Page 1

TL-ER604W
Wireless N Gigabit Broadband VPN Router
REV1.2.2
1910011343
Page 2

COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS
Specifications are subject to change without notice. is a registered
trademark of TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Other brands and product names are
trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
No part of the specifications may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to
make any derivative such as translation, transformation, or adaptation without permission
from TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Copyright © 2015 TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES
CO., LTD. All rights reserved.
FCC STATEMENT
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/ TV technician for help.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions:
1) This device may not cause harmful interference.
2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference
that may cause undesired operation.
Page 3

Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Note: The manufacturer is not responsible for any radio or TV interference caused by
unauthorized modifications to this equipment. Such modifications could void the user’s
authority to operate the equipment.
FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This device and its antenna must not be co-located or
operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
“To comply with FCC RF exposure compliance requirements, this grant is applicable to
only Mobile Configurations. The antennas used for this transmitter must be installed to
provide a separation distance of at least 20 cm from all persons and must not be
co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.”
CE Mark Warning
This is a class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio
interference, in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Industry Canada Statement
Complies with the Canadian ICES-003 Class B specifications.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
This device complies with RSS 210 of Industry Canada. This Class B device meets all the
requirements of the Canadian interference-causing equipment regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la Classe B respecte toutes les exigences du Règlement sur le
matériel brouilleur du Canada.
NCC Notice & BSMI Notice
注意!
依據 低功率電波輻射性電機管理辦法
Page 4

第十二條 經型式認證合格之低功率射頻電機,非經許可,公司、商號或使用者均不得擅自
變更頻率、加大功率或變更原設計之特性或功能。
第十四條 低功率射頻電機之使用不得影響飛航安全及干擾合法通行;經發現有干擾現象時,
應立即停用,並改善至無干擾時方得繼續使用。前項合法通信,指依電信規定作業之無線電
信。低功率射頻電機需忍受合法通信或工業、科學以及醫療用電波輻射性電機設備之干擾。
減少電磁波影響,請妥適使用。
安全諮詢及注意事項
●請使用原裝電源供應器或只能按照本產品注明的電源類型使用本產品。
●清潔本產品之前請先拔掉電源線。請勿使用液體、噴霧清潔劑或濕布進行清潔。
●注意防潮,請勿將水或其他液體潑灑到本產品上。
●插槽與開口供通風使用,以確保本產品的操作可靠並防止過熱,請勿堵塞或覆蓋開口。
●請勿將本產品置放於靠近熱源的地方。除非有正常的通風,否則不可放在密閉位置中。
●請不要私自打開機殼,不要嘗試自行維修本產品,請由授權的專業人士進行此項工作。
此為甲類資訊技術設備,于居住環境中使用時,可能會造成射頻擾動,在此種情況下,使用
者會被要求採取某些適當的對策。
Продукт сертифіковано згідно с правилами системи УкрСЕПРО на відповідність
вимогам нормативних документів та вимогам, що передбачені чинними
законодавчими актами України.
Safety Information
When product has power button, the power button is one of the way to shut off the
product; When there is no power button, the only way to completely shut off power is
to disconnect the product or the power adapter from the power source.
Don’t disassemble the product, or make repairs yourself. You run the risk of electric
shock and voiding the limited warranty. If you need service, please contact us.
Page 5

Avoid water and wet locations.
Page 6

CONTENTS
Package Contents
Chapter 1 About this Guide
1.1 Intended Readers .................................................................................................................. 2
1.2 Conventions ........................................................................................................................... 2
1.3 Overview of this Guide ........................................................................................................... 2
Chapter 2 Introduction
2.1 Overview of the Router .......................................................................................................... 3
2.2 Features ................................................................................................................................. 4
2.3 Appearance ............................................................................................................................ 6
2.3.1 Front Panel ................................................................................................................ 6
2.3.2 Rear Panel ................................................................................................................. 7
Chapter 3 Configuration
.................................................................................................................. 1
................................................................................................... 2
.......................................................................................................... 3
........................................................................................................ 8
3.1 Network .................................................................................................................................. 8
3.1.1 Status ......................................................................................................................... 8
3.1.2 System Mode ............................................................................................................. 8
3.1.3 WAN ........................................................................................................................ 10
3.1.4 LAN .......................................................................................................................... 26
3.1.5 IPTV ......................................................................................................................... 29
3.1.6 MAC Address ........................................................................................................... 30
3.1.7 Switch ...................................................................................................................... 31
3.2 Wireless ............................................................................................................................... 37
3.2.1 Wireless Setting ....................................................................................................... 37
3.2.2 MAC Filtering ........................................................................................................... 51
3.2.3 Host Status .............................................................................................................. 52
3.3 User Group .......................................................................................................................... 53
3.3.1 Group ....................................................................................................................... 53
3.3.2 User ......................................................................................................................... 54
-IV-
Page 7

3.3.3 View ......................................................................................................................... 55
3.4 Advanced ............................................................................................................................. 56
3.4.1 NAT .......................................................................................................................... 56
3.4.2 Traffic Control .......................................................................................................... 64
3.4.3 Session Limit ........................................................................................................... 67
3.4.4 Load Balance ........................................................................................................... 68
3.4.5 Routing .................................................................................................................... 73
3.5 Firewall ................................................................................................................................. 78
3.5.1 Anti ARP Spoofing ................................................................................................... 78
3.5.2 Attack Defense ........................................................................................................ 81
3.5.3 MAC Filtering ........................................................................................................... 82
3.5.4 Access Control ......................................................................................................... 83
3.5.5 App Control .............................................................................................................. 88
3.6 VPN...................................................................................................................................... 90
3.6.1 IKE ........................................................................................................................... 90
3.6.2 IPsec ........................................................................................................................ 94
3.6.3 L2TP/PPTP ............................................................................................................ 100
3.7 Services ............................................................................................................................. 104
3.7.1 PPPoE Server ........................................................................................................ 104
3.7.2 E-Bulletin ............................................................................................................... 109
3.7.3 Dynamic DNS ........................................................................................................ 111
3.7.4 UPnP ..................................................................................................................... 117
3.8 Maintenance ...................................................................................................................... 118
3.8.1 Admin Setup .......................................................................................................... 118
3.8.2 Management .......................................................................................................... 122
3.8.3 SNMP .................................................................................................................... 124
3.8.4 Statistics ................................................................................................................. 125
3.8.5 Diagnostics ............................................................................................................ 127
-V-
Page 8

3.8.6 Time ....................................................................................................................... 130
3.8.7 Logs ....................................................................................................................... 132
3.8.8 NAT Table .............................................................................................................. 134
Chapter 4 Application
4.1 Network Requirements ....................................................................................................... 135
4.2 Network Topology ............................................................................................................... 136
4.3 Configurations .................................................................................................................... 136
4.3.1 Internet Setting ...................................................................................................... 136
4.3.2 VPN Setting ........................................................................................................... 138
4.3.3 Network Management ............................................................................................ 146
4.3.4 Network Security .................................................................................................... 150
Appendix A Hardware Specifications
Appendix B FAQ
Appendix C Glossary
........................................................................................................ 135
........................................................................... 156
......................................................................................................... 157
.................................................................................................. 159
-VI-
Page 9

Package Contents
The following items should be found in your package:
One TL-ER604W Router
One Power Adapter
One RJ45 Ethernet Cable
Quick Installation Guide
Resource CD
Note:
Make sure that the package contains the above items. If any of the listed items is damaged or missing,
please contact your distributor.
-1-
Page 10
on the
Provides the possible solutions to the problems that may
Chapter 1 About this Guide
This User Guide contains information for setup and management of TL-ER604W router. Please read
this guide carefully before operation.
1.1 Intended Readers
This Guide is intended for Network Engineer and Network Administrator.
1.2 Conventions
In this Guide the following conventions are used:
The router or TL-ER604W mentioned in this Guide stands for TL-ER604W SafeStream Wireless
N Gigabit Broadband VPN Router without any explanation.
Menu Name→Submenu Name→Tab page indicates the menu structure. Advanced→N AT
→NAT Setup means the N AT Setup page under the NAT menu option that is located under the
Advanced menu.
Bold font indicates a toolbar icon, menu or menu item.
<Font> indicate a button.
Symbols in this Guide:
Symbol Description
Note:
Tips:
Ignoring this type of note might result in a malfunction or damage to the device.
This format indicates important information that helps you make better use of your device.
1.3 Overview of this Guide
Chapter 1 About This Guide Introduces the guide structure and conventions.
Chapter 2 Introduction Introduces the features and appearance of this router.
Chapter 3 Configuration Introduces how to configure the router via Web management
page.
Chapter 4 Application
Appendix A Hardware Specifications Lists the hardware specifications of this router.
Appendix B FAQ
Appendix C Glossary Lists the glossary used in this guide.
Introduces the practical application of the router
enterprise network.
occur during the installation and operation of the router.
-2-
Page 11

Chapter 2 Introduction
Thanks for choosing the SafeStream Wireless N Gigabit Broadband VPN Router TL-ER604W.
2.1 Overview of the Router
The SafeStream Wireless N Gigabit Broadband VPN Router TL-ER604W from TP-LINK supports
Wireless N speed and Gigabit wired speeds on all ports. It integrates multiple VPN protocols,
high-security and high-performance VPN capabilities, making it an ideal choice for branch offices in
need of cost-effective secure remote connections to headquarters or remote offices. Furthermore,
together with many useful features including hardware-based WiFi On/Off button, Guest Networking,
App Control, IPTV, and PPPoE Server functions, TL-ER604W is an ideal network solution for home or
small office consumers.
● Powerful Data Processing Capability
+ Built-in MIPS 32 network processor and 64MB DDRII high-speed RAM allows the stability and
reliability for operation.
● Wireless Feature
+ Wireless N speed provides an incredible high speed experience.
+ Supporting Guest Networking feature, which provides a secure network for guests outside of the
existing, potentially sensitive LAN.
+ Hardware Wi-Fi On/Off button provides an easy way to turn wireless radio on or off
● Virtual Private Network (VPN)
+ Providing comprehensive IPsec VPN with DES/3DES/AES encryptions, MD5/SHA1
identifications and automatically/manually IKE Pre-Share Key exchanges.
+ Supporting PPTP/L2TP VPN Server mode to allow the staff on business or remote branch office
to access the headquarter network.
● Online Behavior Management
+ Complete Functions of Access Rules can allow managers to select the network service levels to
block or allow applications of FTP downloading, Email, Web browsing and so on.
+ Deploying One-Click restricting of IM/P2P applications to save time & energy while reserving
exceptional groups for certain users.
+ Supporting URL Filtering to prevent potential hazards from visiting the malicious Web sites.
● Powerful Firewall
+ Supporting One-Click IP-MAC Binding to avoid ARP spoofing and guarantee a network without
stagnation.
-3-
Page 12

+ Featured Attack Defense to protect the network from a variety of flood attack and packet
anomaly attack.
+ Possessing MAC Filtering function to block the access of illegal hosts.
● Flexible Traffic Control
+ Featured Bandwidth Control with flexible bandwidth management to automatically control the
bandwidth of the host in bi-direction to avoid bandwidth over occupation, as well as optimize
bandwidth usage.
+ Supporting Session Limit to avoid the complaint of a few people to force whole sessions.
● Dual-WAN P orts
+ Providing two 10/100/1000M WAN ports for users to connect two Internet lines for bandwidth
expansion.
+ Supporting multiple Load Balance modes, including Bandwidth Based Balance Routing,
Application Optimized Routing, and Policy Routing to optimize bandwidth usage.
+ Featured Link Backup to switch all the new sessions from dropped line automatically to another
for keeping an always on-line network.
● Easy-to-use
+ Providing easy-to-use GUI with clear configuration steps and detailed help information for the
users to configure the router simply.
+ Helping administrators to monitor the whole network status and take actions to malfunctions
according to the recorded log information.
+ Supporting remote management to manage the router from remote places.
2.2 Features
Hardware
1 fixed gigabit WAN port, 1 interchangeable gigabit WAN/LAN port, 3 fixed gigabit LAN ports
Fanless Design for Quiet Operation
Hardware Wi-Fi On/Off button provides an easy way to turn wireless radio on or off
Supports Professional 4kV common mode
lightning protection
Complies with IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3u, IEEE 802.3ab, IEEE 802.11 b/g/n standards
Supports AH, ESP, IKE, PPP protocols
Supports TCP/IP, DHCP, ICMP, NAT, NAPT protocols
Supports PPPoE, SNTP, HTTP, HTTPS, DDNS, UPnP, NTP protocols
-4-
Page 13

