
FOREWORD
This repair manual has been prepared to provide essential information on body panel repair methods (including cutting and
welding operations, but excluding painting) for the TOYOTA
AVALON.
Applicable models: GSX30 series
This manual consists of body repair methods, exploded diagrams and illustrations of the body components and other information relating to body panel replacement such as handling
precautions, etc. However, it should be noted that the front fenders of the TOYOTA model is bolted on and require no welding.
When repairing, don’t cut and join areas that are not shown in
this manual. Only work on the specified contents to maintain
body strength.
Body construction will sometimes differ depending on specifications and country of destination. Therefore, please keep in mind
that the information contained herein is based on vehicles for
general destinations.
For the repair procedures and specifications other than collisiondamaged body components of the TOYOTA AVALON refer to
the repair manuals.
If you require the above manuals, please contact your TOYOTA
Dealer.
All information contained in this manual is the most up-to-date at
the time of publication. However, specifications and procedures
are subject to change without prior notice.
VIEWS OF THIS TEXT
Scope of the repair work explanation
This text explains the welding panel replacement instructions from the vehicle’s white body condi-
tion. W e have abbreviated the explanations of the removal and reinstallation of the equipment parts
up to the white body condition and of the installation, inspection, adjustment and final inspection of
equipment parts after replacing the weld panel.
Section categories
Each section has been divided as shown below.
Section Title Contents Examples
INTRODUCTION
BODY PANEL REPLACEMENT
BODY DIMENSIONS Body aligning measurements. Dimension diagrams.
PAINT COATING
Explanation of general body repair.
Views of weld panel replacement instructions.
Instructions for replacing the weld panels
from the white body condition, from which
bolted parts have been removed, with
individual supply parts.
Scope and type of anti-rust treatment, etc.
together with weld panel replacement.
Abbreviation of contents in this text.
The following essential procedures have been abbreviated. When actually working, conduct this
work properly.
(1) Jack and lift operations.
(2) Clean and wash removed parts, if necessary.
(3) Visual inspection.
Cautionary items.
Views of weld panel replacement instructions.
Front side member replacement.
Quarter panel replacement.
Under coat.
Body sealer.

Glass Cover
INTRODUCTION
GENERAL REPAIR INSTRUCTIONS
1. WORK PRECAUTIONS
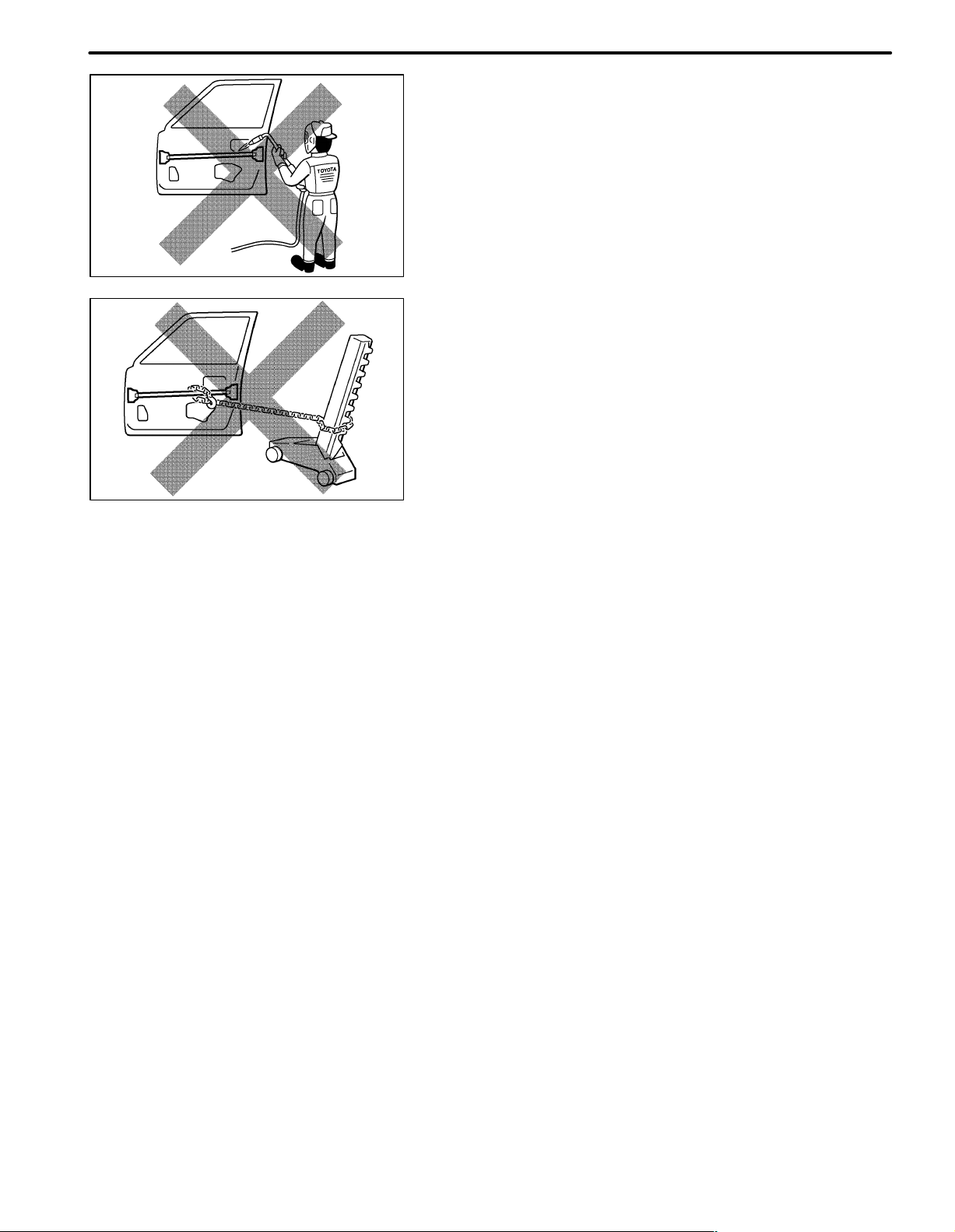
(a) VEHICLE PROTECTION
(1) When welding, protect the painted surfaces, windows,
seats and carpet with heat resistant, fire-proof covers.
IN-1
WRONG
Seat Cover
F10001A
(b) SAFETY
(1) Never stand in direct line with the chain when using a
puller on the body or frame, and be sure to attach a
safety cable.
F10002A
(2) Before performing repair work, check for fuel leaks.
If a leak is found, be sure to close the opening totally.
(3) If it is necessary to use a flame in the area of the fuel
tank, first remove the tank and plug the fuel line.
WRONG
F10003A
F10004A
(c) SAFETY WORK CLOTHES
(1) In addition to the usual mechanic’s wear, cap and
safety shoes, the appropriate gloves, head protector,
glasses, ear plugs, face protector, dust-prevention
mask, etc. should be worn as the situation demands.
Code Name
A Dust-Prevention Mask
B Face Protector
C Eye Protector
D Safety Shoes
E Welder’s Glasses
F Ear Plugs
G Head Protector
H Welder’s Gloves

