Page 1

DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTION MANUAL
FOR
MODEL SSA-340A
SERVICE TEST SYSTEM
(ZD730=136E*C)
No. 2D730-I 36E*C
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
@ TOSHIBA CORPORATION 1995
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
Page 2
REVISION RECORD
No. 2D730-136E*C
REV. DATE
(hlAliYY)
INI. 02/'95
*A
111'95 121'95 upgrade is supported.
REASON
Mr. Nakajima
Mr. Yamazaki
"B lo/'96 121'96 upgrade is supported.
"C 071'98 101'98 upgrade is supported.
PAGE
/AUTHOR CHANGED No.
-_-----
P. 4-113 to
115
Mr. Okumoto
Mr. Okumoto
SER.
DOC.
PRODUCT.
TM-WW
R-l
*
Page 3

CONTENTS
No. 2D730-136E
Page
INTRODUCTION
1.
OUTLINE OF THE TEST SYST~_~~~_____~~~~~__~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~2~1
2.
____________________-------
2.1 Configuration of the Test System
____________________~~~~~~~~
____________________~~~~~~~~~~
2.2 Diagnostic Items and Nature of Tests in the Test System-------2-l
2.3 Test Modes (ALL, SUB)
TROUBLESHOOTING _______~____~~~~___~~~~~_~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~____~3~1
3.
--------------
3.1 Preparatory Work ---------------
____________________-------
____________________~~~~~~~~~~~
3.2 Operating Precautions for the Test Systems --------------------3-3
3.3 Operating Procedure ___~~~~__~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~_~~~3~4
3.3.1 Procedure until the menu message is displayed ----------3-4
3.3.2 Flowchart of the ALL mode ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~__~~3~6
3.3.3 Flowchart of the SUB mode ~~~~_~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~___~3~6
3.3.4 Command ___________________________--____----___~~~~____3_S
l-l
2-l
2-12
3-3
3.3.5 Changing the frequency of test execution---------------3-10
3.4 Error Code Table ______~~~~_~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~3~13
FLOWCHARTS FOR IDENTIFYING MALFUNCTIONS
4.
4.1 Identifying Faults in the CPU Unit
4.1.1 Preparatory work________~_____~~~~~_~~~~~~_______~_____4~~
____________________~~~~~~~~
_______________--___~~~~~~~~
4.1.2 Flowchart for identifying malfunctions -----------------4-l
4.1.3 Decision criteria____~~~~_-__~~~~~~~~~~~~~_~_~~~~~_~~~~4~3
4.1.4 Supplement----------- ____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 4-13
4.2 Identifying Faults in the PANEL Unit
____________________------
4.2.1 Preparatory work_~_______~___~_~--~~---------------~~~-4-13
4.2.2 Flowchart for identifying faults -----------------------4-13
4.2.3 Criteria ____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 4-14
4.2.4 Sunnlement ____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 4-16
4-l
4-l
4-13
-a-
Page 4

CONTENTS - continued
No. 2D730-136E
Page
4.3 Identifying Faults in RPG ____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
4.3.1 Preparatory work ____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
4.3.2 Troubleshooting flowchart ____________________~~~~~~~~~~
4-18
4-18
4-18
4.3.3 Decision tree ______-__-__________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 4-20
4.3.4 Supplement _________-__________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 4-21
4.4 Identifying Faults in the DSC Unit
____________________~~~~~~~~
4-23
4.4.1 Preparations _______-____________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 4-23
4.4.2 Troubleshooting flowchart------------------------------4-23
4.4.3 Criteria ____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
4-25
4.5 Identifying Faults in the T/R Unit----------------------------4-56
4.5.1 Preparations
_______-____________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
4.5.2 Fault diagnosis flow chart ____________________~~~~~~~~~
4.5.3 Criteria ____________________~-~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
____4_56
4-56
4-59
4.5.4 Supplement ____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 4-71
4.6 Identifying Faults in the FFT Unit----------------------------4-76
4.6.1 Preparatory work
____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
--m-4-76
4.6.2 Flowchart for identifying faults -----------------------4-76
4.6.3 Criteria ____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 4-79
4.6.4 Supplement ~~~~~~~~~~___~__~~~~~~~~~~~__~~~~~~~~~_~~~~~~4~~~
4.7 Identifying Faults in the CFM Unit ----------------------------4-87
4.7.1 Preparatory work_~_~________~~~~~_~~~______~~~_____~~~~4~87
4.7.2 Flowchart for identifying faults -----------------------4-87
4.7.3
4.7.4 Results of the diagnostic tests ------------------------4-105
4.7.5 Supplement
4.8 Maintenance
____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
----4-111
4-113
-b-
Page 5

CONTENTS - continued
No. 2D730-136E
Page
5. APPENDIX ____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~-~~~~~~~
5.1 Error Codes for Self-diagnosis ___-________________~~~~~~~~~~~~
5.2 Patch Menu Operation ____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
<.
5.2.1 Applicable equipment ____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
5.2.2 Starting ____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
5.2.3 Memory R/W & dump ____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
5.2.4 Coordinate check (X,Y) ____________________~~~~~~~~~~~~~
5.2.5 Image cant external value set
5.2.6 Address & data value save
____________________------
______________________________5_g
5-1
5-1
5-5
5-5
5-5
5-6
5-7
5-7
- c -
Page 6

INTRODUCTION
1.
No. 2D730-136E
Test systems are service
test units for the ultrasonic diagnostic
equipment model SSA-340A.
This manual explains the diagnostic procedures.
Furthermore,
operates normally,
since certain PWBs can be checked only if the system
it is necessary to perform testing in the following
order.
(1) CPU unit
(2) RPG
(3) DSC unit
(4) T/R unit
(5) FFT unit
(6) CFM unit
(7) PANEL unit
l-1
Page 7

OUTLINE OF THE TEST SYSTEM
;2-----_
2.
No. 2D730-136E
If a malfunction occurs,
with respect to PWBs and PWB blocks,
responsible for the malfunction by displaying error codes.
the test system will indicate the test results
identifying those which are
Alternately,
the test system will indicate a pattern which permits assessment of the
quality of each block.
Tests principally involve the CPU unit, PANEL unit, RPG, DSC unit, T/R
unit, FFT unit, and CFM unit.
Although not all units are included, it is
possible to test the basic units required for generating an image.
Therefore,
troubleshooting is expedited if the test system succeeds in
helping identify faulty units.
Furthermore,
at the time of maintenance and checking it is possible to
assess changes in ultrasonic wave transmission which-are difficult to
observe during- the normal service period; degradation of system
performance;
and memory errors of any addresses caused by faulty
reception.
In addition,
there are guidelines for test performance frequency.
is useful for checking faults that occur infrequently, caused by RS-232C
communication errors.
2.1 Configuration of the Test System
This
This test system is incorporated in the main unit of the diagnostic
ultrasound system.
This manual describes the operating procedures for the test system.
