TW100-P1W1
NWay Internet/Print
Multiple Server
User’s Guide
Rev. 01 (July, 1998)
6ETH802H.01
Printed In Taiwan
RECYCLABLE

Wichtige Sicherheitshinweise
1. Bitte lesen Sie sich diese Hinweise sorgfältig durch.
2. Heben Sie diese Anleitung für den spätern Gebrauch auf.
3. Vor jedem Reinigen ist das Gerät vom Stromnetz zu trennen. Vervenden Sie keine Flüssigoder Aerosolreiniger. Am besten dient ein angefeuchtetes Tuch zur Reinigung .
4. Um eine Beschädigung des Gerätes zu vermeiden sollten Sie nur Zubehörteile verwenden,
die vom Hersteller zugelassen sind.
5. Das Gerät is vor Feuchtigkeit zu schützen.
6. Bei der Aufstellung des Gerätes ist auf sichern Stand zu achten. Ein Kippen oder Fallen
könnte Verletzungen hervorrufen. Verwenden Sie nur sichere Standorte und beachten Sie
die Aufstellhinweise des Herstellers.
7. Die Belüftungsöffnungen dienen zur Luftzirkulation die das Gerät vor Überhitzung schützt.
Sorgen Sie dafür, daß diese Öffnungen nicht abgedeckt werden.
8. Beachten Sie beim Anschluß an das Stromnetz die Anschlußwerte.
9. Die Netzanschlußsteckdose muß aus Gründen der elektrischen Sicherheit einen
Schutzleiterkontakt haben.
10. Verlegen Sie die Netzanschlußleitung so, daß niemand darüber fallen kann. Es sollete auch
nichts auf der Leitung abgestellt werden.
11. Alle Hinweise und Warnungen die sich am Geräten befinden sind zu beachten.
12. Wird das Gerät über einen längeren Zeitraum nicht benutzt, sollten Sie es vom Stromnetz
trennen. Somit wird im Falle einer Überspannung eine Beschädigung vermieden.
13. Durch die Lüftungsöffnungen dürfen niemals Gegenstände oder Flüssigkeiten in das Gerät
gelangen. Dies könnte einen Brand bzw. Elektrischen Schlag auslösen.
14. Öffnen Sie niemals das Gerät. Das Gerät darf aus Gründen der elektrischen Sicherheit nur
von authorisiertem Servicepersonal geöffnet werden.
15. Wenn folgende Situationen auftreten ist das Gerät vom Stromnetz zu trennen und von einer
qualifizierten Servicestelle zu überprüfen:
a– Netzkabel oder Netzstecker sint beschädigt.
b– Flüssigkeit ist in das Gerät eingedrungen.
c– Das Gerät war Feuchtigkeit ausgesetzt.
d– Wenn das Gerät nicht der Bedienungsanleitung ensprechend funktioniert oder Sie mit
Hilfe dieser Anleitung keine Verbesserung erzielen.
e– Das Gerät ist gefallen und/oder das Gehäuse ist beschädigt.
f– Wenn das Gerät deutliche Anzeichen eines Defektes aufweist.
ii

16. Bei Reparaturen dürfen nur Orginalersatzteile bzw. den Orginalteilen entsprechende Teile
verwendet werden. Der Einsatz von ungeeigneten Ersatzteilen kann eine weitere
Beschädigung hervorrufen.
17. Wenden Sie sich mit allen Fragen die Service und Repartur betreffen an Ihren
Servicepartner. Somit stellen Sie die Betriebssicherheit des Gerätes sicher.
iii

Quick Installation
This section takes you through a step-by-step minimum installation
and setup procedure for the internet/print multiple server. Please
refer to the main text of this manual for detailed information about
the setup and oper ation of this device.
Getting Started
Step 1: Unpack the device. Make certain no components have been
lost or damaged. A packing list is provided on page 7.
Step 2: Choose an installation site on a flat, level surface or wall
near the modem or ISDN/TA you plan to use for internet
connections or near the network line you plan to use for a
LAN connection, and near the printer you would like to share
through the server. Note that the internet/print multiple
server can be hung on a wall using the wall mounting
equipment included with the product.
Making Connections
Step 3: Connect the internet/print multiple server to your LAN
using a Category 3, 4 or 5, twisted-pair cable and the device’s
single RJ-45 LAN port. This connection should be made to
an Ethernet or Fast Ethernet switch or hub. (The RJ-45 port
looks like a phone jack.)
Step 4: Connect the internet/print multiple server to the printer
using the LPT port and a parallel cable. See Chapter 5 for
information on how to setup the print server variables and
see the IS Admin User’s Guide for information on shared
print services.
iv
Step 5: Connect the internet/print multiple server to a modem or
ISDN/TA using the device’s serial port (COM). (Note that
your modem or ISDN/TA should already be connected and
setup according to the instructions included with it.)
Step 6: Plug the power adapter into the device and into an outlet.
Configuring
Step 7: Before your can use your internet/print multiple server, IP
addresses on your LAN’s PCs must be set so that they are
compatible with the internet/print multiple server’s settings.
The internet/print multiple server comes with the default local IP address: 192.168.100.1 and the default subnet mask
setting: 255.255.255.0. Computer stations on your LAN that
will use the internet/print multiple server for internet access
must modify their IP settings to 192.168.100.xxx (where xxx
is a number between 2 and 255). All stations must also modify their subnet mask settings to match the internet/print
multiple server subnet mask setting, and set their default
gateway to the local IP address (in this case the default address listed above) used by the internet/print multiple server.
If you want to use a different IP address range, see “Setting
IP Addresses” on page 16.
Step 8: The internet/print multiple server can be configured and
operated via Telnet or a web browser once PC IP addresses
have been properly set. (Note that some device settings can
be manipulated using the IS Admin program included with
the device.) Start your Telnet or browser software and enter
the IP address of the internet/print multiple server (either
the default IP listed above or the new address you assigned
using IS Admin). This should bring up the internet/print
multiple server start menu. See the next series of steps for
information about variables that must be set for the device to
work properly.
v

Key Variables
Step 9: ISP Account -> Phone Number, when you signed-up for
an account with your ISP (internet service provider), you
should have been given an access phone number that your
modem will dial. Look under the “WAN Port Variables”
menu for this variable and enter the phone number provider
by your ISP.
Step 10: ISP Account -> User ID , your ISP should also have as-
signed a User ID (aka, a username) that you will use for
logging-in. Also under “WAN Port Variables,” enter this user
ID exactly as it was provided to you.
Step 11: ISP Account -> Password, finally, to complete the ISP
login process, the internet/print multiple server must provide
the password associated with the user ID assigned by your
ISP. Enter it.
You have now completed the basic steps necessary to install, configure, and begin using the internet/print multiple server. Note that,
with respect to steps 9–11, it may be necessary for you to use a
“Login Script” instead. If you enter the information required in those
three variables correctly and still have trouble logging-in, see the
“Login Script” section on page 23 to create a login script.
vi

Trademarks
Contents subject to change without prior notice.
All trademarks belong to their respective proprietors.
Copyright Statement
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any
means or used to make any derivative such as translation, transformation, or adaptation without per mission from the manufacturer, as
stipulated by the United States Copyright Act of 1976.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with this user’s guide, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is
likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be
required to correct the interference at his own expense.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product
may cause radio interference in which case the user may be required
to take adequate measures.
VCCI A Warning
vii
TABLE OF C ONTENTS
QUICK INSTALLATION................................................................III
0ABOUT THIS GUIDE...............................................................XIII
Audience................................................................................xiii
Overview of the User’s Guide..................................................xiii
1CHAPTER 1 : INTRODUCTION...................................................1
Product Description..................................................................1
Product Features......................................................................1
Internet Server Technology.......................................................2
2CHAPTER 2 : INSTALLATION....................................................7
Unpacking ................................................................................7
Desktop / Shelf Installation ......................................................8
Wall Installation .......................................................................8
Port Description........................................................................9
Serial – WAN...................................................................................................9
Parallel – Printer...........................................................................................10
RJ-45 – LAN...................................................................................................10
LED Description ..................................................................... 10
Pw/Tx................................................................................................................10
Link/Rx.............................................................................................................10

COM .................................................................................................................11
LPT...................................................................................................................11
Normal LED Flash Pattern.........................................................................11
Connecting to the Local Network............................................. 11
Connecting to the Internet....................................................... 12
Connecting Power................................................................... 12
3CHAPTER 3 : SYSTEM SETUP ...............................................15
Setting IP Addresses ...............................................................16
Default Addressing.......................................................................................16
Configuring LAN IP Addresses..................................................................16
Using In-Band Telnet to Configure the Server ......................... 18
Using a Browser to Configure the Server .................................18
Minimum Configuration.......................................................... 19
DNS IP Address.............................................................................................20
ISP Account -> Phone Number....................................................................20
ISP Account -> User ID.................................................................................21
ISP Account -> Password.............................................................................22
Login Script.....................................................................................................23
Operation................................................................................ 24
4CHAPTER 4 : CONFIGURATION VARIABLES..........................25
System Variables .................................................................... 25
Server Name...................................................................................................25
Local LAN -> IP Address.............................................................................26
Local LAN -> Subnet Mask .........................................................................26
DNS IP Address.............................................................................................27
Maximum Idle Time.....................................................................................27
Operation Mode.............................................................................................28
Change Password..........................................................................................29
WAN Port Variables ................................................................29
ix

