Page 1

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Cover Page
Page 2

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Table of Contents
i
Contents
Product Overview ........................................................................... 1
Package Contents .......................................................................................................... 1
Features ......................................................................................................................... 1
Product Hardware Features........................................................................................... 2
Client Bridge + AP Mode .............................................................................................. 26
WISP (CPE) + AP Mode ................................................................................................ 26
Router Mode ............................................................................................................... 27
CAP (Control AP) Mode ............................................................................................... 27
Access your access point management page .................................. 28
AP Management Settings .............................................................. 29
Application Diagram ...................................................................................................... 4
Management Setup ..................................................................................................... 29
Primary Product Application ........................................................... 5
Set the device date and time ....................................................................................... 30
Minimum Installation Requirements ............................................... 5
Model Differences ........................................................................... 6
TEW-740APBO ............................................................................................................... 6
TEW-740APBO2K ........................................................................................................... 6
SNMP Settings ............................................................................................................. 31
SNMP v2c ........................................................................................................... 31
SNMP v3 ............................................................................................................ 32
SNMP Trap ......................................................................................................... 32
Backup and restore your AP configuration settings .................................................... 33
TEW-740APBO Setup & Installation ................................................. 7
Note the WiFi MAC Addresses ....................................................................................... 7
TEW-740APBO #1 .......................................................................................................... 8
TEW-740APBO #2 ........................................................................................................ 13
Confirm Connectivity ................................................................................................... 14
Ground Wire and Pole Mount Installation .................................................................. 15
Completed Installation Reference ............................................................................... 16
TEW-740APBO2K Setup and Installation ........................................ 17
Backup configuration settings ........................................................................... 33
Restore configuration settings .......................................................................... 33
Reset your AP to factory defaults ................................................................................ 33
Soft reboot your AP ..................................................................................................... 33
Upgrade your AP firmware .......................................................................................... 34
Network Utilities .......................................................................................................... 34
View system information............................................................................................. 35
View currently connected wireless client devices ....................................................... 36
Setup and Confirm Connectivity .................................................................................. 18
Ground Wire and Pole Mount Installation .................................................................. 21
Completed Installation Reference ............................................................................... 22
Wireless Installation Tips............................................................... 23
Application Modes ........................................................................ 24
AP Mode (Access Point Mode) .................................................................................... 24
WDS Mode (Pure WDS) ............................................................................................... 25
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
View currently connected authenticated users .......................................................... 36
View authentication log information .......................................................................... 36
View the device system log information ..................................................................... 36
Configuring additional application modes ..................................... 37
Access Point (AP) Mode ............................................................................................... 37
Set the device to AP mode ................................................................................ 37
Set the device LAN IP address ........................................................................... 37
Page 3

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Table of Contents
ii
Configure primary wireless network settings .................................................... 38
MAC Address Filter ............................................................................................ 39
DHCP Server ....................................................................................................... 40
DHCP Reservation/Static Lease.......................................................................... 41
802.11r/802.11k Fast Roaming .......................................................................... 42
Additional Wireless Settings .............................................................................. 43
Advanced Wireless Settings ............................................................................... 45
Wireless WMM QoS Setup ................................................................................ 46
WDS (Wireless Distribution System) .................................................................. 48
Authentication/Captive Portal ........................................................................... 50
Guest Authentication ......................................................................................... 51
OAuthentication 2.0 .......................................................................................... 52
POP3 Server ....................................................................................................... 53
Customize Page .................................................................................................. 54
Multiple Language ............................................................................................. 55
Walled Garden ................................................................................................... 55
Privilege Address ............................................................................................... 56
Backup/Restore Authentication Profile & Customized Pages ........................... 56
Client Bridge + AP Mode .............................................................................................. 57
Set the device to Client Bridge + AP mode ........................................................ 57
Set the device IP address settings ..................................................................... 57
Connect the device to your wireless network ................................................... 58
Configure your wireless network settings (WLAN) ............................................ 58
WISP (CPE) + AP Mode ................................................................................................. 59
Set the device LAN IP address settings .............................................................. 59
Configure the LAN DHCP Server ........................................................................ 59
DHCP Reservation/Static Lease.......................................................................... 60
Configure WAN connection settings for WISP ................................................... 61
Connect to your WISP (Wireless Internet Service Provider) .............................. 61
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) .................................................................................. 62
Technical Specifications ................................................................ 80
Appendix ...................................................................................... 82
IP Filter ............................................................................................................... 63
MAC Filter .......................................................................................................... 63
Virtual Server ..................................................................................................... 64
Access Control ................................................................................................... 64
Time Policy / Schedule ....................................................................................... 65
Router Mode ............................................................................................................... 67
Set the device LAN IP address settings .............................................................. 67
Configure the LAN DHCP Server ........................................................................ 67
DHCP Reservation/Static Lease ......................................................................... 69
Configure WAN connection settings.................................................................. 69
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) .................................................................................. 70
IP Filter ............................................................................................................... 71
MAC Filter .......................................................................................................... 71
Virtual Server ..................................................................................................... 72
Access Control ................................................................................................... 72
Time Policy / Schedule ....................................................................................... 73
CAP (Control AP) Mode ............................................................................................... 75
Scan and Import CAP Mode compatible APs ..................................................... 76
Modify and view your managed AP list ............................................................. 77
Batch Configuration Settings ............................................................................. 77
Group Setup ....................................................................................................... 78
Map Setup ......................................................................................................... 78
Authentication Profile ....................................................................................... 79
Managed AP Status ............................................................................................ 79
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 4

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
1
Product Overview
Features
TRENDnet’s 10 dBi Outdoor PoE Access Point, model TEW-740APBO, provides wireless
N300 point-to-point connectivity. A variety of installation scenarios are facilitated with
Access Point (AP), Wireless Distribution System (WDS), Client Bridge + AP, Wireless ISP
(WISP) + AP, CPE + AP, and control AP (CAP) modes. The IPX6 rated housing comes with
wall and pole mounting hardware.
Wireless Modes
Supports Access Point (AP), Wireless Distribution System (WDS), Client Bridge + AP,
Wireless ISP (CPE) + AP, Router, and control AP (CAP) modes
TEW-740APBO TEW-740APBO2K
Package Contents
TEW-740APBO package includes:
1 x TEW-740APBO
CD-ROM (User’s Guide)
Quick Installation Guide
Proprietary PoE injector
Power adapter (12V DC, 1A)
Mounting hardware
Grounding wire
TEW-740APBO2K package includes:
2 x TEW-740APBO (Preconfigured WDS Bridge)
CD-ROM (User’s Guide)
Quick Installation Guide
Proprietary PoE injectors
Power adapters (12V DC, 1A)
Mounting hardware
Grounding wires
Wireless N300 (2.4 GHz)
Compliant with 802.11b/g/n technology (2.4 GHz) with data rates up to 300 Mbps*
Outdoor Rated
Durable enclosure with an IPX6 outdoor weather rating
Directional Antenna
Built in 10 dBi directional antenna
PoE Power Adapter
Proprietary PoE power adapter included
Logs
Real time logs and statistics help troubleshooting
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 5

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
2
IPX6 Weather
Rated Housing
with built-in
directional sector
Encrypted Wireless
Support for wireless encryption of up to WPA2
Product Hardware Features
Front View
Multiple SSIDs
Create up to eight additional SSIDs
Compatibility
Compatible with legacy wireless devices
Mounting Hardware
Pole and wall mount hardware included
* Effective wireless coverage may vary depending on the wireless device's output
power, antenna gain, antenna alignment, receiving sensitivity, and radio interference.
Additionally environmental factors such as weather conditions, physical obstacles, and
other considerations may affect performance. For optimal results, we recommended
consulting a professional installer for site survey, safety precautions, and proper
installation.
Bottom View (Closed)
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 6

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
3
Bottom View (Open)
LAN1 (PoE) Port – This Ethernet interface will be used to power the access
point through the P+DATA OUT proprietary PoE injector and provide
10/100Mbps network connectivity to the access point. Router mode only: The
LAN1 port interface will be used for wired WAN Internet connectivity when the
access point is configured in Router mode and wired LAN connectivity can be
used on the LAN2 port interface.
LAN2 Port – This Ethernet interface is a secondary 10/100Mbps LAN port
interface and can be used to also access the access point. The LAN2 port and
LAN1 (PoE) port are bridged for all modes except Router mode where LAN2 will
function as a wired LAN port and LAN1 port will function as wired WAN
Internet port.
LAN1 LED – When the LED is on, this indicates an active network connection to
the LAN1 port. If there is no active network connection to 10/100 DATA IN on
the proprietary PoE injector, there is no active link to the LAN1 port and LED
will be off. When the LED is blinking, this indicates data is being transmitted or
received on the LAN1 port.
LAN2 LED - When the LED is on, this indicates an active network connection to
the LAN2 port. If the LED is off, there is no active network connection to the
Important Note:
It is recommended to use RJ-45 cables without any additional caps, molded caps, or
boots specifically on the connector side that will be connected to the access point LAN1
(PoE) port to avoid any cable fitment issues inside the access point enclosure.
LAN2 port. When the LED is blinking, this indicates data is being transmitted or
received on the LAN2 port.
Power (PWR) LED – When the LED is on, this will indicate that the device is
receiving power and off if the device is not receiving power.
Reset Button – The reset button resets the access point to factory default
settings. Using a paper clip, push and hold the reset button for 15 sec. and
release. The LEDs will flash when the device reset has been initiated.
Connection Quality Indicators – These LEDs will indicate the wireless
connection quality to the wireless ISP network when using WISP (CPE) mode.
Grounding Screw – The grounding point/screw allows you to attach the unit to
a proper ground point.
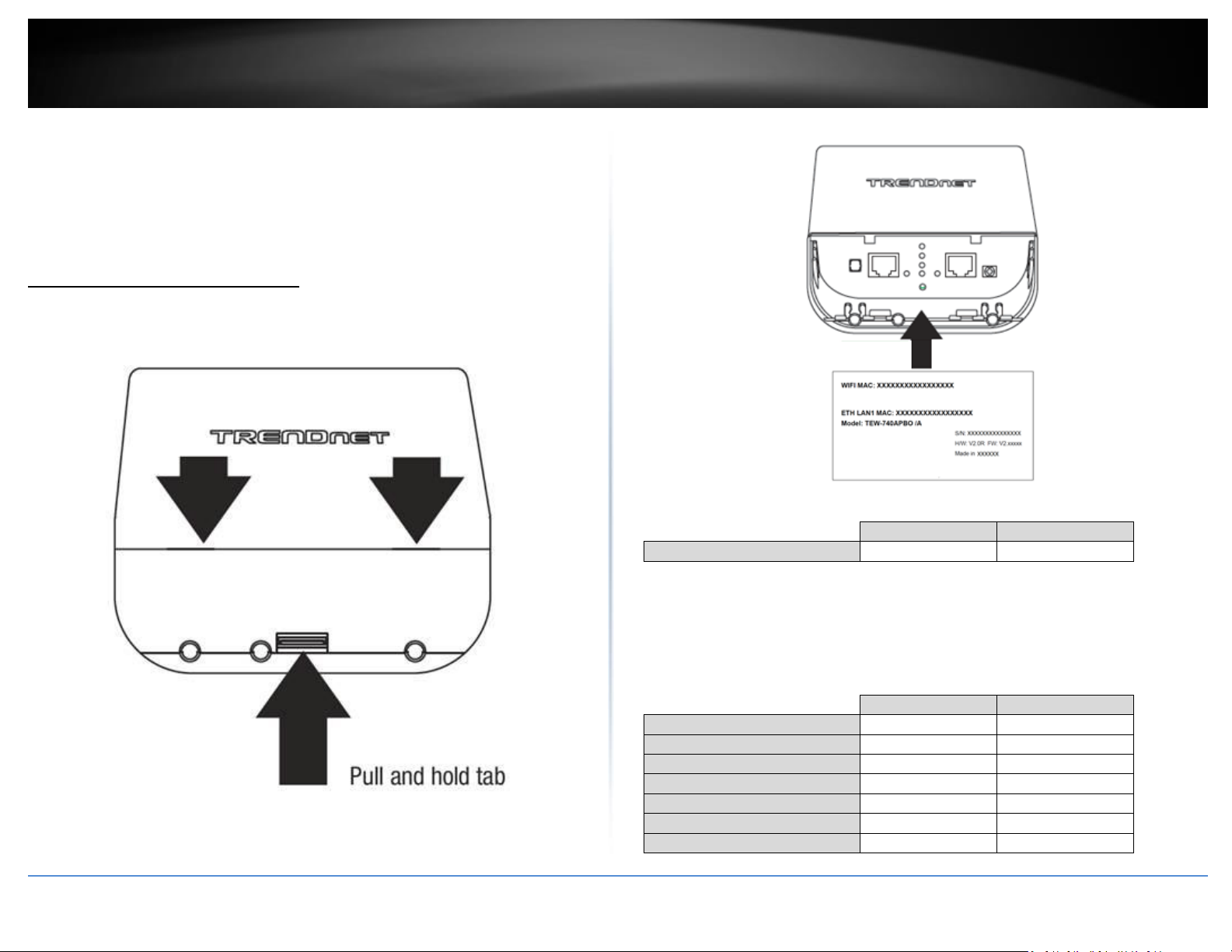
Cable Guides/Removable tabs – With the enclosure cover installed, the cable
guides and removable tabs allows you to route RJ-45 cables and the ground
cable externally from the device while protecting the internal port connection
of the device to the network.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 7

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
4
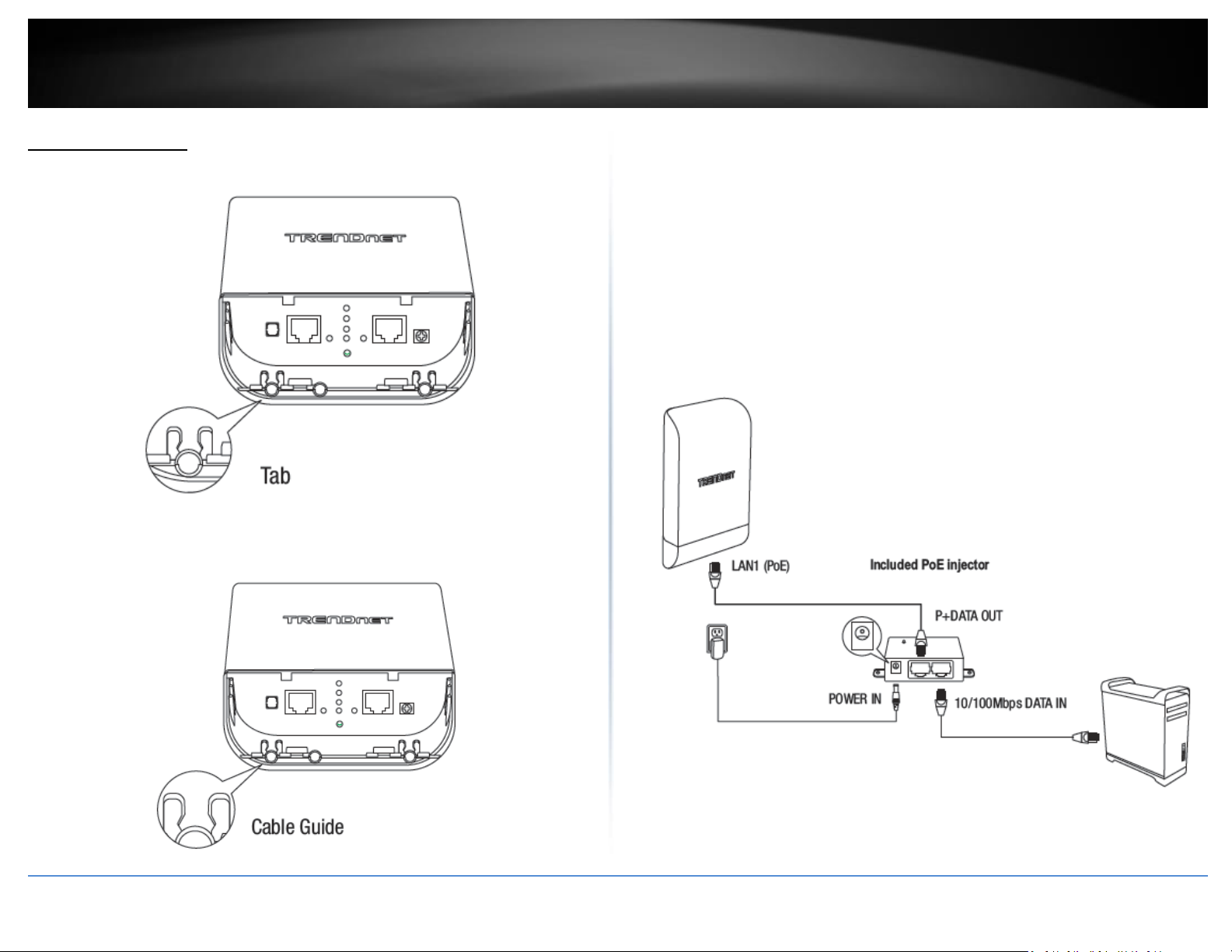
Proprietary PoE Injector –
Important Note:
The access point does not support standard IEEE 802.3at/af PoE/PoE+. Only the
included proprietary PoE injector may be used to supply power to the access point.
For safety, use only the included PoE injector to supply power to the access point.
o POWER IN – Connect the included power adapter connector to this
input and adapter side into an AC power source to supply power to
the injector.
o P+DATA OUT – Connect an Ethernet RJ-45 cable to this output and the
other side to the device LAN1 (PoE) port to supply power to the
device. Please note that the RJ-45 Ethernet cable between the
proprietary PoE injector and the LAN1 (PoE) port of the access points
supports a maximum length of up to 60 m (197 ft.). RJ-45 Ethernet
cables longer than the maximum length specified may result in
insufficient power to the device, intermittent connectivity/power loss,
and unstable physical link.
o 10/100 DATA IN – Connect an Ethernet RJ-45 cable to this input and
connect the other to your network or directly to a computer for initial
device setup.
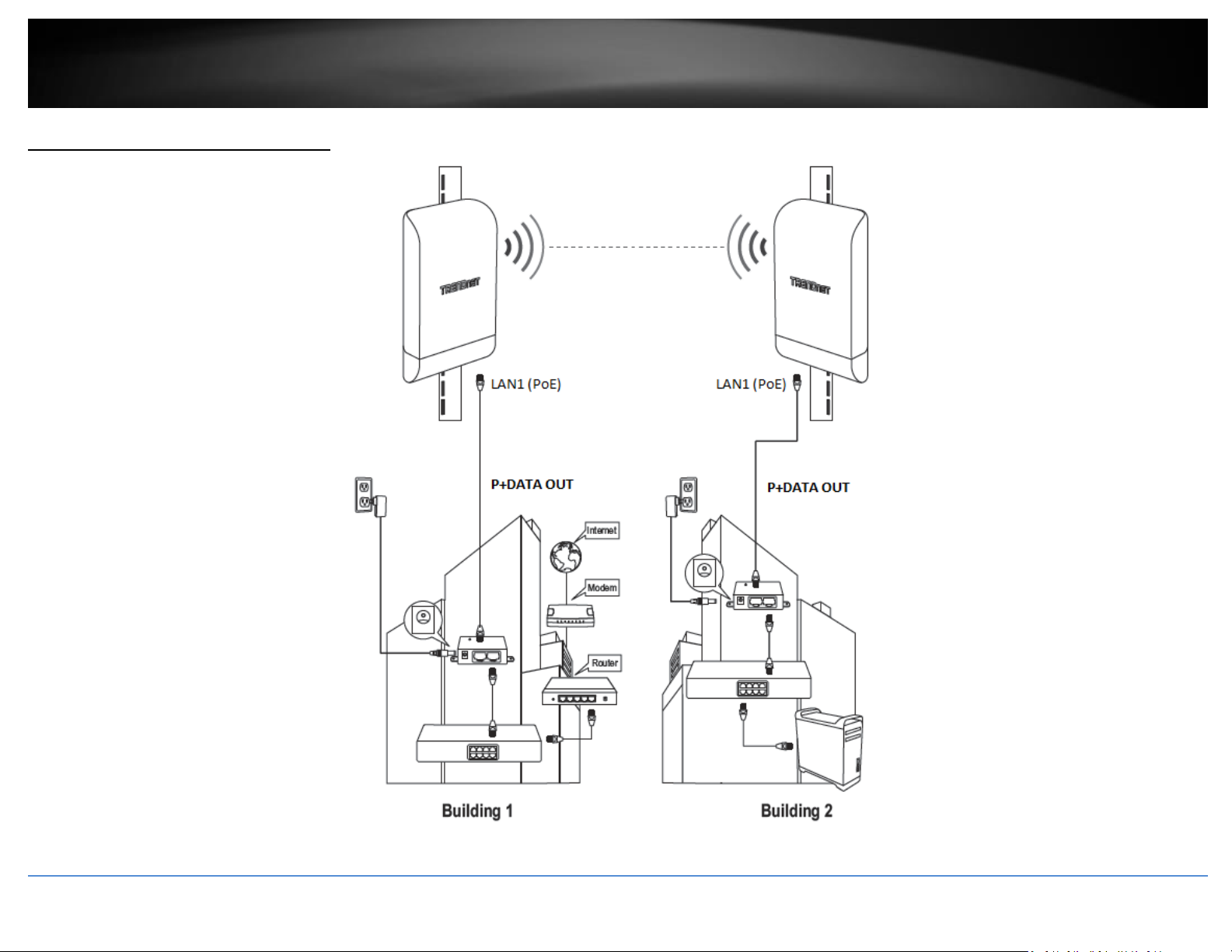
Application Diagram
The example application displays two TEW-740APBO access points are configured in WDS pointto-point bridge mode and establishing a wireless link between each and other, allowing for
network connectivity between two buildings over a point-to-point wireless link.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 8

