Trendnet TEW-829DRU User's Guide

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Cover Page

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Table of Contents
Product Overview ........................................................................... 1
Package Contents .......................................................................................................... 1
Features ......................................................................................................................... 1
Product Hardware Features........................................................................................... 3
Applications ................................................................................................................... 5
Router Installation .......................................................................... 2
Desktop Hardware Installation ...................................................................................... 2
Rack Mount Hardware Installation ................................................................................ 2
Basic Installation and Configuration .............................................................................. 3
Basic Router Settings ....................................................................... 8
Access your router management page .......................................................................... 8
Saving and applying router configuration changes ....................................................... 8
Change your administrator password ........................................................................... 8
Set your router date and time ....................................................................................... 9
Application layer gateway (ALG) ................................................................................. 26
UPnP and NAT-PMP ..................................................................................................... 27
Static routes ................................................................................................................. 27
Dynamic routing protocols .......................................................................................... 28
Routing Information Protocol (RIP).................................................................................. 28
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) ...................................................................................... 29
Quality of Service (QoS) ............................................................................................... 30
Dynamic DNS ............................................................................................................... 32
File sharing server ........................................................................................................ 33
Wake on LAN (WoL) ..................................................................................................... 34
Wireless Networking and Security ................................................. 35
Wireless Settings ......................................................................................................... 35
Primary SSID ..................................................................................................................... 35
Multiple SSID .................................................................................................................... 37
How to choose the type of wireless security ............................................................... 38
Secure your wireless network ..................................................................................... 39
Table of Contents
Create time schedules ................................................................................................. 10
Change LAN IPv4 address settings ............................................................................... 11
Configure LAN IPv4 DHCP server settings .................................................................... 12
Add static DHCP reservations ...................................................................................... 15
Add static host name entries ....................................................................................... 15
Add static ARP entries ................................................................................................. 16
Configure WAN1 / WAN2 interfaces for Internet connectivity ................................... 17
IPv6 settings ................................................................................................................. 19
Virtual LANs (VLANs) .................................................................................................... 20
Create a port-based VLAN ................................................................................................ 20
Create a port-based VLAN with 802.1Q tagging .............................................................. 21
Assigning VLAN IDs to Wireless SSIDs .............................................................................. 24
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Guest Network............................................................................................................. 41
WiFi client bridge mode .............................................................................................. 42
Connect wireless devices using WPS ........................................................................... 43
Steps to improve wireless connectivity ....................................................................... 45
Firewall & security settings ........................................................... 46
General settings ........................................................................................................... 46
Port forwarding rules................................................................................................... 47
Port trigger rules .......................................................................................................... 48
IP filtering .................................................................................................................... 49
MAC filtering ................................................................................................................ 50
Denial of service (DoS) prevention .............................................................................. 51
DMZ Host ..................................................................................................................... 51
i

TRENDnet User’s Guide
One-to-One NAT .......................................................................................................... 52
RADIUS Authentication ................................................................................................ 54
Multiple WAN Configuration ......................................................... 55
Multiple WAN Management Settings .......................................................................... 55
MWAN Status ................................................................................................................... 55
Link Tracking .................................................................................................................... 55
Default Traffic Rule .......................................................................................................... 56
Web Management System (Router Limits™) .................................. 57
Setup your router with Router Limits .......................................................................... 57
Router Limits Content Management ........................................................................... 59
Virtual Private Networking (VPN) .................................................. 62
Creating a Virtual Private Network (VPN) .................................................................... 62
PPTP VPN Server .......................................................................................................... 63
Setting up the PPTP VPN server ....................................................................................... 63
Setting up the PPTP VPN client (Windows) ...................................................................... 65
L2TP VPN Server .......................................................................................................... 66
IPsec ................................................................................................................................. 88
OpenVPN .......................................................................................................................... 89
Router Maintenance and Monitoring ............................................ 90
Managing access to the router management interface .............................................. 90
Local Access Management ............................................................................................... 90
Remote Access Management .......................................................................................... 90
Diagnostic tools ........................................................................................................... 91
Backup and restore your router configuration settings .............................................. 92
Reboot your router ...................................................................................................... 92
Scheduled automatic reboot ....................................................................................... 93
Console access ............................................................................................................. 93
Command Line Interface ............................................................................................. 93
Router Default Settings ............................................................................................... 94
Reset your router to factory defaults .......................................................................... 94
Upgrade your router firmware .................................................................................... 95
Ping Watchdog ............................................................................................................ 97
Table of Contents
Setting up the L2TP VPN server without IPsec encryption .............................................. 66
Setting up the L2TP VPN server with IPsec encryption (PSK) ........................................... 68
Setting up the L2TP VPN client (Windows) with IPsec encryption (PSK) ......................... 70
IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) ................................................................................ 72
Setting up IPsec site-to-site VPN (PSK) ............................................................................. 72
Setting up IPsec server VPN (PSK with xAUTH) ................................................................ 75
Setting up IPsec site-to-site VPN Failover (PSK) ............................................................... 78
Secure Socket Layer VPN (SSL) / OpenVPN.................................................................. 83
SSL VPN Server Setup ....................................................................................................... 83
SSL VPN Client Setup (Windows)...................................................................................... 84
Certificate Management .............................................................................................. 88
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Local Access Management ............................................................................................... 97
Check the router status information ........................................................................... 98
View routing table and ARP entries ........................................................................... 100
View your router logging ........................................................................................... 101
Configure router logging settings and setup external syslog server .............................. 101
Technical Specifications .............................................................. 102
Troubleshooting ......................................................................... 105
Appendix .................................................................................... 106
ii

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Product Overview
Features
TRENDnet’s AC3000 Tri-Band Wireless Gigabit Dual-WAN VPN SMB Router, model TEW829DRU, features three concurrent WiFi bands to maximize device networking speeds:
two separate high performance 802.11ac networks (5GHz1: 1733Mbps / 5GHz2:
867Mbps), and a 400Mbps Wireless N network. It features dual-WAN ports for load
balancing or fail-over modes, and encrypted Virtual Private Network (VPN) access for
remote users. Dual-WAN ports smooth network loading, minimize network downtime,
and allow employees to access your network from the Internet—all with a single router.
This wireless router features advanced management, QoS, VLAN, VPN, and other
capabilities to ensure optimal performance, scalability, and protection of your network.
Intelligently manage your offices’ web access with our advanced contenting filtering
tool, increase employee productivity and finally take control of your internet.
TEW-829DRU
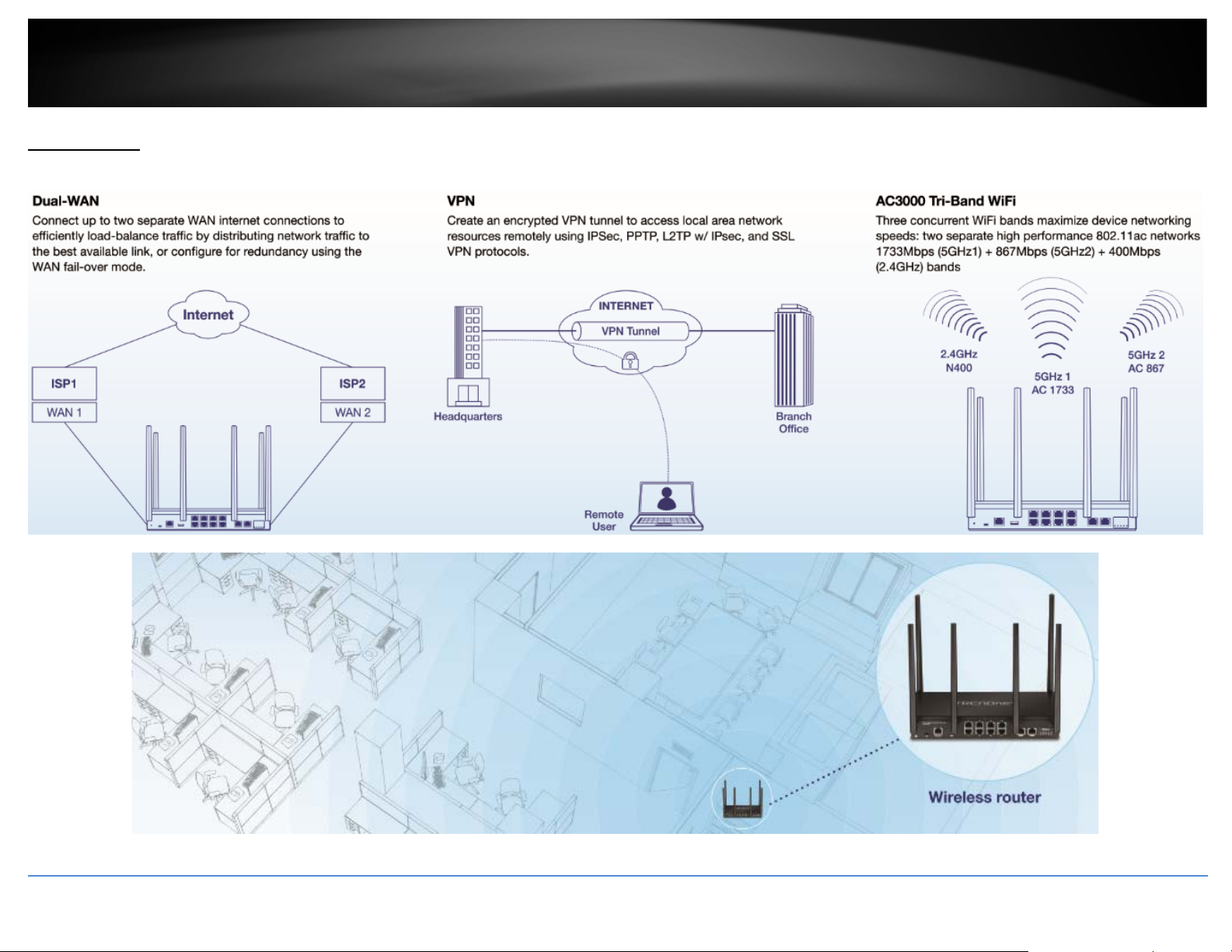
Dual-WAN
Supports up to two separate WAN internet connections for load-balancing or fail-over
modes
Ports
TEW-829DRU
Package Contents
In addition to your router, the package includes:
• Quick Installation Guide
• 6 x detachable high gain antennas
• Network cable (1.5 m/5 ft.)
• RJ-45 to RS-232 console cable (1.5m / 5 ft.)
• Power adapter (12V DC, 3 A)
• Rack mount kit
If any package contents are missing or damaged, please contact the retail store, online
retailer, or reseller/distributor from which the product was purchased.
2 x Gigabit WAN ports, 8 x Gigabit LAN ports, 1 x USB 3.0 port, 1 x Console port
Tri-Band WiFi
Three concurrent WiFi bands maximize device networking speeds: two separate high
performance 802.11ac networks 1733Mbps (5GHz1) + 867Mbps (5GHz2) + 400Mbps
(2.4GHz) bands
Pre-Encrypted Wireless
For your convenience the router’s WiFi bands are pre-encrypted with their own unique
passwords
VPN
Supports IPsec, PPTP, L2TP w/ IPsec, and SSL VPN protocols for encrypted remote access
to local area network (LAN) resources over the internet
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
1

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Inter-VLAN Routing
Provides routing capabilities between VLANs
TEW-829DRU
QoS
Intelligently prioritize voice, video, and other data traffic to improve network efficiency
and overall performance
Rack Mount Design
Sturdy metal housing with rack mount brackets included
Wall Mountable
Wall mount ready
Online Firmware Updates
Automatic notification of firmware updates
Management
Supports web browser (HTTP, HTTPS), CLI, SSH and Telnet management
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
2
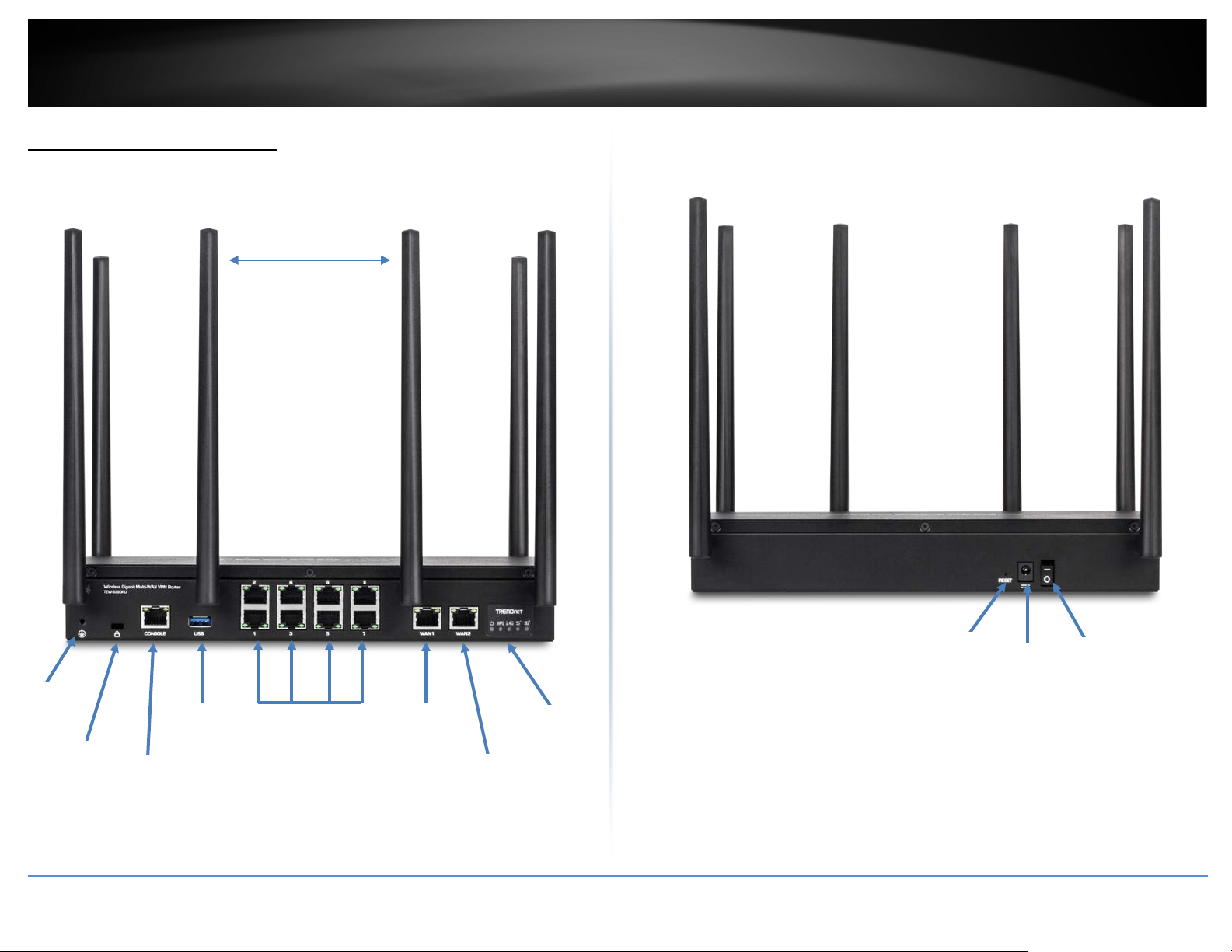
Port
Port
1-8
Port
Indicators
Antennas
Button
Port
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Product Hardware Features
Front Panel View
Rear Panel View
TEW-829DRU
High Gain
Detachable
Ground
Point
Security
Slot
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Console
RJ-45
USB 3.0
Gigabit
LAN Ports
WAN1
Port
WAN2
LED
Reset
Power
On(-)/Off(o)
3
LED
Description
Solid Blue – Device is receiving power and turned on.
