble CU ready for robotic operation.
5. Remove the Trimble CU from the instrument.
To connect to the Trimble S6 total station through robotics:
1. Attach the Trimble CU to the Advanced CU holder.
2. Press on the Trimble CU. The Trimble Survey Controller software
automatically powers on the Advanced CU holder radio and connects to the
instrument.
To use the map to assist robotic oper ation once a survey has been started:
1. Select Map to open the map display. Once the station setup is completed, the current
orientation of the instrument is shown by a dotted line extending from the
instrument to the end of the screen. The target is shown as a cross when a distance is
measured.
2. Make sure there is nothing selected on the map. Tap and hold a blank part of the
map that corresponds to your approximate location. The tap and hold action
displays a menu of options available from the map.
3. Select Turn to from the tap and hold menu. The instrument turns to your
approximate location.
Highlight this technique as a very useful method of re-establishing lock during robotics.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 17
Page 18

Overview Session: Features of the Trimble S6 To tal Station – Summary
10.1 Summary
This section described the following key features and benefits of the Trimble S6 total
station.
Feature Benefits
MagDrive servo technology Integrated angle and servo system. The next generation in servo-driven total
stations. Extremely fast, accurate, and quiet movement.
SurePoint technology Accurate aiming is retained providing confidence in obtaining accurate
measurements.
MultiTrack technology Improved flexibility, range, and accuracy to conventional prisms.
Trimble DR technology Fast, accurate, long range measurements.
Integrated surveying Seamless integration with conventional, GPS, and office software.
Servo focus Improved ergonomics for fast, easy, and convenient focusing.
Target ID Search with Target ID to always locate and track the correct target.
Coaxial optics, EDM,
Autolock, Laser P ointer
High-capacity internal Battery Li-ion internal “smart” battery provides long operation time with accurate
Trimble CU—detachable
WindowsCE controller
Tracklight High visibility red/green tracklight for aligning pole person on line.
Face 2 display View measurements and perform survey tasks without having to view only
Built-in rotating optical
plummet
Ergonomic offset handle Perform efficient surface scans or vertical measurements without being
Fully coaxial instrument provides ideal measurement confidence.
battery discharge information.
The Trimble CU is a rugged controller that incorporates a sophisticated
graphical display and Bluetooth® wireless technology to interface to Trimble
sensors.
the face 1 display.
Built in optical plummet provide s high accu racy centering tool to ensure
accurate results.
obstructed by the handle.
18 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 19

Field Sessions – Session 1: Basic station setup, and topographic measurement
1.1 Field Sessions
The following field sessions describe how to best demonstrate the Trimble S6 total
station using the Trimble Survey Controller software for various applications. It is not
intended that you complete all field sessions during a demonstration. Use the sessions to
tailor a demonstration to suit your customers’ applications and needs.
The sessions can also be performed using a Servo, Autolock, or Robotic instrument.
Before you start the field session, connect or configure the instrument using the method
that you will demonstrate.
11.1 Session 1: Basic station setup, and topographic measurement
Objective – To describe how to create a job, set up a station, and measure topographic
points:
• Applications – Basic control, topographic surveys
• Features – Instrument and software functionality
• Benefits – Ease of use, functionality, productivity
This session should take approximately 20-30 minutes to demonstrate.
Creating a job
Note – When you create a new job, settings from the previous job are used as the
defaults.
Create a new job using a coordinate system of scale factor only (1.000000), link the
Survey Control.CSV file, select the Road and Boundary.DXF background map, and
select the Default Feature and Attribute library:
1. Tap
$ to exit Survey Controller Basic mode. The main Trimble Survey
Controller menu appears, and you can begin a survey.
2. Select Files / New job and then enter a job name.
3. Select the button next to Coord. Sys:
a. Select Scale factor only and then tap
n.
b. Enter a scale factor as required (1.000000).
c. Tap
q to accept and use the scale factor.
4. Select the button next to Units:
a. Demonstrate and verify the various units.
b. Tap a to accept the units.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 19
Page 20

Field Sessions – Session 1: Basic station setup, and topographic measurement
5. Select the button next to Linked files:
a. Tap the file Survey Control.CSV so that it is selected (indicated by the
check mark 9).
b. Tap a to accept the linked file.
6. Select the button next to Background files:
a. Tap the file Road and Boundary.dxf so that the file is selected (indicated
by the check mark 9).
b. Tap a to accept the background file.
7. Select the button next to Feature library:
–Tap Default to select the default feature code library.
8. Tap a to create the job.
Note – To modify the properties of this new job at any stage, select Files / Properties of
current job. Each button displays the current settings. Tap a button to change the
settings.
Setting up a station
Perform a station setup on point 1, with point 2 as the backsight:
1. Place two markers in the ground to use as point 1 and point 2 from the training data.
Place point 2 approximately 40 meters from point 1.
2. Set up the instrument on point 1 and then place the prism or target on point 2.
3. From the Trimble Survey Controller main menu, select Survey / Station setup.
4. Set appropriate Corrections values and then tap a.
5. Enter the station setup details:
a. Enter the instrument point name (1), or tap the field pop-up arrow, then tap
List and select Point 1.
b. Enter the instrument height.
Note – The instrument height can be defined as measured to the True Height or
to the Bottom Notch. Use True Height when measuring to the cross that
corresponds to the centre of the trunnion axis. Use Bottom Notch when
measuring to the bottom notch of the instrument. Use the advanc ed pop-up
menu to select the measurement method (True Height is used by default).
c. Enter the backsight point name (2) and the backsight height.
d. Enter the Azimuth to the backsight point (2) as 0.
e. Select a measurement method of Angles and Distance.
20 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 21

