Page 1

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Cover Page
Page 2

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Table of Contents
i
Contents
Product Overview ........................................................................... 1
Package Contents .......................................................................................................... 1
Features ......................................................................................................................... 1
Product Hardware Features........................................................................................... 2
Application Diagram ...................................................................................................... 3
Switch Installation .......................................................................... 4
Desktop Hardware Installation ...................................................................................... 4
Rack Mount Hardware Installation ................................................................................ 4
Basic Installation ............................................................................................................ 5
Connect additional devices to your switch .................................................................... 6
Configure your switch ..................................................................... 7
Access your switch management page .......................................................................... 7
System Info .................................................................................................................... 7
View your switch status information ................................................................... 7
System ........................................................................................................................... 9
Set your system information ............................................................................... 9
Set your IPv4 settings ........................................................................................ 10
Set your IPv6 settings ........................................................................................ 11
Add IPv6 neighbors ............................................................................................ 12
Set your DNS server settings.............................................................................. 13
Restrict access to switch management page ..................................................... 13
Restrict access to switch management page ..................................................... 14
Change administrator password and add accounts........................................... 15
Enable or disable SNMP and modify idle timeout settings ................................ 16
Set the switch date and time ............................................................................. 17
Enable HTTPS/SSL (Secure Socket Layer) management access ......................... 18
Enable DHCP Auto Configuration....................................................................... 19
View and setup your switch logging .................................................................. 19
Physical Interface ......................................................................................................... 20
Configure your switch ports and view port status............................................. 20
Spanning Tree (STP, RSTP, MSTP) ................................................................................ 22
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol settings ....................................................... 22
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol port settings................................................ 23
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol MST settings (MSTP) ................................... 25
View your Spanning Tree Protocol Instance Information (MSTP) ..................... 26
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol MST Port Settings (MSTP) ........................... 26
Trunk Config (Link Aggregation) .................................................................................. 27
Configure port trunk settings ............................................................................ 27
View your trunk group status information ........................................................ 28
Configure your port priority .............................................................................. 28
Mirroring ..................................................................................................................... 29
Configure port mirror settings ........................................................................... 29
Loopback Detection ..................................................................................................... 30
Enable loopback detection ................................................................................ 30
Static Unicast ............................................................................................................... 31
Add static unicast entries to the switch ............................................................ 31
Static Multicast ............................................................................................................ 32
Add static multicast entries to the switch ......................................................... 32
IGMP Snooping ............................................................................................................ 33
Configure IGMP Snooping Settings .................................................................... 33
Configure IGMP Snooping Router Ports ............................................................ 33
Bandwidth Control ...................................................................................................... 34
Configure Storm Control .................................................................................... 34
Set Ingress Rate Limiting.................................................................................... 35
Set Egress Rate Limiting ..................................................................................... 35
VLAN ............................................................................................................................ 36
Add, modify, and remove VLANs ....................................................................... 36
Configure VLAN Port Settings ............................................................................ 37
Configure the VLAN Forwarding Table Mode .................................................... 38
View the switch VLAN dynamic forwarding table ............................................. 38
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 3

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Table of Contents
ii
Create a private VLAN ........................................................................................ 39
View the current VLAN database ....................................................................... 40
GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protcol) ..................................................................... 40
Enable GVRP ...................................................................................................... 40
Set GVRP port settings ....................................................................................... 41
Set GVRP time settings ...................................................................................... 42
QoS (Quality of Service) ............................................................................................... 43
Set CoS priority settings ..................................................................................... 43
Set Port Priority ................................................................................................. 44
Set DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point) Class Mapping settings ............ 44
Set the Scheduling Algorithm ............................................................................ 45
Configure the IPv6 Traffic Class Priority Settings ............................................... 46
SNMP ........................................................................................................................... 47
Set the SNMP Engine ID ..................................................................................... 47
Configure the SNMP View Table ........................................................................ 47
Configure the SNMP Group Access Table .......................................................... 48
Configure the SNMP User/Group Table ............................................................. 49
Configure the SNMP Community Table ............................................................. 50
Configure the SNMP Trap Management ............................................................ 51
Access Control Config .................................................................................................. 52
Configure Policy Settings ................................................................................... 52
Configure Rate Control ...................................................................................... 56
View your policy database ................................................................................. 57
RMON .......................................................................................................................... 57
Switch Maintenance ..................................................................... 82
Configure Port Access Control ........................................................................... 66
Create Dial-In Users (Local Authentication Method) ......................................... 67
Add RADIUS Servers (RADIUS Authentication Method) .................................... 68
Add TACACS+ Servers (TACACS+ Authentication Method)................................ 69
Destination MAC Filter ...................................................................................... 70
Denial of Service (DoS) ...................................................................................... 71
PoE Configuration ........................................................................................................ 72
Configure PoE settings ....................................................................................... 73
DHCP Snooping ............................................................................................................ 74
Enable DHCP Snooping ...................................................................................... 74
Enable DHCP Snooping ...................................................................................... 75
Set Trusted Interfaces ........................................................................................ 76
Configure Binding Database .............................................................................. 76
LLDP (Link-Layer Discovery Protocol) .......................................................................... 78
Enable and configure LLDP ................................................................................ 78
View LLDP Neighbor Information ...................................................................... 80
Statistic ........................................................................................................................ 80
View Traffic Information Statistics..................................................................... 80
View Error Information Statistics....................................................................... 81
Upgrade your switch firmware .................................................................................... 82
Firmware Upgrade via HTTP Settings ................................................................ 82
Firmware Upgrade via TFTP Settings ................................................................. 83
Enable RMON ..................................................................................................... 57
Configure parameters for RMON Ethernet statistics ......................................... 58
Configure parameters for RMON history control settings ................................. 59
Configure parameters for RMON alarms ........................................................... 60
Configure parameters for RMON events ........................................................... 62
Voice VLAN .................................................................................................................. 63
Create a Voice VLAN .......................................................................................... 64
Configure Voice VLAN OUI settings ................................................................... 65
Security ........................................................................................................................ 66
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Backup and restore your switch configuration settings .............................................. 83
Backup/Restore via HTTP Settings ..................................................................... 83
Backup/Restore via TFTP Settings ..................................................................... 84
Cable Diagnostics Test ................................................................................................. 85
Enable IEEE 802.3az Power Saving Mode .................................................................... 86
Reboot/Reset to factory defaults ................................................................................ 86
Network Connectivity Test (Ping Tool) ........................................................................ 87
Using the Web Smart Switch Management Utility ......................... 88
Page 4

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Table of Contents
iii
System Requirements .................................................................................................. 88
Installation ................................................................................................................... 88
Using the Utility ........................................................................................................... 89
Launching the Utility .......................................................................................... 89
Discovery List ..................................................................................................... 90
Monitor List ....................................................................................................... 90
Device Setting .................................................................................................... 91
Main Menu Options ........................................................................................... 92
Switch Management Page Structure .............................................. 93
Technical Specifications................................................................. 94
Troubleshooting ............................................................................ 96
Appendix ...................................................................................... 97
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 5

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
1
Product Overview
Features
TRENDnet’s 10-Port Gigabit Web Smart PoE+ Switch, model TPE-1020WS, delivers a 20
Gbps switching capacity with eight PoE+ Gigabit ports and two Gigabit Ethernet uplink
ports shared with two SFP slots. This IPv6 ready switch offers advanced traffic
management, troubleshooting, security, energy saving GREENnet, and monitoring
features at a reduced cost.
Hardware Design
Fanless rack mountable housing features eight Gigabit PoE+ ports (automatically
supplies PoE+ (30 Watts) and PoE (15 Watts)) and two Gigabit Ethernet uplink ports
shared with two SFP slots.
IPv6 Ready
This switch supports IPv6 configuration and IPv6 neighbor discovery.
TPE-1020WS
Package Contents
In addition to your switch, the package includes:
Quick Installation Guide
CD-ROM (Utility & User’s Guide)
Power cord (1.8 m / 6 ft.)
Rack mount kit
If any package contents are missing or damaged, please contact the retail store, online
retailer, or reseller/distributor from which the product was purchased.
Traffic Management
A broad range of network configurations are supported by: 802.3ad link aggregation,
Asymmetric VLAN, 802.1Q VLAN, Voice VLAN, GVRP, 802.1p Class of Service (CoS), and
QoS queue scheduling.
Troubleshooting
Real time traffic comparison charts, error group charts, and a convenient cable
diagnostic test aid in rapid troubleshooting.
Security
Features such as ACL, SSL, MAC / port filtering, 802.1X, TACACS+, and RADIUS are
compatible with layered security controls.
Monitoring
RMON, SNMP, SNMP Trap, and Port Mirroring support administrator monitoring
solutions.
Energy Savings
Up to 70% energy saving GREENnet technology
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 6

