TRENDnet TEW-659BRN User Manual

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Cover Page

© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Table of Contents
i
Contents
Product Overview ........................................................................... 1
Package Contents .......................................................................................................... 1
Features ......................................................................................................................... 1
Product Hardware Features........................................................................................... 2
Application Diagram ...................................................................................................... 4
Basic Router Setup .......................................................................... 5
Creating a Home Network ............................................................................................. 5
Router Installation ......................................................................................................... 6
Connect additional wired devices to your network ..................................................... 12
Wireless Networking and Security ................................................. 13
How to choose the type of security for your wireless network .................................. 13
Secure your wireless network ..................................................................................... 14
Connect wireless devices to your router ..................................................................... 17
Connect wireless devices using WPS ........................................................................... 18
Basic wireless settings ................................................................................................. 19
Steps to improve wireless connectivity ....................................................................... 21
Advanced wireless settings .......................................................................................... 22
Multiple SSID ........................................................................................................... 22
Wireless Scheduling ................................................................................................ 23
Wireless bridging using WDS (Wireless Distribution System) ................................. 24
Virtual Private Networking (VPN) .................................................. 26
Creating a Virtual Private Network .............................................................................. 26
IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) ................................................................................ 27
Site-to-Site VPN ....................................................................................................... 27
Client-Server VPN (Server Mode) ............................................................................ 31
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) ................................................................... 33
Client-Server VPN (Server Mode) ............................................................................ 33
Client-Server VPN (Client Mode) ............................................................................. 35
L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) ............................................................................... 38
Client-Server VPN (Server Mode) ............................................................................ 38
Client-Server VPN (Client Mode) ............................................................................. 39
GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation)Tunneling .......................................................... 42
Access Control Filters .................................................................... 45
Access control basics ................................................................................................... 45
MAC Control ............................................................................................................ 45
URL Filters ............................................................................................................... 46
Keyword Blocking .................................................................................................... 47
Packet Outbound/Inbound Filters .......................................................................... 47
Advanced Router Setup ................................................................ 50
Access your router management page ........................................................................ 50
Change your router login password ............................................................................ 50
Set your router date and time ..................................................................................... 51
Manually configure your Internet connection ............................................................ 52
Clone a MAC address ................................................................................................... 52
Change your router IP address .................................................................................... 53
Set up the DHCP server on your router ....................................................................... 53
Set up DHCP reservation ............................................................................................. 55
Enable/disable UPnP on your router ........................................................................... 56
Allow/deny VPN connections through your router ..................................................... 57
Allow/deny multicast streaming through your router ................................................ 57
Enable/disable DoS (Denial of Service) Prevention ..................................................... 58
Allow/deny ping requests to your router from the Internet ....................................... 58

© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Table of Contents
ii
Identify your network on the Internet ......................................................................... 59
Allow remote access to your router management page ............................................. 60
Open a device on your network to the Internet .......................................................... 61
DMZ ......................................................................................................................... 61
Virtual Computers ................................................................................................... 61
Virtual Server........................................................................................................... 62
Special Applications................................................................................................. 63
Prioritize traffic using QoS (Quality of Service) ............................................................ 64
Create schedules.......................................................................................................... 65
Add static routes to your router .................................................................................. 66
Enable dynamic routing on your router ...................................................................... 67
Enable route mode on your router .............................................................................. 68
Using WoL (Wake on LAN) on your router .................................................................. 68
Router Maintenance & Monitoring ................................................ 69
Reset your router to factory defaults .......................................................................... 69
Router Default Settings ............................................................................................... 69
Backup and restore your router configuration settings .............................................. 70
Upgrade your router firmware .................................................................................... 71
Restart your router ...................................................................................................... 72
Check connectivity using the router management page ............................................. 72
Check the router status information ........................................................................... 73
View your router log .................................................................................................... 75
Configure your router log ............................................................................................ 76
Enable SNMP on your router ....................................................................................... 78
Router Management Page Structure ............................................. 79
Technical Specifications................................................................. 80
Troubleshooting ............................................................................ 81
Appendix ...................................................................................... 82

© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
1
Product Overview
TEW-659BRV
Package Contents
In addition to your router, the package includes:
• Muti-Language Quick Installation Guide
• CD-ROM (User’s Guide)
• Network cable (1.5m / 5ft)
• Power adapter (12V DC, 1A)
If any package contents are missing or damaged, please contact the retail store, online
retailer, or reseller/distributor that the item was purchased.
Features
The 300Mbps Wireless N VPN Router, model TEW-659BRV, provides the ability to define
up to 80 Virtual Private Network (VPN) tunnels*, all while generating a high speed
wireless network. IPSec, L2TP, and PPTP VPN pass-through sessions are supported and a
configurable firewall ensures the highest level of security.
This router provides powerful 300Mbps wireless connectivity and a WPS button on the
front of the router takes that hassle out of connecting to it. Four Fast Ethernet ports on
the back of the router help extend a wired network. Advanced Stateful Packet
Inspection (SPI) and Network Address Translation (NAT) encryption protects your digital
network. Advanced features include GRE tunneling, advanced Quality of Service (QoS)
controls, Domain filtering, packet filtering, and more.
• High-speed wireless data rates up to 300Mbps** using an IEEE 802.11n
connection
• 4 x 10/100 Mbps Auto-MDIX LAN ports
• 1 x 10/100 Mbps WAN port (Internet)
• Compatible with most popular cable/DSL Internet service providers using
Dynamic/Static IP, PPPoE, PPTP and L2TP protocols
• Firewall protection with Network Address Translation (NAT), Stateful Packet
Inspection (SPI), and Denial of Service (DoS) prevention
• Supports up to 80* PPTP/L2TP/IPsec tunnels
• Supports up to 100 PPTP/L2TP/IPsec VPN pass through sessions
• Supports up to 8 Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) tunnels
• Access Control: Virtual Servers, MAC/IP Packet Filters, URL/Keyword Filters,
Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) host, and One-to-One NAT
• Set device time using Network Time Protocol (NTP) and define schedules for
Wireless, Virtual Server, Packet Filters, and Quality of Service (QoS)
• Broadcast up to 4 SSIDs with different wireless encryption
• Supports Access Point (AP) and Wireless Distribution System (WDS) modes
• Quality of Service (QoS) traffic prioritization via IP/(TCP/UDP) Ports with 3
priority queues and wireless WiFi Multimedia (WMM) support
• Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) for auto discovery and support for device
configuration of Internet applications
• Supports Internet Group Multicast Protocol IGMPv1/2 pass through for
multicast applications

© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
2
• Supports static and dynamic RIP v1/2 routing
• Dynamic DNS Client for dynamic Internet IP resolution
• Device monitoring using the Internal System Log, External Syslog, E-mail Alert,
and SNMPv1/2c
• Local/Remote management via Web browser, upgrade firmware, and
backup/restore configuration
• One-touch Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) button connects wireless clients
quickly
• Complete wireless security with WPA/WPA2, WPA/WPA2-PSK, and WEP
*The number of supported concurrent VPN tunnels is dependent upon available bandwidth
**Maximum wireless signal rates are referenced from IEEE 802.11 theoretical specifications.
Actual data throughput and coverage will vary depending on interference, network traffic,
building materials and other conditions.
Product Hardware Features
Rear Panel View
• LAN Ports – Connect Ethernet cables (also called network cables) from your
router LAN ports and to your wired network devices.
• WAN Port - Connect an Ethernet cable (also called network cable) from your
router WAN port and to your xDSL/Cable modem.
• Power Port – Connect the included power adapter from your router power
port and to an available power outlet.
Note: Use only the adapter that came with your router.
• On/Off Power Switch – Push your router On/Off push button power switch to
turn your router “On” (Inner position) or “Off” (Outer position).
• Antennas – The antennas broadcasts wireless signals to allow your wireless
clients and wireless network devices to connect to your router.

© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
3
Front Panel View
Front Panel Button and LEDs
Reset Button / WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) Button – Push and hold this
button for 3 seconds to activate WPS. The wireless LED will be blinking green
rapidly when WPS is activated. Push and hold this button for 20 seconds and
release to reset your router to its factory defaults. The LEDs will blink rapidly
when the reset process is activated.
Wireless (Link/Activity) / WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) – This LED indicator is
blinking green when the wireless is “On” and functioning properly on your
router. This LED indicator will be blinking green rapidly while data is
transmitted or received by your wireless clients or wireless network devices
connected to your router. This LED indicator will also be blinking green rapidly
when WPS is activated.
WAN (Link/Activity) – This LED indicator is solid green when your router WAN
port is physically connected to the xDSL/Cable modem Ethernet port (also
called network port) successfully with an Ethernet cable (also called network
cable). The LED indicator will be blinking green while data is transmitted or
received through the WAN port of your router.
LAN 1-4 (Link/Activity) – These LED indicators are solid green when the LAN
ports are physically connected to your wired network devices successfully with
an Ethernet cable (also called network cable). These LED indicators will be
blinking green while data is transmitted or received through your router LAN
ports.
Status - This LED indicator is blinking green when your router is ready and
working successfully. If this LED indicator is solid green on or off, your router is
not receiving power or not working properly.

© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
4
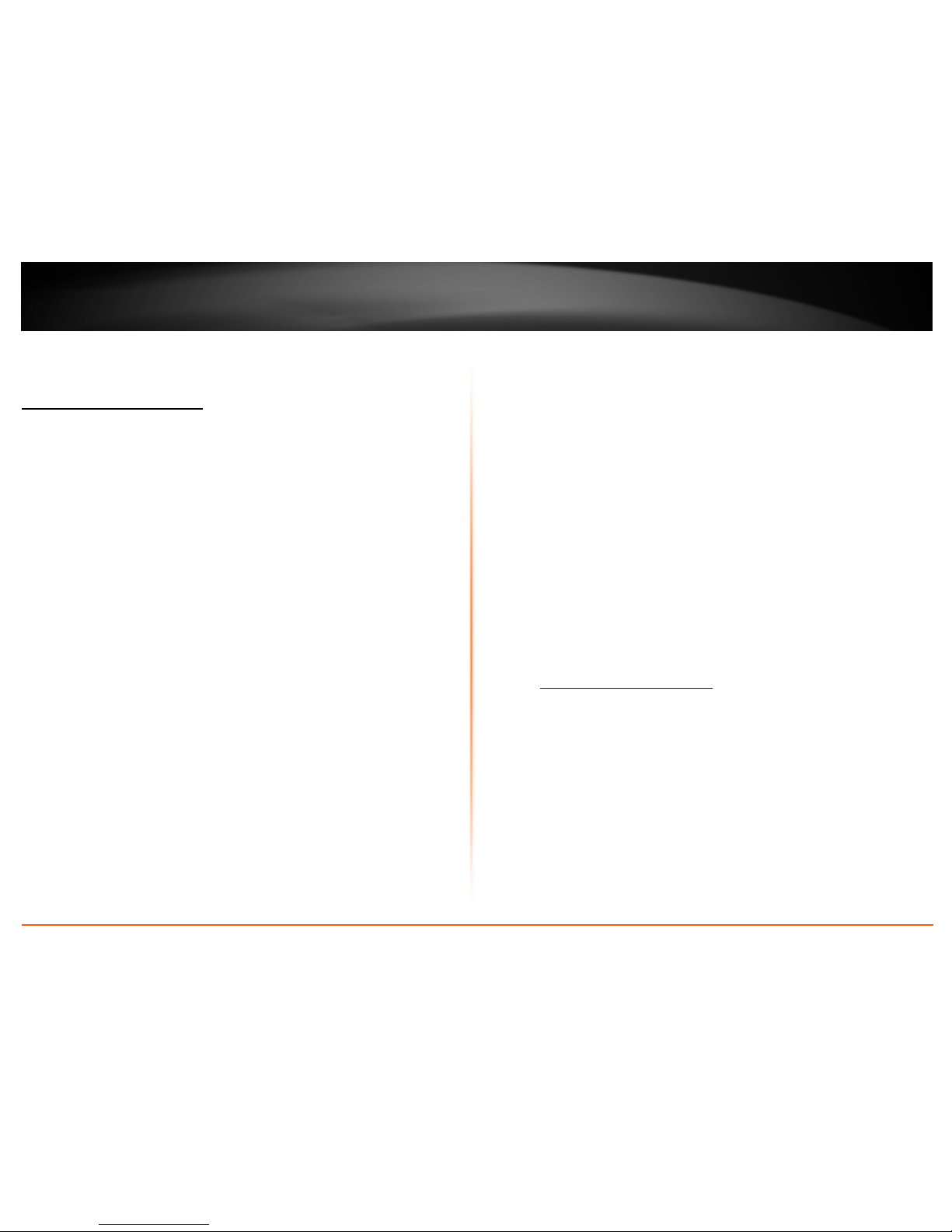
Application Diagram
The router is installed in a main office location which is connected to the Internet. A
desktop computer is connected to one of the four LAN ports of the router using an
Ethernet cable (also called network cable) and a laptop is connected wirelessly using its
integrated wireless adapter to connect to the router allowing these computers to access
the Internet. The router is also configured as a Virtual Private Network (VPN) server to
allow secure remote access (over the Internet) to work related files and media located
at the main office to an employee working from an outside home office location.
