Toyota 4 Runner 1993 User Manual

ST–1
–STARTING SYSTEM
STARTING SYSTEM
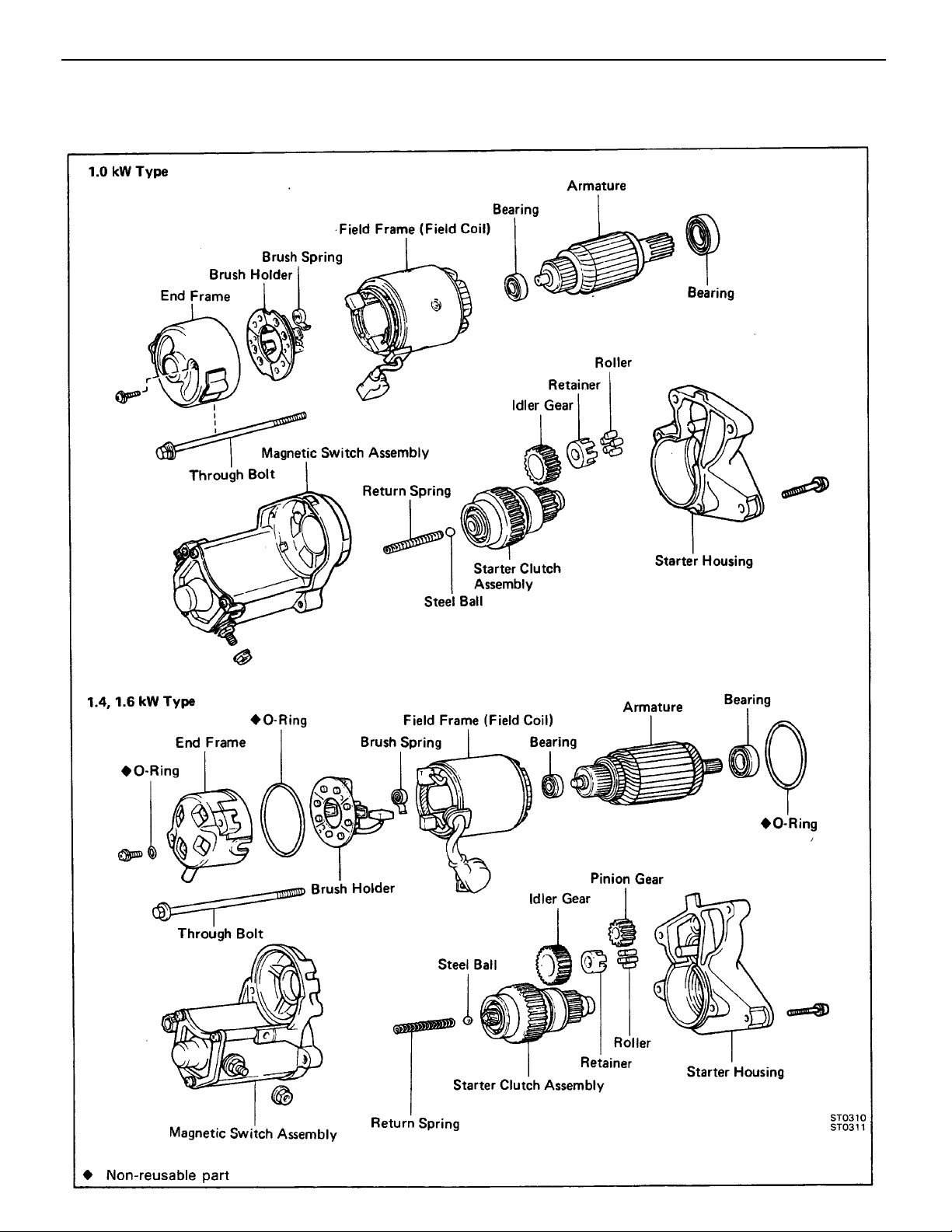
ST–2
–STARTING SYSTEM Starter
STARTER
COMPONENTS
–STARTING SYSTEM Starter
ST–3
REMOVAL OF STARTER
1. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE TERMINAL OF
BATTERY
2. DISCONNECT TWO WIRES FROM STARTER
(a) Remove the nut and disconnect the battery cable from
the magnetic switch on the starter motor.
(b) Disconnect the other wire from terminal 50.
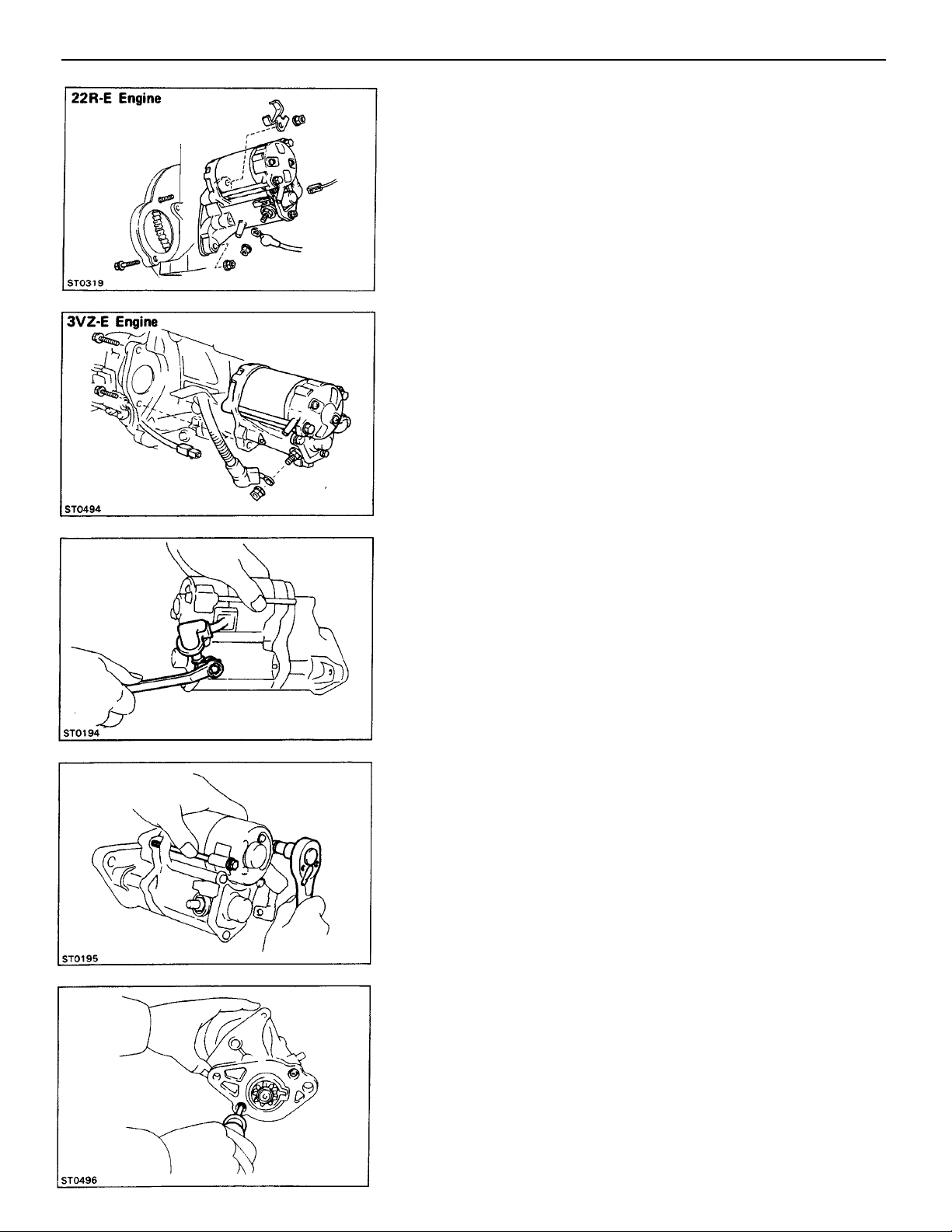
3. REMOVE STARTER MOTOR
(22R–E Engine)
Remove the nut and bolt, and remove the starter motor
from the flywheel bellhousing.
(3VZ–E Engine)
Remove the two mounting bolts, and remove the starter
motor from flywheel bellhousing.
DISASSEMBLY OF STARTER
(See page ST–2)
1. REMOVE FIELD FRAME WITH ARMATURE FROM
MAGNETIC SWITCH ASSEMBLY
(a) Remove the nut and disconnect the lead wire from
the magnetic switch terminal.
(b) Remove the two through bolts. Pullout the field
frame
with the armature from the magnetic switch assembly.
(c) (1.4,
1. 6 kW )
Remove the O–ring.
2. REMOVE STARTER HOUSING FROM MAGNETIC
SWITCH ASSEMBLY
(a) Remove the two screws.
ST–4
–STARTING SYSTEM Starter
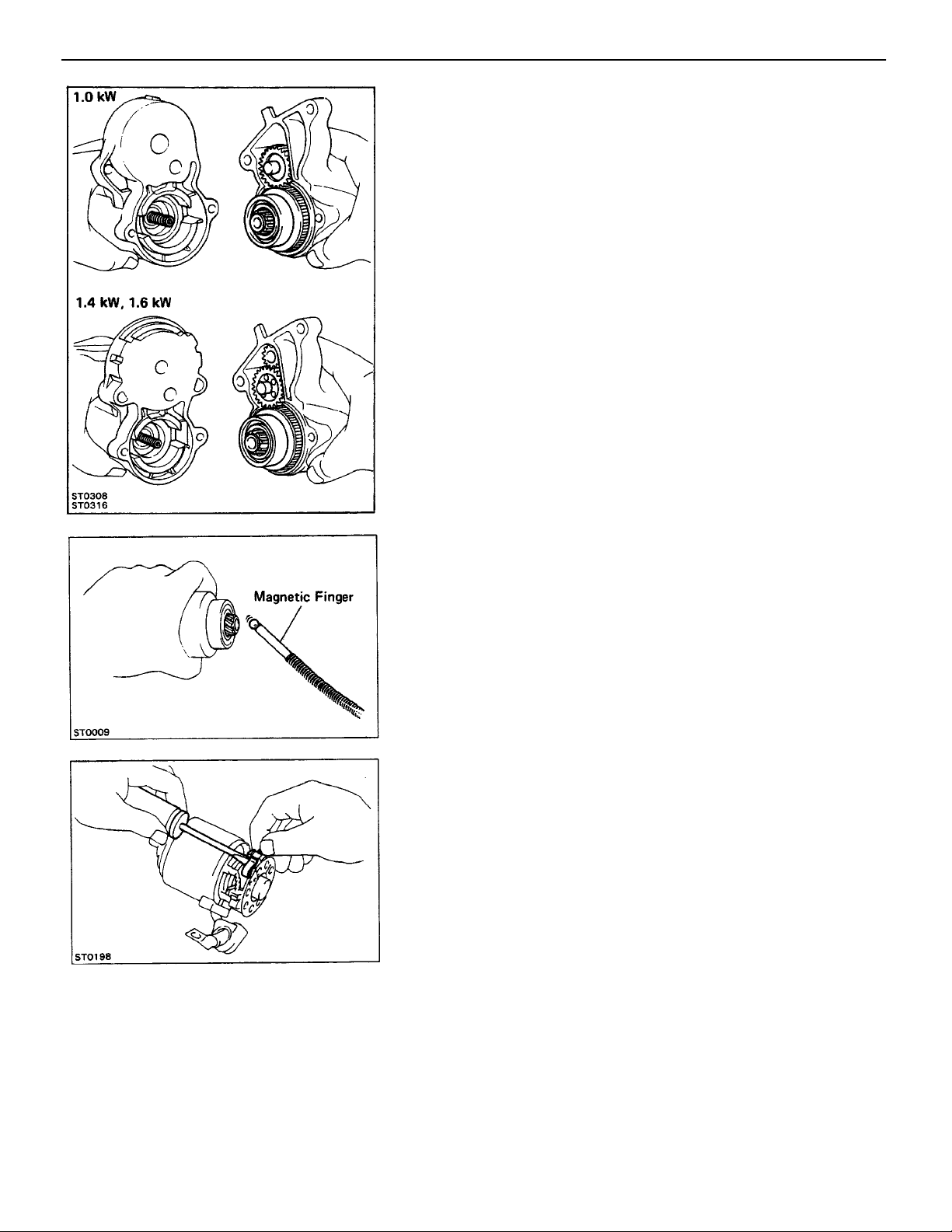
(b) Remove the starter housing with the pinion gear
(1.4, 1.6 kW), idler gear, bearing and clutch assembly.
3. REMOVE CLUTCH ASSEMBLY AND GEARS FROM
STARTER HOUSING
4. REMOVE STEEL BALL AND SPRING
Using a magnetic finger, remove the spring and steel ball
from the clutch shaft hole.
5. REMOVE BRUSHES AND BRUSH HOLDER
(a) Remove the two screws and pull the end cover with
0–ring (1.4, 1.6 kW) off the field frame.
(b) Using a screwdriver, hold the spring back and discon–
nect the brush from the brush holder. Disconnect the
four brushes and remove the brush holder.