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
2
On
:
When the Power LED lights on, the device is receiving
power.
Off
:
When the Power turns off or the power cord is not
connected
On (Red)
:
When reaching near the max PoE power budget provided
68W or above, the LED will turn on and the system will
not provide power additional PD (PoE client devices)
after max PoE budget is reached..
Off
:
When the PoE power provided is below the 68W PoE
power budget.
On
:
When the Link/ACT LED lights on, the respective port is
successfully connected to an Ethernet network.
Blinking
:
When the Link/ACT LED is blinking, the port is
transmitting or receiving data on the Ethernet network.
Off : No link.
Green
on
:
When the Green LED lights on, the respective port is
connected to a 1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet network.
Amber
on
:
When the respective port is connected to a 10Mbps or
100Mbps Ethernet network.
Green
:
When the PoE powered device (PD) is connected and the
port supplies power normally.
AC Power Connector
Gigabit
Ports
PoE+ Gigabit
Ports
Reset
Button
Diagnostic
LEDs
SFP
Slots
Product Hardware Features
Rear View
Diagnostic LED Indicators
Power LED
AC Power Connector – Connect the AC power cord to the connector and the
other side into a power outlet. (Input: 100~240VAC, 50/60Hz)
Front View
Reset Button – Press and hold this button for 10 seconds and release to
reset the switch to factory defaults.
PoE+ Gigabit Ports (1-8) – Connect PoE and non-PoE network devices.
Gigabit Ports (9R-10R) – Connect non-PoE devices or uplinks. Disabled
when SFP slots (9-10) are in use.
SFP slots (9-10) – Supports optional 1000BASE-SX/LX mini-GBIC modules.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
PoE MAX (Power over Ethernet Max.)
PoE+ Gigabit Ports (1-8)
L/A: Link/Activity
SPD: Speed
PoE (Power over Ethernet)
Page 7
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
3
Amber
:
PoE port has may have one of the following issues:
PoE power circuit shortage.
Power over current: over the power current of PD’s
classification.
Out of PoE voltage of 44 ~ 57 VDC output.
Cause fail.
Off
No PoE powered device (PD) connected or unplugged the
PoE output port.
On
:
When the Link/ACT LED lights on, the respective port is
successfully connected to an Ethernet network.
Blinking
:
When the Link/ACT LED is blinking, the port is
transmitting or receiving data on the Ethernet network.
Off : No link.
Green
on
:
When the Green LED lights on, the respective port is
connected to a 1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet network.
Amber
on
:
When the respective port is connected to a 10Mbps or
100Mbps Ethernet network
Green on
:
When the mini-GBIC Green LED lights on, the
respective port is inserted mini-GBIC Gigabit
module.
Green blinking
:
When the mini-GBIC Green LED is blinking, the
port is transmitting or receiving data on the
Gigabit network.
Amber on
When the mini-GBIC Amber LED lights on, the
respective port is inserted mini-GBIC 100Mbps
module.
Amber blinking
When the mini-GBIC Amber LED is blinking, the
port is transmitting or receiving data on the
Ethernet network.
Off No link
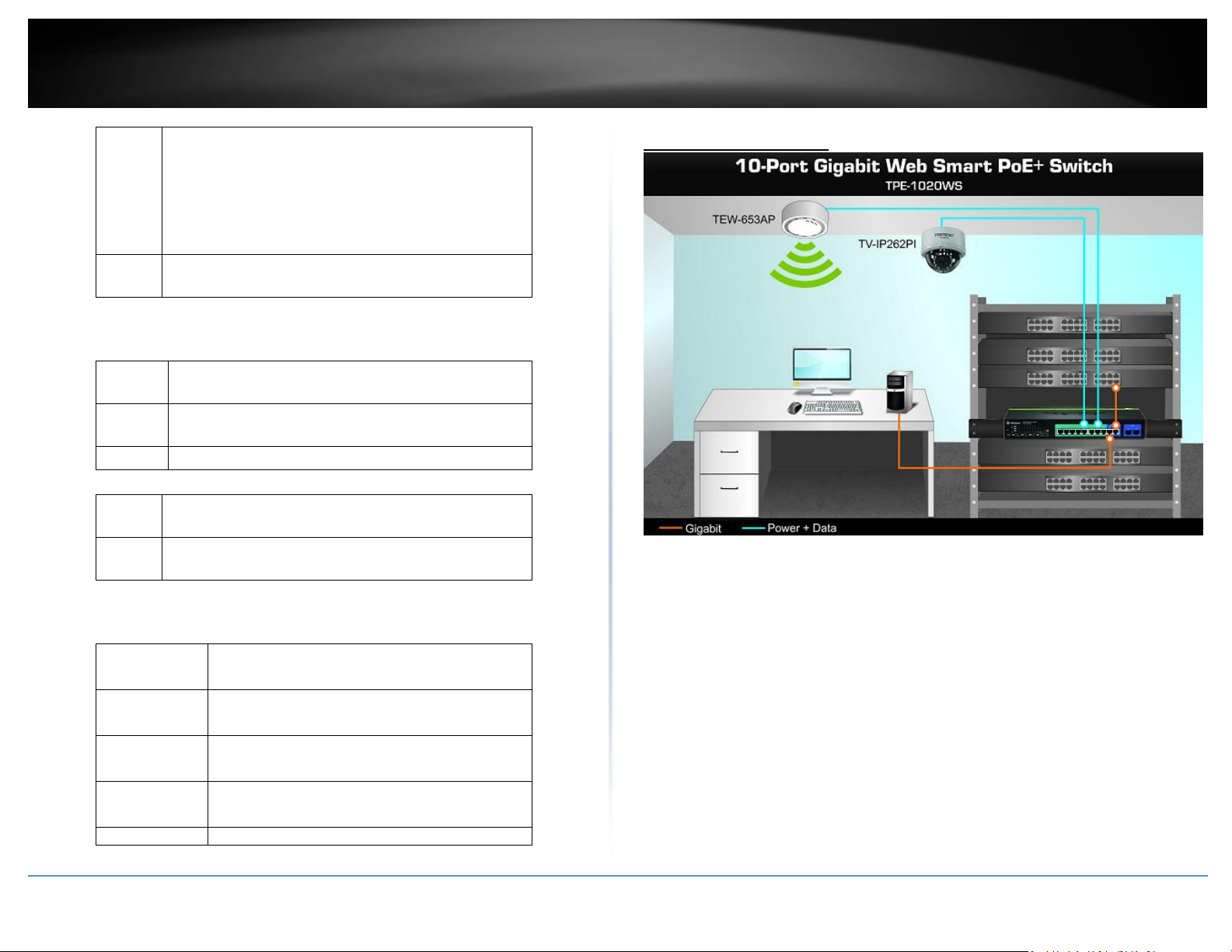
Application Diagram
Gigabit Ports (9R-10R)
L/A: Link/Activity
SPD:Speed
The PoE WebSmart switch is installed a server room within an EIA standard-size, 19-inch rack
SFP Slots Shared (9-10)
SFP
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
The PoE switch supplying power and providing data connectivity to through Ethernet to PoE
devices (access point and IP camera). The PoE connects the PoE devices to your network through
the non-PoE Gigabit Ethernet uplink port to a switch that is connected to your network..
Page 8
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
4
Switch Installation
Desktop Hardware Installation
The site where you install the hub stack may greatly affect its performance. When
installing, consider the following pointers:
Install the Switch in a fairly cool and dry place.
Install the Switch in a site free from strong electromagnetic field generators (such
as motors), vibration, dust, and direct exposure to sunlight.
Leave at least 10cm of space at the front and rear of the hub for ventilation.
Install the Switch on a sturdy, level surface that can support its weight, or in an
EIA standard-size equipment rack. For information on rack installation, see the
next section, Rack Mounting.
When installing the Switch on a level surface, attach the rubber feet to the
bottom of each device. The rubber feet cushion the hub and protect the hub
case from scratching.
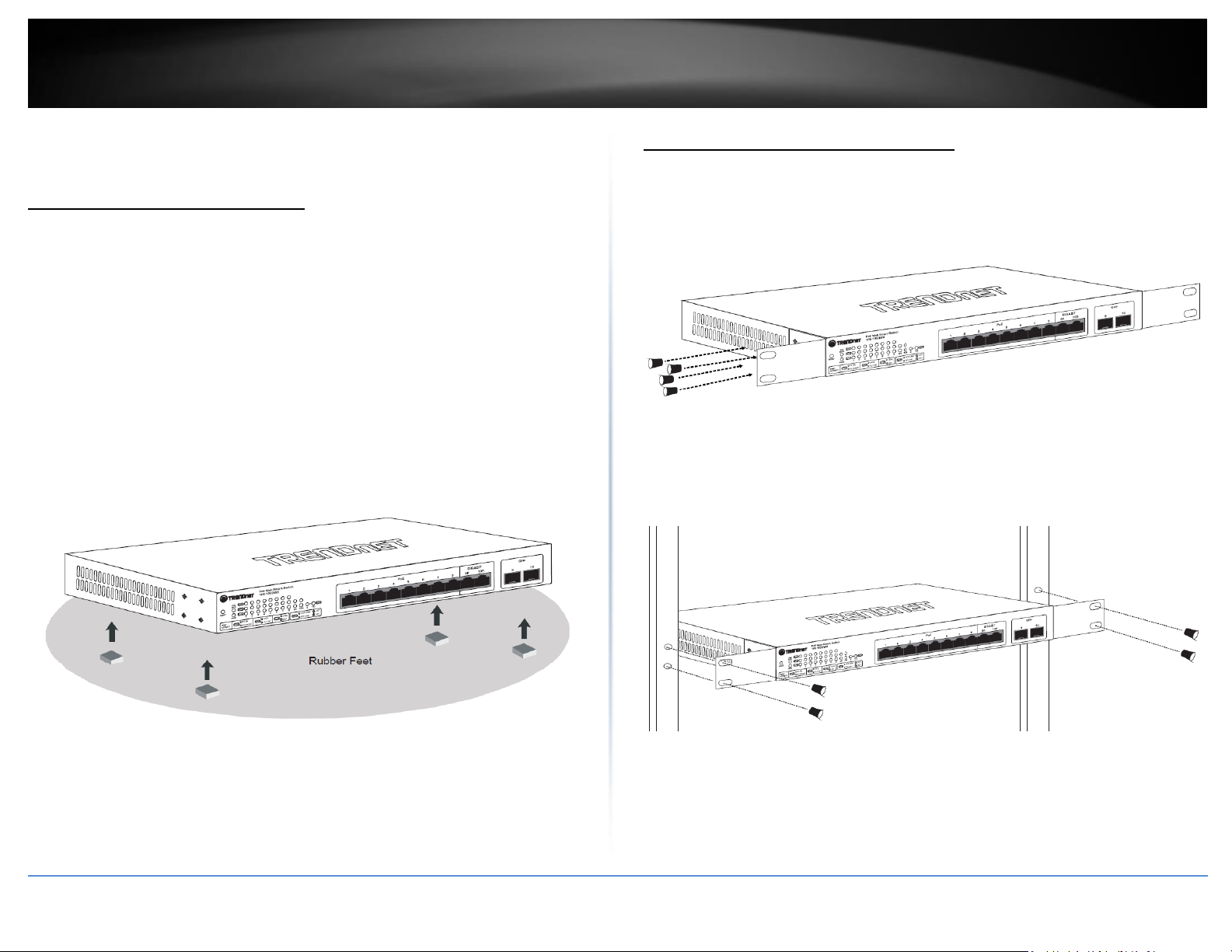
Rack Mount Hardware Installation
The switch can be mounted in an EIA standard-size, 19-inch rack, which can be placed in
a wiring closet with other equipment. Attach the mounting brackets at the switch’s
front panel (one on each side), and secure them with the provided screws.
Then, use screws provided with the equipment rack to mount each switch in the rack.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 9
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
5
Basic Installation
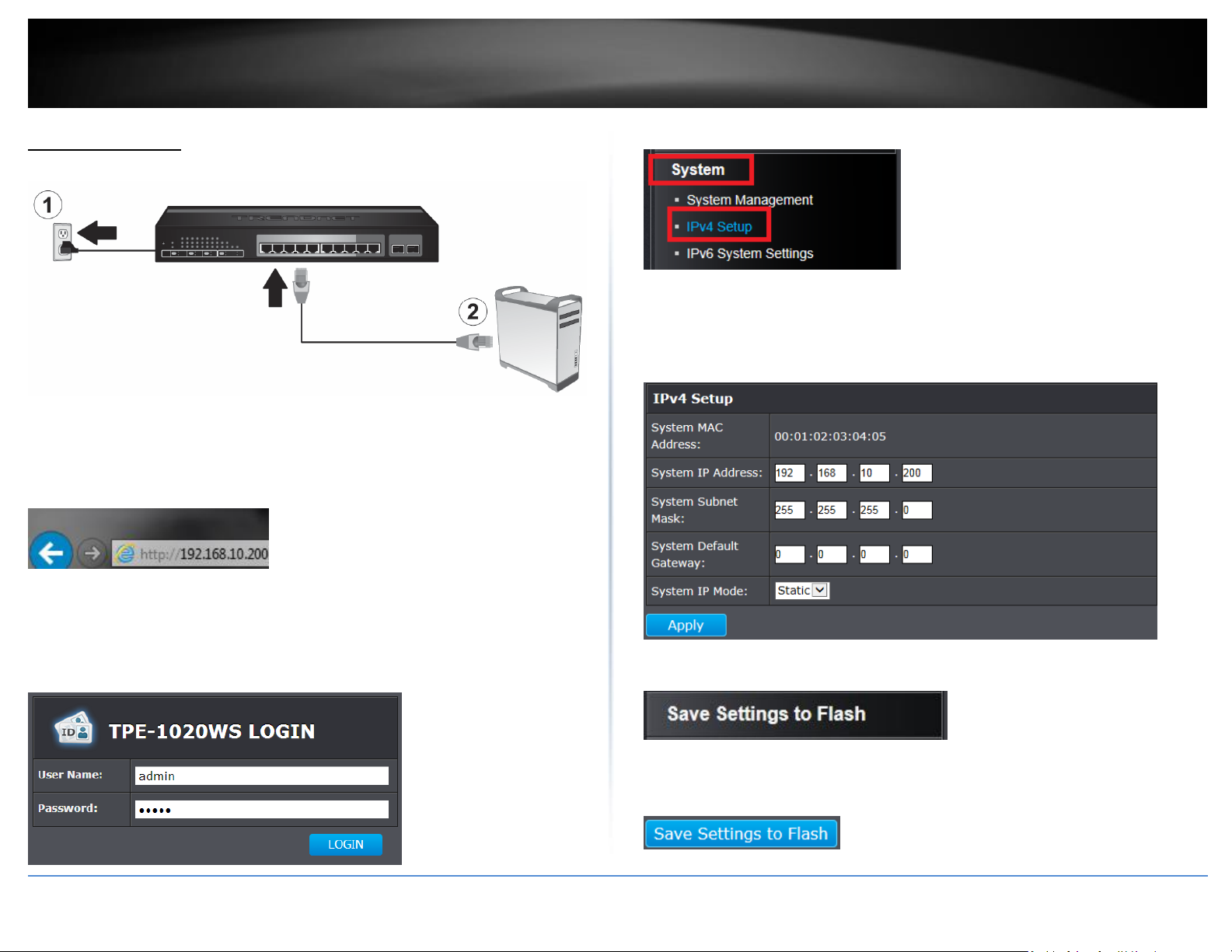
3. Assign a static IP address to your computer’s network adapter in the subnet of
192.168.10.x (e.g. 192.168.10.25) and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
4. Open your web browser, and type the IP address of the switch in the address bar, and
then press Enter. The default IP address is 192.168.10.200.
5. Enter the User Name and Password, and then click Login. By default:
User Name: admin
Password: admin
Note: User name and password are case sensitive.
6. Click System and then click IPv4 Setup.
7. Configure the switch IP address settings to be within your network subnet, then click
Apply.
Note: You may need to modify the static IP address settings of your computer’s network
adapter to IP address settings within your subnet in order to regain access to the switch.
8. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
9.Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: Once the settings are saved, you can connect the switch to your network.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 10
6
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
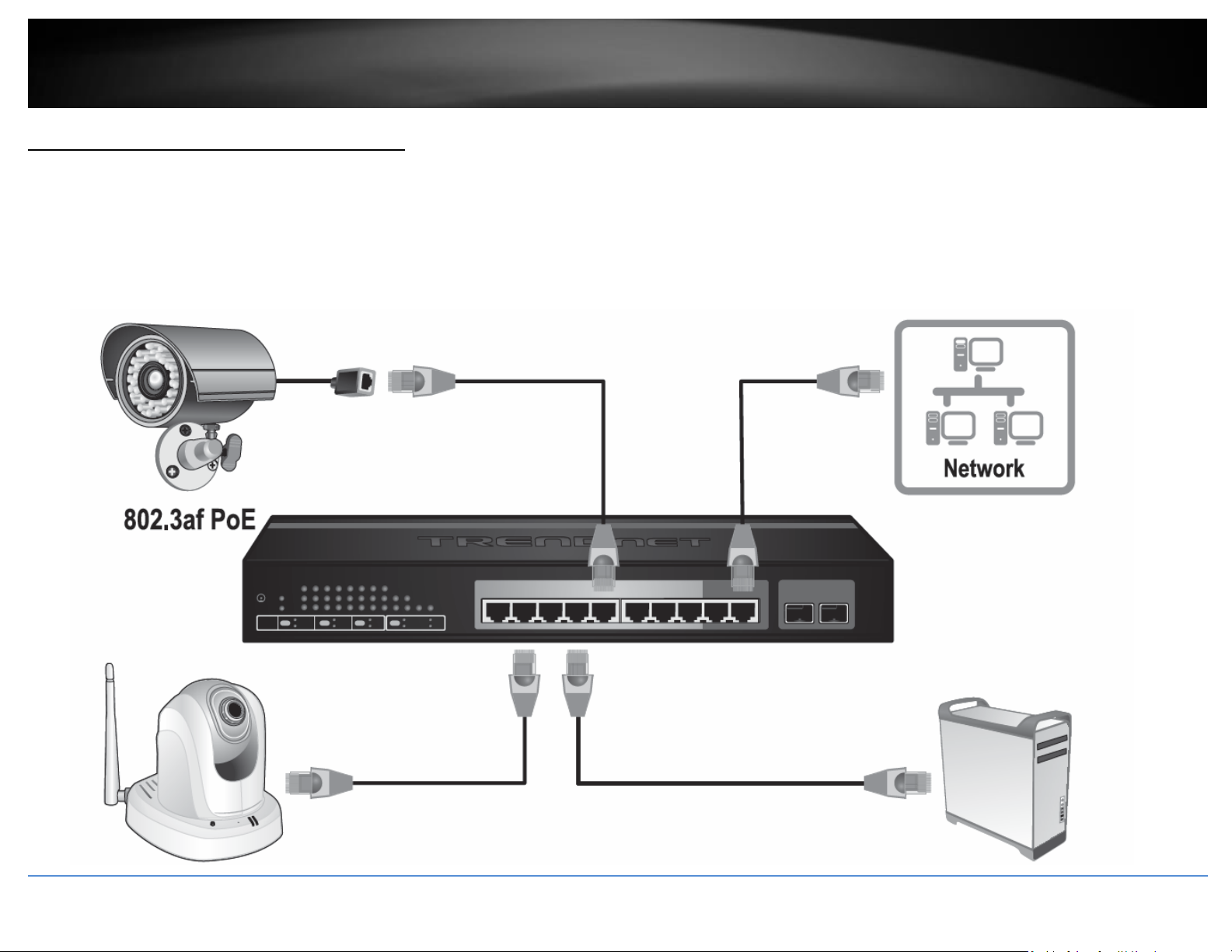
Connect additional devices to your switch
You can connect additional computers or other network devices PoE (Power over Ethernet) or non-PoE devices to your switch using Ethernet cables to connect them to one of the
available PoE+ Gigabit Ports (1-8) or Gigabit ports (9R-10R). Check the status of the LED indicators on the front panel of your switch to ensure the physical cable connection from your
computer or device.
Note: If you encounter issues connecting to your network, there may be a problem with your computer or device network settings. Please ensure that your computer or device network
settings (also called TCP/IP settings) are configured properly within the network subnet your switch is connected.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 11
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
7
Configure your switch
Access your switch management page
Note: Your switch default management IP address http://192.168.10.200 is accessed
through the use of your Internet web browser (e.g. Internet Explorer®, Firefox®,
Chrome™, Safari®, Opera™) and will be referenced frequently in this User’s Guide.
1. Open your web browser and go to the IP address http://192.168.10.200. Your switch
will prompt you for a user name and password.
2. Enter the user name and password. By default:
User Name: admin
Password: admin
Note: User Name and Password are case sensitive.
System Info
View your switch status information
System Info
You may want to check the general system information of your switch such as firmware
version, boot loader information and system uptime. Other information includes H/W
version, RAM/Flash size, administration information, IPv4 and IPv6 information.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on System Info.
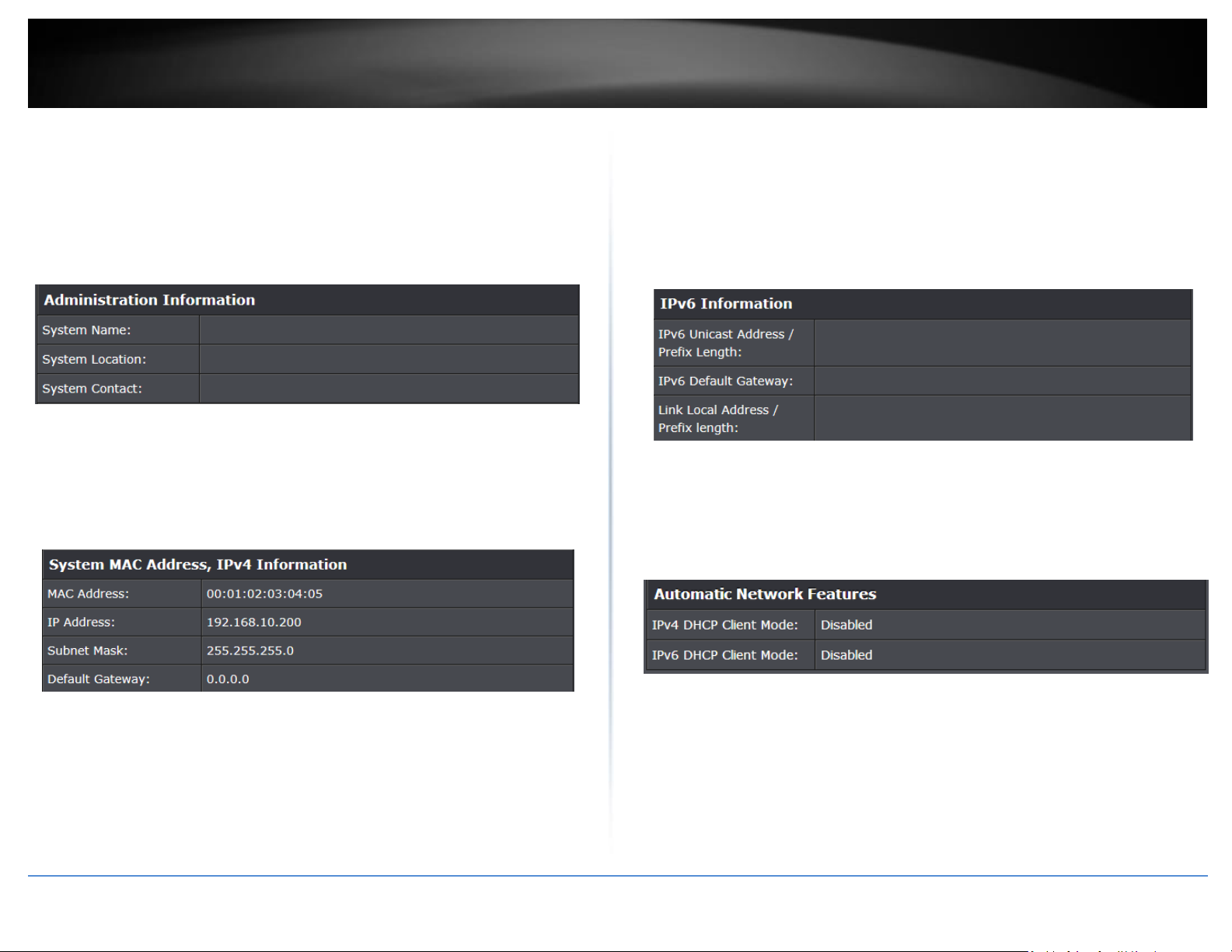
System Information
System Up For – The duration your switch has been running continuously without
a restart/power cycle (hard or soft reboot) or reset.
Runtime Image: The current software or firmware version your switch is running.
Boot Loader – The current boot loader version your switch is running.
Hardware Information
Version: Displays your switch hardware version.
DRAM Size: Displays your switch RAM memory size.
Flash Size: Displays your switch Flash memory size.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 12
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
8
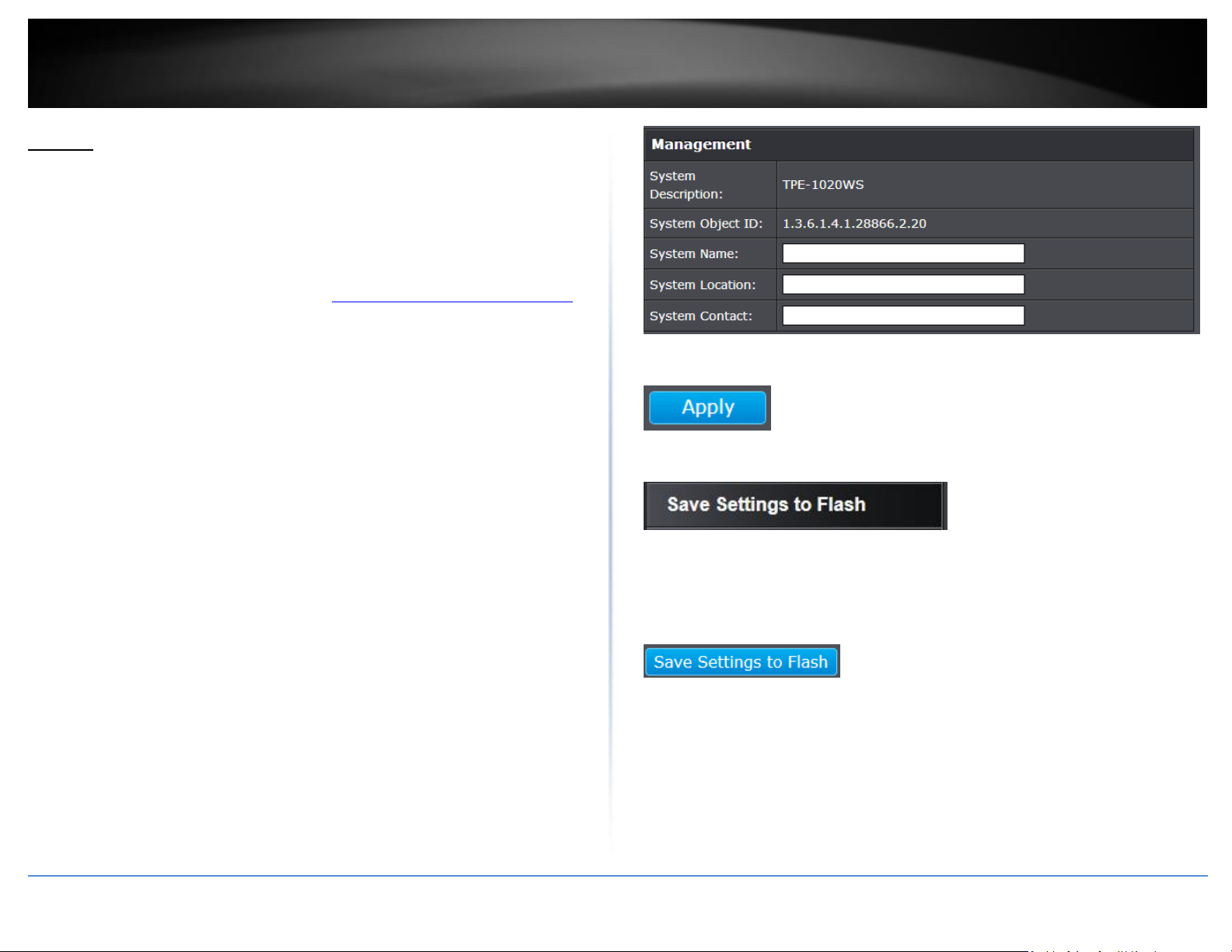
Administration Information
System Name – Displays the identifying system name of your switch. This
information can be modified under the System section.
System Location - Displays the identifying system location of your switch. This
information can be modified under the System section.
System Contact – Displays the identifying system contact or system administrator
of your switch. This information can be modified under the System section.
System MAC Address, IPv4 Information
MAC Address: Displays the switch system MAC address.
IP Address – Displays the current IPv4 address assigned to your switch.
Subnet Mask – Displays the current IPv4 subnet mask assigned to your switch.
Default Gateway – Displays the current gateway address assigned to your switch.
IPv6 Information
IPv6 Unicast Address / Prefix Length: Displays the current IPv6 address and
prefix assigned to your switch.
IPv6 Default Gateway: Displays the current IPv6 default gateway address
assigned to your switch.
Link Local Address / Prefix Length: Displays the current Link Local address and
prefix length assigned to your switch
Automatic Network Features
IPv4 DHCP Client Mode: Displays if your switch IPv4 address setting is set to
DHCP client.
IPv6 DHCP Client Mode: Displays if your switch IPv6 address setting is set to
DHCP client.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 13
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
9
System
Set your system information
System > System Management
This section explains how to assign a name, location, and contact information for the
switch. This information helps in identifying each specific switch among other switches
in the same local area network. Entering this information is optional.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on System, and click on Settings.
3. Review the settings. When you have completed making changes, click Apply to save
the settings.
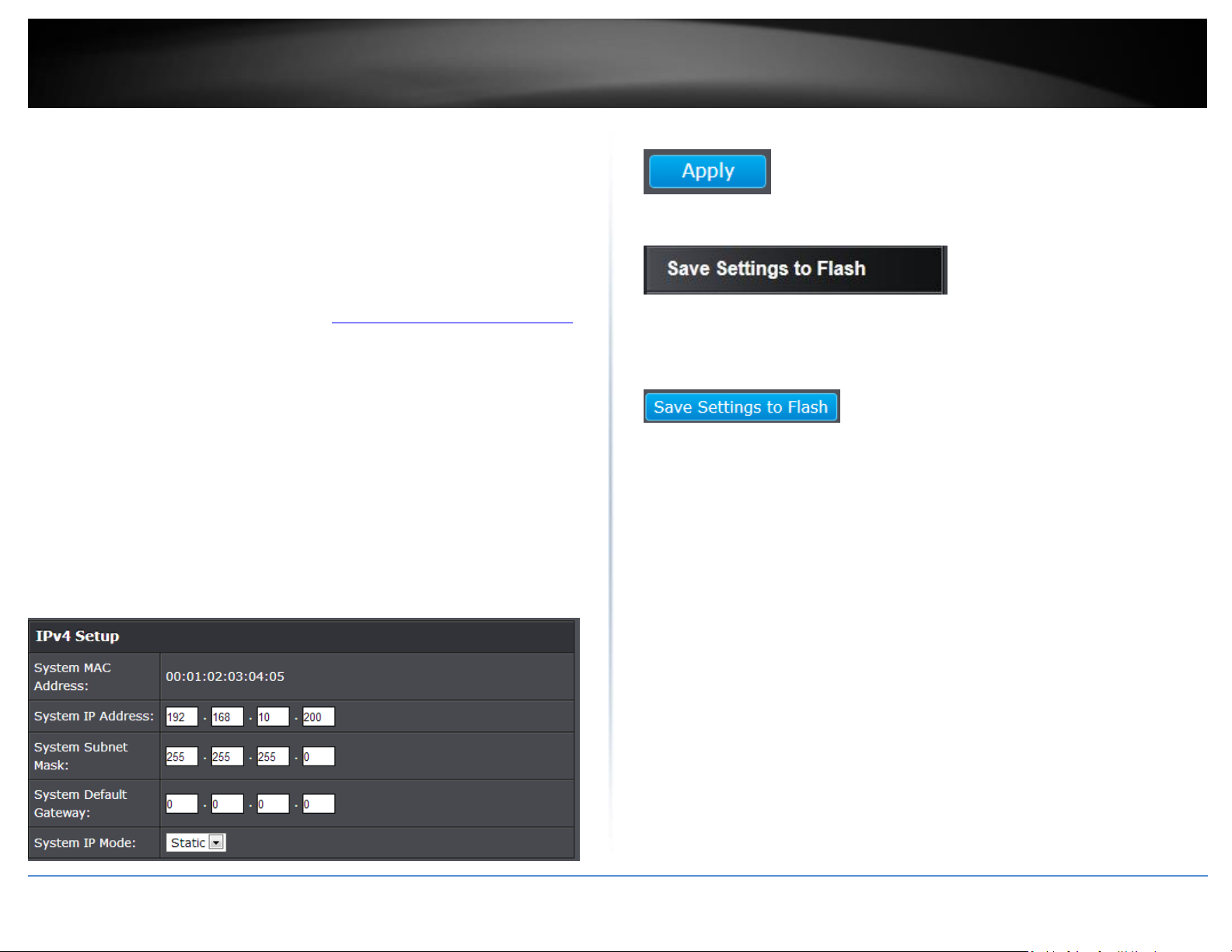
System Description - Specifies the Switch model. You cannot change this
parameter.
System Object ID - Indicates the unique SNMP MIB object identifier that
identifies the switch model. You cannot change this parameter.
System Name - Specifies a name for the switch, the name is optional and may
contain up to 15 characters.
System Location - Specifies the location of the switch. The location is optional
and may contain up to 30 characters.
System Contact - Specifies the name of the network administrator responsible
for managing the switch. This contact name is optional and may contain up to
30 characters.
4. Click Apply.
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
6. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that the
changes are permanent. If you do not complete this step, rebooting or power cycling the
switch will lose all of your current configuration changes.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 14
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
10
Set your IPv4 settings
System > IPv4 Setup
This section allows you to change your switch IPv4 address settings. Typically, the IP
address settings should be changed to match your existing network subnet in order to
access the switch management page on your network.
Default Switch IPv4 Address: 192.168.10.200
Default Switch IPv4 Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on System, and click on IPv4 Setup.
3. Review the settings. When you have completed making changes, click Apply to save
the settings.
System MAC Address: Displays the switch MAC address information.
System IP Address: Enter the new switch IP address. (e.g. 192.168.200.200)
System Subnet Mask: Enter the new switch subnet mask. (e.g. 255.255.255.0)
System Default Gateway: Enter the default gateway IP address. (e.g.
192.168.200.1 or typically your router/gateway to the Internet).
System IP Mode: Click the drop-down list and select Static to manually specify
your IP address settings or DHCP to allow your switch to obtain IP address
settings automatically from a DHCP server on your network.
4. Click Apply.
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
6. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 15
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
11
Set your IPv6 settings
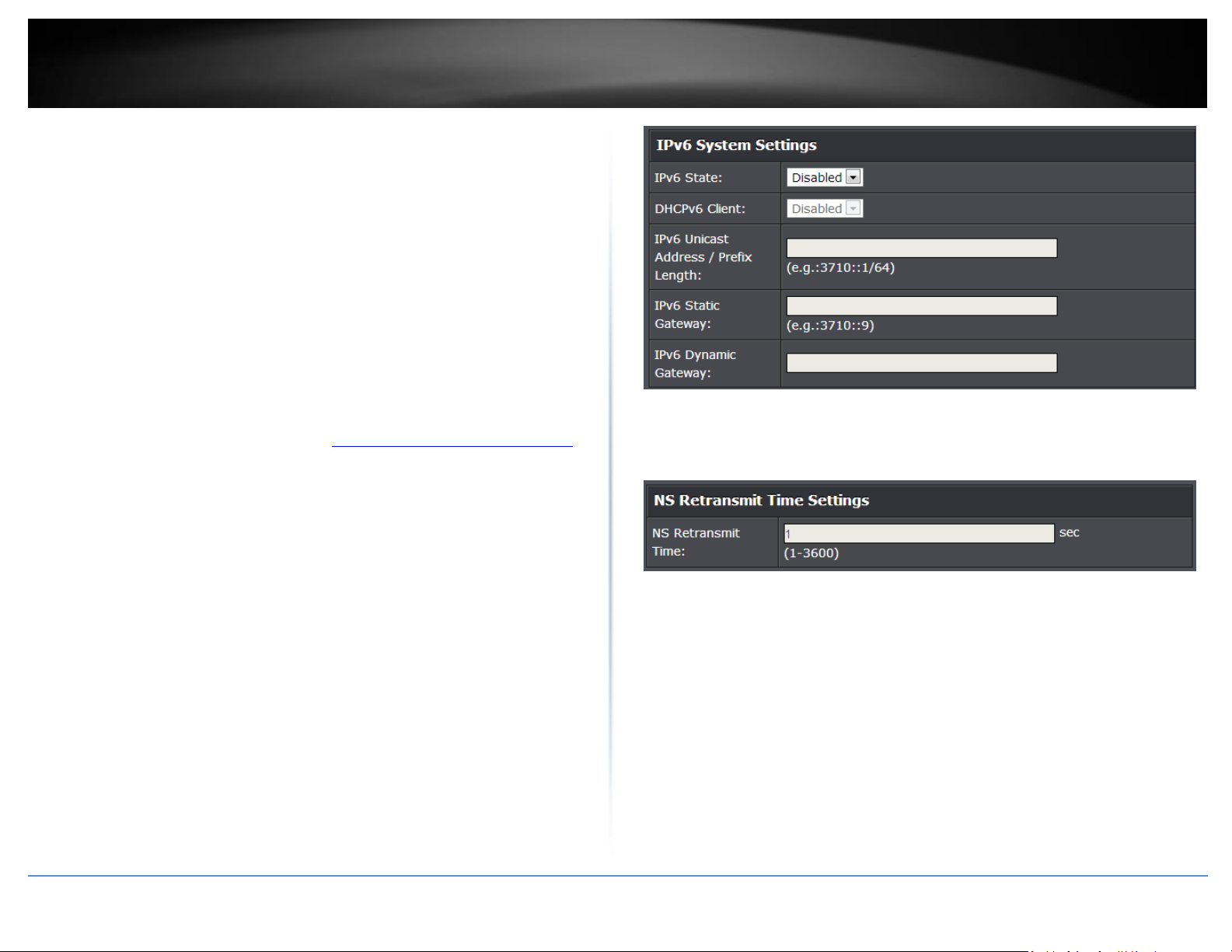
System > IPv6 System Settings
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is a new IP protocol designed to replace IP version 4
(IPv4). The IPv6 address protocol meets the current requirements of new applications
and the never ending growth of the Internet. The IPv6 address space makes more
addresses available but it must be approached with careful planning. Successful
deployment of IPv6 can be achieved with existing IPv4 infrastructures. With proper
planning and design, the transition between IP version 4 and 6 is possible today as well.
Use the IPv6 System Settings page to configure the IPv6 network interface, which is the
logical interface used for in-band connectivity with the switch via all of the switch's
front-panel ports. The configuration parameters associated with the switch's network
interface do not affect the configuration of the front-panel ports through which traffic is
switched or routed.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on System, and click on IPv6 System Settings.
3. Review the settings. When you have completed making changes, click Apply to save
the settings.
IPv6 State: The IPv6 address for the IPv6 network interface is set in auto
configuration mode if this option is enabled. The default value is Disable. Auto
configuration can be enabled only when DHCPv6 is not enabled on any of the
management interfaces. DHCPv6 Client: This option only displays when
DHCPv6 is enabled.
IPv6 Unicast Address / Prefix Length: The IPv6 Unicast Address is an identifier
for a single interface, on a single node. A packet that is sent to a unicast
address is delivered to the interface identified by that address. Add the IPv6
prefix and prefix length to the IPv6 System Settings interface.
IPv6 Static Gateway: Specifies the corresponding Gateway of the IP address
entered into the field.
IPv6 Dynamic Gateway: To configure the switch to automatically obtain its IP
configuration from a DHCP server on your network.
NS Retransmit Time Settings: A constant that defines a nonzero number of
seconds between periodic reauthentication of the client. The field is 1~3600
seconds. The default setting is 1 second.
Link Local Address Settings: A link-local address is an IPv6 unicast address that
can be automatically configured on any interface using the link-local prefix
FE80::/10 (1111 1110 10) and the interface identifier in the modified EUI-64
format. Link-local addresses are used in the neighbor discovery protocol and
the stateless autoconfiguration process. Nodes on a local link can use link-local
addresses to communicate; the nodes do not need globally unique addresses
to communicate. IPv6 devices must not forward packets that have link-local
source or destination addresses to other links.
Automatic Link Local Address: A link local address has a prefix of FE80, is not
routable, and can be used for communication only on the local network. Only
one link local address is supported. If a link local address exists on the interface,
this entry replaces the address in the configuration.
Link Local Address/Prefix length: Enter the Link Local Address/Prefix Length.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 16