Solid Blue – WPS connection process was successful. WPS
activated.
Solid Blue – 2.4GHz (2-stream) wireless radio is turned on.
Off – 2.4GHz (2-stream) wireless radio turned off.
Solid Blue – 5GHz1 (4-stream) wireless radio is turned on.
Solid Blue – 5GHz2 (2-stream) wireless radio is turned on.
LAN 1-8, WAN1 & WAN2 Ports
Blinking Green - Data activity/transmission on port.
Ports/Buttons
Description
Grounding Point
Allows the device chassis to be connected to a known ground
Security Slot
Allows for an optional cable lock attachment to secure the
device to a physical location.
RJ-45 Console
Using the included RJ-45 to RS-232 console cable, this
Baud: 115200 / Data: 8 / Stop: 1 / Parity: None / Flow: None
USB 3.0 Port
Allows for an optional USB storage device (flash drive,
share through the Samba protocol. (FAT32/NTFS format only)
LAN Interface
Connect network devices to the LAN interface ports 1-8 at
via default LAN IP address: 192.168.10.1 / 255.255.255.0
WAN1 Interface
Connects to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) equipment
primary WAN link for Internet connectivity.
WAN2 Interface
Connects to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) equipment
secondary WAN link for Internet connectivity.
Reset Button
Resets device to factory defaults. Using a paperclip, push and
device to factory defaults.
Power Port
Connects the included power adapter to supply device
power.
On(-)/Off(o)
Power Switch
Turns the device power On(-) or Off(o).
TRENDnet User’s Guide
LED Indicators
Off – Device is not receiving power or turned off.
LED will remain on after successful connection for 2 minutes.
Blinking Blue – WPS is activated and setup process has
started. Within 2 minutes, start the WPS process on your
WPS client device to connect.
Off – WPS setup process has stopped or has not been
Blinking Blue – Data transmission on 2.4GHz radio.
Blinking Blue – Data transmission on 5GHz1 radio.
Off – 5GHz
Blinking Blue – Data transmission on 5GHz2 radio.
Off – 5GHz
1
(4-stream) wireless radio turned off.
2
(2-stream) wireless radio turned off.
Port/Button Description
point for electrical safety and protection possible shock or
surge during device operation and handling. (Grounding wire
and screw not included.)
Port
Ports 1-8
interface provides console/terminal (command line interface)
access to the device for management and troubleshooting
purposes.
Terminal Settings:
external HDD, etc.) to be connected and used as a network
Gigabit, 10Mbps/100Mbps Full/Half Duplex. By default,
management access to the GUI and command line interface
TEW-829DRU
Port LEDs
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
LED (Right Side)
Solid Green – Port is connected at 1Gbps link speed.
Off – Port is connected at 10Mbps or 100Mbps link speed.
LED (Left Side)
Port
Port
for Internet connectivity such as modem. By default, WAN
mode is set for failover and WAN1 is configured as the
for Internet connectivity such as modem. By default, WAN
mode is set for failover and WAN2 is configured as the
hold the reset button for 15 seconds and release to reset the
4
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-829DRU
Applications
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
5
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Router Installation
Desktop Hardware Installation
The site where you install the hub stack may greatly affect its performance. When
installing, consider the following pointers:
Note: The router model may be different than the one shown in the example
illustrations.
• Install the Router in a fairly cool and dry place.
• Install the Router in a site free from strong electromagnetic field generators (such
as motors), vibration, dust, and direct exposure to sunlight.
• Leave at least 10cm of space at the front and rear of the hub for ventilation.
• Install the Router on a sturdy, level surface that can support its weight, or in an
EIA standard-size equipment rack. For information on rack installation, see the
next section, Rack Mounting.
• When installing the Router on a level surface, attach the rubber feet to the
bottom of each device. The rubber feet cushion the hub and protect the hub
case from scratching.
Rack Mount Hardware Installation
The router can be mounted in an EIA standard-size, 19-inch rack, which can be placed in
a wiring closet with other equipment. Attach the mounting brackets at the router’s
front panel (one on each side), and secure them with the provided screws.
Then, use screws provided with the equipment rack to mount each router in the rack.
TEW-829DRU
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Note: The look of the router may be different than what is actually displayed.
2
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Basic Installation and Configuration
Note: It is recommended that you configured the wireless router from a wired computer.
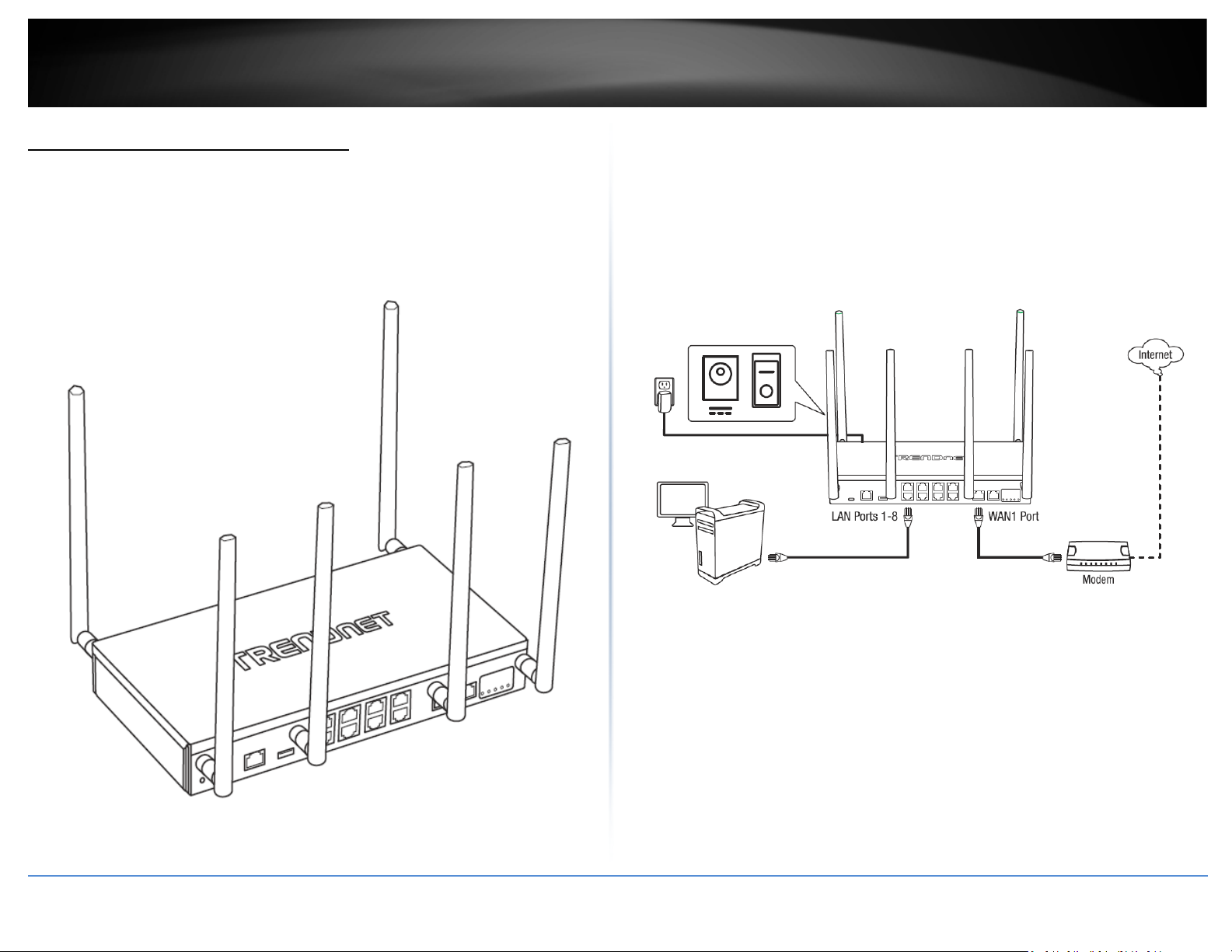
1. Attach the antennas to the front and back of the router and position them for the
best WiFi coverage. It is recommended that you position all antennas vertically as
shown for initial installation and adjust as needed later on.
2. Connect a network cable from the WAN1 port of your router to your modem.
3. Connect a network cable from one of the LAN ports (1-8) of your router to your
computer.
4. Connect the includes power adapter from a power outlet to your router power port
and push the Power On(-)/Off(o) switch into the On(-) position.
TEW-829DRU
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
3
TRENDnet User’s Guide
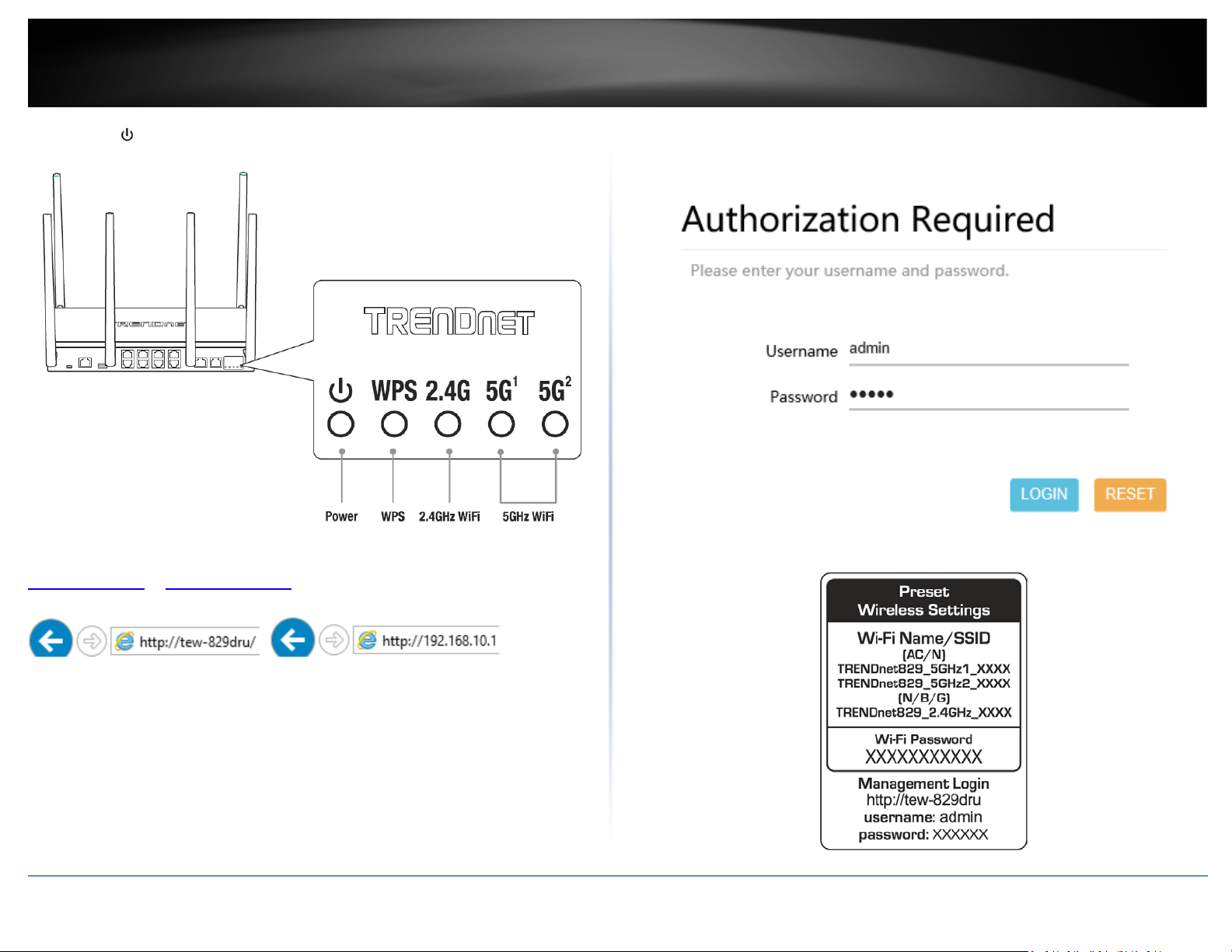
5. The Power ( ), 2.4G, 5G1, 5G2 LEDs will turn on solid indicating that the router is
ready.
6. Open your web browser on the connected computer and in the address bar, enter
http://tew-829dru or http://192.168.10.1
configuration page.