6. REMOVE ARMATURE FROM FIELD FRAME
–STARTING SYSTEM Starter
INSPECTION OF STARTER
Armature Coil
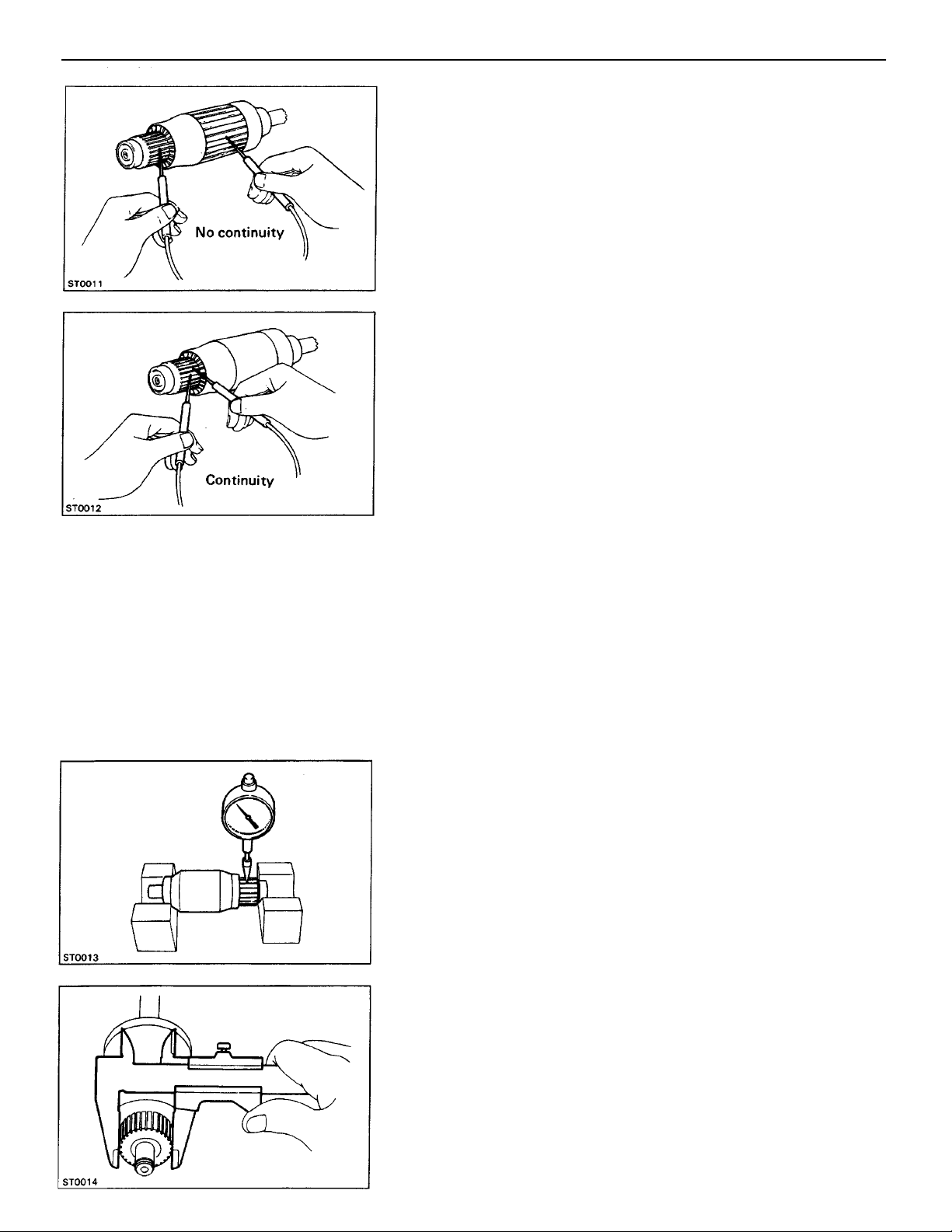
1. INSPECT THAT COMMUTATOR IS NOT GROUNDED
Using an ohmmeter, check that there is no continuity be–
tween the commutator and armature coil core.
If there is continuity, replace the armature.
2. INSPECT COMMUTATOR FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
Using an ohmmeter, check that there is continuity between
the segments of the comrnutator.
If there is no continuity between any segment, replace the
armature.
ST–5
Commutator
1. INSPECT COMMUTATOR FOR DIRTY AND BURNT
SURFACES
If the surface is dirty or burnt, correct it with sandpaper
(No.400) or on a lathe.
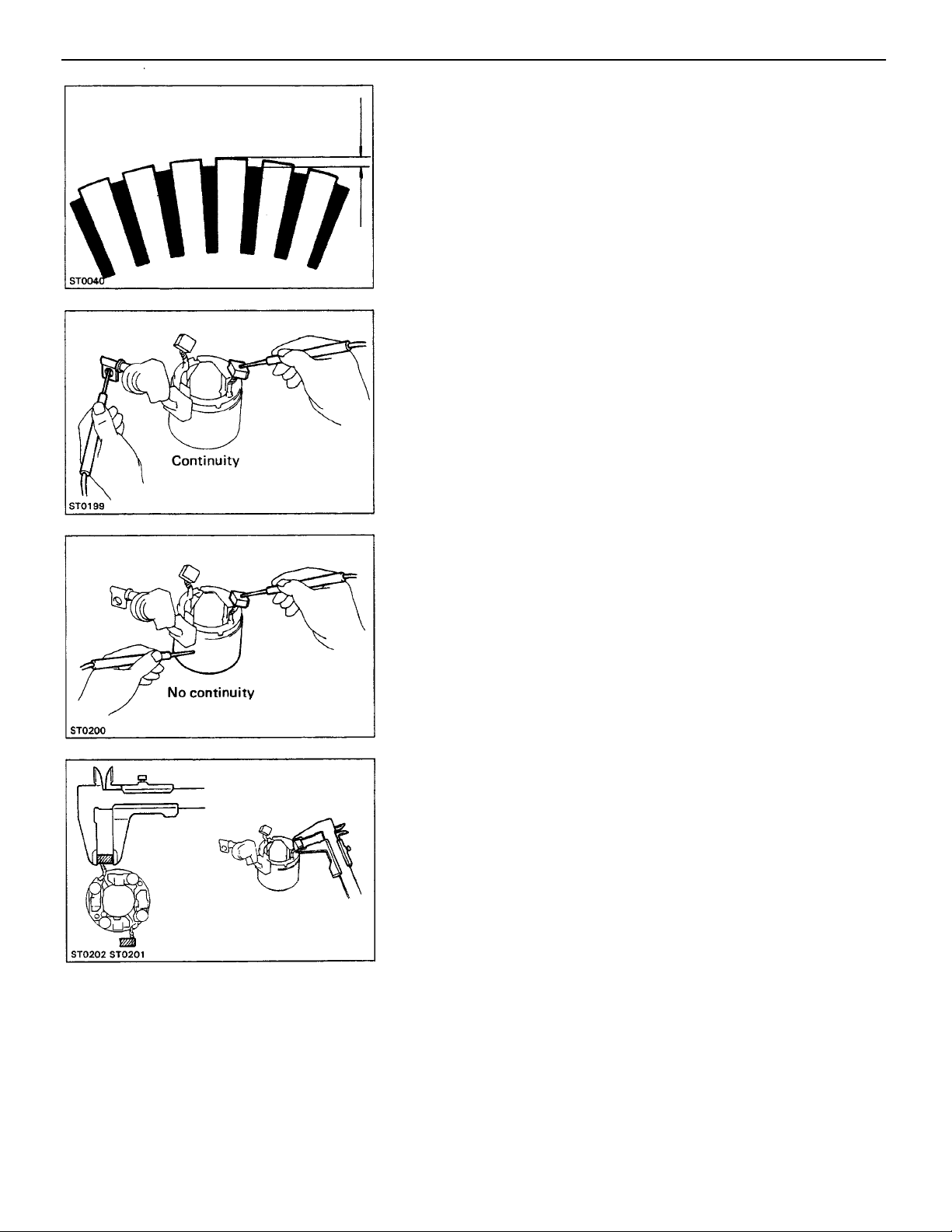
2. INSPECT COMMUTATOR CIRCLE RUNOUT
(a) Place the commutator on V–blocks.
(b) Using a dial indicator, measure the circle runout.
Maximum circle runout: 0.05 mm (0.0020 in.)
If the circle runout is greater than maximum, correct it on
a lathe.
3. INSPECT COMMUTATOR DIAMETER
Using vernier calipers, measure the commutator diameter.
Standard diameter: 30 mm (1.18 in.)
Minimum diameter: 29 mm (11.14 in.)
If the diameter is less than minimum, replace the armature.
ST–6
–STARTING SYSTEM Starter
4. INSPECT UNDERCUT DEPTH OF SEGMENT
Check that the undercut depth is clean and free of foreign
material. Smooth out the edge.
Standard undercut depth: 0.6 mm (0.024 in.)
Minimum undercut depth: 0.2 mm (0.008 in.)
If the undercut depth is less than minimum, correct it with
a hacksaw blade.
Field Frame (Field Coil)
1. INSPECT FIELD COIL FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
Using an ohmmeter, check that there is continuity between
the lead wire and field coil brush lead.
If there is no continuity, replace the field frame.
2. INSPECT THAT FIELD COIL IS NOT GROUNDED
Using an ohmmeter, check that there is no continuity be–
tween the field coil end and field frame.
If there is continuity, repair or replace the field frame.
Brushes
INSPECT BRUSH LENGTH
Using vernier calipers, measure the brush length.
Standard length: 1.0 kW 13.5 mm (0.531 in.)
1.4 kW 15.5 mm (0.610 in.)
1.6 kW 15.5 mm (0.610 in.)
Minimum length: 1.0 kW 8.5 mm (0.335 in.)
1.4 kW 10.0 mm (0.394 in.)
1.6 kW 10.0 mm (0.394 in.)
If the length is less than minimum, replace the brush holder
and field frame.
–STARTING SYSTEM Starter
Brush Springs
INSPECT BRUSH SPRING LOAD
Take the pull scale reading the instant the brush spring
separates from the brush.
Standard installed load:
18 – 24 N (1.785 – 2.415 kgf, 3.9 – 5.3 1bf)
Minimum installed load:
12 N (1.2 kgf, 2.6 Ibf)
If the installed load is less than minimum, replace the brush
springs.
HINT: Take the pull scale reading the instant the brush
spring separates from the brush.
Brush Holder
INSPECT INSULATION OF BRUSH HOLDER
Using an ohmmeter, check that there is no continuity be–
tween the positive (+) and negative (–) brush holders.
If there is continuity, repair or replace the brush holder.
ST–7
Clutch and Gears
1. INSPECT GEAR TEETH
Check the gear teeth on the pinion gear, idler gear and
clutch assembly for wear or damage.
If damaged, replace the gear or clutch assembly.
If damaged, also check the flywheel ring gear for wear or
damage.
2. INSPECT CLUTCH
Rotate the clutch pinion gear clockwise and check that it
turns freely. Try to rotate the clutch pinion counterclock–
wise and check that it locks.
If necessary, replace the clutch assembly.
Bearings
1. INSPECT BEARINGS
Turn each bearing by hand while applying inward force.
If the resistance is felt or if the bearing sticks, replace the
bearing.
ST–8
–STARTING SYSTEM Starter
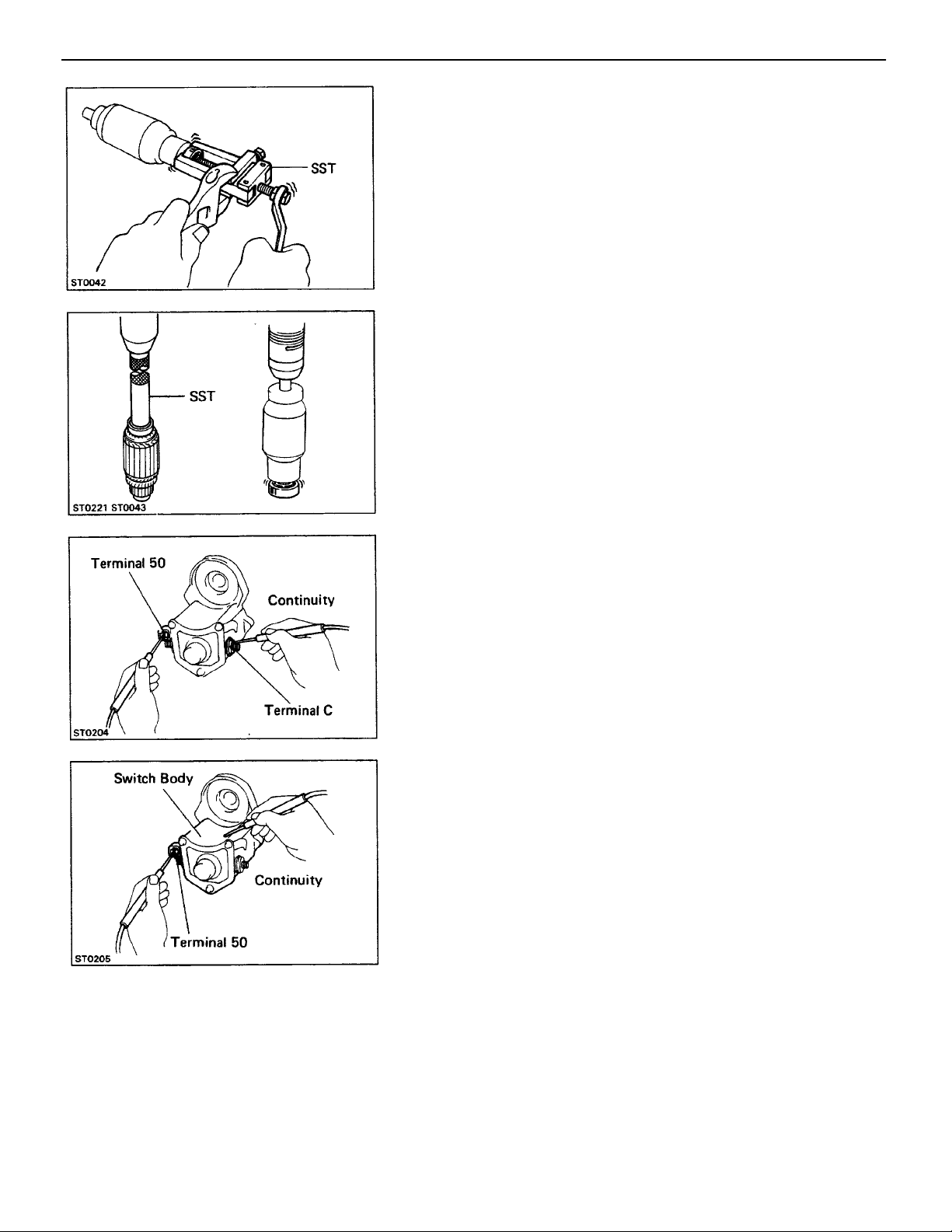
2. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE BEARINGS
(a) Using SST, remove the bearing.
