TRENDnet TEW-740APBO User Manual

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Cover Page

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
2
Contents
Product Overview ........................................................................... 4
Package Contents .......................................................................................................... 4
Features ......................................................................................................................... 4
Product Hardware Features........................................................................................... 5
Application Diagram ...................................................................................................... 7
Setup & Installation ........................................................................ 8
Note the Wireless MAC Addresses ................................................................................ 8
Setup Guide Assumed Defaults ........................................................................... 8
TEW-740APBO #1 Configuration ................................................................................... 9
TEW-740APBO #2 Configuration ................................................................................. 11
Verify Point-to-Point Configuration/Connectivity ....................................................... 12
Grounding Wire Installation ........................................................................................ 13
Waterproof Kit Installation .......................................................................................... 13
Mounting Hardware Installation ................................................................................. 16
Pole Mounting ................................................................................................... 16
Wall Mounting ................................................................................................... 17
Completed Point to Point Setup and Pole Mount Installation Example ...................... 18
Installation Tips ............................................................................................................ 19
Application Modes ........................................................................ 20
AP Mode (Access Point Mode) .................................................................................... 20
WDS Mode (Pure WDS) ............................................................................................... 21
Client Bridge + Universal Repeater Mode ................................................................... 22
CPE + AP Mode (Router Client + Access Point) ............................................................ 22
AP Mode Configuration ................................................................. 23
External Network Connection...................................................................................... 23
Network Requirement ....................................................................................... 23
Configure LAN IP .......................................................................................................... 23
Wireless LAN Network ................................................................................................. 25
Wireless General Setup ..................................................................................... 25
Wireless Advanced Setup .................................................................................. 25
Wireless WMM QoS Setup ................................................................................ 27
Create Virtual AP (VAP) ..................................................................................... 29
Virtual AP Setup ................................................................................................. 30
Wireless MAC Filter Setup ................................................................................. 32
Wireless Network Expansion ............................................................................. 32
System Status .............................................................................................................. 33
System Overview ............................................................................................... 33
Associated Clients Status ................................................................................... 34
Show WDS Link Status ....................................................................................... 34
Extra Information............................................................................................... 35
Event Log ........................................................................................................... 36
WDS Mode Configuration ............................................................. 37
External Network Connection ..................................................................................... 37
Network Requirement ....................................................................................... 37
Configure LAN IP .......................................................................................................... 37
Wireless Network Expansion ....................................................................................... 38
Wireless General Setup ..................................................................................... 38
Wireless Advanced Setup .................................................................................. 39
Wireless WMM QoS Setup ................................................................................ 40
WDS Setup ......................................................................................................... 42
System Status .............................................................................................................. 42
System Overview ............................................................................................... 42
Extra Information............................................................................................... 43
Event Log ........................................................................................................... 44
WDS Link Status ................................................................................................. 45
Repeater Mode ............................................................................. 46
External Network Connection ..................................................................................... 46
Network Requirement ....................................................................................... 46
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
3
Configure LAN IP .......................................................................................................... 46
Access Control ............................................................................................................. 74
Wireless Network Expansion ....................................................................................... 47
Wireless General Setup ..................................................................................... 47
Wireless Advanced Setup .................................................................................. 48
Wireless WMM QoS Setup ................................................................................ 50
Site Survey ......................................................................................................... 51
Repeater AP Setup ............................................................................................. 52
Wireless MAC Filter Setup ................................................................................. 54
Create Wireless Profile ...................................................................................... 54
Bandwidth Control ............................................................................................. 56
Configure SNMP Setup ...................................................................................... 56
Configure Time Policy ........................................................................................ 57
System Status .............................................................................................................. 58
System Overview ............................................................................................... 58
DHCP Client ........................................................................................................ 59
Extra Information ............................................................................................... 59
Event Log ........................................................................................................... 60
Associated Client List ......................................................................................... 60
Remote AP status............................................................................................... 61
CPE + AP Mode Configuration ........................................................ 61
External Network Connection...................................................................................... 61
Network Requirement ....................................................................................... 61
Configure CPE Setup .................................................................................................... 62
Configure DDNS Setup ....................................................................................... 63
Configure LAN IP ................................................................................................ 63
Configure Static IP address ................................................................................ 65
Access Point Association .............................................................................................. 65
Wireless General Setup ..................................................................................... 65
Wireless Advanced Setup .................................................................................. 66
Wireless WMM QoS Setup ................................................................................ 67
Site Survey ......................................................................................................... 69
Create Wireless Profile ...................................................................................... 69
AP Setup ............................................................................................................. 71
Wireless AP MAC Filter Setup ............................................................................ 73
DMZ ................................................................................................................... 74
IP Filter Setup .................................................................................................... 74
MAC Filter Setup ................................................................................................ 75
Virtual Server ..................................................................................................... 75
Bandwidth Control ............................................................................................. 76
Routing .............................................................................................................. 76
Status ........................................................................................................................... 76
System Overview ............................................................................................... 77
DHCP Client ........................................................................................................ 77
Extra Information............................................................................................... 78
Event Log ........................................................................................................... 79
Associated Client List ......................................................................................... 79
Remote AP status .............................................................................................. 79
System Management .................................................................... 81
Configure Management ..................................................................................... 81
Configure System Time ...................................................................................... 82
Configure SNMP Setup ...................................................................................... 82
Enable UPNP ...................................................................................................... 83
Backup / Restore and Reset to Factory ............................................................. 83
Firmware Upgrade ............................................................................................. 84
Network Utility .................................................................................................. 84
Reboot ............................................................................................................... 85
Technical Specifications ................................................................ 86
Appendix ...................................................................................... 88
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
4
Product Overview
Features
TRENDnet’s 10dBi Wireless N300 Outdoor PoE Access Point., model TEW-740APBO,
provides Wireless N300 building-to-building connectivity. A variety of installation
scenarios are facilitated with Access Point (AP), Wireless Distribution System (WDS),
Repeater, and CPE + AP modes. The IP67 rated housing comes with wall and pole
mounting hardware.
Multi-Mode Support
Supports Access Point (AP), Wireless Distribution System (WDS), Repeater, and Wireless
Client modes
Wireless N300 (2.4 GHz)
Compliant with 802.11n/g/b technology (2.4 GHz) with data rates up to 300 Mbps*
Outdoor Rated
Durable enclosure with an IP67 outdoor weather rating
TEW-740APBO
Package Contents
TEW-740APBO
CD-ROM (Software & User’s Guide)
Quick Installation Guide
Power adapter (48V DC, 0.5A)
Proprietary PoE injector
Waterproof RJ-45 kit
Grounding wire
Mounting hardware
Directional Antenna
Built in 10 dBi directional antenna
Power over Ethernet (PoE)
Comes with a proprietary PoE injector, so that it can connect a regular non-PoE switch
Logs
Real time logs and statistics help troubleshooting
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
5
IP67 Weather
Rated Housing
with built-in
directional sector
Encrypted Wireless
Support for wireless encryption of up to WPA2
Product Hardware Features
Front View
Multiple SSIDs
Create up to eight additional SSIDs
Compatibility
Compatible with legacy wireless devices
Mounting Hardware
Pole and wall mount hardware included
* Effective wireless coverage may vary depending on the wireless device's output
power, antenna gain, antenna alignment, receiving sensitivity, and radio interference.
Additionally environmental factors such as weather conditions, physical obstacles, and
other considerations may affect performance. For optimal results, we recommended
consulting a professional installer for site survey, safety precautions, and proper
installation.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
6
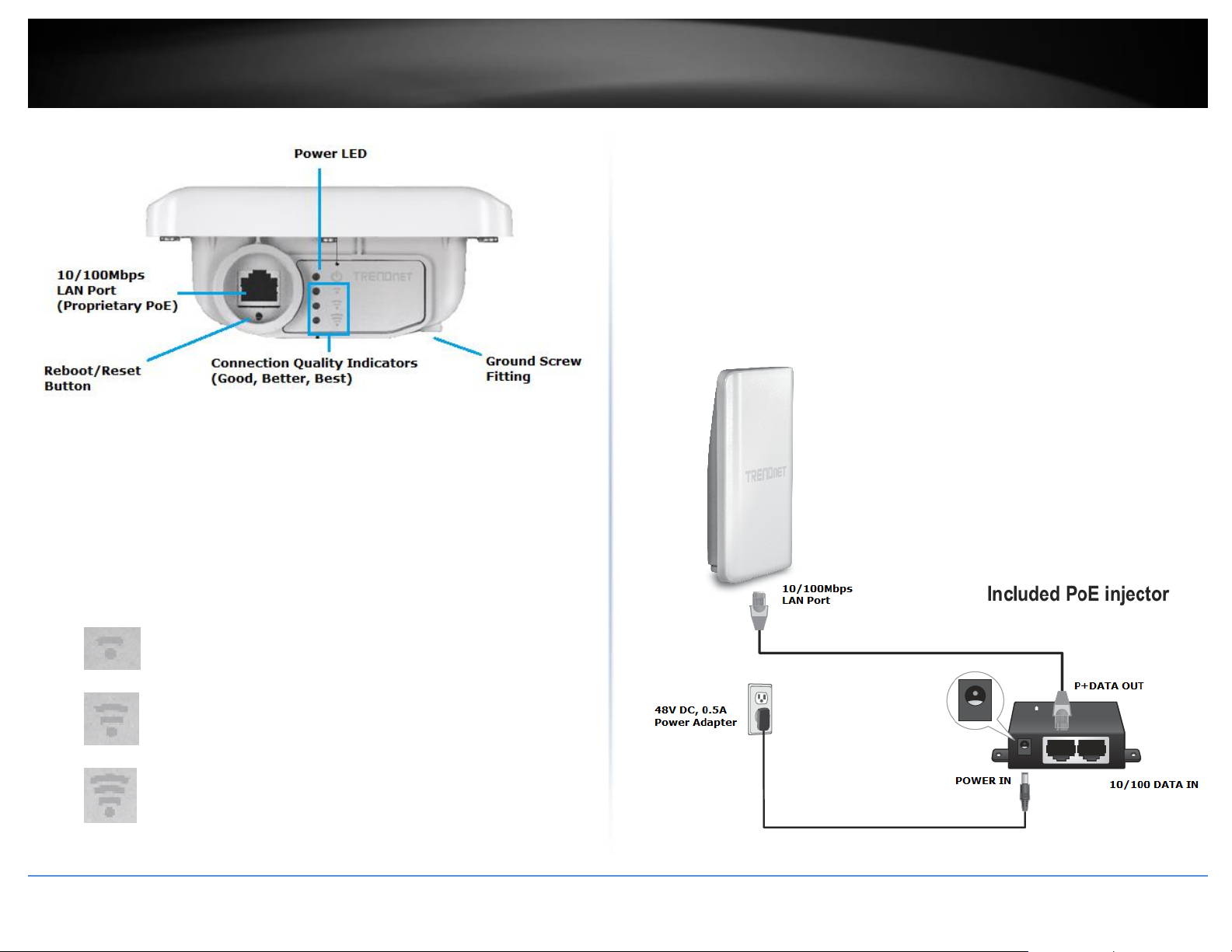
Bottom View
LAN Port – You will need to unscrew the protective cover to gain access to this
port. The Ethernet LAN port operates at 10/100Mbps and is also used to supply
power to the device using only the included proprietary PoE injector.
Proprietary PoE Injector –
o POWER IN – Connect the included power adapter connector to this
input and adapter side into an AC power source to supply power to
the injector.
o P+DATA OUT – Connect an Ethernet RJ-45 cable to this output and the
other side to the device LAN port to supply power to the device.
o 10/100 DATA IN – Connect an Ethernet RJ-45 cable to this input and
connect the other to your network or directly to computer for initial
device setup.
Reboot/Reset Button – You will need to unscrew the protective cover or
disconnect the RJ-45 waterproof kit if it is installed to gain access to this
button. Press and hold this button for 2 seconds and release to reboot the
device. Press and hold this button for 10 seconds and release to reset the
device to factory defaults.
Power LED – The indicator will turn when the device is powered on.
WLAN Connection Quality Indicators – The connection quality indicators will
turn on depending on the connection quality during installation. These
indicators can help to assist with optimal placement and positioning during
mounting/hardware installation.
