Page 1

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Table of Contents
Page 2

2
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Contents
Introduction ........................................................................................................... 4
Package Contents .......................................................................................................... 4
Hardware Feature .......................................................................................................... 5
System Concept...................................................................................................... 6
Product Benefit .............................................................................................................. 7
Installation Considerations ............................................................................................ 7
Installation ..................................................................................................................... 7
Configuration ................................................................................................................. 8
Applications ........................................................................................................... 9
AP Mode (including Access Point + WDS) ...................................................................... 9
WDS Mode (Pure WDS) ............................................................................................... 10
Client Bridge + Universal Repeater Mode ................................................................... 10
CPE + AP Mode (Router Client + Access Point) ............................................................ 11
Web Management Interface Instructions ............................................................. 11
AP Mode Configuration ........................................................................................ 12
External Network Connection...................................................................................... 12
Network Requirement ................................................................................................. 12
Configure LAN IP ...................................................................................................... 12
Wireless LAN Network ................................................................................................. 15
Wireless General Setup ............................................................................................ 15
Wireless Advanced Setup ......................................................................................... 15
Wireless WMM QoS Setup ....................................................................................... 17
Create Virtual AP (VAP) ............................................................................................ 19
Virtual AP Setup ....................................................................................................... 20
Wireless MAC Filter Setup........................................................................................ 22
Wireless Network Expansion ................................................................................... 22
System Status .............................................................................................................. 23
System Overview ...................................................................................................... 23
Associated Clients Status ......................................................................................... 24
Show WDS Link Status .............................................................................................. 24
Extra Information ..................................................................................................... 25
Event Log .................................................................................................................. 26
WDS Mode Configuration..................................................................................... 26
External Network Connection ..................................................................................... 26
Network Requirement ............................................................................................. 26
Configure LAN IP ...................................................................................................... 27
Wireless Network Expansion ....................................................................................... 27
Wireless General Setup ............................................................................................ 27
Wireless Advanced Setup......................................................................................... 28
Wireless WMM QoS Setup ....................................................................................... 29
WDS Setup ............................................................................................................... 31
System Status .............................................................................................................. 32
System Overview ..................................................................................................... 32
Extra Information ..................................................................................................... 33
Event Log .................................................................................................................. 34
WDS Link Status ....................................................................................................... 34
Repeater Mode .................................................................................................... 35
External Network Connection ..................................................................................... 35
Network Requirement ............................................................................................. 35
Configure LAN IP ...................................................................................................... 35
Wireless Network Expansion ....................................................................................... 36
Wireless General Setup ............................................................................................ 36
Wireless Advanced Setup......................................................................................... 37
Wireless WMM QoS Setup ....................................................................................... 39
Site Survey ............................................................................................................... 40
Repeater AP Setup ................................................................................................... 41
Wireless MAC Filter Setup ....................................................................................... 43
Create Wireless Profile ............................................................................................ 43
Bandwidth Control ................................................................................................... 45
Configure SNMP Setup ............................................................................................. 45
Configure Time Policy .............................................................................................. 46
System Status .............................................................................................................. 47
Table of Contents
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 3

3
TRENDnet User’s Guide
System Overview ...................................................................................................... 47
DHCP Client .............................................................................................................. 48
Extra Information ..................................................................................................... 48
Event Log .................................................................................................................. 49
Associated Client List ............................................................................................... 49
Remote AP status ..................................................................................................... 50
CPE + AP Mode Configuration .............................................................................. 50
External Network Connection...................................................................................... 50
Network Requirement ............................................................................................. 50
Configure CPE Setup................................................................................................. 51
Configure DDNS Setup ............................................................................................. 52
Configure LAN IP ...................................................................................................... 53
Configure Static IP address ...................................................................................... 54
Access Point Association .............................................................................................. 54
Remote AP status ..................................................................................................... 68
System Management ........................................................................................... 68
Configure Management ........................................................................................... 68
Configure System Time ............................................................................................ 70
Configure SNMP Setup ............................................................................................. 70
Enable UPNP ............................................................................................................ 71
Backup / Restore and Reset to Factory .................................................................... 71
Firmware Upgrade ................................................................................................... 72
Network Utility ......................................................................................................... 72
Reboot ...................................................................................................................... 73
Mounting bracket installation .............................................................................. 73
Package contents ......................................................................................................... 73
Wall mount bracket ..................................................................................................... 74
Pole mount bracket ..................................................................................................... 74
Table of Contents
Wireless General Setup ............................................................................................ 54
Wireless Advanced Setup ......................................................................................... 55
Wireless WMM QoS Setup ....................................................................................... 56
Site Survey ................................................................................................................ 58
Create Wireless Profile ............................................................................................. 58
AP Setup ................................................................................................................... 60
Wireless AP MAC Filter Setup .................................................................................. 62
Access Control ............................................................................................................. 62
DMZ .......................................................................................................................... 62
IP Filter Setup ........................................................................................................... 63
MAC Filter Setup ...................................................................................................... 63
Virtual Server ........................................................................................................... 64
Bandwidth Control ................................................................................................... 64
Routing ..................................................................................................................... 65
Status ........................................................................................................................... 65
System Overview ...................................................................................................... 65
DHCP Client .............................................................................................................. 66
Extra Information ..................................................................................................... 67
Event Log .................................................................................................................. 68
Associated Client List ............................................................................................... 68
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Appendix .............................................................................................................. 75
Windows TCP/IP Settings ............................................................................................ 75
Enabling UPnP in Windows XP ..................................................................................... 76
Limited Warranty ......................................................................................................... 78
Page 4

TRENDnet User’s Guide
4
Introduction
Multiple SSIDs
Create up to seven additional SSIDs
TRENDnet’s 10 dBi Outdoor PoE Access Point, model TEW-738APBO,
provides Wireless N300 building-to-building connectivity for clear line of
sight distances of up to 8 km (5 miles)*. A variety of installation scenarios
are facilitated with Access Point (AP), Wireless Distribution System
(WDS), Repeater, and CPE + AP modes. The rugged aluminum IP67 rated
housing comes with wall and pole mounting hardware.
Compatibility
Compatible with legacy wireless devices
Mounting Hardware
Pole and wall mount hardware included
* Effective wireless coverage may vary depending on the wireless
device's output power, antenna gain, antenna alignment, receiving
Performance
Multi-Mode Support
Supports Access Point (AP), Wireless Distribution System (WDS), WDS +
AP, and CPE + AP modes
Wireless N300 (2.4 GHz)
Compliant with 802.11n/g/b technology (2.4 GHz) with data rates up to
300 Mbps
sensitivity, and radio interference. Additionally environmental factors
such as weather conditions, physical obstacles, and other considerations
may affect performance. For optimal results, we recommended
consulting a professional installer for site survey, safety precautions, and
proper installation.
**Recommended max. PoE cable length of 70 m
Outdoor Rated
Durable aluminum enclosure with an IP67 outdoor weather rating
Directional Antenna
Built in 10 dBi directional antenna
Distance Rating
When networked to the same unit, this unit is rated for connecting over
clear line-of-sight distances of up to 8 km (5 miles)*
Power over Ethernet (PoE)
Comes with a proprietary PoE injector, so that it can connect a regular
non-PoE switch
Logs
Real time logs and statistics help troubleshooting
Encrypted Wireless
Support for wireless encryption of up to WPA2
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Package Contents
The standard package contents
• TEW-738APBO
• Multi-Language Quick Installation Guide
• CD-ROM (User’s Guide)
• PoE Injector &Power cord (All in one type)
• Mounting Kit
• Grounding wire
• Waterproof kit
TEW-738APBO
Page 5

TRENDnet User’s Guide
5
Housing
Hardware Feature
Front Panel
Bottom Panel
TEW-738APBO
LAN/WLAN/PWR
LEDs
Reset Button
• LED
o LAN: Turns on when there is a LAN connection and blinks when data is running
through the LAN port.
o WLAN: Turns on when wireless is enabled and blinks during wireless transmission
occur.
o PWR: Indicates the unit is powered on.
• Reset Button (unscrew cap)
o Reboot: Press and hold the reset button for 2 seconds to restart the unit. All LEDs
• Housing: IP 66/67 housing
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
except PWR will turn off before the unit turns back on and wireless transmission
occur.
o Reset – Press and hold the reset button for more than 10 seconds to restore the
unit back to factory default settings.
• PoE Port (unscrew cap) – Connect the network cable that is connected to the
provided PoE injector to power and configure the unit.
PoE Port
Page 6

TRENDnet User’s Guide
6
TEW-738APBO
System Concept
The TEW-738APBO is not only designed and used as a traditional outdoor AP, but also
with rich features tailored for WISP applications. The two-level management capability
and access control ease WISP and owners to maintain and manage wireless network in a
more controllable fashion. Main applications are listed as follows with illustration:
• Wireless CPE for Multi Dwelling Unit/Multi-Te n an t Unit (MDU/MTU) complexes
including apartments, dormitories, and office complexes.
• Outdoor Access Point for school campuses, enterprise campuses, or manufacture
plants.
• Indoor Access Point for hotels, factories, or warehouses where industrial grade
devices are preferred.
• Public hotspot operation for café, parks, convention centers, shopping malls, or
airports.
• Wireless coverage for indoor and outdoor grounds in private resorts, home yards,
or gulf course communities.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 7

TRENDnet User’s Guide
7
TEW-738APBO
Installation
Product Benefit
The 10 dBi Outdoor PoE Access Point is the point of connection to Wireless Outdoor
Network for service provider deploying last mile services to business or residential
broadband subscribers.. Network administrators can create multiple subscriber service
tier using per-subscriber rate limiting features, and manage centrally.
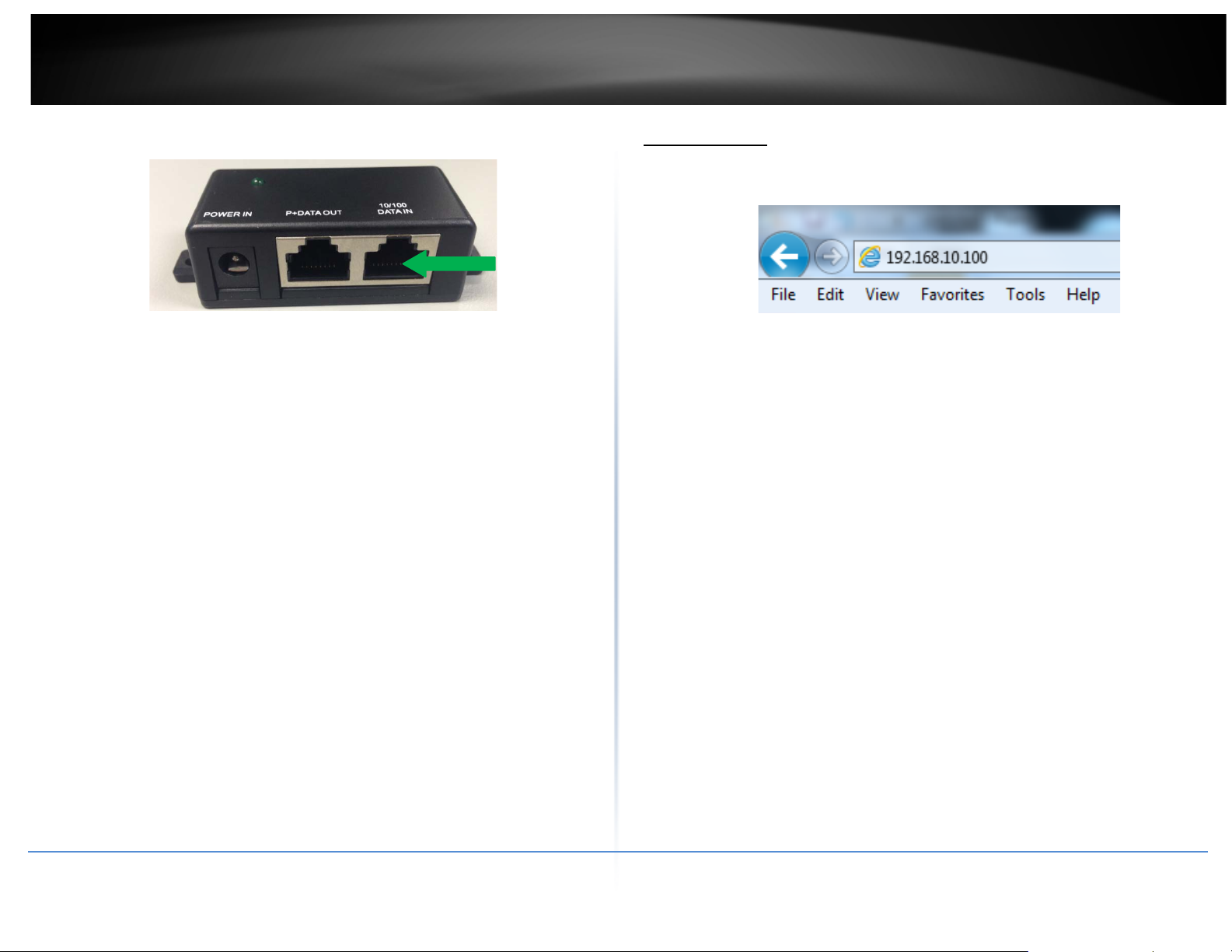
1. Unscrew the black cap covering the PoE port of the TEW-738APBO
2. Install the waterproof kit and insert one end of an Ethernet cable through the kit.
Installation Considerations
There are a number of factors that can impact the range of wireless devices.
1. Adjust your wireless devices so that the signal is traveling in a straight path, rather
than at an angle. The more material the signal has to pass through the more signal
you will lose.
2. Keep the number of obstructions to a minimum. Each obstruction can reduce the
range of a wireless device. Position the wireless devices in a manner that will
minimize the amount of obstructions between them.
3. Building materials can have a large impact on your wireless signal. In an indoor
environment, try to position the wireless devices so that the signal passes through
less dense material such as dry wall. Dense materials like metal, solid wood, glass
or even furniture may block or degrade the signal.
4. Antenna orientation can also have a large impact on your wireless signal. Use the
wireless adapter’s site survey tool to determine the best antenna orientation for
your wireless devices.
5. Interference from devices that produce RF (radio frequency) noise can also impact
your signal. Position your wireless devices away from anything that generates RF
noise, such as microwaves, radios and baby monitors.
If you are still experiencing low or no signal consider repositioning the wireless devices
or installing additional access points. The use of higher gain antennas may also provide
the necessary coverage depending on the environment.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
3. Connect the Ethernet cable to the PoE port of the TEW-738APBO
4. Tighten and secure the seal nut of the waterproof kit.
5. Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to the P+DATA Out port on the PoE
injector.
Page 8
TRENDnet User’s Guide
8
6. Using another Ethernet cable, connect one end to the DATA IN port of the injector.
Configuration
1. Open a web browser, type the IP address of the Access Point and then press Enter.
The default IP address is 192.168.10.100.
TEW-738APBO
7. Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to the LAN port of your network.
8. Plug the power cord into the injector. Then connect the plug into a power outlet.
2. Enter the Username and Password and click OK. By default the Username: root and
Password: root.
3. Click the Wizard button and follow the setup wizard instructions. Click Finish to
complete installation.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 9
TRENDnet User’s Guide
9
Main
WDS
Remote
Main
Remote
Applications
TEW-738APBO is multiple mode system which can be configured either as a wireless
gateway or an access point as desired. It also can be used as a WDS link for Ethernet
network expansion. This section depicts different applications on Router AP Mode, AP
Mode, WDS Mode, CPE Mode, Client Bridge + Universal Repeater Mode and CPE + AP
Mode.
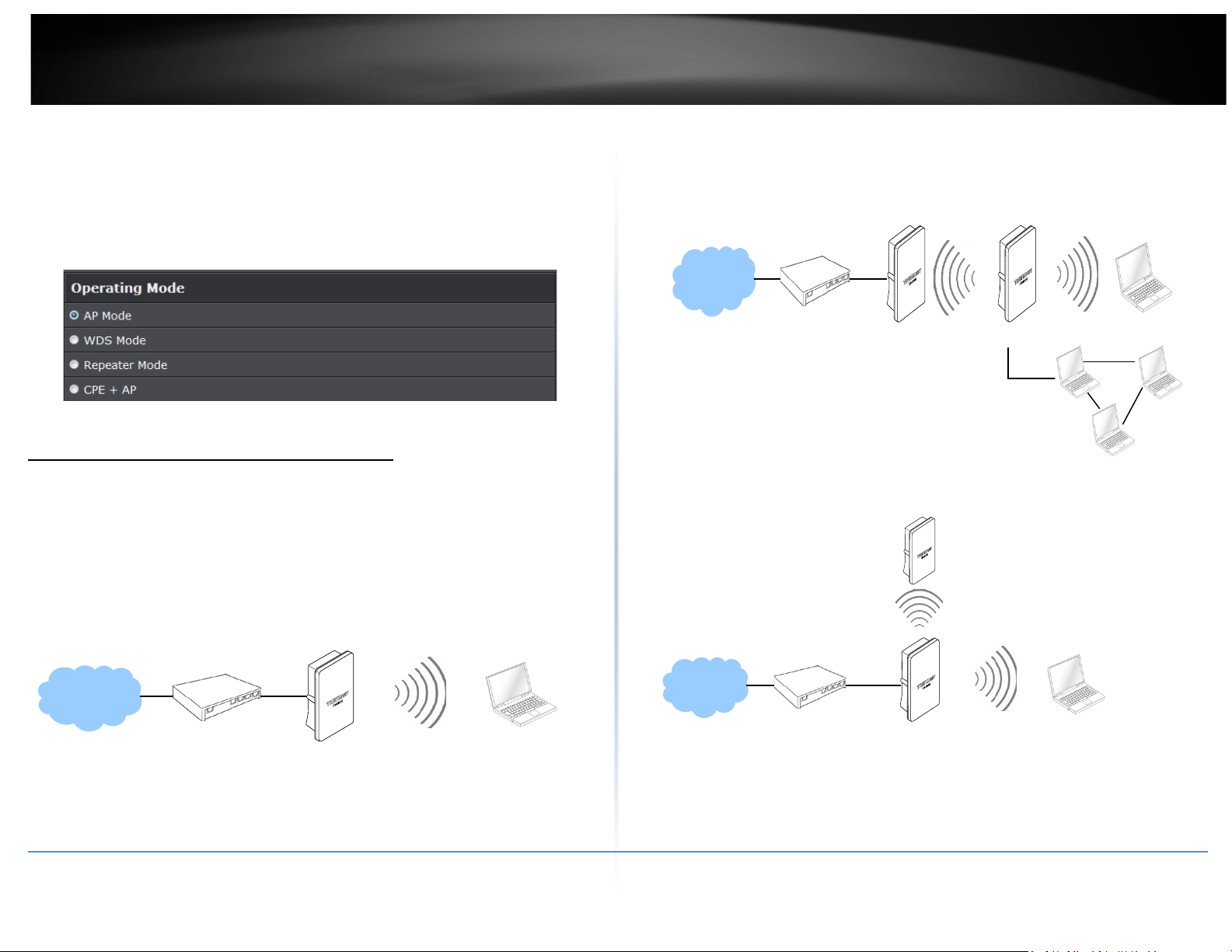
AP Mode (including Access Point + WDS)
An access point can be either a main, relay or remote base station. A main base
station is typically connected to a wired network via the Ethernet port. A relay base
station relays data between main base stations and relay stations or remote base
stations with clients. A remote base station is the end point to accept connections
from wireless clients and pass data upwards to a network wirelessly.
Example 1: Access Point without WDS
• It can be deployed as a tradition fixed wireless Access Point
Example 2: Access Point with WDS
• It can be deployed as a tradition fixed wireless Access Point and provides WDS link
to expand network
WDS
TEW-738APBO
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 10
TRENDnet User’s Guide
10
Inter
WIFI WAN
Main Base
LAN
NA
WDS
Main
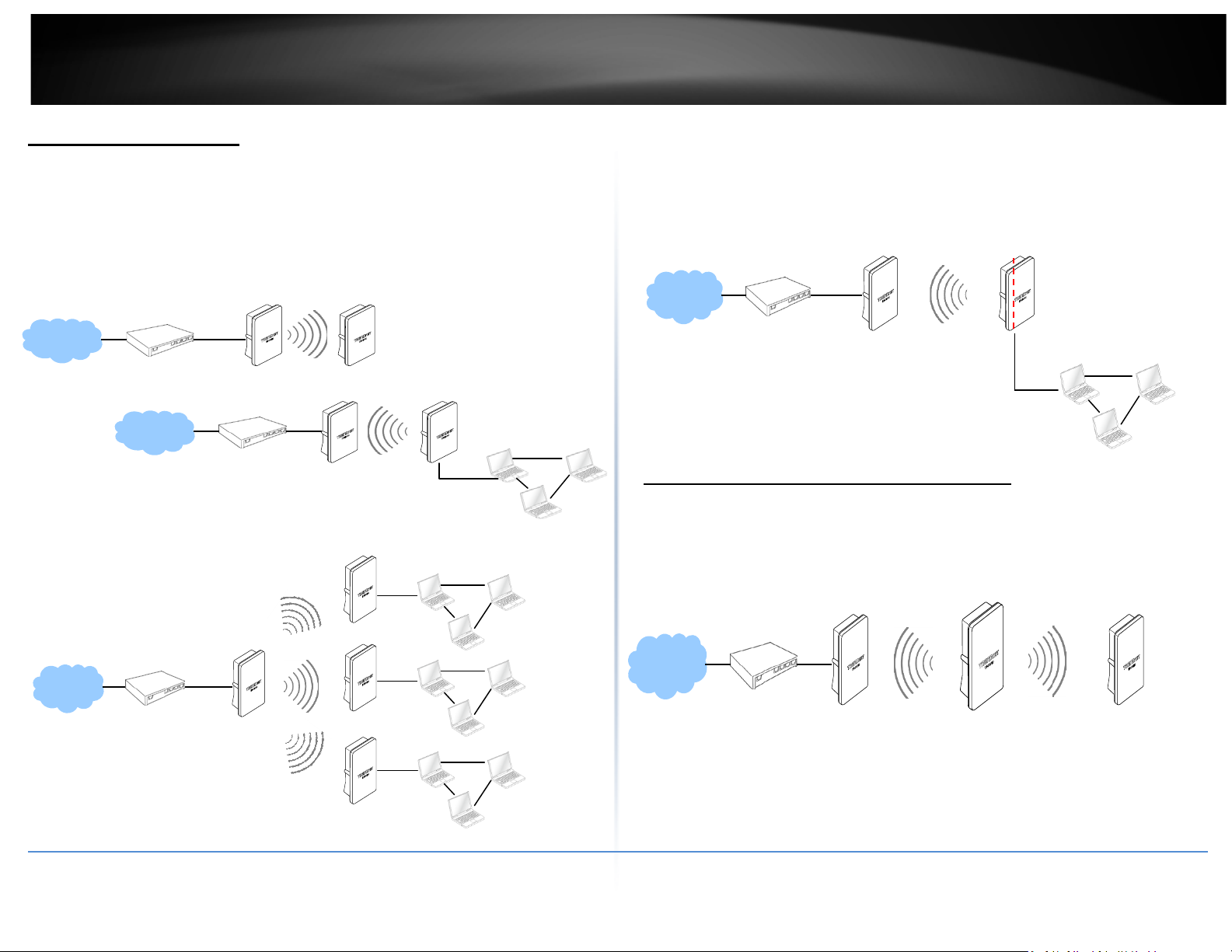
WDS Mode (Pure WDS)
An access point can be either a main, relay or remote base station. A main base station
is typically connected to a wired network via the Ethernet port. A relay base station
relays data between main base stations and relay stations or remote base stations with
clients. A remote base station is the end point to accept connections from wireless
clients and pass data upwards to a network wirelessly. In this mode, it can support single
or multiple WDS links and no wireless clients can associate with it.
Example 1: Point-to-Point
Example 2 : Point-to-Multi-Point
Example 3 : Multi-Point Repeating bridge
Station
Client Bridge + Universal Repeater Mode
It can be used as an Client Bridge + Universal Repeater to receive wireless signal
over last mile applications, helping WISPs deliver wireless broadband Internet
service to new residential and business customers. In this mode, TEW-738APBO is
enabled with DHCP Server functions. The wired clients of TEW-738APBO are in the
same subnet from Main Base Station and it accepts wireless connections from
client devices.
TEW-738APBO
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 11
TRENDnet User’s Guide
11
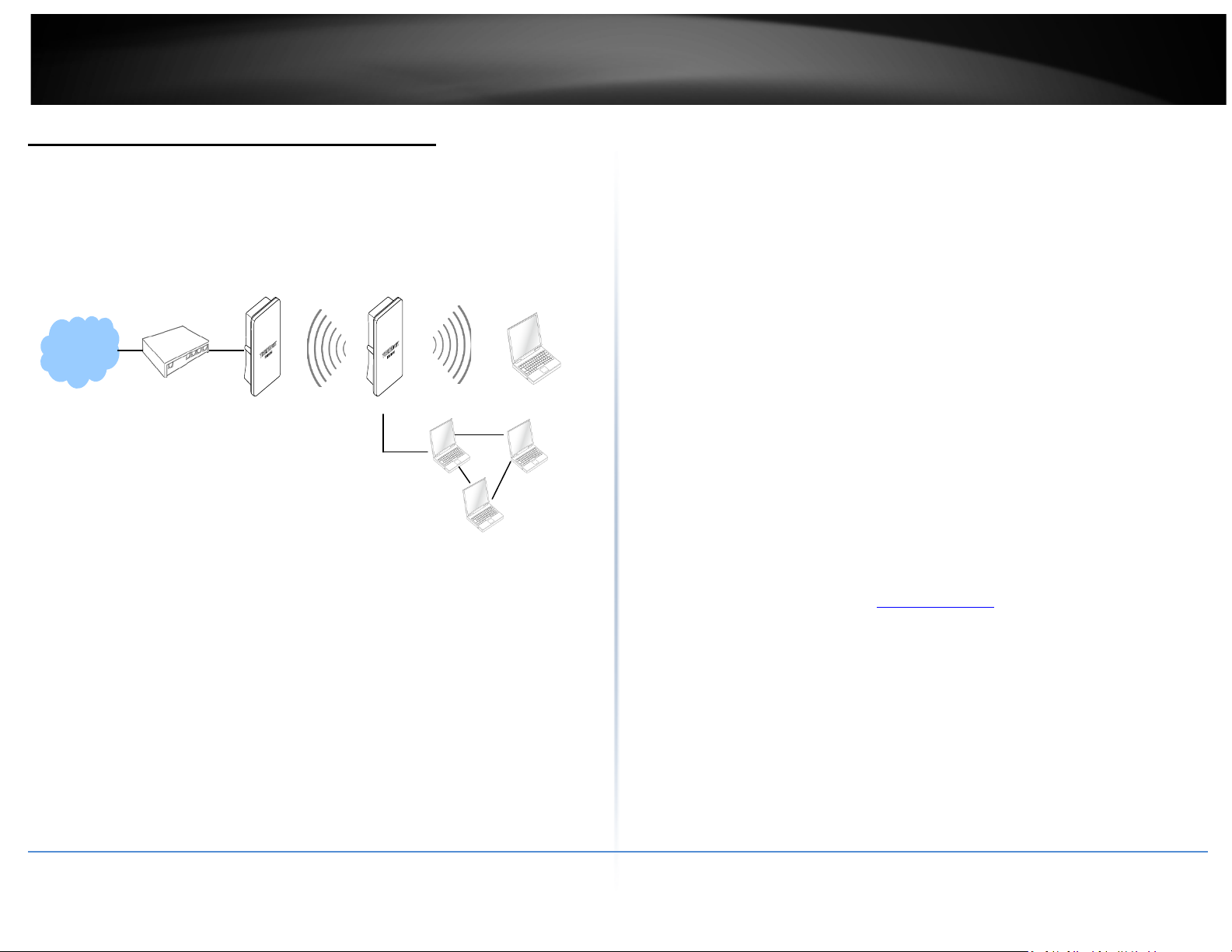
CPE + AP Mode (Router Client + Access Point)
It can be used as an Outdoor Customer Premised Equipment (CPE) to receive
wireless signal over the last mile, helping WISPs deliver wireless broadband Internet
service to new residential and business customers. In this mode, theTEW-738APBO
is a gateway with NAT and DHCP Server functions. The wireless and wired clients of
TEW-738APBO are on the different subnet from Main Base Station and it accepts
wireless connections from client devices.
Web Management Interface Instructions
TEW-738APBO supports web-based configuration. Upon the completion of hardware
installation, TEW-738APBO can be configured through a PC/NB by using its web browser
such as Internet Explorer version 6.0.
• Default IP Address : 192.168.10.100
• Default IP Netmask : 255.255.255.0
• Default User Name and Password : admin/admin
Step
• IP Segment Set-up for Administrator's PC/NB: Set the IP segment of the
administrator's computer to be in the same range as TEW-738APBO for accessing
the system. Do not duplicate the IP Address used here with IP Address of TEW738APBO or any other device within the network
Example of Segment:
The valid range is 1 ~ 254 and 192.168.10.254 shall be avoided because it is already
assigned to TEW-738APBO. 192.168.10.10 is used in the example below.
o IP Address : 192.168.10.10
o IP Netmask : 255.255.255.0
• Launch Web Browser
Launch web browser to access the web management interface of system by
entering the default IP Address,
press Enter.
• System Login: The system manager Login Page then appears.
Enter “admin” as User name and “admin” as Password, and then click OK to login
to the system; the root manager account is used as an example here.
• Login Success: System Overview page will appear after successful login.
http://192.168.10.100, in the URL field, and then
TEW-738APBO
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 12