SST 09286–46011
(b) Using SST and a press, press in a new bearing.
SST 1.0 kW 09285–76010
1.4 kW, 1.6 kW 09201–41020
Magnetic Switch
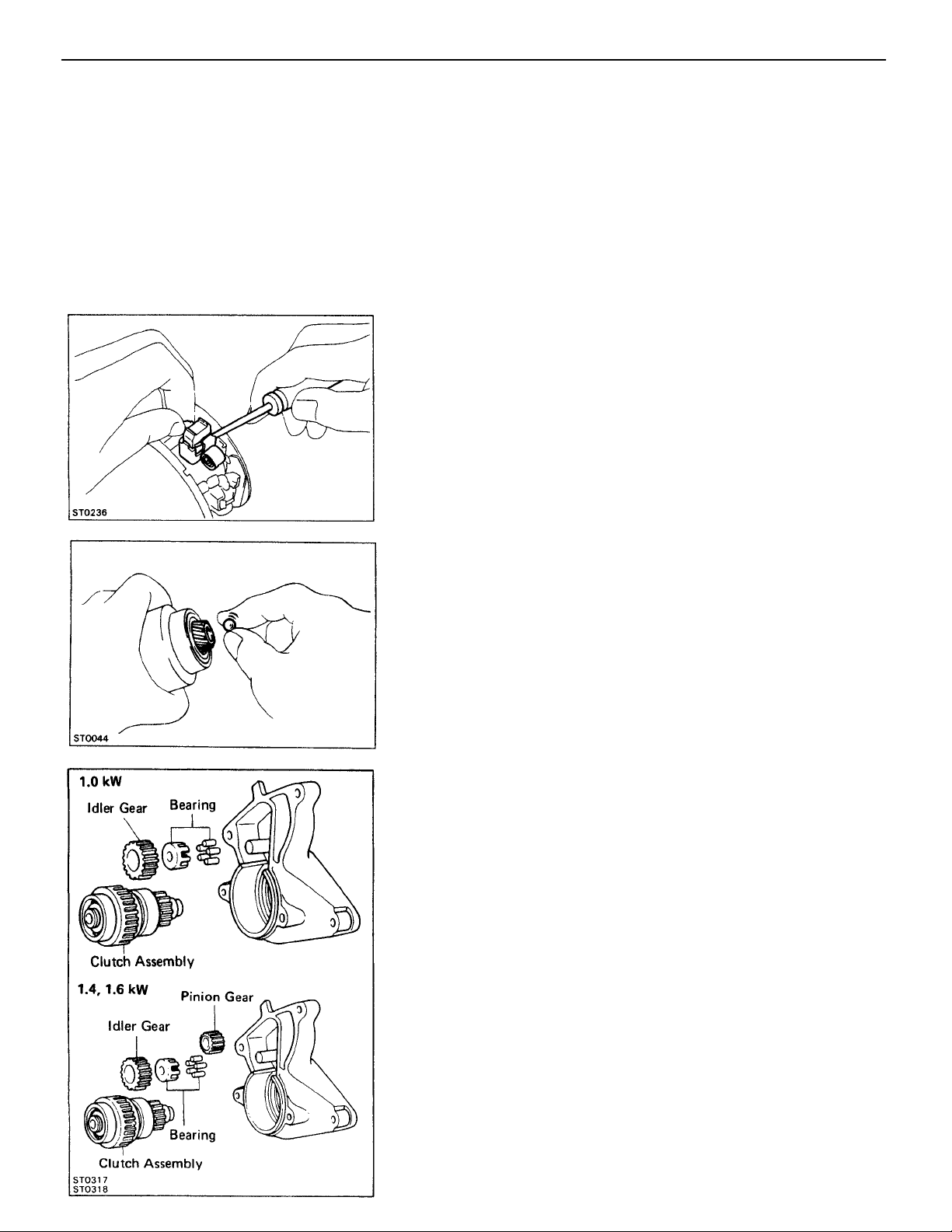
1. PERFORM PULL–IN COIL OPEN CIRCUIT TEST
Using an ohmmeter, check that there is continuity between
terminals 50 and C.
Ifthere is no continuity, replace the magnetic switch as–
sembly.
2. PERFORM HOLD–IN COIL CIRCUIT TEST
Using an ohmmeter, check that there is continuity between
terminal 50 and the switch body.
If there is no continuity, replace the magnetic switch as–
sembly.
–STARTING SYSTEM Starter
ASSEMBLY OF STARTER
(See page ST–2)
HINT: Use high–temperature grease to lubricate the bear–
ings and gears when assembling the starter.
1. PLACE ARMATURE INTO FIELD FRAME
Apply grease to the armature bearings and insert the ar–
mature into the field frame.
2. INSTALL BRUSH HOLDER
(a) Place the brush holder over the frame.
(b) Using a screwdriver, hold the brush spring back, and
connect the brush into the brush holder. Connect the
four brushes.
HINT: Check that the positive (+) lead wires are not
grounded.
(c) (1.4 kW, 1.6 kW)
Place the 0–ring on the field frame.
(d) Install the end cover to the field frame with the two
screws.
ST–9
3. INSERT STEEL BALL INTO CLUTCH SHAFT HOLE
(a) Apply grease to the steel ball.
(b) Insert the steel ball into the clutch shaft hole.
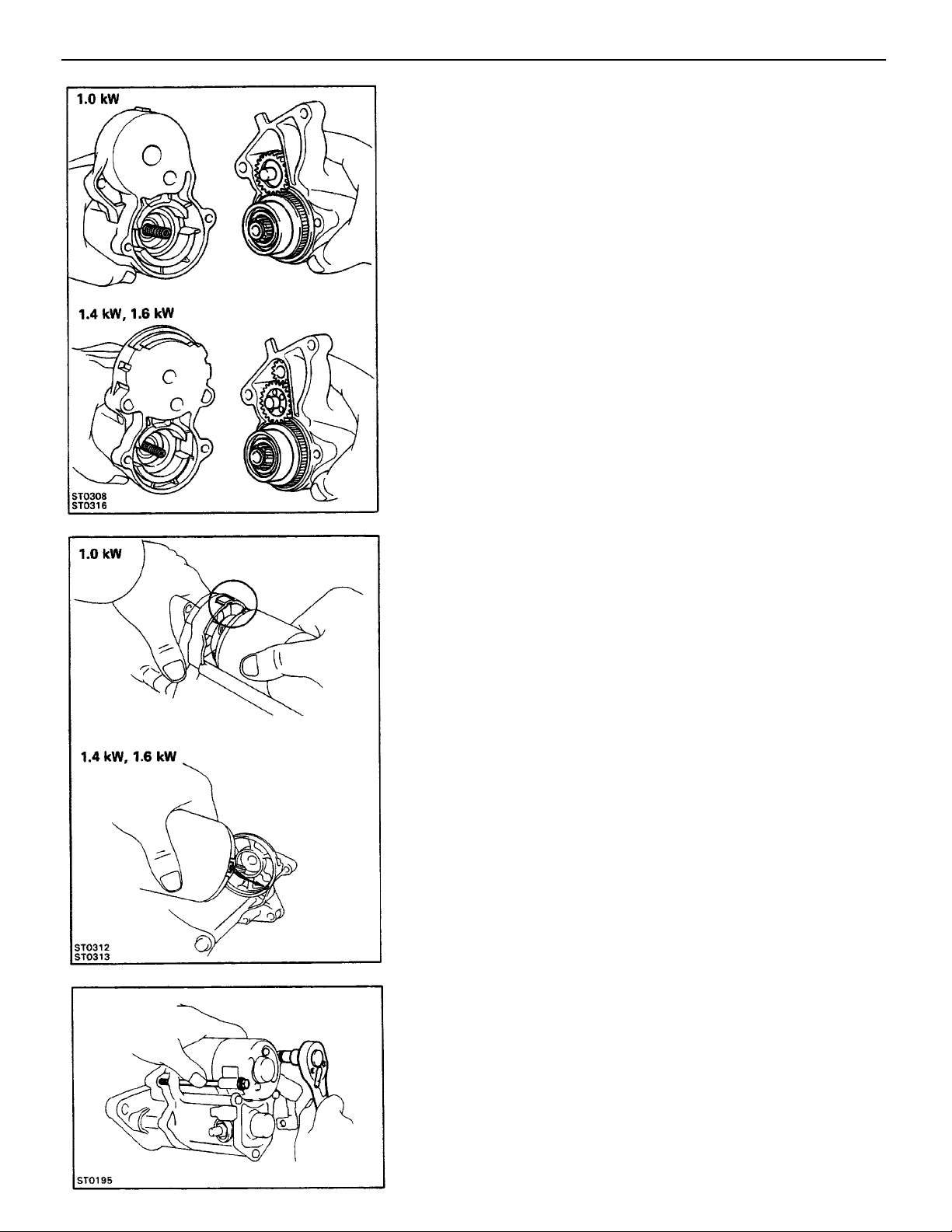
4. INSTALL GEARS AND CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
(a) Apply grease to the gears and clutch assembly.
(b) Place the clutch assembly, idler gear, bearing and pin–
ion gear 11.4, 1.6 kW) in the starter housing.
ST–10
–STARTING SYSTEM Starter
5. INSTALL STARTER HOUSING
(a) Apply grease to the return spring.
(b) Insert the return spring into the magnetic hole.
(e) Place the starter housing on the magnetic switch and
install the two screws.
6. INSTALL FIELD FRAME WITH ARMATURE TO
MAGNETIC SWITCH ASSEMBLY
(a) (1.4, 1. 6 kW)
Place the O–ring on the field frame.
(b) Align the protrusion of the field frame with the cutout
of the magnetic switch.
(c) Install the two through bolts.
(d) Connect the lead wire to the magnetic switch ter-
mi¿na1 C, and install the nut.
–STARTING SYSTEM Starter
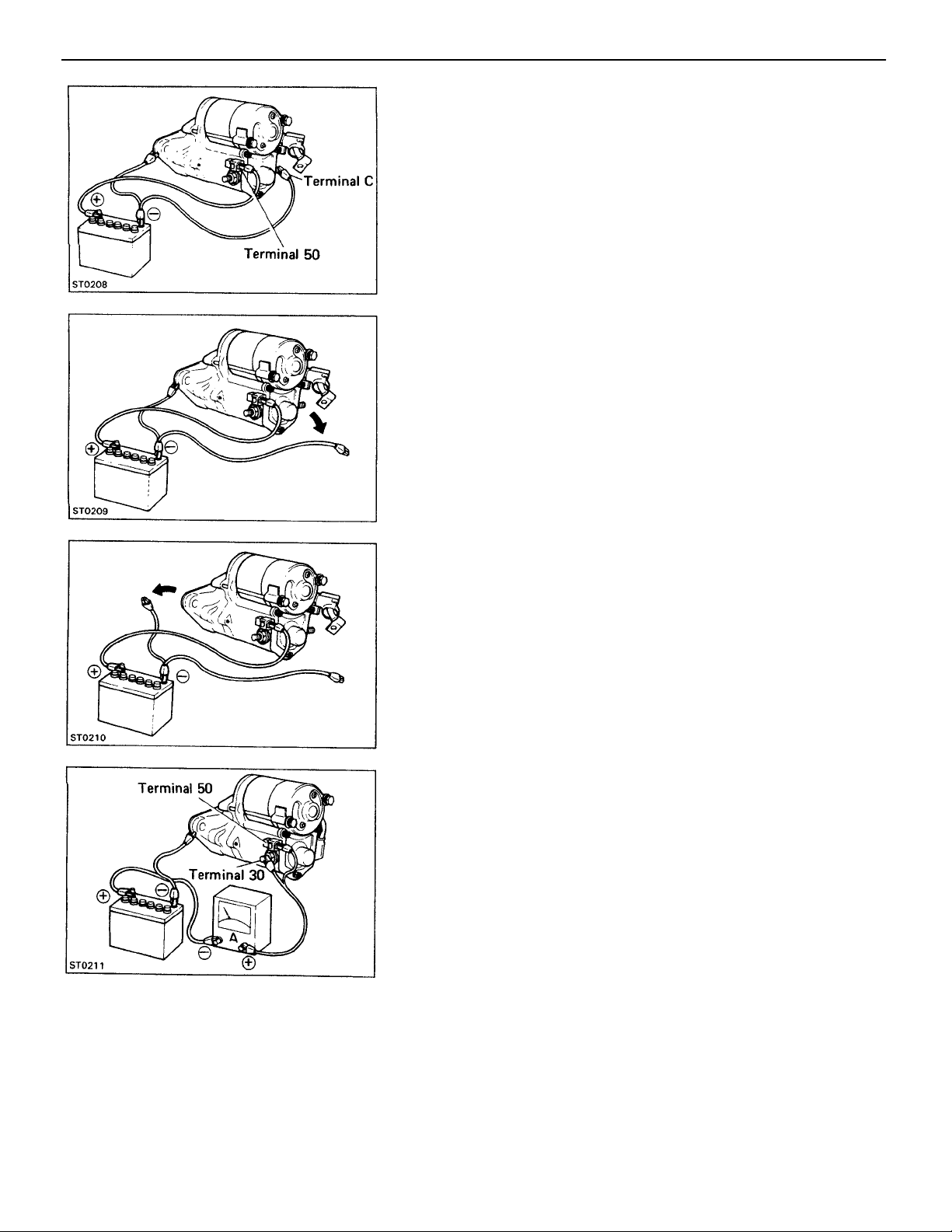
PERFORMANCE TEST OF STARTER
NOTICE: These tests must be performed within 3 to 5
seconds to avoid burning out the coil.