Field Sessions – Session 1: Basic station setup, and topographic measurement
6. Aim to the backsight point and then tap m. The measurement result appears:
7. Tap
q to accept and complete the station setup.
Measuring topographic points
Set up three prisms or targets within the survey area to use for this and later tasks. These
points will be measured and can be used later as control for a resection. To do this:
1. Identify three evenly spaced locations around point 1 so that sound geometry is
available for a resection performed later at point 1. For example, see Figure 1.8.
Figure 1.8 Prism or target locations
2. Place a prism at each location.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 21
Page 22

Field Sessions – Session 1: Basic station setup, and topographic measurement
3. From the main menu, select Survey / Measur e topo and then enter the details for the
point to measure:
a. Enter the point name (for example, 1001) and then select a feature code
from the default library (for example, SS for Survey Station).
b. Select a measurement method of Angles and distance.
c. Enter the target height. Make a note of the point name and target height if
you intend to use this for resection later.
B
Tip – To alternate between targets or to edit the target height and the prism constant:
1. Tap the target icon on the status bar .
2. Select the target name to change to that target.
3. To open the Target Details form for editing, select the target height or prism constant.
You can create up to five non-DR targets.
4. Aim to the first point and then tap m.
While the instrument is measuring, the instrument icon becomes animated and
Measuring appears on the status line during a measurement. Once the measurement
is completed, the angles and distance appear.
5. Tap
s to store the point.
6. Measure the second point:
a. Modify the target height as necessary for the second point (1002). Make a
note of the point name and target height if you intend to use this for
resection later.
b. Aim to the point 1002 and then tap
c. Tap
s to store the point.
m.
7. Measure the third point:
a. Modify the target height as necessary for the third point (1003). Make a
note of the point name and target height if you intend to use this for
resection later.
b. Aim to point 1003 and then tap
c. Tap
Measuring topographic points: fast method
To measure topographic points quickly, use the TRK EDM mode:
1. Tap the Trimble key to display the Trimble functions form and then tap
Distances are now continuously measured and displayed on the status line.
2. Change the measurement method to Angles and Distance. The current measurement
is displayed and continuously updated.
3. Tap
s to store points as required. The fast update rate and continuous display of
the measurement allows points to be stored almost instantaneously.
22 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
m.
s to store the point.
TRK.
Page 23

Field Sessions – Session 1: Basic station setup, and topographic measurement
4. Tap the Trimble key to display the Trimble functions form and then tap STD to
change the EDM mode back to a standard measurement.
Measuring offset points
Objects such as trees, posts, or power poles cannot be directly measured because you
cannot place a prism at the centre of the object. This section describes some of the offset
measurement options and instrument modes that you can use for inaccessible objects.
H. Angle offset
The distance to a prism beside an object, and the horizontal angle to the centre of the
object are used to determine the measurement to the center of the object. See Figure 1.9.
Figure 1.9 H. Angle offset
1. Change the measurement method to H. Angle Offset.
2. Aim to the prism beside the cylindrical object (1) and then tap
m. Turn to the
centre of the object (2) and then tap Measure HA.
The measurement to the centre of the object (3) is displayed.
3. Tap
s to store the point.
Single dist offset
A defined offset distance and the measured distance to a prism at an offset point are used
to determine the measurement to the center of the object. See Figure 1.10.
Figure 1.10 Single distance offset
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 23
Page 24

Field Sessions – Session 1: Basic station setup, and topographic measurement
1. Change the measurement method to Single dist offset.
2. In the Measure topo dialog, enter a distance Out from the offset point to the centre
of the object (1):
3. Aim to a prism located at the front of the cylindrical object (2) and then tap
The measurement to the centre of the object (3) is displayed.
4. Tap
s to store the point.
Circular object - Direct Reflex
This method is specific to the use of Direct Reflex (DR) measurements. The distance to
the face of a circular object, and the horizontal angle to the edge of the object, are used to
determine the radius of the object and hence the distance to the center of the object. See
Figure 1.11.
Figure 1.11 Circular object - DR
1. Change the measurement method to Circular object.
2. Select the Trimble key to display the Trimble functions form and then tap the
DR icon to measure to non reflective surfaces using Direct Reflex.
m.
3. Aim to the face of the cylindrical object (1) and then tap
4. Turn to the edge of the object (2) and then tap Measure HA.
24 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
m.
Page 25