Basic Functions
Supports Static IP, Dynamic IP, PPPoE/Russian PPPoE, L2TP/Russian L2TP, PPTP/Russian
PPTP, Dual Access, BigPond Internet connections
Supports IPTV Function
Supports Virtual Server, Port Triggering, ALG, Static Route and RIP v1/v2
Built-in Switch supporting Port Mirror, Port VLAN, Rate Control and so on
Supports to change the MAC address of LAN and WAN port
Supports Logs, Statistics, Time setting
Supports Remote and Web management
Supports SNMP v1/v2c
Supports Daylight Saving Time
Supports Diagnostics (Ping/Tracert) and Online Detection
Wireless
Supports Wireless N speed and 2 detachable 5dBi antennas
Supports WEP, WPA/WPA2, WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK Encryption
Supports WDS, Multi-SSID, Guest Network
VPN
Supports IPsec VPN and provides up to 30 IPsec VPN tunnels
Supports IPSec VPN in LAN-to-LAN or Client-to-LAN
Provides DES, 3DES, AES128, AES192, AES256 encryption, MD5, SHA1 authentication
Supports IKE Pre-Share Key and DH1/DH2/DH5 Key Exchanges
Supports PPTP/L2TP Server/Client
Traffic Control
Supports Bandwidth Control
Supports Session Limit
Security
Built-in firewall supporting URL/MAC Filtering
Supports Access Control
Supports Attack Defense
-5-
Page 14
On
The router is powered on.
Flashing
The router works properly.
On(Green)
The wireless function is enabled.
Off
There is no device linked to the corresponding port.
Supports IP-MAC Binding
Supports GARP (Gratuitous ARP)
Deploys One-Click restricting of IM/P2P applications
2.3 Appearance
2.3.1 Front Panel
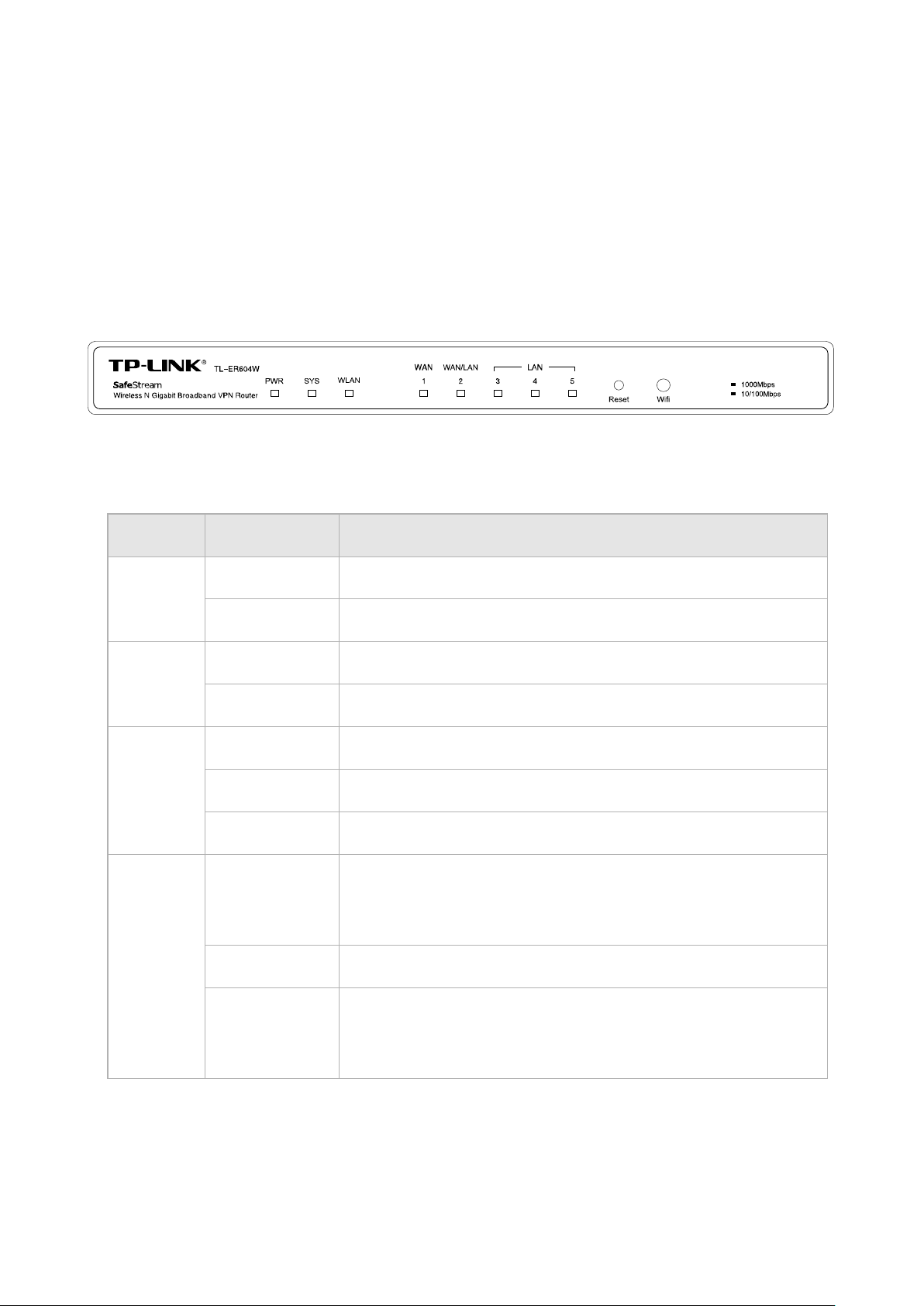
The front panel of TL-ER604W is shown as the following figure.
Figure 2-1 Front Panel
●
LEDs
LED Status Indication
PWR
Off The router is powered off or power supply is abnormal.
SYS
On/Off The router works improperly.
WLAN
WAN,LAN
Off The wireless function is disabled.
Flashing(Green) There is data being transferred through wireless.
On
(Green/Yellow)
There is a device linked to the corresponding port but no activity.
(Green light indicates the linked device is running at 1000Mbps,
and yellow indicates the linked device is running at 10/100Mbps.)
Flashing
(Green/Yellow)
●
Reset button
Use the button to restore the router to the factory defaults. With the router powered on, use a pin to
press and hold the Reset button (about 4~5 seconds). After the SYS LED goes out, release the Reset
button. If the SYS LED is flashing with a high frequency about two or three seconds, it means the router
is restored successfully.
The corresponding port is transmitting or receiving data. (Green
light indicates the linked device is running at 1000Mbps, and
yellow indicates the linked device is running at 10/100Mbps.)
-6-
Page 15
The WAN port is for connecting the router to a DSL/Cable modem or
The LAN port is for connecting the router to the local PCs or switches by
●
Wifi button
Press this button to enable or disable Wi-Fi. WLAN LED will light up when the wireless function is
enabled.
2.3.2 Rear Panel
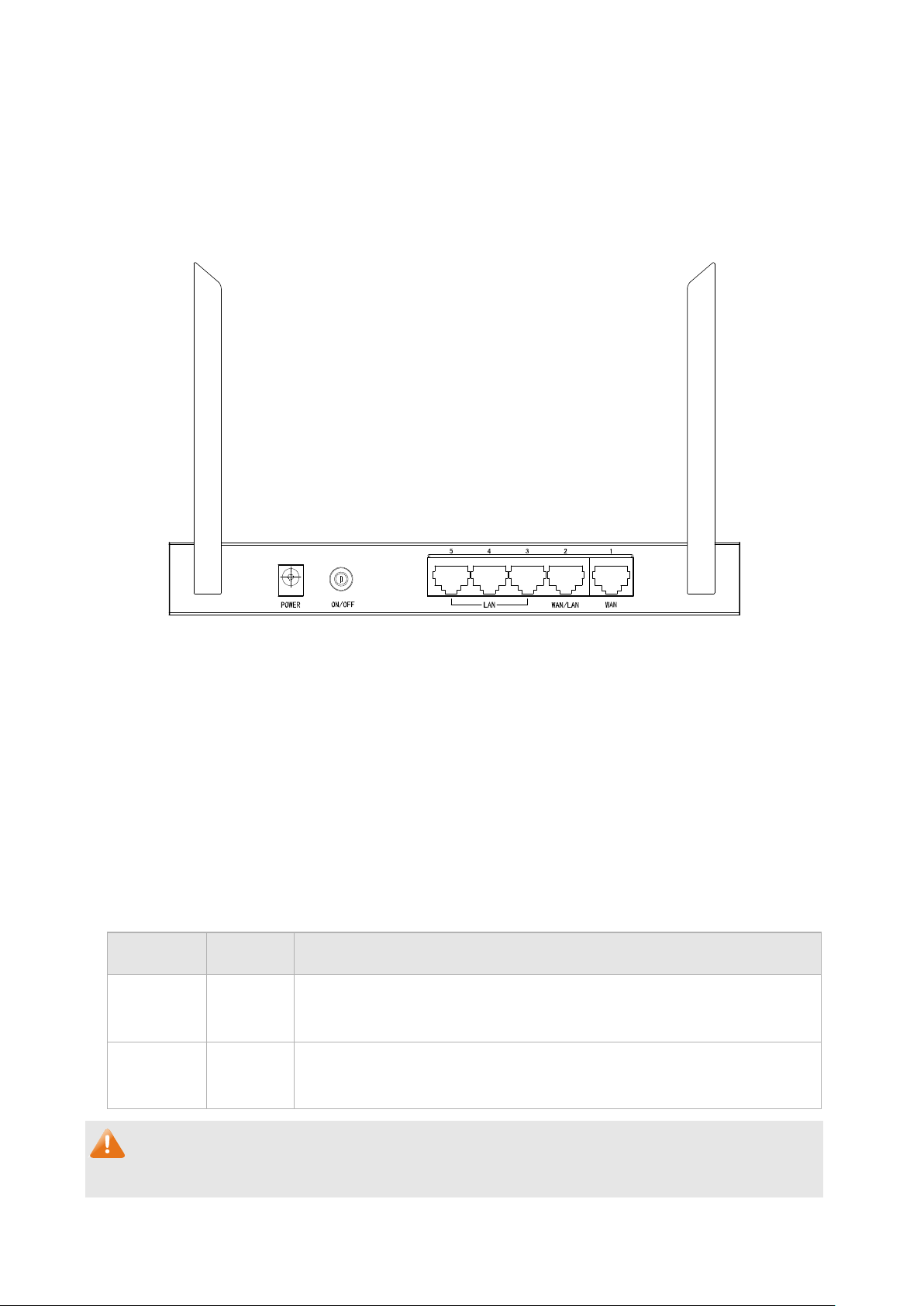
The rear panel of TL-ER604W is shown as the following figure.
Figure 2-2 Rear Panel
●
Antenna
The router provides two external detachable antennas for receiving and transmitting the wireless data.
●
POWER
The power socket is where you will connect the power adapter. Please use the power adapter provided
with this TL-ER604W SafeStream Wireless N Gigabit Broadband VPN Router.
●
ON/OFF
Press this button to turn on or turn off the router. All LEDs will be off when turning off the router.
●
Interface Description
Interface Port Description
WAN 1~2
Ethernet by the RJ45 cable.
LAN 2~5
the RJ45 cable.
Note:
Please only use the power adapter provided with this router.
-7-
Page 16
Chapter 3 Configuration
3.1 Network
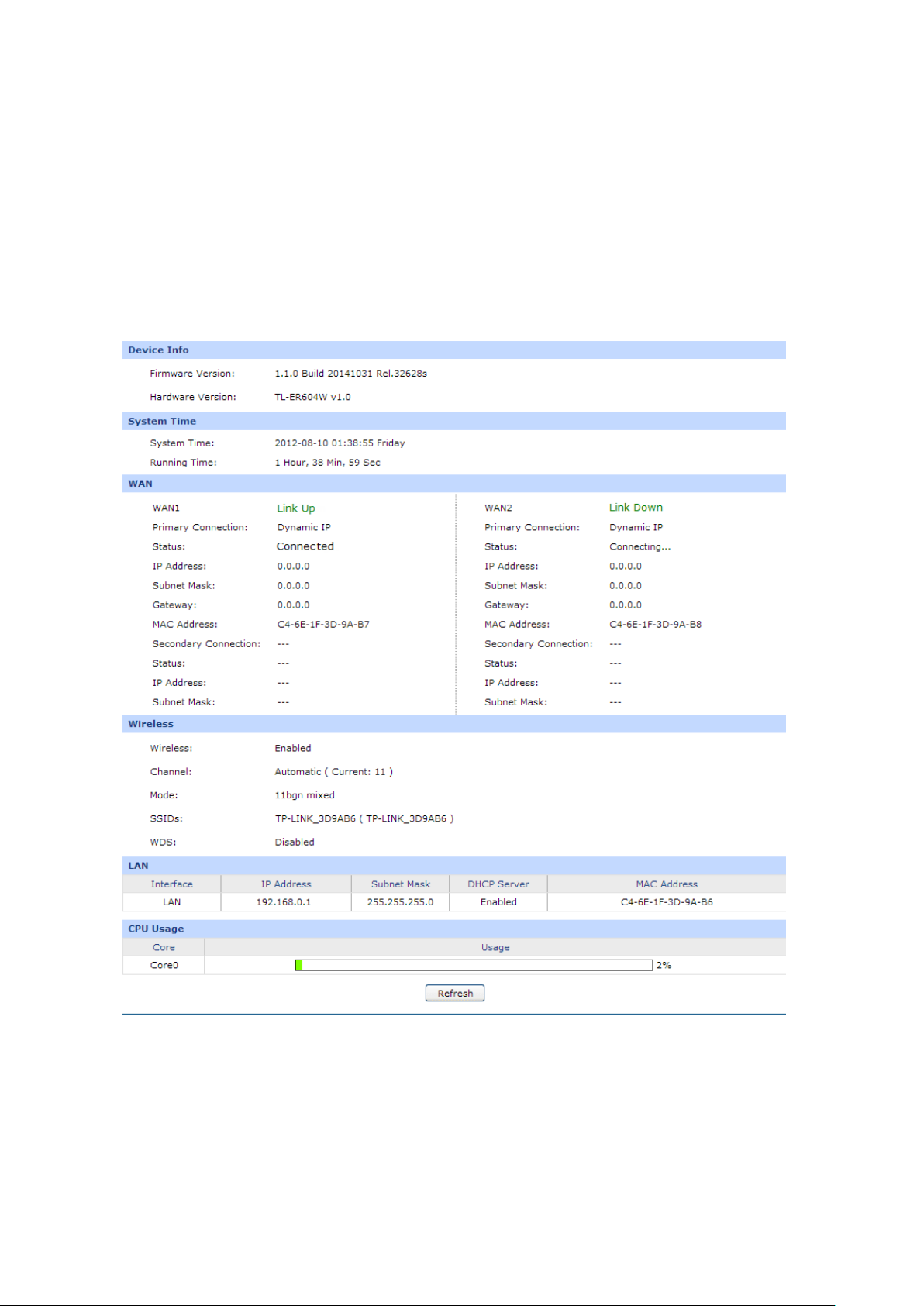
3.1.1 Status
The Status page shows the system information, the port connection status and other information
related to this router.
Choose the menu Network→Status→System Status to load the following page.
Figure 3-1 Status
3.1.2 System Mode
The TL-ER604W can work in three modes: NAT, Non-NAT and Classic.
If your router is hosting your local network’s connection to the Internet with a network topology as the
Figure 3-2 shows, you can set it to NAT mode.
-8-
Page 17
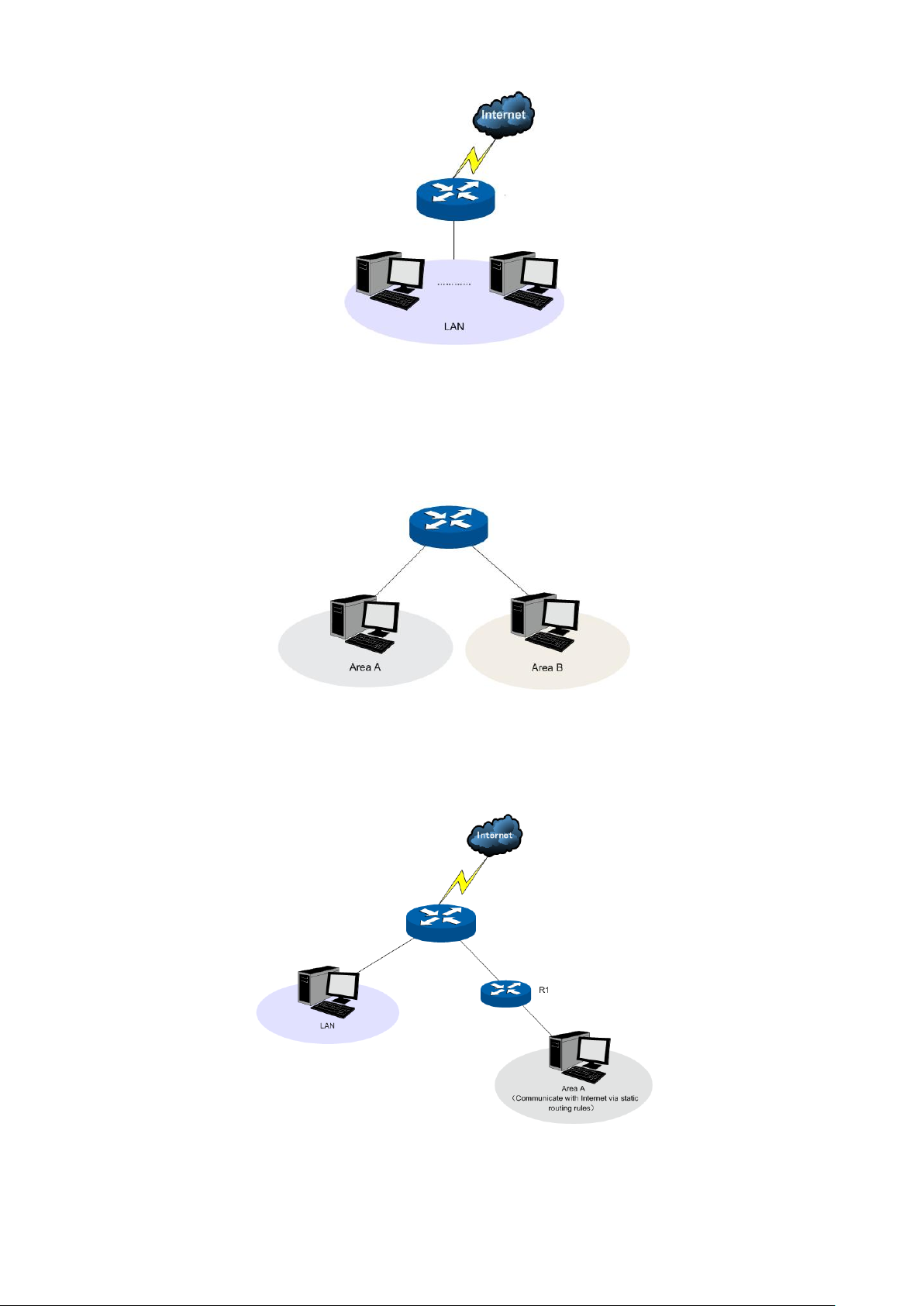
Figure 3-2 Network Topology - NAT Mode
If your router is connecting the two networks of different areas in a large network environment with a
network topology as the Figure 3-3 shows, and forwards the packets between these two networks by
the Routing rules, you can set it to Non-NAT mode.
Figure 3-3 Network Topology – Non-NAT Mode
If your router is connected in a combined network topology as the Figure 3-4 shows, you can set it to
Classic Mode.
Figure 3-4 Network Topology – Classic Mode
Choose the menu Network→System Mode to load the following page.
-9-
Page 18
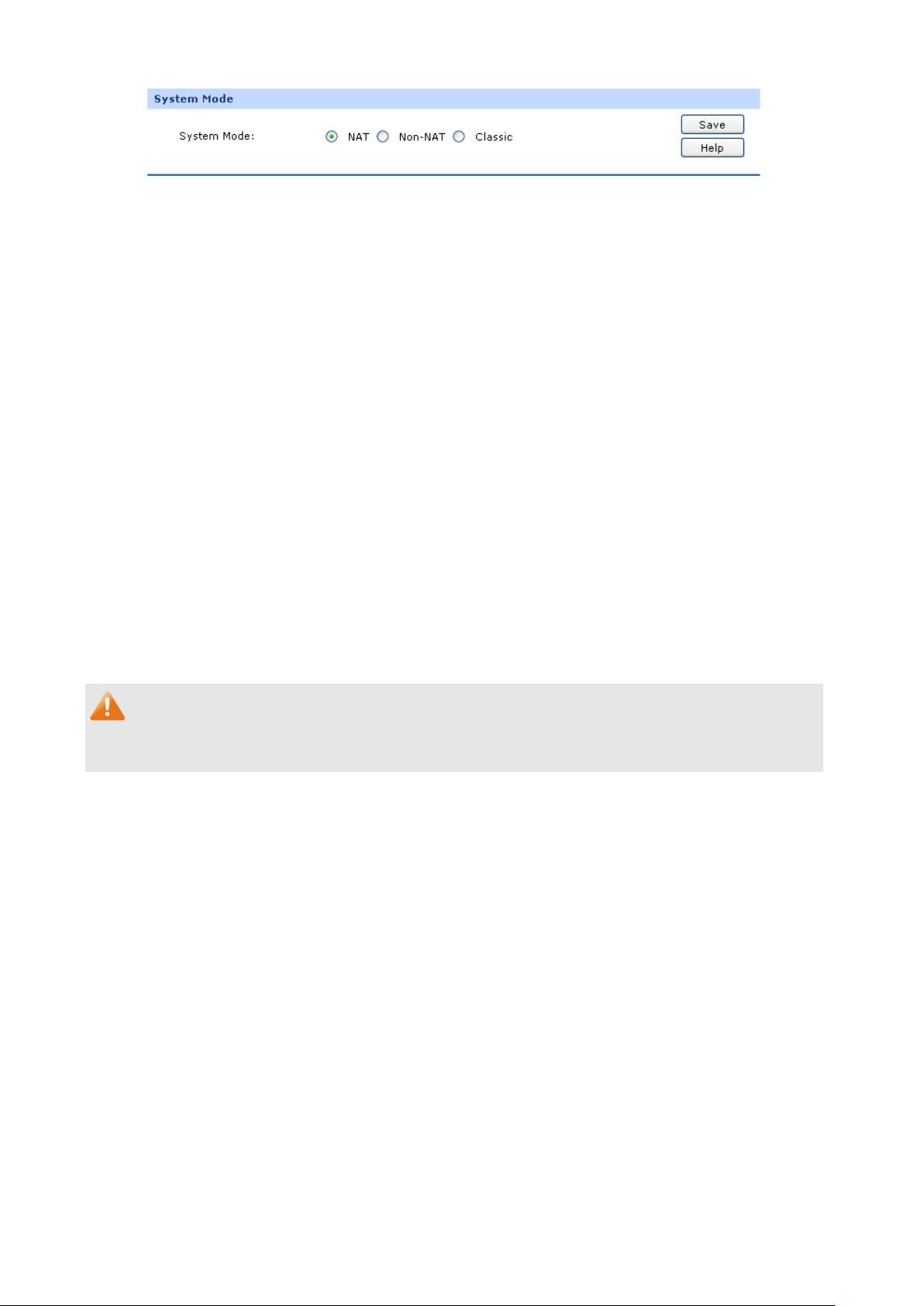
Figure 3-5 System Mode
You can select a System Mode for your router according to your network need.
NAT Mode
NAT (Network Address Translation) mode allows the router to translate private IP addresses within
internal networks to public IP addresses for traffic transport over external networks, such as the
Internet. Incoming traffic is translated back for delivery within the internal network. However, the router
will drop all the packets whose source IP addresses are in different subnet of LAN port. For example: If
the LAN port of the router is set to 192.168.0.1 for IP address and 255.255.255.0 for the Subnet Mask,
then the subnet of LAN port is 192.168.0.0/24. The packet with 192.168.0.123 as its source IP address
can be transported by NAT, whereas the packet with 20.31.76.80 as its source IP address will be
dropped.
Non-NAT Mode
In this mode, the router functions as the traditional Gateway and forwards the packets via routing
protocol. The Hosts in different subnets can communicate with one another via the routing rules
whereas no NAT is employed.
Note:
In Non-NAT mode, all the NAT forwarding rules will be disabled.
Classic Mode
It's the combined mode of NAT mode and Non-NAT mode. In Classic mode, the router will first
transport the packets which are compliant with NAT forwarding rules and then match the other packets
to the static routing rules. The matched packets will be transmitted based on the static routing rules
and the unmatched ones will be dropped. In this way, the router can implement NAT for the packets
without blocking the packets in the different subnet of the ports.
3.1.3 WAN
3.1.3.1 WAN Mode
TL-ER604W provides two adjustable WAN ports. You can set the number of WAN ports on this page.
Choose the menu Network→WAN→WAN Mode to load the following page.
-10-
Page 19
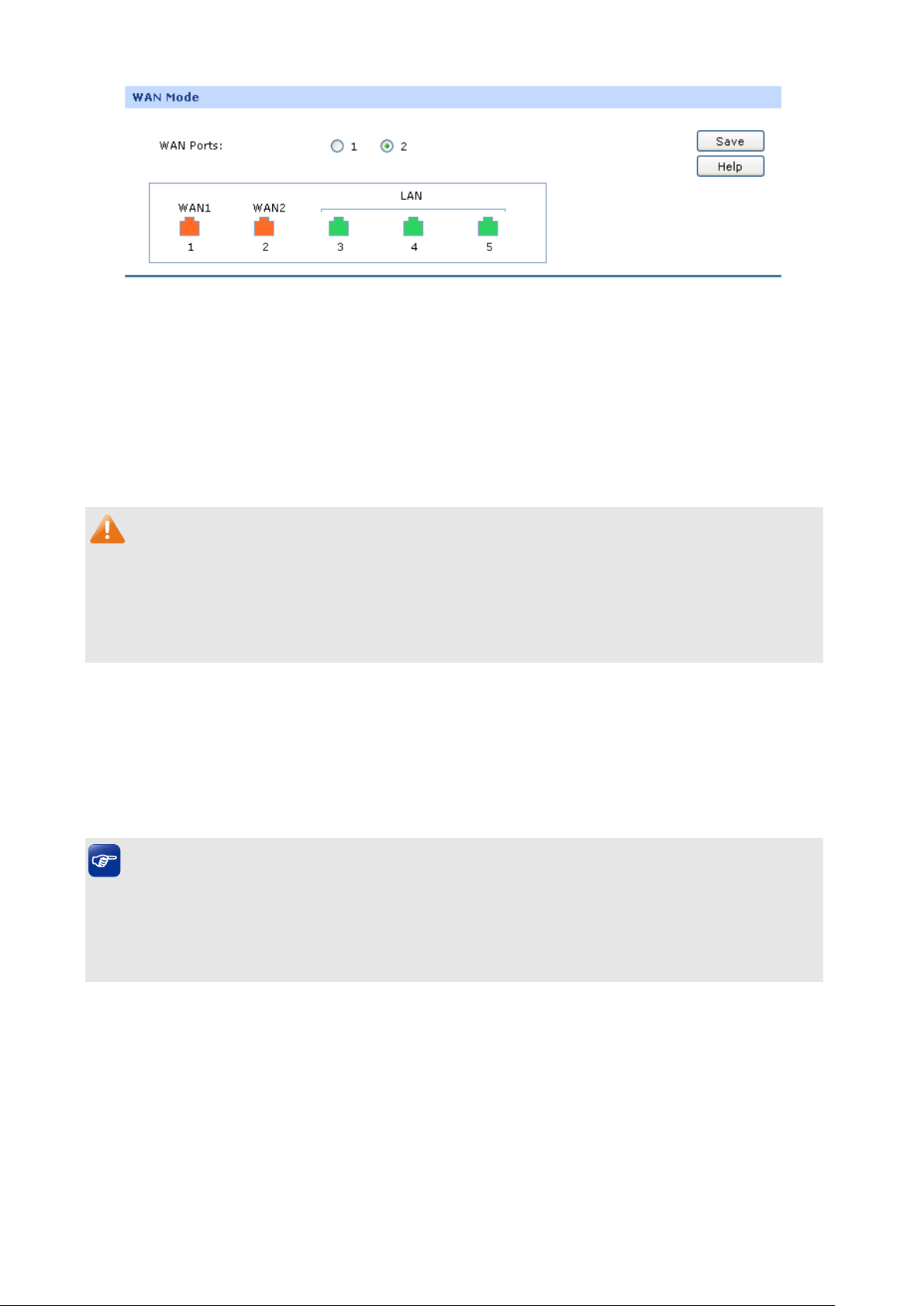
WAN Mode
Figure 3-6 WAN Mode
WAN Ports:
Select the total number of WAN ports you prefer to use. The router
support one WAN and dual WAN. The router will adjust the physical
ports accordingly, which can be illustrated on the following port sketch.
Note:
By default, TL-ER604W is set to work in the mode of dual WAN ports.
Any change to the number of WAN ports may lead to a loss of current configurations. Please be
sure to back up your configurations in advance.
3.1.3.2 WAN1
TL-ER604W provides the following six Internet connection types: Static IP, Dynamic IP,
PPPoE/Russian PPPoE, L2TP/Russian L2TP, PPTP/Russian PPTP and BigPond. To configure the
WAN, please first select the type of Internet connection provided by your ISP (Internet Service
Provider).
Tips:
It’s allowed to set the IP addresses of both the WAN ports within the same subnet. However, to
guarantee a normal communication, make sure that the WAN ports can access the same network,
such as Internet or a local area network.
Choose the menu Network→WAN→WAN1 to load the configuration page.
1) Static IP
If a static IP address has been provided by your ISP, please choose the Static IP connection type to
configure the parameters for WAN port manually.
-11-
Page 20
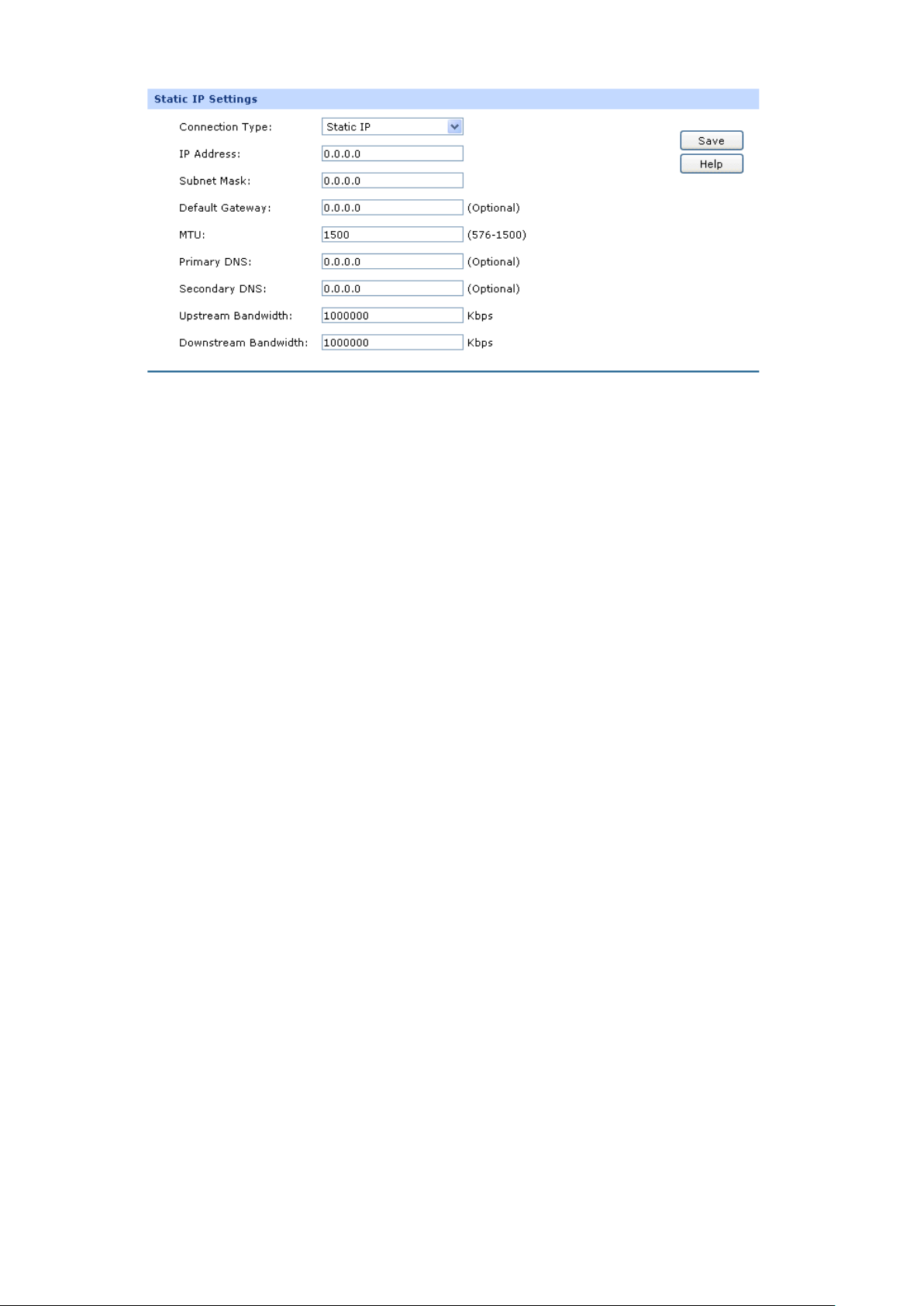
Figure 3-7 WAN – Static IP
ata unit
(Domain Name
The following items are displayed on this screen:
Static IP
Connection Type:
IP Address:
Subnet Mask:
Default Gateway:
MTU:
Primary DNS:
Select Static IP if your ISP has assigned a static IP address for your
computer.
Enter the IP address assigned by your ISP. If you are not clear, please
consult your ISP.
Enter the Subnet Mask assigned by your ISP.
Optional. Enter the Gateway assigned by your ISP.
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) is the maximum d
transmitted by the physical network. It can be set in the range of
576-1500. The default MTU is 1500. It is recommended to keep the
default value if no other MTU value is provided by your ISP.
Enter the IP address of your ISP’s Primary DNS
Server). If you are not clear, please consult your ISP. It’s not allowed to
access the Internet via domain name if the Primary DNS field is blank.
Secondary DNS:
Upstream
Bandwidth:
Downstream
Bandwidth:
Optional. If a Secondary DNS Server address is available, enter it.
Specify the bandwidth for transmitting packets on the port.
Specify the bandwidth for receiving packets on the port.
-12-
Page 21
mic IP if your ISP assigns the IP address automatically.
<Obtain> to get the IP address from your ISP’s server. Click
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) is the maximum data unit
2) Dynamic IP
If your ISP (Internet Service Provider) assigns the IP address automatically, please choose the
Dynamic IP connection type to obtain the parameters for WAN port automatically.
Figure 3-8 WAN – Dynamic IP
The following items are displayed on this screen:
Dynamic IP
Connection Type:
Select Dyna
Click
<Release> to release the current IP address of WAN port.
Host Name:
Optional. This field allows you to give a name for the router. It's blank
by default.
MTU:
transmitted by the physical network. It can be set in the range of
576-1500. The default MTU is 1500. It is recommended to keep the
default value if no other MTU value is provided by your ISP.
Get IP Address by
Unicast:
The broadcast requirement may not be supported by a few ISPs.
Select this option if you cannot get the IP address from your ISP even if
with a normal network connection. This option is not required generally.
-13-
Page 22

(Domain Name
outer is obtaining the IP
Use the following
DNS Server:
Primary DNS:
Secondary DNS:
Upstream
Bandwidth:
Downstream
Bandwidth:
Dynamic IP Status
Select this option to enter the DNS (Domain Name Server) address
manually.
Enter the IP address of your ISP’s Primary DNS
Server). If you are not clear, please consult your ISP.
Optional. If a Secondary DNS Server address is available, enter it.
Specify the bandwidth for transmitting packets on the port.
Specify the bandwidth for receiving packets on the port.
Status:
IP Address:
Subnet Mask:
Displays the status of obtaining an IP address from your ISP.
“Disabled” indicates that the Dynamic IP connection type is not
applied.
“Connecting” indicates that the r
parameters from your ISP.
“Connected” indicates that the router has successfully obtained the
IP parameters from your ISP.
“Disconnected” indicates that the IP address has been manually
released or the request of the router gets no response from your ISP.
Please check your network connection and consult your ISP if this
problem remains.
Displays the IP address assigned by your ISP.
Displays the Subnet Mask assigned by your ISP.
Gateway Address:
Primary DNS:
Secondary DNS:
Displays the Gateway Address assigned by your ISP.
Displays the IP address of your ISP’s Primary DNS.
Displays the IP address of your ISP’s Secondary DNS.
-14-
Page 23
3) PPPoE
If your ISP (Internet Service Provider) has provided the account information for the PPPoE connection,
please choose the PPPoE connection type (Used mainly for DSL Internet service).
Figure 3-9 WAN - PPPoE
The following items are displayed on this screen:
PPPoE Settings
Connection Type:
Select PPPoE if your ISP provides xDSL Virtual Dial-up connection.
Click <Connect> to dial-up to the Internet and obtain the IP address.
Click <Disconnect> to disconnect the Internet connection and release
the current IP address.
-15-
Page 24

Account Name:
Enter the Account Name provided by your ISP. If you are not clear,
established automatically when it is
alive packets
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) is the maximum data unit
k. It can be set in the range of
Optional. Enter the ISP address provided by your ISP. It's null by
Optional. Enter the Service Name provided by your ISP. It's null by
please consult your ISP.
Password:
Active Mode:
PPPoE Advanced
Settings:
Keep Alive:
Enter the Password provided by your ISP.
You can select the proper Active mode according to your need.
Manual: Select this option to manually activate or terminate the
Internet connection by the <Connect> or <Disconnect> button. It is
optimum for the dial-up connection charged on time.
Always-on: Select this option to keep the connection always on.
The connection can be re-
down.
Time-based: Select this option to keep the connection on during
the Active time you set.
Check here to enable PPPoE advanced settings.
Once PPPoE is connected, the router will send keep-
every "Keep Alive Interval" sec and "Keep Alive Retry Times" to make
sure the connection is still alive. If the router does not get the response
from ISP after sending keep-alive packets, then the router will terminate
the connection.
MTU:
transmitted by the physical networ
576-1492. The default MTU is 1480. It is recommended to keep the
default value if no other MTU value is provided by your ISP.
ISP Address:
default.
Service Name:
default.
Primary DNS:
Secondary DNS:
Secondary
Connection:
Enter the IP address of your ISP’s Primary DNS.
Optional. Enter the IP address of your ISP’s Secondary DNS.
Here allows you to configure the secondary connection. Dynamic IP
and Static IP connection types are provided.
-16-
Page 25

Connection Type:
Select the secondary connection type. Options include Disable,
e the IP address of WAN port. If
Dynamic IP is selected, the obtained IP address of WAN port is
If Static IP is selected, configure the subnet address of WAN port. If
“Disabled” indicates that the PPPoE connection type is not
outer is obtaining the IP
Dynamic IP and Static IP.
IP Address:
Subnet Address:
Status:
Upstream
Bandwidth:
Downstream
Bandwidth:
PPPoE Status
If Static IP is selected, configur
displayed.
Dynamic IP is selected, the obtained subnet address of WAN port is
displayed.
Displays the status of secondary connection.
Specify the bandwidth for transmitting packets on the port.
Specify the bandwidth for receiving packets on the port.
Status:
Displays the status of PPPoE connection.
applied.
“Connecting” indicates that the r
parameters from your ISP.
“Connected” indicates that the router has successfully obtained the
IP parameters from your ISP.
“Disconnected” indicates that the connection has been manually
terminated or the request of the router has no response from your
ISP. Please ensure that your settings are correct and your network
is connected well. Consult your ISP if this problem remains.
IP Address:
Gateway Address:
Primary DNS:
Displays the IP address assigned by your ISP.
Displays the Gateway Address assigned by your ISP.
Displays the IP address of your ISP’s Primary DNS.
Secondary DNS:
Displays the IP address of your ISP’s Secondary DNS.
-17-
Page 26
t connection and release the current IP
4) L2TP
If your ISP (Internet Service Provider) has provided the account information for the L2TP connection,
please choose the L2TP connection type.
Figure 3-10 WAN - L2TP
The following items are displayed on this screen:
L2TP Settings
Connection Type:
Select L2TP if your ISP provides a L2TP connection. Click <Connect>
to dial-up to the Internet and obtain the IP address. Click <Disconnect>
to disconnect the Interne
address.
-18-
Page 27

Account Name:
Enter the Account Name provided by your ISP. If you are not clear,
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) is the maximum data unit
established automatically when it is
Select the secondary connection type. Options include Disable,
If Static IP is selected, configure the IP address of WAN port. If
port obtained is
If Static IP is selected, configure the subnet mask of WAN port. If
Dynamic IP is select, the subnet mask of WAN port obtained is
please consult your ISP.
Password:
Server IP:
MTU:
Active Mode:
Enter the Password provided by your ISP.
Enter the Server IP provided by your I S P.
transmitted by the physical network. It can be set in the range of
576-1460. The default MTU is 1460. It is recommended to keep the
default value if no other MTU value is provided by your ISP.
You can select the proper Active Mode according to your need.
Manual: Select this option to manually activate or terminate the
Internet connection by the <Connect> or <Disconnect> button. It is
optimum for the dial-up connection charged on time.
Always-on: Select this option to keep the connection always on.
The connection can be re-
down.
Secondary
Connection:
Connection Type:
IP Address:
Subnet Mask:
Default Gateway:
Here allows you to configure the secondary connection. Dynamic IP
and Static IP connection types are provided.
Dynamic IP and Static IP.
Dynamic IP is selected, the IP address of WAN
displayed.
displayed.
If Static IP is selected, configure the default gateway. If Dynamic IP is
selected, the obtained default gateway is displayed.
Primary DNS/
Secondary DNS:
If Static IP is selected, configure the DNS. If Dynamic IP is selected, the
obtained DNS is displayed.
-19-
Page 28

outer is obtaining the IP
Upstream
Specify the bandwidth for transmitting packets on the port.
Bandwidth:
Downstream
Specify the bandwidth for receiving packets on the port.
Bandwidth:
L2TP Status
Status:
Displays the status of PPPoE connection.
“Disabled” indicates that the L2TP connection type is not applied.
“Connecting” indicates that the r
“Connected” indicates that the router has successfully obtained the
“Disconnected” indicates that the connection has been manually
parameters from your ISP.
IP parameters from your ISP.
terminated or the request of the router has no response from your
ISP. Please ensure that your settings are correct and your network
is connected well. Consult your ISP if this problem remains.
IP Address:
Primary DNS:
Secondary DNS:
Displays the IP address assigned by your ISP.
Displays the IP address of your ISP’s Primary DNS.
Displays the IP address of your ISP’s Secondary DNS.
5) PPTP
If your ISP (Internet Service Provider) has provided the account information for the PPTP connection,
please choose the PPTP connection type.
-20-
Page 29
Select PPTP if your ISP provides a PPTP connection. Click
Figure 3-11 WAN - PPTP
The following items are displayed on this screen:
PPTP Settings
Connection Type:
<Connect> to dial-up to the Internet and obtain the IP address. Click
<Disconnect> to disconnect the Internet connection and release the
current IP address.
Account Name:
Enter the Account Name provided by your ISP. If you are not clear,
please consult your ISP.
Password:
Enter the Password provided by your ISP.
-21-
Page 30

MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) is the maximum data unit
Select the secondary connection type. Options include Disable,
of WAN port. If
Dynamic IP is selected, the IP address of WAN port obtained is
Dynamic IP is select, the subnet mask of WAN port obtained is
Server IP:
MTU:
Active Mode:
Secondary
Connection:
Enter the Server IP provided by your ISP.
transmitted by the physical network. It can be set in the range of
576-1460. The default MTU is 1460. It is recommended to keep the
default value if no other MTU value is provided by your ISP.
You can select the proper Active mode according to your need.
Manual: Select this option to manually activate or terminate the
Internet connection by the <Connect> or <Disconnect> button.
It’s optimum for the dial-up connection charged on time.
Always-on: Select this option to keep the connection always on.
The connection can be re-established automatically when it is
down.
Here allow you to configure the secondary connection. Dynamic IP
and Static IP connection types are provided.
Connection Type:
IP Address:
Subnet Mask:
Default Gateway:
Primary DNS/
Secondary DNS:
Dynamic IP and Static IP.
If Static IP is selected, configure the IP address
displayed.
If Static IP is selected, configure the subnet mask of WAN port. If
displayed.
If Static IP is selected, configure the default gateway. If Dynamic IP is
selected, the obtained default gateway is displayed.
If Static IP is selected, configure the DNS. If Dynamic IP is selected,
the obtained DNS is displayed.
Upstream Bandwidth:
Downstream
Specify the bandwidth for transmitting packets on the port.
Specify the bandwidth for receiving packets on the port.
Bandwidth:
-22-
Page 31

PPTP Status
outer is obtaining the IP
Status:
IP Address:
Primary DNS:
Secondary DNS:
Displays the status of PPTP connection.
“Disabled” indicates that the PPTP connection type is not applied.
“Connecting” indicates that the r
parameters from your ISP.
“Connected” indicates that the router has successfully obtained the
IP parameters from your ISP.
“Disconnected” indicates that the connection has been manually
terminated or the request of the router has no response from your
ISP. Please ensure that your settings are correct and your network
is connected well. Consult your ISP if this problem remains.
Displays the IP address assigned by your ISP.
Displays the IP address of your ISP’s Primary DNS.
Displays the IP address of your ISP’s Secondary DNS.
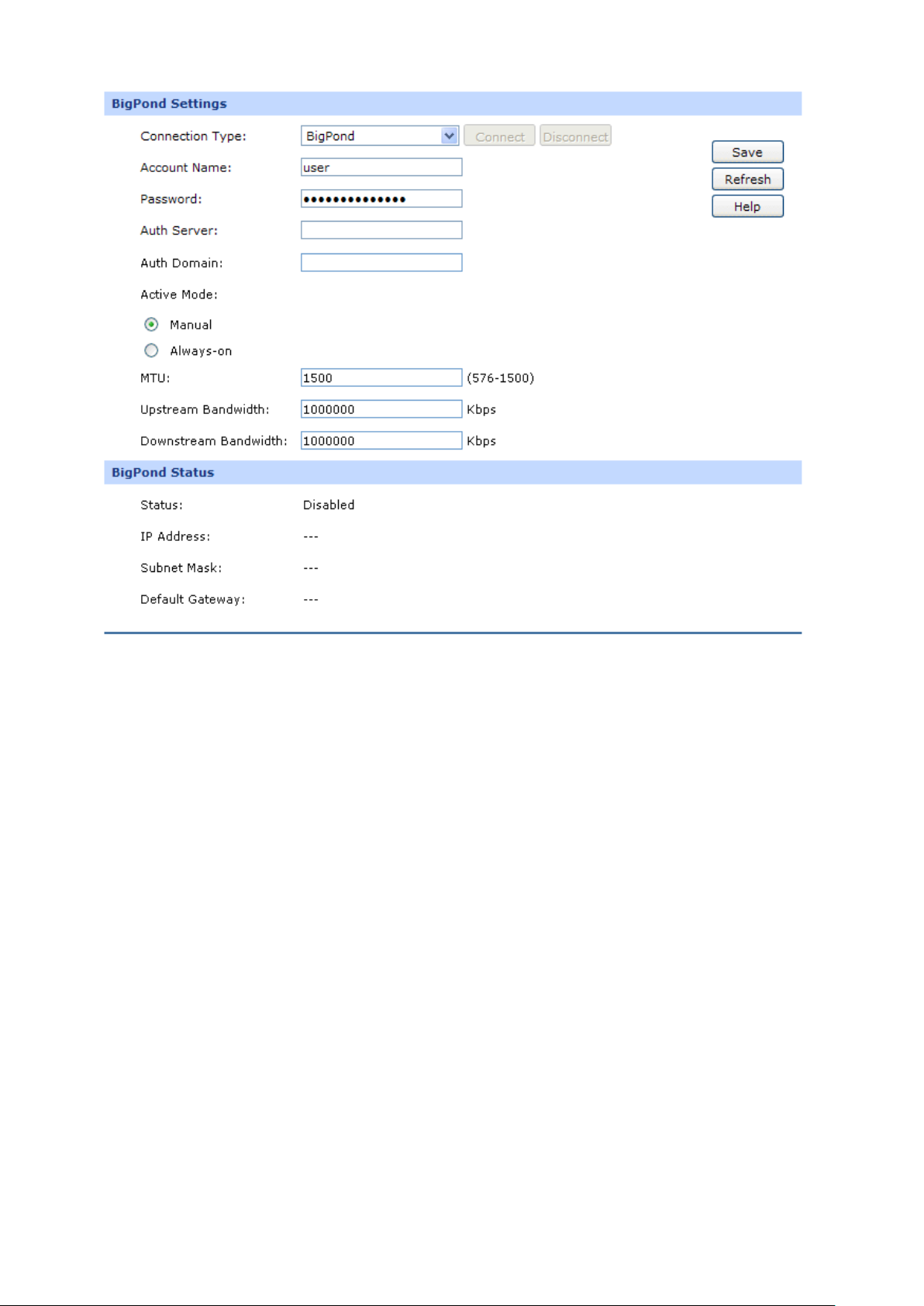
6) BigPond
If your ISP (Internet Service Provider) has provided the account information for the BigPond
connection, please choose the BigPond connection type.
-23-
Page 32
Enter the Password provided by your ISP. If you are not clear,
Figure 3-12 WAN – Bigpond
The following items are displayed on this screen:
BigPond Settings
Connection Type:
Select BigPond if your ISP provides a BigPond connection. Click
<Connect> to dial-up to the Internet and obtain the IP address. Click
<Disconnect> to disconnect the Internet connection and release the
current IP address.
Account Name:
Enter the Account Name provided by your ISP. If you are not clear,
please consult your ISP.
Password:
please consult your ISP.
Auth Server:
Enter the address of authentication server. It can be IP address or
server name.
-24-
Page 33

U (Maximum Transmission Unit) is the maximum data unit
Upstream/Downstream
ad Balance" and "Bandwidth Control" take effect, please set
“Disabled” indicates that the BigPond connection type is not
outer is obtaining the IP
Auth Domain:
Auth Mode:
MTU:
Enter the domain name of authentication server. It's only required
when the address of Auth Server is a server name.
You can select the proper Active mode according to your need.
Manual: Select this option to manually activate or terminate the
Internet connection by the <Connect> or <Disconnect> button.
It is optimum for the dial-up connection charged on time.
Always-on: Select this option to keep the connection always on.
The connection can be re-established automatically when it is
down.
MT
transmitted by the physical network. It can be set in the range of
576-1500. The default MTU is 1500.
Specify the Upstream/Downstream Bandwidth for the port. To make
Bandwidth:
"Lo
these parameters correctly.
BigPond Status
Status:
Displays the status of BigPond connection.
applied.
“Connecting” indicates that the r
parameters from your ISP.
“Connected” indicates that the router has successfully obtained the
IP parameters from your ISP.
“Disconnected” indicates that the connection has been manually
terminated or the request of the router has no response from your
ISP. Please ensure that your settings are correct and your network
is connected well. Consult your ISP if this problem remains.
IP Address:
Subnet Mask:
Displays the IP address assigned by your ISP.
Displays the Subnet Mask assigned by your ISP.
-25-
Page 34
Default Gateway:
Note:
To ensure the BigPond connection re-established normally, please restart the connection at least 5
seconds after the connection is off.
Displays the IP address of the default gateway assigned by your ISP.
3.1.4 LAN
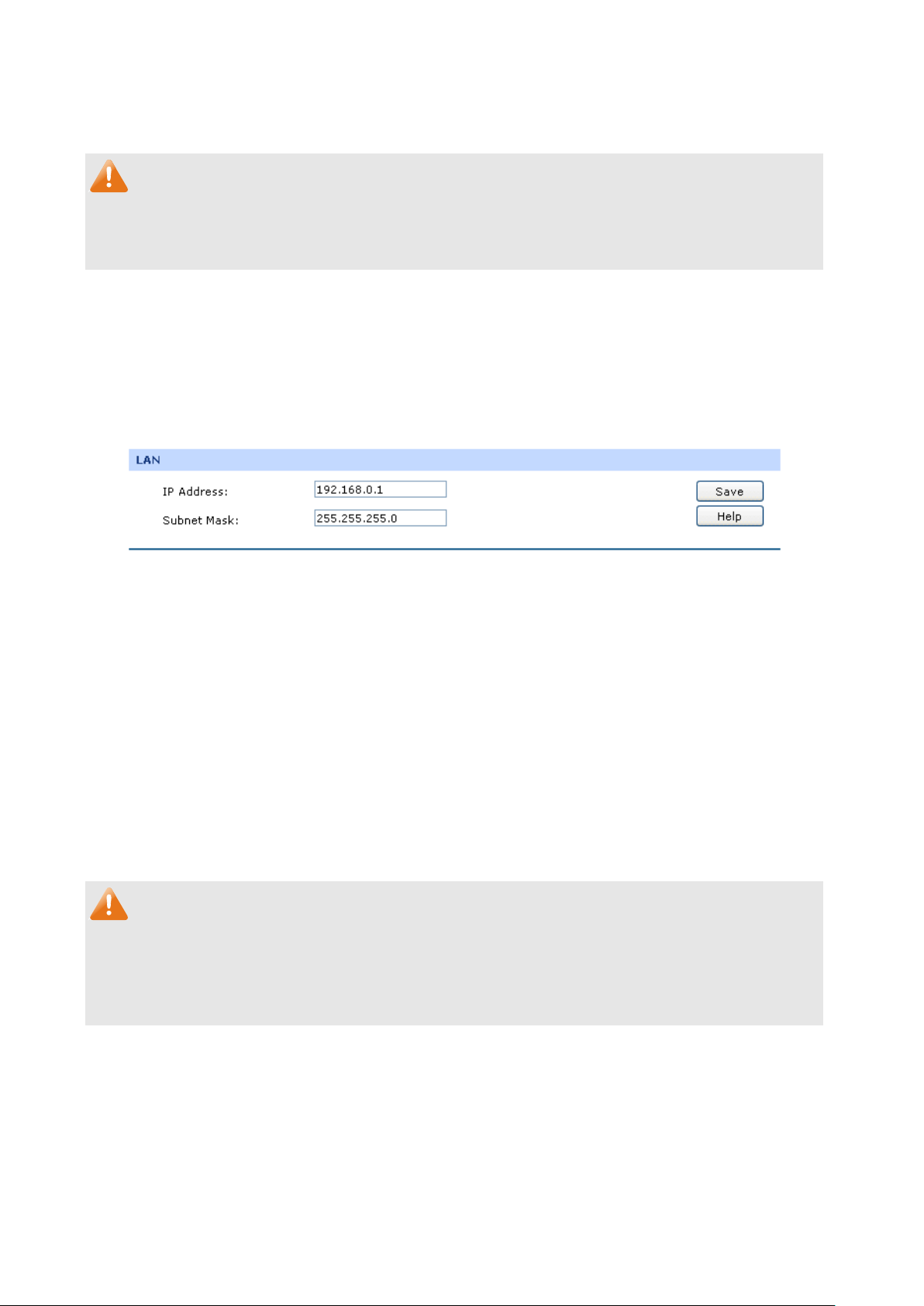
3.1.4.1 LAN
On this page, you can configure the parameters for LAN port of this router.
Choose the menu Network→LAN→LAN to load the following page.
Figure 3-13 LAN
The following items are displayed on this screen:
LAN
IP Address:
Subnet Mask:
Note:
If the LAN IP address is changed, you must use the new IP address to login the router. To guarantee a
normal communication, be sure to set the Gateway address and the Subnet Mask of the Hosts on the
LAN to the new LAN IP address and the Subnet Mask of the router.
Enter the LAN IP address of the router. 192.168.0.1 is the default IP
address. The Hosts in LAN can access the router via this IP address. It
can be changed according to your network.
Enter the Subnet Mask. The default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
3.1.4.2 DHCP
The router with its DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server enabled can automatically
assign an IP address to the computers in the local area network.
Choose the menu Network→LAN→DHCP to load the following page.
-26-
Page 35
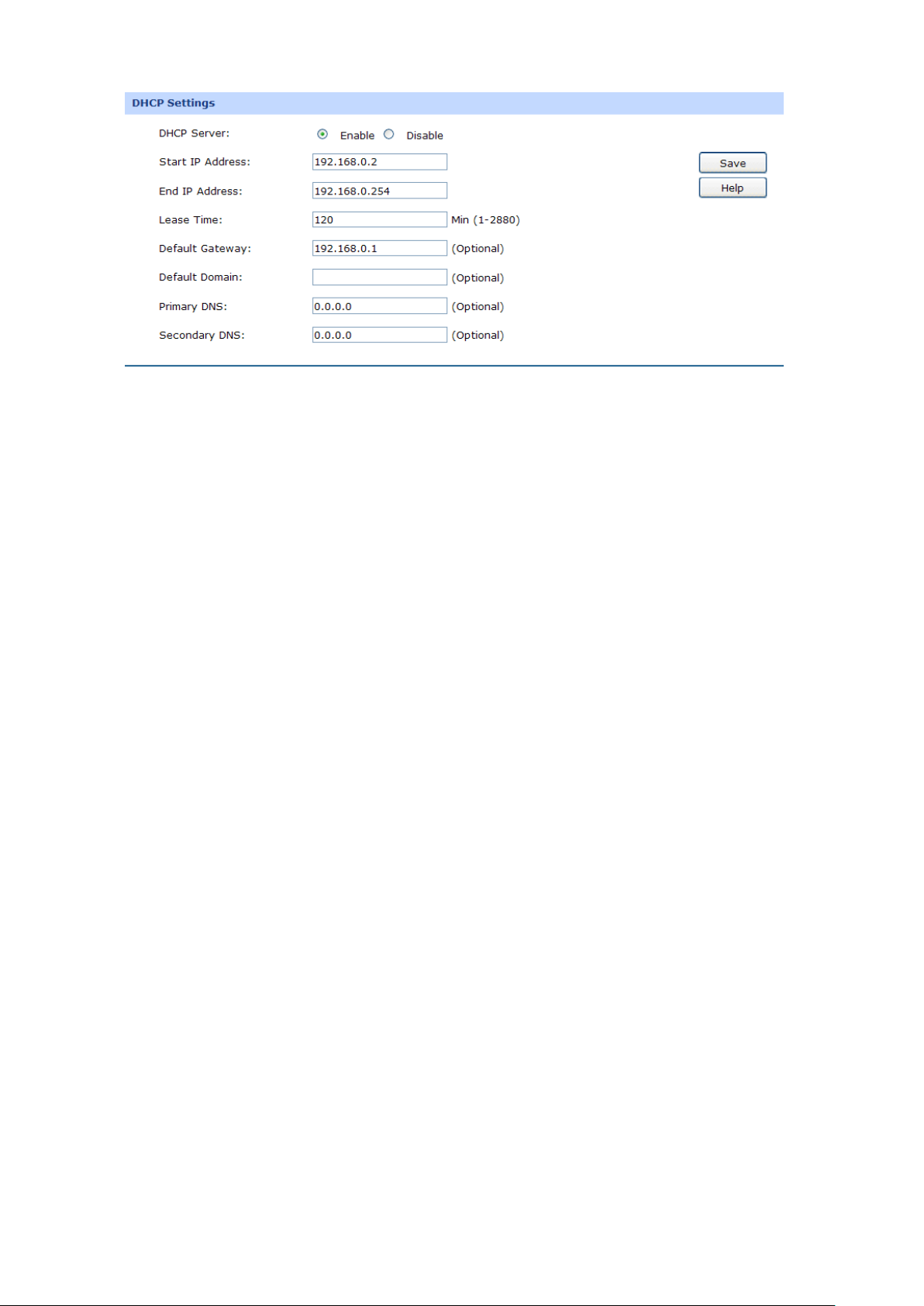
Figure 3-14 DHCP Settings
arameters to the computers in the LAN
for each computer. After the IP address expired, the client will be
ter the Gateway address to be assigned. It is
The following items are displayed on this screen:
DHCP Settings
DHCP Server:
Start IP Address:
End IP Address:
Lease Time:
Enable or disable the DHCP server on your router. To enable the router
to assign the TCP/IP p
automatically, please select Enable.
Enter the Start IP address to define a range for the DHCP server to
assign dynamic IP addresses. This address should be in the same IP
address subnet with the router’s LAN IP address. The default address
is 192.168.0.2.
Enter the End IP address to define a range for the DHCP server to
assign dynamic IP addresses. This address should be in the same IP
address subnet with the router’s LAN IP address. The default address
is 192.168.0.254.
Specify the length of time the DHCP server will reserve the IP address
automatically assigned a new one.
Default Gateway:
Optional. En
recommended to enter the IP address of the LAN port of the router.
Default Domain:
Optional. Enter the domain name of your network.
-27-
Page 36
Primary DNS:
Secondary DNS:
Optional. Enter the Primary DNS server address provided by your ISP.
It is recommended to enter the IP address of the LAN port of the router.
Optional. If a Secondary DNS Server address is available, enter it.
3.1.4.3 DHCP Client
On this page, you can view the information about all the DHCP clients connected to the router.
Choose the menu Network→LAN→DHCP Client to load the following page.
Figure 3-15 DHCP Client
You can view the information of the DHCP clients in this table. Click the <Refresh> button for the
updated information.
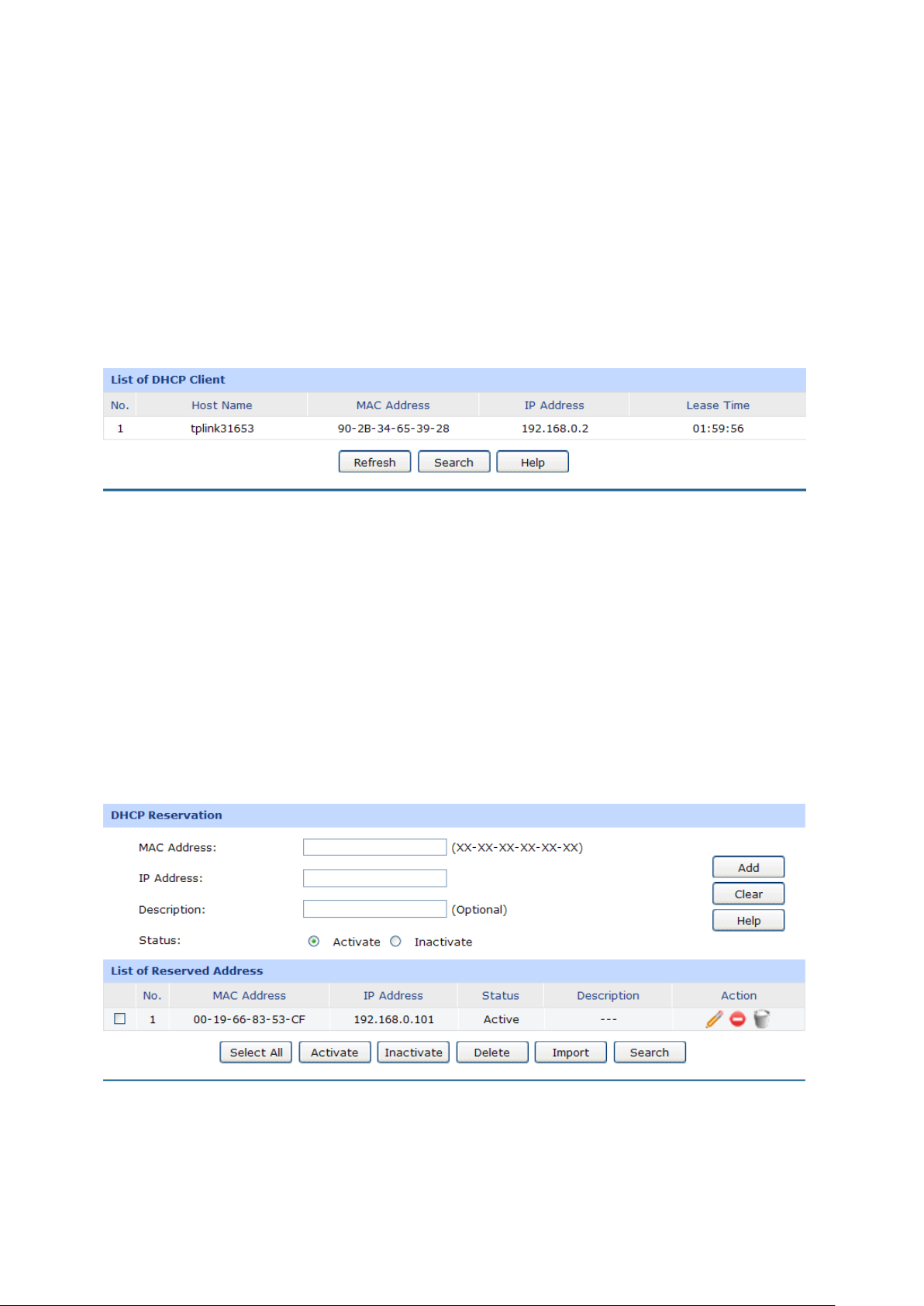
3.1.4.4 DHCP Reservation
DHCP Reservation feature allows you to reserve an IP address for the specified MAC address. The
client with this MAC address will always get the same IP address every time when it accesses the
DHCP server.
Choose the menu Network→LAN→DHCP Reservation to load the following page.
Figure 3-16 DHCP Reservation
-28-
Page 37
The following items are displayed on this screen:
DHCP Reservation
MAC Address:
IP Address:
Description:
Status:
List of Reserved Address
In this table, you can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
The first entry in Figure 3-16 indicates: The IP address 192.168.0.101 is reserved for the
computer with the MAC address 00-19-66-83-53-CF, and this entry is activated.
Enter the MAC address of the computer for which you want to reserve
the IP address.
Enter the reserved IP address.
Optional. Enter a description for the entry. Up to 28 characters can be
entered.
Activate or Inactivate the corresponding entry.
Note:
It's recommended that users bind the IP address and the MAC address in 3.5.1.1 IP-MAC Binding ,
then import the entries from the IP-MAC binding table to the List of Reserved Address in buck by
clicking the <Import> button in Figure 3-16 DHCP Reservation.
3.1.5 IPTV
On this page, you can set up the IPTV function.
Choose the menu Network→IPTV→IPTV to load the page.
Figure 3-17 IPTV
-29-
Page 38
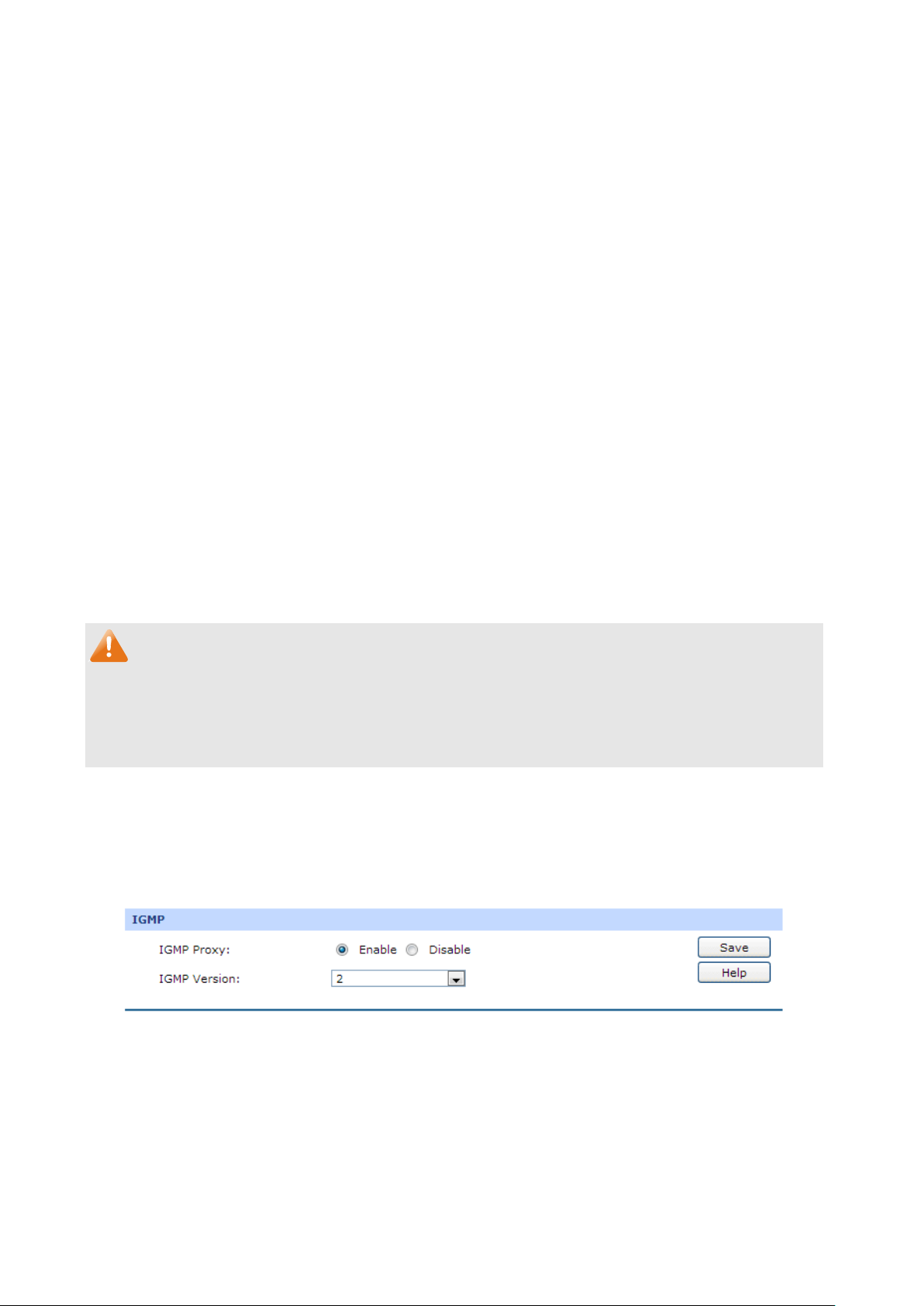
The following items are displayed on this screen:
IGMP
IGMP Proxy:
IGMP Version:
Tips:
Among the WAN ports, only WAN1(Port1) can be used for IPTV service.
When IGMP Proxy option is enabled, you need to ensure the Block IP options under the
Firewall→Attack Defense→Attack Defense is not selected.
If the data traffic is heavy when you use IPTV function, it is recommended to increase the
parameters of Stationary source UDP Flood and Multi-connections UDP Flood on the page of
Firewall→Attack Defense→Attack Defense, or deselect the options.
IGMP Proxy is to act as a multicast proxy for hosts on the LAN side. It
is recommended to enable the IGMP Proxy, otherwise you will not be
able to use IPTV service.
You can choose the highest IGMP version that the system supports:
IGMPv2 or IGMPv3.
3.1.6 MAC Address
The MAC (Media Access Control) address, as the unique identifier of the router in network, does not
need to be changed commonly.
Set the MAC Address for LAN port:
In a complex network topology with all the ARP bound devices, if you want to use TL-ER604W instead
of the current router in a network node, you can just set the MAC address of TL-ER604W‘s LAN port
the same to the MAC address of the previous router, which can avoid all the devices under this
network node to update their ARP binding tables.
Set the MAC Address for WAN port:
In the condition that your ISP has bound the account and the MAC address of the dial-up device, if you
want to change the dial-up device to be TL-ER604W, you can just set the MAC address of
TL-ER604W’s WAN port the same to the MAC address of the previous dial-up device for a normal
Internet connection.
Choose the menu Network→MAC Address→MAC Address to load the following page.
-30-
Page 39