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
Line Type.........................................................................................................29
Baud Rate.......................................................................................................29
ISP Account -> Phone Number....................................................................30
ISP Account -> User ID.................................................................................30
ISP Account -> Password.............................................................................31
ISP Account -> IP Address..........................................................................31
Modem AT Command..................................................................................31
Login Script.....................................................................................................32
Print Server Variables............................................................. 33
Parallel Port -> Port Name.........................................................................33
Parallel Port -> Speed..................................................................................34
Parallel Port -> PJL Printer........................................................................34
NetBEUI -> Workgroup Name....................................................................35
NetBEUI -> Maximum Connected Stations............................................35
AppleTalk -> Printer Type...........................................................................35
AppleTalk -> Postscript Level....................................................................36
AppleTalk -> Font Group.............................................................................36
DHCP Server Variables ...........................................................37
Enable..............................................................................................................37
IP Address Range -> Start...........................................................................38
IP Address Range -> End.............................................................................38
IP Lease Time.................................................................................................38
IP Reserve Table............................................................................................39
Server Address Variables ........................................................ 39
System Monitoring ................................................................. 41
Displaying Information................................................................................41
Tools.................................................................................................................42
Navigation Controls................................................................ 43
5CHAPTER 5 : PRINT SERVER FUNCTION...............................45
Print Server Features ............................................................. 45
Connecting for Print Service ................................................... 46
Print Server Configuration...................................................... 47
x

6APPENDIX A : TROUBLESHOOTING.......................................49
System POST......................................................................... 49
Device Installation Problems................................................... 50
WAN .................................................................................................................50
Print Server.....................................................................................................51
LAN..................................................................................................................51
Station Configuration Problems.............................................. 51
Operating Problems ................................................................ 52
7APPENDIX B : SPECIFICATIONS............................................53
General................................................................................... 53
Environmental and Physical ................................................... 54
8APPENDIX C : AT COMMANDS .............................................55
Basic AT Command Set .......................................................... 55
Extended AT& Command Set ................................................. 59
9APPENDIX D : PORT PINOUTS..............................................61
Serial Ports ............................................................................ 61
Parallel Port........................................................................... 62
RJ-45 Port ..............................................................................63
10APPENDIX E : GLOSSARY...................................................65
INDEX.........................................................................................66
xi

0 A BOUT THIS GUIDE
This guide explains how to install and use the NWay port internet/print multiple server.
Audience
This manual assumes basic familiarity with LANs, the internet, and
ISPs. It has, however, been designed for basic-level users.
Overview of the User’s Guide
? ?Chapter 1, Introduction. Provides information on the inter-
net/print multiple server and internet server technology.
? ?Chapter 2, Installation. Helps you unpack, understand and
install the device.
? ?Chapter 3, System Setup. Explains how to set necessary op-
tions on the internet/print multiple server.
? ?Chapter 4, Configuration Variables. Explains all available
variables on the internet/print multiple server and what options exist for configuration and use.
? ?Chapter 5, Print Server Function. Describes how to use the
device as a print server.

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
xiv
? ?Appendix A, Troubleshooting. Provides direction and assis-
tance for locating the source of problems and solving them.
? ?Appendix B, Specifications. Lists the device’s specifications.
? ?Appendix C, AT Commands. Lists the basic and extended AT
command sets.
? ?Appendix D, Port Pinouts. Provides pinout data for the de-
vice’s ports.
? ?Appendix E, Glossary. Provides the meaning for some net-
working terms used in this manual.
About This Guide
1
1 INTRODUCTION
This chapter introduces the internet/print multiple server, as well as
some of the tec hnology that underlies it.
Product Description
The internet/print multiple server is designed to provide a singlepoint access to the internet for multiple, networked PCs. One of the
primary features of the internet/print multiple server is that it pr ovides multi-user access to the internet through a single user account
and one connection. More simply put, an internet/print multiple
server takes a single internet connection that without it could only
be used by one person and allows it to be used by multiple stations on
the same network simultaneously.
The internet/print multiple server also supports local network print
server operations.
Product Features
The list below highlights the features and specifications of the internet/print multiple server.
Introduction 1
Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
? ?Compatible with the IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T Ethernet and
802.3u 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet industry standards for interoperability with other Ethernet/Fast Ethernet network
devices.
? ?Internet protocol support for: PPP, PAP/CHAP, NAT, TCP/IP,
DHCP, ARP, ICMP, SMTP, POP3, FTP, Telnet, and HTTP.
? ?Support for device configuration via Telnet, web browser, or IS
Admin program (included).
? ?NWay TP port for LAN connection.
? ?Ethernet connections support Category 3 or better twisted-pair
cables.
? ?Fast Ethernet connections support both shielded twisted pair
and Category 5 unshielded twisted-pair cables.
? ?56K (maximum) modem speed support
? ?128K (maximum) ISDN/TA speed support
? ?Internet Features include: Dial-On-Demand, NAT internet
access, DHCP server, and virtual server.
? ?Print Server support includes the following print server pr oto-
cols: TCP/IP, NetBEUI, and AppleTalk.
? ?Flash memory for easy firmware upgrades.
Internet Server Technology
The concept behind internet/print multiple servers is to provide a
single, shared access point for multiple users. Without an internet/print multiple server, each end point (i.e., PC or workstation) on
a LAN must have it’s own public domain IP address.
Introduction 2
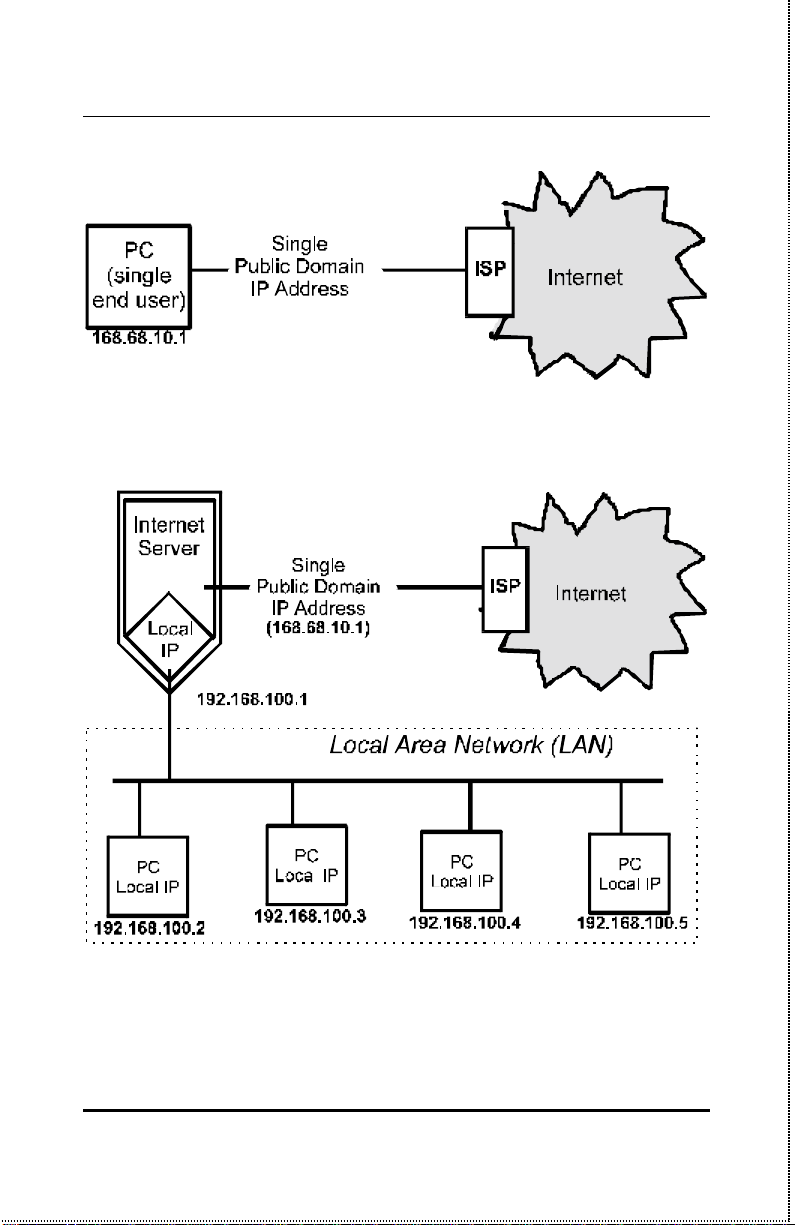
Using an internet/print multiple server allows a single public IP address to be shared by multiple local end points simultaneously.
Since the same range of local IP addresses can be used at as many
multiple locations as necessary, available IP addresses can increase.
Introduction 3
Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
4
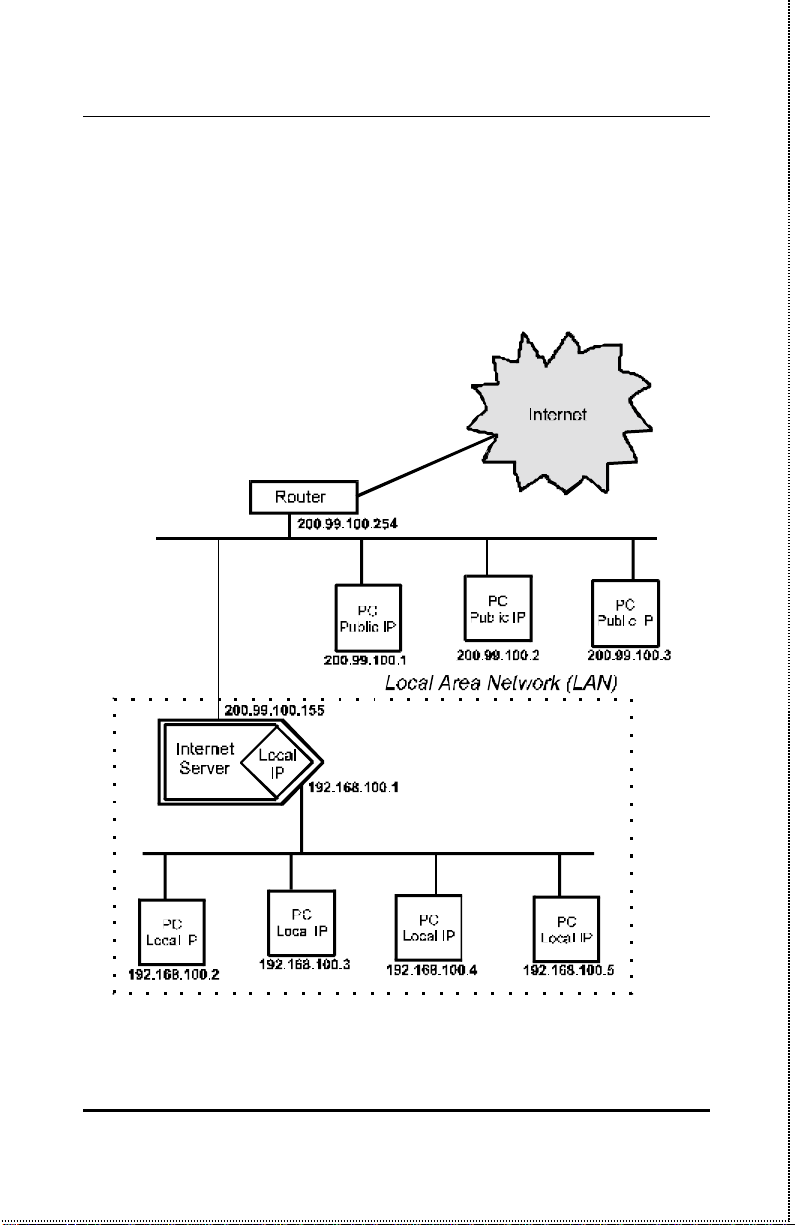
Also, it is only necessary for a company to pay for a single internet
access account even though many people will be able to use it.
An internet/print multiple server can also be used to expand a LAN
by providing a means to create localized “sub-groups” in a LAN-toLAN configuration. The internet/print multiple server acts as a sin-
gle public IP address access point for the sub-group LAN. The subgroup LAN can then use local IP addresses from the available
Introduction

