
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Cover Page
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
Table of Contents
Advanced Settings ........................................................................ 24
Manually configure your Internet connection ............................................................ 24
Product Overview ........................................................................... 3
Package Contents .......................................................................................................... 3
Features ......................................................................................................................... 3
Product Hardware Features........................................................................................... 4
Application Diagram ...................................................................................................... 5
Creating a Network ........................................................................................................ 6
Hardware Installation .................................................................................................... 7
Basic Settings .................................................................................. 7
Access your management page ..................................................................................... 7
Network Status .............................................................................................................. 8
How to choose the type of security for your wireless network .................................... 9
Steps to improve wireless connectivity ....................................................................... 10
Router Mode Setup ....................................................................... 10
Before you Install in router mode ...................................................................... 10
Router Mode Installation ............................................................................................. 11
Wireless Settings ......................................................................................................... 14
Wireless Networking and Security ................................................. 15
Secure your wireless network ..................................................................................... 15
Connect wireless devices to your router ..................................................................... 17
Connect wireless devices using WPS ........................................................................... 17
Guest Network ............................................................................................................. 19
Parental Control ........................................................................................................... 20
IPv6 Settings ................................................................................................................ 24
Clone a MAC address ................................................................................................... 25
Change your router IP address .................................................................................... 26
Set up the DHCP server on your router ....................................................................... 26
Set up DHCP reservation ............................................................................................. 27
Enable/disable UPnP on your router ........................................................................... 28
Enable/disable Application Layer Gateways (ALG) ...................................................... 28
Allow/deny multicast streaming.................................................................................. 29
Identify your network on the Internet ........................................................................ 29
Set your router date and time ..................................................................................... 29
Create schedules ......................................................................................................... 30
Access Control (IP Protocol Filter) ............................................................................... 31
Inbound Filter .............................................................................................................. 32
Open a device on your network to the Internet .......................................................... 33
DMZ ................................................................................................................... 33
Virtual Server ..................................................................................................... 33
Special Applications ........................................................................................... 34
Gaming............................................................................................................... 35
Allow remote access to your router management page ................................... 36
Allow/deny ping requests tofrom the Internet ........................................................... 36
Add static routes ......................................................................................................... 37
Enable Dynamic Routing .............................................................................................. 37
AP/WISP Mode Setup ................................................................... 38
Access Rule (MAC/IP Filter) ............................................................................... 20
Website Filter..................................................................................................... 21
MAC Filter (Wireless) ................................................................................................... 21
Advanced wireless settings .......................................................................................... 22
Multiple SSID...................................................................................................... 22
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Advanced Settings ............................................................................................. 23
AP/WISP Mode Installation ......................................................................................... 38
Access Point Mode ........................................................................ 40
Wireless Settings ......................................................................................................... 41
Wireless Networking and Security ................................................. 42
Secure your wireless network ..................................................................................... 42

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
Connect wireless devices using WPS ........................................................................... 44
Upgrade firmware ....................................................................................................... 65
Change your access point IP address ........................................................................... 45
Configure your Internet connection ............................................................................ 46
IPv6 Connection Settings ............................................................................................. 46
Advanced Settings ....................................................................................................... 47
WISP Mode ................................................................................... 48
Wireless Settings ......................................................................................................... 49
Wireless Networking and Security ................................................. 50
Secure your wireless network ..................................................................................... 50
Connect wireless devices to your router ..................................................................... 52
Connect wireless devices using WPS ........................................................................... 52
Change your access point IP address ........................................................................... 53
Configure your Internet connection ............................................................................ 54
IPv6 Connection Settings ............................................................................................. 54
Advanced Settings ....................................................................................................... 55
Repeater Mode ............................................................................. 56
Wireless Settings ......................................................................................................... 57
Wireless Networking and Security ................................................. 58
Wireless Client List ...................................................................................................... 66
Check system information ........................................................................................... 66
View logs ...................................................................................................................... 68
Technical Specifications ................................................................ 69
Troubleshooting ........................................................................... 71
Appendix ...................................................................................... 72
Secure your wireless network ..................................................................................... 58
Change your access point IP address ........................................................................... 61
Configure your Internet connection ............................................................................ 61
IPv6 Connection Settings ............................................................................................. 62
Advanced Settings ....................................................................................................... 62
Maintenance & Monitoring ........................................................... 63
Change your router login password ............................................................................ 63
Reset your router to factory defaults .......................................................................... 63
Default Settings ........................................................................................................... 64
Backup and restore configuration settings .................................................................. 64
Reboot ......................................................................................................................... 65
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
3
Product Overview
Features
TRENDnet’s AC750 Wireless Travel Router, model TEW-817DTR, is a powerful travel
router for on the go professionals. Concurrent high performance WiFi AC and N bands
network all wireless devices. Router mode turns a wired internet connection into a
wireless network. Wireless ISP (WISP) mode shares a single password protected hotel
WiFi connection with multiple users*. The compact router plugs directly into an outlet
and interchangeable North America, Euro, and UK power prongs work on all continents.
Easy Setup
Get up and running in minutes with the intuitive guided setup
Wireless AC750
Concurrent high speed 433 Mbps WiFi AC + 300 Mbps WiFi N bands
Pre-Encrypted Wireless
For your convenience the wireless network arrives pre-encrypted with its own unique
password
Router Mode
Turns a single wired internet connection into a shared wireless network
TEW-817DTR
Package Contents
In addition to your router, the package includes:
TEW-817DTR
North America, Euro, UK Power Plugs adapter
Multi-Language Quick Installation Guide
CD-ROM (User’s Guide)
Network cable Ethernet Cable (1.5m / 5ft.)
If any package contents are missing or damaged, please contact the retail store, online
retailer, or reseller/distributor from which the product was purchased.
WISP Mode
Shares a single password protected hotel WiFi connection with multiple users*
Access Point/Repeater Modes
Access Point and Repeater modes add device versatility
Toggle Switch
A convenient external switch sets the TEW-817DTR to Router mode, to
WISP/AP/Repeater mode, or turns it off
Power Plugs
Stay connected on all continents with interchangeable North America, Euro, and UK
power plugs
Ethernet Port
Router mode: WAN port used to connect to a wired internet connection
WISP/AP/Repeater mode: LAN port used to connect a wired device to the internet
One Touch Connection
Connect at the touch of the Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) button
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
4
Reset button
Guest Network
Create an isolated network for guest internet access only (router mode only)
VPN Passthrough Support
Secure remote access with IPsec, PPTP, and L2TP VPN passthrough support
IPv6
IPv6 network support
*WISP mode is not compatible with captive portal wireless login pages
**Maximum wireless signal rates are referenced from IEEE 802.11 theoretical
specifications. Actual data throughput and cover-age will vary depending on
interference, network traffic, building materials and other conditions. For maximum
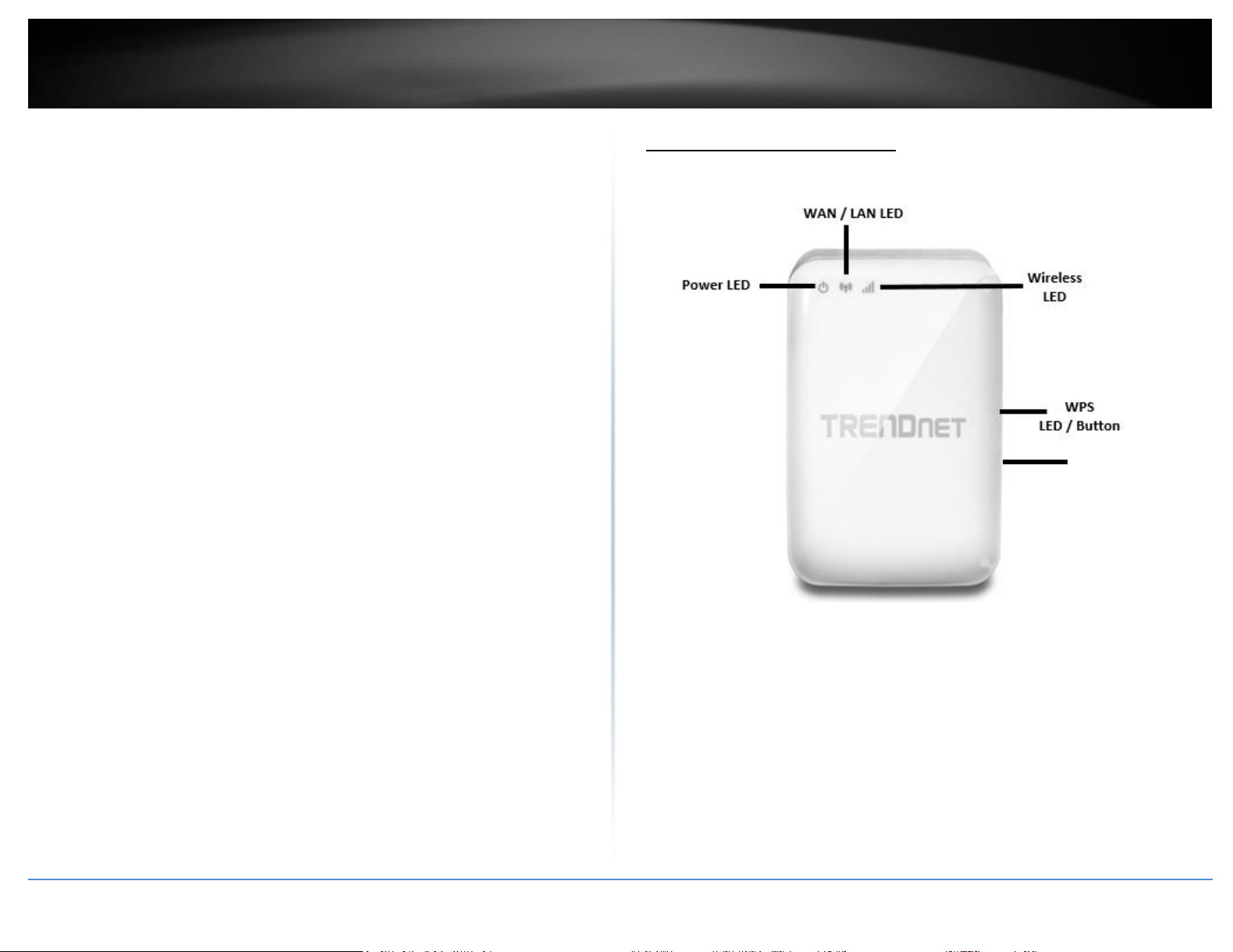
Product Hardware Features
Front View
performance of up to 1.3 Gbps use with a 1.3 Gbps 802.11ac wireless adapter.
Power LED: LED turns blue when the unit is on.
WAN / LAN LED: LED lights blue when the Ethernet port is connected. Blinks during
data transmission.
Wireless LED: Blinks blue during wireless data transmission
WPS LED/Button: Blinks when WPS is activated. Press and hold for 5 seconds to
activate WPS.
Reset button: Press and hold for 10 seconds to reset the device into default
settings.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
5
Off / Mode
Switch
Ethernet
Port
Bottom View
Ethernet Port: Connect Ethernet cables (also called network cables) from your
router LAN ports to your wired network devices. When Router mode is selected the
port becomes WAN port that allows you to connect to the Internet. When AP+WISP
mode is selected the port becomes a LAN port that allows you to connect wired
clients of to connect to an existing network.
Mode Switch: Router mode allows you to connect the device to an existing
network. AP + WISP mode sets the device into Access Point mode where you can
configure the device into an access point, WISP client or Repeater. Select Off to turn
off the device.
Application Diagram
The router is installed near the hotel’s internet connection port which connects to the Internet.
2.4GHz wireless signals from the router are broadcasted to wireless clients such as laptops (with
wireless capability) and the less congested 5GHz wireless signals from the router are broadcasted
to other wireless client devices such as TVs, game consoles, or media bridges thereby providing
Internet access for all wireless client devices.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
6
Creating a Network
What is a network?
A network is a group of computers or devices that can communicate with each other. A
home network of more than one computer or device also typically includes Internet
access, which requires a router.