IN-2
INTRODUCTION
2. HANDLING PRECAUTIONS OF PLASTIC BODY PARTS
(1) The repair procedure for plastic body parts must conform with the type of plastic material.
(2) Plastic body parts are identified by the codes in the following table.
(3) When repairing metal body parts adjoining plastic body parts (by brazing, frame cutting, welding, paint-
ing etc.), consideration must be given to the property of the plastic.
*
Heat
Code
Material
name
resistant
temperature
limit C (F)
Resistance to
alcohol or gasoline
Notes
AAS
ABS
AES
ASA
CAB
EPDM
FRP
Acrylonitrile
Acrylic Styrene
Acrylonitrile
Butadiene Styrene
Acrylonitrile
Ethylene Styrene
Acrylonitrile
Styrene
Acrylate
Cellulose
Acetate
Ethylene
Propylene
Fiber
Reinforced
Plastics
80
(176)
80
(176)
80
(176)
80
(176)
80
(176)
100
(212)
180
(356)
Alcohol is harmless if applied only for
short time in small amounts (e.g., quick
wiping to remove grease).
Alcohol is harmless if applied only for
short time in small amounts (e.g., quick
wiping to remove grease).
Alcohol is harmless if applied only for
short time in small amounts (e.g., quick
wiping to remove grease).
Alcohol is harmless if applied only for
short time in small amounts (e.g., quick
wiping to remove grease).
Alcohol is harmless if applied only for
short time in small amounts (e.g., quick
wiping to remove grease).
Alcohol is harmless.
Gasoline is harmless if applied only for
short time in small amounts.
Alcohol and gasoline are harmless. Avoid alkali.
Avoid gasoline and organic
or aromatic solvents.
Avoid gasoline and organic
or aromatic solvents.
Avoid gasoline and organic
or aromatic solvents.
Avoid gasoline and organic
or aromatic solvents.
Avoid gasoline and organic
or aromatic solvents.
Most solvents are harmless
but avoid dipping in gasoline,
solvents, etc.
EVA
E/VAC
PA
PBT
PC Polycarbonate
*Temperatures higher than those listed here may result in material deformation during repair.
Ethylene
Acetate
Ethylene/
Vinyl
Acetate
Copolymer
Resin
Polyamide
(Nylon)
Polybutylene
Terephthalate
70
(158)
70
(158)
80
(176)
160
(320)
120
(248)
Alcohol is harmless if applid only for short
time in small amounts (e.g., quick wiping
to remove grease).
Alcohol is harmless if applid only for short
time in small amounts (e.g., quick wiping
to remove grease).
Alcohol and gasoline are harmless. Avoid battery acid.
Alcohol and gasoline are harmless. Most solvents are harmless.
Alcohol is harmless.
Avoid gasoline and organic
or aromatic solvents.
Avoid gasoline and organic
or aromatic solvents.
Avoid gasoline brake fluid,
wax, wax removers and
organic solvents. Avoid alkali.
Code
Material
name
*
Heat
resistant
temperature
limit C (F)
INTRODUCTION
Resistance to
alcohol or gasoline
IN-3
Notes
PE Polyethylene
PET
PMMA
POM
PP Polypropylene
PPF
PPO
PS Polystyrene
Polyethylene
Terephthalate
Polymethyl
Methacrylate
Polyoxymethylene
(Polyacetal)
Composite
Reinforced
Polypropylene
Modified
Polyphenylene
Oxide
80
(176)
75
(167)
80
(176)
100
(212)
80
(176)
80
(176)
100
(212)
60
(140)
Alcohol and gasoline are harmless. Most solvents are harmless.
Alcohol and gasoline are harmless. Avoid dipping in water.
Alcohol is harmless if applied only for
short time in small amounts.
Alcohol and gasoline are harmless. Most solvents are harmless.
Alcohol and gasoline are harmless. Most solvents are harmless.
Alcohol and gasoline are harmless. Most solvents are harmless.
Alcohol is harmless.
Alcohol and gasoline are harmless if
applied only for short time in small
amounts.
Avoid dipping or immersing
in alcohol, gasoline,
solvents, etc.
Gasoline is harmless if
applied only for quick wiping
to remove grease.
Avoid dipping or immersing
in alcohol, gasoline,
solvents, etc.
PUR Polyurethane
PVC
SAN
TPO
TPU
TSOP
UP
Polyvinylchloride
(Vinyl)
Styrene
Acrylonitrile
Thermoplastic
Olefine
Thermoplastic
Polyurethane
TOYOTA
Super
Olefine Polymer
Unsaturated
Polyester
80
(176)
80
(176)
80
(176)
80
(176)
80
(176)
80
(176)
110
(233)
Alcohol is harmless if applied only for very
short time in small amounts (e.g., quick
wiping to remove grease).
Alcohol and gasoline are harmless if
applied only for short time in small
amounts (e.g., quick wiping to remove
grease).
Alcohol is harmless if applied only for
short time in small amounts (e.g., quick
wiping to remove grease).
Alcohol is harmless.
Gasoline is harmless if applied only for
short time in small amounts.
Alcohol is harmless if applied only for
short time in small amounts (e.g., quick
wiping to remove grease).
Alcohol and gasoline are harmless. Most solvents are harmless.
Alcohol and gasoline are harmless. Avoid alkali.
Avoid dipping or immersing
in alcohol, gasoline,
solvents, etc.
Avoid dipping or immersing
in alcohol, gasoline,
solvents, etc.
Avoid dipping or immersing
in alcohol, gasoline, solvents
etc.
Most solvents are harmless
but avoid dipping in gasoline,
solvents, etc.
Avoid dipping or immersing
in alcohol, gasoline,
solvents, etc.
*Temperatures higher than those listed here may result in material deformation during repair.
IN-4
INTRODUCTION
3. LOCATION OF PLASTIC BODY PARTS
Parts Name Code
Radiator Grille ABS
Front Bumper Cover TSOP
Front Bumper Hole Cover PC/ABS
Headlight PP/PC
Foglight PC/PE
Cowl Top Ventilator Louver TSOP
Door Window Frame Moulding ASA
Door Outside Handle PA
Outer Rear View Mirror ABS PPO
Door Outside Moulding TPO
Body Rocker Panel Moulding TPO
Rocker Panel Moulding Protector PP
License Plate Light PC
Rear Combination Light PMMA/ASA
Rear Light PMMA/ASA
Rear Bumper Cover TSOP
HINT:
Resin material differs with model.
/ Made up of 2 or more kind of materials.

