Page 1

REV1.0.0
1910011922
User Guide
EAP115-Wall
Page 2

CONTENTS
Chapter 1 Introduction ...................................................................................................................... 1
Chapter 2 Network Topology .......................................................................................................... 2
Chapter 3 Management Mode ........................................................................................................ 4
3.1 Standalone Mode ................................................................................................................ 4
3.2 Managed Mode .................................................................................................................... 4
3.3 Switch to Standalone Mode ............................................................................................ 4
Chapter 4 Network .............................................................................................................................. 5
Chapter 5 Wireless .............................................................................................................................. 6
5.1 Wireless Settings ................................................................................................................ 7
5.1.1 Wireless Basic Settings ....................................................................................... 8
5.1.2 SSIDs .......................................................................................................................... 9
5.1.3 Wireless Advanced Settings ............................................................................ 13
5.1.4 Load Balance ......................................................................................................... 14
5.2 Portal ..................................................................................................................................... 15
5.2.1 Portal Configuration ............................................................................................ 16
5.2.2 Free Authentication Policy ................................................................................ 20
5.3 MAC Filtering ...................................................................................................................... 22
5.4 Scheduler ............................................................................................................................. 25
5.5 QoS ........................................................................................................................................ 28
5.5.1 AP EDCA Parameters ......................................................................................... 29
5.5.2 Station EDCA Parameters ................................................................................. 30
5.6 Rogue AP Detection ......................................................................................................... 31
5.6.1 Settings ................................................................................................................... 32
5.6.2 Detected Rogue AP List..................................................................................... 32
5.6.3 Trusted AP List ...................................................................................................... 33
5.6.4 Download/Backup Trusted AP List ................................................................ 34
Chapter 6 Monitoring ....................................................................................................................... 35
6.1 AP ........................................................................................................................................... 35
6.1.1 AP List ...................................................................................................................... 35
6.2 SSID ....................................................................................................................................... 40
6.2.1 SSID List .................................................................................................................. 40
Page 3

6.3 Client...................................................................................................................................... 41
6.3.1 User List .................................................................................................................. 41
6.3.2 Portal Authenticated Guest .............................................................................. 42
Chapter 7 Management................................................................................................................... 44
7.1 System Log ......................................................................................................................... 44
7.1.1 Log List .................................................................................................................... 44
7.1.2 Log Settings ........................................................................................................... 45
7.2 Web Server .......................................................................................................................... 46
7.3 Management Access ....................................................................................................... 47
7.4 LED ON/OFF ........................................................................................................................ 48
7.5 Wi-Fi Control ....................................................................................................................... 48
7.6 SSH ........................................................................................................................................ 49
7.7 Management VLAN .......................................................................................................... 50
7.8 SNMP ..................................................................................................................................... 50
Chapter 8 System .............................................................................................................................. 53
8.1 User Account ...................................................................................................................... 53
8.2 Time Settings ...................................................................................................................... 53
8.2.1 Time Settings ........................................................................................................ 54
8.2.2 Daylight Saving ..................................................................................................... 55
8.3 Reboot/Reset ..................................................................................................................... 57
8.4 Backup & Restore .............................................................................................................. 57
8.5 Firmware Upgrade ............................................................................................................ 58
Page 4

Chapter 1 Introduction
Auranet series products provide wireless coverage solutions for small-medium
business. They can either work independently as standalone APs or be centrally
managed by the EAP Controller software, providing a flexible, richly-functional but
easily-configured enterprise-grade wireless network for small and medium business.
“Celling lamp” appearance and easily mounting design with chassis make the EAP easy
to be installed on a wall or ceiling and blend in with most interior decorations.
With two built-in omnidirectional antennas, EAP115-Wall operates at 2.4GHz, and apply
802.11 standards and 2*2MIMO technology, allowing packet transmission at up to
300Mbps.
EAP115-Wall can only be powered via a PSE* device.
*PSE: Power Sourcing Equipment, a device (switch or hub for instance) that will provide
power in a PoE setup
1
Page 5
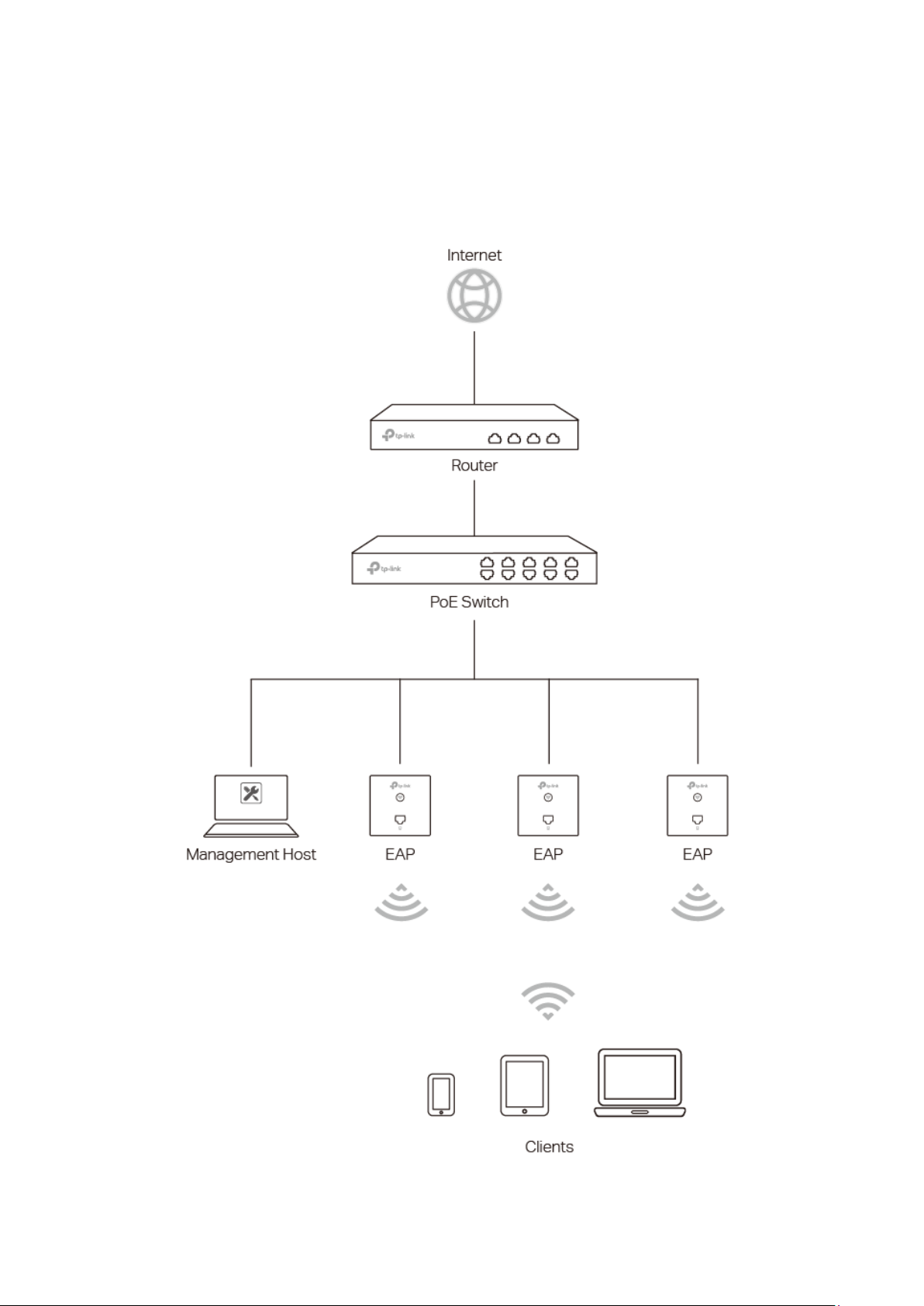
Chapter 2 Network Topology
A typical network topology for EAP115-Wall is shown below.
Figure 2-1 Typical Topology
2
Page 6

To deploy the EAP in your local network, a DHCP server is required to assign IP
addresses to the EAP and clients. Typically, a router acts as the DHCP server. A
computer running the EAP Controller software can locate in the same or different subnet
with the EAPs.
The EAP can be managed by the EAP Controller software, which is a management
software specially designed for the TP-Link EAP devices on a local wireless network,
allowing you to centrally configure and monitor mass EAP devices using a web browser
on your PC. For more information about the EAP Controller, please find the EAP
Controller User Guide from our official website:
http://www.tp-link.com/en/support/download/
3
Page 7