2.2 Diagnostic Items and-Nature of Tests in the Test System
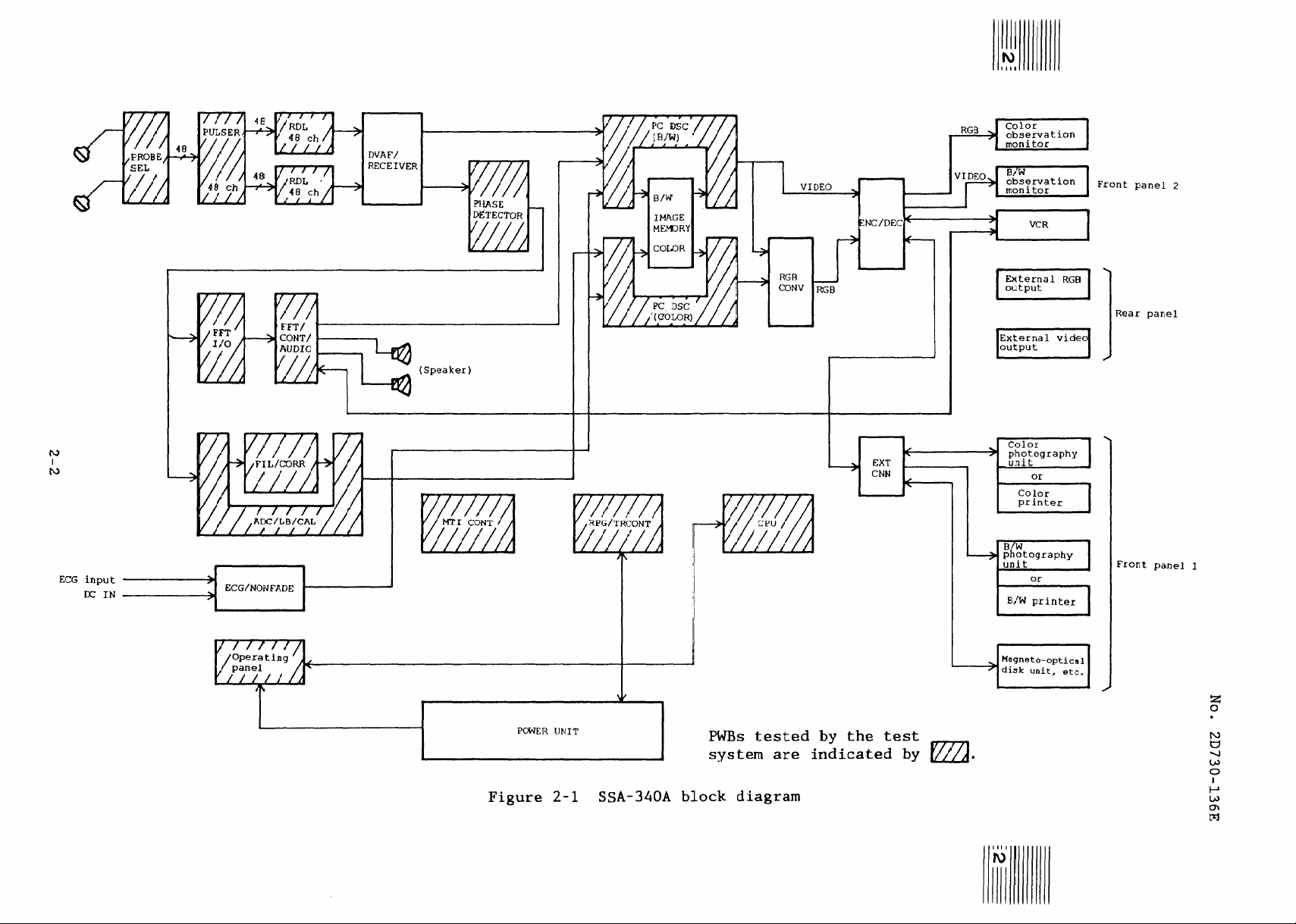
PWBs which are tested by the test system are shown in figure 2-1 to
figure 2-3.
Details concerning each test item are given in tables 2-1
and 2-2.
2-l
Page 8
No. 2D730-136E
Page 9
No. 2D730-136E
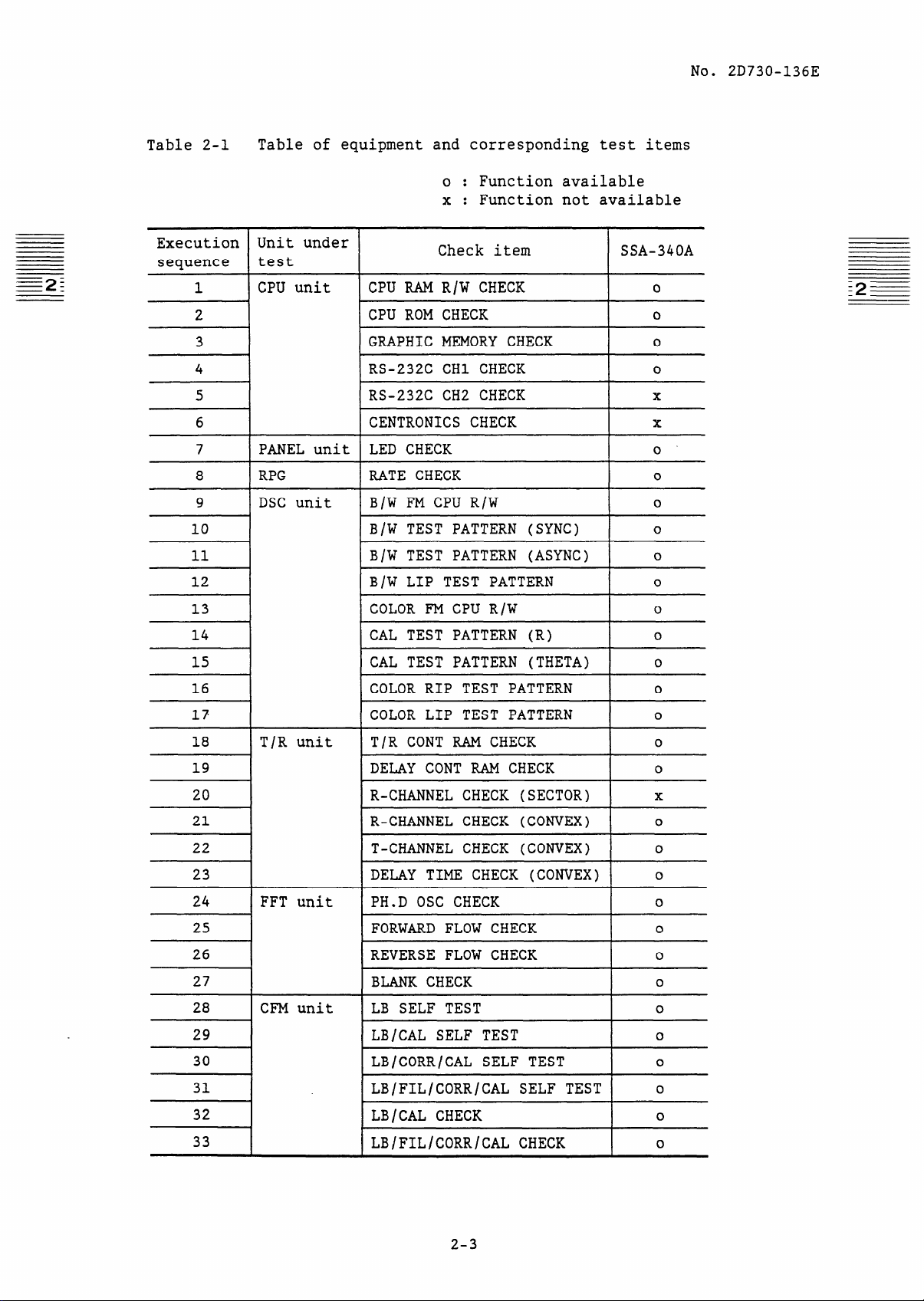
Table 2-1
Execution Unit under
seauence
3 GRAPHIC MEMORY CHECK 0
4 RS-232C CHl CHECK 0
5
6 CENTRONICS CHECK X
7 PANEL unit LED CHECK 0
8
-4 DSC unit
Table of equipment and corresponding test items
test
RS-232C CH2 CHECK X
RPG
I ~
RATE CHECK
T
1 B/W FM CPU R/W
B/W TEST PATTERN (SYNC)
r- ~~
1 B/W TEST PATTERN (ASYNC) 1 o
B/W LIP TEST PATTERN
I
COLOR FM CPU R/W
I
CAL TEST PATTERN (R)
I
1 CAL TEST PATTERN (THETA) ) o
0 : Function available
x: Function not available
Check item SSA-340A
0
I
0
I
0
I_
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
COLOR RIP TEST PATTERN
I
COLOR LIP TEST PATTERN
I
T/R unit 1 T/R CONT RAM CHECK
DELAY CONT RAM CHECK 0
R-CHANNEL CHECK (SECTOR) X
1 R-CHANNEL CHECK (CONVEX) 1 o
1 T-CHANNEL CHECK (CONVEX) 1 o
1 DELAY TIME CHECK (CONVEX) 1 o
FFT unit
CFM unit
PH.D OSC CHECK
I
FORWARD FLOW CHECK
I
REVERSE FLOW CHECK
I
I
I
I
1 LB/FIL/CORR/CAL SELF TEST 1 o
LB/CAL CHECK
LB/FIL/CORR/CAL CHECK
I
I
I
I
I
I
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2-3
Page 10
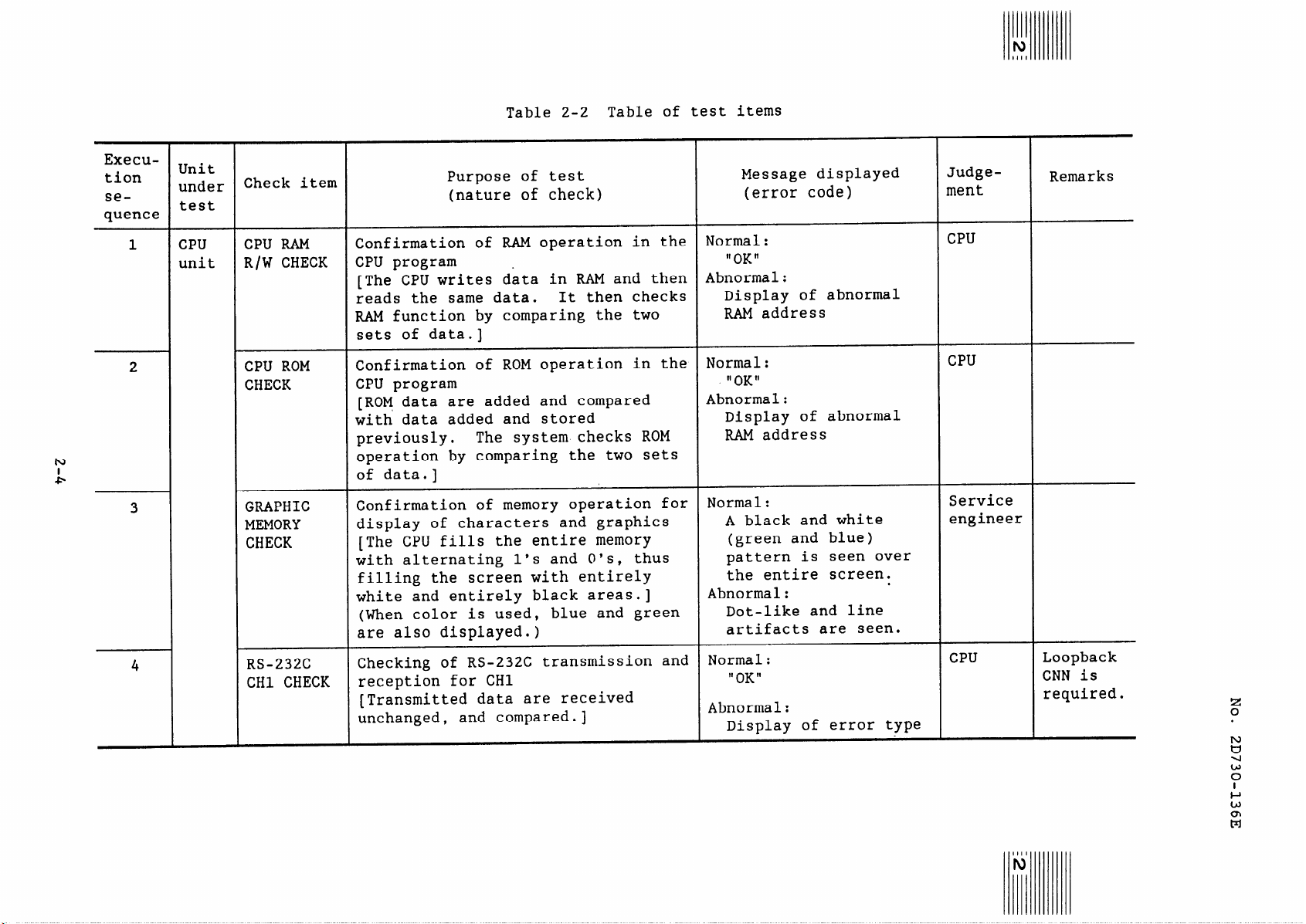
Table 2-2 Table of test items
Execution
se-
quence
1
2
3
4
Unit
under
test
CPU
unit
Check item
CPU RAM
R/W CHECK
CPU ROM
CHECK
GRAPHIC
MEMORY
CHECK
RS-232C
CHl CHECK
Purpose of test
(nature of check)