Good Connection Quality
Better Connection Quality
Best Connection Quality
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
7
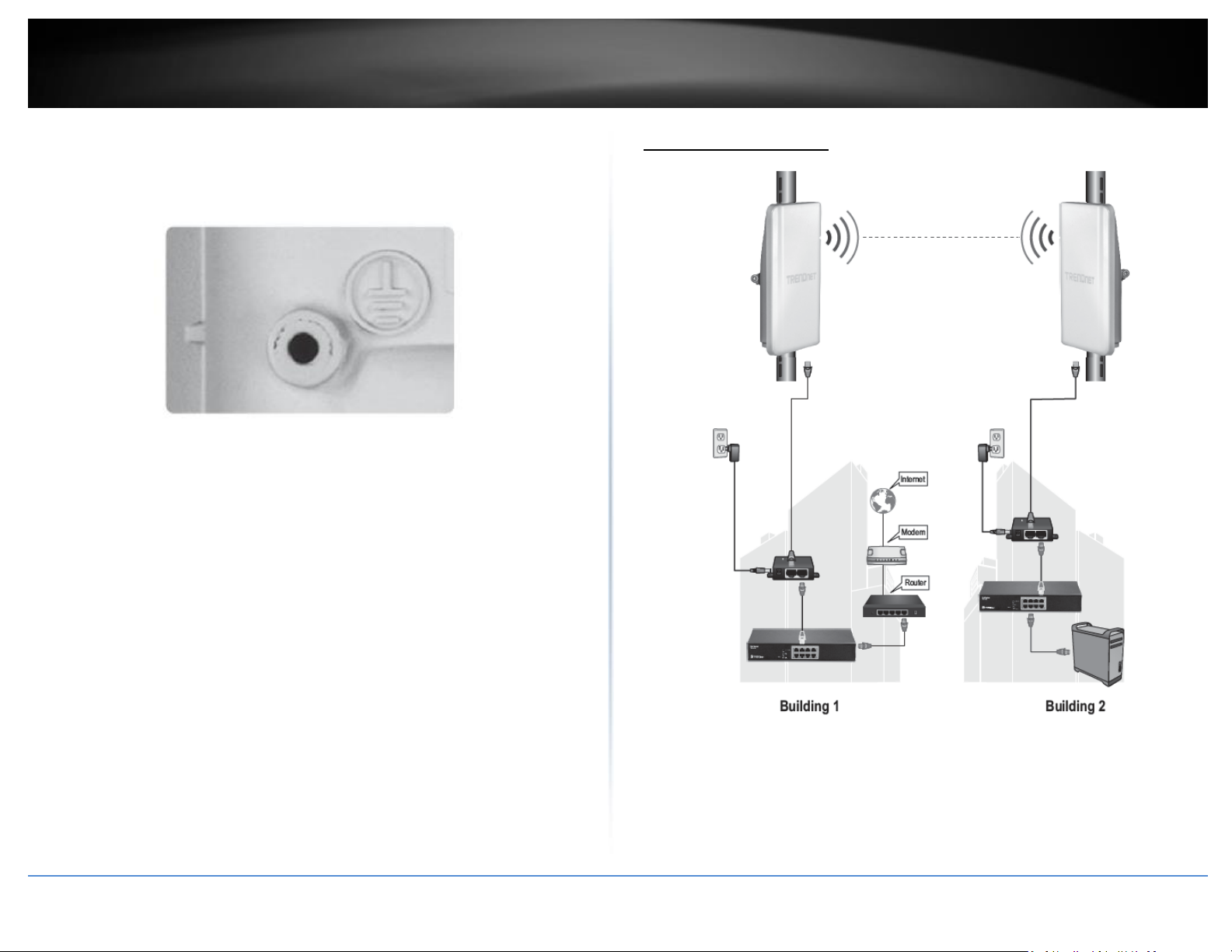
Ground Screw Fitting – The ground screw is built into the device housing. The
fitting can be identified on the back of the housing by checking for the ground
symbol. The included ground screw and wire can be used to attached the
device to a known grounding point. (ex. Earth driven rod, grounded electrical
system, building frame, etc.)
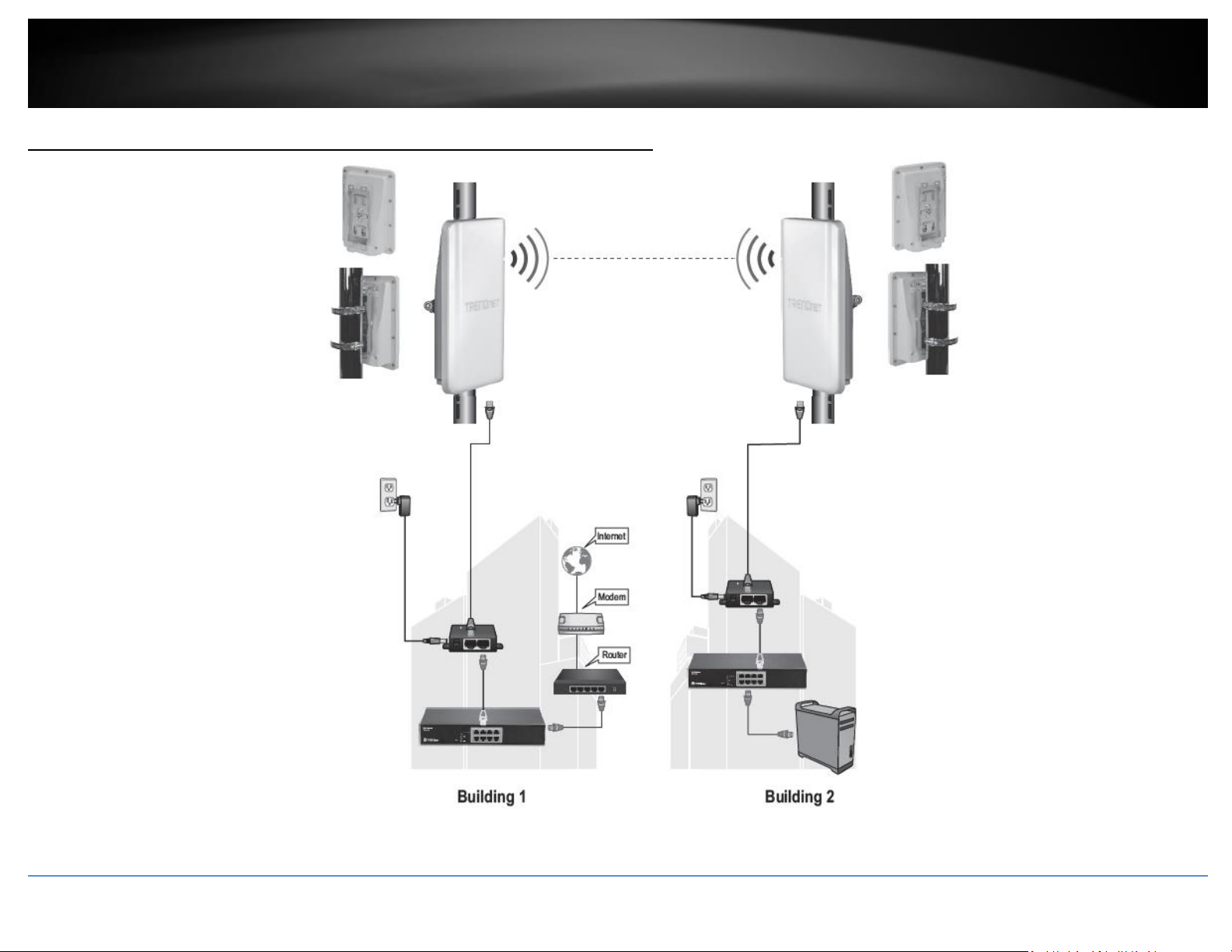
Application Diagram
The example application displays two TEW-740APBO access points are configured in WDS pointto-point bridge mode and establishing a wireless link between each and other, allowing for
network connectivity between two buildings over a point-to-point wireless link.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
8
Setup & Installation
The intended purpose and application for this product is to extend network connectivity
across long physical distances outside of an area or building that lacks local connectivity
using point to point wireless bridge capability using 802.11 standards.
Although this product supports multiple wireless modes, the basic installation will only
cover the primary application of point to point wireless connectivity.
Minimum Requirements
Computer with RJ-45 Ethernet port and web browser
2 x RJ-45 Ethernet cables (not included)
Phillips screwdriver (not included)
Important Note:
The access point does not support standard IEEE 802.3at/af PoE/PoE+. Only the included
proprietary PoE injector may be used to supply power to the access point. For safety,
use only the included PoE injector to supply power to the access point.
It is strongly recommended that you configure the access points first before mounting
them in their desired locations.
Access Point Default Settings
LAN IP Address: 192.168.10.100
LAN Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
User: admin
Password: admin
The following steps assume you are setting up and installation two TRENDnet TEW740APBO access points in point to point configuration.
Note the Wireless MAC Addresses
Please check the device label on both access points and write down or note the item
labeled MAC1 from both access points. MAC1 is the wireless MAC address assigned to
each access point and will be used later in the configuration steps.
Setup Guide Assumed Defaults
In this guide, we will assume the following defaults and settings:
TEW-740APBO #1 MAC1: 00:11:22:33:44:55
TEW-740ABPO #2 MAC1: AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF
Network Router/Gateway IP Address/Netmask: 192.168.10.1 / 255.255.255.0
Network Router/Gateway DHCP IP Pool: 192.168.10.101-192.168.10.199
Note: Please note that if your existing network router/gateway IP address/subnet
settings are different than the network settings assumed above, you will need to modify
the assigned IP configuration to each access point accordingly to within you specific
subnet.
Before mounting the access points in their desired locations, please configure access
points first.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
9
TEW-740APBO #1 Configuration
1. Connect the power adapter connector side to the POWER IN on the included
proprietary PoE injector and the adapter to an AC power source.
Note: EU model also include an on/off power switch. Please make sure to switch to the
(On/-) position.
2. Connect an RJ-45 Ethernet cable from the access point LAN port to the P+DATA OUT
on the included proprietary PoE injector.
3. Connect an RJ-45 Ethernet cable from the computer to the 10/100 DATA IN on the
included proprietary PoE injector.
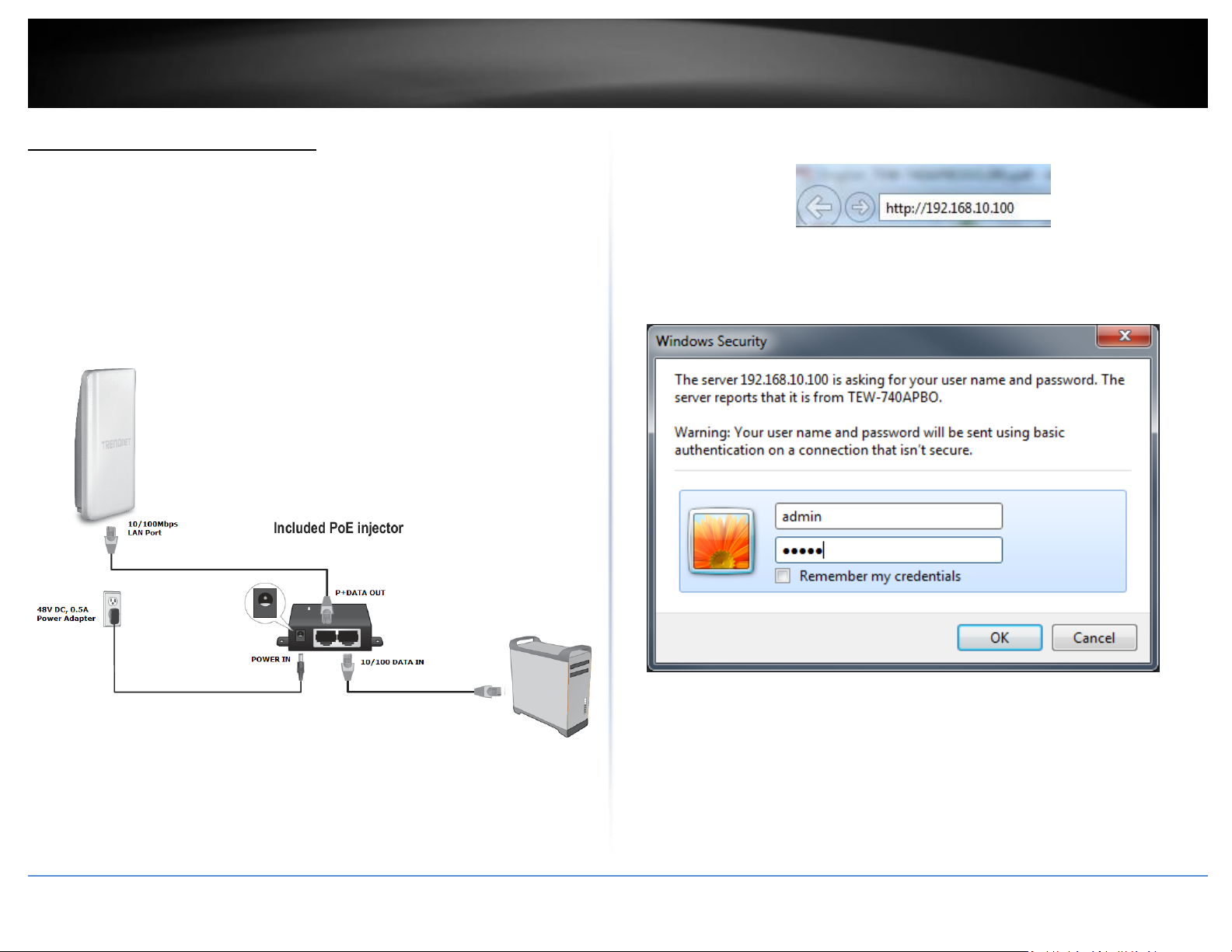
6. Open your web browser and type in the IP address of the access point in the address
bar, then press Enter. The default IP address of the access point is 192.168.10.100.