TIPS:
Proceed to the following chapters for information on using the EAP in standalone mode.
Chapter 3 Management Mode
300Mbps Wireless N Wall-Plate Access Point EAP115-Wall can either work under the
control of the EAP Controller software or work independently as a standalone access
point.
When user establishes a large-scale wireless network, the management of every single
EAP in the network is complex and complicated. With the EAP Controller software, you
can centrally manage the mass EAPs simply in a web browser.
The Standalone mode applies to a relatively small-sized wireless network. EAPs in the
Standalone mode cannot be managed centrally by the EAP Controller software.
3.1 Standalone Mode
By default, the EAP works independently as a standalone access point. By entering the
IP address of the standalone EAP, you can log in to its web interface and perform
configurations.
The factory default IP address configuration of the EAP is DHCP (Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol). Before you access the web interface of the EAP, please make
sure the DHCP server works properly. Typically, a router acts as the DHCP server.
Follow the steps below to log in to the web interface of a standalone EAP.
1. Launch a web browser, enter the DHCP address in the address field and press the
Enter key.
2. Enter admin (all lowercase) for both username and password.
3.2 Managed Mode
The EAP will become a managed EAP once it is adopted via the EAP Controller software.
Users can manage the EAP via a web browser. Refer to the EAP Controller User Guide
from our website at www.tp-link.com to know more about EAP Controller software.
3.3 Switch to Standalone Mode
The web interface of a specific EAP is not available once this EAP is adopted by the EAP
Controller. You can
AP. Refer to the EAP Controller User Guide from our website at www.tp-link.com to learn
more.
Forget
the EAP via the EAP Controller to turn it back as a standalone
4
Page 8
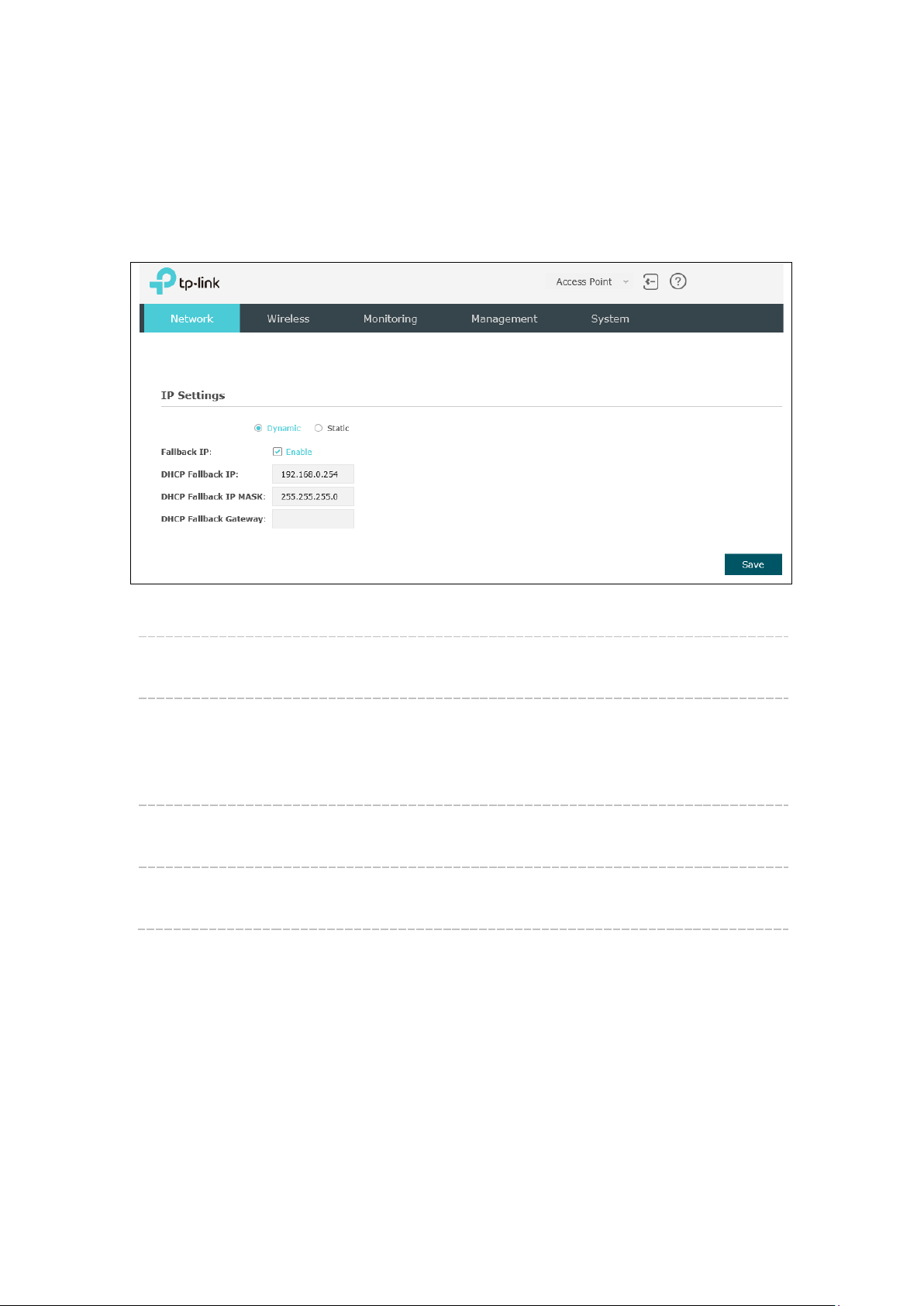
On
Network
DHCP Fallback
DHCP Fallback
Chapter 4 Network
page you can configure the IP address of the standalone EAP.
Figure 4-1 Network Page
Dynamic/Static: By default, the EAP obtains an IP address from a DHCP server (typically
a router). Select Static to configure IP address manually.
Fallback IP: If the EAP fails to get a dynamic IP address from a DHCP server within
ten seconds, the fallback IP will work as the IP address of the device.
After that, however, the device will keep trying to obtain an IP address
from the DHCP server until it succeeds.
Enter the fallback IP/IP mask.
IP/IP MASK:
Enter the fallback gateway.
Gateway:
5
Page 9
Wireless
Chapter 5 Wireless
and Rogue AP Detection, is shown below.
page, consisting of Wireless Settings, Portal, MAC Filtering, Scheduler, QoS
Figure 5-1 Wireless Page
6
Page 10
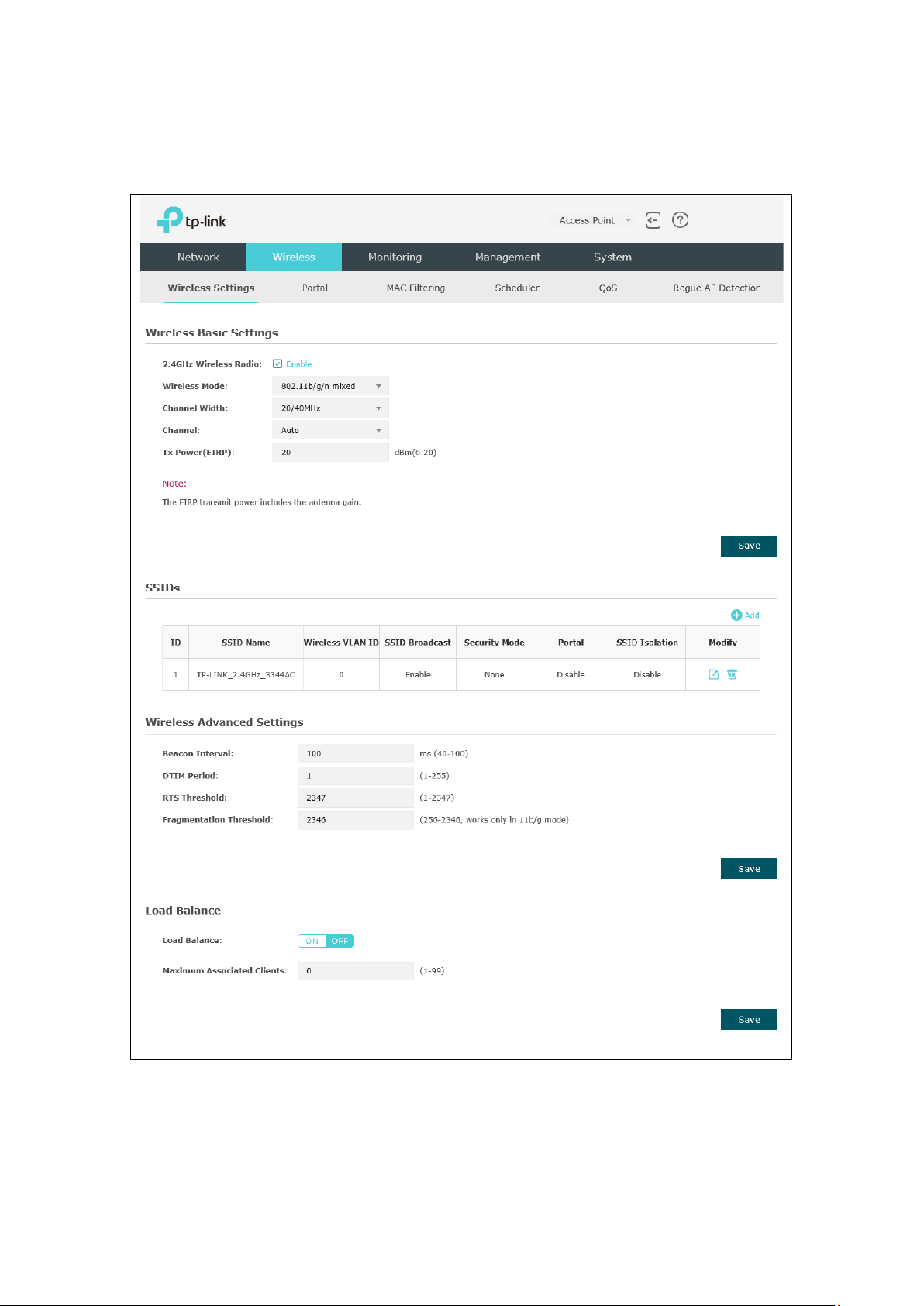
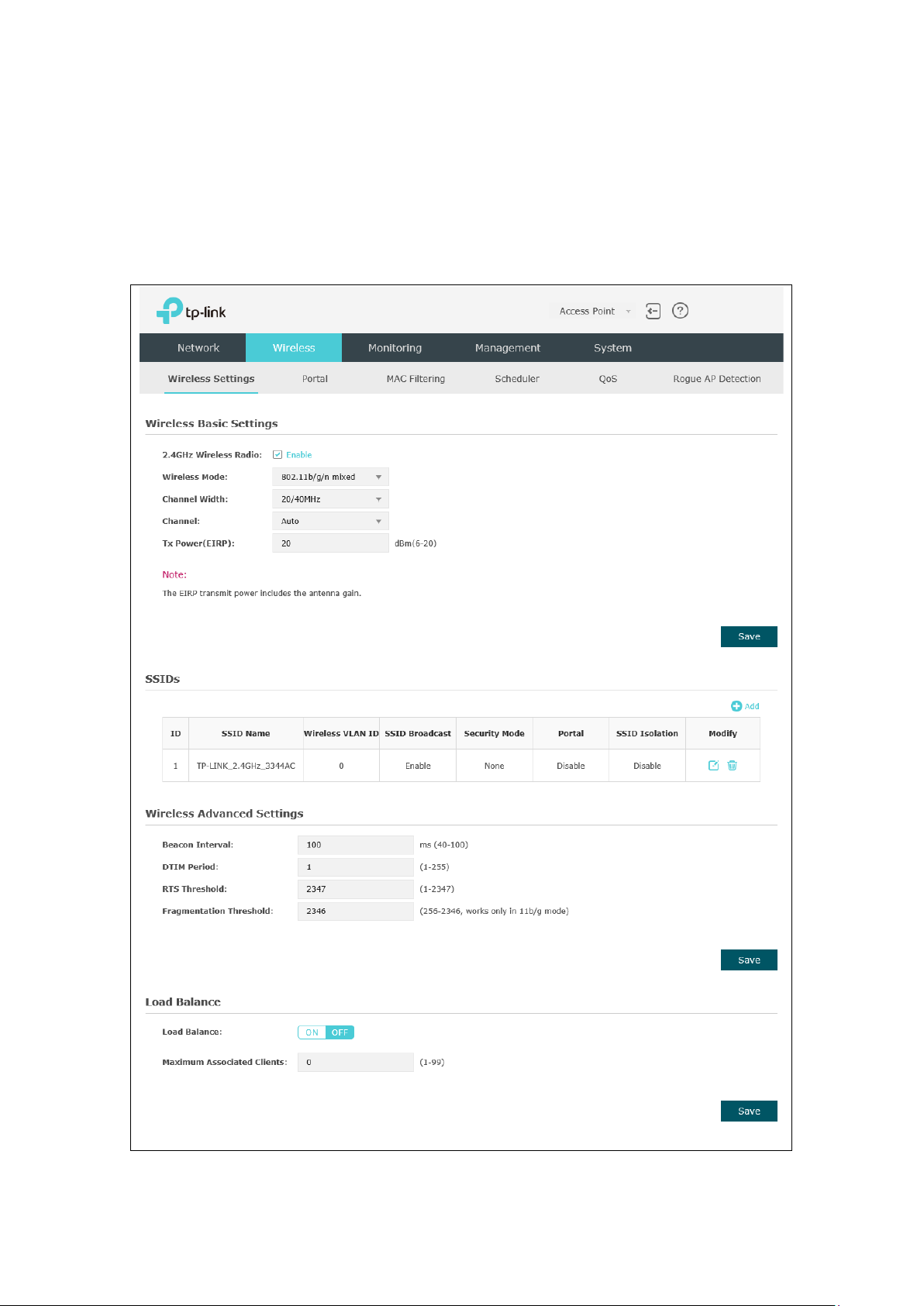
5.1 Wireless Settings
Wireless Settings
Following is the page of
.
Figure 5-2 Wireless Settings Page
7
Page 11

supports 802.11b/g/n, 802.11b/g, and 802.11n standards. It is
include 20MHz, 40MHz and 20/40MHz (this device
ate higher transmit power,
TIPS:
the EAP.
Proceed to the following chapter for information on configuring the wireless network of
5.1.1 Wireless Basic Settings
Figure 5-3 Wireless Basic Settings
2.4GHz
Wireless Radio:
Wireless Mode: Select the protocol standard for the wireless network.
Channel Width: Select the channel width of this device.
Check the box to enable 2.4GHz Wireless Radio.
Wireless network created by the EAP work within 2.4GHz. The EAP
recommended to select 802.11b/g/n, in which way clients supporting
11b, 11g or 11n mode can access your wireless network.
Options
automatically selects 20MHz or 40MHz, and 20MHz will be used if
40MHz is not available).
According to IEEE 802.11n standard, using a channel width of 40MHz
can increase wireless throughput. However, users may choose lower
bandwidth due to the following reasons:
1. To increase the available number of channels within the limited total
bandwidth.
2. To avoid interference from overlapping channels occupied by other
devices in the environment.
3. Lower bandwidth can concentr
increasing stability of wireless links over long distances.
8
Page 12
Select the channel used by this device to improve wireless
allows, the maximum Tx power regulated will be applied in actual
NOTE
reduce longevity of the device. Select a certain transmit power is
Channel:
performance. 1/2412MHz means the Channel is 1 and the frequency is
2412MHz. By default, channel is automatically selected.
Tx Power(EIRP): Enter the transmit power value. By default, the value is 20.
If the maximum transmit power is set to be larger than local regulation
situation.
: In most cases, it is unnecessary to select maximum transmit
power. Selecting larger transmit power than needed may cause
interference to neighborhood. Also it consumes more power and will
enough to achieve the best performance.
5.1.2 SSIDs
SSIDs can work together with switches supporting 802.1Q VLAN. The EAP can build up
to eight virtual wireless networks per radio for users to access. At the same time, it adds
different VLAN tags to the clients which connect to the corresponding wireless network.
It supports maximum 8 VLANs per radio. The clients in different VLAN cannot directly
communicate with each other.
Clients connected to the device via cable do not belong to any VLAN. Thus wired client
can communicate with all the wireless clients despite the VLAN settings.
Click in the Modify column, the following content will be shown.
Figure 5-4 SSIDs
Click to add up to 8 wireless networks per radio.
9
Page 13
PSK is
NOTE:
may work at a low transmission rate.
SSID Name: Enter up to 32 characters as the SSID name.
Wireless
VLAN ID:
SSID
Broadcast:
Set a VLAN ID (ranges from 0 to 4094) for the wireless network. Wireless
networks with the same VLAN ID are grouped to a VLAN.
Enable this function, AP will broadcast its SSID to hosts in the surrounding
environment, as thus hosts can find the wireless network identified by this
SSID. If SSID Broadcast is not enabled, hosts must enter the AP’s SSID
manually to connect to this AP.
Security
Mode:
Select the security mode of the wireless network. For the security of
wireless network, you are suggested to encrypt your wireless network. This
device provides three security modes: WPA-Enterprise, WPA-PSK (WPA
Pre-Shared Key) and WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy). WPArecommended. Settings vary in different security modes as the details are
in the following introduction. Select None and the hosts can access the
wireless network without password.
Portal: Portal provides authentication service for the clients who want to access
the wireless local area network. For more information, refer to 5.2 Portal
After Portal is enabled, the configurations in 5.2 Portal will be applied.
SSID
Isolation:
After enabling SSID Isolation, the devices connected in the same SSID
cannot communicate with each other.
.
Modify:
Click to open the page to edit the parameters of SSID.
Click to delete the SSID.
Following is the detailed introduction of security mode: WEP, WPA-Enterprise and
WPA-PSK.
WEP
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), based on the IEEE 802.11 standard, is less safe than
WPA-Enterprise or WPA-PSK.
WEP is not supported in 802.11n mode. If WEP is applied in 802.11n mode, the clients may
not be able to access the wireless network. If WEP is applied in 11b/g/n mode, the device
10
Page 14
password. However, correct password is necessary for data
Hexadecimal format stands for any combination of
Figure 5-5 Security Mode-WEP
Type: Select the authentication type for WEP.
Auto: The default setting is Auto, which can select Open System or
Shared Key automatically based on the wireless station's capability and
request.
Open System: After you select Open System, clients can pass the
authentication and associate with the wireless network without
transmission.
Shared Key: After you select Shared Key, clients has to input password
to pass the authentication, or it cannot associate with the wireless
network or transmit data.
Key Selected: You can configure four keys in advance and select one as the present
valid key.
Wep Key
Format:
Select the wep key format as ASCII or Hexadecimal.
ASCII: ASCII format stands for any combination of keyboard characters
in the specified length.
Hexadecimal:
hexadecimal digits (0-9, a-f, A-F) in the specified length.
Key Type: Select the WEP key length for encryption.
64 Bit: You can enter 10 hexadecimal digits (any combination of 0-9, a-
f, A-F without null key) or 5 ASCII characters.
128 Bit: You can enter 26 hexadecimal digits (any combination of 0-9,
a-f, A-F without null key) or 13 ASCII characters.
152 Bit: You can enter 32 hexadecimal digits (any combination of 0-9,
a-f, A-F without null key) or 16 ASCII characters.
Key Value: Enter the key value.
11
Page 15