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
12
Link Layer MAC Address: Specifies the link layer MAC address.
Click Add to save the entry to the list.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
You can type in the specific address and click Find to find the entry to modify or
click Delete or delete the address. If the entries span multiple pages, you can
navigate page number in the Page field and click Go or you can click First,
Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
Add IPv6 neighbors
System > IPv6 Neighbor Settings
This settings allows you to manually define IPv6 supported neighboring devices on your
network.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on System, and click on IPv6 Neighbor Settings.
3. Review the settings. When you have completed making changes, click Apply to save
the settings.
Neighbor IPv6 Address: Specifies the neighbor IPv6 address.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Page 17
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
13
Set your DNS server settings
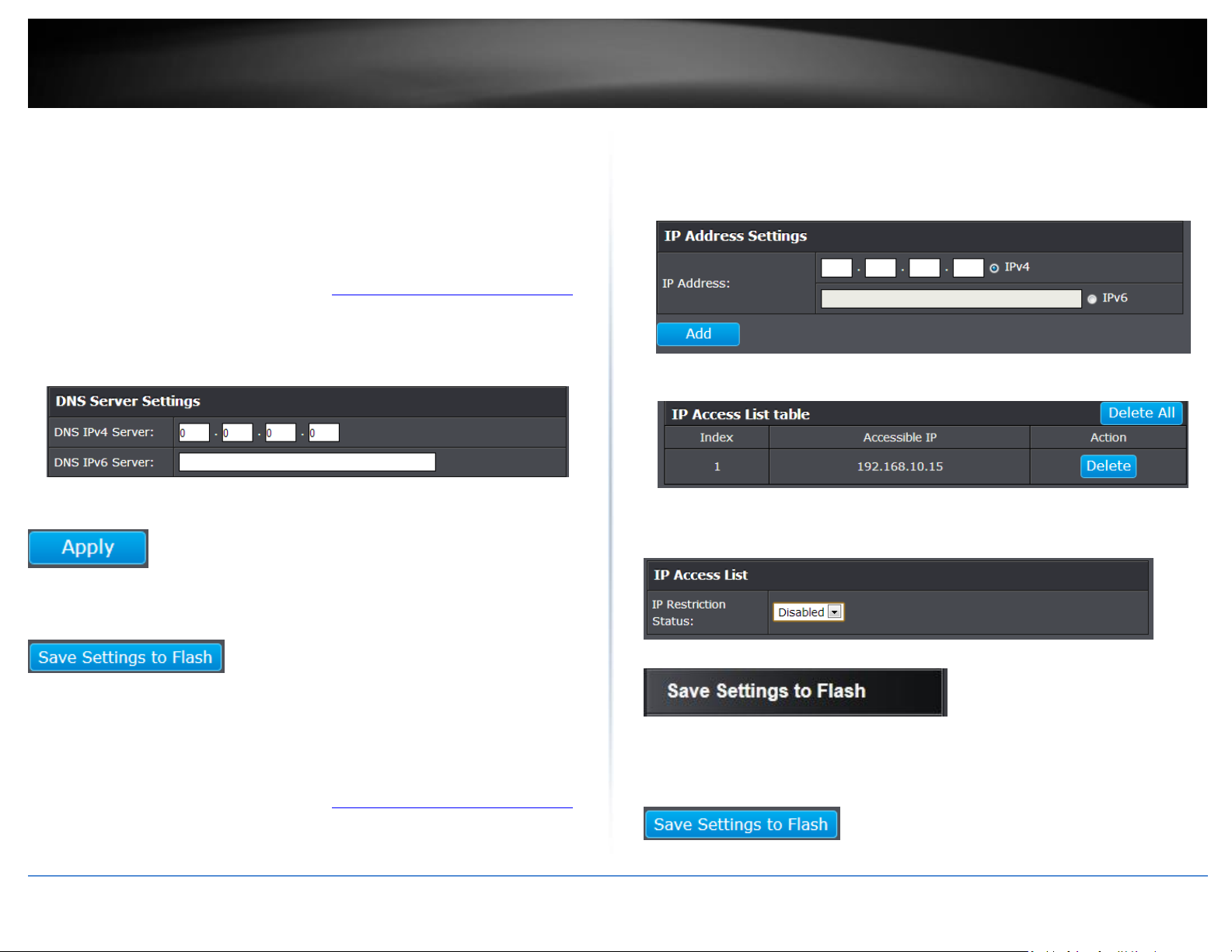
System > DNS Settings
This setting allows you to configure your IPv4/IPv6 DNS server settings for the purpose
or resolving hostnames. For example, when specifying your SNTP server time settings
via domain name, the switch will not be able to resolve the SNTP domain name specified
until you configure the switch DNS server setting.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on System, and click on DNS Settings.
3. Enter your DNS IPv4 Server address and/or DNS IPv6 Server address in the provided
fields.
2. Click on System, and click on IP Access List.
3. Review the settings.
First, enter the IPv4 or IPv6 address to allow access and click Add for each entry.
For each entry, the access list will populate. You can click Delete next to the entry to
delete the entry or Delete All to delete all entries in the table.
4. Click Apply to save the settings.
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Restrict access to switch management page
System > IP Access List
This section allows you to define or restrict access to the switch management page to a
list of specific IP addresses.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
When you have completed entering the IPv4 and IPv6 address entries, click the IP
Restriction Status drop-down list at the top and select Enabled, then click Apply.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK. Note: This step saves all
configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the switch is rebooted or power
cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Page 18

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
14
Restrict access to switch management page
System > IP Access List
This section allows you to define or restrict access to the switch management page to a
list of specific IP addresses.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on System, and click on IP Access List.
3. Review the settings.
First, enter the IPv4 or IPv6 address to allow access and click Add for each entry.
For each entry, the access list will populate. You can click Delete next to the entry to
delete the entry or Delete All to delete all entries in the table.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
When you have completed entering the IPv4 and IPv6 address entries, click the IP
Restriction Status drop-down list at the top and select Enabled, then click Apply.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 19
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
15
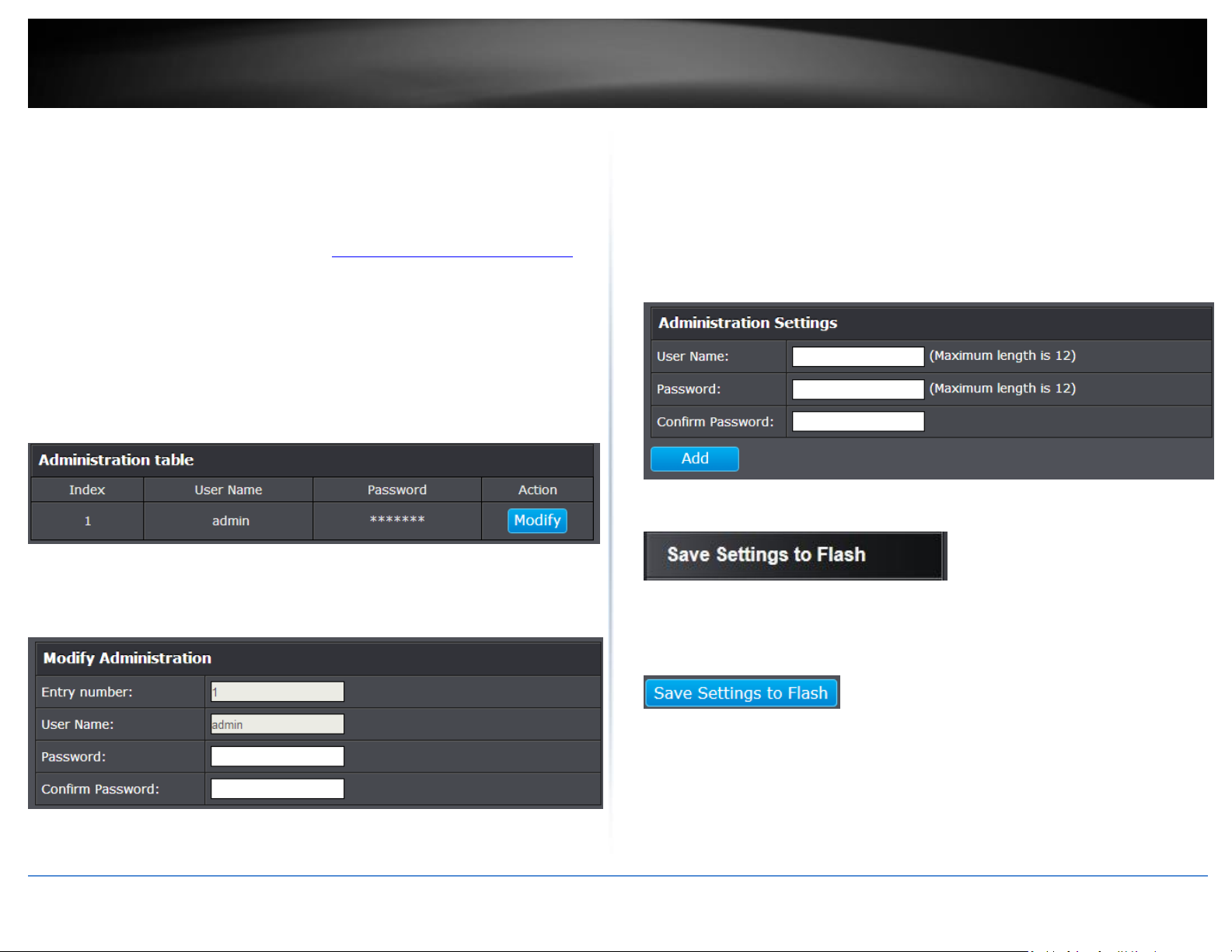
Change administrator password and add accounts
System > Administration
This section explains how to change the administrator password create additional
administrative user accounts for access to the switch management page.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on System, and click on Administration.
3. Review the settings.
To change the administrator password, in the “admin” entry in the table, click on
Modify. Note: This default administrator account cannot be deleted.
In the Password field, enter the new password and enter the new password again the
Confirm Password field to verify. Then, click Apply.
Note: The password consists of up to 12 alphanumeric characters.
To create additional administrative user accounts:
User Name: Enter the user name of the new account.
Password: Enter the password for the new acocunt and enter the password
again the Confirm Password field to verify. Then, click Add to add to the table.
For additional user accounts, you will be provided the option to Modify or
Delete to remove the account.
Note: The password consists of up to 12 alphanumeric characters.
.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 20

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
16
Enable or disable SNMP and modify idle timeout settings
System > User Interface
This section explains how to enable SNMP on the switch and modify the switch
management page idle timeout settings.
Note: If you disable the SNMP on the switch, the switch will not be manageable via
SNMP using MIBs.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on System, and click on User Interface.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save changes.
SNMP Agent: Click the drop-down list to one of the following options.
o Enabled - When you enable this parameter, the SNMP agent is active.
You can manage the switch with SNMP network management
software and the switch’s private MIB.
o Disabled - When you enable this parameter, the SNMP agent is
inactive.
Web Server Status – Displays the current SNMP status.
Web Idle Timeout - Enter the idle period in minutes, when the switch will
automatically log out a user from the switch management page.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 21
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
17
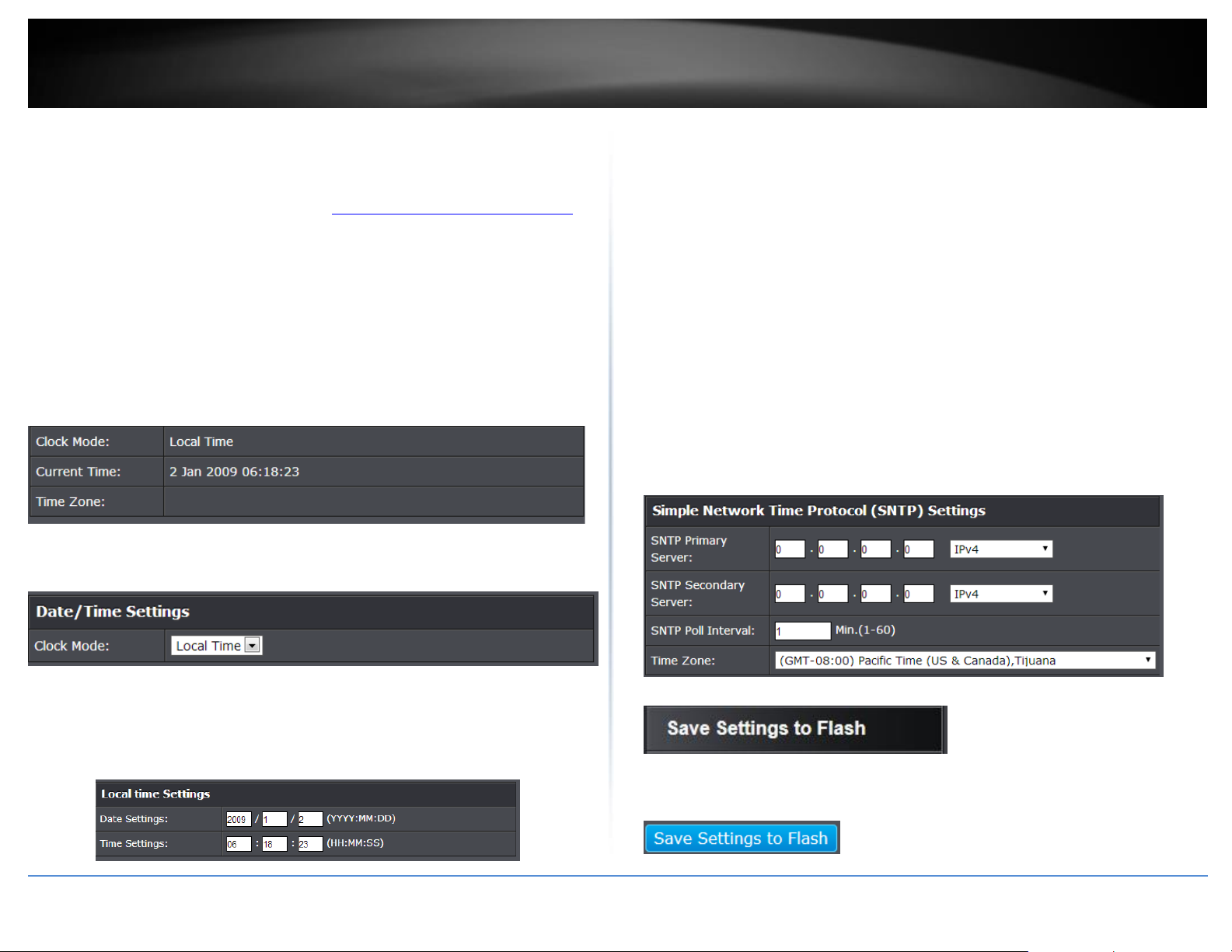
Set the switch date and time
System > System Time
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on System, and click on System Time.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save changes.
Clock Mode - Displays if system time and date is set manually Local Time or
obtained automatically from a network time server SNTP.
Current Time – Displays the current system time and date.
Time Zone – Displays the current system time zone.
Clock Mode: Select Local Time to manually configure your date and time
settings or select SNTP to configure your switch to automatically obtain
settings from an network time server.
o SNTP – Allows you to configure your switch to pull time and date
settings automatically from a network time server. If selecting this
option, under Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) Settings, enter
your time server settings.
Note: Please note that in order for the switch to communicate to
Internet SNTP time servers, the switch must have valid IPv4/IPv6
address settings including a default gateway address for Internet
access. Additionally, if using a domain name, the switch must be
configured with valid DNS server settings in order to resolve
host/domain names.
SNTP Primary Server – Enter the primary network time server
IPv4 address, IPv6 address, or Domain Name.
SNTP Secondary Server – Enter the secondary network time
server IPv4 address, IPv6 address, or Domain Name..
SNTP Poll Interval – Enter the interval time when your switch
will update the time and date settings with the time server.
Time Zone – Click the drop-down list to select your time
zone. Additionally, you can set your Daylight Savings Time.
o Local Time – Allows you to manually set the time settings. If selecting
this option, under Local Time Settings, manually enter your date and
time settings.
Date Settings – Enter your date settings (YYYY/MM/DD).
Time Settings – Enter your time settings (HH:MM:SS)
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK. Note: This step saves all
configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the switch is rebooted or power
cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Page 22
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
18
Enable HTTPS/SSL (Secure Socket Layer) management access
System > SSL Settings
By default, your switch management page can be accessed using standard web HTTP
protocol which is unsecure. Enabling HTTPS/SSL management access allows access to
the switch management page using secure encrypted communication which prevents
unauthorized users from intercepting user name and password credentials. Typically,
the switch is accessed within the local network only by system administrators which
does not necessarily require additional security. It is recommended to only enable this
feature, if allowing switch management access from other networks or over the
Internet.
Note: Once HTTPS/SSL management access is enabled, HTTP management access will be
disabled forcing all access to the switch management page using secure encryption
communication only.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on System, and click on SSL Settings.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save changes.
SSL Status:
o Enabled – Enables HTTPS/SSL management access and disables HTTP
unsecured mode.
o Disabled – Disabled HTTPS/SSL management access and enabled HTTP
unsecured mode. (Default setting).
Click Continue, Proceed to this website, and accept the certificate if prompted.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
If enabling SSL management access, you will need to access the switch management
page using HTTPS instead of HTTP. (e.g. https://192.168.10.200)
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 23
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
19
Enable DHCP Auto Configuration
System > DHCP Auto Configuration
If you need to automatically update the switch configuration files via a remote server,
the DHCP Auto Configuration feature is available for this purpose via the DHCP server.
Your IP address settings must enable the DHCP client so that this feature can operate
with your DHCP server.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on System, and click on DHCP Auto Configuration.
3. Click the Auto Configuration State drop-down list and select Enabled. Click Apply to
save changes.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
View and setup your switch logging
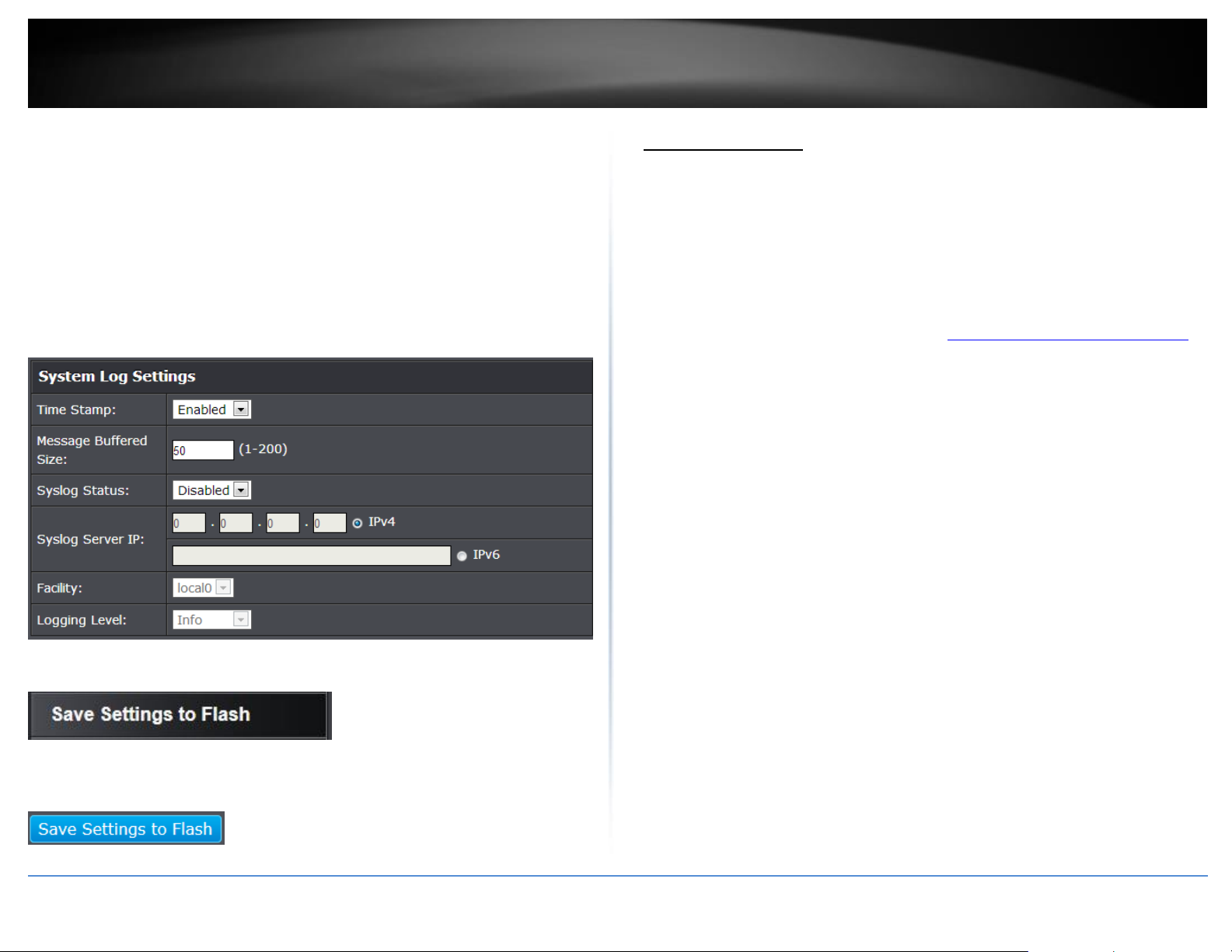
System > System Log Settings
The system log is designed to monitor the operation the switch by recording the event
messages it generates during normal operation. These events may provide vital
information about system activity that can help in the identification and solutions of
system problems.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on System, and click on System Log Settings.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save changes.
Time Stamp
o Enable - Each event message recorded in the log will have a time
stamp.
o Disable - No time stamp will be included with the event messages.
Message Buffered Size - Enter the message buffer size. (Range: 1-200)
Syslog - Allows you to send device logging to an external log (Syslog) server for
troubleshooting or monitoring.
o Syslog Status –
Enable – Enable syslog and in the Syslog Server IP section,
enter the IPv4 or IPv6 address of the external syslog server to
send logging.
Disable – Disable syslog functionality.
o Facility - Click the drop-down list and which facility to store the
logging. (Options: local0 – local7)
Note: You can define the facility to store logging on your external
syslog server. This helps to ensure you have separate logging sections
for different devices.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 24
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
20
o Logging Level – Click the drop-down list to select what level of event
messages that will be logged.
0 Emergency - The system is unusable.
1 Alert - Action must be taken immediately.
2 Critical - Critical conditions are displayed.
3 Error - Error conditions are displayed.
4 Warning - Warning conditions are displayed.
5 Notice - Normal but significant conditions are displayed.
6 Informational - Informational messages are displayed
7 Debug - Debug-level messages are displayed.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Physical Interface
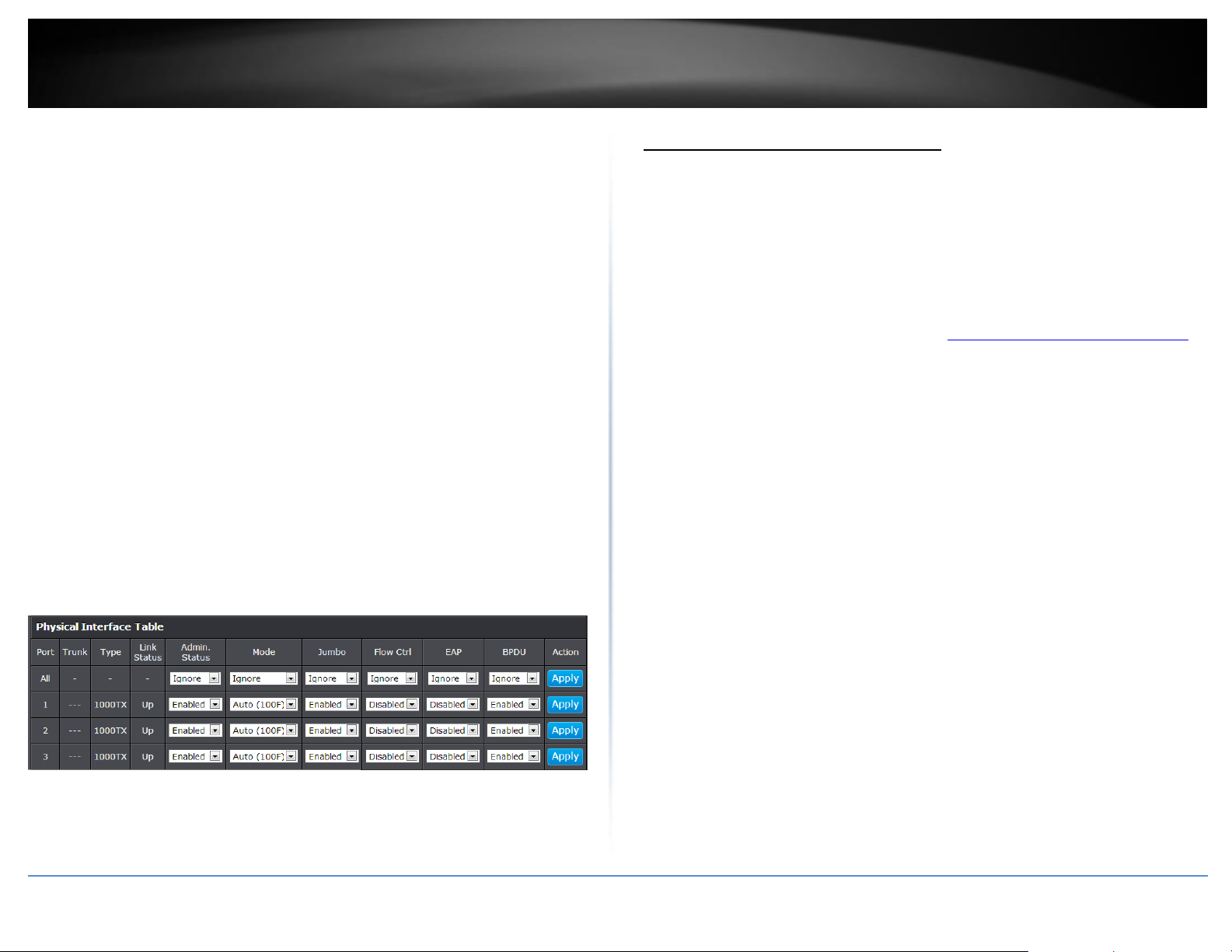
Configure your switch ports and view port status
Physical Interface
This section allows you to configure the physical port parameters such as speed, duplex,
flow control, and jumbo frames. This section also reports the current link status of each
port and negotiated speed/duplex. Additionally you will be able to set your BPDU ports
for Spanning Tree Configuration and EAP ports for 802.1x port-based authentication
configuration.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Physical Interface.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save changes.
Port - Specifies the port number. The All value indicates ports 1 through 10 on
the Switch. You cannot change this parameter. You can use the All row value in
the Port column to apply Admin Status, Mode, Jumbo, Flow Contrl, EAP, BPDU
settings to all ports at the same time.
Trunk - This parameter indicates the trunk group number. A number in this
column indicates that the port has been added to a trunk using static or
dynamic 802.3ad LACP link aggregation.
Type - This parameter indicates the port type. On the Switch, the port type is
1000TX for 10/100/1000Base-T twisted-pair ports (1 through 8, 9R and 10R)
and 100FX or 1000TX for the SFP ports (9 and 10) for copper or fiber SFP type.
Link Status - This parameter indicates the status of the link between the port
and the end node connected to the port. The possible values are:
o Up -This parameter indicates a valid link exists between the port and
the end node.
o Down -This parameter indicates the port and the end node have not
established a valid link.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 25