7. When prompted to login, enter the default user name and password and click OK.
Default User Name: admin
Default Password: admin
4. The access point power LED will turn on to indicate the device is receiving power.
5. Assign a static IP address to your computer network adapter in the subnet of
192.168.10.x (ex. 192.168.10.10) and subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
10
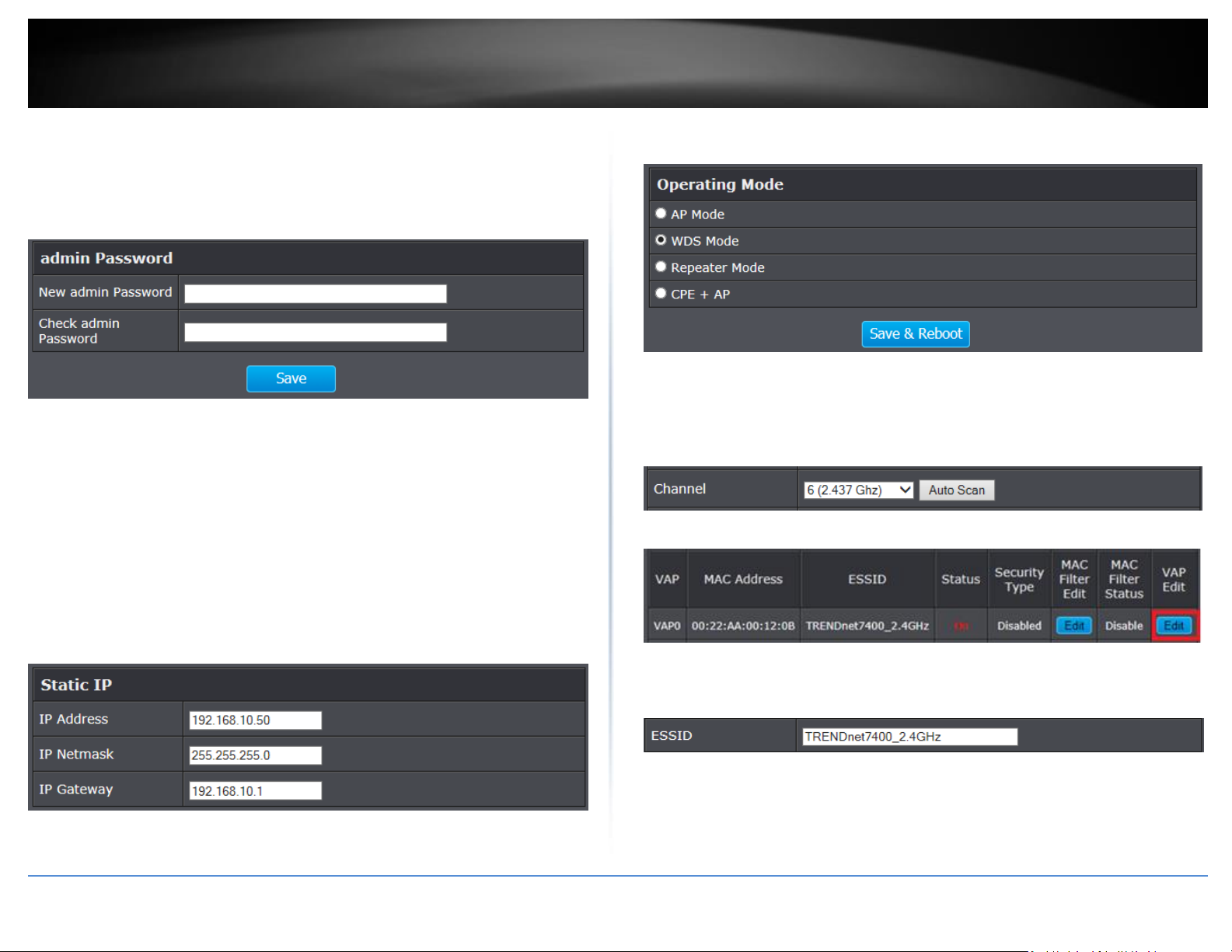
8. At the Password Setup page, enter your new password in the New admin Password
field and once again in the Check admin Password field to confirm, then click Save to
apply the new password settings.
Note: It is recommended to change to a strong admin password. This is the password
that will be used to login to the access point management configuration web page.
11. Click System and click on Operating Mode. In the list, select WDS and click on Save
& Reboot to apply the settings.
9. In the access point management web page, click on System and click on LAN.
10. Under Static IP, enter the IP address settings below, then scroll down and click Save
to apply the settings. After changes are applied, you will need to login to the new IP
address assigned.
Note: Please note that if your existing network IP subnet is different. You must assign IP
addresses available in your IP subnet to the access points accordingly.
TEW-740ABO #1 IP Configuration
IP Address: 192.168.10.50
IP Netmask: 255.255.255.0
IP Gateway: 192.168.10.1
12. Click on Wireless and click on General.
You can choose to change the Channel settings but they must match on both access
points to establish a point-to-point WDS configuration. For this example, we will leave
as the default channel 6. If you decide to change it, make sure to scroll down and click
Save to apply the setting.
13. Click on Wireless and click on Virtual AP. For VAP0, click on Edit.
14. You can choose to change the ESSID (Wireless Network Name) settings but they
must match on both access points to establish a point-to-point WDS configuration. For
this example, we will leave as the default setting TRENDnet7400_2.4GHz.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
11
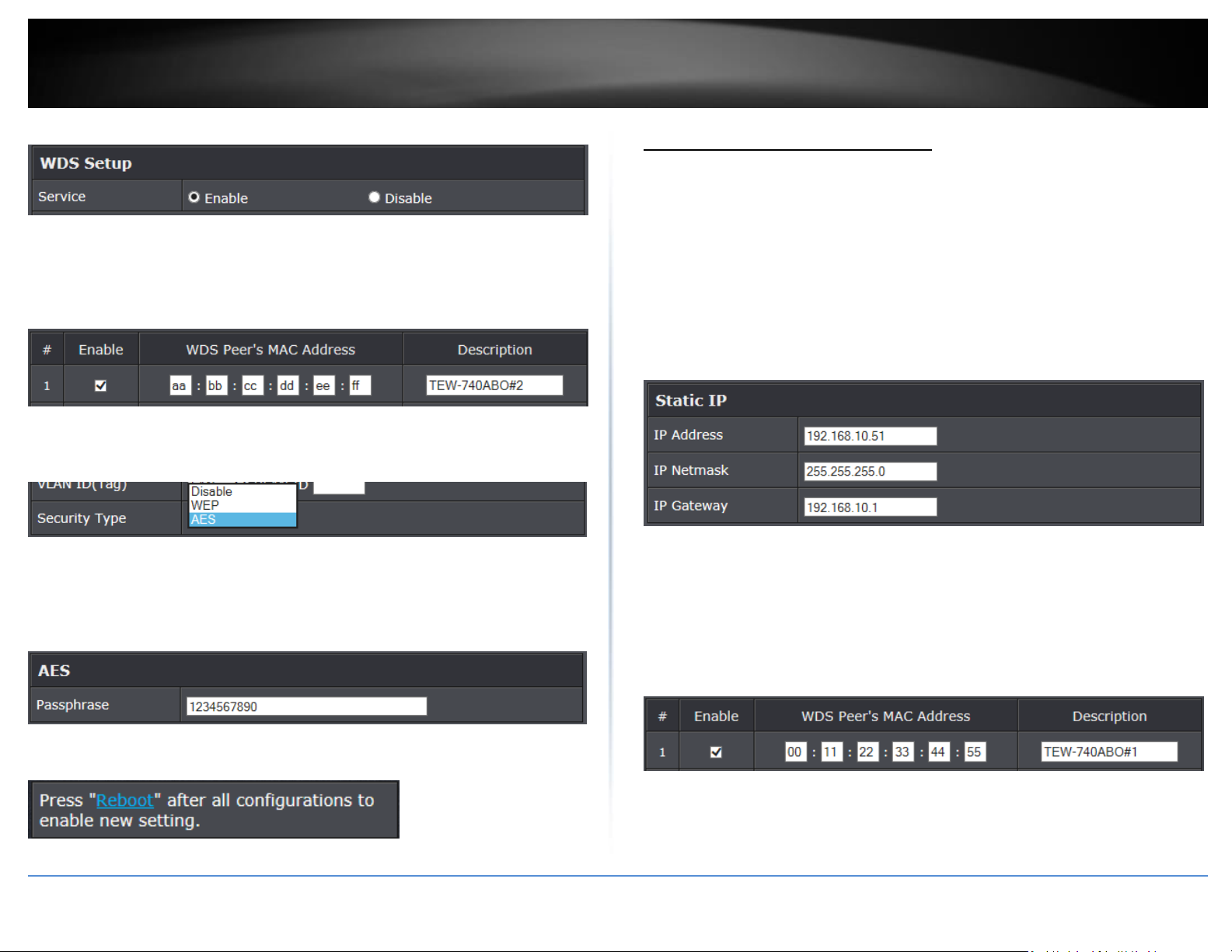
15. Under WDS Setup, set the Service setting to Enable.
16. In the first field for item 1, check the Enable option and in the WDS Peer’s MAC
Address fields, enter the MAC address of the 2nd TEW-740ABPO (TEW-740APBO #2
MAC1: AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF) noted earlier in this guide. Description field is optional.
Note: You will need to enter the wireless MAC address of your 2nd access point as the one
below is only used as an example in this guide.
TEW-740APBO #2 Configuration
1. Repeat the same TEW-740APBO #1 configuration steps 1-9 for TEW-740ABPO #2.
2. On the TEW-740APBO #1 configuration step 10, use the IP configuration settings
below for TEW-740APBO #2.
Note: Please note that if your existing network IP subnet is different. You must assign IP
addresses available in your IP subnet to the access points accordingly.
TEW-740ABO #2 IP Configuration
IP Address: 192.168.10.51
IP Netmask: 255.255.255.0
IP Gateway: 192.168.10.1
17. In the Security Type field above, it is recommended to select AES and assign a
passphrase. It is not required to create a point-to-point WDS link but strongly
recommended. This setting must match on both access points.
If you decide to apply encryption and assign a passphrase, select AES. Then scroll down
to the bottom under the AES section and enter Passphrase. The security type and key
must match on both access points. Then click Save to save the settings.
Note: It is strongly recommended to assign strong passphrase. We are only using the
encryption key 1234567890 as an example in this guide.
18. At the top of the page, click Reboot, then click the Reboot button on the GUI page
to commit all of the changes. This completes the configuration for TEW-740APBO #1.
3. Repeat the same TEW-740APBO #1 configuration steps 11-15 for TEW-740ABPO #2.
4. On the TEW-740APBO #1 configuration step 16, enter the MAC address of the 1st
TEW-740ABPO (TEW-740APBO #1 MAC1: 00:11:22:33:44:55) noted earlier in this guide.
Description field is optional.
Note: You will need to enter the wireless MAC address of your 1st access point as the one
below is only used as an example in this guide.
5. Repeat the same TEW-740APBO #1 configuration steps 11-18 to complete the TEW740ABPO #2 configuration. This completes the configuration for TEW-740APBO #2
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
12
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
Verify Point-to-Point Configuration/Connectivity
1. Make sure both access points (TEW-740APBO #1 and TEW-740APBO #2) powered on and positioned pointing toward each other.
2. With the static IP address still assigned from the setup guide, connect your computer to one of the access points via LAN port.
3. On your computer, open a command prompt/terminal window and run a ping command to test connectivity to both access point IP addresses 192.168.10.50 and 192.168.10.51.
Example of successful ping replies below from both access points. You can also check if you can access both access point web management pages through a web browser.