A typical home network may include multiple computers, a media player/server, a
printer, a modem, and a router. A large home network may also have a switch,
additional routers, access points, and many Internet-capable media devices such as TVs,
game consoles, and Internet cameras.
Modem: Connects a computer or router to the Internet or ISP (Internet Service
Provider).
Router: Connects multiple devices to the Internet.
Switch: Connect several wired network devices to your home network. Your
router has a built-in network switch (the LAN port 1-4). If you have more wired
network devices than available Ethernet ports on your router, you will need an
additional switch to add more wired connections.
How to set up a home network
1. For a network that includes Internet access, you’ll need:
Computers/devices with an Ethernet port (also called network port) or wireless
networking capabilities.
A modem and Internet service to your home, provided by your ISP (modem
typically supplied by your ISP).
A router to connect multiple devices to the Internet.
2. Make sure that your modem is working properly. Your modem is often provided by
your Internet Service Provider (ISP) when you sign up for Internet service. If your
modem is not working contact your ISP to verify functionality.
3. To set up wireless security on your router, see “Wireless Networking and Security” on
page 8.
How to setup your device in router mode
Refer to the Quick Installation Guide or continue to the next section “Router Mode” on
page 11 for more detailed installation instructions.
How to setup your device in AP/WISP mode
Refer to the Quick Installation Guide or continue to the next section “AP/WISP Mode”
on page 40 for more detailed installation instructions.
Where to find more help
In addition to this User’s Guide, you can find help below:
http://www.trendnet.com/support (documents, downloads, and FAQs are
available from this Web page)
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
7
Hardware Installation
1. Verify that you have an Internet connection when connecting your computer directly
to your Internet connection port.
2. Attached the appropriate power adapter for your region.
3. Make sure the switch on the unit is set to the appropriate (Router / AP+WISP) mode.
Please refer to the specific mode section for proper installation.
Basic Settings
Access your management page
Note: Your router management page URL/domain name http://tew-817dtr or IP
address http://192.168.10.1 is accessed through the use of your Internet web browser
(e.g. Internet Explorer®, Firefox®, Chrome™, Safari®, Opera™) and will be referenced
frequently in this User’s Guide.
1. Open your web browser and go to URL/domain name http://tew-817dtr or IP address
http://192.168.10.1. Your router will prompt you for a user name and password.
2. For added security, the router is preconfigured with a unique password. You can find
the Password on a sticker on the side of the router and on the label on the bottom of
the router. Enter your Username and Password, select your preferred language, and
then click Login.
User Name: admin
Password: (xxxxxxxx)
Note: User Name and Password are case sensitive.
4. Plug the TEW-817DTR into a power outlet.
8. Verify that the LED indicators on the front of the unit are illuminated: Power, and
Internet.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
8
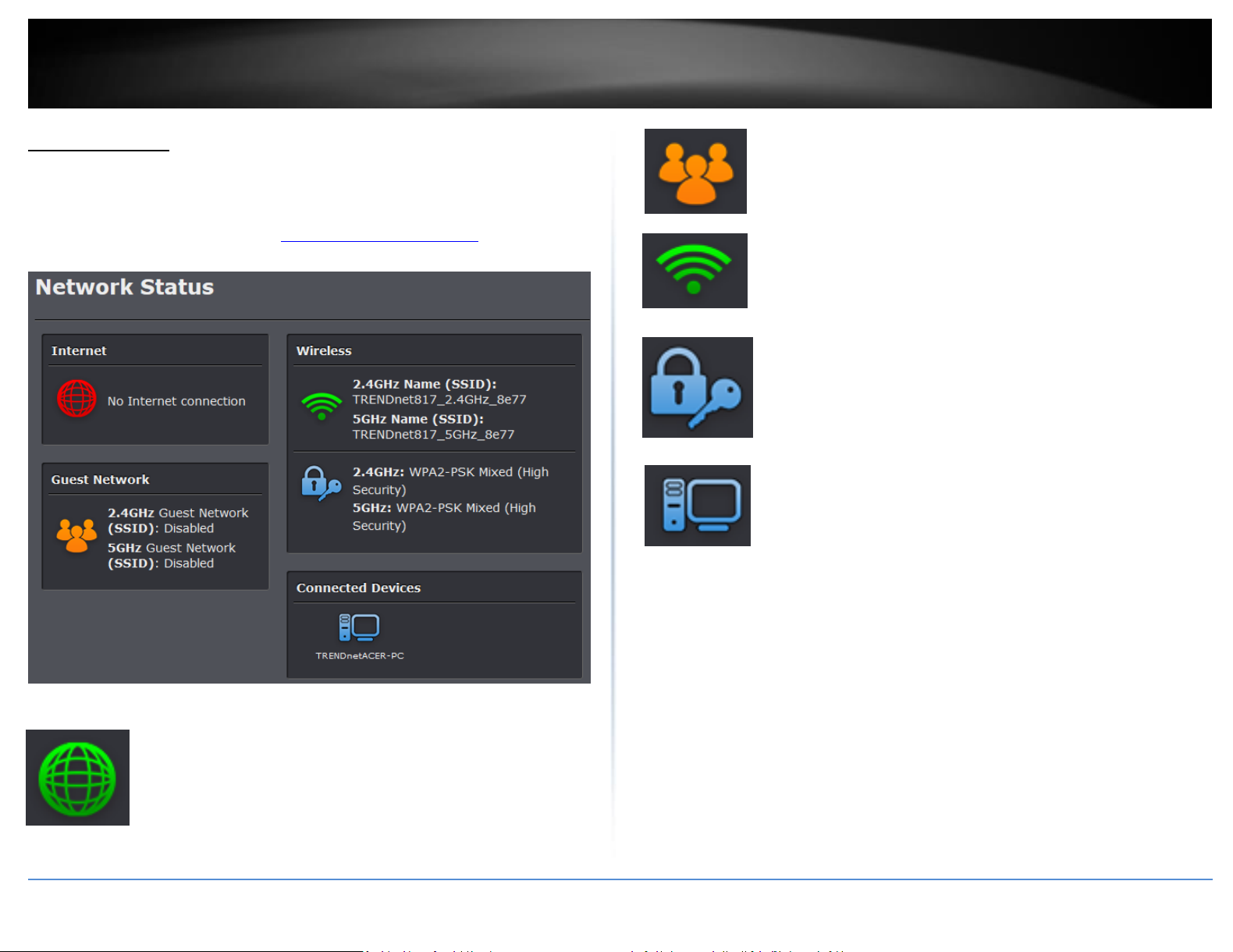
Network Status
Basic > Network Status
This section displays a brief summary of the router’s basic settings and the connected
devices.
1. Log into the management page (see “Access your management page” on page 7).
2. Click on Basic and click on Network Status.
Internet: The Internet icon displays green to indicate that your router
has successfully established an Internet connection. The Internet icon
displays orange to indicate that a physical connection has been
established on the Internet port of the router but with no successful
Internet connection has been established. The Internet icon displays
red to indicate that the Internet is physically disconnected.
Guest Network (Available in Router mode): The Guest Network icon
displays orange to indicate that there are no wireless guest networks
currently enabled. The Guest Network icon will display green to
indicate that you have at least one wireless guest network currently
enabled.
Wireless: The wireless icon displays green to indicate that wireless is
enabled on both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands. The wireless icon displays
orange to indicate that only wireless band is enabled (2.4GHz or
5GHz). The wireless icon will display red to indicate that wireless is
disabled on both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands.
Wireless Security: The wireless security section will display the
current security settings configured for your wireless networks. It is
strongly recommended to enable security on your wireless networks.
Connected Devices: The connected devices section displays the list of
network devices currently connected to your router.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
9
Security Standard
WEP
WPA
WPA2
Compatible
Wireless
Standards
IEEE 802.11a/b/g
(802.11n devices
will operate at
802.11g to connect
using this standard)
IEEE 802.11a/b/g
(802.11n devices
will operate at
802.11g to connect
using this
standard)
IEEE
802.11a/b/g/n/ac
Highest
Performance
Under This
Setting
Up to 54Mbps
Up to 54Mbps
Up to 450Mbps (11n)
or 1.3 Gbps (11ac)
Encryption
Strength
Low
Medium
High
Additional
Options
Open System or
Shared Key,
HEX or ASCII,
Different key sizes
TKIP or AES,
Preshared Key or
RADIUS
TKIP or AES,
Preshared Key or
RADIUS
Recommended
Configuration
Open System ASCII
13 characters
TKIP
Preshared Key
8-63 characters
AES
Preshared Key
8-63 characters
*Dependent on the maximum 802.11n data rate supported by the device (150Mbps,
300Mbps, 450Mbps) or maximum 802.11ac data rate supported by the device
(433Mbps, 867Mbps, 1.3Gbps)
How to choose the type of security for your wireless network
Setting up wireless security is very important. Leaving your wireless network open and
unsecure could expose your entire network and personal files to outsiders. TRENDnet
recommends reading through this entire section and setting up wireless security on your
new router.
There are a few different wireless security types supported in wireless networking each
having its own characteristics which may be more suitable for your wireless network
taking into consideration compatibility, performance, as well as the security strength
along with using older wireless networking hardware (also called legacy hardware).
It is strongly recommended to enable wireless security to prevent unwanted users from
accessing your network and network resources (personal documents, media, etc.).
In general, it is recommended that you choose the security type with the highest
strength and performance supported by the wireless computers and devices in your
network. Please review the security types to determine which one you should use for
your network.
Wireless Encryption Types
WEP: Legacy encryption method supported by older 802.11b/g hardware. This is
the oldest and least secure type of wireless encryption. It is generally not
recommended to use this encryption standard, however if you have old 802.11 b or
802.11g wireless adapters or computers with old embedded wireless cards(wireless
clients), you may have to set your router to WEP to allow the old adapters to
connect to the router.
Note: This encryption standard will limit connection speeds to 54Mbps.
WPA: This encryption is significantly more robust than the WEP technology. Much
of the older 802.11g hardware was been upgraded (with firmware/driver upgrades)
to support this encryption standard. Total wireless speeds under this encryption
type however are limited to 54Mbps.
WPA-Auto: This setting provides the router with the ability to detect wireless
devices using either WPA or WPA2 encryption. Your wireless network will
automatically change the encryption setting based on the first wireless device
connected. For example, if the first wireless client that connects to your wireless
network uses WPA encryption your wireless network will use WPA encryption. Only
when all wireless clients disconnect to the network and a wireless client with WPA2
encryption connects your wireless network will then change to WPA2 encryption.
Note: WPA2 encryption supports 802.11n speeds and WPA encryption will limit
your connection speeds to 54Mbps
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
WPA2: This is the most secure wireless encryption available today, similar to WPA
encryption but more robust. This encryption standard also supports the highest
connection speeds. TRENDnet recommends setting your router to this encryption
standard. If you find that one of your wireless network devices does not support
WPA2 encryption, then set your router to either WPA or WPA-Auto encryption.
Note: Check the specifications of your wireless network adapters and wireless
appliances to verify the highest level of encryption supported.Below is brief
comparison chart of the wireless security types and the recommended
configuration depending on which type you choose for your wireless network.

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
10
Steps to improve wireless connectivity
There are a number of factors that can impact the range of wireless devices. Follow
these tips to help improve your wireless connectivity:
1. Keep the number of obstructions to a minimum. Each obstruction can reduce the
range of a wireless device. Position the wireless devices in a manner that will
minimize the amount of obstructions between them.
a. For the widest coverage area, install your router near the center of your
home, and near the ceiling, if possible.
b. Avoid placing the router on or near metal objects (such as file cabinets and
metal furniture), reflective surfaces (such as glass or mirrors), and masonry
walls.
c. Any obstruction can weaken the wireless signal (even non-metallic objects),
so the fewer obstructions between the router and the wireless device, the
better.
d. Place the router in a location away from other electronics, motors, and
fluorescent lighting.
e. Many environmental variables can affect the router’s performance, so if your
wireless signal is weak, place the router in several locations and test the
signal strength to determine the ideal position.