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
5
Basic Router Setup
Creating a Home Network
What is a network?
A network is a group of computers or devices that can communicate with each other. A
home network of more than one computer or device also typically includes Internet
access, which requires a router.
A typical home network may include multiple computers, a media player/server, a
printer, a modem, and a router. A large home network may also have a switch,
additional routers, access points, and many Internet-capable media devices such as TVs,
game consoles, and web cameras.
• Modem – Connects a computer or router to the Internet or ISP (Internet
Service Provider).
• Router – Connects your wireless and wired network devices to each other and
to the modem.
• Switch – Allows you to connect several wired network devices to your home
network. Your router has a built-in network switch (the LAN port 1-4). If you
have more wired network devices than available Ethernet ports on your router,
you will need an additional switch to add more wired connections.
How to set up a home network
1. For a network that includes Internet access, you’ll need:
• Computers/devices with an Ethernet port (also called network port) or wireless
networking capabilities
• A modem and Internet service to your home, provided by your ISP (modem
typically supplied by your ISP)
• A router to connect your computers and devices and also connects to the
modem.
2. Make sure that your modem is working. Your ISP can help you set up your modem
and verify that it’s working correctly.
3. Set up your router. See “How to setup your router” below.
4. To connect additional wired computers or wired network devices to your network,
see “Connect additional wired devices to your network” on page 12.
5. To set up wireless networking on your router, see “Wireless Networking and Security”
on page 13.
How to setup your router
The easiest way and fastest way to follow the included Quick Installation Guide or
continue to the next section “Router Installation” on page 6, and complete the
remaining sections of “Router Installation”.
Where to find more help
In addition to this User’s Guide, you can find help below:
• http://www.trendnet.com/support
(documentation, downloads, FAQs, how to contact technical support)
• Internet service to your home, provided by an ISP (Internet Service Provider)
• Autorun CD (Quick Installation Guide)

© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
6
Router Installation
Before you Install
It is recommended, that you verify your Internet connection type with your ISP (Internet
Service Provider) and ensure you have all the information for one of the following
connection types below before proceeding with the router installation.
1. Obtain IP Address Automatically (DHCP)
Host Name (Optional)
Clone Mac Address (Optional)
2. Fixed IP address
WAN IP Address: _____. _____._____._____
(e.g. 215.24.24.129)
WAN Subnet Mask: _____. _____._____._____
WAN Gateway IP Address: _____. _____._____._____
DNS Server Address 1: _____. _____._____._____
DNS Server Address 2: _____. _____._____._____
3. PPPoE to obtain IP automatically
User Name: _________
Password: ________________
4. PPPoE with a fixed IP address
User Name: _________
Password: ________________
IP Address: ____. _____._____._____ (e.g. 215.24.24.129)
5. PPTP
Type (Dynamic IP or Static IP )
My IP Address: _____. _____._____._____
(e.g. 215.24.24.129)
Subnet Mask:_____. _____._____._____
Gateway:_____. _____._____._____
Server IP: _____. _____._____._____
PPTP Account: ________________
PPTP Password: ________________
6. L2TP
Type (Dynamic IP or Static IP)
My IP Address: _____. _____._____._____
(e.g. 215.24.24.129)
Subnet Mask:_____. _____._____._____
Gateway:_____. _____._____._____
Server IP: _____. _____._____._____
L2TP Account: ________________
L2TP Password: ________________
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
7
Hardware Installation
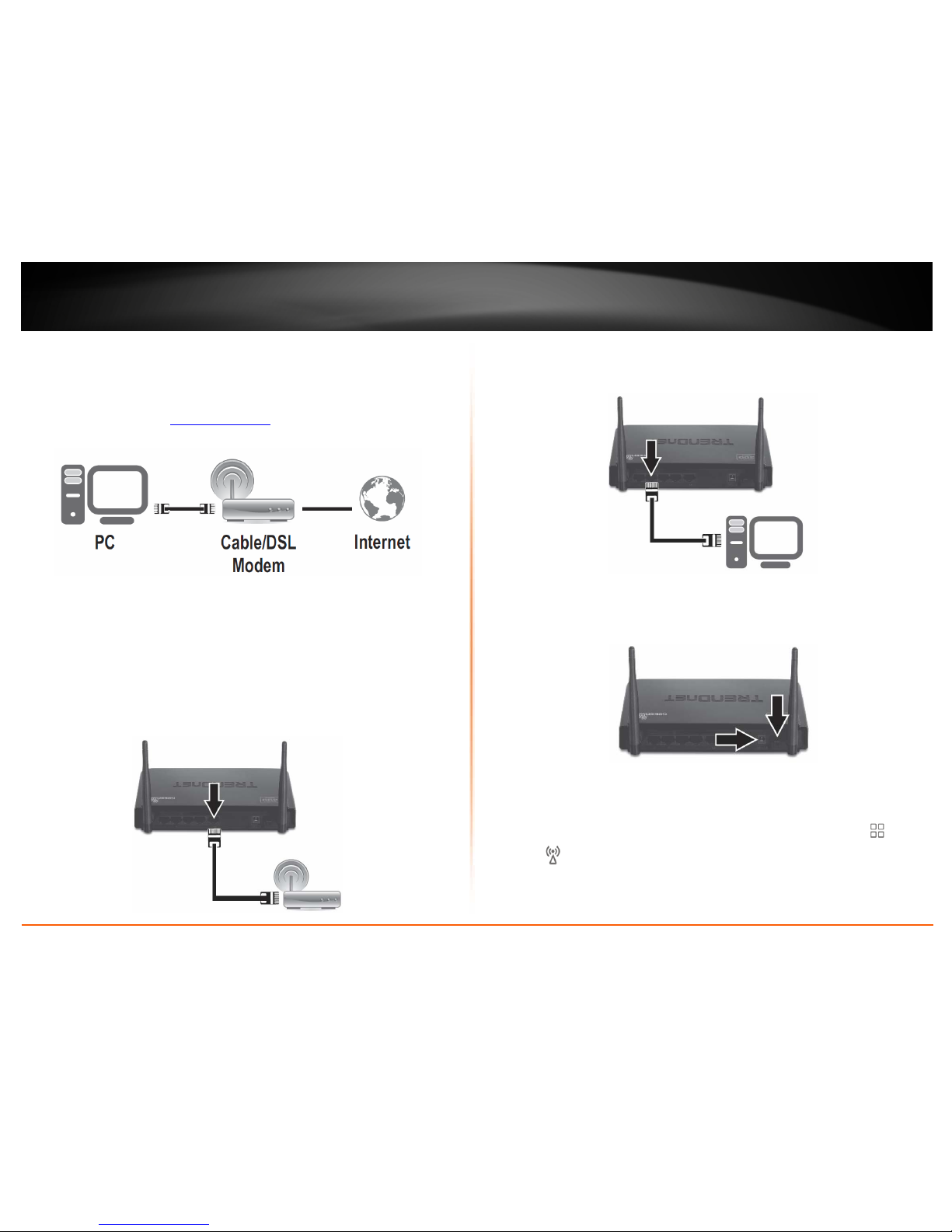
1. Verify that you have an Internet connection when connecting your computer directly
to the modem. Open your browser (e.g. Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome, Safari, or
Opera) and type in a URL (e.g.
http://trendnet.com) in the address bar.
2. Turn off your modem.
3. Disconnect the Ethernet cable (also called network cable) from your modem and your
computer.
4. Connect one end of a network cable to your router WAN port. Connect the other end
of the network cable to your Cable modem network port.
5. Connect one end of a network cable to one of your router LAN ports (1-4). Connect
the other end of the network cable to the computer Ethernet port (also called network
port).
6. Connect the included power adapter to your router Power Port and then to an
available power outlet. Push the On/Off Power Switch on your router to the “On”
(inner) position.
7. Turn on your modem.
8. Verify that the following front panel LED indicators on your router (Status
and
Wireless
is blinking green, WAN is solid green, and the LAN port for which your
computer is connected is solid green.
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
8
Setup Wizard
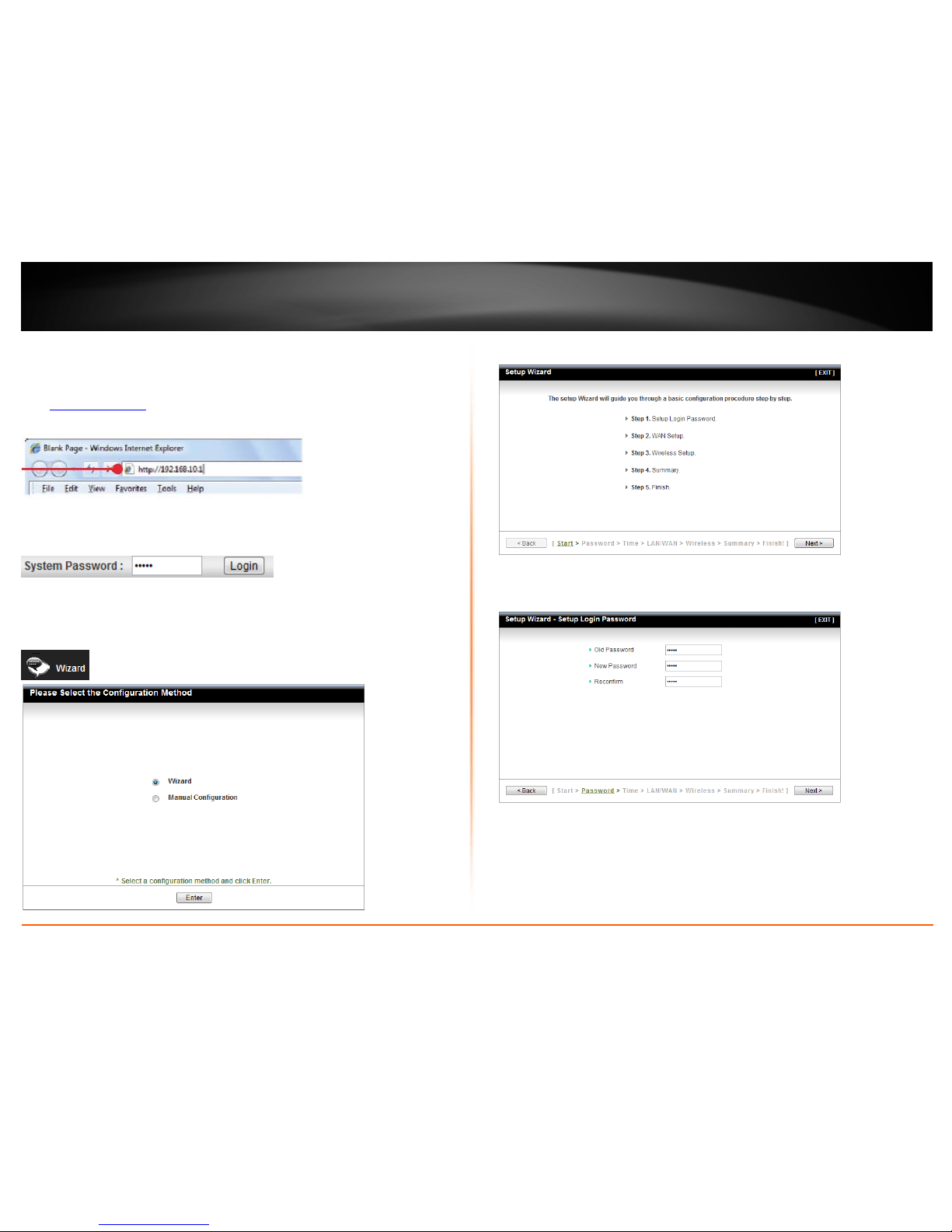
1. Open your web browser (e.g. Internet Explorer, Firefox, Safari, Chrome, or Opera) and
go to
http://192.168.10.1. Your router will prompt you for a password.
2. Enter the System Password and click Login.
Default System Password: admin
3. Make sure the Wizard option is selected and then click Enter.
Note: If the Setup Wizard does not automatically appear, click Wizard at the top of the
page.