ranges. The effect of this is to expand the number of stations that
can use IP addresses assigned to the LAN.
Introduction 5

2
2 INSTALLATION
This chapter provides information on the unpacking and initial installation of your internet/print multiple server .
Unpacking
Open the shipping carton of your internet/print multiple server and
carefully unpack the contents. The carton should contain the following items:
? ?One internet/print multiple server device
? ?One AC power adapter, suitable for your area’s electrical
power connections
? ?One 3.5” diskette with IS Admin software
? ?IS Admin User’s Guide
? ?Wall mount hardware
? ?This User’s Guide
? ?One lpr software diskette
? ?One lpr User’s Guide
Installation 7
Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
Inspect the device and all accompanying items. If any item is damaged or missing, report the problem to your dealer immediately.
Desktop / Shelf Installation
The unit has rubber feet attached to the bottom to cushion it. Allow
enough ventilation space between the device and the objects around
it. Choose a sturdy, level surface in a ventilated area that is dust
free and away from heat vents, warm air exhaust from other devices
and direct sunlight. Avoid proximity to large electric motors or other
electromagnetic equipment.
Observe the following guidelines when choosing an installation loc ation:
?? Air temperature should range from 32? to 122? F (0? to 50? C).
?? Humidity should be less than 90%, non -condensing.
?? Site should not exceed the electromagnetic field (RFC) standards
for IEC 801-3, Level 2 (3V/M) field strength.
For a detailed list of the product’s technical specifications, refer to
Appendix B, Specifications.
Wall Installation
The product can be installed on a wall. When installing, you need to
attach two tapping screws and two screw anchors to the bottom of
the device. Wall mount supplies are included.
Installation 8
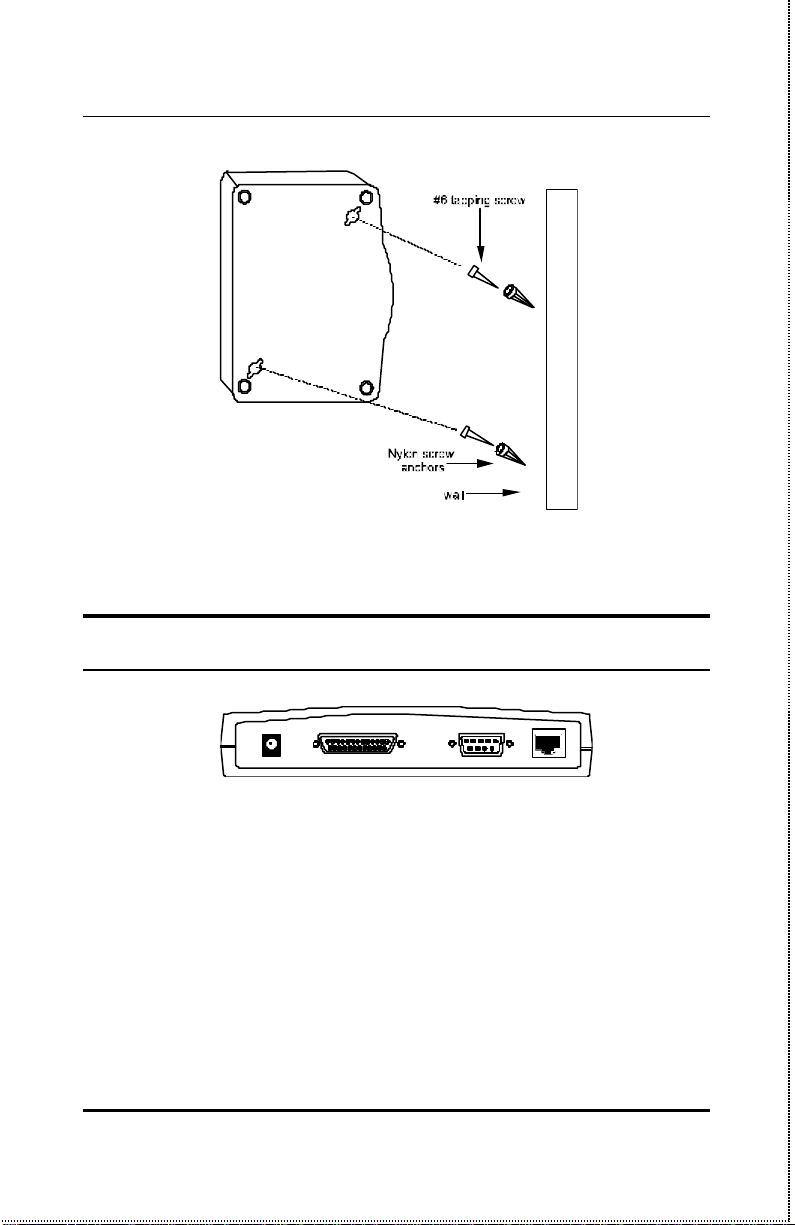
Installing the Internet/Print Multiple Server on a Wall
Port Description
Rear Panel
Serial – WAN
The serial port is used for a WAN connection either to a modem or
an ISDN terminal adapter. The serial port is a standard male 9-pin
RS-232 connector.
Installation 9
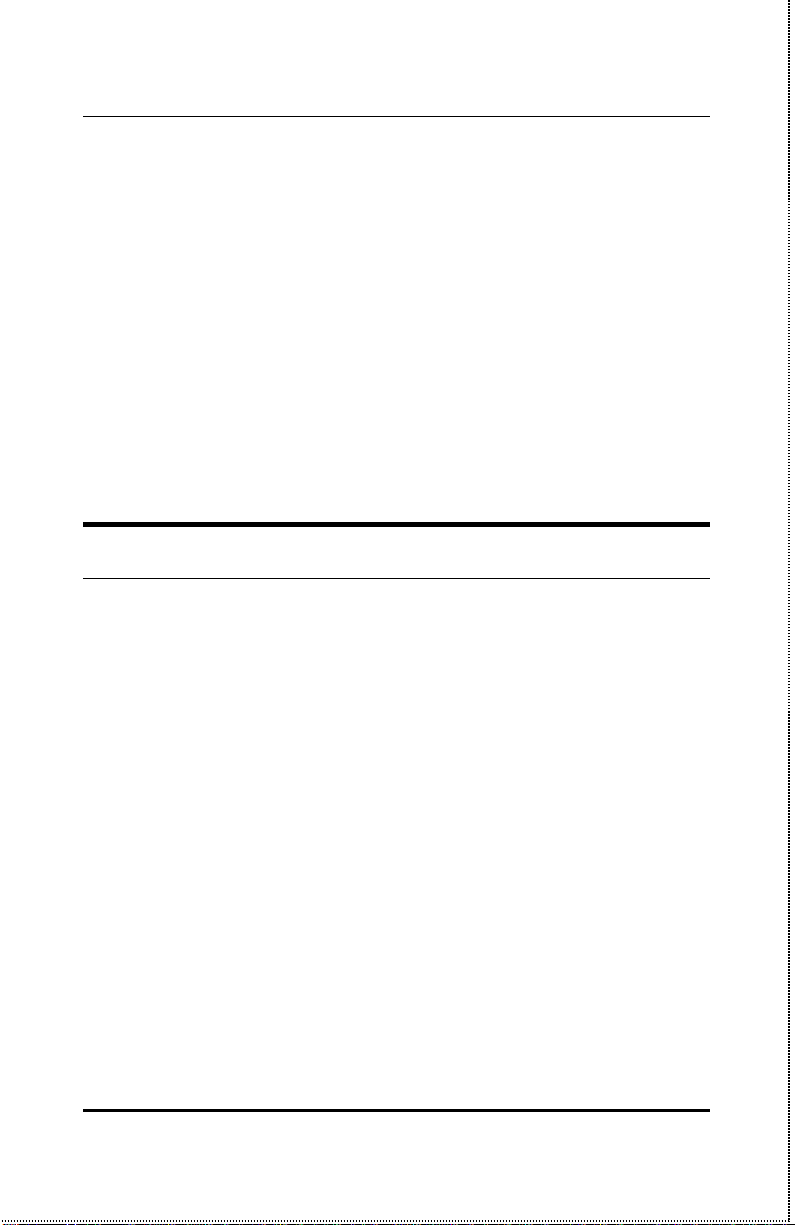
Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
Parallel – Printer
The parallel port is used for connecting to a printer for sharing to the
LAN. This port is a standard female 25-pin parallel connector.
RJ-45 – LAN
The internet/print multiple server has a single, NWay RJ-45 LAN
port. This port is 10Mbps and 100Mbps capable (auto-detect, autoconfigure) and designed for use in an Ethernet or Fast Ethernet LAN
via a network hub. The port has standard RJ-45 pinouts.
LED Description
The internet/print multiple server has a small LED array for indicating current port and transmission status. The power/transmit
(Pw/Tx) and connect/receive (Link/Rx) LEDs only relate to activity
on the LAN port. All other LED indicators display information about
their related ports as labeled.
Pw/Tx
The Pw/Tx (power/transmit) LED lights when power is supplied to
the device and flashes when the LAN port transmits data.
Link/Rx
The Link/Rx (link/receive) indicator will light up when a good connection is made at the LAN port with an operating and compatible
Ethernet or Fast Ethernet device. This indicator flashes when the
LAN port receives data from the network.
Installation 10