2. Building materials can have a large impact on your wireless signal. In an indoor
environment, try to position the wireless devices so that the signal passes through
less dense material such as dry wall. Dense materials like metal, solid wood, glass
or even furniture may block or degrade the signal.
3. Antenna orientation can also have a large impact on your wireless signal. Use the
wireless adapter’s site survey tool to determine the best antenna orientation for
your wireless devices.
4. Interference from devices that produce RF (radio frequency) noise can also impact
your signal. Position your wireless devices away from anything that generates RF
noise, such as microwaves, radios and baby monitors.
If possible, upgrade wireless network interfaces (such as wireless cards in computers)
from older wireless standards to 802.11n or 802.11ac. If a wirelessly networked device
uses an older standard, the performance of the entire wireless network may be slower.
If you are still experiencing low or no signal consider repositioning the wireless devices,
installing additional access points or wireless extenders.
Router Mode Setup
Before you Install in router mode
Many Internet Service Providers (ISPs) allow your router to connect to the Internet
without verifying the information fields listed below. Skip this section for now and if
your router cannot connect to the Internet using the standard installation process, come
back to this page and contact your ISP to verify required ISP specification fields listed
below.
1. Obtain IP Address Automatically (Dynamic IP/DHCP)
Host Name:_______________ (Optional, if required by ISP for Compatibilty)
Primary DNS Server Address: _____. _____._____._____ (Optional)
Secondary DNS Servers Address : _____. _____._____._____ (Optional)
MTU:_______ (Default: 1500, change if required by ISP)
MAC Address: ___:___:___:___:___:___ Clone your PC MAC Address (Optional)
2. Static IP/Fixed IP address
IP Address: _____. _____._____._____ (e.g. 215.24.24.129)
Subnet Mask: _____. _____._____._____
Default Gateway IP Address: _____. _____._____._____
Primary DNS Server Address: _____. _____._____._____
Secondary DNS Servers Address : _____. _____._____._____ (Optional)
MTU:_______ (Default: 1500, change if required by ISP)
MAC Address: ___:___:___:___:___:___ Clone your PC MAC Address (Optional)
3. PPPoE Dynamic IP (DHCP) / PPPoE Static IP – Standard & Russian
Type (Dynamic IP/DHCP or Static IP)
IP Address (Static IP): _____. _____._____._____ (e.g. 215.24.24.129)
Username: _________
Password: ________________
Service Name: _________________ (Optional)
DNS Servers Address 1 (Static IP): _____. _____._____._____
DNS Servers Address 2 (Static IP): _____. _____._____._____ (Optional)
Reconnect Mode: Always / On Demand / Manual (Optional)
MTU:_______ (Default: 1500, change if required by ISP)
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
11
MAC Address: ___:___:___:___:___:___ Clone your PC MAC Address (Optional)
4. PPTP - Standard & Russian
Type (Dynamic IP/DHCP or Static IP)
PPTP IP Address: _____. _____._____._____ (e.g. 215.24.24.129)
PPTP Subnet Mask: _____. _____._____._____ (e.g. 255.255.255.0)
PPTP Gateway:_____. _____._____._____ (e.g. 215.24.24.1)
PPTP Server: _____________________ (e.g. 215.24.24.150)
Username: _________
Password: ________________
Reconnect Mode: Always / On Demand / Manual (Optional)
DNS Servers Address 1 (Static IP): _____. _____._____._____
DNS Servers Address 2 (Static IP): _____. _____._____._____ (Optional)
MTU:_______ (Default: 1500, change if required by ISP)
MAC Address: ___:___:___:___:___:___ Clone your PC MAC Address (Optional)
MPPE (Microsoft® Point-to-Point Encryption) w/ MS-CHAPv2 Enabled:____(Yes or No)
5. L2TP - Standard & Russian
Type (Dynamic IP/DHCP or Static IP)
L2TP IP Address: _____. _____._____._____ (e.g. 215.24.24.129)
L2TP Subnet Mask: _____. _____._____._____ (e.g. 255.255.255.0)
L2TP Gateway:_____. _____._____._____ (e.g. 215.24.24.1)
L2TP Server: _____________________ (e.g. 215.24.24.150)
Username: _________
Password: ________________
Reconnect Mode: Always / On Demand / Manual (Optional)
DNS Servers Address 1 (Static IP): _____. _____._____._____
DNS Servers Address 2 (Static IP): _____. _____._____._____ (Optional)
MTU:_______ (Default: 1500, change if required by ISP)
MAC Address: ___:___:___:___:___:___ Clone your PC MAC Address (Optional)
MPPE (Microsoft® Point-to-Point Encryption) w/ MS-CHAPv2 Enabled:____(Yes or No)
Router Mode Installation
In router mode, the TEW-817DTR serves as your typical network router. In this mode the
TEW-817DTR offers advance configurations from setting specific WAN types to opening
certain ports for your applications.
1. Verify that you have an Internet connection when connecting your computer directly
to your Internet connection port.
2. Attached the appropriate power adapter for your region.
3. Make sure the switch on the unit is set to Router mode.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
12
4. Plug the TEW-817DTR into a power outlet.
5. Connect the TEW-817DTR to an available Internet connection port provided by your
hotel.
5. Connect your wireless computer to the TEW-817DTR’s wireless network.
6. When prompted, enter the WiFi password from the sticker on the device.
6. Open your internet browser and verify you can access the Internet. Congratulations,
you are now connected to the Internet using the TEW-817DTR.
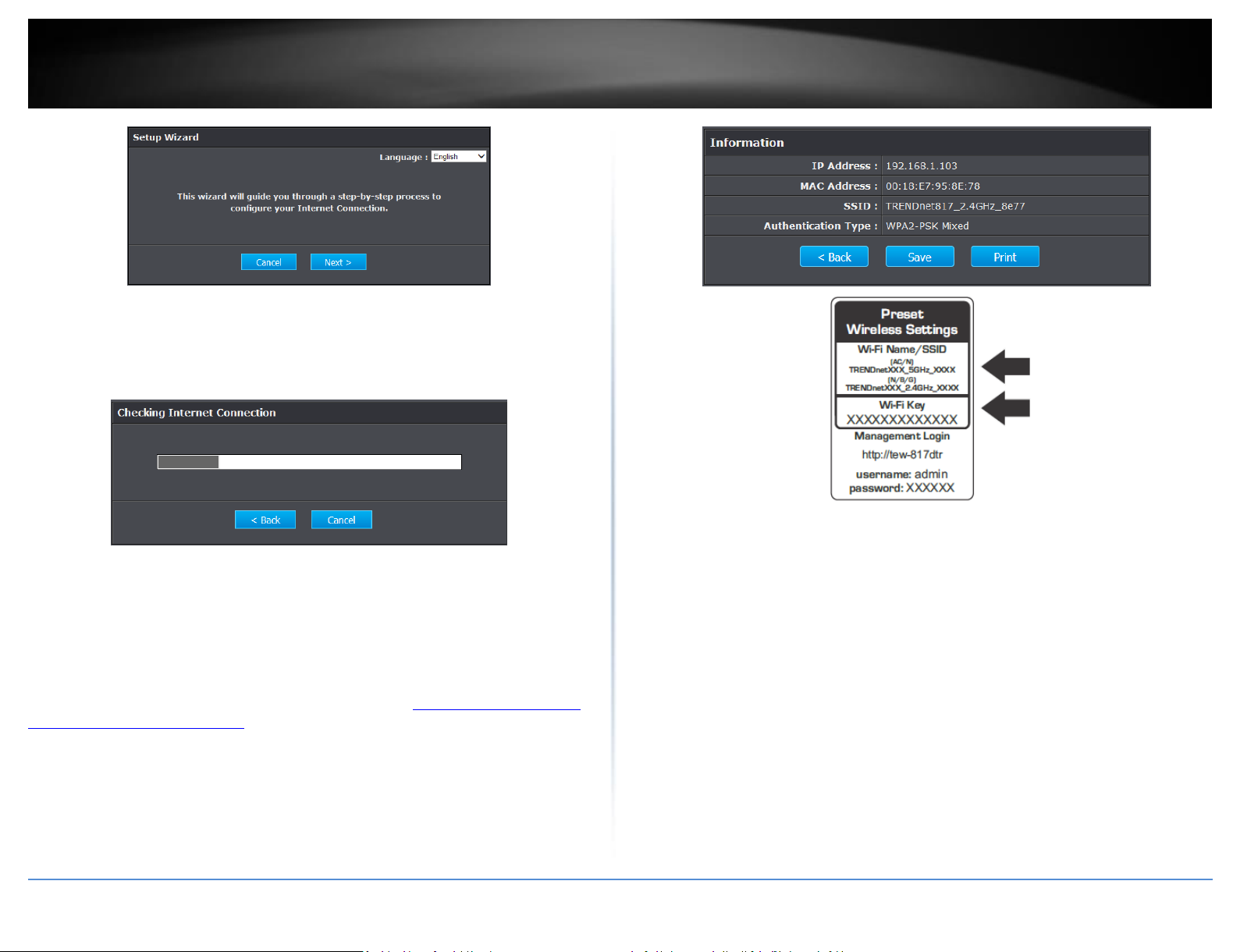
Setup Wizard
1. Open your web browser (e.g. Internet Explorer, Firefox, Safari, Chrome, or Opera) and
the wizard will automatically appear.
Note: If you have already configured your router before, the wizard will no longer
appear automatically. In your web browser, go to http://tew-817dtr/ or you can
access the router management using the default IP address http://192.168.10.1. Your
router will prompt you for a user name and password. Enter your user name and
password and click Advanced > Setup > Wizard.
2. Select your Language and click Next..
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
13
3. If the wizard is unable to detect your Internet connection type, you will be prompted
to select it. Select your Internet connection type and click Next.
Note: Dynamic IP (DHCP) is typical for most Internet services. You can verify your
settings with your Internet Service Provider.
4. Confirm your settings. This window displays your predefined router wireless settings
and click Exit to complete the wizard.
Note: For added security, the router wireless network is pre-encrypted with its own
unique wireless network security key. You can find the unique network security key and
the pre-assigned network name (SSID) on a sticker on the side of the router and on a
label on the bottom of the router. You will need this information to connect to the
router. To change the network security key, refer to page 9 “How to choose the type of
security for your wireless network”. If the router is reset to factory defaults, the wireless
encryption will reset to the network security key printed on the product labels of the
router.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
14
Wireless Settings
Basic > Wireless (2.4GHz or 5GHz)
This section outlines available management options under basic wireless sub tab for
both 2.4GHz and 5GHz wireless sections. You can refer to the page 15 Secure your
Wireless network to configure your wireless security settings.