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
5
Primary Product Application
The intended purpose and application for this product is to extend network connectivity
across long physical distances outside of an area or building that lacks local connectivity
using point-to-point wireless bridge capability using 802.11 standards. Essentially, two
access points configured in point-to-point bridge capability can connect/link the two
physical locations or buildings together through an encryption wireless connection.
Although this product supports multiple wireless modes, the basic installation will only
cover the primary application of point to point wireless connectivity in WDS (Wireless
Distribution System) Bridge Mode using AES encryption for security.
Minimum Installation Requirements
Computer with RJ-45 Ethernet port and web browser
4 x RJ-45 Ethernet cables (not included)
Phillips screwdriver (not included, for grounding wire installation only)
Additional TRENDnet TEW-740APBO H/W: v2.XR N300 directional wireless
access point (For TEW-740APBO single unit only, TEW-740APBO2K model
includes two preconfigured access points)
For wall mounting only (included wall mounting kit for drywall installations only)
Power drill/driver
7/16 in (2.75 mm) straight drill bit for hard wood or 3/32 in (2.35 mm) bit for
soft wood (for mounting screws)
11/16 in (4.3 mm) straight drill bit for hard wood or 5/32 in (4 mm) bit for soft
wood (if required for drywall anchors)
Philips driver bit or screwdriver
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 9

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
6
Model Differences
TEW-740APBO
Single Unit Model
The single access point requires another TEW-740APBO H/W: v2.XR N300 additional
access point to create a WDS point-to-point wireless link.
Important Note:
Purchasing this model requires the access points to be properly configured to establish
the wireless link/bridged connection to each other and verifying connectivity first before
mounting the access points in their desired locations.
Single Unit Default Settings
LAN IP Address: 192.168.10.100
LAN Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Mode: Access Point (AP) Mode
User: admin
Password: admin
Preconfigured Kit Default Settings
TEW-740APBO #1
LAN IP Address: 192.168.10.50
LAN Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Mode: WDS Bridge Mode
WDS AES Encryption Key: <predefined>
User: admin
Password: <predefined>
TEW-740APBO #2
LAN IP Address: 192.168.10.51
LAN Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Mode: WDS Bridge Mode
WDS AES Encryption Key: <predefined>
User: admin
Password: <predefined>
TEW-740APBO2K
Preconfigured Bridge Kit Model
The two access points in the kit model are preconfigured to establish a WDS bridged
connection to each using a unique AES encryption key. For convenience, a unique
predefined administrator password is also assigned. The predefined AES encryption key
and administrator password can be found on the included wireless settings sticker or on
the device label.
Important Note:
Purchasing this model does not require any additional configuration to establish the
wireless link/bridged connection between the two access points but it is strongly
recommended that you verify connectivity first between the two access points first
before mounting them in their desired locations.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 10
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
7
TEW-740APBO #1
TEW-740APBO #2
WiFi MAC Address
00:11:22:33:44:00
00:11:22:33:44:11
TEW-740APBO #1
TEW-740APBO #2
IP Address
192.168.10.50
192.168.10.51
Netmask (Subnet Mask)
255.255.255.0
255.255.255.0
IP Gateway (Default Gateway)
192.168.10.1
192.168.10.1
Primary DNS
192.168.10.1
192.168.10.1
Wireless Channel (Default)
1
1
Mode
WDS
WDS
WDS Encryption
AES
AES
TEW-740APBO Setup & Installation
The following installation procedure assumes you are setting up and installing two
TRENDnet TEW-740APBO H/W: v2.XR access points in WDS bridge point-to-point
configuration.
2. On the device label located inside, write down the WiFi MAC of each access point.
Note the WiFi MAC Addresses
1. Remove the cover of the access points by pulling and holding the tab in the vertical
direction upward (as shown in the picture below) and sliding the cover in the two
locations noted away from the access point.
Note: In this installation procedure example, we will assume the WiFi MAC addresses:
Router Settings:
Router/Default Gateway IP Address: 192.168.10.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
In this installation procedure example, we will configure the TEW-740APBO access points
will be configured with the following settings:
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 11
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
8
TEW-740APBO #1
1. Remove the tab on the far left by gently bending it back and forth until the tab is
removed. This will create the opening the RJ-45 network cable to be routed through.
3. Connect the other end of the RJ-45 network cable to the P+DATA OUT port on the
included PoE injector.
4. Using another RJ-45 network cable, connect one end of the 10/100 DATA IN port on
the included PoE injector.
5. Connect the other end of the RJ-45 network cable to your computer’s Ethernet port.
6. Connect the included power adapter to the PoE injector POWER IN on the included
PoE injector.
7. Plug the connected power adapter into a power outlet.
8. Confirm the device is powered on through the PWR LED indicator.
2. Using a RJ-45 network cable, connect one end of the cable to the LAN (PoE) port and
push the cable into the guide on the far left, then through the opening that was created
in the previous step.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 12

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
9
9. Assign a static IP address to your computer’s network adapter in the subnet of
192.168.10.x (e.g. 192.168.10.10) and subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
Note: For information on how to statically assign your IP address, see the Appendix
section.
10. Open your web browser and type in the default IP address of the access point in the
address bar, then press Enter. The default IP address is 192.168.10.100.
11. When prompted, login to the access point management page using the default user
name and password settings.
User Name: admin
Password: admin
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 13

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
10
12. Click on the System tab and select Management.
14. Click on the System tab and click on Mode Setup.
13. Under Administrator Password, change the default administrator password by
typing in the new password in the fields provided and then click the Save button at the
bottom of the page.
15. Click on the Mode field and in the drop-down list click on WDS Mode, then click on
Save & Reboot. When prompted to change the mode, click Yes and wait for the device
to apply changes and reboot.
Note: After the device reboots, you may need to login to the management page again.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 14

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
11
16. After device saves changed and reboots, click on System and click on VLAN Setup.
18. In the IP Setup section, enter the IP Address 192.168.10.50, then click Save. In the
menu located at the top, you will be prompted to reboot the device. Click the Reboot
button and in the following page, click Reboot. When prompted to reboot, click Yes
apply changes and reboot.
Note: After the device reboots, you will need to reconnect to the access point
configuration page using the new IP address setting and login. When configuring TEW740APBO #2, enter the IP address 192.168.10.51.
17. For the first entry in the VLAN List under the action column, click Network.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 15

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
12
19. Click on Wireless and click WDS Setup.
21. Under WDS Client Setup, check the first entry and enter the WiFi MAC address of
TEW-740APBO #2 00:11:22:33:44:11. Then click Save. In the menu located at the top,
you will be prompted to reboot the device. Click the Reboot button and in the following
page, click Reboot. When prompted to reboot, click Yes apply changes and reboot.
Note: When configuring TEW-740APBO #2, enter the WiFi MAC address of TEW740APBO #1.
20. Click Enabled for the WDS Setup and under Authentication, select AES. Enter a WDS
Passphrase. (8-63 alphanumeric characters)
Note: When configuring TEW-740APBO #2, the WDS passphrase must be the same
passphrase configured on TEW-740APBO #1.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 16

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
13
TEW-740APBO #2
When configuring TEW-740APBO #2, repeat all steps in previous section same as TEW740APBO #1 and make sure to follow the noted differences below for steps 18, 20-21.
18. In the IP Setup section, enter the IP Address 192.168.10.51, then click Save. In the
menu located at the top, you will be prompted to reboot the device. Click the Reboot
button and in the following page, click Reboot. When prompted to reboot, click Yes
apply changes and reboot.
Note: After the device reboots, you will need to reconnect to the access point
configuration page using the new IP address setting and login.
20. Click Enabled for the WDS Setup and under Authentication, select AES. Enter a WDS
Passphrase. (8-63 alphanumeric characters)
Note: When configuring TEW-740APBO #2, the WDS passphrase must be the same
passphrase configured on TEW-740APBO #1.
21. Under WDS Client Setup, check the first entry and enter the WiFi MAC address of
TEW-740APBO #1 00:11:22:33:44:00. Then click Save. In the menu located at the top,
you will be prompted to reboot the device. Click the Reboot button and in the following
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
page, click Reboot. When prompted to reboot, click Yes apply changes and reboot.
Page 17
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
14
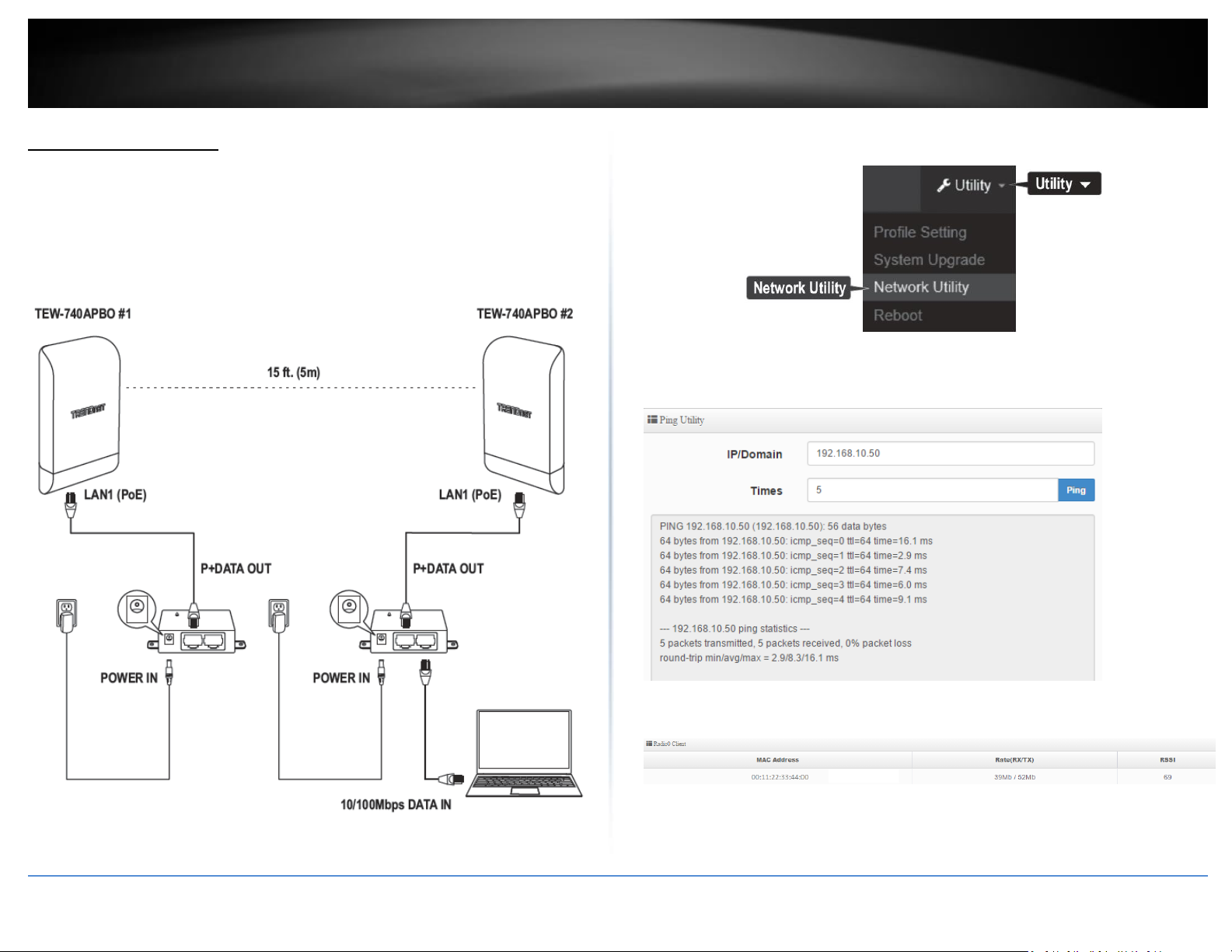
Confirm Connectivity
1. Leave your computer connected to TEW-740APBO #2 and keep the access point
management page open.
2. Make sure both TEW-740APBO #1 and TEW-740APBO #2 access point are powered on
and approximately 15 ft. (5 m) apart from one another with the front of access points
directly facing each other.
3. To verify connectivity, in the TEW-740APBO #2 access point management page, click
on Utility and click on Network Utility.
4. In the IP/Domain field, enter the IP address 192.168.10.50. Next to Times, click Ping.
Ping replies and 0% packet loss will indicate a successful WDS point to point bridge has
been established between the two access points as shown below.
You can also check under Wireless and WDS Status the status of the wireless point to
point bridge between the two access points.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Note: If the connectivity test fails, wait for about 1 minute and try again. Make sure
there are no obstacles between two access points and that they are not too close
together.
Page 18

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
15
Ground Wire and Pole Mount Installation
1. Locate the grounding point located in bottom section of the enclosure. Using a
Phillips screwdriver, remove the ground point screw (counter clockwise) and attach the
included grounding wire to the ground point screw. Reattach the ground screw
(clockwise) along with the grounding wire. After installing the grounding wire, remove
another tab on the enclosure by gently bending back and forth until the tab is removed.
This will create the opening for the ground cable to be routed through.
Note: The ground wire may need to be cut and extended using additional ground wire in
order to reach a proper ground point.
2. Reinstall the cover by lining up the guides into the notches as shown and push the
cover down until the cover clips in and is secured.
3. Insert the included fasteners through the holes located at the back of the access
point.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
4. Wrap the fasteners around the pole where the access point will be installed. On the
fasteners, insert the open end into the locking mechanism and pull tight until the point
is secured.
5. After the access points are properly mounted, you can connect the grounding wires to
the proper ground points and RJ-45 cables from each access point PoE injector to your
network.
Page 19

16
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
Completed Installation Reference
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 20

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
17
TEW-740APBO #1
TEW-740APBO #2
IP Address
192.168.10.50
192.168.10.51
Netmask (Subnet Mask)
255.255.255.0
255.255.255.0
IP Gateway (Default Gateway)
192.168.10.1
192.168.10.1
Primary DNS
192.168.10.1
192.168.10.1
Wireless Channel (Default)
1
1
Mode
WDS
WDS
WDS Encryption
AES
AES
TEW-740APBO2K Setup and Installation
When purchasing the access point bridge kit, mode TEW-740ABPO2K, by default, the
TEW-740APBO access points are preconfigured to establish a point-to-point WDS bridge
between each other using a unique predefined AES encryption key. For convenience, a
unique predefined admin password has already been assigned to both access points.
You can find the preconfigured access point settings on the wireless sticker or on the
device label beneath the cover where the Ethernet ports and LEDs are located. No
additional configuration is required. Ma
On the device label located inside, you can also find the preconfigured default settings
of each access point.
The TEW-740APBO access points will be preconfigured with the following settings:
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 21

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
18
Setup and Confirm Connectivity
1. Remove the cover of the access points by pulling and holding the tab in the vertical
direction upward (as shown in the picture below) and sliding the cover in the two
locations noted away from the access point.
2. Remove the tab on the far left by gently bending it back and forth until the tab is
removed. This will create the opening the RJ-45 network cable to be routed through.
3. Using a RJ-45 network cable, connect one end of the cable to the LAN (PoE) port and
push the cable into the guide on the far left, then through the opening that was created
in the previous step.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 22

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
19
4. Connect the other end of the RJ-45 network cable to the P+DATA OUT port on the
included PoE injector.
5. Connect the included power adapter to the PoE injector POWER IN on the included
PoE injector.
6. Plug the connected power adapter into a power outlet.
7. Confirm the device is powered on through the PWR LED indicator.
8. Assign a static IP address to your computer’s network adapter in the subnet of
192.168.10.x (e.g. 192.168.10.10) and subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
9. Using another network cable, connect one end to the 10/100 DATA IN port on the
included PoE injector for either the first or second access point.
10. Connect the other end of the network cable to your computer’s Ethernet port.
Note: Repeat steps 1-7 to power on and connect the second access point.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 23