TRENDnet User’s Guide
12
AP Mode Configuration
When AP mode is chosen, the system can be configured as an Access Point. This section
provides detailed explanation for users to configure in the AP mode with help of
illustrations. In the AP mode, functions listed in the table below are also available from
the Web-based GUI interface.
Configure LAN IP
Here are the instructions to setup the local IP Address and Netmask.
Please click on System -> LAN and follow the below setting.
• Mode: Check either “Static IP” or “Dynamic IP” button as desired to set up the
system IP of LAN port.
TEW-738APBO
External Network Connection
Network Requirement
Normally, TEW-738APBO connects to a wired LAN and provides a wireless connection
point to associate with wireless client as shown in Figure 3-1. Then, Wireless clients
could access to LAN or Internet by associating themselves with TEW-738APBO set in AP
mode.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
• Static IP: The administrator can manually setup the LAN IP address when static IP
is available/ preferred.
o IP Address : The IP address of the LAN port; default IP address is
192.168.2.254
o IP Netmask : The Subnet mask of the LAN port; default Netmask is
255.255.255.0
o IP Gateway : The default gateway of the LAN port; default Gateway is
192.168.2.1
• Dynamic IP: This configuration type is applicable when the TEW-738APBO is
connected to a network with the presence of a DHCP server; all related IP
information will be provided by the DHCP server automatically.
o Hostname : The Hostname of the LAN port
Page 13
TRENDnet User’s Guide
13
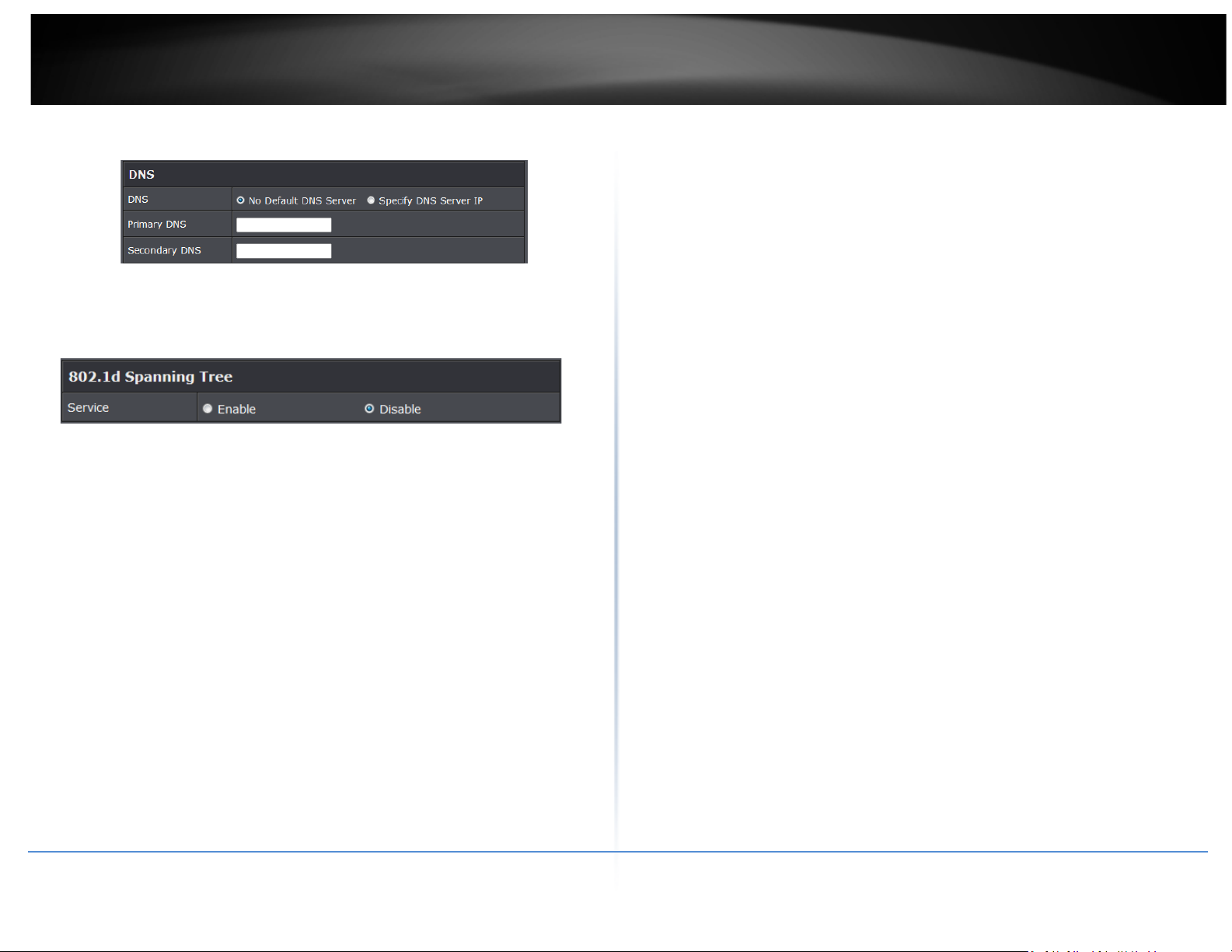
• DNS: Check either “No Default DNS Server” or “Specify DNS Server IP” button as
desired to set up the system DNS.
TEW-738APBO
o Primary: The IP address of the primary DNS server.
o Secondary: The IP address of the secondary DNS server.
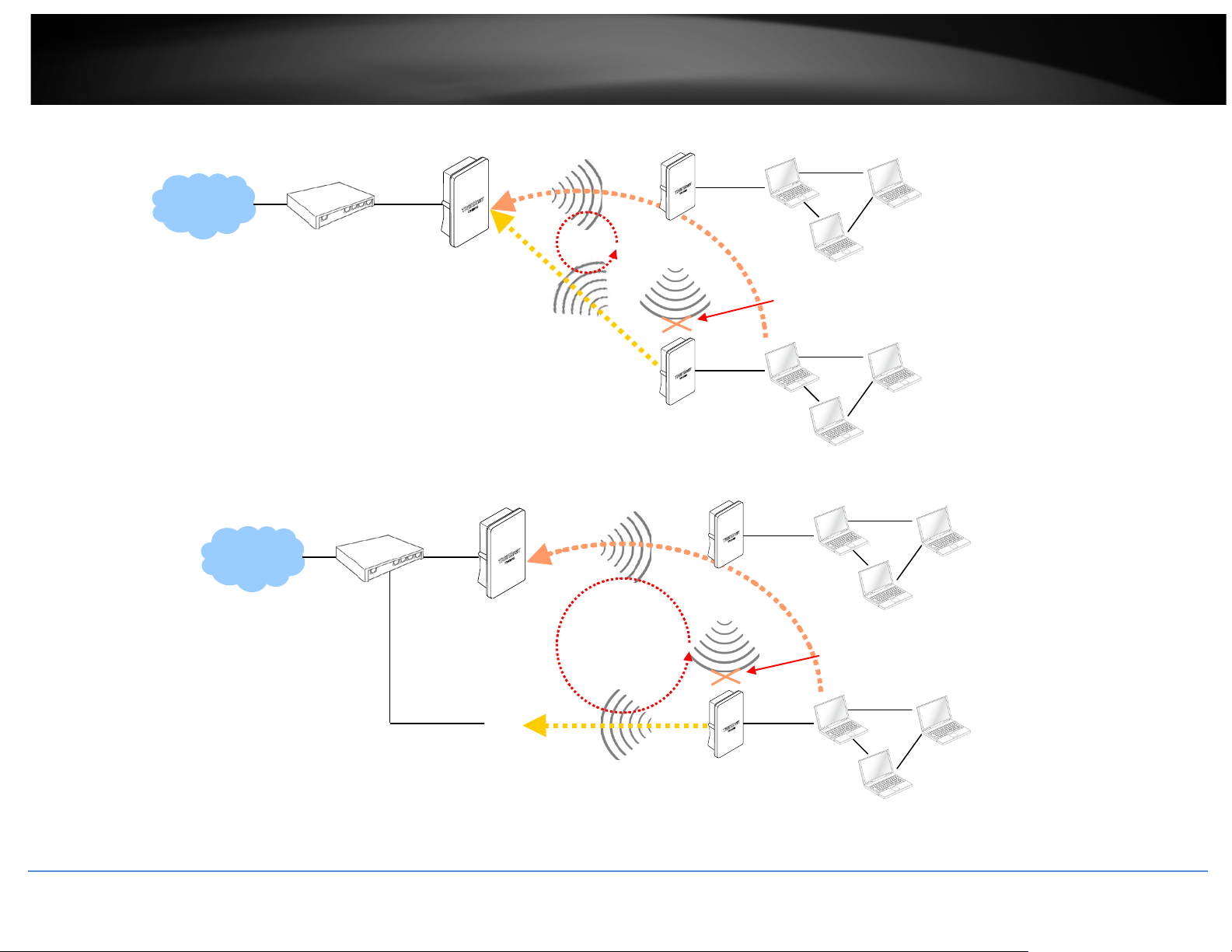
• 802.1d Spanning Tree
The spanning tree network protocol provides a loop free topology for a bridged LAN
between LAN interface and 4 WDS interfaces from wds0 to wds3. The Spanning
Tree Protocol, which is also referred to as STP, is defined in the IEEE Standard
802.1d. The Spanning tree always enabled on TEW-738APBO. Below Figures depict
a loop for a bridged LAN between LAN and WDS link
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 14
TRENDnet User’s Guide
14
WDS
Remote Base Station
WDS
locked by
WDS
Remote Base Station
Base Station
Remote Base Station
WDS
WDS
Remote Base Station
LOOP
WDS
Blocked by
Spanning Tree Protocol
TEW-738APBO
LOOP
B
Spanning Tree Protocol
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 15
15
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-738APBO
Wireless LAN Network
The network manager can configure related wireless settings, General Settings,
Advanced Settings, Virtual AP (VAP) Setting, Security Settings and MAC Filter Settings.
Wireless General Setup
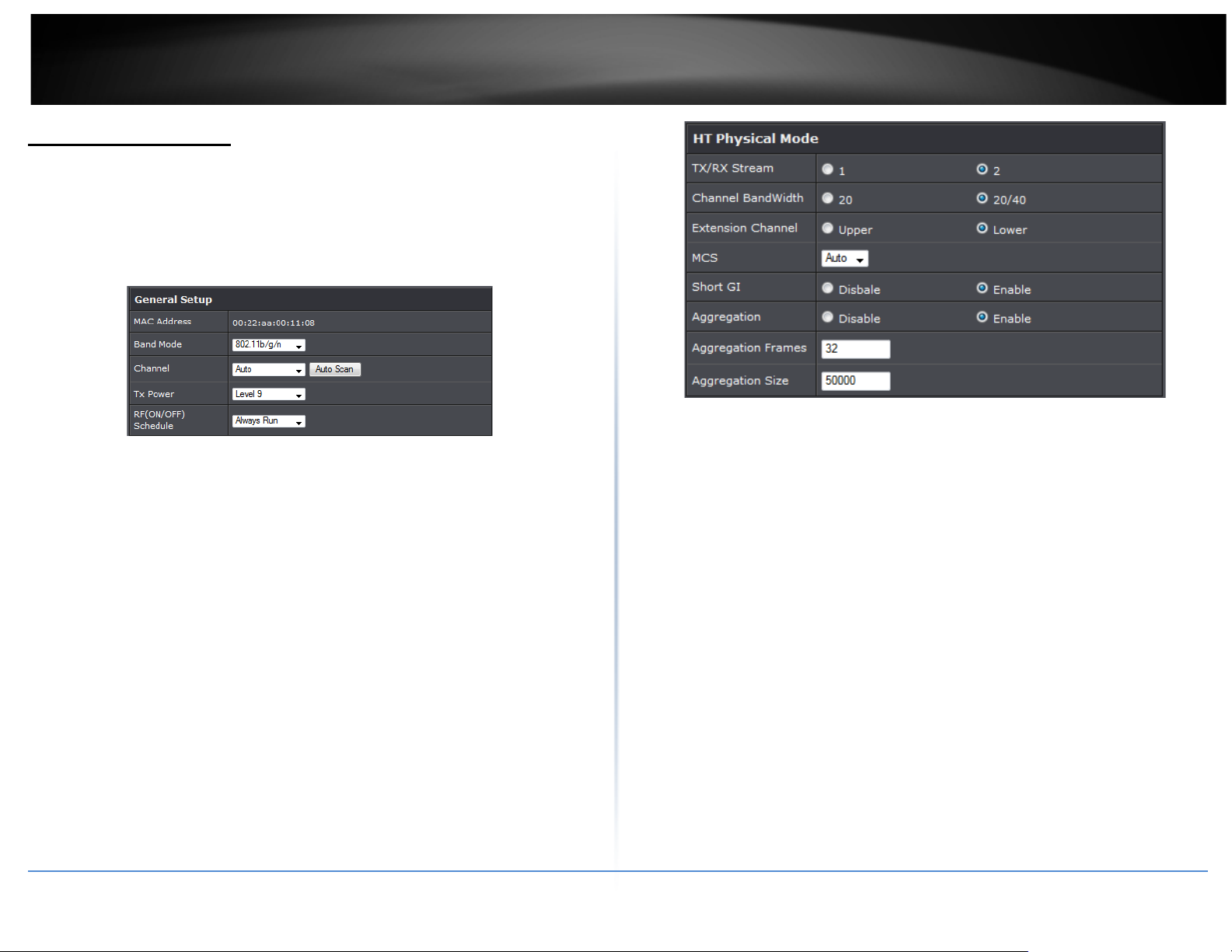
The administrator can change the data transmission, channel and output power settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> General Setup and follow the below setting.
• MAC Address: The MAC address of the Wireless interface is displayed here.
• Band Mode: Select an appropriate wireless band; bands available are 801.11b,
802.11b/g, 802.11b/g/n or 802.11n only.
• Channel: Select the desired channel from the drop-down list to have the access
point operate on. Click Auto Scan to scan for the best available channel to use based
on the environment.
• Tx Power: Yo u can adjust the output power of the system to get the appropriate
coverage for your wireless network. Specify digit numbers between 1 to 100 (the
unit is %) for your environment. If you are not sure which setting to choose, then
keep the default setting, 100%.
• RF (ON/OFF) Schedule: Select an assigned schedule of when to have the access
point turn on. Select Always Run to have the access point always on.
When Band Mode select in 802.11a only mode, the HT(High Throughput) settings
should be hidden immediately.
3
• TxStream/Rx Stream: Select the amount of transmit (TX) and Receive (RX) streams.
By default, it's 2.
• Channel Bandwidth: The "20/40” MHz option is usually best. The other option is
available for special circumstances.
• Extensions Channel: Select which section of channels to use for extension channels.
• MCS: This parameter represents transmission rate. By default (Auto) the fastest
possible transmission rate will be selected. You have the option of selecting the
speed if necessary. (Refer to Appendix C. MCS Data Rate)
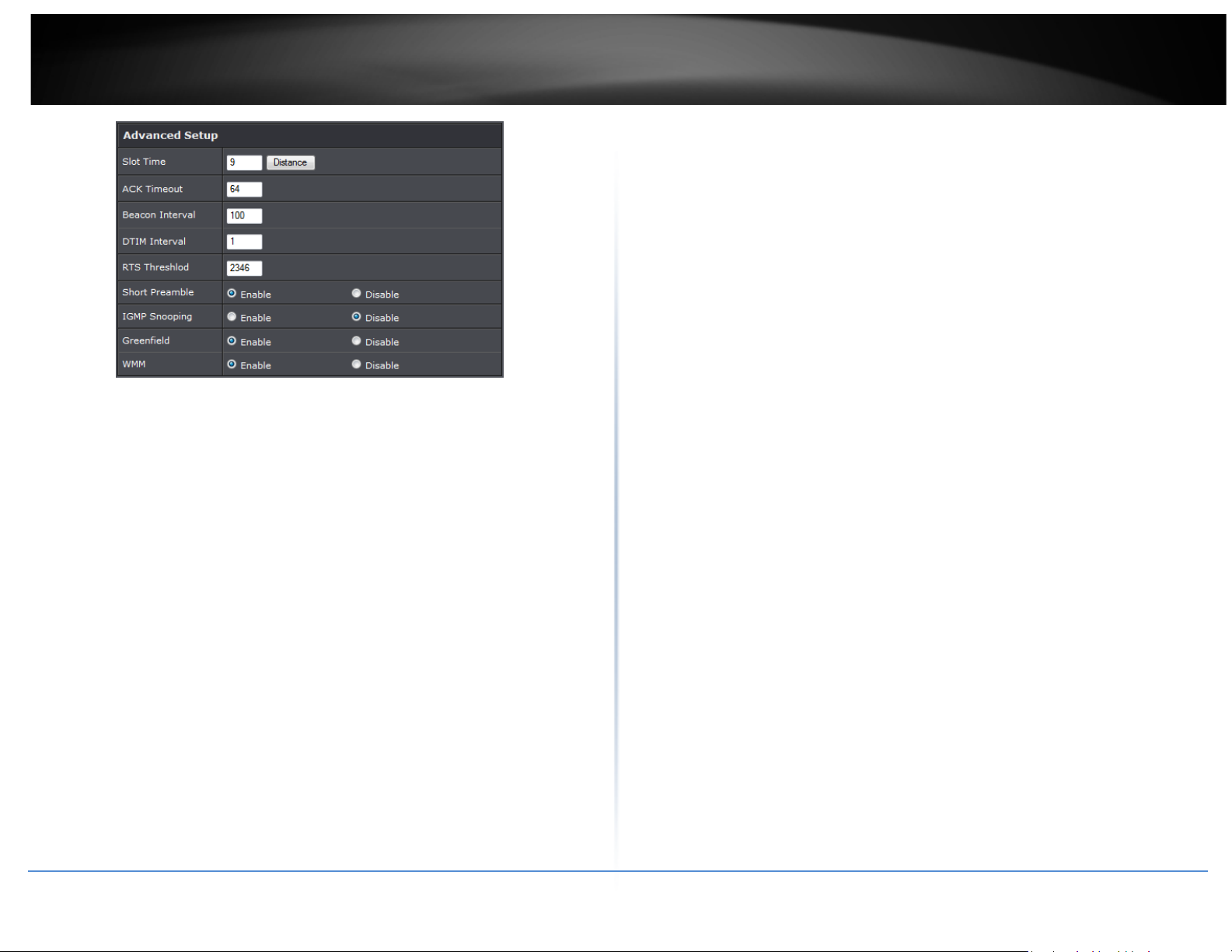
Wireless Advanced Setup
To achieve optimal wireless performance, it is necessary to tweak advance setting per
requirements properly, not necessary higher the better or lower.
The administrator can change the RTS threshold and fragmentation threshold settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> Advanced Setup and follow the below setting.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 16
16
TRENDnet User’s Guide
will start to “Resend” packet before ACK is received, and throughputs become low
due to excessively high re-transmission. ACK Timeout is best determined by
distance between the radios, data rate of average environment. The Timeout value
is calculated based on round-trip time of packet with a little tolerance, So, if
experiencing re-transmissions or poor performance the ACK Timeout could be
made longer to accommodate.
• Beacon Interval: Beacon Interval is in the range of 20~1024 and set in unit of
millisecond. The default value is 100 msec.
Access Point (AP) in IEEE 802.11 will send out a special approximated 50-byte
frame, called “Beacon”. Beacon is broadcast to all the stations, provides the basic
information of AP such as SSID, channel, encryption keys, signal strength, time
stamp, support data rate.
• Short Slot: By default, it’s “Enable” for reducing the slot time from the standard 20
microseconds to the 9 microsecond short slot time. Slot time is the amount of time a
device waits after a collision before retransmitting a packet. Reducing the slot time
decreases the overall back-off, which increases throughput. Back-off, which is a
multiple of the slot time, is the random length of time a station waits before
sending a packet on the LAN. For a sender and receiver own right of the channel the
shorter slot time help manage shorter wait time to re-transmit from collision
because of hidden wireless clients or other causes. When collision sources can be
removed sooner and other senders attempting to send are listening the channel
(CSMA/CA) the owner of the channel should continue ownership and finish their
transmission and release the channel. Then, following ownership of the channel will
be sooner for the new pair due to shorter slot time. However, when long duration of
existing collision sources and shorter slot time exist the owners might experience
subsequent collisions. When adjustment to longer slot time can’t improve
performance then RTS/CTS could supplement and help improve performance.
• ACK Timeout: ACK timeout is in the range of 1~255 and set in unit of microsecond.
The default value is 32 microsecond. All data transmission in 802.11b/g request an
“Acknowledgement” (ACK) send by receiving radio. The transmitter will resend the
original packet if correspondent ACK failed to arrive within specific time interval,
also refer to as “ACK Timeout”.
ACK Timeout is adjustable due to the fact that distance between two radio links
may vary in different deployment. ACK Timeout makes significant influence in
performance of long distance radio link. If ACK Timeout is set too short, transmitter
All the radio stations received beacon recognizes the existence of such AP, and may
proceed next actions if the information from AP matches the requirement. Beacon
is sent on a periodic basis, the time interval can be adjusted.
By increasing the beacon interval, you can reduce the number of beacons and
associated overhead, but that will likely delay the association and roaming process
because stations scanning for available access points may miss the beacons. You
can decrease the beacon interval, which increases the rate of beacons. This will
make the association and roaming process very responsive; however, the network
will incur additional overhead and throughput will go down.
• DTIM Interval: The DTIM interval is in the range of 1~255. The default is 1.
DTIM is defined as Delivery Traffic Indication Message. It is used to notify the
wireless stations, which support power saving mode, when to wake up to receive
multicast frame. DTIM is necessary and critical in wireless environment as a
mechanism to fulfill power-saving synchronization. A DTIM interval is a count of the
number of beacon frames that must occur before the access point sends the
buffered multicast frames. For instance, if DTIM Interval is set to 3, then the Wi-Fi
clients will expect to receive a multicast frame after receiving three Beacon frame.
The higher DTIM interval will help power saving and possibly decrease wireless
throughput in multicast applications.
• RTS Threshold: TRTS Threshold is in the range of 1~2347 byte. The default is 2347
byte. The main purpose of enabling RTS by changing RTS threshold is to reduce
possible collisions due to hidden wireless clients. RTS in AP will be enabled
automatically if the packet size is larger than the Threshold value. By default, RTS is
disabled in a normal environment supports non-jumbo frames.
• Short Preamble: By default, it’s “Enable”. To Disable is to use Long 128-bit Preamble
TEW-738APBO
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 17
17
TRENDnet User’s Guide
queue (FTP data, for example).
data is sent to this queue
Minimum delay. Time-sensitive video data is
Synchronization field. The preamble is used to signal "here is a train of data coming"
to the receiver. The short preamble provides 72-bit Synchronization field to improve
WLAN transmission efficiency with less overhead.
• WMM: By default, it's “Enabled”.
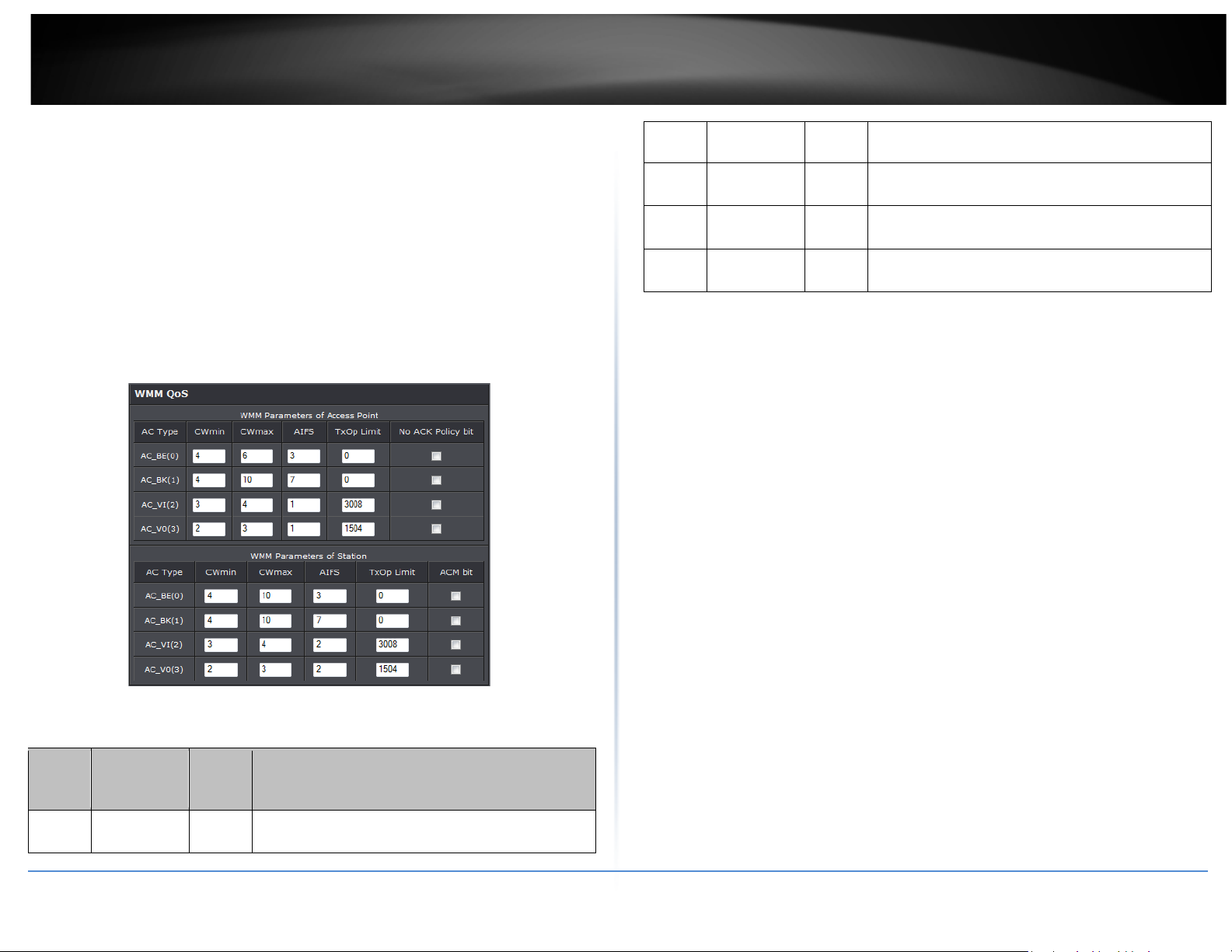
Wireless WMM QoS Setup
To achieve optimal wireless performance, it is necessary to tweak advance setting per
requirements properly, not necessary higher the better or lower.
The administrator can change the RTS threshold and fragmentation threshold settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> Advanced
• WMM Parameters of Access Point : This affects traffic flowing from the access point
to the client station
Data
Queue
AC_BK Background. Low
Transmitted
AP to Clients
Priority Description
High throughput. Bulk data that requires maximum
throughput and is not time-sensitive is sent to this
AC_BE Best Effort Medium
AC_VI Video High
AC_VO Voice High
Configuring QoS options consists of setting parameters on existing queues for different
types of wireless traffic. You can configure different minimum and maximum wait
times for the transmission of packets in each queue based on the requirements of the
media being sent. Queues automatically provide minimum transmission delay for
Voice, Video, multimedia, and mission critical applications, and rely on best-effort
parameters for traditional IP data.
As an Example, time-sensitive Voice & Video, and multimedia are given effectively
higher priority for transmission (lower wait times for channel access), while other
applications and traditional IP data which are less time-sensitive but often more dataintensive are expected to tolerate longer wait times.
o Aifsn: The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing Number specifies a wait time (in
milliseconds) for data frames
o CWmin: Minimum Contention Window. This parameter is input to the algorithm
that determines the initial random back-off wait time ("window") for retry of a
transmission. The value specified here in the Minimum Contention Window is the
upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from which the initial random back-off
wait time is determined.
o CWmax: Maximum Contention Window. The value specified here in the
Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling
of the random back-off value. This doubling continues until either the data frame
is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached. Once the Maximum
Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a maximum number
of retries allowed is reached. Valid values for the "cwmax" are 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63,
127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for "cwmax" must be higher than the value for
"cwmin".
o Txop: Transmission Opportunity is an interval of time when a WME AP has the
right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium (WM). This value
specifies (in milliseconds) the Transmission Opportunity (TXOP) for AP; that is, the
Medium throughput and delay. Most traditional IP
automatically sent to this queue
Time-sensitive data like VoIP and streaming media
are automatically sent to this queue
TEW-738APBO
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 18
18
TRENDnet User’s Guide
interval of time when the WMM AP has the right to initiate transmissions on the
wireless network.
o ACM: Admission Control Mandatory, ACM only takes effect on AC_VI and AC_VO.
When you do not click Checkbox, it means that the ACM is controlled by the
connecting AP. If you click Checkbox, it means that the Client is in charge.
o AckPolicy: Acknowledgment Policy, WMM defines two ACK policies: Normal ACK
and No ACK. Click “Checkbox” indicates “No ACK”
Data
Queue
AC_BK Background. Low
AC_BE Best Effort Medium
AC_VI Video High
AC_VO Voice High
When the no acknowledgment (No ACK) policy is used, the recipient does not
acknowledge received packets during wireless packet exchange. This policy is
suitable in the environment where communication quality is fine and interference
is weak. While the No ACK policy helps improve transmission efficiency, it can
cause increased packet loss when communication quality deteriorates. This is
because when this policy is used, a sender does not retransmit packets that have
not been received by the recipient. When the Normal ACK policy is used, the
recipient acknowledges each received unicast packet.
• WMM Parameters of Station: This affects traffic flowing from the client station to
the access point.
o Aifsn: The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing Number specifies a wait time (in
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Transmitted
Clients to AP
Priority Description
High throughput. Bulk data that
requires maximum
throughput and is not timesensitive is sent to this queue
(FTP data, for example).
Medium throughput and delay.
Most traditional IP data is
sent to this queue
Minimum delay. Time-sensitive
video data is automatically
sent to this queue
Time-sensitive data like VoIP
and streaming media are
automatically sent to this
queue
milliseconds) for data frames
o CWmin: Minimum Contention Window. This parameter is input to the
algorithm that determines the initial random backoff wait time ("window")
for retry of a transmission. The value specified here in the Minimum
Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from
which the initial random backoff wait time is determined.
o CWmax: Maximum Contention Window. The value specified here in the
Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling
of the random backoff value. This doubling continues until either the data frame
is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached. Once the Maximum
Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a maximum number
of retries allowed is reached. Valid values for the "cwmax" are 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63,
127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for "cwmax" must be higher than the value for
"cwmin".
o Txop: Transmission Opportunity is an interval of time when a WME AP has the
right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium (WM). This value
specifies (in milliseconds) the Transmission Opportunity (Txop) for AP; that is, the
interval of time when the WMM AP has the right to initiate transmissions on the
wireless network.
o ACM: Admission Control Mandatory, ACM only takes effect on AC_VI and AC_VO.
When you do not click Checkbox, it means that the ACM is controlled by the
connecting AP. If you click Checkbox, it means that the Client is in charge.
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes.
The items in this page are for AP's RF advanced settings and will be applied to all VAPs
and WDS Links.
TEW-738APBO
Page 19
19
TRENDnet User’s Guide
VLA
N #5
VLA
N #4
VLA
N #3
VLA
N #2
VLA
N #1
SSID 5
SSID 4
SSID 1
Market Network
Guest Network
WPA2PSK/AES
WPA2PSK/TKIP
WPA-
WPAPSK/TKIP
W
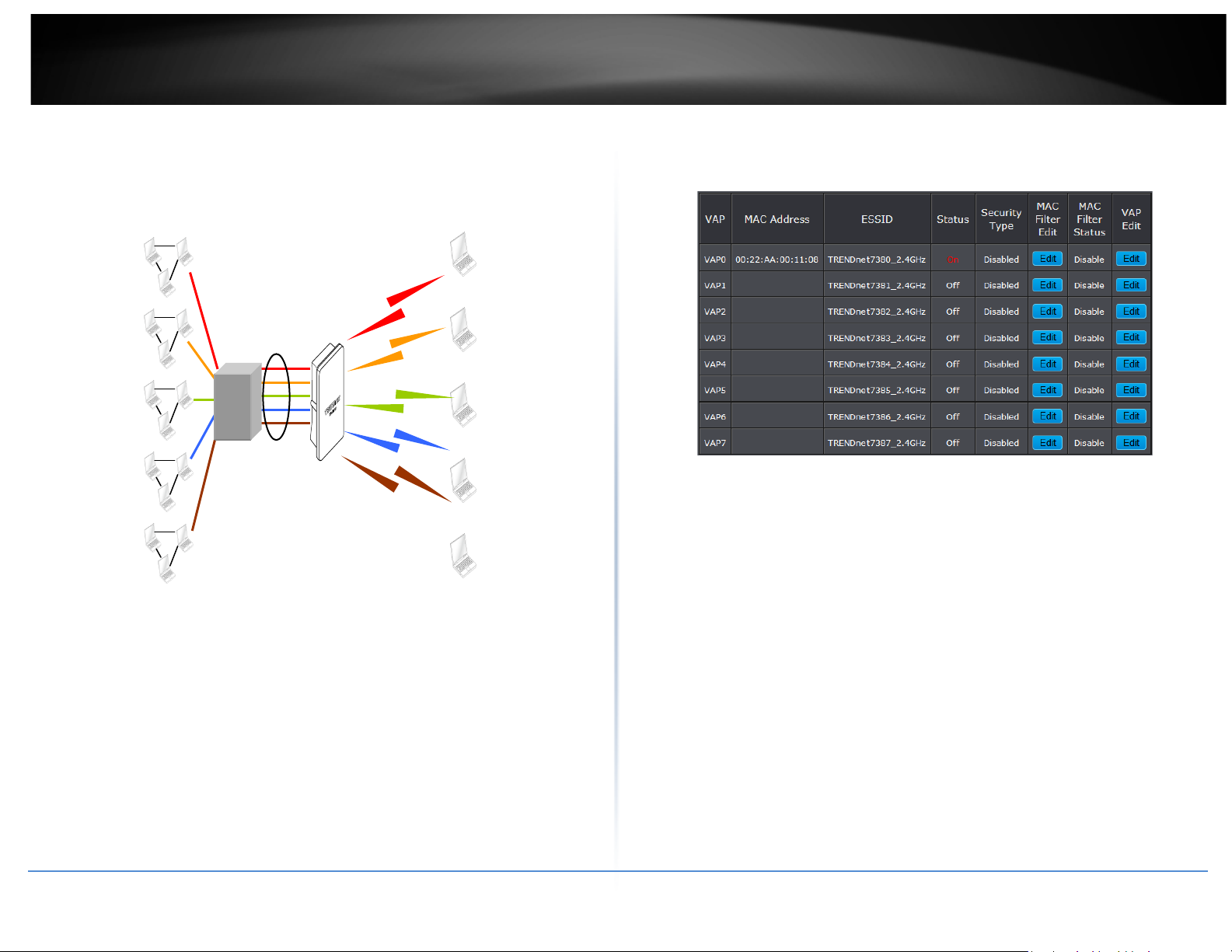
Create Virtual AP (VAP)
Virtual AP Overview
TEW-738APBO
The TEW-738APBO support broadcasting multiple SSIDs, allowing the creation of Virtual
Access Points, partitioning a single physical access point into 7 logical access points, each
of which can have a different set of security, VLAN Tag(ID) and network settings. Figure
3-2 shows multiple SSIDs with different security type and VLAN settings.
Sales Network
Engineer Network
E
SSID 2
PSK/AES
SSID 3
Accounting Network
Multiple SSIDs with different Security Type and VLAN Tag
The administrator can view all of the Virtual AP's settings via this page.
Please click on Wireless -> Virtual AP Setup and the Virtual AP Overview Page appears.
• VAP: Indicate the system's Virtual AP.
• MAC Address: The MAC address of the VAP Interface is displayed here. When you
enable AP and reboot system, the MAC address will display here.
• ESSID: Indicate the ESSID of the respective Virtual AP
• Status: Indicate the Status of the respective Virtual AP. The Primary AP always on.
• Security Type: Indicate a used security type of the respective Virtual AP.
• MAC Filter: Indicate a used MAC filter of the respective Virtual AP.
• Edit: Click Edit button to configure Virtual AP's settings, including security type and
MAC Filter.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 20
20
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Virtual AP Setup
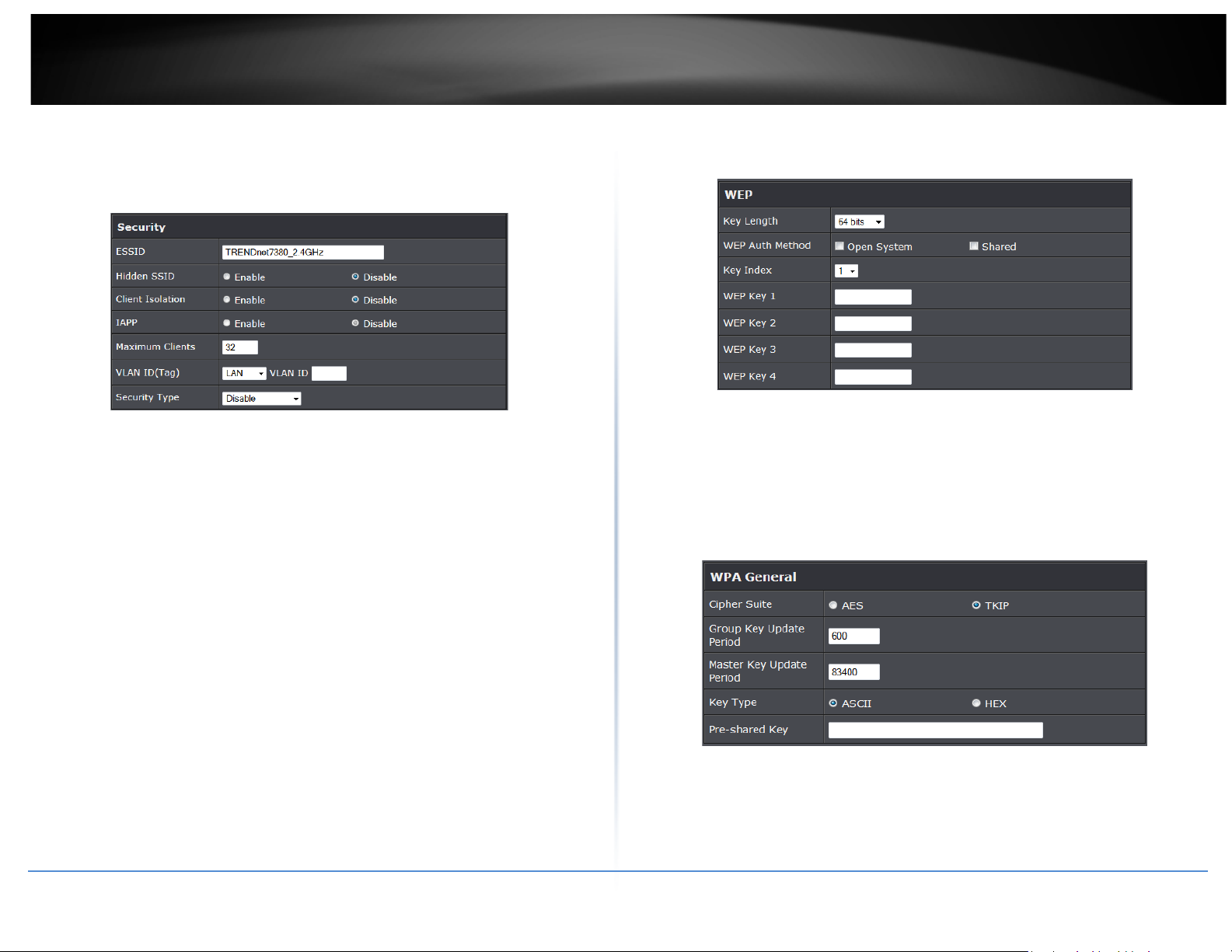
For each Virtual AP, administrators can configure SSID, VLAN tag(ID), SSID broadcasting,
Maximum number of client associations, security type settings.
Click Edit button on the Edit column, and then a Virtual AP setup page appears.
are Disable, WEP, WPA -PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA -Enterprise, WPA2-Enterprise and
WEP 802.1X.
o Disable: Data are unencrypted during transmission when this option is selected.
TEW-738APBO
• ESSID: Extended Service Set ID, when clients are browsing for available wireless
networks, this is the SSID that will appear in the list. ESSID will determine the
service type available to AP's clients associated with the specified VAP.
• Hidden SSID: By default, it’s “Disable”. Enable this option to stop the SSID broadcast
in your network. When disabled, people could easily obtain the SSID information
with the site survey software and get access to the network if security is not turned
on. When enabled, network security is enhanced. It’s suggested to enable it after AP
security settings are archived and setting of AP clients could make to associate to it.
• Client Isolation: Select Enable, all clients will be isolated from each other, that mean
all clients cannot reach to other clients. Below Figures depict Client Isolation and AP
Isolation
• IAPP:
• Maximum Clients: The default value is 32. You can enter the number of wireless
clients that can associate to a particular SSID. When the number of client is set to 5,
only 5 clients at most are allowed to connect to this VAP.
• VLAN Tag (ID) : By default, it’s selected “Disable”.
This system supports tagged Virtual LAN (VLAN). A valid number of 1 to 4094 can be
entered after it’s enabled. If your network utilize VLANs you could tie a VLAN Tag to
a specific SSID, and packets from/to wireless clients belonging to that SSID will be
tagged with that VLAN Tag. This enables security of wireless applications by
applying VLAN Tag.
• Security Type: Select the desired security type from the drop-down list; the options
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
• WEP Auth Method: Enable the desire option among OPEN or SHARED
o Key Index: Key index is used to designate the WEP key during data transmission. 4
different WEP keys can be entered at the same time, but only one is chosen.
o WEP Key #: Enter HEX or ASCII format WEP key value; the system supports up to 4
sets of WEP keys.
• WPA -PSK (or WPA2-PSK) : WPA (or WPA2) Algorithms, allows the system accessing
the network by using the WPA-PSK protected access.
o Cipher Suite: By default, it is AES. Select either AES or TKIP cipher suites
o Group Key Update Period: By default, it is 600 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
Page 21
21
TRENDnet User’s Guide
o Master Key Update Period: By default, it is 83499 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o Pre-shared Key: Enter the pre-shared key; the format shall go with the selected
key type.
• WPA -Enterprise (or WPA2-Enterprise): The RADIUS authentication and encryption
will be both enabled if this is selected.
• Radius Server Settings :
o IP Address: Enter the IP address of the Authentication RADIUS server.
o Port: By default, it’s 1812. The port number used to communicate with RADIUS
server.
o Shared secret: A secret key used between system and RADIUS server. Supports 8
to 64 characters.
o Accounting RADIUS Server: Enable to set Account RADIUS server.
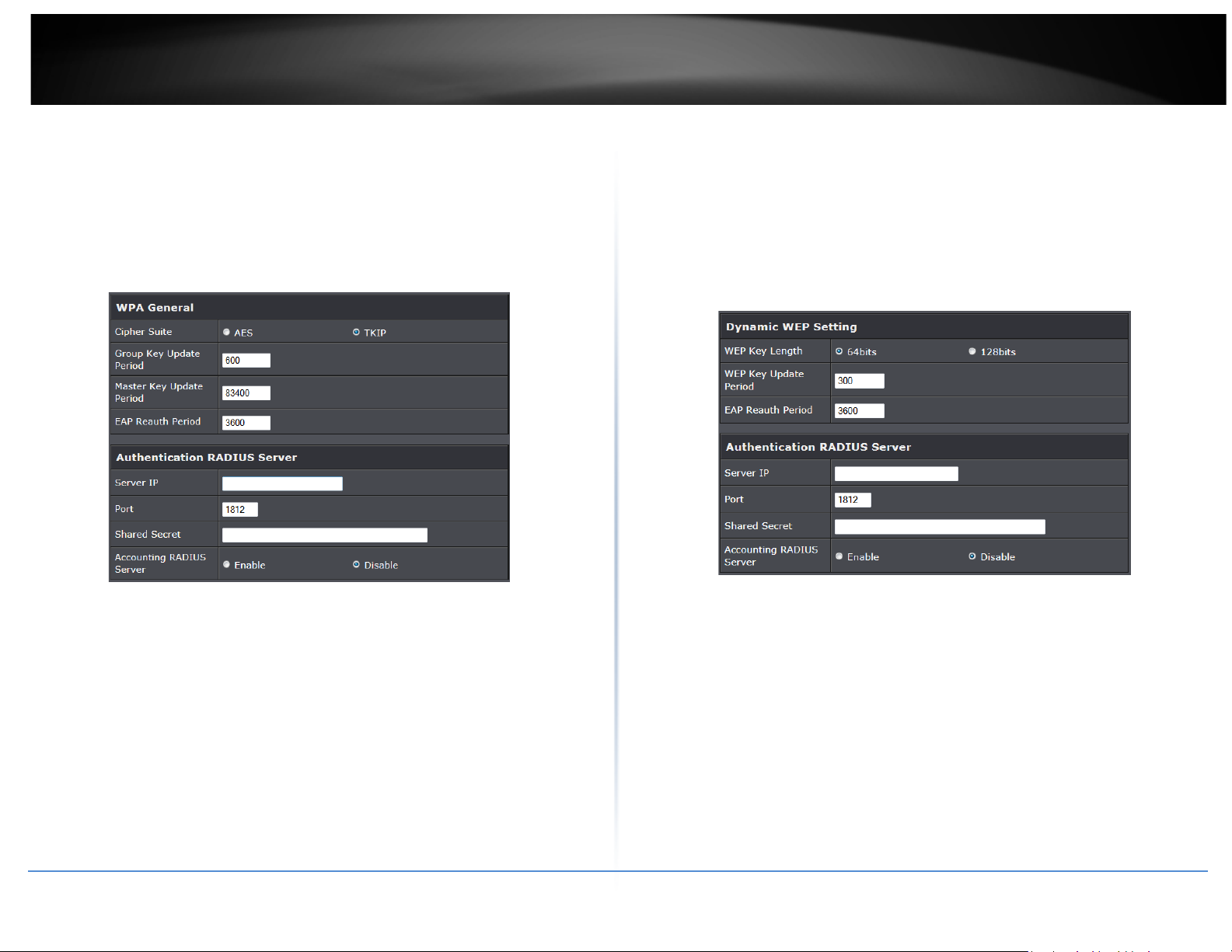
• WEP 802.1X: When WEP 802.1x Authentication is enabled, please refer to the
following Dynamic WEP and RADIUS settings to complete configuration.
TEW-738APBO
• WPA General Settings:
o Cipher Suite: By default, it is AES. Select either AES or TKIP cipher suites
o Group Key Update Period: By default, it’s 3600 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o Master Key Update Period: By default, it is 83499 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o EAP Reauth Period: By default, it's 3600 seconds. Set WPA2 PMKID cache
timeout period, after time out, the cached key will be deleted.
o Pre-Authentication: By default, it's “Disable”. To Enable is use to speed up
roaming before pre-authenticating IEEE 802.1X/EAP part of the full RSN
authentication and key handshake before actually associating with a new AP.
• Radius Server Settings:
o IP Address: Enter the IP address of the Authentication RADIUS server.
o Port: By default, it’s 1812. The port number used to communicate with RADIUS
server.
o Shared secret: A secret key used between system and RADIUS server. Supports 8
to 64 characters.
o Accounting RADIUS Server: Enable to set Account RADIUS server.
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 22
22
TRENDnet User’s Guide
WDS
Remote Bass Station
Wireless MAC Filter Setup
Wireless Network Expansion
TEW-738APBO
Continue Virtual AP Setup section. For each Virtual AP setting, the administrator can
allow or reject clients to access each Virtual AP.
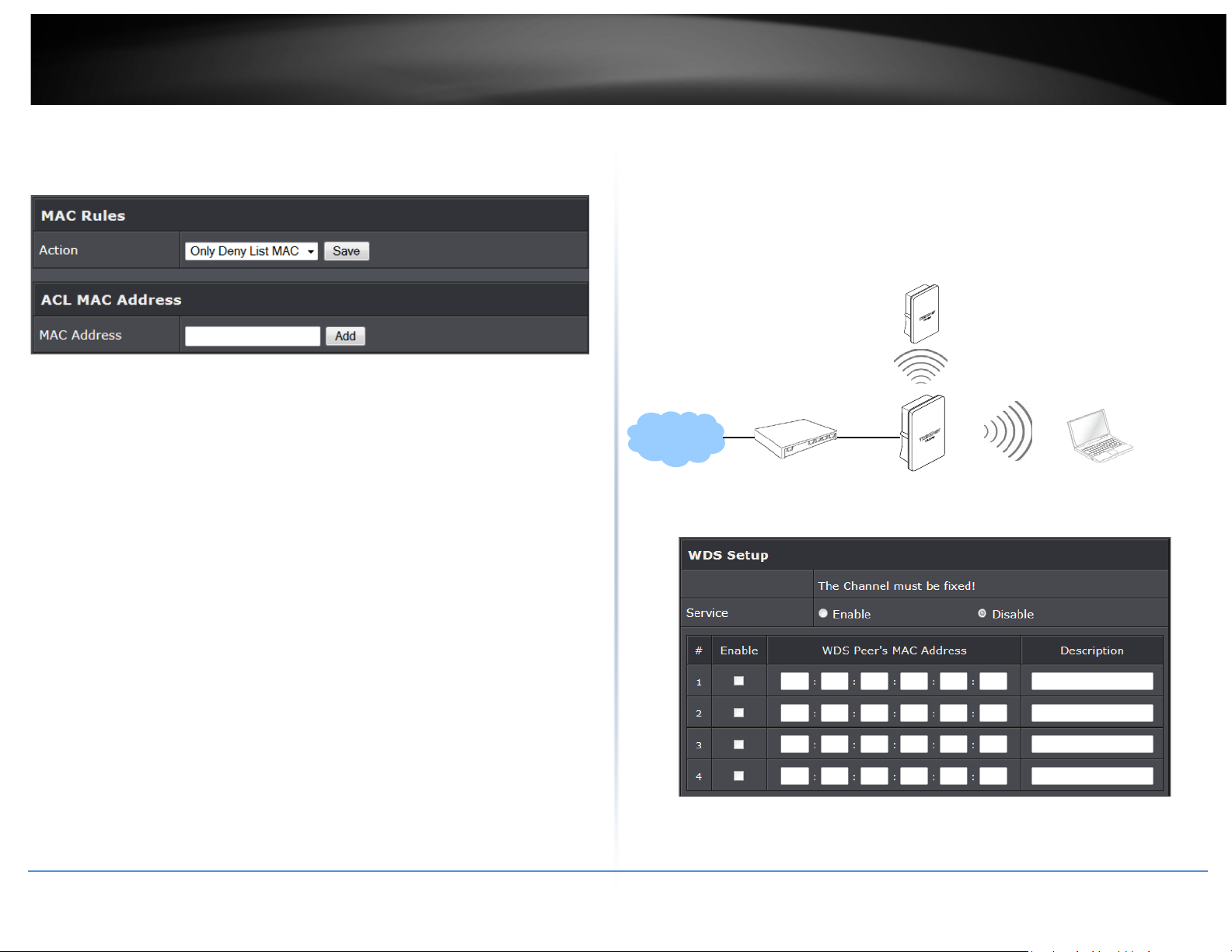
• MAC Filter Setup: By default, it’s “Disable”. Options are Disable, Only Deny List
MAC or Only Allow List MAC.
Two ways to set MAC filter rules:
o Only Allow List MAC: The wireless clients in the “Enable” list will be allowed to
access the Access Point; All others or clients in the “Disable” list will be denied.
o Only Deny List MAC: The wireless clients in the “Enable” list will be denied to
access the Access Point; All others or clients in the “Disable” list will be allowed.
Add a station MAC: Enter MAC address (e.g. aa:bb:cc:00:00:0a) and click “Add” button,
then the MAC address should display in the “Enable” List.
There are a maximum of 20 clients allowed in this “Enable” List. The MAC addresses of
the wireless clients can be added and removed to the list using the Add and Remove
buttons. Click Reboot button to activate your changes
The administrator could create WDS Links to expand wireless network. When WDS is
enabled, access point functions as a wireless bridge and is able to communicate with
other access points via WDS links. A WDS link is bidirectional and both side must
support WDS. Access points know each other by MAC Address. In other words, each
access point needs to include MAC address of its peer. Ensure all access points are
configured with the same channel and own same security type settings.
Please click on Wireless -> WDS Setup and follow the below setting.
• Security Type: Option is “Disable”, “ WEP”, “TKIP”o r “AES” from drop-down list.
Needs the same type to build WDS links. Security type takes effect when WDS is
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 23
23
TRENDnet User’s Guide
enabled.
o WEP Key: Enter 5 / 13 ASCII or 10 / 26 HEX format WEP key.
o TKIP Key: Enter 8 to 63 ASCII or 64 HEX format TKIP key.
o AES Key: Enter 8 to 63 ASCII or 64 HEX format AES key.
• WDS MAC List
o Enable: Click Enable to create WDS link.
o WDS Peer's MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of WDS peer.
o Description: Description of WDS link.
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes
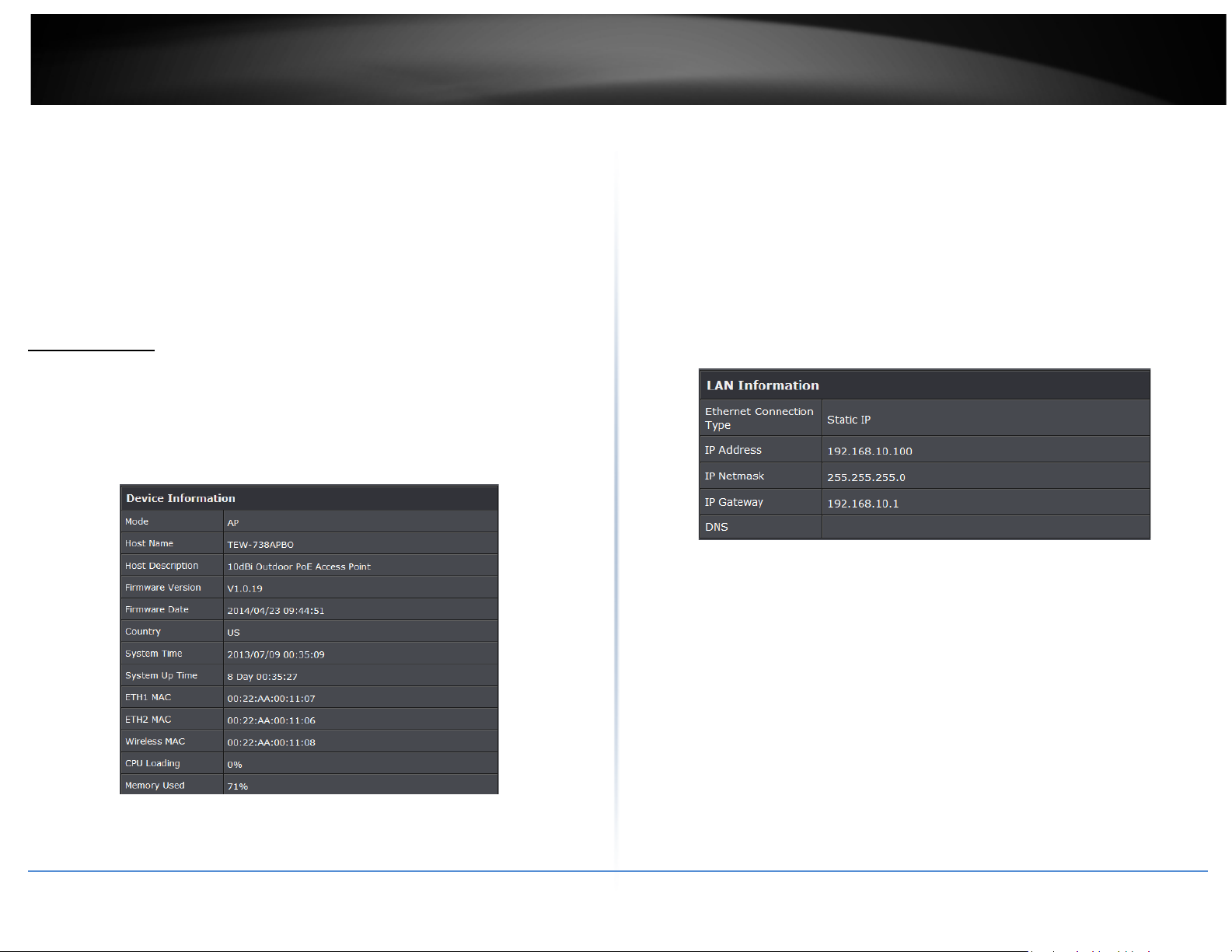
o Host Description: A description of the system.
o Firmware Version: The current installed firmware version.
o Firmware Date: The build time of installed firmware.
o Device Time: The current time of the system.
o System Up Time: The time period that system has been in service since last
reboot.
o ETH1/ETH2MAC: Ethernet MAC address of the access point.
o Wireless MAC: Wireless MAC address of the access point
o CPU Loading: The CPU loading of the access point
o Memory Used: Memory usage of the access point.
System Status
This section breaks down into subsections of System Overview, Associated Clients
• LAN Information: Display total received and transmitted statistics on the LAN
interface.
Status, WDS Link Status, Extra Information and Event Log.
TEW-738APBO
System Overview
Display detailed information of System, Network, LAN and Wireless in the System
Overview page.
• Device Information: Display the information of the system.
o Ethernet Connection Type: The connection applied on the access point.
o IP Address: The management IP of system. By default, it’s 192.168.2.254.
o IP Netmask: The network mask. By default, it’s 255.255.255.0.
o IP Gateway: The gateway IP addresses and by default, it’s 192.168.2.1.
o Primary DNS: The primary DNS server in service.
o Operating Mode: The mode currently in service.
o Host Name: The name of the system.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 24
24
TRENDnet User’s Guide
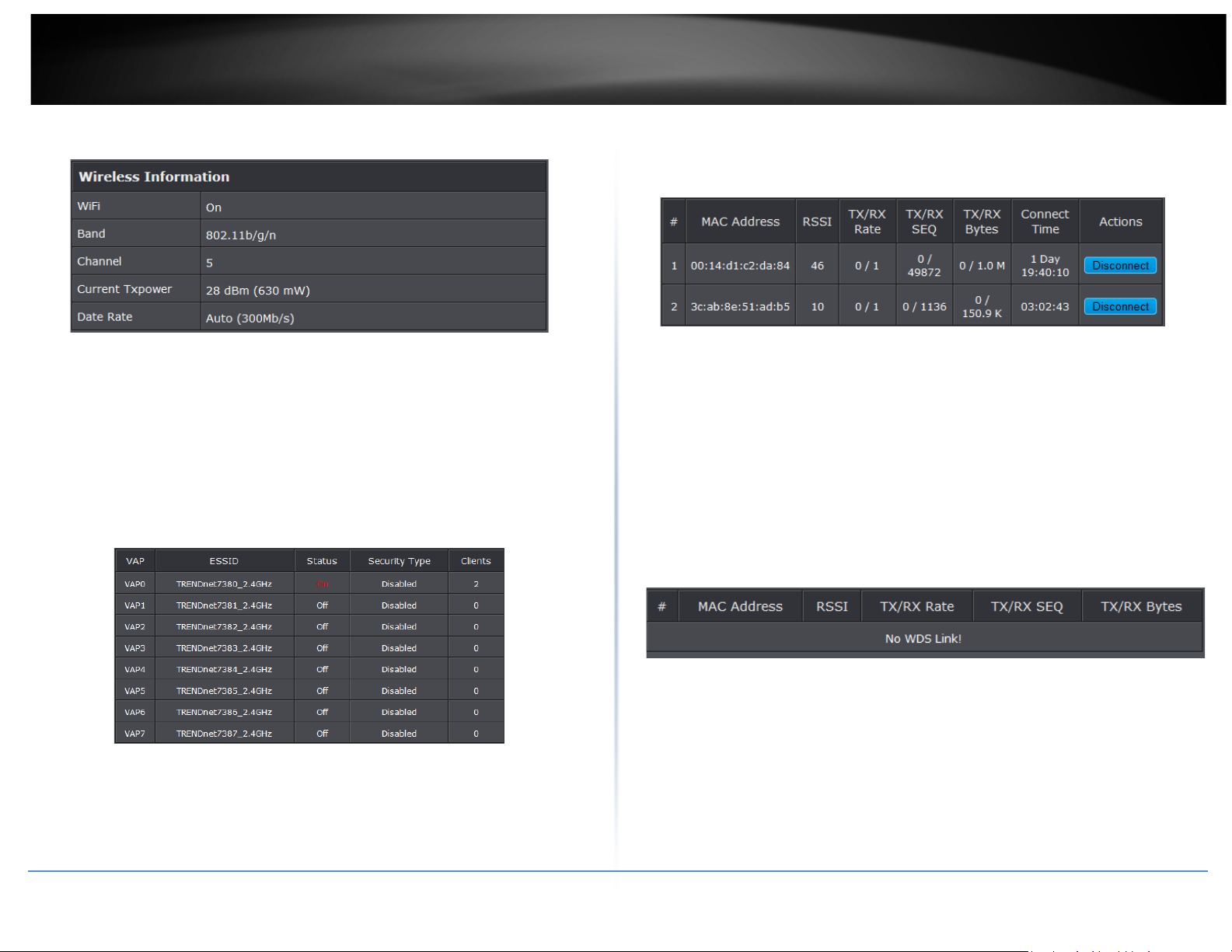
• Wireless Information: Display total received and transmitted statistics on available
Virtual AP.
Enterprise.
o Clients: Display total number of wireless connections for each VAP.
• VAP Clients: Display all associated clients on each Virtual AP.
TEW-738APBO
o WiFi: Wireless status of the access point.
o Band: Operating wireless band of the access point.
o Channel: Operating channel of the access point.
o Current Tx Power: Transmit power of the access point.
o Data Rate: Current wireless data rate of the access point.
Associated Clients Status
It displays ESSID, on/off Status, Security Type, total number of wireless clients associated
with all Virtual AP.
• VAP Information: Highlights key VAP information.
o VAP: Available VAP from Primary AP to VAP6.
o ESSID: Display name of ESSID for each VAP.
o Status : On/Off
o Security Type: Display chosen security type; WEP, WPA/WPA2-PSK, WPA/WPA2-
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
o MAC Address: MAC address of associated clients
o RSSI: Signal Strength of from associated clients.
o TX/RX Rate: Transmit and receive connection rate
o TX/RX SEQ: Transmit and receive sequence.
o TX/RX Bytes: Tra n s m i t and receive bytes
o Connect Time: Connection time
o Disconnect: Click “Disconnect” button to manually disconnect a wireless client in
a Virtual AP.
Show WDS Link Status
Peers MAC Address, antenna 0/1 received signal strength, phy mode and channel
bandwidth for each WDS are available.
o MAC Address: Display MAC address of WDS peer.
o RSSI: Indicate the signal strength of the respective WDS links.
o TX/RX SEQ: Transmit and receive sequence.
o TX/RX Bytes: Transmit and receive bytes
Page 25