INTRODUCTION
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
1. BODY PANEL REPLACEMENT THIS MANUAL
IN-5
F13890A
IN-6
INTRODUCTION
F13891A
INTRODUCTION
IN-7
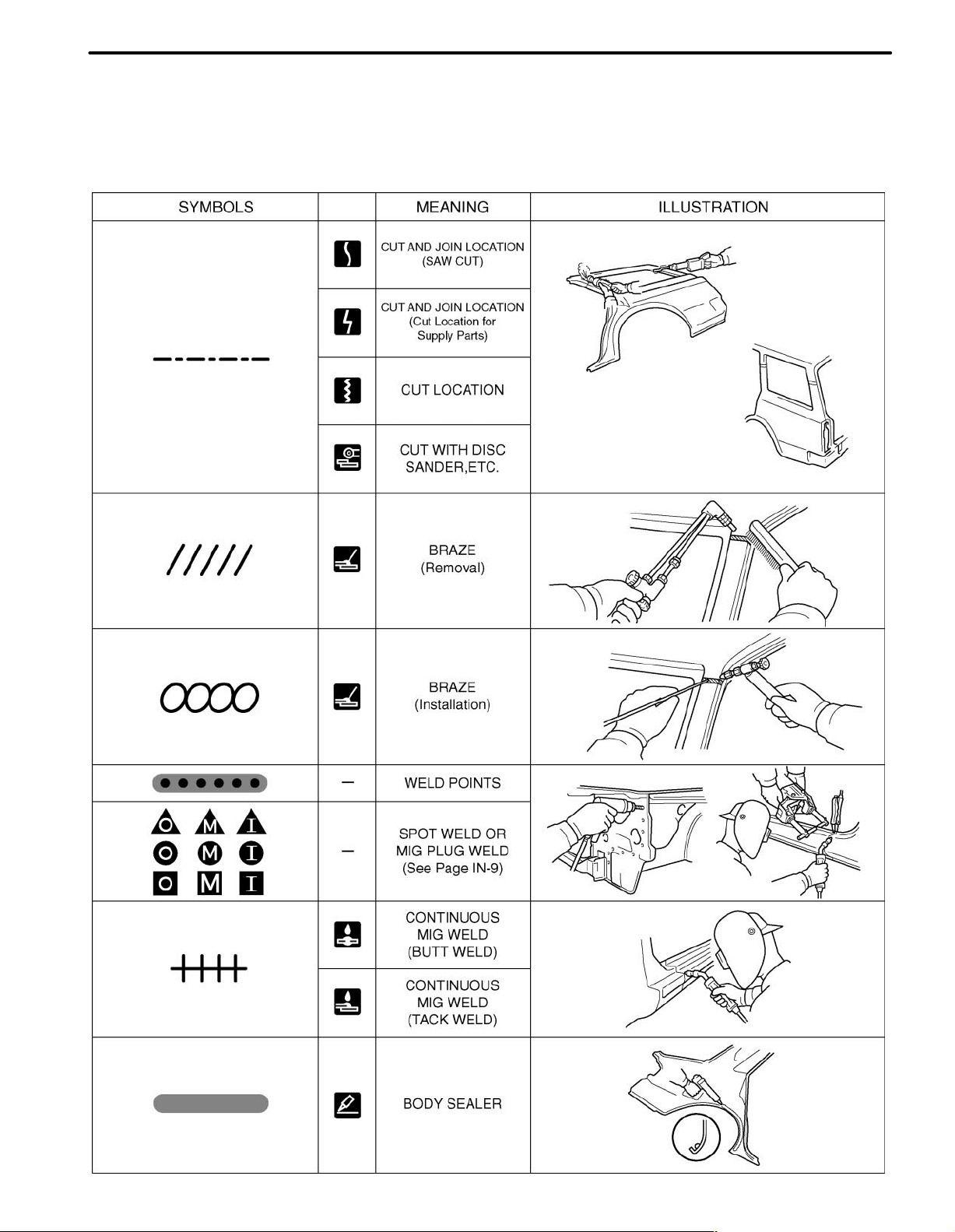
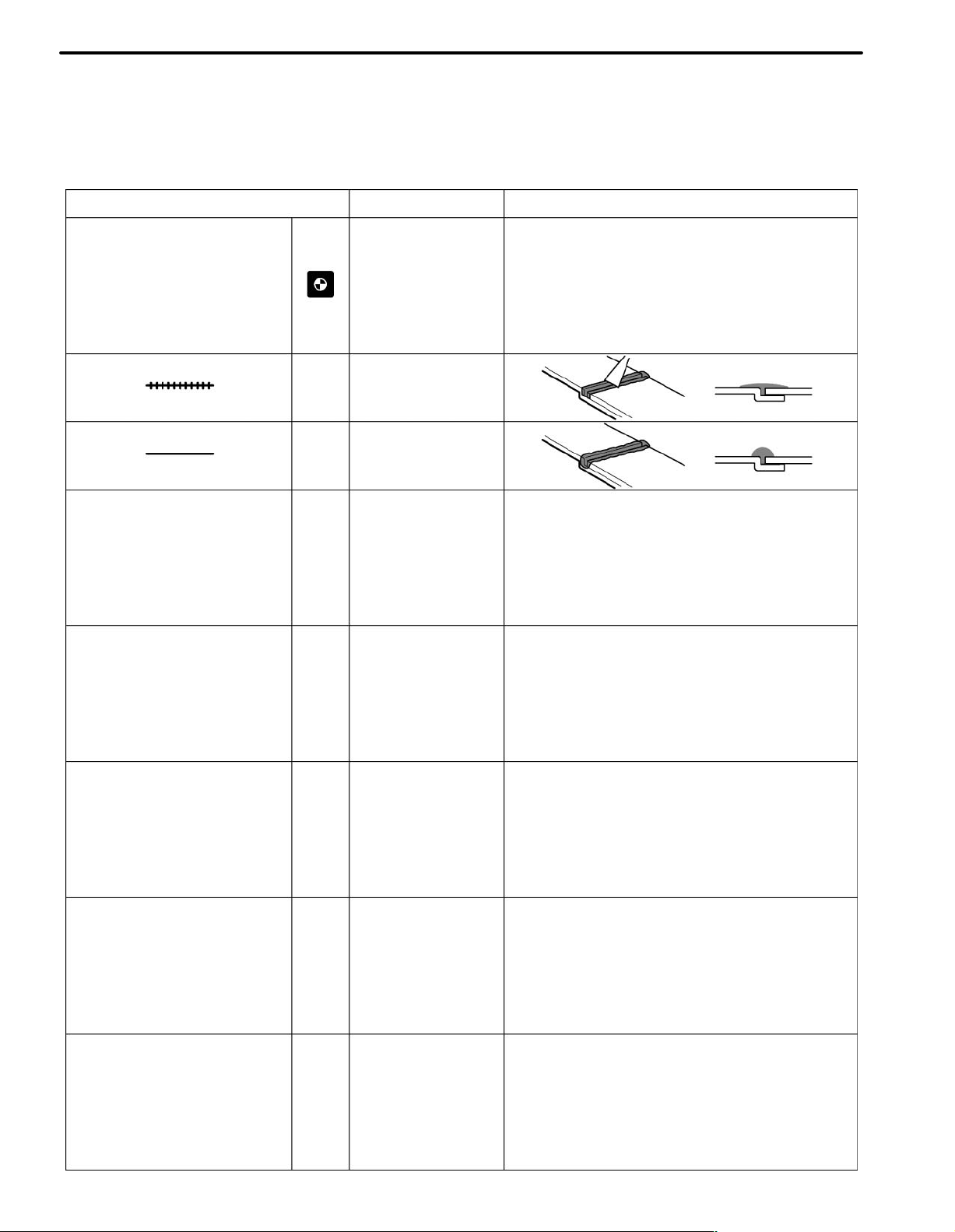
2. SYMBOLS
The following symbols are used in the welding diagrams in section BP of this manual to indicate cutting areas