Confirmation of RAM operation in the
CPU program
[The CPU writes data in RAM and then
reads the same data.
It then checks
RAM function by comparing the two
sets of data.]
Confirmation of ROM operation in the
CPU program
[ROM data are added and compared
with data added and stored
previously.
The system checks ROM
operation by comparing the two sets
of data.]
Confirmation of memory operation for
display of characters and graphics
[The CPU fills the entire memory
with alternating l's and O's, thus
filling the screen with entirely
white and entirely black areas.]
(When color is used, blue and green
are also displayed.)
Checking of RS-232C transmission and
reception for CHl
[Transmitted data are received
unchanged,
and compared.]
Message displayed
(error code)
Normal:
'OK"
Abnormal:
Display of abnormal
RAM address
Normal:
11 OK II
Abnormal:
Display of abnormal
RAM address
Normal:
A black and white
(green and blue)
pattern is seen over
the entire screen.
Abnormal:
Dot-like and line
artifacts are seen.
Normal:
” OK "
Abnormal:
Display of error type
Judge-
Remarks
ment
CPU
CPU
Service
engineer
.
CPU
Loopback
CNN is
required.
Page 11
Execution
sequence
Unit
under
test
Check item
Purpose of test
(nature of check)
Message displayed
(error code)
Judgement
Remarks
5
CPU
unit
RS-232C
CH2 CHECK
6 CENTRONICS
CHECK
7 RPG
8
DSC
unit
9
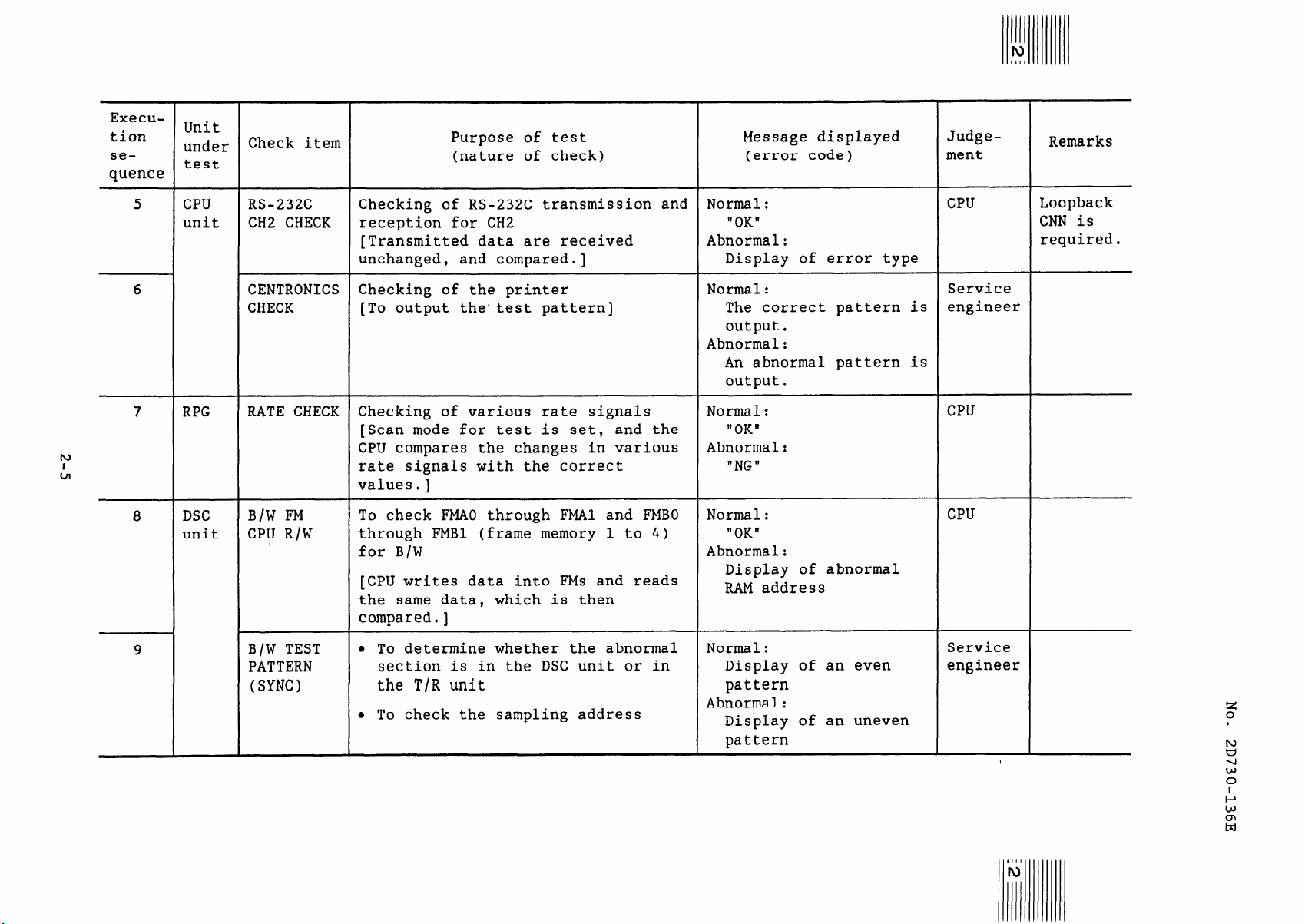
RATE CHECK Checking of various rate signals
B/W FM
CPU R/W
B/W TEST
PATTERN
(SYNC)
Checking of RS-232C transmission and
reception for CH2
[Transmitted data are received
unchanged, and compared.]
