Page 1

Installation and operating instructions
TOUCH800®
Version: V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN Read and follow these instructions. Keep these instructions in a
safe place for later reference. Please note that there might be a
more recent version of these instructions on the homepage.
Page 2

Document
Copyright ©
Company details
Installation and operating instructions
Product: TOUCH800®
Document number: 30322538-02-EN
As of software version: 02.20.17
Original instructions
Original language: German
Müller-Elektronik GmbH & Co.KG
Franz-Kleine-Straße 18
33154 Salzkotten
Germany
Phone: ++49 (0) 5258 / 9834 - 0
Fax: ++49 (0) 5258 / 9834 - 90
Email: info@mueller-elektronik.de
Homepage: http://www.mueller-elektronik.de
Page 3

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
3
1
For your safety
7
1.1
Basic safety instructions
7
1.2
Intended use
7
1.3
Layout and meaning of warnings
8
1.4
Disposal
8
1.5
Instructions on retrofitting
8
1.6
EU declaration of conformity
9
2
About these Operating Instructions
10
2.1
Target group of these Operating Instructions
10
2.2
Layout of operating instructions
10
2.3
Layout of references
10
2.4
Directional information in these instructions
10
3
Product description
11
3.1
Scope of delivery
11
3.2
Terminal buttons
11
3.3
Terminal ports
11
3.4
Applications on the terminal
12
3.5
Information on the rating plate
14
4
Mounting and installation
15
4.1
Mounting the terminal in the vehicle cab
15
4.1.1
Mounting the standard bracket
15
4.1.2
Mounting the optional bracket
16
4.1.3
Mounting the optional adapter
16
4.2
Connecting the terminal to the ISOBUS
17
4.3
Inserting micro-SD card
18
4.4
Using two terminals
18
5
Basic control principles
19
5.1
Switching on the terminal
19
5.2
Initial start-up
19
5.2.1
Using the terminal for parallel driving
19
5.2.2
Operating ISOBUS implement
20
5.2.3
Terminal for automatic section control
20
5.2.4
Terminal for task management
21
5.3
Switching off the terminal
22
5.4
Terminal screen layout
22
5.5
Opening applications
23
5.6
Moving an application
24
5.7
Saving and loading window arrangements
24
Table of contents
Table of contents
Page 4

4
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
5.8
Hiding an application
25
5.9
Using the keyboard
25
5.10
Using a memory device
26
5.10.1
Using SD card
26
5.10.2
Folders on the USB memory device
26
5.10.3
Displaying the content of the memory device on the terminal
27
6
Connecting and configuring external devices
28
6.1
GPS receiver
28
6.1.1
Connecting the GPS receiver to the terminal
28
6.1.2
Changing the driver for the GPS receiver
28
6.1.3
Configuring the GPS receiver
30
Parameters for the GPS receiver
30 RTK or L band licence for SMART-6L
33
GSM modem for SMART-6L
33
Configuring the GPS receiver for the steering system
34
6.1.4
Recording GPS position
35
6.1.5
Configuring the “GPS TILT-Module” tilt module
36
6.2
Configuring the joystick button allocations
36
6.3
Connecting sensors to the terminal
37
6.4
Camera
38
6.4.1
Connecting the camera to the terminal
38
Connecting the camera HQ2
38
Connecting the camera NQ
39
6.4.2
Activating a camera
39
6.4.3
Operating the camera
40
6.5
External lightbar
40
6.5.1
Connecting the external lightbar to the terminal
40
6.5.2
Activating an external lightbar
41
6.6
Connecting the on-board integrated display/controller to the terminal
41
6.7
ISO Printer
42
6.7.1
Connecting the ISO printer to the terminal
42
6.7.2
Activating ISO Printer
43
6.8
Configuring the Bluetooth connection in the Connection Center
43
6.9
Crop protection sensors
43
7
Configuring the terminal in the Service application
45
7.1
Changing the language
45
7.2
Basic terminal settings
45
7.3
Activating and deactivating applications
47
7.4
Unlocking licenses for full versions
48
7.5
Creating screenshots
49
7.6
Deleting pools
49
7.7
Using the Open Data Interface
49
7.7.1
Activating ME ODI
50
7.7.2
Opening ME ODI
50
Table of contents
Page 5

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
5
8
Tractor-ECU application
51
8.1
Work screen
51
8.2
Managing the tractor profiles
51
8.3
Parameter
53
8.3.1
Calibrating the speed sensor
55
8.3.2
Calibrating an analog work position sensor
56
8.3.3
Tractor geometry
56
Configuring the tractor connector types
57
Configuring the tractor geometry
58
8.4
Results
59
8.4.1
Trip counter
59
8.4.2
Task-related counter
59
9
Virtual ECU application
61
9.1
Managing virtual job computers
61
9.2
Parameter
62
9.3
Work screen
65
10
Task management (ISOBUS-TC)
66
10.1
Configuring ISOBUS-TC
66
10.1.1
The “farmpilot” parameter
66
10.1.2
“Operating Mode” parameter
66
10.1.3
“TC number” parameter
67
10.1.4
“Prefer internal Tractor-ECU?” parameter
67
10.1.5
“Save finished tasks as a file?” parameter
67
10.1.6
“Validation of the device description” parameter
67
10.1.7
“Simplified target rate assignment?” parameter
68
10.2
Configuring the list of connections
68
10.3
Using fields and shp data
69
10.3.1
What is field data for?
70
10.3.2
Creating fields
70
10.3.3
Activating and deactivating fields
71
10.3.4
Importing field data (*.shp)
72
10.3.5
Exporting field data
72
10.3.6
Data on the memory device
73
10.3.7
Transferring field data to a different terminal
73
10.4
Using prescription maps
73
10.4.1
Importing shape prescription maps
74
10.4.2
Selecting shape prescription maps
75
10.4.3
Editing shape prescription maps
75
10.4.4
ISO-XML prescription maps
76
10.5
MULTI-Control
76
11
FILE-Server application
78
12
Technical specifications
79
12.1
Technical specifications of the terminal
79
Table of contents
Page 6

6
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
12.2
Pin-out diagrams
80
12.2.1
Port A (CAN bus)
80
12.2.2
Port B
80
12.2.3
Port C
81
12.2.4
CAM port
82
12.2.5
ETH (Ethernet) port
83
12.3
Licence conditions
83
13
Troubleshooting
84
Table of contents
Page 7

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
7
1
1.1
1.2
For your safety
For your safety
Basic safety instructions
1
Basic safety instructions
Please read the following safety instructions carefully before using the product for the first time.
▪ Do not operate the terminal while driving in road traffic. Come to a standstill in order to use the
unit.
▪ Before maintenance or repair to the tractor, always disconnect the connection between the
tractor and the terminal.
▪ Before charging the tractor battery, always disconnect the connection between the tractor and
the terminal.
▪ Before welding on the tractor or implement, always disconnect the power supply to the terminal.
▪ Do not make any unauthorized modifications to the product. Unauthorized modifications or use
may impair safety and reduce the service life or operability of the unit. Modifications are
considered unauthorized if they are not described in the product documentation.
▪ Follow all recognised safety, industrial and medical rules as well as all road traffic laws.
▪ The product does not include any user-serviceable parts. Do not open the casing. If the casing is
opened, its imperviousness can be changed.
▪ Read the operating instructions to the agricultural device which you want to control by using the
product.
Using a camera
The camera serves solely for observing the implement functions in non-safety-related working areas
of the agricultural implement.
In certain situations, the camera image may appear on the screen with a delay. The delay depends
on the respective use of the terminal and can also be affected by external factors and devices.
For this reason, please note the following information:
▪ Do not use the camera to assist with steering the vehicle: not in road traffic, and not on private
properties.
▪ Do not use the camera to watch the road traffic or when driving into intersections.
▪ Do not use the camera as a rear view camera.
▪ Do not use the camera as a visual aid for controlling the implement, especially when a delayed
reaction can lead to risks.
▪ Using a camera does not exempt you from your due diligence obligation to pay attention to
safety when operating the implement.
Intended use
The terminal is used to operate implements equipped with ISOBUS job computers.
Intended use also includes compliance with the conditions for operation and repairs prescribed by the
manufacturer.
The manufacturer cannot be held liable for any personal injury or property damage resulting from
such non-compliance. All risk arising from improper use lies with the user.
All applicable accident prevention regulations and all other generally recognized safety, industrial,
and medical standards as well as all road traffic laws must be observed. Any unauthorized
modifications made to the equipment will void the manufacturer's warranty.
Page 8
8
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
WARNING
This signal word identifies medium-risk hazards, which could potentially cause death or serious
physical injury, if not avoided.
CAUTION
damage to property, if not avoided.
NOTICE
This signal word identifies hazards that could potentially cause damage to property, if not avoided.
1.3
Example
1.4
1.5
Selecting components
For your safety
1
Layout and meaning of warnings
Layout and meaning of warnings
All safety instructions found in these Operating Instructions are composed in accordance with the
following pattern:
This signal word identifies hazards that could potentially cause minor or moderate physical injury or
There are some actions that need to be performed in several steps. If there is a risk involved in
carrying out any of these steps, a safety warning appears in the instructions themselves.
Safety instructions always directly precede the step involving risk and can be identified by their bold
font type and a signal word.
1. NOTICE! This is a notice. It warns that there is a risk involved in the next step.
2. Step involving risk.
Disposal
When it has reached the end of its service life, please dispose of this product as
electronic scrap in accordance with all applicable waste management laws.
Instructions on retrofitting
Instructions on how to retrofit electrical and electronic farm equipment and/or
components
Agricultural equipment used today features electronic components and parts whose function can be
affected by other farm equipment which emits electromagnetic waves. Such effects could lead to
personnel being put in danger, if the following safety instructions are not adhered to.
When selecting components, make sure first of all that the retrofitted electrical and electronic
components comply with the current version of the EMC Directive 2004/108/EC and carry the CE
marking.
Page 9

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
9
(EMC Directive 2014/30/EU)
User responsibility
Additional requirements
1.6
For your safety
EU declaration of conformity
1
When retrofitting a machine with electrical and electronic farm equipment and/or components
connected to the vehicle's electrical system, it is your own responsibility to check whether the
installation causes interference with the vehicle's electronic system or other components. This
applies, in particular, to the electronic control of:
▪ electronic hitch control (EHR),
▪ Front lifting gear,
▪ PTO shafts,
▪ Motor,
▪ Gear.
The following requirements must be met in order to retrofit mobile communication systems (e.g. radio,
phone):
▪ Only approved devices complying to national regulations (e.g. BZT approval in Germany) are to
be installed;
▪ The equipment must be installed as a fixed installation.
▪ The use of portable or mobile devices inside the vehicle is permissible only via a connection to
the permanently installed outside antenna;
▪ The transmitting part must be spatially separated from the vehicle's electronic system.
▪ When attaching the antenna, pay attention to proper installation, including a sound ground
connection between the antenna and the vehicle's ground wire.
For information on wiring and installation as well as the maximum allowable current consumption,
please also refer to the installation guide provided by the machine manufacturer.
EU declaration of conformity
Herewith we declare that the design and construction of this product and its identical variants, as well
as the form brought onto the market by us, is in accordance with the relevant safety and health
requirements of the EU Directive of Electromagnetic Compatibility 2014/30/EU. If alterations are
made to the product without prior consultations with us, this declaration becomes invalid.
TOUCH800®
Harmonised standards applied: EN ISO 14982:2009
Page 10
10
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Type of depiction
Meaning
2.
⇨
This will happen when you perform an action.
⇨
steps.
can be performed.
2
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
About these Operating Instructions
2
Target group of these Operating Instructions
About these Operating Instructions
Target group of these Operating Instructions
These Operating Instructions are intended for personnel entrusted with installing and operating the
terminal.
Layout of operating instructions
The operating instructions explain step by step how you can perform certain operations with the
product.
We use the following symbols throughout these Operating Instructions to identify different operating
instructions:
1.
Actions that must be performed in succession.
Result of the action.
Result of an operating instruction.
This will happen when you have completed all
Requirements.
In the event that any requirements have been
specified, these must be met before an action
Layout of references
If any references are given in these Operating Instructions, they appear as:
Example of a reference: [➙ 10]
References can be identified by their square brackets and an arrow. The number following the arrow
shows you on what page the section starts where you can find further information.
Directional information in these instructions
All directional information in these instructions, such as “left”, “right”, “forward”, “back”, is relative to
the movement direction of the vehicle.
Page 11

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
11
3
3.1
3.2
3.3
Product description
Product description
Scope of delivery
3
Scope of delivery
The following items are included in delivery:
▪ TOUCH800 terminal
▪ VESA holder and screws
▪ Bracket for mounting the terminal
▪ USB memory device
▪ Installation and Operating Instructions
▪ Operating instructions for the ISOBUS-TC application - as a separate document.
Terminal buttons
You will find a number of buttons on the housing of the terminal that are used to operate the terminal.
Terminal buttons
Function of the buttons
Switches the terminal on and off.
Creates screenshots.
Saves the window layout.
Terminal ports
Terminal ports
Page 12

12
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
- Connection to the tractor CAN bus
- Lightbar [➙ 40]
- Ethernet
3.4
Full versions
Product description
3
Applications on the terminal
USB port for:
- USB memory device [➙ 26]
Port A
CAN bus port for:
- ISOBUS basic vehicle harness [➙ 17]
Port C
Serial port for:
- GPS receiver [➙ 28]
Port B
See section: Pin assignment connector B [➙
80]
- GPS TILT-Module
ETH port
M12 port for:
CAM port
Port for an analog camera
Slot with the SD card
Applications on the terminal
The terminal is delivered with a range of installed application (apps). Most of these can be used
immediately. Even the non-activated applications can generally be tested for 50 hours. If a specific
application works well for you, a license can be ordered from Müller-Elektronik to activate the full
version of the application.
The full versions of the following applications are installed on the terminal:
▪ ISOBUS interface (ISOBUS-UT)
The terminal enables you to operate ISOBUS job computers which are ISO 11783 compliant.
The user interfaces for operating a job computer are shown on the terminal screen if this is
connected to the ISOBUS connector of the vehicle.
The ISOBUS interface has no icon of its own. The icon for the connected job computer will
always be displayed in the selection menu.
▪
- Service application.
The Service application allows you to:
– Configure the terminal.
– Enable and disable other applications.
– Enter license activation codes.
– Enable drivers for connected devices.
– Configuration of the GPS settings
▪
- Tractor-ECU application
The Tractor-ECU application is used to record all settings around the tractor.
Here, you can e.g.:
– Enter the position of the GPS receiver.
– Set the GPS receiver as the speed signal source.
– Select which sensor signals are received by the terminal.
– View the speed and PTO shaft rotational speed on the screen.
More about this in section: Tractor-ECU application [➙ 51]
Page 13