and the types of weld required.
F13893A
IN-8
INTRODUCTION
SYMBOLS MEANING ILLUSTRATION
—
—
—
Assembly Mark
BODY SEALER
(Flat Finishing)
BODY SEALER
(No flat Finishing)
—
F13894A
INTRODUCTION
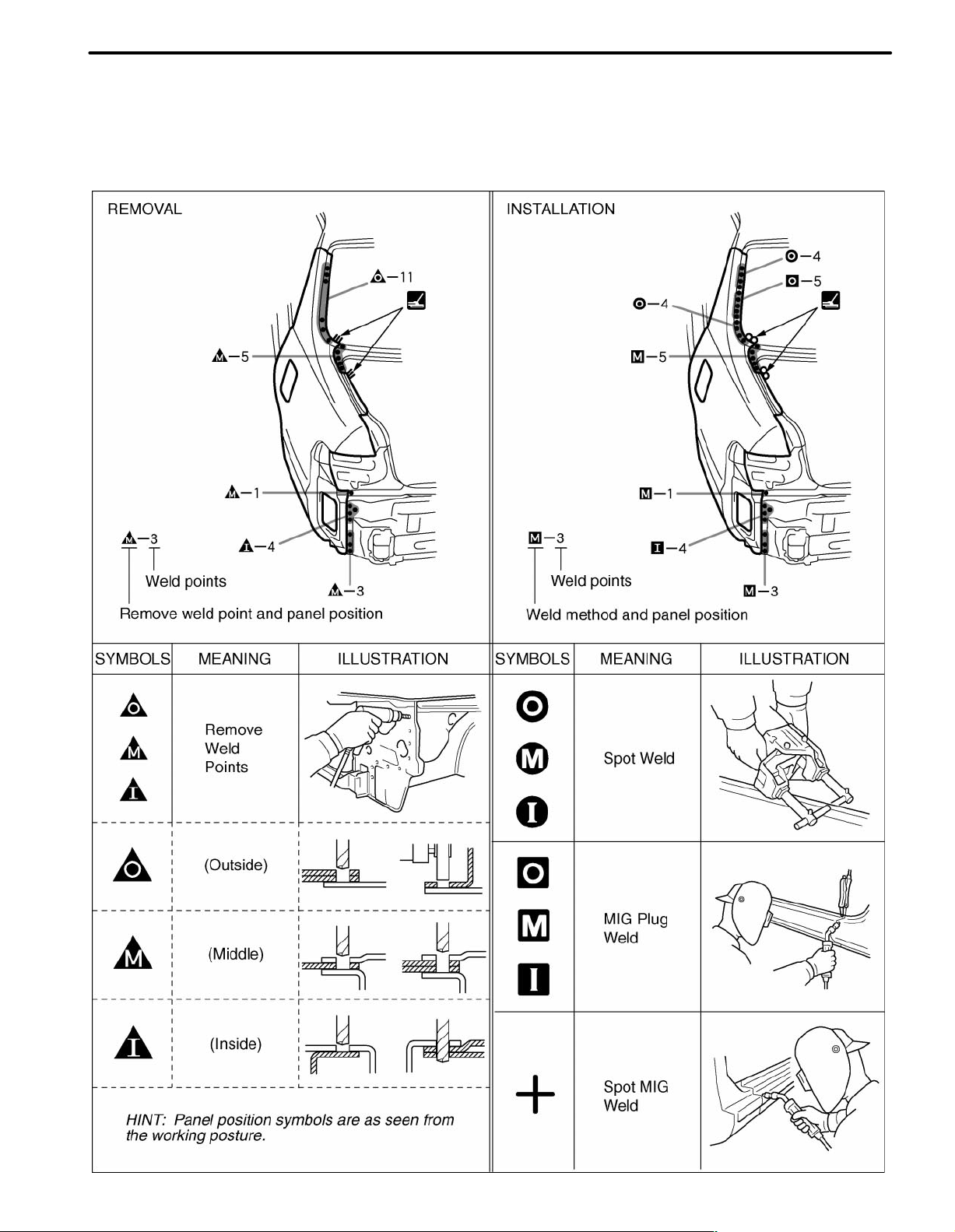
3. ILLUSTRATION OF WELD POINT SYMBOLS
EXAMPLE:
IN-9
F13892A