1. PERFORM PULL–IN TEST
(a) Disconnect the field coil lead wire from terminal C.
(b) Connect the battery to the magnetic switch as shown.
Check that the clutch pinion gear moves outward.
If the clutch pinion gear does not move, replace the mag–
netic switch assembly.
2. PERFORM HOLD–IN TEST
With battery connected as above with the clutch pinion
gear out, disconnect the negative (–) lead from terminal
C. Check that the pinion gear remains out.
If the clutch pinion gear returns inward, replace the mag–
netic switch assembly.
ST–11
3. INSPECT CLUTCH PINION GEAR RETURN
Disconnect the negative (–) lead from the switch body.
Check that the clutch pinion gear returns inward.
If the clutch pinion gear does not return, replace the mag–
netic switch assembly.
4. PERFORM NO–LOAD PERFORMANCE TEST
(a) Connect the battery and ammeter to the starter as
shown. .
(b) Check that the starter rotates smoothly and steadily
with the pinion gear moving out. Check that the am–
meter reads the specified current.
Specified current:
90 A or less at 11.5 V
ST–12
–STARTING SYSTEM Starter
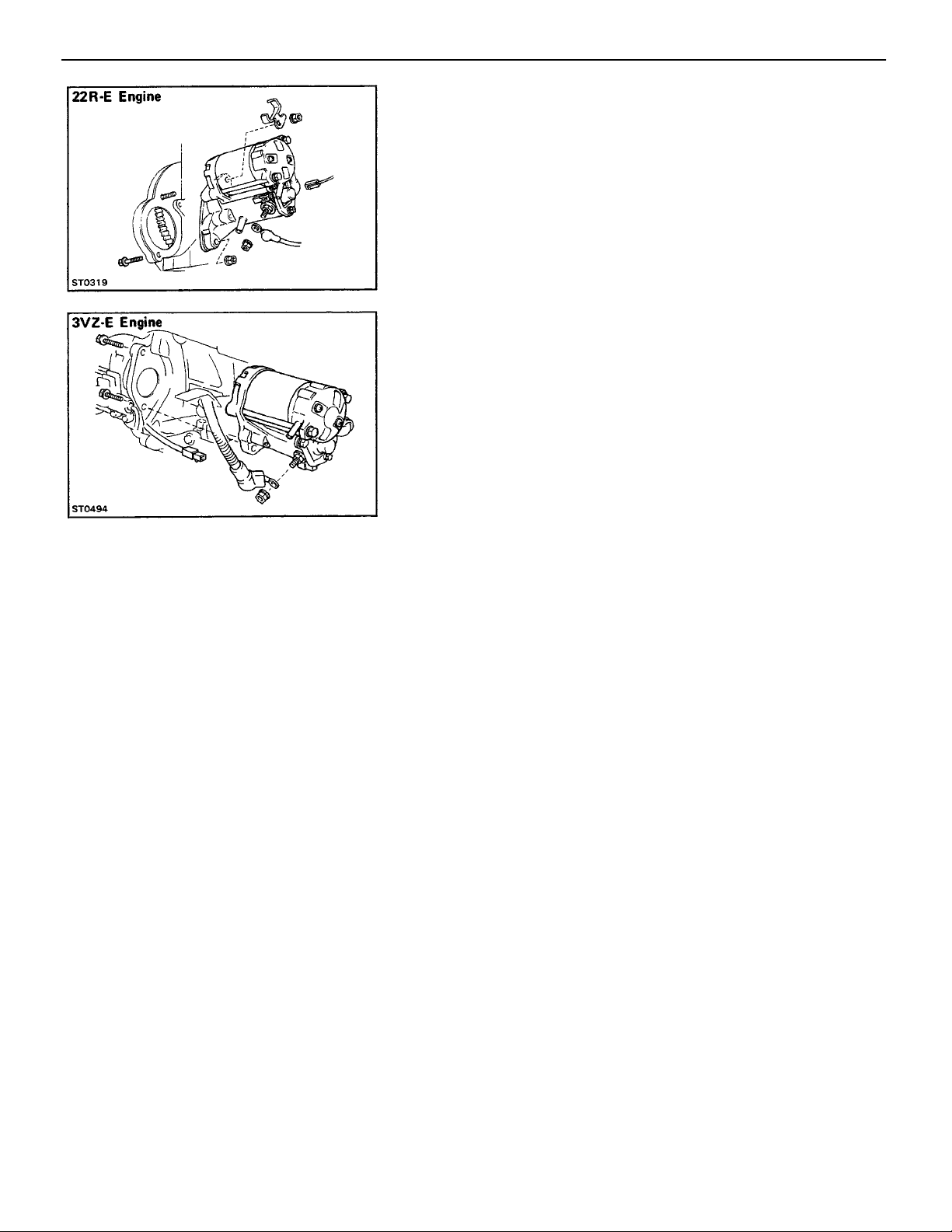
INSTALLATION OF STARTER
1. INSTALL STARTER MOTOR ON TRANSAXLE
(22R–E Engine)
Place the starter motor in the flywheel bellhousing.
Install and torque the bolt and nut.
(3VZ–E Engine)
Place the starter motor in the flywheel bellhousing, and in–
stall and torque the starter mounting bolts.
Torque: 39 N–m (400 kgf–cm, 29 ft–lbf)
2. CONNECT TWO WIRES TO STARTER
Connect the connector to the terminal on the magnetic
switch. Connect the cable from the battery to the termi–
nal on the switch, and install the nut.
3. CONNECT CABLE TO NEGATIVE TERMINAL OF BATTERY
Check that the engine starts.
–STARTING SYSTEM Starter Relay, Clutch Start Switch
ST–13
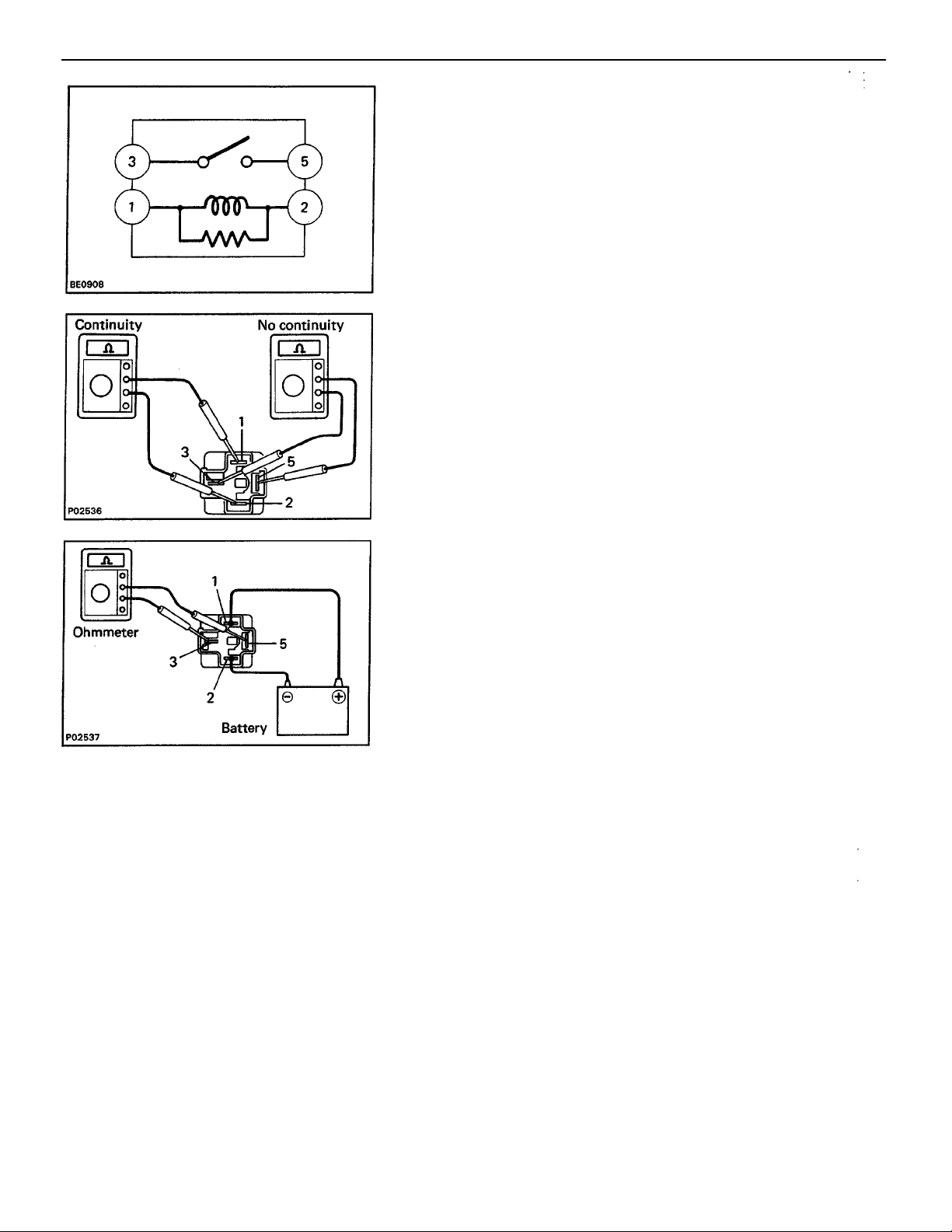
STARTER RELAY
INSPECTION OF STARTER RELAY
LOCATION: The relay is located in the No. 1 junction block
on the driver’s side.
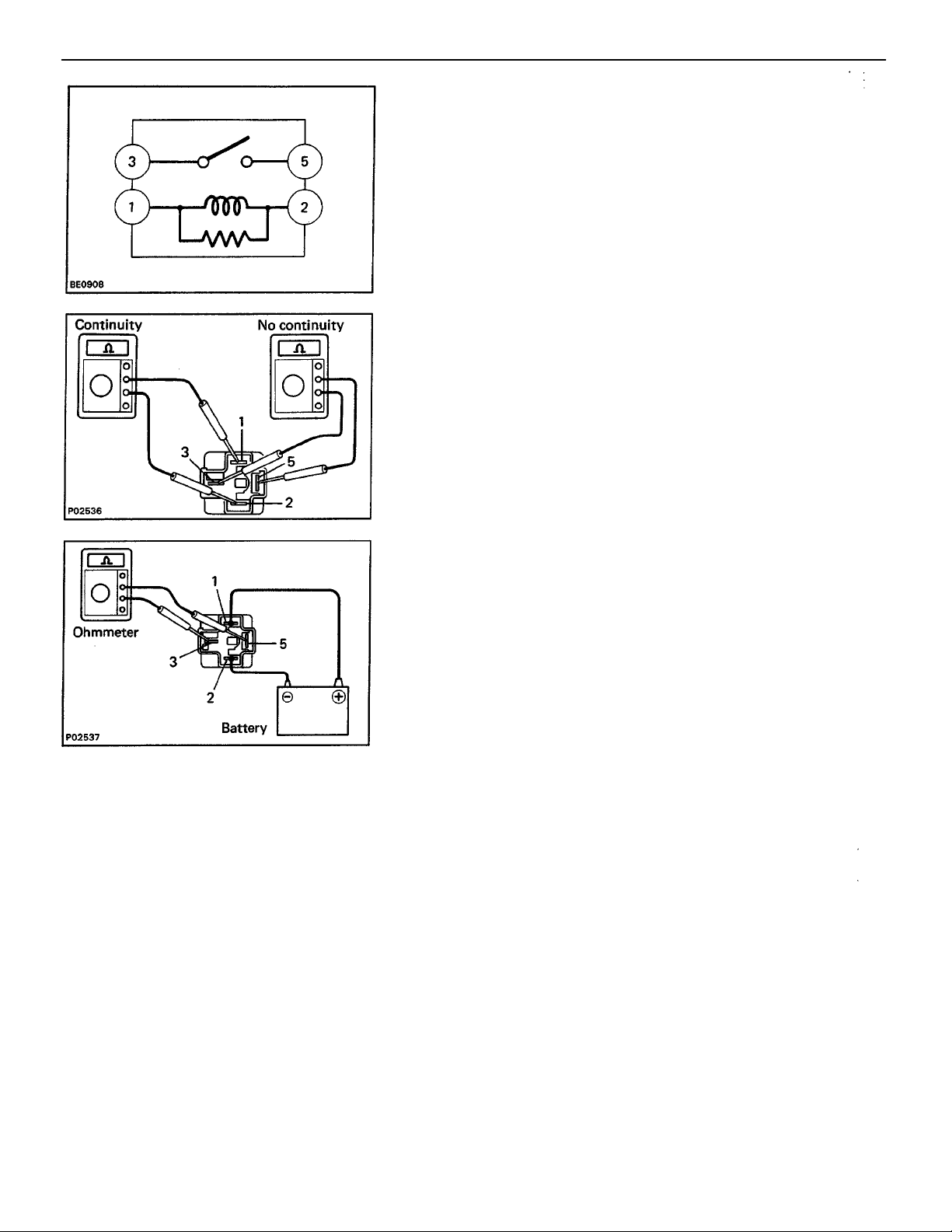
1. INSPECT RELAY CONTINUITY
(a) Using an ohmmeter, check that there is continuity be–
tween terminals 1 and 2.