COM
The COM port LED provides an indication of the operating status of
the WAN port. When the WAN port is transmitting data, the COM
port will light. If no data is being transmitted, the COM LED will be
off.
LPT
The LPT port LED lights to indicate when data is being sent to the
network printer it is connected to. If no data is being transmitted,
the LPT LED will be off.
Normal LED Flash Pattern
Immediately after power-up, all four of the LEDs should display
steady green for several seconds. Then the COM LED and LPT LED
should flash simultaneously three times. This sequence of flashes
should be followed by first the COM LED flashing once and then LPT
LED flashing once, repeated three times in succession. If as problem with the device is detected during this time, the LED flashes will
display an error pattern (see Appendix A: Troubleshooting for more
information on POST error indications). If no errors are detected,
the internet/print multiple server will begin operating normally.
Connecting to the Local Network
The internet/print multiple server includes one RJ-45 NWay LAN
port. To connect the device to your LAN, use a standard Category
3, 4, 5 UTP, or STP twisted-pair cable to link the device to an
Ethernet or Fast Ethernet hub or switch.
Installation 11
Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
Cable length limits must conform to Ethernet and Fast Ethernet
wiring rules. Ethernet cable segments can be a maximum of 100
meters. Fast Ethernet wiring rules also limit the maximum
length of cabling segments to 100 meters.
Once the internet/print multiple server is physically connected to
a local network and you have used the IS Admin software included to assign an IP address to the device (or simply
reconfigured your PC’s IP address, subnet mask and gateway to
match the default settings of the internet/print multiple server),
you may configure other parameter variables from your network
station using Telnet or a web browser.
Connecting to the Internet
The internet/print multiple server must be connected to the internet
(this is also known as a “Wide Area Network or ‘WAN’” connection)
using the COM serial port. The COM port can either be connected to
the serial port of a modem (or fax/modem), or to an ISDN terminal
adapter. The faster the WAN connection is, the faster access will be
and the more users will be able to get on the internet simultaneously.
Connect the COM port of the internet/print multiple server to a modem or ISDN terminal adapter using a standard serial cable.
Connecting Power
Power is supplied to the internet/print multiple server through an
AC power adapter. Check the technical specifications section for information about the AC power input voltage.
Installation 12

Since the internet/print multiple server does not include a power
switch, plugging its power adapter into a power outlet will immediately power it on.
Installation 13


3
3 S YSTEM SETUP
Before it can be used, the internet/print multiple server has some
variables that need to be properly set. This chapter describes how to
change default IP settings and then how to use Telnet or a web
browser to manipulate the internet/print multiple server. A description of the minimum setup required to operate is also provided. A
full listing of all variables on the internet/print multiple server is
provided in Chapter 4. Note that the variables and their options are
the same regardless of whether you are using Telnet or a web
browser although they are displayed in different formats.
Usage Note: Throughout this user’s guide, we refer to
“your ISP.” An ISP is a company that provides internet services, normally for a fee,
and usually via modems connected over
telephone lines. From the ISP’s point of
view, the internet/print multiple server is a
single user (with a single username and
password). The purpose of the server is to
allow you to get access as a single user for
multiple actual users.
System Setup 15

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
Setting IP Addresses
The internet/print multiple server comes with a default IP address
and subnet mask assigned. If you would prefer not to use the internet/print multiple server’s default IP address, it will be necessary for
you to change that address using the IS Admin program included
with the device. Regardless, it will be necessary for you to configure
one PC with an IP address and subnet mask that are compatible
with the settings of the internet/print multiple server. (Note that
your PC’s IP address, subnet mask, and IP gateway must be hand
set; The IS Admin pr ogram does not include this function.)
Once the server and a management PC have compatible IP address
and subnet mask settings, and are connected through the LAN, either an in-band Telnet session or a web browser can be used to set
the device’s configurable variables and view its current operating
status.
Default Addressing
The internet/print multiple server comes with a preset default IP
address setting of 192.168.100.1. In order to configure the internet/print multiple server, you must set at least one computer on your
LAN to an IP address in the same subnet (192.168.xxx.xxx).
Configuring LAN IP Addresses
Before you can use Telnet or a browser to configure the internet/print
multiple server, it is necessary for you to change your PC’s IP address to the same subnet as the LAN IP used by the server. Each
operating system and network software suite will have a different
procedure/application for setting the system IP.
System Setup 16

Under TCP/IP (many Windows 3.1 and 3.11 users), the system IP
and subnet mask are configured under “Setup” in the TCP manager.
In Windows 95, users must go to the Control Panel and Network
settings; Under Network settings, you must modify the TCP/IP
properties for the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
The IP address should be on the same subnet as the local address
assigned to the internet/print multiple server, the subnet mask setting should be the same as the internet/print multiple server, and
the default gateway setting should be the local IP address assigned to
the internet/print multiple server.
Since the principle behind internet/print multiple server technology
is the use of local IP addresses that are never seen or used on public
systems, you must use IP addresses from the ranges below. The following three IP address blocks have been set aside by internet
regulatory authorities specifically for local-only use:
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
All local stations using the server to access the internet must have
an IP address within these three ranges, as well as an IP address on
the same subnet as the internet/print multiple server.
Important: If the server’s IP address is 10.10.1.150, all
local stations must have an IP address as:
10.10.1.xxx, the subnet mask setting must
be the same, and the default gateway of
each station needs to be set to the local IP
address assigned to the internet/print multiple server.
System Setup 17

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
We recommend that you make a note of each device’s IP address for
reference during troubleshooting or when adding new stations or devices.
Using In-Band Telnet to Configure
the Server
Once your PC is configured with an IP address on the same subnet
as the server, start your Telnet program and enter the IP address
assigned to the server when you are prompted for a host address.
You should immediately see the internet/print multiple server Telnet
Interface console greeting screen.
Enter the password to access the device parameters. There is no default password. Once you have access, use the menu item numbers
to set the variables which are described later in this chapter.
Note: When using Telnet to modify device
parameters, saving those parameters
immediately ends the Telnet session.
Using a Browser to Configure the
Server
Once your PC is configured with an IP address on the same subnet
as the server, start your browser program and enter the “http://” pr e-
System Setup 18
fix, followed by the IP address assigned to the server, in the address
window.
You should immediately see the internet/print multiple server web
browser interface menu. Note that the internet/print multiple server
IP can be bookmarked for future access so that it doesn’t need to be
entered each time.
The browser interface uses frames, so it is best if you use a framescapable browser program. Also, we advise you to temporarily suspend the use of proxies – if you are using them – while accessing the
internet/print multiple server as proxy settings may interfere with
browser access to local devices.
If you use a non -frames browser, when you receive the initial internet/print multiple server screen, you should see the main navigation
menu rather than the navigation menu and the system status
screen. The functions are the same, only the appearance will be different.
After you have access to the browser interface, use the menu options
in the left-hand frame to choose the variables you want to view, set
or modify. Some variables have limited options that must be selected
from a pull-down list.
Minimum Configuration
Regardless of how you intend to use the internet/print multiple
server, you will need to consider and set some basic system variables.
This section is concerned with describing only those variables that
are critical to proper functioning of the internet/print multiple
server.
System Setup 19

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
The following variables need to be configured for the internet/print
multiple server to operate correctly (the first is a System variable,
the others are WAN port variables):
DNS IP Address
Domain Name Service (DNS) servers are used on the internet to
maintain information about which Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
name relates to which internet IP address. For example, the URL:
WWW.CNN.COM, is a pseudonym for the IP address: 207.25.71.25.
DNS entries allow users to access resources using URLs instead of
IPs.
Options: Any internet DNS server IP address available
through the WAN connection. This address should be provided by your ISP. (Note that without a DNS server IP,
internet sites will only be available using IP addresses and will
not be available using URLs.)
Default Value: 0.0.0.0
Must Be User Modified? Yes.
Description: A Domain Name Service (DNS) server address is
used to translate URLs into their corresponding IP addresses.
ISP Account -> Phone Number
In order for the internet/print multiple server to control the modem
to dial the phone, you must enter the dial-up phone number for you r
ISP. If you need to dial an area code in order to call the number, it
must be included in this variable. If you must dial “#”, 0, 9 or some
other number in order to get an outside phone connection, that information must be included in how this variable is configured.
System Setup 20