7. Enter the default User Name and Password, then click LOGIN. By default, the preconfigured user name and password are located on the included preset wireless settings
sticker or device label located on the bottom of the router.
and press Enter to access the router web
TEW-829DRU
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
4
TRENDnet User’s Guide
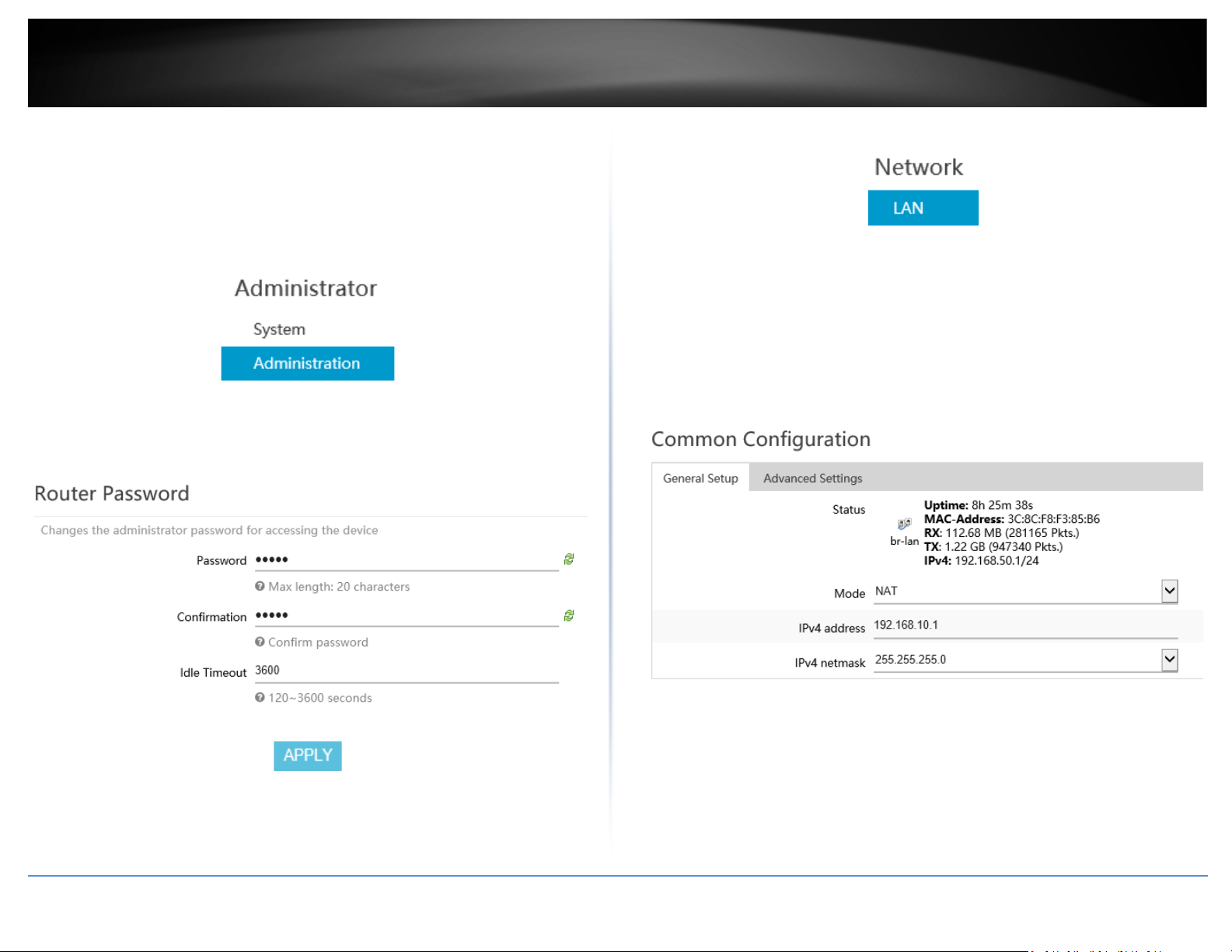
8. To change the administrator password for the router configuration, click
Administrator and click Administration.
Note: By default, the administrator password has been pre-configured for your
convenience and can be located on the included wireless settings sticker or on the device
label located on the bottom of the router. If you are modifying the administrator
password, you will need to log into the router configuration using the new password.
9. Enter the new administrator password in the Password field and re-type the new
password in the Confirmation field. Click Apply to save and commit the changes.
10. To change your router’s LAN IPv4 address settings, click on Network and click LAN.
11. Under Common Configuration and General Setup, enter the new LAN IPv4 address
and subnet mas in the IPv4 address and IPv4 netmask fields. Click Apply to save and
commit the changes. Please wait for the new address settings to be applied and log back
into the router web configuration page using the new LAN IPv4 address.
Note: If your computer IP address settings are not automatically updated to the new
settings, you may need to manually renew your computer IP address settings in order
for your to log back into the router web configuration with the new LAN IPv4 address
settings.
TEW-829DRU
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
5
TRENDnet User’s Guide
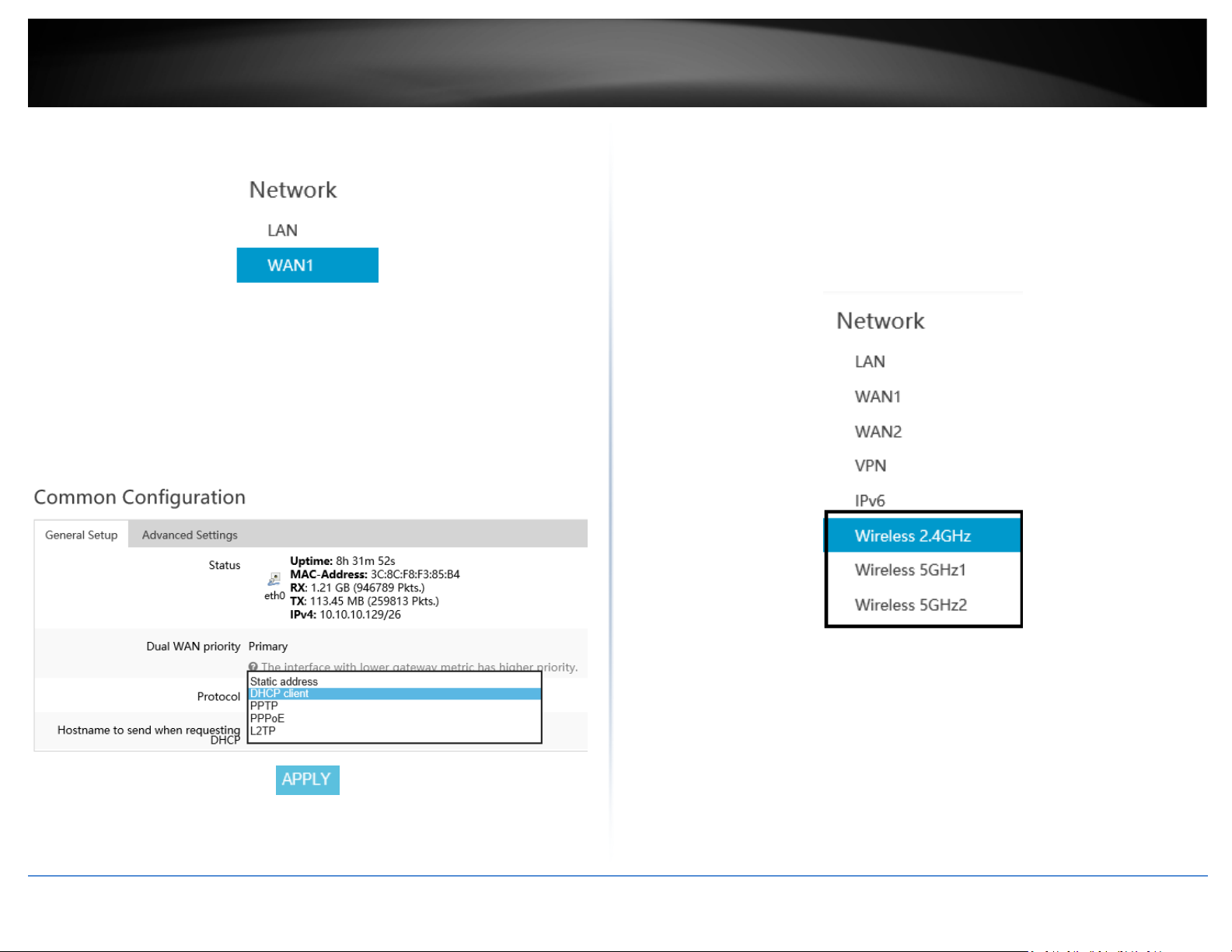
12. To configure your WAN1 Internet connection settings, click Network and click
WAN1.
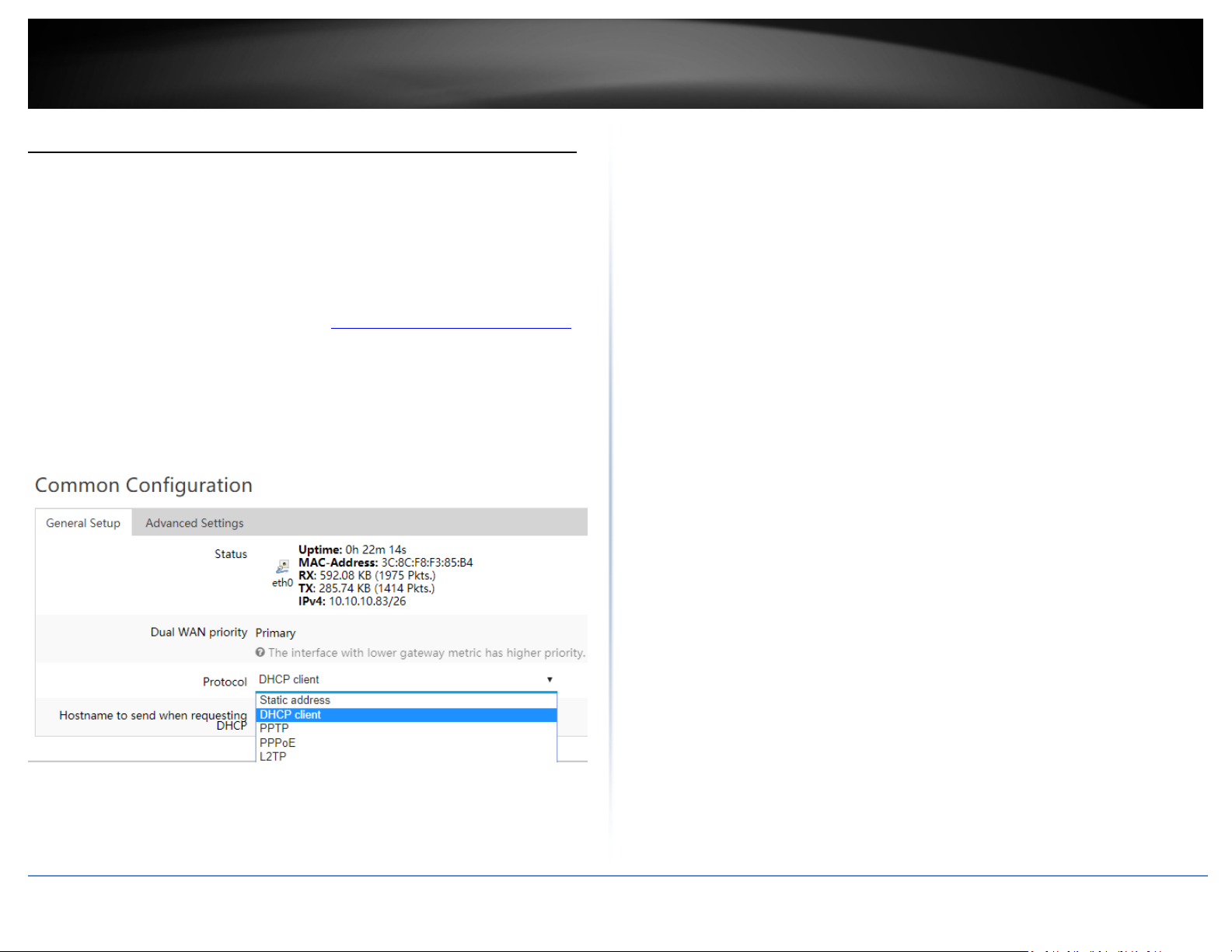
13. Under Common Configuration and General Setup, click the Protocol drop-down list
and select the appropriate protocol (Static address, DHCP client, PPTP, PPPoE, L2TP) for
yoru Internet connection. DHCP client is the typical protocol in which the connection
settings are automatically obtained by your ISP (Internet Service Provider). If you are
unsure about the Internet connection settings, please contact your ISP for details. After
you have completed the Internet connection settings, click Apply to save and commit
the changes.
14. To configure your wireless network name/SSID and wireless encryption settings,
click Network and click the wireless band you would like to configure. Wireless 2.4GHz,
Wireless 5GHz1, or Wireless 5GHz2.
Note: By default, the wireless network name/SSID has been pre-configured for your
convenience and can be located on the included wireless settings sticker or on the device
label located on the bottom of the router. If you are modifying the wireless settings, you
will need to connect to the router with your WiFi clients using the new settings.