C:\Users\trendnet>ping 192.168.10.50
Pinging 192.168.10.50 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.10.50: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.10.50: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
C:\Users\trendnet>ping 192.168.10.51
Pinging 192.168.10.51 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.10.51: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.10.51: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
13
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
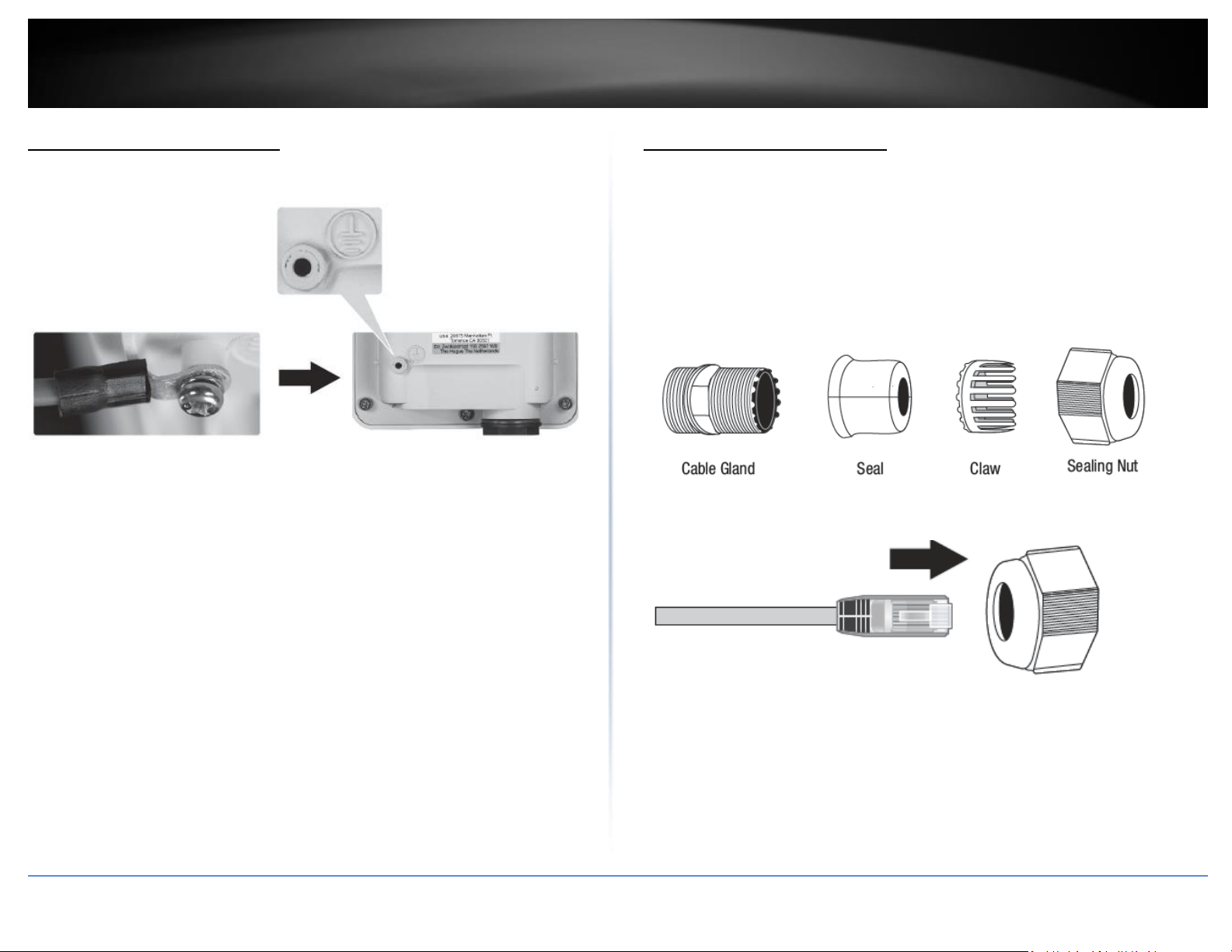
Grounding Wire Installation
To install the grounding wire, align one end of the ground wire over the ground fitting,
then secure the wire using the included screw and washer as shown below.
Waterproof Kit Installation
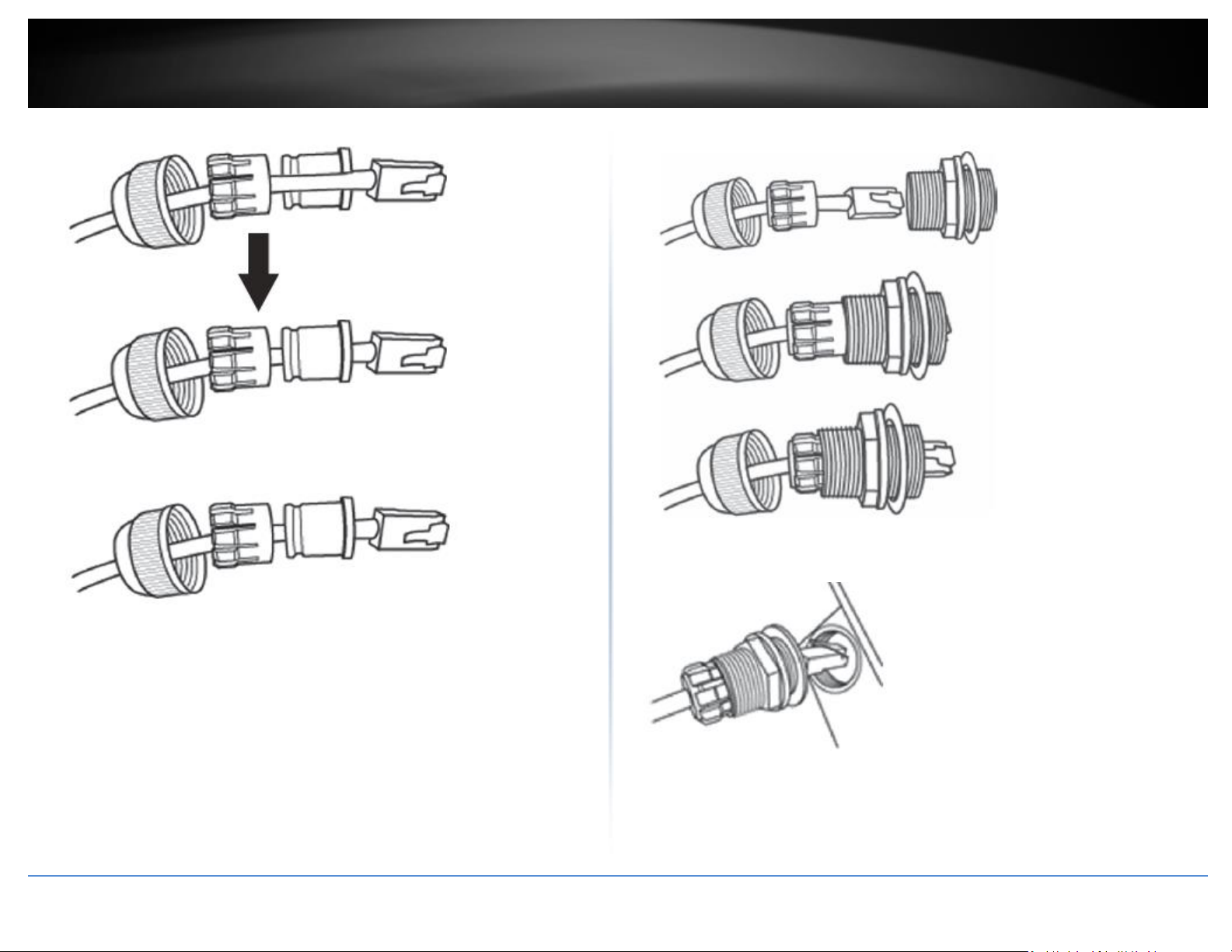
1. Unscrew the sealing nut from the main body.
2. Separate rubber seal from the claw.
3. Verify that you have the following parts as shown below:
Cable Gland
Seal
Claw
Sealing Nut
4. Insert one end of an Ethernet cable into the sealing nut.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
14
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
5. Insert the Ethernet cable into the seal.
7. Insert the seal/rubber claw into the cable gland.
6. Insert the seal into the claw.
8. Connect the Ethernet cable to the LAN port on the bottom of the access point.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
15
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
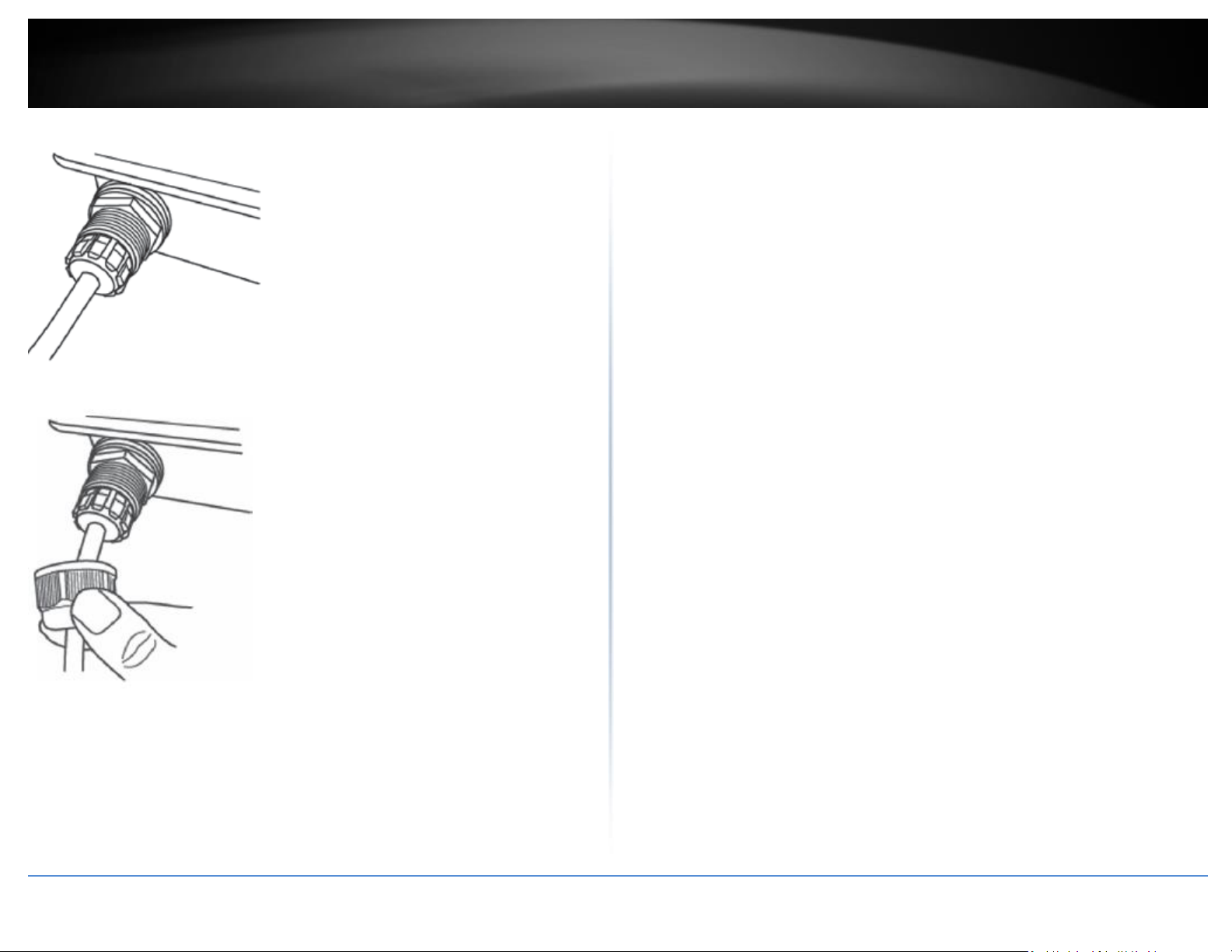
9. Fasten and tighten the plug to the housing of the access point.
10. Fasten and tighten the cap to the weather proof plug.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
16
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
Mounting Hardware Installation
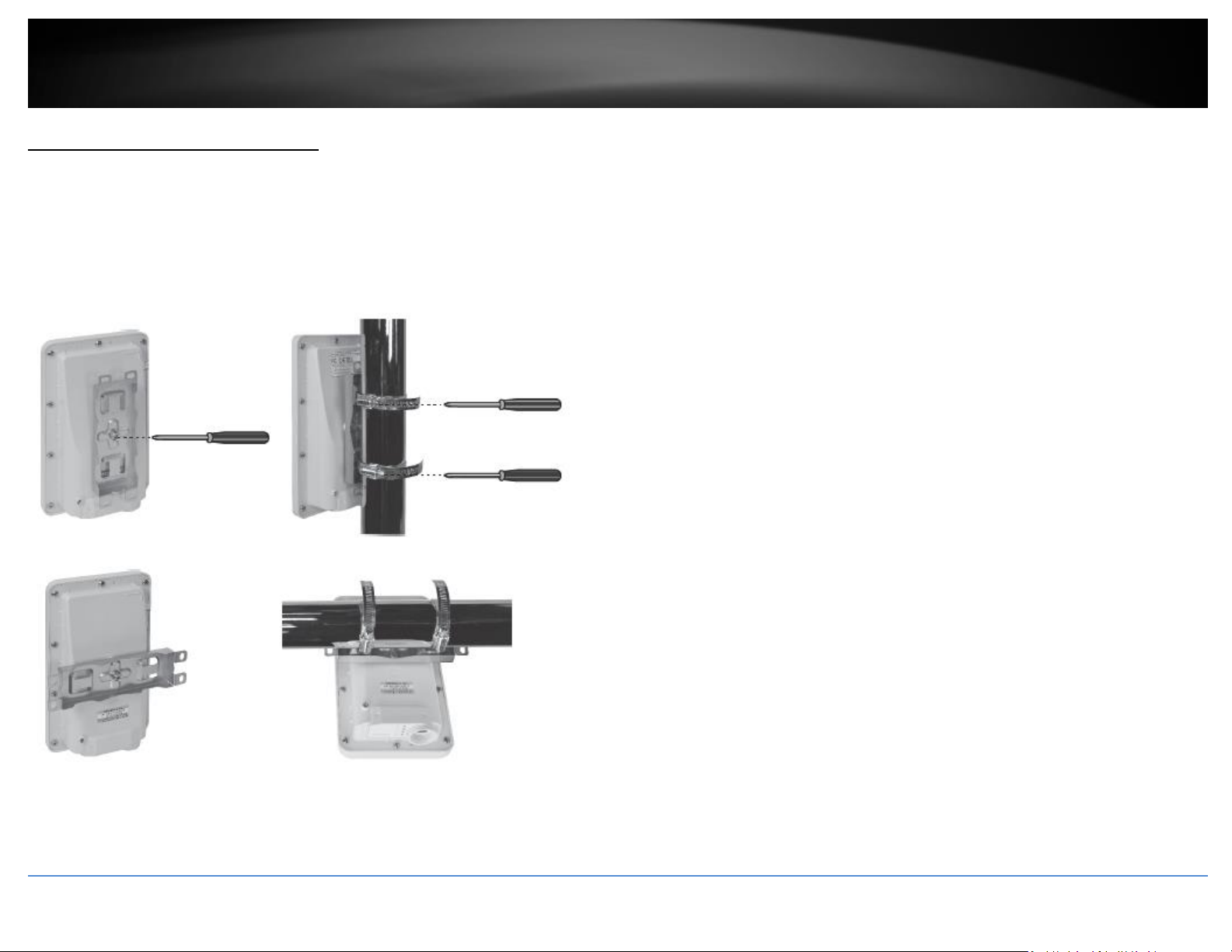
Pole Mounting
Note: The pole mounting clamp supports poles with a maximum diameter of 101 mm (3.98 in.)