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
13
Test versions
Optional software
Product description
Applications on the terminal
3
▪ - Virtual ECU application
The Virtual ECU application is a central hub where virtual job computers can be created for
machines and devices that do not communicate through ISOBUS.
The Virtual ECU enables the use of apps such as TRACK-Leader, ISOBUS-TC and SECTIONControl with non-ISO machines.
More about this in section: Virtual ECU application [➙ 61]
▪
FILE-Server application
This application is used to define a storage location on the terminal. This storage location can be
used by ISOBUS job computers that support the FILE-Server functionality. The options for use
depend on the ISOBUS job computer.
▪
- Camera
The Camera application displays on the screen the image from the camera which is connected
to the terminal.
You can use the test versions of the following applications:
▪
- TRACK-Leader application.
The TRACK-Leader application allows you to work the field on exact parallel tracks.
The app contains several modules for which a license can also be activated:
– SECTION-Control: Automatic section control in order to minimize overlaps.
– TRACK-Leader AUTO: Automatic vehicle steering on the field.
– TRACK-Leader AUTO CLAAS: Automatic vehicle steering on the field for CLAAS tractors.
– TRACK-Leader TOP: Automatic vehicle steering on the field.
– TRAMLINE-Management: Tramline control using the current GPS position.
▪
- ISOBUS-TC application (ISOBUS task controller)
The ISOBUS-TC application serves as an interface between the terminal applications
(SECTION-Control, TECU, VECU) and ISOBUS devices (job computers, crop protection
sensors). Moreover, the app enables data transfer between the terminal and electronic Farm
Management Information Systems.
The scope of functions depends on the activated licenses and the configuration.
More about this in section: Task management (ISOBUS-TC) [➙ 66]
▪ MULTI-Control – This license extends the functionality of ISOBUS-TC. It enables the assignment
of prescription maps to individual metering units on a machine.
▪ ASD protocol – The license enables communication between the terminal and a serially
connected on-board integrated display/controller. The terminal knows the position of the machine
on the field (GPS) and can transmit the target application rate of a product (from the prescription
map) or the section status to the on-board integrated display/controller. In this way, you can use
the SECTION-Control app for section control, among other things.
More about this in section: Connecting the on-board integrated display/controller to the terminal [
➙ 41]
▪ ME ODI – This license activates the ME ODI application. It is used to connect the terminal with
the Internet via Ethernet or Bluetooth.
Optionally you can activate the following software:
▪
- FIELD-Nav application
Page 14
14
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Abbreviation
Meaning
Service application:
Hardware version
The terminal may only be connected to voltages within this range.
will be shown here.
Serial number
3.5
Product description
3
Information on the rating plate
FIELD-Nav – Road navigation for agricultural purposes. The map material can be edited with the
corresponding PC software FIELD-Nav Desktop. All field tracks, small bridges and other
restrictions can then be integrated in the map material and be considered when mapping the
route.
You will find the operating instructions on the Müller-Elektronik website.
▪
- Agricon plugin
Enables coupling with crop protection sensors (Yara-N, P3US, P3ALS etc.) manufactured by
Agricon.
Information on the rating plate
You will find a nameplate sticker on the back of the terminal. On this sticker, you can find all the
information you need to definitively identify the product.
Have these details ready when you contact Customer Services.
Abbreviations on the rating plate
Software version
You can see the installed software version on the Start Screen of the
Operating voltage
Customer number
If the terminal was manufactured for an agricultural machinery
manufacturer, the agricultural machinery manufacturer's item number
Page 15

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
15
Item number
Type
Scope of
delivery?
Properties
31322506
Standard bracket
Yes
terminal.
▪ Is mounted around a pipe.
4
4.1
4.1.1
Procedure
Mounting and installation
Mounting and installation
Mounting the terminal in the vehicle cab
4
Mounting the terminal in the vehicle cab
You need a bracket to mount the terminal in the vehicle cab. The following brackets are available.
31322507 Optional bracket No
31322508 Optional adapter No
▪ For a more sturdy attachment of the
▪ Is mounted on bracket 31322507.
▪ Suitable for vehicles without a B
column.
Mounting the standard bracket
You have the VESA bracket assembly kit within reach.
1. Assemble the bracket together.
2. Secure the bracket with the four screws on the back side of the terminal.
3. Secure the terminal in the vehicle cab. You can, for example, use the ME mounting bracket for
this purpose. It is included in the scope of delivery of the ISOBUS basic vehicle harness.
⇨ Your terminal should be mounted as follows:
4. Check that your terminal is firmly mounted.
⇨ You can now connect cables to the terminal. [➙ 11]
Page 16

16
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
4.1.2
Procedure
4.1.3
Mounting and installation
4
Mounting the terminal in the vehicle cab
Mounting the optional bracket
You have the bracket assembly kit within reach.
1. Assemble the bracket together.
2. Secure the bracket with the four screws on the back side of the terminal.
3. Put the bracket into the desired position. For example:
4. Secure the terminal in the vehicle cab. You can, for example, use the ME mounting bracket for
this purpose. It is included in the scope of delivery of the ISOBUS basic vehicle harness.
5. Check that your terminal is firmly mounted.
Mounting the optional adapter
If you want to mount your terminal in a vehicle that does not have a B column, you can install an
adapter onto bracket 31322507. This adapter can be mounted around a pipe.
Page 17

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
17
Procedure
4.2
Mounting and installation
Connecting the terminal to the ISOBUS
4
▪ Adapter for round pipe systems, for pipes with a diameter of 20, 25 or 30 mm, item number:
31322508
1. Assemble the adapter together.
2. Connect the adapter with the bracket.
3. Put the bracket and the adapter in the desired position.
4. Check that everything is firmly mounted.
Connecting the terminal to the ISOBUS
Connection to the ISOBUS serves to:
▪ supply the terminal with power,
▪ enable communication with other ISOBUS components.
You will need a different connection cable for this, depending on the model of your tractor.
▪ In tractors that have been retroactively upgraded with an ISOBUS basic vehicle harness
manufactured by Müller-Elektronik, use connector cable A from the ISOBUS basic vehicle
harness.
▪ In tractors that are equipped as standard with ISOBUS and that have an ISOBUS in-cab
connector, you will need the following connector cable:
Connector cable D-Sub <-> CPC Item no. 30322541
Page 18

18
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Possible purpose
Setting of the ME terminal
Setting of the in-cab terminal
Activate the ISOBUS terminal (JohnDeere:
Task Controller; Fendt: Taskcontroller).
Greenstar, Original Greenstar
Procedure
4.3
Procedure
4.4
Mounting and installation
4
Inserting micro-SD card
When there is more than one terminal in the tractor cab, you may need to change certain settings in
order to enable two-way communication. Find out more: Using two terminals [➙ 18]
1. Connect the 9-pin connector A of the basic vehicle harness to the CAN port of the terminal.
2. Tighten the safety screws on the connector.
Inserting micro-SD card
The micro-SD card serves as internal storage for the terminal.
To change the SD card:
1. Switch off the terminal and disconnect all cable connections.
2. Unscrew the cover on the rear of the terminal.
3. Use your finger to press on the SD card in the slot.
⇨ The SD card is unlocked and now protrudes by approx. 1 mm.
4. You can remove the card.
5. To lock the card again, press the card lightly into the slot until it is locked again.
6. Screw the cover back onto the rear of the terminal.
Using two terminals
The following table will tell you which settings you need to configure to be able to use two terminals,
and the sections in which these are described. The specifications on the in-cab terminals are without
liability.
Settings for the ME terminal and in-cab terminal
TRACK-Leader and SECTION-Control on
Login as ISOBUS terminal: No [➙ 45]
the ME terminal.
Operation of the job computer on the incab terminal.
TRACK-Leader, SECTION-Control, and
Login as ISOBUS terminal: Yes [➙ 45]
job computer operation on the ME
terminal.
Implement Bus; Fendt: Fendt ISOBUS
terminal).
Deactivate Task Controller (JohnDeere:
Deactivate the ISOBUS terminal
(JohnDeere: Implement Bus; Fendt: Fendt
ISOBUS terminal).
Deactivate Task Controller (JohnDeere:
Task Controller; Fendt: Taskcontroller).
For JohnDeere, also deactivate:
Page 19
30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
19
Setting
Where?
Purpose
receiver must be activated.
5
5.1
Procedure
5.2
5.2.1
Basic control principles
Basic control principles
Switching on the terminal
5
Switching on the terminal
To switch on the terminal:
The terminal is installed and connected to the ISOBUS basic vehicle harness.
1. Press and hold the
button for approx. 3 seconds.
⇨ The terminal will beep briefly.
⇨ The terminal screen remains dark for approx. 10 seconds until the applications are loaded in
the background.
⇨ The Start screen of the terminal appears:
⇨ You have started the terminal.
Initial start-up
The next step to perform after switching on the terminal depends on the purpose of the terminal:
▪ Parallel driving
▪ Operation of ISOBUS implements
▪ Automatic section control
▪ Task management and documentation
These cases will be described in the following sections.
Using the terminal for parallel driving
If you want to use the terminal for parallel driving, TRACK-Leader is the most important app for you.
Most important settings
Select the GPS driver.
/ Driver / GPS [➙ 28]
The standard driver works in
most cases for the receivers
sold by ME. However, to
change the correction signal, a
fitting driver for the GPS
Page 20

20
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Setting
Where?
Purpose
- Tractor geometry [➙ 56]
61]
Setting
Where?
Commentary
receiver must be activated.
- Tractor geometry [➙ 56]
5.2.2
Procedure
5.2.3
Basic control principles
5
Initial start-up
Enter the tractor geometry and
activate the tractor profile.
/ Settings
See:
- Managing the tractor profiles [
➙ 51]
Virtual job computer
/ Settings
For the system to be able to
know the working width and
other parameters of the
machine, you must create a
virtual job computer for every
non-ISOBUS-compatible
machine that you use.
Virtual ECU application [
See:
Other settings must be made in the TRACK-Leader application.
➙
Operating ISOBUS implement
To operate an ISOBUS job computer with the terminal, it is sufficient to connect the job computer to
the rear ISOBUS socket. As a standard, the terminal disposes of the required licences.
The “ISOBUS-UT” licence is activated.
1. Insert the ISOBUS cable of the job computer into the ISOBUS rear socket.
2. Switch on the terminal.
3. Wait until the job computer application has copied all of the relevant data on the terminal.
4. Open the job computer application using the selection menu [➙ 23].
Terminal for automatic section control
Most important settings
Select the GPS driver
(optional).
Enter the tractor geometry and
activate the tractor profile.
/ Driver / GPS [➙ 28]
/ Settings
The standard driver works in
most cases for the receivers
sold by ME. However, to
change the correction signal, a
fitting driver for the GPS
See:
- Managing the tractor profiles [
➙ 51]
Page 21

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
21
Setting
Where?
Commentary
the ISOBUS.
parameters in the profile.
Setting
Where?
Purpose
“Standard”.
without a USB memory device.
Procedure
5.2.4
Procedure
Basic control principles
Initial start-up
5
Connecting the job computer to
Job computer profile in
SECTION-Control
/ Settings / SECTION-
Control
Search for a profile and set the
“Machine model” parameter.
For more precise operation,
configure all of the other
The “ISOBUS-UT”, “TRACK-Leader” and “SECTION-Control” licenses are activated.
1. Insert the ISOBUS cable into the ISOBUS rear socket.
2. Switch on the terminal.
3. Wait until the job computer application has copied all of the relevant data on the terminal.
4.
- Open the TRACK-Leader application using the selection menu [➙ 23].
5. Configure the settings from the table above.
6. Start a new navigation.
You can read how to proceed in the operating instructions for TRACK-Leader.
Terminal for task management
You can always use ISOBUS-TC task management, regardless of whether you are driving in parallel,
switching sections or simply operating an ISOBUS job computer. However, the most important
settings mentioned in the previous sections must be made for each of these applications.
Important for ISOBUS-TC:
▪ Always remember to start and stop the tasks.
▪ After finishing work, you must save all of the tasks on the USB memory device (log out the USB
memory device) before you remove the USB memory device or transmit new tasks onto the
terminal.
Most important settings
Set the operating mode to
“Extended”.
Insert the USB memory device
with task data or create tasks
/ Settings
Activates and deactivates task
management in the ISOBUSTC application.
If you do not want to create
tasks, set the operating mode to
The “ISOBUS-TC” licence is activated.
Page 22
22
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Menu” area.
applications.
Icon
Meaning
When this icon appears in other areas, it is used for confirmation
5.3
Procedure
5.4
Basic control principles
5
Switching off the terminal
1. Switch on the terminal.
2.
- Open the ISOBUS-TC application using the selection menu [➙ 23].
3. Insert a USB memory device with task data.
4. Start a task.
Switching off the terminal
To switch off the terminal:
1. Press and hold the
⇨ You have now switched off the terminal.
button for approx. 3 seconds.
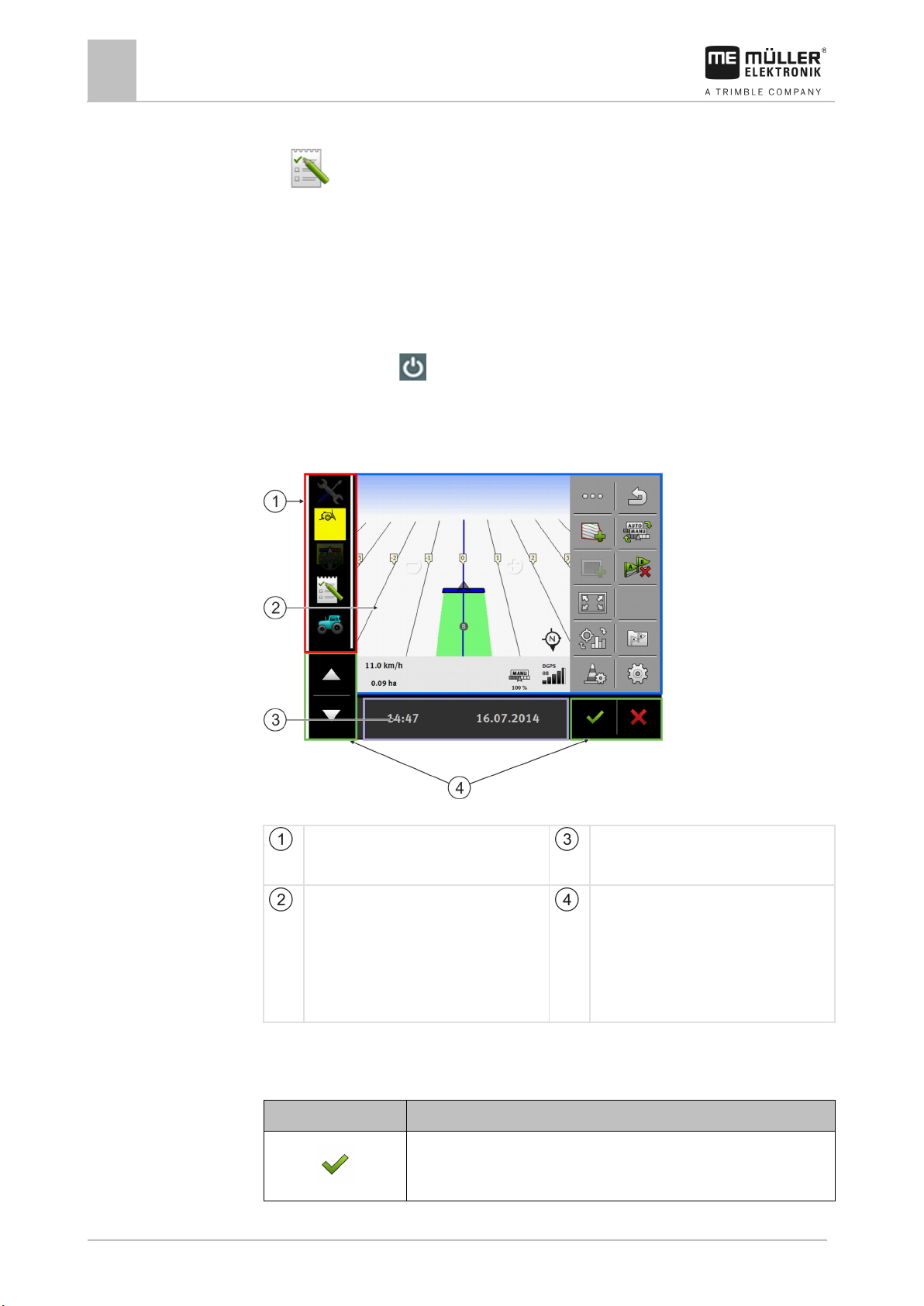
Terminal screen layout
Terminal screen layout
Selection menu
You can open applications in the “Selection
Main window
This area enables you to operate applications.
Touching the terminal screen in the “Main
window” area will actuate the function whose
icon you have touched.
The controls depend on the opened
Wide additional window
System icons
System icons
Has no function in this area.
Page 23
30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
23
Icon
Meaning
purposes.
deletion purposes.
5.5
Procedure
Basic control principles
Opening applications
5
Has no function in this area.
When this icon appears in other areas, it is used for cancellation or
Has no function in the current software version.
Has no function in the current software version.
Opening applications
An application opens when it appears in the main window or in an additional window.
To open an application:
1. Find the function icon for the desired application in the Selection menu area. For example, the
icon:
2. Tap the function icon of the application:
⇨ The application appears in the main window:
⇨ The function icon of the application in the Selection menu now appears darker. This tells
you that this application is already open. You will no longer be able to open it from the
Selection menu.
⇨ If the main window is occupied, the application that is already opened will be moved to a
free additional window. If this is occupied, the application that is already opened will be
moved back to the Selection menu. Their icon becomes bright again. However, it can
continue to work in the background.
Page 24
24
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
5.6
Procedure
5.7
Procedure
Basic control principles
5
Moving an application
Moving an application
You can move any application from the main window to one of the additional windows or to the MEHeader.
To move an application from the main window to an additional window:
You have opened an application in the main window. For example, the Service application:
1. Tap the additional window:
⇨ The application will now appear in the additional window:
2. Tap the additional window with the application.
⇨ The application will once again appear in the main window.
Saving and loading window arrangements
You can save and load the arrangement of the applications in the windows.
To save the arrangement:
1. Hold the button
pressed down until the terminal beeps twice.
Page 25
30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
25
Icon
Meaning
Abc
Procedure
5.8
Procedure
5.9
Basic control principles
⇨ The arrangement will be saved.
Hiding an application
5
To load a saved arrangement:
1. Briefly press the button:
⇨ The arrangement will be loaded.
Hiding an application
If you do not have enough space on the terminal screen to open new applications, you can hide an
application. The application will not be shut down, but will instead continue to run in the background.
To hide an application:
1. Open the application in the additional window.
2. Move the application to the selection menu.
Using the keyboard
In order to enable you to also write numbers or text on the terminal, a keyboard appears on the
terminal screen whenever this is necessary.
Major icons
Changes the buttons on the keyboard.
12#
Deletes a character.
Moves the cursor.
Saves the input.
Cancels the input.
Switches between upper and lower case letters.
Page 26