TEW-829DRU
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
6
TRENDnet User’s Guide
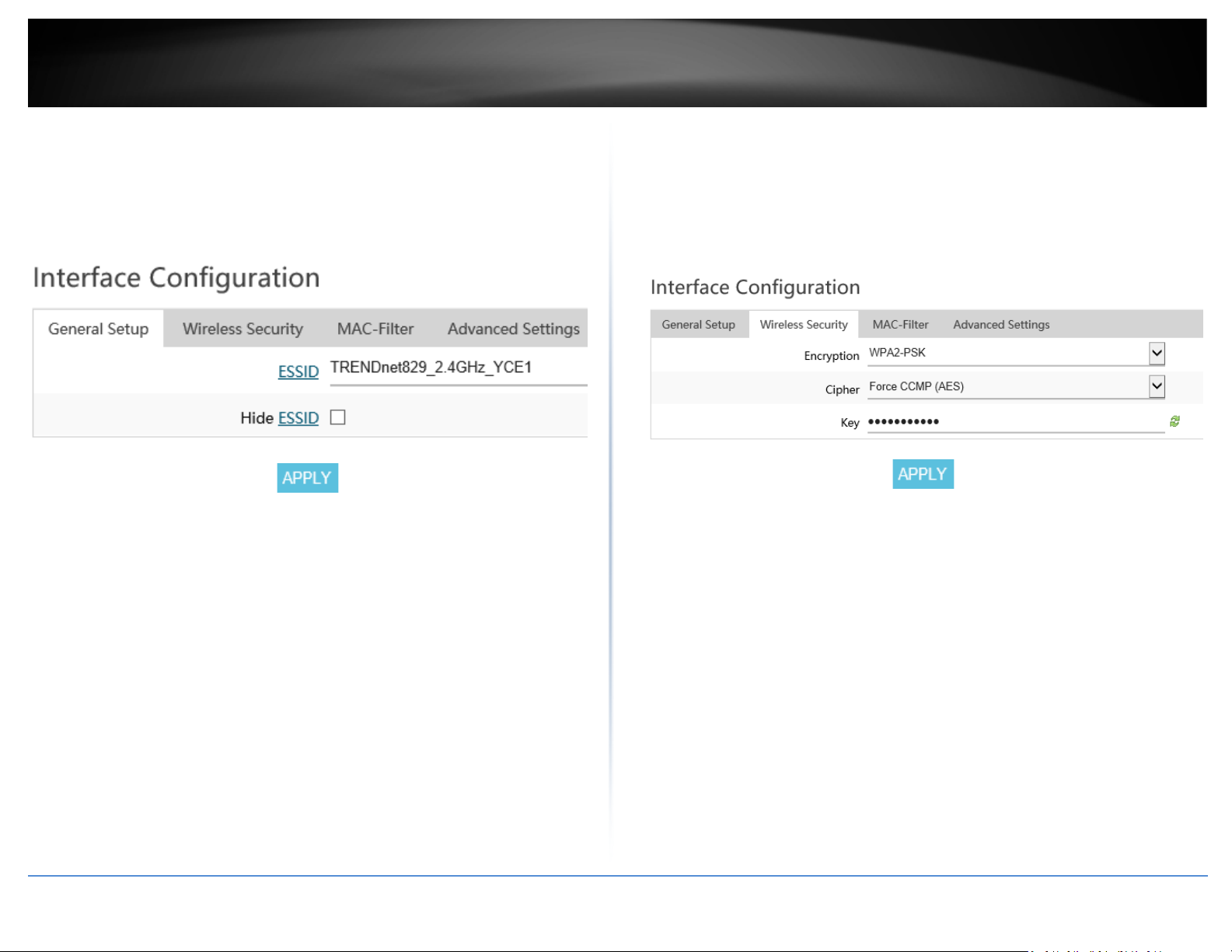
15. To change the wireless network name/SSID for the selected wireless band, under
Interface Configuration and General Setup, enter the new name in the ESSID field and
click Apply to save and commit the changes.
Note: The wireless network name/SSID is the name your WiFi clients will need to search
and discover when connecting to your router wireless network.
16. To change the wireless encryption key for the selected wireless band, under
Interface Configuration Wireless Security, enter the new encryption in the Key field and
click Apply to save and commit the changes.
Note: WPA2-PSK AES wireless encryption is strongly recommended. The wireless
encryption key is the key your WiFi clients will need to enter when connecting to your
router wireless network.
TEW-829DRU
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
7
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Basic Router Settings
Access your router management page
Note: Your router management page URL/domain name http://tew-829dru or IP
address http://192.168.10.1 is accessed through the use of your Internet web browser
(e.g. Internet Explorer®, Firefox®, Chrome™, Safari®, Opera™) and will be referenced
frequently in this User’s Guide.
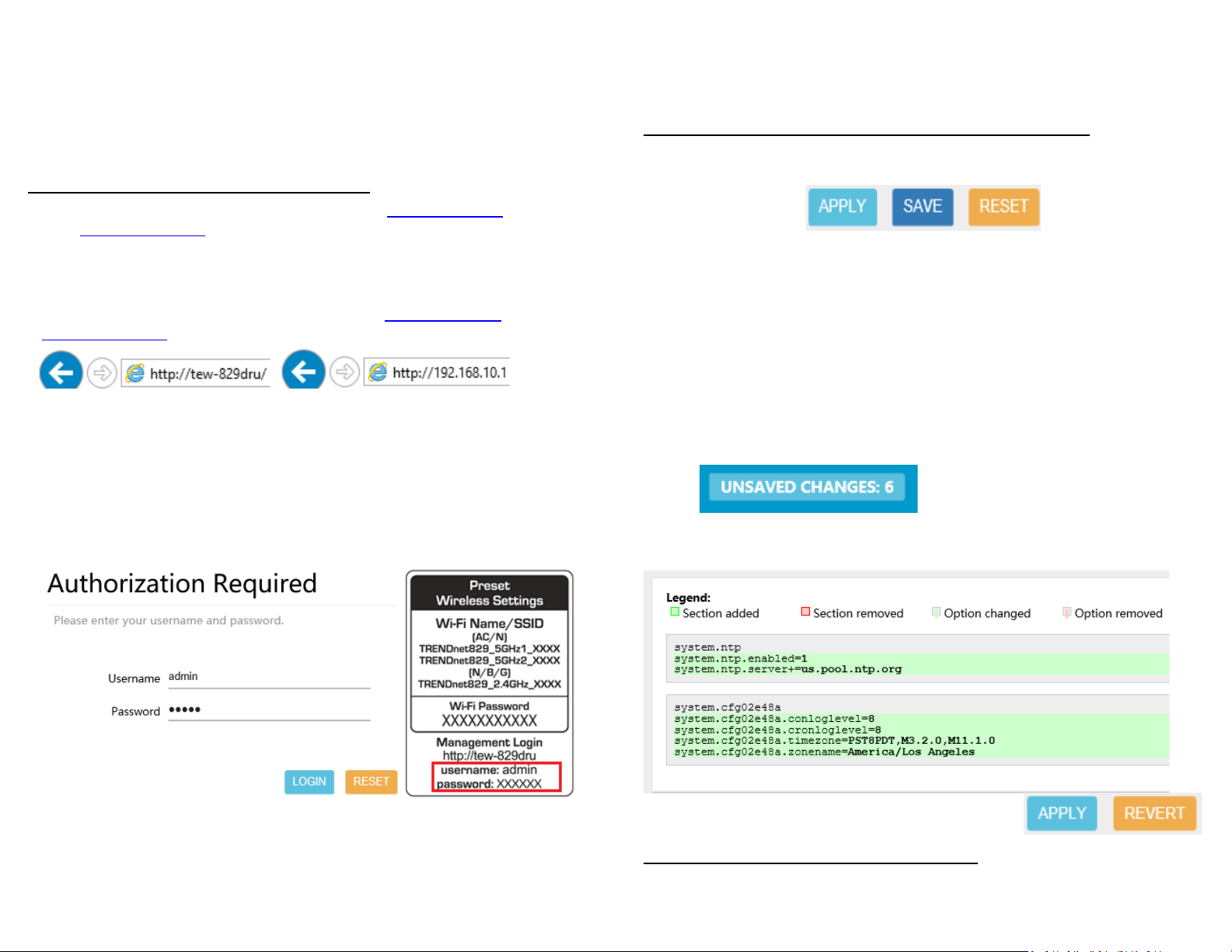
1. Open your web browser and go to URL/domain name http://tew-829dru
http://192.168.10.1. Your router will prompt you for a user name and password.
2. For added security, the router is pre-configured with a unique administrator
password. You can find the Password on the sticker included in the router package
contents or on the device label located on the bottom of the router. Enter your
Username and Password, then click LOGIN.
• User Name: admin
• Password: (xxxxxxxx)
Note: User Name and Password are case sensitive.
or IP address
TEW-829DRU
Saving and applying router configuration changes
In the router management page, pages may include all, some, or one of the options
below. Some configuration changes may require a device reboot.
• Reset – Clicking this option will reset all settings to their previous configuration
on a specific page.
• Apply – Clicking this option will save and apply the configuration changes on a
specific page which will take effect immediately.
• Save – Clicking this option will temporarily save the changes and allow you to
temporarily save multiple configuration changes and apply all configuration
changes at the same time. When a configuration setting has been temporarily
saved, a notification will appear in the top right corner of the router
management page indicated that there are unsaved changes and the number
of pending configuration changes. When you are ready to save and apply the
configuration changes permanently, click on the notification in the top right
corner.
A list of all pending configuration changes will be displayed. If you are ready to
permanently save all configuration changes, click Apply. Otherwise, to discard
changes, click Revert to discard all pending configuration changes.
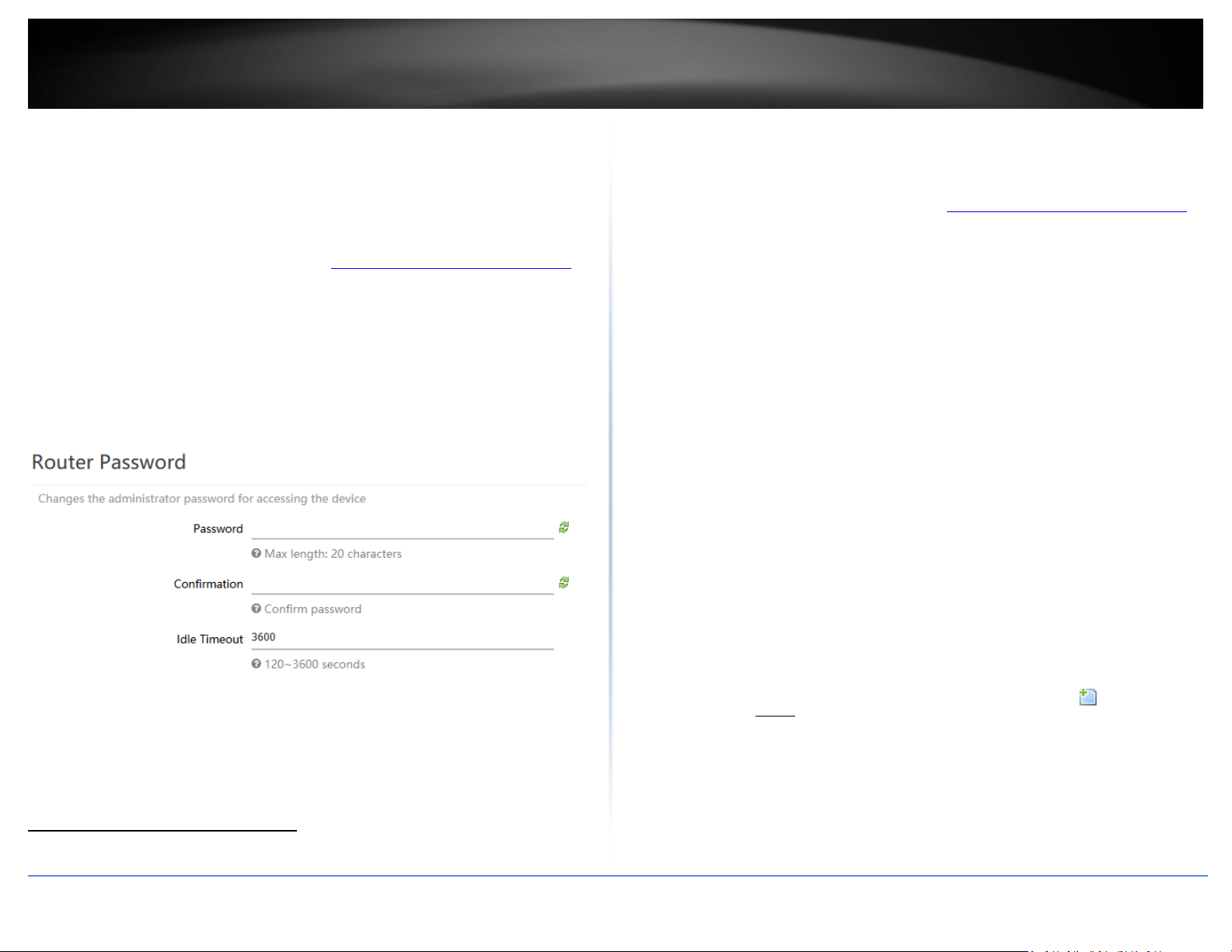
Change your administrator password
Administrator > Administration
TRENDnet User’s Guide
By default, the administrator password has been pre-configured a unique password for
your convenience. You can find the pre-configured administrator password on the
wireless sticker included in your router package contents or also located on the router
device label located on the bottom of the device. This section will allow you to change
the default administrator password used to log into your router management page.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page
on page 8).
2. Click on Administrator and click on Administration.
3. Enter the new administrator password in the Password and re-enter the new
password in the Confirmation field. Click Apply to save and commit the changes
Note: The idle timeout setting is used to define the period of inactivity in the router
management page before automatically logging out.
Note: If you change the administrator password, you will need to access the router
management page using the User Name “admin” and the new password instead of the
pre-configured default password. If you reset the device to factory defaults, you will
need to access the router management page using the pre-configured settings on the
included wireless sticker in the router package contents or on device label located on the
bottom of the router.
It is recommended to set the router date and time for scheduling functions and logging
functions for monitoring and troubleshooting.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page
on page 8).