Figure 3-18 MAC Address
button to clone the MAC
The following items are displayed on this screen:
MAC Address
Port:
Current MAC Address:
MAC Clone:
Note:
To avoid a conflict of MAC address on the local area network, it’s not allowed to set the MAC address
of the router’s LAN port to the MAC address of the current management PC.
Displays the port type of the router.
Displays the current MAC address of the port.
It’s only available for WAN port. Click the <Restore Factory MAC>
button to restore the MAC address to the factory default value or
click the <Clone Current PC’s MAC>
address of the PC you are currently using to configure the router.
Then click <Save> to apply.
3.1.7 Switch
Some basic switch port management functions are provided by TL-ER604W, which facilitates you to
monitor the traffic and manage the network effectively.
3.1.7.1 Statistics
Statistics screen displays the detailed traffic information of each port, which allows you to monitor the
traffic and locate faults promptly.
Choose the menu Network→Switch→Statistics to load the following page.
-31-
Page 40
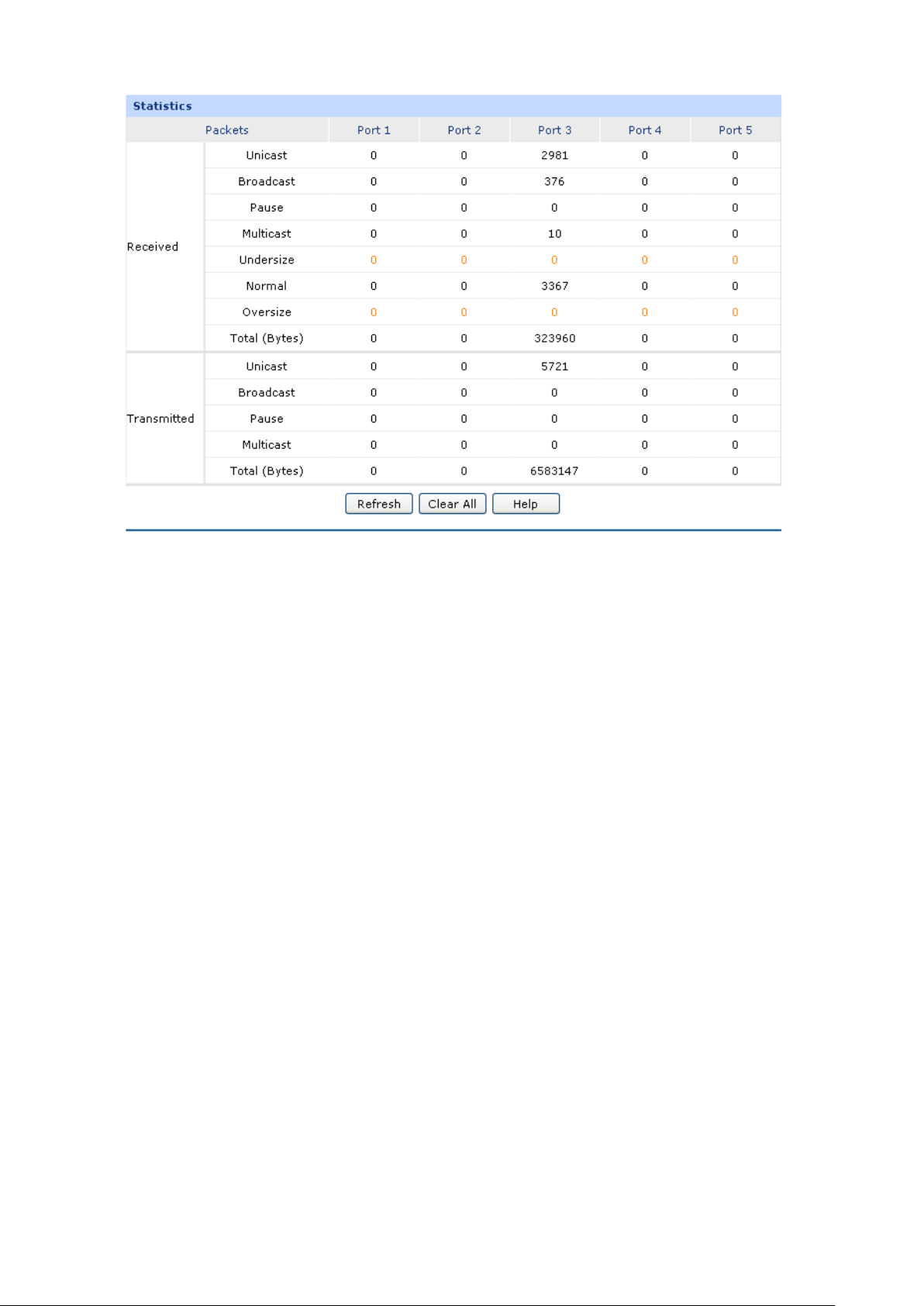
Displays the number of normal broadcast packets received or
Displays the number of normal multicast packets received or
Figure 3-19 Statistics
The following items are displayed on this screen:
Statistics
Unicast:
Displays the number of normal unicast packets received or transmitted
on the port.
Broadcast:
transmitted on the port.
Pause:
Displays the number of flow control frames received or transmitted on
the port.
Multicast:
transmitted on the port.
Undersize:
Displays the number of the received frames (including error frames)
that are less than 64 bytes long.
Normal:
Displays the number of the received packets (including error frames)
that are between 64 bytes and the maximum frame length. The
maximum untagged frame this router can support is 1518 bytes long
and the maximum tagged frame is 1522 bytes long.
-32-
Page 41

Displays the total number of the received or transmitted packets
Oversize:
Displays the number of the received packets (including error frames)
that are longer than the maximum frame.
Total (Bytes):
(including error frames).
Click the <Clear All> button to clear all the traffic statistics.
Tips:
The Port 1/2/3/4/5 mentioned in this User Guide refers to the WAN1/2 port and LAN1/2/3 port on the
router.
3.1.7.2 Port Mirror
Port Mirror, the packets obtaining technology, functions to forward copies of packets from one/multiple
ports (mirrored port) to a specific port (mirroring port). Usually, the mirroring port is connected to a data
diagnose device, which is used to analyze the mirrored packets for monitoring and troubleshooting the
network.
Choose the menu Network→Switch→Port Mirror to load the following page.
Figure 3-20 Port Mirror
The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
Enable Port Mirror:
Check the box to enable the Port Mirror function. If unchecked, it will
be disabled.
-33-
Page 42

When this mode is selected, both the
Mode:
Port Mirror
Mirroring Port:
Mirrored Port:
Select the mode for the port mirror function. Options include:
Ingress: When this mode is selected, only the incoming packets
received by the mirrored port will be copied to the mirroring port.
Egress: When this mode is selected, only the outgoing packets
sent by the mirrored port will be copied to the mirroring port.
Ingress & Egress:
incoming and outgoing packets through the mirrored port will be
copied to the mirroring port.
Select the Mirroring Port to which the traffic is copied. Only one port
can be selected as the mirroring port.
Select the Mirrored Port from which the traffic is mirrored. One or
multiple ports can be selected as the mirrored ports.
The entry in Figure 3-20 indicates: The outgoing packets sent by port 1, port 2, port 3 and port 5
(mirrored ports) will be copied to port 4 (mirroring port).
Application Example
To monitor all the traffic and analyze the network abnormity for an enterprise’s network, please set the
Port Mirror function as below:
1) Check the box before Enable Port Mirror to enable the Port Mirror function and select the
Ingress & Egress mode.
2) Select Port 3 to be the Mirroring Port to monitor all the packets of the other ports.
3) Select all the other ports to be the Mirrored Ports.
4) Click the <Save> button to apply.
-34-
Page 43

3.1.7.3 Rate Control
On this page, you can control the traffic rate for the specific packets on each port so as to manage your
network flow.
Choose the menu Network→Switch→Rate Control to load the following page.
Figure 3-21 Rate Control
The following items are displayed on this screen:
Rate Control
Port:
Ingress Limit:
Ingress Rate:
Egress Limit:
Egress Rate:
The first entry in Figure 3-21 indicates: The Ingress and Egress Limits are enabled for port 1. The
Ingress and Egress Rates are 1Mbps. That is, the receiving rate for the ingress packets will not exceed
1Mbps, and the transmitting rate for all the egress packets will not exceed 1Mbps.
Displays the port number.
Specify whether to enable the Ingress Limit feature.
Specify the limit rate for the ingress packets.
Specify whether to enable Egress Limit feature.
Specify the limit rate for the egress packets.
3.1.7.4 Port Config
On this page, you can configure the basic parameters for the ports.
Choose the menu Network→Switch→Port Config to load the following page.
-35-
Page 44

Figure 3-22 Port Config
The following items are displayed on this screen:
Port Config
Status:
Specify whether to enable the port. The packets can be transported via
this port after being enabled.
Flow Control:
Negotiation Mode:
All Ports:
Allows you to enable/disable the Flow Control function.
Select the Negotiation Mode for the port.
Allows you to configure the parameters for all the ports at one time.
3.1.7.5 Port Status
On this page, you can view the current status of each port.
Choose the menu Network→Switch→Port Status to load the following page.
Figure 3-23 Port Status
-36-
Page 45

3.1.7.6 Port VLAN
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a network topology configured according to a logical scheme
rather than the physical layout, which allows you to divide the physical LAN into multiple logical LANs
so as to control the communication among the ports
The VLAN function can prevent the broadcast storm in LANs and enhance the network security. By
creating VLANs in a physical LAN, you can divide the LAN into multiple logical LANs, each of which
has a broadcast domain of its own. Hosts in the same VLAN communicate with one another as if they
are in a LAN. However, hosts in different VLANs cannot communicate with one another directly.
Therefore, broadcast packets are limited in a VLAN.
TL-ER604W provides the Port VLAN function, which allows you to create multiple logical VLANs for
the LAN ports based on their port numbers.
Choose the menu Network→Switch→Port VLAN to load the following page.
.
Figure 3-24 Port VLAN
The following items are displayed on this screen:
Port VLAN
Network:
VLAN:
Tips:
The Port VLAN can only be created among the LAN ports.
Only the ports in the same VLAN can communicate with each other. The ports in different VLAN
cannot communicate directly.
Displays the current logical network of the physical port.
Select the desired VLAN for the port.
3.2 Wireless
3.2.1 Wireless Setting
3.2.1.1 Wireless Setting
On this page you can configure the basic parameters of the wireless network.
-37-
Page 46

down list. This field specifies the region
outer can be used. It may be illegal to
outer in a region other than one of those
is field. If your country or region is not listed, please contact
Choose the menu Wireless→Wireless Setting→Wireless Setting to load the following page.
Figure 3-25 Wireless Setting
The following items are displayed on this screen:
Wireless Setting
Wireless:
Region:
Enable or disable the Wireless function.
Select your region from the drop-
where the wireless function of the r
use the wireless function of the r
specified in th
your local government agency for assistance.
-38-
Page 47

Channel:
This field determines which operating frequency will be used. The default
nel
automatically. It is not necessary to change the wireless channel unless you
Select if you are using both 802.11b and 802.11g wireless
d 11n
Select the desired wireless mode. When 802.11b mode is selected, only
outer. When 802.11g mode is
outer. When
selected, only 802.11n wireless stations can connect to
,
and all of 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n wireless stations can connect to
down list. The default setting is
, which can adjust the channel width for your clients
in
Considering your wireless network security, the default
_XXXXXX (XXXXXX indicates the last unique
outer’s MAC address). This value is
channel is automatic and the router will choose the best chan
notice interference problems with another nearby access point.
Mode:
Select the desired mode.
11b only - Select if all of your wireless clients are 802.11b.
11g only - Select if all of your wireless clients are 802.11g.
11n only- Select only if all of your wireless clients are 802.11n.
11bg mixed -
clients.
11bgn mixed - Select if you are using a mix of 802.11b, 11g, an
wireless clients.
802.11b wireless stations can connect to the r
selected, only 802.11g wireless stations can connect to the r
802.11n mode is
the router. It is strongly recommended that you set the Mode 11bgn mixed
the router.
Channel Width:
Select the channel width from the drop-
automatic
automatically.
Wireless Parameter
SSID:
Enter a name for the wireless network. The same name of SSID
(Service Set Identification) must be assigned to all wireless devices
your network.
SSID is set to be TP-LINK
six numbers of each r
case-sensitive. For example, TEST is NOT the same as test.
Description:
Enter the description for the SSID.
-39-
Page 48

local area for wireless networks to associate with, they will detect the
, the
can isolate wireless
, otherwise select one
down list. It’s strongly recommended to
outer:
WPA/WPA2 and WEP. It is recommend to
The detail information of the three security options will be introduced
PSK security on the
shared key of
SSID Broadcast:
AP Isolation
Security:
Enable or disable the SSID Broadcast. When wireless clients survey the
SSID broadcast by the router. If the SSID Broadcast is enabled
Wireless router will broadcast its name (SSID) on the air.
Enable or disable the AP Isolation. This function
stations in your network from each other. Wireless devices will be able to
communicate with the router but not with each other.
Specify the security option of the wireless network. If you do not want to
use wireless security, select “Disable Security”
Security option from the drop-
choose one of the security options to enable security.
There are three wireless security options supported by the r
WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK,
choose WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK.
below.
1) WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
It’s the WPA/WPA2 authentication type based on pre-shared passphrase. The default security
option of the router is WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK.
Auth Type:
Choose the Auth type of the WPA-PSK/WPA2-
drop-down list. The default setting is Automatic, which can select
WPA-PSK (Pre-shared key of WPA) or WPA2-PSK (Pre-
WPA) automatically based on the wireless station's capability and request.
-40-
Page 49
Temporal Key
automatically
used in the IEEE 802.11 wireless
S is a specification for the encryption of electronic data
The
t PIN code, which is labeled
Group Key Update
Specify the group key update interval in seconds. The value should be 30
security on the
) automatically based
Encryption: Select the Encryption type, including Automatic, TKIP, AES.
The default setting is Automatic, which can select TKIP (
Integrity Protocol) or AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
based on the wireless station's capability and request.
TKIP – TKIP is a security protocol
networking standard.
AES – AE
established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Password:
Period:
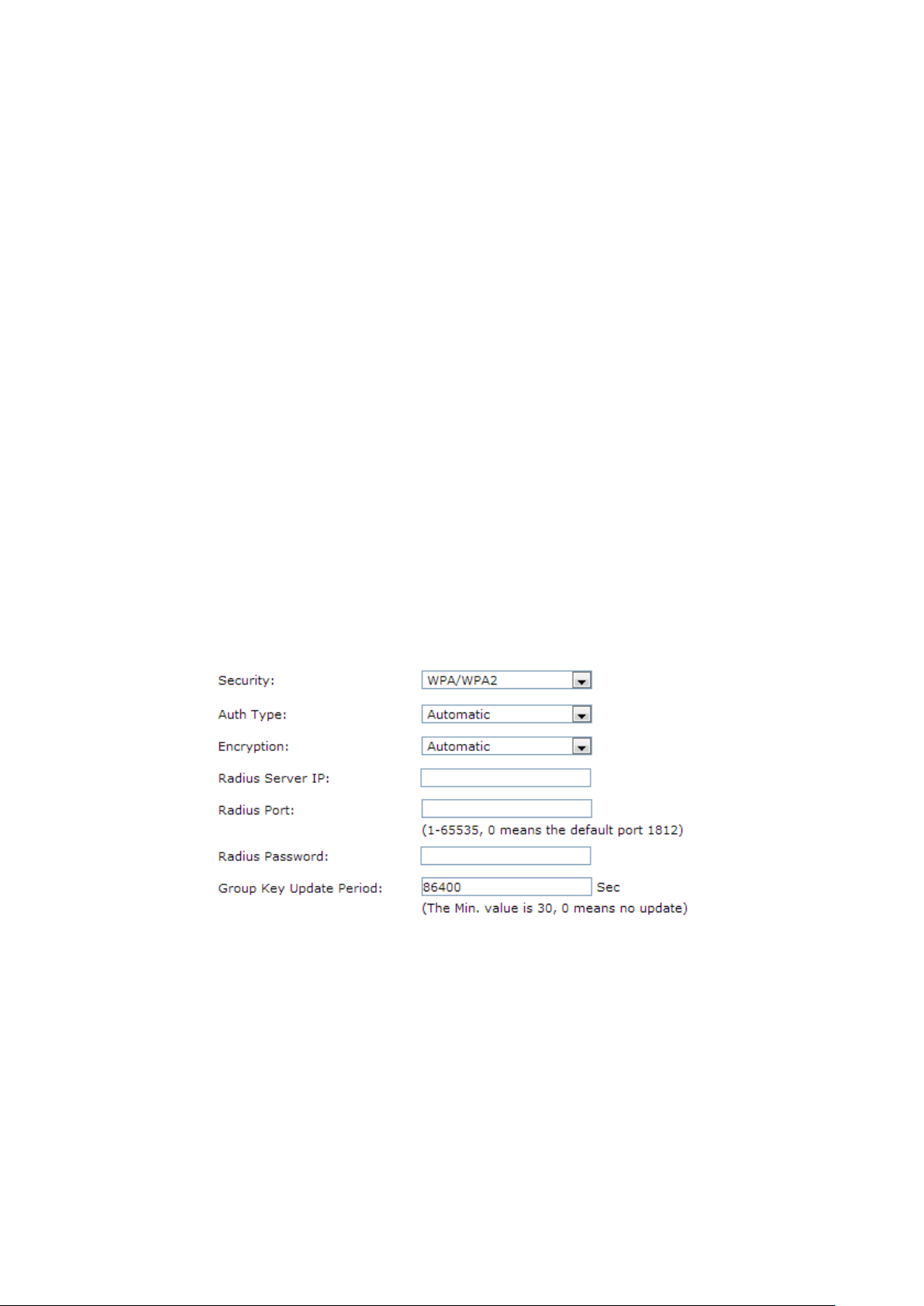
2) WPA/WPA2
It’s based on Radius Server.
Enter 8 to 63 ASCII characters or 8 to 64 Hexadecimal characters.
default password is the same with the defaul
on the bottom of the router
or above. Enter 0 to disable the update.
Auth Type:
You can choose the Auth type of the WPA/WPA2
drop-down list. The default setting is Automatic, which can select WPA
(Wi-Fi Protected Access) or WPA2 (WPA version 2
on the wireless station's capability and request.
-41-
Page 50

Temporal Key
automatically
TKIP is a security protocol used in the IEEE 802.11 wireless
AES is a specification for the encryption of electronic data
Group Key Update
down list.
automatically based on the wireless
Encryption: Select the Encryption type, including Automatic, TKIP, AES.
The default setting is Automatic, which can select TKIP (
Integrity Protocol) or AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
based on the wireless station's capability and request.
TKIP –
networking standard.
AES –
established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Radius Server IP:
Radius Port:
Radius Password:
Enter the IP address of the Radius server.
Enter the port number of the Radius server.
Enter the password for the Radius server.
Specify the group key update interval in seconds. The value should be 30
Period:
or above. Enter 0 to disable the update.
3) WEP
It is based on the IEEE 802.11 standard.
Auth Type:
You can choose the Auth type of the WEP security on the drop-
The default setting is Automatic, which can select Open System or
Shared Key authentication type
station's capability and request.
-42-
Page 51