1. Log into the management page (see “Access your management page” on page 7).
2. Click on Wireless and click on Basic scroll down to Wireless Network Settings (2.4GHz
or 5GHz)
3. To save changes to this section, click Apply when finished.
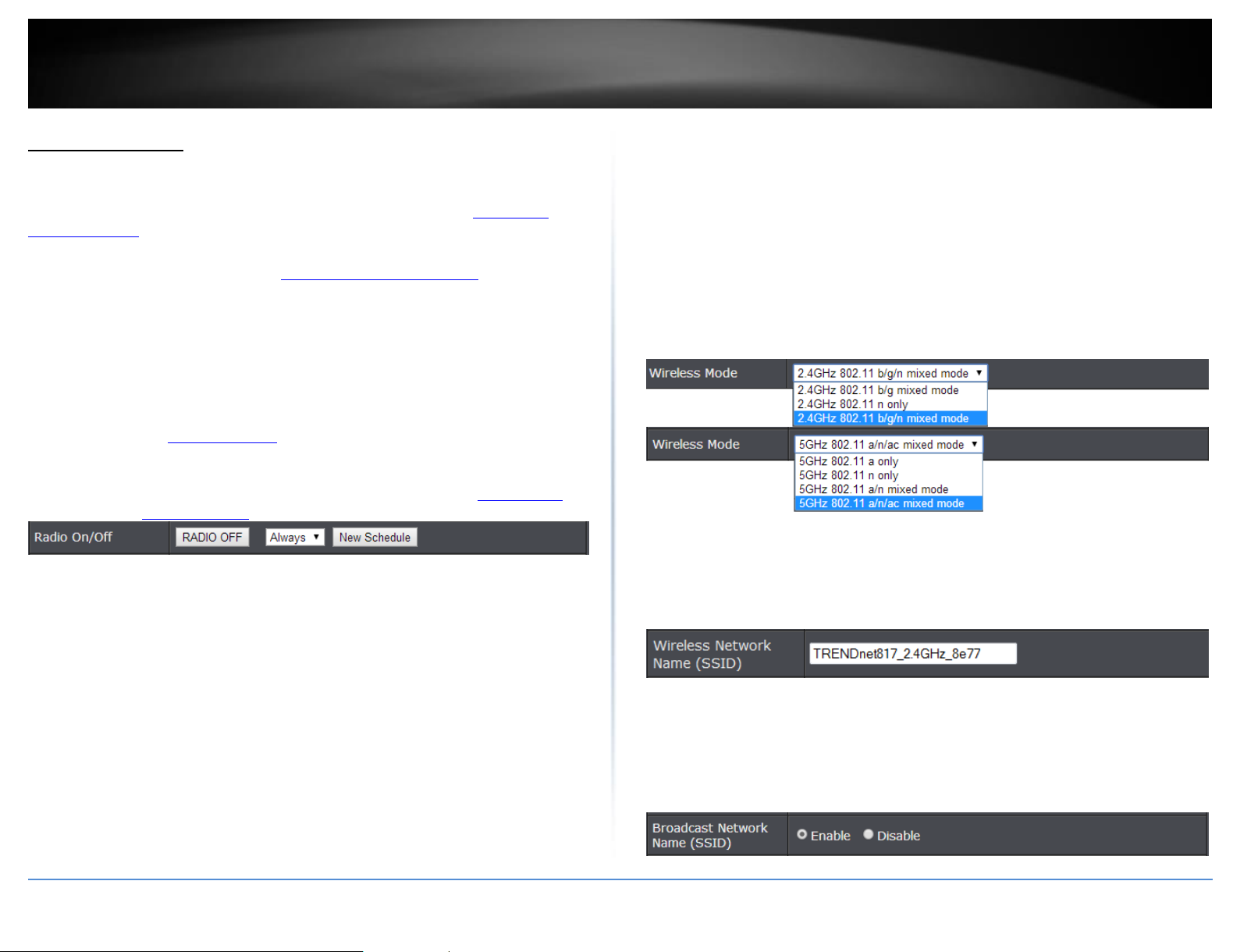
Radio On/Off:– Click the radio on/off button to enable/disable the wireless radio.
Note: It is recommended to keep wireless radios enabled.
New Schedule: The schedule function allows you to define a schedule when the
wireless should be turned on. To define a new schedule, click New Schedule and
refer to page 31 “Create Schedules”. After you have created a new schedule, click
the drop-down list and the new schedule will be available for selection.
Note: Before applying scheduling, please ensure your Time settings are configured
correct and you have defined a schedule. See page 30 to configure Time Settings and
see page 31 “Create Schedules” to create a schedule.
Wireless Mode: When applying the Wireless Mode setting, please keep in mind the
following:
Wireless devices that support 802.11n are backwards compatible and can connect
wirelessly at 802.11g or 802.11b.
Wireless devices that support 802.11ac are backwards compatible and can connect
wirelessly at 802.11n or 802.11a.
Connecting at 802.11b or 802.11g will limit the capability of your 802.11n
supported wireless devices from obtaining higher performance and data rates.
Connecting at 802.11a or 802.11n will limit the capability of your 802.11ac
supported wireless devices from obtaining higher performance and data rates.
Allowing 802.11b or 802.11g devices to connect to an 802.11n capable wireless
network may degrade the wireless network performance below the higher
performance and data rates of 802.11n.
Allowing 802.11a or 802.11n devices to connect to an 802.11ac capable wireless
network may degrade the wireless network performance below the higher
performance and data rates of 802.11ac.
Wireless devices that only support 802.11n or 802.11a will not be able to connect
to a wireless network that is set to 802.11ac only mode.
Wireless devices that only support 802.11b or 802.11g will not be able to connect
to a wireless network that is set to 802.11n only mode.
Wireless devices that only support 802.11b will not be able to connect to a wireless
network that is set to 802.11g only mode.
Wireless devices that only support 802.11a will not be able to connect to a wireless
network that is set to 802.11n only mode.
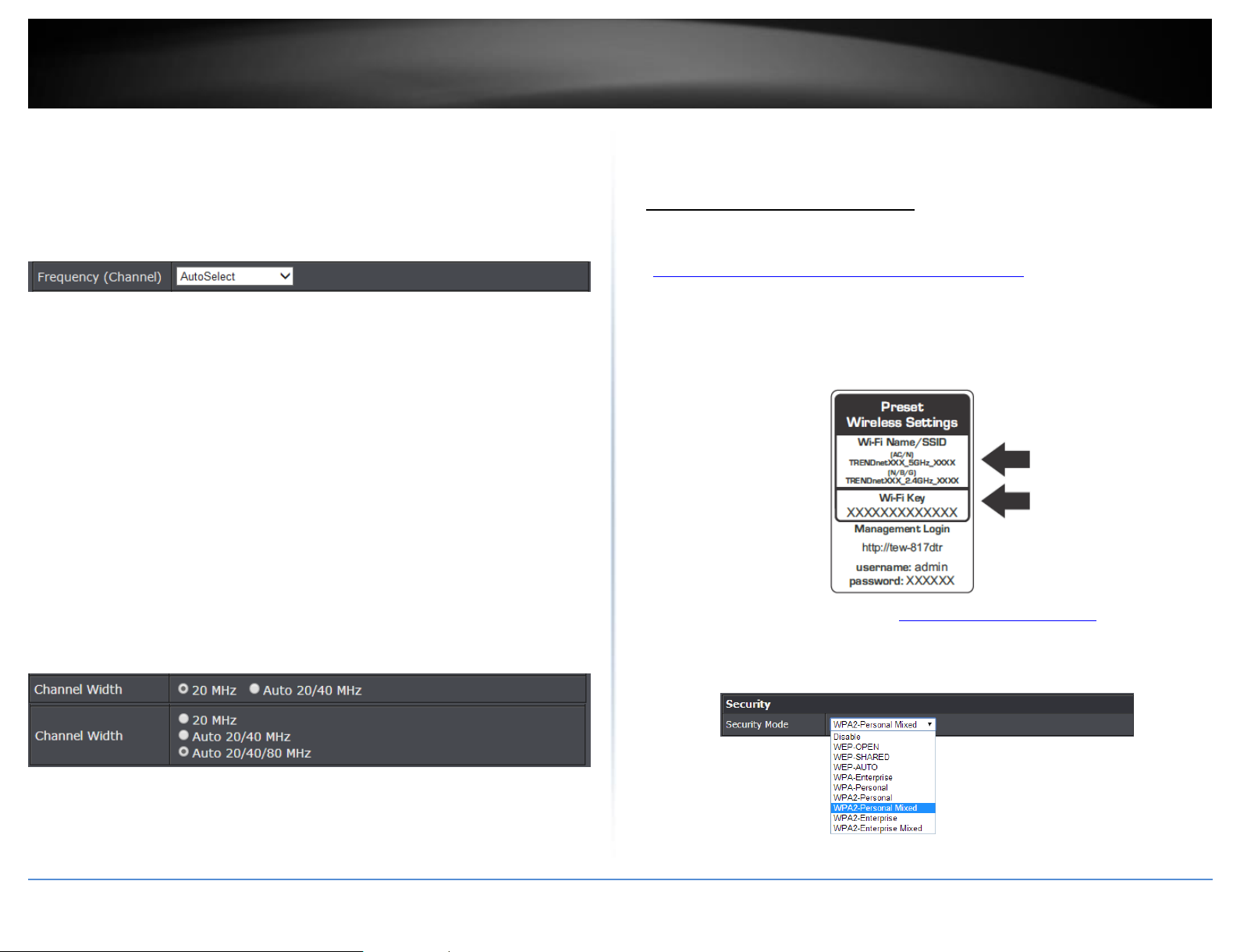
Wireless Network Name (SSID): Enter the wireless name (SSID) for your wireless
network. This acronym stands for Service Set Identifier and is the name of your
wireless network. It differentiates your wireless network from others around you.
By default, the router’s wireless name is unique to the device. If you choose to
change the SSID, change it to a name that you can easily remember.
Broadcast Network Name (SSID)
o Visible: Allows wireless devices to search and discover your wireless network
name (also called SSID) broadcasted by your router.
o Invisible: Turns off the ability for wireless devices to find your network. It is still
possible for wireless devices to be configured to connect to your wireless
network. Disabling this setting will disable WPS functionality.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
15
Enable Auto Channel Scan – Check this option to set your router to scan for which
wireless channels to use automatically.
Frequency (Channel) – Selecting the Auto option will set your router to scan for the
appropriate wireless channel to use automatically. Click the drop-down list and
select the desired Channel for wireless communication. The goal is to select the
Channel that is least used by neighboring wireless networks.
Channel Width: Select the appropriate channel width for your wireless network.
This setting only applies to 802.11n and 802.11ac. For greater 802.11n
performance, select Auto 20/40MHz (Options: 20MHz or Auto 20/40MHz). It is
recommended to use the default channel bandwidth settings.
For greater 802.11ac performance, select Auto 20/40/80MHz (Options: 20MHz,
Auto 20/40MHz, Auto 20/40/80MHz). It is recommended to use the default channel
width settings.
Note: Please note that the default settings may provide more stability than the
higher channel bandwidth settings such as Auto 20/40/80MHz for connectivity in
busy wireless environments where there are several wireless networks in the area.
o 20 MHz: This mode operates using a single 20MHz channel for wireless devices
connecting at 802.11n on both 2.4GHz and 5GHz. This setting may provide more
stability than 20/40MHz (Auto) for connectivity in busy wireless environments
where there are several neighboring wireless networks in the area.
o Auto 20/40MHz (11n) or Auto 20/40/80MHz (11ac): When this setting is active,
this mode is capable of providing higher performance only if the wireless devices
support the channel width settings. Enabling Auto 20/40MHz or Auto 20/40/80
MHz typically results in substantial performance increases when connecting an
802.11ac/n wireless client.
Wireless Networking and Security
Secure your wireless network
Basic > Wireless
After you have determined which security type to use for your wireless network (see
“How to choose the security type for your wireless network” on page 9), you can set up
wireless security.
Note: By default, your router is configured with a predefined wireless network name
(SSID) and security key using WPA2-Personal. The predefined wireless network name and
security can be found on the sticker on the side of the router or on the device label at the
bottom of the router.
1. Log into the management page (see “Access your management page” on page 7).
2. Click on Basic, and click on Wireless.
3. Under Security, click on the Security Mode drop-down list to select your wireless
security type.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
16
WEP Key Format
HEX
ASCII
Character set
0-9 & A-F, a-f only
Alphanumeric (a,b,C,?,*, /,1,2, etc.)