”
2. Click on Administrator and click on System.
3. Review the settings below. Click Apply to save and commit the changes.
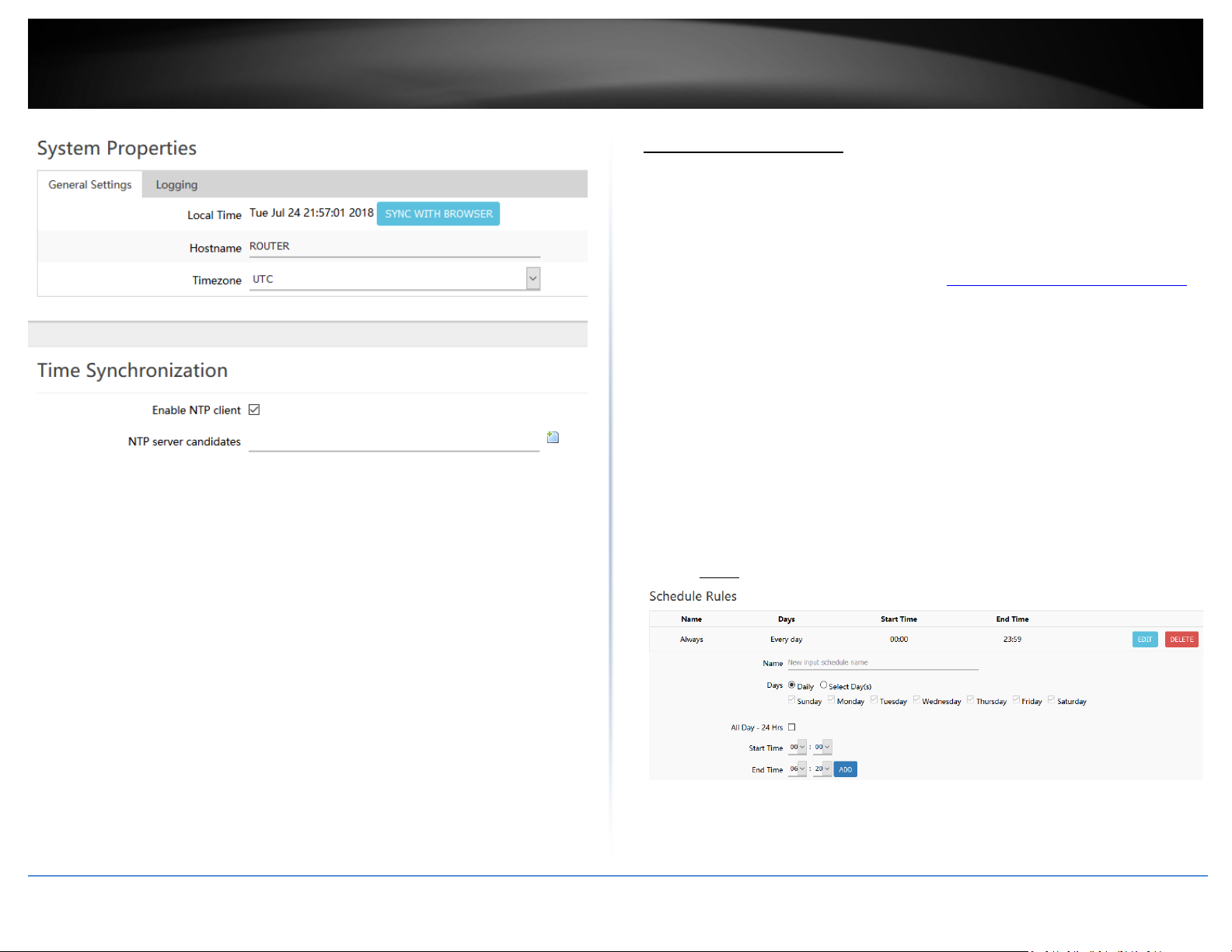
System Properties
• Local Time – Displays the current day, date, and time. Clicking the SYNC WITH
BROWSER button will automatically copy the current day, date, and time
settings from the web browser and allows the time to be set manually.
• Hostname – Modifies the router host name. The host name identifies is the
name used to identify the router to other computer or devices on the network.
Modifying this setting will modify the hostname used when accessing the
router management page using the hostname or when using the Samba USB
share feature.
• Timezone – Click the drop-down list to select the appropriate time zone.
Time Synchronization
• Enable NTP client – Enables the NTP client to configure router to obtain time
and date settings from an external network time server.
o NTP server candidates – Enter the domain name of the network time
server to obtain time and settings. (e.g. pool.ntp.org)
Note: You can add multiple time servers by clicking . If one server
is not available, your router will try the next available server in the list.
Limited Warranty
”
Set your router date and time
Administrator > System
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
9
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Limited Warranty
Create time schedules
Administrator > Schedule
Your router allows you to create schedules to specify a time period when a feature
should be activated and deactivated. Before you use the scheduling feature on your
router, ensure that your router system time and date settings are configured correctly.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page
on page 8).
2. Click on Administrator and click Schedule.
3. Review the settings below. Click Add to add the new schedule to the list and Apply to
save and commit the changes.
• Name – Enter a name for the new schedule rule.
• Days – Choosing Daily will set the set the schedule rule to occur at the specified
time every day. Choosing Select Day(s) will allow to manually select which
specific days for the schedule.
• All Day – 24 Hrs – Checking this option will set the schedule to run all 24 hours
instead of manually configured a specified time period.
• Start Time / End Time – Manually define a time period for the schedule.
Note: The time period is specified in 24 hour format.
”
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
10
TRENDnet User’s Guide
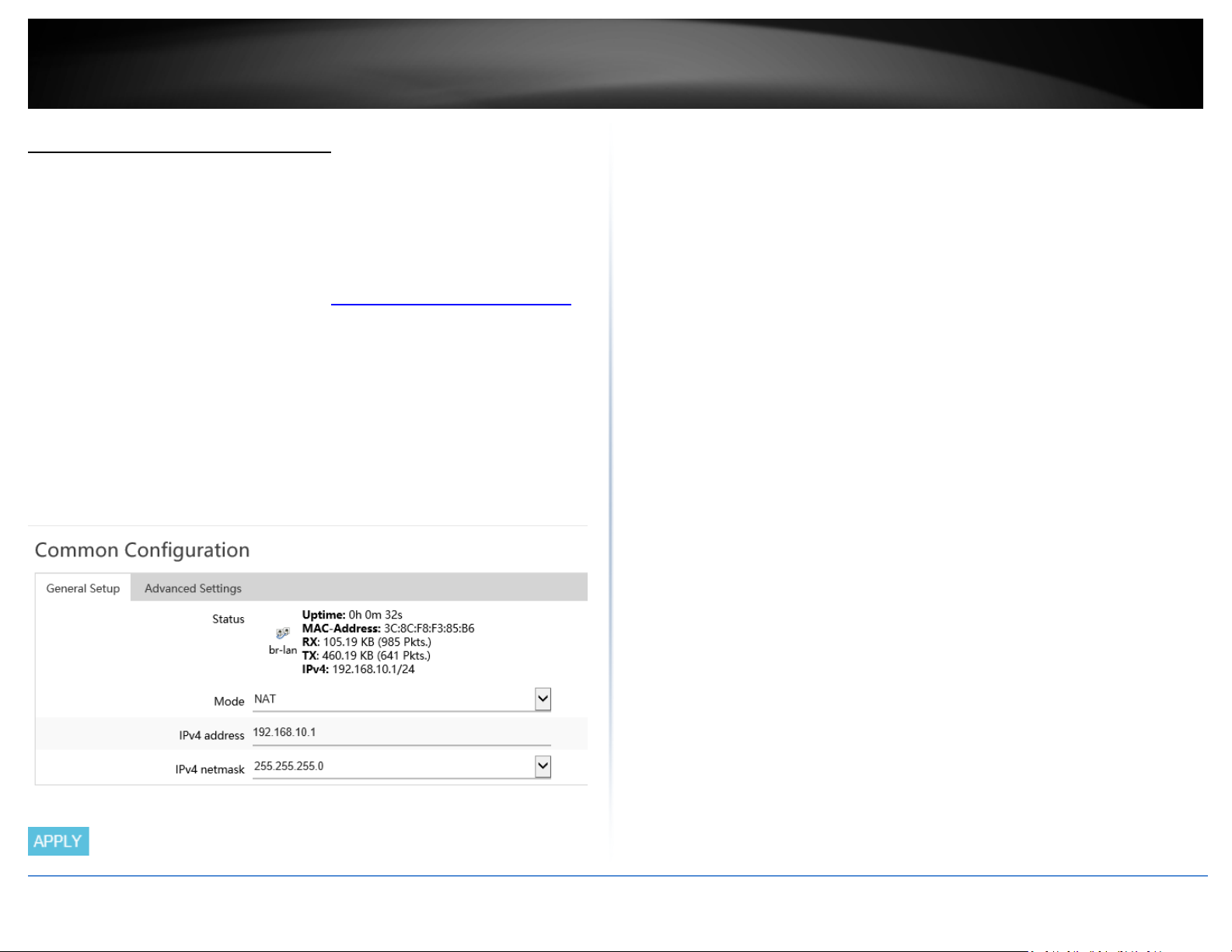
Change LAN IPv4 address settings
Network > LAN
Note: The default LAN interface IPv4 address settings is 192.168.10.1 / 255.255.255.0
and also assigned to LAN ports 1-8 by default. If the LAN IPv4 address settings are
modified, you will need to log into the router management page with the new IPv4
address settings.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page
on page 8).
2. Click on Network and click LAN.
3. Under the Common Configuration section, you can enter the new LAN interface IP
address settings.
• IPv4 address – Enter the new LAN IPv4 address. (e.g. 192.168.50.1)
• IPv4 netmask – Select or Enter the new LAN IPv4 subnet mask. The drop-down
menu will list class A, B, C, or custom which will allow you to manually enter a
custom subnet mask. (e.g. 255.255.255.0)
4. Click Apply to
Below is a reference of the additional LAN settings if you choose to make other
configuration changes to these sections.
General Setup
• Status – LAN Interface (br-lan)
o Uptime – Displays the amount time the LAN interface has been up and
continuously running. This time will reset if the router is powered off
”
• Mode – Allows you to change the function between NAT mode or Route Only
(NAT-less).
Advanced Settings
• Override MAC Address – This parameter allows you to assign a new LAN
interface (br-lan) MAC address. Typically, this parameter does not need to be
modified. (e.g. AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF)
• Override MTU – The default MTU (maximum transfer unit) or frame size is set
to 1500 bytes. This parameter allows you to assign a new MTU size. Typically,
this parameter does not need to be modified.
• Use gateway metric – This is automated metric or priority value assigned to the
LAN network interface route in the routing table. Typically, this parameter does
or router is rebooted.
o MAC-Address – Displays the current MAC address assigned to the LAN
interface.
o Rx – Displays the total amount of data received by the LAN interface in
MB (# of packets) since the start of the currently displayed uptime.
o Tx – Displays the total amount of data transmitted by the LAN
interface in MB (# of packets) since the start of the currently displayed
uptime.
o IPv4: Displays the current IPv4 address settings assigned to the LAN
interface.
o NAT – The default router mode which uses network address
translation between the local internal (LAN/VLAN) interfaces and
external (WAN1/WAN2) interfaces translating public and private IP
addressing.
o Route Only (NAT-less) – This mode disables the NAT function between
internal and external interfaces and may also be known as classical
routing mode. This mode should only be used when the router is using
for local internal IP routing only
Limited Warranty
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
11

TRENDnet User’s Guide
not need to be modified. (Lower value = Higher priority in route table, 0 being
the highest priority.)
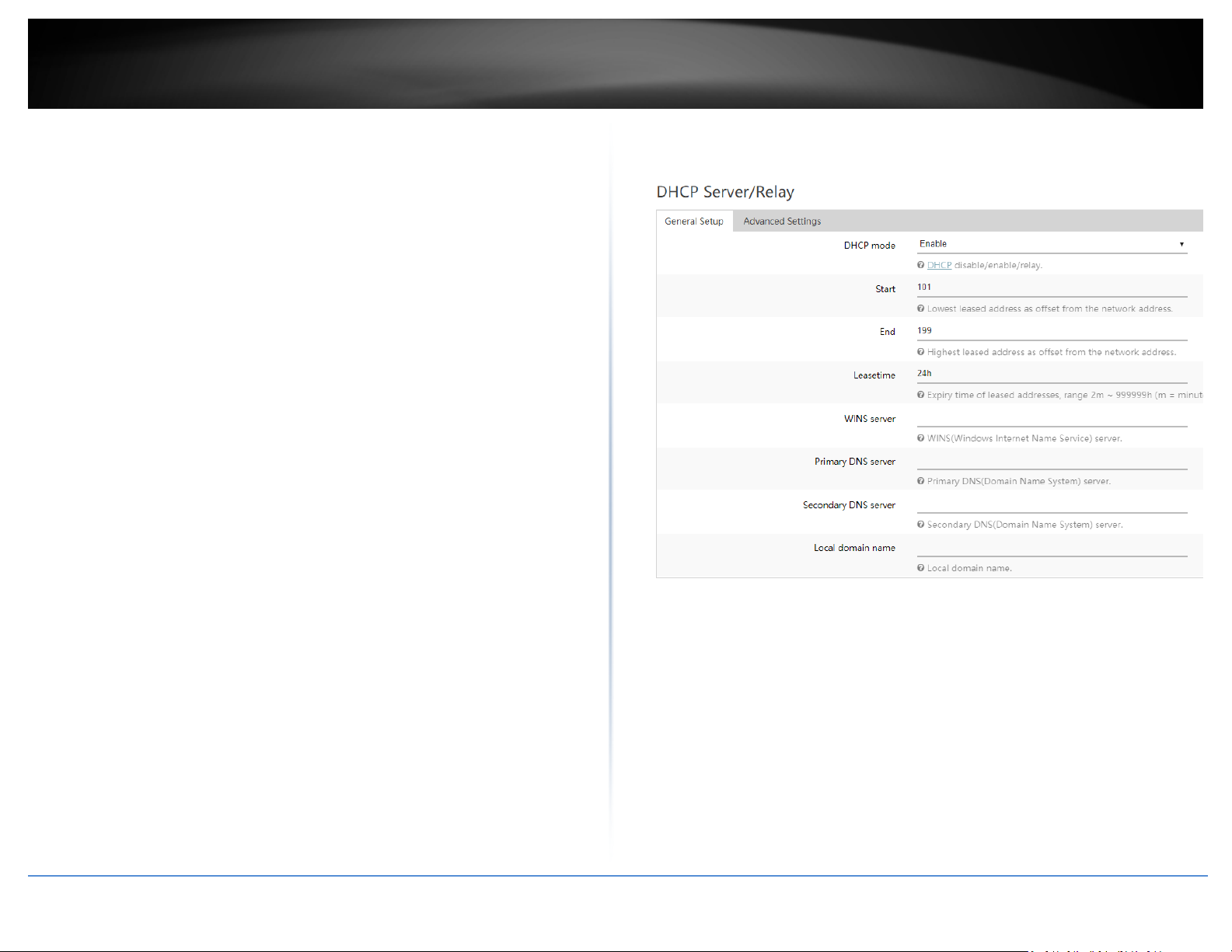
Configure LAN IPv4 DHCP server settings
Network > LAN
Note: The internal DHCP server function is enabled by default on the LAN interface to
automatically distribute IP address settings to network devices connected to the LAN and
wireless LAN interfaces. The internal DHCP server only supports only class C IP address
range. The default IP range is 101 – 199 (192.168.10.101 – 192.168.10.199)
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page
on page 8).