4. Click Next.
5. Enter the Old Password (Default: admin), enter a New Password and enter the
password again next to Reconfirm to verify the New Password.
Note:
1. Setting a password prevents other users from accessing the router management page.
2. It is recommended that you enter a new password. If you decide to change the default
password, please write down the new password.
3. Password is limited up to 9 characters.
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
9
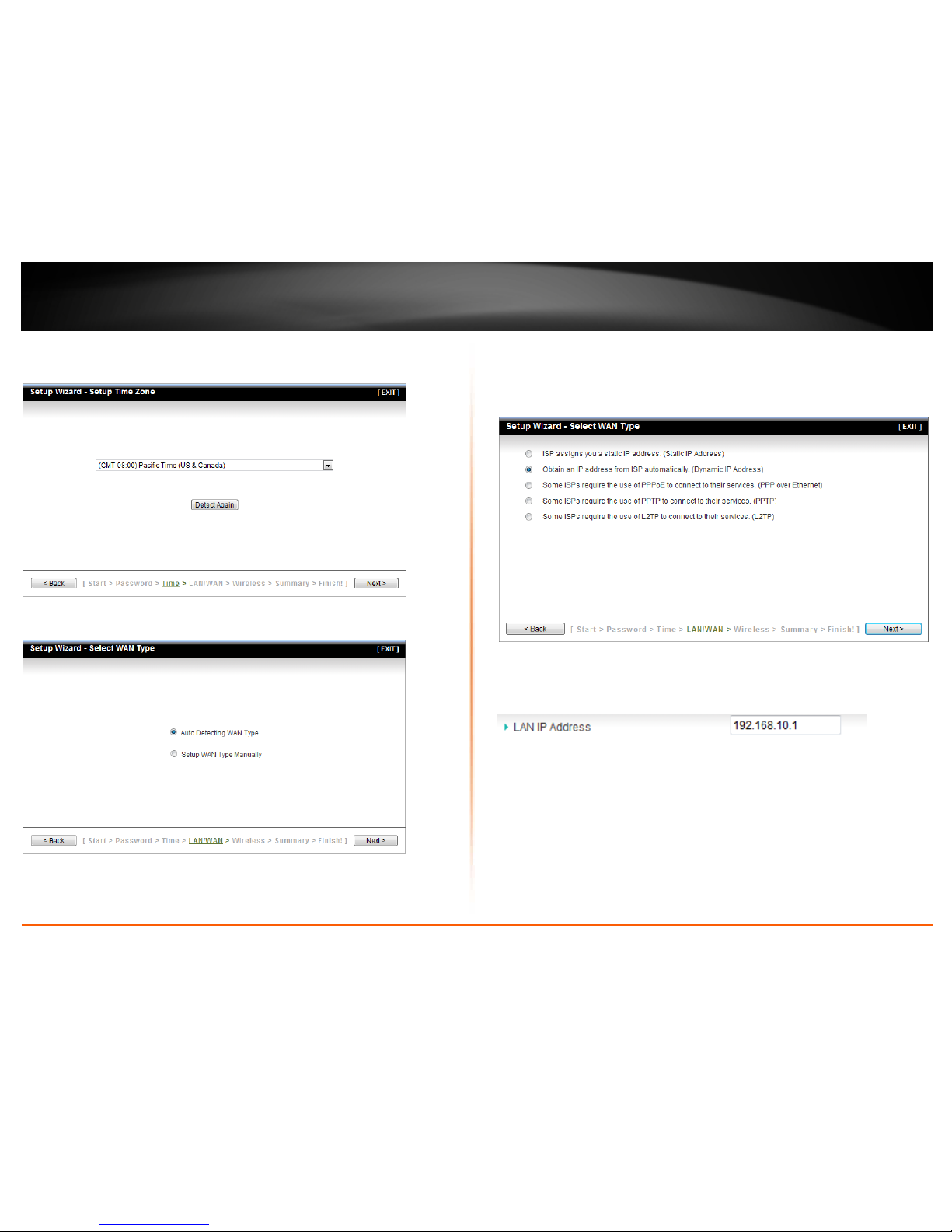
6. Click the drop-down list and select your Time Zone. Click Next.
7. Select Auto Detecting WAN Type and the click Next.
8. Configure the settings based on information provided by your Internet Service
Provider (ISP). Follow the wizard instructions to complete your configuration.
Note: Each Internet connection type may have different options.
Note: When configuring your Internet connection settings. It is optional to change your
LAN IP network settings. It is recommended to leave this setting at default.
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
10
9. You will need to configure the following:
• Wireless LAN: Select Enable for Wireless LAN.
• Note: Selecting Disable will disable the wireless functionality of the router and
will not allow wireless devices to connect.
• Network ID (SSID): The SSID is your wireless network name. Enter a unique
SSID. Choose something that you would easily identify when searching for
available wireless networks.
• Channel: It is recommended to leave this setting as Auto.
Note:
1. To protect your network from any unauthorized access, it is recommended to enable
wireless encryption.
2. The example below is for WPA-PSK/WP2-PSK (AES) security. If you select WPA-PSK or
WPA2-PSK, make sure your wireless adapters support WPA or WPA2. If you wireless
adapters do not support WPA or WPA2, then select WEP.
3. WEP security only supports 802.11b/g speed of up to 54Mbps.
4. Once encryption is enabled on the router, each wireless computer or device must be
configured with the same encryption key.
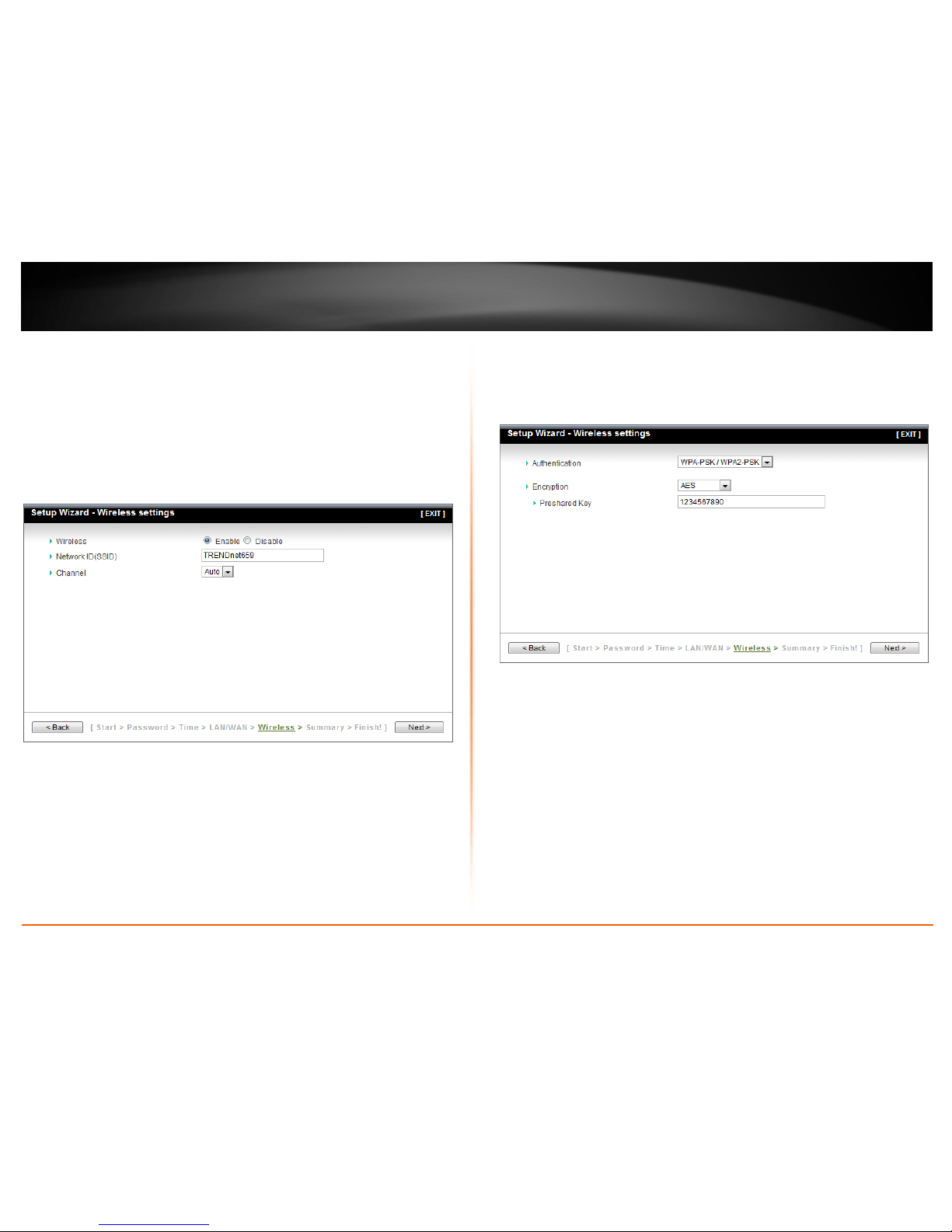
10. Select the desired Authentication mode, select the Encryption type, enter characters
for your Preshared key and then click Next. For WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK, the Preshared
key length is 8-63 characters ASCII or 64 HEX characters. Make sure to copy down your
Preshared key. You will need the Preshared key when you configure your wireless
computer or devices.

© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
11
11. Click Apply Settings.
Note: You can check the network testing option to run an Internet connection test before
applying the settings.
12. Please wait until the router applies the changes and reboots.
Note: If you checked the option to run network testing (Internet connection test), you
will see the status message below.
13. Click Finish.
Note: If you checked the option to run network testing (Internet connection test) and the
test is success, you will receive the message below along with your Internet connection
settings.

© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
12
Connect additional wired devices to your network
You can connect an additional computer or device to your network by connecting one
end of an Ethernet cable (also called network cable) from your computer or device
Ethernet port (also called network port) to one of the available LAN ports labeled 1,2,3,4
on your router. Check the status of the LED indicators (1, 2, 3, or 4) on the front panel of
your router to ensure the physical cable connection from your computer or device.
Note: If you encounter issues connecting to your network, there may be a problem with
your computer or device network settings. Please ensure that your computer or device
network settings (also called TCP/IP settings) are configured to obtain IP address settings
automatically (also called dynamic IP address or DHCP) and to Obtain DNS Server
address settings automatically.

© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
13
Wireless Networking and Security
How to choose the type of security for your wireless network
There are a few different wireless security types supported in wireless networking
each having its own characteristics which may be more suitable for your wireless
network taking into consideration compatibility, performance, as well as the security
strength along with using older wireless networking hardware (also called legacy
hardware).
It is strongly recommended to enable wireless security to prevent unwanted users
from accessing your network and network resources (personal documents, media, etc.).
In general, it is recommended that you choose the security type with the highest
strength and performance supported by the wireless computers and devices in your
network. Please review the security types to determine which one you should use for
your network.
• WEP: Legacy encryption method supported by most 802.11b/g hardware.
Older hardware may only support up to WEP encryption.
• WPA: Legacy encryption method supported in most 802.11g hardware.
• WPA2: Currently the most secure method of wireless security and required for
802.11n performance.
Note: Check the specifications of your wireless network adapters and wireless appliances
to verify the highest level of encryption supported.
Below is brief comparison chart of the wireless security types and the recommended
configuration depending on which type you choose for your wireless network.
Security
Comparison
WEP WPA WPA2
Wireless Standard IEEE 802.11a/b/g IEEE 802.11a/b/g IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n
Performance Up to 54Mbps Up to 54Mbps Up to 450Mbps*
Strength Low Medium High
Additional
Options
Open System or
Shared Key,
HEX or ASCII,
Different key sizes
TKIP or AES,
Preshared Key or
RADIUS
TKIP or AES,
Preshared Key or
RADIUS
Recommended
Configuration
Open System ASCII
13 characters
TKIP
Preshared Key
8-63 characters
AES
Preshared Key
8-63 characters
*Dependent on the maximum 802.11n data rate supported by the device (150Mbps,
300Mbps, or 450Mbps)
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
14
Secure your wireless network
Configuration > Basic Setting > Wireless
After you have determined which security type to use for your wireless network (see
“How to choose the security type for your wireless network” on page 13), you can set up
wireless security.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on
page 50).
2. Click on Configuration at the top of the page, then click on Basic Setting, and click on
Wireless.