Group Key
NOTE:
11b/g/n mode, the device may work at a low transmission rate.
WPA-Enterprise
Based on RADIUS server, WPA-Enterprise can generate different passwords for
different users and it is much safer than WPA-PSK. However, it costs much to maintain
and is more suitable for enterprise users. At present, WPA-Enterprise has two versions:
WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK.
Figure 5-6 Security Mode_WPA-Enterprise
Version: Select one of the following versions:
Auto: Select WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK automatically based on the
wireless station's capability and request.
WPA-PSK: Pre-shared key of WPA.
WPA2-PSK: Pre-shared key of WPA2.
Encryption: Select the encryption type, including Auto, TKIP, and AES. The default
setting is Auto, which can select TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol)
or AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) automatically based on the
wireless station's capability and request. AES is more secure than TKIP
and TKIP is not supported in 802.11n mode. It is recommended to select
AES as the encryption type.
RADIUS Server
Enter the IP address/port of the RADIUS server.
IP/Port:
RADIUS
Enter the shared secret of RADIUS server to access the RADIUS server.
Password:
Specify the group key update period in seconds. The value can be either
Update period:
0 or 30-8640000 seconds.
Encryption type TKIP is not supported in 802.11n mode. If TKIP is applied in 802.11n mode,
the clients may not be able to access the wireless network of the EAP. If TKIP is applied in
12
Page 16
automatically based on the
Group Key
WPA-PSK
Based on pre-shared key, security mode WPA-PSK is characterized by high security and
simple configuration, which suits for common households and small business. WPA-PSK
has two versions: WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK.
Figure 5-7 Security Mode_WPA-PSK
Version:
Auto: Select WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK
wireless station's capability and request.
WPA-PSK: Pre-shared key of WPA-PSK.
WPA2-PSK: Pre-shared key of WPA2-PSK.
Encryption: Select the encryption type, including Auto, TKIP, and AES. The default
setting is Auto, which can select TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) or
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) automatically based on the wireless
station's capability and request. AES is more secure than TKIP and TKIP
is not supported in 802.11n mode. It is recommended to select AES as
the encryption type.
Wireless
Password:
Configure the WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK password with ASCII or Hexadecimal
characters. For ASCII, the length should be between 8 and 63 characters
with combination of numbers, letters (case-sensitive) and common
punctuations. For Hexadecimal, the length should be 64 characters (caseinsensitive, 0-9, a-f, A-F).
Specify the group key update period in seconds. The value can be either
Update Period:
0 or 30-8640000 seconds.
5.1.3 Wireless Advanced Settings
Figure 5-8 Wireless Advanced Settings
13
Page 17
wireless performance caused by the excessive packets. The
Beacon
Interval:
DTIM Period: This value indicates the number of beacon intervals between successive
RTS
Threshold:
Beacons are transmitted periodically by the device to announce the
presence of a wireless network for the clients. Beacon Interval value
determines the time interval of the beacons sent by the device. You can
specify a value from 40 to 100. The default value is 100 milliseconds.
Delivery Traffic Indication Messages (DTIMs) and this number is included
in each Beacon frame. A DTIM is contained in Beacon frames to indicate
whether the access point has buffered broadcast and/or multicast data for
the client devices. Following a Beacon frame containing a DTIM, the
access point will release the buffered broadcast and/or multicast data, if
any exists. You can specify the value between 1-255 Beacon Intervals. The
default value is 1, indicating the DTIM Period is the same as Beacon
Interval. An excessive DTIM period may reduce the performance of
multicast applications. It is recommended to keep it by default.
When the RTS threshold is activated, all the stations and APs follow the
Request to Send (RTS) protocol. When the station is to send packets, it will
send a RTS to AP to inform the AP that it will send data. After receiving the
RTS, the AP notices other stations in the same wireless network to delay
their transmitting of data. At the same time, the AP inform the requesting
station to send data. The value range is from 1 to 2347 bytes. The default
value is 2347, which means that RTS is disabled.
Fragmentation
Threshold:
Specify the fragmentation threshold for packets. If the size of the packet
is larger than the fragmentation threshold, the packet will be fragmented
into several packets. Too low fragmentation threshold may result in poor
recommended and default value is 2346 bytes.
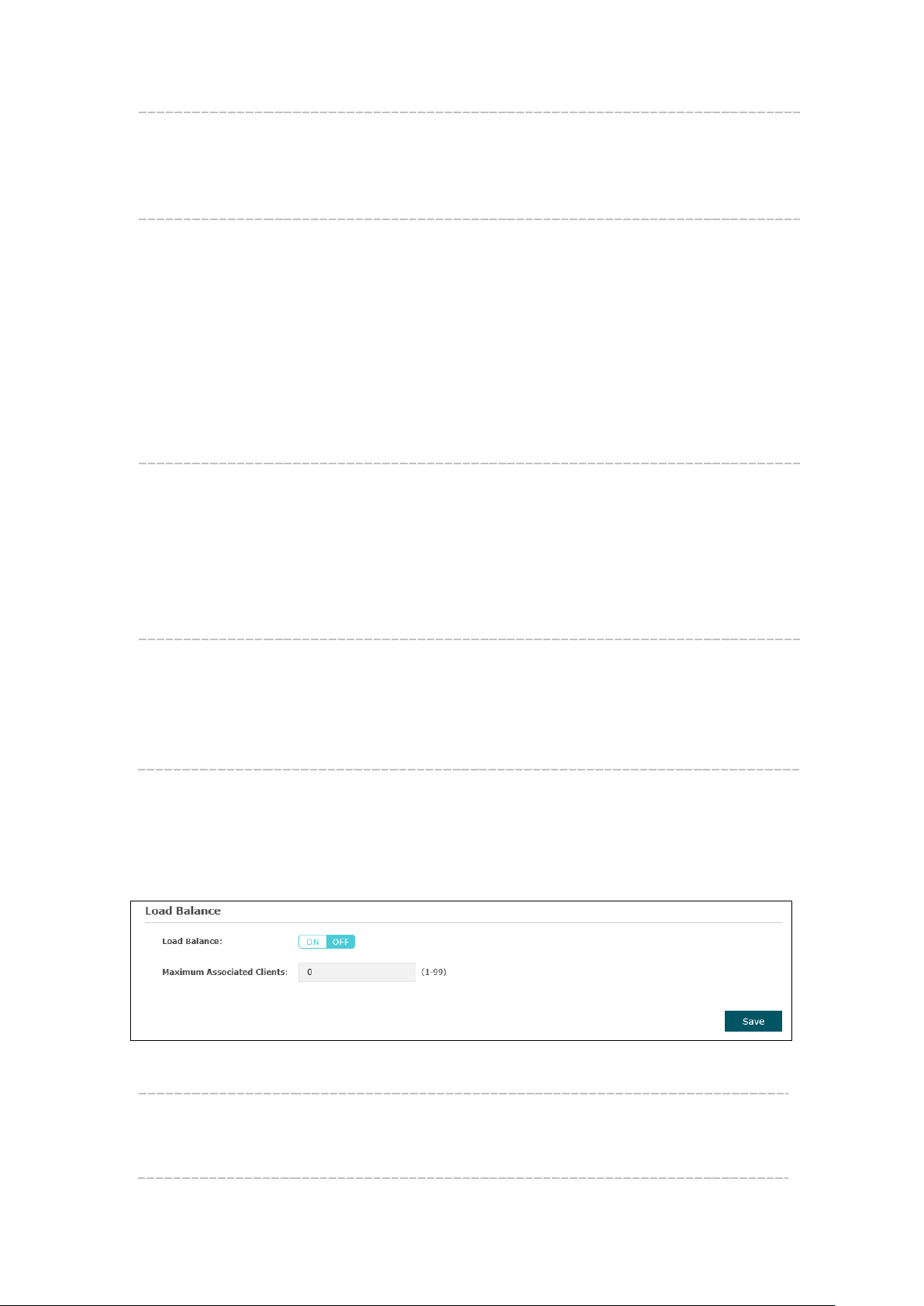
5.1.4 Load Balance
By restricting the maximum number of clients accessing the EAPs, Load Balance helps
to achieve rational use of network resources.
Figure 5-9 Load Balance
Load Balance: Disable by default. Click ON to enable the function. After enabling it,
you can set a number for maximum associated clients to control the
wireless access.
14
Page 18
Portal
Maximum
Associated
Clients:
Enter the number of clients to be allowed for connection to the EAP.
The number ranges from 1 to 99.
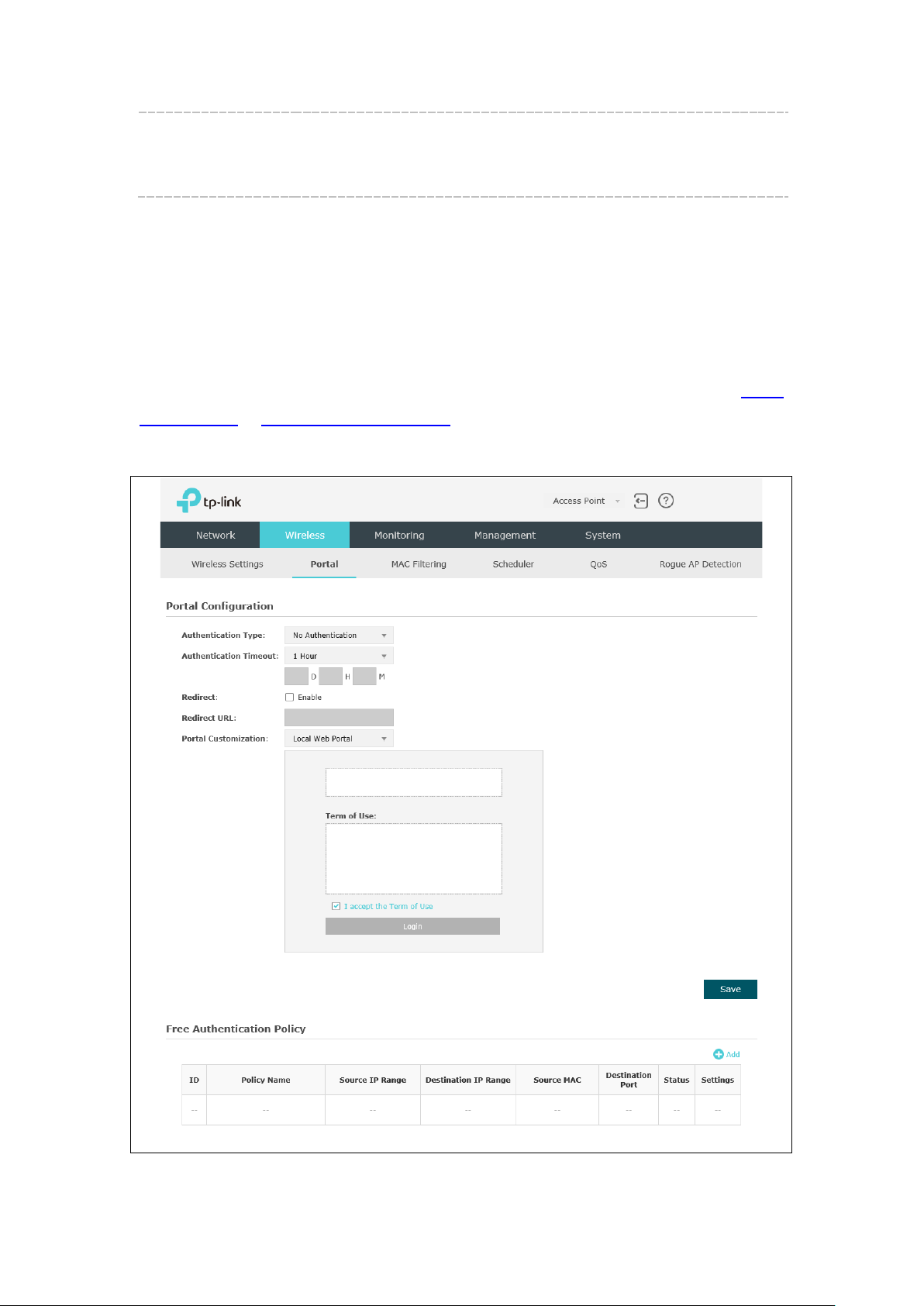
5.2 Portal
Portal authentication enhances the network security by providing authentication service
to the clients that just need temporary access to the wireless network. Such clients have
to log into a web page to establish verification, after which they will access the network
as guests. What's more, you can customize the authentication login page and specify a
URL which the newly authenticated clients will be redirected to. Please refer to
Configuration or Free Authentication Policy according to your need.
Following is the page of
.
Portal
Figure 5-10 Portal Page
15
Page 19
NOTE:
to enable Portal of a selected SSID.
No Authentication
Local Password
External RADIUS Server
To apply Portal in a wireless network, please go to Wireless→Wireless Settings→SSIDs
5.2.1 Portal Configuration
Three authentication types are available: No Authentication, Local Password and
External RADIUS Server.
1.
protocol and click the Login button.
2.
in the EAP.
3.
password, which are saved in the database of the RADIUS server. The RADIUS
server acts as the authentication server, which allows you to set different
usernames and passwords for different users.
:Users are required to finish only two steps: agree with the user
:Users are required to enter the preset password, which are saved
:Users are required to enter the preset user name and
Refer to the following content to configure Portal based on actual network situations.
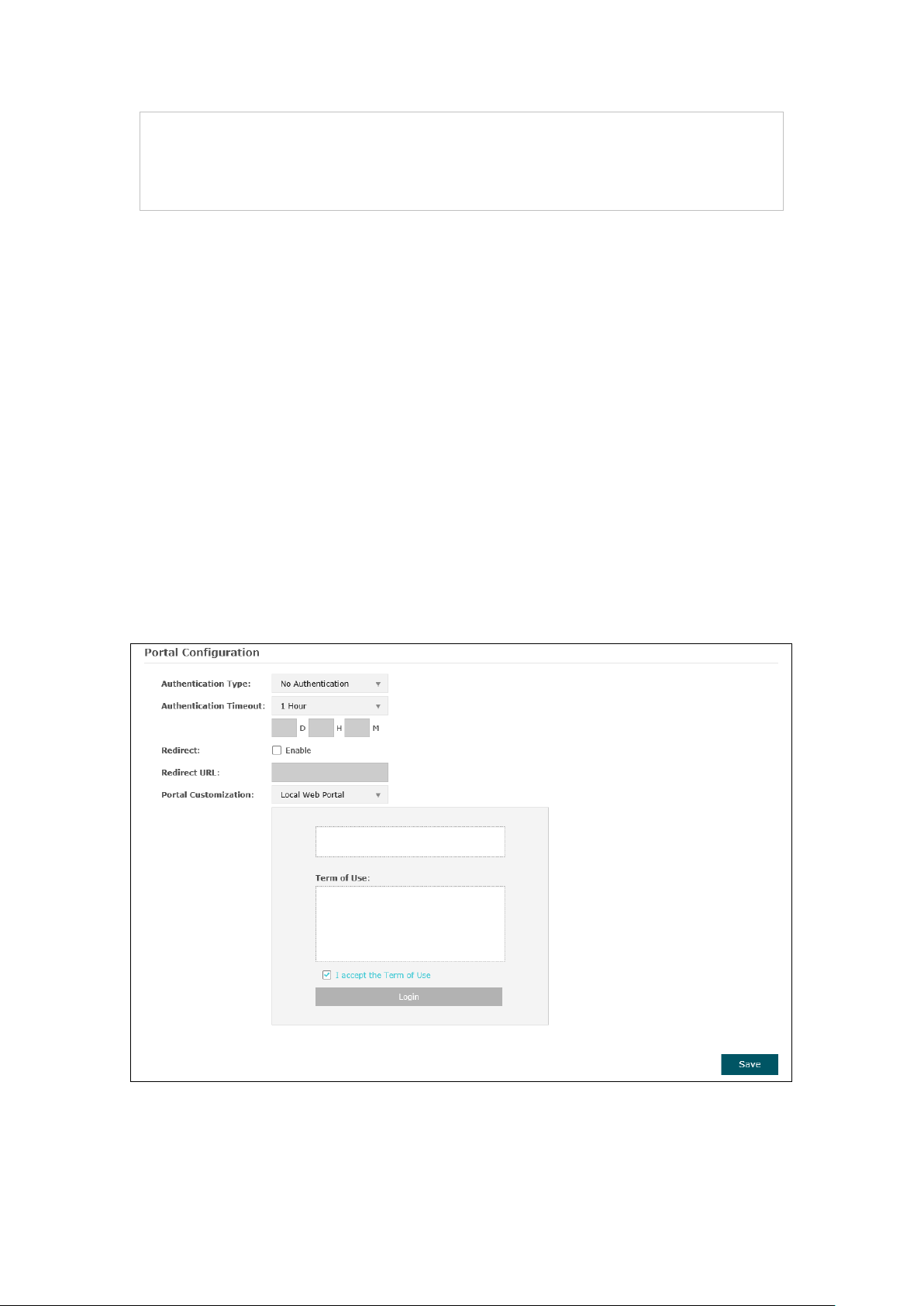
No Authentication
Figure 5-11 Portal Configuration_No Authentication
16
Page 20
Authentication
Select No Authentication.
Type:
Authentication
Timeout:
After successful verification, an authentication session is established.
Authentication Timeout decides the active time of the session. Within
the active time, the device keeps the authentication session open with
the associated client. To reopen the session, the client needs to log in
the web authentication page and enter the user name and password
again once authentication timeout is reached.
By default, authentication timeout is one hour. Select Custom from the
drop-down list to customize the parameter.
Redirect: Disable by default. Redirect specifies that the portal should redirect the
newly authenticated clients to the configured URL.
Redirect URL: If you enable the Redirect function, please enter the URL that a newly
authenticated client will be directed to.
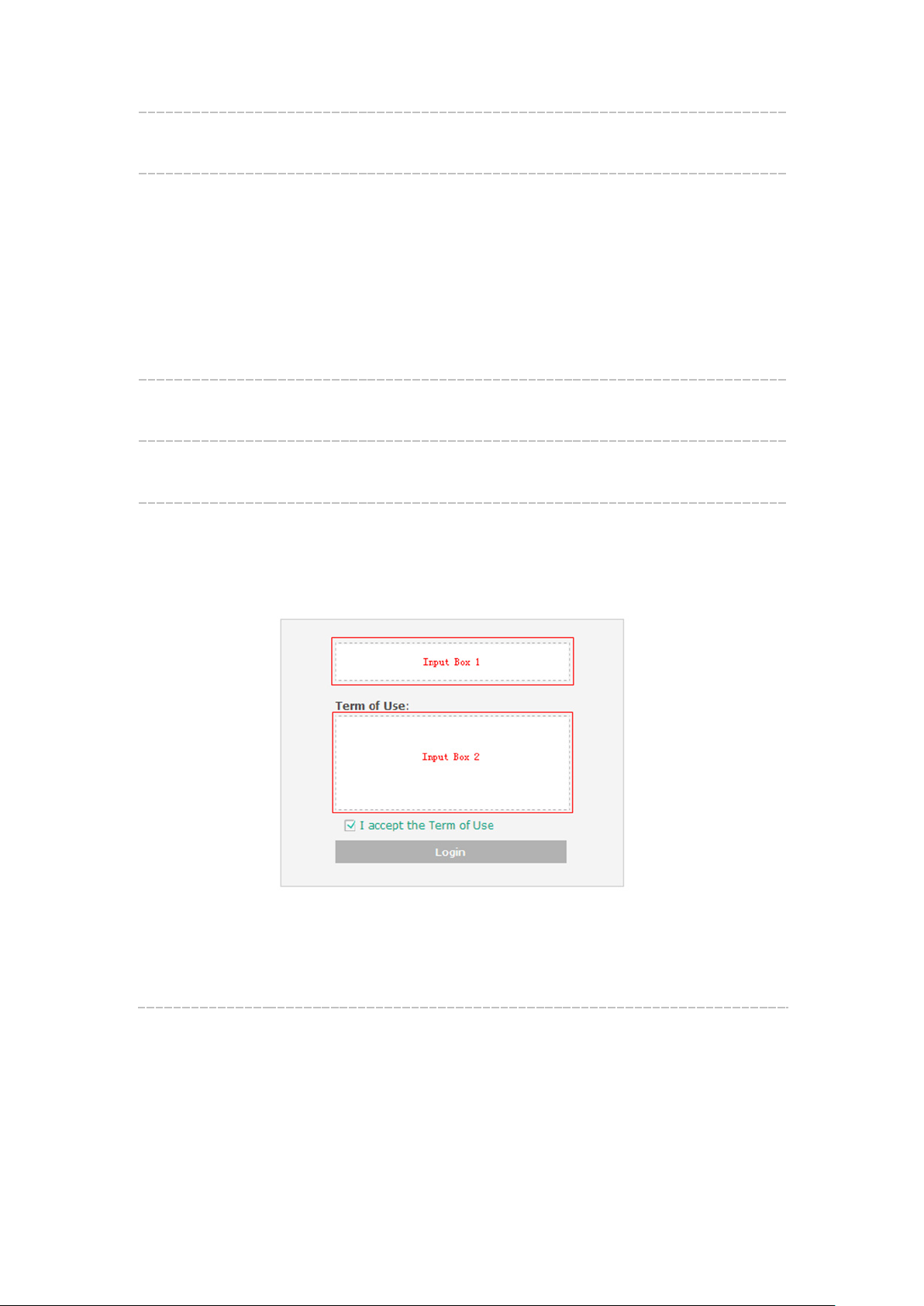
Portal
Customization:
Select Local Web Portal, the authentication login page will be provided
by the built-in web server.
The page configured below will be presented to users as the login page.
Words can be filled in Input Box 1 and Input Box 2.
Enter up to 31 characters as the title of the authentication login page in
Input Box 1, like “Guest Portal of TP-Link”.
Enter the terms presented to users in Input Box 2. The terms can be 1 to
1023 characters long.
17
Page 21