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
20
11. Make sure both access points are powered on approximately 15 ft. (5 m) apart from
one another with front of access points directly facing each other.
12. To verify connectivity on your computer, open a command prompt or terminal
application window and type in the following commands.
Note: In Windows®, you can use the Command Prompt application and in Mac®, you can
use the Terminal application to run the commands for connectivity testing.
ping 192.168.10.50
<Press Enter and wait for result>
ping 192.168.10.51
<Press Enter and wait for result>
A successful connectivity test will appear similar to the result below for each access
point. Ping replies and 0% packet loss will indicate a successful point to point bridge
connection between the two access points.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Note: If the connectivity test fails, wait for about 1 minute and try again. Make sure
there are no obstacles between two access points and that they are not too close
together.
Page 24

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
21
Ground Wire and Pole Mount Installation
1. Locate the grounding point located in bottom section of the enclosure. Using a
Phillips screwdriver, remove the ground point screw (counter clockwise) and attach the
included grounding wire to the ground point screw. Reattach the ground screw
(clockwise) along with the grounding wire. After installing the grounding wire, remove
another tab on the enclosure by gently bending back and forth until the tab is removed.
This will create the opening for the ground cable to be routed through.
Note: The ground wire may need to be cut and extended using additional ground wire in
order to reach a proper ground point.
2. Reinstall the cover by lining up the guides into the notches as shown and push the
cover down until the cover clips in and is secured.
3. Insert the included fasteners through the holes located at the back of the access
point.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
4. Wrap the fasteners around the pole where the access point will be installed. On the
fasteners, insert the open end into the locking mechanism and pull tight until the point
is secured.
5. After the access points are properly mounted, you can connect the grounding wires to
the proper ground points and RJ-45 cables from each access point PoE injector to your
network.
Page 25
22
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
Completed Installation Reference
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 26

23
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
Wireless Installation Tips
There are a number of factors that can impact the range of wireless devices.
1. Adjust your wireless devices so that the signal is traveling in a straight path, rather than at an angle. The more material the signal has to pass through the more signal you will lose.
2. Keep the number of obstructions to a minimum. Each obstruction can reduce the range of a wireless device. Position the wireless devices in a manner that will minimize the amount
of obstructions between them.
3. Building materials can have a large impact on your wireless signal. In an indoor environment, try to position the wireless devices so that the signal passes through less dense material
such as dry wall. Dense materials like metal, solid wood, glass or even furniture may block or degrade the signal.
4. Antenna orientation can also have a large impact on your wireless signal. Use the wireless adapter’s site survey tool to determine the best antenna orientation for your wireless
devices.
5. Interference from devices that produce RF (radio frequency) noise can also impact your signal. Position your wireless devices away from anything that generates RF noise, such as
microwaves, radios and baby monitors.
If you are still experiencing low or no signal consider repositioning the wireless devices or installing additional access points. The use of higher gain antennas may also provide the
necessary coverage depending on the environment. Please note to use the wireless connection quality indicators during installation to determine the optimal positioning when mounting
your access points.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 27

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
24
Application Modes
Although the access point is intended to be used for primarily WDS point-to-point bridging, the access point offers other operating modes. The access point multiple mode system which
can be configured either as a wireless gateway or an access point as desired. It also can be used as a WDS (Wireless Distribution System) link for Ethernet network expansion. This section
explains the different modes the access point has available, Access (AP) Mode, AP + WDS Mode, WDS Mode, Client Bridge + AP Mode, WISP (CPE) + AP Mode, Router Mode, and CAP
(Control AP) Mode.
The different modes can be found under System > Mode Setup in the access point web management page.
AP Mode (Access Point Mode)
An access point can be either a main, relay or remote base station. A main base station is typically connected to a wired network via the Ethernet port. A relay base station relays data
between main base stations and relay stations or remote base stations with clients. A remote base station is the end point to accept connections from wireless clients and pass data
upstream to a network wirelessly.
Example 1: Access Point Only
It can be deployed as a traditional fixed wireless access point.
Example 2: Access Point + WDS Bridging
It can be deployed as a traditional fixed wireless access point and establish WDS bridging to an upstream access point to expand a network.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 28

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
25
WDS Mode (Pure WDS)
This is the primary application mode for the TEW-740ABPO and TEW-740APBO2K. The built-in high gain directional antenna makes this access point an ideal solution for
establishing a single WDS point-to-point wireless bridge or link between two physical locations that are a great distance from one another.
Example 1: Point-to-Point
Example 2 : Point-to-Multi-Point
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 29

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
26
Client Bridge + AP Mode
It can be used as an Client Bridge + AP to receive wireless signal over last mile applications, helping WISPs deliver wireless broadband Internet service to new residential and business
customers. In this mode, the access point is enabled with DHCP Server functions. In this mode, the AP functions similar to that of a wireless client or station such as mobile phone, tablet,
or notebook computer, however is also capable of broadcasting wireless signal for other wireless clients to connect. The wired ports LAN1 (PoE) and LAN2 are logically bridged to the
wireless interface. The wired clients of access point are in the same subnet from Main Base Station and it accepts wireless connections from client devices.
WISP (CPE) + AP Mode
It can be used as an Outdoor Customer Premised Equipment (CPE) to receive wireless signal over the last mile, helping WISPs deliver wireless broadband Internet service to new
residential and business customers. This In this mode, the access point wireless interface connects to the wireless Internet service provider (WISP) and acts as the Internet or WAN
Interface. The wired interfaces LAN1 (PoE) and LAN2 operate as the LAN local interface with NAT and DHCP Server functions and wireless interface operates as the WAN Internet interface.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 30

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
27
Router Mode
Router mode allows you to use the access point as a NAT router/gateway. LAN1 (PoE) operates as the wired WAN Internet interface and LAN2 and wireless interfaces operates as the LAN
local interface with NAT and DHCP Server functions.
CAP (Control AP) Mode
CAP mode functions in AP mode but in addition, this mode allows you to manage, monitor, and control other APs using the same firmware/software. You can configure multiple settings
for multiple APs at the same time, push out batch firmware upgrades from one convenient GUI interface. The CAP Mode AP can discover and manage any CAP mode compatible APs on
any of interfaces including WDS bridged links. Note: Currently, the only TRENDnet TEW-740APBO (H/W: v2.XR) is CAP mode firmware/software compatible.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 31

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
28
Access your access point management page
Note: TEW-740APBO Users: Your access point management page default IP address http://192.168.10.100 is accessed through the use of your Internet web browser (e.g. Internet
Explorer®, Firefox®, Chrome™, Safari®, Opera™) and will be referenced frequently in this User’s Guide.
TEW-740APBO2K Users: Your access point management page default IP addresses are http://192.168.10.50 and http://192.168.10.51. Additionally, the pre-defined user name and
password will be unique. This information will be printed on both the wireless stickers and device label located inside the access point enclosure.
If you have changed the default IP address, you will need to ensure that your computer is configured with IP address settings in the same subnet as the as the access point in order to
access the access point management page. Also, make sure your access point is powered on through the included PoE injector and your computer is connected to the 10/100 DATA IN port
on injector or connect to LAN2 Ethernet port. (Ex. Access Point IP address changed to 192.168.0.100 / 255.255.255.0, example computer address 192.168.0.25 / 255.255.255.0).
1. Open your web browser and go to the address http://192.168.10.100 (TEW-740APBO) or http://192.168.10.50 and http://192.168.10.51 (TEW-740APBO2K). Your access point will
prompt you for a user name and password.
2. TEW-740APBO Users: By default, the user name is admin and password is admin. TEW-740APBO2K Users: You can also find the wireless settings sticker included with the access points
and on the device inside the access point enclosure. Enter your Username and Password, then click Login.
Note: If you have changed the password already such as in the Setup Wizard, you will need to login using the new password. User Name and Password are case sensitive.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 32

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
29
AP Management Settings
Management Setup
System > Management
These settings will allow you to configure the AP system information, administrator
password, management access methods, external logging, and automatic reboot
schedule.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on Management. Review the settings and click Save to apply
the changes.
System Information
System Name – Specifies the device or hostname of the AP for easily
identifying the device and network management purposes.
Description – Specifies a brief description of the device for easily identifying
the device and network management purposes.
Location – Specifies the location of the device relative to the network for easily
identify the device and network management purposes.
Administrator Password
New/Check Admin Password – To change the default administrator password,
enter the new password in the field provide and again in the check field to
confirm the password change.
Login Methods
HTTP – The standard unsecured web GUI method is enabled by default. Check
the box to enable or disable management access to the device via http web GUI
access. You can also check the default port used for management access.
HTTPS – This type of management access is also through the web GUI but
secured using SSL (Secure Socket Layer) encryption. The default port may also
be changed. Additionally, you can upload your own SSL certificate under Utility
> Profile Settin.
Telnet – This type of unsecured management access is through the CLI
(Command Line Interface) through the AP IP address and has been disabled by
default for security purposes. The default port may also be changed.
SSH – This type of secured and encrypted management access is also through
the CLI (Command Line Interface) through the AP IP address. The default port
may also be changed. For additional security, the Host Key Footprint may also
be changed by clicking Generate Key.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 33

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
30
System Log Setup
Remote Server – To enable external logging to be sent, check the option and
enter the IP address of the remote logging server (Syslog Server).
Port – By default, Syslog logging uses port UDP 514 but can be changed. Please
note the port would also need to be changed on external Syslog server.
Auto Reboot
Type – Click the drop-down list and select the frequency of when the AP will
auto reboot, Daily, Weekly, or Monthly.
o Daily – The AP will auto reboot once a day. Specify the time when to
initiate the device reboot.
o Weekly – The AP will auto reboot once a week. Specify the day of the
week and time when to initiate the device reboot.
o Monthly - The AP will auto reboot once a month. Specify the day of
the month and the time to initiate the device reboot.
Set the device date and time
System > Time
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on Time. Review the settings and click Save to apply the
changes.
Local Time – Displays the current device date and time.
Mode:
NTP Server – The device will obtain the date and time information automatically
from an external NTP server. Please note that the default gateway IP address and
DNS must be configured properly to access an NTP server located on the Internet.
o Default NTP Server – Click the drop-down list and select an available NTP
server from the list.
o NTP Server – Allows you to manually enter an NTP server that is not
available in the predefined NTP server list.
o Time Zone – Click the drop-down list and select the correct Time Zone.
o Daylight Savings Time – Enable or Disable the daylight savings time
function if it is currently active in your region.
Manual – Allows you to manually set the device date and time.
o Date (Y/M/D) – Click drop-down lists to set the correct date manually.
Year / Month / Day
o Time (H:M:S) – Click the drop-down lists to set the correct time manually.
Hour:Minute:Second.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 34

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
31
SNMP Settings
System > SNMP
SNMP v2c
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on SNMP. Review the settings and click Save to apply the
changes.
Active – Enable or disable SNMP version 2c.
RO Community – Enter the read only community name.
RW Community – Enter the ready/write community name.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 35

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
32
SNMP v3
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on SNMP. Review the settings and click Save to apply the
changes.
Active – Enable or disable SNMP version 3.
RO Username – Enter the read only user name.
RO Password – Enter the read only password.
RW Username – Enter the read/write user name.
RW Password – Enter the read/write password.
SNMP Trap
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on SNMP. Review the settings and click Save to apply the
changes.
Active – Enable or disable SNMP Trap.
Community – Enter the community name for SNMP trap.
IP 1 – Enter the IP address of the 1
IP 2 – Enter the IP address of the additional SNMP trap receiver.
IP 1 – Enter the IP address of the additional SNMP trap receiver.
IP 1 – Enter the IP address of the additional SNMP trap receiver.
st
SNMP trap receiver.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 36

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
33
Backup and restore your AP configuration settings
Utility > Profile Setting
Backup configuration settings
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Utility and click on Profile Setting.
3. Next to Save Settings To PC, click Save.
Depending on your web browser settings, you may be prompted to save a file (specify
the location) or the file may be downloaded automatically to the web browser settings
default download folder. (Default Filename: config.bin)
Restore configuration settings
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Utility and click on Profile Setting.
3. Next to Load Settings From PC, click Browse or Choose File.
4. A separate file navigation window should open.
5. Select the configuration file to restore and click Upload. (Default Filename:
config.bin). If prompted, click Yes or OK.
6. Wait for the device restore settings.
Reset your AP to factory defaults
Utility > Profile Setting
You may want to reset your device to factory defaults if you are encountering difficulties
and have attempted all other troubleshooting. Before you reset to defaults, if possible,
you should backup your router configuration first. If you are using are resetting an AP
from the TEW-740APBO2K Bridge Kit, the APs will default to the original predefined
settings which can be located on the device label inside the enclosure or predefined
sticker.
There are two methods that can be used to reset your device to factory defaults.
Reset Button – Located inside the enclosure where Ethernet ports and LEDs are
located. Use this method if you are encountering difficulties with accessing your
router management page.
OR
Management Page
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Utility and click on Profile Setting.
3. Next to Reset To Factory Default, click Default.
Soft reboot your AP
Utility > Reboot
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Utility and click on Network Utility.
3. Click Reboot.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 37

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
34
Upgrade your AP firmware
Utility > System Upgrade
TRENDnet may periodically release firmware upgrades that may add features or fix
problems associated with your TRENDnet device and date/version. To check if there is a
firmware upgrade available for your device, please check your TRENDnet model and
version using the link. http://www.trendnet.com/downloads/
In addition, it is also important to verify if the latest firmware version is newer than the
one your AP is currently running. To identify the firmware that is currently loaded on
your AP, log in to the AP, click on Utility > Status. The firmware version and date used by
the AP will be displayed. If there is a newer version available, also review the release
notes to check if there were any new features you may want or if any problems were
fixed that you may have been experiencing.
1. If a firmware upgrade is available, download the firmware to your computer.
2. Unzip the file to a folder on your computer.
Please note the following:
Do not interrupt the firmware upgrade process. Do not turn off the device or
press the Reset button during the upgrade.
If you are upgrade the firmware using a laptop computer, ensure that the laptop
is connected to a power source or ensure that the battery is fully charged.
Disable sleep mode on your computer as this may interrupt the firmware upgrade
process.
Do not upgrade the firmware using a wireless connection, only using a wired
network connection.
Any interruptions during the firmware upgrade process may permanently
damage your router.
3. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
4. Click Utility and click on System Upgrade.
5. Next to Upgrade Via Local PC, click Browse or Choose File.
6. A separate file navigation window should open.
7. Select the firmware file to restore and click Upload. If prompted, click Yes or OK.
Other Firmware Upgrade Methods:
Via TFTP Server – If you have a computer running as a TFTP server or running
third party TFTP server software, you can copy the file to your TFTP server
computer, enter the TFTP server IP address and firmware filename, then click
Upload.
Via HTTP URL – If you have the firmware file loaded to an HTTP web server and
the file is downloadable via link, enter the URL link to the firmware download
and click Upload.
Network Utilities
Utility > Network Utility
The built-in network test utilities ping and traceroute can be used for troubleshooting
purposes.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Utility and click on Network Utility.
Ping Utility – Enter the IP/Domain address to test connectivity and enter the
amount of ping requests sent, click Ping.
Traceroute – Enter the Destination Host IP address to test and enter the
maximum number of router hops allowed.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 38

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
35
View system information
Status > Overview
This page will display the AP system summary information such as the currently
operating mode, system time, firmware version, MAC and IP address settings WiFi
information.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Status and click on Overview.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 39

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
36
View currently connected wireless client devices
Status > Wireless Client
This page will display the wireless client devices that are currently connected to your AP.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Status and click on Wireless Client.
Radio – Displays the radio the wireless client device is connected. Since the
TEW-740APBO only has one radio (Radio 0), only Radio 0 will be shown for this
model.
MAC Address – Displays the wireless client device MAC address.
Rate (RX/TX) – Displays the estimated receive and transmission rates at which
the wireless client device is connected.
RSSI – Displays the estimated signal strength of the wireless client device
relative to the AP. The value is a negative number, therefore, the lower the
value, the better signal and connectivity of the client device.
View currently connected authenticated users
Status > Online Users
Only when using the guest or user authentication feature, this page will display
information about the currently connected authenticated users.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Status and click on Online Users.
View authentication log information
Status > Authentication Log
Only when using the guest or user authentication feature and authentication log has
been enabled, this page will displayed authentication status logs and attempts for each
VLAN.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Status and click on Authentication Log.
View the device system log information
Status > System Log
This page will display general device logging information about the system operation,
functions, and status.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Status and click on System Log.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 40
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
37
Configuring additional application modes
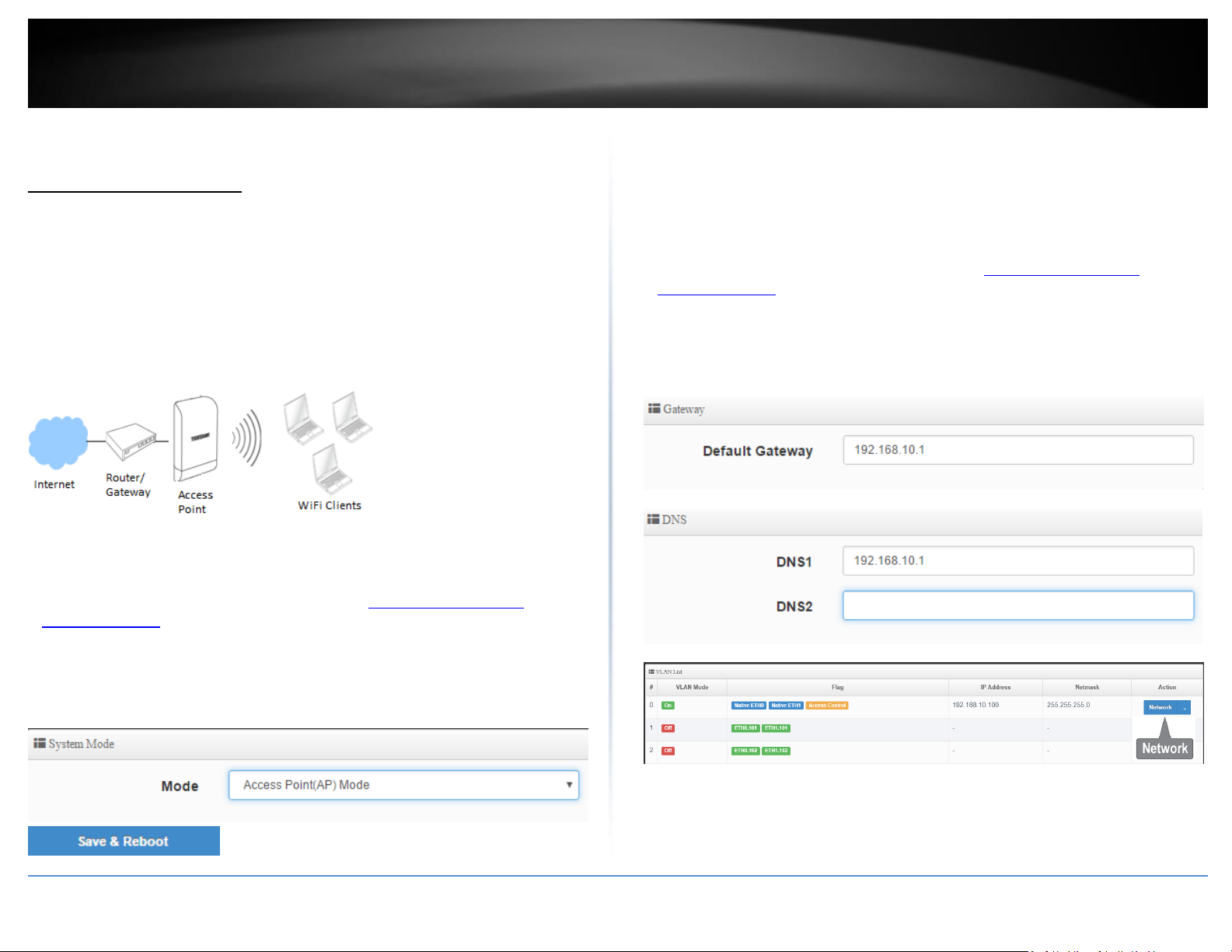
Access Point (AP) Mode
In AP mode, the access point creates a wireless network to allow wireless devices to
connect and access your network. The access point allows wireless connectivity to your
existing wired network by connecting directly to your wired network’s router/gateway
or network switch via the access point RJ-45 Ethernet port using the 10/100 DATA IN on
the PoE injector or LAN2 port.
The diagram below shows your access point to your router/gateway and functioning in
AP mode creating a wireless network for your wireless clients (ex. laptops, smart
phones, etc.) to connect and adding wireless connectivity to an existing wired network.
Set the device LAN IP address
System > VLAN Setup
By default, the primary LAN interface and management interface is set to VLAN 0. You
can configure up to 7 VLAN tagged interfaces. Each VLAN can be configured with it’s
own IP address settings and SSID.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on VLAN Setup. In this page, you can configure the
router/Internet gateway/default gateway IP address and DNS server IP addresses.
(ex. 192.168.10.1)
Set the device to AP mode
System > Mode Setup
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on Mode Setup.
3. Select Access Point (AP) Mode in the mode drop down list. Then click Save & Reboot.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
(ex. 192.168.10.1)
3. For the first entry in the list VLAN #0, under the Action column, click Network.
Page 41