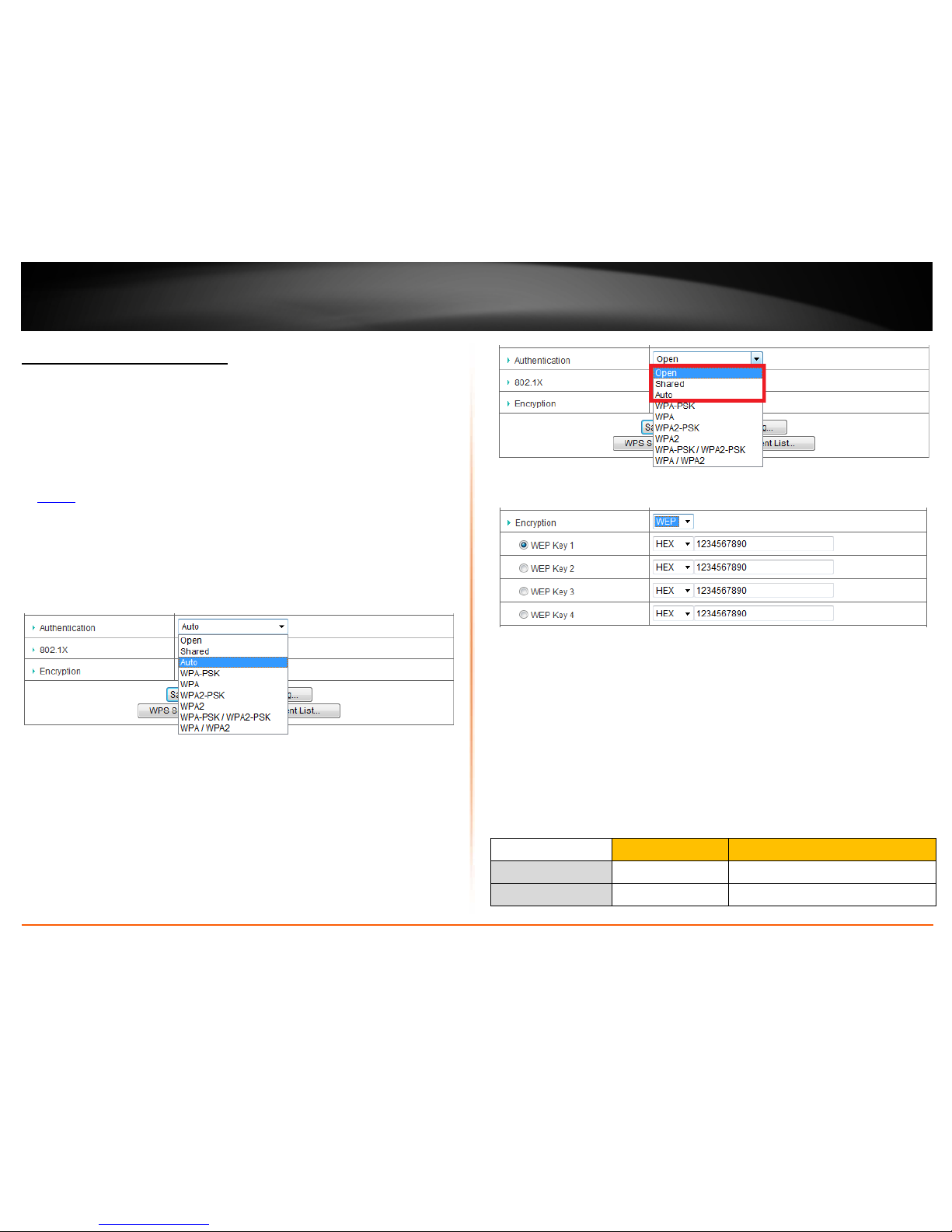
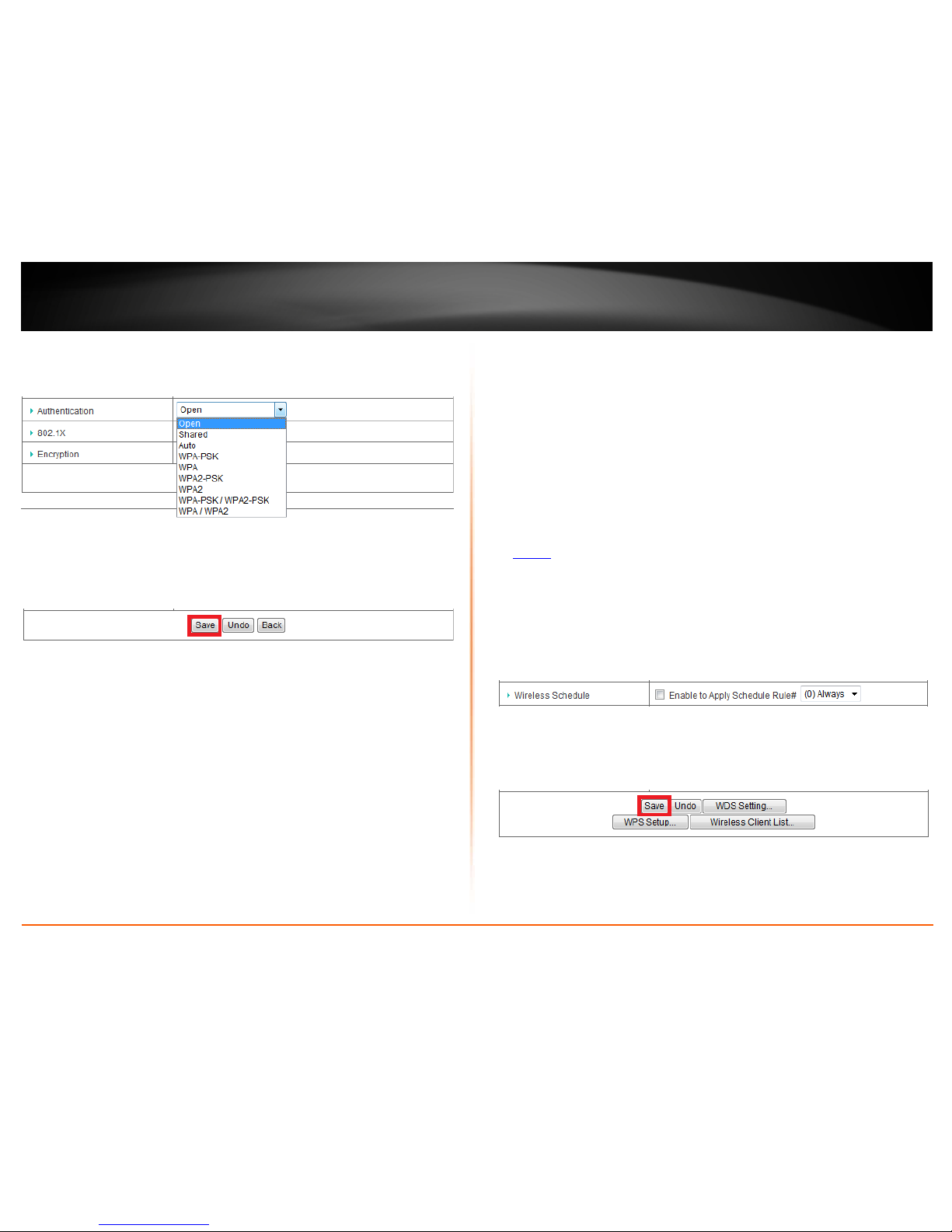
3. Click on the Authentication drop-down list to select your wireless security type.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
To select and configure WEP, select Open (Recommended), Shared, or Auto in the
Authentication drop-down list.
Note: It is recommended to use Open System because it is known to be more secure than
Shared Key. Selecting Auto will automatically determine which authentication type to
use between Open and Shared Key.
Then click on the Encryption drop-down list and select WEP.
• WEP Key 1-4 – Choose a key index 1,2,3, or 4.
Note: The Key Index # must also match when configuring wireless devices to
connect to your wireless network.
• Choose HEX or ASCII.
Note: It is recommended to use ASCII because of the much larger character set
that can be used to create the key.
• Enter a WEP Key.
Note: Once you select HEX or ASCII, you will need to enter the WEP key using
the HEX or ASCII format described in the table below.
WEP Key Format
HEX ASCII
Character set 0-9 & A-F, a-f only alphanumeric (a,b,C,?,*, /,1,2, etc.)
Key Length 10 or 26 characters 5 or 13 characters
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
15
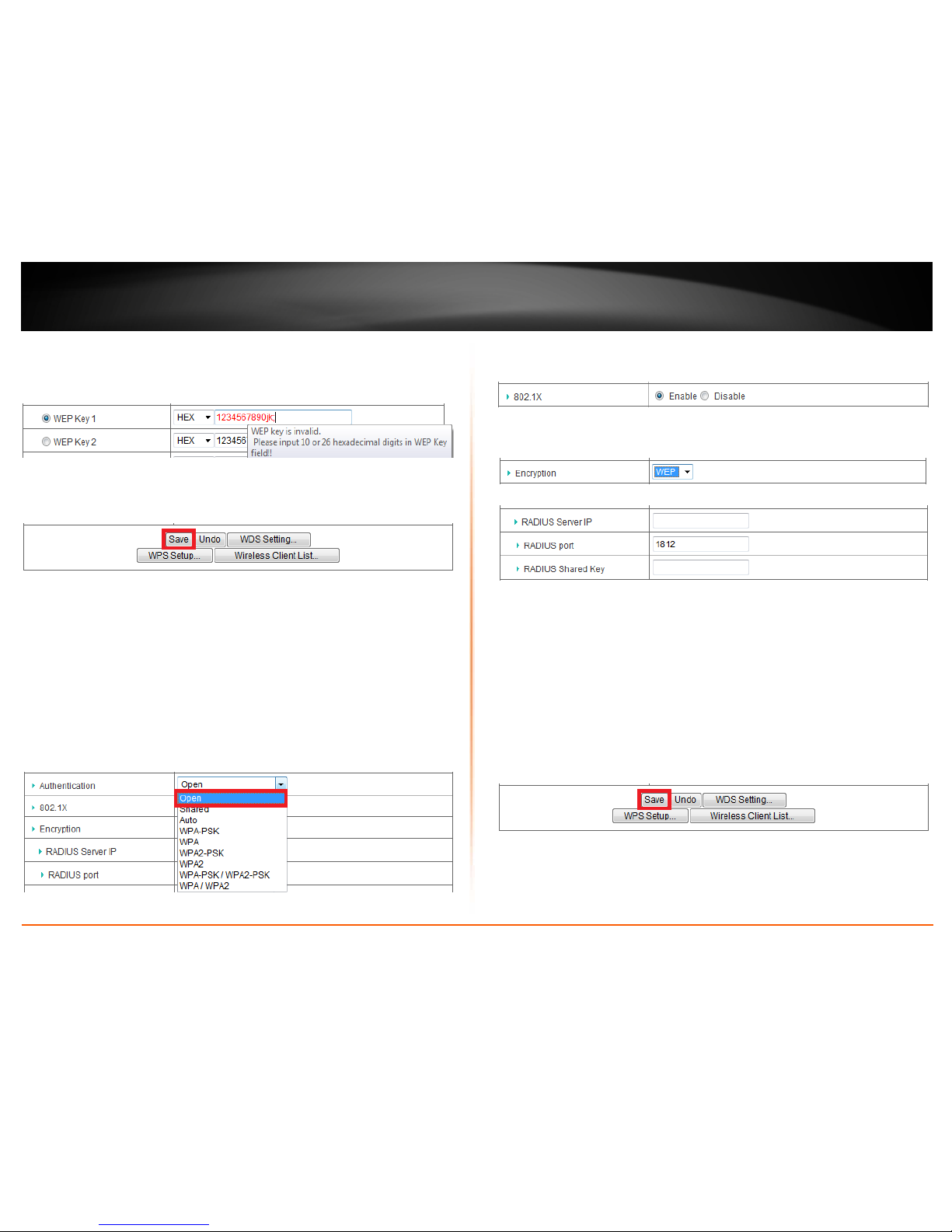
Note: If the WEP key you have entered does not meet the correct format, the
text color will change to red. Moving your cursor over the WEP Key field will
provide you with helpful tips as to why the key format is incorrect.
Click Save to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Save.
For advanced users, to select and configure WEP (Wired Equivalent) with 802.1x which
is the standard for port-based access control (PNAC), also known as Extensible
Authentication Protocol,or called RADIUS, Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service),
select Open, in the Authentication drop-down list.
Note: It is recommended to use WEP using a HEX or ASCII key because it is easier to
setup and simply requires you to create a key compared to 802.1x which requires you to
connect an external RADIUS server and requires more configuration.
Select Open in the Authentication drop-down list.
Note: The 802.1x option is only available when using Open Authentication.
Select the Enable option for 802.1X.
Then click on the Encryption drop-down list and select WEP.