26
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
5.10
5.10.1
5.10.2
Basic control principles
5
Using a memory device
Keyboard for inputting text and numbers.
Keyboard for inputting text.
Using a memory device
The terminal can work with two kinds of memory devices:
1. With an integrated micro-SD card. This will be used as storage for most applications.
2. With an inserted USB memory device.
The USB memory device is used only for the following purposes:
▪ For data transfer [➙ 26] between the terminal and PC
▪ For saving screenshots
Using SD card
The terminal applications save most data [➙ 26] directly onto the SD card.
In order to exchange data between the terminal and a PC, you will need to proceed differently for
each application. You can find out more about this in the instructions for each application.
Folders on the USB memory device
As soon as you insert the USB memory device into the terminal, several folders will be created on the
USB memory device. You will need to set up other folders by yourself.
Each folder may only contain certain data, so that the applications on the terminal can use this data.
▪ “documents”
– Files: .txt
– Purpose: Records for all completed tasks are saved in this folder.
▪ “FIELDNav”
– Files: .iio, .data
– Purpose: Map material will be saved in this folder.
– The folder will be created when the FIELD-Nav license is activated.
Page 27

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
27
5.10.3
Procedure
Basic control principles
Using a memory device
5
▪ “fileserver”
– Files: All file formats are acceptable.
– Purpose: Files which are to be imported or exported in the FILE-Server application are
saved in this folder.
▪ "GPS"
– Files: .txt
– Purpose: GPS positions are saved in a file in the folder. This will enable Customer Service
to reconstruct the traveled distance.
– The folder will be created if you activate the “Record and save data” parameter.
▪ “NgStore”
– Files: .iio, .data
– Purpose: TRACK-Leader. Standard folder for saved routes and fields.
▪ “Screencopy”
– Files: .bmp
– Purpose: Screenshots are saved here.
– The terminal will create this folder automatically when the “Screenshot” parameter is
activated in the “Terminal” menu and you create a screenshot.
▪ "SHP"
This folder replaces the “GIS” folder that was used in previous versions.
– Files: .dbf, .kml, .prj, .shp, .shx
– Purpose: TRACK-Leader: After saving with the SD card, the field data will be stored here.
For example: Field boundaries, applied areas, headlands, etc.
ISOBUS-TC: The shp files must be stored in this folder.
▪ “Taskdata”
– Files: .xml
– Purpose: The folder may only contain XML files which originate from an ISO-XML
compatible FMIS. The ISOBUS-TC application accesses this data.
– You must create this folder yourself.
Displaying the content of the memory device on the terminal
You can view the content of the memory device directly on the terminal.
1. Insert the memory device (USB memory device or SD card) into the terminal.
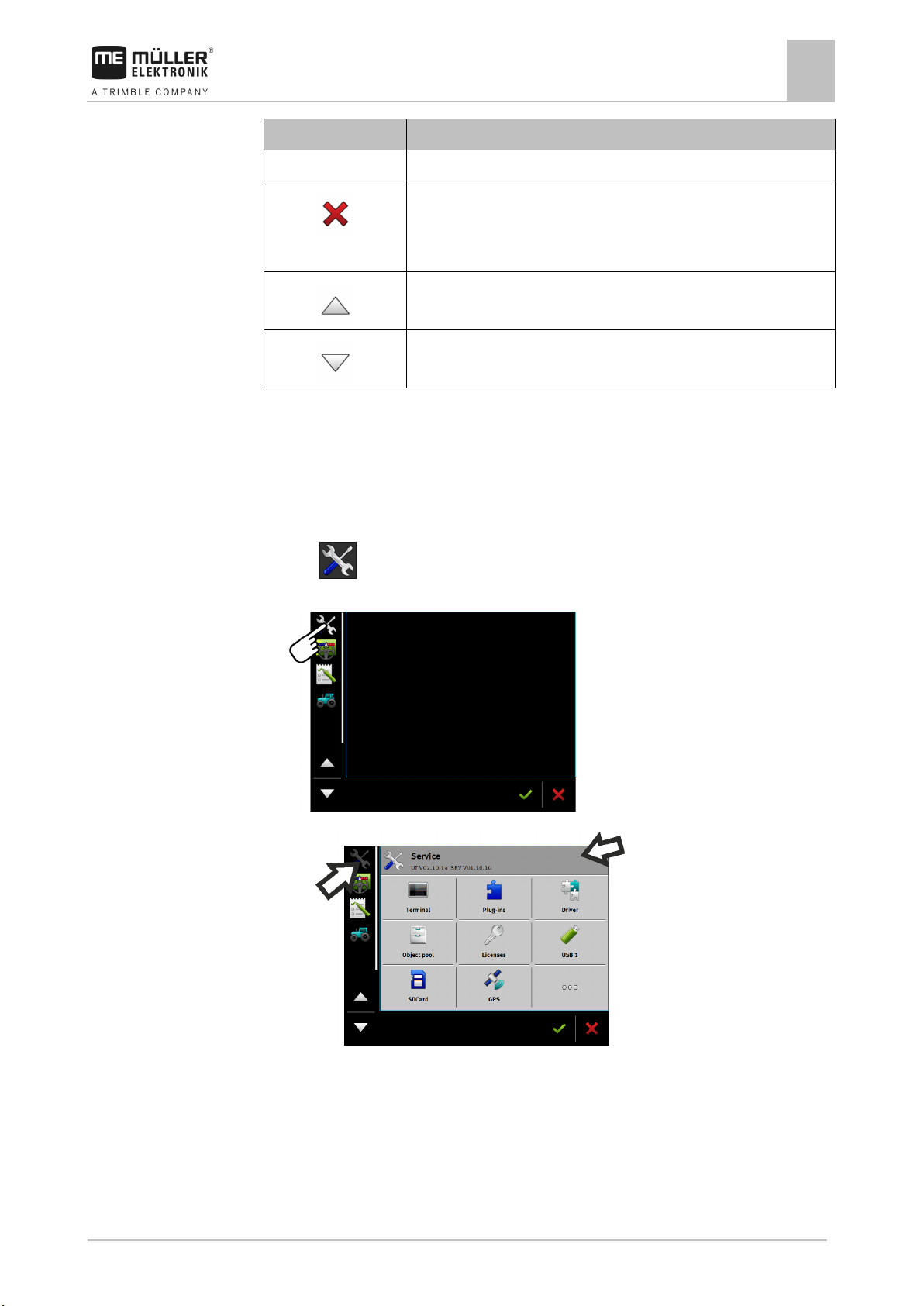
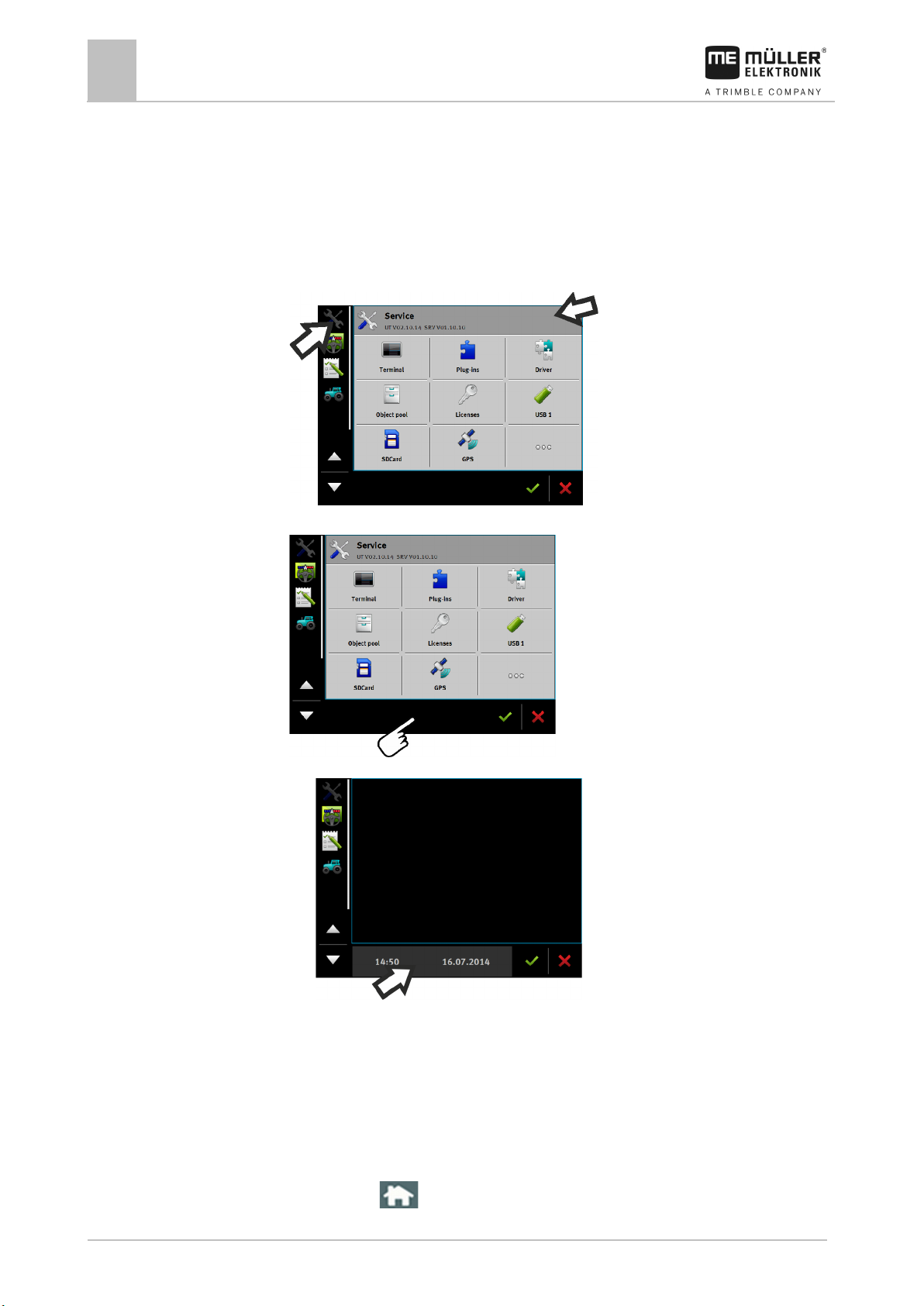
2. Open the “Service” application.
3. Tap on “USB 1” or on “SDCard”.
⇨ The content of the USB memory device will be displayed.
⇨ The content of the SD card can be found in the “ME-TERMINAL” folder.
Page 28

28
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
5 Hz (GPGGA, GPVTG)
1 Hz (GPGSA, GPZDA)
Transmission rate
19200 baud
Data bits
8
Parity
No
Stop bits
1
Flow control
None
6
6.1
6.1.1
Procedure
6.1.2
Connecting and configuring external devices
6
GPS receiver
Connecting and configuring external devices
GPS receiver
Connecting the GPS receiver to the terminal
Find out how to connect a GPS receiver from Müller-Elektronik to the terminal from the operating
instructions for the GPS receiver.
When mounting the terminal in a vehicle which is already fitted with a GPS receiver and another
ISOBUS terminal, you must:
▪ connect the GPS signal to the terminal manufactured by Müller-Elektronik.
▪ configure the GPS receiver.
To connect the terminal to a GPS receiver which is already installed on the vehicle:
1. Find out how you can direct the signal from the GPS receiver to the terminal. This can differ for
every vehicle or GPS receiver: Vehicles can be fitted with a GPS socket in the cab, a GPS
receiver with a serial output or serial outputs to the ISOBUS terminal.
2. Check what cable you will use to connect GPS signal to the serial socket on the terminal
manufactured by Müller-Elektronik.
3. Connect the GPS signal to the serial socket of the terminal manufactured by Müller-Elektronik.
4. Configure the GPS receiver so that it can communicate with the terminal manufactured by
Müller-Elektronik. You can find the necessary specifications for this in the table below.
5. Activate the “Standard” GPS driver on the terminal.
Configuration
Frequencies
Changing the driver for the GPS receiver
Upon delivery, the “Standard” driver is activated on the terminal. You must change this driver if you
want to reconfigure the GPS receiver, for example, to change the correction signal. In this case, you
must select a driver that is fitting for the GPS receiver.
Page 29

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
29
Driver name
GPS receiver
deactivated
No GPS receiver is connected.
Elektronik, if they are connected to the serial interface.
Müller-Elektronik, if they are connected to the serial interface.
external lightbar.
cannot thus be configured.
external lightbar.
NOTICE
driver.
Procedure
Connecting and configuring external devices
Available drivers
GPS receiver
6
A100, A101 Drivers for the A100 and A101 GPS receivers from Müller-
AG-STAR, SMART-6L Drivers for the AG-STAR and SMART-6L GPS receivers from
PSR CAN Select this driver if the GPS receiver is connected to the PSR
steering job computer. PSR is a steering job computer by the
Reichhardt company. The signals are transmitted to the terminal
through the CAN cable. The receiver will be configured directly in
the PSR application.
Please note that you cannot use this driver together with an
Standard Drivers for unknown GPS receivers, if they are connected to the
serial interface.
This driver is activated by default. The connected GPS receiver
TRACK-Leader AUTO® Select this driver if a GPS receiver is connected to the TRACK-
Leader AUTO® steering job computer.
Please note that you cannot use this driver together with an
Incorrect driver
Damage to the GPS receiver.
◦ Before connecting a GPS receiver to the terminal, you must always activate the appropriate
To activate the driver:
1.
- Open the “Service” application.
2. Tap "Driver".
3. Tap “GPS”.
⇨ The installed drivers appear.
4. Tap the appropriate driver.
5.
- Confirm.
6. Restart the terminal.
Page 30