64-bit key length
10 characters
5 characters
128-bit key length
26 characters
13 characters
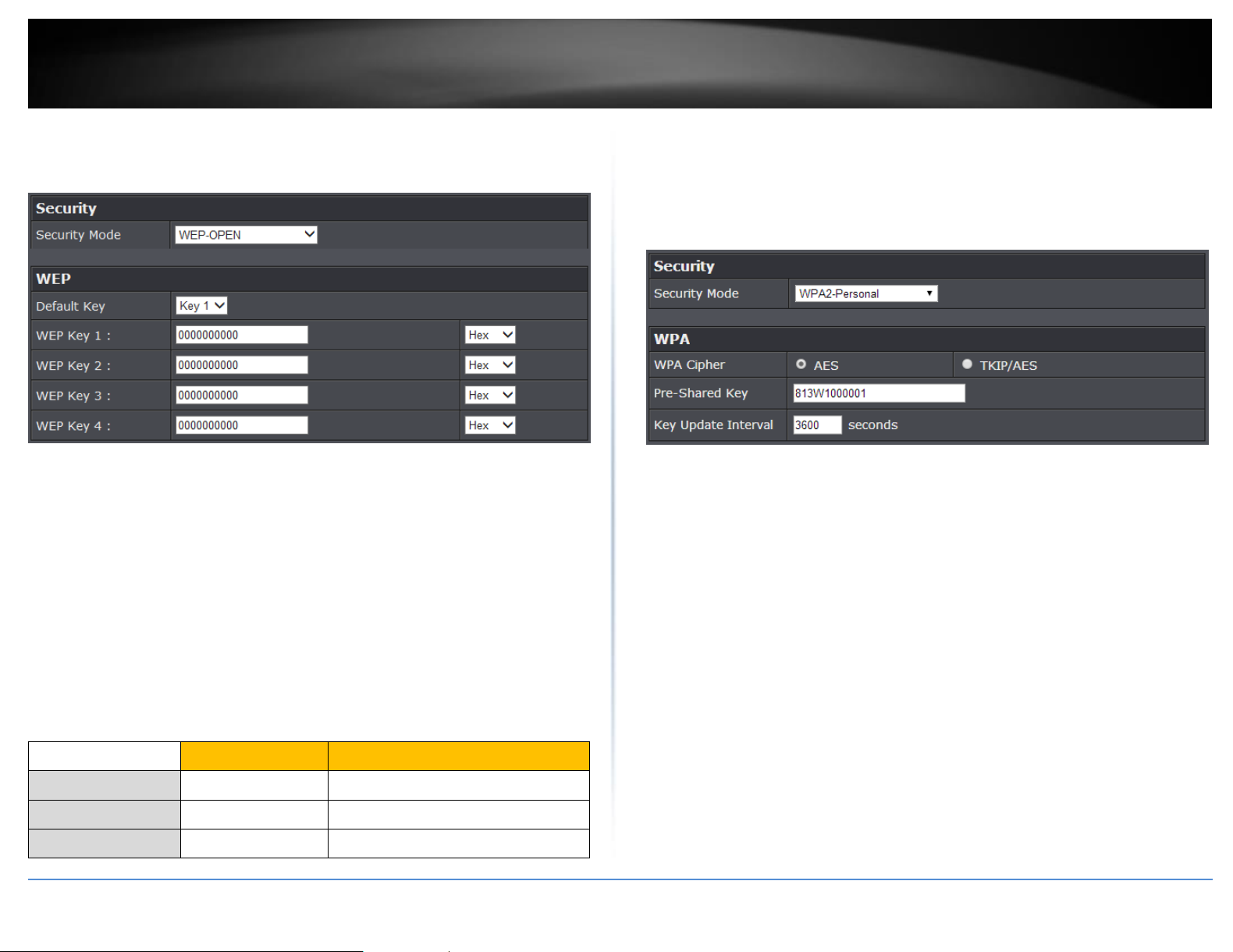
Selecting WEP:
If selecting WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), please review the WEP settings to configure
and click Apply to save the changes.
Selecting WPA-Personal / WPA2-Personal / WPA2-Personal Mixed
(WPA2-Personal recommended):
In the Security Mode drop-down list, select WPA-Personal, WPA2-Personal, or WPA2Personal Mixed. Please review the WPA-Personal settings to configure and click Apply
to save the changes.
Security Mode: Choose WEP-OPEN, WEP-SHARED, or WEP-AUTO.
Note: It is recommended to use Open since it is known to be more secure than
Shared Key.
Default Key: Choose the key index to use for security to the corresponding WEP
Keys 1-4. You can only use one key at any given time.
Note: Please note that they wireless client key index 1-4 should also match the key
index chosen here in order to establish connection.
WEP Key 1-4: Enter the WEP key. This is the password or key that is used to
connect your computer to this router wirelessly. You can enter 64-bit or 128-bit
key. You can enter up to four keys but only the one chosen as the Default Key will
be used.
Note: It is recommended to use 128-bit because it is more secure to use a key that
consists of more characters.
Hex/ASCII: Enter the WEP key format. See the table below for the acceptable
characters and lengths for each format.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
The following section outlines options when selecting WPA-Personal, WPA2-Personal,
or WPA2-Personal Mixed (Preshared Key),
WPA Cipher: Select a Cipher Type to use.
o When selecting WPA2-Personal Mixed security, it is recommended to use
TKIP/AES.
o When selecting WPA2-Personal security, it is recommended to use AES.
WPA Pre-Shared Key: Enter the passphrase.
o This is the password or key that is used to connect your computer to this router
wirelessly
Key Format: 8-63 alphanumeric characters (a,b,C,?,*, /,1,2, etc.)
Key Update Interval: Enter the time interval (seconds) of when the network
passphrase will rotate.
Note: It is recommended to use the default interval time. Your passphrase will not
change, rotation of the key is part of the WPA protocol and designed to increase
security.
Selecting WPA-Enterprise / WPA2-Enterprise / WPA2-Enterprise Mixed
(WPA2-Personal recommended):
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
17
Connect wireless devices to your router
A variety of wireless network devices can connect to your wireless network such as:
Gaming Consoles
Internet enabled TVs
Network media players
Smart Phones
Wireless Laptop computers
Wireless IP cameras
Each device may have its own software utility for searching and connecting to available
wireless networks, therefore, you must refer to the User’s Manual/Guide of your
wireless client device to determine how to search and connect to this router’s wireless
network.
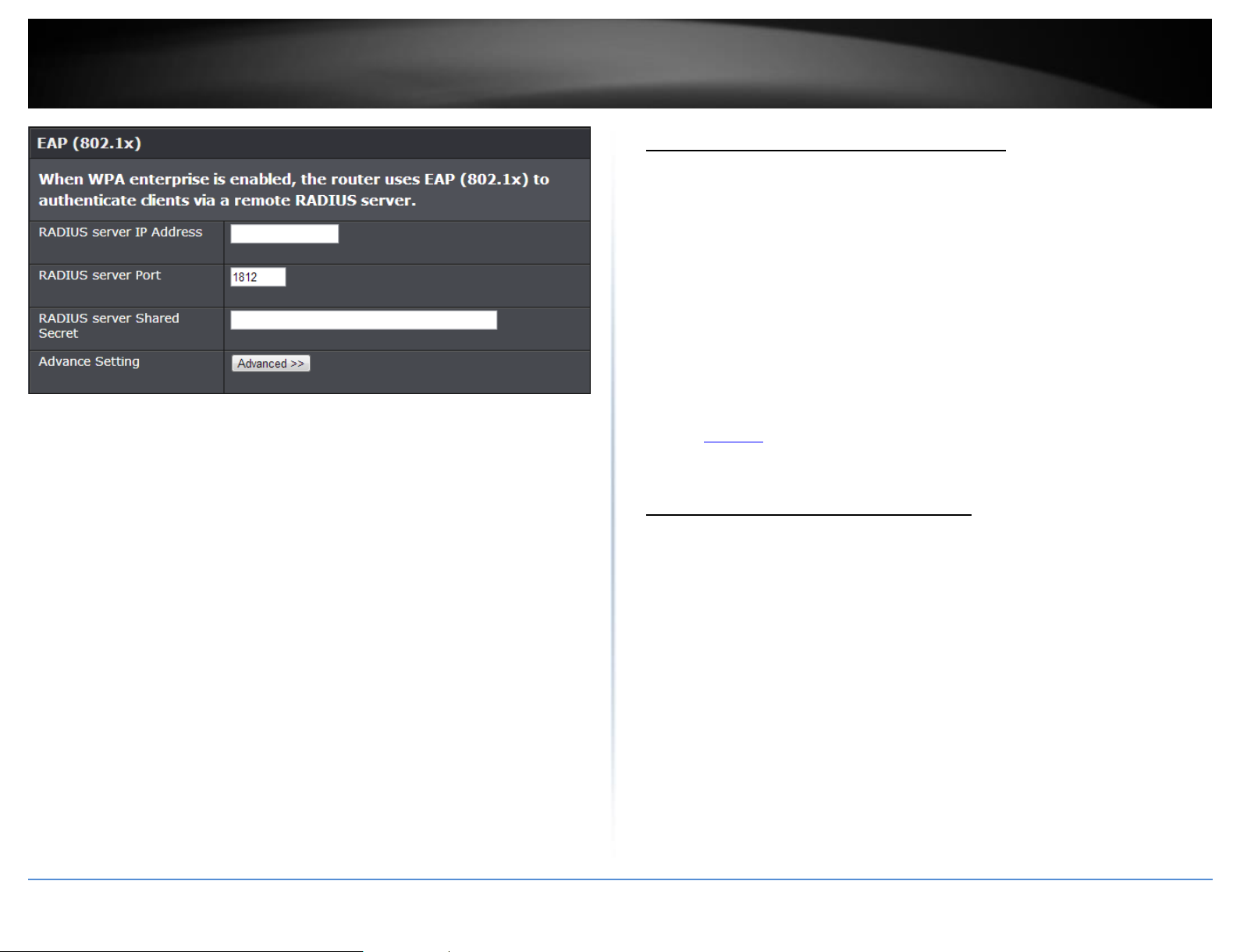
The following section outlines options when selecting WPA-Enterprise, WPA2-
Enterprise, or WPA2-Enterprise Mixed (EAP or RADIUS). This security type is also known
as EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) or Remote Authentication Dial-In User
Service or RADIUS.
Note: This security type requires an external RADIUS server, Pre-Shared Key only requires
you to create a passphrase.
WPA Cipher: Select a Cipher Type to use.
o When selecting WPA2-Personal Mixed security, it is recommended to use
TKIP/AES.
o When selecting WPA2-Personal security, it is recommended to use AES.
Key Update Interval: Enter the time interval (seconds) of when the network
passphrase will rotate.
Note: It is recommended to use the default interval time. Your passphrase will not
change, rotation of the key is part of the WPA protocol and designed to increase
security.
RADIUS Server Address: Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server. (e.g.
192.168.10.250)
RADIUS Port: Enter the port your RADIUS server is configured to use for RADIUS
authentication.
Note: It is recommended to use port 1812 which is typical default RADIUS port.
RADIUS Server Shared Secret: Enter the shared secret used to authorize your
router with your RADIUS server.
You can view the currently connected wireless client devices under Advanced > Wireless
(2.4GHz or 5GHz) > Station List in the router management page.
See the “Appendix” on page 77 for general information on connecting to a wireless
network.
Connect wireless devices using WPS
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) is a feature that makes it easy to connect devices to your
wireless network. If your wireless devices support WPS, you can use this feature to
easily add wireless devices to your network.
Note: You will not be able to use WPS if you set the SSID Broadcast setting to Disabled or
if you are using WEP security.
There are two methods the WPS feature can easily connect your wireless devices to
your network.
Push Button Configuration (PBC) method
o (RECOMMENDED) Hardware Push Button method–with an external button
located physically on your router and on your client device
o WPS Software/Virtual Push Button - located in router management page
PIN (Personal Identification Number) Method - located in router management page
Note: Refer to your wireless device documentation for details on the operation of
WPS.