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
21
Admin. Status: This parameter indicates the operating status of the port. You can use
this parameter to enable or disable a port. You may want to disable a port and prevent
packets from being forwarded if a problem occurs with the node or cable connected to
the port. You can enable the port to resume normal operation after the problem has
been fixed. You can also disable an unused port to secure it from unauthorized
connections. The possible values are:
o Ignore -This parameter applies to the All row only and indicates that
the Admin. Status field must be set individually for each port.
o Enabled - This parameter indicates the port is able to send and receive
Ethernet frames.
o Disabled - This parameter indicates the port is not able to send and
receive Ethernet frames.
Mode: This parameter indicates the speed and duplex mode settings for the
port. You can use this parameter to set the speed and duplex mode of a port.
The possible settings are:
o Ignore -This parameter indicates that the All setting does not apply to
the Mode field. In other words, each port is set individually.
o Auto -This parameter indicates the port is using Auto-Negotiation to
set the operating speed and duplex mode. The actual operating speed
and duplex mode of the port are displayed in parentheses (for
example, “1000/F” for 1000 Mbps full duplex mode) after a port
establishes a link with an end node.
o Auto (1000F) -This parameter indicates the port is configured for
1000Mbps operation in Auto-Negotiation mode.
o 1000/Full -This parameter indicates the port is configured for
1000Mbps operation in full-duplex mode.
o 100/Full -This parameter indicates the port is configured for 100Mbps
operation in full-duplex mode.
o 10/Full -This parameter indicates the port is configured for 10Mbps
operation in full-duplex mode.
o 1000/Half -This parameter indicates the port is configured for
1000Mbps operation in half-duplex mode.
o 100/Half -This parameter indicates the port is configured for 100Mbps
operation in half-duplex mode.
Note: When selecting a Mode setting, the following points apply:
Jumbo: This parameter i Indicates whether or not jumbo frames can be
Flow Ctrl: Flow Control, This parameter reflects the current flow control setting
o 10/Half -This parameter indicates the port is configured for 10Mbps
operation in half-duplex mode.
o When a twisted-pair port is set to Auto-Negotiation, the end node should
also be set to Auto-Negotiation to prevent a duplex mode mismatch.
o A switch port using Auto-Negotiation defaults to half-duplex if it detects
that the end node is not using Auto-Negotiation. This can result in a
mismatch if the end node is operating at a fixed duplex mode of full-duplex.
To avoid this problem when connecting an end node with a fixed duplex
mode of full-duplex to a switch port, disable Auto-Negotiation on the port
and set the port’s speed and duplex mode manually.
o The only valid setting for the SFP ports is Auto-Negotiation.
accepted by the switch. You may want to activate jumbo frames when your
switch will transmit video and audio files. The possible values are:
o Ignore -This parameter i Indicates that the All setting does not apply
to the Jumbo field. In other words, each port is set individually.
o Enabled -This parameter i Indicates the port is permitted to accept
jumbo frames.
o Disabled -This parameter i Indicates the port is not permitted to
accept jumbo frames.
Note: When QoS is enabled on a port, the Jumbo frame parameter can not be
enabled.
on the port. The switch uses a special pause packet to notify the end node to
stop transmitting for a specified period of time. The possible values are:
o Ignore - This parameter indicates that the All setting does not apply to
the Flow Control field. In other words, each port is set individually.
o Enabled - This parameter indicates that the port is permitted to use
flow control.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 26
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
22
o Disabled - This parameter indicates that the port is not permitted to
use flow control.
EAP: This parameter reflects the current Extensible Authentication Protocol
(EAP) setting on the port. The possible values are:
o Ignore - This parameter indicates that the All setting does not apply to
the EAP field. In other words, each port is set individually.
o Enabled - This parameter indicates that the port is able to send and
receive EAP packets.
o Disabled - This parameter indicates that the port is disabled and is not
able to send or receive EAP packets.
BPDU: This parameter reflects the current BPDU setting on the port.The
possible values are:
o Ignore - This parameter indicates that the All setting does not apply to
the BPDU field. In other words, each port is set individually.
o Enabled - This parameter indicates that the switch will pass BPDU
frames through the switch and broadcast them through all other
ports.
o Disabled - This parameter indicates that the switch will not pass BPDU
frames through the switch, With RSTP or STP enabled, the switch will
receive BPDU frames and process them according to the spanning tree
protocol.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Spanning Tree (STP, RSTP, MSTP)
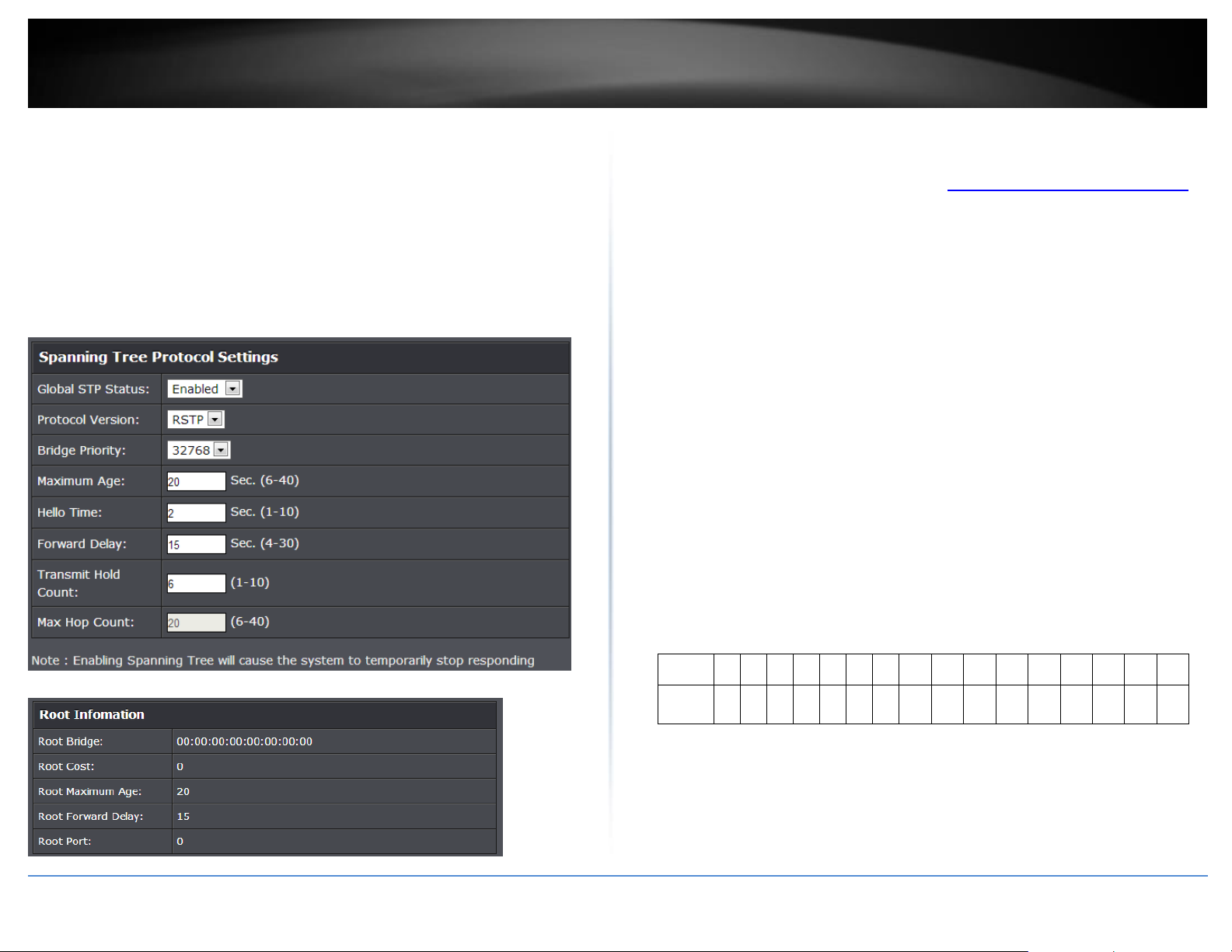
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol settings
Bridge > Spanning Tree > Protocol Settings
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) provides network topology for any arrangement of
bridges/switches. STP also provides a single path between end stations on a network,
eliminating loops. Loops occur when alternate routes exist between hosts. Loops in an
extended network can cause bridges to forward traffic indefinitely, resulting in
increased traffic and reducing network efficiency.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save changes.
Global STP Status: Select the STP state on the device. The possible field values
are:
o Disable – Disables STP on the device. This is the default value.
o Enable – Enables STP on the device.
Protocol Version: Specifies the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) mode to enable
on the switch. The possible field values are:
o STP – Enables STP 802.1d on the device.
o RSTP – Enables Rapid STP 802.1w on the device. This is the default
value.
o MSTP – Enables Multiple STP 802.1s on the device.
Bridge Priority: The Bridge Priority has a range 0 to 61440 in increments of
4096. To make this easier for you, the Web Management Utility divides the
range into increments. You specify the increment that represents the desired
bridge priority value.
Maximum Age: The Maximum Age defines the amount of time a port will wait
for STP/RSTP information. MSTP uses this parameter when interacting with
STP/RSTP domains on the boundary ports. Its range is 6 - 40 seconds
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 27
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
23
Step
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Port
Priority
0
16
32
48
64
80
96
112
128
144
160
176
192
208
224
240
Hello Time: The Hello Time is frequency with which the root bridge sends out a
BPDU.
Forward Delay: The Forward Delay defines the time that the bridge spends in
the listening and learning states. Its range is 4 - 30 seconds.
Transmit Hold Count: The Transmit Hold Count specifies the maximum number
of BPDUs that the bridge can send per second. Its range is 1 - 10.
Max Hop Count: The Max Hop Count is a parameter set in a BPDU packet when
it originates. It is decremented by 1each time it is retransmitted by the next
bridge. When the Hop Count value reaches zero, the bridge drops the BPDU
packet. Its range is 6 - 40 hops.
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol port settings
Bridge > Spanning Tree > Port Settings
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on Spanning Tree, and click on Port Settings.
3. Review the settings. For each entry, click Apply to save changes.
STP Status: Indicates if spanning tree protocol is active or not on the port.
Select one of the following choices from the pull-down menu:
o Enable - The spanning tree protocol is enabled on the port.
o Disabled - The spanning tree protocol is disabled on the port. Enable
Disable
Note: BPDU passthrough must be disabled for all ports under Physical
interface for STP can be enabled.
Priority: Indicates the port priority. If two paths have the same port cost, the
bridges must select a preferred path. In some instances this can involve the use
of the port priority parameter which is used as a tie breaker when two paths
have the same cost.
The range for port priority is 0 to 240. As with bridge priority, this range is
broken into increments, in this case multiples of 16. To select a port priority for
a port, you enter the desired value. Table 1 lists the values that are valid.
Valid Port Priority Values
In addition, this section also displays the spanning tree root information.
Admin Cost (0 = Auto): The administratively assigned value for the contribution
of this port to the path cost of paths towards the spanning tree root. Writing a
value of '0' assigns the automatically calculated default Path Cost value to the
port. If the default Path Cost is being used, this object returns '0' when read.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 28

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
24
External Cost: This defines a metric that indicates the relative cost of
forwarding packets to the specified port list. Port cost can be set automatically
or as a metric value. Define a value between 1 and 200000000 to determine
the external cost. The lower the number, the greater the probability the port
will be chosen to forward packets. The default port cost: 100Mbps port =
200000. Gigabit port = 20000.
State – Displays the current port spanning tree state.
o Blocking - A blocking state does not allow network traffic to be sent or
received on a the port except for BPDU data. A port with a higher path
cost to the root bridge than another on the switch causes a switching
loop and is placed in the blocking state by the Spanning Tree
algorithm. The port’s state may change to the forwarding state if the
other links in use fail and the Spanning Tree algorithm determines the
port may transition to the forwarding state.
o Listening - This state occurs on a port during the convergence process.
The port in the listening state processes BPDUs and awaits new
information that would cause the port to return to the blocking state.
o Learning - While the port does not yet forward frames (packets), in
this state the port does learn source addresses from frames received
and adds them to the filtering (switching) database.
o Forwarding - A port that both receives and sends data. This indicates
normal operation. STP continues to monitor the port for incoming
BPDUs that indicate the port should return to the blocking state to
prevent a loop.
o Disabled - This state is not strictly part of STP. However, a network
administrator can manually disable a port.
Edge: Indicates if a port is connected to an edge device in the network topology
or not. Selecting the Forcetrue parameter designates the port as an edge port.
Edge ports cannot create loops, however an edge port can lose edge port
status if a topology change creates a potential for a loop. An edge port
normally should not receive BPDU packets. If a BPDU packet is received, it
automatically loses edge port status. Selecting the Forcefalse parameter
indicates that the port does not have edge port status. Selecting the Auto
parameter indicates that the port have edge port status or not have edge port
status automatically. The default setting for this parameter is Auto.
P2P: Choosing the Forcetrue parameter indicates a point-to-point (P2P) shared
link. P2P ports are similar to edge ports however they are restricted in that a
P2P port must operate in full-duplex.
Like edge ports, P2P ports transition to a forwarding state rapidly thus
benefiting from RSTP. A P2P value of Forcefalse indicates that the port cannot
have P2P status. Auto allows the port to have P2P status whenever possible
and operate as if the P2P status were true. If the port cannot maintain this
status, (for example if the port is forced to half-duplex operation) the P2P
status changes to operate as if the P2P value were Forcefalse.
The default setting for this parameter is Auto.
Restricted Role: Toggle between True and False to set the restricted role state
of the packet. If set to True, the port will never be selected to be the Root port.
The default value is False.
Restricted TCN: Toggle between True and False to set the restricted TCN of the
packet. Topology Change Notification (TCN) is a BPDU that a bridge sends out
to its root port to signal a topology change. If set to True, it stops the port from
propagating received TCN and to other ports. The default value is False.
Migrate: Indicates if the port is configured to accept RSTP and STP BPDUs.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 29
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
25
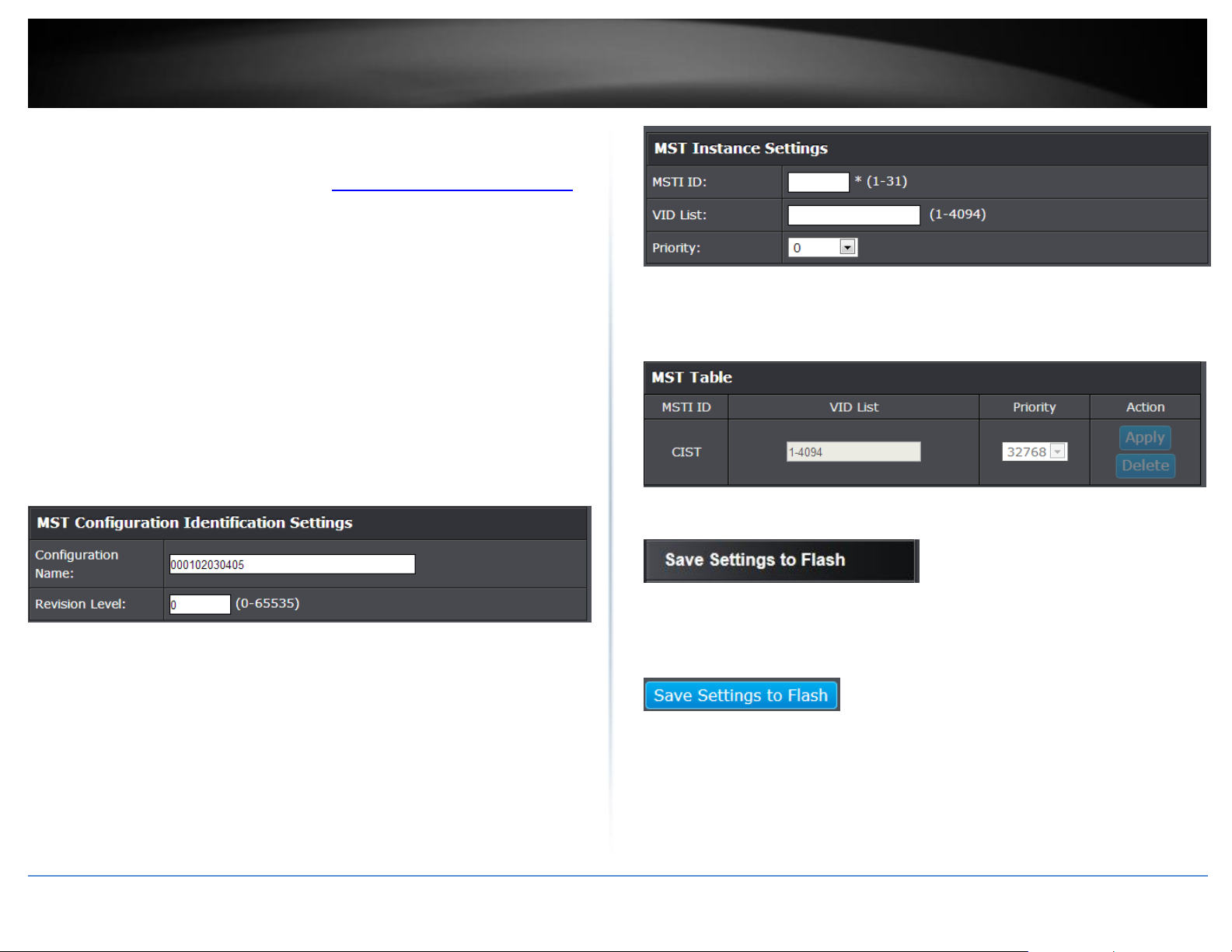
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol MST settings (MSTP)
Bridge > Spanning Tree > MST Settings
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on Spanning Tree, and click on MST Settings.
3. Review the settings. For each section, click Apply to save changes.
MST Configuration Identification Settings
Configuration Name: A configured name set on the switch to uniquely identify
the MSTI (Multiple Spanning Tree Instance). If a configuration name is not set,
this field shows the MAC address of the device running MSTP.
Revision Level (0-65535): This value, together with the configuration name,
and identical vlans mapped for STP instance IDs identifies the MST region
configured on the switch.
MST Table: Make changes to the table entry, and click Apply modify or click
Delete to remove the ID entry.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
MST Instance Settings
MSTI ID (1 - 31): Displays the MSTI ID associated with the VID List. The possible
field range is 1-31.
VID List (1 - 4094): Displays the VID List. Click Add to add into MST Table below.
Priority: Enter the new priority in the Priority field. The user may set a priority
value between 0-61440.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Page 30
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
26
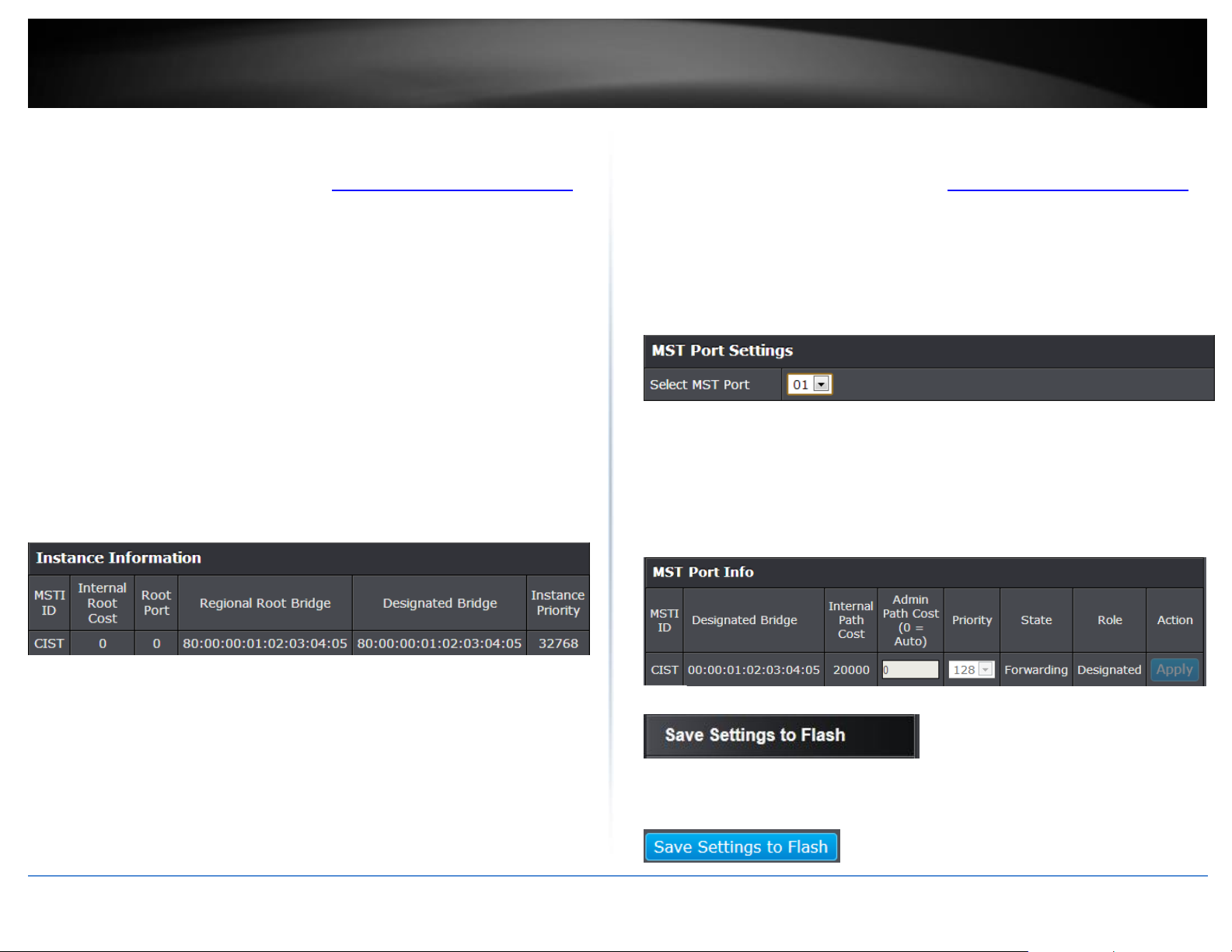
View your Spanning Tree Protocol Instance Information (MSTP)
Bridge > Spanning Tree > MST Settings
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on Spanning Tree, and click on Instance Information.
3. View your MSTP instance information.
MSTI ID – Specifies the instance to which the VLAN is assigned.
Internal Root Cost
Root Port – Indicates the selected instance’s root port.
Regional Root Bridge
Designated Bridge – Displays the ID of the bridge that connects the link or
shared LAN to the root.
Instance Priority – Specifies the selected spanning tree instance device priority.
The field range is 0-61440. The field default is 32768.
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol MST Port Settings (MSTP)
Bridge > Spanning Tree > MST Settings
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on Spanning Tree, and click on MST Port Settings.
3. Review the settings. For each entry, click Apply to save changes.
Select MST Port – Click the drop-down to select which MST port to configure.
MST Port Info - The MST Port Information page provides user to configure the
MSTP Interface settings.
o Admin Path Cost (0 = Auto) - This is the port cost used by MSTP when
calculating path cost to the root bridge.
o Priority - This is the port priority used by MSTP in calculating path
costs when two ports on the switch have the same port cost.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Page 31
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
27
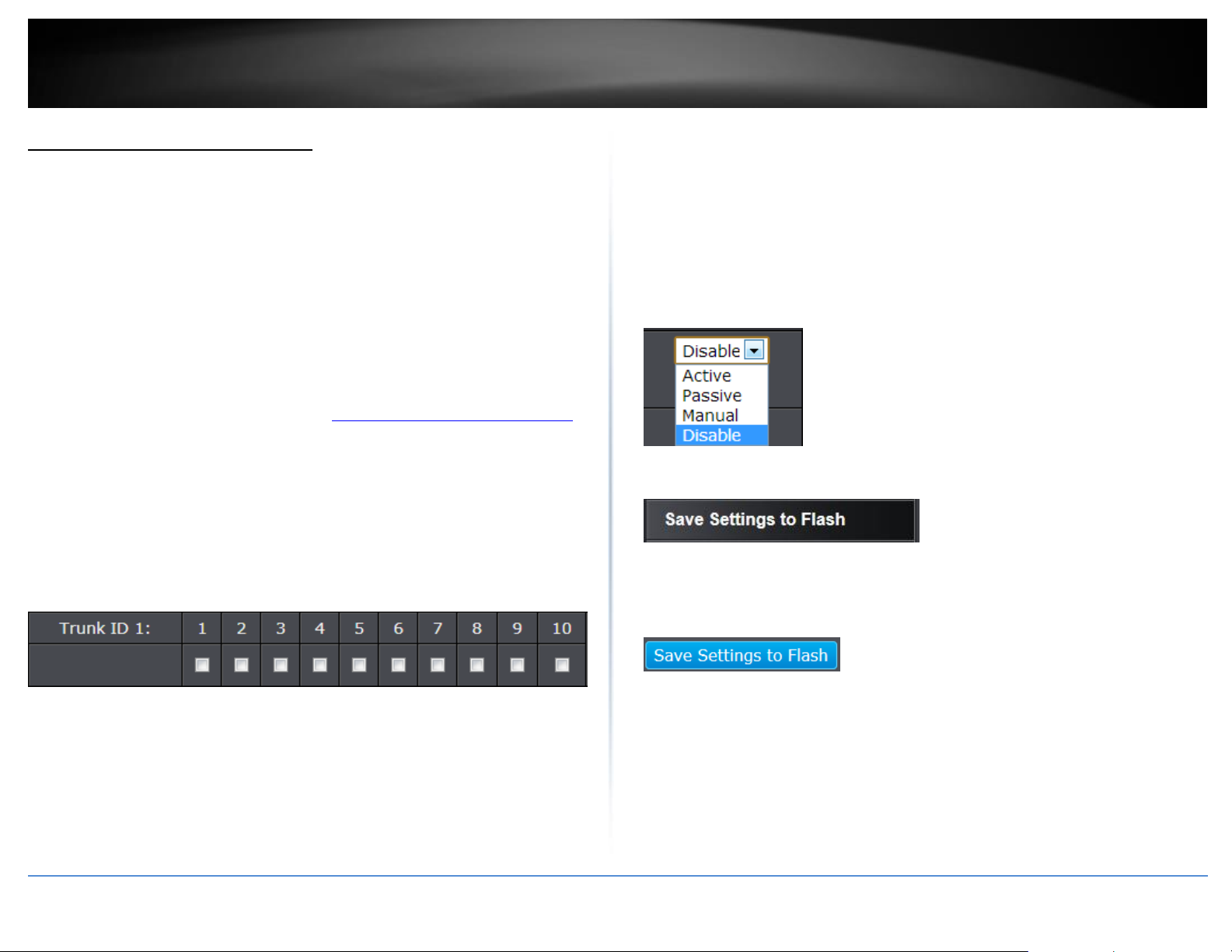
Trunk Config (Link Aggregation)
Configure port trunk settings
Bridge > Trunk Config > Trunking
The trunking function enables the cascading of two or more ports for a combined larger
total bandwidth. Up to 4 trunk groups may be created, each supporting up to 8 ports.
Add a trunking Name and select the ports to be trunked together, and click Apply to
activate the selected trunking groups.
Important Note: Do not connect the cables of a port trunk to the ports on the switch
until you have configured the ports on both the switch and the end nodes. Connecting
the cables prior to configuring the ports can create loops in your network topology.
Loops can result in broadcast storms which can severely limited the effective bandwidth
of your network.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on Trunk Config, and click on Trunking.
3. Review the settings. For each trunk group, click Apply to save changes.
For each Trunk ID/Group, check the port numbers to add for each trunk group.
Click the drop-down list and select one of the following options.
Active - The specific aggregator will broadcast and respond to LACPDU (LACP
Data Unit) packets. This setting enables the dynamic LACP feature for the trunk.
Passive - The specific aggregator will not broadcast LACPDU packets, but it will
respond to them. This setting disables the LACP feature for the trunk
Manual - Enables static port trunking and disables the LACP feature for the
trunk. (Static link aggregation).
Disable - Disables the static port trunk and disables the LACP feature.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 32