30
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Function icon
Meaning
activation license.
6.1.3
Procedure
Connecting and configuring external devices
6
GPS receiver
Configuring the GPS receiver
The internal software for each GPS receiver must be configured. You can configure the following
GPS receivers offered by Müller-Elektronik via the terminal:
▪ A100, A101
▪ AG-STAR, SMART-6L
All other GPS receivers must be configured in accordance with their manufacturer's instructions.
Reads the configuration of the GPS receiver.
Restores the manufacturer's default settings.
Opens the license menu.
Only appears on SMART-6L DGPS/GLONASS receivers for entering an
Resets the baud rate.
The GPS receiver is connected to the terminal.
The GPS receiver is connected directly to the terminal. Additional devices such as an external
lightbar or tilt module may not be connected in between.
The correct GPS driver is activated.
1.
- Open the “Service” application.
2. Tap “GPS”.
⇨ The “Settings” screen appears.
⇨ The following message appears during initial configuration: “GPS receiver detected. Read
the configuration?”
3. To confirm, tap “Yes”. To cancel, tap “No”.
⇨ The terminal reads the current configuration of the GPS receiver.
⇨ You can now see all of the configurable parameters.
4. Configure the parameters. The parameters can be found in the following section.
5. Reconnect all of the additional devices that you had disconnected for the configuration.
Parameters for the GPS receiver
Baud rate
Only appears when the “Standard” driver is selected.
Setting for the speed at which the GPS receiver sends data to the terminal. The parameter sets the
baud rate for the terminal.
Satellite 1 and Satellite 2
Page 31

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
31
Connecting and configuring external devices
GPS receiver
6
Satellite 1 – primary DGPS satellite. The DGPS receiver will connect to this satellite in the first
instance.
Satellite 2 – secondary DGPS satellite. The DGPS receiver will only connect to this satellite in the
event that the primary satellite fails.
Your satellite selection will depend on which satellite currently has the best availability in your region.
Possible values:
▪ “Auto”
The software automatically selects the current best satellite.
▪ Name of the satellite. Which satellites are shown here is dependent on the driver and correction
signal that you have activated.
Steering
This parameter activates the “Automatic steering” assistance function in the GPS receiver.
If you want to connect your existing GPS receiver to a steering job computer, you have to configure
the “Steering” parameter.
Possible values:
▪ “Without automatic steering”
Deactivates automatic steering assistance.
▪ “TRACK-Leader TOP”
Activates automatic steering assistance with TRACK-Leader TOP.
▪ “TRACK-Leader AUTO”
Activates automatic steering assistance with TRACK-Leader AUTO.
Correction signal
Type of correction signal for the DGPS receiver.
The correction signals which are available is dependent on the activated driver.
Possible values:
▪ For the “A100, A101” driver:
– “WAAS/EGNOS”
Correction signal for Europe, North America, Russia and Japan.
– “E-DIF”
Internal calculation of correction data.
Only functions with a special version of the A100 DGPS receiver, item no. 30302464. This
receiver is no longer sold by Müller-Elektronik.
▪ For the “AG-STAR, SMART-6L” driver
When a DGPS/GLONASS AG-STAR receiver is connected:
– “EGNOS-EU”
– “WAAS-US”
– “MSAS-JP”
– “EGNOS-EU + GLIDE”
– “WAAS-US + GLIDE”
– “MSAS-JP + GLIDE”
– “GPS/GLONASS GLIDE 1”
Page 32

32
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Connecting and configuring external devices
6
GPS receiver
– “GPS/GLONASS GLIDE 2”
When a DGPS/GLONASS receiver SMART-6L receiver is connected:
– EGNOS/WAAS
– EGNOS/WAAS + GLIDE
– GLIDE
– RTK radio(RTK licence required)
– RTK GSM(RTK licence required)
– TerraStar (RTK or L band licence required)
Information for GLIDE
If you have selected a correction signal with GLIDE, please note:
▪ Switch the GPS receiver off when driving on roads.
▪ After starting the systems each time, it takes ca. 5 minutes until the system is ready for
operation. Wait on the field to be worked during this time, before you start working.
▪ Ensure that the GPS receiver does not lose the GPS signal during work. (e.g. due to shadowing
by buildings or trees). If the signal gets lost, it can cause the GLIDE to restart. This can lead to
track offset.
Information for TerraStar
If you have selected “TerraStar” as a correction signal, please note:
▪ There are two different TerraStar correction signals: TerraStar-C and TerraStar-L. These differ
mainly in their accuracies.
▪ The accuracies are available ca. 5 to 10 minutes after switching on the GPS receiver under the
open sky.
▪ If the GPS signal fails due to shadowing by buildings or trees, the full accuracy is available again
at the latest after ca. 5 minutes. For this reason, you should avoid driving along rows of trees or
buildings.
▪ During the convergence, the GPS receiver and the vehicle should not be moved and the location
should not be changed.
Baud rate of the receiver on port B
Only appears when the “RTK radio” correction signal is selected.
If you are using a GPS receiver with a radio modem from a third-party manufacturer, the baud rate
must be adjusted in some cases. The baud rate must then correspond to that of the radio modem.
The baud rate for radio modems manufactured by Müller-Elektronik is always 19.200 baud.
Correction during RTK failure
This parameter is only required if you are using the SMART-6L DGPS receiver with a steering
system.
Possible values:
▪ automatic
The parameter is activated.
When there is an RTK failure, a deviation arises between the current position of the vehicle and
the GPS position.
Page 33

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
33
Procedure
Procedure
Connecting and configuring external devices
GPS receiver
6
If the parameter is set to “automatic”, you prevent the vehicle from driving directly to the new
GPS position. The system will then gradually steer towards the new GPS position. This prevents
the occurrence of large track offsets in case of RTK failure.
When the RTK signal is available again, the vehicle will be gradually steered towards the original
GPS position.
▪ deactivated
The parameter is deactivated.
Tilt module
The GPS TILT-Module is configured using this parameter.
You can order the tilt module from Müller Elektronik with the following item number: 30302495.
RTK or L band licence for SMART-6L
You will need a SMART-6L DGPS/GLONASS receiver and RTK license in order to work with RTK
correction signals.
To work with TerraStar correction signals, you need a SMART-6L DGPS/GLONASS receiver and at
least an L band license.
When purchasing a GPS receiver with an RTK or L band license, the licence from Müller-Elektronik
will be entered. You only have to enter the licence yourself when it is purchased at a later date.
1. - Open the “Service” application.
2. Tap “GPS”.
⇨ The “Settings” screen appears.
3.
- Open the license menu.
4. Tap “License code”.
⇨ The “License menu” screen appears.
⇨ You can see the serial number and firmware version on the screen. You will need these
when ordering the license code.
⇨ If you are using the TerraStar correction signal, you will see information on the TerraStar
service and the expiry date of the TerraStar service.
⇨ Optionally, you can open the “Model number” screen to obtain information on the current
activation of the GPS receiver.
5. Enter the license code.
6.
- Confirm.
GSM modem for SMART-6L
If you are using the DGPS/GLONASS SMART-6L receiver with a GSM modem, you can adjust the
existing configuration.
1. - Open the “Service” application.
2. Tap “GPS”.
3. The “Settings” screen appears.
Page 34

34
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Parameter
Meaning
Possible entries
APN
Connection to the provider.
Provider URL or IP address.
same for all users of a provider.
providers do not require entering a name.
password.
URL/IP
Connection to the correction data server.
Correction data server URL or IP address.
Port
Port at the correction data server.
Port number
customer account.
use of upper and lower case letters.
use of upper and lower case letters.
only with GPRS connections.
stream.
Procedure
Connecting and configuring external devices
6
GPS receiver
4. - Open the configuration menu.
5. Configure the parameters. The explanations for the individual parameters can be found in the
table at the end of this section.
6.
- Save the changes.
⇨ The following message appears: “Should the data be transmitted to the modem?”
7. “Yes” - to confirm.
⇨ The data is being transmitted to the modem. This will take approx. 30 seconds.
User Name for the Internet access. The name is the
Password Password for the Internet access. The password is
the same for all users of a provider.
NTRIP user Name from the correction service to identify the
Name that was given by the provider. Some
Password that was given by the provider.
Some providers do not require entering a
Letters and numbers. Pay attention to the
NTRIP password Password for the identification name. Letters and numbers. Pay attention to the
Mountpoint Manual entry of a correction data source available
Name of the correction data source / data
Configuring the GPS receiver for the steering system
To be able to use a GPS receiver with automatic steering, it must previously be configured for this
use. The configuration adjusts the internal settings of the GPS receiver.
You can use the following GPS receivers for the steering system:
▪ A101
▪ AG-STAR
▪ SMART-6L
To configure the GPS receiver for automatic steering:
1. Activate the driver for the respective GPS receiver [➙ 28] to establish a connection between
the terminal and the GPS receiver.
2. Configure the GPS receiver. [➙ 30]
3. Tap “Steering” in the configuration.
4. Select the automatic steering that you are using.
Page 35

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
35
Procedure
6.1.4
Procedure
Connecting and configuring external devices
GPS receiver
6
5. - Confirm.
6. For TRACK-Leader AUTO® systems, tap
and adjust the baud rate of the receiver to the
automatic steering.
⇨ The following message appears: “You can now disconnect the GPS receiver.”
7. Confirm using “OK”.
8. Switch off the terminal.
9. Now connect the GPS receiver to the cable harness of the steering job computer.
10. Start the terminal.
11. Depending on the steering job computer, activate the “PSR CAN” or “TRACK-Leader AUTO”
driver. [➙ 28]
12.
- Confirm.
13. Restart the terminal.
⇨ The GPS receiver is now configured for automatic steering.
To change parameters for the GPS receiver after the GPS receiver has been configured for
automatic steering, you must restore the internal settings of the GPS receiver.
1. Connect the GPS receiver to the terminal.
2. Activate the driver for the respective GPS receiver. [➙ 28]
3. Restart the terminal.
4.
- Open the “Service” application.
5. Tap “GPS”.
6.
- Reset the baud rate.
7. The following message appears: “Should the standard baud rate be restored?”
8. Confirm using “OK”.
9. Restart the terminal.
⇨ You can now change the individual parameters for the GPS receiver.
⇨ After you have changed the parameters, you can reconfigure the GPS receiver for the steering.
Recording GPS position
Certain faults can require recording of the position data from the GPS receiver.
A USB memory device is inserted into the terminal.
1.
2. Tap “GPS”.
3. Tap “GPS data”.
⇨ The “GPS data” screen appears.
- Open the “Service” application.
Page 36

36
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
6.1.5
Procedure
6.2
Procedure
Connecting and configuring external devices
6
Configuring the joystick button allocations
4. Scroll down.
5. Tap “Trace data”.
⇨ The “Trace data” screen appears.
6. Scroll down.
7. Checkmark the “Record and save data” button.
⇨ The terminal will immediately begin to record the data. This will be saved in the “GPS” folder
on the USB memory device.
⇨ The function will be deactivated following any restart.
Configuring the “GPS TILT-Module” tilt module
The “GPS TILT-Module” tilt module is connected.
The tractor is positioned on level ground.
The lightbar driver is configured as a “screen lightbar”.
1. If additional devices (e.g. external lightbar) are connected to the cable between the terminal and
the tilt module, disconnect them. The tilt module must be connected directly to the terminal. After
the tilt module has been configured, these additional devices must be reconnected.
2. Measure the distance between the GPS receiver and the ground on which the tractor is
positioned.
3. Switch on the terminal.
4.
- Open the “Service” application.
5. Tap “GPS”.
⇨ The “Settings” screen appears.
6. Scroll down until the “Tilt module” parameter appears on the screen.
7. Tap “Tilt module”.
8. Enter the measured distance on the “GPS receiver height” line.
9. Tap
.
⇨ Message: “Tilt module will be configured.” is displayed.
10. To confirm, tap “Yes”.
⇨ The position of the tilt module on level ground is being calibrated.
⇨ After calibration, the angle 0 will appear on the “Angle” line. The displayed angle will change
with any tilt of the tractor.
11. Reconnect all of the additional devices that you had disconnected for the configuration.
Configuring the joystick button allocations
The terminal offers you the possibility of assigning the functions of an ISOBUS job computer to the
buttons of the joystick. To do so, the ISOBUS job computer and the joystick must fulfil the Auxiliary 2
specification requirements from the ISOBUS standard.
To activate the driver for this function:
The joystick and ISOBUS job computer are connected and both support the Auxiliary 2 protocol.
Page 37

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
37
Procedure
6.3
Connecting and configuring external devices
Connecting sensors to the terminal
6
1. - Open the “Service” application.
2. Tap "Driver".
3. Tap “Auxiliary”.
4. Mark “Auxiliary2”.
5.
6. Restart the terminal.
- Confirm.
To configure the button assignment:
You have activated the “Auxiliary2” driver
1.
- Open the “Service” application.
2. Tap “Auxiliary”.
3. Tap “Auxiliary Editor”.
⇨ If the ISOBUS job computer supports the Auxiliary 2 protocol, a list appears of the job
computer functions.
⇨ If no list appears, the ISOBUS job computer does not support this protocol.
4. Tap the function which you want to assign to this button on the joystick.
⇨ A list of the buttons on the joystick appears.
⇨ You have two options for assigning the function to the joystick.
5. Option 1: On the joystick, press the button to which you want to assign the function.
Option 2: On the terminal, select the button to which the selected function should be assigned
and confirm with
.
⇨ The function will be assigned to the button and you can continue with the next function, until
you have assigned all of the functions.
6. Restart the terminal.
⇨ After restarting, the following notification appears on the main terminal screen: “Confirm the
assignments.” This notification appears after any restart.
7. “OK” - acknowledge the notification.
⇨ A list of recognized assignments appears on the terminal screen.
8.
- Confirm the assignments.
Connecting sensors to the terminal
The terminal provides you with the possibility of connecting a sensor or the tractor's 7-pin signal
socket to port B. This allows you for example to use the work position signal in the TRACK-Leader
parallel guide.
The work position sensor sold by Müller-Elektronik is fitted with a round 3-pin connector. You will
need an adapter cable to connect it to the terminal.
Page 38

38
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Adapter cable
Item number
3-pin to 9-pin
31302499
Ports
Connection
Item number
position.
CAM port
6.4
6.4.1
Procedure
Connecting and configuring external devices
6
Camera
Adapter cable for the ME sensor Y work position sensor
You can also connect the terminal to the signal socket.
Cable to the signal socket
7-pin to 9-pin socket Cable directly to the signal socket
30322548
Transmits the speed and work
You must activate the work position sensor [➙ 54] and possibly the wheel sensor [➙ 53] or radar
sensor in the Tractor-ECU app and calibrate if necessary.
Camera
Connecting the camera to the terminal
Connecting the camera HQ2
Camera HQ2 - Connection to the Touch Terminal
Connector for connection to the terminal.
Extension cable
Camera HQ2
Camera connector
Connector for the camera plug
1. Assemble the camera together with its bracket, as described in the assembly instructions of the
camera manufacturer.
2. Connect the camera to the extension cable.
3. CAUTION! When laying out the extension cable, ensure that there are no kinks and that
no one can stumble over the laid-out cable.
4. Connect the extension cable to the CAM port of the terminal.
5. Secure the camera.
6. Activate the camera. [➙ 39]
Page 39