(b) Check that there is no continuity between terminals
3 and 5.
If continuity is not as specified, replace the relay.
2. INSPECT RELAY OPERATION
(a) Apply battery voltage across terminals 1 and 2.
(b) Check that there is continuity between terminals 3 and*
5.
If operation is not as described, replace the relay.
CLUTCH START SWITCH (M/T only)
(See page CL–4)
–STARTING SYSTEM Starter Relay, Clutch Start Switch
ST–13
STARTER RELAY
INSPECTION OF STARTER RELAY
LOCATION: The relay is located in the No. 1 junction block
on the driver’s side.
1. INSPECT RELAY CONTINUITY
(a) Using an ohmmeter, check that there is continuity be–
tween terminals 1 and 2.
(b) Check that there is no continuity between terminals
3 and 5.
If continuity is not as specified, replace the relay.
2. INSPECT RELAY OPERATION
(a) Apply battery voltage across terminals 1 and 2.
(b) Check that there is continuity between terminals 3 and*
5.
If operation is not as described, replace the relay.
CLUTCH START SWITCH (M/T only)
(See page CL–4)

AC–1
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM
AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM
AC–2
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM General Information
GENERAL INFORMATION
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
Prevention of Refrigerant Release and Excessive quantities
Refrigerant (CFCs) for automobile air conditionings is be–
lieved to cause harm by depleting the ozone layer which
helps to protect us from the ultraviolet rays of the sun.
Therefore, it is necessary to prevent release of refrigerant
to the atmosphere and to use the minimum amount when
servicing the air conditioning.
1. USE RECOVERY MACHINE TO RECOVER REFRIGERANT
When discharging refrigerant from the system as follows,
use a recovery machine to recover the refrigerant.
• Before replacing parts on the refrigerant line.
• When moisture or air gets in the refrigerant line.
• When excess refrigerant is charged.
NOTICE:
• When handling the recovery machine, always follow
the directions given in the instruction manual.
• After recovery, the amount of compressor oil removed
must be measured and the same amount added to the
system.
2. USE CHARGING HOSES WITH STOP VALVE WHEN
INSTALLING MANIFOLD GAUGE SET
To prevent release of refrigerant, using charging hoses
with a stop valve when installing the manifold gauge set
to the service valves on the refrigerant line.
3. TIGHTEN CONNECTING PARTS SECURELY
Follow the notices about tightening connecting parts in
step 6 on page AC–4.
4. PROPERLY EVACUATE AIR FROM REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM
To prevent release and wasteful use of refrigerant, evac–
uate air with care from refrigeration system as follows;
• Do not evacuate before recovering refrigerant in
system.
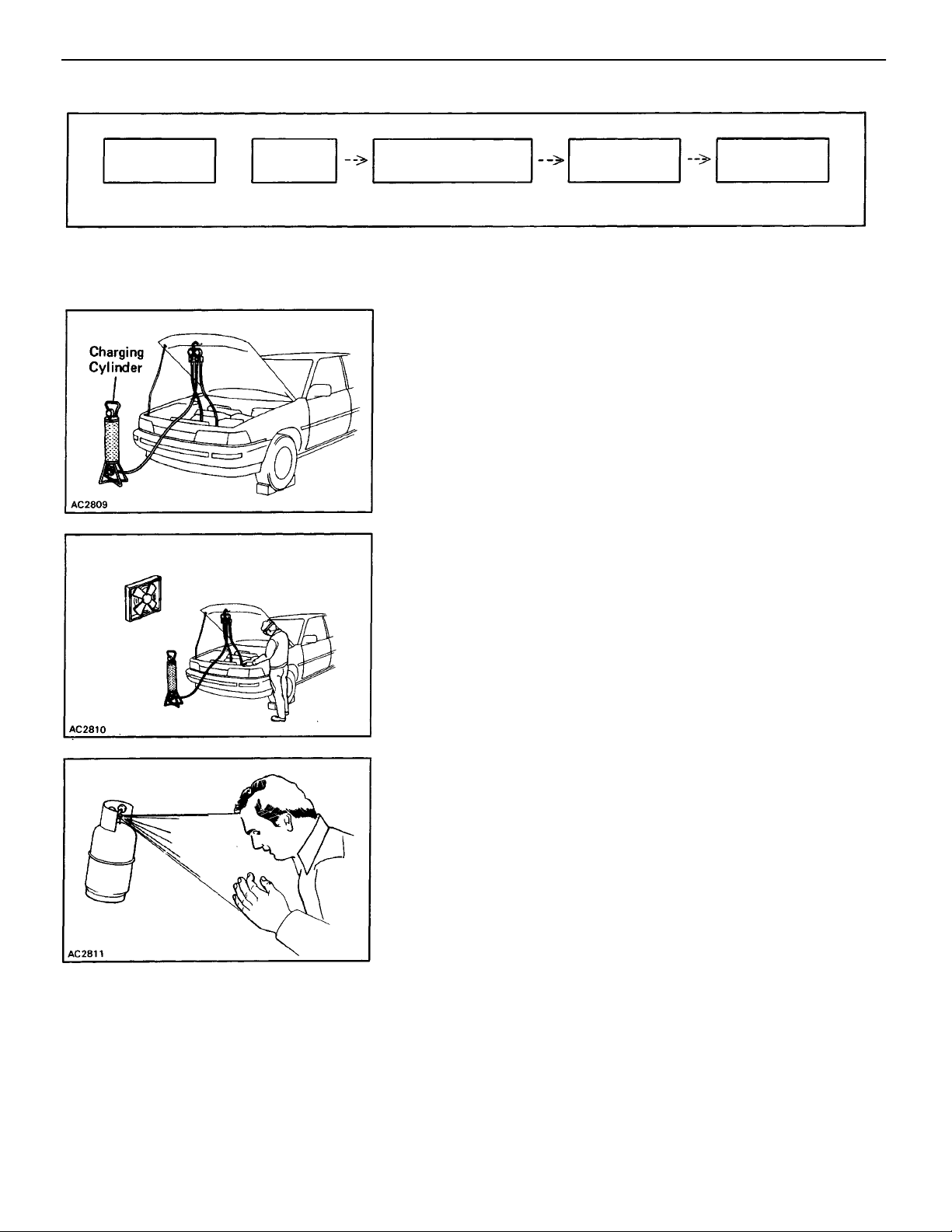
Evacuation Process
Evacuation
10 minutes
or more
Airtight
Check
Leave for 5
minutes
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM General Information
• Do not perform repeat evacuation of system.
Top–Up Charging of
Refrigerant
Refrigerant
Leak Check
Charging
Refrigerant
6. USE CHARGING CYLINDER TO CHARGE PROPER
AMOUNT OF REFRIGERANT
To prevent excessive use of refrigerant due to overcharg–
ing, use a charging cylinder to charge the proper amount
of refrigerant.
AC–3
Handling Precautions for Refrigerant
1. DO NOT HANDLE REFRIGERANT IN AN ENCLOSED
AREA OR NEAR AN OPEN FLAME
2. ALWAYS WEAR EYE PROTECTION
3. BE CAREFUL THAT LIQUID REFRIGERANT DOES NOT
GET IN YOUR EYES OR ON YOUR SKIN
If liquid refrigerant gets in your eyes or on your skin;
(a) Wash the area with lots of cool water.
CAUTION: Do not rub your eyes or skin.
(b) Apply clean petroleum jelly to the skin.
(c) Go immediately to a physician or hospital for profes–
sional treatment.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to treat yourself.
Handling Precautions for Refrigerant Container
1. NEVER HEAT CONTAINER OR EXPOSE IT TO NAKED
FLAME
2. BE CAREFUL NOT TO DROP CONTAINER AND NOT TO
APPLY PHYSICAL SHOCKS TO IT
AC–4
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM General Information
Handling Precautions for Gas–Cylinder Type Gas
Leak Tester
1. BEFORE USING TESTER MAKE SURE THAT THERE ARE
NO FLAMMABLE SUBSTANCES NEARBY
2. BE CAREFUL NOT TO INHALE POISONOUS GAS
If refrigerant gas comes in contact with flame, a poison–
ous gas is produced. During leak tests, do not inhale any
gas.
Precautions When Replacing Parts in
Refrigerant line
1. RECOVER REFRIGERANT IN SYSTEM BEFORE REMOV–
ING PARTS
Using a recovery machine, recover refrigerant in system
before removing the parts.
NOTICE: Do not release refrigerant to atmosphere.
2. INSERT PLUG IMMEDIATELY IN DISCONNECTED PARTS
Insert a plug immediately in the disconnected parts to
prevent the entry of moisture and dust.
3. DO NOT REMOVE PLUG FROM NEW PARTS UNTIL IM–
MEDIATELY BEFORE INSTALLATION
4. DO NOT USE BURNER FOR BENDING OR LENGTHENING
OPERATIONS ON TUBE
If the tubes are heated with a burner, a layer of oxidation
forms inside the tube, causing the same kind of trouble
as an accumulation of dust.
5. DISCHARGE GAS IN NEW COMPRESSOR FROM
CHARGING VALVE BEFORE INSTALLING IT
If the gas in new compressor is not discharged first, com–
pressor oil will spray out with gas when the plug is re–
moved.
6. TIGHTEN CONNECTING PARTS SECURELY
Securely tighten the connecting parts to prevent leaking
of refrigerant gas.
• Apply a few drops of compressor oil to 0–ring fittings
for easy tightening and to prevent leaking of refriger–
ant gas.
• Tighten the nuts using two wrenches to avoid twisting
the tube.
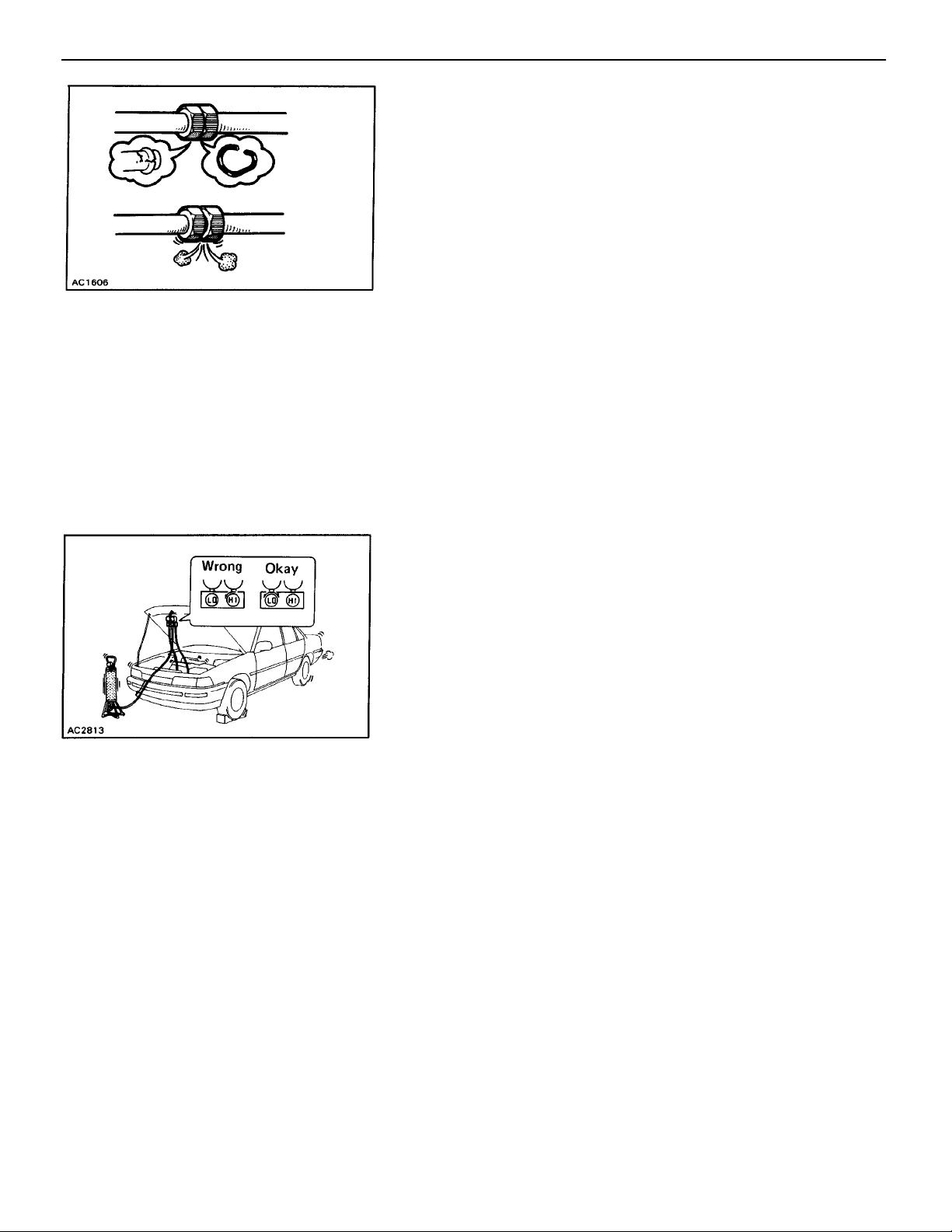
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM General Information
• Tighten the O–ring fittings or the bolted type fittings to
the specified torque.