IN-10
Cutting Okay
Reinforcement
INTRODUCTION
PROPER AND EFFICIENT WORK
PROCEDURES
1. REMOVAL
(a) PRE-REMOVAL MEASURING
(1) Before removal or cutting operations, take measure-
ments in accordance with the dimension diagram. Always use a puller to straighten a damaged body or
frame.
F10007A
(b) CUTTING AREA
(1) Always cut in a straight line and avoid reinforced area.
WRONG
Corners
F10008A
(c) PRECAUTIONS FOR DRILLING OR CUTTING
(1) Check behind any area to be drilled or cut to insure
that there are no hoses, wires, etc., that may be damaged.
HINT: See “Handling Precautions on Related Components” on page IN-15.
F10009A
(d) REMOVAL OF ADJACENT COMPONENTS
(1) When removing adjacent components, apply protec-
tive tape to the surrounding body and your tools to prevent damage.
HINT: See “Handling Precautions on Related Components” on page IN-15.
F10010A

Less than
3 mm
F10011A
F10012A
INTRODUCTION
2. PREPARATION FOR INSTALLATION
(a) SPOT WELD POINTS
(1) When welding panels with a combined thickness of
over 3 mm (0.12 in.), use a MIG (Metal Inert Gas)
welder for plug welding.
HINT: Spot welding will not provide sufficient durability
for panels over 3 mm (0.12 in.) thick.
(b) APPLICATION OF WELD-THROUGH PRIMER
(SPOT SEALER)
(1) Remove the paint from the portion of the new parts
and body to be welded, and apply weld-through primer.
IN-11
Air Saw
Puncher
20 − 30 mm
F10013A
F10014A
Overlap
(c) MAKING HOLES FOR PLUG WELDING
(1) For areas where a spot welder cannot be used, use a
puncher or drill to make holes for plug welding.
REFERENCE: mm (in.)
Thickness of welded portion Size of plug hole
1.0 (0.04) under 5 (0.20) ø over
1.0 (0.04) − 1.6 (0.06) 6.5 (0.26) ø over
1.7 (0.07) − 2.3 (0.09) 8 (0.31) ø over
2.4 (0.09) over 10 (0.39) ø over
(d) SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR ELECTRICAL COM-
PONENTS
(1) When welding, there is a danger that electrical compo-
nents will be damaged by the electrical current flowing
through the body.
(2) Before starting work, disconnect the negative terminal
of the battery and ground the welder near the welding
location of the body.
(e) ROUGH CUTTING OF JOINTS
(1) For joint areas, rough cut the new parts, leaving 20 −
30 mm (0.79 − 1.18 in.) overlap.
F10015A

IN-12
INTRODUCTION
Body Measurement Diagrams
WRONG
3. INSTALLATION
(a) PRE-WELDING MEASUREMENTS
(1) Always take measurements before installing under-
body or engine components to insure correct assembly. After installation, confirm proper fit.
F10016A
(b) WELDING PRECAUTIONS
(1) The number of welding spots should be as follows.
Spot weld: 1.3 X No. of manufacturer’s spots.
Plug weld: More than No. of manufacturer’s plugs.
(2) Plug welding should be done with a MIG (Metal Inert
Gas) welder. Do not gas weld or braze panels at areas
other than specified.
F10017A
(c) POST-WELDING REFINISHING
(1) Always check the welded spots to insure they are se-
cure.
(2) When smoothing out the weld spots with a disc grind-
er, be careful not to grind off too much as this would
weaken the weld.
CORRECT WRONG
New Spot
Old
Spot
Locations
Locations
F10018A
(d) SPOT WELD LOCATIONS
(1) Try to avoid welding over previous spots.
F10020A
(e) SPOT WELDING PRECAUTIONS
(1) The shape of the welding tip point has an effect on the
strength of the weld.
(2) Always insure that the seams and welding tip are free
of paint.
Tip Cutter
F10019A

INTRODUCTION
IN-13
Sealer Gun
4. ANTI-RUST TREATMENT
(a) BODY SEALER APPLICATION
(1) For water-proofing and anti-corrosion measures, al-
ways apply the body sealer to the body panel seams
and hems of the doors, hoods, etc.
F10021A
(b) UNDERCOAT APPLICATION
(1) To prevent corrosion and protect the body from dam-
age by flying stones, always apply sufficient undercoat to the bottom surface of the under body and inside of the wheel housings.
F10022A
5. ANTI-RUST TREATMENT AFTER PAINTING
PROCESS
(a) ANTI-RUST AGENT (WAX) APPLICATION
(1) To preserve impossible to paint areas from corrosion,
always apply sufficient anti-rust agent (wax) to the inside of the hemming areas of the doors and hoods,
and around the hinges, or the welded surfaces inside
the boxed cross-section structure of the side member,
body pillar, etc.
F10023A

IN-14
INTRODUCTION
6. ANTI-RUST TREATMENT BY PAINTING
REFERENCE:
Painting prevents corrosion and protect the sheet
metal from damage. In this section, anti-chipping paint
only for anti-corrosion purpose is described.
(a) ANTI-CHIPPING PAINT
(1) To prevent corrosion and protect the body from dam-
age by flying stones, etc., apply anti-chipping paint to
the rocker panel, wheel arch areas, balance panel,
etc.
HINT:
Depending on the model or the application area, there
are cases where the application of anti-chipping paint
is necessary before the second coat or after the top
coat.
Apply the anti-chipping paint after
the top coat.
Anti-Chipping Paint
Top Coat
Second Coat
Under Coat (ED Primer)
Steel Metal
Apply the anti-chipping paint before
the second coat.
Top Coat
Second Coat
Anti-Chipping Paint
Under Coat (ED Primer)
Steel Metal
F10024A
INTRODUCTION
HANDLING PRECAUTIONS ON RELATED COMPONENTS
1. BRAKE SYSTEM
The brake system is one of the most important safety components. Always follow the directions and
notes given in brake (32) section of the repair manual for the relevant model when handling brake system
parts.
NOTICE: When repairing the brake master cylinder or TRAC system, bleed the air out of the TRAC system.
2. DRIVE TRAIN AND CHASSIS
The drive train and chassis are components that can have great effects on the running performance and
vibration resistance of the vehicle. After installing components in the sections listed in the table below,
perform alignments to ensure correct mounting angles and dimensions. Particularly accurate repair of
the body must also be done to ensure correct alignment.
HINT: Correct procedures and special tools are required for alignment. Always follow the directions given in the repair manual for the relevant model during alignment and section DI of this section.
IN-15
Component to be aligned
Front Wheels Front Suspension (26) section
Rear Wheels Rear Suspension (27) section
Section of repair manual
for relevant model
3. COMPONENTS ADJACENT TO THE BODY PANELS
Various types of component parts are mounted directly on or adjacently to the body panels. Strictly observe the following precautions to prevent damaging these components and the body panels during handling.
Before repairing the body panels, remove their components or apply protective covers over the com-
ponents.
Before prying components off using a screwdriver or a scraper, etc., attach protective tape to the tool
tip or blade to prevent damaging the components and the body paint.
Before removing components from the outer surface of the body, attach protective tape to the body to
ensure no damage to painted areas.
HINT: Apply touch-up paint to any damaged paint surfaces.
Before drilling or cutting sections, make sure that there are no wires, etc. on the reverse side.
4. ECU (ELECTRONIC CONTROL UNIT)
Many ECUs are mounted in this vehicle.
Take the following precautions during body repair to prevent damage to the ECUs.
Before starting electric welding operations, disconnect the negative (−) terminal cable from the bat-
tery.
When the negative (−) terminal cable is disconnected from the battery, memory of the clock and audio
systems will be cancelled. So before starting work, make a record of the contents memorized by each
memory system. Then when work is finished, reset the clock and audio systems as before.
When the vehicle has tilt and telescopic steering, power seat and outside rear view mirror, which are
all equipped with memory function, it is not possible to make a record of the memory contents.
So when the operation is finished, it will be necessary to explain this fact to the customer, and request
the customer to adjust the features and reset the memory.
Do not expose the ECUs to ambient temperatures above 80C (176F).
NOTICE: If it is possible the ambient temperature may reach 80C (176F) or more, remove the ECUs
from the vehicle before starting work.
Be careful not to drop the ECUs and not to apply physical shocks to them.