25
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-738APBO
Extra Information
Users could pull out information such as Route table, ARP table, MAC table, Bridge table
or STP available in the drop-down list from system. The “Refresh” button is used to
retrieve latest table information.
• Bridge table information: Select “Bridge Table information” on the drop-down list
to display bridge table. Bridge table will show Bridge ID and STP's Status on the
each Ethernet bridge and its attached interfaces, the Bridge Port should be
attached to some interfaces (e.g. eth2, ra0~ra6 and wds0~wds3).
• Route table information: Select “Route table information” on the drop-down list
to display route table. TEW-738APBO could be used as a L2 or L3 device. It doesn’t
support dynamic routing protocols such as RIP or OSPF. Static routes to specific
hosts, networks or default gateway are set up automatically according to the IP
configuration of system's interfaces. When used as a L2 device, it could switch
packets and, as L3 device, it’s capable of being a gateway to route packets inward
and outward.
• ARP table Information: Select “ARP Table Information” on the drop-down list to
display ARP table. ARP associates each IP address to a unique hardware address
(MAC) of a device. It is important to have a unique IP address as final destination to
switch packets to.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
• Bridge MAC information: Select “Bridge MACs Information” on the drop-down list
to display MAC table.
This table displays local MAC addresses associated with wired or wireless interfaces,
but also remember non-local MAC addresses learned from wired or wireless
interfaces. Ageing timers will be reset when existing MAC addresses in table are
learned again or added when new MAC addresses are seen from wired or wireless
interfaces as well. When time runs out for a particular entry, it will be pruned from
the table. In that situation, switching packet to that particular MAC address will be
dropped.
Page 26