Precautions When Charging Refrigerant
1. DO NOT OPERATE COMPRESSOR WITHOUT ENOUGH
REFRIGERANT IN REFRIGERANT CYCLE
If there is not enough refrigerant in the refrigerant cycle,
oil lubrication will be insufficient and compressor burnout
may occur, so take care to avoid this.
AC–5
2. DO NOT OPEN HIGH PRESSURE VALVE OF MANIFOLD
GAUGE WITH COMPRESSOR OPERATING
If the high pressure valve is opened, refrigerant flows in
the reverse direction and could cause the charging cylin–
der to rupture, so open and close the low pressure valve
only.
3. BE CAREFUL NOT TO OVERCHARGE WITH REFRIGER–
ANT IN SYSTEM
If refrigerant is overcharged, it causes trouble such as in–
sufficient cooling, poor fuel economy, engine overheating
etc.
ELECTRICAL PARTS
Before removing and inspecting the electrical parts, set
the ignition switch to the LOCK position and disconnect
the negative (–) terminal cable from the battery..
AC–6
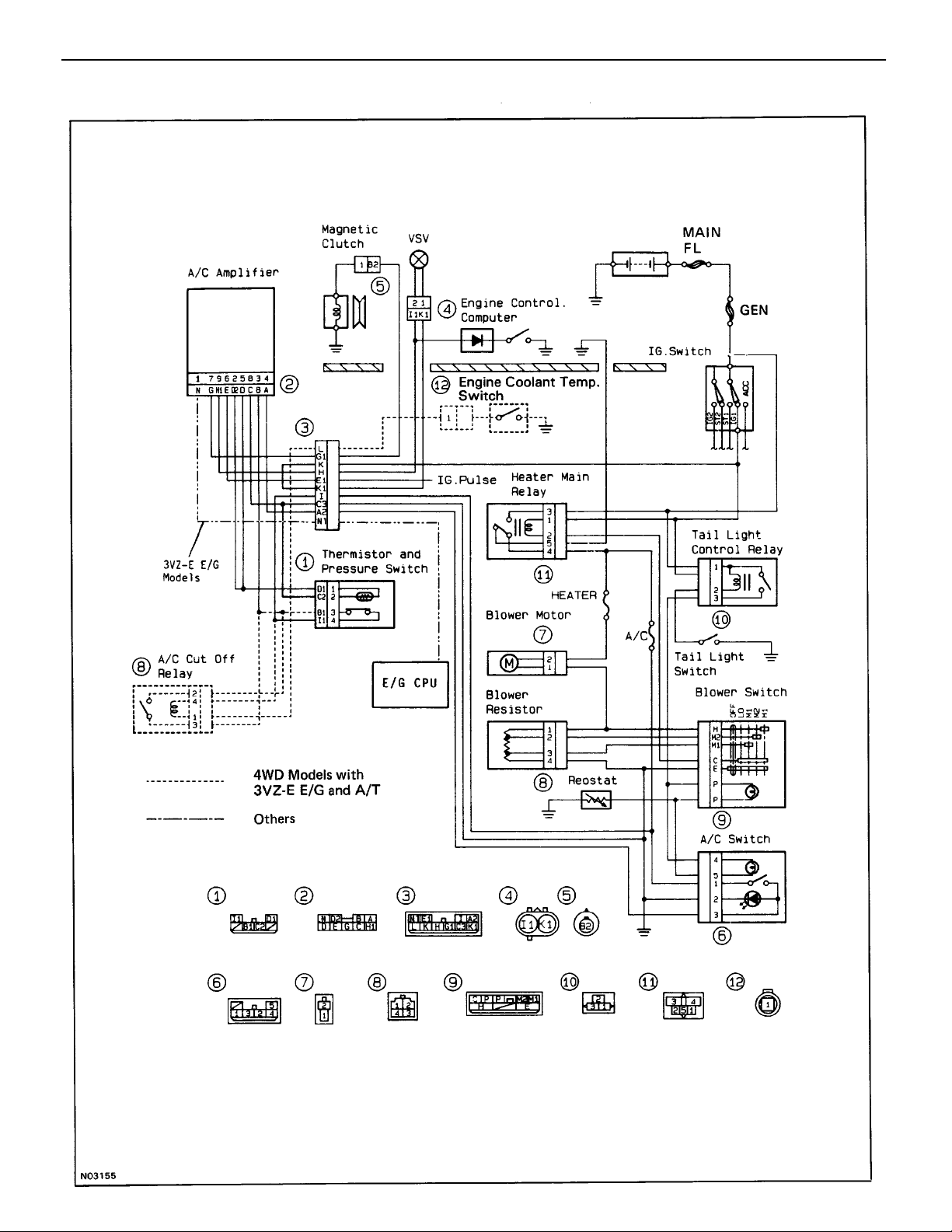
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM Air Conditioning System Circuit
AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM CIRCUIT
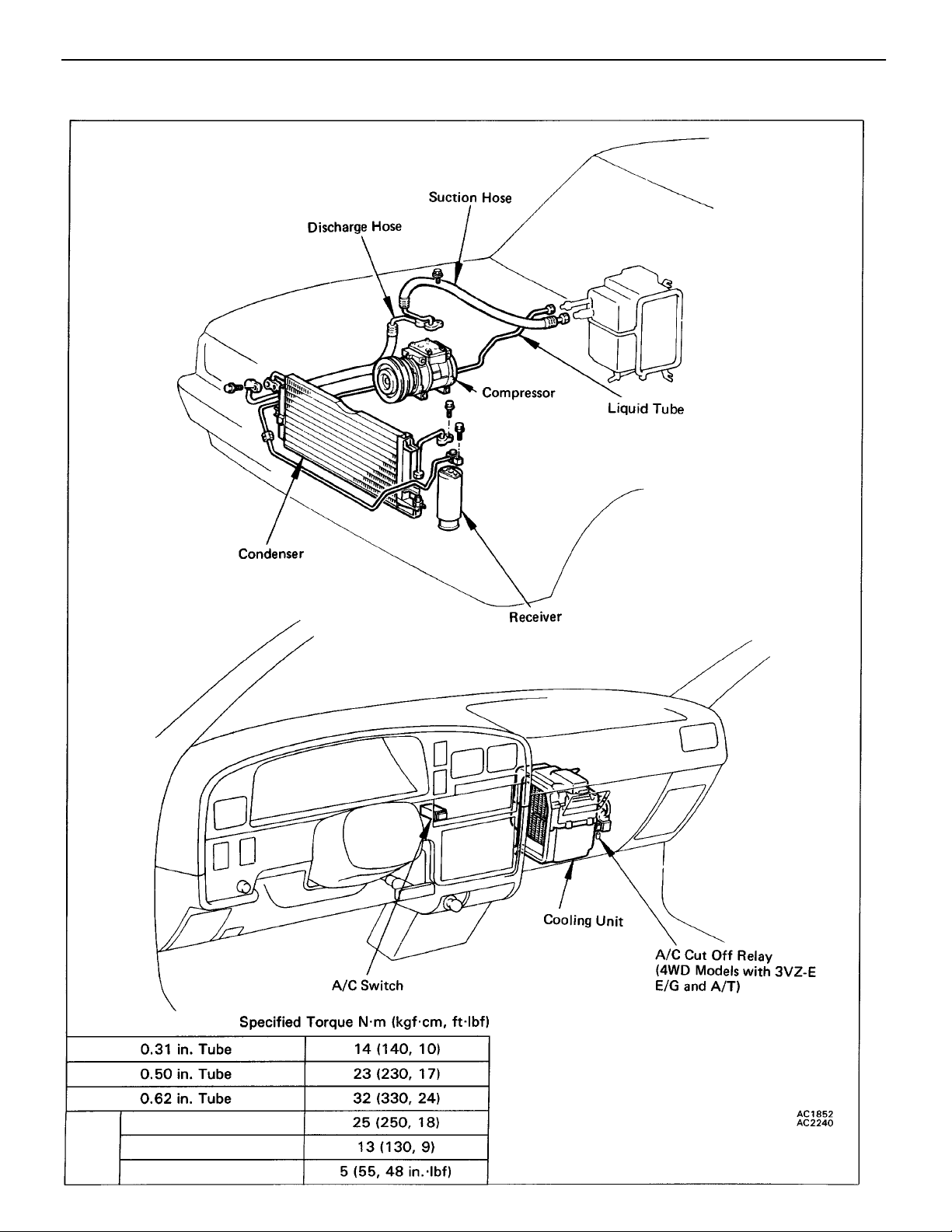
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM System Components
SYSTEM COMPONENTS
AC–7
Bolted
Type
For Compressor
For Condenser
For Receiver
AC–8
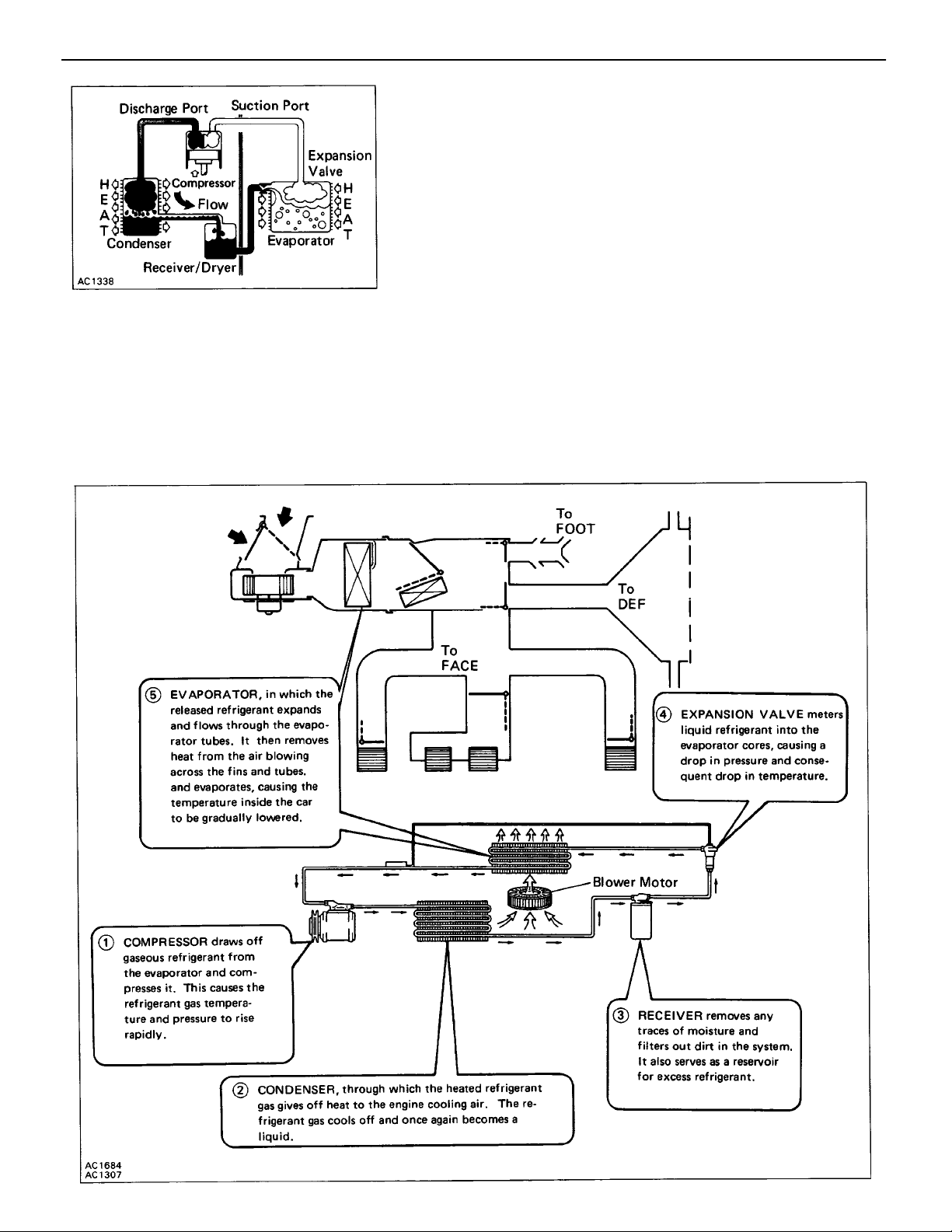
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM General Description
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
REFRIGERATION CYCLE
1. The compressor discharges high temperature and high
pressure refrigerant containing the heat absorbed from
the evaporator plus the heat created by the compressor
in a discharge stroke.
2. This gaseous refrigerant flows into the condenser. In the
condenser, the gaseous refrigerant condenses into liquid
refrigerant.