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
38
4. Under IP Setup, enter the primary LAN IP address and Subnet Mask of the device.
Then click Save. When prompted to reboot, reboot and apply the changes.
Note: Please note you will need to log back into the access point management page
using the new IP address settings. (ex. 192.168.10.50 / 255.255.255.0)
Additional Network Settings
VLAN Mode – For each virtual AP interface, enable or disable tagged VLAN
traffic.
IP Setup – For each virtual AP interface, aside from the primary IP address
settings assigned for VLAN 0, you can assign an IP interface for each virtual AP
which can be used for management access over different VLANs/IP subnets.
Note: It is recommended to leave VLAN #0 enabled for management purposes.
Access Point – Enable or Disable the wireless network interface.
802.1d Spanning Tree – Enable this setting only if you are using redundant
wired and wireless bridged links (WDS) to prevent loops and multiple paths.
Example below with redundant WDS bridge link between 3 access points.
Control Port (Used CAP Mode Only) – Enable this setting to allow management
access from another TEW-740ABPO AP running in CAP (Control AP) mode. This
will allow the management AP to push settings the current AP on the selected
VLAN interface.
LAN1/LAN2 VLAN Tag Setup – By default, VLANs are setup as untagged ports.
To set the LAN2 Ethernet interface as a tagged member of specified VLAN,
check the VLAN Tag option and enter the VLAN ID. This will allow you to map a
specific wireless network to specific VLAN IDs on LAN1/2 Ethernet interfaces.
Note: The example diagram below displays the access point broadcasting
multiple SSIDs mapped to specific VLANs.
Configure primary wireless network settings
System > VLAN Setup > VLAN # > Access Point
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on VLAN Setup.
Page 42

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
39
3. For the first entry in the list VLAN #0, under the Action column, click the arrow next to
the Network button and select Access Point.
Note: If you under the Network section in the VLAN 0 configuration, you can click VLAN 0
at the top and click on Access Point in the drop-down list.
4. Review the settings, click Save when finished.
Access Point – Enable or Disable the wireless network interface.
Wireless Network Name (ESSID): Enter the wireless name (SSID) for your wireless
network. It differentiates your wireless network from others around you.
SSID Visibility – Enable or disable your wireless network name from being
discovered by wireless scanning or client devices. Please note that this does not
disable your radio, only hides the network name.
Client Isolation – When isolation is enabled, this restricts wireless client devices
from communicating to each other when connected to the same wireless network
providing an extra level of security. If disabled, this allows wireless client devices to
communicate to each other when connected to the same wireless network.
Connection Limit – The maximum number of connected wireless client devices can
be set using this setting for additional control and prevention of overloading the
wireless network with too many client connections. Check the Enable option, and
enter the maximum number of connections in the User Limit field
Authentication – Set the wireless encryption for the wireless network.
o Open System – No encryption required to connect to wireless
network.
MAC Address Filter
System > VLAN Setup > VLAN # > MAC Filter
This feature will add another layer of security by restricting access by WiFi MAC address.
You can specify either which MAC addresses to allow or which MAC addresses to deny
access.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on VLAN Setup.
3. For the first entry in the list VLAN #0, under the Action column, click the arrow next to
the Network button and select MAC Filter.
Note: First, decide whether you would like to specify only MAC addresses allow or
MAC addresses to deny and add them to the list. It is easier to specify only MAC
addresses to allow and deny all other since the MAC addresses are known.
4. In the Add MAC Address section, enter the first MAC address to allow or deny in the
MAC address field in the following format (XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX). Click Add to add the
MAC address to the MAC address list. Repeat to add additional MAC addresses.
o WPA/WPA2 Personal – Applies standard WPA or WPA2 wireless
security requiring a specifically assigned passphrase to connect to the
wireless network. (Passphrase: 8-63 alphanumeric characters).
o WPA/WPA2 Enterprise – Applies standard WPA or WPA2 wireless
security requiring the use of the third party RADIUS authentication
server to authenticate wireless clients connecting to the wireless
network. The third party RADIUS authentication server is external to
the access point and must be set up and configured separately. Once
the RADIUS is properly set up on the network, the access point will
forward and authentication requests to the external RADIUS server via
IP address and shared secret.
o 802.1X – This authentication method is similar to WPA/WPA2
enterprise in that it requires an external third party RADIUS
authentication server. Standard WPA/WPA2 encryption is not applied,
only the requirement for RAIDUS.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 43

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
40
Mode – Enable or Disable the DHCP service.
5. In the MAC Rules, select the rule action.
Only Allow List MAC – This rule only allows listed MAC addresses to connect and denies
all others.
Only Deny List MAC – This rule denies all listed MAC addresses and allows all others to
connect.
DHCP Server
System > VLAN Setup > VLAN # > DHCP Server
This feature will allow to distribute IP address automatically on the selected interface.
Typically, your network router will already be automatically distribute IP address
settings via DHCP.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on VLAN Setup.
3. For the first entry in the list VLAN #0, under the Action column, click the arrow next to
the Network button and select DHCP Server. Review the settings below and click Save
when completing the changes.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Start IP: Enter the first IP address of the IP address range/pool to distribute to DHCP
client devices. (ex. 192.168.10.101)
End IP: Enter the last IP address of the IP address range/pool to distribute to DHCP
client devices. (ex. 192.168.10.199)
Netmask: Enter the subnet mask to distribute to DHCP client devices. (ex.
255.255.255.0)
Gateway: Enter the default gateway IP address to distribute to DHCP client devices.
(ex. 192.168.10.1)
DNS1 IP: Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server to distribute to DHCP client
devices.
DNS2 IP: Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS server to distribute to DHCP
client devices.
WINS IP: Enter the IP address of the WINS (Windows Internet Name Service) server
to distribute to DHCP client devices. Typically this is used on a Windows network to
allow the resolution of computer and device names.
Domain: Enter the domain name to distribute to DHCP client devices. (ex.
trendnet.com)
Lease Time: Enter the time in seconds how long DHCP client devices will retain their
settings assigned by the DHCP service before expiration. Upon expiration, DHCP
client devices will initiate new requests for DHCP client settings.
Page 44

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
41
DHCP Reservation/Static Lease
System > VLAN Setup > VLAN # > DHCP Server
From the DHCP IP address range, you can set a permanent IP address assignment to a
specific client device MAC address so the IP address assignment will not change.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on VLAN Setup.
3. For the first entry in the list VLAN #0, under the Action column, click the arrow next to
the Network button and select DHCP Server. In the Static Lease IP Setup section,
please review the settings below and click Save when completing the changes.
Comment: Add a comment or name to help easily identify the device or purpose of
the DHCP static IP lease/reservation.
IP Address: Enter the IP address from the DHCP server IP address range/pool to
permanently assign. (ex. 192.168.10.20)
MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of the client device to assign the permanent
lease in the example format provided and click Add to add the static IP lease to the
list. (ex. 00:11:22:AA:BB:CC). Repeat to add additional static IP leases.
After the DHCP server settings have been configured and changes have been applied,
dynamic DHCP client leases will appear in the DHCP Client List table.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 45

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
42
802.11r/802.11k Fast Roaming
System > VLAN Setup > VLAN # > 802.11r Fast Roaming
When the APs are configured with the same SSID and encryption, these settings enable
WiFi clients to seamlessly roam between APs with minimal or no downtime during
transitions. For these fast roaming functions to work properly, the WiFi clients must also
support 802.11r and 802.11k. 802.11r speeds up WiFi client roaming and transition by
pre-authentication eliminating the need for the client to pre-authenticate at every
access point. 802.11k enhances roaming efficiency by providing information (signal
strength & utilization) to WiFi clients about APs in the network allowing the clients
choose the next AP to connect to or transition.
Note: Please note that fast roaming features require the WiFi clients to also support
802.11r and 802.11k. Please check your wireless client device or adapter specifications.
3. For the first entry in the list VLAN #0, under the Action column, click the arrow next to
the Network button and select 802.11r Fast Roaming. In the Static Lease IP Setup
section, please review the settings below and click Save when completing the
changes.
Fast Roaming: Enable or Disable the fast roaming features.
Mobility Domain: The identifier used to indicate a domain or group of access points.
Enter the ID (2 octets) as a 4-digit hexadecimal string. (Hex Format: 0-9 and A-F) (ex.
a1b2)
Note: When enabling roaming, the domain ID must be the same on all APs in same
wireless roaming group.
Reassoc Deadline: Re-association deadline time units (TU2 / 1.024 ms; range 1000 –
65535).
R0/NAS Identifier: PMK-R0 Key Holder Identifier. When using IEEE 802.11R, this value
must be configured and must be between 1 to 48 octets long alphanumeric
characters. (ex. ap.example.com) This value will need to be entered in other APs in
the same mobility domain as the R0 Key Holder NAS identifier.
R1 Identifier: PMK-R1 Key Holder ID (6 octets) as a 12-digit hexadecimal string. (Hex
Format: 0-9 and A-F) (ex. 000102030405)
R1 Push: Enables or disables the R1 key to automatically be sent. Enable this setting if
you are only configuring roaming between APs without a wireless controller.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on VLAN Setup.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 46

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
43
In the R0 Key Holders field, you will need to enter in all other APs in the Mobility
Domain for roaming. To add an AP, enter the MAC address, NAS identifier, and 128-bit
key (26 hexadecimal characters, Hex Format: 0-9 and A-F)
MAC Address: Enter the WiFi MAC address of the remote AP to add.
NAS Identifier: Enter the NAS identifier of the remote AP.
128-bit Key: Enter the 128-bit key of the remote AP. (26 hexadecimal characters, Hex
Format: 0-9 and A-F)
In the R1 Key Holders field, enter a unified set of R1 Key Holder information, enter the
MAC address, NAS identifier, and 128-bit key (26 hexadecimal characters, Hex Format:
0-9 and A-F)
Additional Wireless Settings
Wireless > Radio 0 Basic Setup
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Wireless and click on Radio 0 Basic Setup.
3. Review the settings, click Save when finished.
MAC Address: Displays the WiFi MAC address of the access point.
MAC Address: Enter the main roaming device MAC address.
R1 Identifier: Enter the Shared Identifier.
128-bit Key: Enter the 128-bit key. (26 hexadecimal characters, Hex Format: 0-9 and
A-F)
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Country – Displays the current country/region the access point is set to currently
operate.
Band Mode – Allows you to set which wireless client devices are able to connect to
the access point. 802.11b/g/n, 802.11b/g. Wireless client devices that do not
support the 802.11 mode specified will not be able to connect to the access point.
Auto Channel – Enables your access point to automatically scan for which wireless
channel to operate automatically. Please note for WDS bridging only, the wireless
channel must match on both sides of the wireless WDS bridge link.
Page 47

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
44
Channel – If Auto Channel is disabled, select the wireless channel the access point
will operate.
Tx Power – You can adjust the wireless output power of the access point to achieve
the appropriate wireless coverage. It is recommended to keep the default setting,
level 9.
Slot Time: By default, the slot time is set to 9 microsecond. Slot time is the amount
of time a device waits after a collision before retransmitting a packet. Reducing the
slot time decreases the overall back-off, which increases throughput. Back-off,
which is a multiple of the slot time, is the random length of time a station waits
before sending a packet on the LAN. For a sender and receiver own right of the
channel the shorter slot time help manage shorter wait time to re-transmit from
collision because of hidden wireless clients or other causes. When collision sources
can be removed sooner and other senders attempting to send are listening the
channel (CSMA/CA) the owner of the channel should continue ownership and finish
their transmission and release the channel. Then, following ownership of the
channel will be sooner for the new pair due to shorter slot time. However, when
long duration of existing collision sources and shorter slot time exist the owners
might experience subsequent collisions. When adjustment to longer slot time can’t
improve performance then RTS/CTS could supplement and help improve
performance. Additionally, if you are encountering wireless connection issues
specifically with wireless WDS bridge linked connectivity, you can click distance and
enter the distance in m (meters) and slot time will be automatically adjusted
accordingly. It is recommended to keep the default setting.
ACK Timeout: ACK timeout is in the range of 1~255 and set in unit of microsecond.
The default value is 85 microsecond. All data transmission in 802.11b/g request an
“Acknowledgement” (ACK) send by receiving radio. The transmitter will resend the
original packet if correspondent ACK failed to arrive within specific time interval,
also refer to as “ACK Timeout”.
ACK Timeout is adjustable due to the fact that distance between two radio links
may vary in different deployment. ACK Timeout makes significant influence in
performance of long distance radio link. If ACK Timeout is set too short, transmitter
will start to “Resend” packet before ACK is received, and throughputs become low
due to excessively high re-transmission. ACK Timeout is best determined by
distance between the radios, data rate of average environment. The Timeout value
is calculated based on round-trip time of packet with a little tolerance, So, if
experiencing re-transmissions or poor performance the ACK Timeout could be
made longer to accommodate.
TX/RX Stream: This will allow you to set the number of wireless streams. By default,
this is set to 2T2R (2 Transmit / 2 Receive) streams approximately 300Mbps
operating @ 64 QAM. If using 1T1R (1 Transmit / 1 Receive) streams the maximum
possible speed is approximately 150Mbps.
Channel Width: Select the appropriate channel width for your wireless network.
This setting only applies to 802.11n. For greater 802.11n performance, select
20/40MHz (Auto) (Options: 20MHz or 20/40MHz (Auto)). It is recommended to use
the default channel bandwidth settings.
Note: Please note that this setting may provide more stability than the higher
channel bandwidth settings such as 20/40MHz (Auto) for connectivity in busy
wireless environments where there are several wireless networks in the area.
o 20 MHz – This mode operates using a single 20MHz channel for
wireless devices connecting at 802.11n on both 2.4GHz and 5GHz. This
setting may provide more stability than 20/40MHz (Auto) for
connectivity in busy wireless environments where there are several
neighboring wireless networks in the area.
o 20/40MHz (Auto) –When 20/40MHz (Auto) is active, this mode is
capable of providing higher performance only if the wireless devices
support the channel bandwidth settings. Enabling 20/40MHz (Auto)
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 48

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
45
typically results in substantial performance increases when connecting
an 802.11n client.
Short GI – Short GI standard for short guard interval. Enabling this setting may
increase wireless throughput in less busy wireless environments by decreasing the
standard guard interval time to ensure distinct transmissions do not interfere with
each other. Although enabling this setting may slightly increase wireless
throughput, it may also increase errors depending on the wireless environment.
Aggregation – This setting may increase wireless throughput by sending additional
frames in a single transmission. This maximum number of aggregation frames and
total aggregation size can also be set for single transmission.
Advanced Wireless Settings
Wireless > Advanced Setup
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Wireless and click on Radio 0 Basic Setup.
3. Review the settings, click Save when finished.
Beacon Interval: Beacon Interval is in the range of 20~1024 and set in unit of
millisecond. The default value is 100 msec.
Access Point (AP) in IEEE 802.11 will send out a special approximated 50-byte
frame, called “Beacon”. Beacon is broadcast to all the stations, provides the basic
information of AP such as SSID, channel, encryption keys, signal strength, time
stamp, support data rate.
All the radio stations received beacon recognizes the existence of such AP, and may
proceed next actions if the information from AP matches the requirement. Beacon
is sent on a periodic basis, the time interval can be adjusted.
By increasing the beacon interval, you can reduce the number of beacons and
associated overhead, but that will likely delay the association and roaming process
because stations scanning for available access points may miss the beacons. You can
decrease the beacon interval, which increases the rate of beacons. This will make the
association and roaming process very responsive; however, the network will incur
additional overhead and throughput will go down.
DTIM Interval: The DTIM interval is in the range of 1~255. The default is 1.
DTIM is defined as Delivery Traffic Indication Message. It is used to notify the
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 49