26
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Option
System
Wireless
Utilities
Status
SNMP
WDS
Event Log
The Event log displays system events when system is up and running. Also, it becomes
very useful as a troubleshooting tool when issues are experienced in system.
• Time: The date and time when the event occurred.
• Facility: It helps users to identify source of events such “System” or “User”
• Severity: Severity level that a specific event is associated such as “info”, “error”,
“warning”, etc.
• Message: Description of the event.
Click Refresh button to renew the log, or click Clear button to clear all the record.
WDS Mode Configuration
Please refer to illustrations of the section 1.3 for possible applications in the WDS mode.
This section provides detailed explanation for users to configure in the WDS mode with
help of illustrations. In the WDS mode, functions listed in the table below are also
available from the Web-based GUI interface.
WDS Mode Functions
Operating General Setup Profiles Settings System
LAN Advanced Setup Firmware WDS Status
Functions
External Network Connection
Network Requirement
You could expand your Ethernet network via WDS link. In this mode, the TEW-738APBO
connects directly to a wired LAN, and wirelessly bridges to a remote access point via a
WDS link as shown in Figure 4-1. In the mode, it can’t associate with any wireless clients.
Management WDS Setup Network Utility Extra Info
Time Server Reboot Event Log
Point to Point network Configuration
TEW-738APBO
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 27