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
39
Connector for connection to the terminal.
CAM port
Camera
Procedure
6.4.2
Procedure
Connecting and configuring external devices
Camera
6
Connecting the camera NQ
Camera with adapter cable
Connector for the adapter cable
Connector for the extension cable
Camera connector
Connector for the camera plug
1. Connect the cables to each other as shown in the figure. Pay attention to cable lengths when
doing so.
2. CAUTION! When laying out the cable, ensure that there are no kinks in the cable and that
no one can stumble over the laid-out cable.
3. Lay out the cable. Ensure that the cable reaches the terminal and is not pulled out during
operation.
4. Attach the cable with the provided cable ties.
5. Secure the camera. Use the white cardboard drilling template from the quick start guide for this
purpose.
6. Connect the camera to the terminal. Use the CAM port to do this.
7. Activate the camera. [➙ 39]
8. When disconnecting the cable from the terminal, use the enclosed rubber gasket to seal the
exposed connector.
Activating a camera
In order to activate a camera, you must activate the “Camera_ME” plug-in.
1. - Open the “Service” application.
2. Tap “Plug-ins”.
3. Tap “Camera”.
⇨ The plug-in is marked with a green tick.
4. Restart the terminal.
Page 40

40
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
WARNING
Accident due to delayed image transmission
reaction can lead to risks.
Function icon
Meaning
6.4.3
6.5
6.5.1
Connecting and configuring external devices
6
External lightbar
⇨ After restarting, the icon for the camera application appears in the selection menu.
5.
- Open the Camera application.
Operating the camera
The camera serves solely for observing the implement functions in non-safety-related working areas
of the agricultural implement.
In certain situations, the camera image may appear on the screen with a delay. The delay depends
on the respective use of the terminal and can also be affected by external factors and devices.
Rapidly moving objects may be detected too late.
◦ Do not use the camera as an aid for steering the vehicle.
◦ Do not use the camera in road traffic.
◦ Do not use the camera when driving into intersections.
◦ Do not use the camera as a rear view camera.
◦ Do not use the camera as a visual aid for controlling the implement, especially when a delayed
You have connected and activated the camera.
External lightbar
Connecting the external lightbar to the terminal
The external lightbar is a parallel driving display made by Müller-Elektronik, which can be mounted
near the windshield.
The external lightbar works with position data and guidance lines that are provided by the TRACKLeader app. This is why you need the TRACK Leader App to be able to use the external lightbar.
Mirrors the image horizontally.
Mirrors the image vertically.
1.
- Open the Camera application.
⇨ The filmed image appears in the main window.
2. Tap on the main window.
⇨ Function icons appears on the side for 10 seconds, with which you can actuate the camera.
Page 41

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
41
6.5.2
Procedure
6.6
Connecting and configuring external devices
Connecting the on-board integrated display/controller to the terminal
6
External lightbar
Connector for connecting a GPS receiver
Connector for connection to the terminal
Serial port
Activating an external lightbar
If you connected an external ME Lightbar to the terminal, you must activate it.
To activate the external lightbar, you must first activate its driver.
You can order the external lightbar from Müller-Elektronik with the following item number: 30302490.
1. - Open the “Service” application.
2. Tap "Driver".
3. Tap “Lightbar”.
⇨ The installed drivers appear.
4. Tap “Lightbar”.
5.
- Confirm.
6. Restart the terminal.
Connecting the on-board integrated display/controller to the
terminal
You can connect a range of on-board integrated display/controllers (non-ISO computers), which
communicate using the LH5000 protocol or the ASD interface, to the terminal.
An appropriate connector cable for each on-board integrated display/controller which can be
connected is available from Müller-Elektronik. Our sales team will be glad to advise you.
Page 42

42
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
3032254800
ISOBUS
Procedure
6.7
6.7.1
Connecting and configuring external devices
6
ISO Printer
On-board integrated display/controller
Adapter cable*
Available as a set with Cable 3, item number:
Null modem cable
Connector B of the terminal
*When using an Amatron3 or Amatron+ as on-board integrated display/controller, you will only need a
traditional null modem cable. (Amatron3 and Amatron+ are on-board integrated display/controller
from Amazone)
1. After connecting the on-board integrated display/controller to the terminal, create a virtual job
computer for the machine. More about this in section: Virtual ECU application [➙ 61]
ISO Printer
Connecting the ISO printer to the terminal
The ISO printer is used to print out information from an ISO-XML task.
9-pin Sub-D connector for connection to
ISO Printer
ISO Printer socket
Connector for connection to ISO printer socket
Connector for connection to the terminal
CAN Bus port
Page 43

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
43
6.7.2
Procedure
6.8
Procedure
6.9
Procedure
Connecting and configuring external devices
Configuring the Bluetooth connection in the Connection Center
6
Activating ISO Printer
In order to activate the ISO printer, you must activate its driver.
1. - Open the “Service” application.
2. Tap "Driver".
3. Tap “ISOPrinter”.
⇨ The installed drivers appear.
4. Tap “ISO Printer”.
5.
6. Restart the terminal.
- Confirm.
Configuring the Bluetooth connection in the Connection Center
If you connect a bluetooth stick to the terminal, you can couple the terminal with another bluetooth
device (e.g. a smartphone).
This allows you to use the ME ODI (Müller Elektronik Open Data Interface) [➙ 13] application.
1. Connect the USB bluetooth stick to the terminal.
2.
- Open the “Service” application.
3. Tap "Driver".
4. Activate the “Connection Center” driver (value: Connection Center)
5. Restart the terminal.
6.
- Open the “Service” application.
7. Tap on “...”.
8. Tap on “Connection Center”.
⇨ The “Connection Center” screen appears.
9. Tap on “Bluetooth”.
Crop protection sensors
Crop protection sensors measure the plant requirements during operation. Depending on the sensor,
the results are transmitted as a target rate to the job computer of the fertilizer spreader or sprayer.
The terminal can communicate with crop protection sensors through two interfaces:
▪ ISOBUS - If a sensor communicates via ISOBUS, it is automatically detected by the terminal.
The target rates are transmitted directly to the job computer.
▪ Serial - If a sensor only communicates through the serial interface, you must connect it to the
serial port on the terminal [➙ 81]. Then you must create a virtual job computer for the sensor in
the Virtual ECU [➙ 61] app. Activate the virtual job computer before starting operation.
To work with ISOBUS sensors:
Page 44

44
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Procedure
Procedure
Connecting and configuring external devices
6
Crop protection sensors
1. Connect the sensor to the ISOBUS.
2. Follow the instructions from the sensor manufacturer. The terminal does not need to be
configured.
To work with serial connection sensors:
1. Connect the sensor to the serial port of the terminal.
2. Create a virtual job computer in the Virtual ECU app. [➙ 61]
3. In the “External controller” [➙ 62] parameter, select the sensor type.
4. Activate the job computer for the sensor.
⇨ You have activated the sensor.
⇨ The terminal transmits all target rates to ISOBUS-TC, the ISOBUS job computer and TRACK-
Leader.
Special case
If you are working with your machine in mixed operation, with ISOBUS and serially connected
sensors, you must observe the following sequence:
The serial sensor is connected to the serial interface of the terminal.
1. Connect the ISOBUS components to the ISOBUS.
2. Start the Virtual ECU [➙ 61] app.
3. Create a virtual job computer in the Virtual ECU app. [➙ 61]
4. In the “External controller” [➙ 62] parameter, select the sensor type.
5. Activate the job computer for the sensor.
⇨ You have activated the sensor.
6. Set the connectors in the list of connections.
⇨ The terminal transmits all target rates to ISOBUS-TC, the ISOBUS job computer and TRACK-
Leader.
Page 45

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
45
7
7.1
Procedure
7.2
Procedure
Configuring the terminal in the Service application
Configuring the terminal in the Service application
Changing the language
7
Changing the language
If you change the language in the Service application, you also change the language for all
applications and the ISOBUS job computer.
If a connected ISOBUS job computer cannot activate the selected language, a standard language will
be activated.
1. - Open the “Service” application.
⇨ The application start screen appears:
2. Tap “Terminal”.
⇨ A list of parameters appears.
3. Slide your finger over the terminal screen from the bottom to the top.
⇨ New parameters appear.
4. Tap “Language”.
⇨ A list of abbreviations of available languages appears.
5. Tap the abbreviation for your language.
⇨ The abbreviation is marked with a green dot.
6.
- Confirm.
⇨ The “Terminal” screen appears.
7. Restart the terminal.
Basic terminal settings
The basic settings include: Language, Time, Measurement units.
All settings which you make here will also apply to other applications and in connected ISOBUS job
computers.
1. - Open the “Service” application.
Page 46

46
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Parameter name
Function
Brightness Day
Brightness of the terminal screen during the day.
Brightness Night
Brightness of the terminal screen at night.
Keyboard brightness
Lighting of the buttons.
Volume
Volume of the terminal.
Date
Current date.
Time
Current time.
Time zone
Time difference in relation to GMT.
Language
Language of the applications on the terminal screen.
Measurement units
Measurement system.
the terminal.
Number that should be given to the terminal on the ISOBUS.
the parameter must be deactivated.
Configuring the terminal in the Service application
7
Basic terminal settings
⇨ The application start screen appears:
2. Tap “Terminal”.
⇨ A list of parameters appears. See the table below.
3. To change the value of any of the parameters, tap the desired parameter.
⇨ A window appears, into which you can input the value of the parameter as a number, or
select from a list.
4.
- Confirm.
5. Restart the terminal.
Parameters in the “Terminal” menu
Screenshot When this parameter is activated, you can create screenshots on
VT number Parameters from the ISO standard
Login as ISOBUS-VT Activate this parameter if you want the ISOBUS job computer to
be displayed on the terminal. This parameter must be activated in
most instances. On very few self-propelled agricultural machines,
Page 47

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
47
Parameter name
Function
between multiple pages with function icons.
Character representation
Character representation on the terminal.
Name of the plug-in
Activates the following applications
TRACK-Leader AUTO
ISOBUS-TC
Task management (ISOBUS-TC) [➙ 66]
Tractor-ECU
Tractor-ECU application [➙ 51]
camera.
FIELD-Nav
FIELD-Nav
FILE-Server
FILE-Server application [➙ 78]
Virtual ECU
Virtual ECU application [➙ 61]
7.3
Procedure
Configuring the terminal in the Service application
Activating and deactivating applications
7
Number of navigation buttons The terminal provides a maximum of 12 function icons in each
application.
When you connect an ISOBUS job computer that has more
functions in a single screen to the terminal, their function icons
are spread over multiple pages. Furthermore, navigation buttons
appear that can be used to scroll to the next page.
The number indicates how many buttons should be used to scroll
Activating and deactivating applications
In the “Service” application you can activate and deactivate other applications that are installed on the
terminal.
The applications are installed in packages, in so-called plug ins. A plug in can contain several
applications.
You can for example deactivate a plugin if you do not want to use it. The plug-in will then not be
displayed in the selection menu.
TRACK-Leader TRACK-Leader
SECTION-Control
TRACK-Leader TOP
Camera The terminal screen will show the image from the connected
To activate and deactivate plug-ins:
1.
- Open the “Service” application.
2. Tap “Plug-ins”.
⇨ Screen “Plug-ins” appears.
3. To activate or disable a plug-in, tap it.
Page 48

48
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
marks.
version in the brackets: in hours and minutes.
7.4
Procedure
Configuring the terminal in the Service application
7
Unlocking licenses for full versions
⇨ A plug-in is activated when a checkmarker appears in front of its name.
4. Restart the terminal.
Unlocking licenses for full versions
Several applications are pre-installed on the terminal, which you can use for trial purposes for up to
50 hours. After this time has elapsed, they will be automatically deactivated.
“Licenses” screen
Screen name
Unlocked applications are marked with check
Un-checked applications are locked.
Name of the application
You can see how long you can still use a test
18-digit alphabetical code of the application
You will need an activation key to unlock a license. To receive this, you will need to purchase a
license from Müller-Elektronik.
If you request the activation key by phone or by email, you will be required to give our staff the
following information:
▪ The name of the application for which you require a license.
▪ The 18-digit alphabetical code of the application. You will find this on the “Licenses” screen.
▪ Serial number of the terminal – Found on the nameplate on the reverse of the terminal.
▪ Item number of the terminal – Found on the nameplate on the back of the terminal.
To unlock a license:
1.
- Open the “Service” application.
2. Tap “Licenses”.
3. Order an activation key from Müller-Elektronik using the 18-digit alphabetical code.
4. Tap the name of the license that you want to unlock.
⇨ The keyboard appears.
5. Enter the activation key.
6.
- Confirm.
⇨ The “Licenses” screen appears.
7. Restart the terminal.
⇨ The full version of the application is now unlocked.
Page 49

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
49
7.5
Procedure
7.6
When to delete?
Procedure
7.7
Configuring the terminal in the Service application
Creating screenshots
7
Creating screenshots
A screenshot is a photo of the screen being displayed.
1. Insert a USB memory device into the terminal.
2.
- Open the “Service” application.
3. Tap “Terminal”.
4. Set the “Screenshot” parameter to “Activated”.
5. To create a screenshot, press the
button.
⇨ The content of the terminal screen will be saved as an image file on the USB memory
device in the “Screencopy” folder.
Deleting pools
Pools are the intermediate storage for the terminal. Pools are used to temporarily store graphics or
text. Over time, the pools will become too large and slow down the operation of the terminal.
You can delete the pools to speed up the terminal's operation.
Delete the pools:
▪ After updating the software of a connected job computer.
▪ If the terminal operates more slowly than usual.
▪ When asked to do so by Customer Services.
To delete the pools:
1.
- Open the “Service” application.
2. Tap “Object pool”.
⇨ A list with the ISO names of ISOBUS job computers appears, whose graphics and text can
be found in the storage of the terminal. You can determine from the icon which farm
implement is being controlled by the job computer.
3. Tap the object pool which you want to delete.
4.
- Delete the object pool.
⇨ Nothing happens if you delete the wrong object pool.
⇨ The following message appears: “Do you want to delete the folder?”
5. To confirm, tap “Yes”.
6. The current pool of the job computer will be loaded after the next restart.
Using the Open Data Interface
Müller-Elektronik Open Data Interface (short: ME ODI or ODI) is a driver that activates an interface to
Internet services.
Through this interface, data can be exchanged between the terminal applications and external
Internet-based services.
Page 50

50
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
7.7.1
Procedure
7.7.2
Procedure
Configuring the terminal in the Service application
7
Using the Open Data Interface
Examples: Transmitting tasks to the ISOBUS-TC, sending target rates to the job computer, etc.
Activating ME ODI
Please note that you can only activate the driver for ME ODI if the driver for farmpilot is deactivated.
To activate ME ODI:
1.
- Open the “Service” application.
2. Tap “Driver”.
3. Tap “Open Data Interface”.
⇨ The installed drivers appear.
4. Tap “ME ODI”.
5.
6. Restart the terminal.
Opening ME ODI
- Confirm.
To open ME ODI:
1.
- Open the “Service” application.
2. Tap on “...”.
3. Tap “Open Data Interface”.
⇨ The “Settings” screen appears.
The overall configuration of the connection must take place through the online service. On the
“Settings” screen, you can see information on the established connections:
▪ “Client” - Services that are presently connected to the terminal.
▪ “Diagnostics” - Here, you can record the connection sequence to be able to find the cause in
case of an error.
Page 51