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
46
wireless stations, which support power saving mode, when to wake up to receive
multicast frame. DTIM is necessary and critical in wireless environment as a
mechanism to fulfill power-saving synchronization. A DTIM interval is a count of the
number of beacon frames that must occur before the access point sends the
buffered multicast frames. For instance, if DTIM Interval is set to 3, then the Wi-Fi
clients will expect to receive a multicast frame after receiving three Beacon frame.
The higher DTIM interval will help power saving and possibly decrease wireless
throughput in multicast applications.
Fragment Threshold: The default range for the fragment threshold isf
256~2346 bytes. The default is 2346 byte. This setting is used to specify the
maximum size for a data packet before being fragmented into multiple data
packets.
RTS Threshold: RTS Threshold is in the range of 1~2347 byte. The default is
2346 byte. The main purpose of enabling RTS by changing RTS threshold is to
reduce possible collisions due to hidden wireless clients. RTS in AP will be
enabled automatically if the packet size is larger than the Threshold value. By
default, RTS is disabled in a normal environment supports non-jumbo frames.
Short Preamble: By default, it’s “Enable”. To Disable is to use Long 128-bit
Preamble Synchronization field. The preamble is used to signal "here is a train
of data coming" to the receiver. The short preamble provides 72-bit
Synchronization field to improve WLAN transmission efficiency with less
overhead.
IGMP Snooping – Enabling this setting identifies multicast traffic transmitted
over the access point and filter accordingly to prevent multicast flooding.
Greenfield – When enabled, restricts the access point to communicate only
with other 802.11n devices. Other pre-802.11n clients such as 802.11b/g will
be ignored.
Wireless WMM QoS Setup
Wireless > WMM Setup
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Wireless and click on WMM Setup.
3. Review the settings, click Save when finished.
To achieve optimal wireless performance, it is necessary to tweak advance setting per
requirements properly, not necessary higher the better or lower.
The administrator can change the RTS threshold and fragmentation threshold settings
for the system.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 50

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
47
Queue
Data
Transmitted
AP to Clients
Priority
Description
AC_BK
Background.
Low
High throughput. Bulk data that requires maximum
throughput and is not time-sensitive is sent to this
queue (FTP data, for example).
AC_BE
Best Effort
Medium
Medium throughput and delay. Most traditional IP
data is sent to this queue
AC_VI
Video
High
Minimum delay. Time-sensitive video data is
automatically sent to this queue
AC_VO
Voice
High
Time-sensitive data like VoIP and streaming media
are automatically sent to this queue
Queue
Data
Transmitted
Clients to AP
Priority
Description
AC_BK
Background.
Low
High throughput. Bulk data that
requires maximum
throughput and is not timesensitive is sent to this queue
(FTP data, for example).
AC_BE
Best Effort
Medium
Medium throughput and delay.
Most traditional IP data is
sent to this queue
AC_VI
Video
High
Minimum delay. Time-sensitive
video data is automatically
sent to this queue
AC_VO
Voice
High
Time-sensitive data like VoIP
and streaming media are
automatically sent to this
queue
WMM Parameters of Access Point : This affects traffic flowing from the access
point to the client station
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Configuring QoS options consists of setting parameters on existing queues for different
types of wireless traffic. You can configure different minimum and maximum wait
times for the transmission of packets in each queue based on the requirements of the
media being sent. Queues automatically provide minimum transmission delay for
Voice, Video, multimedia, and mission critical applications, and rely on best-effort
parameters for traditional IP data.
As an Example, time-sensitive Voice & Video, and multimedia are given effectively
higher priority for transmission (lower wait times for channel access), while other
applications and traditional IP data which are less time-sensitive but often more dataintensive are expected to tolerate longer wait times.
o Aifsn: The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing Number specifies a wait time (in
milliseconds) for data frames
o CWmin: Minimum Contention Window. This parameter is input to the algorithm
that determines the initial random back-off wait time ("window") for retry of a
transmission. The value specified here in the Minimum Contention Window is the
upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from which the initial random back-off
wait time is determined.
o CWmax: Maximum Contention Window. The value specified here in the
Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling
of the random back-off value. This doubling continues until either the data frame
is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached. Once the Maximum
Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a maximum
number of retries allowed is reached. Valid values for the "cwmax" are 1, 3, 7, 15,
31, 63, 127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for "cwmax" must be higher than the
value for "cwmin".
o Txop: Transmission Opportunity is an interval of time when a WME AP has the
right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium (WM). This value
specifies (in milliseconds) the Transmission Opportunity (TXOP) for AP; that is, the
interval of time when the WMM AP has the right to initiate transmissions on the
wireless network.
o ACM: Admission Control Mandatory, ACM only takes effect on AC_VI and AC_VO.
When you do not click Checkbox, it means that the ACM is controlled by the
connecting AP. If you click Checkbox, it means that the Client is in charge.
o AckPolicy: Acknowledgment Policy, WMM defines two ACK policies: Normal ACK
and No ACK. Click “Checkbox” indicates “No ACK”
When the no acknowledgment (No ACK) policy is used, the recipient does not
acknowledge received packets during wireless packet exchange. This policy is
suitable in the environment where communication quality is fine and interference
Page 51

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
48
is weak. While the No ACK policy helps improve transmission efficiency, it can
cause increased packet loss when communication quality deteriorates. This is
because when this policy is used, a sender does not retransmit packets that have
not been received by the recipient. When the Normal ACK policy is used, the
recipient acknowledges each received unicast packet.
WMM Parameters of Station: This affects traffic flowing from the client station to
the access point.
o Aifsn: The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing Number specifies a wait time (in
milliseconds) for data frames
o CWmin: Minimum Contention Window. This parameter is input to the algorithm
that determines the initial random backoff wait time ("window") for retry of a
transmission. The value specified here in the Minimum Contention Window is the
upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from which the initial random backoff wait
time is determined.
o CWmax: Maximum Contention Window. The value specified here in the
Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling
of the random backoff value. This doubling continues until either the data frame
is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached. Once the Maximum
Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a maximum
number of retries allowed is reached. Valid values for the "cwmax" are 1, 3, 7, 15,
31, 63, 127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for "cwmax" must be higher than the
value for "cwmin".
o Txop: Transmission Opportunity is an interval of time when a WME AP has the
right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium (WM). This value
specifies (in milliseconds) the Transmission Opportunity (Txop) for AP; that is, the
interval of time when the WMM AP has the right to initiate transmissions on the
wireless network.
o ACM: Admission Control Mandatory, ACM only takes effect on AC_VI and AC_VO.
When you do not click Checkbox, it means that the ACM is controlled by the
connecting AP. If you click Checkbox, it means that the Client is in charge.
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes.
The items in this page are for AP's RF advanced settings and will be applied to all VAPs
and WDS Links.
WDS (Wireless Distribution System)
Wireless > WDS Setup
When in AP (Access Point) mode, you can also configure the access point to establish
wireless WDS bridged links at the same time (AP + WDS mode).
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Wireless and click on WDS Setup.
3. Review the settings, click Save when finished.
WDS Setup – Enable or Disable WDS functionality.
ESSID – The SSID or wireless network name for WDS connections only.
Authentication – Specifies the type of security used for the WDS link. None or
AES. Please note this is not the same as WPA/WPA2 and can only be used for
WDS connections to this access, not standard wireless client devices.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 52

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
49
VLAN Setup – Allows you to configure VLANs that will communicate across the
wireless WDS link. See the example diagrams below.
WDS Client Setup – Enter the remote access points wireless MAC addresses in
the table to establish the wireless WDS link.
MAC Address – Displays the currently managed access point wireless MAC
address or BSSID.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
WDS Status – Displays information about currently established wireless WDS
links to the managed access point.
Page 53

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
50
Authentication/Captive Portal
System > Authentication > VLAN #
On each VLAN interface/SSID, guest authentication can be used using either the local
user database, RADIUS, or OAuth 2.0 Authentication Server (ex. Google, Facebook, etc.)
Additionally, you can use the built-in page template for captive portal/wall garden user
login or upload your own customized page.
Authentication
System > Authentication > VLAN # > Authentication
This section allows you to configure the user name and password type authentication
method through either the local user database or external RADIUS server.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System, click on Authentication, and in the first entry VLAN 0, in the Action
column, and click on Authentication. Review the settings and click Save to apply the
changes.
Authentication - Enable or disable the authentication function on the interface.
There are 2 methods to authenticate users you can choose, Local User or RADIUS. If you
are running your own external RAIDIUS server for authentication, you can choose the
RADIUS option and configure server settings accordingly.
Local User – Enable or disable local user authentication. This will authenticate users
through the internal local user database.
Multiple Login – Check the option to allow multiple logins concurrently with the
same user.
Login Timeout – Enter the idle timeout period before automatically logging out
users in minutes.
Redirect URL – Enter the URL of the web page to automatically redirect users
after successful login.
Login URL – Enter the URL of the login page for users.
Authentication Log – Enable or disable authentication logging.
Session Log – Enable or disable session logging.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
If using Local User, create your user accounts System > Authentication > VLAN # > Local
User.
Page 54

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
51
RADIUS Setup – Enable or disable RADIUS authentication. This will authenticate users
through the external RADIUS authentication server and require that you have already a
server set up manually.
Primary Server IP – Enter the IP address of the primary RADIUS.
Secondary Server IP – If you have a secondary or backup RADIUS server, enter
the IP address.
Authentication Port – Enter the authentication port number used by your
RADIUS server for authentication requests. Typically, the default RADIUS server
port is 1812.
Accounting Service – If your RADIUS server also has accounting enabled, check
the option and enter the accounting port. Typically, the default RADIUS server
account port is 1813.
Authentication – Select the authentication type used by your RADIUS server for
user authentication. Typically, CHAP is used since it is more secure than PAP.
Secret Key – Enter the shared secret required by your RADIUS server.
If you have bandwidth restriction limits for your guest users, you can specify those limits
per user and total allocated bandwidth in Kbps.
Guest Authentication
System > Authentication > VLAN # > Guest
This section allows you configure the guest authentication function.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System, click on Authentication, and in the first entry VLAN 0, in the Action
column, and click on drop-down list and click Guest. Review the settings and click
Save to apply the changes.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 55

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
52
Service – Enable or disable the guest authentication function.
Login Type:
o One Time – Allows a single user account to be logged in only one instance.
o Multiple Time – Allows a single user account to be logged in at multiple
instances.
Count Limit – Specifies the maximum amount of connected users at any given
time. Once the maximum is reached, other users will not be able to log on until of
the existing users logs out or disconnects.
Login Time - Specifies the maximum amount of time users can be logged on
before automatically disconnected.
QoS – Allows use to specify the maximum total amount of upload and download
bandwidth allowed for guest authenticated users in Kbps.
OAuthentication 2.0
System > Authentication > VLAN # > OAuth 2.0
OAuthentication is an open standard for authorization for allowing users to authenticate
to third-party websites using their Microsoft, Google, Facebook, Twitter accounts etc.
without exposing their passwords. Additionally, these providers may allow for methods
of creating a custom walled garden/splash page. By default, Google and Facebook
provider entries have already been created but you may add more providers to the list.
Assuming you have the developer API account and splash page already set up with your
provider.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System, click on Authentication, and in the first entry VLAN 0, in the Action
column, and click on drop-down list and click OAuth 2.0. Review the settings and click
Save to apply the changes.
Create New Provider – Click this option to create a new provider if it is not listed
in the table.
Provider – Enter the provider name to easily identify.
Active – Enable or disable OAuth 2.0 authorization with the provider.
Client ID – Enter the client ID used with the provider.
Client Secret – Enter the client secret or password used with the provider.
Advanced – Click the Advanced button to specify the Scope, Auth URL, Token
URL, User Info URL, and Revoke URL used for the provider.
Walled URL – Enter in the URLs used for your walled garden with the providers
and click Add to add them to the list.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 56

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
53
POP3 Server
System > Authentication > VLAN # > POP3
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System, click on Authentication, and in the first entry VLAN 0, in the Action
column, and click on drop-down list and click POP3 Server. Review the settings and
click Save to apply the changes.
Service – Enable or disable POP3.
Display Name – Enter the name displayed for the POP3 user.
Host – Enter the server domain or IP address.
Port – Enter the port used for incoming POP3 traffic. Default for POP3 is port 110.
Connect Type – Click the drop-down and select the connection type used for
POP3 incoming services, none, STARTTLS, or SSL/TTL.
POP3 Server Test
Email – To test the POP3 server settings, enter the email address used to test the
settings.
Password – to test the POP3 server settings, enter the along with the email
account used to test the settings.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 57

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
54
Customize Page
System > Authentication > VLAN # > Customize Page
This section allows you to customize the captive portal login page using the default
template or apply your own code.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System, click on Authentication, and in the first entry VLAN 0, in the Action
column, and click on drop-down list and click Customize Page. Review the settings
and click Save to apply the changes.
Template – Enable or disable the built-in login page template. The preview area
will display a preview of the built-in login page. Disabling the template option will
allow you to enter in your own code for customization.
o Style – Select one the predefined color schemes for the built-in page
template.
o Body Background – Enter the HTML color code for the built-in login page
background.
o Content Background – Enter the HTML color code for the built-in login
page content area background.
o Font Color – Enter the HTML color code for the built-in login page font.
o Content Width – Enter the pixel width for the entire built-in login page.
o AD Background– Enter the HTML color code for the ad background.
o AD Font Color – Enter the HTML color code for the ad font.
Multiple Language – Enable or disable multiple languages on the built-in login
page. To define additional languages, go to System > Authentication > VLAN # >
Language.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 58

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
55
Multiple Language
System > Authentication > VLAN # > Multiple Language
This section allows you to create additional languages when using the multiple language
option for the built-in captive portal login page template.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System, click on Authentication, and in the first entry VLAN 0, in the Action
column, and click on drop-down list and click Multiple Language. Review the settings
and click Save to apply the changes.
Create New Language – By default, English has already been added to the list. To
create a new language, click this option and enter in the text strings for the new
language. The preview window will display the current built-in login page
template.
Walled Garden
System > Authentication > VLAN # > Walled Garden
This section can allow you to provide content such as advertisement web pages for
users to access the websites listed before login and authentication.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System, click on Authentication, and in the first entry VLAN 0, in the Action
column, and click on drop-down list and click Walled Garden. Review the settings and
click Add to add the entry to the walled garden list and click Save to apply the
changes.
Display Name – Enter display name to easily identify the wall garden entry.
IP Address/Domain: Enter the IP address or domain/URL of the website to add to
the walled garden.
Full URL: Enter the full URL or website name.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 59

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
56
Privilege Address
System > Authentication > VLAN # > Privilege Address
This section can allow you to set a privileged host addresses that may connect to your
network without the need for authentication.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System, click on Authentication, and in the first entry VLAN 0, in the Action
column, and click on drop-down list and click Privilege Address. Review the settings
and click Add to add the entry to the device list and click Save to apply the changes.
Device Name – Enter device name to easily identify device in the list.
IP Address: Enter the IP address of the privileged host device.
MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of the privileged host device.
Backup/Restore Authentication Profile & Customized Pages
System > Authentication > VLAN # > Profile
This section can allow you to backup/restore the authentication profile to your local
drive and also backup/store customized captive portal pages.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System, click on Authentication, and in the first entry VLAN 0, in the Action
column, and click on drop-down list and click Profile.
Download Profile Setting – Click download to back up the authentication profile
to your local drive.
Upload Profile Setting - Click Browse or Choose File to restore a previously
backed up authentication profile. Click Upload to start the restore process.
Download Customize Page – Click download to back up the customized captive
portal pages to your local drive.
Upload Customize Page - Click Browse or Choose File to restore a previously
backed up captive portal page. Click Upload to start the restore process.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 60
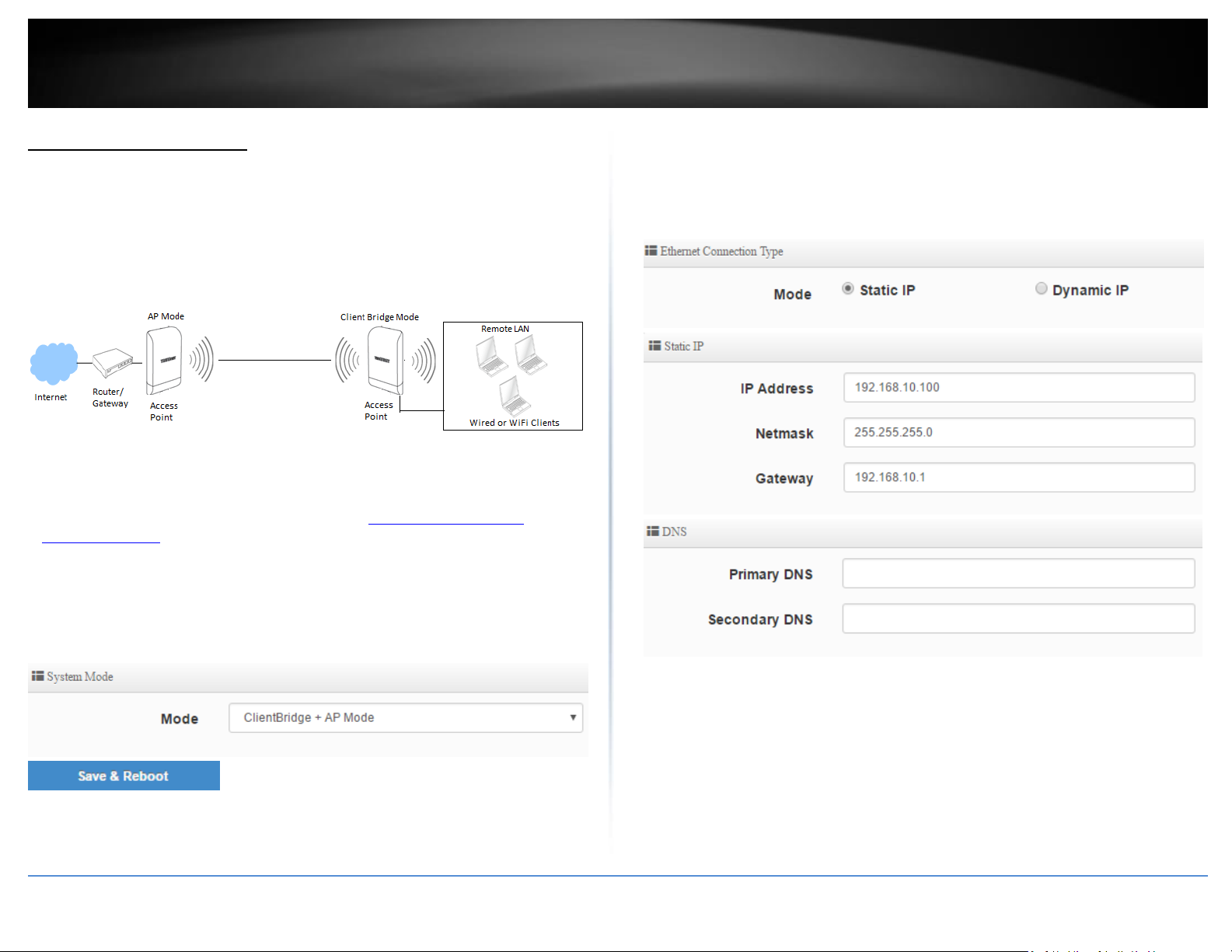
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
57
Client Bridge + AP Mode
Client Bridge mode functions similar to that of a wireless client adapter like the one built
into your notebook PC or mobile device. It wireless connects to a wireless network
provided by a wireless AP or router and bridges this connection to the device Ethernet
ports. Additionally, in Client Bridge mode, the device can function as an AP and create
another wireless network to also bridge over it’s connection from the wireless AP or
router.
Set the device IP address settings
System > LAN Setup
To set the IP address, gateway, and DNS settings, click on System and click on LAN
Setup. Click Save when you have completed your settings.
Set the device to Client Bridge + AP mode
System > Mode Setup
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on Mode Setup.
3. Select Client Bridge + AP Mode in the mode drop down list. Then click Save &
Reboot.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 61