27
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-738APBO
Configure LAN IP
Here are the instructions to setup the local IP Address and Netmask.
Please click on System -> LAN and follow the below setting.
• Mode: Check either “Static IP” or “Dynamic IP” button as desired to set up the
system IP of LAN port.
• Static IP : The administrator can manually setup the LAN IP address when static IP
is available/ preferred.
o IP Address : The IP address of the LAN port; default IP address is
192.168.2.254
o IP Netmask : The Subnet mask of the LAN port; default Netmask is
255.255.255.0
o IP Gateway : The default gateway of the LAN port; default Gateway is
192.168.2.1
• Dynamic IP : This configuration type is applicable when the TEW-738APBO is
connected to a network with the presence of a DHCP server; all related IP
information will be provided by the DHCP server automatically.
o Hostname : The Hostname of the LAN port
• DNS : Check either “No Default DNS Server” or “Specify DNS Server IP” button as
desired to set up the system DNS.
o Primary: The IP address of the primary DNS server.
o Secondary: The IP address of the secondary DNS server.
• 802.1d Spanning Tree
The spanning tree network protocol provides a loop free topology for a bridged LAN
between LAN interface and 4 WDS interfaces from wds0 to wds3. The Spanning
Tree Protocol, which is also referred to as STP, is defined in the IEEE Standard
802.1d. The Spanning tree always enabled on TEW-738APBO. Below Figures depict
a loop for a bridged LAN between LAN and WDS link
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes
Wireless Network Expansion
The network manager can configure related wireless settings, General Settings,
Advanced Settings and WDS Settings.
Wireless General Setup
The administrator can change the data transmission, channel and output power settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> General Setup and follow the below setting.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 28

28
TRENDnet User’s Guide
By default, it's 2.
• Channel Bandwidth: The "20/40” MHz option is usually best. The other option is
available for special circumstances.
• Extensions Channel: Select which section of channels to use for extension channels.
• MCS: This parameter represents transmission rate. By default (Auto) the fastest
possible transmission rate will be selected. You have the option of selecting the
speed if necessary. (Refer to Appendix C. MCS Data Rate)
• MAC Address: The MAC address of the Wireless interface is displayed here.
• Band Mode: Select an appropriate wireless band; bands available are 801.11b,
802.11b/g, 802.11b/g/n or 802.11n only.
• Channel: Select the desired channel from the drop-down list to have the access
point operate on. Click Auto Scan to scan for the best available channel to use based
on the environment.
• Tx Power: Yo u can adjust the output power of the system to get the appropriate
coverage for your wireless network. Specify digit numbers between 1 to 100 (the
unit is %) for your environment. If you are not sure which setting to choose, then
keep the default setting, 100%.
• RF (ON/OFF) Schedule: Select an assigned schedule of when to have the access
point turn on. Select Always Run to have the access point always on.
When Band Mode select in 802.11a only mode, the HT(High Throughput) settings
should be hidden immediately.
Wireless Advanced Setup
To achieve optimal wireless performance, it is necessary to tweak advance setting per
requirements properly, not necessary higher the better or lower.
The administrator can change the RTS threshold and fragmentation threshold settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> Advanced Setup and follow the below setting.
TEW-738APBO
• Short Slot: By default, it’s “Enable” for reducing the slot time from the standard 20
microseconds to the 9 microsecond short slot time. Slot time is the amount of time a
device waits after a collision before retransmitting a packet. Reducing the slot time
decreases the overall back-off, which increases throughput. Back-off, which is a
multiple of the slot time, is the random length of time a station waits before
sending a packet on the LAN. For a sender and receiver own right of the channel the
shorter slot time help manage shorter wait time to re-transmit from collision
• TxStream/Rx Stream: Select the amount of transmit (TX) and Receive (RX) streams.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
because of hidden wireless clients or other causes. When collision sources can be
removed sooner and other senders attempting to send are listening the channel
Page 29

29
TRENDnet User’s Guide
(CSMA/CA) the owner of the channel should continue ownership and finish their
transmission and release the channel. Then, following ownership of the channel will
be sooner for the new pair due to shorter slot time. However, when long duration of
existing collision sources and shorter slot time exist the owners might experience
subsequent collisions. When adjustment to longer slot time can’t improve
performance then RTS/CTS could supplement and help improve performance.
• ACK Timeout: ACK timeout is in the range of 1~255 and set in unit of microsecond.
The default value is 32 microsecond. All data transmission in 802.11b/g request an
“Acknowledgement” (ACK) send by receiving radio. The transmitter will resend the
original packet if correspondent ACK failed to arrive within specific time interval,
also refer to as “ACK Timeout”.
ACK Timeout is adjustable due to the fact that distance between two radio links
may vary in different deployment. ACK Timeout makes significant influence in
performance of long distance radio link. If ACK Timeout is set too short, transmitter
will start to “Resend” packet before ACK is received, and throughputs become low
due to excessively high re-transmission. ACK Timeout is best determined by
distance between the radios, data rate of average environment. The Timeout value
is calculated based on round-trip time of packet with a little tolerance, So, if
experiencing re-transmissions or poor performance the ACK Timeout could be
made longer to accommodate.
• Beacon Interval:: Beacon Interval is in the range of 20~1024 and set in unit of
millisecond. The default value is 100 msec.
Access Point (AP) in IEEE 802.11 will send out a special approximated 50-byte
frame, called “Beacon”. Beacon is broadcast to all the stations, provides the basic
information of AP such as SSID, channel, encryption keys, signal strength, time
stamp, support data rate.
All the radio stations received beacon recognizes the existence of such AP, and may
proceed next actions if the information from AP matches the requirement. Beacon
is sent on a periodic basis, the time interval can be adjusted.
By increasing the beacon interval, you can reduce the number of beacons and
associated overhead, but that will likely delay the association and roaming process
because stations scanning for available access points may miss the beacons. You
can decrease the beacon interval, which increases the rate of beacons. This will
make the association and roaming process very responsive; however, the network
will incur additional overhead and throughput will go down.
• DTIM Interval: The DTIM interval is in the range of 1~255. The default is 1.
DTIM is defined as Delivery Traffic Indication Message. It is used to notify the
wireless stations, which support power saving mode, when to wake up to receive
multicast frame. DTIM is necessary and critical in wireless environment as a
mechanism to fulfill power-saving synchronization. A DTIM interval is a count of the
number of beacon frames that must occur before the access point sends the
buffered multicast frames. For instance, if DTIM Interval is set to 3, then the Wi-Fi
clients will expect to receive a multicast frame after receiving three Beacon frame.
The higher DTIM interval will help power saving and possibly decrease wireless
throughput in multicast applications.
• RTS Threshold: TRTS Threshold is in the range of 1~2347 byte. The default is 2347
byte. The main purpose of enabling RTS by changing RTS threshold is to reduce
possible collisions due to hidden wireless clients. RTS in AP will be enabled
automatically if the packet size is larger than the Threshold value. By default, RTS is
disabled in a normal environment supports non-jumbo frames.
• Short Preamble: By default, it’s “Enable”. To Disable is to use Long 128-bit Preamble
Synchronization field. The preamble is used to signal "here is a train of data coming"
to the receiver. The short preamble provides 72-bit Synchronization field to improve
WLAN transmission efficiency with less overhead.
• WMM: By default, it's “Enabled”.
Wireless WMM QoS Setup
To achieve optimal wireless performance, it is necessary to tweak advance setting per
requirements properly, not necessary higher the better or lo wer.
The administrator can change the RTS threshold and fragmentation threshold settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> Advanced
TEW-738APBO
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 30

30
TRENDnet User’s Guide
AP to Clients
queue (FTP data, for example).
parameters for traditional IP data.
As an Example, time-sensitive Voice & Video, and multimedia are given effectively
higher priority for transmission (lower wait times for channel access), while other
applications and traditional IP data which are less time-sensitive but often more dataintensive are expected to tolerate longer wait times.
o Aifsn: The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing Number specifies a wait time (in
milliseconds) for data frames
o CWmin: Minimum Contention Window. This parameter is input to the algorithm
that determines the initial random back-off wait time ("window") for retry of a
transmission. The value specified here in the Minimum Contention Window is the
upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from which the initial random back-off
wait time is determined.
o CWmax: Maximum Contention Window. The value specified here in the
Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling
of the random back-off value. This doubling continues until either the data frame
• WMM Parameters of Access Point : This affects traffic flowing from the access point
to the client station
Data
Queue
AC_BK Background. Low
AC_BE Best Effort Medium
AC_VI Video High
AC_VO Voice High
Configuring QoS options consists of setting parameters on existing queues for different
types of wireless traffic. You can configure different minimum and maximum wait
times for the transmission of packets in each queue based on the requirements of the
media being sent. Queues automatically provide minimum transmission delay for
Voice, Video, multimedia, and mission critical applications, and rely on best-effort
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Transmitted
Priority Description
High throughput. Bulk data that requires maximum
throughput and is not time-sensitive is sent to this
Medium throughput and delay. Most traditional IP
data is sent to this queue
Minimum delay. Time-sensitive video data is
automatically sent to this queue
Time-sensitive data like VoIP and streaming media
are automatically sent to this queue
is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached. Once the Maximum
Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a maximum number
of retries allowed is reached. Valid values for the "cwmax" are 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63,
127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for "cwmax" must be higher than the value for
"cwmin".
o Txop: Transmission Opportunity is an interval of time when a WME AP has the
right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium (WM). This value
specifies (in milliseconds) the Transmission Opportunity (TXOP) for AP; that is, the
interval of time when the WMM AP has the right to initiate transmissions on the
wireless network.
o ACM: Admission Control Mandatory, ACM only takes effect on AC_VI and AC_VO.
When you do not click Checkbox, it means that the ACM is controlled by the
connecting AP. If you click Checkbox, it means that the Client is in charge.
o AckPolicy: Acknowledgment Policy, WMM defines two ACK policies: Normal ACK
and No ACK. Click “Checkbox” indicates “No ACK”
TEW-738APBO
Page 31

31
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Data
Clients to AP
High throughput. Bulk data that
sent to this queue
sent to this queue
Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling
Queue
AC_BK Background. Low
AC_BE Best Effort Medium
AC_VI Video High
AC_VO Voice High
When the no acknowledgment (No ACK) policy is used, the recipient does not
acknowledge received packets during wireless packet exchange. This policy is
suitable in the environment where communication quality is fine and interference
is weak. While the No ACK policy helps improve transmission efficiency, it can
cause increased packet loss when communication quality deteriorates. This is
because when this policy is used, a sender does not retransmit packets that have
not been received by the recipient. When the Normal ACK policy is used, the
recipient acknowledges each received unicast packet.
• WMM Parameters of Station: This affects traffic flowing from the client station to
the access point.
o Aifsn : The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing Number specifies a wait time (in
milliseconds) for data frames
o CWmin : Minimum Contention Window. This parameter is input to the
algorithm that determines the initial random backoff wait time ("window")
for retry of a transmission. The value specified here in the Minimum
Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from
which the initial random backoff wait time is determined.
o CWmax : Maximum Contention Window. The value specified here in the
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Transmitted
Priority Description
requires maximum
throughput and is not timesensitive is sent to this queue
(FTP data, for example).
Medium throughput and delay.
Most traditional IP data is
Minimum delay. Time-sensitive
video data is automatically
Time-sensitive data like VoIP
and streaming media are
automatically sent to this
queue
of the random backoff value. This doubling continues until either the data frame
is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached. Once the Maximum
Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a maximum number
of retries allowed is reached. Valid values for the "cwmax" are 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63,
127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for "cwmax" must be higher than the value for
"cwmin".
o Txop : Transmission Opportunity is an interval of time when a WME AP has the
right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium (WM). This value
specifies (in milliseconds) the Transmission Opportunity (Txop) for AP; that is, the
interval of time when the WMM AP has the right to initiate transmissions on the
wireless network.
o ACM: Admission Control Mandatory, ACM only takes effect on AC_VI and AC_VO.
When you do not click Checkbox, it means that the ACM is controlled by the
connecting AP. If you click Checkbox, it means that the Client is in charge.
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes.
The items in this page are for AP's RF advanced settings and will be applied to all VAPs
and WDS Links.
WDS Setup
The administrator could create WDS Links to expand wireless network. When WDS is
enabled, access point functions as a wireless bridge and is able to communicate with
other access points via WDS links. A WDS link is bidirectional and both side must
support WDS. Access points know each other by MAC Address. In other words, each
access point needs to include MAC address of its peer. Ensure all access points are
configured with the same channel and own same security type settings.
TEW-738APBO
Page 32

32
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-738APBO
• Security Type: Option is “Disable”, “ WEP”, “TKIP” or “AES” from drop-down list.
Needs the same type to build WDS links. Security type takes effect when WDS is
enabled.
o WEP Key: Enter 5 / 13 ASCII or 10 / 26 HEX format WEP key.
o TKIP Key: Enter 8 to 63 ASCII or 64 HEX format TKIP key.
o AES Key: Enter 8 to 63 ASCII or 64 HEX format AES key.
• WDS MAC List
o Enable: Click Enable to create WDS link.
o WDS Peer's MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of WDS peer.
o Description: Description of WDS link.
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes
System Status
This section breaks down into subsections of System Overview, Associated Clients
Status, WDS Link Status, Extra Information and Event Log.
System Overview
Display detailed information of System, Network, LAN and Wireless in the System
Overview page.
• Device Information: Display the information of the system.
o Operating Mode: The mode currently in service.
o Host Name: The name of the system.
o Host Description: A description of the system.
o Firmware Version: The current installed firmware version.
o Firmware Date: The build time of installed firmware.
o Device Time: The current time of the system.
o System Up Time: The time period that system has been in service since last
reboot.
o ETH1/ETH2MAC: Ethernet MAC address of the access point.
o Wireless MAC: Wireless MAC address of the access point
o CPU Loading: The CPU loading of the access point
o Memory Used: Memory usage of the access point.
• LAN Information: Display total received and transmitted statistics on the LAN
interface.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 33

33
TRENDnet User’s Guide
or STP available in the drop-down list from system. The “Refresh” button is used to
retrieve latest table information.
TEW-738APBO
o Ethernet Connection Type: The connection applied on the access point.
o IP Address: The management IP of system. By default, it’s 192.168.2.254.
o IP Netmask: The network mask. By default, it’s 255.255.255.0.
o IP Gateway: The gateway IP addresses and by default, it’s 192.168.2.1.
o Primary DNS: The primary DNS server in service.
• Wireless Information: Display total received and transmitted statistics on available
Virtual AP.
o WiFi: Wireless status of the access point.
o Band: Operating wireless band of the access point.
o Channel: Operating channel of the access point.
o Current Tx Power: Transmit power of the access point.
o Data Rate: Current wireless data rate of the access point.
Extra Information
• Route table information: Select “Route table information” on the drop-down list
to display route table. TEW-738APBO could be used as a L2 or L3 device. It doesn’t
support dynamic routing protocols such as RIP or OSPF. Static routes to specific
hosts, networks or default gateway are set up automatically according to the IP
configuration of system's interfaces. When used as a L2 device, it could switch
packets and, as L3 device, it’s capable of being a gateway to route packets inward
and outward.
• ARP table Information: Select “ARP Table Information” on the drop-down list to
display ARP table. ARP associates each IP address to a unique hardware address
(MAC) of a device. It is important to have a unique IP address as final destination to
switch packets to.
Users could pull out information such as Route table, ARP table, MAC table, Bridge table
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 34

34
TRENDnet User’s Guide
• Bridge table information: Select “Bridge Table information” on the drop-down list
to display bridge table. Bridge table will show Bridge ID and STP's Status on the
each Ethernet bridge and its attached interfaces, the Bridge Port should be
attached to some interfaces (e.g. eth2, ra0~ra6 and wds0~wds3).
Event Log
The Event log displays system events when system is up and running. Also, it becomes
very useful as a troubleshooting tool when issues are experienced in system.
TEW-738APBO
• Bridge MAC information: Select “Bridge MACs Information” on the drop-down list
to display MAC table.
• Time: The date and time when the event occurred.
• Facility: It helps users to identify source of events such “System” or “User”
• Severity: Severity level that a specific event is associated such as “info”, “error”,
“warning”, etc.
• Message: Description of the event.
Click Refresh button to renew the log, or click Clear button to clear all the record.
WDS Link Status
Peers MAC Address, antenna 0/1 received signal strength, phy mode and channel
This table displays local MAC addresses associated with wired or wireless interfaces,
but also remember non-local MAC addresses learned from wired or wireless
interfaces. Ageing timers will be reset when existing MAC addresses in table are
learned again or added when new MAC addresses are seen from wired or wireless
interfaces as well. When time runs out for a particular entry, it will be pruned from
the table. In that situation, switching packet to that particular MAC address will be
dropped.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
bandwidth for each WDS are available.
o MAC Address: Display MAC address of WDS peer.
o RSSI: Indicate the signal strength of the respective WDS links.
o TX/RX SEQ: Transmit and receive sequence.
o TX/RX Bytes: Transmit and receive bytes
Page 35

35
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Main
SSID:
Repeater Mode
When Universal Repeater mode is activated, the system can be configured as an Access
Point and Client Station simultaneously. This section provides information in configuring
the Client Bridge+Universal Repeater mode with graphical illustrations. TEW-738APBO
provides functions as stated below where they can be configured via a user-friendly web
based interface.
Configure LAN IP
Here are the instructions to setup the local IP Address and Netmask.
Please click on System -> LAN and follow the below setting.
• Mode: Check either “Static IP” or “Dynamic IP” button as desired to set up the
system IP of LAN port.
TEW-738APBO
External Network Connection
Network Requirement
It can be used as a Client Bridge or Universal Repeater to receive and repeat wireless
signal over last mile applications, helping WISPs deliver wireless broadband Internet
service to new residential and business customers. In this mode, TEW-738APBO is
enabled with DHCP Server functions. The wired clients of TEW-738APBO are in the same
subnet from Main Base Station and it accepts wireless connections from wireless client
devices.
Universal Repeater mode network Configuration
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
• Static IP: The administrator can manually setup the LAN IP address when static IP is
available/ preferred.
o IP Address : The IP address of the LAN port; default IP address is 192.168.2.254
o IP Netmask : The Subnet mask of the LAN port; default Netmask is 255.255.255.0
o IP Gateway : The default gateway of the LAN port; default Gateway is 192.168.2.1
• Dynamic IP : This configuration type is applicable when the TEW-738APBO is
connected to a network with the presence of a DHCP server; all related IP
information will be provided by the DHCP server automatically.
o Hostname : The Hostname of the LAN port
• DNS: Check either “No Default DNS Server” or “Specify DNS Server IP” button as
desired to set up the system DNS.
Page 36

36
TRENDnet User’s Guide
o Primary: The IP address of the primary DNS server.
o Secondary: The IP address of the secondary DNS server.
• 802.1d Spanning Tree
The spanning tree network protocol provides a loop free topology for a bridged LAN
between LAN interface and 4 WDS interfaces from wds0 to wds3. The Spanning Tree
Protocol, which is also referred to as STP, is defined in the IEEE Standard 802.1d.
Spanning tree always disabled on TEW-738APBO. Below Figures depict a loop for a
bridged LAN between LAN and WDS link
• DHCP Setup: Devices connected to the system can obtain an IP address
automatically when this service is enabled.
o Domain: Enter the domain name for this network.
o Lease Time: The IP addresses given out by the DHCP server will only be valid for
the duration specified by the lease time. Increasing the time ensure client
operation without interruptions, but could introduce potential conflicts. Lowering
the lease time will avoid potential address conflicts, but might cause more
interruptions to the client while it will acquire new IP addresses from the DHCP
server. Default is 86400 seconds
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes
Wireless Network Expansion
The network manager can configure related wireless settings, General Settings,
Advanced Settings and WDS Settings.
Wireless General Setup
The administrator can change the data transmission, channel and output power settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> General Setup and follow the below setting.
TEW-738APBO
o DHCP: Check Enable button to activate this function or Disable to deactivate this
service.
o Start IP / End IP: Specify the range of IP addresses to be used by the DHCP server
when assigning IP address to clients. The default range IP address is 192.168.2.10
to 192.168.2.70, the netmask is 255.255.255.0
o DNS1 IP: Enter IP address of the first DNS server; this field is required.
o DNS2 IP: Enter IP address of the second DNS server; this is optional.
o WINS IP: Enter IP address of the Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) server;
this is optional.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
• MAC Address: The MAC address of the Wireless interface is displayed here.
• Band Mode: Select an appropriate wireless band; bands available are 801.11b,
802.11b/g, 802.11b/g/n or 802.11n only.
• Channel: Select the desired channel from the drop-down list to have the access
point operate on. Click Auto Scan to scan for the best available channel to use based
on the environment.
• Tx Power: Yo u can adjust the output power of the system to get the appropriate
coverage for your wireless network. Specify digit numbers between 1 to 100 (the
unit is %) for your environment. If you are not sure which setting to choose, then
keep the default setting, 100%.
• RF (ON/OFF) Schedule: Select an assigned schedule of when to have the access
Page 37

37
TRENDnet User’s Guide
point turn on. Select Always Run to have the access point always on.
When Band Mode select in 802.11a only mode, the HT(High Throughput) settings
should be hidden immediately.
• Short Slot: By default, it’s “Enable” for reducing the slot time from the standard 20
• TxStream/Rx Stream: Select the amount of transmit (TX) and Receive (RX) streams.
By default, it's 2.
• Channel Bandwidth: The "20/40” MHz option is usually best. The other option is
available for special circumstances.
• Extensions Channel: Select which section of channels to use for extension channels.
• MCS: This parameter represents transmission rate. By default (Auto) the fastest
possible transmission rate will be selected. You have the option of selecting the
speed if necessary. (Refer to Appendix C. MCS Data Rate)
Wireless Advanced Set up
To achieve optimal wireless performance, it is necessary to tweak advance setting per
requirements properly, not necessary higher the better or lower.
The administrator can change the RTS threshold and fragmentation threshold settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> Advanced Setup and follow the below setting.
microseconds to the 9 microsecond short slot time. Slot time is the amount of time a
device waits after a collision before retransmitting a packet. Reducing the slot time
decreases the overall back-off, which increases throughput. Back-off, which is a
multiple of the slot time, is the random length of time a station waits before
sending a packet on the LAN. For a sender and receiver own right of the channel the
shorter slot time help manage shorter wait time to re-transmit from collision
because of hidden wireless clients or other causes. When collision sources can be
removed sooner and other senders attempting to send are listening the channel
(CSMA/CA) the owner of the channel should continue ownership and finish their
transmission and release the channel. Then, following ownership of the channel will
be sooner for the new pair due to shorter slot time. However, when long duration of
existing collision sources and shorter slot time exist the owners might experience
subsequent collisions. When adjustment to longer slot time can’t improve
performance then RTS/CTS could supplement and help improve performance.
• ACK Timeout: ACK timeout is in the range of 1~255 and set in unit of microsecond.
The default value is 32 microsecond. All data transmission in 802.11b/g request an
“Acknowledgement” (ACK) send by receiving radio. The transmitter will resend the
original packet if correspondent ACK failed to arrive within specific time interval,
also refer to as “ACK Timeout”.
ACK Timeout is adjustable due to the fact that distance between two radio links
may vary in different deployment. ACK Timeout makes significant influence in
performance of long distance radio link. If ACK Timeout is set too short, transmitter
TEW-738APBO
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 38