IN-16
INTRODUCTION
PRECAUTIONS FOR REPAIRING BODY
STRUCTURE PANELS
1. HEAT REPAIR FOR BODY STRUCTURE
PANELS
Toyota prohibits the use of the heat repair method on body
structure panels when repairing a vehicle damaged in a collision.
Panels that have high strength and rigidity, as well as a long
life span for the automobile body are being sought after.
At Toyota, in order to fulfill these requirement, we use high
tensile strength steel sheets and rust preventive steel
sheets on the body.
High tensile steel sheets are made with alloy additives and
a special heat treatment in order to improve the strength.
To prevent the occurrence of rust for a long period of time,
the surface of the steel is coated with a zinc alloy.
If a body structure parts are heat repaired with an acetylene
torch or ot h e r heating source, the crystalline organization of
the steel sheet will change and the strength of the steel
sheet will be reduced.
The ability of the body to resist rust is significantly lowered
as well since the rust resistant zinc coating is destroyed by
heat and the steel sheet surface is oxidized.
2. STRUCTURE PANEL KINKS
A sharp deformation angle on the panel that cannot be returned to its original shape by pulling or hammering is
called kink.
Since structure parts are designed to exhibit its performance in their original shape, if parts are deformed in an
accident, or if the deformed parts are repaired and reused,
the parts may become unable to exhibit the same performance as intended in the design.
It is necessary to replace the part where the kink has occurred.
INTRODUCTION
3. IMPACT BEAM REPAIR
The impact beam and bracket are necessary and important
parts that help reduce the probability of injury to passengers in side collisions.
For impact beam, we use special high tensile strength
steel.
The high tensile strength steel maintains its special crystalline organization by heat treatment or alloy additives.
Since these parts are designed to exhibit its performance in
their origi n a l shape, if parts are deformed in an accident, or
if the deformed parts are repaired and reused, the parts
may become unable to exhibit the same performance as intended in the design.
If the impact beam or bracket is damaged, replace the door
assembly which has the damaged beam.
Also, the bumper reinforcement is a necessary and important part that helps reduce the probability of injury to passengers in front collisions, and for the same reasons explained above, should be replaced if damaged.
IN-17

IN-18
INTRODUCTION
ABBREVIATIONS USED IN THIS MANUAL
For convenience, the following abbreviations are used in this
manual.
ABS Antilock Brake System
A/C Air Conditioner
assy assembly
ECT Electronic Controlled Transmission
ECU Electronic Control Unit
e.g. Exempli Gratia (for Example)
Ex. Except
FWD Front Wheel Drive Vehicles
2WD Two Wheel Drive Vehicles
4WD Four Wheel Drive Vehicles
in. inch
LH Left-hand
LHD Left-hand Drive
MIG Metal Inert Gas
M/Y Model Year
PPS Progressive Power Steering
RH Right-hand
RHD Right-hand Drive
SRS Supplemental Restraint System
SSM Special Service Materials
w/ with
w/o without

BODY PANEL REPLACEMENT
FIT STANDARDS
3.7 mm
IN-81
4.2 mm
5.4 mm
5.75 mm
4.8 mm
4.8 mm
4.2 mm
4.2 mm
5.2 mm
5.2 mm
3.7 mm (0.146 in.) 4.2 mm (0.165 in.) 4.8 mm (0.189 in.)
5.2 mm (0.205 in.) 5.4 mm (0.213 in.) 5.75 mm (0.226 in.)
F22065

IN-82
BODY PANEL REPLACEMENT
3.7 mm
4.5 mm
5.75 mm
3.7 mm (0.146 in.) 4.5 mm (0.177 in.) 5.75 mm (0. 226 in.)
F22066