3. This liquid refrigerant flows into the receiver which stores
and filters the liquid refrigerant till the evaporator requires
the refrigerant.
4. The liquid refrigerant is changed by the expansion valve into a low temperature, low pressure liquid
and gaseous mixture.
5. This cold and foggy refrigerant flows to the evaporator. Vaporizing the liquid in the evaporator, the
heat from the warm air stream passing through the evaporator core is transferred to the refrigerant. All
the liquid is changed into the gaseous refrigerant in the evaporator and only heat–laden gaseous
refrigerant is drawn into the compressor. Then the process is repeated again.
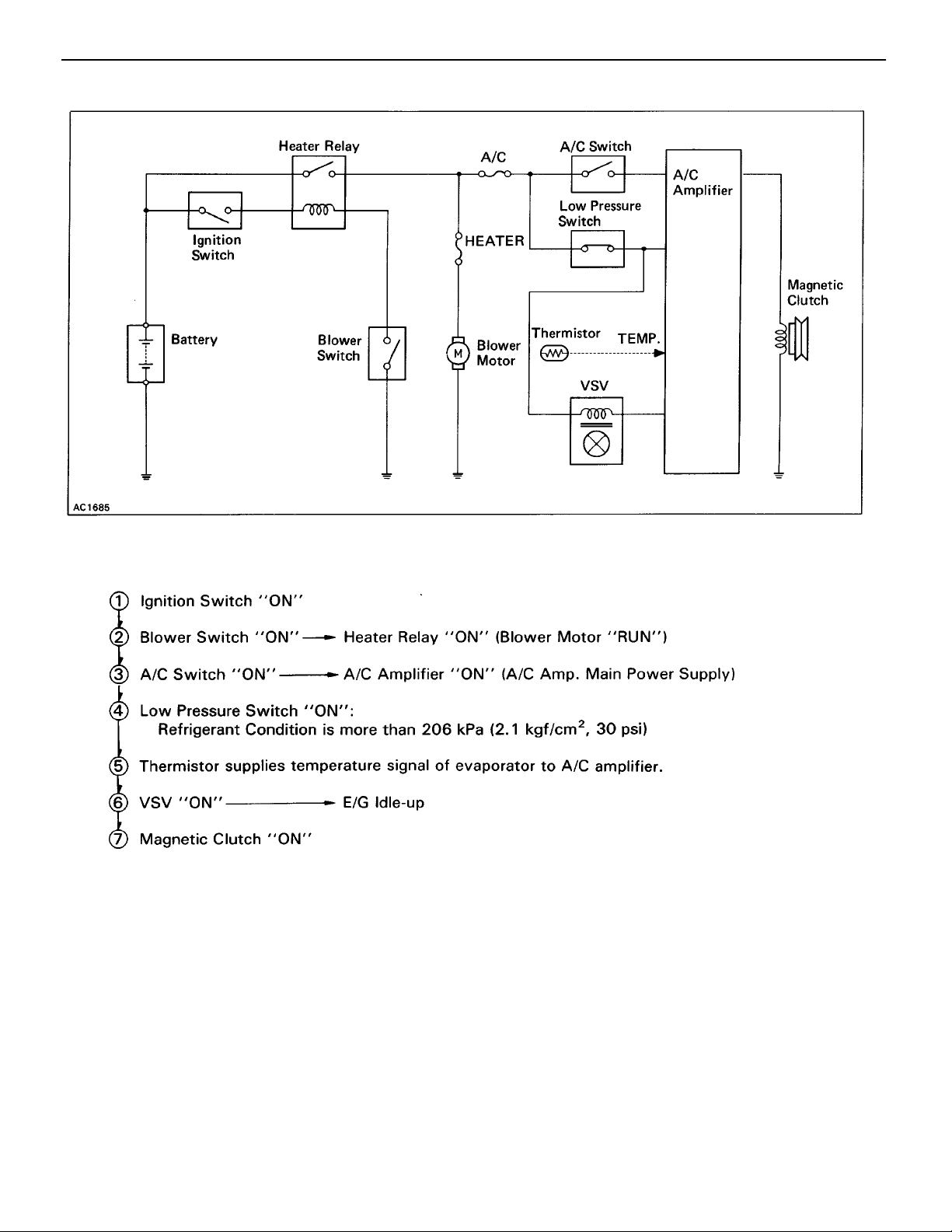
1. PRINCIPLE OF A/C ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM General Description
AC–9
2. HOW IS MAGNETIC CLUTCH ENERGIZED?
The general process until the magnetic clutch is energized as shown below.
AC–10
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM Special Tools and Equipment
SPECIAL TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT
Tool
Ohmmeter
Voltage meter
Air conditioning service tool set
Magnetic clutch remover
Magnetic clutch stopper
Snap ring pliers
Part Name
ND OIL6,
SUNISO No.5GS or equivalent
Problem
No cooling or warm
air
Magnetic clutch does not engage
(a) A/C fuse blown
(b) Magnetic clutch faulty
(c) A/C switch faulty
(d) A/C amplifier faulty
(e) Wiring or ground faulty
(f) Refrigerant empty
(g) Heater relay faulty
(h) Pressure switch faulty
Compressor does not rotate properly
(a) Drive belt loose or broken
(b) Compressor faulty
Expansion valve faulty
Leak in system
Fusible plug on receiver blown or clogged
screen
Blower does not operate
(a) HEATER fuse blown
(b) A/C switch faulty
(c) Heater relay faulty
(d) Blower motor faulty
(e) Wiring or ground faulty
SSM (SPECIAL SERVICE MATERIALS)
07117–68040
TROUBLESHOOTING
Possible cause
SST No.
To diagnosis electrical system
To diagnosis electrical system
07110–58011
07112–66040
07112–76060
07114–84020
Part No. Use etc.
To evacuate and charge system
To remove pressure plate
To remove and install pressure plate
To remove pressure plate
Compressor
Remedy
Replace fuse and check for
short
Check magnetic clutch
Check switch
Check amplifier
Repair as necessary
Check refrigerant volume
Check heater relay
Check pressure switch
Adjust or replace drive belt
Check compressor
Check expansion valve
Test system for leaks
Check receiver
Replace fuse and check for
short
Check switch
Check heater relay
Check blower motor
Repair as necessary
Use
Page
AC–6
AC–17
AC–29
AC–31
AC–6
AC–16
AC–37
AC–29
AC–15
AC–17
AC–25
AC–23
AC–6
AC–29
AC–37
AC–37
AC–6
Cool air comes out
intermittently
Magnetic clutch slipping
Expansion valve faulty
Wiring connection faulty
Excessive moisture in system
A/C amplifier faulty
Check magnetic clutch
Check expansion valve
Repair as necessary
Evacuate and charge system
Check amplifier
AC–17
AC–25
AC–6
AC–31
AC–10
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM SSM (Special Service Materials)
SPECIAL TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT
Tool
Ohmmeter
Voltage meter
Air conditioning service tool set
Magnetic clutch remover
Magnetic clutch stopper
Snap ring pliers
Part Name
ND OIL6,
SUNISO No.5GS or equivalent
Problem
No cooling or warm
air
Magnetic clutch does not engage
(a) A/C fuse blown
(b) Magnetic clutch faulty
(c) A/C switch faulty
(d) A/C amplifier faulty
(e) Wiring or ground faulty
(f) Refrigerant empty
(g) Heater relay faulty
(h) Pressure switch faulty
Compressor does not rotate properly
(a) Drive belt loose or broken
(b) Compressor faulty
Expansion valve faulty
Leak in system
Fusible plug on receiver blown or clogged
screen
Blower does not operate
(a) HEATER fuse blown
(b) A/C switch faulty
(c) Heater relay faulty
(d) Blower motor faulty
(e) Wiring or ground faulty
SSM (SPECIAL SERVICE MATERIALS)
07117–68040
TROUBLESHOOTING
Possible cause
SST No.
To diagnosis electrical system
To diagnosis electrical system
07110–58011
07112–66040
07112–76060
07114–84020
Part No. Use etc.
To evacuate and charge system
To remove pressure plate
To remove and install pressure plate
To remove pressure plate
Compressor
Remedy
Replace fuse and check for
short
Check magnetic clutch
Check switch
Check amplifier
Repair as necessary
Check refrigerant volume
Check heater relay
Check pressure switch
Adjust or replace drive belt
Check compressor
Check expansion valve
Test system for leaks
Check receiver
Replace fuse and check for
short
Check switch
Check heater relay
Check blower motor
Repair as necessary
Use
Page
AC–6
AC–17
AC–29
AC–31
AC–6
AC–16
AC–37
AC–29
AC–15
AC–17
AC–25
AC–23
AC–6
AC–29
AC–37
AC–37
AC–6
Cool air comes out
intermittently
Magnetic clutch slipping
Expansion valve faulty
Wiring connection faulty
Excessive moisture in system
A/C amplifier faulty
Check magnetic clutch
Check expansion valve
Repair as necessary
Evacuate and charge system
Check amplifier
AC–17
AC–25
AC–6
AC–31
AC–10
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM Troubleshooting
SPECIAL TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT
Tool
Ohmmeter
Voltage meter
Air conditioning service tool set
Magnetic clutch remover
Magnetic clutch stopper
Snap ring pliers
Part Name
ND OIL6,
SUNISO No.5GS or equivalent
Problem
No cooling or warm
air
Magnetic clutch does not engage
(a) A/C fuse blown
(b) Magnetic clutch faulty
(c) A/C switch faulty
(d) A/C amplifier faulty
(e) Wiring or ground faulty
(f) Refrigerant empty
(g) Heater relay faulty
(h) Pressure switch faulty
Compressor does not rotate properly
(a) Drive belt loose or broken
(b) Compressor faulty
Expansion valve faulty
Leak in system
Fusible plug on receiver blown or clogged
screen
Blower does not operate
(a) HEATER fuse blown
(b) A/C switch faulty
(c) Heater relay faulty
(d) Blower motor faulty
(e) Wiring or ground faulty
SSM (SPECIAL SERVICE MATERIALS)
07117–68040
TROUBLESHOOTING
Possible cause
SST No.
To diagnosis electrical system
To diagnosis electrical system
07110–58011
07112–66040
07112–76060
07114–84020
Part No. Use etc.