Options: For dial-up connections, the local ISP phone num-
ber, complete without spaces, hyphens or other punctuation
(commas may be used to indicate a pause). The maximum
length is 20 characters.
Example: Your ISP phone number is a local call to 916-5555
and you must dial 0 in order to get an outside line from the office where you want to use the internet/print multiple server.
You would enter 0,,9165555 in the “ISP Account -> Phone
Number” variable. The two commas instruct the modem to
pause between dialing the 0 and dialing the rest of the number. This pause is necessary if there is normally a moment or
two between dialing 0 and getting an outside dial tone.
Default Value: (none)
Must Be User Modified? Yes.
Description: The phone number entered in this variable is
the number the internet/print multiple server will dial to establish its internet (WAN) connection.
Note: If the ISP phone line is busy, the inter-
net/print multiple server will automatically
redial. Three successive redial attempts will
be made.
ISP Account -> User ID
Just as the internet/print multiple server needs to know what phone
number to dial to access your ISP, it also needs to know what username to login under. This variable is the username the ISP has
assigned to you or your company.
System Setup 21

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
Options: Needed for dial-up connections. The ISP assigned
user ID name exactly as provided (i.e., all letters capitalized
where necessary, underscores and other punctuation included).
The maximum length is 16 characters.
Default Value: (none)
Must Be User Modified? Yes.
Description: This variable is the user ID that will be pro-
vided to the ISP once the modem connection is established.
Notes: It may not be possible with some ISPs to use this
variable to allow the internet/print multiple server to automatically login. In that case, it will be necessary to use the
Login Script as described below.
ISP Account -> Password
The password is the final step in the ISP dial-up login process. As
with the username, this password should have been assigned to you
by your ISP when you registered for the service.
Options: For dial-up connections, the ISP user access pass-
word exactly as provided (i.e., all letters capitalized where
necessary, underscores and other punctuation included). The
maximum length is 16 characters.
Default Value: (none)
Must Be User Modified? Yes.
Description: This variable is the user password that will be
provided to the ISP once the modem connection is established
and the username has been accepted.
Notes: It may not be possible with some ISPs to use this
variable to allow the internet/print multiple server to auto-
System Setup 22

matically login. In that case, it will be necessary to use the
Login Script as described below.
Login Script
The login script allows you to list prompts generated by the ISP each
time a user dials-up and then provide the right responses so that the
internet/print multiple server can login. The login script should be
used when the Username and Password variables above don’t work
with your ISP or if your ISP’s login procedure includes additional
prompts (for example, a transmission protocol choice).
Options: For each line item, a prompt string and a keyin
string must be provided. The prompt string is the text displayed by the ISP requesting that something be entered. The
keyin string is what should be entered. Prompt strings can be
up to 25 characters long including punctuation. Keyin strings
can be up to 20 characters long including punctuation (a
maximum of 8 separate line entries).
Example: If your ISP asks you to input a user ID, password,
and to choose from a list of available communications protocols
each time you dial-up, your login script would look like som ething like this:
No. Prompt Keyin
1 Username Andy
2 Password abcd
3 Choice --> 2
With each prompt being the text of the prompt provided by the
ISP, and each keyin being the exact data you would enter.
Default Value: (none)
System Setup 23

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
24
Must Be User Modified? No (unless your ISP login proc e-
dure requires you to use a login script).
Description: A login script is used to provide login prompt
responses when required by the ISP login procedures. Each
line item in the script table should correspond with a prompt
that the ISP makes once the modem connection is established.
The prompt string information entered in the table should include an indication of what data is being asked for at each step
in the login process. Reply string data should be provided exactly as it would be if it were hand entered.
Operation
To access the internet, do the following at each station that will use
the internet/print multiple server for internet access:
1. Make sure that TCP/IP settings are configured properly. IP parameters that must be set:
?? IP Address – must be a unique IP address chosen from the
three reserved IP ranges set aside for local network only use.
See “Setting IP Addresses” earlier in this chapter.
?? Default Gateway – should be set to the IP address assigned
to the internet/print multiple server’s LAN interface.
?? DNS (Domain Name Service) – an IP address provided by
your ISP.
2. Activate your browser and use normally.
System Setup

4
4 C ONFIGURATION
VARIABLES
This chapter provides information about all of the configuration settings available on the internet/print multiple server. Information
about the range of values, default setting, and purpose for each variable is given. Sections and variable order correspond with the menu
listings presented by the internet/print multiple server Telnet console program. Note that those variables which must be user
configured are further detailed in Chapter 3.
System Variables
Server Name
Options: An fifteen -character string of letters and numbers.
Default Value: IS-xxxxxx (where “xxxxxx” is the last six
digits of the device’s MAC address).
Description: The server name is used to identify the inter-
net/print multiple server on network management lists of
active devices.
Configuration Variables 25

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
Local LAN -> IP Address
The Local LAN IP Address variable defines the unique IP address
that your network will use to identify the internet/print multiple
server.
Options: Any IP address from within the local-only ranges
(10.0.0.0.– 10.255.255.255 ; 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 ;
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255).
Default Value: 192.168.100.1
Must Be User Modified? No.
Description: The IP address assigned to the internet/print
multiple server must be consistent with the addresses to be
used by other devices on the network. That is, if the internet/print multiple server address is 192.168.100.1, all other
addresses assigned to local network devices must start with
192.168.100 and have a final number between 2 and 255.
Local LAN -> Subnet Mask
This variable defines the subnet level the internet/print multiple
server will share with other devices on the network.
Options: Any subnet address which identifies a subnet level.
Default Value: 255.255.255.0
Must Be User Modified? No.
Description: The subnet mask is used to identify subgroups
on a LAN. A subgroup is a set of network nodes that can receive broadcast messages (i.e., messages not requiring a
specific IP).
Configuration Variables 26

DNS IP Address
Domain Name Service (DNS) servers are used on the internet to
maintain information about which Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
name relates to which internet IP address. For example, the URL:
WWW.CNN.COM, is a pseudonym for the IP address: 207.25.71.25.
DNS entries allow users to access resources using URLs instead of
IPs.
Options: Any internet DNS server IP address available
through the WAN connection. This address should be provided by your ISP. (Note that without a DNS server IP,
internet sites will only be available using IP addresses and will
not be available using URLs.)
Default Value: 0.0.0.0
Must Be User Modified? Yes.
Description: A Domain Name Service (DNS) server address
is used to translate URLs into their corresponding IP addresses.
Maximum Idle Time
This variable allows you to set an idle time after which the internet/print multiple server will automatically disconnect the WAN
connection. Setting an idle time lets you keep from staying logged-in
to your ISP when no one is using the internet.
Options: A time duration from 3 to 65535 minutes.
Default Value: 30 minutes
Must Be User Modified? No.
Configuration Variables 27

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
Description: The system will automatically disconnect the
WAN link if the port is inactive for the time set.
Operation Mode
Options (sub-menus):
? ?Mode: LAN -to-WAN / LAN-to-LAN; Default is LAN-to-
WAN operation.
? ?LAN-to-LAN Internet Server -> Global IP Address:
Internet/print multiple server’s address for the router
segment when used in LAN -to-LAN mode only.
? ?LAN-to-LAN Internet Server -> Subnet Mask: (as
subnet mask above)
? ?LAN-to-LAN Internet Server -> Default Gateway:
Router’s IP Address.
Default Value: Mode
LAN -to-WAN
=
Description: This option only needs to be changed if the
internet/print multiple server isn’t going to be used to connect
directly to an ISP. Enabling LAN -to-LAN mode automatically
disables the LAN-to-WAN and Server Address Mapping functions.
LAN-to-LAN mode should be used when you need to expand
your LAN but have limited IP addresses available and internet
access is provided via a router.
Note: In LAN-to-LAN mode, you cannot let users
outside of the LAN have access to services
(e.g., Telnet, FTP, or web servers).
Configuration Variables 28

Change Password
Options: An eight-character string of letters and numbers.
Case sensitive.
Default Value: (none – no password)
Must Be User Modified? No (but it is highly recommend to
protect your internet/print multiple server’s settings).
Description: Prevents unauthorized access to the device.
WAN Port Variables
Line Type
Options: Disable, Dialup, Lease Line.
Default Value: Dialup
Description: The WAN port must be configured for use as
either a dial-up connection or a leased-line connection.
Baud Rate
Options: 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, 230400,
460800 bps.
Default Value: 115200 bps
Description: The setting of this variable sets the maximum
bits per second data transmission rate on the line. Generally,
the rate should be set equal to or greater than the maximum
Configuration Variables 29

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
possible transmission rate of the device (e.g., the modem) connected to the WAN port.
ISP Account -> Phone Number
Options: For dial-up connections, the local ISP phone num-
ber, complete without spaces, hyphens or other punctuation
(commas may be used to indicate a pause). The maximum
length is 20 characters.
Default Value: (none)
Description: The phone number entered in this variable is
the number the internet/print multiple server will dial to establish its internet (WAN) connection.
Note: If the ISP phone line is busy, the inter-
net/print multiple server will automatically
redial. Three successive redial attempts will
be made.
ISP Account -> User ID
Options: For dial-up connections, the ISP assigned user ID
name exactly as provided (i.e., all letters capitalized where
necessary, underscores and other punctuation included). The
maximum length is 16 characters.
Default Value: (none)
Description: This variable is the user ID that will be pro-
vided to the ISP once the modem connection is established.
Configuration Variables 30

ISP Account -> Password
Options: For dial-up connections, the ISP user access pass-
word exactly as provided (i.e., all letters capitalized where
necessary, underscores and other punctuation included). The
maximum length is 16 characters.
Default Value: (none)
Description: This variable is the user password that will be
provided to the ISP once the modem connection is established
and the username has been accepted.
ISP Account -> IP Address
Options: The IP address the ISP has assigned to this ac-
count.
Default Value: 0.0.0.0
Description: Dial-up con nections should use address 0.0.0.0
if the IP will be dynamically assigned at each connection.
Otherwise, enter the IP address assigned by your ISP.
Modem AT Command
Options (sub-variables):
? ?Initial String: <AT &F> (default)
? ?Dial Prefix String: <ATDT> (default)
? ?Hangup String: <~~~+++~~~ATH0> (default)
Description: Modem AT commands are used to configure
and operate the modem when it is necessary to control settings
Configuration Variables 31