1. Align the mounting bracket with the hole on the unit and secure it with the M6x8 screw and washer provided.
2. Slide the two provided pole mounting clamps around the pole. Place the mounting bracket at the desired height and position.
3. Secure the TEW-740APBO to the pole mounting bracket using mounting clamp screws.
4. Adjust the orientation of the access point as necessary.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.

17
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
Wall Mounting
1. Align the mounting bracket with the hole on the unit and secure it with the M6x8 screw and washer provided.
2. Position the provided mounting bracket to the desired location and wall mount with screws or fasteners using the four mounting bracket holes.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
18
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
Completed Point to Point Setup and Pole Mount Installation Example
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.

19
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
Installation Tips
There are a number of factors that can impact the range of wireless devices.
1. Adjust your wireless devices so that the signal is traveling in a straight path, rather than at an angle. The more material the signal has to pass through the more signal you will lose.
2. Keep the number of obstructions to a minimum. Each obstruction can reduce the range of a wireless device. Position the wireless devices in a manner that will minimize the amount
of obstructions between them.
3. Building materials can have a large impact on your wireless signal. In an indoor environment, try to position the wireless devices so that the signal passes through less dense material
such as dry wall. Dense materials like metal, solid wood, glass or even furniture may block or degrade the signal.
4. Antenna orientation can also have a large impact on your wireless signal. Use the wireless adapter’s site survey tool to determine the best antenna orientation for your wireless
devices.
5. Interference from devices that produce RF (radio frequency) noise can also impact your signal. Position your wireless devices away from anything that generates RF noise, such as
microwaves, radios and baby monitors.
If you are still experiencing low or no signal consider repositioning the wireless devices or installing additional access points. The use of higher gain antennas may also provide the
necessary coverage depending on the environment. Please note to use the wireless connection quality indicators during installation to determine the optimal positioning when mounting
your access points.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
20
Main
WDS
Remote
Application Modes
Although the access point is intended to be used for WDS point-to-point bridging, the access point offers other operating modes. The access point multiple mode system which can be
configured either as a wireless gateway or an access point as desired. It also can be used as a WDS (Wireless Distribution System) link for Ethernet network expansion. This section
depicts different applications on Router AP Mode, AP Mode, WDS Mode, CPE Mode, Client Bridge + Universal Repeater Mode and CPE + AP Mode.
The different modes can be found under System > Operating Mode in the access point web management page.
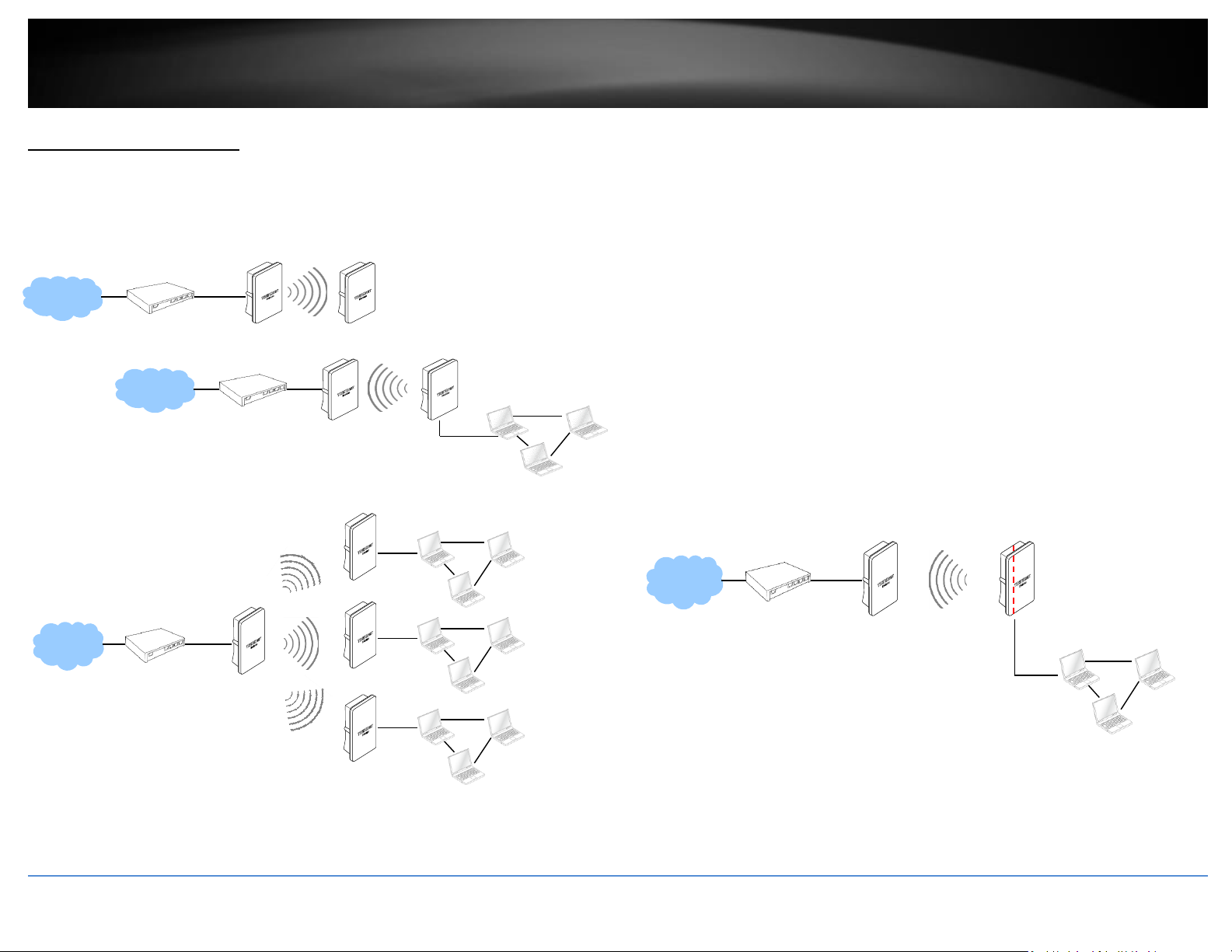
AP Mode (Access Point Mode)
An access point can be either a main, relay or remote base station. A main base station is typically connected to a wired network via the Ethernet port. A relay base station relays data
between main base stations and relay stations or remote base stations with clients. A remote base station is the end point to accept connections from wireless clients and pass data
upstream to a network wirelessly.
Example 1: Access Point Only
It can be deployed as a traditional fixed wireless access point.
Example 2: Access Point + WDS Bridging
It can be deployed as a traditional fixed wireless access point and establish WDS bridging to an upstream access point to expand a network.
Main
Remote
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
21
Station
NA
WDS
Main
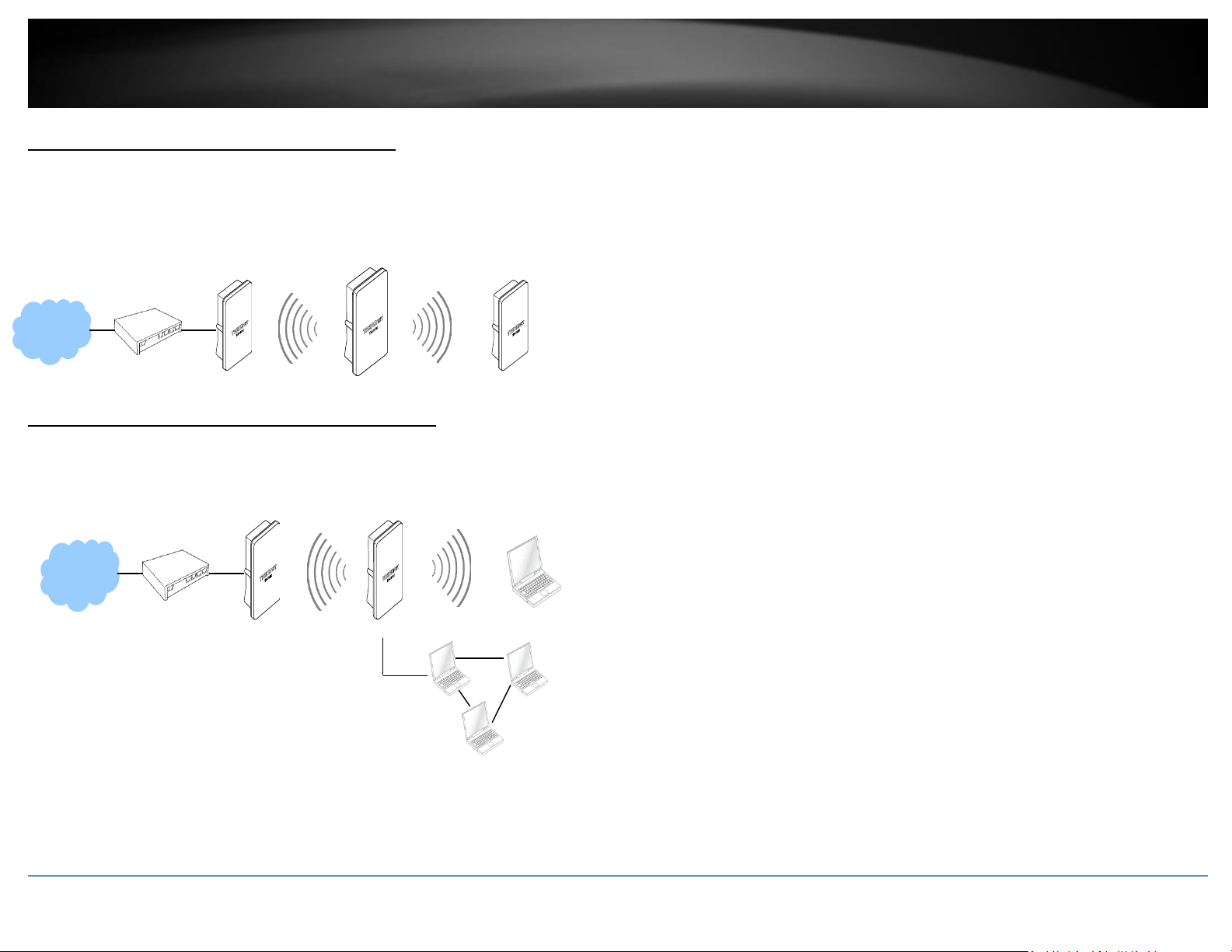
WDS Mode (Pure WDS)
An access point can be either a main, relay or remote base station. A main base station is typically connected to a wired network via the Ethernet port. A relay base station relays data
between main base stations and relay stations or remote base stations with clients. A remote base station is the end point to accept connections from wireless clients and pass data
upwards to a network wirelessly. In this mode, it can support single or multiple WDS links and no wireless clients can associate with it.