2. Click on Network and click LAN.
3. Under the DHCP Server/Relay section, you can modify or enter the new DHCP settings
and click Apply to save and commit the changes.
• DHCP mode – Allows you to set the mode to Enable, Disable, or Relay.
o Enable – Using this setting enables the DHCP server function the LAN
interface.
o Disable - Using this setting disabled the DHCP server function on the
LAN interface.
o Relay – Using this setting allows you to use an external DHCP server
instead of your router’s internal DHCP server to distribute IP address
settings on the LAN interface. If choosing this setting, enter the IP
address of your external DHCP relay server.
• Start – Enter the starting value of DHCP IPv4 address range. (e.g. If your LAN
IPv4 address is 192.168.50.1, entering 120 will define the first IP address of the
DHCP pool is 192.168.50.120)
• End – Enter the ending value of DHCP IPv4 address range. (e.g. If your LAN IPv4
address is 192.168.50.1, entering 200 will define the last IP address of the DHCP
pool is 192.168.50.200)
Limited Warranty
”
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
12
TRENDnet User’s Guide
• Lease Time – Enter the lease time in hours (h) or minutes (m) DHCP clients will
hold their IP address settings before automatically requesting a new lease (IP
address settings) from the internal DHCP server. (e.g. To specify 24 hours, enter
24h. To specify 480 minutes, enter 480m.)
• WINS server – Enter the IPv4 address of your WINS (Windows Internet Name
Server) for internal host name resolution on your local network to be
distributed to DHCP clients. The WINS server provides host name to IP address
resolution for the NetBIOS naming service. This parameter is optional. (e.g.
192.168.50.250)
• Primary DNS – Enter the IPv4 address of your primary DNS (Domain Name
System) server for Internet domain name resolution to be distributed to DHCP
clients. By default, the internal DHCP server uses DNS relay and provides the
router LAN IPv4 address as the primary DNS server to DHCP clients. The DNS
server provides Internet domain name to IP address resolution when
computers are accessing or browsing Internet websites. This parameter is
optional. (e.g. If entering 8.8.8.8, this DNS server will be provided DHCP clients
instead of the router’s LAN IPv4 address to resolve Internet domain names such
as trendnet.com )
• Secondary DNS – Enter the IPv4 address of your secondary DNS (Domain Name
System) server for Internet domain name resolution to be distributed to DHCP
clients. If the primary DNS server cannot be reached, the secondary DNS server
will be used. This parameter is optional. (e.g. 8.8.4.4)
• Local domain name – Enter a domain name to distribute to DHCP clients. This
parameter is optional. (e.g. trendnet.com)
Below is a reference of the additional DHCP Server/Relay settings if you choose to make
other configuration changes to these sections.
Limited Warranty
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
13

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Advanced Settings
• Dynamic DHCP – Checking this option the enables the DHCP server to
distribute IPv4 address settings dynamically to clients. If this option is
unchecked, IPv4 address settings will only be assigned to DHCP clients with a
static DHCP reservation. Typically, this parameter does not need to be
modified.
• Log Queries – Checking this option will enable generate logging to internal or
syslog of any DNS queries. Typically, this parameter does not need to be
modified.
Limited Warranty
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
14
TRENDnet User’s Guide
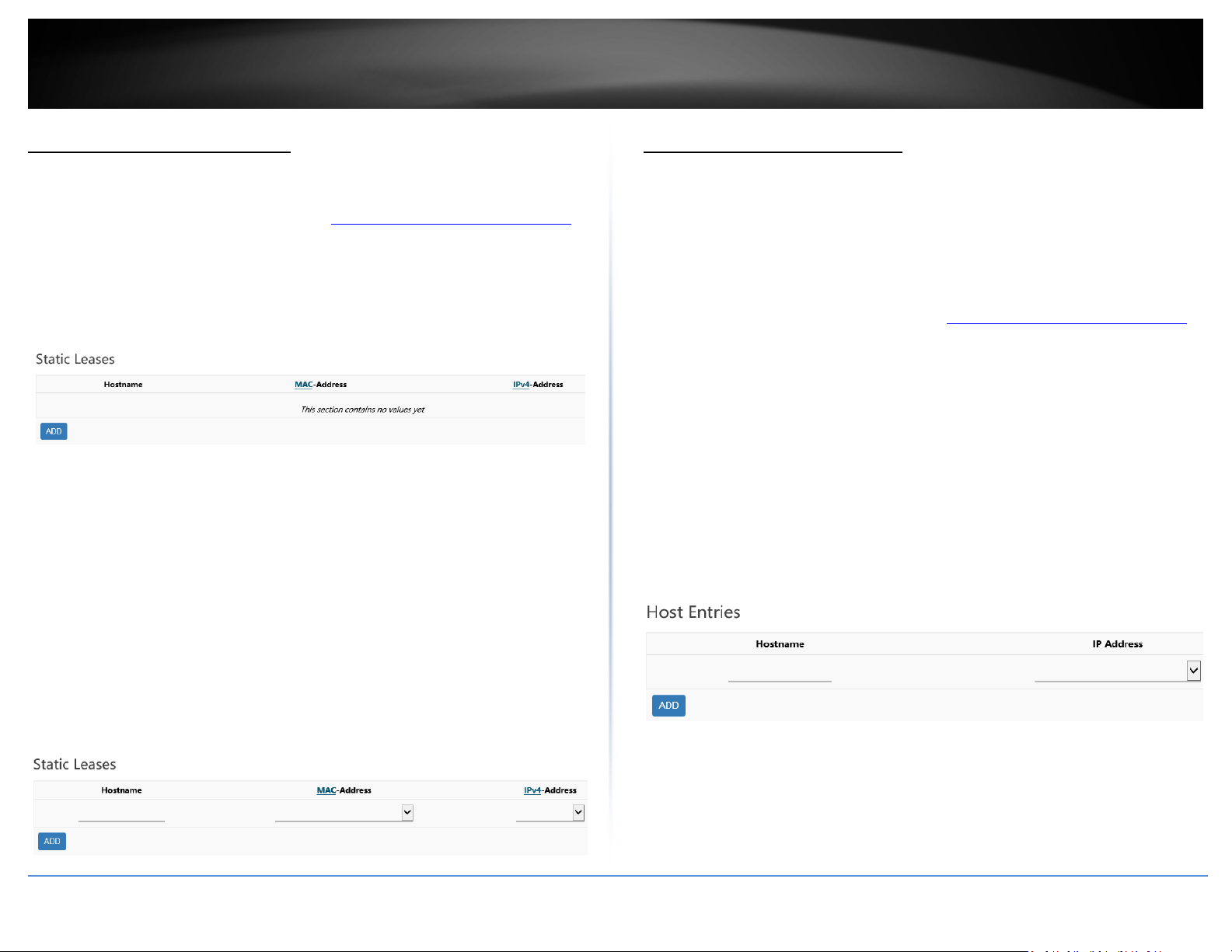
Add static DHCP reservations
Network > LAN
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page
on page 8).
2. Click on Network and click LAN.
3. Under the Static Leases section, click Add.
4. Enter the parameters for the static DHCP reservation and click Apply to save and
commit the changes.
Note: The network device or computer the reservation is created will need to release and
renew the IPv4 address settings in order to obtain the new IP address settings.
• Hostname – Enter a name for the DHCP reservation. (e.g. trendnetpc)
• MAC-Address – Enter the MAC (Media Access Control) address of the
computer or network device to assign to the reservation. You can also click the
drop-down list to select from a list of network devices detected by the router
that have been assigned IPv4 address settings through DHCP. (e.g.
AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF)
• IPv4-Address – Enter the IPv4 address to assign to the computer or network
device for the reservation. You can also click the drop-down list to select from
list o of network devices detected by the router through DHCP. (e.g.
192.168.50.150)
Add static host name entries
Network > LAN
The router can be used for host name to IP address resolution of computers or network
”
devices on your local network similar to a WINS server however, entries will not
dynamically populate and each entry must be manually entered. For clients to resolve
the manually entered static entries, DHCP clients must use the router LAN IPv4 address
as the WINS server.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page
on page 8).
2. Click on Network and click LAN.
3. Under the Host Entries section, click Add.
4. Enter the parameters for the static host name entry and click Apply to save and
commit the changes.
• Hostname – Enter the host name. (e.g. trendnetpc)
• IPv4-Address – Enter the IPv4 address to resolve to host name. (e.g.
192.168.50.150)
Limited Warranty
”
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
15
TRENDnet User’s Guide
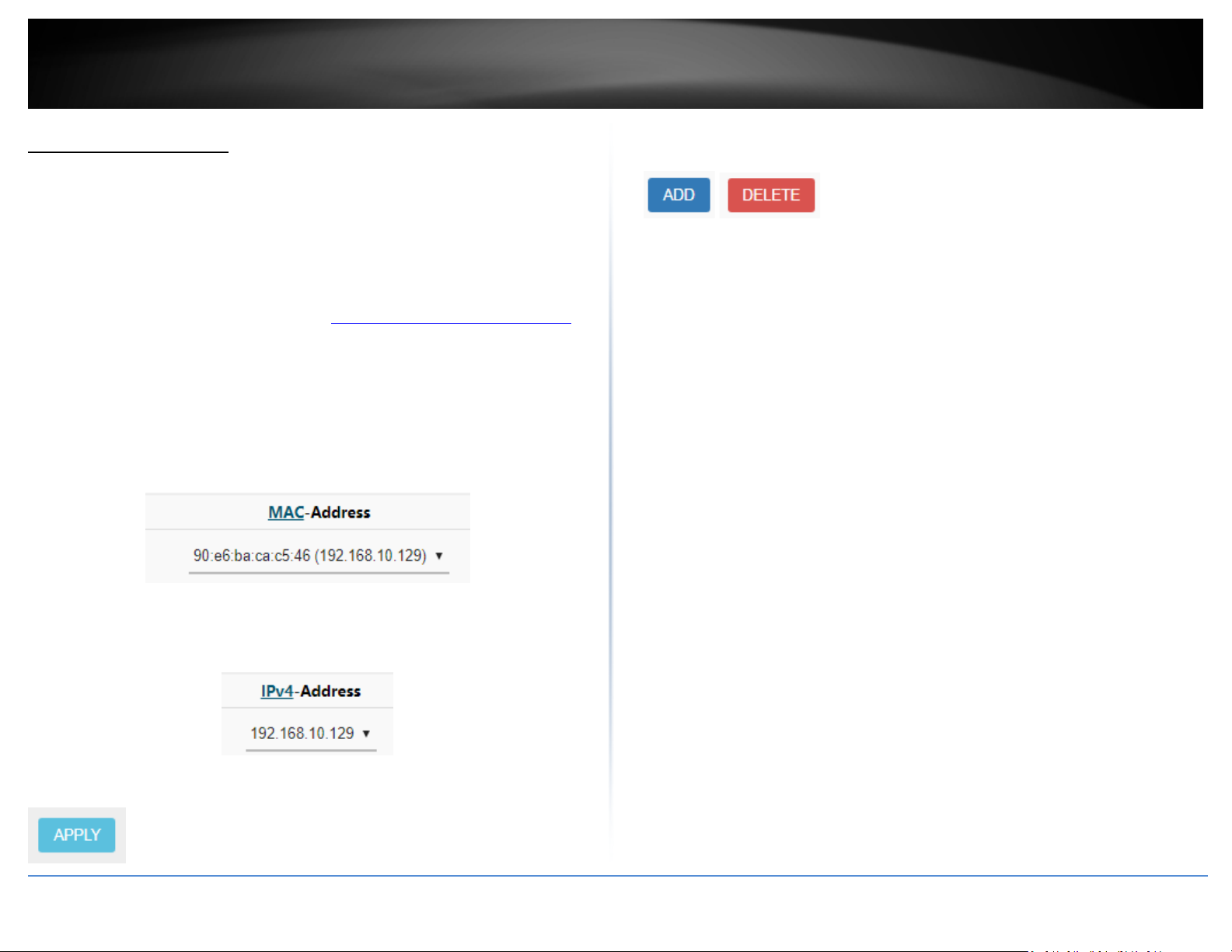
Add static ARP entries
Network > LAN
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is the protocol responsible for resolve IP addresses to
hardware MAC addresses. Typically, ARP entries are dynamically learned and refreshed
in the ARP table however, in the case where your application requires static ARP entries
to always be present in the router ARP table, you can manually enter and add them to
the router. (ex. applications: WoL (Wake on LAN) or Wake on WAN)
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page
on page 8).
2. Click on Network and click LAN.
3. Under the Static ARP section, click the MAC-Address drop-down list to select a MAC
address from the list or select customer to manually enter a MAC address (format
example: aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff).
Note: You can specify additional static ARP entries by clicking Add. Delete existing
entries by clicking the Delete button next to the entry to be removed.
”
Limited Warranty
4. Click the IPv4-Address drop-down list and select the IPv4 address to assign to the
MAC address ARP table entry or select custom to manually enter an IPv4 address
(format example: 192.168.10.129)
5. Click Apply to save and commit the changes.
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
16
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Configure WAN1 / WAN2 interfaces for Internet connectivity
Network > WAN1/WAN2
By default, the WAN configuration is set to use WAN1 as the primary connection for
Internet connectivity and failover to WAN2 secondary if there is fault in connectivity to
WAN1. This section will explain how to set up the WAN1 or WAN2 interfaces for
Internet connectivity to your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page
on page 8).
2. Click on Network and click WAN1 or WAN2.
3. Under the Common Configuration section, click the Protocol drop-down list and
select the Internet connection provided by your ISP.
4. Complete all of the fields required by your ISP and click Apply to save and commit the
changes.
Below is a reference of the additional WAN settings if you choose to make other
configuration changes to these sections.
General Setup
• Status – LAN Interface (br-lan)
o Uptime – Displays the amount time the WAN1/WAN2 interface has
been up and continuously running. This time will reset if the router is
powered off or router is rebooted.
o MAC-Address – Displays the current MAC address assigned to the
”
• Dual WAN priority – Displays the current priority assignment for the selected
WAN interface. The WAN priority settings can be configured under Network >
Multiple WAN. By default, the WAN configuration is set to use WAN1 as the
primary connection for Internet connectivity and failover to WAN2 secondary if
there is fault in connectivity to WAN1.