format
F) in the
format stands for any combination of keyboard
Select which of the four keys will be used and enter the matching WEP
es are identical on all wireless
bit.) for
9,
You can enter 26 hexadecimal digits (any combination of
any combination of
Key Format:
Key Selected:
WEP Key:
Key Type:
Hexadecimal and ASCII formats are provided. Hexadecimal
stands for any combination of hexadecimal digits (0-9, a-f, A-
specified length. ASCII
characters in the specified length.
You can select the key based on need.
key that you create. Make sure these valu
stations in your network.
You can select the WEP key length (64-bit, or 128-bit, or 152-
encryption. "Disabled" means this WEP key entry is invalid.
64-bit - You can enter 10 hexadecimal digits (any combination of 0-
a-f, A-F, zero key is not promoted) or 5 ASCII characters.
128-bit -
0-9, a-f, A-F, zero key is not promoted) or 13 ASCII characters.
152-bit - You can enter 32 hexadecimal digits (
0-9, a-f, A-F, zero key is not promoted) or 16 ASCII characters.
Tips:
The modification of the Wireless Setting will take effect only after the router is rebooted.
The WEP Auth type is not supported by 802.11n mode.
The TKIP is not supported by 802.11n mode. The TKIP cannot be selected if 11n only mode is
selected. The router will not work in 11n mode if bgn mixed mode and TKIP encryption are both
selected. TKIP is an encryption option of the WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK2 and WPA/WPA2 Auth type.
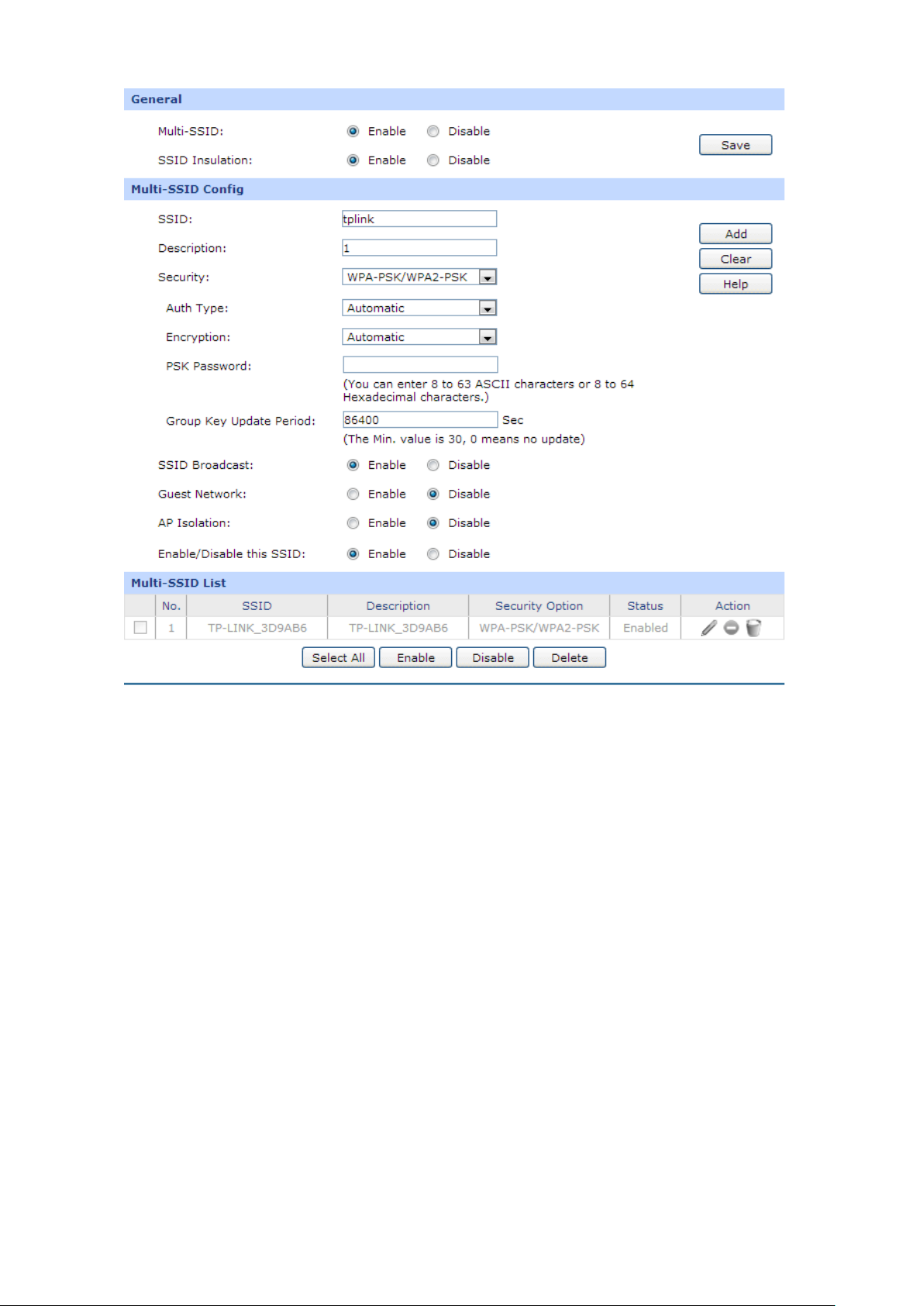
3.2.1.2 Multi-SSID
On this page you can configure the Multi-SSID.
Choose the menu Wireless→Wireless Setting→Multi-SSID to load the following page.
-43-
Page 52
establish multiple wireless
Enable or disable the SSID Insulation. If enabled, the hosts accessing to
Figure 3-26 Multi-SSID
The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
Multi-SSID:
Enable or disable the Multi-SSID. You can
networks if Multi-SSID is enabled.
SSID Insulation:
the different SSID cannot be communicate with each other.
Multi-SSID Config
SSID:
Description:
Specify a name for the wireless network.
Enter a description for this SSID.
-44-
Page 53
Security:
Specify the security option of the wireless network. If you do not want to
“Disable Security”, otherwise select one
down list. It’s strongly recommended to
outer:
The detail information of the three security options will be introduced
,
hosts in this network cannot communicate with the LAN port or other
from each other.
outer but not with
Enable/Disable this
Enable or disable this SSID. If you select this option, the host which
otherwise,
use wireless security, select
Security option from the drop-
choose one of the security options to enable security.
There are three wireless security options supported by the r
WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK, WPA/WPA2 and WEP. It is recommend to choose
WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK.
below.
SSID Broadcast:
Guest Network:
AP Isolation:
SSID
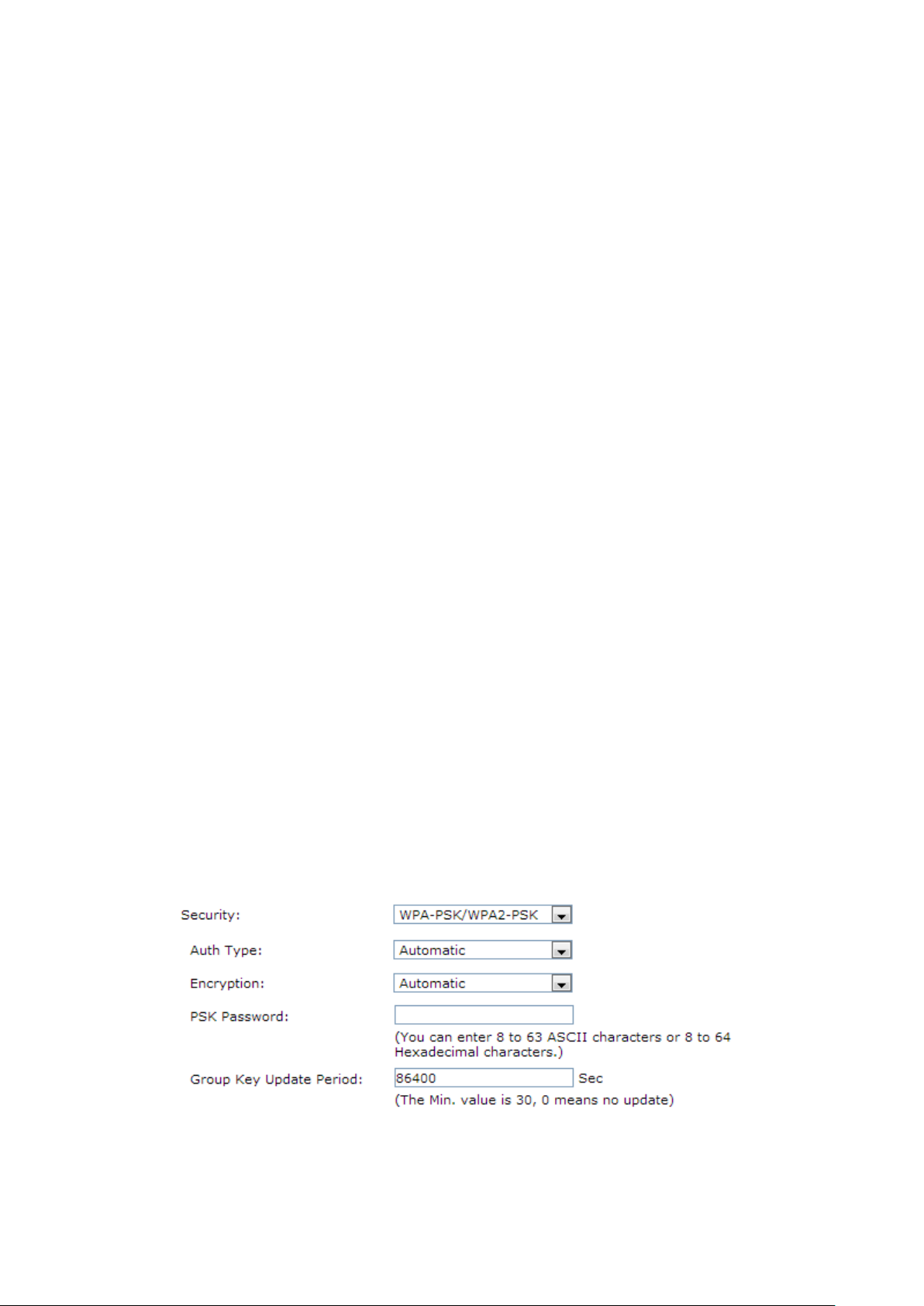
1) WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
Enable or disable the SSID Broadcast. If you enable the SSID Broadcast
the Wireless router will broadcast its name (SSID) on the air.
Enable or disable the Guest Network. If the Guest Network is enabled, the
SSIDs.
This function can isolate wireless stations in your network
Wireless devices will be able to communicate with the r
each other.
passed the validation will be allowed to connect to this SSID;
the router will refuse this host's request.
It’s the WPA/WPA2 authentication type based on pre-shared passphrase.
-45-
Page 54
PSK security on the
shared key of
Temporal Key
automatically
EE 802.11 wireless
AES is a specification for the encryption of electronic data
Group Key Update
You can choose the Auth type of the WPA/WPA2 security on the
) automatically based
Auth Type:
Encryption: Select the Encryption type including Automatic, TKIP, AES.
Password:
Choose the Auth type of the WPA-PSK/WPA2-
drop-down list. The default setting is Automatic, which can select
WPA-PSK (Pre-shared key of WPA) or WPA2-PSK (Pre-
WPA) automatically based on the wireless station's capability and request.
The default setting is Automatic, which can select TKIP (
Integrity Protocol) or AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
based on the wireless station's capability and request.
TKIP – TKIP is a security protocol used in the IE
networking standard.
AES –
established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Enter 8 to 63 ASCII characters or 8 to 64 Hexadecimal characters.
Period:
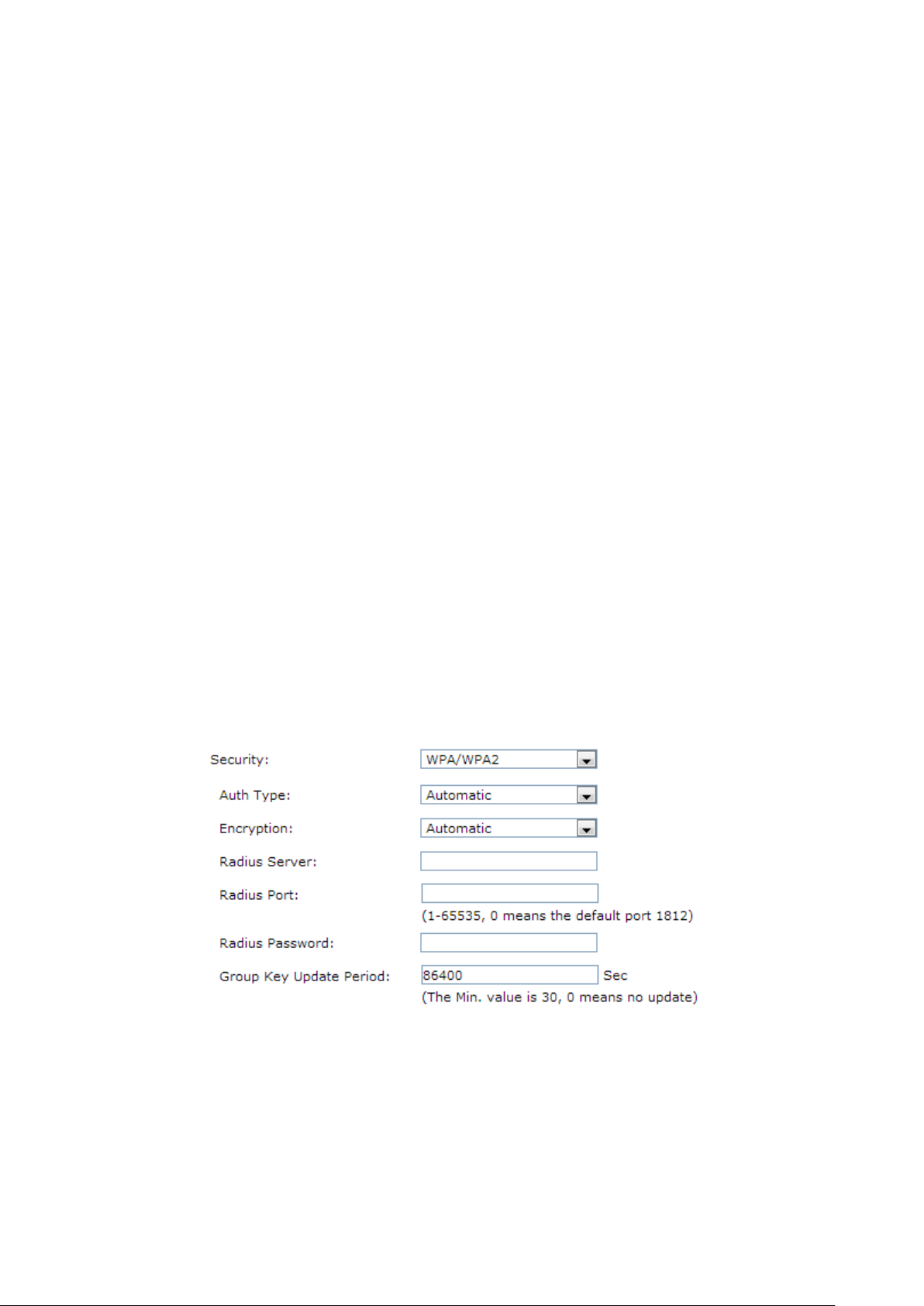
2) WPA/WPA2
It’s based on Radius Server.
Specify the group key update interval in seconds. The value should be 30
or above. Enter 0 to disable the update.
Auth Type:
drop-down list. The default setting is Automatic, which can select WPA
(Wi-Fi Protected Access) or WPA2 (WPA version 2
on the wireless station's capability and request.
-46-
Page 55
Temporal Key
automatically
802.11 wireless
AES is a specification for the encryption of electronic data
Group Key Update
down list.
automatically based on the wireless
Encryption: Select the Encryption type, including Automatic, TKIP, AES.
The default setting is Automatic, which can select TKIP (
Integrity Protocol) or AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
based on the wireless station's capability and request.
TKIP – TKIP is a security protocol used in the IEEE
networking standard.
AES –
established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Radius Server IP:
Radius Port:
Radius Password:
Enter the IP address of the Radius server.
Enter the port number of the Radius server.
Enter the password for the Radius server.
Specify the group key update interval in seconds. The value should be 30
Period:
or above. Enter 0 to disable the update.
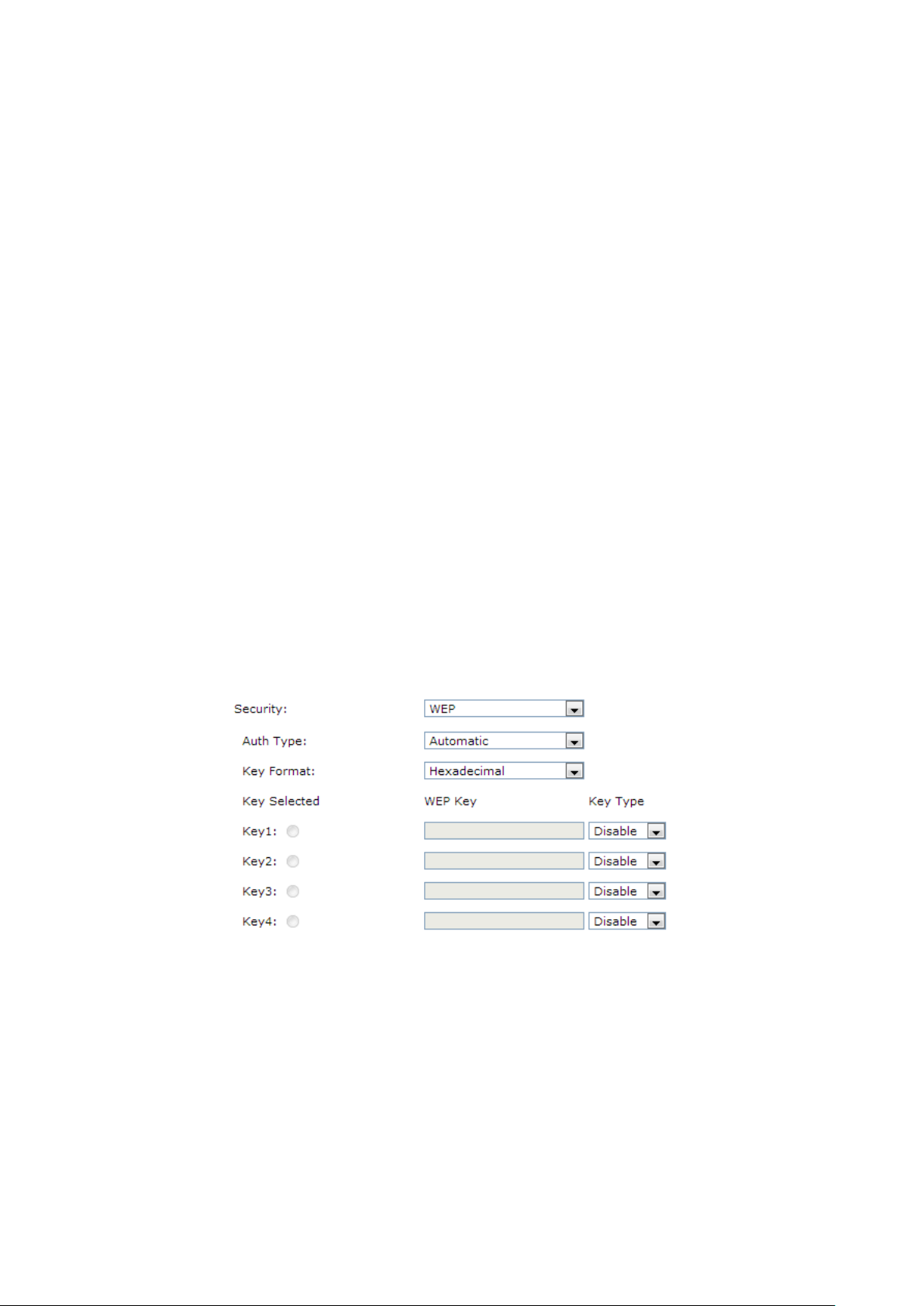
3) WEP
It is based on the IEEE 802.11 standard.
Auth Type:
You can choose the Auth type of the WEP security on the drop-
The default setting is Automatic, which can select Open System or
Shared Key authentication type
station's capability and request.
-47-
Page 56

format
F) in the
format stands for any combination of keyboard
Select which of the four keys will be used and enter the matching WEP
key that you create. Make sure these values are identical on all wireless
bit.) for
9,
You can enter 26 hexadecimal digits (any combination of
You can enter 32 hexadecimal digits (any combination of
Key Format:
Key Selected:
WEP Key:
Key Type:
Hexadecimal and ASCII formats are provided. Hexadecimal
stands for any combination of hexadecimal digits (0-9, a-f, A-
specified length. ASCII
characters in the specified length.
You can select the key based on need.
stations in your network.
You can select the WEP key length (64-bit, or 128-bit, or 152-
encryption. "Disabled" means this WEP key entry is invalid.
64-bit - You can enter 10 hexadecimal digits (any combination of 0-
a-f, A-F, zero key is not promoted) or 5 ASCII characters.
128-bit -
0-9, a-f, A-F, zero key is not promoted) or 13 ASCII characters.
152-bit -
0-9, a-f, A-F, zero key is not promoted) or 16 ASCII characters.
Tips:
The parameters of the host which desires to connect to the router must be the same as the
parameter configured here.
The WEP Auth type is not supported by 802.11n mode.
The TKIP is not supported by 802.11n mode. The TKIP cannot be selected if 11n only mode is
selected. The router will not work in 11n mode if bgn mixed mode and TKIP encryption are both
selected. TKIP is an encryption option of the WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK2 and WPA/WPA2 Auth type.
List of Group
In this table, you can view the information of the multi-SSID and edit them by the Action buttons.
The first entry in Figure 3-26 cannot be configured here. To edit it, please go to 3.2.1.1 Wireless
Setting.
Tips:
The WDS function will be disabled if Multi-SSID is enabled.
UP to 7 new SSIDs can be added to the router.
The router allows only one SSID to use WEP Auth.
-48-
Page 57
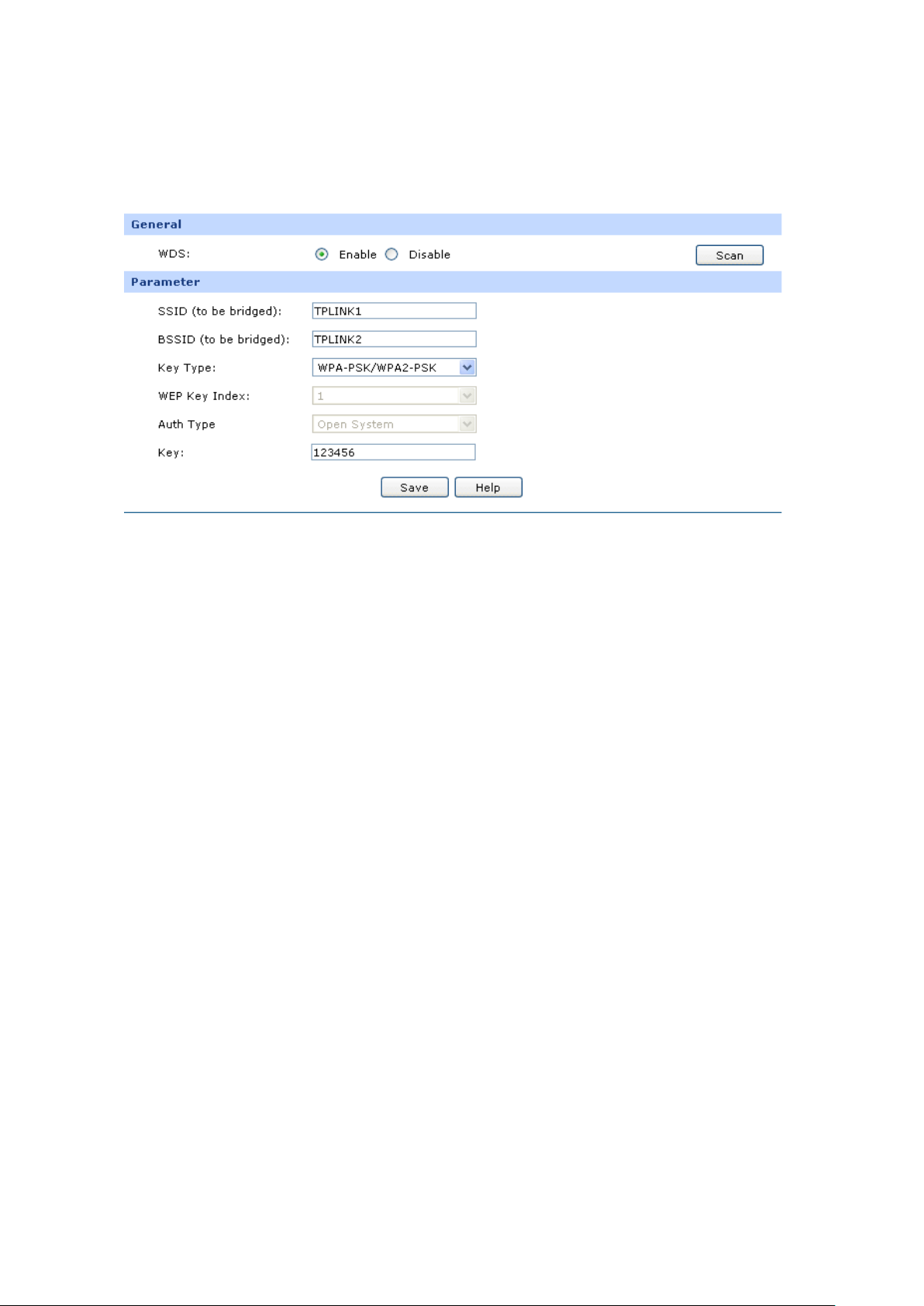
outer can
s
ter is going to connect to as a client. You can
outer is going to connect to as a client. You
be chosen according to the AP's security
configuration. It is recommended that the security type is the same as
3.2.1.3 WDS
With the WDS function, the router can bridge two or more WLANs.
Choose the menu Wireless→Wireless Setting→WDS to load the following page.
Figure 3-27 WDS Configuration
The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
WDS:
Enable or disable the WDS function. With this function, the r
bridge two or more WLANs.
Scan:
Click this button, and you can search the APs that run in the channel
this device supports.
Parameter
SSID(to be bridged):
The SSID of the AP your rou
also use the search function to select the SSID to join.
BSSID(to be bridged):
The BSSID of the AP your r
can also use the search function to select the BSSID to join.
Key Type:
This option should
your AP's security type
-49-
Page 58

This option should be chosen if the key type is WEP (ASCII) or WEP
This option should be chosen if the key type is WEP (ASCII) or WEP
outer is going to connect needs password, you need to fill
priority
to enable
WEP Key Index:
(HEX).It indicates the index of the WEP key.
Auth Type:
(HEX).It indicates the authorization type of the Root AP.
Key: If the AP your r
the key in this blank.
Tips:
The Multi-SSID function will be disabled if WDS is enabled.
3.2.1.4 Wireless Advanced
On this page, you can configure the wireless advanced parameters.
Choose the menu Wireless→Wireless Setting→Wireless Advanced to load the following page.
Figure 3-28 Wireless Advanced
The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
WMM: WMM (Wi-Fi MultiMedia) can guarantee the packets with high-
messages transmitted preferentially. You are recommended
this function.
-50-
Page 59

Short GI:
This function will increase the data capacity by reducing the guard
outer. You can select High,
Middle or Low which you would like. High is the default setting and is
n Interval here.
The beacons are the packets sent by the router to synchronize a
wireless network. Beacon Interval value determines the time interval of
Threshold. If the
packet is larger than the specified RTS Threshold size, the router will
send RTS frames to a particular receiving station and negotiate the
aximum size determining whether packets will be
fragmented. Setting the Fragmentation Threshold too low may result in
poor network performance since excessive packets. 2346 is the default
he interval of the Delivery Traffic Indication
of
the next window for listening to broadcast and multicast messages.
outer has buffered broadcast or multicast messages for
ated clients, it sends the next DTIM with a DTIM Interval value.
255 Beacon Intervals. The default
value is 1, which indicates the DTIM Interval is the same as Beacon
Wireless Advanced
interval time. You are recommended to enable it.
Transmit Power:
Beacon Interval:
RTS Threshold:
Fragmentation
Threshold:
Here you can specify the transmit power of r
recommended.
Enter a value between 40-1000 milliseconds for Beaco
the beacons. The default value is 100.
Here you can specify the RTS (Request to Send)
sending of a data frame. The default value is 2346.
This value is the m
setting and is recommended.
DTIM Interval:
This value determines t
Message (DTIM). A DTIM field is a countdown field informing clients
When the r
associ
You can specify the value between 1-
Interval.
Tips:
The modification of the Wireless Advanced will take effect only after the router is rebooted.
3.2.2 MAC Filtering
On this page, you can control the wireless access by configuring the MAC Filtering.
-51-
Page 60

Choose the menu Wireless→MAC Filtering to load the following page.
Figure 3-29 MAC Filtering
The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
Each SSID can be configured the MAC Address Filtering rules. You can select an SSID in the
SSID drop-down list. To create a new SSID, please refer to 3.2.1.2 Multi-SSID.
To control some of the hosts to access the wireless network, it is recommended to select “Enable
Wireless MAC Address Filtering” and select one filtering rule according to need.
Click <Save> button to apply the setting.
Filtering Rules
MAC Address:
Description:
Enter the MAC Address of the host to be filtered.
Enter a description for the entry. Up to 28 characters can be entered.
Rule List
In this table, you can view the information of the Filtering Rules and edit them by the Action
buttons.
3.2.3 Host Status
On this page, you can view the information of all the hosts connected to the wireless network.
Choose the menu Wireless→Host Status to load the following page.
-52-
Page 61

outer by
Figure 3-30 Host Status
The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
Select an SSID, the status of the host in this wireless network will display on the following table.
Host Status
MAC Address: Displays the MAC address of the host which access the r
wireless connection.
SSID: Displays the name of the SSID to which the host connects.
Current Status: Displays the Status of the wireless connection.
Received Packets: Displays the total packets received by the host.
Transmitted Packets: Displays the total packets transmitted by the host.
Bytes Tx: Displays the total bytes transmitted by the host.
Bytes Rx: Displays the total bytes received by the host.
Rate Tx: Displays the rate for transmitting data frames.
Rate Rx: Displays the rate for receiving data frames.
3.3 User Group
The User Group function is used to group different users for unified management, so that you can
perform other applications such as Bandwidth Control, Session Limit, and Access Control etc. on per
group.
3.3.1 Group
On this page you can define the group for management.
Choose the menu User Group→Group to load the following page.
-53-
Page 62

t be the network address or
Figure 3-31 Group Configuration
The following items are displayed on this screen:
Group Config
Group Name: Specify a unique name for the group.
Description: Give a description for the group. It's optional.
List of Group
In this table, you can view the information of the Groups and edit them by the Action buttons.
3.3.2 User
On this page, you can configure the User for the group.
Choose the menu User Group→User to load the following page.
Figure 3-32 User Configuration
The following items are displayed on this screen:
User Config
User Name:
IP Address:
Specify a unique name for the user.
Enter the IP Address of the user. It canno
broadcast address of the port.
-54-
Page 63