• RADIUS Server IP - Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server.
(e.g. 192.168.10.250)
• RADIUS Port – Enter the port your RADIUS server is configured to use for
RADIUS authentication. Note: It is recommended to use port 1812
• RADIUS Shared Key– Enter the shared secret used to authorize your router
with your RADIUS server.
Click Save to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Save.

© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
16
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
To select and configure WPA or WPA2 PSK (Preshared Key), select WPA-PSK, WPA2PSK, or WPA-PSK / WPA2-PSK, in the Authentication drop-down list.
Note: It is recommended to choose the specific security type WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK,
instead of choosing WPA-PSK / WPA2-PSK.
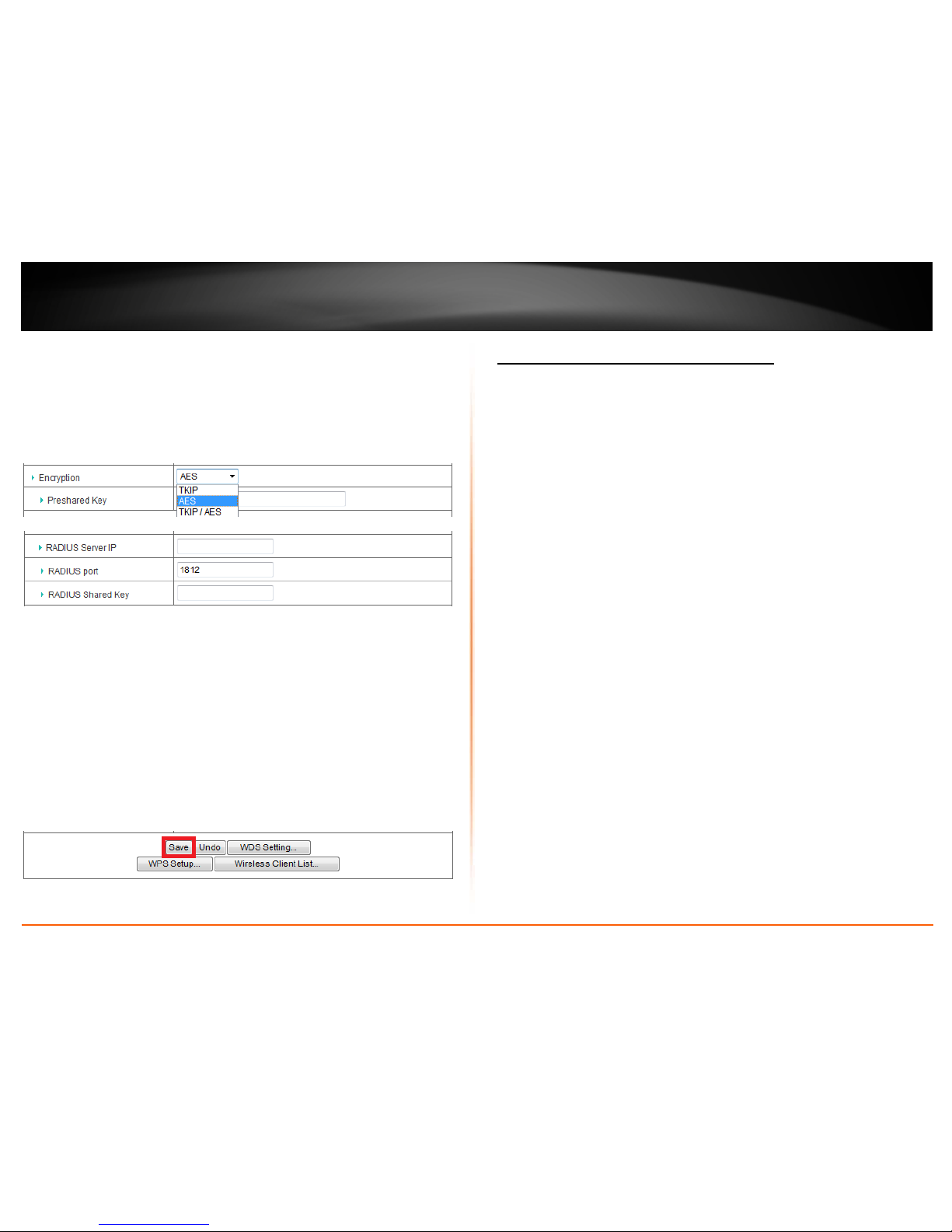
• Encryption – Choose TKIP, AES, or TKIP / AES.
Note: For best the wireless performance and compatibility with wireless devices:
o When selecting WPA security, it is recommended to use TKIP.
o When selecting WPA2 security, it is recommended to use AES.
o It is recommended to configure the specific encryption type instead of
choosing TKIP / AES.
• Preshared Key – Enter the passphrase.
Note: 8-63 alphanumeric characters (a,b,C,?,*, /,1,2, etc.)
Click Save to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Save.
For advanced users, to select and configure WPA or WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access) EAP
(Extensible Authentication Protocol, also called RADIUS, Remote Authentication Dial-In
User Service), select WPA, WPA2, or WPA / WPA2, in the Authentication drop-down
list.
Note: It is recommended to use PSK because it is easier to setup and simply requires you
to create a passphrase compared to EAP which requires you to connect an external
RADIUS server and requires more configuration.
Note: If you select this security type, it is recommended to choose the specific security
type WPA or WPA2, instead of choosing WPA / WPA2.
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
17
• Encryption – Choose TKIP, AES, or TKIP / AES.
Note: For best the wireless performance and compatibility with wireless
devices:
o When selecting WPA security, it is recommended to use TKIP.
o When selecting WPA2 security, it is recommended to use AES.
o It is recommended to configure the specific encryption type instead of
choosing TKIP / AES.
• RADIUS Server IP - Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server.
(e.g. 192.168.10.250)
• RADIUS Port – Enter the port your RADIUS server is configured to use for
RADIUS authentication.
Note: It is recommended to use port 1812
• RADIUS Shared Key– Enter the shared secret used to authorize your router
with your RADIUS server.
Click Save to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Save.
Connect wireless devices to your router
There is a variety of wireless network devices that can connect to your wireless network
such as:
• Gaming Consoles
• Internet enabled TVs
• Network media players
• Smart Phones
• Wireless Laptop computers
Each device may have its own software utility for searching and connecting to available
wireless networks, therefore, you must refer to the User’s Manual/Guide of your
wireless capable laptop/computer or wireless adapter to determine how to search and
connect to available wireless networks.
See the “Appendix” section for general information on connecting to a wireless
network.
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
18
Connect wireless devices using WPS
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) is a feature that makes it easy to connect devices to your
wireless network. If your wireless devices support WPS, you can use this feature to
easily add wireless devices to your network.
Note: You will not be able to use WPS if you set the SSID Broadcast setting to Disabled.
There are two methods the WPS feature can easily connect your wireless devices to
your network.
• PBC (Push Button Configuration) Method
o Hardware Push Button - located physically on your router
o WPS Software/Virtual Push Button - located in router management
page
• PIN (Personal Identification Number) Method - located in router management
page
Note: Refer to your wireless device documentation for details on the operation of WPS.
PBC (Hardware Push Button)
To add a wireless device to your network, simply push the WPS button on the wireless
device you are connecting, then push and hold the WPS button located on your router
for 3 seconds and release it. The Wireless
LED will be blinking green rapidly on your
router indicating that the WPS setup process has been activated on your router. (See
the “Product Hardware Features” section for the details on LEDs.)
For connecting additional WPS supported devices, repeat this process for each
additional device.
PBC (Software/Virtual Push Button)
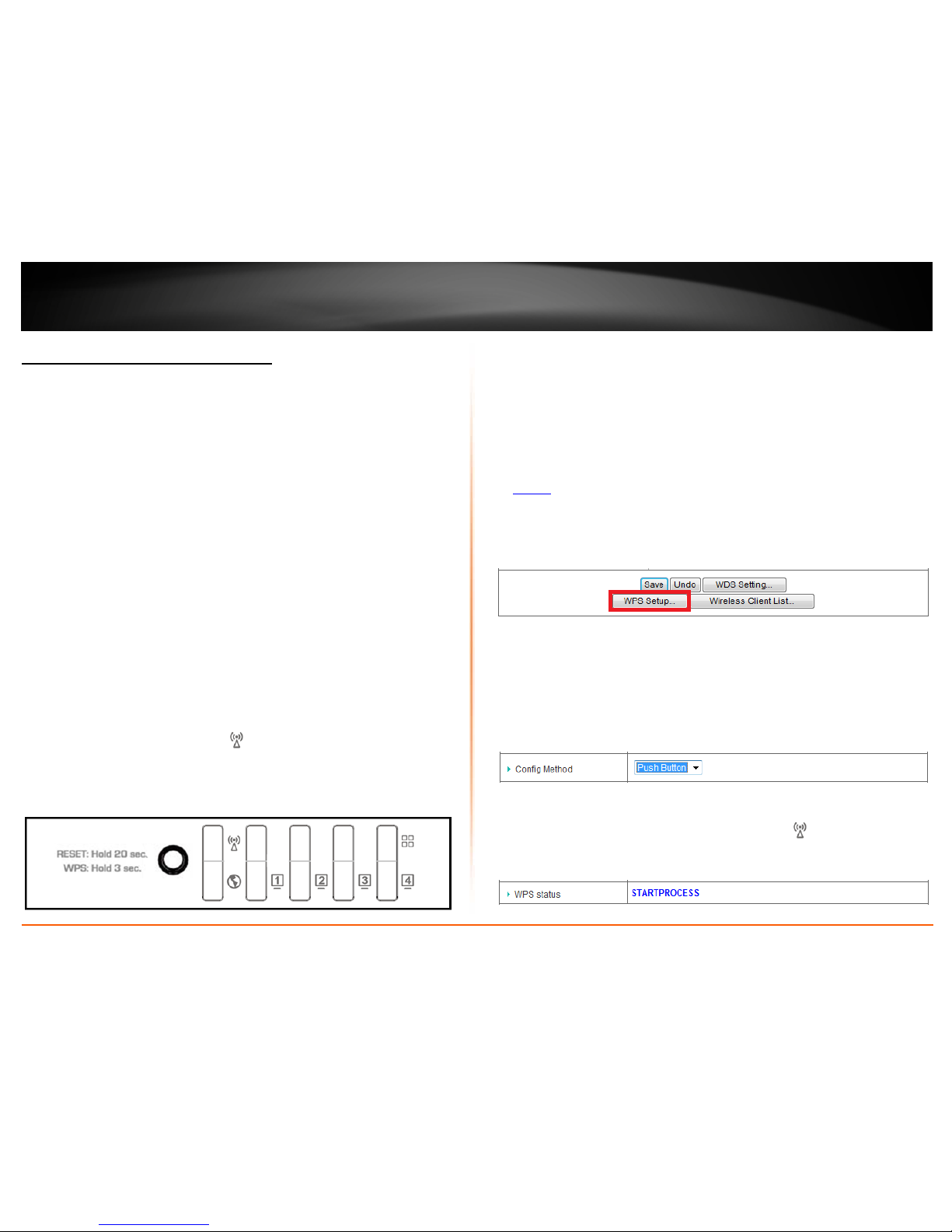
Configuration > Basic Setting > Wireless > WPS Setup
In addition to the hardware push button located physically on your router, the router
management page also has push button which is a software or virtual push button you
can click to activate WPS on your router.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on
page 50).
2. Click on Configuration at the top of the page, click on Basic Setting, then click on
Wireless, and click on WPS Setup at the bottom of the page.
3. To add a wireless device to your network, simply the push the WPS button on the
wireless device you are connecting, then, in your router management page next to
Config Method, make sure Push Button is selected in the drop-down list. Then click
Start PBC.
Note: If the Push Button option is not selected, first select Push Button in the drop-down
list and click Save at the bottom of the page before clicking Start PBC.
4. Next to WPS Status, you will receive a status message indicating the WPS process is
activated on your router or you can check that the Wireless
LED is blinking green
rapidly.
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
19
5. You will receive a message indicating that the WPS status is Configured if the wireless
device is able to connect successfully using WPS.