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
such as the speaker volume, line modulation, or handshaking
protocol.
Note: See your modem user’s guide for informa-
tion about initial string settings and other
modem commands.
Note that the initial string modem command must set the following:
1. Fixed baud rate (i.e., serial data rate adjustment dis-
abled).
2. Data Carrier Detect (DCD) to follow carrier signal
status.
3. Data Set Ready (DSR) to on while the modem is on.
4. Data Terminal Ready (DTR) to off to hang-up.
5. Enable RTS/CTS flow control.
Login Script
Options: For each line item, a prompt string and a keyin
string must be provided. The prompt string is the text displayed by the ISP requesting that something be entered. The
keyin string is what should be entered. Prompt strings can be
up to 25 characters long including punctuation. Keyin strings
can be up to 20 characters long including punctuation (a
maximum of 8 separate line entries).
Example: If your ISP asks you to input a user ID, password,
and to choose from a list of available communications protocols
each time you dial-up, your login script would look like som ething like this:
Configuration Variables 32

No. Prompt Keyin
1 Username Andy
2 Password abcd
3 Choice --> 2
With each prompt being the text of the prompt provided by the
ISP, and each keyin being the exact data you would enter.
Default Value: (none)
Description: A login script is used to provide login prompt
responses when required by the ISP login procedures. Each
line item in the script table should correspond with a prompt
that the ISP makes once the modem connection is established.
The prompt string information entered in the table should include an indication of what data is being asked for at each step
in the login process. Reply string data should be provided exactly as it would be if it were hand entered.
Print Server Variables
The variables listed here are those available for print server control.
Refer to Chapter 5 for more information about setting-up and using
the print server functions of the internet/print multiple server.
Parallel Port -> Port Name
Options: A string of letters and numbers up to 32 characters
long.
Default Value: IS-xxxxxx-P1 (where “xxxxxx” is the last six
digits of the device’s MAC address).
Configuration Variables 33

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
34
Description: An identifying label for the print server port.
Important: If the port will be used for Windows NT 4.0
clients, the port name cannot exceed 12
characters. If the port will be used for LAN
manager clients, the port name cannot exceed eight characters.
Parallel Port -> Speed
Options: High/Low.
Default Value: High
Description: The parallel port speed setting controls the rate
(in general) at which print job data will be transmitted to the
printer. Most newer printers can accept high speed data
transmission; If your printer loses characters, then you may
need to choose low speed mode.
Parallel Port -> PJL Printer
Options: Yes/No.
Default Value: No
Description: If the printer being used is compatible with the
HP PJL (Printer Job Language) protocol, enabling this variable will allow the printer to provide information to the
internet/print multiple server about the printer model, status,
and other details.
Configuration Variables

NetBEUI -> Workgroup Name
Options: A string of letters and numbers up to 15 characters
long.
Default Value: WORKGROUP
Must Be User Modified? No (unless you want the print
server to be assigned to another network group).
Description: Each Microsoft Networking workstation or
server has a workgroup name. Workgroup names determine
what servers and resources will appear by default in lists of
accessible resources. You should assign to the print server the
same workgroup name as the users who will be accessing it
most often.
NetBEUI -> Maximum Connected Stations
Options: A number between 16 and 100.
Default Value: 32
Description: The NetBEUI protocol allows you to limit the
number of connections to a shared printer to prevent queue
overloads.
AppleTalk -> Printer Type
Options: A string of letters and numbers up to 32 characters
long.
Default Value: LaserWriter
Configuration Variables 35

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
Must Be User Modified? No (unless your printer is not a
postscript printer).
Description: The AppleTalk protocol requires that the type
of printer being used be identified. Most postscript printers
should use the “Laserwriter” type.
AppleTalk -> Postscript Level
Options: Level 1, Level 2
Default Value: Level 2
Description: The AppleTalk print protocol requires that
shared postscript printers be identified as to whether they are
Level 1 or Level 2 postscript.
AppleTalk -> Font Group
Options: No font, All fonts, Standard 35, Standard 13
Default Value: Standard 35
Description: The AppleTalk print protocol requires that
shared postscript printers be identified as to what font group is
supported by the printer. Most postscript printers support
Standard 35 (Adobe 35N font set). The option, “No font” will
force Macintoshes to load fonts to the printer, and the option,
“All fonts” will prevent Macintoshes from loading any fonts to
the printer.
Configuration Variables 36

DHCP Server Variables
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allows servers
and devices like the internet/print multiple server to dynamically
assign IP addresses to network devices. Dynamic IP assignment
alleviates the need for the network administrator to maintain and
monitor IP address assignments and simplifies IP use because IP
address are automatically and dynamically assigned when a station
powers-on. DHCP is factory defaulted to OFF.
Important Note: If you use DHCP to set your local
IP addresses, the software IP settings of all
stations on the network will need to be
manually configured to 0.0.0.0., or, as in the
case of Windows 95 users, the “Obtain an IP
address automatically” option under TCP/IP
will have to be selected.
Enable
Options: Yes/No
Default Value: No
Description: This variable is the “on/off” switch for using a
DHCP server. DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
allows IP addresses to be dynamically assigned. Rather than
assigning a specific local IP address to each station, the internet/print multiple server will assign IPs to each station
dynamically if the DHCP server function is enabled.
Configuration Variables 37

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
IP Address Range -> Start
The range of IP addresses available to the internet/print multiple
server for DHCP allocation is set using two variables. This is the
first.
Options: Any IP address within the three reserved IP
ranges. The IP chosen must correlate with the End of the
range.
Default Value: 192.168.100.101
Must Be User Modified? No.
Description: This variable indicates the beginning of the
range of IP addresses available for DHCP use in assigning IPs.
It is paired with the next variable to create an address range.
IP Address Range -> End
This is the second of the DHCP IP address range variables.
Options: Any IP address within the three reserved IP
ranges. The IP address used must correlate with the IP set in
the Beginning range variable.
Default Value: 192.168.100.150
Description: This variable indicates the end of the range of
IP addresses available for DHCP use in assigning IPs. It is
paired with the previous variable to create an address range.
IP Lease Time
Options: An amount of time, measured in minutes, from 5 to
65535.
Configuration Variables 38

Default Value: 1440 (24 hours)
Description: Dynamically assigned addresses can be peri-
odically “refreshed” by a DHCP server. The IP Lease Time
variable allows you to set that time limit. If a time is entered
in this variable, each dynamically assigned address will be recycled at the end of the lease time.
IP Reserve Table
Options: Local IP Address, MAC Address (a maximum of 16
separate line entries).
Default Value: (none)
Description: The IP reserve table specifies ownership of par-
ticular IP addresses by particular stations or servers
(identified by MAC address) so that those IP addresses will not
be used by other devices on the LAN under any circumstances.
(Note that devices listed in the Server Address Variables table
should have their IP addresses listed here if DHCP is going to
be used so that their IP addresses don’t get assigned to other
network stations.)
Server Address Variables
The Server Address Configuration table allows you to setup local
servers, for example an FTP or web site, and provide non -local access
to them through the internet/print multiple server. Entries in the
table associate a port number with the local IP of a particular LAN
server so that users not on the LAN can access that server.
The internet/print multiple server supports virtual internet ser vers
so that your single-point ISP internet access can be used to provide
Configuration Variables 39

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
externally-accessible servers for FTP and HTTP. “Virtual Servers”
in this context are “virtual” because they don’t have their own public
domain IP addresses in the typical internet fashion. Rather, their
local IP address, with an access port number, is listed in a table inside the internet/print multiple server. The port number provides
the internet/print multiple server with the reference to correctly
route data requests.
Note that in LAN-to-LAN mode, this function is disabled and no
LAN devices can be accessed from the internet.
? ? No.
Item number used for entry editing. Maximum of 16 en-
tries.
? ? Local IP Address
The LAN IP address for the server entered. Any resource
which will be shared to the internet through the server
should have a dedicated IP address.
? ? Protocol
The type of server protocol being used: TCP or UDP
? ? Port Number
The server port number assigned to provide outside connec-
tions (from 1 to 65535).
A Server Addr ess Variable table example:
No Local IP Address Protocol Port Number
1 192.168.100.11 TCP 23
2 192.168.100.50 TCP 21
Configuration Variables 40

3 192.168.100.101 TCP 80
Note: The port numbers in the above example are
those commonly used for Telnet, FTP, and
web servers respectiv ely, but the port number should correspond to that assigned when
the server is setup.
System Monitoring
The internet/print multiple server provides a display function which
shows the current setting and operational status of all of its functions. In display mode, it is only possible to view the status of
variables and functions, it is not possible to modify or control them.
Displaying Information
? ?Monitor WAN Port Link
Provides a display of the current WAN port link status (i.e.,
whether or not the WAN port is connected).
? ?Display Configuration
Displays all configuration data for the device (addresses,
ports, links, etcetera). Configuration data is a readout of the
variables that are user -set as described in this chapter.
? ?DHCP Server Status
Configuration Variables 41

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
Displays a table of DHCP servers with the following infor-
mation: IP Address, MAC Address, and Lease Time.
? ?User Connection Status
Displays a table of current user connections with the follow-
ing data: Source IP, Destination IP, Protocol, Path, and Idle.
Each user connected to the internet through the server will
be listed.
? ?Print Server Status
Displays current print server statistics and information on
any jobs currently printing or spooled including their size.
Tools
Each of the management items listed below allows you to ‘force’ some
action. Each of them prompt for confirmation before executing.
? ?Dial Up – Dial the ISP phone access for one or the other
WAN port using the configuration stored under the WAN
port control.
? ?Hang Up – Send the phone disconnect command string to
the modem immediately to end the current session.
? ?Reset – Return the internet/print multiple server’s set-
tings to their state prior to changes made this session and
restart the device.
? ?Factory Reset – Return the internet/print multiple
server’s settings to their original factory values and restart
the device. Note that this will wipe out all information about
how the variables are currently set.
Configuration Variables 42