38
TRENDnet User’s Guide
will start to “Resend” packet before ACK is received, and throughputs become low
due to excessively high re-transmission. ACK Timeout is best determined by
distance between the radios, data rate of average environment. The Timeout value
is calculated based on round-trip time of packet with a little tolerance, So, if
experiencing re-transmissions or poor performance the ACK Timeout could be
made longer to accommodate.
• Beacon Interval:: Beacon Interval is in the range of 20~1024 and set in unit of
millisecond. The default value is 100 msec.
Access Point (AP) in IEEE 802.11 will send out a special approximated 50-byte
frame, called “Beacon”. Beacon is broadcast to all the stations, provides the basic
information of AP such as SSID, channel, encryption keys, signal strength, time
stamp, support data rate.
All the radio stations received beacon recognizes the existence of such AP, and may
proceed next actions if the information from AP matches the requirement. Beacon
is sent on a periodic basis, the time interval can be adjusted.
By increasing the beacon interval, you can reduce the number of beacons and
associated overhead, but that will likely delay the association and roaming process
because stations scanning for available access points may miss the beacons. You
can decrease the beacon interval, which increases the rate of beacons. This will
make the association and roaming process very responsive; however, the network
will incur additional overhead and throughput will go down.
• DTIM Interval: The DTIM interval is in the range of 1~255. The default is 1.
DTIM is defined as Delivery Traffic Indication Message. It is used to notify the
wireless stations, which support power saving mode, when to wake up to receive
multicast frame. DTIM is necessary and critical in wireless environment as a
mechanism to fulfill power-saving synchronization. A DTIM interval is a count of the
number of beacon frames that must occur before the access point sends the
buffered multicast frames. For instance, if DTIM Interval is set to 3, then the Wi-Fi
clients will expect to receive a multicast frame after receiving three Beacon frame.
The higher DTIM interval will help power saving and possibly decrease wireless
throughput in multicast applications.
• RTS Threshold: TRTS Threshold is in the range of 1~2347 byte. The default is 2347
byte. The main purpose of enabling RTS by changing RTS threshold is to reduce
possible collisions due to hidden wireless clients. RTS in AP will be enabled
automatically if the packet size is larger than the Threshold value. By default, RTS is
disabled in a normal environment supports non-jumbo frames.
• Short Preamble: By default, it’s “Enable”. To Disable is to use Long 128-bit Preamble
Synchronization field. The preamble is used to signal "here is a train of data coming"
to the receiver. The short preamble provides 72-bit Synchronization field to improve
WLAN transmission efficiency with less overhead.
• WMM: By default, it's “Enabled”.
• Signal LED Threshold:
o LED1: Set the RSSI reading when LED1 will activate.
o LED2: Set the RSSI reading when LED2 will activate.
o LED3: Set the RSSI reading when LED3 will activate.
Change these settings as described here and click Save button to save your changes.
Click Reboot button to activate your changes.
TEW-738APBO
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 39

39
TRENDnet User’s Guide
data is sent to this queue
Time-sensitive data like VoIP and streaming media
Wireless WMM QoS Setup
To achieve optimal wireless performance, it is necessary to tweak advance setting per
requirements properly, not necessary higher the better or lower.
The administrator can change the RTS threshold and fragmentation threshold settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> Advanced
• WMM Parameters of Access Point : This affects traffic flowing from the access point
to the client station
Data
Queue
AC_BK Background. Low
AC_BE Best Effort Medium
AC_VI Video High
Transmitted
AP to Clients
Priority Description
High throughput. Bulk data that requires maximum
throughput and is not time-sensitive is sent to this
queue (FTP data, for example).
Medium throughput and delay. Most traditional IP
Minimum delay. Time-sensitive video data is
automatically sent to this queue
AC_VO Voice High
Configuring QoS options consists of setting parameters on existing queues for different
types of wireless traffic. You can configure different minimum and maximum wait
times for the transmission of packets in each queue based on the requirements of the
media being sent. Queues automatically provide minimum transmission delay for
Voice, Video, multimedia, and mission critical applications, and rely on best-effort
parameters for traditional IP data.
As an Example, time-sensitive Voice & Video, and multimedia are given effectively
higher priority for transmission (lower wait times for channel access), while other
applications and traditional IP data which are less time-sensitive but often more dataintensive are expected to tolerate longer wait times.
o Aifsn: The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing Number specifies a wait time (in
milliseconds) for data frames
o CWmin: Minimum Contention Window. This parameter is input to the algorithm
that determines the initial random back-off wait time ("window") for retry of a
transmission. The value specified here in the Minimum Contention Window is the
upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from which the initial random back-off
wait time is determined.
o CWmax: Maximum Contention Window. The value specified here in the
Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling
of the random back-off value. This doubling continues until either the data frame
is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached. Once the Maximum
Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a maximum number
of retries allowed is reached. Valid values for the "cwmax" are 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63,
127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for "cwmax" must be higher than the value for
"cwmin".
o Txop: Transmission Opportunity is an interval of time when a WME AP has the
right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium (WM). This value
specifies (in milliseconds) the Transmission Opportunity (TXOP) for AP; that is, the
interval of time when the WMM AP has the right to initiate transmissions on the
wireless network.
o ACM: Admission Control Mandatory, ACM only takes effect on AC_VI and AC_VO.
When you do not click Checkbox, it means that the ACM is controlled by the
connecting AP. If you click Checkbox, it means that the Client is in charge.
o AckPolicy: Acknowledgment Policy, WMM defines two ACK policies: Normal ACK
and No ACK. Click “Checkbox” indicates “No ACK”
are automatically sent to this queue
TEW-738APBO
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 40

40
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Data
Clients to AP
High throughput. Bulk data that
sent to this queue
sent to this queue
Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling
Queue
AC_BK Background. Low
AC_BE Best Effort Medium
AC_VI Video High
AC_VO Voice High
When the no acknowledgment (No ACK) policy is used, the recipient does not
acknowledge received packets during wireless packet exchange. This policy is
suitable in the environment where communication quality is fine and interference
is weak. While the No ACK policy helps improve transmission efficiency, it can
cause increased packet loss when communication quality deteriorates. This is
because when this policy is used, a sender does not retransmit packets that have
not been received by the recipient. When the Normal ACK policy is used, the
recipient acknowledges each received unicast packet.
• WMM Parameters of Station: This affects traffic flowing from the client station to
the access point.
o Aifsn : The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing Number specifies a wait time (in
milliseconds) for data frames
o CWmin : Minimum Contention Window. This parameter is input to the
algorithm that determines the initial random backoff wait time ("window")
for retry of a transmission. The value specified here in the Minimum
Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from
which the initial random backoff wait time is determined.
o CWmax : Maximum Contention Window. The value specified here in the
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Transmitted
Priority Description
requires maximum
throughput and is not timesensitive is sent to this queue
(FTP data, for example).
Medium throughput and delay.
Most traditional IP data is
Minimum delay. Time-sensitive
video data is automatically
Time-sensitive data like VoIP
and streaming media are
automatically sent to this
queue
of the random backoff value. This doubling continues until either the data frame
is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached. Once the Maximum
Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a maximum number
of retries allowed is reached. Valid values for the "cwmax" are 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63,
127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for "cwmax" must be higher than the value for
"cwmin".
o Txop: Transmission Opportunity is an interval of time when a WME AP has the
right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium (WM). This value
specifies (in milliseconds) the Transmission Opportunity (Txop) for AP; that is, the
interval of time when the WMM AP has the right to initiate transmissions on the
wireless network.
o ACM: Admission Control Mandatory, ACM only takes effect on AC_VI and AC_VO.
When you do not click Checkbox, it means that the ACM is controlled by the
connecting AP. If you click Checkbox, it means that the Client is in charge.
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes.
The items in this page are for AP's RF advanced settings and will be applied to all VAPs
and WDS Links.
Site Survey
Use this tool to scan and locate WISP Access Points and select one to associate with.
Please click on Wireless -> Site Survey. Below depicts an example for site survey.
• ESSID: Available Extend Service Set ID of surrounding Access Points.
• MAC Address: MAC addresses of surrounding Access Points.
• Signal: Received signal strength of all found Access Points.
TEW-738APBO
Page 41

41
TRENDnet User’s Guide
• Channel: Channel numbers used by all found Access Points.
• Security: Security type by all found Access Points.
• Band: Wireless band used by all found Access Points.
• Network Type: Network type used by all found Access Points.
• Select: Click “Select” to configure settings and associate with chosen AP.
TEW-738APBO
Repeater AP Setup
The administrator can configure station profiles via this page.
Please click on Wireless -> Wireless Profile and follow the below setting.
• WEP Auth Method: Enable the desire option among OPEN or SHARED
o Key Index: Key index is used to designate the WEP key during data transmission. 4
different WEP keys can be entered at the same time, but only one is chosen.
o WEP Key #: Enter HEX or ASCII format WEP key value; the system supports up to 4
sets of WEP keys.
• WPA -PSK (or WPA2-PSK): WPA (or WPA2) Algorithms, allows the system accessing
the network by using the WPA-PSK protected access.
• ESSID: Assign Service Set ID for the wireless system.
• Enable Repeater SSID: Select Enable to broadcast the repeated signal.
• Hidden SSID: Select Enable to broadcast the access point’s SSID.
• Client Isolation: Select Enable to isolate wireless clients from each other.
• IAPP:
• Maximum Clients: Enter the amount of wireless clients allowed to connect to the
access point.
• Security Type: Select the desired security type from the drop-down list; the options
are Disable, WEP, WPA -PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA -Enterprise, WPA2-Enterprise and
WEP 802.1X.
o Disable: Data are unencrypted during transmission when this option is selected.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
o Cipher Suite: By default, it is AES. Select either AES or TKIP cipher suites
o Group Key Update Period: By default, it is 600 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o Master Key Update Period: By default, it is 83499 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
Page 42

42
TRENDnet User’s Guide
o Pre-shared Key: Enter the pre-shared key; the format shall go with the selected
key type.
• WPA -Enterprise (or WPA2-Enterprise): The RADIUS authentication and encryption
will be both enabled if this is selected.
o Shared secret: A secret key used between system and RADIUS server. Supports 8
to 64 characters.
o Accounting RADIUS Server: Enable to set Account RADIUS server.
• WEP 802.1X: When WEP 802.1x Authentication is enabled, please refer to the
following Dynamic WEP and RADIUS settings to complete configuration.
TEW-738APBO
• WPA General Settings:
o Cipher Suite: By default, it is AES. Select either AES or TKIP cipher suites
o Group Key Update Period: By default, it’s 3600 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o Master Key Update Period: By default, it is 83499 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o EAP Reauth Period: By default, it's 3600 seconds. Set WPA2 PMKID cache
timeout period, after time out, the cached key will be deleted.
o Pre-Authentication: By default, it's “Disable”. To Enable is use to speed up
roaming before pre-authenticating IEEE 802.1X/EAP part of the full RSN
authentication and key handshake before actually associating with a new AP.
• Radius Server Settings:
o IP Address: Enter the IP address of the Authentication RADIUS server.
o Port: By default, it’s 1812. The port number used to communicate with RADIUS
• Radius Server Settings:
o IP Address: Enter the IP address of the Authentication RADIUS server.
o Port: By default, it’s 1812. The port number used to communicate with RADIUS
server.
o Shared secret: A secret key used between system and RADIUS server. Supports 8
to 64 characters.
o Accounting RADIUS Server: Enable to set Account RADIUS server.
o Key Index: key index is used to designate the WEP key during data transmission.
4 different WEP keys can be entered at the same time, but only one is chosen.
o WEP Key # : Enter HEX or ASCII format WEP key value; the system supports up to
4 sets of WEP keys.
o WPA-PSK (or WPA2-PSK): WPA (or WPA2) Algorithms, allows the system accessing
the network by using the WPA-PSK protected access.
server.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 43

43
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Wireless MAC Filter Setup
The administrator can allow or reject clients to access Repeater AP.
• General Configuration:
TEW-738APBO
• MAC Filter Setup: By default, it’s “Disable”. Options are Disable, Only Deny List
• MAC or Only Allow List MAC.
Two ways to set MAC filter rules:
o Only Allow List MAC: The wireless clients in the “Enable” list will be allowed to
access the Access Point; All others or clients in the “Disable” list will be denied.
o Only Deny List MAC: The wireless clients in the “Enable” list will be denied to
access the Access Point; All others or clients in the “Disable” list will be allowed.
• MAC: Enter MAC address (e.g. aa:bb:cc:00:00:0a) and click “Add” button, then the
MAC address should display in the “Enable” List.
There are a maximum of 20 clients allowed in this “Enable” List. The MAC addresses of
the wireless clients can be added and removed to the list using the Add and Remove
buttons. Click Apply button to activate your changes
Create Wireless Profile
The administrator can configure station profiles via this page.
Please click on Wireless -> Wireless Profile and follow the below setting.
• Connection Setup: Select the repeater connection type.
• MAC Address: The MAC address of the Wireless Station is displayed here.
• Profile Name: Set different profiles for quick connection uses.
• ESSID: Assign Service Set ID for the wireless system.
• Lock to AP MAC: This allows the station to always maintain connection to a
particular AP with a specific MAC address. This is useful as sometimes there can be
few identically named SSID's (AP's) with different MAC addresses. With AP lock on,
the station will lock to MAC address and not roam between several Access Points
with the same ESSID.
• Security Type: Select the desired security type from the drop-down list; the options
are Disable, WEP, WPA -PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA -Enterprise, WPA2-Enterprise and
WEP 802.1X.
o Disable: Data are unencrypted during transmission when this option is selected.
o Fix: Select to have access point fixed on one profile to repeat
o Cycle: Select to have access point cycle through different profiles.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
• WEP Auth Method: Enable the desire option among OPEN or SHARED
o Key Index: Key index is used to designate the WEP key during data transmission. 4
different WEP keys can be entered at the same time, but only one is chosen.
Page 44

44
TRENDnet User’s Guide
o WEP Key #: Enter HEX or ASCII format WEP key value; the system supports up to 4
sets of WEP keys.
• WPA -Enterprise (or WPA2-Enterprise): The RADIUS authentication and encryption
will be both enabled if this is selected.
• WPA -PSK (or WPA2-PSK): WPA (or WPA2) Algorithms, allows the system accessing
the network by using the WPA-PSK protected access.
TEW-738APBO
o Cipher Suite: By default, it is AES. Select either AES or TKIP cipher suites
o Group Key Update Period: By default, it is 600 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o Master Key Update Period: By default, it is 83499 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o Pre-shared Key: Enter the pre-shared key; the format shall go with the selected
key type.
• WPA General Settings:
o Cipher Suite: By default, it is AES. Select either AES or TKIP cipher suites
o Group Key Update Period: By default, it’s 3600 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o Master Key Update Period: By default, it is 83499 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o EAP Reauth Period: By default, it's 3600 seconds. Set WPA2 PMKID cache
timeout period, after time out, the cached key will be deleted.
o Pre-Authentication: By default, it's “Disable”. To Enable is use to speed up
roaming before pre-authenticating IEEE 802.1X/EAP part of the full RSN
authentication and key handshake before actually associating with a new AP.
• Radius Server Settings :
o IP Address: Enter the IP address of the Authentication RADIUS server.
o Port: By default, it’s 1812. The port number used to communicate with RADIUS
server.
o Shared secret: A secret key used between system and RADIUS server. Supports 8
to 64 characters.
o Accounting RADIUS Server: Enable to set Account RADIUS server.
• WEP 802.1X: When WEP 802.1x Authentication is enabled, please refer to the
following Dynamic WEP and RADIUS settings to complete configuration.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 45

45
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-738APBO
Bandwidth Control
Bandwidth control allows you to control the bandwidth going through the access point.
• Radius Server Settings:
o IP Address: Enter the IP address of the Authentication RADIUS server.
o Port: By default, it’s 1812. The port number used to communicate with RADIUS
server.
o Shared secret: A secret key used between system and RADIUS server. Supports 8
to 64 characters.
o Accounting RADIUS Server: Enable to set Account RADIUS server.
o Key Index: key index is used to designate the WEP key during data transmission.
4 different WEP keys can be entered at the same time, but only one is chosen.
o WEP Key #: Enter HEX or ASCII format WEP key value; the system supports up to 4
sets of WEP keys.
o WPA-PSK (or WPA2-PSK): WPA (or WPA2) Algorithms, allows the system accessing
the network by using the WPA-PSK protected access.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
• Service: Select Enable to turn on bandwidth control through the access point.
• Mode: Select the bandwidth control mode to use through the access point.
• Upload: Enter the upload bandwidth speeds
• Download: Enter the download bandwidth speeds
Configure SNMP Setup
SNMP is an application-layer protocol that provides a message format for
communication between SNMP managers and agents. By enabling SNMP function, the
administrator can obtain the system information remotely.
Please click on System -> SNMP Setup and follow the below setting.
Page 46

46
TRENDnet User’s Guide
• SNMP v2c Enable: Check to enable SNMP v2c.
TEW-738APBO
o ro community: Set a community string to authorize read-only access.
o rw community: Set a community string to authorize read/write access.
• SNMP v3 Enable: Check to enable SNMP v3.
SNMPv3 supports the highest level SNMP security.
o SNMP ro user: Set a community string to authorize read-only access.
o SNMP ro password: Set a password to authorize read-only access.
o SNMP rw user: Set a community string to authorize read/write access.
o SNMP rw password: Set a password to authorize read/write access.
• SNMP Trap: Events such as cold start, interface up & down, and association &
disassociation will report to an assigned server.
o Community: Set a community string required by the remote host computer that
will receive trap messages or notices send by the system.
o IP: Enter the IP addresses of the remote hosts to receive trap messages.
Click Save button to save changes and click Reboot button to activate.
Configure Time Policy
Configure time policy to apply on settings like access point Radio Schedule.
• Policy: Select the policy to configure. Click Save Action to save settings.
• Schedule Rule:
o On Schedule: Select to have policy run on exact schedule
o Out of Schedule: Select to have policy run outside of schedule.
• Time Schedule:
o Day of week: Select the days of the week to apply time policy
o Start From: Enter time policy start time
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 47

47
TRENDnet User’s Guide
o End at: Enter the end time of time policy
o CPU Loading: The CPU loading of the access point
o Memory Used: Memory usage of the access point.
System Status
This section breaks down into subsections of System Overview, Associated Clients
• LAN Information: Display total received and transmitted statistics on the LAN
interface.
Status, WDS Link Status, Extra Information and Event Log.
TEW-738APBO
System Overview
Display detailed information of System, Network, LAN and Wireless in the System
Overview page.
• Device Information: Display the information of the system.
o Operating Mode: The mode currently in service.
o Host Name: The name of the system.
o Host Description: A description of the system.
o Firmware Version: The current installed firmware version.
o Firmware Date: The build time of installed firmware.
o Device Time: The current time of the system.
o System Up Time: The time period that system has been in service since last
reboot.
o ETH1/ETH2MAC: Ethernet MAC address of the access point.
o Wireless MAC: Wireless MAC address of the access point
o Ethernet Connection Type: The connection applied on the access point.
o IP Address: The management IP of system. By default, it’s 192.168.2.254.
o IP Netmask: The network mask. By default, it’s 255.255.255.0.
o IP Gateway: The gateway IP addresses and by default, it’s 192.168.2.1.
o Primary DNS: The primary DNS server in service.
• Wireless Information: Display total received and transmitted statistics on available
Virtual AP.
o WiFi: Wireless status of the access point.
o Band: Operating wireless band of the access point.
o Channel: Operating channel of the access point.
o Current Tx Power: Transmit power of the access point.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 48

48
TRENDnet User’s Guide
o Data Rate: Current wireless data rate of the access point.
DHCP Client
Display detailed information of the access point’s DHCP server.
Extra Information
Users could pull out information such as Route table, ARP table, MAC table, Bridge table
or STP available in the drop-down list from system. The “Refresh” button is used to
retrieve latest table information.
TEW-738APBO
• Service: Status of access point’s DHCP server
• Start IP: Starting IP address of access point’s DHCP server
• End IP: Last IP address used on the access point’s DHCP server
• Default Gateway: Assigned gateway address to the access point
• DNS1/2: Assigned DNS to the access point’s DHCP server
• WINS: Assigned WINS to the access point’s DHCP server
• Domain: Domain assigned to access point
• Lease Time: DHCP lease time of access point’s DHCP server
• DHCP Client list: List of clients connected to the access point
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
• Route table information: Select “Route table information” on the drop-down list
to display route table. TEW-738APBO could be used as a L2 or L3 device. It doesn’t
support dynamic routing protocols such as RIP or OSPF. Static routes to specific
hosts, networks or default gateway are set up automatically according to the IP
configuration of system's interfaces. When used as a L2 device, it could switch
packets and, as L3 device, it’s capable of being a gateway to route packets inward
and outward.
• ARP table Information: Select “ARP Table Information” on the drop-down list to
display ARP table. ARP associates each IP address to a unique hardware address
(MAC) of a device. It is important to have a unique IP address as final destination to
switch packets to.
Page 49

49
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-738APBO
Event Log
The Event log displays system events when system is up and running. Also, it becomes
• Bridge table information: Select “Bridge Table information” on the drop-down list
to display bridge table. Bridge table will show Bridge ID and STP's Status on the
each Ethernet bridge and its attached interfaces, the Bridge Port should be
attached to some interfaces (e.g. eth2, ra0~ra6 and wds0~wds3).
• Bridge MAC information: Select “Bridge MACs Information” on the drop-down list
to display MAC table.
very useful as a troubleshooting tool when issues are experienced in system.
• Time: The date and time when the event occurred.
• Facility: It helps users to identify source of events such “System” or “User”
• Severity: Severity level that a specific event is associated such as “info”, “error”,
“warning”, etc.
• Message: Description of the event.
Click Refresh button to renew the log, or click Clear button to clear all the record.
Associated Client List
List of all clients associated to the access point.
This table displays local MAC addresses associated with wired or wireless interfaces,
but also remember non-local MAC addresses learned from wired or wireless
interfaces. Ageing timers will be reset when existing MAC addresses in table are
learned again or added when new MAC addresses are seen from wired or wireless
interfaces as well. When time runs out for a particular entry, it will be pruned from
the table. In that situation, switching packet to that particular MAC address will be
dropped.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
o MAC Address: Display MAC address of WDS peer.
o RSSI: Indicate the signal strength of the respective WDS links.
o TX/RX SEQ: Transmit and receive sequence.
o TX/RX Bytes: Transmit and receive bytes
Page 50

50
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Remote AP status
List the current status of the remote access point.
o ESSID: SSID of remote access point
o MAC Address: Display MAC address of WDS peer.
o RSSI: Indicate the signal strength of the respective WDS links.
o TX/RX SEQ: Transmit and receive sequence.
o TX/RX Bytes: Transmit and receive bytes
o Status: Display current association status of remote access point
CPE + AP Mode Configuration
When CPE+AP mode is chosen, the system can be configured as a Customer Premises
Equipment (CPE). This section provides detailed explanation for users to configure in the
CPE+AP mode with help of illustrations. In the CPE+AP mode, functions listed in the
table below are also available from the Web-based GUI interface.
External Network Connection
Network Requirement
It can be used as an Outdoor Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) to receive and repeat
wireless signal over last mile application, helping WISPs deliver wireless broadband
Internet service to residents and business customers. In the CPE+AP mode, TEW738APBO is a gateway enabled with NAT and DHCP Server functions. The wired and
wireless clients connected to TEW-738APBO are in different subnet from those
connected to Main Base Station, and, in CPE+AP mode, it accepts wireless connections
from wireless client devices.
TEW-738APBO
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 51

51
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Configure CPE Setup
There are three connection types for the WAN port: Static IP, Dynamic IP, PPPoE and
PPTP,
Please click on System -> WA N and follow the below setting.
• Mode: Check “Static IP”, “Dynamic IP”, “PPPoE” or “PPTP”to set up system WAN IP.
• PPPoE : To create wireless PPPoE WAN connection to a PPPoE server in network.
TEW-738APBO
• Static IP: Users can manually setup the WAN IP address with a static IP provided by
W I SP.
o IP Address: The IP address of the WAN port; default IP address is 192.168.1.254
o IP Netmask: The Subnet mask of the WAN port; default Netmask is 255.255.255.0
o IP Gateway : The default gateway of the WAN port; default Gateway is
192.168.1.1
• Dynamic IP: Please consult with WISP for correct wireless settings to associate with
WISP AP before a dynamic IP, along with related IP settings including DNS can be
available from DHCP server. If IP Address is not assigned, please double check with
your wireless settings and ensure successful association. Also, you may go to
“WAN Information” in the Overview page to click Release button to release IP
address and click Renew button to renew IP address again.
o Hostname : The Hostname of the WAN port
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
• User Name : Enter User Name for PPPoE connection
• Password : Enter Password for PPPoE connection
• Reconnect Mode:
o Always on: A connection to Internet is always maintained.
o On Demand: A connection to Internet is made as needed.
o Manual: Click the “Connect” button on “WAN Information” in the Overview page
to connect to the Internet.
• Idle Time: Time to last before disconnecting PPPoE session when it is idle. Enter
preferred Idle Time in minutes. Default is “0”, indicates disabled. When Idle time is
disabled, the “Reconnect Mode” will turn out “Always on”
• MTU: By default, it’s 1492 bytes. MTU stands for Maximum Transmission Unit.
Consult with WISP for a correct MTU setting.
Page 52