Local Password
External RADIUS Server
Figure 5-12 Portal Configuration_Local Password
Authentication Type: Select Local Password.
Password: Enter the password for local authentication.
Please refer to No Authentication to configure Authentication Timeout, Redirect,
Redirect URL, and Portal Customization.
External RADIUS Server
provides two types of portal customization: Local Web Portal
and External Web Portal. The authentication login page of Local Web Portal is provided
by the built-in portal server of the EAP, as
Figure 5-13 shown. The authentication login
page of External Web Portal is provided by external portal server, as Figure 5-14 shown.
18
Page 22
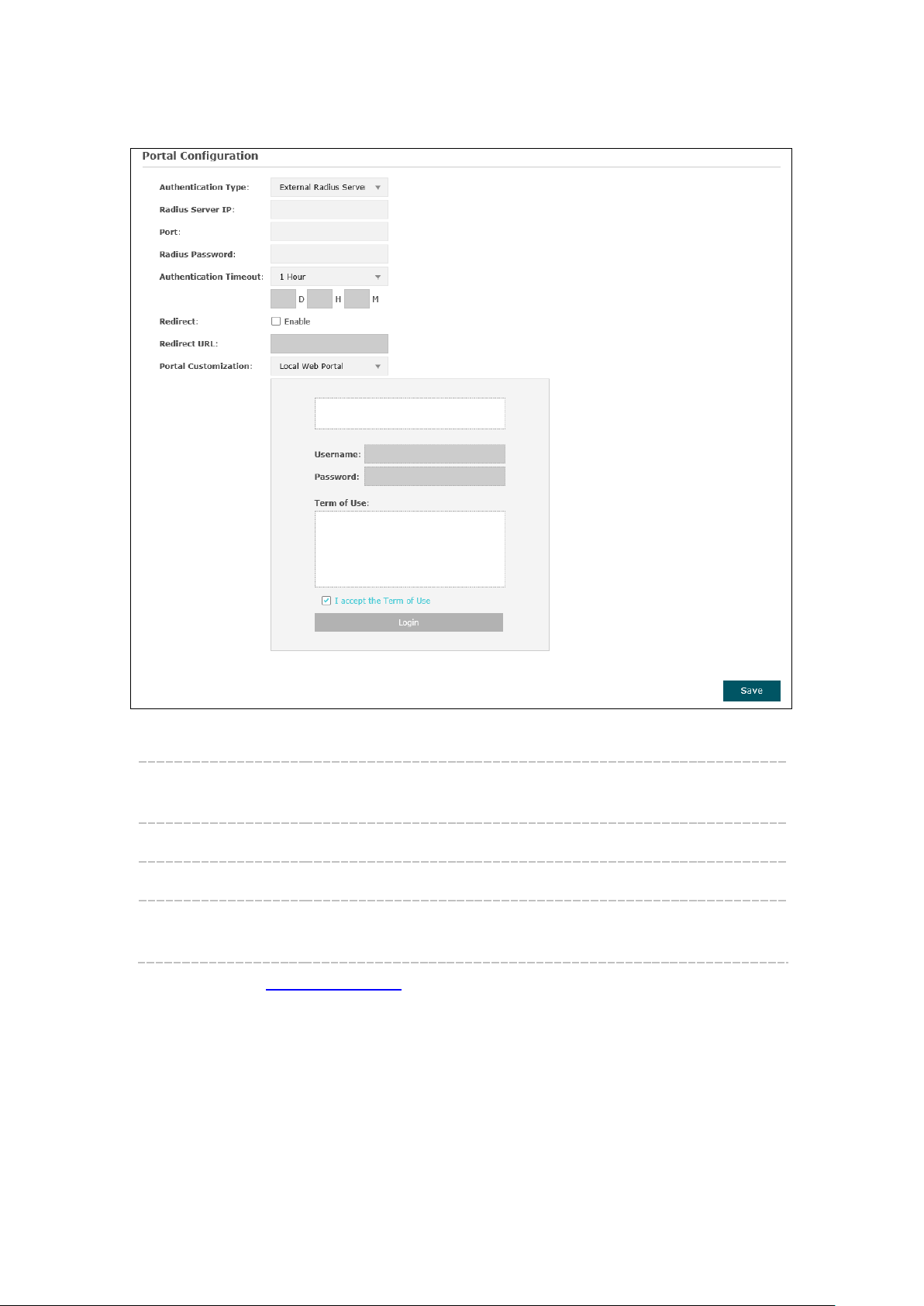
1. Local Web Portal
Figure 5-13 Portal Configuration_External RADIUS Server_Local Web Portal
Authentication
Type:
RADIUS Server IP: Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server.
Port: Enter the port for authentication service.
RADIUS Password: Enter the shared secret of RADIUS server to log in to the RADIUS
Select External RADIUS Server.
server.
Please refer to No Authentication to configure Authentication Timeout, Redirect,
Redirect URL, and Portal Customization.
19
Page 23
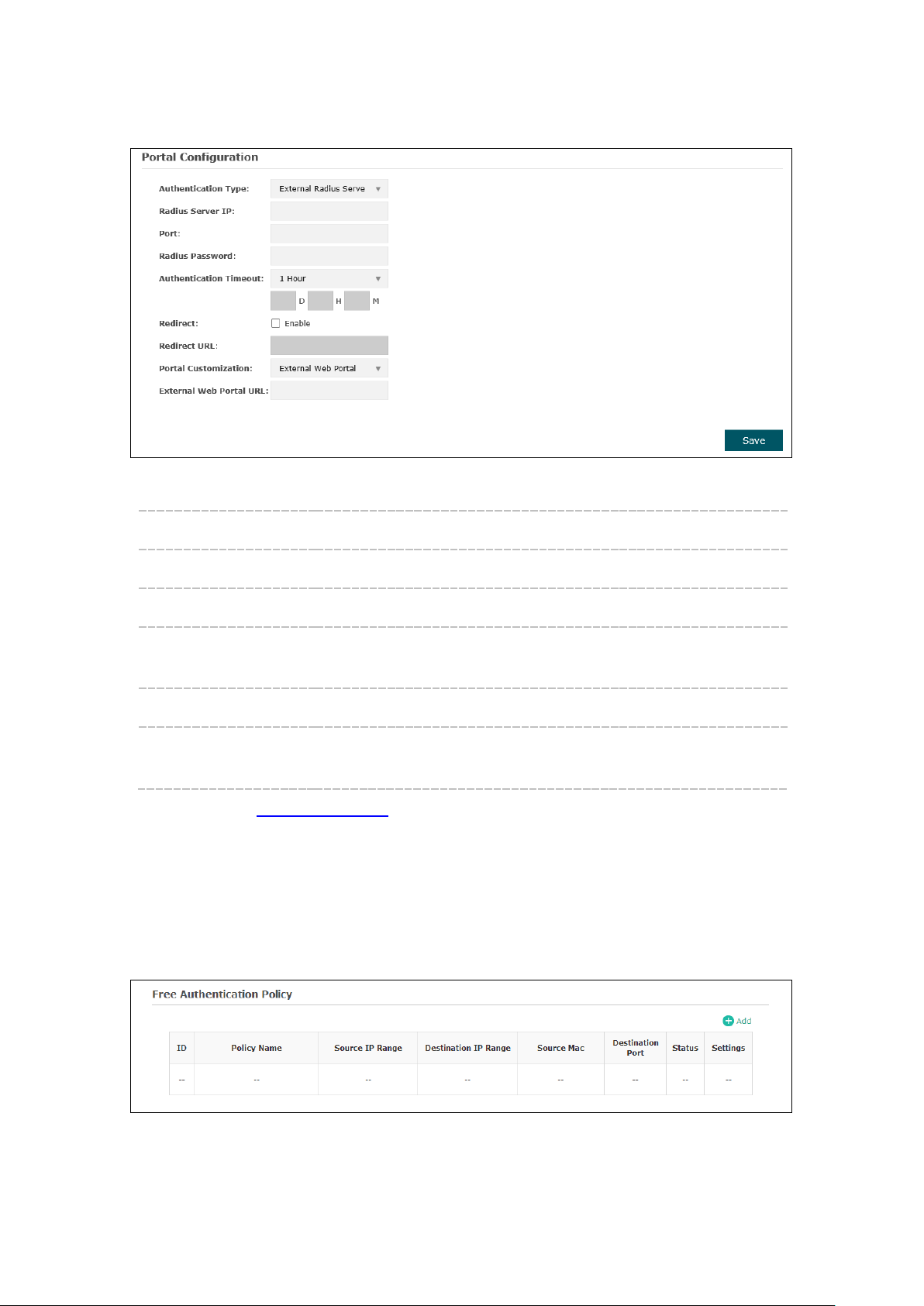
External Web Portal
2. External Web Portal
Figure 5-14 Portal Configuration_External RADIUS Server_External Web Portal
Authentication Type: Select External RADIUS Server.
RADIUS Server IP: Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server.
Port: Enter the port for authentication service.
RADIUS Password: Enter the shared secret of RADIUS server to log in to the RADIUS
server.
Portal Customization: Select External Web Portal.
Enter the authentication login page’s URL, which is provided by
URL:
the remote portal server.
Please refer to No Authentication to configure Authentication Timeout, Redirect and
Redirect URL.
5.2.2 Free Authentication Policy
Free Authentication Policy allows clients to access network resources for free. On the
lower part of the Portal page you can configure and view free authentication policies.
Figure 5-15 Free Authentication Policy
20
Page 24