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
28
View your trunk group status information
Bridge > Trunk Config > LACP Group Status
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on Trunk Config, and click on LACP Group Status.
3. View your trunk group status information.
System Priority - Preassigned setting that cannot be modified. This value
applies to the switch.
System ID - MAC address value assigned to the individual switch. This value
cannot be modified.
Group: # The ID number of the trunk (link aggregation group).
Configure your port priority
Bridge > Trunk Config > Port Priority
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on Trunk Config, and click on Port Priority.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save changes.
To assign a port higher priority within a trunk group, find the port number and in the
priority column, enter a priority value 0-65535 (65535 being the highest priority).
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Page 33

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
29
Mirroring
Configure port mirror settings
Bridge > Mirroring
Port mirroring allows you to monitor the ingress and egress traffic on a port by having
the traffic copied to another port where a computer or device can be set up to capture
the data for monitoring and troubleshooting purposes.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on Trunk Config, and click on Port Priority.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save changes.
Status – Click the drop-down and list and select one of the following options:
o Enable - This parameter activates the Port Mirroring feature and the
rest of the configuration parameters become active on the page.
o Disable - This parameter de-activates the Port Mirroring feature and
the rest of the configuration parameters become inactive on the page.
Mirror Target Port – Click the drop-down and list and select the port to send
the copied ingress/egress packets/data. (e.g. Computer or device with packet
capture or data analysis program.)
To copy data transmitted on specific port, check the port number under the Egress Port
section or you could click All to copy data transmitted on all ports.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Check the port to monitor or copy inormation from. (Source)
To copy data received on a specific port, check the port number(s) under the Ingress
Port section or you could click All to copy data received on all ports.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 34

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
30
Loopback Detection
Enable loopback detection
Bridge > Loopback Detection
The loopback detection feature allows the switch to detect and prevent disruption from
loops that occur on uplink or downlink switches directly connected to your switch.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge and click on Loopback Detection.
3. Review the settings.
State – Select Enabled to enable the loopback detection feature. Select
Disabled to disabled the loopback detection feature.
Interval – Defines the interval your switch will check for loops.
Recover Time – Defines the time period when connectivity will be restored to a
port where a loop was previously detected and blocked.
Click Apply to save changes.
In the Loopback Detection table, select one of the Loopback Detection State choices
from the pull down menu:
Ignore: This parameter indicates that the setting in the All row do not apply to the
Loopback Detection State field. In other words, each port is set individually.
Enabled: This selection enables the Loopback Detection feature for each port.
This state must be enabled along with the State field at the top of the page
before this feature can be active on the selected port.
Disabled: This selection disables the Loopback Detection feature on the
selected port.
Note: In the All row when you select Enable or Disable instead of Ignore, the
selection applies to all of the Switch ports.
Next to each entry modified, under the Action column, click Apply to save the changes.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Page 35

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
31
Static Unicast
Add static unicast entries to the switch
Bridge > Static Unicast
In this section, you can add static unicast entries to the switch configuration.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge and click on Static Unicast.
3. Review the settings.
802.1Q VLAN – Enter the VLAN ID where the MAC address will reside.
Note: By default, all switch ports are part of the default VLAN, VLAN ID 1.
MAC Address – Enter the MAC address of the device to add.
Port Member – Select the port where the MAC address will reside.
Click Apply to add the Static Unicast entry to the list.
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry.
You can also click Delete All to delete all the entries in the list. If the entries span
multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and click Go or you can
click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 36

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
32
Static Multicast
Add static multicast entries to the switch
Bridge > Static Multicast
In this section, you can add static multicast entries to the switch configuration.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge and click on Static Multicast.
3. Review the settings.
802.1Q VLAN – Enter the VLAN ID where the multicast group MAC address will
reside.
Note: By default, all switch ports are part of the default VLAN, VLAN ID 1.
MAC Address – Enter the multicast group MAC address.
Group Member – Check the port(s) where the MAC address will reside.
Note: You can click All to select all ports.
Click Apply to add the Static Multicast Group entry to the list.
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry. If
the entries span multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and
click Go or you can click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 37

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
33
IGMP Snooping
Configure IGMP Snooping Settings
Bridge > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Settings
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge and click on IGMP Snooping.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save the settings.
Status – Click the drop-down list and select Enabled to enable the IGMP
snooping feature or Disabled to disable the feature.
Age-Out Timer – Enter the amount of time in seconds that you want your
switch to wait before it purges an inactive dynamic MAC address.
Querier Status – Click the drop-down list and select Enabled to enable the
Querier Status or Disabled to disable this feature.
Querier Interval – Enter the amount of time you want your switch to send
IGMP queries.
The table below displays the static multicast address groups defined in your switch for
reference and can be modified on under Bridge > Static Multicast or dynamically
updated with the active multicast address groups.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Configure IGMP Snooping Router Ports
Bridge > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Router Port
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge and click on IGMP Snooping.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save the settings.
In the VLAN ID router port list, you can configure your Static and Dynamic Router ports.
IGMP Snooping Router Port configured manually is a Static Router Port, and a Dynamic
Router Port is dynamically configured by the Switch when a query control message is
received.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 38

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
34
To modify an entry, click Modify to add statically add router ports.
Check the static router ports to add and click Apply to save the settings.
Note: You can click on All to add all ports. Clicking Restore will restore the static router
port settings to default.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Bandwidth Control
Configure Storm Control
Bridge > Bandwidth Control > Storm Control
This section allows you to configure the DLF (Destination Lookup Failure), broadcast,
and multicast storm settings for each switch port.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on Bandwidth Control, and click on Storm Control.
3. Review the settings for each port. Click Apply to save the settings.
DLF (Destination Lookup Failure) – Click the drop-down list and select Enabled
to enable DLF storm control.
Broadcast – Click the drop-down list and select Enabled to enable broadcast
storm control.
Multicast – Click the drop-down list and select Enabled to enable multicast
storm control.
Threshold – Enter the pps (packets per second) threshold.
Note: Modifying settings in the row marked All, will apply the settings to all
ports.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Page 39

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
35
Set Ingress Rate Limiting
Bridge > Bandwidth Control > Ingress Rate Limiting
This section allows you to set the ingress (receive) rate for each switch port.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on Bandwidth Control, and click on Ingress Rate Limiting.
3. Review the settings for each port. Click Apply to save the settings.
Bandwidth – Enter the ingress rate limit value.
Status – Click the drop-down list and select Enabled to enable ingress rate
limiting or select Disabled to disable ingress rate limiting.
Note: Modifying settings in the row marked All, will apply the settings to all
ports.
Set Egress Rate Limiting
Bridge > Bandwidth Control > Egress Rate Limiting
This section allows you to set the egress (transmit) rate for each switch port.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on Bandwidth Control, and click on Egress Rate Limiting.
3. Review the settings for each port. Click Apply to save the settings.
Bandwidth – Enter the egress rate limit value.
Status – Click the drop-down list and select Enabled to enable egress rate
limiting or select Disabled to disable egress rate limiting.
Note: Modifying settings in the row marked All, will apply the settings to all
ports.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Page 40

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
36
VLAN
Add, modify, and remove VLANs
Bridge > VLAN > Tagged VLAN
A VLAN is a group of ports that can be anywhere in the network, but communicate as
though they were in the same area.
VLANs can be easily organized to reflect department groups (such as R&D, Marketing),
usage groups (such as e-mail), or multicast groups (multimedia applications such as
video conferencing), and therefore help to simplify network management by allowing
users to move devices to a new VLAN without having to change any physical
connections.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on VLAN, and click on Tagged VLAN.
3. Review the settings.
VLAN ID – Enter the VLAN ID for the new VLAN.
VLAN Name – Enter the VLAN name.
Management VLAN – Click the drop-down list and select Enabled to allow
access to the switch management page through the new VLAN. If you want to
restrict management access through this VLAN, select Disabled.
Note: By default, the default VLAN VID 1 is set as the Management VLAN.
Tagged/Untagged/Not Member VLAN Ports
On a port, the tag information within a frame is examined when it is received to
determine if the frame is qualified as a member of a specific tagged VLAN. If it is, it is
eligible to be switched to other member ports of the same VLAN. If it is determined that
the frame’s tag does not conform to the tagged VLAN, the frame is discarded.
Since these VLAN ports are VLAN aware and able to read VLAN VID tagged information
on a frame and forward to the appropriate VLAN, typically tagged VLAN ports are used
for uplink and downlink to other switches to carry and forward traffic for multiple VLANs
across multiple switches. Tagged VLAN ports can be included as members for multiple
VLANs. Computers and other edge devices are not typically connected to tagged VLAN
ports unless the network interface on these device can be enabled to be VLAN aware.
Select the tagged VLAN ports to add to the new VLAN.
Untagged VLAN ports are used to connect edge devices (VLAN unaware) such as
computers, laptops, and printers to a specified VLAN. It is required to modify the Port
VID settings accordingly for untagged VLAN ports under Bridge > VLAN > Port Settings.
(e.g. If the VID for the VLAN is 2, the PVID should also be set to 2)
Select the untagged VLAN ports to add to the new VLAN.
Select the not member ports to restrict from the new VLAN.
In the sections Static Tagged, Static Untagged, and Not Member, you can add the type
of VLAN ports to add to the new VLAN (Tagged or Untagged) and assign ports that are
not members (Forbidden) of the new VLAN.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 41

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
37
Click Apply to save the new VLAN to the table.
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry. If
the entries span multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and
click Go or you can click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
Note: The default VLAN VID1 cannot be removed.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Configure VLAN Port Settings
Bridge > VLAN > Port Settings
In this section, you can modify the port VID settings, acceptable frame types, and
ingress filtering.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on VLAN, and click on Port Settings.
3. Review the settings for each port. Click Apply to save settings.
PVID – Enter the port VLAN ID. Note: Required for untagged VLAN ports.
Acceptable Frame Type – Click the drop-down list and select which type of
frames can be accepted.
o All – The port can accept all frame types.
o Tagged – The port can accept tagged frames only. Untagged frames
are discarded.
o Untagged & Priority Tagged – The port can accept untagged frames
and frames with tagged priority information only such as 802.1p.
Ingress Filtering –Click the drop-down list and select Enabled to enable ingress
filtering or Disabled to disable ingress filtering.
Note: Modifying settings in the row marked All, will apply the settings to all
ports.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 42

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
38
Configure the VLAN Forwarding Table Mode
Bridge > VLAN > Forwarding Table Mode
This section allows you to configure your switch to standard 802.1Q VLAN mode (IVL) or
Asymmetric VLAN mode (SVL). Asymmetric VLAN allows the configuration of
overlapping untagged VLAN ports in order to create VLAN groups. It is recommended to
use the standard 802.1Q VLAN mode when possible.
IVL – Independent VLAN Learning
SVL – Shared VLAN Learning
Please note the following when switching between forwarding table modes:
FDB (Forwarding Database) will be cleared.
Static Unicast Address entries will be cleared.
Static Multicast Address entries will be cleared.
802.1X authenticated records will be cleared.
IGMP Snooping multicast group addresses will be cleared
When using SVL mode, Voice VLAN will not be supported.
When using SVL mode, the VID field on 802.1Q-VLAN mode will be displayed as
"N/A".
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on VLAN, and click on Forwarding Table Mode.
3. Click the learning mode drop-down list to select the forwarding table mode and click
Apply to save settings.
Note: The default mode is IVL.
View the switch VLAN dynamic forwarding table
Bridge > VLAN > Dynamic Forwarding Table
This section allows you to view the VLAN forwarding table with dynamically generated
forwarding table entries as devices more devices are connected to your switch.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on VLAN, and click on Dynamic Forwarding Table.
3. By default, forwarding entries for all ports are listed. You can click the Port drop-
down list to select a specific port to view only the forwarding entries for the selected
port.
If the entries span multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and
click Go or you can click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 43

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
39
Create a private VLAN
Bridge > VLAN > Private VLAN
The private VLAN feature allows you to create a more secure VLAN that is completely
isolated to it’s members and cannot communicate with other VLANs. A private VLAN
partitions the Layer 2 broadcast domain of a VLAN into subdomains, allowing you to
isolate the ports on the switch from each other. A subdomain consists of a primary
VLAN and one or more secondary VLANs. All VLANs in a private VLAN domain share the
same primary VLAN. The secondary VLAN ID differentiates one subdomain from
another. The secondary VLANs may either be isolated VLANs or community VLANs. A
host on an isolated VLAN can only communicate with the associated promiscuous port
in its primary VLAN. Hosts on community VLANs can communicate among themselves
and with their associated promiscuous port but not with ports in other community
VLANs.
The following guidelines apply when configuring private VLANs: The default VLAN 1
cannot be a private VLAN. The management VLAN 4095 cannot be a private VLAN. The
management port cannot be a member of a private VLAN.IGMP Snooping must be
disabled on isolated VLANs. Each secondary port's (isolated port and community ports)
PVID must match its corresponding secondary VLAN ID. Ports within a secondary VLAN
cannot be members of other VLANs. All VLANs that make up the private VLAN must
belong to the same Spanning Tree Group.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on VLAN, and click on Private VLAN.
3. To configure Private VLAN Settings, perform the following procedure:
Select Private VLAN status from the Status radio button choices that you want
to change.
o Enable: Enable Private VLAN settings.
o Disable: Disable Private VLAN settings.
Press Apply for changes to take effect.
Set the Source Port to one of the following choices from the pull-down menu:
All, 01 – 10.
Click on the Forwarding Ports ratio button that applies to your configuration.
Click Apply.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 44

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
40
View the current VLAN database
Bridge > VLAN > VLAN Database
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on VLAN, and click on Private VLAN.
3. View the current VLAN database in the table.
If the entries span multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and
click Go or you can click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protcol)
The GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) allows network devices to share VLAN
information and to use the information to modify existing VLANs or create new VLANs,
automatically. This makes it easier to manage VLANs that span more than one switch.
Without GVRP, you have to manually configure your switches to ensure that the various
parts of the VLANs can communicate with each other across the different switches.
With GVRP, which is an application of the Generic Attribute Registration Protocol
(GARP), this is done for you automatically.
Enable GVRP
Bridge > GVRP > GVRP Global Settings
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on GVRP and click on GVRP Global Settings.
3. Click the GVRP Status drop-down list and select Enabled to activate GVRP or disabled
to deactivate GVRP. Click Apply to save the settings.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 45

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
41
Set GVRP port settings
Bridge > GVRP > Port Settings
This section will allow you to select which ports will have GVRP enabled or will be
restricted from using GVRP.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on GVRP and click on Port Settings.
3. Review the settings for each port. Click Apply to save the settings.
Port - This parameter displays the ports on the switch.
Dynamic Vlan Status - This parameter defines the GVRP status of the port.
From the Dynamic Vlan Status field, select one of the following choices from
the pull-down menu:
o Ignore - This parameter indicates that the setting in the All row does
not apply to the Dynamic Vlan Status field. In other words, each port
is set individually.
o Enable - The Dynamic Vlan is activated for the port row selected.
o Disable - The Dynamic Vlan is de-active for the port row selected.
Restricted VLAN Registration - This parameter controls if the VLAN registration
on the port is restricted or not.
o Ignore - This parameter indicates that the setting in the All row does
not apply to the Restricted VLAN Registration field. In other words,
each port is set individually.
o Enable - The Restricted VLAN Registration is active for the port row
selected.
o Disable - The Restricted VLAN Registration is de-active for the port
row selected.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 46

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
42
Set GVRP time settings
Bridge > GVRP > Time Settings
This section will allow you to define the GARP Join, Leave, and Leave All Time for each
port.
Note: The GARPLeaveTimer must be greater than (GARPJoinTimer x2 + 10) and the
GARPLeaveAllTimer must be greater than (GARPLeaveTimer + 10). The acceptable input
values are multiples of 10. If you try to enter a value that is not a multiple of 10, the
value is rounded down
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on GVRP and click on Time Settings.
3. Review the settings for each port. Click Apply to save the settings.
Port - This parameter displays the ports on the switch.
JoinTime - This parameter is the GARP Join Timer. Its range is 10 - 1073741810
milli-seconds.
LeaveTime - This parameter is the GARP Leave Timer. Its range is 30 -
2147483630 milli-seconds. This timer must be set in relation to the GVRP Join
Timer according to the following equation:
GARPLeaveTimer >= (GARPJoinTimer X 2) + 10
GarpLeaveAllTime - This parameter is the GARP Leave Timer. Its range is 30 -
2147483630 milli-seconds. This timer must be set in relation to the GVRP Leave
Timer according to the following equation:
GARPLeaveAllTimer > (GARPLeaveTimer + 10)
Note: To ensure compatibility between network devices, you need
to configure the same values for the GARP Join Timer, GARP Leave Timer, and GARP
Leave All Timer on all participating GVRP devices in your network.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 47

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
43
QoS (Quality of Service)
When a port on an Ethernet switch becomes oversubscribed, its egress
queues contain more packets than the port can handle in a timely manner. In this
situation, the port may be forced to delay the transmission of some packets, resulting in
the delay of packets reaching their destinations. A port may be forced to delay
transmission of packets while it handles other traffic, and, in some situations, some
packets destined to be forwarded to an oversubscribed port from other switch ports
may be discarded.
Minor delays are often of no consequence to a network or its performance. But there
are applications, referred to as delay or time sensitive applications, which can be
impacted by packet delays. Voice transmission and video conferences are two examples.
If packets carrying data in either of these cases are delayed from reaching their
destination, the audio or video quality may suffer.
This is where Cost of Service (CoS) is of value. It allows you to manage the flow of traffic
through a switch by having the switch ports give higher priority to some packets, such as
delay sensitive traffic, over other packets. This is referred to as prioritizing traffic.
Set CoS priority settings
Bridge > QoS > CoS
Note: Before mapping the CoS priorities and the egress queues, you must disable the
Jumbo frame parameter on each port. When Jumbo frames are enabled, COS cannot be
enabled.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on QoS and click on CoS.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save the settings.
For each Traffic Class whose queue you want to change, click on the CoS Table
(Low, Medium, High, or Highest) radio button that applies to your
configuration.
After you have completed this mapping process, select Enabled in the QoS
Status field.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 48

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
44
Set Port Priority
Bridge > QoS > Port Priority
The Port Priority values are assigned to an untagged frame at ingress for internal
processing in the switch. This procedure explains how to change the default mappings of
port priorities to the User Priority. This is set at the switch level. You cannot set this at
the per-port level. To change the port priority mappings, perform the following
procedure.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on QoS and click on Port Priority.
3. For each port whose priority you want to change, select a priority (0-7) in the User
Priority column. Click Apply to save the settings.
Set DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point) Class Mapping settings
Bridge > QoS > DSCP
If you choose to use the DSCP tags in your Access Control policy configuration, each
DSCP value (0-63) that is relevant to your configuration needs to be mapped to one of
the four egress queues(Low, Medium, High, or Highest). The default queue for all DSCP
values is 0.To assign the queue mappings to the DSCP values, perform the following
procedure.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on QoS and click on DSCP.
3. For each DSCP In value that is relevant to your configuration, select a queue (Low,
Medium, High, or Highest) in the Queue column. Select Enabled in the DSCP Mapping
drop-down list. Click Apply to save the settings.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 49

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
45
Set the Scheduling Algorithm
Bridge > QoS > Scheduling Algorithm
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on QoS and click on Scheduling Algorithm.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save the settings.
Strict Priority - The port transmits all packets out of higher priority queues
before transmitting any from the lower priority queues.
WRR (Weighted RoundRobin) - The port transmits a set number of packets
from each queue, in a round robin fashion, so that each has a chance to
transmit traffic.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Page 50

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
46
Configure the IPv6 Traffic Class Priority Settings
Bridge > QoS > IPv6 Traffic Class Priority Settings
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Bridge, click on QoS and click on IPv6 Traffic Class Priority Settings.
3. Review the settings.
IPv6 Traffic Class Global Settings: Select Enable or Disable. Click Apply to save
the settings.
IPv6 Traffic Class (0-255): Specify the value of IPv6 class.
Class ID: Defines the priority assigned to the port. The priorities are Highest,
High, Medium and Low.
Click Add to add the traffic class setting entry to the table.
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry.
You can also click Delete All to delete all of the entries in the table. If the entries span
multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and click Go or you can
click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 51