Field Sessions – Session 1: Basic station setup, and topographic measurement
The radius and measurement to the centre of the object (3) appears in the Measure
topo dialog:
5. Tap
s to store the point.
Note – Additional offset methods are available in COGO / Compute point. Use the Fast
Fix or Measure options in the pop-up menu to measure points from within Compute
Point.
Check backsight
A common survey practice is to perform a check measurement to the backsight point.
This check measurement is often performed before ending the current survey. To do this:
1. Tap the
2. Tap the
Ï softkey. A topographic point can be entered and checked.
Ð softkey. The backsight point details are automatically entered and the
instrument automatically turns to the backsight point.
3. Tap
m to measure to the backsight point. Measurement deltas to the backsight
point are displayed and can be stored.
4. Tap
s to store the check measurement to the backsight point and re-orientate if
required.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 25
Page 26

Field Sessions – Session 2: Advanced station setup, and automated roun ds
10.1 Session 2: Advanced station setup, and automated rounds
Objective – To describe advanced station setup (resection) and how to control
measurements:
• Applications – Traversing, control surveys
• Features – Autolock technology, automa ted rounds, instrument speed
• Benefits – Accuracy, speed, productivity
This session should take approximately 30 minutes to demonstrate.
Resection
A resection uses measurements to known points to determine the coordinates of the
instrument point and the horizontal orientation. Perform a resection using three
previously measured points.
1. Although not essential for the resection, set up the instrument on point 1. You can
then use the resection result to compare to the original coordinates of point 1.
2. Set up prisms or targets on three known or pre viously measured points. These points
will be used as the backsight points during the resection.
3. To start the resection:
a. From the main menu, select Survey / Resection.
b. Set appropriate Corrections values and then tap a.
c. Enter the instrument details including the Point name (for example, 10)
and the Instrument height.
d. Tap
o to highlight the resection options available:
e. In the Face order field, select F1…F2…
f. In the Number of rounds field, select 2 and then tap
g. Tap
resection points.
26 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
E.
C to accept the instrument details and proceed to measuring the
Page 27

Field Sessions – Session 2: Advanced station setup, and automated rounds
4. Measure the first resection point:
a. Enter the details of the first backsight point including the Point name and
the correct Target height.
B
Tip – To easily select the Point name, tap the pop-up arrow and then select List from the
menu that appears. Tap the point and then select Accept to add the point to the Point name
field.
b. Use the coarse sight to aim the instrument to the target at the first
backsight point.
c. Select the Trimble key to display the Trimble functions form. Tap
Autolock. The instrument automatically locks onto the target.
d. Tap
5. Measure the second resection point:
a. Enter the details of the second backsight point, including the Point name
b. Aim the instrument to the target at the second backsight point. The
c. Tap
Note – The resection calculation requires a minimum of two points to determine a
solution. Once two points have been measured, the Resection – Residuals are displayed.
Additional points can be added, measurements and residuals reviewed, or the current
solution accepted.
m to measure to the first backsight point.
and the correct Target height.
instrument automatically locks onto the target.
m to measure to the second backsight point.
B
6. Add the third point to the resection:
a. Tap the [+Point] softkey.
b. Enter the details of the third backsight point, including the P o int name and
the correct Target height.
Tip – Once a resection solution appears, the field software uses the current result to turn the
instrument to the next point. Enter the point name and the correct target height to allow the
instrument to turn to the correct location.
c. Tap m to measure to the third backsight point.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 27
Page 28

Field Sessions – Session 2: Advanced station setup, and automated roun ds
All backsight points have now been measured and the resection residuals appear:
7. If required, to add more backsight or foresight points, tap [+Point]; to accept the
resection results, tap
`; to begin rounds of observations, tap é.
8. Tap
` to display the resection results. Since the instrument is set up above
point 1, the coordinates from the resection result should closely match the
coordinates for point 1 (1000, 1000, 100):
9. Tap
s to accept the resection results and complete the station setup.
Automated rounds
The Rounds option enables you to measure multiple observations to multiple targ ets on
face 1, or on both face 1 and face 2.
28 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 29