Click this button to view the tree structure of this group. All the members of
Groups. The Group
Description:
List of User
Give a description to the user for identification. It's optional.
In this table, you can view the information of the Users and edit them by the Action buttons.
3.3.3 View
On this page, you can configure the User View or Group View.
Choose the menu User Group→View to load the following page.
Figure 3-33 View Configuration
The following items are displayed on this screen:
View Config
View:
User Name:
Available Group:
Selected Group:
Group Name:
Select the desired view for configuration.
Select the name of the desired User.
Displays the Groups that the User can join.
Displays the Groups to which this User belongs.
Select the name of the desired Group.
Group Structure:
this group will be displayed, including Users and sub-
Names are displayed in bold.
-55-
Page 64
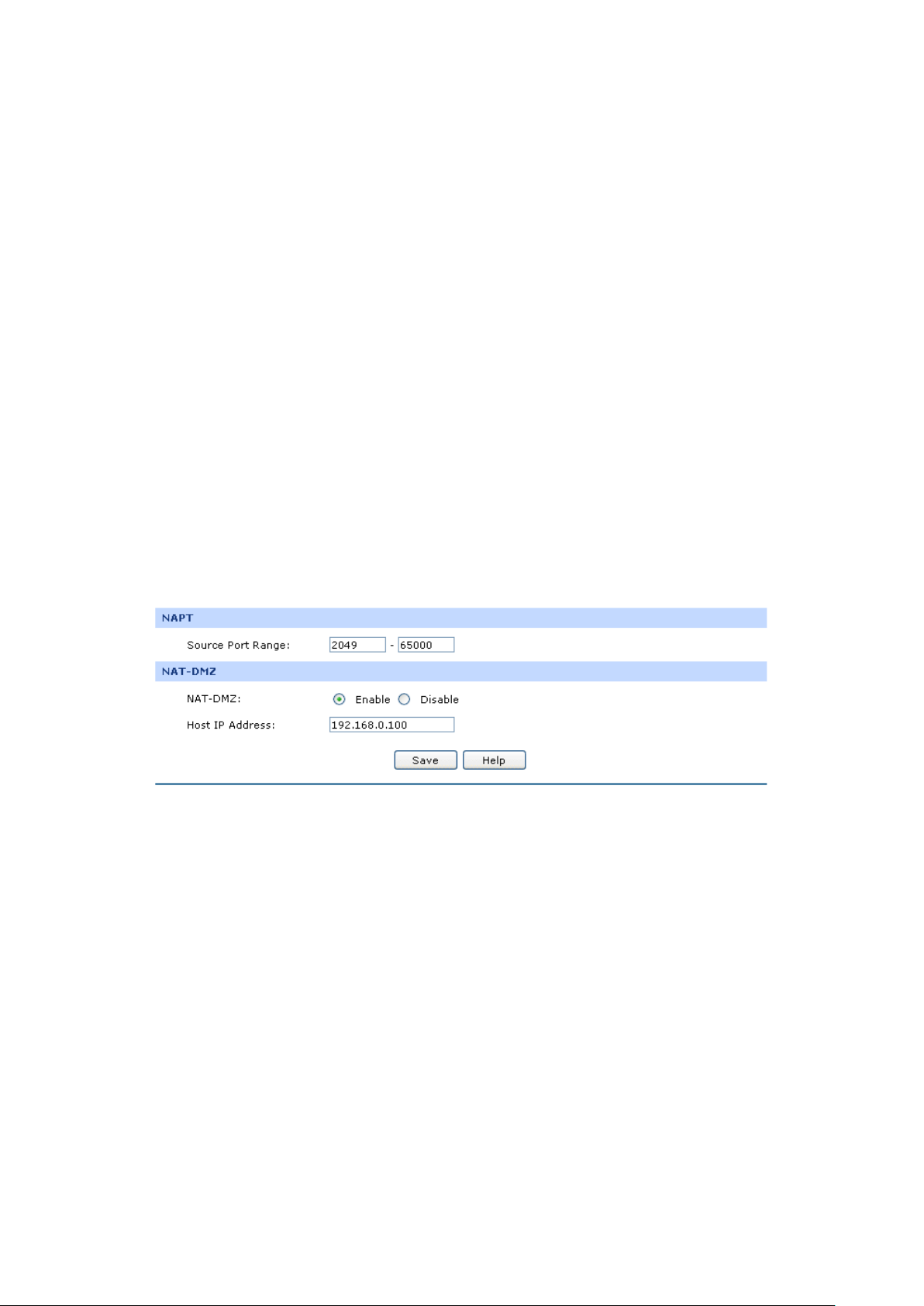
ich
DMZ. NAT DMZ is a special service of NAT
application, which can be considered as a default forwarding rule. When
NAT DMZ (Pseudo DMZ) is enabled, all the data initiated by external
Available Member:
Selected Member:
Displays the Users and the Groups which can be added into this group.
Displays the members of this group, including Users and Groups.
3.4 Advanced
3.4.1 NAT
NAT (Network Address Translation) is the translation between private IP and public IP, which allows
private network users to visit the public network using private IP addresses.
With the explosion of the Internet, the number of available IP addresses is not enough. NAT provides a
way to allow multiple private hosts to access the public network with one public IP at the same time,
which alleviates the shortage of IP addresses. Furthermore, NAT strengthens the LAN (Local Area
Network) security of the network since the address of LAN host never appears on the Internet.
3.4.1.1 N AT Setup
On this page, you can set up the NAT function.
Choose the menu Advanced→NAT →NAT Setup to load the following page.
Figure 3-34 NAT Setup
The following items are displayed on this screen:
NAPT
Source Port Range:
Enter the source port range between 2049 and 65000, the span of wh
must be not less than 100.
NAT-DMZ
NAT-DMZ:
Enable or disable NAT-
network falling short of the current connections or forwarding rules will be
forwarded to the preset NAT DMZ host.
-56-
Page 65
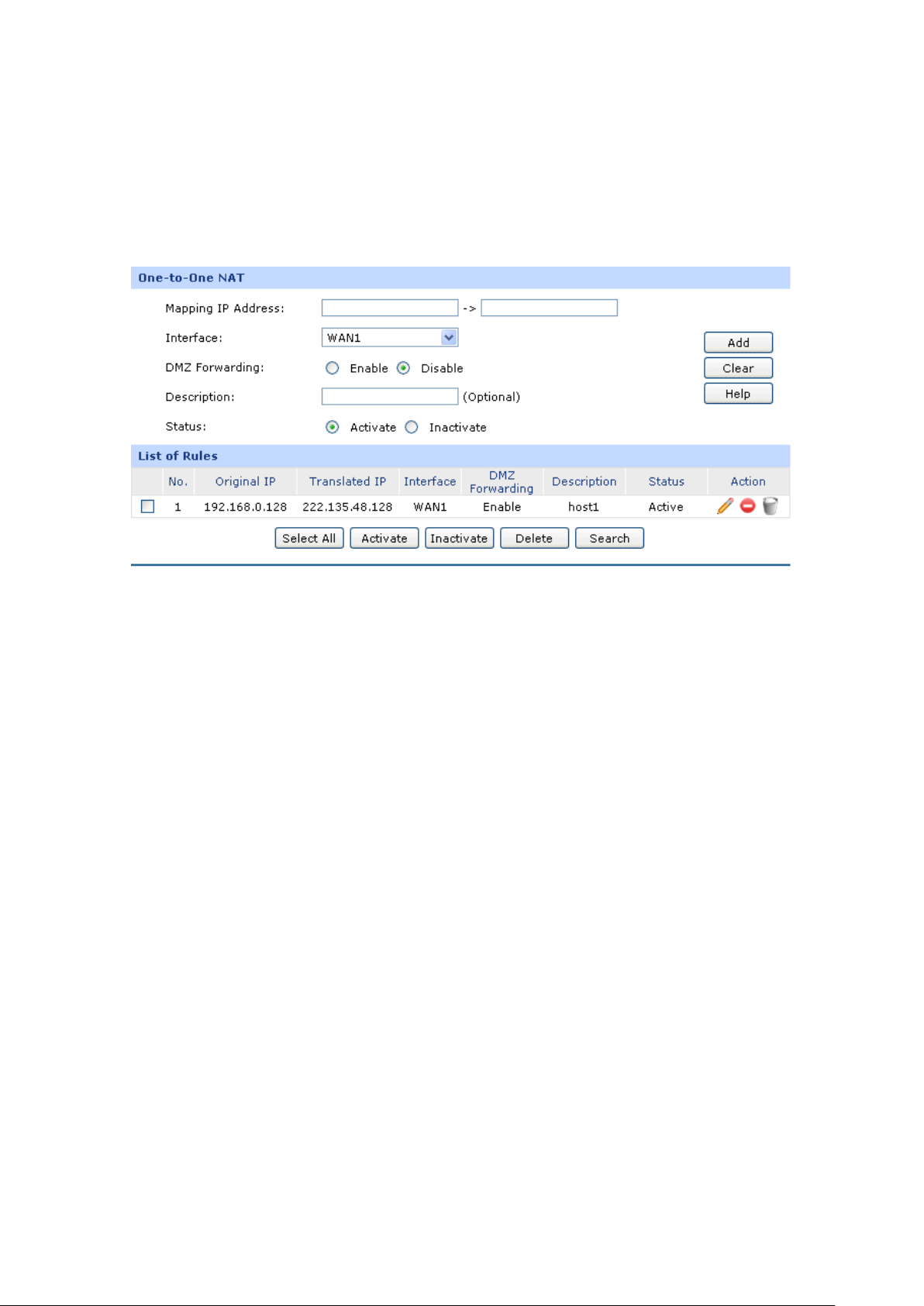
allows mapping from
Enable or disable DMZ Forwarding. The packets transmitted to the
Translated IP Address will be forwarded to the host of Original IP if DMZ
Host IP Address:
Enter the IP address of the host specified as NAT DMZ server.
3.4.1.2 One-to-One NAT
On this page, you can configure the One-to-One NAT.
Choose the menu Advanced→NAT →One-to-One NAT to load the following page.
Figure 3-35 One to One NAT
The following items are displayed on this screen:
One-to-One NAT
Mapping IP Address:
Enter the Original IP Address in the first checkbox and Translated
IP Address in the second checkbox. TL-ER604W
LAN port to WAN port in LAN Mode.
Interface:
Select an interface for forwarding data packets.
DMZ Forwarding:
Forwarding is enabled.
Description:
Status:
Give a description for the entry.
Activate or inactivate the entry.
List of Rules
In this table, you can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
The first entry in Figure 3-35 indicates: The IP address of host1 in local network is 192.168.0.128
and the WAN IP address after NAT mapping is specified to be 222.135.48.128. The data packets
are transmitted from WAN1 port. DMZ Forwarding and this entry are both activated.
-57-
Page 66
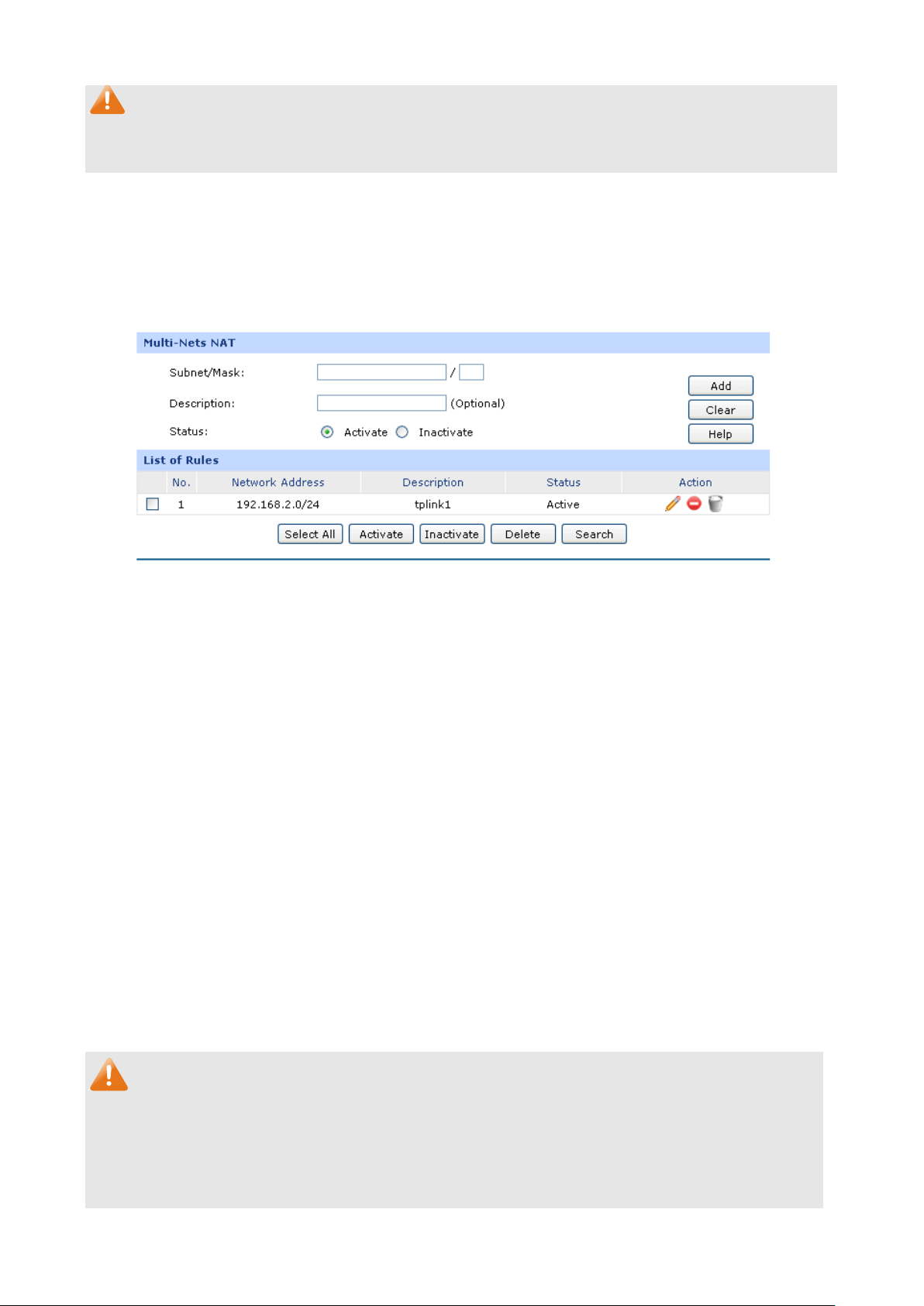
Note:
One-to-One NAT entries take effect only when the Connection Type of WAN is Static IP. Changing the
Connection type from Static IP to other ones will make the entries attached to the interface disabled.
3.4.1.3 Multi-Nets NAT
Multi-Nets NAT function allows the IP under LAN port within multiple subnets to access the Internet via
NAT.
Choose the menu Advanced→NAT →Multi-Nets NAT to load the following page.
Figure 3-36 Multi-Nets NAT
The following items are displayed on this screen:
Multi-Nets NAT
Subnet/Mask:
Description:
Status:
list of Rules
Enter the subnet/mask to make the address range for the entry.
Give a description for the entry.
Activate or inactivate the entry.
You can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
The first entry in Figure 3-36 indicates that: This is a Multi-Nets NAT entry named tplink1. The
subnet under the LAN port of the router is 192.168.2.0/24 and this entry is activated. After the
corresponding Static Route entry is set, the hosts within this subnet can access the Internet
through the router via NAT.
Note:
Multi-Nets NAT entry takes effect only when cooperating with the corresponding Static Route
entries.
For detailed setting of subnet mask, please refer to the Appendix B FAQ.
-58-
Page 67
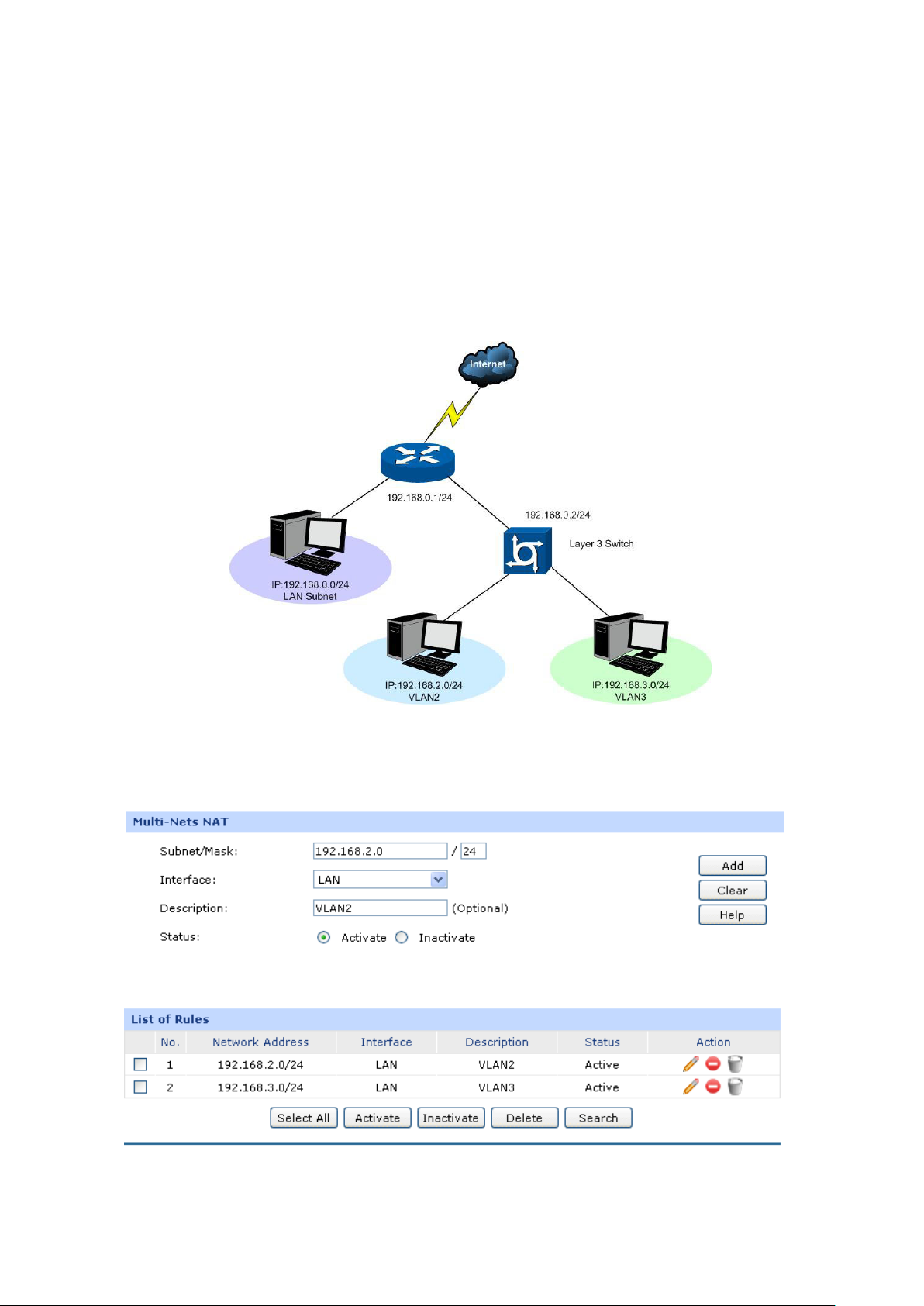
Application Example
Network Requirements
The LAN subnet of TL-ER604W is 192.168.0.0 /24, the subnet of VLAN2 under a three layer switch is
192.168.2.0 /24, while the subnet of VLAN3 is 192.168.3.0 /24. The IP of VLAN for cascading the
switch to the router is 192.168.0.2. Now the hosts within VLAN2 and VLAN3 desire to access the
Internet.
The network topology is shown as the following:
Configuration procedure
1. Establish the Multi-Nets NAT entries with Subnet/Mask of VLAN2 and VLAN3.
The configured entries are as follows:
2. Then set the corresponding Static Route entry, enter the IP address of the interface connecting
the router and the three layer switch into the Next Hop field.
-59-
Page 68
Choose the menu Advanced→Routing→Static Route to load the following page.
The Static Route entry is as follows:
3.4.1.4 Virtual Server
Virtual server sets up public services in your private network, such as DNS, Email and FTP, and
defines a service port. All the service requests to this port will be transmitted to the LAN server
appointed by the router via IP address.
Choose the menu Advanced→NAT→Virtual Server to load the following page.
Figure 3-37 Virtual Server
The following items are displayed on this screen:
Virtual Server
Name:
Enter a name for Virtual Server entries. Up to 28 characters can be
entered.
-60-
Page 69

Interface:
External Port:
Internal Port:
Protocol:
Internal Server IP:
Status:
Note:
Select an interface for forwarding data packets.
Enter the service port or port range the router provided for accessing
external network. All the requests from Internet to this service port or
port range will be redirected to the specified server in local network.
Specify the service port of the LAN host as virtual server.
Specify the protocol used for the entry.
Enter the IP address of the specified internal server for the entry. All the
requests from the Internet to the specified LAN port will be redirected to
this host.
Activate or inactivate the entry.
The External port and Internal Port should be set in the range of 1-65535.
The external ports of different entries should be different, whereas the internal ports can be the
same.
List of Rules
In this table, you can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
The first entry in Figure 3-37 indicates: This is a Virtual Server entry named host, all the TCP data
packets from WAN1 to port 65534-65535 of the router will be redirected to the port 65534-65535
of the LAN host with IP address of 192.168.0.103, and this entry is activated.
3.4.1.5 Port Triggering
Some applications require multiple connections, such as Internet games, video conferencing, Internet
calling, P2P download and so on. Port Triggering is used for those applications requiring multiple
connections.
When an application initiates a connection to the trigger port, all the ports corresponding to the
incoming port will open for follow-up connections.
Choose the menu Advanced→NAT →Port Triggering to load the following page.
-61-
Page 70
Figure 3-38 Port Triggering
Enter the incoming port number or range of port numbers. The
The following items are displayed on this screen:
Port Triggering
Name:
Enter a name for Port Triggering entries. Up to 28 characters can be
entered.
Interface:
Trigger Port:
Select an interface for forwarding data packets.
Enter the trigger port number or the range of port. Only when the trigger
port initiates connection will all the corresponding incoming ports open
and provide service for the applications, otherwise the incoming ports
will not open.
Trigger Protocol:
Select the protocol used for trigger port.
Incoming Port:
incoming port will open for follow-up connection after the trigger port
initiates connection.
Incoming Protocol:
Status:
Select the protocol used for incoming port.
Activate or inactivate the entry.
Note:
The Trigger Port and Incoming Port should be set in the range of 1-65535. The Incoming Port can
be set in a continuous range such as 8690-8696.
-62-
Page 71
. It is
. It is
. It is
It is
The router supports up to 16 Port Triggering entries. Each entry supports at most 5 groups of
trigger ports and overlapping between the ports is not allowed.
Each entry supports at most 5 groups of incoming ports and the sum of incoming ports you set for
each entry should not be more than 100.
List of Rules
In this table, you can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
The first entry in Figure 3-38 indicates that: This is a Port Triggering entry named host1, When the
LAN host initiates a TCP request via port of 5354, and the incoming port 5355 of WAN1 will open
for TCP and UDP protocol. This entry is activated.
3.4.1.6 ALG
Some special protocols such as FTP, H.323, SIP, IPsec and PPTP will work properly only when ALG
(Application Layer Gateway) service is enabled.
Choose the menu Advanced→NAT →ALG to load the following page.
Figure 3-39 ALG
The following items are displayed on this screen:
ALG
FTP ALG:
H.323 ALG:
SIP ALG:
IPsec ALG:
Enable or disable FTP ALG. The default setting is enabled
recommended to keep the default setting if no special requirement.
Enable or disable H.323 ALG. The default setting is enabled. H.323 is
used for various applications such as NetMeeting and VoIP.
Enable or disable SIP ALG. The default setting is enabled
recommended to keep the default setting if no special requirement.
Enable or disable IPsec ALG. The default setting is enabled
recommended to keep default if no special requirement.
PPTP ALG:
Enable or disable PPTP ALG. The default setting is enabled.
recommended to keep default if no special requirement.
-63-
Page 72
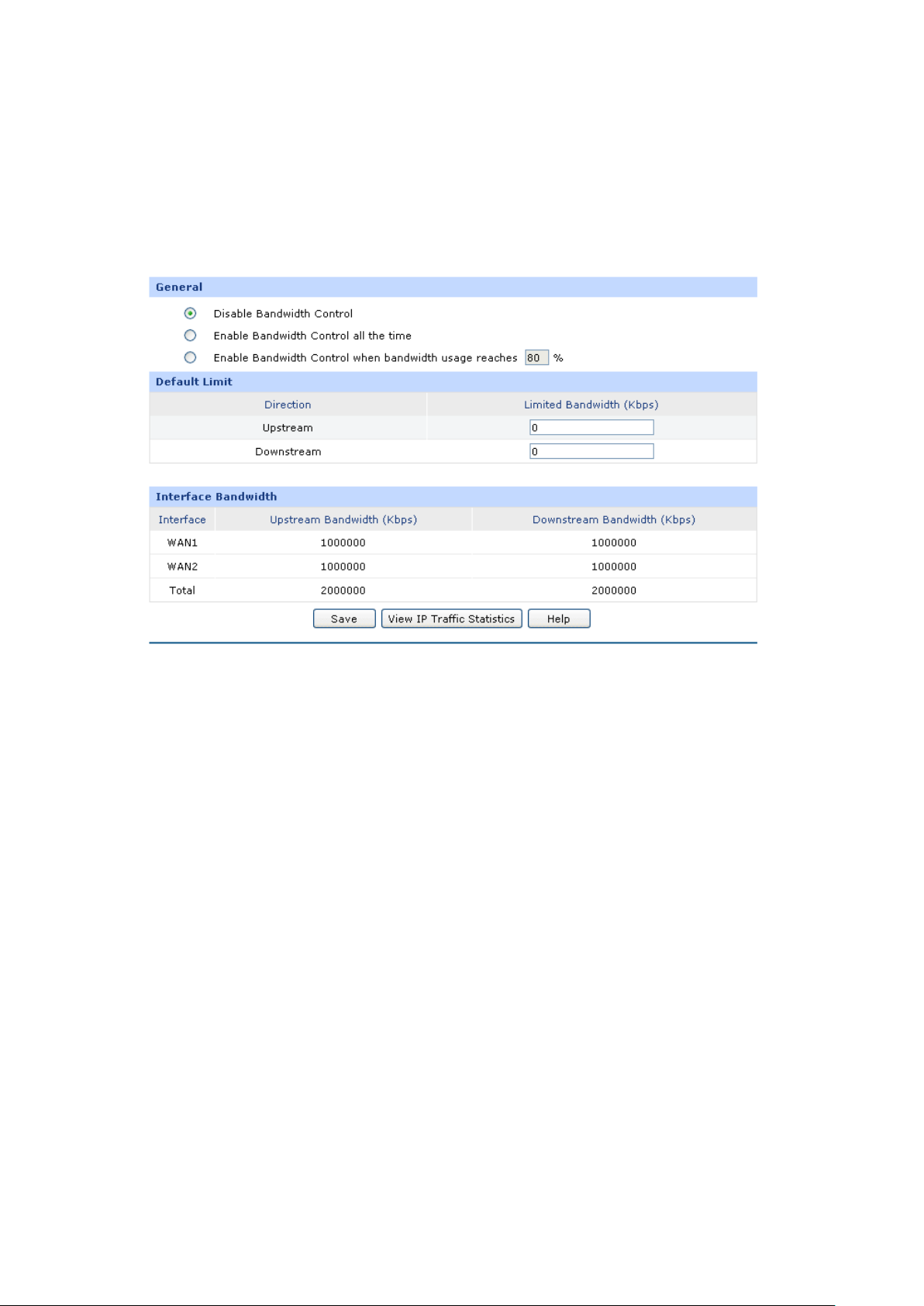
Disable Bandwidth
Default Limit applies only for users that are not constrained by
3.4.2 Traffic Control
Traffic Control functions to control the bandwidth by configuring rules for limiting various data flows. In
this way, the network bandwidth can be reasonably distributed and utilized.
3.4.2.1 Setup
Choose the menu Advanced→Traffic Control→Setup to load the following page.
Figure 3-40 Configuration
The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
Select this option to disable Bandwidth Control.
Control:
Enable Bandwidth
Control all the time:
Enable Bandwidth
Control When:
Default Limit
Select this option to enable Bandwidth Control all the time.
With this option selected, the Bandwidth Control will take effect when
the bandwidth usage reaches the specified value.
Limited Bandwidth:
Bandwidth Control Rules. These users share certain bandwidth with
upper limit configured here. Value 0 means all the remained bandwidth
is available to use.
-64-
Page 73
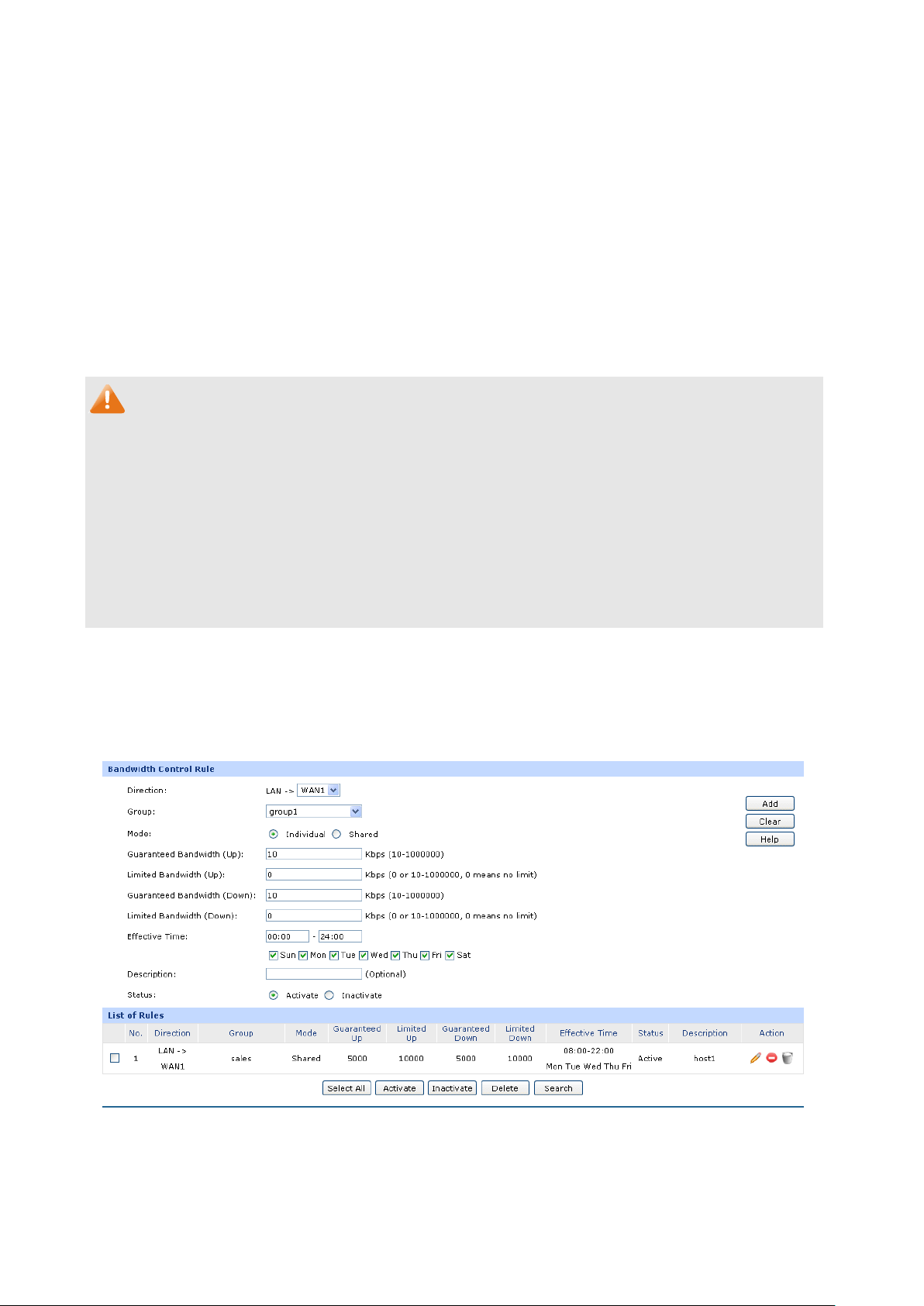
Interface Bandwidth
Displays the bandwidth of each WAN port for receiving data. The
Interface:
Upstream
Bandwidth:
Downstream
Bandwidth:
Note:
The Upstream/Downstream Bandwidth of WAN port you set must not be more than the bandwidth
provided by ISP. Otherwise the Traffic Control will be invalid.
If there are data flowing into the router from interface A and out from interface B while the
downstream bandwidth of A is different from the upstream bandwidth of B, then the smaller one
should be considered as the effective bandwidth, and vice versa.
Displays the current enabled WAN port(s). The Total bandwidth is equal
to the sum of bandwidth of the enabled WAN ports.
Displays the bandwidth of each WAN port for transmitting data. The
Upstream Bandwidth of WAN port can be configured on WAN page.
Downstream Bandwidth of WAN port can be configured on WAN page.
Click the <View IP Traffic Statistics> button to jump to IP Traffic Statistics page.
3.4.2.2 Bandwidth Control
On this page, you can configure the Bandwidth Control function.
Choose the menu Advanced→Traffic Control→Bandwidth Control to load the following page.
Figure 3-41 Bandwidth Control
-65-
Page 74