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
47
SNMP
You can manage a switch by viewing and configuring the management information base
(MIB) objects on the device with the Simple Network Management Program (SNMP).
This chapter describes how to configure SNMP. A Group Name, IP address of the switch
and at least one community string is the minimum required to manage the switch using
SNMP.
Set the SNMP Engine ID
SNMP > Engine ID
The SNMP Engine ID screen allows network managers to define the SNMP Engine ID or
to assign the default Engine ID to SNMP.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on SNMP and click on Engine ID.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save the settings.
Engine ID (10-64 Hex Characters) – Enter the local device Engine ID. The field
value is a hexadecimal string. Each byte in hexadecimal character strings is two
hexadecimal digits. The Engine ID must be defined before SNMP is enabled.
Reset to Default – Use the device-generated Engine ID (Reset to Default will
override any entry in the Engine ID field).
Configure the SNMP View Table
SNMP > View Table
The SNMP View table specifies the MIB object access criteria for each View Name. If the
View Name is not specified on this page, then it has access to all MIB objects. You can
specify specific areas of the MIB that can be accessed or denied based on the entries in
this table. You can create and delete entries in the View table.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on SNMP and click on View Table.
3. Review the settings.
Creating SNMP View Table Entries
This procedure explains how to create entries in the SNMP View Table.
Enter the View Name. This entry must be pre-defined on the SNMP
User/Group page.
Enter the Subtree OID.
Enter “1” for the OID Mask.
Enter the View Type. Choose from the following options, and then click Add.
o Included: This selection allows the specified MIB object to be included
in the view.
o Excluded: This selection blocks the view of the specified MIB object.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 52

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
48
Modifying SNMP View Table Entries
If you need to modify an entry in the View Table page, you must first delete the entry
and then re-enter it.
Deleting SNMP View Table Entries
In the Action column of the table, click Delete for the View table entry that you want to
remove.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Configure the SNMP Group Access Table
SNMP > Group Access Table
The SNMP View Names are defined in the SNMP Group Access table and are based on
the User and Group Names
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on SNMP and click on Group Access Table.
3. Review the settings.
Creating SNMP View Names
Before you can create an SNMP View name, you must define a Group Name using the
SNMP User/Group page.
Enter the Group Name. This entry must be pre-defined on the SNMP
User/Group page.
Enter the Read View Name. This name is an optional field. It can be up to 31
characters in length.
Enter the Write View Name. This name is an optional field. It can be up to 31
characters in length.
Enter the Notify View Name. This name is an optional field. It can be up to 31
characters in length.
From the Security Model pull-down menu, select v3.
Enter the Security Level from the pull-down menu. The selection options are:
o NoAuthNoPriv: This selection is the appropriate selection when no
Auth-Protocol or Priv-Protocol (no encryption) are selected on the
SNMP User/Group page.
o AuthNoPriv: Choose this selection when encryption has been enabled
but only the Auth-Protocol has a password assigned and the Priv-
Protocol has been selected as none on the SNMP User/Group page.
o AuthPriv: When the Auth-Protocol or Priv-Protocol have been
enabled, choose this selection.
Click the Add button.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 53

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
49
Configure the SNMP User/Group Table
SNMP > SNMP User/Group
An SNMP User Name and Group Name definition is the basis for all the other SNMP
tables. You can create and delete View Names by following the procedures in the
following sections:
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on SNMP and click on SNMP User/Group.
Modifying SNMP View Names
If you need to modify an entry in the SNMP Group Access page, you must first delete the
entry and then re-enter it.
Deleting SNMP View Names
In the Action column of the table, click Delete for the View Name that you want to
remove.
Note: The views corresponding to the ReadOnly and ReadWrite Group Names are
default values and cannot be removed.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
3. Review the settings.
Creating SNMP User and Group Names
Note: There are no default User Names or Group Names defined for SNMP.
Type a new User Name. Enter a name up to 31 characters in length.
Type a new Group Name. Enter a name up to 31 characters in length.
From the SNMP Version pull down menu, select v3. The encryption check-box
becomes active.
o Check the encryption check-box. The Auth-Protocol, Priv-Protocol,
and associated password fields become active.
Select one of the following choices for the Auth-Protocol field:
o MD5 - The MD5 authentication protocol. SNMP Users are
authenticated with the MD5 authentication protocol after a message
is received.
o SHA - The SHA authentication protocol. Users are authenticated with
the SHA authentication protocol after a message is received.
Enter the password for the Auth-Protocol.
Select one of the following choices for the Priv-Protocol field:
o DES - Specifies DES encryption scrambles the SNMP data so that
outside observers are prevented from seeing the data content.
o none - Specifies no encryption is applied to SNMP data.
Page 54
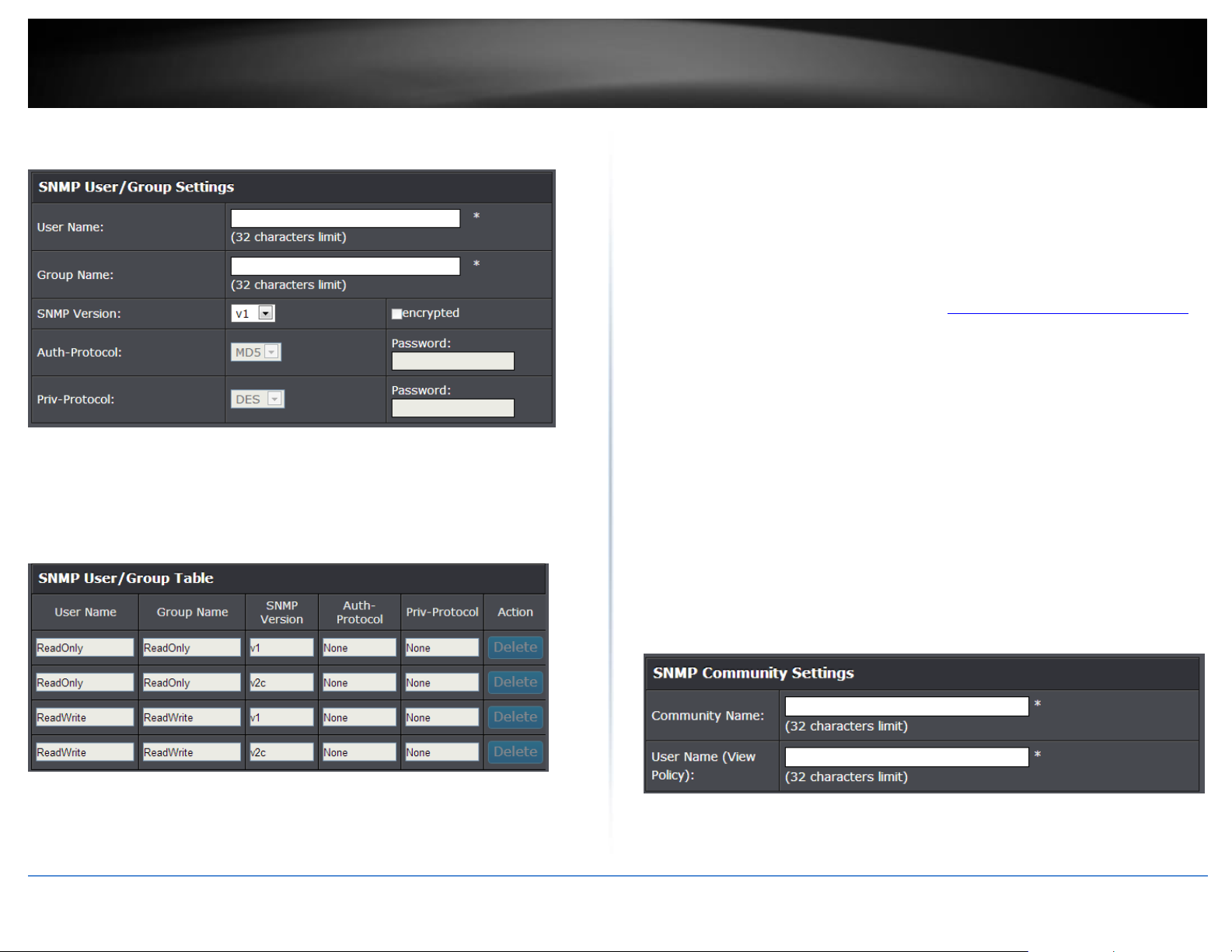
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
50
Click Add. The new User Name and Group Name are displayed on the SNMP
User/Group page.
Modifying SNMP User and Group Names
If you need to modify an entry in the SNMP User/Group page, you must first delete the
entry and then re-enter it.
Deleting SNMP User and Group Names
In the Action column of the table, click Delete for the User Name and Group Name that
you want to remove.
Configure the SNMP Community Table
SNMP > Community Table
A community string has attributes for controlling who can use the string and what the
string will allow a network management station to do on the switch. The Web
Management Utility does not provide any default community strings. You must first
define an SNMP User and Group Name on the SNMP User/Group page and then define a
Community Name on the SNMP Community Table page.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on SNMP and click on SNMP User/Group.
3. Review the settings.
Create SNMP Community Settings
Enter a new Community Name. A name can be up to 31 characters in length.
Enter a User Name(View Policy) that has been previously defined. This name
must match one of the User Names displayed on the
Note: SNMP User/Group page. If you enter a user name that has not been predefined on the SNMP User/Group page, the Community entry is displayed, but
the agent/manager communication fails.
Click Add. The values of the new Community Name and User Name are
displayed.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 55

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
51
Modify SNMP Community Settings
If you need to modify a Community Table entry, you must first delete the entry by using
the procedure below and then re-enter it with the modification by creating a new
Community table entry.
Delete SNMP Community Settings
To delete a Community Name, click Delete next to the entry in the table that
you want to remove.
The deleted Community Name is no longer displayed in the Community table.
No confirmation message is displayed.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Configure the SNMP Trap Management
SNMP > Trap Management
A Host IP address is used to specify a management device that needs to receive SNMP
traps sent by the switch. This IP address is associated with the SNMP Version and a valid
Community Name in the Host table of the switch.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on SNMP and click on Trap Management.
3. Review the settings.
Create Trap Host Table Entry
Use the following procedure to create a trap Host table entry:
Enable trap management by selecting the radio button next to Enabled at the
top of the page. By default, trap management is enabled.
Enter the Host IP Address for the management device that is toreceive the
SNMP traps.
Enter the SNMP Version, either v1 or v2c, that is configured for the host
management device.
Enter a Community Name that you have defined previously in the SNMP
Community table. The Community Name must correlate with one of the
communities displayed on the SNMP Community Table page. If you enter a
Community Name that has not been pre-defined, the Trap Host entry is
displayed, but agent/manager communication fails.
Click Add. The new host is added to the table.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 56

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
52
Access Control Config
Access Control configuration allows you to control different aspects of the Ethernet
traffic as it enters the switch ports and is process through the Switch. You can specify
what traffic is permitted or denied to flow through the switch by setting up specific filter
criteria at an ingress port. You can also manage the switching priority of Ethernet
packets. All of this is done by specifying policies that define the filtering and priority
behavior.
Configure Policy Settings
Access Control Config > Policy Settings
The Policy Settings page allows you to specify the filtering criteria for one policy. You
can create, modify or delete a Policy by following the procedures in the following
sections:
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
Modify a Trap Host Table Entry
If you need to modify an SNMP Trap entry, you must first delete the entry by using the
procedure below and then re-enter it with the modification by creating a new SNMP
trap.
Delete a Trap Host Table Entry
To delete an entry in the host table, click Delete next to the entry in the table that you
want to remove. The Host table entry is removed from the table. No confirmation
message is displayed.
2. Click on Access Control Config and click on Policy Settings.
3. Review the settings.
Choose the type of policy to create:
Add L2+IPv4
Add IPv6
Note: Please note that when adding polices, it is important to note that the rule/policy
order of priority in which the rules/policies are evaluated by the switch, 1 being the
highest priority.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 57

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
53
Add L2+IPv4
To add an L2+IPv4 policy, use the following procedure:
Click Add L2+ IPv4, The Policy Settings page.
Enter a number in the Policy Index field. The Policy Index is a unique number
within the range of 1 – 65535 which identifies the policy. This field is
mandatory.
Choose the parameters to add for the policy, and enter data one or more of the
parameters required for your policy. They are listed here:
o Source MAC Address - Specifies the source MAC address. The format
is xx.xx.xx.xx.xx.xx.
o Source MAC Mask Length - Indicates the length of the Source MAC
Mask ranging from 1- 48.
o Destination MAC Address - Specifies the destination MAC address.
The format is xx.xx.xx.xx.xx.xx.
o Destination MAC Mask Length - Indicates the length of the
Destination MAC Mask ranging from 1 - 48.
o VLAN ID - A unique number identifying a VLAN ranging from 1 to
4094.
o 802.1p Priority - 802.1p priority level of the frame ranging from 0 to 7.
o Ether Type - Indicates the protocol of the ethernet frame protocol
ranging from 0000 to FFFF.
o Protocol - Indicates the packet protocol ranging from 0 to 255.
o Source IP Address - Specifies the source IP address.
o Source IP Mask Length - Specifies the mask length of the source IP
address ranging from 0 - 32.
o Destination IP Address - Specifies the destination IP address.
o Destination IP MAC Mask Length - Specifies the mask length of the
destination IP address ranging from 0 - 32.
o DSCP - The DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point) value in the IP
header ranging from 0 - 63.
o Source Layer 4 Port - Indicates the source layer 4 port ranging from 1 -
65535.
Click Add to add the policy to the Policy Table.
o Destination Layer 4 Port - Indicates the destination layer 4 port
ranging from 1 - 65535.
o Policy Sequence: Enter a number in the Policy Sequence field. The
Policy Sequence must be a unique number within the range of 1 -
65535. This field is mandatory.
o Policy Action: In the Permit/Deny field, use the pull down menu to
select one of the following parameters:
o Deny - This selection drops ingress packets that conform to the
specified Replaced-CoS or Replaced-DSCP.
o Permit - This selection allows ingress packets that conform to the
specified Replaced-CoS or Replaced-DSCP to be processed by the
switch.
Note: You must enter a selection for Deny/Permit field even if the
Profile Action ID that you have entered ignores both the Replaced-
DSCP and Replaced-CoS fields.
o Replaced-CoS: Enter a number in the Replaced-CoS field ranging from
0 to 7. This field indicates the CoS level of interest. This field is not
mandatory and you may elect to leave it blank
o Replaced-DSCP: Enter a number in the Replaced-DSCP field within the
range of 0 to 63. This field indicates the DSCP level of interest. This
field is not mandatory and you may elect to leave it blank.
o Rate Control Index: The Rate Control Index is a unique number within
the range of 1 - 65535. This field is mandatory and must match a Port
List Index that has been previously entered on the Policy Index.
o Port List: Select the interface for which you want to display data.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 58

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
54
Add IPv6
To add an IPv6 policy, use the following procedure:
Click Add IPv6, The Policy Settings page.
Enter a number in the Policy Index field. The Policy Index is a unique number
within the range of 1 – 65535 which identifies the policy. This field is
mandatory.
Choose the parameters to add for the policy, and enter data one or more of the
parameters required for your policy. They are listed here:
o VLAN ID - A unique number identifying a VLAN ranging from 1 to 4094.
o 802.1p Priority - 802.1p priority level of the frame ranging from 0 to 7.
o Protocol - Indicates the packet protocol ranging from 0 to 255.
o IPv6 Source IP Address - Specifies the IPv6 Source IP address.
o Prefix Length - Indicates the length of the Source IP ranging from 1-
128.
o IPv6 Destination IP Address - Specifies the IPv6 Destination IP
address.
o Prefix Length - Indicates the length of the Destination IP ranging from
1- 128.
o Source Layer 4 Port - Indicates the source layer 4 port ranging from 1 -
65535.
o Destination Layer 4 Port - Indicates the destination layer 4 port
ranging from 1 - 65535.
o Policy Sequence: Enter a number in the Policy Sequence field. The
Policy Sequence must be a unique number within the range of 1 -
65535. This field is mandatory.
o Policy Action: In the Permit/Deny field, use the pull down menu to
select one of the following parameters:
o Deny - This selection drops ingress packets that conform to the
specified Replaced-CoS or Replaced-DSCP.
o Permit - This selection allows ingress packets that conform to the
specified Replaced-CoS or Replaced-DSCP to be processed by the
switch.
Note: You must enter a selection for Deny/Permit field even if the
Profile Action ID that you have entered ignores both the Replaced-
DSCP and Replaced-CoS fields.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 59

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
55
o Replaced-CoS: Enter a number in the Replaced-CoS field ranging from
0 to 7. This field indicates the CoS level of interest. This field is not
mandatory and you may elect to leave it blank
o Replaced-DSCP: Enter a number in the Replaced-DSCP field within the
range of 0 to 63. This field indicates the DSCP level of interest. This
field is not mandatory and you may elect to leave it blank.
o Rate Control Index: The Rate Control Index is a unique number within
the range of 1 - 65535. This field is mandatory and must match the
Rate Control Settings page.
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry.
You can also click Delete All to delete all of the entries in the table. If the entries span
multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and click Go or you can
click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
o Port List: Select the interface for which you want to display data.
Click Add to add the policy to the Policy Table.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 60

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
56
Configure Rate Control
Access Control Config > Rate Control
The Policy Settings page allows you to specify the filtering criteria for one policy. You
can create, modify or delete a Policy by following the procedures in the following
sections:
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Access Control Config and click on Rate Control.
3. Review the settings.
Enter a number in the Index field. The Index is a unique number within the
range of 1–65535 which identifies the policy. This field is mandatory.
Enter a number in the Committed Rate column ranging from 1 to 15625.
Click Add to add the rate control settings to the Rate Control Table.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry.
You can also click Delete All to delete all of the entries in the table. If the entries span
multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and click Go or you can
click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 61

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
57
View your policy database
Access Control Config > Policy Database
Allows you to view current policies assigned to each port by Index or Sequence.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Access Control Config and click on Policy Database.
3. Click the Select Port drop-down list to select the port you would like to view
associated with the selected port. Then select the order to sort Index or Sequence.
Note: The Any option will display policies for all ports.
4.View the active poicies associated with the specified port.
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
6. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
RMON
The RMON (Remote MONitoring) MIB is used with SNMP applications to monitor the
operations of network devices. The Switch supports the four RMON MIB groups listed
here:
Statistic group— This group is used to view port statistics remotely with SNMP
programs.
History group— This group is used to collect histories of port statistics to
identify traffic trends or patterns.
Event group— This group is used with alarms to define the actions of the
switch when packet statistic thresholds are crossed.
Alarm group—This group is used to create alarms that trigger event log
messages or SNMP traps when statistics thresholds are exceeded.
You can use your SNMP Network Management System (NMS) software and the RMON
section of the MIB tree to view the RMON statistics, history and alarms associated with
specific ports. Since RMON uses the SNMP agent for communicating with your NMS
software, the SNMP Agent must be enabled and the SNMP feature must be configured
on your switch. Since RMON works in conjunction with the SNMP agent, the SNMP
agent must be enabled for the RMON feature to be active.
Enable RMON
RMON > Global Settings
This section allows you to enable or disable RMON functionality.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on RMON and click on Global Settings.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 62

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
58
3. Click the RMON Status drop-down list and select Enabled to enable RMON. Click
Apply to save settings.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Configure parameters for RMON Ethernet statistics
RMON > Statistics
You can remotely view individual port statistics with RMON by using your SNMP NMS
software and the RMON portion of the MIB tree.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on RMON and click on Statistics.
3. Review the settings.
Index: This parameter specifies the ID number of the new group. The range is 1
to 65535.
Port: This parameter specifies the port where you want to monitor the
statistical information of the Ethernet traffic.
Owner: This parameter is used to identify the person who created an entry. It is
primarily intended for switches that are managed by more than one person,
and is an optional field.
Click Add to add the entry to the table.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 63

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
59
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry. If
the entries span multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and
click Go or you can click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Configure parameters for RMON history control settings
RMON > History
RMON histories are snapshots of port statistics. They are taken by the switch at
predefined intervals and can be used to identify trends or patterns in the numbers or
types of ingress packets on the ports on the switch. The snapshots can be viewed with
your SNMP NMS software with the history group of the RMON portion of the MIB tree.
A history group is divided into buckets. Each bucket stores one snapshot of statistics of a
port. A group can have from 1 to 50 buckets. The more buckets in a group, the more
snapshots it can store.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on RMON and click on History.
3. Review the settings.
Index: This parameter specifies the ID number of the new group. The range is 1
to 65535.
Port: This parameter specifies the port where you want to monitor the
statistical information of the Ethernet traffic.
Buckets Requested: This parameter defines the number of snapshots of the
statistics for the port. Each bucket can store one snapshot of RMON statistics.
Different ports can have different numbers of buckets. The range is 1 to 50
buckets.
Interval: This parameter specifies how frequently the switch takes snapshots of
the port’s statistics. The range is 1 to 3600 seconds (1 hour). For example, if
you want the switch to take one snapshot every minute on a port, you specify
an interval of sixty seconds.
Owner: This parameter is used to identify the person who created an entry. It is
primarily intended for switches that are managed by more than one person,
and is an optional field.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 64

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
60
Click Add to add the entry to the table.
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry.
You can also click Delete All to delete all of the entries in the table. If the entries span
multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and click Go or you can
click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Configure parameters for RMON alarms
RMON > Alarm
RMON alarms are used to generate alert messages when packet activity on designated
ports rises above or falls below specified threshold values. The alert messages can take
the form of messages that are entered in the event log on the switch or traps that are
sent to your SNMP NMS software or both.
RMON alarms consist of two thresholds. There is a rising threshold and a falling
threshold. The alarm is triggered if the value of the monitored RMON statistic of the
designated port exceeds the rising threshold. The response of the switch is to enter a
message in the event log, send an SNMP trap, or both. The alarm is reset if the value of
the monitored statistic drops below the falling threshold.
The frequency with which the switch samples the thresholds of an alarm against the
actual RMON statistic is controlled by a time interval parameter. You can adjust this
interval for each alarm.
Here are the three components that comprise RMON alarms:
RMON statistics group: A port must have an RMON statistics group configured
if it is to have an alarm. When you create an alarm, you specify the port to
which it is to be assigned not by the port number, but rather by the ID number
of the port’s statistics group.
RMON event: An event specifies the action of the Switch when the ingress
packet activity on a port crosses a statistical threshold defined in an alarm. The
choices are to log a message in the event log of the Switch, send an SNMP trap
to an SNMP workstation, or both. Since there are only three possible actions
and since events can be used with more than one alarm, you probably will not
create more than three events.
Alarm: The last component is the alarm itself. It defines the port statistic to be
monitored and the rising and falling thresholds that trigger the switch to
perform an event. The thresholds of an alarm can have the same event or
different events. The switch supports up to eight alarms.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 65

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
61
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on RMON and click on Alarm.
3. Review the settings.
Index: This parameter specifies the ID number of the new group. The range is 1
to 65535.
Interval: This parameter specifies the time (in seconds) over which the data is
sampled. Its range is 1 to 2147483647 seconds.
Variable: This parameter specifies the RMON MIB object that the event is
monitoring.
Sample type: This parameter defines the type of change that has to occur to
trigger the alarm on the monitored statistic. There are two choices from the
pull-down menu - Delta value and Absolute value. Delta value- setting
compares a threshold against the difference between the current and previous
values of the statistic. Absolute value- setting compares a threshold against the
current value of the statistic.
Rising Threshold: This parameter specifies a specific value or threshold level of
the monitored statistic. When the value of the monitored statistic becomes
greater than this threshold level, an alarm event is triggered. The parameter’s
range is 1 to 2147483647.
Falling Threshold: This parameter specifies a specific value or threshold level of
the monitored statistic. When the value of the monitored statistic becomes less
than this threshold level, an alarm event is triggered. The parameter’s range is
1 to 2147483647.
Rising Event Index: This parameter specifies the event index for the rising
threshold. Its range is 1 to 65535. This field is mandatory and must match an
Event Index that you previously entered in “Events”.
Falling Event Index: This parameter specifies the event index for the falling
threshold. Its range is 1 to 65535. This field is mandatory and must match an
Event Index that you previously entered in “Events”.
Owner: This parameter is used to identify the person who created an entry. It is
primarily intended for switches that are managed by morethan one person,
and is an optional field.
Click Add to add the entry to the table.
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry.
You can also click Delete All to delete all of the entries in the table. If the entries span
multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and click Go or you can
click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 66

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
62
Configure parameters for RMON events
RMON > Event
An event specifies the action of the switch when the ingress packet activity on a port
crosses a statistical threshold defined in an alarm. The choices are to log a message in
the event log of the switch, send an SNMP trap to an SNMP workstation, or both. Since
there are only three possible actions and since events can be used with more than one
alarm, you probably will not create more than three events - one for each of the three
actions.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on RMON and click on Event.
3. Review the settings.
Index: This parameter specifies the ID number of the new group. The range is 1
to 65535.
Description: This parameter specifies a text description of the event that you
are configuring.
Type: This parameter specifies where to log the event when it occurs. The
choices are to log a message in the event log of the Switch, send an SNMP trap
to the SNMP NMS software, or both.
Community: This parameter specifies the community where you want to send
the SNMP trap.
Owner: This parameter is used to identify the person who created an entry. It is
primarily intended for switches that are managed by more than one person,
and is an optional field.
Click Add to add the entry to the table.
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry.
You can also click Delete All to delete all of the entries in the table. If the entries span
multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and click Go or you can
click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 67