Source IP
Destination IP
Click to add a new authentication policy and configure its parameters.
Figure 5-16 Configure Free Authentication Policy
Policy Name: Enter a policy name.
Enter the source IP address and subnet mask of the clients who can
Range:
enjoy the free authentication policy. Leaving the field empty means all IP
addresses can access the specific resources.
Enter the destination IP address and subnet mask for free authentication
Range:
policy. Leaving the field empty means all IP addresses can be visited.
When External Radius Server is configured and External Web Portal is
selected, please set the IP address and subnet mask of your external
web server as the Destination IP Range.
Source MAC: Enter the source MAC address of the clients who can enjoy the free
authentication policy. Leaving the field empty means all MAC addresses
can access the specific resources.
Destination
Port:
Enter the destination port for free authentication policy. Leaving the field
empty means all ports can be accessed.
Status: Check the box to enable the policy.
21
Page 25

Click the button OK in Figure 5-16 and the policy is successfully added as Figure 5-17
shows.
Figure 5-17 Add Free Authentication Policy
Here is the explanation of Figure 5-17: The policy name is Policy 1. Clients with IP
address range 192.168.2.0/24 are able to visit IP range 10.10.10.0/24. Policy 1 is enabled.
Click to edit the policy. Click to delete the policy.
5.3 MAC Filtering
MAC Filtering uses MAC addresses to determine whether one host can access the
wireless network. Thereby it can effectively control the user access to the wireless
network.
Figure 5-18 MAC Filtering Page
22
Page 26

Settings
Enable MAC
Check the box to enable MAC Filtering.
Filtering:
Station MAC Group
Follow the steps below to add MAC groups.
Step 1:
Click , two tables will be shown.
Figure 5-19 Station MAC Group
Step 2:
Click and fill in a name for the MAC group.
Figure 5-20 Add a Group
Step 3:
Select one MAC group, click and input the MAC address you want
to organize into this group.
23
Page 27
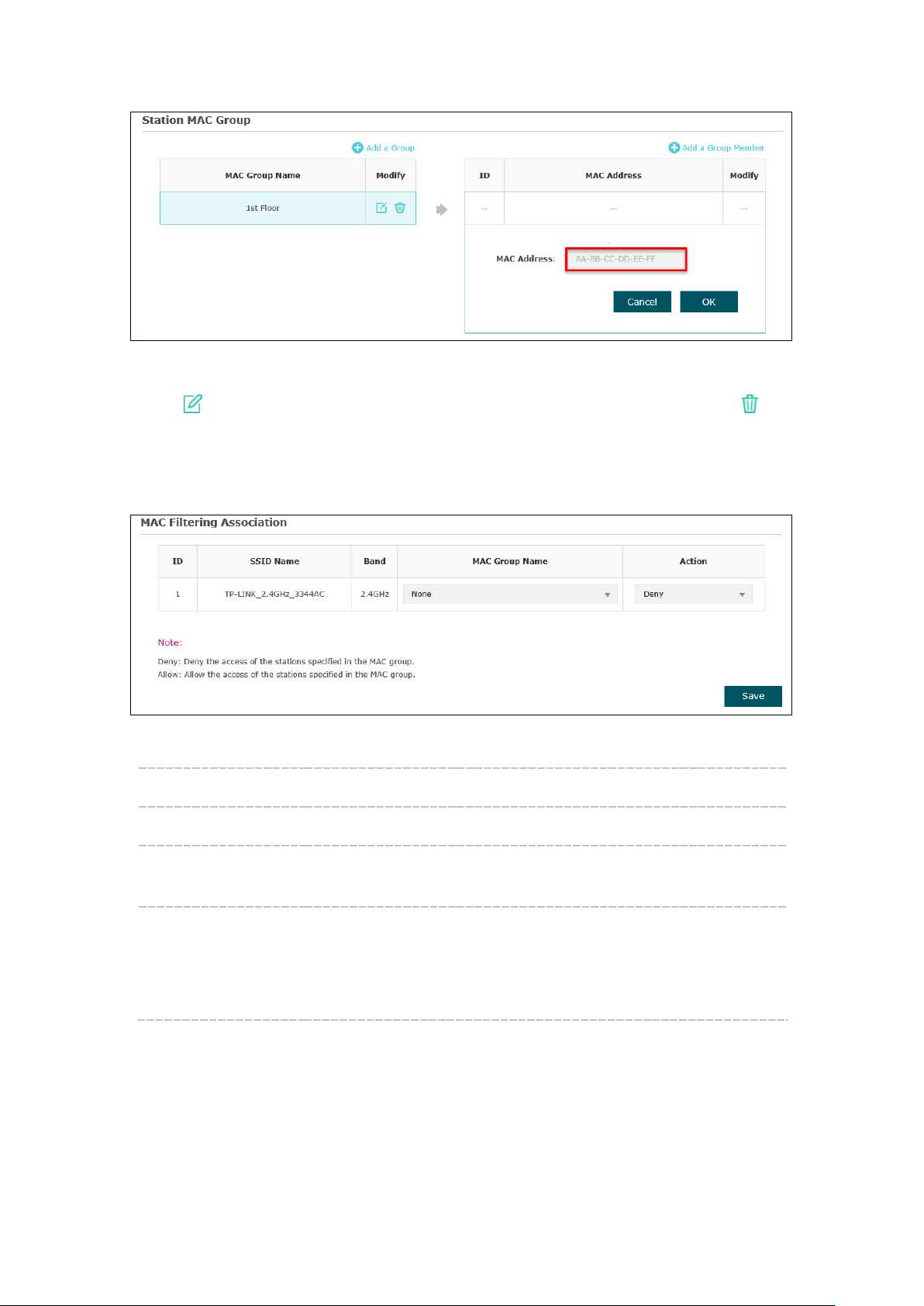
Figure 5-21 Add a Group Member
Click in Modify column to edit the MAC group name or MAC address. Click to
delete the MAC group or group member.
MAC Filtering Association
Figure 5-22 MAC Filtering Association
SSID Name: Displays the SSID of the wireless network.
Band: Displays the frequency band the wireless network operates at.
MAC Group Name: Select a MAC group from the drop-down list to allow or deny its
members to access the wireless network.
Action:
Allow: Allow the access of the stations specified in the MAC
group.
Deny: Deny the access of the stations specified in the MAC
group.
24
Page 28

5.4 Scheduler
Scheduler allows you to configure rules with specific time interval for radios to operate,
which automates the enabling or disabling of the radio.
Figure 5-23 Scheduler Page
Settings
Scheduler: Check the box to enable Scheduler.
Association Mode: Select Associated with SSID/AP, you can perform configurations on
the SSIDs/AP. The display of Scheduler Association is based on your
option here.
Scheduler Profile Configuration
Follow the steps below to add rules.
Step 1:
Click , two tables will be shown.
25
Page 29

Figure 5-24 Scheduler Profile Configuration
Step 2:
Click and input a profile name for the rule.
Figure 5-25 Add a Profile
Step 3:
Select one profile, and click and configure the recurring schedule for the
rule.
Figure 5-26 Add a Rule
26
Page 30

down list. Profile name is
Scheduler Association
This zone will display different contents based on your selection of association mode in
Settings
.
1. Associated with SSID
Figure 5-27 Scheduler Association_Associated with SSID
SSID Name: Displays the SSID of the standalone AP.
Band: Displays the frequency band which the wireless network operates at.
Profile Name: Select a profile name from the drop-
configured in Scheduler Profile Configuration.
Action: Select Radio On/Off to turn on/off the wireless network during the time
interval set for the profile.
2. Associated with AP
Figure 5-28 Scheduler Association_Associated with AP
AP: Displays the name of the device.
AP MAC: Displays the MAC address of the device.
Profile Name: Select a profile name from the drop-down list. Profile name is configured
in Scheduler Profile Configuration.
Action: Select Radio On/Off to turn on/off the wireless network during the time
interval set for the profile.
27
Page 31