BODY PANEL REPLACEMENT
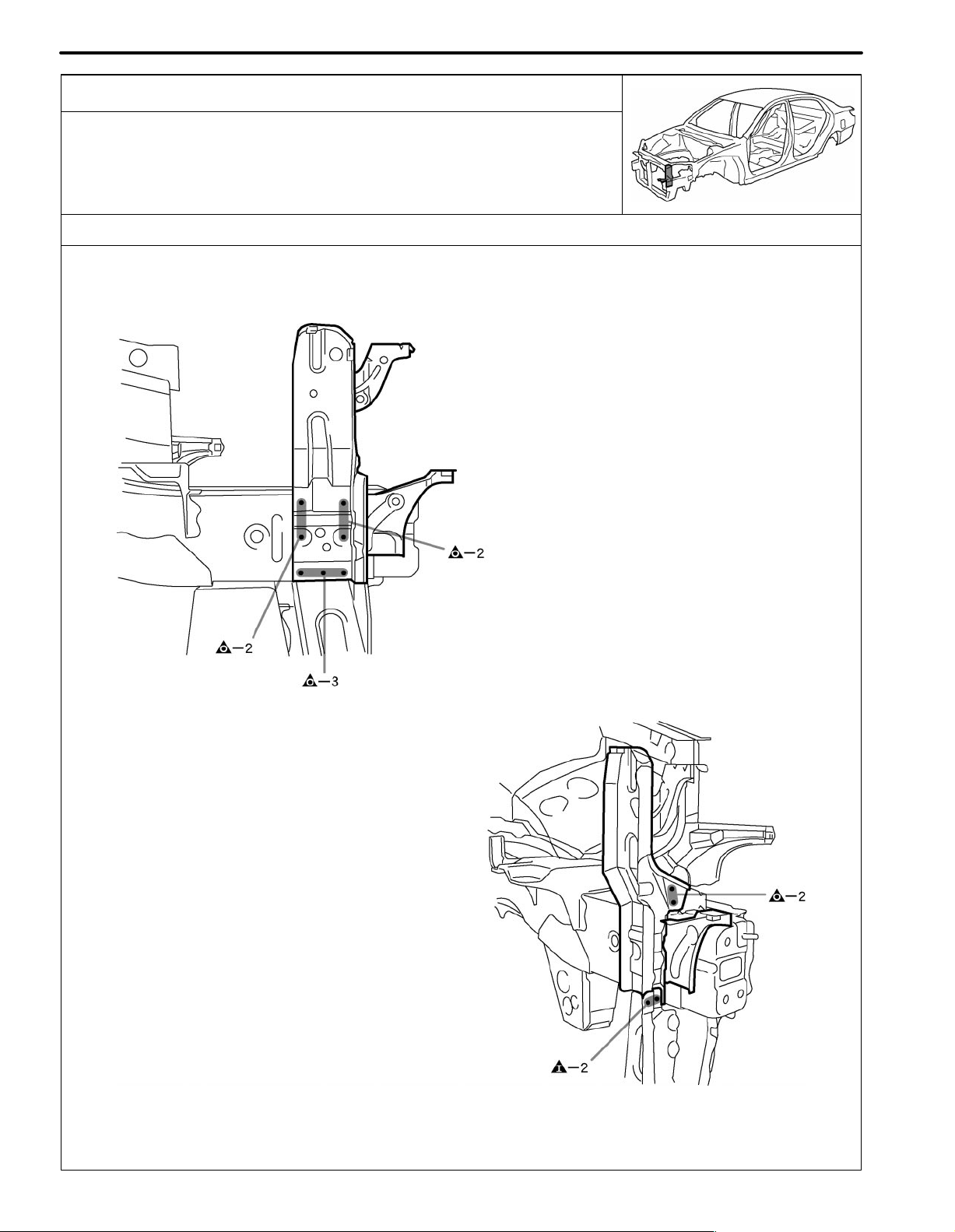
RADIATOR UPPER SUPPORT (ASSY)
REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
BP-1
F22067A
F22067

BP-2
BODY PANEL REPLACEMENT
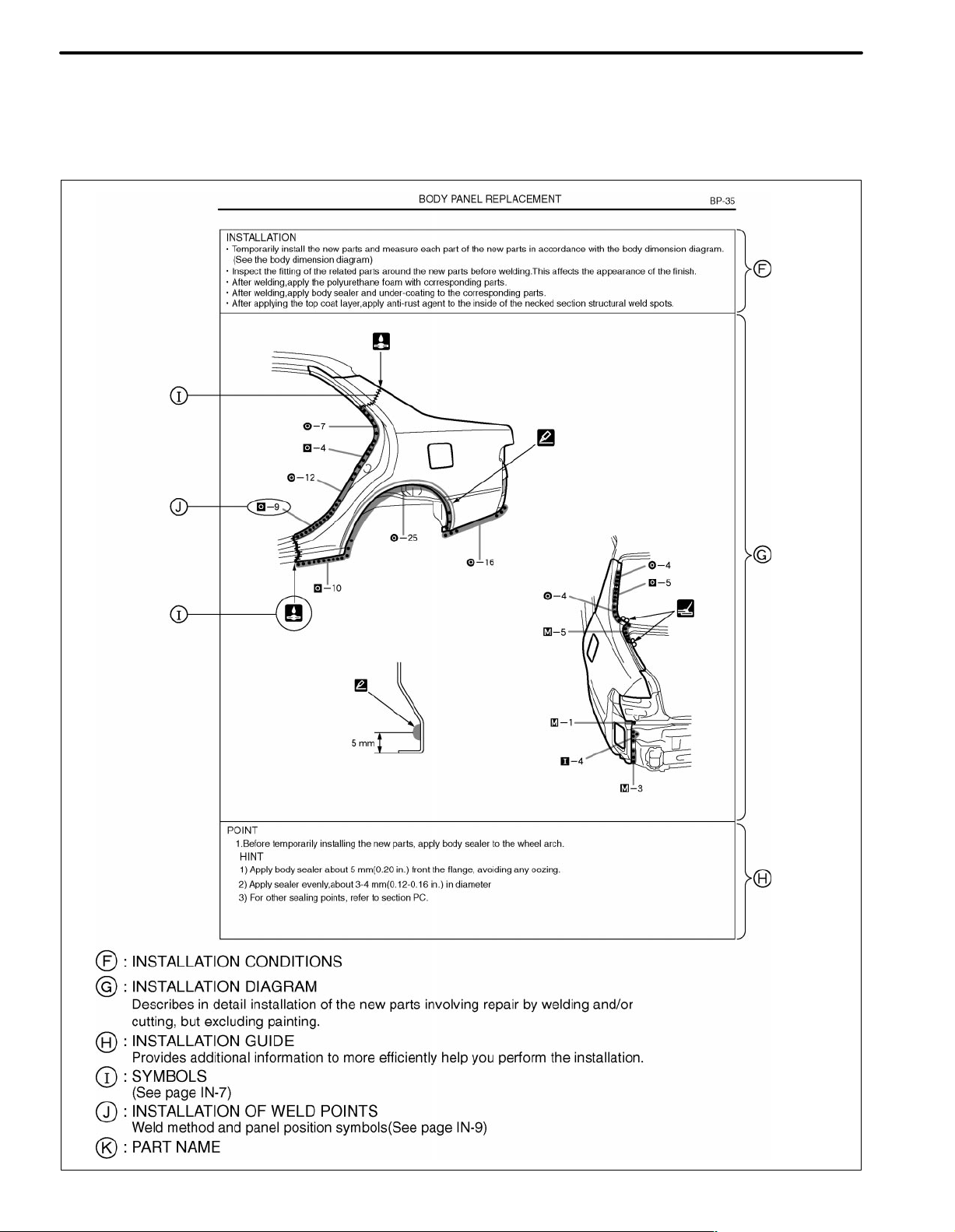
INSTALLATION
Temporarily install the new parts and measure each part of the new parts in accordance with the body dimension
diagram. (See the body dimension diagram)
Inspect the fitting of the related parts around the new parts before welding. This affects the appearance of the
finish.
After welding, apply the polyurethane foam to the corresponding parts.
After welding, apply body sealer and under-coating to the corresponding parts.
After applying the top coat layer, apply anti-rust agent to the inside of the necked section structural weld spots.
F22068
POINT
1 Inspect the fitting of the headlight, front fender and hood, etc., before welding, since this affects the appear-
ance of the finish.
PART NAME
[A] Radiator Support Apron Brace