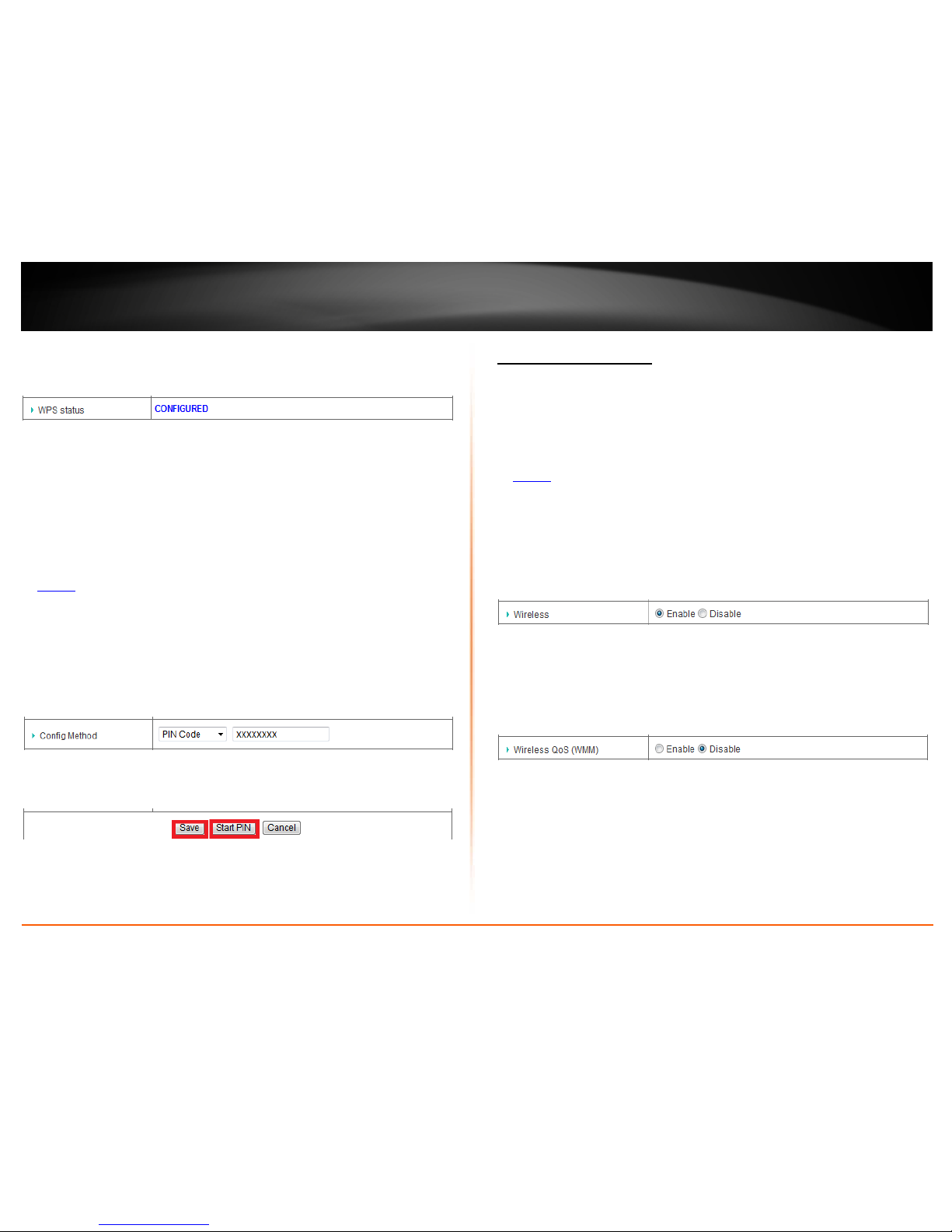
PIN (Personal Identification Number)
Configuration > Basic Setting > Wireless > WPS Setup
If your wireless device has WPS PIN (typically an 8-digit code printed on the wireless
device product label or located in the wireless device wireless software utility), you can
use this method.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on
page 50).
2. Click on Configuration at the top of the page, click on Basic Setting, then click on
Wireless, and click on WPS Setup at the bottom of the page.
3. Next to Config Method, in the drop-down list, select PIN Code and in the empty field,
enter the WPS PIN of the wireless device you are connecting.
4. Click Save. Then click Start PIN to activate WPS using the PIN.
Note: You can click Cancel to discard the changes before clicking Save.
Note: You may need to initiate the WPS PIN on your wireless device first when using this
method. Refer to your wireless device documentation for details on the operation of
WPS.
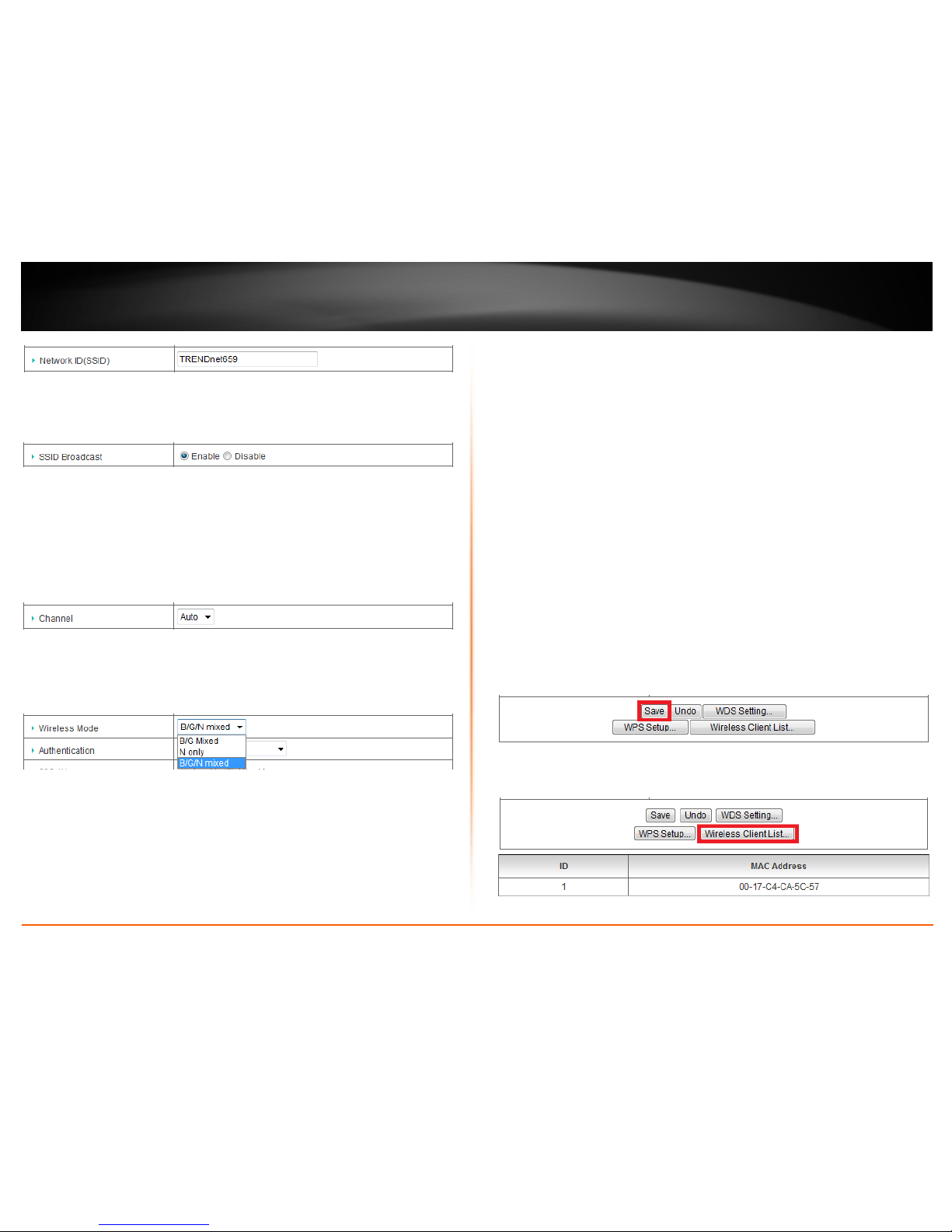
Basic wireless settings
Configuration > Basic Setting > Wireless
You can change the wireless network settings on your router such as the SSID (also
called wireless network name), wireless/802.11 modes, channel, and multiple SSID.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on
page 50).
2. Click on Configuration at the top of the page, click on Basic Setting, and click on
Wireless.
3. Please review the basic wireless settings to configure and click Save at the bottom of
the page to save the changes.
• Wireless –Enable turns on the wireless networking on your router and Disable
turns off wireless networking on your router.
Note: It is recommended to leave the wireless setting to Enable unless you do not
plan on connecting any wireless computers or devices to your network.
• Wireless QoS (WMM) - Wi-Fi Multimedia is a QoS feature that improves quality
of audio, video, and voice applications by prioritizing wireless traffic. This
feature requires the wireless device to also support WMM. Click Enable or
Disable to turn this feature on or off on your router.
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
20
• Network ID (SSID) – The Service Set Identifier or name of your primary wireless
network. Identifies your wireless network when connecting with wireless
devices. Enter the wireless network name.
• SSID Broadcast – Enable allows wireless devices to search and discover your
primary wireless network name (also called SSID) broadcasted by your router.
Disable turns off the ability for wireless devices to find your wireless network
when scanning for available wireless networks. It is still possible for wireless
devices to be configured to connect to your wireless network.
Note: Setting this option to Disable, will disable WPS.
• Channel – Choosing Auto in the drop-down list will allow your router to
automatically select the best channel for wireless communication. To manually
set a specific wireless channel, click the drop-down list and select the channel
for wireless communication.
• Wireless Mode - Select the appropriate mode for your network.
o B/G/N Mixed – Select this mode for the best compatibility. This mode
allows 802.11b, 11g, and 11n wireless devices to connect your wireless
network.
o B/G Mixed – This mode allows wireless devices to connect to your
wireless network at only 802.11b and 802.11g.
o N only – This mode allows wireless devices to connect to your wireless
network at only 802.11n.
Note: Please check the specifications on your wireless devices for the highest wireless
capability supported first before applying these settings. If you are unsure, it is
recommended that you keep the default setting for the best compatibility.
When applying the 802.11 mode setting, please keep in mind the following:
• Wireless devices that support 802.11n are backwards compatible and can
connect wirelessly at 802.11g or 802.11b.
• Connecting at 802.11b or 802.11g will limit the capability of your 802.11n
supported wireless devices from obtaining higher performance and data rates.
• Allowing 802.11b or 802.11g devices to connect to an 802.11n capable wireless
network may degrade the wireless network performance below the higher
performance and data rates of 802.11n.
• Wireless devices that only support 802.11b or 802.11g will not be able to
connect to a wireless network that is set to N only mode.
When you finished configuring your basic wireless settings, click Save to save the
changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Save.
To view wireless devices that are currently connected to your router, click Wireless
Client List. The MAC address of the wireless client will be listed.

© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
21
Steps to improve wireless connectivity
There are a number of factors that can impact the range of wireless devices. Follow
these tips to help improve your wireless connectivity:
1. Adjust your wireless devices so that the signal is traveling in a straight path,
rather than at an angle. The more material the signal has to pass through the
more signal you will lose.
2. Keep the number of obstructions to a minimum. Each obstruction can reduce
the range of a wireless device. Position the wireless devices in a manner that
will minimize the amount of obstructions between them.
3. Building materials can have a large impact on your wireless signal. In an indoor
environment, try to position the wireless devices so that the signal passes
through less dense material such as dry wall. Dense materials like metal, solid
wood, glass or even furniture may block or degrade the signal.
4. Antenna orientation can also have a large impact on your wireless signal. Use
the wireless adapter’s site survey tool to determine the best antenna
orientation for your wireless devices.
5. Interference from devices that produce RF (radio frequency) noise can also
impact your signal. Position your wireless devices away from anything that
generates RF noise, such as microwaves, radios and baby monitors.
6. Any device operating on the 2.4GHz frequency will cause interference. Devices
such as 2.4GHz cordless phones or other wireless remotes operating on the
2.4GHz frequency can potentially drop the wireless signal.
7. Although the phone may not be in use, the base can still transmit wireless
signal. Move the phone’s base station as far away as possible from your
wireless devices.
8. Make sure that your router is in a good location.
a. For the widest coverage area, install your router near the center of your
home, and near the ceiling, if possible.
b. Avoid placing the router on or near metal objects (such as file cabinets and
metal furniture), reflective surfaces (such as glass or mirrors), and masonry
walls.
c. Any obstruction can weaken the wireless signal (even non-metallic
objects), so the fewer obstructions between the router and the wireless
device, the better.
d. Place the router in a location away from other electronics, motors, and
fluorescent lighting.
e. Many environmental variables can affect the router’s performance, so if
your wireless signal is weak, place the router in several locations and test
the signal strength to determine the ideal position.