52
TRENDnet User’s Guide
• PPTP: The Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) mode enables the implementation of
secure multi-protocol Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
through public networks.
security for the PPTP connection that is between the VPN client and the VPN server.
• DNS: Check “No Default DNS Server” or “Specify DNS Server IP” radial button as
desired to set up system DNS.
• Primary: The IP address of the primary DNS server.
• Secondary: The IP address of the secondary DNS server.
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes
TEW-738APBO
Configure DDNS Setup
Dynamic DNS allows you to map domain name to dynamic IP address.
• IP Address: The IP address of the WAN port
• IP Netmask: The Subnet mask of the WAN port
• PPTP Server IP Address: The IP address of the PPTP server
• User Name : Enter User Name for PPTP connection
• Password: Enter Password for PPTP connection
• Reconnect Mode:
o Always on: A connection to Internet is always maintained.
o On Demand: A connection to Internet is made as needed.
o Manual: Click the “Connect” button on “WAN Information” in the Overview page
to connect to the Internet.
• Idle Time: Time to last before disconnecting PPPoE session when it is idle. Enter
preferred Idle Time in minutes. Default is “0”, indicates disabled. When Idle time is
disabled, the “Reconnect Mode” will turn out “Always on”
• MTU: By default, it’s 1460 bytes. MTU stands for Maximum Transmission Unit.
Consult with WISP for a correct MTU setting.
• MPPE Encryption: Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption (MPPE) encrypts data in
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)-based dial-up connections or Point-to-Point Tunneling
Protocol (PPTP) virtual private network (VPN) connections. 128-bit key (strong) and
40-bit key (standard) MPPE encryption schemes are supported. MPPE provides data
Please click on System -> DDNS Setup and follow the below setting.
• Enabled: By default, it’s “Disable”. The mapping domain name won’t change when
dynamic IP changes. The beauty of it is no need to remember the dynamic WAP IP
while accessing to it.
• Service Provider: Select the preferred Service Provider from the drop-down list
including dyndns, dhs, ods and tzo
• Hostname: Host Name that you register to Dynamic-DNS service and export.
• User Name & Password: User Name and Password are used to login DDNS service.
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 53

53
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Configure LAN IP
Here are the instructions to setup the local IP Address and Netmask.
Please click on System -> LAN and follow the below setting.
• Mode: Check either “Static IP” or “Dynamic IP” button as desired to set up the
system IP of LAN port.
• Static IP: The administrator can manually setup the LAN IP address when static IP is
available/ preferred.
o IP Address: The IP address of the LAN port; default IP address is 192.168.2.254
o IP Netmask: The Subnet mask of the LAN port; default Netmask is 255.255.255.0
o IP Gateway : The default gateway of the LAN port; default Gateway is 192.168.2.1
• Dynamic IP: This configuration type is applicable when the TEW-738APBO is
connected to a network with the presence of a DHCP server; all related IP
information will be provided by the DHCP server automatically.
o Primary: The IP address of the primary DNS server.
o Secondary: The IP address of the secondary DNS server.
• 802.1d Spanning Tree
The spanning tree network protocol provides a loop free topology for a bridged LAN
between LAN interface and 4 WDS interfaces from wds0 to wds3. The Spanning Tree
Protocol, which is also referred to as STP, is defined in the IEEE Standard 802.1d.
Spanning tree always disabled on TEW-738APBO. Below Figures depict a loop for a
bridged LAN between LAN and WDS link
• DHCP Setup: Devices connected to the system can obtain an IP address
automatically when this service is enabled.
TEW-738APBO
o Hostname : The Hostname of the LAN port
• DNS: Check either “No Default DNS Server” or “Specify DNS Server IP” button as
desired to set up the system DNS.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
o DHCP: Check Enable button to activate this function or Disable to deactivate this
service.
o Start IP / End IP: Specify the range of IP addresses to be used by the DHCP server
when assigning IP address to clients. The default range IP address is 192.168.2.10
to 192.168.2.70, the netmask is 255.255.255.0
o DNS1 IP: Enter IP address of the first DNS server; this field is required.
o DNS2 IP: Enter IP address of the second DNS server; this is optional.
o WINS IP: Enter IP address of the Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) server;
this is optional.
Page 54

54
TRENDnet User’s Guide
o Domain: Enter the domain name for this network.
o Lease Time: The IP addresses given out by the DHCP server will only be valid for
the duration specified by the lease time. Increasing the time ensure client
operation without interruptions, but could introduce potential conflicts. Lowering
the lease time will avoid potential address conflicts, but might cause more
interruptions to the client while it will acquire new IP addresses from the DHCP
server. Default is 86400 seconds
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes
Access Point Association
Wireless General Setup
The administrator can change the data transmission, channel and output power settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> General Setup and follow the below setting.
TEW-738APBO
Configure Static IP address
Assign static IP address to associated clients through the access point.
• Comment: Enter a note of assigned IP address
• IP Address: Enter the IP address to assign
• MAC address: Enter the client MAC address to the assigned IP address. Click Add to
enter settings.
• MAC Address: The MAC address of the Wireless interface is displayed here.
• Band Mode: Select an appropriate wireless band; bands available are 801.11b,
802.11b/g, 802.11b/g/n or 802.11n only.
• Channel: Select the desired channel from the drop-down list to have the access
point operate on. Click Auto Scan to scan for the best available channel to use based
on the environment.
• Tx Power: Yo u can adjust the output power of the system to get the appropriate
coverage for your wireless network. Specify digit numbers between 1 to 100 (the
unit is %) for your environment. If you are not sure which setting to choose, then
keep the default setting, 100%.
• RF (ON/OFF) Schedule: Select an assigned schedule of when to have the access
point turn on. Select Always Run to have the access point always on.
When Band Mode select in 802.11a only mode, the HT(High Throughput) settings
should be hidden immediately.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 55

55
TRENDnet User’s Guide
• TxStream/Rx Stream: Select the amount of transmit (TX) and Receive (RX) streams.
By default, it's 2.
• Channel Bandwidth: The "20/40” MHz option is usually best. The other option is
available for special circumstances.
• Extensions Channel: Select which section of channels to use for extension channels.
• MCS: This parameter represents transmission rate. By default (Auto) the fastest
possible transmission rate will be selected. You have the option of selecting the
speed if necessary. (Refer to Appendix C. MCS Data Rate)
Wireless Advanced Set up
To achieve optimal wireless performance, it is necessary to tweak advance setting per
requirements properly, not necessary higher the better or lower.
The administrator can change the RTS threshold and fragmentation threshold settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> Advanced Setup and follow the below setting.
• Short Slot : By default, it’s “Enable” for reducing the slot time from the standard 20
microseconds to the 9 microsecond short slot time. Slot time is the amount of time a
device waits after a collision before retransmitting a packet. Reducing the slot time
decreases the overall back-off, which increases throughput. Back-off, which is a
multiple of the slot time, is the random length of time a station waits before
sending a packet on the LAN. For a sender and receiver own right of the channel the
shorter slot time help manage shorter wait time to re-transmit from collision
because of hidden wireless clients or other causes. When collision sources can be
removed sooner and other senders attempting to send are listening the
channel(CSMA/CA) the owner of the channel should continue ownership and finish
their transmission and release the channel. Then, following ownership of the
channel will be sooner for the new pair due to shorter slot time. However, when
long duration of existing collision sources and shorter slot time exist the owners
might experience subsequent collisions. When adjustment to longer slot time can’t
improve performance then RTS/CTS could supplement and help improve
performance.
• ACK Timeout: ACK timeout is in the range of 1~255 and set in unit of microsecond.
The default value is 32 microsecond. All data transmission in 802.11b/g request an
“Acknowledgement” (ACK) send by receiving radio. The transmitter will resend the
original packet if correspondent ACK failed to arrive within specific time interval,
also refer to as “ACK Timeout”.
ACK Timeout is adjustable due to the fact that distance between two radio links
may vary in different deployment. ACK Timeout makes significant influence in
TEW-738APBO
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 56

56
TRENDnet User’s Guide
queue (FTP data, for example).
performance of long distance radio link. If ACK Timeout is set too short, transmitter
will start to “Resend” packet before ACK is received, and throughputs become low
due to excessively high re-transmission. ACK Timeout is best determined by
distance between the radios, data rate of average environment. The Timeout value
is calculated based on round-trip time of packet with a little tolerance, So, if
experiencing re-transmissions or poor performance the ACK Timeout could be
made longer to accommodate.
• Beacon Interval:: Beacon Interval is in the range of 20~1024 and set in unit of
millisecond. The default value is 100 msec.
Access Point (AP) in IEEE 802.11 will send out a special approximated 50-byte
frame, called “Beacon”. Beacon is broadcast to all the stations, provides the basic
information of AP such as SSID, channel, encryption keys, signal strength, time
stamp, support data rate.
All the radio stations received beacon recognizes the existence of such AP, and may
proceed next actions if the information from AP matches the requirement. Beacon
is sent on a periodic basis, the time interval can be adjusted.
By increasing the beacon interval, you can reduce the number of beacons and
associated overhead, but that will likely delay the association and roaming process
because stations scanning for available access points may miss the beacons. You
can decrease the beacon interval, which increases the rate of beacons. This will
make the association and roaming process very responsive; however, the network
will incur additional overhead and throughput will go down.
• DTIM Interval: The DTIM interval is in the range of 1~255. The default is 1.
DTIM is defined as Delivery Traffic Indication Message. It is used to notify the
wireless stations, which support power saving mode, when to wake up to receive
multicast frame. DTIM is necessary and critical in wireless environment as a
mechanism to fulfill power-saving synchronization. A DTIM interval is a count of the
number of beacon frames that must occur before the access point sends the
buffered multicast frames. For instance, if DTIM Interval is set to 3, then the Wi-Fi
clients will expect to receive a multicast frame after receiving three Beacon frame.
The higher DTIM interval will help power saving and possibly decrease wireless
throughput in multicast applications.
• RTS Threshold: TRTS Threshold is in the range of 1~2347 byte. The default is 2347
byte. The main purpose of enabling RTS by changing RTS threshold is to reduce
possible collisions due to hidden wireless clients. RTS in AP will be enabled
automatically if the packet size is larger than the Threshold value. By default, RTS is
disabled in a normal environment supports non-jumbo frames.
• Short Preamble: By default, it’s “Enable”. To Disable is to use Long 128-bit Preamble
Synchronization field. The preamble is used to signal "here is a train of data coming"
to the receiver. The short preamble provides 72-bit Synchronization field to improve
WLAN transmission efficiency with less overhead.
• WMM: By default, it's “Enabled”.
Wireless WMM QoS Setup
To achieve optimal wireless performance, it is necessary to tweak advance setting per
requirements properly, not necessary higher the better or lower.
The administrator can change the RTS threshold and fragmentation threshold settings
for the system. Please click on Wireless -> Advanced
• WMM Parameters of Access Point : This affects traffic flowing from the access point
to the client station
Data
Queue
AC_BK Background. Low
Transmitted
AP to Clients
Priority Description
High throughput. Bulk data that requires maximum
throughput and is not time-sensitive is sent to this
TEW-738APBO
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 57

57
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Medium throughput and delay. Most traditional IP
sent to this queue
sent to this queue
queue
AC_BE Best Effort Medium
AC_VI Video High
Data
Queue
AC_BK Background. Low
AC_BE Best Effort Medium
AC_VI Video High
AC_VO Voice High
AC_VO Voice High
Configuring QoS options consists of setting parameters on existing queues for different
types of wireless traffic. You can configure different minimum and maximum wait
times for the transmission of packets in each queue based on the requirements of the
media being sent. Queues automatically provide minimum transmission delay for
Voice, Video, multimedia, and mission critical applications, and rely on best-effort
parameters for traditional IP data.
As an Example, time-sensitive Voice & Video, and multimedia are given effectively
higher priority for transmission (lower wait times for channel access), while other
applications and traditional IP data which are less time-sensitive but often more dataintensive are expected to tolerate longer wait times.
Transmitted
Clients to AP
data is sent to this queue
Minimum delay. Time-sensitive video data is
automatically sent to this queue
Priority Description
High throughput. Bulk data that
requires maximum
throughput and is not timesensitive is sent to this queue
(FTP data, for example).
Medium throughput and delay.
Most traditional IP data is
Minimum delay. Time-sensitive
video data is automatically
Time-sensitive data like VoIP
and streaming media are
automatically sent to this
Time-sensitive data like VoIP and streaming media
are automatically sent to this queue
o Aifsn: The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing Number specifies a wait time (in
milliseconds) for data frames
o CWmin: Minimum Contention Window. This parameter is input to the algorithm
that determines the initial random back-off wait time ("window") for retry of a
transmission. The value specified here in the Minimum Contention Window is the
upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from which the initial random back-off
wait time is determined.
o CWmax: Maximum Contention Window. The value specified here in the
Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling
of the random back-off value. This doubling continues until either the data frame
is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached. Once the Maximum
Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a maximum number
of retries allowed is reached. Valid values for the "cwmax" are 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63,
127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for "cwmax" must be higher than the value for
"cwmin".
o Txop: Transmission Opportunity is an interval of time when a WME AP has the
right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium (WM). This value
specifies (in milliseconds) the Transmission Opportunity (TXOP) for AP; that is, the
interval of time when the WMM AP has the right to initiate transmissions on the
wireless network.
o ACM: Admission Control Mandatory, ACM only takes effect on AC_VI and AC_VO.
When you do not click Checkbox, it means that the ACM is controlled by the
connecting AP. If you click Checkbox, it means that the Client is in charge.
o AckPolicy: Acknowledgment Policy, WMM defines two ACK policies: Normal ACK
and No ACK. Click “Checkbox” indicates “No ACK”
When the no acknowledgment (No ACK) policy is used, the recipient does not
acknowledge received packets during wireless packet exchange. This policy is
suitable in the environment where communication quality is fine and interference
is weak. While the No ACK policy helps improve transmission efficiency, it can
cause increased packet loss when communication quality deteriorates. This is
because when this policy is used, a sender does not retransmit packets that have
not been received by the recipient. When the Normal ACK policy is used, the
recipient acknowledges each received unicast packet.
• WMM Parameters of Station: This affects traffic flowing from the client station to
the access point.
o Aifsn : The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing Number specifies a wait time (in
milliseconds) for data frames
TEW-738APBO
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 58

58
TRENDnet User’s Guide
o CWmin : Minimum Contention Window. This parameter is input to the
algorithm that determines the initial random backoff wait time ("window")
for retry of a transmission. The value specified here in the Minimum
Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from
which the initial random backoff wait time is determined.
o CWmax : Maximum Contention Window. The value specified here in the
Maximum Contention Window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling
of the random backoff value. This doubling continues until either the data frame
is sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached. Once the Maximum
Contention Window size is reached, retries will continue until a maximum number
of retries allowed is reached. Valid values for the "cwmax" are 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63,
127, 255, 511, or 1024. The value for "cwmax" must be higher than the value for
"cwmin".
o Txop : Transmission Opportunity is an interval of time when a WME AP has the
right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium (WM). This value
specifies (in milliseconds) the Transmission Opportunity (Txop) for AP; that is, the
interval of time when the WMM AP has the right to initiate transmissions on the
wireless network.
o ACM: Admission Control Mandatory, ACM only takes effect on AC_VI and AC_VO.
When you do not click Checkbox, it means that the ACM is controlled by the
connecting AP. If you click Checkbox, it means that the Client is in charge.
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes.
The items in this page are for AP's RF advanced settings and will be applied to all VAPs
and WDS Links.
Site Survey
• ESSID: Available Extend Service Set ID of surrounding Access Points.
• MAC Address: MAC addresses of surrounding Access Points.
• Signal: Received signal strength of all found Access Points.
• Channel: Channel numbers used by all found Access Points.
• Security: Security type by all found Access Points.
• Band: Wireless band used by all found Access Points.
• Network Type: Network type used by all found Access Points.
• Select: Click “Select” to configure settings and associate with chosen AP.
Create Wireless Profile
The administrator can configure station profiles via this page.
Please click on Wireless -> Wireless Profile and follow the below setting.
• Connection Setup: Select the repeater connection type.
o Fix: Select to have access point fixed on one profile to repeat
o Cycle: Select to have access point cycle through different profiles.
• General Configuration:
TEW-738APBO
Use this tool to scan and locate WISP Access Points and select one to associate with.
Please click on Wireless -> Site Survey. Below depicts an example for site survey.
• MAC Address: The MAC address of the Wireless Station is displayed here.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
• Profile Name: Set different profiles for quick connection uses.
Page 59

59
TRENDnet User’s Guide
• ESSID: Assign Service Set ID for the wireless system.
• Lock to AP MAC: This allows the station to always maintain connection to a
particular AP with a specific MAC address. This is useful as sometimes there can be
few identically named SSID's (AP's) with different MAC addresses. With AP lock on,
the station will lock to MAC address and not roam between several Access Points
with the same ESSID.
• Security Type: Select the desired security type from the drop-down list; the options
are Disable, WEP, WPA -PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA -Enterprise, WPA2-Enterprise and
WEP 802.1X.
o Disable: Data are unencrypted during transmission when this option is selected.
o Cipher Suite: By default, it is AES. Select either AES or TKIP cipher suites
o Group Key Update Period: By default, it is 600 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o Master Key Update Period: By default, it is 83499 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o Pre-shared Key: Enter the pre-shared key; the format shall go with the selected
key type.
• WEP Auth Method: Enable the desire option among OPEN or SHARED
o Key Index: Key index is used to designate the WEP key during data transmission. 4
• WPA -Enterprise (or WPA2-Enterprise): The RADIUS authentication and encryption
will be both enabled if this is selected.
different WEP keys can be entered at the same time, but only one is chosen.
o WEP Key #: Enter HEX or ASCII format WEP key value; the system supports up to 4
sets of WEP keys.
• WPA -PSK (or WPA2-PSK) : WPA (or WPA2) Algorithms, allows the system accessing
the network by using the WPA-PSK protected access.
TEW-738APBO
• WPA General Settings:
o Cipher Suite: By default, it is AES. Select either AES or TKIP cipher suites
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 60

60
TRENDnet User’s Guide
o Group Key Update Period: By default, it’s 3600 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o Master Key Update Period: By default, it is 83499 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o EAP Reauth Period: By default, it's 3600 seconds. Set WPA2 PMKID cache
timeout period, after time out, the cached key will be deleted.
o Pre-Authentication: By default, it's “Disable”. To Enable is use to speed up
roaming before pre-authenticating IEEE 802.1X/EAP part of the full RSN
authentication and key handshake before actually associating with a new AP.
• Radius Server Settings :
o IP Address: Enter the IP address of the Authentication RADIUS server.
o Port: By default, it’s 1812. The port number used to communicate with RADIUS
o Shared secret: A secret key used between system and RADIUS server. Supports 8
to 64 characters.
o Accounting RADIUS Server: Enable to set Account RADIUS server.
o Key Index: key index is used to designate the WEP key during data transmission.
4 different WEP keys can be entered at the same time, but only one is chosen.
o WEP Key #: Enter HEX or ASCII format WEP key value; the system supports up to 4
sets of WEP keys.
o WPA-PSK (or WPA2-PSK): WPA (or WPA2) Algorithms, allows the system accessing
the network by using the WPA-PSK protected access.
AP Setup
The administrator can configure station profiles via this page.
Please click on Wireless -> Wireless Profile and follow the below setting.
server.
o Shared secret: A secret key used between system and RADIUS server. Supports 8
to 64 characters.
o Accounting RADIUS Server: Enable to set Account RADIUS server.
• WEP 802.1X: When WEP 802.1x Authentication is enabled, please refer to the
following Dynamic WEP and RADIUS settings to complete configuration.
TEW-738APBO
• ESSID: Assign Service Set ID for the wireless system.
• Enable Repeater SSID: Select Enable to broadcast the repeated signal.
• Hidden SSID: Select Enable to broadcast the access point’s SSID.
• Client Isoltion: Select Enable to isolate wireless clients from each other.
• IAPP:
• Radius Server Settings:
o IP Address: Enter the IP address of the Authentication RADIUS server.
o Port: By default, it’s 1812. The port number used to communicate with RADIUS
server.
• Maximum Clients: Enter the amount of wireless clients allowed to connect to the
access point.
• Security Type: Select the desired security type from the drop-down list; the options
are Disable, WEP, WPA -PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA -Enterprise, WPA2-Enterprise and
WEP 802.1X.
o Disable: Data are unencrypted during transmission when this option is selected.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 61

61
TRENDnet User’s Guide
o Pre-shared Key: Enter the pre-shared key; the format shall go with the selected
key type.
• WPA -Enterprise (or WPA2-Enterprise): The RADIUS authentication and encryption
will be both enabled if this is selected.
TEW-738APBO
• WEP Auth Method: Enable the desire option among OPEN or SHARED
o Key Index: Key index is used to designate the WEP key during data transmission. 4
different WEP keys can be entered at the same time, but only one is chosen.
o WEP Key #: Enter HEX or ASCII format WEP key value; the system supports up to 4
sets of WEP keys.
• WPA -PSK (or WPA2-PSK) : WPA (or WPA2) Algorithms, allows the system accessing
the network by using the WPA-PSK protected access.
• WPA General Settings:
o Cipher Suite: By default, it is AES. Select either AES or TKIP cipher suites
o Group Key Update Period: By default, it’s 3600 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o Master Key Update Period: By default, it is 83499 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o Cipher Suite: By default, it is AES. Select either AES or TKIP cipher suites
o Group Key Update Period: By default, it is 600 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the timelength is required.
o Master Key Update Period: By default, it is 83499 seconds. This time interval for
rekeying GTK, broadcast/multicast encryption keys, in seconds. Entering the time-
o EAP Reauth Period: By default, it's 3600 seconds. Set WPA2 PMKID cache
timeout period, after time out, the cached key will be deleted.
o Pre-Authentication: By default, it's “Disable”. To Enable is use to speed up
roaming before pre-authenticating IEEE 802.1X/EAP part of the full RSN
authentication and key handshake before actually associating with a new AP.
• Radius Server Settings :
o IP Address: Enter the IP address of the Authentication RADIUS server.
o Port: By default, it’s 1812. The port number used to communicate with RADIUS
server.
length is required.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 62

62
TRENDnet User’s Guide
o Shared secret: A secret key used between system and RADIUS server. Supports 8
to 64 characters.
o Accounting RADIUS Server: Enable to set Account RADIUS server.
• WEP 802.1X: When WEP 802.1x Authentication is enabled, please refer to the
following Dynamic WEP and RADIUS settings to complete configuration.
• MAC Filter Setup: By default, it’s “Disable”. Options are Disable, Only Deny List
• MAC or Only Allow List MAC.
Two ways to set MAC filter rules:
o Only Allow List MAC: The wireless clients in the “Enable” list will be allowed to
access the Access Point; All others or clients in the “Disable” list will be denied.
o Only Deny List MAC: The wireless clients in the “Enable” list will be denied to
access the Access Point; All others or clients in the “Disable” list will be allowed.
• MAC: Enter MAC address (e.g. aa:bb:cc:00:00:0a) and click “Add” button, then the
MAC address should display in the “Enable” List.
There are a maximum of 20 clients allowed in this “Enable” List. The MAC addresses of
• Radius Server Settings:
o IP Address: Enter the IP address of the Authentication RADIUS server.
o Port: By default, it’s 1812. The port number used to communicate with RADIUS
server.
o Shared secret: A secret key used between system and RADIUS server. Supports 8
to 64 characters.
o Accounting RADIUS Server: Enable to set Account RADIUS server.
o Key Index : key index is used to designate the WEP key during data transmission.
4 different WEP keys can be entered at the same time, but only one is chosen.
o WEP Key # : Enter HEX or ASCII format WEP key value; the system supports up to
4 sets of WEP keys.
o WPA-PSK (or WPA2-PSK) : WPA (or WPA2) Algorithms, allows the system
accessing the network by using the WPA-PSK protected access.
Wireless AP MAC Filter Setup
The administrator can allow or reject clients to access Repeater AP.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
the wireless clients can be added and removed to the list using the Add and Remove
buttons. Click Apply button to activate your changes
Access Control
DMZ
DMZ is commonly work with the N AT functionality as an alternative of Virtual
Server(Port Forwarding) while wanting all ports of DMZ host visible to Internet users.
Virtual Server rules have precedence over the DMZ rule. In order to use a range of ports
available to access to different internal hosts Virtual Server rules are needed.
• DMZ: By default, it’s “Disable”. Check Enable radial button to enable DMZ.
• IP Address: Enter IP address of DMZ host and only one DMZ host is supported.
TEW-738APBO
Page 63