Field Sessions – Session 2: Advanced station setup, and automated rounds
Highlight the speed and accuracy of the MagDrive servo technology.
In measuring rounds, you must first make one measurement to each of the points to be
measured. Then the instrument takes over, completing the measurement sets
automatically:
1. Set up the instrument on point 1 and then perform a station setup to point 2 (or use
the station setup defined by the resection on page 26).
2. Set up at least two prisms on the site. See Figure 1.12.
Figure 1.12 Site for automated rounds
3. Measure and note the height of targets.
4. From the main menu, select Survey / Rounds.
5. Select Options to configure the Rounds options:
– To measure all face 1 observations followed by all face 2 observations, set
the Face order to F1…F2….
– To define the number of face 1 and face 2 rounds, set the Number of
rounds to 3.
– To observe in a classic first to last point order, set the Observation order to
123…123.
– To have the instrument automatically measure rounds, ensure that the
Automated rounds option is selected.
6. Tap a to accept the rounds options.
7. Measure the first point:
a. Use the coarse sight to aim the instrument to the prism.
b. Select the Trimble key to display the Trimble functions form.
c. Tap
Autolock. The instrument automatically locks onto the target.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 29
Page 30

Field Sessions – Session 2: Advanced station setup, and automated roun ds
d. Enter the details of the point, including the Point name and the correct
Target height.
e. Tap
8. To measure the second point, repeat Step a through Step e above.
9. Measure additional points as required.
10.Tap
The instrument turns and measures all points automatically until the required number of
rounds is completed.
Highlight Use this time to highlight survey appl ication s (control and traversing) that are of
most benefit to this type of measurement. Also highlight the speed and accuracy of the
MagDrive servo technology and the pr oductivity gains that can be achie ved with the T rimbl e
S6 total station.
Reviewing rounds results
Once completed, the rounds results with standard deviations appear:
é to complete the current face and begin measuring automated rounds.
m to measure to the point.
1. Explain that the standard de viations displayed are the result of all the f ace 1 and face
2 observations.
2. Tap a point on the rounds list to show a review of all the face 1 and face 2
observations used to create the resultant mean measurement.
B
30 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Tip – To disable individual measurements, select the measurement and then tap the Use
softkey. The mean is updated using only the enabled measurements.
3. Tap to return to the rounds list.
4. Tap
` to accept the rounds observations and exit.
Page 31

Field Sessions – Session 2: Advanced station setup, and automated rounds
Review stored results
To review and edit survey data after it is stored:
• Select Files / Review current job to review how the data is stored and how it can be
edited. Discuss how the job is like a field book. Changes can be made and
coordinates are recomputed, but the original values are always retained for quality
assurance, for example, a target height change.
• Select Files / Point manager to review and edit data in a tabular view. Tap the
column header to sort the data. T ap + to ex pand the details for a point. Tap the
softkey to select a different view of the data.
• Select Files / QC Graph to review and edit data graphically . For example, to review
target heights. Tap a bar on the gr aph to display the details of the data. Tap
display and edit the full details. Tap the
Ö softkey to select a different view of
the data.
Ö
V to
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 31
Page 32

Field Sessions – Session 3: Staking out points and lines
10.1 Session 3: Staking out points and lines
Objective – To describe common stakeout tasks involving stakeout points and lines:
• Applications – Basic stakeout and construction stakeout applications
• Features – MagDrive servo technology, Target ID, upgradeability
• Benefits – Functionality, productivity
This session should take approximately 20-30 minutes to demonstrate. Use Servo,
Autolock, or Robotics depending on the needs of the users.
Staking out points
Various options can be configured when staking out points. This section describes some
of the common workflows.
Stake out points
Points are commonly staked out to define locations of interest either for construction,
earthwork, or cadastral type applications. In the stakeout workflow, you select a point,
navigate to the point, and then accept the measurement. To do this:
1. Set up the instrument on point 1 and then perform a station setup to point 2.
2. From the main menu select Survey / Stakeout / Points. If enabled, turn off Autolock
technology through Trimble functions.
3. Select the points to add to the stakeout list:
a. Select
A to add points to the stakeout list. Various methods to select
points and add them to the stakeout list are available.
b. Select the Enter single point name method.
c. Enter the name of one of the resection points (or a previously measured
point) and then tap
d. Tap
$ to exit Enter single point name and display the stakeout list.
A to add the point to the stakeout list.
32 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 33

Field Sessions – Session 3: Staking out points and lines
4. Tap S to start staking out the point highlighted in the stakeout list. The stakeout
navigation form appears and the inst rument turns to the stak eout point. The EDM is
put into TRK mode to provide continuous navigation updates:
5. Place a target at the point and then move the instrument slightly to show how the
navigation information updates.
Highlight that the instrument uses voice prompts to help you navigate to the point.
6. Demonstrate that you can select
ã at any stage to re-aim the instrument at the
stakeout point.
7. Tap a to accept the current measurement or, for high precision applications,
m to perform an STD measurement before you select a.
select
The staked deltas appear.
8. Tap
s to store the measurement and staked deltas.
Stake out with a DTM
Stake out with an underlying DTM is often used for earthwork applications that require
the cut or fill to be reported to a design DTM. To stake out a point using an underlying
DTM:
1. Tap a point to start staking out the point.
2. Tap
o and then select the Display cut/fill to DTM check box.
3. Select the DTM of Survey DTM and then tap a. The cut/fill values are
calculated and displayed with respect to the DTM rather than the elevation of the
design point.
4. Navigate to the point. Tap a to accept the current measurement.
5. Tap
s to store the measurement and staked deltas.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 33
Page 34