• Hostname to send when requesting DHCP – If your ISP requires to send
specific hostname with the DHCP request for Internet connectivity, enter the
required host name in the field. Applies to DHCP client/PPTP/L2TP WAN
protocols.
• WAN mode – Applies to PPTP/L2TP WAN protocols.
• Connect mode – Applies to PPPoE/PPTP/L2TP WAN protocols.
WAN1/WAN2 interface.
o Rx – Displays the total amount of data received by the WAN1/WAN2
interface in MB (# of packets) since the start of the currently displayed
uptime.
o Tx – Displays the total amount of data transmitted by the
WAN1/WAN2 interface in MB (# of packets) since the start of the
currently displayed uptime.
o IPv4: Displays the current IPv4 address settings assigned to the
WAN1/WAN2 interface.
o DHCP client – Using this option will set the WAN to obtain IP address
settings automatically from your ISP for Internet connectivity.
o Static IP – Using this option will require you to manually enter the
WAN IP settings required by your ISP for Internet connectivity.
o Keep alive – This option will keep the connection on at all times.
o On demand – This option will automatically disconnect after the max.
idle time is reached and will automatically re-establish connection
when Internet access is used.
Limited Warranty
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
17
TRENDnet User’s Guide
• Access concentrator / Service name – Optional parameters required only if ISP
requires for Internet connectivity. Applies to PPPoE WAN protocol.
• MPPE support– Optional parameter (applies Microsoft Point-to-Point
Encryption) required only if ISP requires for Internet connectivity. Applies to
PPTP WAN protocol.
• Use DNS servers advertised by peer- If checked, automatically obtains DNS
service IP address settings from your ISP. If unchecked, allows you to specify
custom DNS server IP addresses. Applies to PPPoE/PPTP/L2TP WAN protocols.
Advanced Settings
• Bring up on boot – The parameter is enabled to bring the WAN1/WAN2
interface up during device boot. Typically, this parameter does not need to be
modified.
• Use builtin IPv6-management – Enables/disables IPv6 protocol on the
WAN1/WAN2 interface. Typically, this parameter does not need to be
modified.
• Enable IPv6 negotiation on PPP link – Enables/disables IPv6 when using the
PPPoE/L2TP WAN protocols. Typically, this parameter does not need to be
modified.
• Use broadcast flag – Optional parameter if your ISP may requires that DHCP
requests from your device be sent as broadcasts or unicasts for IP address
settings for Internet access.
• Use default gateway – This parameter automatically created a default gateway
route in the device routing table to access the Internet through the selected
WAN interface. If unchecked, the default gateway route for Internet access
must be entered in manually in the device routing table settings. Typically, this
parameter does not need to be modified.
• Use gateway metric – This parameter is the route priority value assigned to the
default gateway route. Range: 0-9999, 0 being the highest priority. Typically,
this parameter does not need to be modified.
• Use DNS servers advertised by peer- If checked, automatically obtains DNS
service IP address settings from your ISP. If unchecked, allows you to specify
custom DNS server IP addresses. Applies to the DHCP client WAN protocol.
• Client ID to send when requesting DHCP – Optional parameter only required if
your ISP requires a specific client ID to be sent when requesting IP address
settings for Internet access. Applies to DHCP client WAN protocol.
• Vendor Class to send when requesting DHCP – Optional parameter only
required if your ISP requires a specific vendor class to be sent when requesting
IP address settings for Internet access. Applies to DHCP client WAN protocol.
• Override MAC address – Optional parameter used to change the WAN
interface MAC address if you are experiencing issues obtaining IP address
settings from your ISP. This parameter is more commonly known as MAC
address cloning where you can assign a LAN computer MAC address to the
WAN interface. Applied to DHCP client WAN protocol.
• Override MTU – The default MTU (maximum transfer unit) or frame size is set
to 1500 bytes. This parameter allows you to assign a new MTU size. For
PPPoE/PPTP/L2TP WAN protocols, if you experience issues accessing SSL/HTTPS
secure websites, you can try lower the MTU value to 1492 to decrease the
amount of packet errors. Typically, this parameter does not need to be
modified.
WAN VLAN Tagging
Some ISPs require VLAN tag assignment of a specific VLAN ID when for Internet access
or other services. You can follow the steps below to assign a specific VLAN ID to the
WAN interface.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page
on page 8).
2. Click on Network and click VLAN.
3. Under the VID, you can enter the VID required by your ISP and set the WAN interface
to tagged or untagged. Click Apply to save and commit the changes.
Limited Warranty
”
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
18
TRENDnet User’s Guide
IPv6 settings
Network > IPv6
IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6) is a new protocol that significantly increases the
number of available Internet public IP addresses due to the 128-bit IP address structure
versus IPv4 32-bit address structure. In addition, there are several integrated
enhancements compared to the most commonly used and well known IPv4 (Internet
Protocol Version 4) such as:
• Integrated IPsec – Better Security
• Integrated Quality of Service (QoS) – Lower latency for real-time applications
• Higher Efficiency of Routing – Less transmission overhead and smaller routing
tables
• Easier configuration of addressing
Note: In order to use IPv6 Internet connection settings, it is required that your ISP
provide you with the IPv6 service. Please contact your ISP for availability and more
information about the IPv6 service.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page
on page 8).
2. Click on Network and click on IPv6.
.
3. Review the IPv6 Internet Connection settings and enter information settings specified
by your ISP. Complete all of the fields required by your ISP and click Apply to save and
commit the changes.
Note: Please contact your ISP for IPv6 service availability.
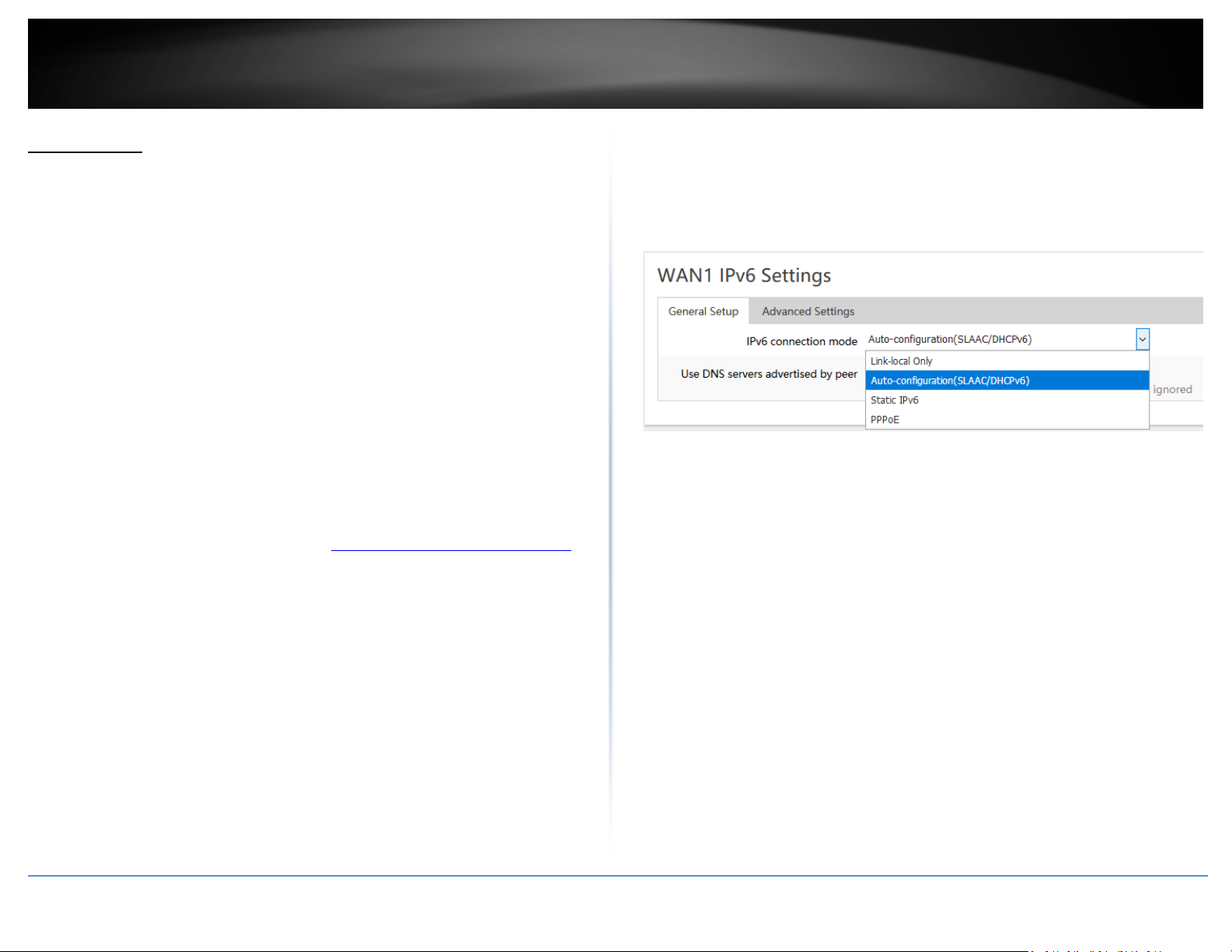
Select the IPv6 WAN connection type provided by your ISP.
”
• Static IPv6
• Auto-configuration (SLAAC/DHCPv6)
• PPPoE
• Link-Local Only
Limited Warranty
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
19
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Virtual LANs (VLANs)
Network > VLAN
Your router supports port-based 802.1Q VLANs as well inter-VLAN routing. VLANs can
be assigned different IP address interfaces in which the router can route be between
VLAN IP subnets.
Create a port-based VLAN
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page
on page 8).
2. Click on Network and click VLAN.
3. Before assigning which untagged and tagged VLAN member ports are assigned to a
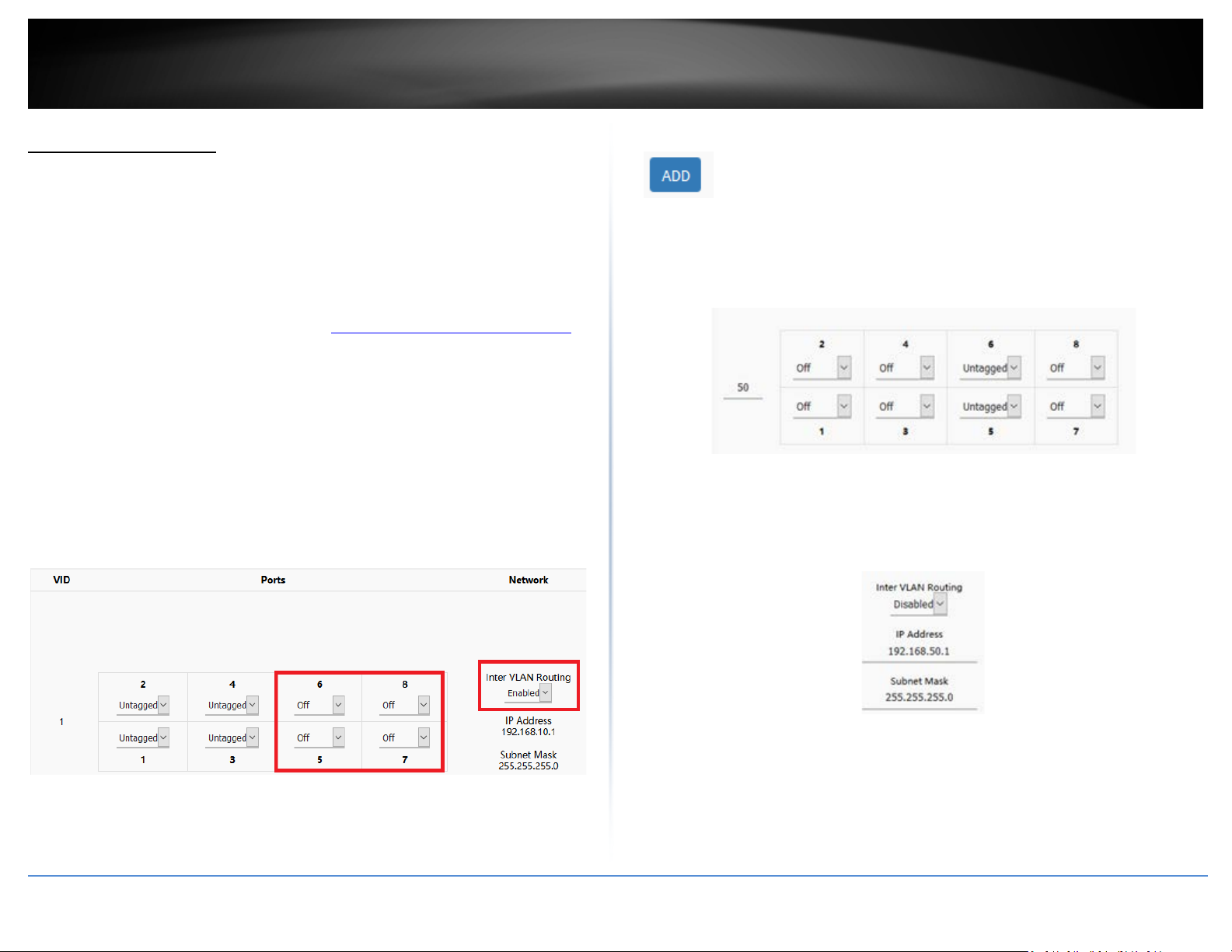
new VLAN, the ports must be set to Off in the default VLAN VID: 1 (LAN). Also, click
the Inter VLAN Routing drop-down list and select Enabled to enable communication
between the LAN and other VLAN interfaces. Click Apply to save and commit the
changes. Example: We will remove ports 5-8 from the default VLAN VID: 1 (LAN)
interface so these ports can be re-assigned as untagged member ports of new VLANs
in example below.