5.5 QoS
The EAP supports Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize voice and video traffic over other
traffic types. In normal use, we recommend you keep the default values for the EAP
devices and station EDCA (Enhanced Distributed Channel Access).
Wi-Fi Multimedia
(WMM):
Figure 5-29 QoS Page
By default, WMM is enabled. After WMM is enabled, the device has the
QoS function to guarantee the transmission of audio and video
packets with high priority.
28
Page 32

sensitive data such as VoIP and streaming media are automatically
A list to the algorithm that determines the initial random backoff wait
5.5.1 AP EDCA Parameters
AP Enhanced Distributed Channel Access (EDCA) parameters affect traffic flowing from
the EAP device to the client station.
Figure 5-30 AP EDCA Parameters
Queue: Queue displays the transmission queue. By default, the priority from
high to low is Data 0, Data 1, Data 2, and Data 3. The priority may be
changed if you reset the EDCA parameters.
Arbitration InterFrame Space:
Minimum
Contention
Window:
Maximum
Contention
Window:
Data 0 (Voice)—Highest priority queue, minimum delay. Time-
sent to this queue.
Data 1 (Video)—High priority queue, minimum delay. Time-sensitive
video data is automatically sent to this queue.
Data 2 (Best Effort)—Medium priority queue, medium throughput and
delay. Most traditional IP data is sent to this queue.
Data 3 (Background)—Lowest priority queue, high throughput. Bulk
data that requires maximum throughput and is not time-sensitive is
sent to this queue (FTP data, for example).
A wait time for data frames. The wait time is measured in slots. Valid
values for Arbitration Inter-Frame Space are from 1 to 15.
time (window) for retry of a transmission.
This value cannot be higher than the value for the Maximum
Contention Window.
The upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling of the random backoff
value. This doubling continues until either the data frame is sent or the
Maximum Contention Window size is reached.
This value must be higher than the value for the Minimum Contention
Window.
29
Page 33

specifies (in milliseconds) the maximum burst length allowed for
decreased overhead results in higher throughput and better
:
:
Maximum Burst The Maximum Burst is an AP EDCA parameter that applies only to
traffic flowing from the EAP devices to the client station. This value
packet bursts on the wireless network. A packet burst is a collection
of multiple frames transmitted without header information. The
performance.
The valid values are multiples of 32 between 0 and 8192.
5.5.2 Station EDCA Parameters
Station EDCA parameters affect traffic flowing from the client station to the EAP device.
Queue
Arbitration InterFrame Space
Figure 5-31 Station EDCA Parameters
Queue displays the transmission queue. By default, the priority
from high to low is Data 0, Data 1, Data 2, and Data 3. The priority
may be changed if you reset the EDCA parameters.
Data 0 (Voice)—Highest priority queue, minimum delay. Timesensitive data such as VoIP and streaming media are automatically
sent to this queue.
Data 1 (Video)—High priority queue, minimum delay. Timesensitive video data is automatically sent to this queue.
Data 2 (Best Effort)—Medium priority queue, medium throughput
and delay. Most traditional IP data is sent to this queue.
Data 3 (Background)—Lowest priority queue, high throughput.
Bulk data that requires maximum throughput and is not timesensitive is sent to this queue (FTP data, for example).
A wait time for data frames. The wait time is measured in slots. Valid
values for Arbitration Inter-Frame Space are from 0 to 15.
30
Page 34

Minimum
:
A list to the algorithm that determines the initial random backoff
:
Transmission Opportunity (TXOP) is an interval of time, in
:
to specify that the EAP device should not
Automatic Power
Detected Rogue AP List
Trusted AP List
Contention
Window
wait time (window) for retry of a transmission. This value cannot be
higher than the value for the Maximum Contention Window.
Maximum
Contention
Window
TXOP Limit:
No
Acknowledgement
Unscheduled
Save Delivery:
The upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling of the random
backoff value. This doubling continues until either the data frame is
sent or the Maximum Contention Window size is reached.
This value must be higher than the value for the Minimum
Contention Window.
The TXOP Limit is a station EDCA parameter and only applies to
traffic flowing from the client station to the EAP device. The
milliseconds, when a WME client station has the right to initiate
transmissions onto the wireless medium (WM) towards the EAP
device.
The valid values are multiples of 32 between 0 and 8192.
Select Enable
acknowledge frames with QosNoAck as the service class value. By
default, it is disabled.
Select Enable to enable APSD, which is a power management
method. APSD is recommended if VoIP phones access the network
through the EAP device. By default, it is enabled.
5.6 Rogue AP Detection
A Rogue AP is an access point that has been installed on a secure network without
explicit authorization from a system administrator.
The EAP device can scan all channels to detect all APs in the vicinity of the network. If
rogue APs are detected, they are shown on the
as a rogue is legitimate, you can add it to the
.
. If an AP listed
31
Page 35

Figure 5-32 Rogue AP Detection Page
5.6.1 Settings
Figure 5-33 Enable Rogue AP Detection
Rogue AP Detection: Check the box to enable Rogue AP Detection, then click Save.
5.6.2 Rogue AP List detected
Information about the detected rogue APs is displayed in the list. By default, the status
of the detected rogue AP is unknown. You can click Known in Action column to move
the AP to the Trusted AP List.
32
Page 36

Figure 5-34 Detected Rogue AP List
Action: Click Known to move the AP to the Trusted AP List. After the configurations
MAC: The MAC address of the rogue AP.
SSID: The SSID of the rogue AP.
Band: Displays the frequency band which the wireless network of the rogue AP
Channel: The channel on which the rogue AP is currently broadcasting.
Security: Displays the enabling or disabling of the security mode of the wireless
Beacon
Interval:
Click to scan rogue APs. Make sure you have enabled Rogue AP Detection
and saved the setting before you click the button.
are saved, the moved AP will not be displayed in the Detected Rogue AP
List.
operates at.
network.
The beacon interval used by the rogue AP.
Beacon frames are transmitted by an AP at regular intervals to announce
the existence of the wireless network. The default behavior is to send a
beacon frame once every 100 milliseconds (or 10 per second).
Signal: The strength of the radio signal emitting from the rogue AP.
5.6.3 Trusted AP List
Information about the trusted APs is displayed in the list.
Figure 5-35 Trusted AP List
Action: Click Unknown to move the AP out of the Trusted AP List.
33
Page 37

Source File
NOTE:
EAP device does not have any control over the APs in the Detected Rogue AP List.
MAC: The MAC address of the trusted AP.
SSID: The SSID of the trusted AP.
Band: Displays the frequency band which the wireless network of the trusted AP
operates at.
Channel: The channel on which the trusted AP is currently broadcasting.
Security: Displays the enabling or disabling of the security mode of the wireless
network.
5.6.4 Download/Backup Trusted AP List
You can import a list of trusted APs from a saved list which is acquired from another AP
or created from a text file. The AP whose MAC address is in the Trusted AP List will not
be detected as a rogue.
You can also backup a list and save it in your PC.
Figure 5-36 Download/Backup Trusted AP List
Save Action: Select Download (PC to AP) to import a trusted AP list to the device.
Select Backup (AP to PC) to copy the trusted AP list to your PC.
Click Browse and choose the path of a saved trusted AP list or to save
Name:
File
Management:
a trusted AP list.
Select Replace to import the list and replace the contents of the
Trusted AP List.
Select Merge to import the list and add the APs in the imported file to
the APs currently shown in the Trusted AP List
34
Page 38

On
Monitoring
AP List
Monitoring
on
AP, SSID and Client.
6.1 AP
Chapter 6 Monitoring
page, you can monitor the network running status and statistics based
number of clients. Below the AP List the AP’s detailed information will be shown,
including
Radio Traffic.
on the
Device Information, Wireless Settings, LAN Information, Client, LAN Traffic and
page displays the device name, its MAC address and the
6.1.1 AP List
Figure 6-1 AP Monitoring
Figure 6-2 AP List
35
Page 39

o preliminarily judge
Device Name: Displays the device name.
MAC: Displays the MAC address of the EAP.
Num of Clients: Displays the number of clients connected to the EAP.
Device Information
Figure 6-3 Device Information
Device Name: Displays the device name.
Device Model: Displays the model of the device.
Firmware
Version:
Displays the firmware version of the device. If you want to upgrade the
firmware, please refer to 8.5 Firmware Upgrade
.
System Time: Displays the system time of the device. If you want to adjust the system
time, please refer to 8.2.1 Time Settings
.
Uptime: Displays the time that has elapsed since the last reboot.
CPU0/CPU1: Displays the CPU occupancy, which helps you t
whether the device functions properly.
Memory: Displays the memory usage , which helps you to preliminarily judge
whether the device functions properly.
36
Page 40

Wireless Settings
Figure 6-4 Wireless Settings
Channel/Frequency: Displays the channel number and the operating frequency. If you
want to change them, please refer to 5.1.1 Wireless Basic Settings
Channel Width: Displays the spectral width of the radio channel used by the device.
If you want to change it, refer to 5.1.1 Wireless Basic Settings
.
.
IEEE802.11 Mode: Displays the radio standard used for operation of your device. If you
want to change it, refer to 5.1.1 Wireless Basic Settings
Max TX Rate: Displays the maximum data rate at which the device should
transmit wireless packets.
Transmit Power: Displays the maximum average transmit power of the device. If you
want to change it, refer to 5.1.1 Wireless Basic Settings
LAN Information
Figure 6-5 LAN Information
.
.
MAC Address: Displays the MAC address of the device.
IP Address: Displays the IP address of the device.
Subnet Mask: Displays the subnet mask of the device.
37
Page 41

LAN Port1/
Displays the maximum transmission rate and duplex mode (half-duplex
LAN Port2:
Client
or full-duplex) of the port.
Figure 6-6 Client
MAC: Displays the MAC address of the client of the AP selected in AP List.
SSID: Displays the SSID the client is connected to.
SNR(dB): Signal to Noise Ratio, the power ratio between the received wireless signal
strength and the environmental noise strength. The bigger the value of SNR
is, the better network performance the device provides.
CCQ(%): Displays the wireless Client Connection Quality (CCQ). CCQ refers to the
ratio of current effective transmission bandwidth and the theoretically
maximum available bandwidth. CCQ reflects the actual link condition.
Rate(Mbps): Displays the data rate at which the client transmits wireless packets.
Down(Byte): Displays the throughput of the downstream data.
Up(Byte): Displays the throughput of the upstream data.
Active Time: Displays the amount of time the client has been connected to the device.
LAN Traffic
Click LAN Traffic and you can monitor the data transmission status of the LAN port.
Figure 6-7 LAN Traffic
Rx/Tx Packets: Displays the total amount of packets received/sent on the LAN port.
38
Page 42

Rx/Tx Dropped
Rx/Tx Bytes: Displays the total amount of data (in bytes) received/sent on the LAN
port.
Displays the total amount of dropped packets received/sent on the
Packets:
LAN port.
Rx/Tx Errors: Displays the total amount of error packets received/sent on the LAN
port.
Radio Traffic
Click Radio Traffic and you can monitor the data transmission status of the wireless
network.
Figure 6-8 Radio Traffic
Rx/Tx Packets: Displays the total amount of packets received/sent by the wireless
network.
Rx/Tx Bytes: Displays the total amount of data (in bytes) received/sent by the
wireless network.
Rx/Tx Dropped
Packets:
Displays the total amount of dropped packets received/sent by the
wireless network.
Rx/Tx Errors: Displays the total amount of error packets received/sent by the
wireless network.
39
Page 43

6.2 SSID
SSID List
6.2.1 SSID List
Figure 6-9 SSID Monitoring
In
SSID Name: Displays the SSID name. If you want to modify it, please refer to
VLAN ID: Displays the VLAN which the SSID belongs to. If you want to change
Num of Clients: Displays the number of clients connected to the SSID. If you want to
SSID
Broadcast:
you can monitor the related parameters of the wireless network.
Figure 6-10 SSID List
SSIDs.
the VLAN ID, please refer to 5.1.2 SSIDs
get more information about these clients, please refer to 5.1.2 SSIDs
Displays the enabling or disabling of SSID broadcast. If you want to
modify it, please refer to 5.1.2 SSIDs
.
.
5.1.2
.
Band: Displays the frequency band the wireless network is operating at.
Security: Displays the security mode the wireless network is applying. If you
want to modify it, please refer to 5.1.2 SSIDs
Portal: Displays the enabling or disabling of Portal. If you want to modify it,
please refer to 5.1.2 SSIDs
.
40
.
Page 44

MAC Filtering:
Displays the enabling or disabling of MAC Filtering. If you want to
Displays the enabling or disabling of SSID Isolation. If you want to
User List
modify it, please refer to 5.1.2 SSIDs.
Isolation:
modify it, please refer to 5.1.2 SSIDs.
Down(Byte): Displays the throughput of the downstream data.
Up(Byte): Displays the throughput of the upstream data.
6.3 Client
From
including those who are authenticated.
, you can monitor the status of all the clients connected to the EAP
Figure 6-11 Client Monitoring
6.3.1 User List
Figure 6-12 User List
MAC: Displays the MAC address of the client.
41
Page 45

Portal Authenticated Guest
Band: Displays the band the client is in.
Access
Point:
SSID: Displays the SSID the client is connected to.
SNR(dB): Signal to Noise Ratio, the power ratio between the received wireless
CCQ(%): Displays the wireless Client Connection Quality (CCQ). CCQ refers to the
Rate(Mbps): Displays the data rate at which the client transmits wireless packets.
Down(Byte): Displays the throughput of the downstream data.
Up(Byte): Displays the throughput of the upstream data.
Active Time: Displays the amount of time the client has been connected to the device.
Displays the name of the device to which the client is connected.
signal strength and the environmental noise strength. The bigger the
value of SNR, the better network performance the device provides.
ratio of current effective transmission bandwidth and the theoretically
maximum available bandwidth. CCQ reflects the actual link condition.
6.3.2 Portal Authenticated Guest
The
displays information about clients that have set up
valid authentication.
Figure 6-13 Portal Authenticated Guest
MAC: Displays the MAC address of the authenticated client.
Band: Displays the band the authenticated client is in.
Access
Point:
SSID: Displays the SSID the authenticated client is connected to.
SNR(dB): Signal to Noise Ratio, the power ratio between the received wireless
Displays the name of the device to which the authenticated client is
connected
signal strength and the environmental noise strength. The bigger the
value of SNR, the better network performance the device provides.
42
Page 46

CCQ(%): Displays the Client Connection Quality (CCQ) of the authenticated client.
CCQ refers to the ratio of current effective transmission bandwidth and
the theoretically maximum available bandwidth. CCQ reflects the actual
link condition.
Rate(Mbps): Displays the data rate at which the authenticated client transmits wireless
packets.
Down(Byte): Displays the throughput of the downstream data.
Up(Byte): Displays the throughput of the upstream data.
Active Time: Displays the amount of time the client has been authenticated on the root
AP.
Action: Click Unauthorize to stop giving authorization to the clients connected to
the wireless network.
43
Page 47
Management
System Log
Log List
Chapter 7 Management
page is mainly used for device management and maintenance.
7.1 System Log
System log records information about hardware, software as well as system issues and
monitors system events. With the help of system log, you can get informed of system
running status and detect the reasons for failure.
Following is the page of
.
7.1.1 Log List
From
issues and so on.
you can view detailed information about hardware, software, system
Figure 7-1 System Log Page
44
Page 48