Field Sessions – Session 3: Staking out points and lines
Stake out from the map
Use the map display to enhance selecting and staking out points, particularly during
robotics. To stake out a point from the map:
1. Select
L to open the map display. The current orientation of the instrument is
shown by a dotted line extending from the instrument to the end of the screen. The
target is shown as a cross when a distance is measured.
2. Tap a point (for example, 105) to select the point:
3. Tap
4. Tap
S to start staking out the point.
Q / L to use the map while in stakeout. Note that the stakeout cut/fill
values are displayed on the map while the stakeo ut form is op en in the back gro un d.
5. Navigate to the point. Select
Q / Stake out points to return to the stakeout
navigation form.
6. Tap a to accept the current measurement.
7. Tap
s to store the measurement and staked deltas.
8. Repeat the stakeout procedure with additional points if necessary.
34 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 35

Field Sessions – Session 3: Staking out points and lines
Stake out lines
Lines are often used as a reference guide, particularly in construction app lications. To
define a position relative to a line or to stake out a line:
1. Create a line between two boundary corner points:
a. Select Keyin / Lines:
b. Enter a Line name and a Code as necessary.
c. Select the Start point and then enter point 103.
d. Select the End point and then select List from the pop-up menu. Tap point
102 to select the point from the list.
e. Enter a Start station of 100 and a Station interval of 5.
f. T ap
g. Tap
Z to calculate the line details.
s to store the line.
2. Set up the instrument on point 1 and then perform a station setup to point 2.
3. Tap
K and then select Survey / Stakeout / Line.
4. Define a location relative to the station and offset from the line:
a. Enter the line name and then select a Stake method of To the line.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 35
Page 36

Field Sessions – Session 3: Staking out points and lines
b. Tap x and move about the line. Demonstrate how the graphic, and
station and offset values update as you move:
B
c. Tap C and then tap
for the point.
5. Stake out a point by defining a design station and offset value:
a. Change the Stake method to Station/Offset from line.
b. Enter the Station (0+105.110 m) and Offset (0.593 m) values
corresponding to the front corner of the building on lot 20.
c. Tap
d. Navigate to the point and then tap C to accept the current
e. Tap
6. Stakeout a slope relative to the line:
a. Change the Stake method to Slope from the line.
b. The slope left and right can be defined by distances or by grade and
c. Enter a Grade of 50% and an H. dist of 10 m for the left slope.
Tip – The format of the grade can be changed through Options or from Properties of current
job / Units.
x and then navigate to the station and offset point.
measurement.
s to store the measurement and staked deltas.
distance. Select the Slope left method of Grade and Horz. Dist.
s to store the measurement and station values
d. Enter the same values of Grade (50%) and an H. dist (10 m) for the right
slope.
36 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 37

Field Sessions – Session 3: Staking out points and lines
e. Tap x to begin staking out the slope from the line. Demonstrate how
the graphic, station, and offset an d grade v alues u pdate as you mo ve ab out
the line:
f. T ap C to store the current measurement and grade.
7. Stakeout additional station and
offset values as necessary. The
station and offset values for the
building on lot 20 are shown in the
following table and in Figure 1.13.
Point Station Offset
a 0+105.110 m 0.593m
b 0+105.076 m 4.103m
c 0+107.182 m 4.125 m
d 0+107.157 m 6.732 m
e 0+118.543 m 6.841 m
f 0+118.603 m 0.722 m
Figure 1.13 Lot 20
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 37
Page 38

Field Sessions – Session 4: Advanced topographic measurements
10.1 Session 4: Advanced topographic measurements
Objective – To demonstrate how to perform advanced topographic measurement using high
speed automated measurement techniques:
• Applications – Advanced topographic measurements for high density / large areas.
• Features – DR technology, MagDrive servo technology, Autolock technology,
software functionality
• Benefits – Productivity, diverse applications, automation
This session should take approximately 15-20 minutes to demonstrate.
Continuous topo
Use continuous topo to automatically measure points based on a defined criteria, such as
time, distance, or time and distance. Continuous topo is best suited to Autolock and
Robotic use and provides an efficient measurement technique that greatly improves
productivity.
1. To perform some continuous to pographic measurements over the site area:
a. Set up the instrument on point 1 and perform a station setup to point 2.
B
b. From the main menu, select Survey / Continuous topo.
c. Enter a Start point name for the first point to be measured. The point name
will automatically increment by 1 from the start point name.
d. Select a Method depending on the measurement control required. In this
case, select Fixed distance.
e. Enter a Distance value. A point is automatically stored when the distance
changes by the amount defined in the Distance field.
f. Select the Trimble key to display the Trimble functions form. Tap
Autolock.
g. Aim to a target. The instrument automatically locks onto the target.
h. Select
x to begin automatic measurement.
i. Move the target around the site to demonstrate points being automatically
stored.
Tip – To demonstrate Continuous topo in DR mode, turn the instrument during continuous
measurement. This is the equivalent of a manually controlled surface scan.
2. To view continuous topo measurements in the map:
a. Select
L to display the map of the current job.
b. Tap
displayed by a cross on the map with the orientation of the instrument
indicated by the red dotted line. See Figure 1.14.
38 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
N to zoom into the current position. The current position is
Page 39