BODY PANEL REPLACEMENT
1,425 mm
1,210 mm
BP-3
POINT
1 Measure the dimensions before installing the headlight.
2 These values are reference values.
296 mm (11.65 in.) 480 mm (18.90 in.) 866 mm (34.09 in.) 1,210 mm (47.64 in.)
F22069
1,425 mm (56.10 in.)
BP-4
BODY PANEL REPLACEMENT
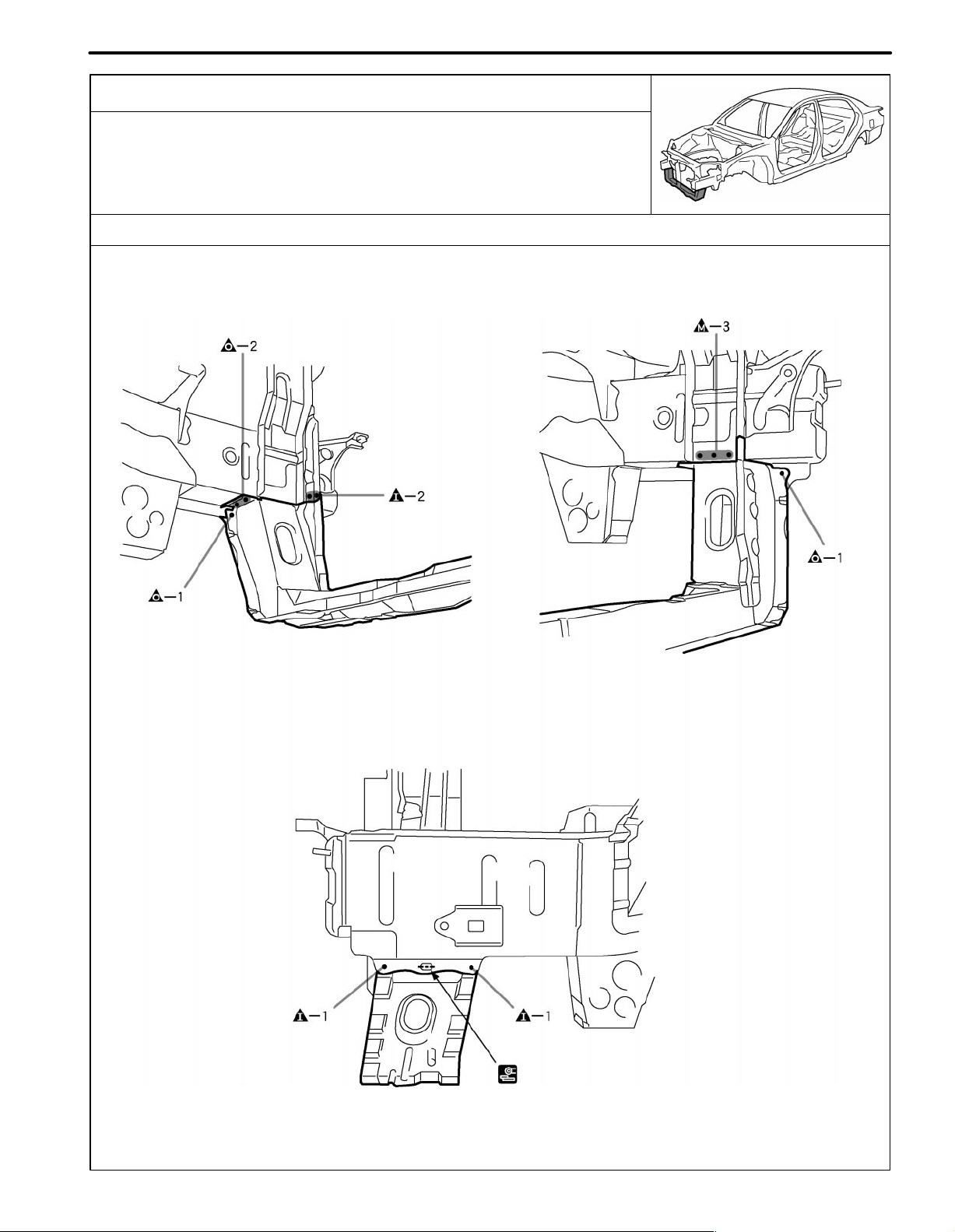
RADIATOR SIDE SUPPORT (ASSY)
REPLACEMENT
With the radiator upper support removed.
REMOVAL
F22070A
F22070

BODY PANEL REPLACEMENT
BP-5
INSTALLATION
Temporarily install the new parts and measure each part of the new parts in accordance with the body dimension
diagram. (See the body dimension diagram)
Inspect the fitting of the related parts around the new parts before welding. This affects the appearance of the
finish.
After welding, apply the polyurethane foam to the corresponding parts.
After welding, apply body sealer and under-coating to the corresponding parts.
After applying the top coat layer, apply anti-rust agent to the inside of the necked section structural weld spots.
PART NAME
[A] Front Bumper Upper Arm
F22071
[B] Front Bumper Side Support
BODY PANEL REPLACEMENT
FRONT CROSSMEMBER (ASSY)
REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
BP-7
F22072A
F22072

BP-8
BODY PANEL REPLACEMENT
INSTALLATION
Temporarily install the new parts and measure each part of the new parts in accordance with the body dimension
diagram. (See the body dimension diagram)
Inspect the fitting of the related parts around the new parts before welding. This affects the appearance of the
finish.
After welding, apply the polyurethane foam to the corresponding parts.
After welding, apply body sealer and under-coating to the corresponding parts.
After applying the top coat layer, apply anti-rust agent to the inside of the necked section structural weld spots.
10 mm (0.39 in.)
F22073

BP-8
BODY PANEL REPLACEMENT
RADIATOR SUPPORT (ASSY)
REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
F22074A
F22074
 Loading...
Loading...