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
51
8
8.1
8.2
Tractor-ECU application
Work screen
8
Tractor-ECU application
The Tractor-ECU application is used to compile all of the information of the vehicle on which the
terminal is mounted. Tractor-ECU can transfer this information to other apps (e.g. the position of the
GPS receiver to TRACK-Leader or SECTION-Control) or to a connected ISOBUS job computer (GPS
signal as a speed source).
The Tractor-ECU application allows you to:
▪ Create a profile for each vehicle, with specific settings.
▪ Input the sensors which are mounted on the vehicle.
▪ Enter the position of the GPS receiver.
▪ Define the GPS signal to determine the speed on the CAN bus.
Work screen
Speed display
Speed Source
Position of the work position sensor
PTO shaft speed
Number of operation hours
Status of the work position sensor
Managing the tractor profiles
Tractor profiles are used to store important features of the tractor on which the terminal is installed.
This offers the following advantages:
▪ You can use the terminal on several tractors. Each time you change tractors, you can activate
the fitting tractor profile.
▪ Even if the terminal is always installed on one tractor, you can create several profiles for one
tractor.
You can use between 1 and 31 tractor profiles.
The number of tractor profiles depends on several factors:
▪ Purpose of the terminal:
– If you switch the mounted implement manually, or are using an implement for which cm-
accuracy is not required, one tractor profile per tractor is enough.
– If you are not using TRACK-Leader and SECTION-Control, you probably do not need
tractor profiles.
▪ Required precision:
Page 52

52
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
profiles)
the stop icon appears.
State of the tractor profile:
restarting the terminal.
Function icon
Function
Tractor-ECU application
8
Managing the tractor profiles
– If you are working with SECTION-Control and ISOBUS planters/seeders or field sprayers,
the distance between the GPS receiver and the coupling is decisive. For this reason, you
need one profile in which you measure the distance to the lower link in the geometry, and
one profile in which you measure the distance to the drawbar.
▪ Number of tractors with different equipment and different geometries.
For self-propelled machines (e.g. field sprayers), you must use a tractor profile with the following
settings:
▪ “Connection with ISOBUS-TC?” parameter - Ensure that this parameter is properly set.
▪ “Speed” parameter
– GPS receiver - If a GPS receiver is connected to the terminal and is used to determine the
speed.
– Wheel sensor, radar sensor via CAN bus - If a speed sensor is connected to the junction
box of the ISOBUS job computer, this setting allows you to use the speed display of the
Tractor-ECU.
▪ Geometry: For self-propelled machines, the geometry is generally entered in the field sprayer job
computer. For this reason, you do not need to enter any distances in the Tractor-ECU.
Name of a tractor profile
Icon for the tractor
Green = Profile is activated;
ISO name of the tractor profile
(The numbers in the middle differ among the
Function icons.
If at least one tractor profile is activated, only
Yellow = Profile will be activated after
Creates a new tractor profile.
Activates the marked tractor profile.
Deactivates the tractor profile.
Calls up the parameters stored in the tractor profile.
Page 53

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
53
Function icon
Function
Procedure
8.3
Procedure
Tractor-ECU application
Parameter
8
Deletes the tractor profile.
1. - Open the Tractor ECU application.
2. Tap “Settings”.
⇨ The existing tractor profiles appear.
⇨ If a tractor profile is activated, most of the other function icons are greyed-out.
3. A maximum of five tractor profiles can be displayed on one page. To view other profiles, swipe
across the screen with your finger from bottom to top.
4. To edit a tractor profile or to create a new one, you must deactivate the activated tractor profile.
Parameter
1. - Open the Tractor ECU application.
2. Tap “Settings”.
⇨ The existing tractor profiles appear.
3.
- If a tractor profile is activated, deactivate it.
4. Tap on the profile to be configured.
⇨ The profile will be marked.
5.
- Call up the parameters for the marked tractor profile.
⇨ The parameters are displayed.
Name
Name of the tractor profile.
Connection with ISOBUS-TC?
With this parameter, you can set whether the Tractor ECU application should communicate with the
ISOBUS-TC application. In doing so, it transmits: Counters, work position, position of the GPS
receiver.
Deactivate this parameter only if the terminal is used as a secondary terminal and the GPS receiver
is connected to a different terminal.
Speed
Configuring the speed sensor. This measures the speed.
Possible values:
▪ “deactivated”
No sensor measures the speed.
▪ “Wheel sensor”
Page 54

54
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Tractor-ECU application
8
Parameter
A wheel sensor is connected to the terminal. The wheel sensor must be calibrated [➙ 55].
▪ “Radar sensor”
A radar sensor is connected to the terminal. The radar sensor must be calibrated [➙ 55].
▪ “GPS receiver”
The speed is calculated using GPS.
▪ “Unknown sensor via CAN”
A wheel sensor or a radar sensor is connected to the terminal via CAN.
▪ “Radar sensor via CAN”
A radar sensor is connected to the terminal via CAN.
▪ “Wheel sensor via CAN”
A wheel sensor is connected to the terminal via CAN.
Pulses per 100 m
This parameter is only required if you have selected one of the following speed sources: Wheel
sensor or radar sensor. In other cases, any value entered here will be ignored.
The speed sensor calibration results appear under this parameter.
Work position sensor
With this parameter, you can set whether there is a work position sensor and how its signal reaches
the terminal.
There are three parameters that can be used to configure the work position sensor:
“Mounting position and connection” parameter
Possible values:
▪ “deactivated”
No sensor measuring the work position.
▪ “Front via connector B”
A work position sensor, is located on the front hitch or on the implement mounted on the front
hitch. It is connected to the terminal via connector B. The work position sensor must be
configured.
▪ “Rear via connector B”
A work position sensor, is located on the rear hitch or on the implement mounted on the front
hitch. It is connected to the terminal via connector B. The work position sensor must be
configured.
▪ “Unknown sensor via CAN”
There is a work position sensor determining the work position of the implement. It is connected
to an ISOBUS job computer or to a different terminal. The signal reaches the terminal via CAN.
▪ “Front via CAN”
There is a work position sensor determining the work position of the implement at the front of the
vehicle. It is connected to an ISOBUS job computer or to a different terminal. The signal reaches
the terminal via CAN.
▪ “Rear via CAN”
There is a work position sensor determining the work position of the implement at the rear of the
vehicle. It is connected to an ISOBUS job computer or to a different terminal. The signal reaches
the terminal via CAN.
▪ “TRACK-Leader AUTO”
As soon as the steering system is activated, the system assumes that the implement is in work
position.
Page 55

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
55
8.3.1
Procedure
Tractor-ECU application
Parameter
8
“Sensor Type” parameter
If a work position sensor is connected to the terminal via connector B, you must tell the terminal the
principle according to which the sensor functions.
Possible values:
▪ “analog”
You are using an analog work position sensor [➙ 56], which measures the height of the hitch
linkage as a percentage.
▪ “digital”
You are using a digital, ISO-compatible work position sensor in accordance with ISO 11786. The
sensor is connected to the terminal via the signal socket.
▪ “ME-sensor Y”
You are using a work position sensor provided by Müller-Electronik. The sensor is connected to
the terminal.
“Inversion” parameter
As a standard, the terminal assumes that the implement is in work position as soon as the work
position sensor sends a signal. However, if the work position sensor functions inversely, you have to
set it here.
Possible values:
▪ “Yes” - implement is in work position when the sensor is not occupied.
▪ “No” - implement is in work position when the sensor is detecting something.
PTO shaft speed
Configuring the PTO (power take-off) rotational speed sensor. It measures the rotational speed of the
PTO.
Possible values:
▪ “deactivated”
No sensor measures the rotational speed of the PTO.
▪ “Revol. sensor - front”
A rotational speed sensor that is fitted onto the front PTO.
▪ “Revol. sensor - rear”
A rotational speed sensor that is fitted onto the rear PTO.
Impulses per revolution
Number of impulses per revolution that are transmitted by the PTO through the selected PTO sensor.
Calibrating the speed sensor
When calibrating the speed sensor using the 328.085ft (100m) method, determine the number of
targets which the speed sensor encounters over a distance of 328.085ft (100m).
If you know the number of targets for the speed sensor, you can also input this manually.
You have measured and marked a distance of 100m. The distance must correspond to the field
conditions. You must therefore drive across a meadow or a field.
The vehicle with the connected implement is operational for a 100m drive and is at the start of
the marked distance.
You have connected a wheel sensor or radar sensor to the terminal.
Page 56

56
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
8.3.2
Procedure
8.3.3
Tractor-ECU application
8
Parameter
You have selected the value "Wheel sensor" or "Radar sensor" in the "Speed" parameter.
1.
- Open the Tractor ECU application.
2. Tap “Settings”.
3. Mark the vehicle for which you want to calibrate the speed sensor.
4. Tap
5. Tap
.
.
6. Follow the instructions on the display screen.
⇨ You have calibrated the speed sensor.
Calibrating an analog work position sensor
If you have connected an analog work position sensor to the terminal, you have to show the terminal
the position as of which the implement is in work position.
You have connected a work position sensor directly to the terminal or via the signal socket to the
terminal.
You have selected the analogue sensor in the “Sensor type” parameter.
1.
- Open the Tractor ECU application.
2. Tap “Settings”.
3. Mark the vehicle for which you want to calibrate the analog work position sensor.
4. Tap
.
5. Move the implement into work position.
6. Tap
to teach-in the work position on the terminal.
7. Confirm.
⇨ You have configured the work position sensor.
Tractor geometry
The tractor geometry represents a series of dimensions on the vehicle.
Examples of tractor geometry
Page 57

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
57
be edited.
B
Distance between the GPS receiver and the rear axle of the vehicle.
C
Distance between the rear axle and the rear mounting or attachment point.
E
Distance between the rear axle and the front mounting or attachment point.
Function icon
Meaning
Procedure
Tractor-ECU application
Parameter
8
A Distance between the centre of the vehicle and the GPS receiver, on the left-right axis.
If the receiver is installed on the left side, enter a negative value.
Users of TRACK-Leader AUTO®: The position of the GPS receiver must also be entered and
calibrated in the steering job computer. For this reason, the A and B boxes are greyed-out and cannot
Configuring the tractor connector types
The connector type can differ among various tractors and mounted or trailed implements. Per default,
the connector type is always set to “Unknown”.
Please note that when you select a different connector type or multiple different connector types, the
automatic list of connections no longer works. You then have to list the connections manually.
The following connector types are possible:
▪ Unknown
▪ Drawbar
▪ 3-point hitch mounted
▪ 3-point hitch semi-mounted
▪ Hitch hook
▪ Clevis coupling
▪ Piton-type coupling
▪ CUNA hitch
▪ Ball-type hitch
Adds a new connector type.
Deletes the marked connector type.
Edits the marked connector type.
1. - Open the Tractor ECU application.
2. Tap “Settings”.
⇨ The existing tractor profiles appear.
⇨ If a tractor profile is activated, most of the other function icons are greyed-out.
3.
- To edit a tractor profile or to create a new one, you must deactivate the activated tractor
profile.
4. Tap on the tractor profile to be edited.
5.
- Call up the parameter list.
⇨ The parameters are displayed.
Page 58

58
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Procedure
Tractor-ECU application
8
Parameter
6. - Open the tractor geometry screen.
7.
- Call up the screen for configuring the front connector types.
⇨ The “Front - connector type” screen appears.
8.
- Add a connector.
9. Select the connector type.
10. Enter the distance between the rear axle and the front mounting or attachment point.
11.
12. Optionally, you can
13.
- Confirm.
edit or delete other connector types.
- Repeat this procedure for the rear connector types. Enter the distance between the rear
axle and the rear mounting or attachment point.
14.
- Terminate the entry.
⇨ The tractor geometry can now be viewed and edited. [➙ 58]
Configuring the tractor geometry
You have configured the connector types of the tractor. [➙ 57]
1.
- Open the Tractor ECU application.
2. Tap “Settings”.
⇨ The existing tractor profiles appear.
⇨ If a tractor profile is activated, most of the other function icons are greyed-out.
3.
- To edit a tractor profile or to create a new one, you must deactivate the activated tractor
profile.
4. Tap on the tractor profile to be edited.
5.
- Call up the parameter list.
⇨ The parameters are displayed.
6.
7.
- Open the tractor geometry screen.
/ - Select the currently used connector type. Per default, the connector type is
always set to “Unknown”. Please note that when you select a different connector type or multiple
different connector types, the automatic list of connections no longer works. You then have to list
the connections manually.
8. Adopt the pre-set distances for the connector types or enter new distances as shown in the
figure above.
Page 59

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
59
Counter designation
This is documented
Applied distance
Distance during which the work position sensor was activated.
basis for the calculation of the area.
Working time
Time during which the work position sensor was activated.
Icon
This counter will be erased
Counter designation
Unit
This is documented
activated.
activated.
8.4
8.4.1
Procedure
8.4.2
Tractor-ECU application
Results
8
Results
The Tractor ECU application documents the work in two counter groups:
▪ Trip counter
▪ Task-related counter
Trip counter
Applied area Area during which the work position sensor was activated.
The Tractor ECU application uses the set working width as a
To clear a trip counter:
1.
2. Tap “Results”.
3. Tap the function icons to clear the trip counters.
- Open the Tractor ECU application.
⇨ The “Results” screen appears with the trip counters.
Applied distance
Working time
All trip counters
Task-related counter
These counters are transmitted to the ISOBUS-TC app. You can activate the counters in a task, and
they will then appear in the additional window as soon as the ISOBUS-TC App is minimized.
Task-related counter
Distance km Distance during which the work position sensor was
Time in work position h Time during which the work position sensor was
Page 60

60
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Counter designation
Unit
This is documented
1 = in work position
Tractor-ECU application
8
Results
Work position 0/1 0 = not in work position
Page 61

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
61
only the stop icon appears.
restarting the terminal.
Function icon
Function
9
9.1
Procedure
Virtual ECU application
Managing virtual job computers
9
Virtual ECU application
The Virtual ECU application (or VECU for short) is used to create virtual job computers for the
following implements:
▪ Implements that do not have their own job computer. For example: Cultivators, ploughs,
mechanical seeders, etc.
▪ Machines that are operated using an on-board integrated display/controller connected to the
serial interface.
▪ Crop protection sensors that are connected serially to the terminal.
Each virtual job computer contains the most important features of the respective machine (working
width, geometry, type of on-board integrated display/controller) and provides these to other
applications if required.
Managing virtual job computers
Name of the virtual job computer
Implement type
State of the virtual job computer:
Green = Profile is activated;
ISO name of the virtual job computer
Function icons.
If at least one virtual job computer is activated,
Yellow = Profile will be activated after
Creates a new job computer.
Activates the marked job computer.
Deactivates the job computer.
Calls up the parameters stored in the virtual job computer.
Deletes the job computer.
1. - Open the “Virtual ECU” app.
Page 62

62
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
9.2
Procedure
Virtual ECU application
9
Parameter
2. Tap “Settings”.
⇨ The existing virtual job computers appear.
⇨ If a job computer is activated, most of the other function icons are greyed-out.
3. A maximum of five job computer profiles can be displayed on one page. To view other profiles,
swipe across the screen with your finger from bottom to top.
4. To edit a job computer profile or to create a new one, you must deactivate the activated job
computer profile.
Parameter
Name
Name of the virtual job computer.
External Controller
If you have connected an on-board integrated display/controller or crop protection sensor to the serial
interface, you must select the model in this parameter.
The list contains the following devices:
▪ On-board integrated display/controllers that can communicate using one of the protocols ASD or
LH5000 and are capable of communicating with the terminal. If you want to connect an on-board
integrated display/controller that supports this protocol, but does not appear in the list, please
contact Müller-Elektronik and perform the steps shown at the end of this section.
▪ Crop protection sensors that can be connected to the serial interface of the terminal.
▪ AMABUS. Please note that to connect the AMABUS, you need a special cable, item number:
30322572
This is how you update the list of on-board integrated display/controllers:
You have contacted Müller-Elektronik and received a USB memory device with the installation
file.
The Virtual ECU application is closed.
1. Insert the USB memory device into the terminal.
2. Start the Virtual ECU application.
⇨ The following message appears: Do you want to update the list of external on-board
integrated display/controllers?
3. Select “Yes” to update the list.
4. Confirm.
5. Restart the terminal.
⇨ You can now also select the added on-board integrated display/controller.
Implement type
Use this parameter to define the type of implement.
The following implement types are available:
▪ Seeder
▪ Fertilizer spreader
Page 63