Checking of the printer
[To output the’ test pattern]
[Scan mode for test is set, and the
CPU compares the changes in various
rate signals with the correct
values.]
To check FMAO through FMAl and FMBO
through FMBl (frame memory 1 to 4)
for B/W
[CPU writes data into FMs and reads
the same data, which is then
compared.]
l To determine whether the abnormal
section is in the DSC unit or in
the T/R unit
l To check the sampling address
Normal:
"OK"
Abnormal:
Display of error type
Normal:
The correct pattern is
output.
Abnormal:
An abnormal pattern is
output.
Normal:
t1 OK II
Abnormal:
"NG"
Normal:
"OK"
Abnormal:
Display of abnormal
RAM address
Normal:
Display of an even
pattern
Abnormal:
Display of an uneven
pattern
CPU
Service
engineer
CPU
CPU
Service
engineer
Loopback
CNN is
required.
Page 12

Execution
se-
quence
Unit
under
test
Check item
Purpose of test
(nature of check)
Message displayed
(error code)
Judge-
ment
Remarks
tu
b
10
11
12
13
DSC
unit
B/W TEST
PATTERN
(ASYNC)
B/W LIP
TEST
PATTERN
COLOR FM
CPU R/W
CAL TEST
PATTERN
(R)
l To determine whether the abnormal
section is in the DSC unit or in
the T/R unit
l To check the multistage
transmission
To determine whether the abnormality
is before the output section or
after in the DSC unit
[The test pattern is input in the
linear interpolation circuit.]
To check FMAO through FM2 and FMBO
through FM82 (frame memory 1 to 6)
for COLOR
[CPU writes data into FMs and reads
the same data, which is then
compared.]
l To check the interpolation
function (RIP) in the DSC unit
l To determine whether the
abnormality is in the MT1 unit or
in the DSC unit
[Interpolation check in the DSC
r-direction and threshold check in
the e-direction]
Normal:
Display of an even
pattern
Abnormal:
Display of an uneven
pattern
Normal:
Display of a pattern
of the interpolated
vertical lines
Abnormal:
Display of an
abnormally
interpolated pattern.
Normal:
” OK ”
Abnormal:
Display of abnormal
RAM address
Normal:
Display of an even
pattern interpolated
in the r-direction
Abnormal:
Display of an
abnormally
interpolated pattern
Service
engineer
Service
engineer
CPU
Service
engineer
(RIP: Radius direction
interpolation)
Page 13
Execution
se-
quence
Unit
under
test
Check item
Purpose of test
(nature of check)
Message displayed
(error code)
Judge-
ment
Remarks
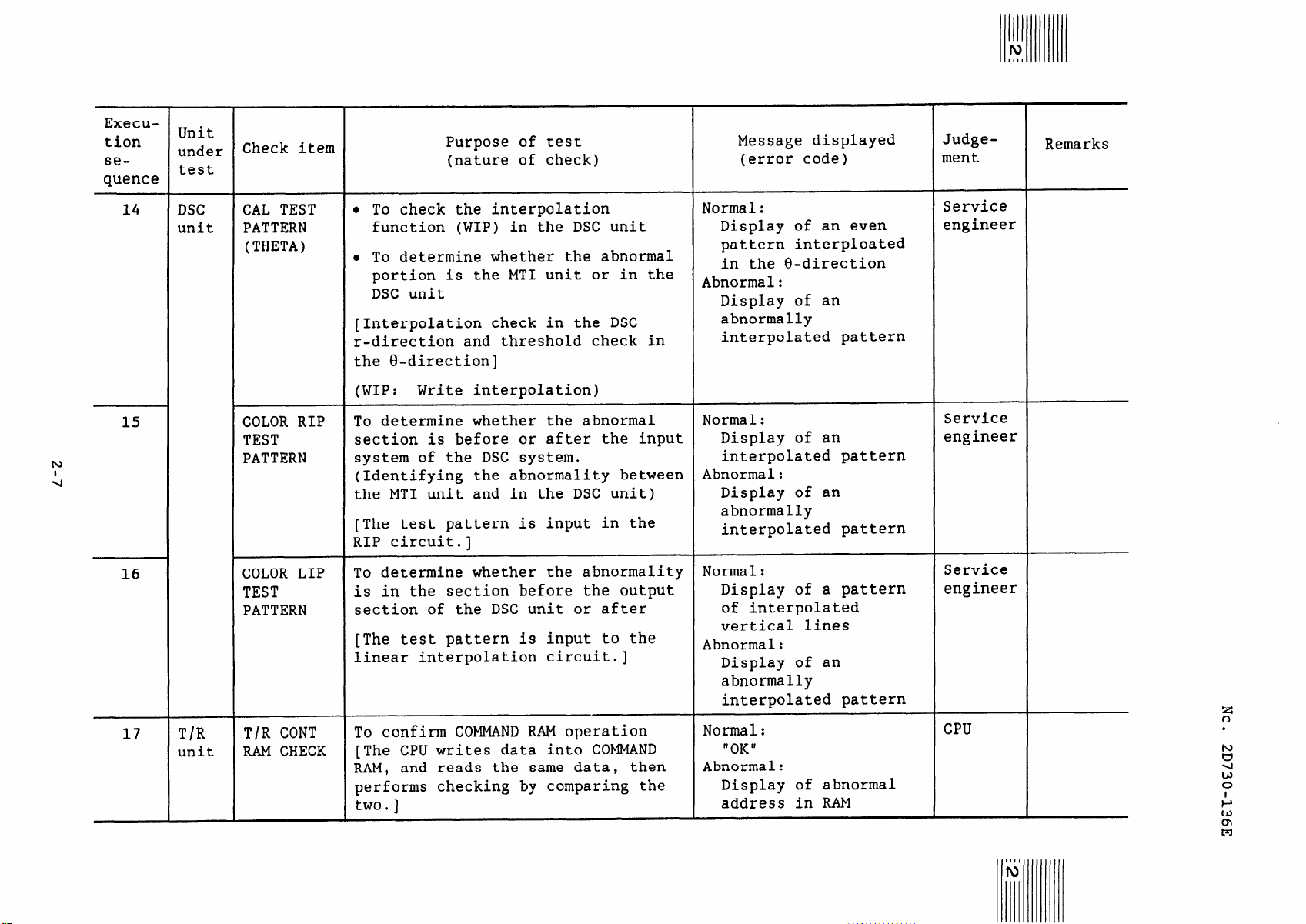
14
15
16
DSC
unit
CAL TEST
PATTERN
(THETA)
COLOR RIP
TEST
PATTERN
COLOR LIP
TEST
PATTERN
l To check the interpolation
function (WIP) in the DSC unit
l To determine whether the abnormal
portion is the MT1 unit or in the
DSC unit
[Interpolation check in the DSC
r-direction and threshold check in
the 8-direction]
(WIP:
Write interpolation)
To determine whether the abnormal
section is before or after the input
system of the DSC system.