7.1.2 Log Settings
Log Settings
Figure 7-2 Log List
You can choose the way to receive system logs in
parameters can be configured:
Enable Auto Mail
Enable Auto Mail, Enable Server and Enable Nvram.
Figure 7-3 Log Settings
zone, where these
If Auto Mail Feature is enabled, system logs will be sent to a mailbox. The following
content will be shown.
Figure 7-4 Enable Auto Mail
From: Enter the sender’s email address.
45
Page 49

System Log Server
Web Server
To: Enter the recipient’s email address, which will receive the system logs.
SMTP Server: Enter the IP address of the SMTP server.
Enable
Authentication:
Generally users are required to log in to the SMTP server by entering
user name and password.
User Name: Enter the sender’s email address.
Password: Enter the password of the sender’s email address.
Confirm Password: Enter the password again for confirmation.
Time Mode: System logs can be sent at specific time or time interval.
Fixation Time: Set a fixed time, for example, 15:00. The recipient will
receive the system logs sent by the device at 15:00 every day.
Period Time: Set a time interval, for example, 5 hours. The recipient
will receive the system logs sent by the device every 5 hours.
Enable Server
System logs can also be sent to a server. After Enable Server is enabled, the following
content will be shown.
Figure 7-5 Enable Server
System Log Server IP: Enter the IP address of the remote server.
Enter the port of the remote server.
Port:
Enable Nvram
By default, Nvram is disabled. Check the box to enable Nvram, system logs will be saved
after power supply is cut.
Nvram (Non-volatile Random Access Memory) is a RAM that can still save data even if a
device is power off. All TP-Link EAPs are equipped with Nvram. With this option enabled,
the Nvram feature can help reserve the system logs when an EAP device is power off.
7.2 Web Server
You can log in web management interface, thereby manage and maintain the device.
Following is the page of
.
46
Page 50

Secure Server
to go back to web
Management Access
Figure 7-6 Web Server Page
HTTPS: HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is enabled by default.
Designate a secure server port for web server in HTTPS mode. By
Port:
default the port is 443.
Server Port: Designate a server port for web server in HTTP mode. By default the port
is 80.
Session
Timeout:
Set the session timeout time. If you do nothing with the web
management page within the timeout time, the system will log out
automatically. Please login again if you want
management page.
7.3 Management Access
Management Access Control allows you to configure up to four MAC addresses of the
hosts that are allowed to log in to the web management page of the EAP. Click Add PC’s
MAC and the MAC address of the current host will be added to MAC address list.
Following is the page of
.
47
Page 51

MAC
Check the box to enable MAC Authentication. After MAC
LED ON/OFF
LED ON/OFF
Wi-Fi Control
Authentication:
Figure 7-7 Management Access Page
Authentication is enabled, only the PCs in MAC address list can log in
the device’s web management page. By default this function is
disabled. All PCs in LAN can log in and manage the device.
MAC1~MAC4: Enter the MAC addresses of the PCs which are authorized to log in the
device.
7.4 LED ON/OFF
can turn on/off the LED by pressing the LED button. When this function is disabled, the
LED button is invalid, and the LED is always off.
Following is the page of
function allows you to control the LED. When this function is enabled, you
.
Figure 7-8 LED ON/OFF
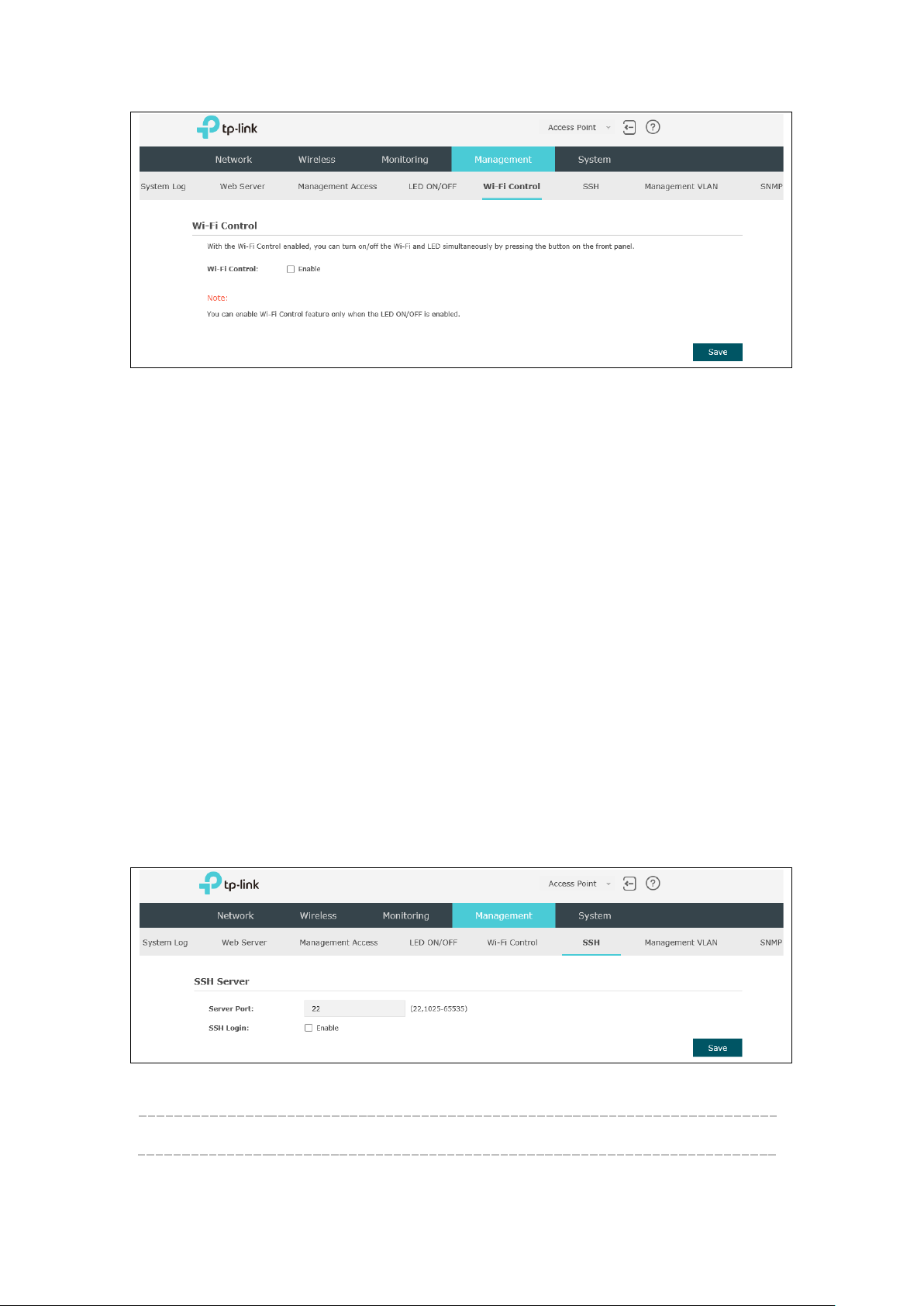
7.5 Wi-Fi Control
Following is the page of
. By default the Wi-Fi Control is disabled.
48
Page 52
SSH
Figure 7-9 Wi-Fi Control
With the Wi-Fi Control enabled, you can turn on/off the Wi-Fi and LED simultaneously
by pressing the button on the front panel.
Note: You can enable Wi-Fi Control feature only when the
LED ON/OFF
is enabled.
7.6 SSH
This device supports the SSH Server function that allows users to login and manage it
through SSH connection on the SSH client software.
SSH (Secure Shell) is a security protocol established on application and transport layers.
SSH-encrypted-connection is similar to a telnet connection, but essentially the old
telnet remote management method is not safe, because the password and data
transmitted with plain-text can be easily intercepted. SSH can provide information
security and powerful authentication when you login this device remotely through an
insecure network environment. It can encrypt all the transmission data and prevent the
information in remote management from being leaked.
Following is the page of
.
Figure 7-10 SSH Page
Server Port: Enter the server port. By default, it is port 22.
49
Page 53

Management VLAN
SSH Login: Check the box to enable SSH Server. By default, it is disabled.
7.7 Management VLAN
Management VLAN provides a safer way for you to manage the EAP. With Management
VLAN enabled, only the hosts in the management VLAN can manage the EAP. Since most
hosts cannot process VLAN TAGs, connect the management host to the network via a
switch, and set up correct VLAN settings for the switches on the network to ensure the
communication between the host and the EAP in the management VLAN.
Following is the page of
Figure 7-11 Management VLAN
.
7.8 SNMP
The device can be configured as an SNMP agent.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), the most widely applied network
management protocol, provides a management framework to monitor and maintain
Internet devices. Main functions of SNMP include monitoring network performance,
detecting and analyzing network error, configuring network devices, and so on. When
networks function properly, SNMP can perform the functions of statistics, configuration
and testing. When networks have troubles, SNMP can detect and restore these troubles.
An SNMP consists of three key components: manager, agent and MIB (Management
Information Base). SNMP manager is a client program operating at workstation, assisting
network administrators to accomplish most network device management tasks. An
agent is a network-management software module that resides on a managed device and
responsible for receiving and dealing with data sent by managing device. Generally the
managed devices are network devices including hosts, bridges, switches and routers.
MIB is the collection of managed devices. It defines a series of properties of the
managed devices. Every SNMP agent has its own MIB.
Once the device has become an SNMP agent, it is able to receive and process request
messages from SNMP manager.
50
Page 54

SNMP
only right of the device's SNMP
Following is the page of
SNMP Agent: Enable SNMP Agent and the SNMP Agent will collect the information of
this device and respond to information requests from one or more
management systems.
.
Figure 7-12 SNMP Page
SysContact: Enter the textual identification of the contact person for this managed
node.
SysName: Enter an administratively-assigned name for this managed node.
SysLocation: Enter the physical location of this managed node.
Get
Community:
Get Source: Defines the IP address (for example, 10.10.10.1) or subnet for
Set
Community:
Community refers to a host group aiming at network management. Get
Community only has the readinformation. The community name can be considered a group
password. The default setting is public.
management systems that can serve as Get Community to read the
SNMP information of this device. The format of subnet is “IP
address/bit” (such as 10.10.10.0/24). The default is 0.0.0.0, which
means all hosts can read the SNMP information of this device.
Set Community has the read and write right of the device's SNMP
information. Enter the community name that allows read/write access
to the device's SNMP information. The community name can be
considered a group password. The default setting is private.
51
Page 55

NOTE:
community is blank, the SNMP Agent will not respond to any community name.
Set Source: Defines the IP address (for example, 10.10.10.1) or subnet for
management systems that can serve as Set Community to read and
write the SNMP information of this device. The format of subnet is “IP
address/bit” (such as 10.10.10.0/24). The default is 0.0.0.0, which
means all hosts can read and write the SNMP information of this
device.
Defining community can allow management systems in the same community to
communicate with the SNMP Agent. The community name can be seen as the shared
password of the network hosts group. Thus, for the security, we suggest modifying the
default community name before enabling the SNMP Agent service. If the field of
52
Page 56

System
Chapter 8 System
time, and realize functions including reboot, reset, backup, restore and upgrade the
device.
page is mainly used to configure some basic information like user account and
8.1 User Account
You can change the username and password to protect your device from unauthorized
login. We recommend that you change the default user password on the very first
system setup.
Figure 8-1 User Account Page
Old User
Name/Password:
New User
Name/Password:
Confirm New
Password:
Enter the present user name and password of the admin account to
get the permission of modification.
Enter a new user name and password for the admin account. Both
values are case-sensitive, up to 64 characters and with no space. New
Password must not be "admin"
Enter the new password again.
8.2 Time Settings
System time represents the device system’s notion of the passing of time. System time
is the standard time for Scheduler and other time-based functions. You can manually set
53
Page 57

the system time, configure the system to acquire its time settings from a preconfigured
NTP server or synchronize the system time with the PC’s clock.
The device supports DST (Daylight Saving Time).
8.2.1 Time Settings
Figure 8-2 Time Settings
Figure 8-3 Time Settings
Click the button and the device will obtain GMT time from NTP
server. IP address of the NTP server has to be filled in.
54
Page 58

Click the button and save the configuration, your PC’s time will
be obtained as the device’s system time.
Time zone: Select your local time zone from the drop-down list.
Date: Set the current date, in format MM/DD/YYYY. For example, for
November 25, 2014, enter 11/25/2014 in the field.
Time: Specify the device’s time. Select the number from the drop-
down list in time format HH/MM/SS.
Primary/Secondary NTP
Server:
If you’ve selected Get GMT from an NTP server, please input
the primary NTP sever address and an alternative NTP server
address.
8.2.2 Daylight Saving
Figure 8-4 Daylight Saving
Daylight Saving: Enable or disable the DST. DST is disabled by default.
Mode: Options include Predefined Mode, Recurring Mode and Date Mode.
Please refer to the following content for more information.
Predefined Mode
Figure 8-5 Predefined Mode
Mode: Select Predefined Mode.
55
Page 59

Sunday in March, 01:00 ~ Last Sunday in
Predefine
Country:
Recurring Mode
Select a predefined DST configuration. Europe is the predefined
country by default.
USA: Second Sunday in March, 02:00 ~ First Sunday in
November, 02:00
European: Last
October, 01:00
Australia: First Sunday in October, 02:00 ~ First Sunday in April,
03:00
New Zealand: Last Sunday in September, 02:00 ~ First Sunday in
April, 03:00
Figure 8-6 Recurring Mode
Mode: Select Recurring Mode. The configuration is recurring in use.
Time Offset: Specify the time adding in minutes when Daylight Saving Time comes.
Start/End: Select starting time and ending time of Daylight Saving Time.
Date Mode
Figure 8-7 Date Mode
Mode: Select Date Mode.
Time Offset: Specify the time adding in minutes when Daylight Saving Time comes.
Start/End: Select starting time and ending time of Daylight Saving Time.
56
Page 60