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
58
Connect the device to your wireless network
Wireless > Station Setup
To connect to a wireless network, click on Wireless and click on Station Setup. In the AP
Station List, click on Site Survey to scan for your wireless network.
Find your wireless network and click Setup within the entry.
The AP Station Security Settings at the top left of the page will populate with the
information of the selected wireless network. If security is enabled on the wireless
network, enter the WPA/WPA2 PassPhrase or WEP key in the field provided. Scroll to
the bottom of the page and click Save when you have completed your settings and click
Reboot in the top right menu to reboot the device and commit the changes.
Configure your wireless network settings (WLAN)
Wireless > AP Setup
Verify you have established wireless bridged connectivity by attempting to
communicate to the Internet or access devices or network resources.
To configure the AP wireless settings to allow other wireless clients to connect, click on
Wireless and click on AP Setup. Click Save when you have completed your settings.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 62

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
59
WISP (CPE) + AP Mode
WISP (CPE) + AP mode is typically used to provide Internet connectivity to buildings in
remote areas where telco hard wired service lines for Internet service (such as DSL or
cable) are scarce or unavailable and Wireless Internet Service Providers (WISPs) are the
only means of establishing Internet connectivity. In this case, the device functions
similar to that of a router except the wireless interface of the AP serves the purpose of
WAN (Internet) connectivity to the WISP wireless network and NAT functions performed
between the wireless WAN connection to the WISP and the LAN (wired Ethernet ports
LAN1/2 and AP wireless WLAN network). Additionally, DHCP server, virtual server/DMZ,
MAC/IP filter functions will be available for access control similar to simple NAT router.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on Mode Setup.
3. Select WISP (CPE) + AP Mode in the mode drop down list. Then click Save & Reboot.
Set the device LAN IP address settings
System > LAN Setup
To set the IP address, gateway, and DNS settings, click on System and click on LAN
Setup. Click Save when you have completed your settings.
Configure the LAN DHCP Server
System > DHCP Setup
To setup the DHCP Server for LAN and WLAN clients, click on System and click on DHCP
Setup.
Mode – Enable or Disable the DHCP service.
Start IP: Enter the first IP address of the IP address range/pool to distribute to DHCP
client devices. (ex. 192.168.10.101)
End IP: Enter the last IP address of the IP address range/pool to distribute to DHCP
client devices. (ex. 192.168.10.199)
Netmask: Enter the subnet mask to distribute to DHCP client devices. (ex.
255.255.255.0)
Gateway: Enter the default gateway IP address to distribute to DHCP client devices.
This should typically be the LAN IP of the device when using WISP (CPE) + AP mode.
(ex. 192.168.10.100)
DNS1 IP: Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server to distribute to DHCP client
devices.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 63

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
60
DNS2 IP: Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS server to distribute to DHCP
client devices.
WINS IP: Enter the IP address of the WINS (Windows Internet Name Service) server
to distribute to DHCP client devices. Typically this is used on a Windows network to
allow the resolution of computer and device names.
Domain: Enter the domain name to distribute to DHCP client devices. (ex.
trendnet.com)
Lease Time: Enter the time in seconds how long DHCP client devices will retain their
settings assigned by the DHCP service before expiration. Upon expiration, DHCP
client devices will initiate new requests for DHCP client settings.
After the DHCP server settings have been configured and changes have been applied,
dynamic DHCP client leases will appear in the DHCP Client List table.
DHCP Reservation/Static Lease
System > DHCP Setup
Comment: Add a comment or name to help easily identify the device or purpose of
the DHCP static IP lease/reservation.
IP Address: Enter the IP address from the DHCP server IP address range/pool to
permanently assign. (ex. 192.168.10.20)
MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of the client device to assign the permanent
lease in the example format provided and click Add to add the static IP lease to the
list. (ex. 00:11:22:AA:BB:CC). Repeat to add additional static IP leases.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 64

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
61
Configure WAN connection settings for WISP
System > WAN Setup
To setup the WAN interface connection method to the WISP, click on System and click
on WAN Setup. The device supports Dynamic IP, Static IP, PPPoE, and PPTP connection
types. Click Save when you have completed the changes.
Note: Please check with your Wireless Internet Service Provider for the required
connection settings and configure them accordingly.
Static IP – Your WISP requires the IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, and
DNS Server IP address settings to be manually entered and statically assigned. If
required by your WISP, specify the MAC address for this interface.
Dynamic – Your WISP will automatically provide you the IP address, Subnet Mask,
Default Gateway, and DNS Server IP address settings. . If required by your WISP,
specify the MAC address for this interface.
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet)– Your WISP requires a specifically
assigned user name and password for authentication in order to establish
connectivity.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Procotol) - Your WISP requires a specifically
assigned user name and password for authentication in order to establish
connectivity similar to PPPoE but a different type of tunneling technology.
Find your wireless network and click Setup within the entry.
The AP Station Security Settings at the top left of the page will populate with the
information of the selected wireless network. If security is enabled on the wireless
network, enter the WPA/WPA2 PassPhrase or WEP key in the field provided. Scroll to
the bottom of the page and click Save when you have completed your settings and click
Reboot in the top right menu to reboot the device and commit the changes.
Connect to your WISP (Wireless Internet Service Provider)
Wireless > Station Setup
To connect to your WISP wireless network to establish Internet connectivity, click on
Wireless and click on Station Setup. In the AP Station List, click on Site Survey to scan
for your wireless network.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 65

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
62
Verify you have established wireless connectivity by attempting to communicate to the
Internet.
To configure the AP wireless settings to allow other wireless clients to connect, click on
Wireless and click on AP Setup. Click Save when you have completed your settings.
Note: Make the computer or network device (for which you are establishing a DMZ link)
has a static IP address or static DHCP Lease.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Advance and click on DMZ.
3. Review the settings below. Click Save when completed.
Automatic Assignment – This option allows you to assign only one DMZ host and
forward all traffic requests received on the WAN side to a single LAN IP address.
o Internal IP Address – Enter the LAN IP address to set as the DMZ host to
forward all traffic.
Static Assignment – If you have multiple WAN static IP addresses assigned by
your Internet provider, this option allows you to assign multiple DMZ hosts and
map them to specific static public/external IP addresses.
o External IP Address – Enter the external public static IP address to map to
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone)
Advance > DMZ
You may want to expose a specific computer or device on your network to the Internet
to allow anyone to access it. The DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) feature that makes all the
ports and services available on the WAN/Internet side and forwards them to a single
LAN IP address (computer or network device) on your network. The DMZ feature is an
easy way of allowing access from the Internet however, it is a very insecure technology
and will open local area network to greater threats from Internet attacks.
It is strongly recommended to use Virtual Server to allow access to your computers or
network devices from the Internet.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
the internal LAN IP address.
o Internal IP Address – Enter the LAN IP address to set as the DMZ host to
forward all traffic.
Page 66

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
63
IP Filter
Advance > IP Filter
The IP filter function allows or denies services (or TCP/UDP ports or ICMP) based on
source and destination IP address.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Advance and click on IP Filter.
3. In the first IP filter rule entry in the list. Click Edit.
Range: 1:65535)
Listen – Enable or disable filtering only TCP packet that contain the SYN flag. (TCP
only).
Interface – Choose the interface the IP filter applies, LAN or WAN.
Schedule – You can specify a schedule under Advance > Time Policy when IP filter
rule is active.
MAC Filter
Advance > MAC Filter
The MAC Filter function allows or denies traffic based on device MAC addresses.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
4. Review the settings below. Click Save when completed.
Active – Enable or disable the IP Filter rule.
Comment – Enter a name for the rule so it can easily be identified.
Policy:
o Deny – This option blocks the port/protocol specified in the rule between
source and destination IP address.
o Pass – This option allows the port/protocol specified in the rule between
source and destination IP address.
In/Out – Specify the traffic direction to apply the filter. In means ingress or
2. Click Advance and click on MAC Filter.
3. Choose the Mode.
Deny – Denies traffic from all specified MAC addresses in the list and allows all
others. (Blacklist)
Allow – Allows traffic from all specified MAC addresses in the list and denies all
others. (Whitelist)
inbound. Out means egress or outbound.
Protocol – Specify the port/protocol to deny or allow.
o ALL – Specifies all TCP/UDP ports and ICMP traffic.
o TCP – Specifies TCP protocol only.
o UDP – Specifies UDP protocol only.
o ICMP – Specifies ICMP traffic only.
Source Address/Mask – Enter the source IP address/Subnet Mask (CIDR). (ex.
192.168.10.15/32 specifies only IP address 192.168.10.15, Any: 0.0.0.0/0)
Source Port – Enter the source port number to apply the filter. (ex. Port Range:
1:65535)
Destination Address/Mask – Enter the destination IP address/Subnet Mask
4. In the MAC Filter List, review the settings below and click Save to apply changes.
Active – Check this option to enable the entry.
Comment – Enter a name for the rule so it can easily be identified.
MAC Address – Enter the MAC address to deny or allow. (00:11:22:AA:BB:CC)
Policy – You can specify a schedule under Advance > Time Policy when the MAC
filter rule is active.
(CIDR). (ex. 10.10.10.30/32)
Destination Port – Enter the destination port number to apply the filter. (ex. Port
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 67

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
64
Virtual Server
Advance > Virtual Server
Virtual Server (also called port forwarding) allows you to define specific ports (used or
required by a specific application) and forward them to a single IP address (a computer
or device) on your network. Using this feature is more secure compared to using DMZ in
which DMZ forwards all ports instead of only specific ports used by an application. An
example would be forwarding a port to an IP camera (TRENDnet IP cameras default to
HTTP TCP port 80 for remote access web requests) on your network to be able to view it
over the Internet.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Advance and click on Virtual Server.
3. In the first Virtual Server entry in the list. Click Edit.
4. Review the settings and click Save when changes are completed.
Active – Enable or disable the virtual server.
Comment – Enter a name for the virtual server so it can easily be identified.
Protocol – Select the protocol required for your device. TCP or UDP.
Public Port – Enter the port number used to access the device from the Internet.
Private IP Address - Enter the IP address of the device to forward the port (e.g.
192.168.10.101).
Private Port – Enter the port number required by your device. Refer to the
connecting device’s documentation for reference to the network port(s) required.
Note: The Public Port can be assigned a different port number than the Private
Port (also known as port redirection), however it is recommended to use the same
port number for both settings. Please refer to the device documentation to
determine which ports and protocols are required. It is recommended to assign a
static IP address to the device or use Static IP Reservation to ensure the IP address
of the device does not change.
Schedule – You can specify a schedule under Advance > Time Policy when Virtual
Server is active.
Access Control
Advance > Access Control
The Access Control function can block TCP/UDP ports and ICMP traffic based on MAC
address and/or IP address but also includes content filtering functions such as URL
blocking, Keyword blocking, and also blocking specific applications. (Listed
applications only)
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Advance and click on Access Control.
3. In the first Access Control entry in the list. Click Edit.
4. Review the settings and click Save when changes are completed.
Active – Enable or disable the access control rule.
Comment – Enter a name for the access control rule it can easily be identified.
Protocol:
o ANY – Block TCP, UDP, and ICMP.
o TCP – Block TCP protocol only.
o UDP – Block UDP protocol only.
o ICMP – Block ICMP traffic only.
o Content Filter – Block web content based on Keyword. Specify the
keywords in the Keyword field and click Add to add them to the list.
o Application – Block applications specified in the predefined list. Select
specified applications to block in the application drop-down list.
o Domain Filter – Block specific web pages. (HTTP only). Specify the
URLs/Domains to block in the Domain field and click Add to add them
to the list.
Schedule - You can specify a schedule under Advance > Time Policy when the
Access Control rule is active.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 68

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
65
MAC Address – Enter the device MAC address to apply the access control rule.
(ex. 00:11:22:AA:BB:CC) and click Add to add it to the list. You can apply the rule
to multiple MAC addresses.
IP Address Setup
o Local IP Address – Enter the IP address range to apply the rule.
o Local Port – Enter the local port number.
o Destination IP Address – Enter the destination IP address to apply the
rule.
o Destination Port – Enter the destination port number.
Time Policy / Schedule
Advance > Time Policy
For additional security control, you can create schedules to specify a time period when a
feature should be activated or deactivated. Before you use the scheduling feature,
ensure that your device/system time is configured correctly under System > Time
Server.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Advance and click on Time Policy.
3. In the first Time Policy entry in the list. Click Edit.
4. Review the settings and click Save when changes are completed.
Comment – Enter a name for the time policy so it can be easily identified.
Mode:
o On Schedule: For the rule used, the schedule will be activated during
the time period defined in the schedule and deactivated any time
period outside of the defined schedule.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 69

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
66
o Out of Schedule: For the rule used, the schedule will be deactivated
during the time period defined in the schedule and activated any time
period outside of the defined schedule.
In the Policy List, click Create New Policy.
Days of Week – Tick the days to apply to the time policy.
Start Time – Define the start time for the time policy. (24-hr format)
End Time – Define the end time for the time policy. (24-hr format)
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 70

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
67
Router Mode
Router Mode functions as a wireless NAT router. LAN2 functions as the primary LAN
interface and LAN1 functions as the WAN interface. VLANs are configurable on the LAN
side and access control functions such as DMZ/Virtual Server, and IP/MAC/Domain
filters are available in this mode.
Set the device LAN IP address settings
System > VLAN Setup > VLAN 0 > Network
To set the IP address, gateway, and DNS settings, click on System and click on VLAN
Setup. You can configure the Default Gateway IP address and DNS addresses on this
page. For the LAN IP address, within the first entry in the list VLAN 0, click on Network.
Click Save when you have completed your settings.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on Mode Setup.
3. Select Router in the mode drop down list. Then click Save & Reboot.
Configure the LAN DHCP Server
System > VLAN Setup > VLAN 0 > DHCP Server
To setup the DHCP Server for LAN and WLAN clients, click on System and click on VLAN
Setup. Within the first entry in the list, VLAN 0, click the arrow next to Network, and
click on DHCP Server.
Mode – Enable or Disable the DHCP service.
Start IP: Enter the first IP address of the IP address range/pool to distribute to DHCP
client devices. (ex. 192.168.10.101)
End IP: Enter the last IP address of the IP address range/pool to distribute to DHCP
client devices. (ex. 192.168.10.199)
Netmask: Enter the subnet mask to distribute to DHCP client devices. (ex.
255.255.255.0)
Gateway: Enter the default gateway IP address to distribute to DHCP client devices.
This should typically be the LAN IP of the device when using WISP (CPE) + AP mode.
(ex. 192.168.10.100)
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 71

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
68
DNS1 IP: Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server to distribute to DHCP client
devices.
DNS2 IP: Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS server to distribute to DHCP
client devices.
WINS IP: Enter the IP address of the WINS (Windows Internet Name Service) server
to distribute to DHCP client devices. Typically this is used on a Windows network to
allow the resolution of computer and device names.
Domain: Enter the domain name to distribute to DHCP client devices. (ex.
trendnet.com)
Lease Time: Enter the time in seconds how long DHCP client devices will retain their
settings assigned by the DHCP service before expiration. Upon expiration, DHCP
client devices will initiate new requests for DHCP client settings.
After the DHCP server settings have been configured and changes have been applied,
dynamic DHCP client leases will appear in the DHCP Client List table.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 72

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
69
DHCP Reservation/Static Lease
System > DHCP Setup
Comment: Add a comment or name to help easily identify the device or purpose of
the DHCP static IP lease/reservation.
IP Address: Enter the IP address from the DHCP server IP address range/pool to
permanently assign. (ex. 192.168.10.20)
MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of the client device to assign the permanent
lease in the example format provided and click Add to add the static IP lease to the
list. (ex. 00:11:22:AA:BB:CC). Repeat to add additional static IP leases.
Configure WAN connection settings
System > WAN Setup
To setup the WAN interface connection method for the LAN1 Ethernet interface, click
on System and click on WAN Setup. The device supports Dynamic IP, Static IP, PPPoE,
and PPTP connection types. Click Save when you have completed the changes.
Note: Please check with your Internet Service Provider for the required connection
settings and configure them accordingly.
Static IP – Your ISP requires the IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, and
DNS Server IP address settings to be manually entered and statically assigned. If
required by your ISP, specify the MAC address for this interface.
Dynamic – Your ISP will automatically provide you the IP address, Subnet Mask,
Default Gateway, and DNS Server IP address settings. . If required by your WISP,
specify the MAC address for this interface.
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet)– Your ISP requires a specifically
assigned user name and password for authentication in order to establish
connectivity.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Procotol) - Your ISP requires a specifically
assigned user name and password for authentication in order to establish
connectivity similar to PPPoE but a different type of tunneling technology.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Verify you have established wireless connectivity by attempting to communicate to the
Internet.
Page 73