(Identifying the abnormality between
the MT1 unit and in the DSC unit)
[The test pattern is input in the
RIP circuit.]
To determine whether the abnormality
is in the section before the output
section of the DSC unit or after
[The test pattern is input to the
linear interpolation circuit.]
Normal:
Display of an even
pattern interploated
in the U-direction
Abnormal:
Display of an
abnormally
interpolated pattern
Normal:
Display of an
interpolated pattern
Abnormal:
Display of an
abnormally
interpolated pattern
Normal:
Display of a pattern
of interpolated
vertical lines
Abnormal:
Display of an
abnormally
interpolated pattern
Service
engineer
Service
engineer
Service
engineer
17
T/R
unit
T/R CONT
RAM CHECK
To confirm COMMAND RAM operation
[The CPU writes data into COMMAND
RAM, and reads the same data, then
performs checking by comparing the
two.]
Normal:
"OK"
Abnormal:
Display of abnormal
address in RAM
CPU
Page 14
Execution
sequence
Unit
under
test
Check item
Purpose of test
(nature of check)
Message displayed
(error code)
Judgement
Remarks
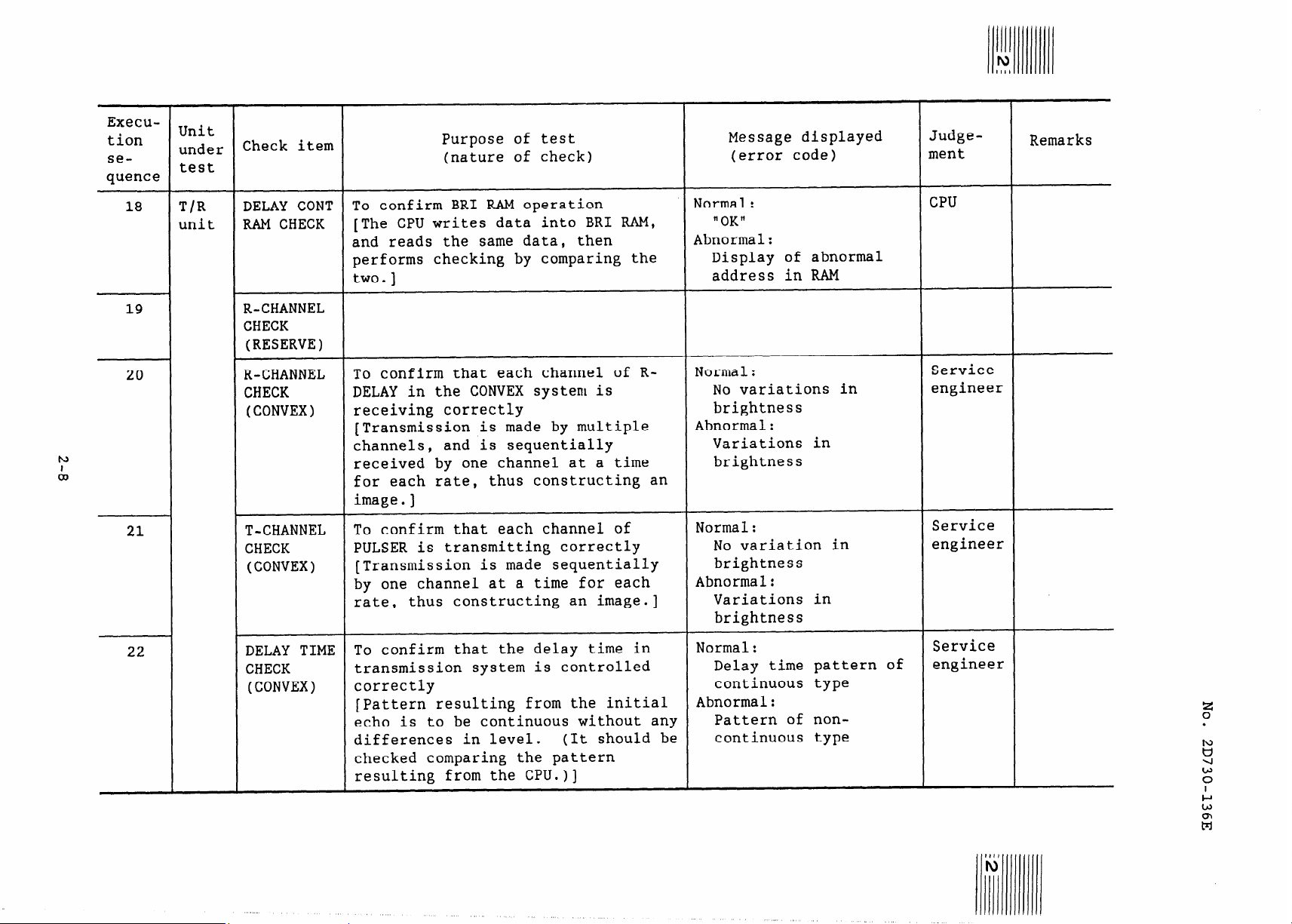
18
19
20
21
T/R
unit
DELAY CONT
RAM CHECK
R-CHANNEL
CHECK
(RESERVE)
R-CHANNEL
CHECK
(CONVEX)
T-CHANNEL
CHECK
(CONVEX)
To confirm BRI RAM operation
[The CPU writes data into BRI RAM,
and reads the same data, then
performs checking by comparing the
two.]
To confirm that each channel of RDELAY in the CONVEX system is
receiving correctly
[Transmission is made by multiple
channels, and is sequentially
received by one channel at a time
for each rate, thus constructing an
image.]
To confirm that each channel of
PULSER is transmitting correctly
(Transmission is made sequentially
by one channel at a time for each
rate,
thus constructing an image.]
Normal:
"OK"
Abnormal:
Display of abnormal
address in RAM
Normal:
No variations in
brightness
Abnormal:
Variations in
brightness
Normal:
No variation in
brightness
Abnormal:
Variations in
brightness
CPU
Service
engineer
Service
engineer
22
DELAY TIME
CHECK
(CONVEX)
To confirm that the delay time in
transmission system is controlled
correctly
[Pattern resulting from the initial
echo is to be continuous without any
differences in level.
checked comparing the pattern
resulting from the CPU.)]