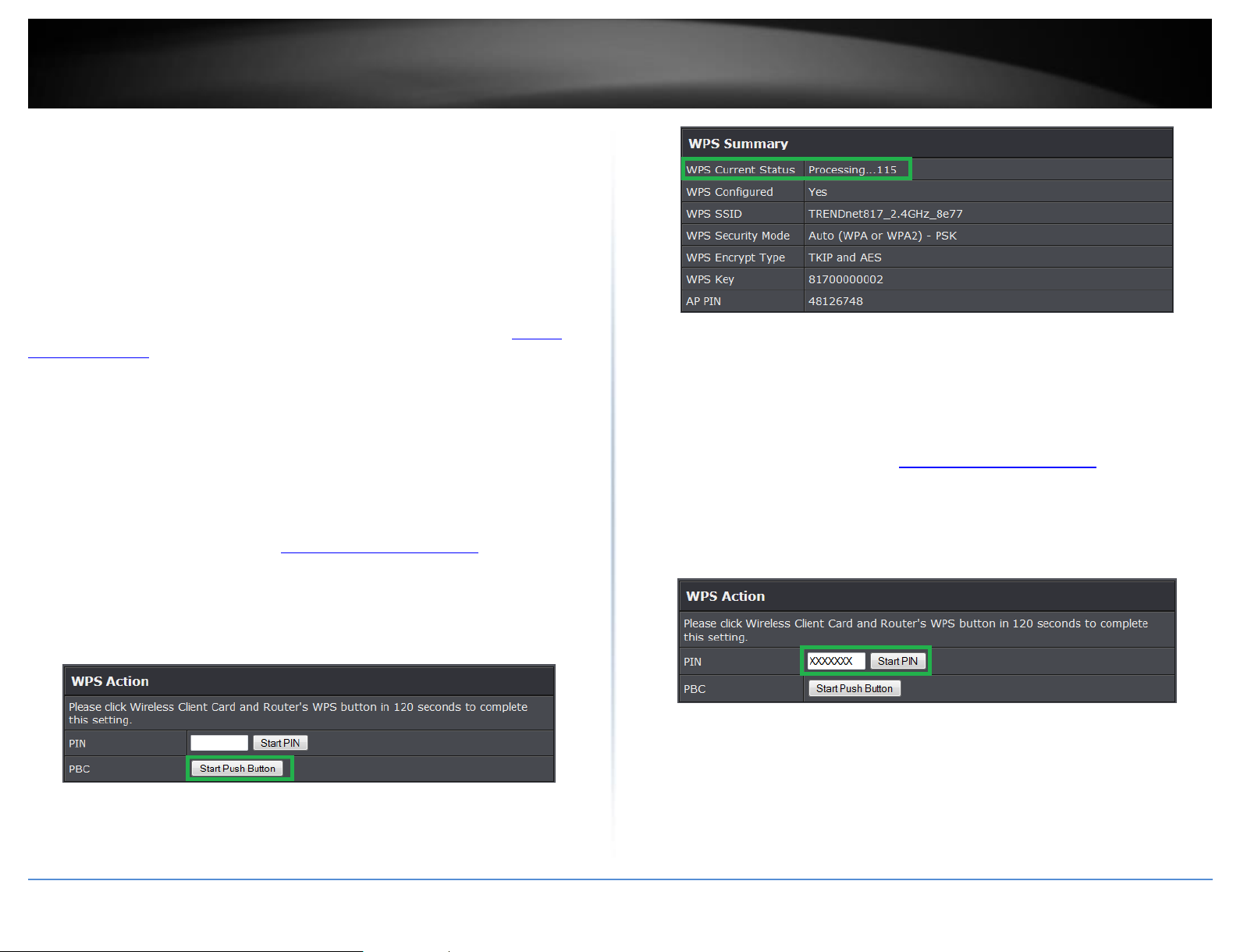
Recommended Hardware Push Button (PBC) Method
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
18
Note: It is recommended that a wireless key (passphrase or password) is created
before connecting clients using the PBC method. By default your router is
preconfigured with a wireless encryption key. If no wireless key is defined when
connecting via PBC, the router will automatically create an encryption key that is 64
characters long. This 64 character key will then have to be used if one has to
connect computers to the router using the traditional connection method.
To add a wireless device to your network, simply push the WPS button on the wireless
device you are connecting (consult client device User’s Guide for length of time), then
push and hold the WPS button located on your router for 3 seconds and release it. The
WPS LED will blink to indicate WPS has been activated on your router. (See “Product
Hardware Features” on page 4)
For connecting additional WPS supported devices, repeat this process for each
additional device.
PBC (Software/Virtual Push Button)
Advanced > Wireless (2.4GHz or 5GHz) > WPS
In addition to the hardware push button located physically on your router, the router
management page also has push button which is a software or virtual push button you
can click to activate WPS on your router.
1. Log into the management page (see “Access your management page” on page 7).
2. Click on Advanced, then click on Wireless (2.4GHz or 5GHz), and click on WPS.
3. To add a wireless device to your network, next to Virtual Push Button, click the Start
Push Button button in the router management page. Then push the WPS button on the
wireless device (consult wireless device’s User’s Guide for length of time) you are
connecting.
PIN (Personal Identification Number)
Advanced > Wireless (2.4GHz or 5GHz) > WPS
If your wireless device has WPS PIN (typically an 8-digit code printed on the wireless
device product label or located in the wireless device wireless software utility), you can
use this method.
1. Log into the management page (see “Access your management page” on page 7).
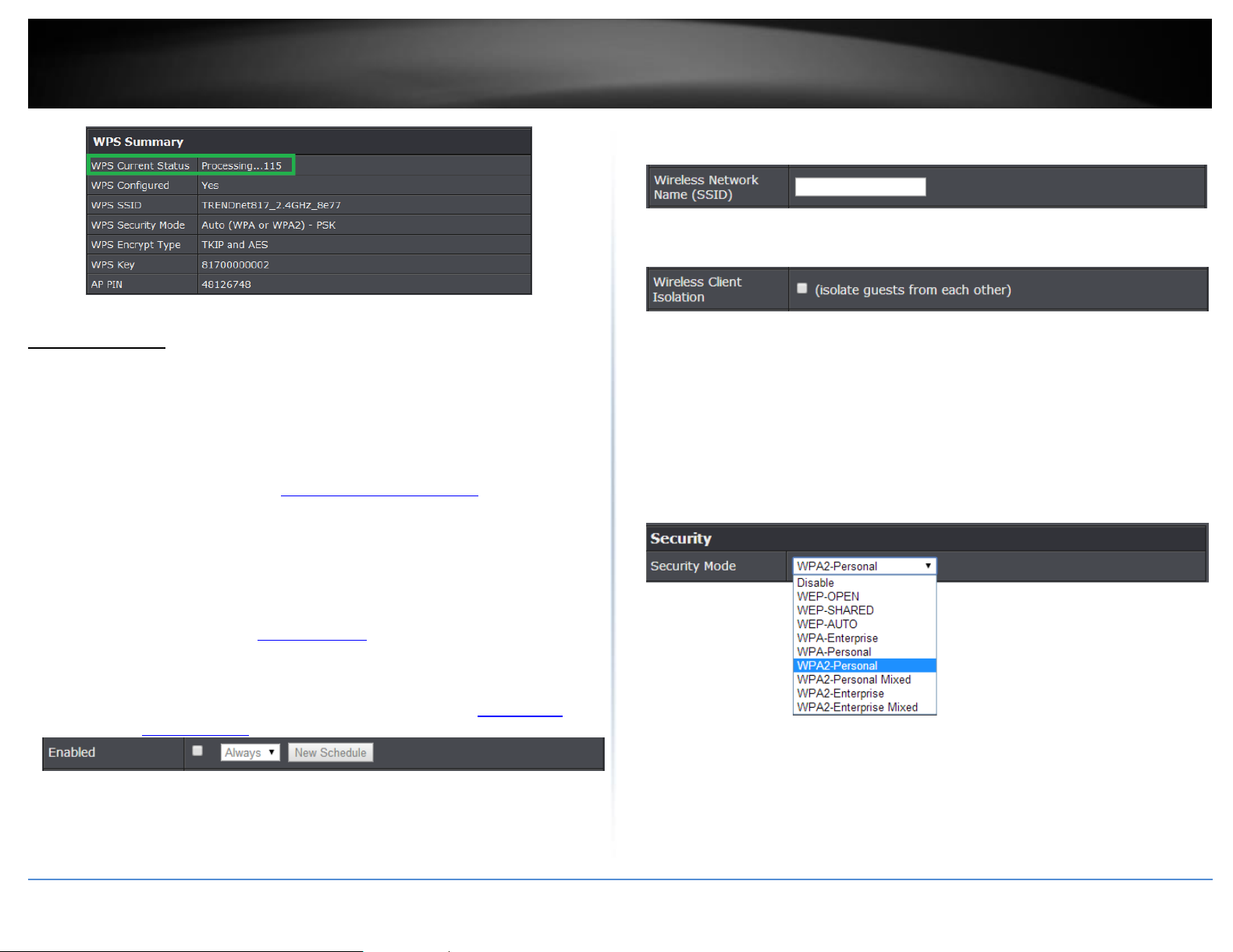
2. Click on Wireless, and click on Wi-Fi Protected Setup.
3. To add a wireless device to your network, next to Client, enter the 8-digit numeric PIN
number of the wireless client device and click Start PIN. Note: You may need to initiate
the WPS PIN on your wireless device first when using this method. Refer to your wireless
device documentation for details on the operation of WPS.
4. Wait for your router to finsh the WPS process.
4. Wait for your router to finsh the WPS process.
Note: You should a message on your WPS client device indicating WPS was successful.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Note: You should a message on your WPS client device indicating WPS was successful.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
19
primary. You can reference your guests to access this network instead of the
primary.
Guest Network
Basic > Guest Network (2.4GHz or 5GHz)
Creating an isolated and separate wireless guest network (2.4GHz or 5GHz) allows
wireless clients to connect to your network for Internet access only and keep your local
LAN network safe by restricting guest access to your LAN network resources such as
shared documents and media files on your computers, network storage, and printers.
1. Log into the management page (see “Access your management page” on page 7).
2. Click on Basic and click on Guest Network.
3. Review the Guest Zone settings, click Apply when finished.
Choose which band to enable the Guest Network (Wireless – 2.4GHz or 5GHz):
Enabled: Check this option to enable the wireless guest network.
New Schedule: The schedule function allows you to define a schedule when the
wireless guest network should be turned on. To define a new schedule, click New
Schedule and refer to page 30 “Create Schedules”. After you have created a new
schedule, click the drop-down list and the new schedule will be available for
selection.
Note: Before applying scheduling, please ensure your Time settings are configured
correct and you have defined a schedule. See page 29 to configure Time Settings and
see page 30 “Create Schedules” to create a schedule.
Wireless Network Name (SSID): This acronym stands for Service Set Identifier and
is the name of your wireless network. It differentiates your wireless network from
others around you. It is recommended to use a different name from your primary
wireless network to a name that you can easily identify and differentiate from the
Wireless Client Isolation: When this option is checked, wireless client devices
connected to your guest network(s) will be restricted from accessing other guests.
Internet Access Only: When this option is checked, wireless client devices
connected to your guest network(s) will be restricted from accessing your private
LAN and wireless clients connected to your primary wireless network, Internet
access only. If unchecked, allows wireless client devices connected your guest
network(s) complete access to your private LAN, primary wireless network, and
Internet.
4. Under Security Mode, you can apply a different wireless security type and key to the
guest network. Please refer to page 12 to find out about different security types and
page 13 for wireless security configuration.
Security Mode: Select the wireless security to use for the guest network.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
20
Parental Control
Basic > Parental Control
Parental control settings allow you to set up restrictions/filters specifically who is
allowed or denied access to your network for a specified period of time and restricted
access to web content.