Field Sessions – Session 4: Advanced topographic measurements
Instrument
orientation indicator
Figure 1.14 Display of current position
c. Move the target around the survey site. The map automatically zooms to
the current location. Points are stored as specified by the continuous topo
measurement form.
B
d. Tap
Q/ Continuous topo to switch back to the continuous topo
controls.
Tip – The map view with Continuous topo is particularly useful for measuring large areas. A
common practice is to store points in a grid pattern to ensure sufficient coverage o v er the site.
The map view allows the measurements to be automatically stored with the map providing a
graphical display of site coverage. The surveyor can then easily control the survey over a
large site, particularly during Robotic operations.
3. To end Continuous topo measurements, tap e.
Surface scan
Use surface scan to automatically measure points over a defined surface area. A vertical
surface, such as a building facade, is often the best type of surface to demonstrate the
scan.
1. Define the scan method:
a. Set up the instrument on point 1 and then perform a station setup to point
2.
b. From the main menu, select Survey / Surface scan.
c. Enter a Start point name for the first point to be measured. The point name
automatically increments by 1 from the start point name.
d. Tap the Scan Method field to identify the scan methods available.
e. Select the Rectangular plane method, which scans a defined plane surface
based on a horizontal and vertical distance interval.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 39
Page 40

Field Sessions – Session 4: Advanced topographic measurements
2. To measure the points used to define the plane, use the Fast fix option from the fi eld
pop-up menu:
a. Aim at the point that will define the top left corner of the rectangular plane
(1). Tap Fast fix from the 1st corner field pop-up menu. The point is
automatically measured and stored with an arbitrary point name. See
Figure 1.15.
Figure 1.15 Rectangular plane
b. Aim at the point that will define the top right corner of the rectangular
plane (2). Tap Fast fix from the 2nd corner (bottom right) field pop-up
menu. The point is automatically measured and stored with an arbitrary
point name.
c. Aim at the point that will define the opposite bottom edge of the
rectangular plane (3). Tap Fast fix from the Point on opposite edge field
pop-up menu. The point is automatically measured and stored with an
arbitrary point name.
3. Define the distance intervals for the scan (4 and 5):
a. Enter a horizontal and a vertical distance interval.
40 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 41

Field Sessions – Session 4: Advanced topographic measurements
b. The total number of points that will be measured, and the estimated time
for the scan appear.
4. Tap
Highlight the speed of the surface scan and the various applications tha t scanning can be
used for.
B
Tip – Turn on TRK mode through Trimble functions to provide continuous distance
measurements that increases the speed of the surface scan.
5. Tap Pause at any stage to temporarily pause the scan.
6. Tap
x to commence the scan.
Information such as the number of points scanned, points skipped, and time to go,
appear during and at the completion of the scan.
` at the completion of the scan to exit.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 41
Page 42

Field Sessions – Session 5: Stakeout roads
10.1 Session 5: Stakeout roads
Objective – To demonstrate staking out roads:
• Applications – Road stakeout
• Features – Instrument speed, accuracy, functionality
• Benefits – Functionality, graphics, productivity
This session should take approximately 15-20 minutes to demonstrate.
Staking out a Trimble road
Trimble roads can be created in Trimble Office Software products or manually entered
from the Trimble Survey Controller software.
To stake out a Trimble road:
1. Set up the instrument on point 1 and then perform a station setup to point 2.
2. Copy the road definition from the Demo Road.job into the current job.
3. From the main menu, select Survey / Stakeout / Road.
4. Stake out a centerline point on the road:
a. Tap the pop-up arrow for the Road name f i eld and th en tap Trimble roads.
A check mark 9 appears next to the selected road type.
b. Select List from the pop-up menu for the Road name field and then select
the road to stake.
c. Select a Stake method of Station and offset.
d. Enter a station value of 1+040.000. Alternativ ely , select List from the f ield
pop-up arrow and tap the station v alue or tap the or softkeys
to increment the station value by the defined station interval.
e. Tap
E to begin staking out the centerline point. The stakeout
navigation screen appears:
42 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 43