Example 1: Point-to-Point
Example 2 : Point-to-Multi-Point
Example 3 : Multi-Point Repeating bridge
Main Base
WIFI WAN
LAN
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
22
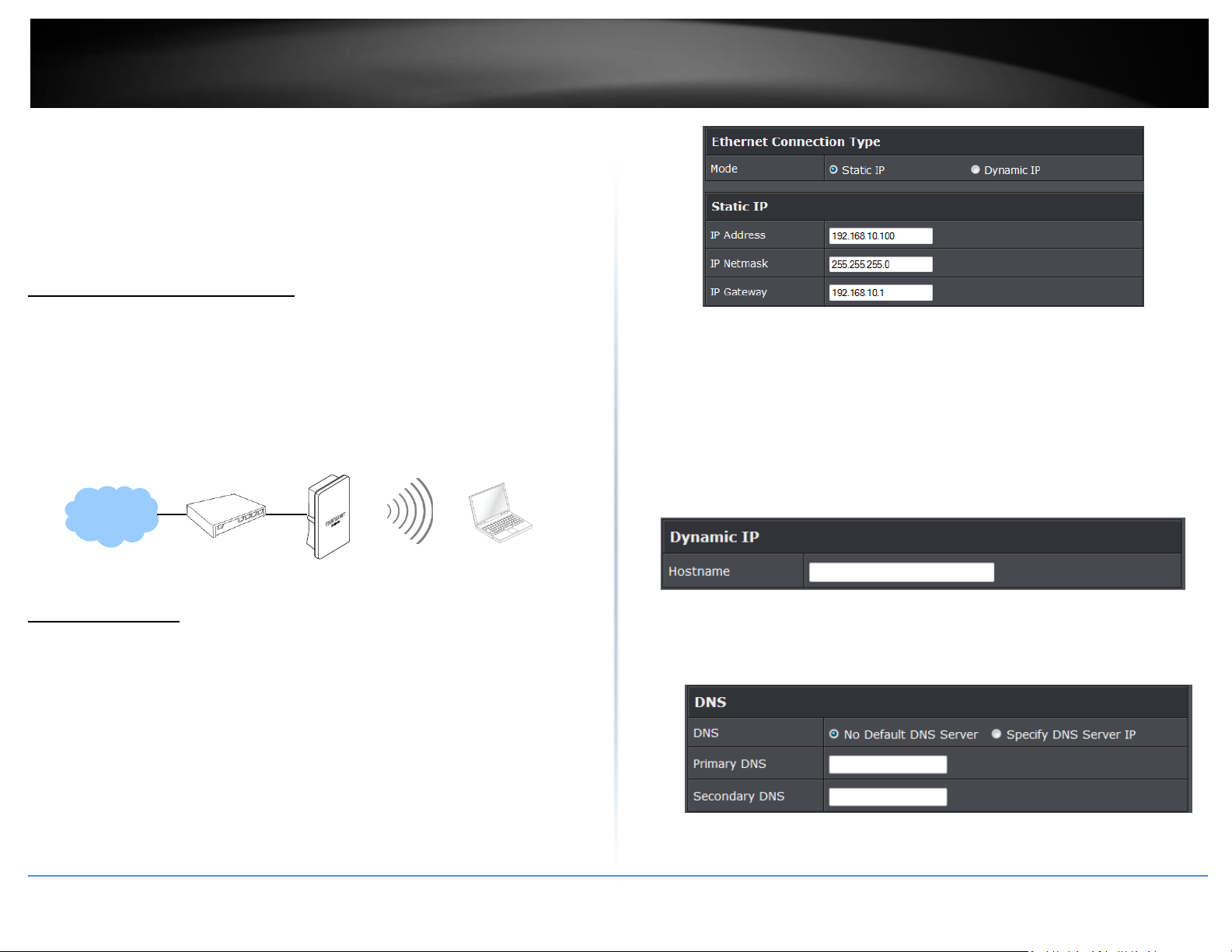
Client Bridge + Universal Repeater Mode
It can be used as an Client Bridge + Universal Repeater to receive wireless signal over last mile applications, helping WISPs deliver wireless broadband Internet service to new
residential and business customers. In this mode, the access point is enabled with DHCP Server functions. The wired clients of access point are in the same subnet from Main Base
Station and it accepts wireless connections from client devices.
CPE + AP Mode (Router Client + Access Point)
It can be used as an Outdoor Customer Premised Equipment (CPE) to receive wireless signal over the last mile, helping WISPs deliver wireless broadband Internet service to new
residential and business customers. In this mode, the access point is a gateway with NAT and DHCP Server functions. The wireless and wired clients of access point are on the
different subnet from Main Base Station and it accepts wireless connections from client devices.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
23
AP Mode Configuration
When AP mode is chosen, the system can be configured as an Access Point. This section
provides detailed explanation for users to configure in the AP mode with help of
illustrations. In the AP mode, functions listed in the table below are also available from
the Web-based GUI interface.
External Network Connection
Network Requirement
Normally, access point connects to a wired LAN and provides a wireless connection
point to associate with wireless client as shown in Figure 3-1. Then, Wireless clients
could access to LAN or Internet by associating themselves with the access point set in AP
mode.
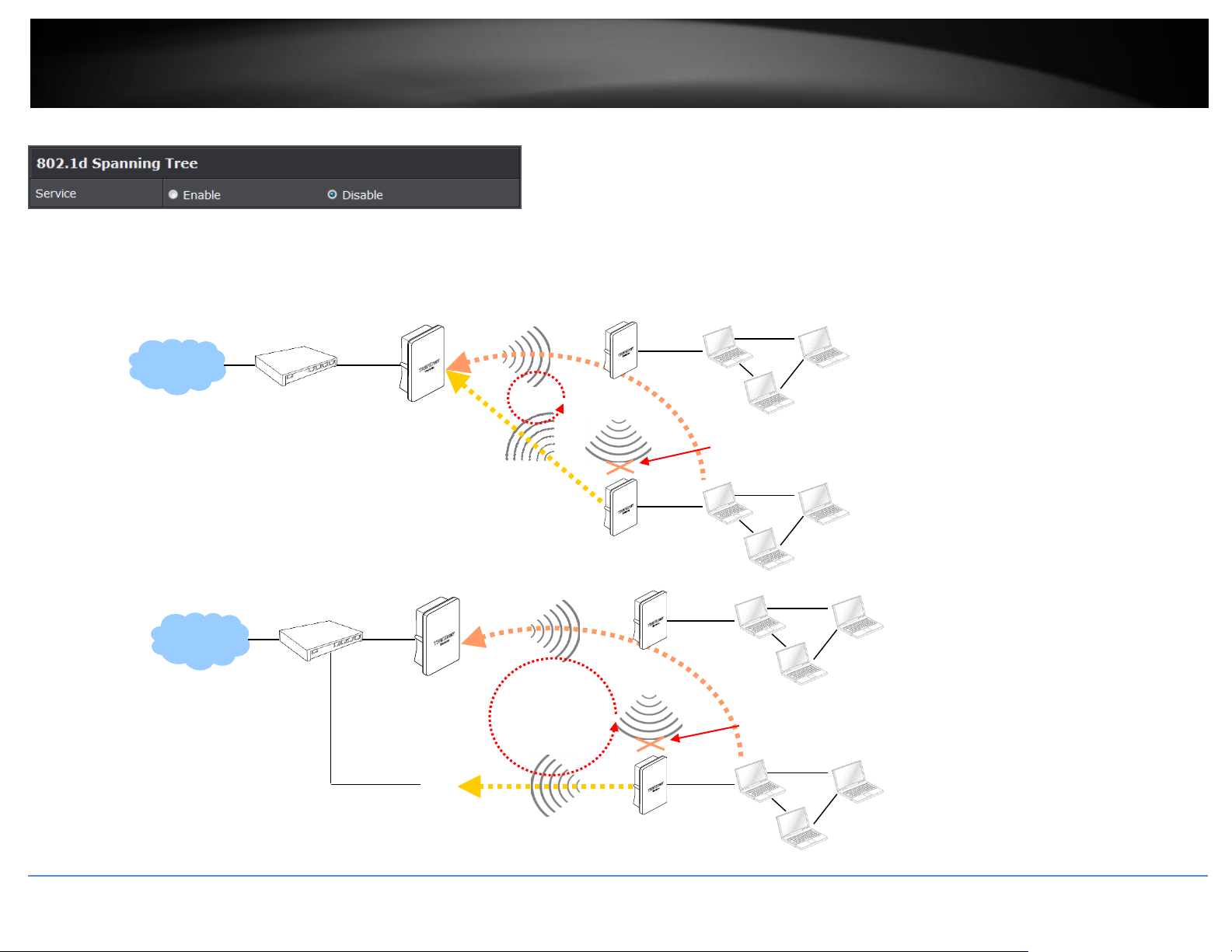
Configure LAN IP
Here are the instructions to setup the local IP Address and Netmask.
Please click on System -> LAN and follow the below setting.
Mode: Check either “Static IP” or “Dynamic IP” button as desired to set up the
system IP of LAN port.
Static IP: The administrator can manually setup the LAN IP address when static IP
is available/ preferred.
o IP Address : The IP address of the LAN port; default IP address is
192.168.2.254
o IP Netmask : The Subnet mask of the LAN port; default Netmask is
255.255.255.0
o IP Gateway : The default gateway of the LAN port; default Gateway is
192.168.2.1
Dynamic IP: This configuration type is applicable when the access point is
connected to a network with the presence of a DHCP server; all related IP
information will be provided by the DHCP server automatically.
o Hostname : The Hostname of the LAN port
DNS: Check either “No Default DNS Server” or “Specify DNS Server IP” button as
desired to set up the system DNS.
o Primary: The IP address of the primary DNS server.
o Secondary: The IP address of the secondary DNS server.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
24
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
WDS
WDS
Spanning Tree Protocol
WDS
Remote Base Station
LOOP
WDS
WDS
Spanning Tree Protocol
WDS
Remote Base Station
LOOP
802.1d Spanning Tree
The spanning tree network protocol provides a loop free topology for a bridged LAN between LAN interface and 4 WDS interfaces from wds0 to wds3. The Spanning Tree Protocol,
which is also referred to as STP, is defined in the IEEE Standard 802.1d. The Spanning tree always enabled on the access point. Below Figures depict a loop for a bridged LAN between LAN
and WDS link
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes.
Blocked by
Remote Base Station
Blocked by
Base Station
Remote Base Station
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
25
Wireless LAN Network
The network manager can configure related wireless settings, General Settings,
Advanced Settings, Virtual AP (VAP) Setting, Security Settings and MAC Filter Settings.
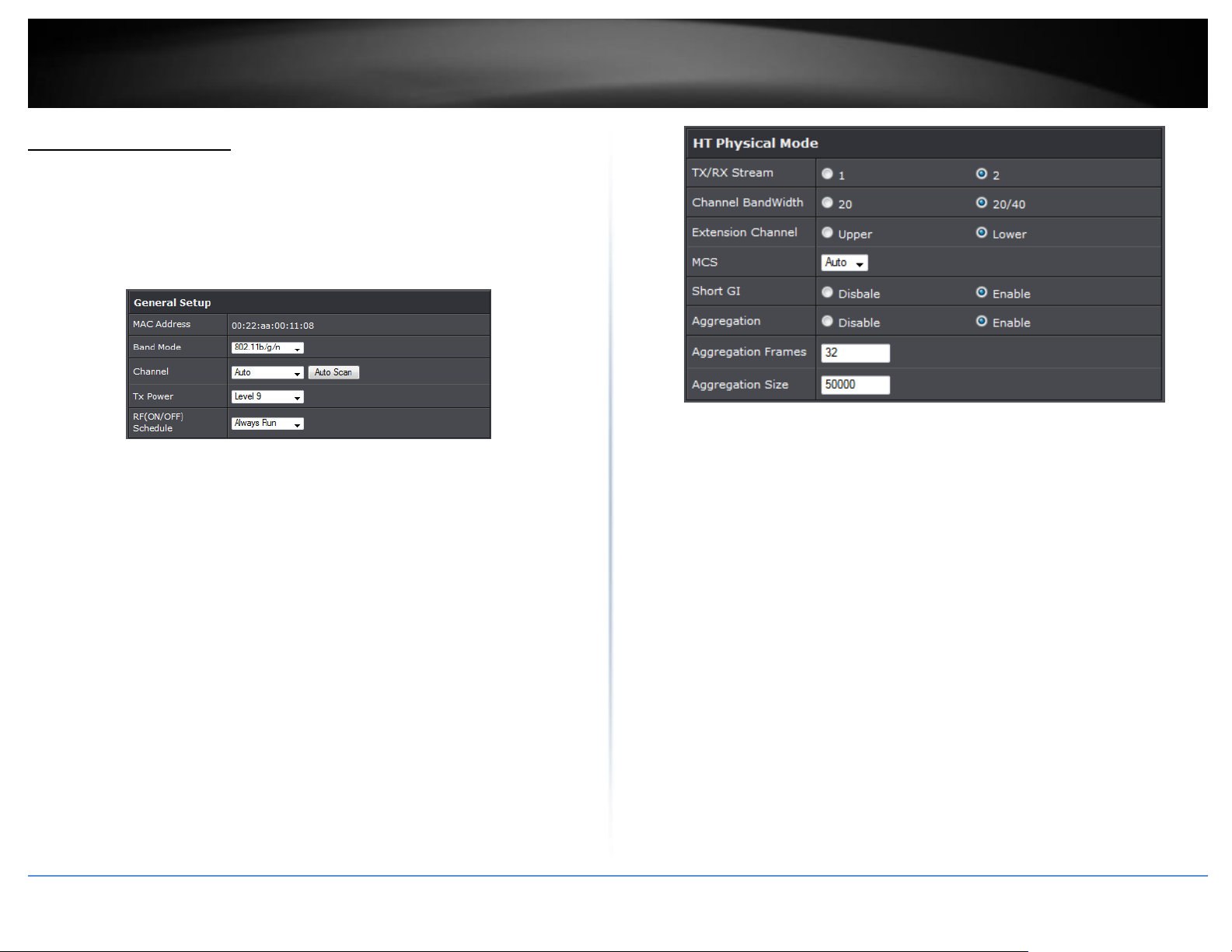
Wireless General Setup
The administrator can change the data transmission, channel and output power settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> General Setup and follow the below setting.
MAC Address: The MAC address of the Wireless interface is displayed here.
Band Mode: Select an appropriate wireless band; bands available are 801.11b,
802.11b/g, 802.11b/g/n or 802.11n only.
Channel: Select the desired channel from the drop-down list to have the access
point operate on. Click Auto Scan to scan for the best available channel to use
based on the environment.