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
63
Virtual ECU application
Parameter
9
▪ Sprayer
▪ Soil tillage
Connector type
Use this parameter to define the connector type of the agricultural implement.
The following connector types are possible:
▪ Unknown
▪ Drawbar
▪ 3-point hitch mounted
▪ 3-point hitch semi-mounted
▪ Hitch hook
▪ Clevis coupling
▪ Piton-type coupling
▪ CUNA hitch
▪ Ball-type hitch
Machine model
This parameter influences how the working bar follows the arrow in TRACK-Leader. The
configuration improves the precision of the recording of applied areas in curves.
After each change, you also need to adjust the geometry.
Possible values:
▪ “mounted”
Setting for implements that are mounted on the tractor three-point hitch.
▪ “trailed”
Settings for implements trailed by a tractor. The working bar is guided like a trailer behind a
tractor.
Working width
This parameter shows the working width set for an implement.
Number of sections
Enter the number of sections that can be switched off on the implement. On a field sprayer, they are
the section valves; on a fertilizer spreader or a planter/seeder, they can be e.g. metering units.
This parameter serves to transmit the proper number of sections to the SECTION-View module, so
that you can switch the sections manually.
Each section appears as part of the working bar on the screen.
Sections
Opens a screen where you can enter the width of the individual sections on the implement.
Geometry
The geometry contains a series of dimensions that help to properly display the vehicle-implement
combination in TRACK-Leader and determine its position.
Page 64

64
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
A
Mounted:
determined individually.
B Mounted
Distance between the pivot point of the machine and the work point.
C
Only for spreaders: Working Length
D
example: - 50 cm.
Display in TRACK-Leader
Virtual ECU application
9
Parameter
To call up the geometry, tap the function icon:
Calls up the machine geometry.
Screen for entering the geometry for different machine models
Distance between the coupling point and the work point of the machine.
Trailed:
Distance between the coupling point and the pivot point of the machine.
For single-axle trailers, the pivot point is located at the centre of the axle, for tandem trailers between
two axles. For planters/seeders, cultivators and other soil tillage implements, the pivot point must be
:
Not available
Trailed:
Lateral offset
If the mounted implement is offset to the left in the direction of travel, enter a negative value. For
Geometry of machines and display in TRACK-Leader
Mounted fertilizer spreader
Trailed sprayer
Page 65

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
65
9.3
Virtual ECU application
Work screen
9
TRAMLINE-View
TRAMLINE-View contains parameters that are used to correctly display tramlines in TRACK-Leader
when using seeders.
To use TRAMLINE-View, the “TRAMLINE-Management” license must be activated.
To call up TRAMLINE-View, tap the function icon:
Calls up TRAMLINE-View.
Parameter:
▪ “Tramline rhythm”
Defines the tramline rhythm to be used for operation.
▪ “Working Start”
Defines the point on the field at which you want to start working.
▪ “Begin with half the working width”
Defines whether you make the first field track after starting to work with only half of the working
width.
Work screen
The following information may appear on the work screen:
▪ Serially transmitted application/spread rates: Target rates and current rates
▪ Section status and number
▪ Implement geometry
Page 66

66
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
10
10.1
10.1.1
10.1.2
Task management (ISOBUS-TC)
10
Configuring ISOBUS-TC
Task management (ISOBUS-TC)
The ISOBUS-TC application has two jobs:
▪ As Task Controller, the application controls all of the relevant data between the terminal and
other implements that are connected to the ISOBUS or terminal (Part 11 of the standard
ISO11783).
▪ As Task Manager, the application enables the creation and editing of ISO-XML tasks. This also
enables communication with Farm Management Information Systems (Part 10 of the standard
ISO11783).
The jobs performed by the application depend on how the “Operating Mode” parameter is configured.
▪ “Standard” - Only the Task-Controller jobs
▪ “Extended” - Task-Controller and Task-Manager jobs
Configuring ISOBUS-TC
The “farmpilot” parameter
This parameter shows the status of the connection to the “farmpilot” portal.
“Operating Mode” parameter
With this parameter, you can set whether the Task Controller of ISOBUS-TC should work in the
background or if you want to work actively with ISO-XML tasks.
▪ “Standard” - Two working methods are possible here.
Working method 1:
– All task data is managed through the “TRACK-Leader” app.
– In ISOBUS-TC, you cannot create any tasks.
– In this operating mode, ISOBUS-TC works in the background.
Working method 2:
– You can load field data from a shape file (field boundaries, guidance lines) in ISOBUS-TC.
This field data is made available in the “TRACK-Leader” app. Also possible without an
ISOBUS-TC license.
– After activating the ISOBUS-TC license, you can edit shape prescription maps.
– In ISOBUS-TC, you cannot create any tasks.
▪ “Extended” - In this operating mode, the ISOBUS-TC menu is extended. The ISOBUS-TC
license is required. In this mode, ISOBUS-TC serves to manage and process ISO-XML tasks.
Two working methods are possible here.
Working method 1:
– You can manage and process ISO-XML tasks using a Farm Management Information
System.
Working method 2:
– You can create and manage master data yourself in the ISOBUS-TC app.
In these instructions, only the standard mode will be explained. The extended mode is described in
the separate instructions for ISOBUS-TC.
Page 67

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
67
Procedure
10.1.3
10.1.4
10.1.5
10.1.6
Task management (ISOBUS-TC)
Configuring ISOBUS-TC
10
1. - Open the ISOBUS-TC application.
2. Tap “Settings”.
3. Tap “Operating Mode”.
4. Tap “Extended” if you want to work with tasks. Tap “Standard” to be able to work without tasks.
5.
- Confirm.
⇨ You will be asked whether you want to change the setting.
6. Tap “Yes” if you want to confirm this.
⇨ All data will be saved and the operating mode will be switched.
7. Wait until all messages have faded out.
What happens with the data?
The data structure is different in the two operating modes. After changing the mode, the task and field
data will be saved. When switching again, the stored data will be loaded.
“TC number” parameter
Number of the Task-Controller. For complex systems with multiple terminals and Task-Controllers,
several Task-Controllers can be distinguished based on this number. If need be, you can control
which Task-Controller the connected job computer should communicate with.
“Prefer internal Tractor-ECU?” parameter
This parameter is important on vehicles that have their own Tractor-ECU in addition to the ME
terminal.
Activate the parameter if the GPS receiver is connected to the ME terminal or to the TRACK-Leader
AUTO steering system. Deactivate the parameter if the GPS receiver is connected to a different
terminal.
“Save finished tasks as a file?” parameter
If this parameter is activated, all ISO-XML tasks are saved on the memory device as a text file.
“Validation of the device description” parameter
Optional parameter. Deactivated per default.
Please note that when the parameter is activated, Task-Controller version 3 is supported. If the
parameter is deactivated, Task-Controller version 2 is supported.
Only activate this parameter if you want to ensure that SECTION-Control and ISOBUS-TC only
communicate with AEF-compliant job computers.
Job computers that are not AEF-compliant are not supported by ISOBUS-TC in this case.
Page 68

68
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Connection between the tractor and the job
- Connected implements
Name of the job computer
- Disconnected implements
10.1.7
10.2
Task management (ISOBUS-TC)
10
Configuring the list of connections
“Simplified target rate assignment?” parameter
Optional parameter. Set to “No” per default.
When you activate this parameter, the target rate settings from the previous task can be adopted for
a new task. To do so, you must set the parameter to “Yes”.
When you then create a new task, the following message appears:
“Should be target rate settings for the implement be adopted from the previous task?”
Confirm this message to adopt the target rate settings.
Configuring the list of connections
The list of connections indicates the ISOBUS job computers from which the terminal will load the
geometries of the connected implements. This geometry is required in order to calculate the position
of all implement components on the basis of the GPS signal. Only in this way are precise parallel
guidance and section control possible.
Icon for the tractor
computer is established
ISO name of the tractor
Icon for the ISOBUS job computer
Not all of the equipment in the list must be
connected.
In simple systems, the terminal can set up the list of connections automatically. In particular, when
the ME terminal is the only unit containing the tractor geometry.
It can however still be necessary to set the list of connections manually in the following instances:
▪ If a tractor job computer (Tractor-ECU), in which the tractor geometry is saved, is mounted as an
independent job computer on the tractor. In this instance, you must decide which Tractor-ECU is
connected in the list of connections with other equipment: the application on the ME terminal or
on the tractor job computer.
▪ If the system cannot organize the ISOBUS job computer by itself. For example when more than
one implement is connected to the tractor (e.g.: slurry tanker and planter/seeder).
▪ When the connection to an ISOBUS job computer is interrupted during the start-up of a ISO-XML
task. In most cases, the list of connections will be set correctly as soon as you reconnect the
ISOBUS job computer.
▪ If this error message appears when starting the terminal: “List of connections is incomplete.”
Page 69

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
69
Icon
Function
Procedure
10.3
Task management (ISOBUS-TC)
Using fields and shp data
10
▪ When the following error message appears when starting a navigation in TRACK-Leader: “The
device data is still loading.” The settings in the list of connections can eliminate this problem.
If you are using the ISOBUS-TC application in “Standard” mode, you can configure the list of
connections as follows:
All ISOBUS job computers and virtual job computers that are required for a field are connected.
1.
- Open the ISOBUS-TC application.
2. Tap “Farm equipment”.
⇨ The “Farm equipment” screen appears.
3.
- Open the list of connections.
⇨ You have called up the list of connections screen.
⇨ A list appears with all of job computers, controllers and ECUs connected to the ISOBUS.
The connectors appear between these devices.
4. Tap the task in the top row in order to select the first implement.
5. The device that is connected to the ME terminal should appear in the second line. Tap the line
with the second implement and select one from this.
6. You now only need to select the appropriate connector between the two devices. Tap the line
between the devices and select the appropriate connector for each device.
7.
- Exit the screen to save the settings.
Using fields and shp data
In the “Fields” category, you can create all of the fields that you want to process. For each field, you
can enter the following properties:
▪ Field name
▪ Code
▪ Area
▪ Field boundary
▪ Guidance lines
▪ Guidance Line Set
▪ Obstacle
▪ Prescription map (ISOBUS-TC license required)
Creates a new field.
Activates the field.
Deactivates the field.
Enables editing of the field properties.
Page 70

70
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Icon
Function
Icon only appears when you tap .
Icon only appears when you tap .
Icon only appears when you tap .
10.3.1
Purpose
10.3.2
Procedure
Task management (ISOBUS-TC)
10
Using fields and shp data
Deletes the field.
Enables the import of field data.
Displays the loaded prescription map.
Displays the imported field data.
Enables the export of field data.
Deletes the selected data.
What is field data for?
All field properties that are stored in this way can be used when working in TRACK-Leader. To do so,
you must activate the field to be processed in ISOBUS-TC before each navigation.
Creating fields
To create a new field:
1.
- Open the ISOBUS-TC application.
2. Tap “Fields”.
⇨ A list with already created fields appears. You can store various field data for each field. For
example: Field name, area, field boundary, prescription map and obstacles. You can access
this data when you work on the same field in the future.
3.
- Create a new field.
⇨ A form for entering the data appears.
4. On the topmost line, enter a field name.
5.
- Exit the screen.
⇨ You will be asked whether you want to save the changes.
6. Confirm.
⇨ A list of created fields appears. The new field appears at the bottom end. Each field is given a
clear PFD number. The fields are sorted according to these numbers. The numbers can be seen
in the field list above the respective field name. Moreover, you can see the number in the header
when you open the field.
Page 71

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
71
10.3.3
Procedure
Procedure
Task management (ISOBUS-TC)
Using fields and shp data
10
PFD numbers
Each PFD number is only given one single time. Even if you delete a field, its PFD will not be used
again.
When processing the fields in TRACK-Leader, this number will also be assigned when saving the
field data in the ngstore database and attached to the field name.
Example:
Work performed on field PFD1 will be saved in TRACK-Leader under “ISOBUS-TC--1”.
Work performed on field PFD50 will be saved in TRACK-Leader under “ISOBUS-TC--50”.
Activating and deactivating fields
You can activate a field as follows:
In the “Virtual ECU” application, you have activated the virtual job computer for the implement to
be used or you have connected an ISOBUS job computer.
Operating mode of ISOBUS-TC: Standard
1.
- Open the ISOBUS-TC application.
2. Tap “Fields”.
⇨ A list with already created fields appears.
3. Tap the entry with the field to be processed.
4.
5.
- Activate the field.
- Open the TRACK-Leader application.
6. Start a new navigation.
⇨ The terminal loads all of the data from the storage: Field boundaries, guidance lines, tracks.
⇨ In doing so, the terminal also takes account of which job computer was used to process the
field. Therefore, if you work on the field two consecutive times with the field sprayer, the
tracks for the field sprayer will be loaded the second time. However, if you work on the field
with a fertilizer spreader, the tracks for the fertilizer spreader will be loaded.
7. Depending on which machine you are working with, you can create or select a suitable guidance
line set in TRACK-Leader. More information on guidance line sets can be found in the
instructions for TRACK-Leader.
If you want to rework the field, you must go to the “Storage” menu in TRACK-Leader and delete the
tracks there with
.
To finish the work:
The navigation screen is called up in TRACK-Leader.
You have worked the field in TRACK-Leader. On the screen, you can see the field with field
boundary, guidance lines and other field data.
1.
- Terminate the navigation in TRACK-Leader.
Page 72

72
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
10.3.4
Procedure
10.3.5
Procedure
Task management (ISOBUS-TC)
10
Using fields and shp data
2. - Open the ISOBUS-TC application.
3. Tap “Fields”.
4. Tap the entry with the field that was just processed.
5.
- Deactivate the field.
⇨ The field will be deactivated. In the process, it will also be saved with all of the current field
Importing field data (*.shp)
data. With the next activation, the data will be automatically loaded again.
To import field data:
The shp files are in WGS84 format.
1. Copy the field data to be imported to the SHP folder on the USB memory device.
2. Please insert the USB memory device.
3.
- Open the ISOBUS-TC application.
4. Tap “Fields”.
5. If you have not created a field yet, create a field. [➙ 70]
6. Tap the field for which you want to load the shp data.
⇨ The field properties appear. You can see the previously entered data and several function
icons on the side.
7.
- Open the import view.
8. Tap “Data type”.
⇨ A list with possible data types appears.
9. Select the type of field data that you want to load.
10. Tap “File selection”.
11. Select the file.
⇨ A preview of the imported data appears.
12.
- Exit the screen.
⇨ The message “Do you want to import the selected file? appears.
13. “Yes” - to confirm.
14. Repeat the import procedure for additional field data.
⇨ The preview of the imported data will be supplemented each time.
⇨ All of the desired field data will be loaded.
If you now activate the field, you can start a new navigation with the loaded field data.
Exporting field data
To export field data:
1. Please insert the USB memory device.
Page 73

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
73
10.3.6
10.3.7
Procedure
10.4
Task management (ISOBUS-TC)
Using prescription maps
10
2. - Open the ISOBUS-TC application.
3. Tap “Fields”.
⇨ A list with already created fields appears.
4. Tap the field for which you want to export data.
⇨ The field properties appear. You can see the previously entered data and several function
icons on the side.
5.
6.
7.
- Open the field view.
- Open the list with all field data.
- Export the field data.
Data on the memory device
During work with TRACK-Leader, two types of data are produced:
▪ Tracks - Everything that is marked in green on the screen. This data describes one single work
process.
– The tracks are automatically saved in TRACK-Leader as soon as the field is deactivated in
ISOBUS-TC.
– You are in the “ngstore” folder on the USB memory device.
– They could be imported for evaluation with TRACK-Guide Desktop.
– Each field is given the name ISOBUS-TC--PFD. Whereby PFD stands for the PFD number
of the field in ISOBUS-TC. For example: ISOBUS-TC--2
▪ Changing of fixed field data: Field boundaries, guidance lines, obstacles. This data is not only
important for one work process, it can also be used in the future.
Transferring field data to a different terminal
To transfer all field data to a different terminal:
Operating mode of ISOBUS-TC: Standard
1. Terminal 1: Export all field data to a USB memory device. [➙ 72]
2. Terminal 2: Create the field profiles once again. [➙ 70]
– This data is saved as shp files in the “SHP” folder.
3. Terminal 2: Import all field boundaries, guidance lines etc. from a USB memory device. [➙ 72]
Using prescription maps
Prescription maps are maps that contain information on the quantity of a product (fertilizer, seed,
pesticide) to be spread/applied on each area of the field.
When the prescription map has been loaded, the terminal checks via GPS coordinates of the vehicle
what application rates are needed according to the prescription map and transfers this information to
the appropriate ISOBUS job computer.
Page 74