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
63
Voice VLAN
This chapter contains a description of the Switch’s Voice VLAN feature and the
procedures to create, modify, and delete a voice VLAN configuration.
The Voice VLAN feature is specifically designed to maintain high quality, uninterrupted
voice traffic through the switch. When talking on a voice over IP phone, a user expects
to have no interruptions in the conversation and excellent voice quality. The Voice VLAN
feature can be configured to meet these requirements.
CoS with Voice VLAN
The Voice VLAN CoS parameter maintains the voice quality between the ingress and
egress ports of the switch. CoS must be enabled for the Voice VLAN CoS priority to take
effect. The CoS priority level that you config is applied to voice traffic on all ports of the
voice VLAN. Normally, most (non-Voice) Ethernet traffic transverses the switch through
lower order egress queues. To avoid delays and interruptions in the voice data flow, the
CoS priority level assigned to the voice VLAN should be mapped to a higher order queue
and the scheduling algorithm should be set to Strict Priority. These settings ensure that
the voice data packets are processed before other types of data so that the voice quality
is maintained as the voice data passes through the switch.
Organization Unique Identifier (OUI)
Each IP phone manufacturer can be identified by one or more Organization Unique
Identifiers (OUIs). An OUI is three bytes long and is usually expressed in hexadecimal
format. It is imbedded into the first part of each MAC address of an Ethernet network
device. You can find the OUI of an IP phone in the first three complete bytes of its MAC
address.
Typically, you will find that all of the IP phones you are installing have the same OUI in
common. The switch identifies a voice data packet by comparing the OUI information in
the packet’s source MAC address with an OUI table that you configure when you initially
set up the voice VLAN. This is important when the Auto-Detection feature for a port and
is a dynamic voice VLAN port.
When you are configuring the voice VLAN parameters, you must enter the complete
MAC address of at least one of your IP phones. An “OUI Mask” is automatically
generated and applied by the Web Management Utility software to yield the
manufacturer’s OUI. If the OUI of the remaining phones from that manufacturer is the
same, then no other IP phone MAC addresses need to be entered into the configuration.
However, it is possible that you can find more than one OUI from the same
manufacturer among the IP phones you are installing. It is also possible that your IP
phones are from two or more different manufacturers in which case you will find
different OUIs for each manufacturer. If you identify more than one OUI among the IP
phones being installed, then one MAC address representing each individual OUI must be
configured in the voice VLAN. You can enter a total of 10 OUIs.
Dynamic Auto-Detection vs Static Ports
Prior to configuring the voice VLAN, you must configure a tagged VLAN which is the
basis for the voice VLAN configuration. The VLAN must be configured with one or more
tagged or untagged ports that will serve as the voice VLAN uplink/downlink. By default,
a tagged or untagged port is a static member of a tagged VLAN. The ports that you
choose to configure as dynamic Auto-Detection ports
must be connected directly to an IP phone. When you initially define the ports of a
tagged VLAN for your voice VLAN configuration, they must be configured as a “Not
Member” ports. The “Not Member” ports are eligible to dynamically join the voice VLAN
when voice data is detected with a predefined OUI in the source MAC address. The port
will leave the voice VLAN after a specified timeout period. This port behavior is
configured with the voice VLAN Auto-Detection feature.
For the Auto-Detection feature to function, your IP phone(s) must be capable of
generating 802.1Q packets with imbedded VLAN ID tags. You must manually configure
your IP phone(s) for the same VLAN ID as the switch’s voice VLAN ID. When voice data is
detected on one of the “Not Member” ports, the packets from the IP phone will contain
the voice VLAN ID so they are switched within the switch’s voice VLAN.
One or more ports in your voice VLAN must be configured as Static tagged or untagged
members. Static VLAN members are permanent member ports of the voice VLAN and
there is no dependency on the configuration of the devices connected to the ports.
These ports might be connected to other voice VLAN network nodes such as other
Ethernet switches, a telephone switch, or a DHCP server. The voice VLAN AutoDetection feature cannot be enabled on Static tagged or tagged ports.
Note: Any Static tagged members of the voice VLAN are required to have the port VLAN
ID (PVID) configured to be the same as the voice VLAN ID. This insures that all untagged
packets entering the port are switched within the voice VLAN as the voice data passes
through the switch.
If the IP phone(s) that you are installing cannot be configured with a VLAN ID, then the
switch ports should be configured as Static tagged ports within the voice VLAN.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 68

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
64
Note: Link Layer Discovery Protocol for Media Endpoint Devices (LLDP- MED) is not
supported on the switch. Each IP phone that is VLAN aware should be manually
configured for the VLAN ID that matches your voice VLAN ID. Each of the voice VLAN
ports connected to an IP phone should be configured as “Not Member” ports of the
tagged VLAN.
Create a Voice VLAN
Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Settings
Note: Prior to configuring your voice VLAN, you must first configure a tagged VLAN. This
VLAN will be used as a basis for your voice VLAN.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Voice VLAN and click on Voice VLAN Settings.
3. Review the settings.
Use the following procedure to configure voice VLAN:
From the Voice VLAN field at the top of the page, select one of the following
radio button choices:
o Enable - The voice VLAN feature is active. The other parameter fields
in the voice VLAN Global Settings section become active and are
eligible for data to be entered.
o Disable - The voice VLAN feature is inactive. The other parameter
fields in the voice VLAN Global Settings section become inactive and
are greyed out so that data cannot be entered.
In the Voice VLAN Global Settings section, enter the configuration information
for the following parameters:
o VLAN ID - This parameter is the tagged VLAN ID that has been
configured in “Tagged VLAN Configuration”. It is a pull-down menu
showing the tagged VLAN IDs that have been defined.
o Aging Time - This parameter indicates the amount of time, in hours,
after the last IP phone's OUI was received on a port, after which this
Click Apply to save the settings.
In the table at the bottom of the page, The voice VLAN Auto- Detection status
is defined. From the Auto-Detection column, select one of the port rows and
then one of the following choices from the pull-down menu:
Note: The voice VLAN Auto-Detection feature can only be enabled on “Not Member”
ports of the voice VLAN. Member ports cannot have the voice VLAN Auto-Detection
feature enabled. The Status column displays Static for the member ports
port will be removed from the voice VLAN. The range is 1 to 120
hours.
o CoS - This parameter is CoS priority level assigned to the voice data
packets received on each voice VLAN port. For the COS priority to be
effective, QoS must be Enabled.
o Ignore - This parameter indicates that the setting in the All row does
not apply to the Dynamic Vlan Status field. In other words, each port
is set individually.
o Enable - The voice VLAN Auto-Detection feature is activated for the
port row selected.
o Disable - The voice VLAN Auto-Detection feature is active for the port
row selected.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 69

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
65
Enter the MAC address in the User Defined OUI - Telephony OUI field of one of
the IP phones with the manufacturer's OUI.
Click Add. The new OUI entry is displayed in the table at the bottom of the
page.
Note: If you find more than one OUI among the IP phones you are installing,
enter one MAC address that represents each individual OUI. You can enter a
total of 10 OUIs.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Configure Voice VLAN OUI settings
Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN OUI Settings
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Voice VLAN and click on Voice VLAN OUI Settings.
3. Review the settings.
Use the following procedure to configure voice VLAN OUIs:
Enter a text description that helps you identify the manufacturer’s OUI in the
User Defined OUI - Description field. This parameter can be up to 20 characters
in length.
Modify OUI Setting
To modify or delete an OUI, it must be first be deleted and then re-created.
Delete OUI Setting
To delete a specific OUI that had already been entered in the table at the bottom of the
page, click on Delete in the Action column of the table. The specific OUI will be deleted
from the table.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 70

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
66
Security
This chapter contains information about the Port-based security features and the
procedures for setting this feature.
Configure Port Access Control
Security > Port Access Control
This section contains information and configuration procedures for the
Port-based Access Control. Port-based Network Access Control (IEEE 802.1x) is used to
control who can send traffic through and receive traffic from a switch port. With this
feature, the switch does not allow an end node to send or receive traffic through a port
until the user of the node logs on by entering a user name and password.
This feature can prevent an unauthorized individual from connecting a computer to a
port or using an unattended workstation to access your network resources. Only those
users to whom you have assigned a user name and password are able to use the switch
to access the network.
This feature can be used with one of two authentication methods:
The RADIUS authentication protocol requires that a remote RADIUS server is
present on your network. The RADIUS server performs the authentication of
the user name and password combinations.
The Dial-in User (local) authentication method allows you to set up the
authentication parameters internally in the switch without an external server.
In this case, the user name and password combinations are entered in the
associated with an optional VLAN when they are defined. Based on these
entries, the authentication process is done locally by the Web Management
Utility using a standard EAPOL transaction.
Note: RADIUS with Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) extensions is the only
supported authentication server for this feature.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Security and click on Port Access Control.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save the settings.
Configure the following parameters as required:
NAS ID - This parameter assigns an 802.1x identifier to the switch that applies
to all ports. The NAS ID can be up to sixteen characters. Valid characters are 0
to 9, a to z, and A to Z. Spaces are allowed. Specifying an NAS ID is optional.
Port Access Control - This parameter enables or disables Port Access Control.
Select one of the following choices from the pulldown menu:
o Enable: The Port Access Control feature is activated.
o Disable: The Port Access Control feature is de-activated.
Authentication Method - This parameter indicates the authentication method
used by the switch. Select one of the following choices:
o RADIUS: This parameter configures port security for remote
authentication. After completing steps, you must configure the
“RADIUS Client” section.
o Local: This parameter configures port security for local authentication.
After completing steps, you must configure the parameters for “Dial-in
User— Local Authentication” section.
o TACACS+: This parameter configures port security for terminal
authentication. After completing steps, you must configure the
“TACACS+ Settings” section.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 71

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
67
Create Dial-In Users (Local Authentication Method)
Security > Dial-in User
Dial-in User feature provides the local authentication server for port security when a
remote (RADIUS) server is not available.
The Dial-in User (local) authentication method allows you to set up 802.1x
authentication parameters internally in the Switch. In this case, the user name and
password combinations are entered with an optional VLAN when they are defined.
Based on these entries, the authentication process of a supplicant is done locally by the
Switch Management Utility using a standard EAPOL (EAP over LAN) transaction.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Security and click on Dial-In User.
3. Review the settings.
To create a dial-in user for local authentication, use the following procedure:
In the User Name field, type a name for the user.
In the Password field, type a password for the user.
In the Dynamic VLAN field, enter the VID of the VLAN which you will allow the
user to access. If you enter 0, this field will be ignored.
Click Add to add the entry to the table.
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry.
You can also click Delete All to delete all of the entries in the table. If the entries span
multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and click Go or you can
click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 72

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
68
Add RADIUS Servers (RADIUS Authentication Method)
Security > RADIUS
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Security and click on RADIUS.
3. Review the settings.
Server Priority – Enter the RADIUS Server priority (Highest: 1, Lowest: 5).
Server IP Address –Select IPv4 or IPv6 and set the RADIUS server IP address
and enter the IP address of the RADIUS server you would like to add.
Server Port (1 - 65535) –Set the RADIUS authentic server(s) UDP port. The
default port is 1812.
Accounting Port (1 - 65535) –Set the RADIUS account server(s) UDP port. The
default port is 1813.
Shared Secret – Enter the default authentication and encryption key for
RADIUS communication between the device and the RADIUS server.
Click Add to add the entry to the table.
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 73

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
69
Add TACACS+ Servers (TACACS+ Authentication Method)
Security > TACACS+
Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS+) provides centralized
security user access validation. The system supports up-to 5 TACACS+ servers.
TACACS+ provides a centralized user management system, while still retaining
consistency with RADIUS and other authentication processes.
The TACACS+ protocol ensures network integrity through encrypted protocol exchanges
between the client and TACACS+ server. The user-assigned TACACS+ parameters are
applied to newly defined TACACS+ servers. If values are not defined, the system defaults
are applied to the new TACACS+ servers.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Security and click on TACACS+.
3. Review the settings.
Server Priority – Enter the TACACS+ Server priority (Highest: 1, Lowest: 5).
Server IP Address – Enter the TACACS+ Server IP address.
Server Port – Enter the port number via which the TACACS+ session occurs. The
default port is port 49.
Timeout – Enter the amount of time (in seconds) the device waits for an
answer from the TACACS+ server before retrying the query, or switching to the
next server. Possible field values are 1-255. The default value is 5.
Shared Secret – Enter the default authentication and encryption key for
TACACS+ communication between the device and the TACACS+ server.
Click Add to add the entry to the table.
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 74

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
70
Destination MAC Filter
Security > Destination MAC Filter
This section contains an explanation of the Destination MAC Filter feature as well a
procedure for configuring it. This section includes the following information:
The Destination MAC Filter feature prevents the switch from forwarding packets to a
specified device. On the Destination MAC Filter Page of the Web Management Utility
software, enter the MAC address of the device that you want to filter.
After the switch receives a packet, it examines the destination MAC address of the
packet. If the destination MAC address matches a MAC address set in the filter, the
software prevents the switch from forwarding it and drops the packet.
You may want to block access to a device within your organization. For instance, you
may not want users on the Sales group switch to have access to a server on the
Accounting group switch. You can enter the MAC address of the Accounting server as a
destination MAC address filter on the Sales group switch. When a packet destined for
the Accounting server is received by the Sales group switch, the switch drops the packet.
The Destination MAC Filter is a subset of the static MAC address.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Security and click on Destination MAC Filter.
4. The MAC address will be added to the table.
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry.
You can also click Delete All to delete all of the entries in the table. If the entries span
multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and click Go or you can
click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
6. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
3. Enter the MAC Address to add to the destination filter table. Click Add.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 75

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
71
Denial of Service (DoS)
Security > Denial of Service
The switch has built-in DoS prevention features to restrict specific type of traffic
associated denial of service attacks on your network. By default, all of the DoS settings
are set to Allow, which allow any type of traffic to pass through the switch. Setting one
of the items to Deny will set the switch to check for traffic matching the selected item
and deny any traffic matching the rule. On the other hand, setting one of rules to Deny
may deny a specific type of traffic that may prevent traffic essential to running your
network such as devices in load balancing configuration using virtual IP addresses (Ex. If
ARP MAC SA Mismatch is set to Deny, it may cause devices in load balance configuration
using shared virtual IP addresses communication issues essential for network server
load balancing.) For additional security, you can set these rules to Deny as necessary.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Security and click on Denial of Service.
3. Next to the DoS item/rule you would like to activate, click the drop-down menu on
the right hand side and select Deny.
4. Click Apply to save the settings.
Note: You can click “Reset to Default” to restore all DoS settings to Allow.
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
6. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 76

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
72
Class
Maximum Power
Output
from a Switch Port
Power Ranges of the PDs
0
15.4W
0.44W to 12.95W
1
4.0W
0.44W to 3.84W
2
7.0W
3.84W to 6.49W
3
15.4W
6.49W to 12.95W
4
34.2W
25.5W to 38.9W
Priority Level
Description
Description
This is the highest priority level. Ports set to
the Critical level are guaranteed to receive
power before any of the ports assigned to
the other priority levels.
High
Ports set to the High level receive power
only when all the ports assigned to the
Critical level are already receiving power.
Low
This is the lowest priority level. Ports set to
the Low level receive power only when all
the ports assigned to the Critical and High
levels are already receiving power. This
level is the default setting.
PoE Configuration
The main advantage of PoE is that it can make installing a network easier. The selection
of a location for a network device is often limited by whether there is a power source
nearby. This constraint limits equipment placement or requires the added time and cost
of having additional electrical sources installed. However, with PoE, you can install
PoEcompatible devices wherever they are needed without having to worry about
whether there is power source nearby.
Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE)
A device that provides PoE to other network devices is referred to as
power sourcing equipment (PSE). The Gigabit Web Smart PoE+ Switch is a PSE
device which provides DC power to the network cable and functions as a central power
source for other network devices.
Powered Device (PD)
A device that receives power from a PSE device is called a powered
device (PD). Examples include wireless access points, IP phones, webcams, and even
other Ethernet switches.
PD Classes PDs are grouped into five classes. The classes are based on the amount of
power that PDs require. The Gigabit Web Smart PoE+ Switch supports all five classes.
Power Budget
Power budget is the maximum amount of power that the PoE switch can provide at one
time to the connected PDs. Port Prioritization As long as the total power requirements
of the PDs is less than the total available power of the switch, it can supply power to all
of the PDs.
However, when the PD power requirements exceed the total available
power, the switch denies power to some ports based on a process called port
prioritization.
The ports on the PoE switch are assigned to one of three priority levels. These levels and
descriptions are listed in Table 3. Without enough power to support all the ports set to
the same priority level
at one time, the switch provides power to the ports based on the port
number, in ascending order. For example, when all of the ports in the
switch are set to the low priority level and the power requirements are
exceeded on the switch, port 1 has the highest priority level, port 2 has the next highest
priority level and so forth.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 77

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
73
Configure PoE settings
PoE Configuration
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on PoE Configuration.
3. Review the settings for each port. Next to each port entry, click Apply to save the
settings.
Power Budget – Displays the maximum PoE power budget in watts.
Power Consumption – Displays the current PoE power provided to PoE devices
or PDs (Powered devices) in watts.
Port - Indicates the port with a specific PoE status and that you are configuring.
Note: You can select the row labled ALL to apply settings to all ports.
Admin - To activate or deactivate PoE on a specific port, select Enable or
Disable. By default the PoE feature is disabled on all switch ports.
Status - The PoE port status is given as follows:
o Power ON - The port is supplying PoE power.
o Power OFF - The port is not supplying PoE power.
Class - The PoE class is indicated the class of the PD. N/A is displayed when the
port is not supplying power.
Priority - Indicates the port priority: Low, High, or Critical.
Power(mW) - Indicates the Power in milliwatts that the port is supplying power
to the PD.
Voltage(V) - Indicates the Voltage in volts as measured at the port when the
port is supplying power to the PD.
Current(mA) - Indicates the Current in milliamps that the port is supplyng to
the PD.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 78

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
74
DHCP Snooping
Here is a summary of the rules to observe when you configure DHCP Snooping:
A trusted port is connected to one of the following:
o Directly to the legitimate trusted DHCP Server.
o A network device relaying DHCP messages to and from a trusted
server.
o Another trusted source such as a switch with DHCP Snooping enabled.
o Untrusted ports are connected to DHCP clients and to traffic that
originates outside of the local area network.
The VLANs to which the DHCP Snooping feature applies must be specified in
the DHCP Snooping VLAN Setting configuration.
Any static IP addresses on the network must be manually added to the Binding
Database.
Enable DHCP Snooping
DHCP Snooping > General Settings
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on DHCP Snooping and click on General Settings.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save the settings.
DHCP Snooping - Select one of the following radio button choices:
o Enabled - This parameter activates the DHCP Snooping feature.
o Disabled - This parameter de-activates the DHCP Snooping
Pass Through Option 82 - Select one of the following choices from the pull-
down menu:
o Enable - Allows an Option 82 packet to be passed through the switch
without being altered.
o Disable - Blocks an Option 82 packet from passing through the switch.
Verify MAC Address - Select one of the following choices from the pull-down
menu:
Backup Database - select one of the following choices from the pull-down
Database Update Interval - Enter the database update interval. The range of
DHCP Option 82 Insertion - select one of the following choices from the pull-
o Enable - The MAC address of each ingress ARP packet is validated
when compared against the Binding Table entries. Invalid ARP packets
are discarded.
o Disable - The MAC address of each ingress ARP packet is not validated
against the Binding Table. All ARP packets are forwarded through the
switch without regard to the IP and MAC Address information in the
packet header.
menu:
o Enable - The Web Management Utility Software saves a backup copy
of the Binding Table to flash at a specified interval (Database Update
Interval) of time.
o Disable - The Web Management Utility Software does not save a
backup copy of the Binding Table to flash.
this interval is 600 to 86400 seconds.
down menu:
o Enable: The Web Management Utility software inserts the DHCP
Option 82 information into the DHCP packets.
o Disable: The Web Management Utility software does not insert the
DHCP Option 82 information into the DHCP packets.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 79

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
75
Enable DHCP Snooping
DHCP Snooping > VLAN Settings
In this section, you can define an existing VLAN to apply DHCP snooping.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on DHCP Snooping and click on VLAN Settings.
3. In the field, enter the existing VLAN ID to apply DHCP Snooping. Then click Add to add
the VLAN entry to the table.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry.
You can also click Delete All to delete all of the entries in the table. If the entries span
multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and click Go or you can
click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 80

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
76
Set Trusted Interfaces
DHCP Snooping > Trusted Interfaces
This section allows you to set trusted port interfaces where DHCP servers can be
connected allows or denies DHCP server information to be received on those ports.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on DHCP Snooping and click on Trusted Interfaces.
3. Next to each port, click the Trust drop-down list and select one of the following
options.
Disable: This parameter defines the port as untrusted for the DHCP Snooping
feature.
Enable: This parameter defines the port as trusted for the DHCP Snooping
feature.
Note: You can select the row labeled ALL to apply settings to all ports.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Configure Binding Database
DHCP Snooping > Binding Database
The Binding Database displays learned and statically assigned MAC
Address and IP Address information for each host on the local area
network. Dynamically assigned IP addresses from the DHCP server will automatically
populate the table on the Binding Database page as they are assigned by the server.
Statically assigned IP addresses are entered manually by entering the host’s address
information and clicking on the Add button.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on DHCP Snooping and click on Binding Database.
3. Review the settings. Click Add to add the database entry to the table.
MAC Address - Enter the host’s MAC Address.
IP Address - Enter the static IP Address assigned to the host.
VLAN - Enter the host’s VLAN ID.
Port - Enter the port number where the host is connected.
Type - Because the IP Address being entered is static, you must select Static.
Lease Time - Enter the time that IP address assignment is valid. The range is 10
to 4294967295 seconds.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 81

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
77
Click Add to add the database entry to the table.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
In the list, you can click Modify to modify an entry or click Delete or delete the entry.
You can also click Delete All to delete all of the entries in the table. If the entries span
multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and click Go or you can
click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
MAC Address: This parameter shows the host’s MAC Address.
VLAN ID: This parameter shows the host’s VLAN ID of which the DHCP client is
a member.
IP Address: This parameter is the IP Address assigned by the DHCP server to
the DHCP client.
Port: This parameter is the port number where the DHCP client is connected.
Type: This parameter indicates the following:
Learned-The host IP Address is dynamically assigned by the DHCP server.
Static- The host IP Address is statically assigned. See “Static IP Addresses” on
page 300 for more information.
Lease Time: This parameter is the time that IP address assignment by the DHCP
server is valid.
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 82

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
78
LLDP (Link-Layer Discovery Protocol)
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) allows Ethernet network devices, such as switches
and routers, to receive and transmit device-related information to directly connected
devices on the network and to store data that is learned about other devices.
Enable and configure LLDP
LLDP > LLDP Global Settings
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on LLDP and click on LLDP Global Settings.
3. Review the settings.
Enabling or Disabling LLDP
From the LLDP parameter, select one of the following radio button choices and
click Apply to save the settings.
Enable: The LLDP feature is active.
Disable: The LLDP feature is inactive.
LLDP Reinit Delay: Sets the reinitialization delay, which is the number of seconds that
must elapse after LLDP is disabled on a port before it can be reinitialized. The range is
from 1 to 10 seconds.
LLDP TX Delay: Sets the value of the transmission delay timer, which is the minimum
time interval between transmissions of LLDP advertisements due to a change in LLDP
local information. The range is from 1 to 8192 seconds.
Click Apply to save the settings.
Configure the LLDP Settings
Message TX Hold Multiplier: Sets the hold multiplier value. The hold time multiplier is
multiplied by the transmit interval to give the Time To Live (TTL) that the switch
advertises to the neighbors. The range is from 2 to 10.
Message TX Interval: Sets the transmit interval, which is the interval between regular
transmissions of LLDP advertisements. The range is from 1 to 10 seconds.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 83

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
79
View LLDP System Information
Chassis ID Subtype: This parameter describes the Chassis ID subtype which is
“macAddress”. You cannot change this parameter.
Chassis ID: This parameter lists the MAC Address of the switch.
You cannot change this parameter.
System Name: This parameter lists the System Name of the switch. You can
assign the system name.
System Description: This parameter lists the product name of the switch. You
cannot change this parameter
Set LLDP Port State
For each port, click the State drop-down list and choose from the following options.
Disabled: Indicates LLDP is disabled on the port. The port cannot receive or
transmit LLDP data packets.
Enabled: Indicates LLDP is enabled on the port. The port can receive and
transmit LLDP data packets.
RxOnly: Indicates LLDP is enabled on the port. The port can receive LLDP data
packets.
TxOnly: Indicates LLDP is enabled on the port. The port can transmit LLDP data
packets.
Note: You can select the row labeled ALL to apply settings to all ports.
Click Apply to save the settings.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 84