If possible, upgrade wireless network interfaces (such as wireless cards in computers)
from older wireless standards to 802.11n. If a wirelessly networked device uses an older
standard, the performance of the entire wireless network may be slower. If you are still
experiencing low or no signal consider repositioning the wireless devices or installing
additional access points.

© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
22
Advanced wireless settings
Configuration > Basic Setting > Wireless
The advanced wireless features provide can provide you with additional options for
setting up your wireless network such as multiple SSID, activate/deactivate wireless
according to schedule, and WDS (Wireless Distribution System) bridging or wireless
bridging.
Multiple SSID
Configuration > Basic Setting > Wireless > Wireless Operation Mode (Multiple SSID)
The multiple SSID feature allows you to broadcast up to four additional SSIDs (or
wireless network names). To wireless devices searching for available wireless networks
to connect to, the SSIDs (or wireless network names) will appear as separate and
different wireless networks. Since they appear as separate wireless networks, they are
also referred to as virtual APs (Access Points). Each virtual AP can be configured each
with a different SSID (or wireless network name), security type and additional settings
for wireless devices to connect. You can use the multiple SSID feature to setup guest
wireless accounts with a different security type to keep your primary wireless network
security information private.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on
page 50).
2. Click on Configuration at the top of the page, click on Basic Setting, click on Wireless,
then next to Wireless Operation Mode, and click on Multiple SSID.
• Wireless Operation Mode – Displays the wireless mode the router is operating.
3. Click the Setup AP drop-down list and select the virtual AP to configure.
4. Select the Enable option to enable wireless networking on your router for the
selected virtual AP.
Note: Selecting Disable will turn off wireless networking for this SSID or virtual AP.
5. Enter the Network ID (SSID) (or wireless network name) to assign to the virtual AP.
6. Select Enable to allow wireless devices to search and discover the SSID (or wireless
network name) of the selected virtual AP. Disable turns off the ability for wireless
devices to find your SSID (or wireless network name) of the selected virtual AP when
scanning for available wireless networks. It is still possible for wireless devices to be
manually configured to connect to the selected virtual AP.
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
23
7. Configure the wireless security for the selected virtual AP. See “Securing your wireless
network” for details on configuring wireless security.
8. Click Save to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Save. You can
also click Back to return to the main wireless configuration page.
Repeat these steps 2-8 to configure the additional virtual APs.
Note: To verify that these virtual APs are active, using a wireless device, scan for
available wireless networks and check if the wireless device is able to discover the virtual
APs. To check connectivity, using a wireless device, connect to these virtual APs using the
wireless security types you have configured.
Wireless Scheduling
Configuration > Basic Setting > Wireless
The wireless scheduling feature allows you to control when the wireless functionality of
your router is enabled and disabled using a predefined time schedule. This can be a
useful security tool to prevent unauthorized access for the duration when the router is
not being used.
Note: Before applying scheduling, please ensure your Time settings are configured
correct and you have defined a schedule. See page 51 to configure Time Settings and see
page 65 to create a schedule.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on
page 50).
2. Click on Configuration at the top of the page, click on Basic Setting, click on Wireless,
then next to Wireless Schedule, check the option Enable to Apply Schedule Rule # and
click the drop-down list to select a predefined schedule.
Note: Wireless functionality will be activated during the time specified in the predefined
schedule and deactivated any time outside of the predefined schedule.
3. Click Save to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Save.
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
24
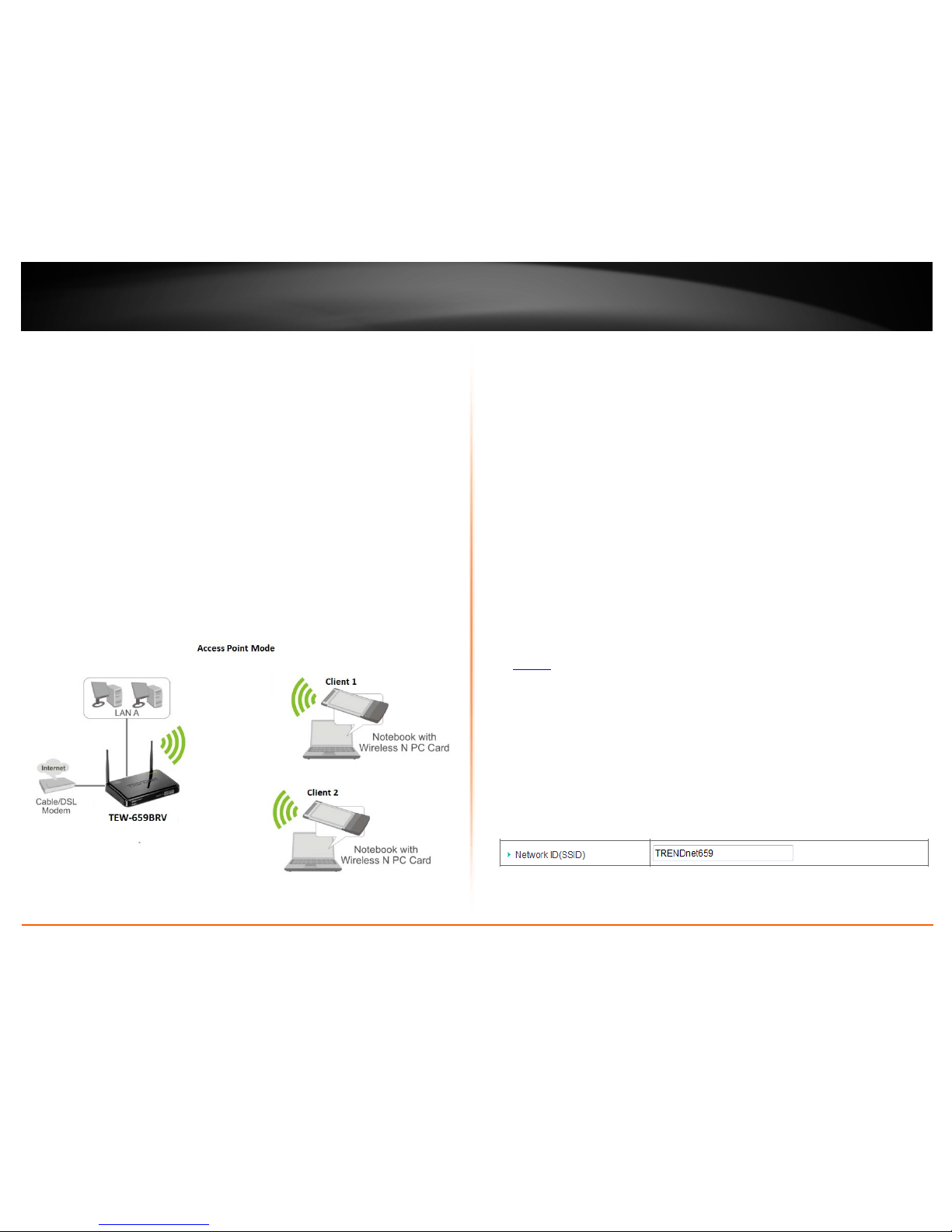
Wireless bridging using WDS (Wireless Distribution System)
Configuration > Basic Setting > Wireless > WDS Setting
Wireless bridging using WDS allows the device to create a wireless bridge with other
WDS supported wireless routers and access points configured in WDS mode to bridge
groups of network devices together wirelessly. Simultaneously, the router will also
function in access point mode allowing wireless client devices such as computers, game
consoles, mobile phones, etc. to connect in order to access network resources from
multiple groups of network devices as well as the Internet.
Note: You can create up to four WDS bridge connections. WDS (Wireless Distribution
System) is not currently standardized and may not connect to different model wireless
routers or access points, therefore, when using WDS, it is recommended to use the same
model and version for wireless bridging.
By default, your router functions in Access Point mode to allow wireless client devices to
connect and access your network resources and access the Internet.
The diagram below shows your router in Access Point mode and clients connecting to
your router.
Note: Before configuring WDS, please ensure the following first:
1. Make sure different IP addresses are assigned to each WDS supported wireless device
used for bridging. (ex. 192.168.10.1,192.168.10.2, 192.168.10.3) to avoid IP address
conflict. See page 53 for changing the LAN IP address.
2. If you are using more than one WDS supported router, please make sure the LAN
DHCP server is enabled on only one and disabled on all others to avoid IP address
conflict. See page 53 for DHCP server options.
3. Configure the same wireless channel and use the same on all WDS supported wireless
devices. See page 19 for configuring basic wireless settings.
4. Configure the same wireless security and key on all WDS supported devices. See page
14 for configuring wireless security settings.
Important Note: Some WDS supported wireless devices require that the same SSID is
used on all WDS supported wireless devices bridging together. For the TEW-659BRV,
when you are using WPA or WPA2 wireless security only, it is required that the same
SSID is used for all WDS supported wireless devices.
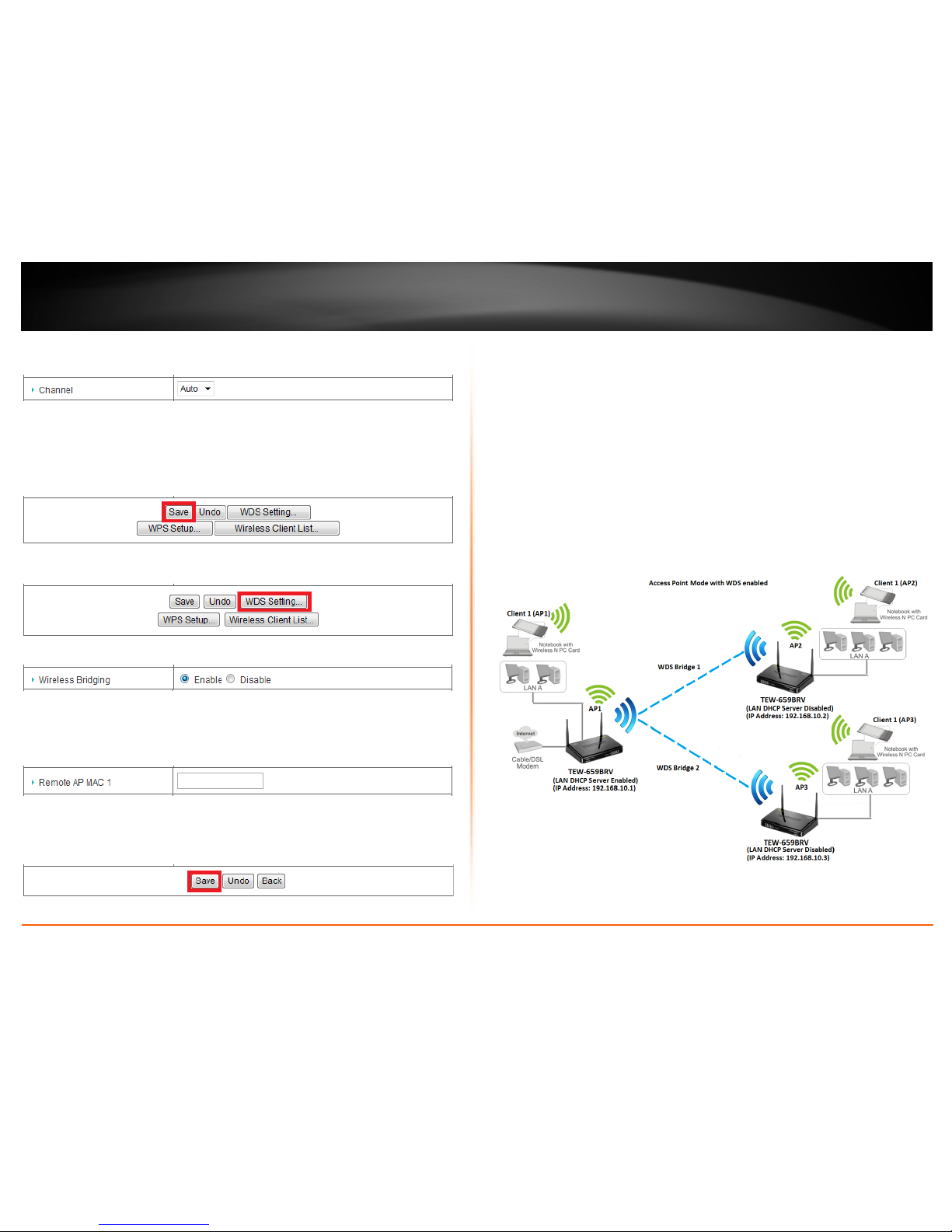
To configure WDS bridging between TEW-659BRV routers:
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on
page 50).
2. Click on Configuration at the top of the page, click on Basic Setting, and click on
Wireless.