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
70
To setup the DHCP Server for LAN and WLAN clients, click on System and click on VLAN
Setup. Within the first entry in the list, VLAN 0, click the arrow next to Network, and
click on DHCP Server.
To configure the AP wireless settings to allow other wireless clients to connect, click on
System and click on VLAN Setup. Within the first entry in the list, VLAN 0, click the
arrow next to Network, and click on Access Point. Click Save when you have completed
your settings.
It is strongly recommended to use Virtual Server to allow access to your computers or
network devices from the Internet.
Note: Make the computer or network device (for which you are establishing a DMZ link)
has a static IP address or static DHCP Lease.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Advance and click on DMZ.
3. Review the settings below. Click Save when completed.
Automatic Assignment – This option allows you to assign only one DMZ host and
forward all traffic requests received on the WAN side to a single LAN IP address.
o Internal IP Address – Enter the LAN IP address to set as the DMZ host to
forward all traffic.
Static Assignment – If you have multiple WAN static IP addresses assigned by
your Internet provider, this option allows you to assign multiple DMZ hosts and
map them to specific static public/external IP addresses.
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone)
Advance > DMZ
You may want to expose a specific computer or device on your network to the Internet
to allow anyone to access it. The DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) feature that makes all the
ports and services available on the WAN/Internet side and forwards them to a single
LAN IP address (computer or network device) on your network. The DMZ feature is an
easy way of allowing access from the Internet however, it is a very insecure technology
and will open local area network to greater threats from Internet attacks.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
o External IP Address – Enter the external public static IP address to map to
the internal LAN IP address.
o Internal IP Address – Enter the LAN IP address to set as the DMZ host to
forward all traffic.
Page 74

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
71
IP Filter
Advance > IP Filter
The IP filter function allows or denies services (or TCP/UDP ports or ICMP) based on
source and destination IP address.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Advance and click on IP Filter.
3. In the first IP filter rule entry in the list. Click Edit.
Range: 1:65535)
Listen – Enable or disable filtering only TCP packet that contain the SYN flag. (TCP
only).
Interface – Choose the interface the IP filter applies, LAN or WAN.
Schedule – You can specify a schedule under Advance > Time Policy when IP filter
rule is active.
MAC Filter
Advance > MAC Filter
The MAC Filter function allows or denies traffic based on device MAC addresses.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
4. Review the settings below. Click Save when completed.
Active – Enable or disable the IP Filter rule.
Comment – Enter a name for the rule so it can easily be identified.
Policy:
o Deny – This option blocks the port/protocol specified in the rule between
source and destination IP address.
o Pass – This option allows the port/protocol specified in the rule between
source and destination IP address.
In/Out – Specify the traffic direction to apply the filter. In means ingress or
2. Click Advance and click on MAC Filter.
3. Choose the Mode.
Deny – Denies traffic from all specified MAC addresses in the list and allows all
others. (Blacklist)
Allow – Allows traffic from all specified MAC addresses in the list and denies all
others. (Whitelist)
inbound. Out means egress or outbound.
Protocol – Specify the port/protocol to deny or allow.
o ALL – Specifies all TCP/UDP ports and ICMP traffic.
o TCP – Specifies TCP protocol only.
o UDP – Specifies UDP protocol only.
o ICMP – Specifies ICMP traffic only.
Source Address/Mask – Enter the source IP address/Subnet Mask (CIDR). (ex.
192.168.10.15/32 specifies only IP address 192.168.10.15, Any: 0.0.0.0/0)
Source Port – Enter the source port number to apply the filter. (ex. Port Range:
1:65535)
Destination Address/Mask – Enter the destination IP address/Subnet Mask
4. In the MAC Filter List, review the settings below and click Save to apply changes.
Active – Check this option to enable the entry.
Comment – Enter a name for the rule so it can easily be identified.
MAC Address – Enter the MAC address to deny or allow. (00:11:22:AA:BB:CC)
Policy – You can specify a schedule under Advance > Time Policy when the MAC
filter rule is active.
(CIDR). (ex. 10.10.10.30/32)
Destination Port – Enter the destination port number to apply the filter. (ex. Port
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 75

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
72
Virtual Server
Advance > Virtual Server
Virtual Server (also called port forwarding) allows you to define specific ports (used or
required by a specific application) and forward them to a single IP address (a computer
or device) on your network. Using this feature is more secure compared to using DMZ in
which DMZ forwards all ports instead of only specific ports used by an application. An
example would be forwarding a port to an IP camera (TRENDnet IP cameras default to
HTTP TCP port 80 for remote access web requests) on your network to be able to view it
over the Internet.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Advance and click on Virtual Server.
3. In the first Virtual Server entry in the list. Click Edit.
4. Review the settings and click Save when changes are completed.
Active – Enable or disable the virtual server.
Comment – Enter a name for the virtual server so it can easily be identified.
Protocol – Select the protocol required for your device. TCP or UDP.
Public Port – Enter the port number used to access the device from the Internet.
Private IP Address - Enter the IP address of the device to forward the port (e.g.
192.168.10.101).
Private Port – Enter the port number required by your device. Refer to the
connecting device’s documentation for reference to the network port(s) required.
Note: The Public Port can be assigned a different port number than the Private
Port (also known as port redirection), however it is recommended to use the same
port number for both settings. Please refer to the device documentation to
determine which ports and protocols are required. It is recommended to assign a
static IP address to the device or use Static IP Reservation to ensure the IP address
of the device does not change.
Schedule – You can specify a schedule under Advance > Time Policy when Virtual
Server is active.
Access Control
Advance > Access Control
The Access Control function can block TCP/UDP ports and ICMP traffic based on MAC
address and/or IP address but also includes content filtering functions such as URL
blocking, Keyword blocking, and also blocking specific applications. (Listed
applications only)
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Advance and click on Access Control.
3. In the first Access Control entry in the list. Click Edit.
4. Review the settings and click Save when changes are completed.
Active – Enable or disable the access control rule.
Comment – Enter a name for the access control rule it can easily be identified.
Protocol:
o ANY – Block TCP, UDP, and ICMP.
o TCP – Block TCP protocol only.
o UDP – Block UDP protocol only.
o ICMP – Block ICMP traffic only.
o Content Filter – Block web content based on Keyword. Specify the
keywords in the Keyword field and click Add to add them to the list.
o Application – Block applications specified in the predefined list. Select
specified applications to block in the application drop-down list.
o Domain Filter – Block specific web pages. (HTTP only). Specify the
URLs/Domains to block in the Domain field and click Add to add them
to the list.
Schedule - You can specify a schedule under Advance > Time Policy when the
Access Control rule is active.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 76

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
73
MAC Address – Enter the device MAC address to apply the access control rule.
(ex. 00:11:22:AA:BB:CC) and click Add to add it to the list. You can apply the rule
to multiple MAC addresses.
IP Address Setup
o Local IP Address – Enter the IP address range to apply the rule.
o Local Port – Enter the local port number.
o Destination IP Address – Enter the destination IP address to apply the
rule.
o Destination Port – Enter the destination port number.
Time Policy / Schedule
Advance > Time Policy
For additional security control, you can create schedules to specify a time period when a
feature should be activated or deactivated. Before you use the scheduling feature,
ensure that your device/system time is configured correctly under System > Time
Server.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click Advance and click on Time Policy.
3. In the first Time Policy entry in the list. Click Edit.
4. Review the settings and click Save when changes are completed.
Comment – Enter a name for the time policy so it can be easily identified.
Mode:
o On Schedule: For the rule used, the schedule will be activated during
the time period defined in the schedule and deactivated any time
period outside of the defined schedule.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 77

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
74
o Out of Schedule: For the rule used, the schedule will be deactivated
during the time period defined in the schedule and activated any time
period outside of the defined schedule.
In the Policy List, click Create New Policy.
End Time – Define the end time for the time policy. (24-hr format)
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 78

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
75
CAP (Control AP) Mode
CAP mode functions in AP mode but in addition, this mode allows you to manage,
monitor, and control other APs using the same firmware/software. You can configure
multiple settings for multiple APs at the same time, push out batch firmware upgrades
from one convenient GUI interface. The CAP Mode AP can discover and manage any CAP
mode compatible APs on any of interfaces including WDS bridged links. Note: Currently,
the only TRENDnet TEW-740APBO (H/W: v2.XR) is CAP mode firmware/software
compatible.
The diagram below displays of a group of CAP mode firmware/software compatible APs
either connected through the wired network interfaces or WDS link. One AP is
configured in CAP mode is able to discover and centrally manage all other APs in this
example scenario.
1. Log into your access point management page (see “Access your access point
management page” on page 28).
2. Click System and click on Mode Setup.
3. Select CAP Mode in the mode drop down list. Then click Save & Reboot.
In the top menu, a new section will be available called AP Control.
Note: You can reference the all the AP mode functions and settings in the AP mode
section. This section will primarily cover the CAP mode features only.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 79

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
76
Scan and Import CAP Mode compatible APs
AP Control > Scan Device
This function allows you to scan for CAP mode compatible remote APs that are available
for management.
Note: Please note that the Control Port function must be enabled on the remote access
points in order for the remote AP to be manageable by the AP set to CAP mode.
Click AP Control and click on Scan Device.
In the Filter Device section, enter the criteria to narrow the scope of discovery.
VLAN# – Click the drop-down to select which VLAN to scan for available APs. If
you have multiple VLAN interfaces configured on the AP, these VLANs will be
available in the drop-down.
Default Password- Enter the default administrator password for the remote APs.
By default, TRENDnet APs use default password: admin. If you are using the kit
(TEW-740APBO2K H/W: v2.0R), the default password will be a unique predefined
administrator password found on the device label or wireless settings sticker.
Sort – Click the drop-down list and select which parameter to use to sort the APs
in the Scan Result list, IP Address or MAC Address
After you have discovered the manageable APs, the Update IP Address & Netmask
section will allow you to assign batch IP address and subnet mask configuration to all of
the APs discovered.
Control Port – Click the drop-down list to select which VLAN and IP subnet the
APs can be managed. By default, TRENDnet APs have the Control Port capability
enabled on native VLAN 0 under the 192.168.10.0/24 IP subnet.
VLAN – If VLAN tagging is enabled on the remote APs along with the control port
feature, check the option and add the correct VLAN tag for the management
VLAN to access the APs. Note: By default, TRENDnet APs have management
enabled on native VLAN 0, untagged VLAN interface.
IP Address – Enter the starting IP address to assign to the listed APs. IP addressing
will automatically assign and auto increment the IP assignment by one for each
AP.
Netmask – Enter the subnet mask to assign to the APs.
To add the AP to the managed list, check the entry under the Device column and click
on Import to add the AP to the managed list.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 80

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
77
Modify and view your managed AP list
AP Control > AP Setup
In this section, you can view the currently managed APs, remove APs, reboot, or
configure settings such as group assignment, IP address, password and GUI HTTP port.
Click AP Control and click on AP Setup. The list displays all of the imported APs to
manage. From the managed AP list, you can delete or reboot the APs in the list. To
select multiple APs, tick the option under the Device column.
For the selected AP entry, click on Setup.
You can change the management settings used to access the AP such as AP group
assignment, IP address, administrator password. Click Save to apply the changes.
Batch Configuration Settings
AP Control > Batch Setup
This section allows you to apply configuration change to multiple APs by VLAN group
including batch configuration and firmware upgrade.
Click AP Control and click on Batch Setup.
VLAN – Select the VLAN group you would like to apply changes. Once selected,
the APs part of the selected VLAN group will appear under the Device List. You
can check which APs in the list you would like to apply the configuration settings.
Group – Click the drop-down list to select the group name assignment. You can
create groups by VLAN under AP Control > Group Setup.
Batch Setup – Click the drop-down list and select which configuration settings to
configure and assign to the selected APs. Enter the settings you would like to
apply, then click Apply to apply the configuration to the seleted APs.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 81

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
78
Group Setup
AP Control > Group Setup
This section allows you to create specific AP groups for batch configuration to be
applied.
Click AP Control and click on Map Setup. Click Create New Map. Click Save to save the
new map reference.
Map Name –Enter a name to identify this map.
Image URL – Enter the URL location of the image to use.
Description – Enter a brief text description to help further provide detail about
the map.
Image – After the correct image URL has been provided, click View to view the
map.
Map Setup
AP Control > Map Setup
This section allows you to reference online maps to help you identify AP deployment
areas and locations. Please note that you can only reference and view maps from
interface only. Map editing is not supported. You will need to create and edit your map
using another third party software.
Click AP Control and click on Map Setup. Click Create New Map. Click Save to save the
new map reference.
Map Name –Enter a name to identify this map.
Image URL – Enter the URL location of the image to use.
Description – Enter a brief text description to help further provide detail about
the map.
Image – After the correct image URL has been provided, click View to view the
map.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 82

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
79
Authentication Profile
AP Control > Authentication Profile
If you are using the AP authentication feature across multiple APs, this section allows
you to create authentication profiles to apply per VLAN to multiple APs through the
Batch Setup section.
Click AP Control and click on Authentication Profile. Click Create New Profile. Click Save
to save the new authentication profile.
Profile Name –Enter a name to identify this authentication profile.
Description – Enter a brief text description to help further provide detail about
the profile.
After you have created the new profile, in the entry in the list, click on the drop-down
arrow next to Authentication. You’ll be able to create the customized authentication
settings for the newly created profile. After you created your customized authentication
profile, the profile can be applied to multiple APs under AP Control > Batch Setup.
Managed AP Status
AP Control > Status
This section provides status information about all of the current APs managed by the
CAP mode AP.
Click AP Control and click on Status.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 83

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
80
Technical Specifications
Standards
IEEE 802.3
IEEE 802.3u
IEEE 802.1d
IEEE 802.1p
IEEE 802.1Q
IEEE 802.1X
IEEE 802.11d
IEEE 802.11e
IEEE 802.11f
IEEE 802.11h
IEEE 802.11i
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n (2.4 GHz up to 300 Mbps)
IEEE 802.11r
IEEE 802.11k
Wireless encryption: WPA/WPA2-PSK, WPA/WPA2-Enterprise, 802.1X
Firewall (CPE Mode): NAT, Virtual Server, DMZ Host, PPTP/L2TP/IPsec VPN
Passthrough
Access Controls: MAC, IP Filter, Layer 2 Client Isolation, Per-SSID client limiting
802.1Q VLAN
OAuthentication 2.0 / Walled Garden for guest authentication
Customizable Captive Portal for guest authentication
QoS
WMM
Operation Modes
Access Point (AP)
Access Point (AP) + WDS
Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
WISP (CPE) + AP
Client Bridge + AP
Router
Control AP (CAP)
Hardware Interface
1 x 10/100 Mbps LAN1 port (proprietary PoE max. cable length 60 m (197 ft.))
1 x 10/100 Mbps LAN2 port
LED indicators
Reset button
Grounding Point
Special Features
IPX6 weather rated
802.1Q VLAN assignment per SSID
Schedule radio on/off time policy
802.11r / 802.11k fast roaming
Access Control
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
SSID
Up to 7 SSIDs
Internet Connection Types (WISP (CPE) + AP & Router modes)
Dynamic IP (DHCP)
Static IP (Fixed)
PPPoE (Dynamic IP/Static IP)
PPTP (Dynamic IP/Static IP)
Management/Monitoring
Local/remote web based management (HTTP, HTTPS)
Local/remote CLI based management (Telnet, SSH)
SNMP v2c/v3
SNMP Trap
Upgrade firmware
Page 84

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
81
Backup/restore configuration
Event logging
Authentication log
Reboot
Restore to factory defaults
Ping test
Traceroute
LED Control
Frequency
FCC: 2.412 - 2.462 GHz
ETSI: 2.412 – 2.472 GHz
IC: 2.412 - 2.462 GHz
Wireless Channels
FCC: 1-11
ETSI: 1-13
Modulation
802.11b: DBPK, DQPSK, CCK with DSSS
802.11g/n: BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM with OFDM
Media Access Protocol
CSMA/CA with ACK
802.11n: FCC/ETSI: FCC: 26 dBm (max.), ETSI: 10.6 dBm (max.), IC: 26 dBm
(max.)/- 69 dBm (typical) @ 300 Mbps
Power
Input: 100 – 220 V, 50 - 60 Hz, 0.5 A
Output: 12V / 1A
Consumption: 13.5 Watts Max.
Operating Temperature
-20 - 60° C (-4 - 140° F)
Operating Humidity
Max. 99 % non-condensing
Certifications
CE
FCC
Dimensions
195 x 118 x 61 mm (7.6 x 4.6 x 2.4 in.)
Antenna Gain
10 dBi internal sector antenna
Wireless Output Power/Receiving Sensitivity
802.11b: FCC/ETSI: FCC: 28 dBm (max.), ETSI: 10.4 dBm (max.), IC: 28 dBm
(max.)/-88 dBm (typical) @ 11 Mbps
802.11g: FCC/ETSI: FCC: 26 dBm (max.), ETSI: 10.5 dBm (max.), IC: 26 dBm
(max.)/- 74 dBm (typical) @ 54 Mbps
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Weight
320 g (0.7 lbs.)
Disclaimer
* Effective wireless coverage may vary depending on the wireless device's output power, antenna
gain, antenna alignment, receiving sensitivity, and radio interference. Additionally, environmental
factors such as weather conditions, physical obstacles, and other considerations may affect
performance. For optimal results, we recommended consulting a professional installer for site
survey, safety precautions, and proper installation.
Page 85

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
82
Appendix
How to find your IP address?
Note: Please note that although the following procedures provided to follow for your
operating system on configuring your network settings can be used as general
guidelines, however, it is strongly recommended that you consult your computer or
operating system manufacturer directly for assistance on the proper procedure for
configuring network settings.
Command Prompt Method
Windows 2000/XP/Vista/7/8.1/10
1. On your keyboard, press Windows Logo+R keys simultaneously to bring up the Run
dialog box.
2. In the dialog box, type cmd to bring up the command prompt.
3. In the command prompt, type ipconfig /all to display your IP address settings.
MAC OS X
1. Navigate to your Applications folder and open Utilities.
2. Double-click on Terminal to launch the command prompt.
3. In the command prompt, type ipconfig getifaddr <en0 or en1> to display the wired
or wireless IP address settings.
Note: en0 is typically the wired Ethernet and en1 is typically the wireless Airport
interface.
Graphical Method
MAC OS 10.6/10.5
1. From the Apple menu, select System Preferences.
2. In System Preferences, from the View menu, select Network.
3. In the Network preference window, click a network port (e.g., Ethernet, AirPort,
modem). If you are connected, you'll see your IP address settings under "Status:"
MAC OS 10.4
1. From the Apple menu, select Location, and then Network Preferences.
2. In the Network Preference window, next to "Show:", select Network Status. You'll see
your network status and your IP address settings displayed.
Note: If you are experiencing difficulties, please contact your computer or operating
system manufacturer for assistance.
How to configure your network settings to obtain an IP address automatically or use
DHCP?
Note: Please note that although the following procedures provided to follow for your
operating system on configuring your network settings can be used as general
guidelines, however, it is strongly recommended that you consult your computer or
operating system manufacturer directly for assistance on the proper procedure for
configuring network settings.
Windows 7/8.1/10
a. Go into the Control Panel, click Network and Sharing Center.
b. Click Change Adapter Settings, right-click the Local Area Connection icon.
c. Then click Properties and click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
d. Then click Obtain an IP address automatically and click OK.
Windows Vista
a. Go into the Control Panel, click Network and Internet.
b. Click Manage Network Connections, right-click the Local Area Connection
icon and click Properties.
c. Click Internet Protocol Version (TCP/IPv4) and then click Properties.
d. Then click Obtain an IP address automatically and click OK.
Windows XP/2000
a. Go into the Control Panel, double-click the Network Connections icon
b. Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and the click Properties.
c. Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
d. Then click Obtain an IP address automatically and click OK.
MAC OS 10.4/10.5/10.6
a. From the Apple, drop-down list, select System Preferences.
b. Click the Network icon.
c. From the Location drop-down list, select Automatic.
d. Select and view your Ethernet connection.
In MAC OS 10.4, from the Show drop-down list, select Built-in
Ethernet and select the TCP/IP tab.
In MAC OS 10.5/10.6, in the left column, select Ethernet.
e. Configure TCP/IP to use DHCP.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 86