To evacuate and charge system
To remove pressure plate
To remove and install pressure plate
To remove pressure plate
Compressor
Remedy
Replace fuse and check for
short
Check magnetic clutch
Check switch
Check amplifier
Repair as necessary
Check refrigerant volume
Check heater relay
Check pressure switch
Adjust or replace drive belt
Check compressor
Check expansion valve
Test system for leaks
Check receiver
Replace fuse and check for
short
Check switch
Check heater relay
Check blower motor
Repair as necessary
Use
Page
AC–6
AC–17
AC–29
AC–31
AC–6
AC–16
AC–37
AC–29
AC–15
AC–17
AC–25
AC–23
AC–6
AC–29
AC–37
AC–37
AC–6
Cool air comes out
intermittently
Magnetic clutch slipping
Expansion valve faulty
Wiring connection faulty
Excessive moisture in system
A/C amplifier faulty
Check magnetic clutch
Check expansion valve
Repair as necessary
Evacuate and charge system
Check amplifier
AC–17
AC–25
AC–6
AC–31
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM Troubleshooting
TROUBLESHOOTING (Cont’d)
AC–11
Problem
Cool air comes out
only at high speed
Insufficient cooling
Insufficient velocity
of cool air
Possible cause
Condenser clogged
Drive belt slipping
Compressor faulty
Insufficient or too much refrigerant
Air in system
Condenser clogged
Drive belt slipping
Magnetic clutch faulty
Compressor faulty
Expansion valve faulty
Insufficient *or too much refrigerant
Air or excessive compressor oil in system
Receiver clogged
Water valve cable faulty
A/C amplifier faulty
Evaporator clogged or frosted
Air leakage from cooling unit or air duct
Air inlet blocked
Blower motor faulty
A/C amplifier faulty
Remedy
Check condenser
Check or replace drive belt
Check compressor
Check refrigerant volume
Evacuate and charge system
Check condenser
Check or replace drive belt
Check magnetic clutch
Check compressor
Check expansion valve
Check refrigerant volume
Evacuate and charge system
Check receiver
Reset water valve cable
Check amplifier
Clean evaporator fins or filters
Repair as necessary
Repair as necessary
Check blower motor
Check amplifier
Page
AC–24
AC–15
AC–17
AC–16
AC–24
AC–15
AC–17
AC–17
AC–25
AC–16
AC–23
AC–36
AC–31
AC–27
AC–37
AC–31
AC–12
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM Troubleshooting
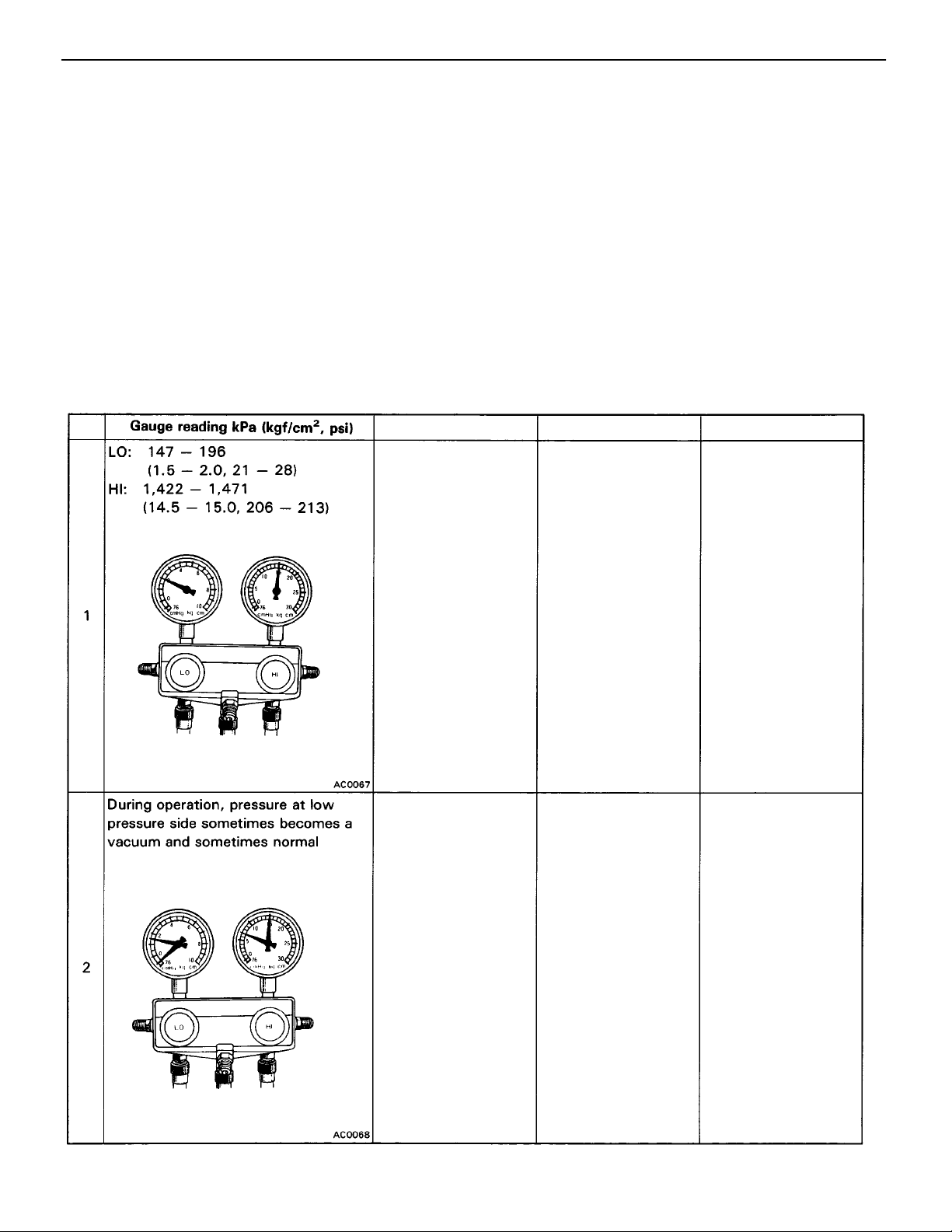
Inspection of Refrigeration System with Manifold Gauge Set
This is a method in which the trouble is located by using a manifold gauge set. (See ”Installation of Mani–
fold Gauge Set” on page AC–16. ) Read the manifold gauge pressure when the following conditions are
established:
(b) Engine running at 2,000 rpm
(a) Temperature at the air inlet with the switch set at RECIRC is 30 – 35
(c) Blower fan speed control switch set at high speed
(d) Temperature control switch set at max. cool side
HINT: It should be noted that the gauge indications may vary slightly due to ambient temperature condi–
tions.
NOTICE:
• Always recover refrigerant before removing the parts in the refrigerant line and evacuating air.
• Evacuate air and charge proper amount of purified refrigerant after installing the parts in the refriger-
ant line.
C (86 – 95F)
No.
Condition
Normal cooling
Periodically cools and
then fails to cool
Probable cause
Normally functioning
system
Moisture present in
refrigeration system
Remedy
(1) Replace receiver
(2) Remove moisture
in system through
repeatedly evacu–
ating air
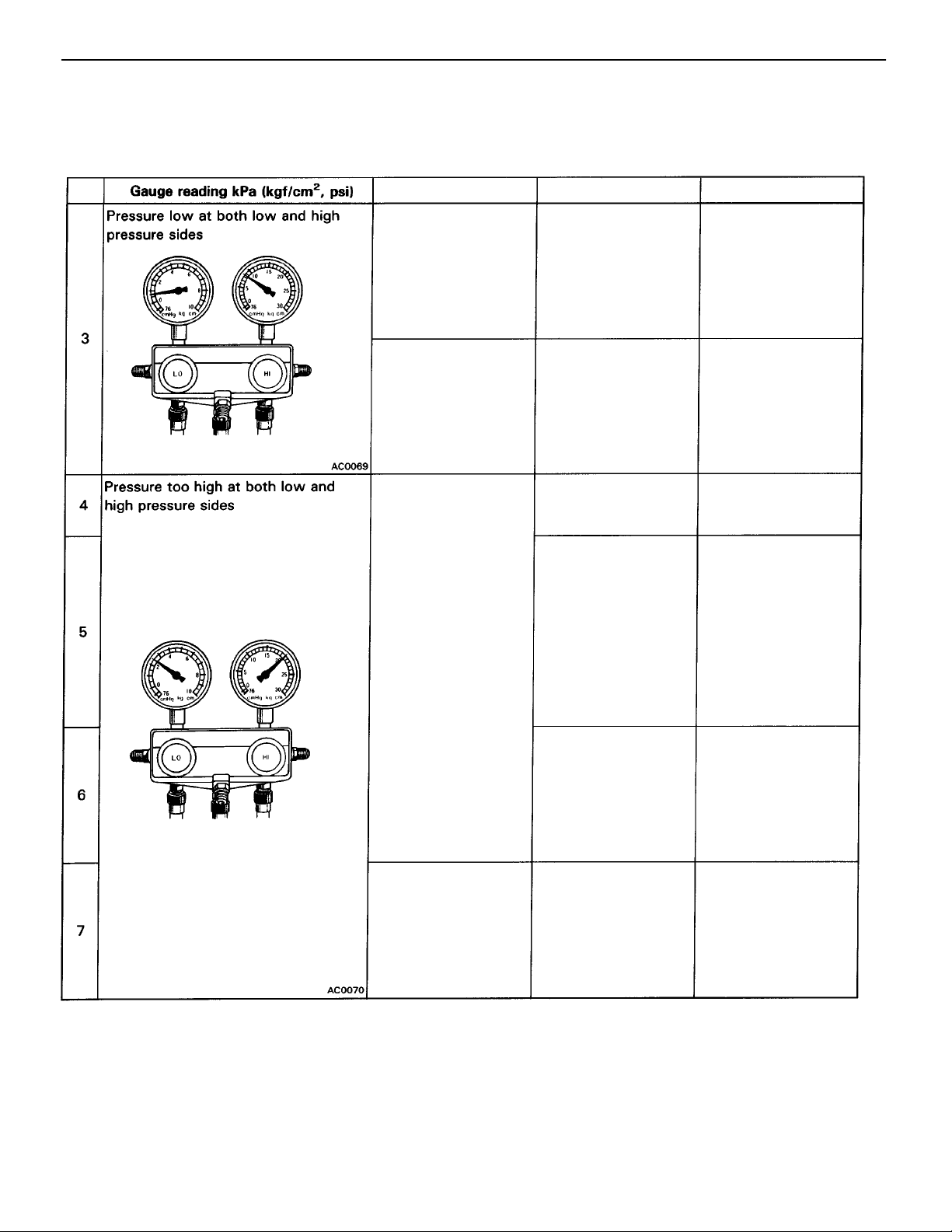
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM Troubleshooting
NOTICE:
• Always recover refrigerant before removing the parts in the refrigerant line and evacuating air.
• Evacuate air and charge proper amount of purified refrigerant after installing the parts in the refrigerant line.
AC–13
No.
• Insufficient cooling
• Bubbles seen in
sight glass
• Insufficient cooling
• Frost on tubes from
receiver to unit
Insufficient cooling
• Insufficient cooling
• Frost or Large
amount of dew on
piping at low pres–
sure side
Probable causeCondition
Insufficient refrigerant
Refrigerant flow ob–
structed by dirt in re
ceiver
Insufficient cooling of
condenser
Refrigerant over–
charged
Air present in system
Expansion valve im–
properly mounted,heat
sensing tube defective
(Opens too wide)
Remedy
(1) Check for gas
leakage with gas
leak tester and
repair if necessary
(2) Add refrigerant
until bubbles dis–
appear
Replace receiver
(1) Clean condenser
(2) Check fan motor
operation
(1) Check amount of
refrigerant
If refrigerant is over–
charged
(2) Recover refriger–
ant
(3) Evacuate air and
charge proper
amount of purified
refrigerant
(1) Replace receiver
(2) Check compressor
oil to see if dirty
(3) Remove air in sys–
tem through re–
peatedly evacuat–
ing air
(1) Check heat sens–
ing tube installa–
tion condition
If (1) is normal
(2) Check expansion
valve and replace
if defective
Hint at 6:
These gauge indications are for when the refrigeration system has been opened and the refrigerant
charged without evacuating air.
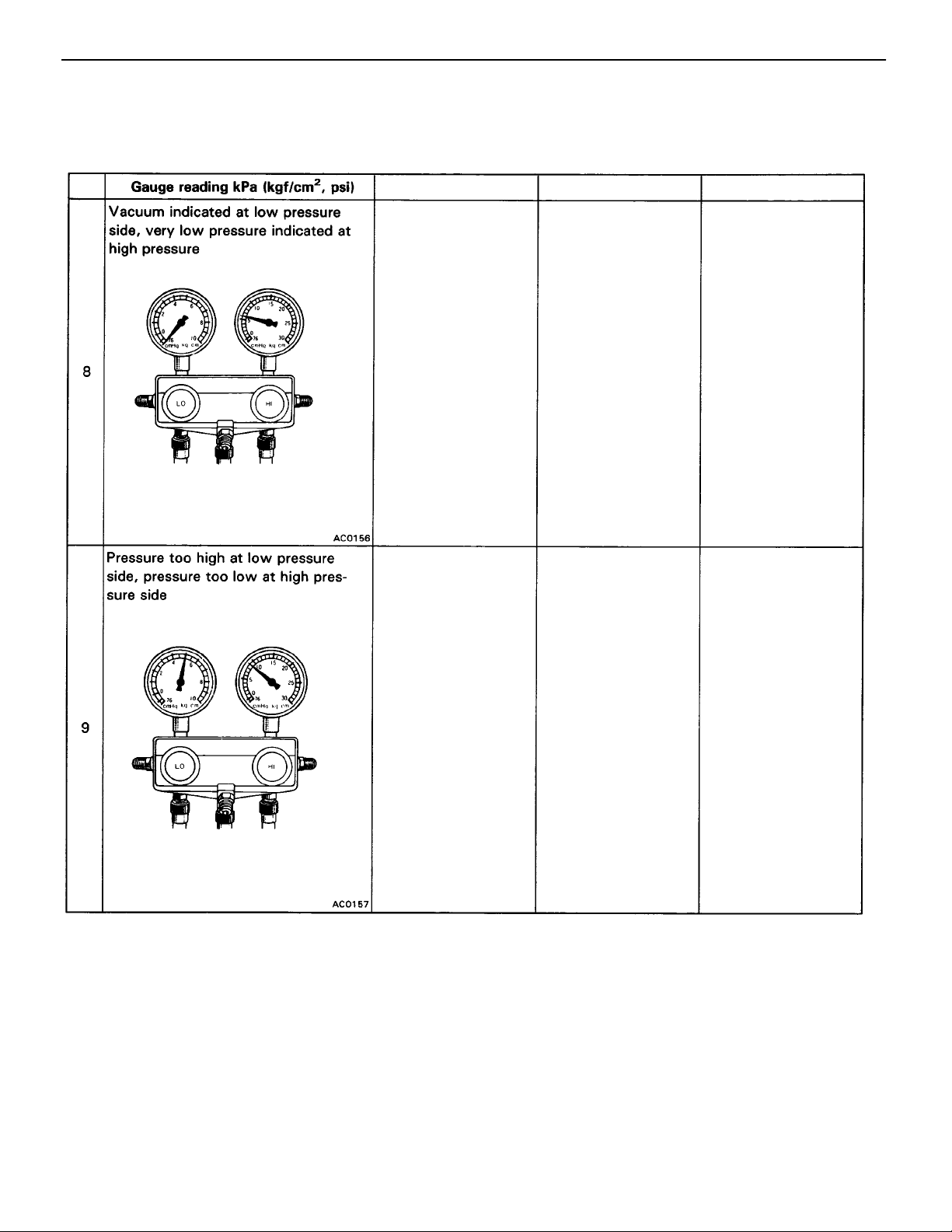
AC–14
–AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM Troubleshooting
NOTICE:
• Always recover refrigerant before removing the parts in the refrigerant line and evacuating air.
• Evacuate air and charge proper amount of purified refrigerant after installing the parts in the
refrigerant line.
No.
Condition
• Does not cool
(Cools from time to
time in some cases)
• Frost or dew seen
on piping before
and after receiver or
expansion valve
Probable cause
Refrigerant does not
circulate
Remedy
(1) Check heat sens–
ing tube for gas
leakage and re–
place expansion
valve if defective
If
(1) is normal
(2) Clean out dirt in
expansion valve
by blowing with
air
If not able to re–
move dirt, replace
expansion valve
(3) Replace receiver
Does not cool
Insufficient compres–
sion
Repair or replace com–
pressor
 Loading...
Loading...