Tx Power: You can adjust the output power of the system to get the appropriate
coverage for your wireless network. Specify digit numbers between 1 to 100 (the
unit is %) for your environment. If you are not sure which setting to choose, then
keep the default setting, 100%.
RF (ON/OFF) Schedule: Select an assigned schedule of when to have the access
point turn on. Select Always Run to have the access point always on.
When Band Mode select in 802.11a only mode, the HT(High Throughput) settings
should be hidden immediately.
3
TxStream/Rx Stream: Select the amount of transmit (TX) and Receive (RX) streams.
By default, it's 2.
Channel Bandwidth: The "20/40” MHz option is usually best. The other option is
available for special circumstances.
Extensions Channel: Select which section of channels to use for extension channels.
MCS: This parameter represents transmission rate. By default (Auto) the fastest
possible transmission rate will be selected. You have the option of selecting the
speed if necessary. (Refer to Appendix C. MCS Data Rate)
Wireless Advanced Setup
To achieve optimal wireless performance, it is necessary to tweak advance setting per
requirements properly, not necessary higher the better or lower.
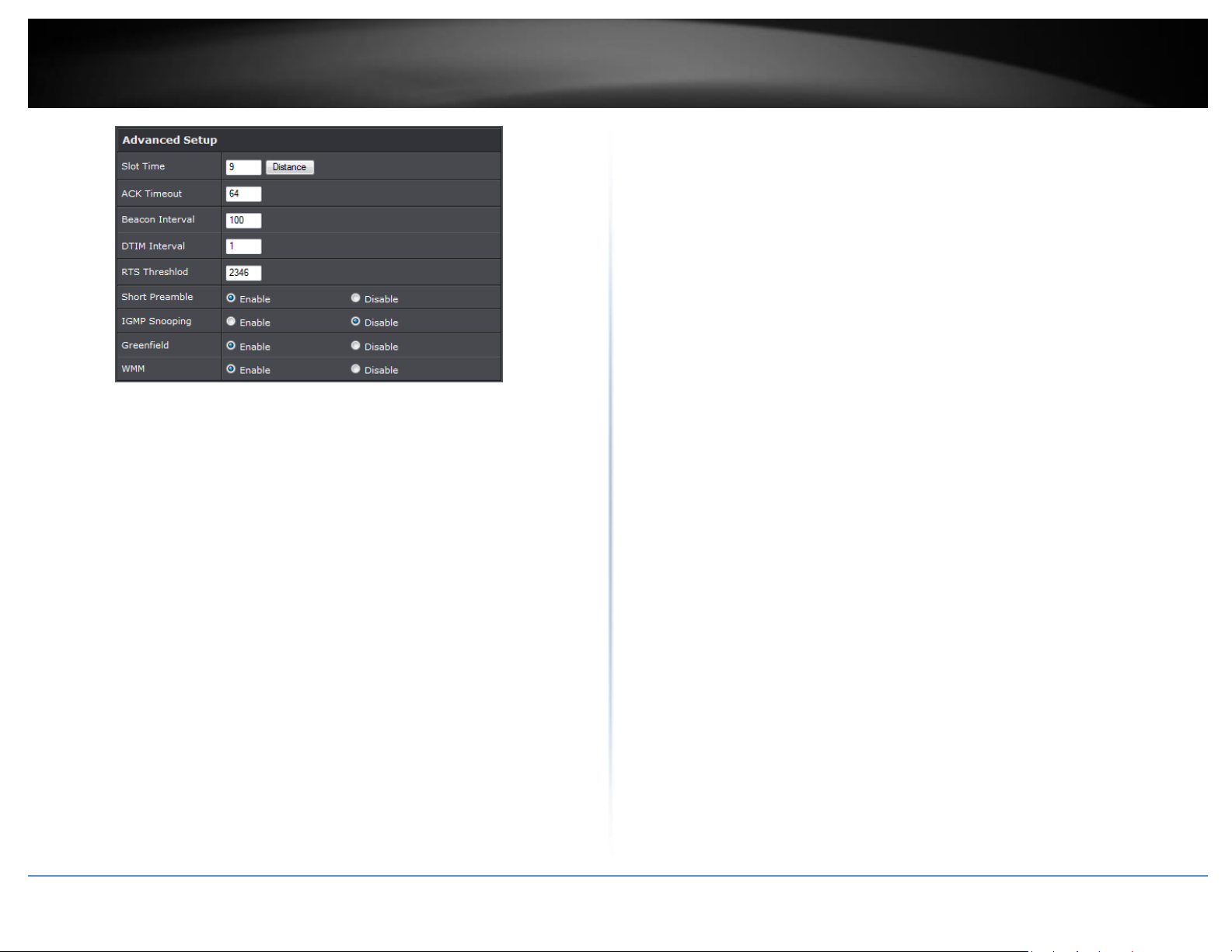
The administrator can change the RTS threshold and fragmentation threshold settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> Advanced Setup and follow the below
setting.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
26
will start to “Resend” packet before ACK is received, and throughputs become low
due to excessively high re-transmission. ACK Timeout is best determined by
distance between the radios, data rate of average environment. The Timeout value
is calculated based on round-trip time of packet with a little tolerance, So, if
experiencing re-transmissions or poor performance the ACK Timeout could be
made longer to accommodate.
Beacon Interval: Beacon Interval is in the range of 20~1024 and set in unit of
millisecond. The default value is 100 msec.
Access Point (AP) in IEEE 802.11 will send out a special approximated 50-byte
frame, called “Beacon”. Beacon is broadcast to all the stations, provides the basic
information of AP such as SSID, channel, encryption keys, signal strength, time
stamp, support data rate.
Short Slot: By default, it’s “Enable” for reducing the slot time from the standard 20
microseconds to the 9 microsecond short slot time. Slot time is the amount of time
a device waits after a collision before retransmitting a packet. Reducing the slot
time decreases the overall back-off, which increases throughput. Back-off, which is
a multiple of the slot time, is the random length of time a station waits before
sending a packet on the LAN. For a sender and receiver own right of the channel the
shorter slot time help manage shorter wait time to re-transmit from collision
because of hidden wireless clients or other causes. When collision sources can be
removed sooner and other senders attempting to send are listening the channel
(CSMA/CA) the owner of the channel should continue ownership and finish their
transmission and release the channel. Then, following ownership of the channel will
be sooner for the new pair due to shorter slot time. However, when long duration
of existing collision sources and shorter slot time exist the owners might experience
subsequent collisions. When adjustment to longer slot time can’t improve
performance then RTS/CTS could supplement and help improve performance.
ACK Timeout: ACK timeout is in the range of 1~255 and set in unit of microsecond.
The default value is 32 microsecond. All data transmission in 802.11b/g request an
“Acknowledgement” (ACK) send by receiving radio. The transmitter will resend the
original packet if correspondent ACK failed to arrive within specific time interval,
also refer to as “ACK Timeout”.
ACK Timeout is adjustable due to the fact that distance between two radio links
may vary in different deployment. ACK Timeout makes significant influence in
performance of long distance radio link. If ACK Timeout is set too short, transmitter
All the radio stations received beacon recognizes the existence of such AP, and may
proceed next actions if the information from AP matches the requirement. Beacon
is sent on a periodic basis, the time interval can be adjusted.
By increasing the beacon interval, you can reduce the number of beacons and
associated overhead, but that will likely delay the association and roaming process
because stations scanning for available access points may miss the beacons. You can
decrease the beacon interval, which increases the rate of beacons. This will make the
association and roaming process very responsive; however, the network will incur
additional overhead and throughput will go down.
DTIM Interval: The DTIM interval is in the range of 1~255. The default is 1.
DTIM is defined as Delivery Traffic Indication Message. It is used to notify the
wireless stations, which support power saving mode, when to wake up to receive
multicast frame. DTIM is necessary and critical in wireless environment as a
mechanism to fulfill power-saving synchronization. A DTIM interval is a count of the
number of beacon frames that must occur before the access point sends the
buffered multicast frames. For instance, if DTIM Interval is set to 3, then the Wi-Fi
clients will expect to receive a multicast frame after receiving three Beacon frame.
The higher DTIM interval will help power saving and possibly decrease wireless
throughput in multicast applications.
RTS Threshold: TRTS Threshold is in the range of 1~2347 byte. The default is 2347
byte. The main purpose of enabling RTS by changing RTS threshold is to reduce
possible collisions due to hidden wireless clients. RTS in AP will be enabled
automatically if the packet size is larger than the Threshold value. By default, RTS is
disabled in a normal environment supports non-jumbo frames.
Short Preamble: By default, it’s “Enable”. To Disable is to use Long 128-bit
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
27
Queue
Data
Transmitted
AP to Clients
Priority
Description
AC_BK
Background.
Low
High throughput. Bulk data that requires maximum
throughput and is not time-sensitive is sent to this
queue (FTP data, for example).
AC_BE
Best Effort
Medium
Medium throughput and delay. Most traditional IP
data is sent to this queue
AC_VI
Video
High
Minimum delay. Time-sensitive video data is
automatically sent to this queue
AC_VO
Voice
High
Time-sensitive data like VoIP and streaming media
are automatically sent to this queue
Preamble Synchronization field. The preamble is used to signal "here is a train of
data coming" to the receiver. The short preamble provides 72-bit Synchronization
field to improve WLAN transmission efficiency with less overhead.
WMM: By default, it's “Enabled”.
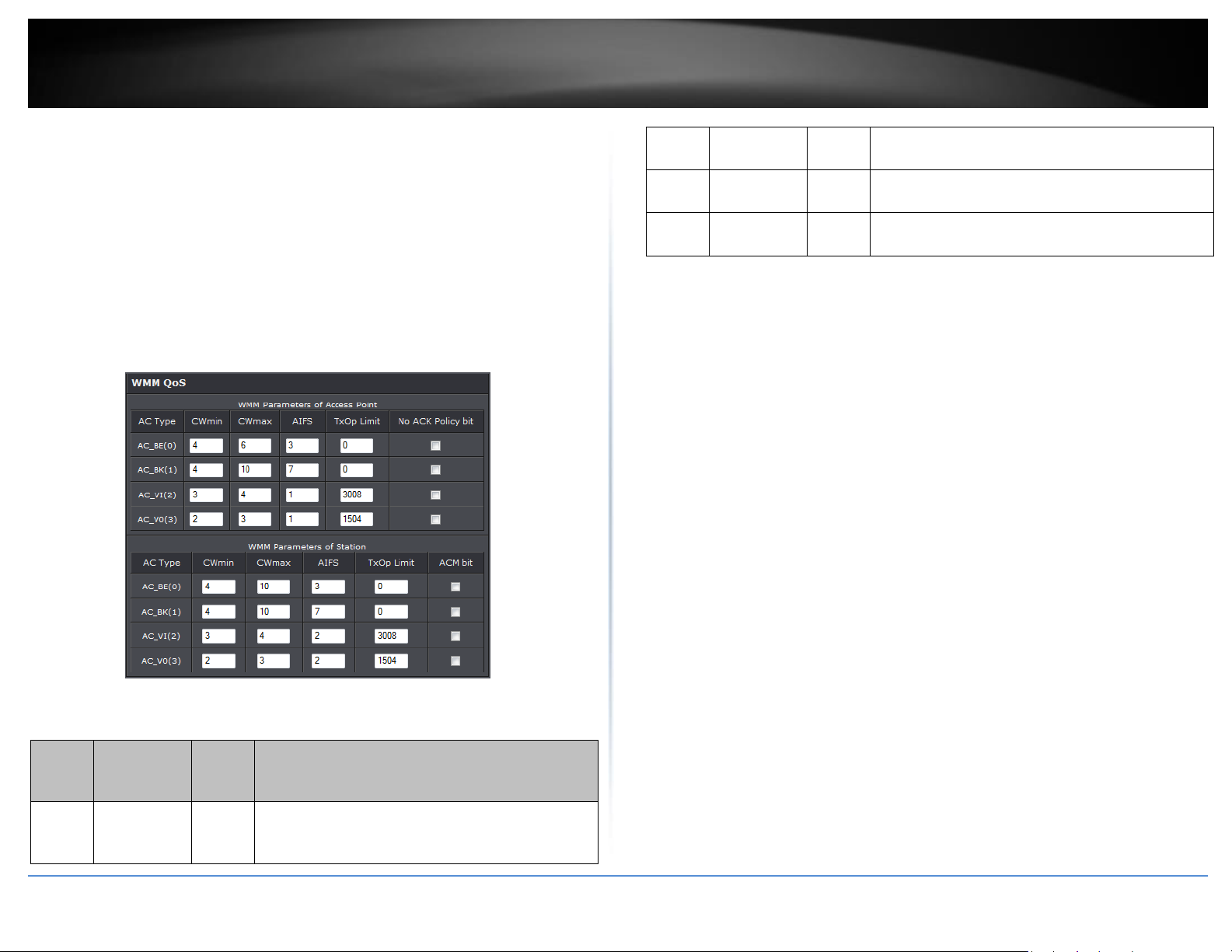
Wireless WMM QoS Setup
To achieve optimal wireless performance, it is necessary to tweak advance setting per
requirements properly, not necessary higher the better or lower.