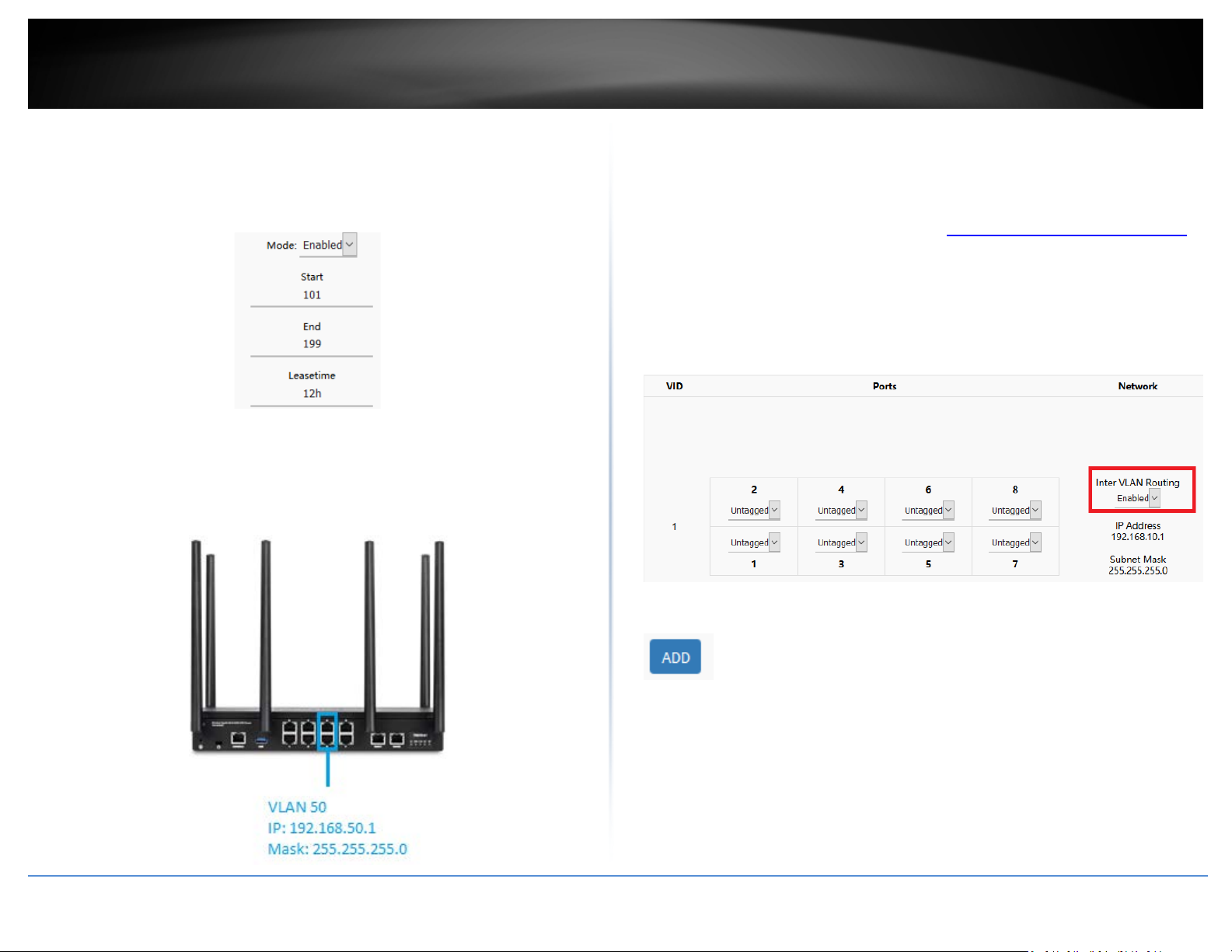
4. To create a new 802.1Q VLAN, under the VLANs section, click Add.
5. Under VID, enter the VLAN ID to assign to the new VLAN (4-4094, VLAN IDs 1-3 are
reserved for use with the default LAN, WAN1, WAN2 interfaces) and set the untagged
VLAN member ports. Example: In the example below, we will create a new VLAN with
VLAN ID: 50 and assign ports 5 & 6 as untagged member ports.
”
6. Enter the VLAN IP interface configuration under IP Address and Subnet Mask.
Example: In the example below, we will enter the VLAN 50 interface IP address as
192.168.50.1 and subnet mask 255.255.255.0.
Limited Warranty
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
20
TRENDnet User’s Guide
7. Under DHCP Server, click the Mode drop-down list and select Enabled to enable the
DHCP server on the VLAN. Click Apply to save and commit the changes.
Example: In the example below, we will enable the DHCP server on VLAN 50 and leave IP
address range and lease defaults. This will assign a DHCP IP range of 101-199 to ensure
any devices connected to this VLAN obtain IP address information via DHCP.
If following the port-based VLAN configuration example, any computers or devices
connecting to ports 5 & 6 will obtain 192.168.50.x/255.255.255.0 address settings and
use the VLAN 50 IP interface 192.168.50.1 as the Internet gateway and gateway to other
local IP subnets.
Create a port-based VLAN with 802.1Q tagging
Your router supports 802.1Q VLAN tagging/trunking to other 802.1Q VLAN devices such
as managed switches.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page
on page 8).
2. Click on Network and click VLAN.
3. Under VLAN VID:1 (LAN), click the Inter VLAN Routing drop-down list and select
Enabled and click Apply to commit and save the changes.
Limited Warranty
”
4. To create a new 802.1Q VLAN, under the VLANs section, click Add.
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
21
TRENDnet User’s Guide
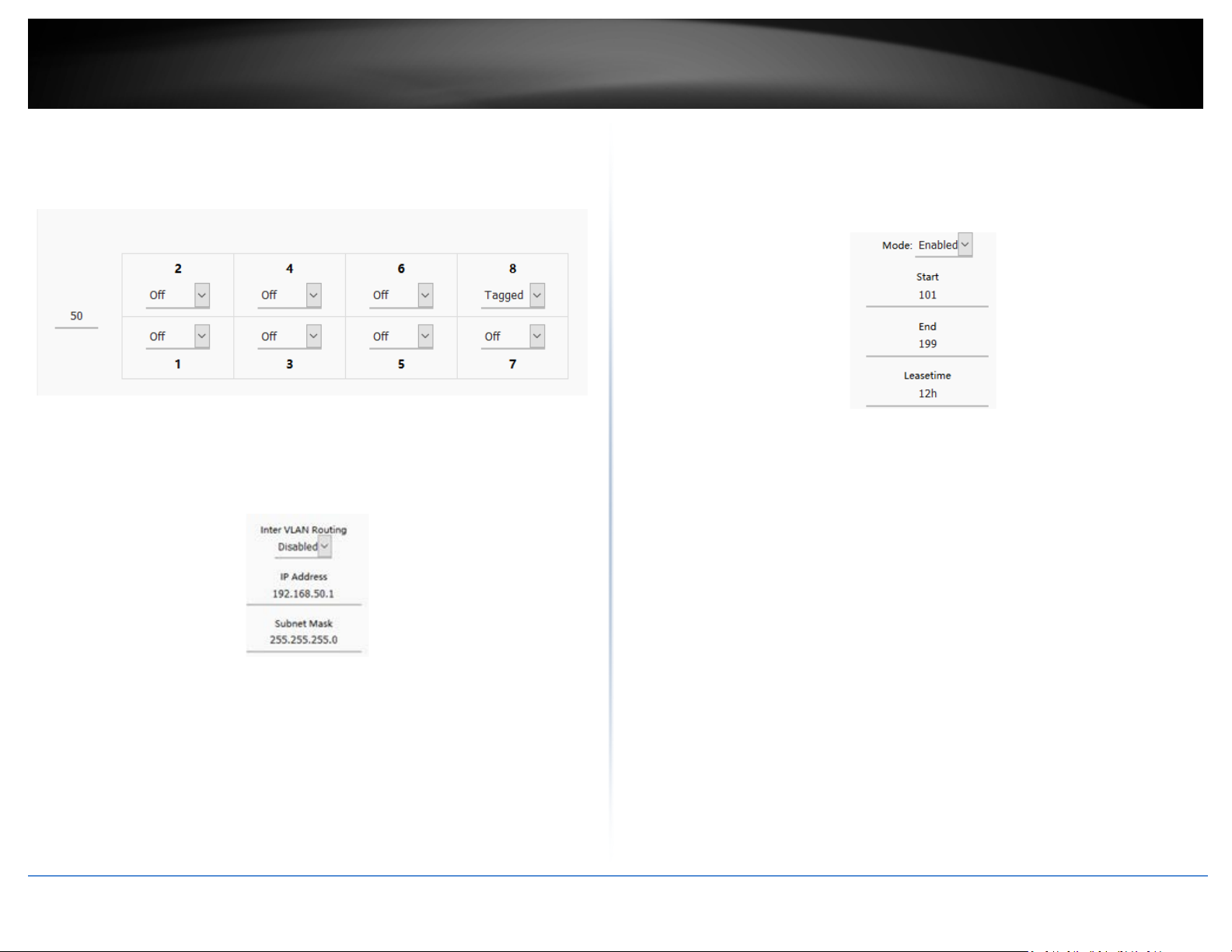
5. Under VID, enter the VLAN ID to assign to the new VLAN (4-4094, VLAN IDs 1-3 are
reserved for use with the default LAN, WAN1, WAN2 interfaces) and set the tagged
VLAN member port. Example: In the example below, we will create a new VLAN with
VLAN ID: 50 and assign port 8 as a tagged VLAN member port.
6. Enter the VLAN IP interface configuration under IP Address and Subnet Mask.
Example: In the example below, we will enter the VLAN 50 interface IP address as
192.168.50.1 and subnet mask 255.255.255.0.
7. Under DHCP Server, click the Mode drop-down list and select Enabled to enable the
DHCP server on the VLAN. Click Apply to save and commit the changes.
Example: In the example below, we will enable the DHCP server on VLAN 50 and leave IP
address range and lease defaults. This will assign a DHCP IP range of 101-199 to ensure
any devices connected to this VLAN obtain IP address information via DHCP.
Limited Warranty
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
22
TRENDnet User’s Guide
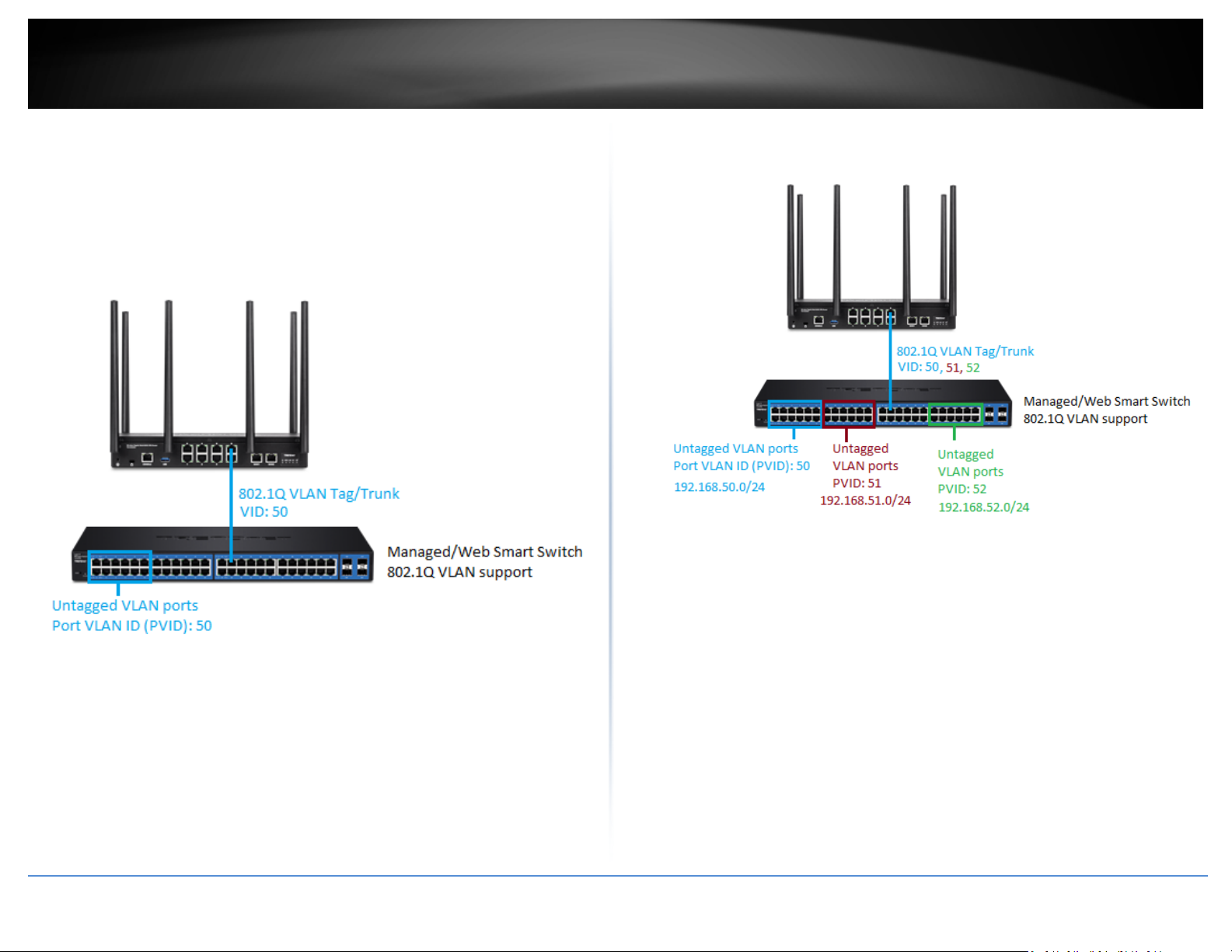
If following the 802.1Q VLAN configuration example, a managed/web smart switch with
802.1Q VLAN support can be connected and pass VLAN 50 traffic between the router
and switch. Any computers or devices connecting to the untagged VLAN ports (PVID: 50)
on the managed/web smart will obtain 192.168.50.x/255.255.255.0 address settings
and use the VLAN 50 IP interface 192.168.50.1 as the Internet gateway and gateway to
other local IP subnets. Additional VLANs can be created on the router and switch in
which 802.1Q VLAN traffic can pass through the same single 802.1Q VLAN tag/trunk
link.
Example below of multiple VLANs configured and passing traffic through the same
802.1Q VLAN tag/trunk link.
Limited Warranty
© Copyright 2019 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
23
 Loading...
Loading...