Access Rule (MAC/IP Filter)
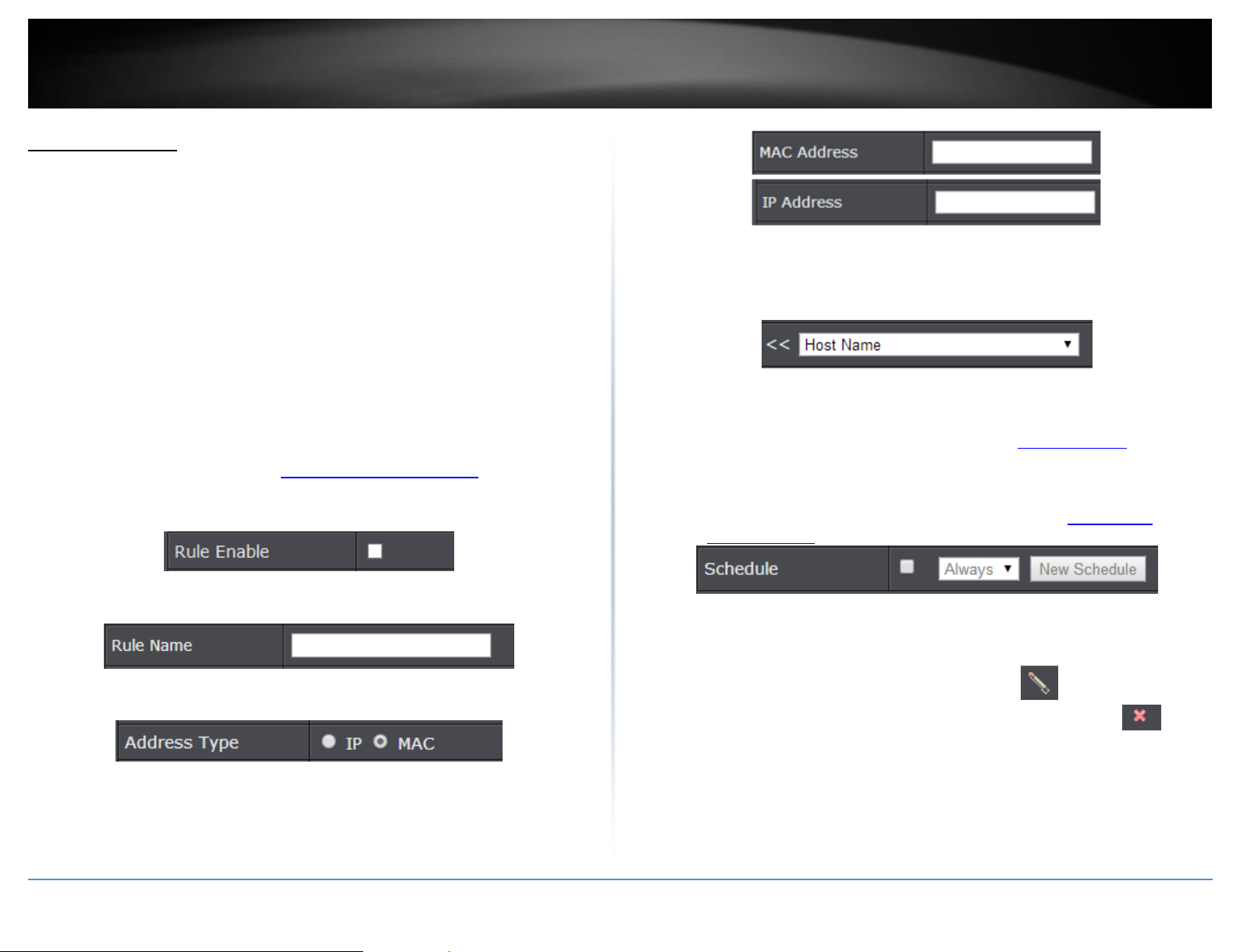
Basic > Parental Control
Every network device has a unique, 12-digit MAC (Media Access Control) address. Every
network device must be assigned or configured with a specific IP address in order to
communicate with your network which is typically assigned by your router DHCP server
automatically. Using access rules, you can deny specific computers and other devices
from using this router’s wired or wireless network by specifying the MAC address or IP
address.
1. Log into the management page (see “Access your management page” on page 7).
2. Click on Basic, click on Parental Control.
3. Check Enabled to enable the access rule.
4. Enter a Rule Name.
5. Select which Address Type to apply the filter. (MAC Address or IP Address)
Note: If you device is not listed, please refer to your computer or device documentation
to find the MAC address.
6. Manually enter the MAC Address or IP Address in the field.
Note: If the network device is connected to your router, you can also click the drop-down
list to choose one of the network devices (MAC Address/IP Address) detected by your
router.
7. Schedule (Optional): The schedule function allows you to define a schedule when the
access should be active and blocking the specified MAC address or IP address. To define
a new schedule, click New Schedule and refer to page 30 “Create Schedules”. After you
have created a new schedule, click the drop-down list and the new schedule will be
available for selection.
Note: Before applying scheduling, please ensure your Time settings are configured
correct and you have defined a schedule. See page 29 to configure Time Settings and see
page 30 “Create Schedules” to create a schedule.
8. Click Add to add the access rule to the Access Rule List. Wait of the rule to be added.
Note: Clicking Reset will discard your settings and clear all fields.
Note: In the Access Rule List, you can edit a rule by clicking under the Edit column
next to the rule you would like to edit. You can also delete a rule by clicking under
the Delete column next to the rule you would like to delete.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
21
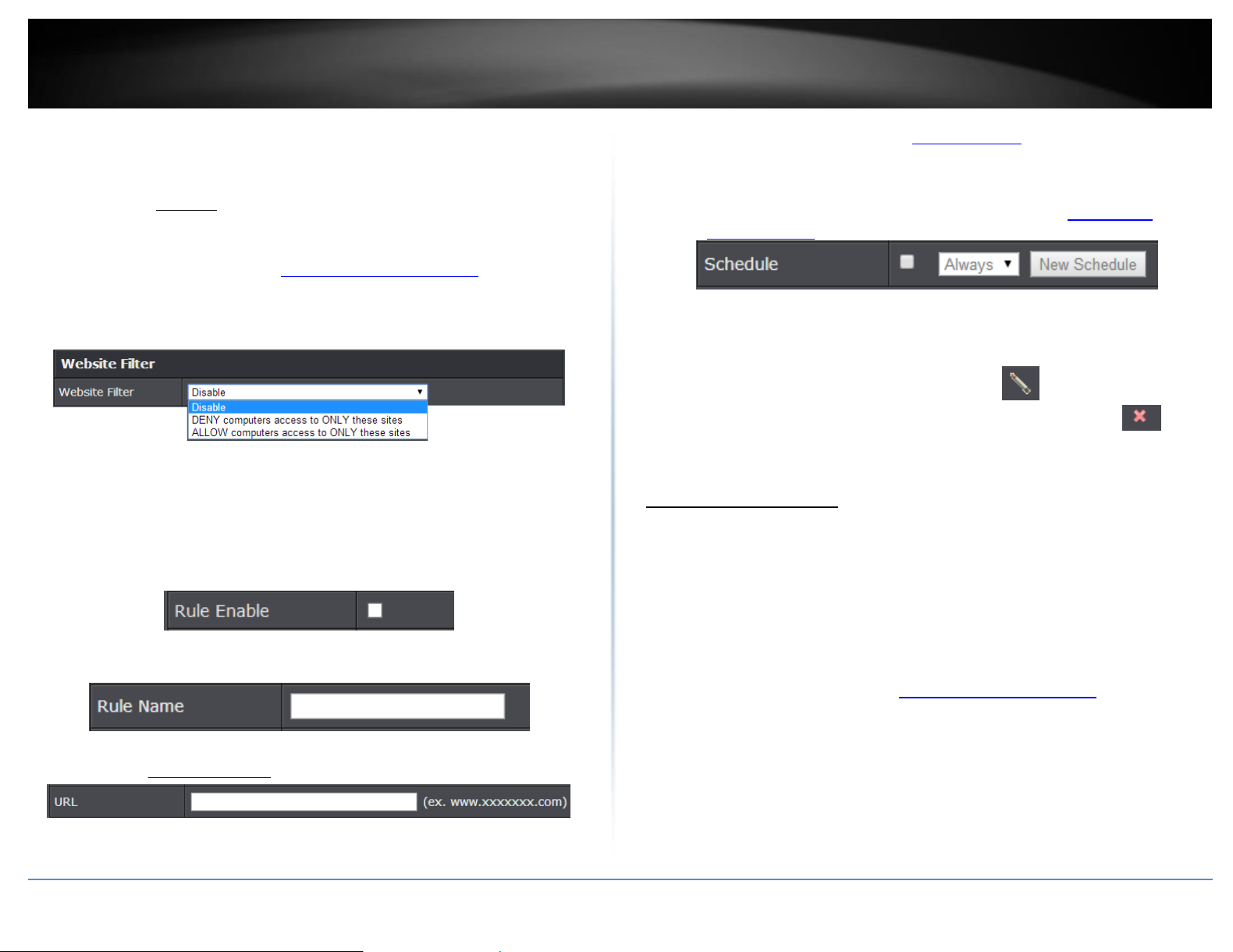
Website Filter
Basic > Parental Control
You may want to block computers or devices on your network access to specific
websites (e.g. www.xxxxxxxxx.com, etc.), also called domains or URLs (Uniform Resource
Locators). You may also apply a schedule when these websites are allowed or denied.
1. Log into the management page (see “Access your management page” on page 7).
2. Click on Basic and click on Parental Control.
3. Under Website Filter, click the Website Filter drop-down list and choose one of the
following options.
click New Schedule and refer to page 30 “Create Schedules”. After you have created a
new schedule, click the drop-down list and the new schedule will be available for
selection.
Note: Before applying scheduling, please ensure your Time settings are configured
correct and you have defined a schedule. See page 29 to configure Time Settings and see
page 30 “Create Schedules” to create a schedule.
8. Click Add to add the access rule to the Access Rule List. Wait of the rule to be added.
Note: Clicking Reset will discard your settings and clear all fields.
Note: In the URL Fille List, you can edit a rule by clicking under the Edit column
Disable: Disables website filtering.
DENY computers access to ONLY these sites: Only Deny computers/devices access
to the listed websites and allow access to others.
ALLOW computers access to ONLY these sites: Only Allow computers/devices
access to the listed websites and deny access to others.
4. Check Enable to enable the access rule.
5. Enter a Rule Name.
6. Enter a URL (ex. www.xxxxxxxx.com) to apply for the filter or block
7. Schedule (Optional): The schedule function allows you to define a schedule when the
access should be active and blocking the specified website. To define a new schedule,
next to the rule you would like to edit. You can also delete a rule by clicking under
the Delete column next to the rule you would like to delete.
MAC Filter (Wireless)
Advanced > Wireless (2.4GHz or 5GHz) > MAC Filter
This MAC filter is dedicated to filter on each band and each SSID. Every network device
has a unique, 12-digit MAC (Media Access Control) address. Every network device must
be assigned or configured with a specific IP address in order to communicate with your
network which is typically assigned by your router DHCP server automatically. Using
access rules, you can deny specific computers and other devices from using this router’s
wired or wireless network by specifying the MAC address or IP address.
1. Log into the management page (see “Access your management page” on page 7).
2. Click on Advanced and click on Wireless (2.4GHz or 5GHz), then click on MAC Filter.
3. Review the MAC Filter options. Click Apply to save settings.
Select SSID: If you have multiple SSIDs configured, click the drop-down list to select
which SSID to apply the MAC filter.
Wireless MAC Filter
o Filter Mode
Disabled: Disables MAC address filter.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
22
Allow listed computers and deny all others: Selecting this function allows
computers/devices with MAC addresses listed to access the local network
(LAN/WLAN), web management, and the Internet.
Deny listed computers and allow all others: Selecting this function denies
computers/devices with MAC addresses listed from access to the local
network (LAN/WLAN), web management, and the Internet.
o MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of the wireless device to apply to this filter.
Advanced wireless settings
The advanced wireless features provide can provide you with additional options for
setting up your wireless network such as multiple SSID and WDS (Wireless Distribution
System) or wireless bridging.