The following items are displayed on this screen:
direction for the entry. The direction of
ALL means all
Bandwidth Control Rule
Direction:
Group:
Mode:
Guaranteed
Bandwidth (Up):
Limited Bandwidth
(Up):
Select the data stream
arrowhead indicates the data stream direction. WAN-
WAN ports through which the data flow might pass. Individual WAN
port cannot be selected if WAN-ALL rules are added.
Select the group to define the controlled users.
Individual: The bandwidth of each user equals to the current bandwidth
of this entry.
Shared: The total bandwidth of all controlled IP addresses equals to the
current bandwidth of this entry.
Specify the Guaranteed Upstream Bandwidth for this entry.
Specify the Limited Upstream Bandwidth for this entry.
Guaranteed
Specify the Guaranteed Downstream Bandwidth for this entry.
Bandwidth (Down):
Limited Bandwidth
Specify the Limited Downstream Bandwidth for this entry.
(Down):
Effective Time:
Description:
Status:
Specify the time for the entry to take effect.
Give a description for the entry.
Activate or inactivate the entry.
List of Rules
You can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
The first entry in Figure 3-41 indicates: The users within group “group1” share the bandwidth and
the Downstream/Upstream Guaranteed Bandwidth is 5000kbps, while the Downstream/Upstream
Limited bandwidth is 10000kbps. This entry takes effect at 8 a.m. to 10 p.m. from Monday to
Friday.
-66-
Page 75

Note:
The premise for single rule taking effect is that the bandwidth of the interface for this rule is
sufficient and not used up.
It is impossible to satisfy all the guaranteed bandwidth if the total guaranteed bandwidth specified
by all Bandwidth Control rules for certain interface exceeds the physical bandwidth of this
interface.
3.4.3 Session Limit
The amount of TCP and UDP sessions supported by the router is finite. If some local hosts transmit
too many TCP and UDP sessions to the public network, the communication quality of the other local
hosts will be affected, thus it is necessary to limit the sessions of those hosts.
3.4.3.1 Session Limit
On this page, you can configure the session limit to specified PCs.
Choose the menu Advanced→Session Limit→Session Limit to load the following page.
Figure 3-42 Session Limit
The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
Enable Session
Limit:
Session Limit
Group:
Check here to enable Session Limit, otherwise all the Session Limit
entries will be disabled.
Select a group to define the controlled users.
-67-
Page 76

Max. Sessions:
Description:
Status:
List of Session Limit
You can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
The first entry in Figure 3-42 indicates: The amount of maximum sessions for the hosts within
group1 is 100 and this entry is enabled.
Enter the max. Sessions for the users.
Give a description for the entry.
Activate or inactivate the entry.
3.4.3.2 Session List
On this page, you can view the Session Limit information of hosts configured with Session Limit.
Choose the menu Advanced→Session Limit→Session List to load the following page.
Figure 3-43 Session List
In this table, you can view the session limit information of users configured with Session Limit. Click
the <Refresh> button to get the latest information.
3.4.4 Load Balance
In this part, you can configure the traffic sharing mode of the WAN ports to optimize the resource
utilization.
3.4.4.1 Configuration
Choose the menu Advanced→Load Balance→Configuration to load the following page.
Figure 3-44 Configuration
-68-
Page 77

With the box before Enable Application Optimized Routing checked, the router will consider the
source IP address and destination IP address of the packets as a whole and record the WAN port they
pass through. And then the packets with the same source IP address and destination IP address or
destination port will be forwarded to the recorded WAN port. This feature is to ensure the
multi-connected applications to work properly.
Check the box before Enable Bandwidth Based Balance Routing and select the WAN port below,
Load Balance of the specified WAN port will be enabled automatically if no routing rules are set.
Then click the <Save> button to apply.
Note:
The WAN ports not connecting to the Internet don’t support Intelligent Balance, please do not select
them.
3.4.4.2 Policy Routing
Policy Routing provides an accurate way to control the routing based on the policy defined by the
network administrator.
Choose the menu Advanced→Load Balance→Policy Routing to load the following page.
Figure 3-45 Policy Routing
The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
Protocol:
Select the protocol for the entry in the drop-down list. If the protocol you
want to set is not in the list, you can add it to the list on 3.4.4.4
Protocol page.
Source IP:
Enter the source IP range for the entry. 0.0.0.0 - 0.0.0.0 means any IP
is acceptable.
-69-
Page 78

Destination IP:
Source Port:
Destination Port:
WAN :
Effective Time:
Status:
Enter the destination IP range for the entry. 0.0.0.0 - 0.0.0.0 means any
IP is acceptable.
Enter the source Port range for the entry, which is effective only when
the protocol is TCP, UDP or TCP/UDP. The default value is 1 – 65535,
which means any port is acceptable.
Enter the destination port range for the entry, which is effective only
when the protocol is TCP, UDP or TCP/UDP. The default value is 1 –
65535, which means any port is acceptable.
Select the WAN port for transmitting packets.
Specify the time for the entry to take effect.
Activate or inactivate the entry.
Priority:
Select this option to specify the priority for the added entries. The latest
enabled entry will be displayed at the end of the list by default.
List of Rules
You can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
The first entry in Figure 3-45 indicates: All the packets with Source IP between 192.168.0.100 and
192.168.0.199 and Destination IP between 116.10.20.28 and 116.10.20.29 will be forwarded from
WAN1 port, regardless of the port and protocol. This entry is activated d and will take effect at 8
am to 10 pm from Monday to Friday.
3.4.4.3 Link Backup
With Link Backup function, the router will switch all the new sessions from dropped line automatically
to another to keep an always on-line network.
On this page, you can configure the Link Backup function based on actual need to reduce the traffic
burden of WAN port and improve the network efficiency.
Choose the menu Advanced→Load Balance→Link Backup to load the following page.
-70-
Page 79

WAN list. The color of WAN button
Figure 3-46 Link Backup
The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
WAN Ports:
Displays all the WAN ports in use. You can drag the light-blue WAN
button to primary and backup
changing to gray indicates that the WAN port is already in the primary
and backup WAN list.
WAN Config:
The WAN port in the secondary WAN list will share the traffic for the
WAN in the primary WAN list under the specified condition.
Mode:
You can select Timing or Failover Mode.
Timing:
Failover:
Link Backup will be enabled if the specified effective time is reached.
All the traffic on the primary WAN will switch to the backup WAN at
the beginning of the effective time; the traffic on the backup WAN will
switch to the primary WAN at the ending of the effective time.
Specify the premise for Failover Mode. The backup WAN port will be
enabled only when the premise is met.
-71-
Page 80
:
Backup Effective
Time:
Specify the backup effective time if Timing Mode has been selected.
Then the backup WAN port will be enabled, while the primary WAN
port is disabled in the specified time period. When the start time you
enter is not earlier than the end time, the default effective time is from
the start time of the day to the end time of the next day.
Status
Activate or inactivate the entry.
List of Rules
You can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
The first entry in Figure 3-46 indicates: WAN1 is the primary port and WAN2 is the backup port.
WAN2 will be enabled while WAN1 is failed. This entry is enabled.
Note:
The same WAN port cannot be added to the primary and secondary WAN lists at the same time, and
one WAN port should be added to only one list.
3.4.4.4 Protocol
On this page, you can specify the protocol for routing rules conveniently. A protocol constitutes of the
name and number. The router predefines four commonly used protocols such as TCP, UDP, TCP/UDP
and IGMP. Moreover, you can also add new protocols as your wish.
Choose the menu Advanced→Load Balance→Protocol to load the following page.
Figure 3-47 Protocol
-72-
Page 81

The following items are displayed on this screen:
Protocol
Name:
Number:
List of Protocol
You can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
Note:
The system predefined protocols cannot be configured.
Enter a name to indicate a protocol. The name will display in the
drop-down list of Protocol on Access Rule page.
Enter the Number of the protocol in the range of 0-255.
3.4.5 Routing
3.4.5.1 Static Route
Routing is the process of selecting optimized paths in a network along which to send network traffic.
Static Route is a kind of special routing configured by the administrator, which is simple, efficient, and
reliable.
Commonly used in small-sized network with fixed topology, Static Route does not change along with
the network topology automatically. The administrator should modify the static route information
manually as long as the network topology or link status is changed.
Choose the menu Advanced→Routing→Static Route to load the following page.
Figure 3-48 Static Route
-73-
Page 82

The following items are displayed on this screen:
Select the physical network interface, through which this route is
Static Route
Destination:
Subnet Mask:
Next Hop:
Interface:
Metric:
Description:
Status:
Enter the destination host the route leads to.
Enter the Subnet Mask of the destination network.
Enter the gateway IP address to which the packet should be sent next.
accessible.
Defines the priority of the route. The smaller the value is, the higher the
priority is. The default value is 0. It is recommended to keep the default
value.
Give a description for the entry.
Activate or inactivate the entry.
List of Rules
You can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
The first entry in Figure 3-48 indicates: If there are packets being sent to a device with IP address
of 211.162.1.0 and subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, the router will forward the packets from WAN1
port to the next hop of 211.200.1.1.
Application Example
Network Requirements
LAN1 is under the router and it uses network segment 192.168.0.0 /24. LAN2 and LAN3 are under a
layer 3 switch and they use network segments 192.168.2.0 /24 and 192.168.3.0 /24 respectively. The IP
address of the cascading LAN port between the layer 3 switch and the router is 192.168.0.2. Now the
hosts within LAN1 desire to access the hosts within LAN2 and LAN3.
-74-
Page 83
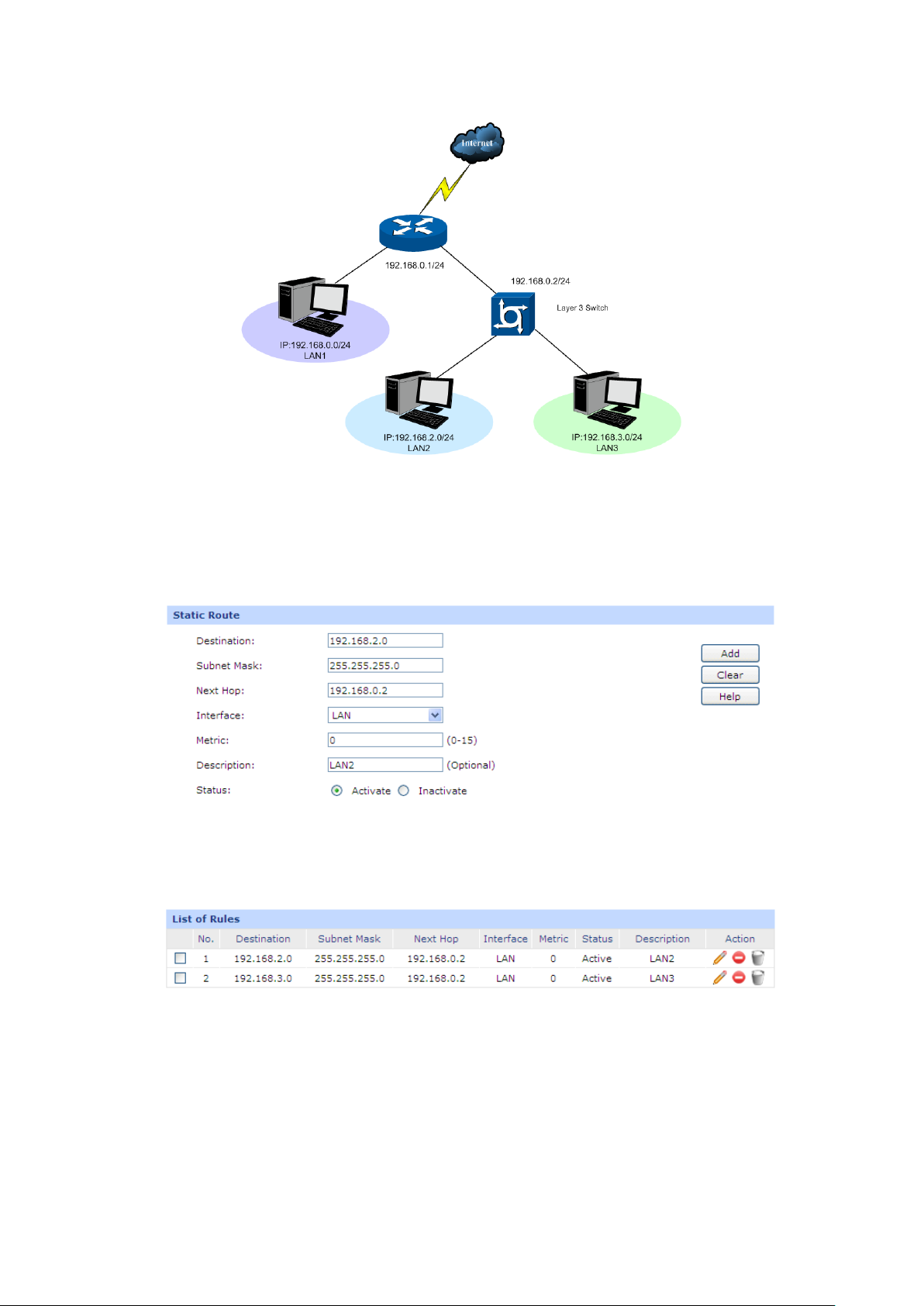
The network topology is shown as the following:
Configuration procedure
On the Static Route page, add a static routing rule for LAN2 with destination address 192.168.2.0
(LAN2’s IP address) and next hop address 192.168.0.2 (IP address of the cascading LAN port) as
shown in the following figure. Then click the <Add> button.
Add a static routing rule for LAN3 by referring to step 2.
The static routing rules are shown in the following figure.
3.4.5.2 RIP
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is a dynamic route protocol using distance vector algorithm to select
the optimal path. With features of easy configuration, management and implementation, it is widely used
in small and medium-sized networks such as the campus network.
The distance of RIP refers to the hop counts that a data packet passes through before reaching its
destination, the value range of which is 1–15. It means the destination cannot be reached if the value is
more than 15. Optimal path indicates the path with the fewest hop counts. RIP exchanges the route
information every 30 seconds by broadcasting UDP packets. If one router has not sent route information
-75-
Page 84
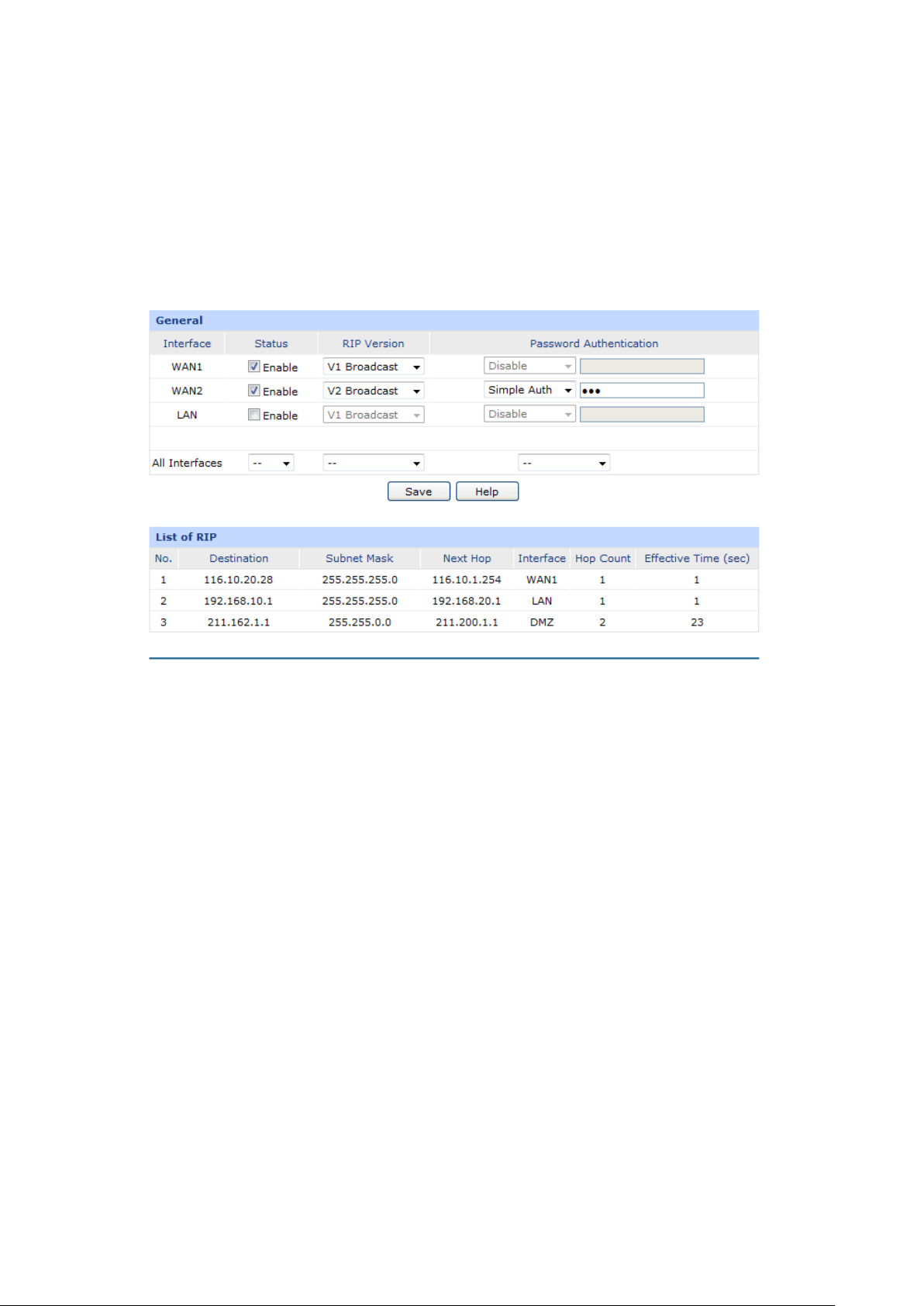
the password should not be more than 15
in 180 seconds, the RIP of the other routers would set the distance to this router into infinity and delete
the corresponding information from route table.
RIP develops from initial RIPv1 to RIPv2 gradually. Compared with RIPv1, RIPv2 supports VLSM
(Variable Length Subnet Mask), simple plain text authentication, MD5 cryptograph authentication, CIDR
(Classless Inter-Domain Routing) and multicast.
TL-ER604W supports both RIPv1 version and RIPv2 version, thus you can configure the RIP version
based on the actual need to improve the network performance.
Choose the menu Advanced→Routing→RIP to load the following page.
Figure 3-49 RIP
The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
Interface:
Displays the interfaces which has been physically connected or assigned
static IP.
Status:
RIP Version:
Password
Authentication:
Enable or disable RIP protocol.
Select RIPv1 or RIPv2. RIPv2 supports multicast and broadcast.
If RIPv2 is enabled, set the Password Authentication according to the actual
network situation, and
characters.
All Interfaces:
Here you can operate all the interfaces in bulk. All the interfaces will not
apply RIP if “Enable” option for All Interfaces is selected.
-76-
Page 85
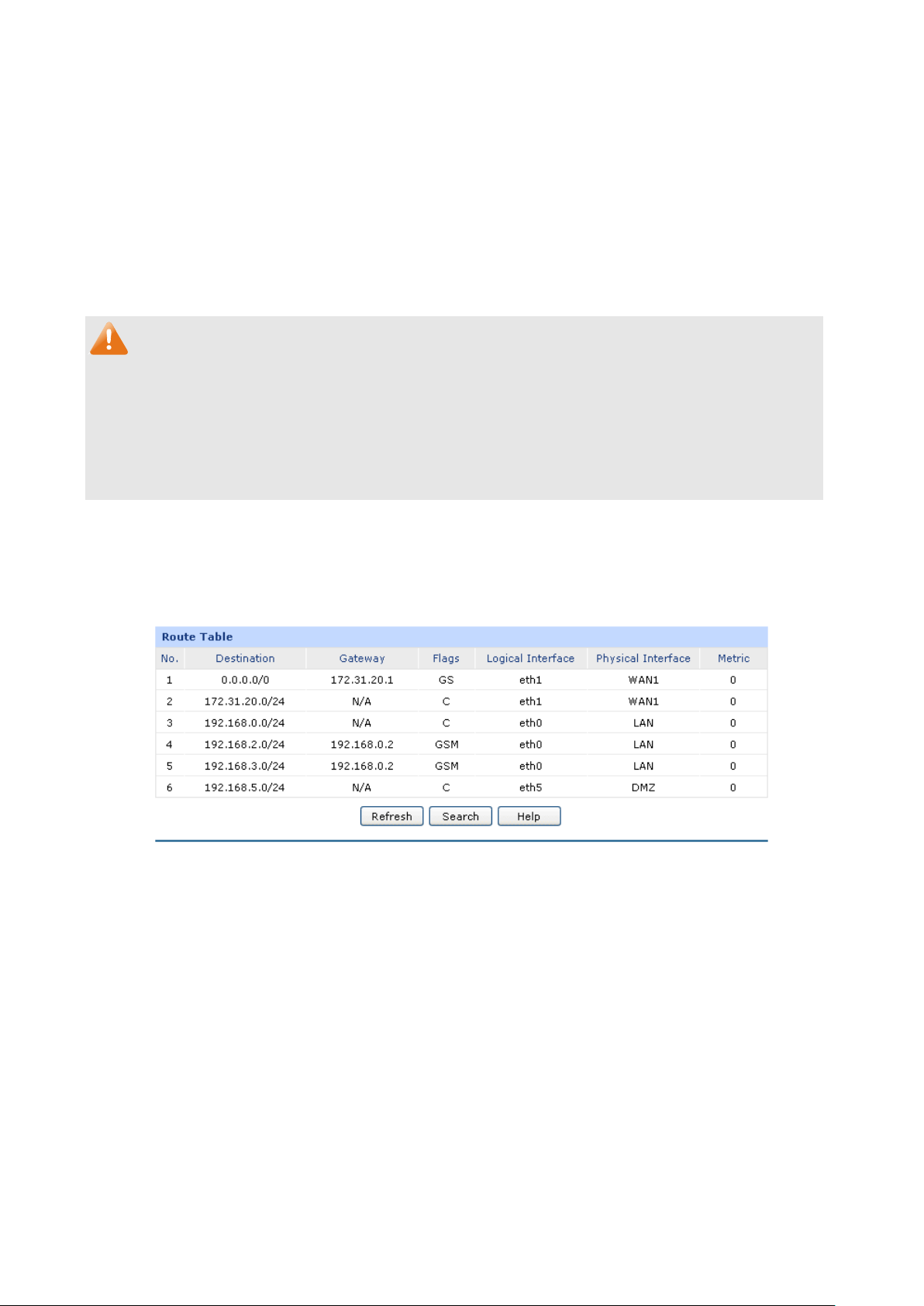
List of RIP
After RIP is enabled, the information of RIP forwarding the packets received by the router will be
displayed in the list.
The first entry in Figure 3-49 indicates: when receiving packets with destination IP is 116.10.20.28,
the router will select WAN1 which is in the same network with the destination IP as next hop and
forward data via this port. The IP address of next hop is 116.10.1.254 and the hop count is 1. The
effective time of this entry is 1 second.
Note:
RIP function cannot be set if the router is in NAT Mode. To set RIP function, please change the
System Mode to Routing or Full Mode.
The RIP function of WAN port takes effects only when the Connection Type of this WAN port is
Static IP.
3.4.5.3 Route Table
This page displays the information of the system route table.
Choose the menu Advanced→Routing→Route Table to load the following page.
Figure 3-50 RIP
The following items are displayed on this screen:
Route Table
Destination:
Gateway:
Flags:
Logical Interface:
The Destination of route entry.
The Gateway of route entry.
The Flags of route entry. The Flags describe certain characteristics of
the route.
The logical interface of route entry.
-77-
Page 86
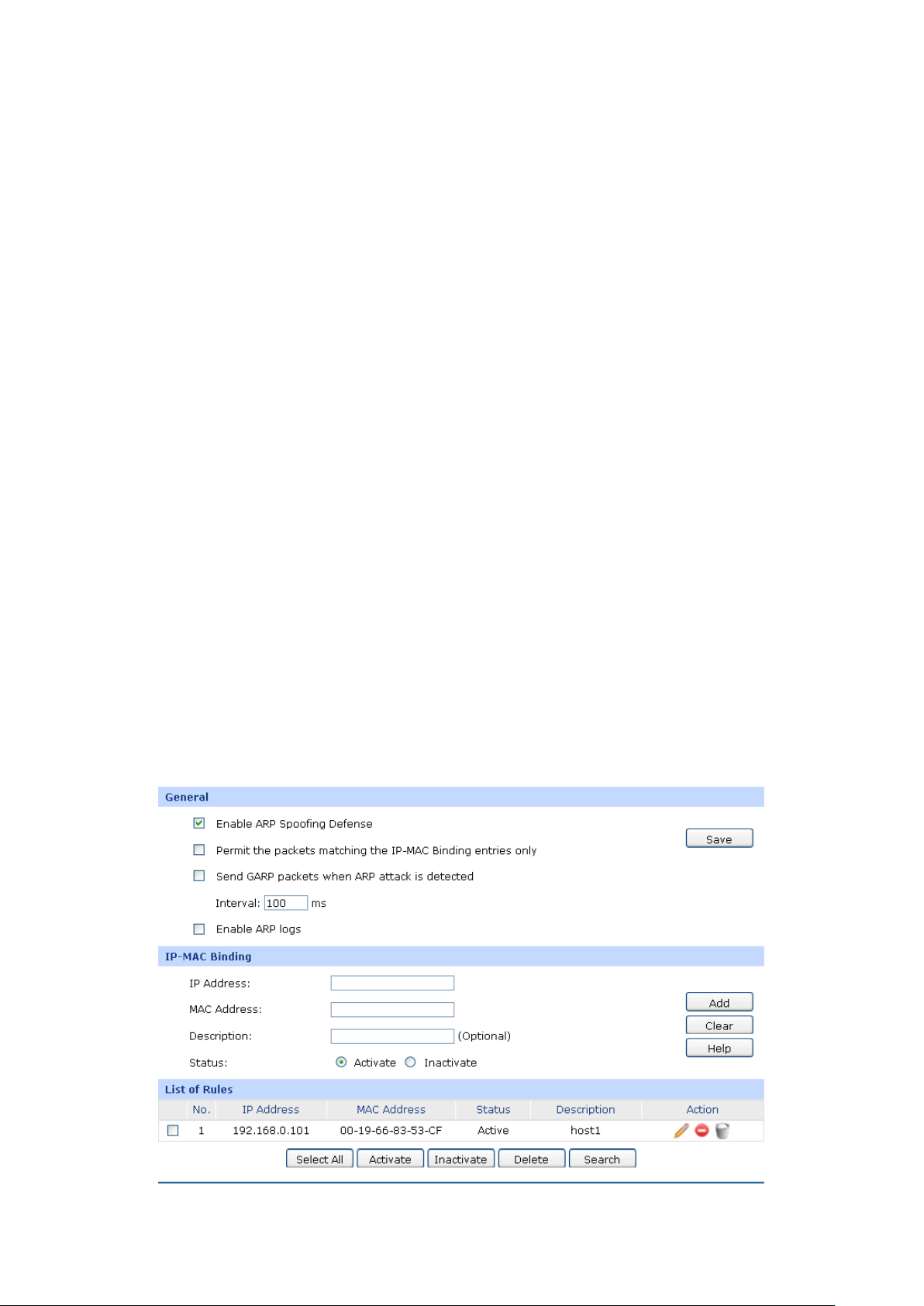
Physical Interface:
Metric
The physical interface of route entry.
The Metric of route entry.
3.5 Firewall
3.5.1 Anti ARP Spoofing
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is used for analyzing and mapping IP addresses to the
corresponding MAC addresses so that packets can be delivered to their destinations correctly.
ARP functions to translate the IP address into the corresponding MAC address and maintain an ARP
Table in which the latest used IP address-to-MAC address mapping entries are stored. ARP protocol
can facilitate the Hosts in the same network segment to communicate with one another or access to
external network via Gateway. However, since ARP protocol is implemented with the premise that all
the Hosts and Gateways are trusted, there are high security risks during ARP Implementation
Procedure in the actual complex network.
The attacker may send the ARP spoofing packets with false IP address-to-MAC address mapping
entries, and then the device will automatically update the ARP table after receiving wrong ARP
packets, which results in a breakdown of the normal communication. Thus, ARP defense technology is
generated to prevent the network from this kind of attack.
3.5.1.1 IP-MAC Binding
IP-MAC Binding functions to bind the IP address, MAC address of the host together and only allows the
Hosts matching the bound entries to access the network.
Choose the menu Firewall→Anti ARP Spoofing→IP-MAC Binding to load the following page.
Figure 3-51 IP-MAC Binding
-78-
Page 87