The administrator can change the RTS threshold and fragmentation threshold settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> Advanced
WMM Parameters of Access Point : This affects traffic flowing from the access
point to the client station
Configuring QoS options consists of setting parameters on existing queues for different
types of wireless traffic. You can configure different minimum and maximum wait
times for the transmission of packets in each queue based on the requirements of the
media being sent. Queues automatically provide minimum transmission delay for
Voice, Video, multimedia, and mission critical applications, and rely on best-effort
parameters for traditional IP data.
As an Example, time-sensitive Voice & Video, and multimedia are given effectively
higher priority for transmission (lower wait times for channel access), while other
applications and traditional IP data which are less time-sensitive but often more dataintensive are expected to tolerate longer wait times.
o Aifsn: The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing Number specifies a wait time (in
milliseconds) for data frames
o CWmin: Minimum Contention Window. This parameter is input to the algorithm
that determines the initial random back-off wait time ("window") for retry of a
transmission. The value specified here in the Minimum Contention Window is the
upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from which the initial random back-off
wait time is determined.
o CWmax: Maximum Contention Window. The value specified here in the
Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling
of the random back-off value. This doubling continues until either the data frame
is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached. Once the Maximum
Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a maximum
number of retries allowed is reached. Valid values for the "cwmax" are 1, 3, 7, 15,
31, 63, 127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for "cwmax" must be higher than the
value for "cwmin".
o Txop: Transmission Opportunity is an interval of time when a WME AP has the
right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium (WM). This value
specifies (in milliseconds) the Transmission Opportunity (TXOP) for AP; that is, the
interval of time when the WMM AP has the right to initiate transmissions on the
wireless network.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
28
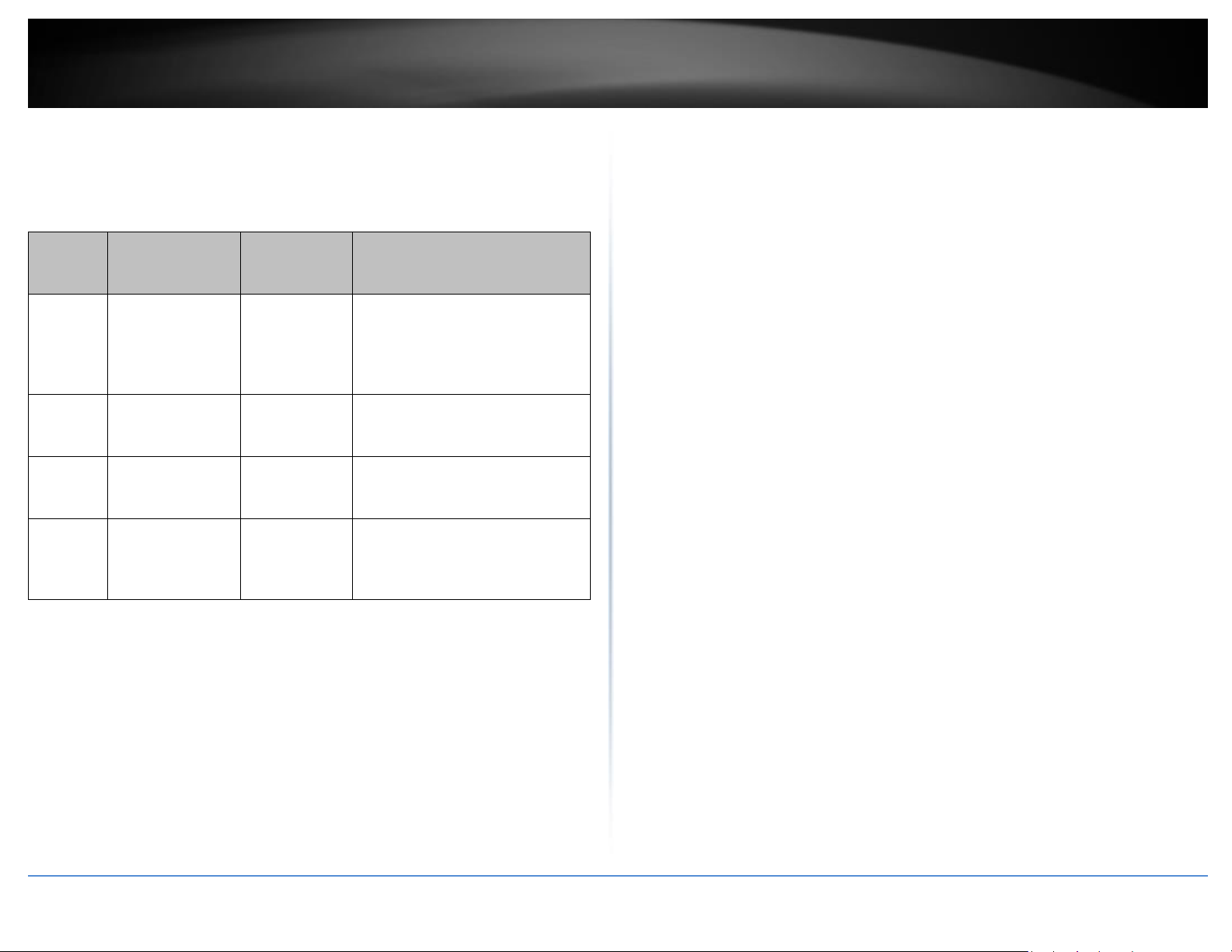
Queue
Data
Transmitted
Clients to AP
Priority
Description
AC_BK
Background.
Low
High throughput. Bulk data that
requires maximum
throughput and is not timesensitive is sent to this queue
(FTP data, for example).
AC_BE
Best Effort
Medium
Medium throughput and delay.
Most traditional IP data is
sent to this queue
AC_VI
Video
High
Minimum delay. Time-sensitive
video data is automatically
sent to this queue
AC_VO
Voice
High
Time-sensitive data like VoIP
and streaming media are
automatically sent to this
queue
o ACM: Admission Control Mandatory, ACM only takes effect on AC_VI and AC_VO.
When you do not click Checkbox, it means that the ACM is controlled by the
connecting AP. If you click Checkbox, it means that the Client is in charge.
o AckPolicy: Acknowledgment Policy, WMM defines two ACK policies: Normal ACK
and No ACK. Click “Checkbox” indicates “No ACK”
When the no acknowledgment (No ACK) policy is used, the recipient does not
acknowledge received packets during wireless packet exchange. This policy is
suitable in the environment where communication quality is fine and interference
is weak. While the No ACK policy helps improve transmission efficiency, it can
cause increased packet loss when communication quality deteriorates. This is
because when this policy is used, a sender does not retransmit packets that have
not been received by the recipient. When the Normal ACK policy is used, the
recipient acknowledges each received unicast packet.
WMM Parameters of Station: This affects traffic flowing from the client station to
the access point.
o Aifsn: The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing Number specifies a wait time (in
milliseconds) for data frames
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
o CWmin: Minimum Contention Window. This parameter is input to the algorithm
that determines the initial random backoff wait time ("window") for retry of a
transmission. The value specified here in the Minimum Contention Window is the
upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from which the initial random backoff wait
time is determined.
o CWmax: Maximum Contention Window. The value specified here in the
Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling
of the random backoff value. This doubling continues until either the data frame
is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached. Once the Maximum
Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a maximum
number of retries allowed is reached. Valid values for the "cwmax" are 1, 3, 7, 15,
31, 63, 127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for "cwmax" must be higher than the
value for "cwmin".
o Txop: Transmission Opportunity is an interval of time when a WME AP has the
right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium (WM). This value
specifies (in milliseconds) the Transmission Opportunity (Txop) for AP; that is, the
interval of time when the WMM AP has the right to initiate transmissions on the
wireless network.
o ACM: Admission Control Mandatory, ACM only takes effect on AC_VI and AC_VO.
When you do not click Checkbox, it means that the ACM is controlled by the
connecting AP. If you click Checkbox, it means that the Client is in charge.
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes.
The items in this page are for AP's RF advanced settings and will be applied to all VAPs
and WDS Links.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-740APBO
29
Sales Network
Engineer Network
Market Network
Guest Network
Accounting Network
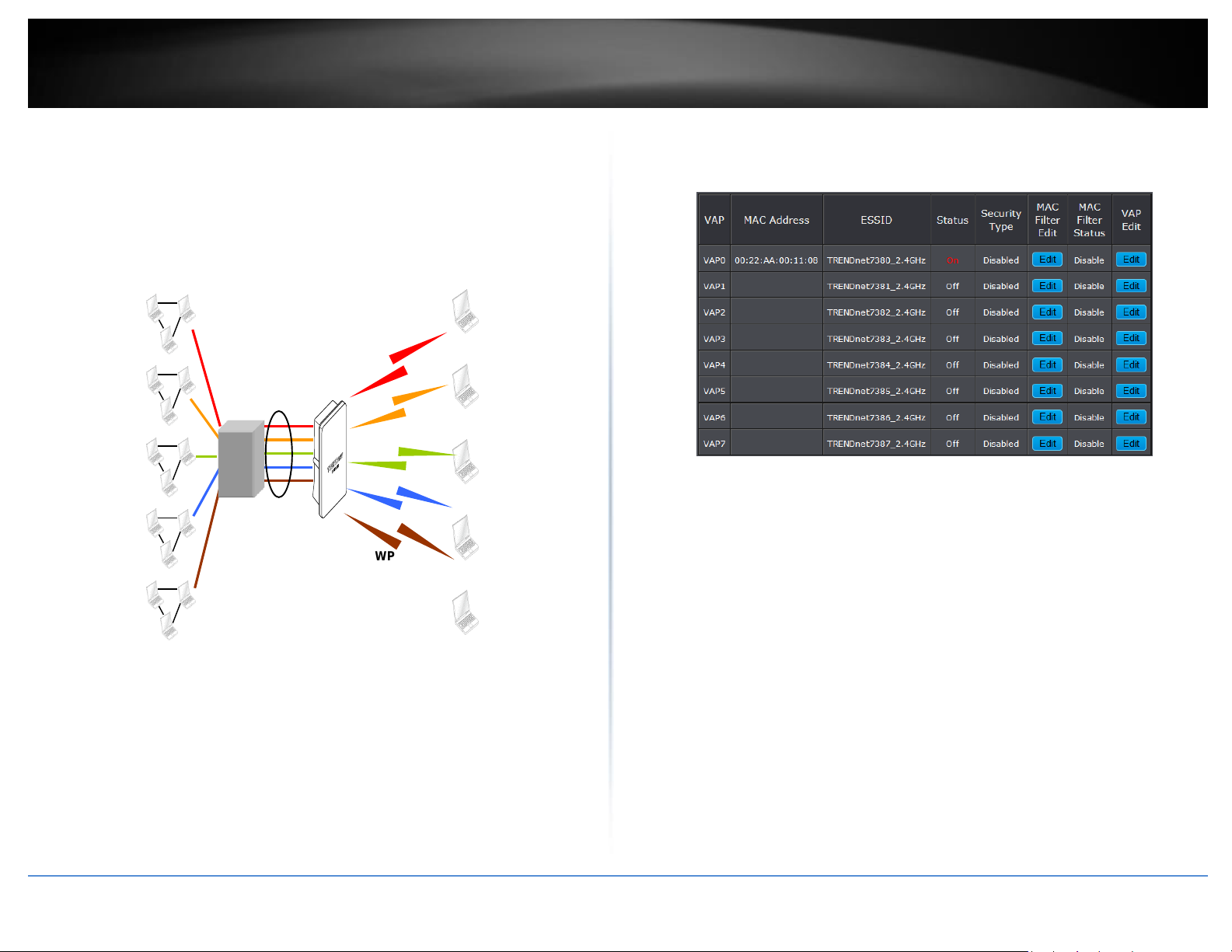
Create Virtual AP (VAP)
Virtual AP Overview
The access point supports broadcasting multiple SSIDs, allowing the creation of Virtual
Access Points, partitioning a single physical access point into 7 logical access points,
each of which can have a different set of security, VLAN Tag(ID) and network settings.
Figure 3-2 shows multiple SSIDs with different security type and VLAN settings.
Multiple SSIDs with different Security Type and VLAN Tag
VLAN #1
WEP
VLAN #2
WPA-PSK/TKIP
SSID 1
SSID 2
VLAN #3
WPA-PSK/AES
WPA2-PSK/TKIP
SSID 3
VLAN #4
WPA2-PSK/AES
SSID 4
VLAN #5
SSID 5
The administrator can view all of the Virtual AP's settings via this page.
Please click on Wireless -> Virtual AP Setup and the Virtual AP Overview Page appears.
VAP: Indicate the system's Virtual AP.
MAC Address: The MAC address of the VAP Interface is displayed here. When you
enable AP and reboot system, the MAC address will display here.
ESSID: Indicate the ESSID of the respective Virtual AP
Status: Indicate the Status of the respective Virtual AP. The Primary AP always on.
Security Type: Indicate a used security type of the respective Virtual AP.
MAC Filter: Indicate a used MAC filter of the respective Virtual AP.
Edit: Click Edit button to configure Virtual AP's settings, including security type and
MAC Filter.
© Copyright 2016 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...