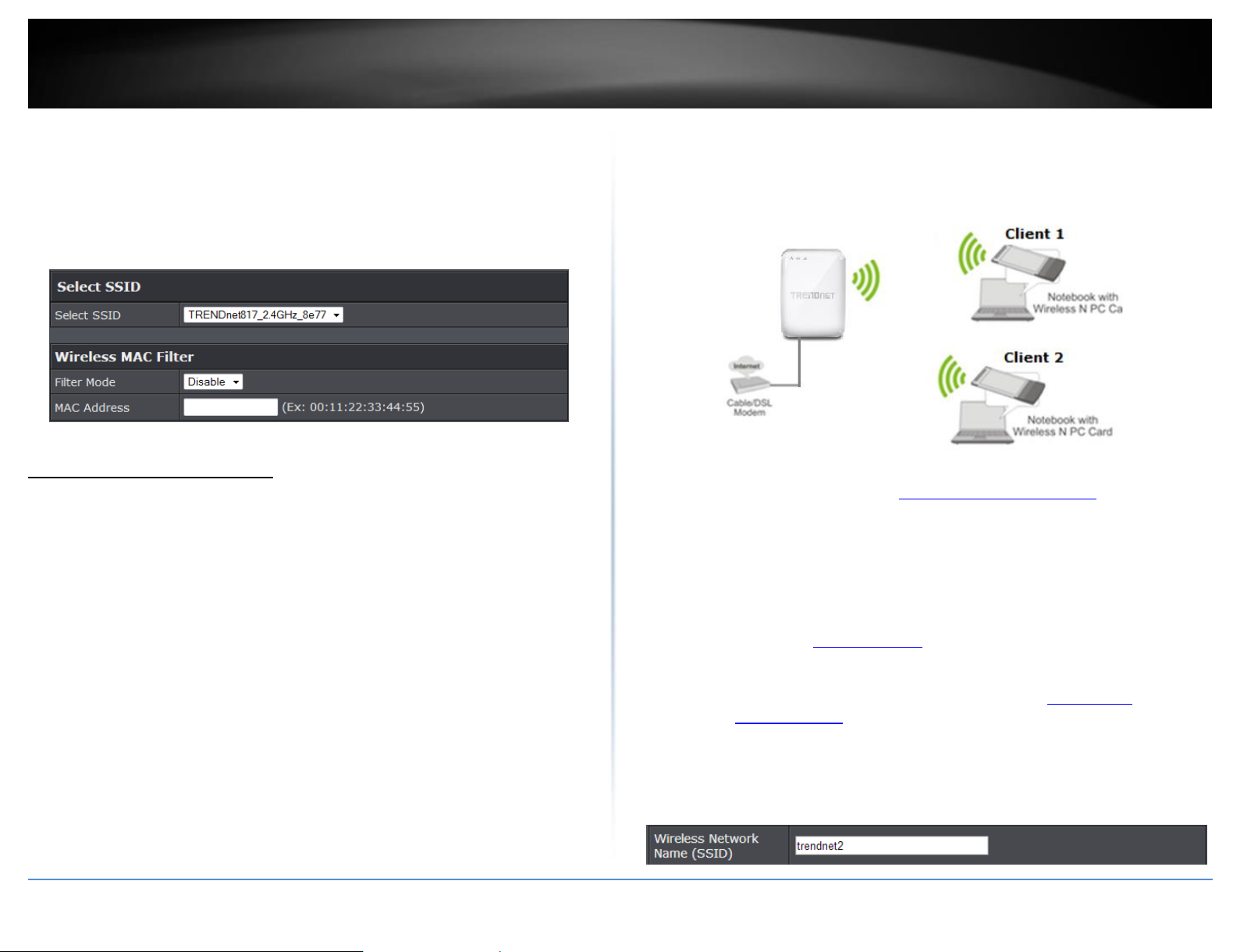
Multiple SSID
Advanced > Wireless (2.4GHz or 5GHz) > Multiple SSID
The multiple SSID feature allows you to broadcast up to 3 SSIDs (or wireless network
names). When wireless devices are searching for available wireless networks to connect
to, the SSIDs (or wireless network names) will appear as separate and different wireless
networks. Since they appear as separate wireless networks, they are also referred to as
virtual APs (Access Points) since they appear as separate wireless access points but are
actually all being broadcasting and managed by a single wireless access point. Each
virtual AP can be configured each with a different SSID (or wireless network name),
security type and additional settings for wireless devices to connect. You can use the
multiple SSID feature to setup guest wireless accounts with a different security type to
keep your primary wireless network security information private. The diagram shows an
example of a client connecting to SSID 1 and another client connecting to SSID 2.
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
By default, your router functions in Access Point mode to allow wireless client devices to
connect and access your network resources and access the Internet using a single SSID.
The diagram below shows your router in Access Point mode and clients connecting to
your router using a single SSID.
To configure multiple SSID on your router:
1. Log into the management page (see “Access your management page” on page 7).
2. Click on Advanced and click on Wireless (2.4GHz or 5GHz), then click on Multiple
SSID.
3. Next to Multiple SSID1 or SSID2, check Radio On/Off option to enable the additional
SSID.
New Schedule: The schedule function allows you to define a schedule when the
additional SSID should be turned on. To define a new schedule, click New Schedule
and refer to page 30 “Create Schedules”. After you have created a new schedule,
click the drop-down list and the new schedule will be available for selection. Note:
Before applying scheduling, please ensure your Time settings are configured correct
and you have defined a schedule. See page 29 to configure Time Settings and see
page 30 “Create Schedules” to create a schedule.
4. Wireless Name (SSID): Enter the wireless name (SSID) for additional SSID. This
acronym stands for Service Set Identifier and is the name of your wireless network. It
differentiates your wireless network from others around you. By default, the router’s
wireless name is unique to the device. It is recommended to change it to a name
different from the primary SSID 1 and one that you can easily remember.
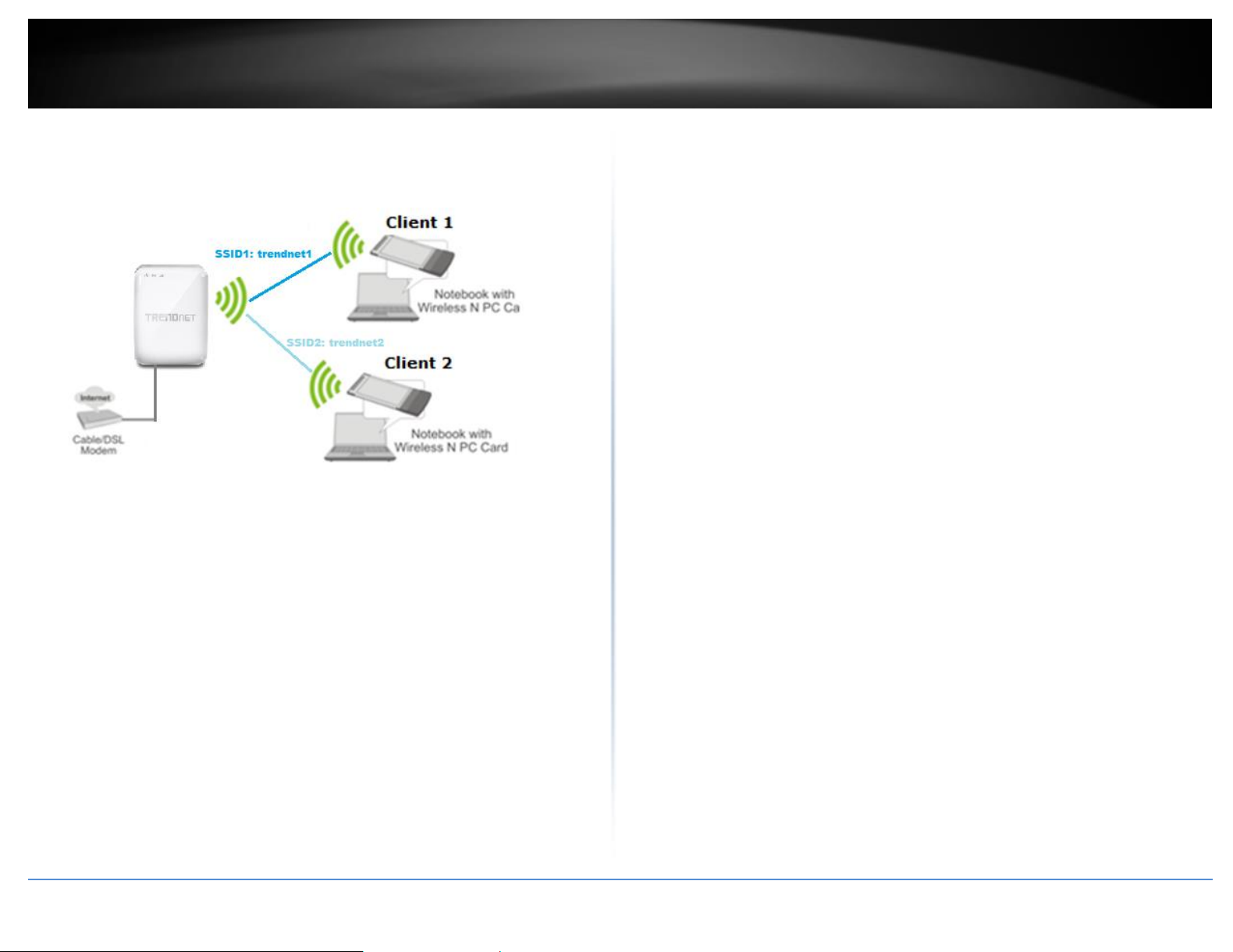
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-817DTR
23
Please refer to page 15 to find out about different security types and page 16 for
wireless security configuration.
The diagram shows an example of a client connecting to SSID 1 and another client
connecting to SSID 2.
5. To save changes, click Apply.
Note: You can repeat the steps to enable and configure additional SSIDs.
Advanced Settings
Advanced > Wireless (2.4GHz or 5GHz) > Advanced
These settings are advanced options that can be configured to change advanced
wireless broadcast specifications. It is recommended that these settings remain set to
their default values unless you are knowledgeable about the effects of changing these
values. Changing these settings incorrectly can degrade performance.
Beacon Period: A beacon is a management frame used in wireless networks that
transmitted periodically to announce the presence and provide information about
the router’s wireless network. The interval is the amount time between each
beacon transmission.
Default Value: 100 milliseconds (range: 100-1000)
DTIM: A DTIM is a countdown informing clients of the next window for listening to
broadcast and multicast messages. When the wireless router has buffered
broadcast or multicast messages for associated clients, it sends the next DTIM with
© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
a DTIM Interval value. Wireless clients detect the beacons and awaken to receive
the broadcast and multicast messages. The default value is 1. Valid settings are
between 1 and 255.
Fragment Threshold: Wireless frames can be divided into smaller units (fragments)
to improve performance in the presence of RF interference and at the limits of RF
coverage. Fragmentation will occur when frame size in bytes is greater than the
Fragmentation Threshold. This setting should remain at its default value of 2346
bytes. Setting the Fragmentation value too low may result in poor performance.
RTS Threshold: The Request To Send (RTS) function is part of the networking
protocol. A wireless device that needs to send data will send a RTS before sending
the data in question. The destination wireless device will send a response called
Clear to Send (CTS). The RTS Threshold defines the smallest data packet size
allowed to initiate the RTS/CTS function. Default Value: 2347 (range: 1-2347)
TX Power: This setting allows you to adjust the wireless transmit power to a lower
setting. In busy wireless environments, lowering the transmit power may improve
better performance and connectivity and decrease interference with neighboring
wireless networks.
Short Preamble: Using a short preamble can potentially increase throughput as the
transfer time is 96 microseconds versus the more commonly used long preamble
192 microseconds. However, using a short preamble is not supported using 802.11b
legacy devices, in some cases cause wireless interoperability issues, and increase
the error rate in some installations. The preamble is the info. sent from the wireless
transmitter to the receiver indicating when data is incoming.
Short Slot: Short Slot Override defines the amount of time a device waits after a
data frame collision before retransmitting the data. Reducing the time from 20
microseconds (standard) to 9 microseconds can potentially increase throughput
however, can also increase the error rate.
20/40 Coexistence (2.4GHz only): 20/40 MHz Coexistence allows for the auto-
fallback from 40MHz to 20MHz channel width operation when neighboring 802.11
wireless networks are detected.
Guard Interval: Using a short (400ns) guard interval can increase throughput.
However, it can also increase error rate in some installations, due to increased
sensitivity to radio-frequency reflections.
MCS – Allows you to lock down the wireless transmission rate.
Extension channel – Allows you to assign either the upper or lower extension
channels to use for channel bonding when establishing connectivity at the higher
channel widths 40MHz and 80MHz.
 Loading...
Loading...