(It should be
Normal:
Delay time pattern of
continuous type
Abnormal:
Pattern of noncontinuous type
Service
engineer
Page 15
Execution
se-
quence
Unit
under
test
Check item
Purpose of test
(nature of check)
Message displayed
(error code)
Judge-
ment
Remarks
N
\o
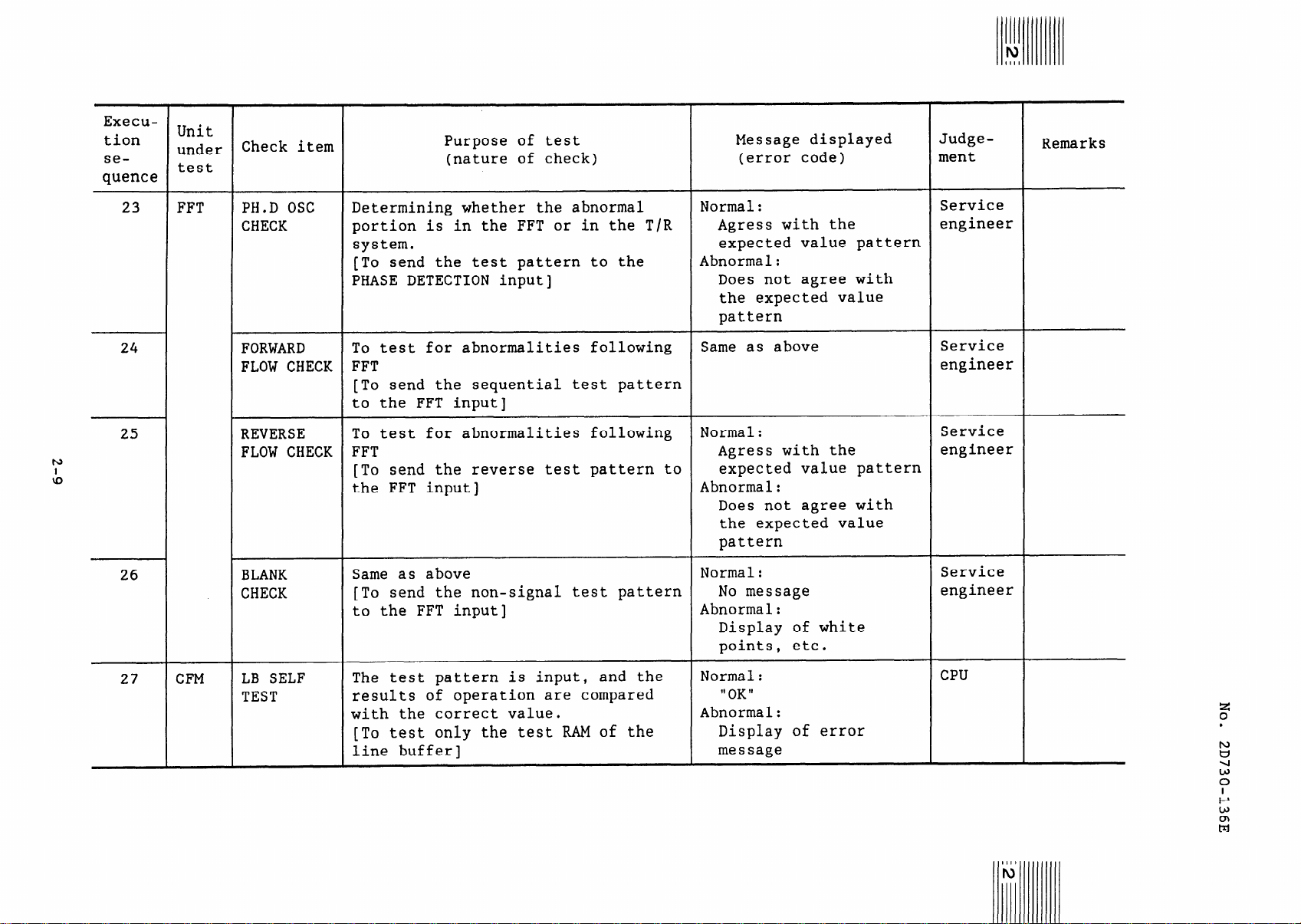
23
24
25
26
FFT
PH.D OSC
CHECK
FORWARD
FLOW CHECK
REVERSE
FLOW CHECK
BLANK
CHECK
Determining whether the abnormal
portion is in the FFT or in the T/R
system.
[To send the test pattern to the
PHASE DETECTION input]
To test for abnormalities following
FFT
[To send the sequential test pattern
to the FFT input]
To test for abnormalities following
FFT
[To send the reverse test pattern to
the FFT input]
Same as above
[To send the non-signal test pattern
to the FFT input]
Normal:
Agress with the
expected value pattern
Abnormal:
Does not agree with
the expected value
pattern
Same as above
Normal:
Agress with the
expected value pattern
Abnormal:
Does not agree with
the expected value
pattern
Normal:
No message
Abnormal:
Display of white
points, etc.
Service
engineer
Service
engineer
Service
engineer
Service
engineer
27
CFM
LB SELF
TEST
The test pattern is input, and the
results of operation are compared
with the correct value.
[To test only the test RAM of the
line buffer]
Normal:
II OK II
Abnormal:
Display of error
message
CPU
Page 16
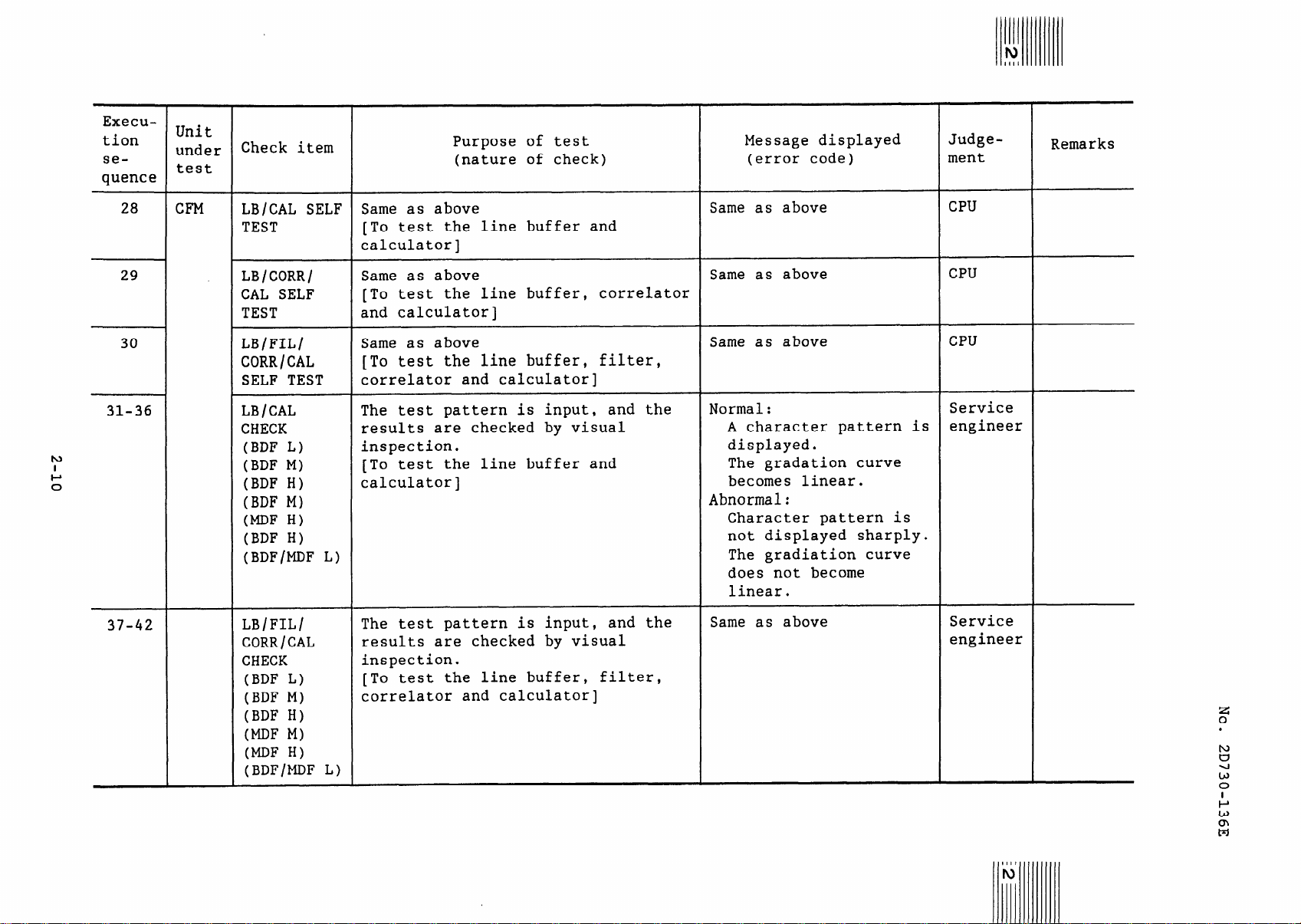
Execution
sequence
Unit
under
test
Check item
Purpose of test
(nature of check)
Message displayed
(error code)
Judge-
ment
Remarks
28
29
30
31-36
37-42
CFM
LB/CAL SELF
TEST
LB/CORR/
CAL SELF
TEST
LB/FIL/
CORR/CAL
SELF TEST
LB/CAL
CHECK
(BDF L)
(BDF M)
(BDF H)
(BDF M)
WDFH)
(BDF H)
(BDF/MDF L
LB/FIL/
CORR/CAL
CHECK
(BDF L)
(BDF M)
(BDF H)
WDFM)
WFH)
(BDF/MDF L)
Same as above
[To test the line buffer and
calculator]
Same as above
[To test the line buffer, correlator
and calculator]
Same as above
[To test the line buffer, filter,
correlator and calculator]
The test pattern is input, and the
results are checked by visual
inspection.
[To test the line buffer and
calculator]
The test pattern is input, and the
results are checked by visual
inspection.