Field Sessions – Sessi on 5: Stakeout roads
Highlight the use of the graphical display and the instrument voice prompts to help you to
navigate to the point.
f. T o accept the current measurement, tap a; to remeasure the point, tap
m.
g. Tap
s to store the measurement and staked deltas.
5. Stake out a template offset point on the road:
a. Enter a station value of 1+040.000.
b. Select List from the Offset field pop-up menu and then tap the 3.000m
Offset (right) value.
c. Tap
E to begin staking out the template point.
d. To accept the current measurement, tap a; to remeasure the point, tap
m.
e. Tap
s to store the measurement and staked deltas.
6. Stake out a road catch point. The road catch point is where the side slope of the
template intersects with the ground.
a. Enter a station value of 1+040.000.
b. Select List from the Offset field pop-up menu and then tap the right (Side
Slope).
c. Tap
x to begin staking out the catch point.
The stakeout navigation form appears:
d. The Slope values at the top of the form show the current side slope (in
blue) and the design side slope (in black). Use the current value when the
design side slope cannot be staked.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 43
Page 44

Field Sessions – Session 5: Stakeout roads
e. Tap the softkey to view a cross-section of the road display. Use the
cross-section view to help stakeout navigation:
f. Select a to accept the current measurement.
g. Tap
s to store the measurement and staked deltas.
7. Stake out a road design point using construction offsets. Construction offsets can be
applied both horizontally and/or vertically to enable stakes to be placed offset to the
actual design.
a. Enter a station value of 1+040.000.
b. Select List from the Offset field pop-up menu and then tap the 3.000m
Offset (right) value.
c. Select a Construction Offsets / Method of Horizontal to define offsets
horizontally from the design.
d. Enter a Horizontal value of 2.000 m and a vertical offset value of 1.000 m.
e. Tap Start to begin staking out the construction offset points. The stakeout
navigation form appears.
44 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 45

Field Sessions – Sessi on 5: Stakeout roads
f. Tap the softkey to view a cross-section of the road display. Use the
cross-section view to help stakeout navigation. The construction offsets
appear in green:
g. To accept the current measurement, tap a; to remeasure the point, tap
m.
h. Tap
s to store the measurement and staked deltas.
Note – If you stake out a construction offsets from a side slope, navigate to the
catch point first. Then select Offset / Add Constr. offsets to Catch pt to
stake out the construction offsets.
Note – The Trimble Survey Controller software supports the use of LandXML and
GENIO road definitions. For more information, refer to the Trimble Survey Controller
Help.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 45
Page 46

Field Sessions – Session 6: COGO and other features
10.1 Session 6: COGO and other features
Objective – To demonstrate COGO, exporting data, and other advanced features of the
Trimble Survey Controller software:
• Applications – Survey computations, data export
• Features – Functionality, ease of use
• Benefits – Functionality
COGO
Coordinate calculations are often performed to provide additional survey information, or
to define or locate points of interest.
1. Calculate an inverse between two points:
a. From the main menu, select COGO / Compute Inverse.
b. Enter a From point or use the pop-up menu to select or measure a point.
c. Enter a To point or use the pop-up menu to select or measure a point.
d. Once you tap C for the To Point field, the inverse details appear.
e. Select
s to store the inverse, or enter additional points to recalculate.
2. Calculate an inverse between two points from the map:
a. Open the Map and then select two points.
b. Tap and hold a point on the screen and then select Compute Inverse.
c. The Compute inverse form appears.
d. Tap
s to store the inverse, or tap $ to exit.
3. Calculate an area from the map:
a. Open the Map and then select three or more points.
b. Tap and hold a point on the screen and then select Compute Area.
c. The Compute Area result form appears.
d. Tap
s to store the area, or tap $ to exit.
Note – The points used in determining an area can also be added through COGO /
Compute Area.
4. Calculate the coordinates of a point using a known angle and distance from a point:
a. From the main menu, select COGO / Compute Point.
b. Enter a Point name for the point to be computed.
c. Select a method of Turned angle and distance.
46 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 47

Field Sessions – Session 6: COGO and other features
d. To explain this me thod, demonstrate the on line help. Select the Trimble
icon in the top left corner of the screen and then tap Help. The help is
context sensitive, which means it automatically scrolls to the topic
corresponding to the area of the software where help was selected.
e. Tap Calculating – points to display the help topic on COGO – Compute
point. Scroll to the list of methods and then tap the HTML link for Turned
angle and distance.
f. T ap
k to close Microsoft® Explorer and then tap $ to close the
Help index.
g. Enter a Start point, and an End point or Azimuth.
h. Key in the Turned angle, Horizontal distance, and Vertical distance
(optional).
i. Tap
j. Tap
È to calculate and view the coordinates for the point.
s to store the coordinates for the point.
Transferring data
You can transfer data to and from the Trimble Survey Controller software and Trimble
office software products using the Trimble Data Transfer utility or through Microsoft
ActiveSync®.
Transferring data into Trimble Geomatics Office
1. If you have not already done so, run the Update Office Software option on the
Trimble Survey Controller installation CD.
2. Make sure that Microsoft ActiveSync is installed on the office computer.
3. Open Trimble Geomatics Office and then create a new project.
4. Place the Trimble CU in the office docking station and then connect the docking
station to the USB port of the office computer.
5. Power on the Trimble CU. When prompted, tap Yes to connect to the desktop. The
Trimble CU now appears as a mobile device on the office computer.
6. In Trimble Geomatics Office™, select Import / Survey Devices.
7. Select Survey Controller on ActiveSync. The files available to download appear.
8. Select the appropriate Survey Controller job file and then select Open. The job file
is imported into the Trimble Geomatics Office project.
Transferring data using the Data Transfer utility
1. If you have not already done so, run the Update Office Software option on the
Trimble Survey Controller installation CD.
2. Make sure that Data Transfer utility is installed on the office computer. Data
Transfer is available on the Trimble Survey Controller installation CD.
3. Make sure that Microsoft ActiveSync is installed on the computer.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 47
Page 48