63
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes.
IP Filter Setup
Allows to create deny or allow rules to filter ingress or egress packets from specific
source and/or to destination IP address on wired (LAN) or Wireless (WAN) ports. Filter
rules could be used to filter unicast or multicast packets on different protocols as shown
in the IP Filter Setup. Important to note that IP filter rules has precedence over Virtual
server rules.
Please click on Advance -> IP Filter Setup and follow the below setting.
Click “Save” button to add IP filter rule. Total of 20 rules maximum allowed in the IP
Filter List. All rules can be edited or removed from the List. Click Reboot button to
activate your changes.
When you create rules in the IP Filter List, the prior rules maintain higher priority. To
allow limited access from a subnet to a destination network manager needs to create
allow rules first and followed by deny rules. So, if you just want one IP address to access
the system via telnet from your subnet, not others, the Example 1 demonstrates it, not
rules in the Example 2.
o Example 1 : Create a higher priority rule to allow IP address 192.168.2.2 Telnet
access from LAN port first, and deny Telnet access from remaining IP addresses in
the same subnet.
o Example 2 : All Telnet access to the system from the IP addresses of subnet
192.168.2.x works with the rule 1 of Example 2. The rule 2 won’t make any
difference.
TEW-738APBO
MAC Filter Setup
Create MAC filter rules to allow or deny unicast or multicast packets from limited
number of MAC addresses. Note that MAC filter rules have precedence over IP Filter
rules.
Please click on Advance -> MAC Filter Setup and follow the below setting.
• Source Address/Mask: Enter desired source IP address and netmask; i.e.
192.168.2.10/32.
• Source Port: Enter a port or a range of ports as start:end; i.e. port 20:80
• Destination Address/Mask: Enter desired destination IP address and netmask; i.e.
192.168.1.10/32
• Destination Port: Enter a port or a range of ports as start:end; i.e. port 20:80
• In/Out: Applies to Ingress or egress packets
• Protocol: Supports TCP, UDP or ICMP.
• Listen: Click Yes radial button to match TCP packets only with the SYN flag.
• Active: Deny to drop and Pass to allow per filter rules
• Interface: The interface that a filter rule applies
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
• MAC Filter Rule: By default, it’s “Disable”. Options are Disabled, Only Deny List
MAC or Only Allow List MAC. Click Save button to save your change.
Two ways to set the MAC Filter List:
o Only Allow List MAC: The wireless clients in the MAC Filter List will be allowed to
Page 64

64
TRENDnet User’s Guide
access to Access Point; All others will be denied.
o Only Deny List MAC: The wireless clients in the MAC Filter List will be denied to
access to Access Point; All others will be allowed.
• MAC Address: Enter MAC address (e.g. aa:bb:cc:00:00:0a) and click “Add” button,
then the MAC address should display in the MAC Filter List.
There are a maximum of 20 clients allowed in this MAC Filter List. The MAC addresses of
the wireless clients can be added and removed to the list using the Add and Delete
buttons.
Click Reboot button to activate your changes
Virtual Server
“Virtual Server” can also referred to as “Port Forward” as well and used interchangeably.
Resources in the network can be exposed to the Internet users in a controlled manner
including on-line gaming, video conferencing or others via Virtual Server setup. Don’t
repeat ports’ usage to avoid confusion.
Suppose you want to assign ports 21-25 to one FTP, Telnet and SMTP server (A in the
example), and port 80 to another (B in the example). You assign the LAN IP addresses
and the ISP assigns the WAN IP address. The NAT network appears as a single host on
the Internet.
multiple private ports.
• Private Port: A port or a range of ports may be specified as start:end; i.e. port
20:80
• Public Port: A port or a range of ports may be specified as start:end; i.e. port 20:80
.Click “Add” button to add Virtual Server rule to List. Total of maximum 20 rules are
allowed in this List. All rules can be edited or removed from the List. Click Reboot button
to activate your changes.
While creating multiple Virtual Server rules, the prior rules have higher priority. The
Virtual server rules have precedence over the DMZ one while both rules exist. Example 1
and 2 demonstrate proper usage of DMZ and Virtual Server rules.
• Example 1: All connections should be redirected to 192.168.2.12 while DMZ is
enabled. Since Virtual Server rules have precedence over the DMZ rule all
connections to TCP port 22 will be directed to TCP port 22 of 192.168.2.10 and
remaining connections to port TCP 20~80 will be redirected to port TCP 20~80 of
192.168.2.11
• Example 2: All connections should be redirected to 192.168.2.12 while DMZ is
enabled. Since Virtual Server rules have precedence over the DMZ rule all other
connections to TCP port 20~80 will be redirected to port 20~80 of 192.168.2.11.
The rule 2 won’t take effect.
TEW-738APBO
Bandwidth Control
Bandwidth control allows you to control the bandwidth going through the access point.
• Virtual Server: By Default, It’s “Disable”. Check Enable radial button to enable
Virtual Server.
• Description: Enter appropriate message for resource sharing via Virtual Server.
• Private IP: Enter corresponding IP address of internal resource to share.
• Protocol Type: Select appropriate sessions, TCP or UDP, from shared host via
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
• Service: Select Enable to turn on bandwidth control through the access point.
• Mode: Select the bandwidth control mode to use through the access point.
• Upload: Enter the upload bandwidth speeds
• Download: Enter the download bandwidth speeds
Page 65

65
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Routing
System Overview
TEW-738APBO
This section allows you to configure the routing of the access point.
• OSPF: Select Enable to enable OSPF setting
• RouterID: Select the ID to configure
• Network (WAN): Select to configure the WAN section, enter the area to assign
• Network (LAN): Select to configure the LAN section, enter the area to assign.
• Distribute RIP over OSPF: Check this option to use RIP protocol
• RIP Settings
• RIP Service: Select Enable to use RIP protocol
• Side: Select the network section to apply RIP.
Status
This section breaks down into subsections of System Overview, Associated Clients
Status, WDS Link Status, Extra Information and Event Log.
Display detailed information of System, Network, LAN and Wireless in the System
Overview page.
• Device Information: Display the information of the system.
o Operating Mode: The mode currently in service.
o Host Name: The name of the system.
o Host Description: A description of the system.
o Firmware Version: The current installed firmware version.
o Firmware Date: The build time of installed firmware.
o Device Time: The current time of the system.
o System Up Time: The time period that system has been in service since last
reboot.
o ETH1/ETH2MAC: Ethernet MAC address of the access point.
o Wireless MAC: Wireless MAC address of the access point
o CPU Loading: The CPU loading of the access point
o Memory Used: Memory usage of the access point.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 66

66
TRENDnet User’s Guide
• LAN Information: Display total received and transmitted statistics on the LAN
DHCP Client
interface.
Display detailed information of the access point’s DHCP server.
TEW-738APBO
o Ethernet Connection Type: The connection applied on the access point.
o IP Address: The management IP of system. By default, it’s 192.168.2.254.
o IP Netmask: The network mask. By default, it’s 255.255.255.0.
o IP Gateway: The gateway IP addresses and by default, it’s 192.168.2.1.
o Primary DNS: The primary DNS server in service.
• Wireless Information: Display total received and transmitted statistics on available
Virtual AP.
o WiFi: Wireless status of the access point.
o Band: Operating wireless band of the access point.
o Channel: Operating channel of the access point.
o Current Tx Power: Transmit power of the access point.
o Data Rate: Current wireless data rate of the access point.
• Service: Status of access point’s DHCP server
• Start IP: Starting IP address of access point’s DHCP server
• End IP: Last IP address used on the access point’s DHCP server
• Default Gateway: Assigned gateway address to the access point
• DNS1/2: Assigned DNS to the access point’s DHCP server
• WINS: Assigned WINS to the access point’s DHCP server
• Domain: Domain assigned to access point
• Lease Time: DHCP lease time of access point’s DHCP server
• DHCP Client list: List of clients connected to the access point
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 67

67
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-738APBO
Extra Information
Users could pull out information such as Route table, ARP table, MAC table, Bridge table
or STP available in the drop-down list from system. The “Refresh” button is used to
retrieve latest table information.
• Bridge table information: Select “Bridge Table information” on the drop-down list
to display bridge table. Bridge table will show Bridge ID and STP's Status on the
each Ethernet bridge and its attached interfaces, the Bridge Port should be
attached to some interfaces (e.g. eth2, ra0~ra6 and wds0~wds3).
• Route table information: Select “Route table information” on the drop-down list
to display route table. TEW-738APBO could be used as a L2 or L3 device. It doesn’t
support dynamic routing protocols such as RIP or OSPF. Static routes to specific
hosts, networks or default gateway are set up automatically according to the IP
configuration of system's interfaces. When used as a L2 device, it could switch
packets and, as L3 device, it’s capable of being a gateway to route packets inward
and outward.
• ARP table Information: Select “ARP Table Information” on the drop-down list to
display ARP table. ARP associates each IP address to a unique hardware address
(MAC) of a device. It is important to have a unique IP address as final destination to
switch packets to.
• Bridge MAC information: Select “Bridge MACs Information” on the drop-down list
to display MAC table.
This table displays local MAC addresses associated with wired or wireless interfaces,
but also remember non-local MAC addresses learned from wired or wireless
interfaces. Ageing timers will be reset when existing MAC addresses in table are
learned again or added when new MAC addresses are seen from wired or wireless
interfaces as well. When time runs out for a particular entry, it will be pruned from
the table. In that situation, switching packet to that particular MAC address will be
dropped.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 68

68
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-738APBO
Event Log
The Event log displays system events when system is up and running. Also, it becomes
very useful as a troubleshooting tool when issues are experienced in system.
o ESSID: SSID of remote access point
o MAC Address: Display MAC address of WDS peer.
• Time: The date and time when the event occurred.
• Facility: It helps users to identify source of events such “System” or “User”
• Severity: Severity level that a specific event is associated such as “info”, “error”,
“warning”, etc.
• Message: Description of the event.
Click Refresh button to renew the log, or click Clear button to clear all the record.
Associated Client List
List of all clients associated to the access point.
o RSSI: Indicate the signal strength of the respective WDS links.
o TX/RX SEQ: Transmit and receive sequence.
o TX/RX Bytes: Transmit and receive bytes
o Status: Display current association status of remote access point
System Management
Configure Management
Administrator could specify geographical location of the system via instructions in this
page. Administrator could also enter new Root and Admin passwords and allow multiple
login methods.
Please click System -> Management and follow the below settings.
• System Information
o MAC Address: Display MAC address of WDS peer.
o RSSI: Indicate the signal strength of the respective WDS links.
o TX/RX SEQ: Transmit and receive sequence.
o TX/RX Bytes: Transmit and receive bytes
Remote AP status
List the current status of the remote access point.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
o System Name: Enter a desired name or use the default one.
o Description: Provide description of the system.
o Location: Enter geographical location information of the system. It helps
administrator to locate the system easier.
• Admin Password:
Page 69

69
TRENDnet User’s Guide
o New Password : Enter a new password if desired
o Check New Password: Enter the same new password again to check.
• Admin Login Methods:
TEW-738APBO
o Enable HTTP: Check to select HTTP Service.
o HTTP Port: The default is 80 and the range is between 1 ~ 65535.
o Enable HTTPS: Check to select HTTPS Service
o HTTPS Port: The default is 443 and the range is between 1 ~ 65535.
o Enable Telnet: Check to select Telnet Service
o Telnet Port: The default is 23 and the range is between 1 ~ 65535.
o Enable SSH: Check to select SSH Service
o SSH Port: The default is 22 and the range is between 1 ~ 65535.
• Ping Watchdog: The ping watchdog sets the TEW-738APBO Device to continuously
ping a user defined IP address (it can be the internet gateway for example). If it is
unable to ping under the user defined constraints, the TEW-738APBO device will
automatically reboot. This option creates a kind of "fail-proof" mechanism.
Ping Watchdog is dedicated for continuous monitoring of the particular connection
to remote host using the Ping tool. The Ping works by sending ICMP “echo request”
packets to the target host and listening for ICMP “echo response” replies. If the
defined number of replies is not received, the tool reboots the device.
o Enable Ping Watchdog: control will enable Ping Watchdog Tool.
o IP Address To Ping: specify an IP address of the target host which will be
monitored by Ping Watchdog Tool.
o Ping Interval: specify time interval (in seconds) between the ICMP “echo
requests” are sent by the Ping Watchdog Tool. Default is 300 seconds.
o Startup Delay: specify initial time delay (in seconds) until first ICMP “echo
requests” are sent by the Ping Watchdog Tool. The value of Startup Delay should
be at least 60 seconds as the network interface and wireless connection
initialization takes considerable amount of time if the device is rebooted. Default
is 300 seconds.
o Failure Count To Reboot: specify the number of ICMP “echo response” replies. If
the specified number of ICMP “echo response” packets is not received
continuously, the Ping Watchdog Tool will reboot the device.
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes
Without a valid certificate, users may encounter the following problem in IE7 when they
try to access system's WMI (
https://192.168.2.254). There will be a “Certificate Error”,
because the browser treats system as an illegal website.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 70

70
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-738APBO
Click “Continue to this website” to access the system's WMI. The system's Overview
page will appear.
Configure System Time
System time can be configured via this page and manual setting or via a NTP server is
supported.
Please click on System -> Time Server and follow the below setting.
• Local Time: Display the current system time.
• NTP Client: To synchronize the system time with NTP server.
o Enable: Check to select NTP client.
o Default NTP Server: Select the NTP Server from the drop-down list.
o Time Zone: Select a desired time zone from the drop-down list.
o Daylight saving time: Enable or disable Daylight saving.
Click Save button to save your changes. Click Reboot button to activate your changes.
Configure SNMP Setup
SNMP is an application-layer protocol that provides a message format for
communication between SNMP managers and agents. By enabling SNMP function, the
administrator can obtain the system information remotely.
Please click on System -> SNMP Setup and follow the below setting.
• SNMP v2c Enable: Check to enable SNMP v2c.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 71

71
TRENDnet User’s Guide
will receive trap messages or notices send by the system.
o IP: Enter the IP addresses of the remote hosts to receive trap messages.
Click Save button to save changes and click Reboot button to activate.
o ro community: Set a community string to authorize read-only access.
o rw community: Set a community string to authorize read/write access.
• SNMP v3 Enable: Check to enable SNMP v3. SNMPv3 supports the highest level
SNMP security.
Enable UPNP
Enable UPNP protocol on the access point.
• Service:
o Enable: Select to enable UPNP through the access point
o Disable: Select to disable UPNP
TEW-738APBO
Backup / Restore and Reset to Factory
o SNMP ro user: Set a community string to authorize read-only access.
o SNMP ro password: Set a password to authorize read-only access.
o SNMP rw user: Set a community string to authorize read/write access.
o SNMP rw password: Set a password to authorize read/write access.
• SNMP Trap: Events such as cold start, interface up & down, and association &
disassociation will report to an assigned server.
o Community: Set a community string required by the remote host computer that
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Backup current configuration, restore prior configuration or reset back to factory default
configuration can be executed via this page.
Please click on Utilities -> Profile Setting and follow the below setting.
• Save Settings to PC: Click Save to save current access point configuration settings to
a computer.
• Load Settings from PC: Click Browse button to locate a configuration file to restore,
and then click Upload button to upload.
• Reset To Factory Default: Click Default button to reset back to the factory default
settings and expect Successful loading message. Then, click Reboot button to
activate.
Page 72

72
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-738APBO
Firmware Upgrade
Firmware is the main software image that system needs to respond to requests and to
manage real time operations. Firmware upgrades are sometimes required to include
new features or bugs fix. It takes around 2 minutes to upgrade due to complexity of
firmware. To upgrade system firmware, click Browse button to locate the new firmware,
and then click Upgrade button to upgrade.
• Firmware Version: Access point’s current firmware version
• Firmware Date: Firmware date of access point
• Select File: Click Browse button to locate a configuration file to restore, and then
click Upgrade button to upload.
• TFTP Server IP: Enter the IP address of the TFTP server to use for firmware upgrade
• File: Enter the location of the firmware file to use, and then click Upgrade button to
upload.
• URL: Enter the URL to use to upgrade access point’s firmware. Then, click Reboot
button to activate.
Network Utility
The administrator can diagnose network connectivity via the PING and TRACEROUTE
utility.
Please click on Utilities -> Network Utility and follow the below setting
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
• Ping: This utility will help ping other devices on the network to verify connectivity.
Ping utility, using ICMP packets, detects connectivity and latency between two
network nodes. As result of that, packet loss and latency time are available in the
Result field while running the PING test.
o Destination IP/Domain: Enter desired domain name, i.e. www.google.com, or IP
address of the destination, and click ping button to proceed. The ping result will
be shown in the Result field.
o Count: By default, it’s 5 and the range is from 1 to 50. It indicates number of
connectivity test.
• Traceroute: Allows tracing the hops from the TEW-738APBO device to a selected
outgoing IP address. It should be used for the finding the route taken by ICMP
packets across the network to the destination host. The test is started using the
Start button, click Stop button to stopped test
o Destination Host: Specifies the Destination Host for the finding the route taken by
ICMP packets across the network.
o MAX Hop: Specifies the maximum number of hops( max time-to-live value)
traceroute will probe.
Page 73

73
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Reboot
This function allows user to restart system with existing or most current settings when
changes are made. Click Reboot button to proceed and take around three minutes to
complete.
Mounting bracket installation
Package contents
TEW-738APBO
A reminder will be available for remaining time to complete. If power cycle is necessary,
please wait till completion of the reboot process.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 74

74
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Wall mount bracket
Pole mount bracket
TEW-738APBO
Align the mounting triangle to the back of the access point. Securely tighten the
mounting triangle by using the M5x10 screws and washers.
Position the provided mounting bracket to the desired location and mount as
shown in the above image using the provided wood scr ews and plugs .
Insert and fasten the provided clamps to the pole as shown in the above image
using the provided screw washers, spring washers and nuts.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 75

75
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Appendix
2. Click right on “Local Area Connection”, and select Properties.
Windows TCP/IP Settings
Windows XP
1. Click Start -> Settings -> Control Panel, and then “Control Panel” window
appears. Click on “Network Connections”, and then “Network Connections”
window appears.
Appendix
3. In “Local Area Connection Properties” window, select “Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP)” and click on Properties button.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
4. Select “Use the following IP address”, and type in
IP address : 192.168.2.100
Page 76

76
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Subnet mask : 255.255.255.0
Appendix
Enabling UPnP in Windows XP
1. Open the “Add/Remove Programs” control panel, and then click on “Add/Remove
Windows Components” in the sidebar. Scroll down and find “Networking Services”,
highlight it, and then click Details.
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
2. In the “Networking Services” window, ensure that the “Internet Gateway Device”
and “UPnP User Interface” options are checked. If they are not, check it to enable
them, as shown below, and click OK to continue.
Page 77

77
TRENDnet User’s Guide
3. Next, in the “Control panel”, open the “Administrative Tools” and then open
“Services”. Scroll down until you find the “SSDP Discovery Interface”. If the Status
is not Started, double-click on SSDP Discovery Interface to open the service
properties. Change the startup type to Automatic, then close the properties. Now,
right-click on SSDP Discovery Services, and choose Start from the pop-up menu. The
SSDP Discovery Service will then be running and start each time you boot.
4. After enabling UPnP and starting the SSDP Discovery Service, it may take few
minutes for the “TEW-675APBO/ TEW-738APBO” to be discovered and appear in
your “My Network Places”.
Appendix
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 78

78
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Limited Warranty
TRENDnet warrants its products against defects in material and workmanship, under
normal use and service, for the following lengths of time from the date of purchase.
TEW-738APBO – 3 Years Warranty
AC/DC Power Adapter, Cooling Fan, and Power Supply carry 1 year warranty.
If a product does not operate as warranted during the applicable warranty period,
TRENDnet shall reserve the right, at its expense, to repair or replace the defective
product or part and deliver an equivalent product or part to the customer. The
repair/replacement unit’s warranty continues from the original date of purchase. All
products that are replaced become the property of TRENDnet. Replacement products
may be new or reconditioned. TRENDnet does not issue refunds or credit. Please
contact the point-of-purchase for their return policies.
TRENDnet shall not be responsible for any software, firmware, information, or memory
data of customer contained in, stored on, or integrated with any products returned to
TRENDnet pursuant to any warranty.
There are no user serviceable parts inside the product. Do not remove or attempt to
service the product by any unauthorized service center. This warranty is voided if (i) the
product has been modified or repaired by any unauthorized service center, (ii) the
product was subject to accident, abuse, or improper use (iii) the product was subject to
conditions more severe than those specified in the manual.
Warranty service may be obtained by contacting TRENDnet within the applicable
warranty period and providing a copy of the dated proof of the purchase. Upon proper
submission of required documentation a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number
will be issued. An RMA number is required in order to initiate warranty service support
for all TRENDnet products. Products that are sent to TRENDnet for RMA service must
have the RMA number marked on the outside of return packages and sent to TRENDnet
prepaid, insured and packaged appropriately for safe shipment. Customers shipping
from outside of the USA and Canada are responsible for return shipping fees. Customers
shipping from outside of the USA are responsible for custom charges, including but not
limited to, duty, tax, and other fees.
WARRANTIES EXCLUSIVE: IF THE TRENDNET PRODUCT DOES NOT OPERATE AS
WARRANTED ABOVE, THE CUSTOMER’S SOLE REMEDY SHALL BE, AT TRENDNET’S
OPTION, REPAIR OR REPLACE. THE FOREGOING WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES ARE
EXCLUSIVE AND ARE IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED,
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
EITHER IN FACT OR BY OPERATION OF LAW, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
TRENDNET NEITHER ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER PERSON TO ASSUME FOR
IT ANY OTHER LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION MAINTENANCE
OR USE OF TRENDNET’S PRODUCTS.
TRENDNET SHALL NOT BE LIABLE UNDER THIS WARRANTY IF ITS TESTING AND
EXAMINATION DISCLOSE THAT THE ALLEGED DEFECT IN THE PRODUCT DOES NOT EXIST
OR WAS CAUSED BY CUSTOMER’S OR ANY THIRD PERSON’S MISUSE, NEGLECT,
IMPROPER INSTALLATION OR TESTING, UNAUTHORIZED ATTEMPTS TO REPAIR OR
MODIFY, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE BEYOND THE RANGE OF THE INTENDED USE, OR BY
ACCIDENT, FIRE, LIGHTNING, OR OTHER HAZARD.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: TO THE FULL EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW TRENDNET ALSO
EXCLUDES FOR ITSELF AND ITS SUPPLIERS ANY LIABILITY, WHETHER BASED IN
CONTRACT OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), FOR INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, OR FOR LOSS OF REVENUE OR
PROFITS, LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF INFORMATION OR DATE, OR OTHER FINANCIAL
LOSS ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION,
MAINTENANCE, USE, PERFORMANCE, FAILURE, OR INTERRUPTION OF THE POSSIBILITY
OF SUCH DAMAGES, AND LIMITS ITS LIABILITY TO REPAIR, REPLACEMENT, OR REFUND
OF THE PURCHASE PRICE PAID, AT TRENDNET’S OPTION. THIS DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY
FOR DAMAGES WILL NOT BE AFFECTED IF ANY REMEDY PROVIDED HEREIN SHALL FAIL
OF ITS ESSENTIAL PURPOSE.
Governing Law: This Limited Warranty shall be governed by the laws of the state of
California.
Some TRENDnet products include software code written by third party developers.
These codes are subject to the GNU General Public License ("GPL") or GNU Lesser
General Public License ("LGPL").
http://www.trendnet.com/gpl or http://www.trendnet.com Download section
Go to
and look for the desired TRENDnet product to access to the GPL Code or LGPL Code.
These codes are distributed WITHOUT WARRANTY and are subject to the copyrights of
the developers. TRENDnet does not provide technical support for these codes. Please go
http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.txt or http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.txt for
to
specific terms of each license.
Warranty
2014/5/05
Page 79

79
Appendix
© Copyright 2014TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...