Navigation Controls
Each of the functions below may be available in various locations and
each is either a configuration control or a navigation control.
? ?Save Configuration – Stores the current settings
into the system firmware. Activation is followed by a prompt
for confirmation.
Note: When using Telnet to modify device
parameters, saving the configuration
immediately ends the Telnet session.
? ?Quit – Quits the current function or the entire manage-
ment system. Activation is followed by a prompt for
confirmation.
? ?Return to Main Menu – Returns the management
console to the first menu screen.
? ?Return to <Previous> Menu – Takes you up one
menu level (generally to the menu immediately preceding
the current menu).
Configuration Variables 43


5
5 P RINT SERVER
F UNCTION
This chapter explains how to use the internet/print multiple server
as a network print server.
Print Server Features
Print servers improve network printing services in three ways:
? ?They pick up the workload of managing print file traffic to
connected printers. This provides workload relief to file ser vers, and allows the file servers’ full capacity to be used for file
access or other direct services to network users.
? ?The internet/print multiple server’s IEEE 1284 compliant,
high-speed, bi-directional parallel printer port can transmit to
high-speed laser printers much faster than a PC's parallel
printer port. A high-speed laser printer can thus be used at its
full capacity.
? ?Because the internet/print multiple server is very portable and
inexpensive compared to a PC-based print server, the printer
Print Server Function 45

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
can be stationed at the location of maximum convenience to
users.
The internet/print multiple server’s print server functionality offers
extraordinary flexibility, operating with most major network operating systems and protocols:
? ?TCP/IP
UNIX lpr/lpd (HP-UX, SunOS, Solaris, SCO, UnixWare, IBM
AIX); Windows NT
? ?NetBEUI
Windows NT, Windows 95/98, Windows for Workgroups, Micro-
soft LAN Manager, IBM LAN Server
? ?AppleTalk
MacOS EtherTalk
The print server configuration, features, and operation can all be
controlled using the same Telnet or browser interface as the WAN
port and other aspects of the internet/print multiple server (see the
previous chapter).
Connecting for Print Service
To connect your printer to the internet/print multiple server, you
should use the standard parallel cable that comes with the printer.
If you need to pu rchase a new parallel cable, be certain that the connectors on both ends of the cable are the right type and that the total
cable length does not exceed 12 feet (approximately 4 meters).
Follow these steps for a trouble-free print-server connection.
Print Server Function 46

1. Confirm proper operation of the printer to be connected to the
internet/print multiple server.
2. When you have confirmed proper operation of the printer,
switch its power off.
3. Confirm that your network is operating normally.
4. Connect the internet/print multiple server to the network
(through the RJ-45 port on the print server’s rear panel).
5. While the printer is power off, install a printer cable to connect
its parallel port to the printer port of the internet/print multiple server.
6. Switch printer power on.
7. Plug the AC power adapter ’s output plug into the power input
socket on the rear panel of the internet/print multiple server.
8. Plug the AC power adapter into an electric service outlet. This
will supply power to the internet/print multiple server. (The
server has no power switch.)
Print Server Configuration
Print server configuration and operation is controlled through the
same Telnet console or browser interface as the WAN port and other
features of the internet/print multiple server. Chapter 4 explains
each operational section of the interface and its variables. Refer to
the section on print server configuration for details. The following
variables and controls are provided for operating and managing the
print server port of the internet/print multiple server:
1. Parallel Port -> Port Name
Print Server Function 47

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
2. Parallel Port -> Speed
3. Parallel Port -> PJL Printer
4. NetBEUI -> Workgroup Name
5. NetBEUI -> Maximum Connected Stations
6. AppleTalk -> Printer Type
7. AppleTalk -> Postscript Level
8. AppleTalk -> Font Group
Print Server Function 48

A
6 T ROUBLESHOOTING
System POST
When the unit is powered on, the system first runs a Power -On Self
Test (POST) as a check of system components. Errors encou ntered
during the POST are indicated by different flashing front panel LED
combinations.
Note: The LEDs flash as a normal part of the sys-
tem initialization. The error flash codes
listed in the table below will be constant and
thus unlike the brief LED indications at initial
power-on.
LED POST Error Indication Table
COM STATE LPT STATE ERROR INDICATED
0 slow flashing slow flashing Need to reload fir m-
ware
1 on on DRAM Error
Troubleshooting 49

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
2 1 long 2 short off Timer INT Error
3 1 long 3 short off Flash Protected
4 1 long 4 short off Flash ID Error
5 1 long 5 short off Flash Erase / Program
Error
6 1 long 6 short off LAN Controller Error
7 1 long 7 short off LAN Memory Error
8 1 long 8 short off IO Controller Error
9 1 long 9 short off LPT Error
10 fast flashing on EEPROM Error
11 1 long 11 short off LAN IO Base Error
Device Installation Problems
WAN
IP ADDRESSES: If you have trouble connecting with or contacting
your ISP, double-check the IP address setting of the internet/print multiple server. Particularly if your ISP is not using
DHCP to dynamically assign IP addresses, make certain that
you are using the right IP for the login you have set.
ACCESS PASSWORD: It is possible that you mis-entered your
ISP login password. Use the Telnet or browser configuration
program to re-enter the login password.
Troubleshooting 50

Print Server
UNSUPPORTED PROTOCOL: The internet/print multiple
server supports the TCP/IP, NetBEUI, and AppleTalk print pr otocols. If your network is using some other print protocol
(NetWare IPX/SPX for example), you will have printing problems. Most platforms should allow you to reconfigure and use a
supported protocol.
LAN
IP ADDRESSES: If stations on your network have trouble connect-
ing with the internet, double check their IP address settings.
Particularly if you are not using the internet/print multiple
server’s DHCP server function, make certain that you are using
only IP addresses from the three reserved ranges and that each
PC’s IP address is within the same subnet as the internet/print
multiple server LAN IP.
Station Configuration Problems
SUSPEND BROWSER PROXIES: When using a browser to con-
figure the internet/print multiple server, we recommend that
you suspend use of proxies until after you have completed the
configuration. If you are using a proxy server on a different
subnet, your browser will have difficulty contacting the internet/print multiple server.
IP ADDRESSES: The PC you are using must have an IP address
on the same subnet as the internet/print multiple server in order
to contact it.
Troubleshooting 51

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
Operating Problems
ISP LOGIN PROCEDURES – LOGIN SCRIPT: It may be neces-
sary for you to create login script entries in order to complete
your login procedure. Some ISPs prompt for a communications
protocol choice or other data after a successful modem connection. Refer to Chapter 4 for more information.
MODEM COMMANDS: It may be necessary for you to reconfigure
the initial modem commands due to operational differences in
your modem. Refer to Appendix C of this User’s Guide and the
documentation provided with your modem for more information.
In particular, check the setting of the initial string for discrepancies with your modem’s operational features.
ISP DETAILS: Double check all ISP login information (i.e., user-
name, password, phone number) for accuracy.
OUTSIDE LINE ACCESS DIALING: If it is necessary for you to
dial a special number in order to dial a phone number outside of
your office, that dialing information will need to be included in
the phone number information provided to the internet/print
multiple server. See Chapters 3 and 4 for more information.
NUMBER OF USERS: While the internet/print multiple server
can handle any number of users, it is recommended that no
more than 50 attempt to access the internet through the device
simultaneously. Note that the more people who access the
internet through the internet/print multiple server the slower
response times will be for all.
Troubleshooting 52

B
7 S PECIFICATIONS
General
Standards: IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T Ethernet repeater, IEEE 802.3u
100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet repeater (Class II); ANSI X3T9.5
Twisted-Pair Transceiver; IEEE 1284 bi-directional parallel interface
Protocol: CSMA/CD
Network Data Transfer Rate: NWay – Fast Ethernet, 100Mbps;
Or Ethernet, 10Mbps
Ports: One RJ-45 NWay LAN port; One RS-232 serial WAN port;
and One 25-pin standard parallel printer port
Network Media: Ethernet: Category 3 or better UTP cable, 100m
maximum; Fast Ethernet: UTP Cat 5 or STP, 100-ohm twisted-pair
100m maximum.
Status LEDs: Pw/Tx (power on/transmit); Link/Rx (connect
o.k./receive); LPT and COM.
Specifications 53

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
54
Environmental and Physical
Power Supply: 12VDC/500mA (external)
Dimensions: 164 x 118.2 x 30 mm (W x L x H)
Weight: 245 grams (approximately 8.6 ounces)
Operating Temp.: 0? to 55?C
Storage Temp.: –25? to 55?C
Humidity: 5% to 95% non -condensing
Emissions: FCC Class A, CE, VCCI Class A, C-Tick
Safety: UL, CSA, CE Mark, TÜV/GS
Specifications

C
8 AT C OMMANDS
The commands provided in the table below are used to control modems and are provided as a supplemental reference to documentation
that should have been included with your modem or fax/modem.
Basic AT Command Set
Each command, except for “+++” and “A/”, must be preceded by “AT”
and ex ecuted when you press the <Enter> key.
Command Var Description
+++ –
A/ –
A –
Bn
0
1
Dstring
P
T
AT Commands 55
Escape to command mode
Repeat last command
Answer command
Protocol for 1200 bps connection
V.22 mode
Bell 212A mode (Default)
Dial Command
Pulse dial, must precede number string
Tone dial, must precede number string

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
W
,
!
;
Fn
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
13
14
15
16
17
Inserted between digit. Wait for dial tone for the
period defined by S7 before dialing.
Inserted between digit. Pause for the period defined by S8.
Flash. Inserted between digit. Cause modem to
go on-hook for 0.5 seconds and return to off-hook.
Command append. Return to command mode
after dialing to allow additional dialing command.
S=n Dial a stored number where n is equal to 0, 1 or 2
corresponding to the slot number.
Select Line Modulation
Auto-detect mode
V.21 or Bell 103
Reserved
V.23
V.22 or Bell 212A 1200 bps line speed
V.22
V.32bis or V.32 4800
V.32 7200
V.32bis or V.32 9600
V.32bis 12000
V.32bis 14400
V.FC 14400
V.FC 16800
V.FC 19200
V.FC 21600
V.FC 24400
AT Commands 56