Field Sessions – Session 6: COGO and other features
4. Place the Trimble CU in the office docking station and then connect the docking
station to the USB port of the office computer.
5. Power on the Trimble CU. When prompted, tap Yes to connect to the desktop. The
Trimble CU now appears as a mobile device on the office computer.
6. Open Data Transfer and then select Survey Controller on ActiveSync from the
device list.
7. Select the connect icon . Once Data Transfer connects to the Trimble CU, the
connection shows in the device state icon .
8. Select Add to view the list of available files on the Trimble CU.
9. Select the file(s) to download and then select Open.
10.Select Transfer All to download the files onto the office computer.
Transferring data directly from the Trimble Survey Controller software
1. From the Trimble Survey Controller main menu, tap Files / Import/Export… /
Custom ASCII export. The Custom ASCII export uses an XML style sheet with the
Survey Controller job file to create customized formats. You can create your own
style sheet to create a customized report or data format.
2. Select an ASCII format from the list that appears.
3. Enter the details for the ASCII format and tap a. The ASCII file is created in
the Trimble Data directory. To view the file on the controller, enable the View file
option.
Copying an ASCII file from a Trimble CU to a USB memory device
1. Connect the USB memory stick to the Robotic holder or Office docking station
through the USB to Hirose connector.
2. Select My Computer on the Trimble CU and then select the file.
3. Copy (
Ctrl+C) and then paste (Ctrl+V) the file to the USB memory device.
Copying an ASCII file from a Trimble CU to a controller that is running the Windows CE
operating system
Note – The Trimble CU runs the Windows CE .Net operating system.
1. Connect the Trimble CU to the second controller through a cable or through
Bluetooth wireless technology.
2. On the second controller, select Start / Programs / Utilities / File Transfer and then
select Receive.
3. On the Trimble CU, select Start / Programs / Utilities / File Transfer and then select
Send.
4. Select the file to transfer between the controllers.
48 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
Page 49

Field Sessions – Session 6: COGO and other features
Tips for Geodimeter CU users
The Trimble Survey Controller software includes functions to help users who are
experienced with the Geodimeter® Control Unit. These functions include:
• GDM CU – PRG links from within the Trimble Survey Controller software.
Demonstrate that you can enter a program number while the Trimble functions form
is displayed to access programs within the Trimble Survey Controller software. For
example, select Trimble Functions + 26 to access Compute Inverse, which is the
equivalent of DistOb on the GDM CU.
• GDM CU – D-bar. To access this mode in the Trimble Survey Controller software,
select the Averaged Observations measurement method from the Station setup,
Resection, Measure topo, or Measure rounds menu. Then select one of the
following:
– To measure a defined number of observations, select Options / Averaged
observations. Standard deviations are updated and displayed during
measurement.
– T o continually measure until the standard deviations are acceptabl e, select
Options and then enter a high number in the Averaged Observations field.
Tap a once the standard deviations are acceptable.
• To automatically change face and retain the point name after completing the face 1
measurement, select Survey / Options. Then select the A uto F1/F2 check box. When
using an instrument that locks to the target, the measurement starts automatically.
When the face 2 measurement is completed, the instrument changes back to face 1.
• GDM CU – GDM file export. You can create a GDM area and GDM job file from a
Survey Controller job file either directly or transferred through the Data Transfer
utility. To create a GDM file directly:
a. Select Files / Import/Export / Custom ASCII export. The Custom ASCII
export uses an XML style sheet with the Survey Controller job file to
create customized formats. Select the GDM job file format. Enter the file
name and then tap a. The file is created in the Trimble Data directory.
b. Connect the Trimble CU to an office computer and then establish an
ActiveSync connection. Run the Trimble Data Transfer application and
then connect to the Trimble CU. Select Receive and then change the Files
of type to GDM job. Select the fil e that you want to do wnload. A GDM job
file is transferred and created.
Trimble S6 T otal Station Demonstration Guide 49
Page 50

Field Sessions – Session 6: COGO and other features
50 Trimble S6 Total Station Demonstration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...