8.3 Reboot/Reset
Figure 8-8 Reboot & Reset
Click Reboot to restart the device. Click Reset to restore the device to factory default
settings.
8.4 Backup & Restore
Figure 8-9 Backup & Restore
You can save the current configuration of the EAP as a backup file and restore the
configuration via a backup file. To prevent the settings from being lost, we recommend
that you back up the settings before you upgrade the device or upload a new
configuration file.
Restore function helps you to restore the device to previous settings by uploading a
backup file.
57
Page 61
NOTE:
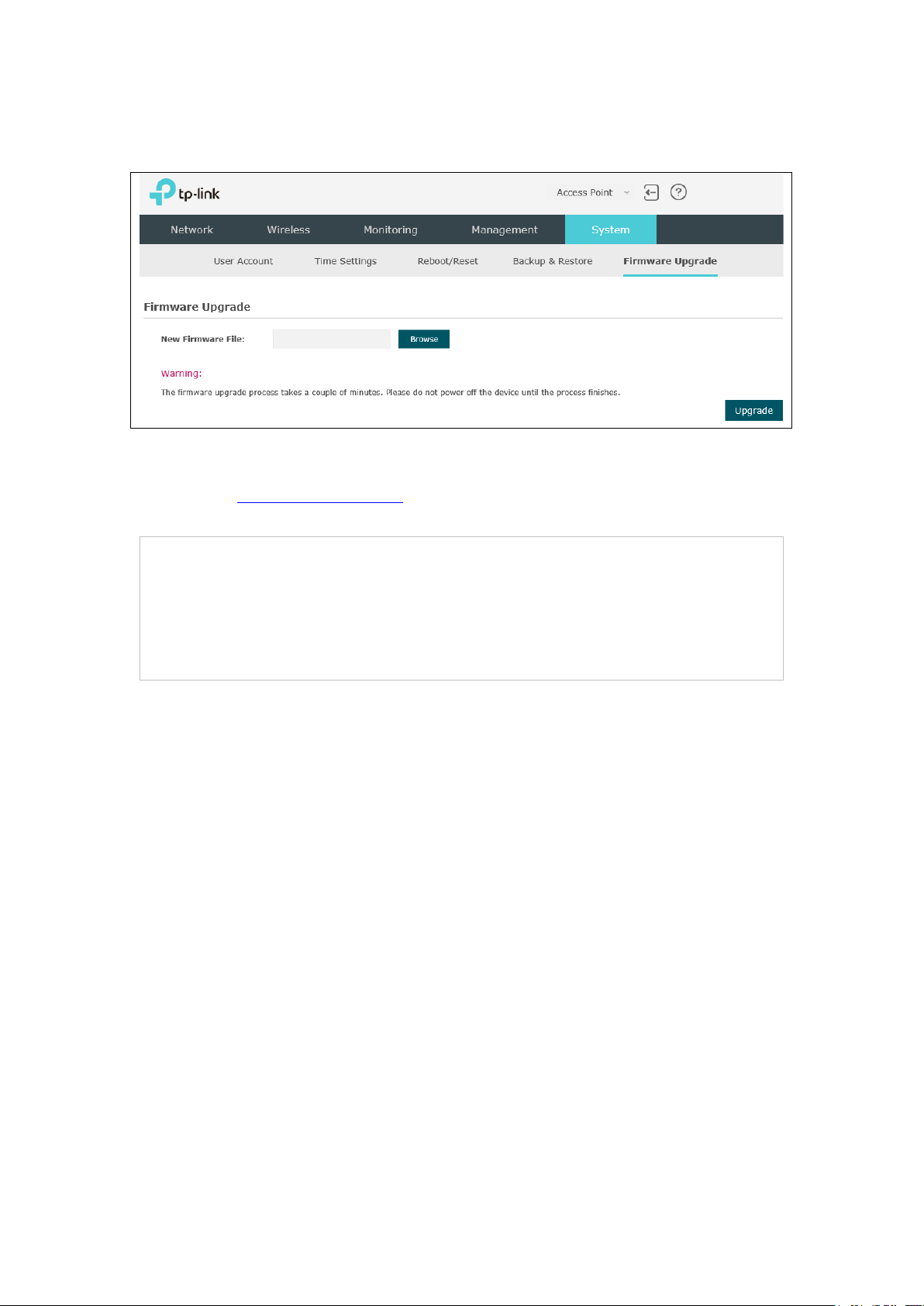
8.5 Firmware Upgrade
Figure 8-10 Firmware Upgrade
Please log in http://www.tp-link.com/ to download the latest system file. Click Browse to
choose the firmware file. Click Upgrade to upgrade the devices.
1. Please select the proper software version that matches your hardware to upgrade.
2. To avoid damage, please do not turn off the device while upgrading.
3. After upgrading, the device will reboot automatically.
58
Page 62

COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS
Specifications are subject to change without notice. is a registered
trademark of TP-Link Technologies CO., LTD. Other brands and product names are
trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
No part of the specifications may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to
make any derivative such as translation, transformation, or adaptation without
permission from TP-Link Technologies CO., LTD. Copyright © 2016 TP-Link
Technologies CO., LTD. All rights reserved.
Page 63

FCC STATEMENT
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/ TV technician for help.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions:
1) This device may not cause harmful interference.
2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Note: The manufacturer is not responsible for any radio or TV interference caused by
unauthorized modifications to this equipment. Such modifications could void the user’s
authority to operate the equipment.
FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This device and its antenna must not be co-located or
operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
“To comply with FCC RF exposure compliance requirements, this grant is applicable to
only Mobile Configurations. The antennas used for this transmitter must be installed to
Page 64

provide a separation distance of at least 20 cm from all persons and must not be co-
located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.”
RF Exposure Information
This device meets the EU requirements (1999/5/EC Article 3.1a) on the limitation of
exposure of the general public to electromagnetic fields by way of health protection.
The device complies with RF specifications when the device used at 20 cm from your
body.
CE Mark Warning
This is a class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio
interference, in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with IC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance
20cm between the radiator & your body.
Déclaration d'exposition aux radiations:
Cet équipement est conforme aux limites d'exposition aux rayonnements IC établies
pour un environnement non contrôlé. Cet équipement doit être installé et utilisé avec un
minimum de 20 cm de distance entre la source de rayonnement et votre corps.
Canadian Compliance Statement
This device complies with Industry Canada license-exempt RSSs. Operation is subject
to the following two conditions:
1) This device may not cause interference, and
2) This device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause
undesired operation of the device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d’Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils
radio exempts de licence. L’exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes :
1) l’appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage;
2) l’utilisateur de l’appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, meme si
le brouillage est susceptible d’en compromettre le fonctionnement.
Page 65

Industry Canada Statement
CAN ICES-3 (B)/NMB-3(B)
Korea Warning Statements
당해 무선설비는 운용중 전파혼신 가능성이 있음.
Продукт сертифіковано згідно с правилами системи УкрСЕПРО на відповідність
вимогам нормативних документів та вимогам, що передбачені чинними
законодавчими актами України.
Safety Information
When product has power button, the power button is one of the way to shut off the
product; When there is no power button, the only way to completely shut off power
is to disconnect the product or the power adapter from the power source.
Don’t disassemble the product, or make repairs yourself. You run the risk of electric
shock and voiding the limited warranty. If you need service, please contact us.
Avoid water and wet locations.
NCC Notice & BSMI Notice
注意!
依據 低功率電波輻射性電機管理辦法
第十二條 經型式認證合格之低功率射頻電機,非經許可,公司、商號或使用者均不得擅自
變更頻率、加大功率或變更原設計之特性或功能。
第十四條 低功率射頻電機之使用不得影響飛航安全及干擾合法通行;經發現有干擾現象時,
應立即停用,並改善至無干擾時方得繼續使用。前項合法通信,指依電信規定作業之無線電
信。低功率射頻電機需忍受合法通信或工業、科學以及醫療用電波輻射性電機設備之干擾。
減少電磁波影響,請妥適使用。
Page 66

Symbol
Explanation
DC voltage
User has the choice to give his product to a competent recycling
organization or to the retailer when he buys a new electrical or
electronic equipment.
BSMI Notice
安全諮詢及注意事項
請使用原裝電源供應器或只能按照本產品注明的電源類型使用本產品。
清潔本產品之前請先拔掉電源線。請勿使用液體、噴霧清潔劑或濕布進行清潔。
注意防潮,請勿將水或其他液體潑灑到本產品上。
插槽與開口供通風使用,以確保本產品的操作可靠並防止過熱,請勿堵塞或覆蓋開口。
請勿將本產品置放於靠近熱源的地方。除非有正常的通風,否則不可放在密閉位置中。
請不要私自打開機殼,不要嘗試自行維修本產品,請由授權的專業人士進行此項工作。
Explanation of the symbols on the product label
Class II equipment
RECYCLING
This product bears the selective sorting symbol for Waste electrical
and electronic equipment (WEEE). This means that this product must
be handled pursuant to European directive 2012/19/EU in order to be
recycled or dismantled to minimize its impact on the environment.
Page 67

COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS
Specifications are subject to change without notice. is a registered
trademark of TP-Link Technologies CO., LTD. Other brands and product names are
trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
No part of the specifications may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to
make any derivative such as translation, transformation, or adaptation without
permission from TP-Link Technologies CO., LTD. Copyright © 2016 TP-Link
Technologies CO., LTD. All rights reserved.
FCC STATEMENT
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/ TV technician for help.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions:
3) This device may not cause harmful interference.
4) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
Page 68

Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Note: The manufacturer is not responsible for any radio or TV interference caused by
unauthorized modifications to this equipment. Such modifications could void the user’s
authority to operate the equipment.
FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This device and its antenna must not be co-located or
operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
“To comply with FCC RF exposure compliance requirements, this grant is applicable to
only Mobile Configurations. The antennas used for this transmitter must be installed to
provide a separation distance of at least 20 cm from all persons and must not be co-
located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.”
RF Exposure Information
This device meets the EU requirements (1999/5/EC Article 3.1a) on the limitation of
exposure of the general public to electromagnetic fields by way of health protection.
The device complies with RF specifications when the device used at 20 cm from your
body.
CE Mark Warning
This is a class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio
interference, in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with IC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance
20cm between the radiator & your body.
Page 69

Déclaration d'exposition aux radiations:
Cet équipement est conforme aux limites d'exposition aux rayonnements IC établies
pour un environnement non contrôlé. Cet équipement doit être installé et utilisé avec un
minimum de 20 cm de distance entre la source de rayonnement et votre corps.
Canadian Compliance Statement
This device complies with Industry Canada license-exempt RSSs. Operation is subject
to the following two conditions:
5) This device may not cause interference, and
6) This device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause
undesired operation of the device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d’Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils
radio exempts de licence. L’exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes :
3) l’appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage;
4) l’utilisateur de l’appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, meme si
le brouillage est susceptible d’en compromettre le fonctionnement.
Industry Canada Statement
CAN ICES-3 (B)/NMB-3(B)
Korea Warning Statements
당해 무선설비는 운용중 전파혼신 가능성이 있음.
Продукт сертифіковано згідно с правилами системи УкрСЕПРО на відповідність
вимогам нормативних документів та вимогам, що передбачені чинними
законодавчими актами України.
Page 70

Safety Information
When product has power button, the power button is one of the way to shut off the
product; When there is no power button, the only way to completely shut off power
is to disconnect the product or the power adapter from the power source.
Don’t disassemble the product, or make repairs yourself. You run the risk of electric
shock and voiding the limited warranty. If you need service, please contact us.
Avoid water and wet locations.
NCC Notice & BSMI Notice
注意!
依據 低功率電波輻射性電機管理辦法
第十二條 經型式認證合格之低功率射頻電機,非經許可,公司、商號或使用者均不得擅自
變更頻率、加大功率或變更原設計之特性或功能。
第十四條 低功率射頻電機之使用不得影響飛航安全及干擾合法通行;經發現有干擾現象時,
應立即停用,並改善至無干擾時方得繼續使用。前項合法通信,指依電信規定作業之無線電
信。低功率射頻電機需忍受合法通信或工業、科學以及醫療用電波輻射性電機設備之干擾。
減少電磁波影響,請妥適使用。
BSMI Notice
安全諮詢及注意事項
請使用原裝電源供應器或只能按照本產品注明的電源類型使用本產品。
清潔本產品之前請先拔掉電源線。請勿使用液體、噴霧清潔劑或濕布進行清潔。
注意防潮,請勿將水或其他液體潑灑到本產品上。
插槽與開口供通風使用,以確保本產品的操作可靠並防止過熱,請勿堵塞或覆蓋開口。
請勿將本產品置放於靠近熱源的地方。除非有正常的通風,否則不可放在密閉位置中。
請不要私自打開機殼,不要嘗試自行維修本產品,請由授權的專業人士進行此項工作。
Page 71

Symbol
Explanation
DC voltage
User has the choice to give his product to a competent recycling
organization or to the retailer when he buys a new electrical or
electronic equipment.
Explanation of the symbols on the product label
Class II equipment
RECYCLING
This product bears the selective sorting symbol for Waste electrical
and electronic equipment (WEEE). This means that this product must
be handled pursuant to European directive 2012/19/EU in order to be
recycled or dismantled to minimize its impact on the environment.
 Loading...
Loading...