74
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
10.4.1
Procedure
Task management (ISOBUS-TC)
10
Using prescription maps
The terminal can open prescription maps in two formats:
▪ Shape format (*.shp)
– The ISOBUS-TC app is used to open a prescription map in shape format.
– Multiple prescription maps can be imported.
– Only one prescription map can be used at a time. If you want to use more than one
prescription map, you need a license for MULTI-Control. This way, for implements that have
more than one metering unit, you can use a prescription map for each metering unit. The
procedure is described in the MULTI-Control II instructions.
▪ ISO-XML format
– The prescription map must be added to an ISO-XML task on a PC.
– The prescription map can only be used in combination with an ISO-XML task through the
ISOBUS-TC application.
– The format is supported by all ISOBUS job computers, regardless of their manufacturer.
– Several prescription maps can be used simultaneously in one task. This way, for
implements that have more than one metering unit, you can use a prescription map for each
metering unit. To do so, you need the MULTI-Control license. The procedure is described in
the MULTI-Control II instructions.
Importing shape prescription maps
You can import more than one prescription map for a field.
To import a prescription map:
The ISOBUS-TC license must be activated.
1. Copy a shape prescription maps to the “SHP” folder on the USB memory device.
2. Please insert the USB memory device.
3.
- Open the ISOBUS-TC application.
4. Tap “Fields”.
5. If you have not created a field yet, create a field. [➙ 70]
6. Tap the field for which you want to load the prescription map.
⇨ The field properties appear. You can see the previously entered data and several function
icons on the side.
⇨ If a prescription map has already been activated for this field, its name appears on the
“Prescription map” line. You can still import another one.
7.
- Open the import view.
8. Tap “Data type”.
⇨ A list with possible data types appears.
9. Select “Prescription map”.
10. Tap “File selection”.
11. Select the prescription map.
⇨ The screen with the properties of the prescription map appears.
Page 75

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
75
10.4.2
Procedure
10.4.3
Procedure
Task management (ISOBUS-TC)
Using prescription maps
10
12. When a prescription map is imported for the first time, first tap “Column selection” to choose the
column with the target rates, then tap “Unit selection” to choose the units. For future imports,
these values will be automatically selected.
13.
- Exit the screen.
14. The overview image of the prescription map appears.
15.
- Exit the screen.
16. You will be asked whether you want to import the file.
17. Confirm.
18. The prescription map has been loaded and stored in the field data.
Selecting shape prescription maps
You can import a multitude of prescription maps for each field. Before starting operation, you must
activate the right prescription map.
If only one prescription map was imported, it will be automatically activated when starting up.
Depending on which work mode you are using, the prescription map is activated either when starting
a field (in “Standard” mode) or when starting a task (in “Extended” mode).
To activate a prescription map:
You have imported several prescription maps.
1.
- Open the ISOBUS-TC application.
2. Tap “Fields”.
3. Tap the field that you want to work on.
⇨ The field properties appear.
⇨ If a prescription map has already been activated for this field, its name appears on the
“Prescription map” line.
4. Tap “Prescription map”.
5. Select a prescription map.
⇨ When you activate the field, this prescription map will be used.
Editing shape prescription maps
After importing the prescription map, you can:
▪ Change all values by a certain percentage point.
▪ Change selected values by an absolute number.
To change all of the values at once:
1.
- Open the ISOBUS-TC application.
2. Tap “Fields”.
3. Tap on the field to be edited.
Page 76

76
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Procedure
10.4.4
10.5
Task management (ISOBUS-TC)
10
MULTI-Control
4. Tap .
5. Tap
.
6. Enter the desired change in value. For example: 50% = halve, 200% = double
7.
- Confirm.
⇨ The “Prescription maps” screen appears.
⇨ All values have been changed.
⇨
- Exit the screen to save the changes.
To change a selected value:
1.
- Open the ISOBUS-TC application.
2. Tap “Fields”.
3. Tap on the field to be edited.
4. Tap
.
5. In the column with the target rates (left), tap the value that you want to change.
⇨ The keyboard appears.
6. Enter the new value.
7.
- Confirm.
⇨ The “Prescription maps” screen appears.
⇨ The new value appears in the cell you have changed.
8.
- Exit the screen to save the changes.
ISO-XML prescription maps
Prescription maps in ISO-XML format are created in an electronic Farm Management Information
System and are transmitted to the terminal with an ISO-XML task.
The ISOBUS-TC license is required to edit them.
Working with ISO-XML tasks is described in the instructions for ISOBUS-TC.
MULTI-Control
After activating the MULTI-Control license, you can use the ISOBUS-TC app to assign multiple
prescription maps to a machine.
This is necessary in two cases:
▪ MULTI-Rate - If the machine applies only one product that is metered by several metering units.
For example, a field sprayer with two tanks and two control manifolds.
▪ MULTI-Product - If the machine has several tanks that are used to apply different products at
different rates. For example: Planter/seeder with liquid fertilizer.
MULTI-Control is described in separate operating instructions.
Page 77

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
77
Function
Operating mode: Standard
Operating mode: Extended
MULTI-Product
not possible
possible
MULTI-Rate
possible
possible
Task management (ISOBUS-TC)
Work modes
MULTI-Control
10
Page 78

78
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
11
Procedure
FILE-Server application
11
FILE-Server application
The FILE-Server application is used to define a save location on the terminal. This save location can
be used by all ISOBUS implements which do not have their own USB interface. This enables the
updating of certain ISOBUS job computers, and also the possibility of saving, for example protocols
or error messages.
A “Fileserver” folder is created for this purpose on the hard disk of the terminal. All ISOBUS
implements can access this folder, and write or read data there.
The folder has a maximum disk space of 5 MB.
If you want to copy files to the terminal, these must be on your USB memory device, in the
“Fileserver” folder.
The “FILE-Server” plug-in is activated.
1.
- Open the FILE-Server application.
⇨ The application start screen appears.
2. Tap “Storage”.
3.
4.
- Copy files from the USB memory device onto the terminal (Import).
- Copy files from the SD card in the terminal to the USB memory device (Export).
⇨ One of the following messages appears: “Start import?” or “Start export?”.
5. To confirm, tap “Yes”.
⇨ The data will be copied.
⇨ Here is an overview of the folders on the USB memory device: Folders on the USB memory
device [➙ 26]
⇨ A report appears.
6. To confirm, tap “OK”.
⇨ You have successfully imported or exported the data.
Page 79

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
79
Operating voltage
10V - 32V
(operation)
Typical: 6W
Maximum: 40W
Ambient temperature
-20°C - +60°C
Storage temperature
-30°C - +80°C
Dimensions (W x H x D)
243mm x 186mm x 69mm
Weight
1.1kg
Protection class
IP6K4 according to ISO 20653:2013
EMC
ISO 14982
ESD protection
ISO 10605:2001 Level IV
with IEC 60068-2-27
Processor
i.MX 515 600MHz
Coprocessor
STM32F205
Storage
256M mDDR
Bootflash
128M SCL-NAND-Flash
Operating system
WinCE 6.0
Display
8'' SVGA TFT
Housing
PC-ABS
1 x Sub-D 9 socket (CAN and power supply)
12
12.1
Technical specifications
Technical specifications
Technical specifications of the terminal
12
Technical specifications of the terminal
Current consumption
Power input
0.5A (typical) - 4A
Environmental testing Vibration:
ISO 15003 Level 1 with Level 2 temperature overlap in accordance
with ISO 15003
Shock:
100 shocks per axis and direction with 15g and 11ms in accordance
Inputs / outputs 1 x USB
Page 80

80
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
1 x M12 (Industrial Ethernet)
Pin
Signal name
Function
1
CAN_L
CAN_L out
6
-Vin
Supply ground
2
CAN_L
CAN_L in
7
CAN_H
CAN_H in
3
CAN_GND
CAN ground, internally connected to the ground
8
CAN_EN_out
Switched input voltage, ≤ 250 mA
4
CAN_H
CAN_H out
9
+Vin
Supply
5
Ignition
Ignition signal
shielding
12.2
12.2.1
12.2.2
Technical specifications
12
Pin-out diagrams
1 x Sub-D 9 connector
1 x Sub-D 9 connector (CAN & signals)
1 x M12 (camera)
Pin-out diagrams
Port A (CAN bus)
9-pin Sub-D socket
Electromagnetic
Electromagnetic shielding ESD/EMV shielding
Port B
9-pin Sub-D connector
Port B is a 9-pin Sub-D connector.
Page 81

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
81
Purpose
Pins used
As second CAN interface
7, 9
As second serial interface
2, 3, 4, 5
signal.
Pin
Signal name
1
Wheel sensor1
6
PTO2
2
/RxD2
7
CAN2_H
3
/TxD2
Reverse signal for determining the course
Switched input voltage, ≤ 250 mA
9
CAN2_L
5
GND
shielding
12.2.3
Technical specifications
The connector can be used for the following purposes depending on its assignment:
Pin-out diagrams
12
As signal input for two digital and one analog
1, 5, 6, 8
8 Work position sensor3 or
4 Voltage supply for GPS receiver
Electromagnetic
ESD/EMV shielding
Legend:
1
) Digital input as per: ISO 11786:1995 chapter 5.2
2
) Digital input as per: ISO 11786:1995 chapter 5.3
3
) Analog input as per: ISO 11786:1995 chapter 5.5
Port C
9-pin Sub-D connector
Page 82

82
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Pin
Signal name
Function
+ Pin 4)
6
DSR
DSR
2
/RxD
/RxD
7
RTS
RTS 3 /TxD
/TxD
8
CTS
CTS
+ Pin 4)
9
(RI)
5 V ≤ 250 mA
5
GND
Signal ground
shielding
Pin
Signal name
Function
1
Power
Voltage supply, max. 250 mA total
2
Power GND
Supply ground
3
FBAS2
Camera
4
FBAS
Camera
5
Signal GND
Signal ground
6
Electromagnetic shielding
ESD/EMV shielding
12.2.4
Technical specifications
12
Pin-out diagrams
1 (DCD1) Switched input voltage, ≤ max. 250 mA total (Pin 1
4 (DTR) Switched input voltage, ≤ max. 250 mA total (Pin 1
Electromagnetic
Electromagnetic shielding ESD/EMV shielding
CAM port
M12 socket: Camera
Page 83

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
83
Pin
Signal name
Function
1
TD+
white-orange
2
RD+
white-green
3
TD-
orange
4
RD-
green
5
Pin not present
Pin not present
shielding
12.2.5
12.3
Technical specifications
Licence conditions
12
ETH (Ethernet) port
M12 socket: Ethernet
Electromagnetic
Electromagnetic shielding ESD/EMV shielding
Licence conditions
The software uses the following open source libraries:
▪ Eigen
http://www.mueller-elektronik.de/LICENCES/eigen/LICENSE.txt
▪ SpatiaLite
http://www.mueller-elektronik.de/LICENCES/spatialite/LICENSE.txt
▪ Proj.4
http://www.mueller-elektronik.de/LICENCES/proj.4/LICENSE.txt
▪ Expat
http://www.mueller-elektronik.de/LICENCES/expat/LICENSE.txt
▪ WCELIBEX
http://www.mueller-elektronik.de/LICENCES/wcelibex/LICENSE.txt
▪ Agg
http://www.mueller-elektronik.de/LICENCES/agg/LICENSE.txt
▪ Poco C++
http://www.mueller-elektronik.de/LICENCES/poco/LICENSE.txt
▪ QT
http://www.mueller-elektronik.de/LICENCES/qt/LICENSE.txt
▪ Boost
http://www.mueller-elektronik.de/LICENCES/boost/LICENSE.txt
Page 84

84
V8.20190731
30322538-02-EN
Error message text
Possible cause
Possible error correction
currently being used.
terminal. [➙ 49]
broken.
The connections between the terminal and
ECU have been broken.
Error message text
Possible cause
Possible error correction
The wrong driver was selected.
Select the correct driver. [➙ 28]
the terminal. [➙ 28]
receiver.
GPS receiver has been broken.
TRACK-Leader AUTO.
[➙ 30]
configuration of the GPS receiver.
settings. [➙ 30]
The wrong driver was selected.
Select the correct driver. [➙ 28]
the terminal. [➙ 28]
activated.
card.
used in the entry.
The wrong driver was selected.
Select the correct driver. [➙ 28]
connected.
13
13
General
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
The following error messages can appear during operation, amongst others:
Some files could not be deleted. The files that should be deleted are
Object pool error Delete the object pool and restart the
ECU: Offline - The connection has been
GPS
Check the connection. [➙ 17]
GPS receiver reset failed.
The external lightbar is activated.
The GPS receiver is not enabled for E-Dif. There is no E-Dif activation on the GPS
GPS receiver has been removed. The connection between the terminal and
Deactivate the external lightbar [➙ 40]
and connect the
GPS receiver directly to
Please contact technical support.
Check the connection. [➙ 28]
The GPS receiver has been configured for
GPS receiver not initialized. The terminal does not recognise the
Timeout.
The external lightbar is activated.
SIM card is not unlocked. The PIN request for the SIM card is
Invalid entry. Unauthorised special characters were
The connected receiver could not be
recognized.
An unknown GPS receiver has been
Reset the baud rate for the GPS receiver.
Reset the GPS receiver to its factory
Deactivate the external lightbar [➙ 40]
and connect the
GPS receiver directly to
Deactivate the PIN request for the SIM
Correct the entry.
Use the default GPS driver. [➙ 28]
Page 85

30322538-02-EN
V8.20190731
85
Error message text
Possible cause
Possible error correction
and GSM modem has been broken.
Please wait for a moment.
Restart the system.
The driver cannot read.
the terminal. [➙ 28]
Error message text
Possible cause
Possible error correction
A vehicle must be activated!
There is currently no activated vehicle.
Activate a vehicle. [➙ 51]
incomplete. Check settings.
Error message text
Possible cause
Possible error correction
machine have been reset.
63]
display/controller has been broken.
Error! There is no active machine.
There is currently no activated machine.
Activate a machine. [➙ 61]
entry?
been used.
entered or are invalid. Abort entry?
sections are incomplete.
and the sections. [➙ 63]
Troubleshooting
13
The modem is not answering. The connection between the GPS receiver
The modem is not ready for
communication yet.
The external lightbar is activated.
The driver cannot write.
Tractor-ECU
Active tractor geometry may be
Virtual ECU
Check the connection.
Deactivate the external lightbar [➙ 40]
and connect the
GPS receiver directly to
Check the tractor geometry. [➙ 56]
Caution! The geometry settings for the
The connection to the external controller
has been interrupted.
This profile name already exists! Abort
Working width or sections have not been
The geometry of the virtual ECU is faulty. Check the geometry of the virtual ECU. [
➙
The connection between the terminal and
Check the connection. [➙ 41]
the external on-board integrated
The identical profile name has already
The entries for the working width and
Enter a different profile name. [➙ 62]
Check the settings for the working width
 Loading...
Loading...