18
19
Hn
0
1
In
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Ln
0
1
2
3
Mn
0
1
2
3
V.FC 24600
V.FC 28800
Hook Switch
Go on-hook (hang-up)
Go off-hook
Identification Command
Display the product identification code.
Report pre-computed checksum.
Report O.K.
Report firmware revision, model and interface
type.
Report response programmed by an OEM.
Report the country code parameter.
Report modem data pump model and code version.
Speaker Volume
Off
Low (Default)
Medium high
High
Speaker Control
Speaker always off
Speaker on during handshaking and off while re-
ceiving carrier. (Default)
Speaker on during handshaking and while receiv-
ing carrier.
Speaker off during dialing and receiving carrier
and turn speaker on during answering.
AT Commands 57

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
Nn
0
1
On
0
1
P
Qn
0
1
Sn
Sn?
Sn=v
=v
?
T
Vn
0
1
Wn
0
1
Automode Detection – This command interacts
with the F command and should be thus used.
Disabled
Enabled (Default)
Return to Data Mode – after using +++ command
to switch to command mode.
Return to data mode.
Perform equalizer retrain sequence, then return to
data mode. A retrain causes the modem to optimize for the best data transmission. This
command works at speeds of 2400 bps or higher.
Force Pulse Dialing
Modem Responses – Determines whether the m o-
dem returns responses after typing a command.
Send responses to local computer (Default)
Do not send response
Select S-Register as default
Display the value of S-Register n
Change the value of Register n to v
Set default S-Register to value v
Display the value of the default S-Register
Force DTMF dialing
Response Format – Used with Q command.
Numeric response format
Word response format (Default)
Extended Response Code
Report DTE speed in EC mode. (Default)
Report line speed, EC protocol and DTE speed.
AT Commands 58

2
Yn
0
1
Report DCE speed in EC mode.
Long Space Disconnect
Modem does not send or respond to break signals.
(Default)
Modem sends break signals for 4 seconds before
disconnecting.
Extended AT& Command Set
Command Var Description
&Bn
1
&Cn
0
1
&Dn
2
&F
&Hn
0
3
4
&Sn
Data rate, terminal-to-modem
DTE/DCE rate fixed at DTE setting
Carrier Detect signal status
Forced to On continuously (Default)
Follows the status of remote carrier signal
Date Terminal Ready (DTR) operations
DTR off causes modem to hang up
Load the default factory settings
Data flow control, DTE/DCE
Flow control disabled
Hardware (RTS/CTS) flow control
Software (Xon/Xoff) flow control
Data Set Ready (DSR)
AT Commands 59

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
0
DSR overridden, DSR always on
AT Commands 60

D
9 P ORT PINOUTS
This appendix provides pinout data for the internet/print multiple
server’s ports.
Serial Ports
The table below shows the pinouts of the internet/print multiple
server’s 9-pin RS-232 serial port. Consult your modem’s documentation for detailed information on how to physically connect the
internet/print multiple server to it.
Pin Signal Function
1 DCD Data Carrier Detected
2 RxD Received Data
3 TxD Transmitted Data
4 DTR Data Terminal Ready
5 Gnd Signal Ground
6 DSR Data Set Ready
7 RTS Request To Send
8 CTS Clear To Send
9 RI Ring Indicator
Port Pinouts 61

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
Parallel Port
The table below lists the pinouts of the internet/print multiple
server’s 25-pin parallel port connector (identical to the parallel port
connector used on most personal computers), and the corresponding
pin numbers for the 36-pin Cen tronics connector used on most printers.
Signal names beginning with n are active-low signals.
25-pin Centronics Signal Source
1 1 nStrobe Host
2 2 Data 1 Bi-directional
3 3 Data 2 Bi-directional
4 4 Data 3 Bi-directional
5 5 Data 4 Bi-directional
6 6 Data 5 Bi-directional
7 7 Data 6 Bi-directional
8 8 Data 7 Bi-directional
9 9 Data 8 Bi-directional
10 10 nAck Printer
11 11 Busy Printer
12 12 PError Printer
13 13 Select Printer
14 14 nAutoFd Host
15 32 nFault Printer
16 31 nInit Host
17 36 nSelectIn Host
18-25 16, 17, 19-30 Ground
Port Pinouts 62

RJ-45 Port
The RJ-45 port of the device is a LAN port designed to use standard,
straight twisted-pair cabling (with different ratings at different
lengths for Ethernet and Fast Ethernet).
Straight Twisted -Pair Cable Pinouts
Contact MDI-X Signal MDI Signal
1 RD+ (receive) TD+ (transmit)
2 RD- (receive) TD- (transmit)
3 TD+ (transmit) RD+ (receive)
4 Not used Not used
5 Not used Not used
6 TD- (transmit) RD- (receive)
7 Not used Not used
8 Not used Not used
RJ-45 Twisted-Pair Cabling Active Pinout Configuration
Port Pinouts 63


E
10 G LOSSARY
Please note that the terms in this glossary are defined according to
their usage in this document and as part of the field of computer
networking. Any meaning or usage outside of these specific areas
may not be included and is not necessarily implied.
#
100BASE -TX 100Mbps Ethernet LAN communications
standard set by the IEEE (in standard
802.3u); also called “Fast Ethernet.”
100Mbps 100 million bits per second; an expression of
transmission speed in a network.
10BASE-T The original Ethernet LAN communications
standard set by the IEEE (in standard
802.3); a 10Mbps standard.
10Mbps 10 million bits per second; an expression of
transmission speed in a network.
A
Address A number, set of numbers, or name which
uniquely identifies a computer, network device, or network resource.

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
B
Bandwidth The range of frequencies available across a
communications channel; in one sense, the
“size” of the communications channel.
C
Category 3, 4, 5 Communication cabling standards referring
to the quality of the transmission medium
and whether or not the cable includes
transmission shielding.
Collision Simultaneous data transmission on a net-
work medium, resulting in a garbled (and
unreadable) transmission. See “CSMA/CD.”
Collision Domain A section of a network isolated from other
sections by a switch, bridge, or hub that detects and resolves collisions locally so that
there is less impact on the entire network.
CSMA/CD Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Colli-
sion Detection; a network communications
protocol in which each transmission source
(i.e., station, server, switch, etc.) monitors
the main data channel for traffic before and
during transmission, postponing transmission when the data channel is in use.
D
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
DHCP is a protocol that allows IP addresses
to be dynam ically assigned.
Glossary 66

DNS Domain Name Service. DNS entries on
internet DNS servers map site names (also
called, “URLs”) to their actual IP addresses.
E
Ethernet A particular type of LAN described in a
standard (802.3) established by the IEEE,
with 10Mbps data transmission.
F
Fast Ethernet An extension of Ethernet LAN (defined in
standard 802.3u) to allow 100Mbps transmissions.
H
Hub The central device in a star-topology LAN
used to connect each station to the network.
I
IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engi-
neers, an accredited professional group of
scientists and engineers who help set standards for LAN communications tec hnology.
In-band Communications with a network device us-
ing the network medium itself. Contrast
with out-of-band.
Internet Server A device designed to provide internet access
to multiple users at multiple stations but
through a single access point (both a single
ISP and only one public domain IP).
Glossary 67

Internet/Print Multiple Server User’s Guide
ISP Internet Service Provider. ISPs are compa-
nies that provide internet access, often
through a modem-to-modem phone line connection.
L
LAN Local Area Network, an interconnected set
of computers and other devices.
Leased-Line A phone line, usually “rented” from a phone
company, which is dedicated to the sole use
of the “renter.” Internet access speeds are
faster using a leased-line, because there is no
bandwidth sharing.
LED Light Emitting Diode – an electronic device
that lights up when electricity is passed
through it. LEDs are commonly used for
status indicators on electronic devices.
M
Mbps Megabits per second; millions of bits per sec-
ond.
T
TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Pro-
tocol; a suite of transport and network layer
communications protoc ols.
Telnet Terminal emulation for the TCP/IP protocol
suite, used for interacting with remote computers and devices.
Twisted-pair Wire such as is commonly used with tele-
phones consisting of pairs of copper wire
Glossary 68

usually terminating in an RJ-45 or RJ-11
connector.
U
UTP/STP UTP – unshielded twisted-pair, twisted pair
wire without shielding. STP – shielded
twisted-pair, twisted-pair wire with shielding.
W
WAN Wide Area Network, an interconnected set of
computers and other devices spread over a
large geographic area. (Often used synon ymously with “internet.”) Compare, “LAN.”
Glossary 69

INDEX
1
100BASE -TX.....................2, 49, 61
100Mbps ..........................49, 61, 63
10BASE -T..........................2, 49, 61
10Mbps ............................49, 61, 63
A
AppleTalk....................................42
B
bidirectional printer port............41
C
cabling..........................................43
CE...........................................vi, 50
CSMA/CD.............................49, 62
D
DC power adapter .......................43
E
EtherTalk......................................42
F
Fast Ethernet...............2, 49, 61, 63
FCC........................................vi, 50
installation.....................................5
L
LED...............................................64
N
NetBEUI.......................................42
P
pinouts.........................................58
power switch (none)..................43
protocols......................................42
R
Rear Panel......................................8
RJ-45.............................................64
S
specifications ................................1
stack ...............................................5
STP.........................................49, 65
T
TCP/IP..........................................42
U
UTP.........................................49, 65
I
IEEE 1284.....................................41
IEEE 802.3................................2, 49
V
VCCI ......................................vi, 50

W WAN......................................16, 23
 Loading...
Loading...