[To test the line buffer, filter,
correlator and calculator]
Same as above
Same as above
Same as above
Normal:
A character pattern is
displayed.
The gradation curve
becomes linear.
Abnormal:
Character pattern is
not displayed sharply.
The gradiation curve
does not become
linear.
Same as above
CPU
CPU
CPU
Service
engineer
Service
engineer
Page 17
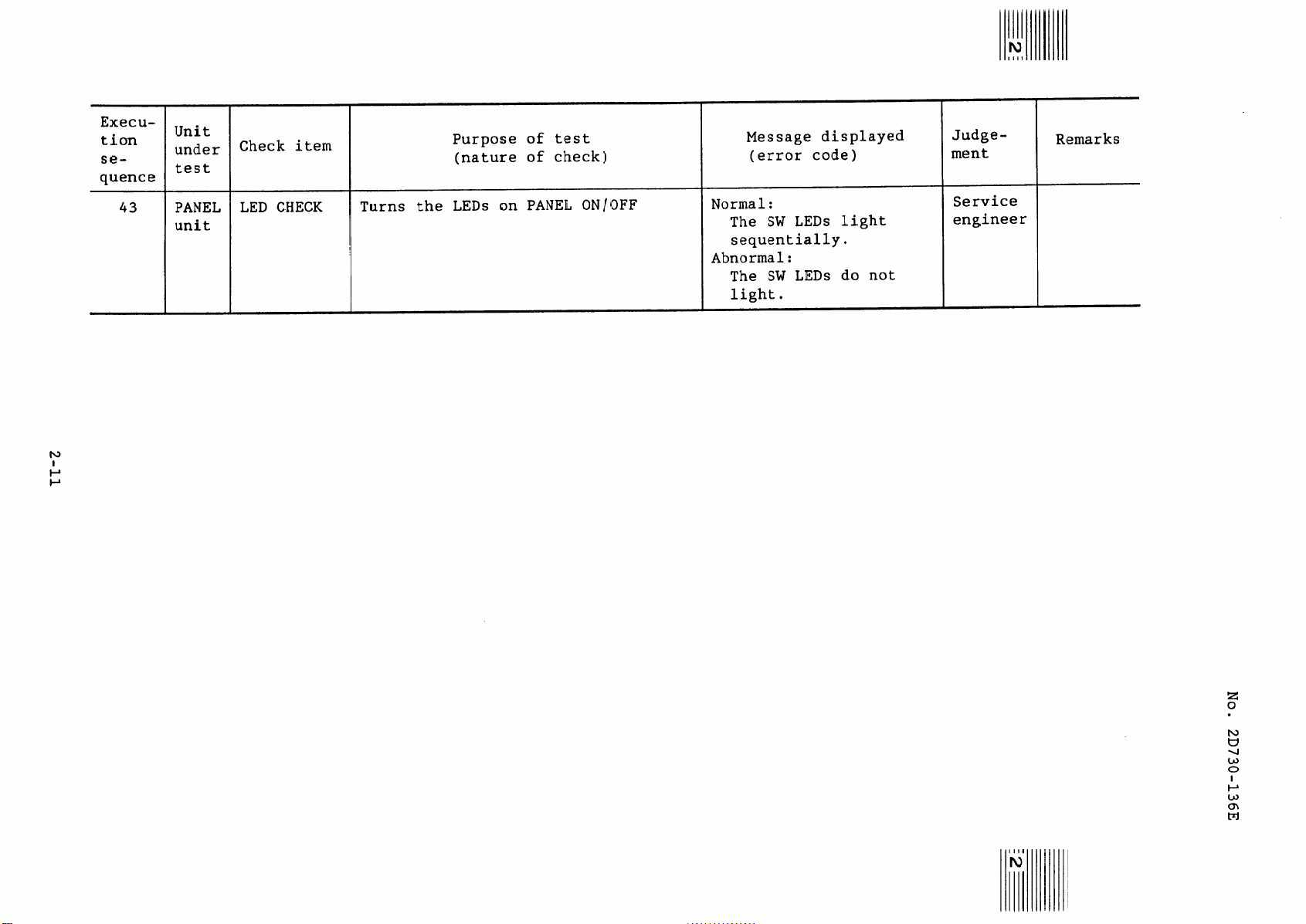
2-11
No. 2D730-136E
Page 18

2.3 Test Modes (ALL, SUB)
(1) ALL mode (general-purpose test mode for beginners)
No. 2D730-136E
All tests are conducted using this test mode.
faulty units are not identified.
This, however,
the serviceman to get the final diagnostic results.
(2) SUB mode (test mode for experts)
Use this test mode to conduct a specific test if the faulty sections
can be guessed from the symptoms.
takes a long time and requires several operations by
Use this mode if the
;2E
2-12
Page 19

TROUBLESHOOTING
3.
Carry out tests to identify malfunctions according to the following
procedure:
(1) Preliminary survey
(2) Preparatory work (with the power off)
(3) Setting of the service mode
(4) Setting of the test mode (ALL, SUB mode)_
(5) Test
*(6) Identification of malfunction based on the error code table
Figure 3-l shows the flowchart for the above procedure.
Preliminary survey
No. 2D730-136E
Survey the stated problems not just by relying on information from the
customer,
function.
but also by checking carefully the status of each mode and
Problems that occur only occasionally cannot be identified by
the test system when it is not actually occurring.
(For tests which are controlled by the CPU, such as the check of the RS232C or the R/W of MM, the test system can provide a means of
reproducing the phenomenon by repeating the test sequence an unlimited
number of times.)
3-1
Page 20
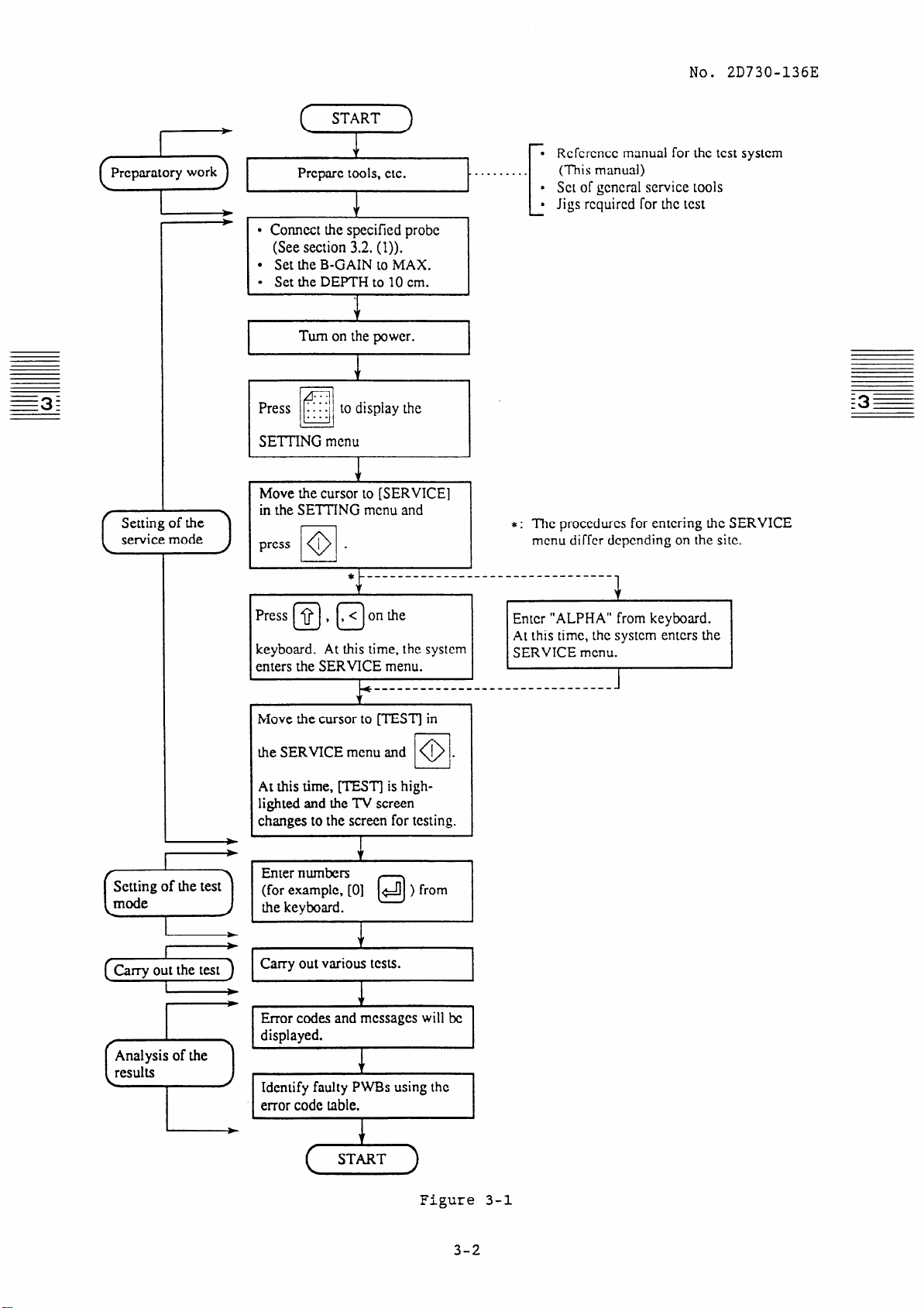
No. 2D730-136E
Preparatory work
(5
,
I
Prcparc tools, etc.