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
80
View LLDP Neighbor Information
LLDP > LLDP Neighbor Information
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on LLDP and click on LLDP Neighbor Information.
3. View the LLDP neighbor information.
Entity: This parameter is a number assigned to the reporting neighbors in the
order that the LLDP information is received from them.
Port: This parameter specifies the TPE-1020WS local port number where the
LLDP information was received.
Chassis ID Subtype: This parameter describes the Chassis ID subtype of the
neighboring network device which is reporting the LLDP information.
Chassis ID: This parameter is the neighboring device’s chassis ID.
Port ID Subtype: This parameter describes the Port ID subtype of the
neighboring network device’s port that is connected directly to the TPE1020WS switch port.
Port ID: This parameter specifies the neighboring network device’s port
number from which the LLDP information was transmitted.
Port Description: This parameter describes the neighboring network device’s
port.
Show Normal: If you click on this button, a detailed report of the neighboring
network device will be displayed.
If the entries span multiple pages, you can navigate page number in the Page field and
click Go or you can click First, Previous, Next, and Last Page to navigate the pages.
Statistic
Statistics provide important information for troubleshooting switch problems at the port
level. The Web Management Utility provides a two statistics charts, including Traffic
Information and Error Information.
View Traffic Information Statistics
Statistic > Traffic Information
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Statistic and click on Traffic Information.
3. View the Traffic Information Statistics.
InOctets: Inbound Octets (Bytes/s), number of inbound octet bits in bytes per
second.
InUcastPkts: Inbound Unicast Packets (Pkts), number of inbound unicast
packets in packets per second.
InNUcastPkts: Inbound Non-unicast Packets (Pkts), number of inbound non-
unicast packets (such as broadcast and multicast packets) in packets per
second.
InDiscards: Inbound Discards (Pkts), number of inbound discarded packets in
packets per second.
OutOctets: Outbound Octets (Bytes/s), rate of outbound octet bits in bytes per
second.
OutUcastPkts: Outbound Unicast Packets (Pkts), number of outbound unicast
packets in packets per second.
OutNUcastPkts: Outbound Non-unicast Packets (Pkts), number of outbound
non-unicast (such as broadcast and multicast packets) packets.
OutDiscards: Outbound Discards (Pkts), number of outbound discarded
packets.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 85

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
81
View Error Information Statistics
Statistic > Error Information
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Statistic and click on Traffic Information.
3. View the Error Information Statistics.
InErrors: Inbound Errors (Pkts), number of inbound errors in packets per
second.
OutErrors: Outbound Errors (Pkts), number of outbound error packets.
DropEvents: Drop Events, number of packets dropped.
CRCAlignErrors: CRC and Align Errors, number of CRC and Align errors that
have occurred.
UndersizePkts: Undersize Packets (Pkts), number of undersized packets (less
than 64 octets) received.
OversizePkts: Oversize Packets (Pkts), number of oversized packets (over 2000
octets) received.
Fragments: Number of fragments (packets with less than 64 octets, excluding
framing bits, but including FCS octets) received.
Collisions: Number of collisions received. If Jumbo Frames are enabled, the
threshold of Jabber Frames is raised to the maximum size of Jumbo Frames.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 86

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
82
Switch Maintenance
Upgrade your switch firmware
Tools > Firmware Upgrade
TRENDnet may periodically release firmware upgrades that may add features or fix
problems associated with your TRENDnet switch model and version. To check if there is
a firmware upgrade available for your device, please check your TRENDnet model and
version using the link. http://www.trendnet.com/downloads/
In addition, it is also important to verify if the latest firmware version is newer than the
one your switch is currently running. To identify the firmware that is currently loaded on
your switch, log in to the switch, click on the System Info section or click on Tools and
click on Firmware Upgrade. The firmware used by the switch is listed as Runtime Image
or Image Version. If there is a newer version available, also review the release notes to
check if there were any new features you may want or if any problems were fixed that
you may have been experiencing.
1. If a firmware upgrade is available, download the firmware to your computer.
2. Unzip the file to a folder on your computer.
Please note the following:
Do not interrupt the firmware upgrade process. Do not turn off the device or
press the Reset button during the upgrade.
If you are upgrade the firmware using a laptop computer, ensure that the laptop
is connected to a power source or ensure that the battery is fully charged.
Disable sleep mode on your computer as this may interrupt the firmware upgrade
process.
Do not upgrade the firmware using a wireless connection, only using a wired
network connection.
Any interruptions during the firmware upgrade process may permanently
damage your switch.
Firmware Upgrade via HTTP Settings
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Tools, click on Firmware Upgrade, and click via HTTP.
3. Depending on your web browser, in the Upload Firmware section, click Browse or
Choose File.
4. Navigate to the folder on your computer where the unzipped firmware file (.hex) is
located and select it.
5. Click Apply. If prompted, click Yes or OK.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 87

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
83
Firmware Upgrade via TFTP Settings
Note: Before using this method, you will require a TFTP server. There are third party
TFTP server applications available for this function. If you are not familiar with the TFTP
protocol, it is recommended to use the HTTP method.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Tools, click on Firmware Upgrade, and click via TFTP.
3. Make sure your TFTP server is running and note the IP address of your server and
firmware file name. The TFTP server should be in the same IP subnet as the switch.
Note: It is recommended to that the firmware file (.hex) is placed in your TFTP server
root directory.
4. Review the settings. Click Apply to start the firmware upgrade.
TFTP Server IP: Enter the IP address of your TFTP server.
Image File Name: Enter the firmware filename with extension. (.hex)
Retry Count: Defined the number of time to attempt to pull the firmware file
from the TFTP server.
5. Click Apply to start the firmware upgrade.
Backup and restore your switch configuration settings
Tools > Config File Backup/Restore
You may have added many customized settings to your switch and in the case that you
need to reset your switch to default, all your customized settings would be lost and
would require you to manually reconfigure all of your switch settings instead of simply
restoring from a backed up switch configuration file.
Backup/Restore via HTTP Settings
To backup your switch configuration:
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Tools, click on Configuration File Backup/Restore, and click on via HTTP.
3. Click Backup to save the configuration file (config.bin) to your local hard drive.
Note: If prompted, choose the location on your local hard drive. If you are not prompted,
the configuration file (config.bin) will be saved to your default downloads folder.
To restore your switch configuration:
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Tools, click on Configuration File Backup/Restore, and click on via HTTP.
3. Next to Select File, depending on your web browser, click on Browse or Choose File.
4. A separate file navigation window should open.
5. Select the switch configuration file to restore and click Restore. (Default Filename:
config.bin). If prompted, click Yes or OK.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
6. Wait for the switch to restore settings.
Page 88

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
84
Backup/Restore via TFTP Settings
Note: Before using this method, you will require a TFTP server. There are third party
TFTP server applications available for this function. If you are not familiar with the TFTP
protocol, it is recommended to use the HTTP method.
To backup your switch configuration:
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Tools, click on Configuration File Backup/Restore, and click on via TFTP.
3. Make sure your TFTP server is running and note the IP address of your server and
firmware file name. The TFTP server should be in the same IP subnet as the switch.
4. Review the settings. Click Backup to save the configuration file (config.bin) to your
local hard drive on your TFTP server root directory.
TFTP Server IP: Enter the IP address of your TFTP server.
Config File Name: Enter the configuration file name for the backup. (Default:
config.bin)
To restore your switch configuration:
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Tools, click on Configuration File Backup/Restore, and click on via HTTP.
3. Make sure your TFTP server is running and note the IP address of your server and
configuration file name. The TFTP server should be in the same IP subnet as the switch.
Note: It is recommended to put the configuration file (config.bin) is placed in your TFTP
server root directory.
4. Review the settings. Click Restore to restore the switch configuration file (config.bin)
from your local hard drive from your TFTP server root directory.
TFTP Server IP: Enter the IP address of your TFTP server.
Config File Name: Enter the configuration file name to restore. (Default:
config.bin)
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
5. Wait for the switch to restore settings.
Page 89

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
85
Cable Diagnostics Test
Tools > Cable Diagnostics
The switch provides a basic cable diagnostic tool in the GUI for verifying the pairs in
copper cabling and estimated distance for troubleshooting purposes.
Note:
1. If the cable length displays N/A, it means that the cable length is Not Available. The
may be due to the port being unable to determine the estimated cable length. If length is
displayed as “N/A” it means the cable length is “Not Available”. This is due to the port
being unable to obtain cable length/either because its link speed is 10M or 100M, or the
cables used are broken and/or of bad in quality.
2. The deviation of “Cable Fault Distance” is +/- 2 meters. No cable may be displayed in
the table when the cable is less than 2 meters in length.
3. The test also measures the cable fault and identifies the fault in length according to
the distance from the switch.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Tools and click on Cable Diagnostic.
3. Click on the Port drop-down list to select which port to run the cable diagnostic and
click Test Now to run the test.
The results will be displayed in the Cable Diagnostic Table below.
Test Results: Displays the diagnostic results for each pair in the cable. One of
the following cable status parameters is displayed:
o OK: There is no problem detected with the cable.
o Open in Cable: There is an open wire within the cable.
o Short in Cable: Two wires are shorted together within the cable.
o Cross talk in Cable: There is crosstalk detected between one pair
o of wires and another pair within the cable.
Cable Fault Distance: This parameter specifies the distance from the switch
port to the cable fault.
Cable Length: This parameter specifies the length of the cable connected to the
switch port.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 90

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
86
Enable IEEE 802.3az Power Saving Mode
Tools > IEEE 802.3az EEE
The IEEE 802.3 EEE standard defines mechanisms and protocols intended to reduce the
energy consumption of network links during periods of low utilization, by transitioning
interfaces into a low-power state without interrupting the network connection. The
transmitted and received sides should be IEEE802.3az EEE compliance. By default, the
switch disabled the IEEE 802.3az EEE function. Users can enable this feature via the
IEEE802.3az EEE setting page.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Tools and click on IEEE 802.3az EEE.
3. Click the IEEE 802.3az EEE Status drop-down list and select Enabled to enable the
power saving feature and click Apply to save the settings.
4. Click Save Settings to Flash (menu).
5. Click Save Settings to Flash (button), then click OK.
Note: This step saves all configuration changes to the NV-RAM to ensure that if the
switch is rebooted or power cycled, the configuration changes will still be applied.
Reboot/Reset to factory defaults
Tools > Reboot
This section provides the procedures for rebooting or resetting the switch to factory
default settings.
To reboot your switch:
You may want to reboot your switch if you are encountering difficulties with your switch
and have attempted all other troubleshooting.
Note: You may want to save the settings to flash before reboot the switch under Save
Settings to Flash (menu) > Save Settings to Flash (button). If you have not saved your
current configuration settings to flash first, the configuration changes will be lost after a
reboot.
There are two methods that can be used to reboot your switch.
Hardware Method: Using a paper clip, on the front panel of the switch, push
and hold the Reset button between 5-9 seconds and release.
Software Method (Switch Management Page):
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Tools and click on Reboot.
3. Click the Reboot Type drop-down list and select Normal and click Apply to initiate a
reboot. Wait for the switch complete the rebooting process.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 91

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
87
Administrator User Name
admin
Administrator Password
admin
Switch IP Address
192.168.10.200
Switch Subnet Mask
255.255.255.0
To reset your switch to factory defaults:
You may want to reset your switch to factory defaults if you are encountering difficulties
with your switch and have attempted all other troubleshooting. Before you reset your
switch to defaults, if possible, you should backup your switch configuration first, see
“Backup and restore your switch configuration settings” on page 44.
There are two methods that can be used to reset your switch to factory defaults.
Hardware Method: Using a paper clip, on the front panel of the switch, push
and hold the Reset button more than 10 seconds and release. Located on the
front panel of your switch, see “Product Hardware Features” on page 6. Use
this method if you are encountering difficulties with accessing your switch
management page.
Software Method (Switch Management Page):
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Tools and click on Reboot.
3. Click the Reboot Type drop-down list and select from one of the following options
Factory Default: Resets all switch configuration settings to factory defaults
including the IP address.
Factory Default Except IP: Resets all switch configuration settings to factory
defaults and leaves the current IP address configuration.
Network Connectivity Test (Ping Tool)
Tools > IEEE 802.3az EEE
This chapter provides the procedure to ping a node on your network from the switch.
This procedure is useful in determining whether an active link exists between the switch
and another network device.
The device you are pinging must be a member of the Default VLAN and within the same
local area network as your switch. In other words, the port on the switch through which
the node is communicating with the switch must be an untagged or tagged member of
the Default VLAN.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 7).
2. Click on Tools and click on Ping.
3. Review the settings. Click Start to start the network connectivity ping test. After the
ping test is activate, you can click Show Ping Results to check the ping test result.
Destination IP Address - The IP address of the node you want to ping in the
IPv4 or IPv6 format.
Timeout Value - Specifies the length of time, in seconds, the switch waits for a
response before assuming that a ping has failed.
Number of Ping Requests - Specifies the number of ping requests you want the
switch to perform.
The switch factory default settings are below.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 92

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
88
Using the Web Smart Switch Management Utility
The Web Smart Switch Management Utility allows you to do the following:
You can easily discover all TRENDnet web smart switches on your network
using the discover feature.
You can modify the IP address settings, change the admin password, and
upgrade firmware for multiple switches.
4. At the Utility installation window, click Next.
System Requirements
Operating System: Windows® 8.1 (32/64-bit), Windows® 8 (32/64-bit), Windows 7
(32/64-bit), Vista (32/64-bit), or XP (32/64-bit)
Installation
1. Insert the included CD-ROM into your computer’s CD-ROM drive.
2. At the CD Autorun Prompt window, click Run Autorun.exe .
Note: If the Autorun prompt does not appear automatically, open the CD contents and
double-click Autorun.exe.
3. At the CD-ROM main menu, click Install Utility.
5. At the Install Location installation window, click Next.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 93

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
89
6. At the Installation, click Install.
Using the Utility
Launching the Utility
Upon completing the software installation, a desktop shortcut is automatically created.
Double-click the icon to start the utility or open the utility if it is already running. Closing
the utility will exit the application. You can also click Exit at the bottom of the utility user
interface to exit the application.
7. In the Completion window, click Finish.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
You can also launch the utility from the Start Menu programs.
Start > Programs (or All Programs) > TRENDnet Management Utility > TRENDnet
Management Utility.exe
Page 94

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
90
Discovery List
This is the list where you can discover all the Web management devices in your network.
By pressing the “Discovery” button, you can list all the Web Smart Management
switches in the discovery list.
Double click or press the “Add to monitor list” button to select a device from the
Discovery List to the Monitor List.
System word definitions in the Discovery List:
MAC Address: Shows the device MAC Address.
IP Address: Shows the current IP address of the device.
Protocol version: Shows the version of the Utility protocol.
Product Name: Shows the device product name.
System Name: Shows the appointed device system name.
IP Mode: Shows the DHCP status of the device.
Location: Shows where the device is located.
Subnet Mask: Shows the Subnet Mask set of the device.
Gateway: Shows the Gateway set of the device.
Group Interval:
Monitor List
All the Web Smart switches in the Monitor List can be monitored; you can also receive
the trap and show the status of the device.
System word definitions in the Monitor List:
S: Shows the system symbol of the Web-Smart device, represent for device
system is not alive.
IP Address: Shows the current IP address of the device.
MAC Address: Shows the device MAC Address.
Protocol version: Shows the version of the Utility protocol.
Product Name: Shows the device product name.
System Name: Shows the appointed device system name.
IP Mode: Shows the DHCP status of the device.
Location: Shows where the device is located.
Subnet Mask: Shows the Subnet Mask set of the device.
Gateway: Shows the Gateway set of the device.
Group Interval:
Add Item: To add a device to the Monitor List manually, enter the IP Address of
the device that you want to monitor.
Delete Item: To delete the device in the Monitor List.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 95

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
91
Device Setting
You can set the device by using the function key in the Device Setting Dialog box.
Configuration Setting: In this Configuration Setting, you can set the IP Address, Subnet
Mask, Gateway, Group Interval, System name, Location and IP Mode.
Select the device in the Discovery list or Monitor List and press this button, then the
Configuration Setting window will appear, after entering the data that you want to
change, you must enter the password and press the “Set” to process the data change
immediately. The default password of TRENDnet Web Smart Switches is “admin”.
Firmware Upgrade: When the device has a new function, there will be a new firmware
to update the device, use this function to update.
Access Web: Double click the device in the Monitor List or select a device in the Monitor
List and press this “Web Access” button to access the device in Web browser.
DHCP Refresh: Press this “DHCP Refresh” button to refresh IP address of selected device
Password Change: You can use this Password Change when you need to change the
password, fill in the password needed in the dialog box and press “Set” button to
proceed the password change immediately.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
form DHCP server. (Only applies if Web Smart switch IP address settings are set to
DHCP).
Page 96

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
92
Main Menu Options
In the “File TAB”, there are Monitor Save, Monitor Save As, Monitor Load and Exit.
Monitor Save: To record the setting of the Monitor List to the default, when you
open the Web Management Utility next time, it will auto load the default
recorded setting.
Monitor Save As: To record the setting of the Monitor List in appointed filename
and file path.
Monitor Load: To manually load the setting file of the Monitor List.
Exit: To exit the Web Management Utility.
In the “View TAB”, there are view log and clear log function, this function will help you
to show trap setting.
View Log: To show the event of the Web Management Utility and the device.
Clear Log: to clear the log.
In the “Option TAB”, there are Refresh Time and Group Interval
Refresh Time: This function helps you to refresh the time of monitoring the
device. Choose 15 secs, 30 secs, 1 min, 2 min and 5 min to select the time of
monitoring.
Group Interval: 120~1225
In the “Help TAB”, there is About function, it will show out the version of the Web
Management Utility.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 97

93
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
Switch Management Page Structure
Switch Info
System
System Management
IPv4 Setup
IPv6 System Settings
IPv6 Neighbor Settings
DNS Settings
IP Access List
Administration
User Interface
System Time
SSL Settings
DHCP Auto Configuration
System Log Settings
Physical Interface
Bridge
Spanning Tree
Trunk Config
IGMP Snooping
Bandwidth Control
VLAN
GVRP
QoS
SNMP
Engine ID
View Table
Group Access Table
SNMP User/Group
Community Table
Trap Management
Access Control Config
Policy Settings
Rate Control Settings
Policy Database
RMON
Global Settings
Statistics
History
Alarms
Event
Voice VLAN
Voice VLAN Settings
Voice VLAN OUI Settings
Security
Port Access Control
Dial-In User
RADIUS
TACACS+
Destination MAC Filter
Denial of Service
PoE Configuration
DHCP Snooping
General Settings
VLAN Settings
Trusted Interfaces
Binding Database
LLDP
LLDP Global Settings
LLDP Neighbor Information
Statistic
Traffic Information
Error Information
Tools
Firmware Upgrade
Config File Backup/Restore
Cable Diagnostics
IEEE 802.3az EEE
Reboot
o Reset to factory defaults
Ping
Save Settings to Flash
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 98

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
94
Technical Specifications
Standards
IEEE 802.1d
IEEE 802.1p
IEEE 802.1Q
IEEE 802.1s
IEEE 802.1w
IEEE 802.1X
IEEE 802.1ab
IEEE 802.3
IEEE 802.3u
IEEE 802.3x
IEEE 802.3z
IEEE 802.3ab
IEEE 802.3ad
IEEE 802.3af
IEEE 802.3at
IEEE 802.3az
Device Interface
8 x Gigabit PoE+ ports (ports 1-8)
2 x Gigabit Ethernet ports (ports 9R - 10R)
2 x Shared SFP slots (shared with ports 9R - 10R)
LED indicators
Data Transfer Rate
Ethernet: 10 Mbps (half duplex), 20 Mbps (full duplex)
Fast Ethernet: 100 Mbps (half duplex), 200 Mbps (full duplex)
Gigabit Ethernet: 2000 Mbps (full duplex)
Performance
Switch fabric: 20 Gbps
Ram buffer: 1 MB
MAC Address Table: 16K entries
Jumbo Frames: 10 KB
HOL Blocking Prevention
Forwarding rates: 14.88 Mpps (64-byte packet size)
Management
HTTP/HTTPS (SSL v2/3 TLS) Web based GUI
SNMP v1, v2c, v3
RMON v1
Static Unicast MAC Address
Enable/disable 802.3az Power Saving
LLDP
Virtual Cable Test
IPv6: IPv6 Neighbor Discovery, IPv6 Static IP, DHCPv6, Auto configuration
MIB
MIB II RFC 1213
Bridge MIB RFC 1493
Bridge MIB Extension RFC 2674
SNMPv2 MIB RFC 1907
Ethernet Interface MIB RFC 1643
Ethernet –like MIB RFC 2863
Interface Group MIB RFC2233
MIB Traps Convention RFC 1215
RMON MIB RFC 1757, RFC 2819
802.1p MIB RFC 2674
RADIUS Client Authentication MIB RFC 2618
LLDP-MIB IEEE 802.1ab
Ping MIB RFC 2925, RFC 4560
Spanning Tree
IEEE 802.1D STP (Spanning Tree protocol)
IEEE 802.1w RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree protocol)
IEEE 802.1s MSTP (Multiple Spanning Tree protocol)
Link Aggregation
Static Link Aggregation
802.3ad Dynamic LACP
Quality of Service (QoS)
802.1p Class of Service (CoS)
DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point)
Bandwidth Control per port
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 99

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
95
Queue Scheduling: Strict Priority, Weighted Round Robin (WRR)
VLAN
Multiple management VLAN assignment
Asymmetric VLAN
802.1Q Tagged VLAN
Dynamic GVRP
Up to 256 VLAN groups, ID Range 1-4094
Private VLAN (Protected Ports)
Voice VLAN (10 user defined OUIs)
Compatibility
Optional Software Utility: Windows® 8.1 (32/64-bit), 8 (32/64-bit), 7 (32/64-bit), Vista (32/64-
bit), XP (32/64-bit), Windows® 2003/2008 Server (32/64-bit)
Special Features
PoE+
Fanless design
IPv6
802.3az power saving
Rack mountable
Multicast
IGMP Snooping v1, v2, v3 (per VLAN)
Static Multicast Address
Up to 256 multicast entries
Port Mirror
RX, TX, or Both
One to one
Many to one
Access Control
802.1X Port-Based Network Access Control, RADIUS, TACACS+
Local Dial In User Authentication
DHCP Snooping (per VLAN)
Loopback Detection
Duplicated Address Detection
Trusted Host
Denial of Service (DoS)
ACL IPv4 L2-L4 & IPv6
MAC Address
VLAN ID
Ether Type (IPv4 only)
IP Protocol 0-255
TCP/UDP Port 1-65535
802.1p
DSCP (IPv4 only)
IPv6 Address (IPv6 only)
Power
Input: 100 - 240 V AC, 50/60 Hz, internal power supply
Consumption: 92.3 Watts (Max)
PoE budget: 75 Watts
Fan/Acoustics
Fanless design
MTBF
545,798 hours
Operating Temperature
0 – 45 °C (32 - 113 °F)
Operating Humidity
Max 90% non-condensing
Dimensions
330 x 183 x 44.45 mm (13 x 7.2 x 1.75 in.)
Rack mountable 1U height
Weight
1.9 kg (4.1 lbs.)
Certifications
CE
FCC
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 100

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-1020WS
96
Troubleshooting
Q: I typed http://192.168.10.200 in my Internet Browser Address Bar, but an error
message says “The page cannot be displayed.” How can I access the switch
management page?
Answer:
1. Check your hardware settings again. See “Switch Installation” on page 8.
2. Make sure the Power and port Link/Activity and WLAN lights are lit.
3. Make sure your network adapter TCP/IP settings are set to Use the following IP
address or Static IP(see the steps below).
4. Make sure your computer is connected to one of the Ethernet switch ports.
5. Since the switch default IP address is 192.168.10.200, make sure there are no other
network devices assigned an IP address of 192.168.10.200
Windows 7/8/8.1
a. Go into the Control Panel, click Network and Sharing Center.
b. Click Change Adapter Settings, right-click the Local Area Connection icon.
c. Then click Properties and click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
d. Then click Use the following IP address, and make sure to assign your
network adapter an IP address in the subnet of 192.168.10.x. Click OK
Windows Vista
a. Go into the Control Panel, click Network and Internet.
b. Click Manage Network Connections, right-click the Local Area Connection
icon and click Properties.
c. Click Internet Protocol Version (TCP/IPv4) and then click Properties.
d. Then click Use the following IP address, and make sure to assign your
network adapter an IP address in the subnet of 192.168.10.x. Click OK
Windows XP/2000
a. Go into the Control Panel, double-click the Network Connections icon
b. Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and the click Properties.
c. Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
d. Then click Use the following IP address, and make sure to assign your
network adapter an IP address in the subnet of 192.168.10.x. Click OK
Note: If you are experiencing difficulties, please contact your computer or operating
system manufacturer for assistance.
Q: If my switch IP address is different than my network’s subnet, what should I do?
Answer:
You should still configure the switch first. After all the settings are applied, go to the
switch configuration page, click on System, click IPv4 Setup and change the IP address of
the switch to be within your network’s IP subnet. Click Apply, then click OK. Then click
Save Settings to Flash (menu) and click Save Settings to Flash to save the IP settings to
the NV-RAM.
Q: I changed the IP address of the switch, but I forgot it. How do I reset my switch?
Answer:
Using a paper clip, push and hold the reset button on the front of the switch and release
after 15 seconds.
The default IP address of the switch is 192.168.10.200. The default user name and
password is “admin”.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...