The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
It is recommended to check all the options. You should import the IP and MAC address of the host to
IP-MAC Binding List and enable the corresponding entry before enabling “Permit the packets
matching the IP-MAC Binding entries only”.
When suffered ARP attack, the correct ARP information will be sent to the device suffering attack
initiatively by GARP (Gratuitous ARP) packets, thus the error ARP information of the device will be
replaced. You can set the packets sending rate in the Interval field.
With the box before Enable ARP Logs checked, the router will send ARP logs to the specified
server. The IP address of server is the Server IP set on 3.8.7 Logs.
IP-MAC Binding
IP Address:
MAC Address:
Description:
Status:
Enter the IP Address to be bound.
Enter the MAC Address corresponding to the IP Address.
Give a description for the entry.
Activate or inactivate the entry.
List of Rules
You can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
The first entry in Figure 3-51 indicates: The IP address of 192.168.1.101 and MAC address of
00-19-66-83-53-CF have been bound and this entry is activated.
Note:
If all the entries in the binding list are disabled and “Permit the packets matching IP-MAC Binding
entries only” option is selected and saved, you cannot login the WEB management page of the router.
At the moment, you should restore the router to factory default and login again.
3.5.1.2 ARP Scanning
ARP Scanning feature enables the router to scan the IP address and corresponding MAC address and
display them on the List of Scanning Result.
Choose the menu Firewall→Anti ARP Spoofing→ARP Scanning to load the following page.
-79-
Page 88
Figure 3-52 ARP Scanning
Enter the start and the end IP addresses into the Scanning IP Range field. Then click the <Scan>
button, the router will scan all the active hosts within the scanning range and display the result in the
list.
The entries displayed on the List of Scanning Result do not mean the IP and MAC addresses are
already bound. The current status for the entry will display in the “Status” field.
--- Indicates that the IP and MAC address of this entry are not bound and may be
replaced by error ARP information.
Indicates that this entry is imported to the list on IP-MAC Binding page, but not
effective yet.
Indicates that the IP and MAC address of this entry are already bound.
To bind the entries in the list, check these entries and click the <Import> button, then the settings will
take effect if the entries do not conflict with the existed entries.
Note:
If the local hosts suffered from ARP attack, you cannot add IP-MAC Binding entries on this page.
Please add entries manually on 3.5.1.1 IP-MAC Binding.
3.5.1.3 ARP List
On this page, the IP-MAC information of the hosts which communicated with the router recently will be
saved in the ARP list.
Choose the menu Firewall→Anti ARP Spoofing→ARP List to load the following page.
-80-
Page 89
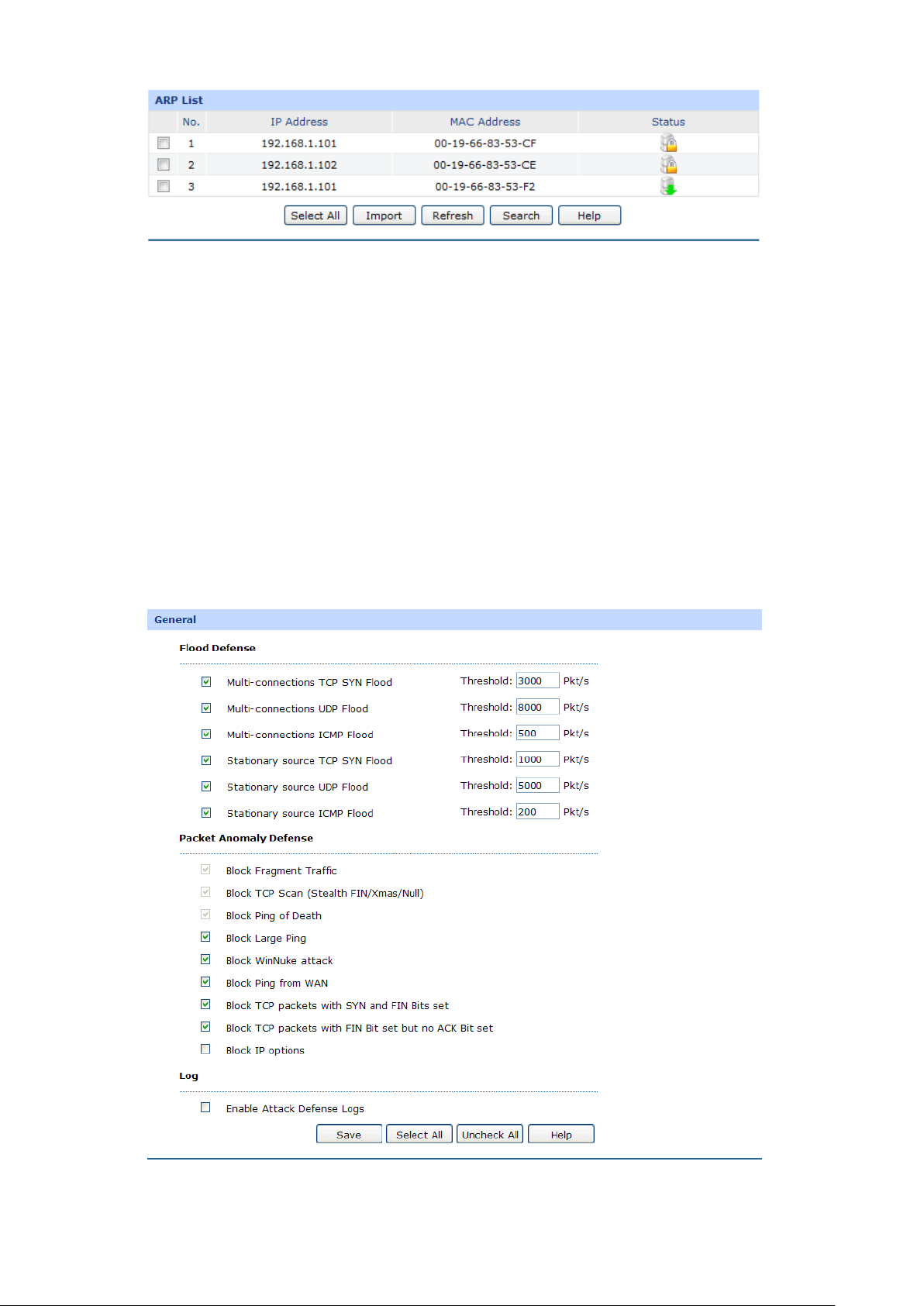
Figure 3-53 ARP List
The configurations for the entries is the same as the configuration of List of Scanning Result on 3.5.1.2
ARP Scanning page.
The unbound IP-MAC information will be replaced by new IP-MAC information or be automatically
removed from the list if it has not been communicated with others for a long time. This period is
regarded as the aging time of the ARP information.
3.5.2 Attack Defense
With Attack Defense function enabled, the router can distinguish the malicious packets and prevent
the port scanning from external network, so as to guarantee the network security.
Choose the menu Firewall→Attack Defense→Attack Defense to load the following page.
Figure 3-54 Attack Defense
-81-
Page 90

The following items are displayed on this screen:
Defense options and specify the corresponding thresholds. Keep the
It is recommended to
General
Flood Defense:
Packet Anomaly
Defense:
Enable Attack
Defense Logs:
Flood attack is a commonly used DoS (Denial of Service) attack, including
TCP SYN, UDP, ICMP and so on. It is recommended to select all the Flood
default settings if you are not sure.
Packet Anomaly refers to the abnormal packets.
select all the Packet Anomaly Defense options.
With this box checked, the router will record the defense logs.
3.5.3 MAC Filtering
On this page, you can control the Internet access of local hosts by specifying their MAC addresses.
Choose the menu Firewall→MAC Filtering→MAC Filtering to load the following page.
Figure 3-55 MAC Filtering
The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
To control the access to Internet for hosts in you private network, it is recommended to check the
box before Enable MAC Filtering and select a filtering mode according to actual situation.
MAC Filtering
MAC Address:
Enter the MAC Address to be filtered.
-82-
Page 91

Description:
Give a description for the entry.
List of Rules
You can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
3.5.4 Access Control
3.5.4.1 URL Filtering
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) specifies where an identified resource is available and the
mechanism for retrieving it. URL Filter functions to filter the Internet URL address, so as to provide a
convenient way for controlling the access to Internet from LAN hosts.
Choose the menu Firewall→Access Control→URL Filtering to load the following page.
Figure 3-56 URL Filtering
The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
To control the access to Internet for hosts in your private network, you are recommended to check
the box before Enable URL Filtering and select a filtering rule based on the actual situation.
URL Filtering Rule
Object:
Select the range in which the URL Filtering takes effect:
ANY: URL Filtering will take effect to all the users.
Group: URL Filtering will take effect to all the users in group.
-83-
Page 92

ill be filtered only when it
Mode:
Select the mode for URL Filtering. “Keyword’’ indicates that all the
URL addresses including the specified keywords will be filtered. “URL
Path” indicates that the URL address w
exactly matches the specified URL.
Effective Time:
Description:
Specify the time for the entry to take effect.
Give a description for the entry.
List of Rules
You can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
Application Example
Network Requirements
Prevent the local hosts from accessing Internet website www.aabbcc.com anytime and downloading
the files with suffix of “exe” at 8:00-20:00 from Monday to Friday.
Configuration Procedure
Select Keywords mode and type ”exe“ in the field, select URL mode and type “www.aabbcc.com” as
the following figure shows, then specify the effective time and click the <Add> button to make the
setting take effect.
-84-
Page 93

3.5.4.2 Web Filtering
On this page, you can filter the desired web components.
Choose the menu Firewall→Access Control→Web Filtering to load the following page.
Figure 3-57 Web Filtering
Check the box before Enable Web Filtering and select the web components to be filtered.
3.5.4.3 Access Rules
Choose the menu Firewall→Access Control→Access Rules to load the following page.
Figure 3-58 Access Rule
The following items are displayed on this screen:
Access Rules
Policy:
Select a policy for the entry:
Block: When this option is selected, the packets obeyed the rule
will not be permitted to pass through the router.
Allow: When this option is selected, the packets obeyed the rule
will be allowed to pass through the router.
-85-
Page 94

. You can add
. You can set the
Select the Destination IP Range for the entries, including the
latest enabled entry will be displayed at the end of the list by default.
Service:
Interface:
Source:
Select the service for the entry. Only the service belonging to the
specified service type is limited by the entry. For example, if you
select “Block” for Policy and only FTP for Service, the packets of
other service types can still pass through the router
new service types on 3.5.4.4 Service.
Select interface for the entry. The entry will take effect when the
interface to which the data is flowing is selected. WAN and LAN
refers to all the WAN and LAN interfaces.
Select the Source IP Range for the entries, including the following
three ways:
IP/MASK: Enter an IP address or subnet mask. ("0.0.0.0/32"
means any IP).
Group: Select a predefined group of users
group on 3.3.1 Group.
Destination:
Effective Time:
Description:
Priority:
List of Rules
ANY: means for any users.
following two ways:
IP/MASK: Enter an IP address or subnet mask. ("0.0.0.0/32"
means any IP is acceptable).
ANY: means for any users.
Specify the time for the entry to take effect.
Give a description for the entry.
Select this option to specify the priority for the added entries. The
You can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons. The smaller the
value is, the higher the priority is.
The first entry in Figure 3-58 indicates: The TELNET packets transmitted from the hosts within the
network of 192.168.0.0/24 will be not allowed to pass through the router at 8:00-20:00 from
Tuesday to Saturday.
-86-
Page 95

Note:
For the users in the private network and not being set access rule, the default Policy is Allow.
To specify all IP addresses, type “0.0.0.0 / 32” in the Policy field.
For detailed setting of subnet mask, please refer to Appendix B FAQ.
3.5.4.4 Service
The Service function allows you to specify the protocol and port number to be filtered for Firewall
function conveniently. Protocol name and port range constitute a service type. The router predefines
three commonly used services such as HTTP, FTP and TELNET and you can also add customized
services if needed.
Choose the menu Firewall→Access Control→Service to load the following page.
Figure 3-59 Service
The following items are displayed on this screen:
Service
Name:
Enter a name for the service. The name should not be more than 28
characters. The name will display in the drop-down list of Protocol on
Access Rule page.
Protocol:
Select the protocol for the service. The system predefined protocols
include TCP, UDP and TCP/UDP.
-87-
Page 96
Dest. Port:
List of Service
You can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
Note:
The service types predefined by the system cannot be modified.
Enter the start and end ports to make a destination port range for the
service. The start port number cannot be greater than the end port
number.
3.5.5 App Control
3.5.5.1 Control Rules
On this page, you can enable the Application Rules function.
Choose the menu Firewall→App Control→Control Rules to load the following page.
Figure 3-60 Application Rules
The following items are displayed on this screen:
General
Check the box before Enable Application Control to make the Application Control function take
effect. The specified application used by the specified local users will be not allowed to access the
Internet if the Application Control entry is enabled.
-88-
Page 97

Control Rules
for the entry. You can select “Group” to limit the
Object:
Group:
Application:
Effective Time:
Description:
Status:
Specify the object
predefined group, or select “ANY” to limit all the users.
If select “Group” as object, you can select the group in the drop-down
list. To establish new group, please refer to 3.3.1 Group.
Click the <Application List> button to select applications from the popup
checkbox. The applications include IM, Web IM, SNS, P2P, Media,
Basic and Proxy. The default setting is to limit all the applications in the
application list except for Basic and Proxy.
Specify the time for the entry to take effect.
Give a description for the entry.
Activate or inactivate the entry.
List of Rules
You can view the information of the entries and edit them by the Action buttons.
The first entry in Figure 3-60 indicates: The group1 is applied with Application Rules. You can click
<View> to view the limited applications in the popup checkbox. The effective time of this entry is
7:00-9:00 on Monday, Tuesday, Friday, Saturday and Sunday. This entry is enabled.
Note:
To set the group and group members, please refer to 3.3.1 Group.
3.5.5.2 Database
On this page, you can upgrade the application database.
Choose the menu Firewall→App Control→Database to load the following page.
Figure 3-61 Database
-89-
Page 98
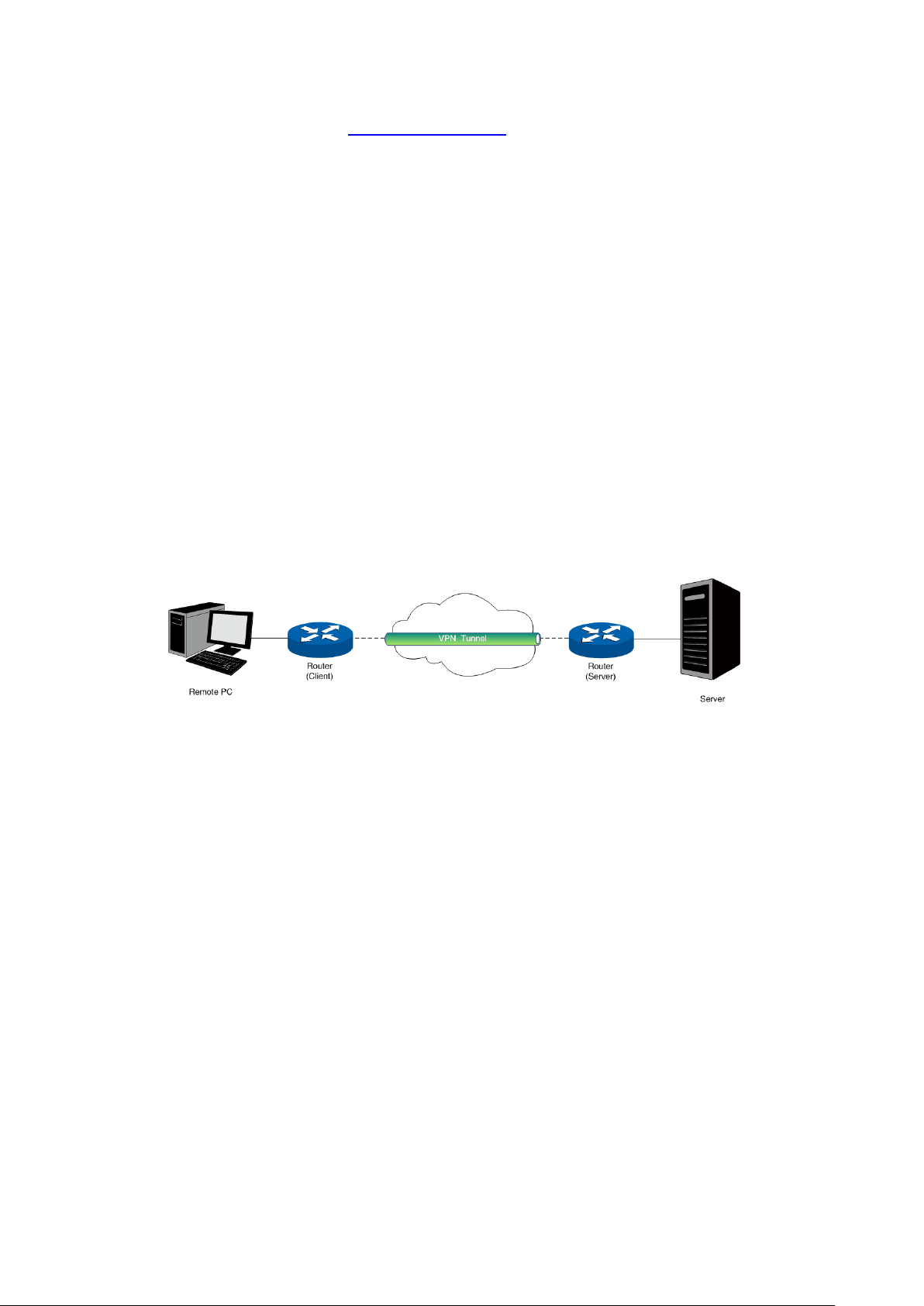
The database refers to all the applications in the application list on the Application Rules page, you can
download the latest database from http://www.tp-link.com
file, and then click the <Save> button to save the database.
. Click the <Browse> button and select the
3.6 VPN
VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a private network established via the public network, generally via the
Internet. However, the private network is a logical network without any physical network lines, so it is
called Virtual Private Network.
With the wide application of the Internet, more and more data are needed to be shared through the
Internet. Connecting the local network to the Internet directly, though can allow the data exchange, will
cause the private data to be exposed to all the users on the Internet. The VPN (Virtual Private Network)
technology is developed and used to establish the private network through the public network, which
can guarantee a secured data exchange.
VPN adopts the tunneling technology to establish a private connection between two endpoints. It is a
connection secured by encrypting the data and using point-to-point authentication. The following
diagram is a typical VPN topology.
Figure 3-62 VPN – Network Topology
As the packets are encapsulated and de-encapsulated in the router, the tunneling topology
implemented by encapsulating packets is transparent to users. The tunneling protocols supported by
TL-ER604W contain Layer 3 IPsec and Layer 2 L2TP/PPTP.
3.6.1 IKE
In the IPsec VPN, to ensure a secure communication, the two peers should encapsulate and
de-encapsulate the packets using the information both known. Therefore the two peers need to
negotiate a security key for communication with IKE (Internet Key Exchange) protocols.
Actually IKE is a hybrid protocol based on three underlying security protocols, ISAKMP (Internet
Security Association and Key Management Protocol), Oakley Key Determination Protocol, and
SKEME Security Key Exchange Protocol. ISAKMP provides a framework for Key Exchange and SA
(Security Association) negotiation. Oakley describes a series of key exchange modes. SKEME
describes another key exchange mode different from those described by Oakley.
-90-
Page 99
n and
IKE consists of two phases. Phase 1 is used to negotiate the parameters, key exchange algorithm and
encryption to establish an ISAKMP SA for securely exchanging more information in Phase 2. During
phase 2, the IKE peers use the ISAKMP SA established in Phase 1 to negotiate the parameters for
security protocols in IPsec and create IPsec SA to secure the transmission data.
3.6.1.1 IKE Policy
On this page you can configure the related parameters for IKE negotiation.
Choose the menu VPN→IKE→IKE Policy to load the following page.
Figure 3-63 IKE Policy
The following items are displayed on this screen:
IKE Policy
Policy Name:
Specify a unique name to the IKE policy for identificatio
management purposes. The IKE policy can be applied to IPsec policy.
-91-
Page 100

with lower security, which applies to scenarios with lower
two peers use the same key. The key should consist of visible
Exchange Mode:
Local ID Type:
Local ID:
Select the IKE Exchange Mode in phase 1, and ensure the remote VPN
peer uses the same mode.
Main: Main mode provides identity protection and exchanges more
information, which applies to the scenarios with higher requirement
for identity protection.
Aggressive: Aggressive Mode establishes a faster connection but
requirement for identity protection.
Select the local ID type for IKE negotiation. IP Address: uses an IP
address as the ID in IKE negotiation. FQDN: uses a name as the ID.
The local WAN IP will be inputted automatically if IP Address type is
selected. If Name type is selected, enter a name for the local device as
the ID in IKE negotiation
Remote ID Type:
Remote ID:
IKE Proposal:
Pre-shared Key:
SA Lifetime:
DPD:
Select the remote ID type for IKE negotiation. IP Address: uses an IP
address as the ID in IKE negotiation. FQDN: uses a name as the ID.
The remote gateway IP will be inputted automatically if IP Address type
is selected. If Name type is selected, enter the name of the remote peer
as the ID in IKE negotiation.
Select the Proposal for IKE negotiation phase 1. Up to four proposals
can be selected.
Enter the Pre-shared Key for IKE authentication, and ensure both the
characters without blank space.
Specify ISAKMP SA Lifetime in IKE negotiation.
Enable or disable DPD (Dead Peer Detect) function. If enabled, the IKE
endpoint can send a DPD request to the peer to inspect whether the
IKE peer is alive.
DPD Interval:
Enter the interval after which the DPD is triggered.
-92-
 Loading...
Loading...