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
83
In MAC 10.4, from the Configure IPv4, drop-down list, select Using
DHCP and click the Apply Now button.
In MAC 10.5, from the Configure drop-down list, select Using DHCP
and click the Apply button.
In MAC 10.6, from the Configure drop-down list, select Using DHCP
and click the Apply button.
f. Restart your computer.
Note: If you are experiencing difficulties, please contact your computer or operating
system manufacturer for assistance.
How to configure your network settings to use a static IP address?
Note: Please note that although the following procedures provided to follow for your
operating system on configuring your network settings can be used as general
guidelines, however, it is strongly recommended that you consult your computer or
operating system manufacturer directly for assistance on the proper procedure for
configuring network settings.
Windows 7/8.1/10
a. Go into the Control Panel, click Network and Sharing Center.
b. Click Change Adapter Settings, right-click the Local Area Connection icon.
c. Then click Properties and click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
d. Then click Use the following IP address, and assign your network adapter a
static IP address. Click OK
Windows Vista
a. Go into the Control Panel, click Network and Internet.
b. Click Manage Network Connections, right-click the Local Area Connection
icon and click Properties.
c. Click Internet Protocol Version (TCP/IPv4) and then click Properties.
d. Then click Use the following IP address, and assign your network adapter a
static IP address. Click OK
Windows XP/2000
a. Go into the Control Panel, double-click the Network Connections icon
b. Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and the click Properties.
c. Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
MAC OS 10.4/10.5/10.6
How to find your MAC address?
In Windows 2000/XP/Vista/7/8,
Your computer MAC addresses are also displayed in this window, however, you can type
getmac –v to display the MAC addresses only.
In MAC OS 10.4,
1. Apple Menu > System Preferences > Network
2. From the Show menu, select Built-in Ethernet.
3. On the Ethernet tab, the Ethernet ID is your MAC Address.
In MAC OS 10.5/10.6,
1. Apple Menu > System Preferences > Network
2. Select Ethernet from the list on the left.
3. Click the Advanced button.
3. On the Ethernet tab, the Ethernet ID is your MAC Address.
d. Then click Use the following IP address, and assign your network adapter a
static IP address. Click OK
a. From the Apple, drop-down list, select System Preferences.
b. Click the Network icon.
c. From the Location drop-down list, select Automatic.
d. Select and view your Ethernet connection.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 87

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
84
How do I use the ping tool to check for network device connectivity?
Windows 2000/XP/Vista/7/8.1/10
1. On your keyboard, press Windows Logo+R keys simultaneously to bring up the Run
dialog box.
2. In the dialog box, type cmd to bring up the command prompt.
3. In the command prompt, type ping <ip_address> with the <ip_address> being the IP
address you want ping and check for connectivity.
Example: Usage of ping command and successful replies from device.
C:\Users>ping 192.168.10.100
Pinging 192.168.10.100 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.10.100: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
Reply from 192.168.10.100: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
Reply from 192.168.10.100: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
Reply from 192.168.10.100: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
Ping statistics for 192.168.10.100:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
MAC OS X
1. Navigate to your Applications folder and open Utilities.
2. Double-click on Terminal to launch the command prompt.
3. In the command prompt, type ping –c <#> <ip_address> with the <#> ping being the
number of time you want to ping and the <ip_address> being the IP address you want
ping and check for connectivity.
Example: ping –c 4 192.168.10.100
How to connect to a wireless network using the built-in Windows utility?
Note: Please note that although the following procedures provided to follow for your
operating system on configuring your network settings can be used as general
guidelines, however, it is strongly recommended that you consult your computer or
operating system manufacturer directly for assistance on the proper procedure for
connecting to a wireless network using the built-in utility.
Windows 7/8.1/10
1. Open Connect to a Network by clicking the network icon ( or ) in the notification
area.
2. In the list of available wireless networks, click the wireless network you would like to
connect to, then click Connect.
4. You may be prompted to enter a security key in order to connect to the network.
5. Enter in the security key corresponding to the wireless network, and click OK.
Windows Vista
1. Open Connect to a Network by clicking the Start Button. and then click Connect
To.
2. In the Show list, click Wireless.
3. In the list of available wireless networks, click the wireless network you would like to
connect to, then click Connect.
4. You may be prompted to enter a security key in order to connect to the network.
5. Enter in the security key corresponding to the wireless network, and click OK.
Windows XP
1. Right-click the network icon in the notification area, then click View Available
Wireless Networks.
2. In Connect to a Network, under Available Networks, click the wireless network you
would like to connect to.
3. You may be prompted to enter a security key in order to connect to the network.
4. Enter in the security key corresponding to the wireless network, and click Connect.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 88

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
85
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is
no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible
for compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with
minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna
or transmitter.
Country Code selection feature to be disabled for products marketed to the US/CANADA
Europe – EU Declaration of Conformity
TRENDnet hereby declare that the product is in compliance with the essential requirements
and other relevant provisions under our sole responsibility.
Safety
EN 60950-1: 2006 + A11: 2010 + A12: 2011 + A2: 2013
EMC
EN 301 489-1 V1.9.2: 09-2011
EN 301 489-17 V2.2.1: 09-2012
EN 55024: 2010 + A1: 2015
EN 55032: 2015
Radio Spectrum & Health
EN 300 328 V1.8.1: 02-2015
EN 62311: 2008
Energy Efficiency
Regulation (EC) No. 1275/2008, No. 801/2013
This product is herewith confirmed to comply with the Directives.
Directives
Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
EMC Directive 2014/30/EU
RED Directive 2014/53/EU
RoHS Directive 2011/65/EU
REACH Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006
This device is designed to provide uninterrupted monitoring and/or recording. This device
does not offer power management functionality such as Off mode or Standby mode.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 89

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
86
Česky [Czech]
TRENDnet tímto prohlašuje, že tento TEW-740APBO je ve shodě se
základními požadavky a dalšími příslušnými ustanoveními směrnice
2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU, 2014/53/EU, a 2011/65/EU.
Dansk [Danish]
Undertegnede TRENDnet erklærer herved, at følgende udstyr TEW740APBO overholder de væsentlige krav og øvrige relevante krav i direktiv
2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU, 2014/53/EU, og 2011/65/EU.
Deutsch
[German]
Hiermit erklärt TRENDnet, dass sich das Gerät TEW-740APBO in
Übereinstimmung mit den grundlegenden Anforderungen und den übrigen
einschlägigen Bestimmungen der Richtlinie 2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU,
2014/53/EU, und 2011/65/EU befindet.
Eesti [Estonian]
Käesolevaga kinnitab TRENDnet seadme TEW-740APBO vastavust direktiivi
2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU, 2014/53/EU, ja 2011/65/EU põhinõuetele ja
nimetatud direktiivist tulenevatele teistele asjakohastele sätetele.
English
Hereby, TRENDnet, declares that this TEW-740APBO is in compliance with
the essential requirements and other relevant provisions of Directive
2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU, 2014/53/EU, and 2011/65/EU.
Español [Spanish]
Por medio de la presente TRENDnet declara que el TEW-740APBO cumple
con los requisitos esenciales y cualesquiera otras disposiciones aplicables o
exigibles de la Directiva 2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU, 2014/53/EU,
2011/65/EU y.
Ελληνική [Greek]
ΜΕ ΤΗΝ ΠΑΡΟΥΣΑTRENDnet ΔΗΛΩΝΕΙ ΟΤΙTEW740APBOΣΥΜΜΟΡΦΩΝΕΤΑΙ ΠΡΟΣ ΤΙΣ ΟΥΣΙΩΔΕΙΣ ΑΠΑΙΤΗΣΕΙΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΙΣ
ΛΟΙΠΕΣ ΣΧΕΤΙΚΕΣ ΔΙΑΤΑΞΕΙΣ ΤΗΣ ΟΔΗΓΙΑΣ 2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU,
2014/53/EU, 2011/65/EU και.
Français [French]
Par la présente TRENDnet déclare que l'appareil TEW-740APBO est
conforme aux exigences essentielles et aux autres dispositions pertinentes
de la 2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU, 2014/53/EU, 2011/65/UE et.
Italiano[Italian]
Con la presente TRENDnet dichiara che questo TEW-740APBO è conforme
ai requisiti essenziali ed alle altre disposizioni pertinenti stabilite dalla
direttiva 2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU, 2014/53/EU, e 2011/65/EU.
Latviski [Latvian]
AršoTRENDnetdeklarē, ka TEW-740APBO atbilstDirektīvas 2014/35/EU,
2014/30/EU, 2014/53/EU, un 2011/65/EU būtiskajāmprasībām un citiemar
to saistītajiemnoteikumiem.
Lietuvių
[Lithuanian]
Šiuo TRENDnet deklaruoja, kad šis TEW-740APBO atitinka esminius
reikalavimus ir kitas 2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU, 2014/53/EU, ir 2011/65/EU
Direktyvos nuostatas.
Nederlands
[Dutch]
Hierbij verklaart TRENDnet dat het toestel TEW-740APBO in
overeenstemming is met de essentiële eisen en de andere relevante
bepalingen van richtlijn 2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU, 2014/53/EU, en
2011/65/EU.
Malti [Maltese]
Hawnhekk, TRENDnet, jiddikjara li dan TEW-740APBO jikkonforma malħtiġijiet essenzjali u ma provvedimenti oħrajn relevanti li hemm fidDirrettiva 2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU, 2014/53/EU, u 2011/65/EU.
Magyar
[Hungarian]
Alulírott, TRENDnet nyilatkozom, hogy a TEW-740APBOmegfelel a
vonatkozó alapvetõ követelményeknek és az 2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU,
2014/53/EU, irányelv és a 2011/65/EU irányelv egyéb elõírásainak.
Polski [Polish]
Niniejszym TRENDnet oświadcza, że TEW-740APBO jest zgodny z
zasadniczymi wymogami oraz pozostałymi stosownymi postanowieniami
Dyrektywy 2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU, 2014/53/EU, i 2011/65/EU.
Português
[Portuguese]
TRENDnet declara que este TEW-740APBO está conforme com os
requisitos essenciais e outras disposições da Directiva 2014/35/EU,
2014/30/EU, 2014/53/EU, e 2011/65/EU.
Slovensko
[Slovenian]
TRENDnet izjavlja, da je ta TEW-740APBO v skladu z bistvenimi zahtevami
in ostalimi relevantnimi določili direktive 2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU,
2014/53/EU, in 2011/65/EU.
Slovensky
[Slovak]
TRENDnettýmtovyhlasuje, že TEW-740APBOspĺňazákladnépožiadavky a
všetkypríslušnéustanoveniaSmernice 2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU,
2014/53/EU, a 2011/65/EU.
Suomi [Finnish]
TRENDnet vakuuttaa täten että TEW-740APBO tyyppinen laite on
direktiivin 2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU, 2014/53/EU, ja 2011/65/EU
oleellisten vaatimusten ja sitä koskevien direktiivin muiden ehtojen
mukainen.
Svenska
[Swedish]
Härmed intygar TRENDnet att denna TEW-740APBO står I
överensstämmelse med de väsentliga egenskapskrav och övriga relevanta
bestämmelser som framgår av direktiv 2014/35/EU, 2014/30/EU,
2014/53/EU, och 2011/65/EU.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 90

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO / TEW-740APBO2K
87
Industry Canada Statement
This device complies with Industry Canada license-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is
subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause interference, and (2)
this device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired
operation of the device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio
exempts de licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) l'appareil
ne doit pas produire de brouillage, et (2) l'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout
brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le
fonctionnement.
Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with IC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance
20cm between the radiator & your body.
Déclaration d'exposition aux radiations:
Cet équipement est conforme aux limites d'exposition aux rayonnements IC établies pour un
environnement non contrôlé. Cet équipement doit être installé et utilisé avec un minimum
de 20 cm de distance entre la source de rayonnement et votre corps.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 91

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Limited Warranty
88
Limited Warranty
TRENDnet warrants only to the original purchaser of this product from a TRENDnet
authorized reseller or distributor that this product will be free from defects in material
and workmanship under normal use and service. This limited warranty is nontransferable and does not apply to any purchaser who bought the product from a
reseller or distributor not authorized by TRENDnet, including but not limited to
purchases from Internet auction sites.
Limited Warranty
TRENDnet warrants its products against defects in material and workmanship, under
normal use and service. Specific warranty periods are listed on each of the respective
product pages on the TRENDnet website.
AC/DC Power Adapter, Cooling Fan, and Power Supply carry a one-year
warranty.
Limited Lifetime Warranty
TRENDnet offers a limited lifetime warranty for all of its metal-enclosed network
switches that have been purchased in the United States/Canada on or after 1/1/2015.
Cooling fan and internal power supply carry a one-year warranty
To obtain an RMA, the ORIGINAL PURCHASER must show Proof of Purchase and return
the unit to the address provided. The customer is responsible for any shipping-related
costs that may occur. Replacement goods will be shipped back to the customer at
TRENDnet’s expense.
Upon receiving the RMA unit, TRENDnet may repair the unit using refurbished parts. In
the event that the RMA unit needs to be replaced, TRENDnet may replace it with a
refurbished product of the same or comparable model.
In the event that, after evaluation, TRENDnet cannot replace the defective product or
there is no comparable model available, we will refund the depreciated value of the
product.
If a product does not operate as warranted during the applicable warranty period,
TRENDnet shall reserve the right, at its expense, to repair or replace the defective
product or part and deliver an equivalent product or part to the customer. The
repair/replacement unit's warranty continues from the original date of purchase. All
products that are replaced become the property of TRENDnet. Replacement products
may be new or reconditioned. TRENDnet does not issue refunds or credit. Please
contact the point-of-purchase for their return policies.
TRENDnet shall not be responsible for any software, firmware, information, or memory
data of customer contained in, stored on, or integrated with any products returned to
TRENDnet pursuant to any warranty.
There are no user serviceable parts inside the product. Do not remove or attempt to
service the product by any unauthorized service center. This warranty is voided if (i) the
product has been modified or repaired by any unauthorized service center, (ii) the
product was subject to accident, abuse, or improper use, or (iii) the product was subject
to conditions more severe than those specified in the manual.
Warranty service may be obtained by contacting TRENDnet within the applicable
warranty period and providing a copy of the dated proof of the purchase. Upon proper
submission of required documentation, a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number
will be issued. An RMA number is required in order to initiate warranty service support
for all TRENDnet products. Products that are sent to TRENDnet for RMA service must
have the RMA number marked on the outside of return packages and sent to TRENDnet
prepaid, insured and packaged appropriately for safe shipment. International customers
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 92

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Limited Warranty
89
shipping from outside of the USA and Canada are responsible for any return shipping
and/or customs charges, including but not limited to, duty, tax, and other fees.
Refurbished product: Refurbished products carry a 90-day warranty after date of
purchase. Please retain the dated sales receipt with purchase price clearly visible as
evidence of the original purchaser's date of purchase. Replacement products may be
refurbished or contain refurbished materials. If TRENDnet, by its sole determination, is
unable to replace the defective product, we will offer a refund for the depreciated value
of the product.
WARRANTIES EXCLUSIVE: IF THE TRENDNET PRODUCT DOES NOT OPERATE AS
WARRANTED ABOVE, THE CUSTOMER'S SOLE REMEDY SHALL BE, AT TRENDNET'S
OPTION, REPAIR OR REPLACE. THE FOREGOING WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES ARE
EXCLUSIVE AND ARE IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED,
EITHER IN FACT OR BY OPERATION OF LAW, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
TRENDNET NEITHER ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER PERSON TO ASSUME FOR
IT ANY OTHER LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION,
MAINTENANCE, OR USE OF TRENDNET'S PRODUCTS.
TRENDNET SHALL NOT BE LIABLE UNDER THIS WARRANTY IF ITS TESTING AND
EXAMINATION DISCLOSE THAT THE ALLEGED DEFECT IN THE PRODUCT DOES NOT EXIST
OR WAS CAUSED BY CUSTOMER'S OR ANY THIRD PERSON'S MISUSE, NEGLECT,
IMPROPER INSTALLATION OR TESTING, UNAUTHORIZED ATTEMPTS TO REPAIR OR
MODIFY, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE BEYOND THE RANGE OF THE INTENDED USE, OR BY
ACCIDENT, FIRE, LIGHTNING, OR OTHER HAZARD.
CONTRACT OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), FOR INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, OR FOR LOSS OF REVENUE OR
PROFITS, LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF INFORMATION OR DATE, OR OTHER FINANCIAL
LOSS ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION,
MAINTENANCE, USE, PERFORMANCE, FAILURE, OR INTERRUPTION OF THE POSSIBILITY
OF SUCH DAMAGES, AND LIMITS ITS LIABILITY TO REPAIR, REPLACEMENT, OR REFUND
OF THE PURCHASE PRICE PAID, AT TRENDNET'S OPTION. THIS DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY
FOR DAMAGES WILL NOT BE AFFECTED IF ANY REMEDY PROVIDED HEREIN SHALL FAIL
OF ITS ESSENTIAL PURPOSE.
Governing Law: This Limited Warranty shall be governed by the laws of the state of
California.
Some TRENDnet products include software code written by third party developers.
These codes are subject to the GNU General Public License ("GPL") or GNU Lesser
General Public License ("LGPL").
Visit http://www.trendnet.com/gpl or the support section on
http://www.trendnet.com and search for the desired TRENDnet product to access to
the GPL Code or LGPL Code. These codes are distributed WITHOUT WARRANTY and are
subject to the copyrights of the developers. TRENDnet does not provide technical
support for these codes. Please visit http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.txt or
http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.txt for specific terms of each license.
PWP07172015v3 2016/12/12
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: TO THE FULL EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW, TRENDNET ALSO
EXCLUDES FOR ITSELF AND ITS SUPPLIERS ANY LIABILITY, WHETHER BASED IN
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 93

 Loading...
Loading...