3. Next to Network ID (SSID), enter the SSID (or wireless network name) of the first
wireless router. (e.g. TRENDnet659_1)
Note: If you are already using or planning to use WPA or WPA2 wireless security, this
must be the same SSID as the other TEW-659BRV routers you are bridging. If wireless
security is disabled or using WEP, the SSID can be different on each router.
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
25
4. Click the Channel drop-down list and select a specific wireless channel.
Note: The wireless channel must be the same on all WDS devices.
5. Configure your wireless security. See page 14 on securing your wireless network.
Note: The wireless security must be the same on all WDS devices.
6. Click Save to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Save.
7. Click on WDS Setting at the bottom of the page.
8. Next to Wireless Bridging, select Enable to enable WDS.
9. Next to a Remote AP MAC #, enter the MAC address of the other WDS supported
wireless device you are bridging. (e.g. 00:11:22:AA:BB:CC)
10. Click Save to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Save. You can
also click Back to return to the main wireless configuration page.
For additional TEW-659BRV routers, make sure to disable the DHCP server first on all
additional routers and configure the LAN IP address to be different on each router. You
will connect devices to the LAN ports 1-4 only on all additional routers and the WAN
port is not used. Then, repeat steps 3-8 for additional TEW-659BRV routers you are
bridging.
In the diagram below, the blue color represents the WDS wireless bridged connections
between the routers. The green color represents access point mode connections
between wireless client devices and the routers.
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
26
Virtual Private Networking (VPN)
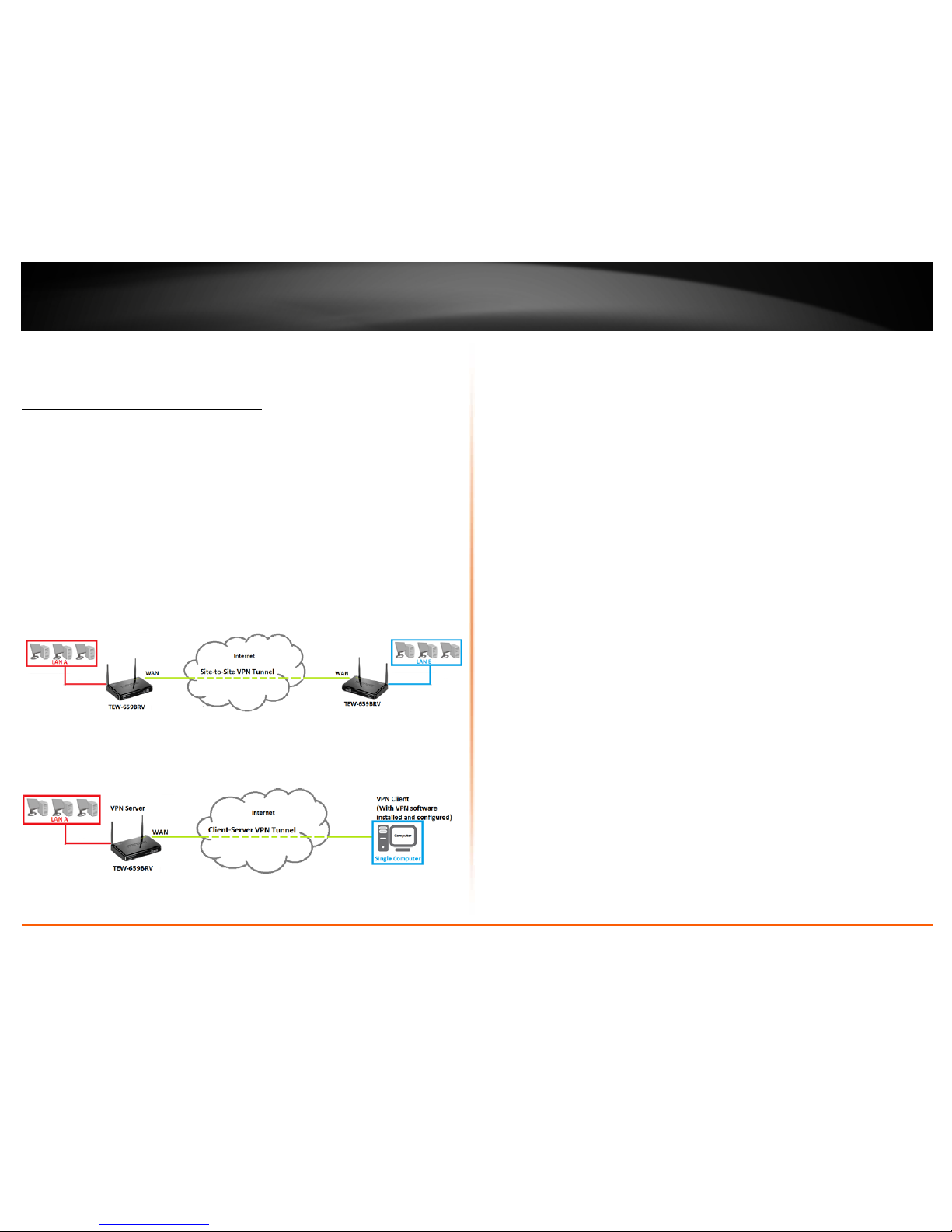
Creating a Virtual Private Network
What is a VPN?
A VPN provides secure communications typically over the Internet by creating a secure
tunnel between two or more VPN routers (gateways) also known as a site-to-site VPN or
between a single client computer and a VPN router (gateway) also known as a clientserver VPN.
On your VPN router, the following types of tunnels can be created:
• Site-to-Site VPN – Connects two or more VPN routers (gateways) allowing the
LAN network from each router to securely communicate to each other over the
Internet.
• Client-Server VPN – A single client computer or device with VPN client software
installed connects to a VPN router (gateway) allow the single client computer
or device to securely communicate to the LAN network of the VPN router over
the Internet.
Tunneling methods supported by your router:
• IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) VPN – This type of VPN can be used for
either Site-to-Site VPN or Client-Server VPN however, the most common
application for this type is a Site-to-Site VPN. This type of VPN can provide
highest degree of security. For a Client-Server VPN, typically, a third party VPN
client software is required to be installed and configured and can be difficult
when installing and configuring on VPN client computers. This VPN type can
provide the highest degree of security.
• PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) VPN – This type of VPN can be used
for Client-Server VPN only however both server mode and client mode are
supported on your router. Most computer operating systems already include a
pre-installed PPTP VPN client software that can be easily configured which
eliminates the need for an additional third party VPN client software to be
purchased and installed. Since it provides less security overall than IPsec VPN, it
is not recommended for a Site-to-Site VPN.
• L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) VPN – This type of VPN is very similar to
PPTP VPN as it is most commonly used for a Client-Server VPN, pre-installed on
most computer operating systems and easy to configure, and provides less
overall security than IPsec VPN. Most of the current operating systems with
L2TP VPN client software pre-installed use L2TP VPN in conjunction with IPsec
VPN to improve the overall security provided. This router does not support the
L2TP over IPsec VPN method.
• GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) Tunneling – This is strictly a tunneling
protocol as it does not provide any security mechanisms and it can only be
used for Site-to-Site tunneling to another router with GRE tunneling support
but in most current implementations can be used in conjunction with IPsec or
PPTP/L2TP to add security mechanisms. Because of the nature of how GRE
works, the benefits include allow multicast traffic and allowing dynamic routing
protocols to pass through the tunnel compared to IPsec VPN. This router does
not support GRE over IPsec VPN or GRE over PPTP/L2TPVPN methods.
Important Note: For any tunneling or VPN method used, to avoid IP address conflict and
to ensure connectivity, it is required that each end (LAN IP network or single client) of the
VPN tunnel is configured with a different IP network or subnet.
© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-659BRV
27
IPsec (Internet Protocol Security)
Site-to-Site VPN
Configuration > Security Setting >VPN-IPsec
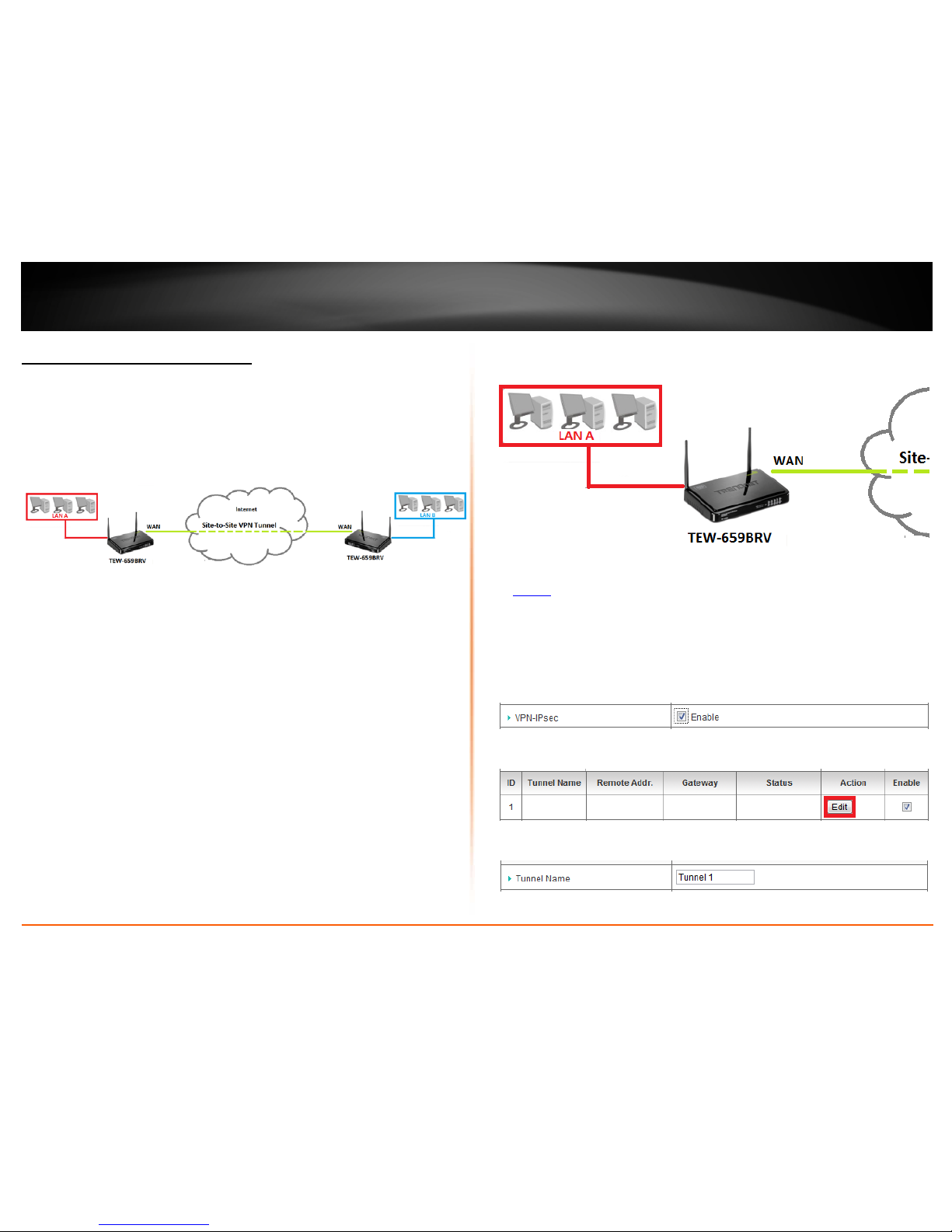
To configure an IPsec Site-to-Site VPN tunnel between two VPN routers:
• Ensure that your router is connected to the Internet and computers and
devices are able to access the Internet through your router and make note of
the WAN (Internet) IP assigned to both routers under the Status page. See page
73 for checking the status page.
Example:
VPN Router A WAN (Internet) IP Address: 10.10.10.10
VPN Router B WAN (Internet) IP Address: 10.10.10.20
• Make sure the LAN IP network on each VPN router is different.
Note: Changing the LAN IP address of your router will change the LAN IP
network of your router. See page 53 for changing the LAN IP address.
Example:
VPN Router A LAN IP Settings: 192.168.10.1 / 255.255.255.0
VPN Router B LAN IP Settings: 192.168.100.1 / 255.255.255.0
VPN Router A Configuration
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on
page 50).
2. Click on Configuration at the top of the page, click on Security Setting, and click on
VPN-IPsec.
3. Next to VPN-IPsec, check the Enable option to enable IPsec.
Note: If Enable is not checked, then this will disable all IPsec functionality on your router.
4. For ID 1, check the Enable option and then click Edit.
5. Next to Tunnel Name, enter the tunnel name in the field. (e.g. Tunnel 1)
 Loading...
Loading...