J.
1
. Connect the specified probe
(See section 3.2. (I)).
l Set the B-GAIN to MAX.
l Set the DEPTH to 10 cm.
3
Turn on the power.
to display the
SETTING menu
Move the cursor to [SERVICE]
in the SETTING menu and
I
press I .
I 0
0
_____-__---____
*
i
4
. ..* . . . . .
t
I
___
. Rcfcrcncc manual for the test system
(This manual)
. Set of gcncral service tools
l Jigs rcquircd Tar the test
* : The proccdurcs for entering the SERVICE
menu differ dcpcnding on the site.
__________----
1
I
(Carry)
Press @ , @ on the
keyboard. At this time, the system
enters the SERVICE menu.
Move the cursor to [TEST] in
the SERVICEmcnu and 1
At this time, WSTj is highlighted and the TV screen
changes to the screen for testing.
t
Enter numbers
(for example, [0]
the keyboard.
Carry out various tests.
I
Error codes and messages will bc
displayed.
I
+
@ ) from
/o/
-
At thus tlmc, the system enters the
_________----- 1
__-
.
I
I
Identify faulty PWBs using the
error code table.
I
I
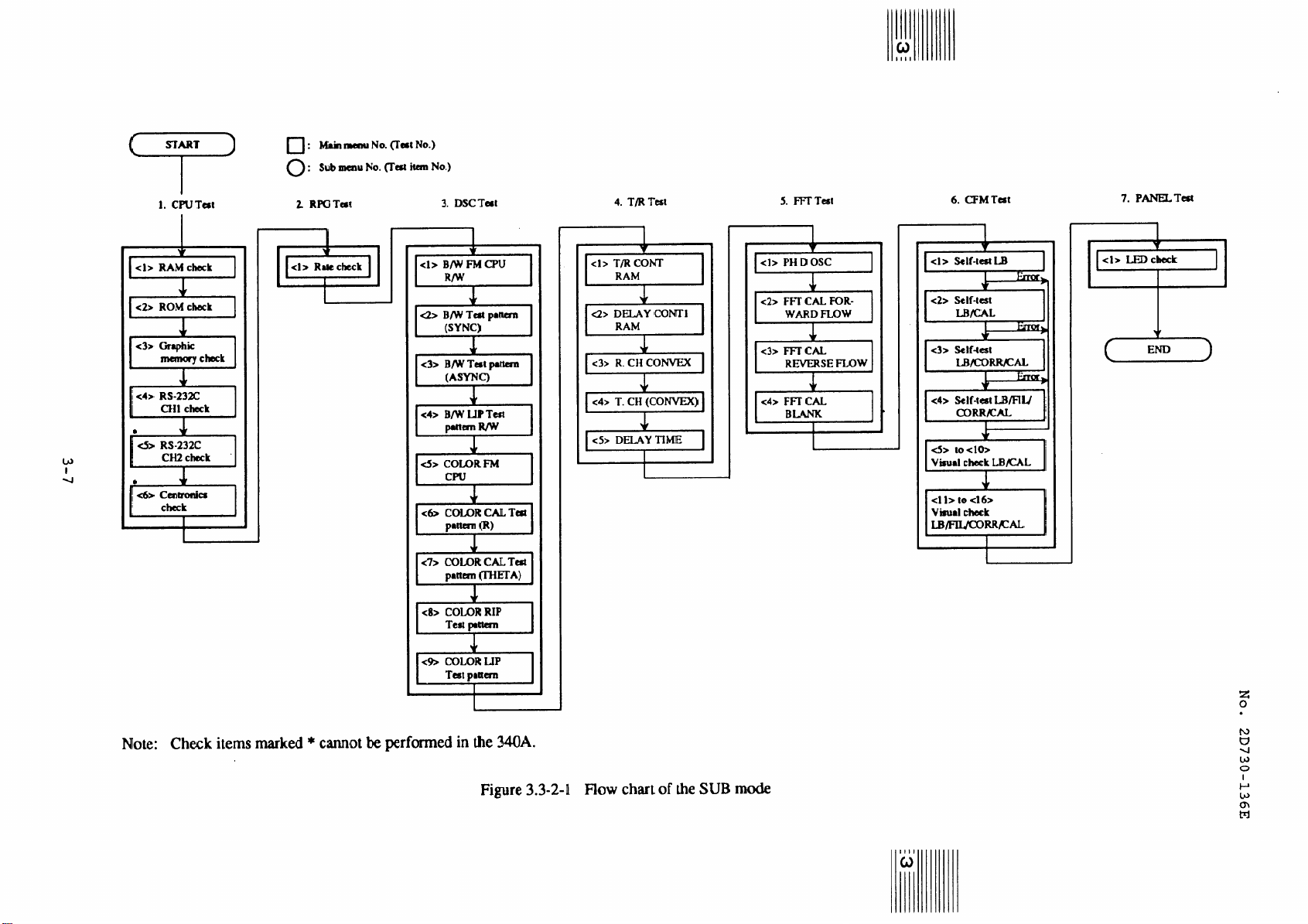
Figure 3-1
3-2
Page 21

3.1 Preparatory Work
Prepare the required tools/devices (such as a return connector) in
accordance with the "Preparatory work" in section 4.
(ex. LOOP BACK CNN)
3.2 Operating Precautions for the Test Systems
No. 2D730-136E*C
(1) Before carrying out tests,
specified below.
unless so instructed,
Do not pull out or connect a probe during the test
otherwise a malfunction may occur.
1 TRANSDUCER C )
SSA-340A
No connection Linear or convex transducer,
the transducer shold be connected as
TRANSDUCER B
TRANSDUCER A
I
PVF-375MT
or no connection
(2) A transient phenomenon is displayed while the test is being carried
out; however,
(3) The time, heart rate, PWR value,
erased.
The ID indication is erased.
this is not abnormal.
ID area and hospital name are not
(4) Pressing (/LJI1 at the graphic check of the CPU may cause a blank area
on the upper right of the image; however, this is not abnormal
(Photo 3.2-l).
(5) Although most switches are disabled during the serviceman test, do
not press the following switches to avoid a malfunction:
l VCR SW (on the panel)
l Palm controller trackball
l Trackball (TRACK BALL FUNCTION)
(6) When the graphic check of the CPU is completed, either of the two
lines for time display may not be displayed; however, this is not
abnormal.
(7) Because peripheral devices may malfunction during testing,
disconnect the control cables of all peripheral devices during
testing. Alternatively,
turn OFF the power of all peripheral
devices.
(8) Be sure to execute New Patient after the test has been completed.
3-3
Page 22

No. 2D730-136E
Photo 3.2-l
3.3 Operating Procedure
3.3.1 Procedure until the menu message is displayed
First perform the
in figure 3-1.
The screen shown in figure 3.3-l-l first appears in the serviceman
test.
Then the caution screen shown in photo 3.3-l-Z appears, requesting
that the following be checked.
(1) The probes specified in section 3.2 (1) have been connected.
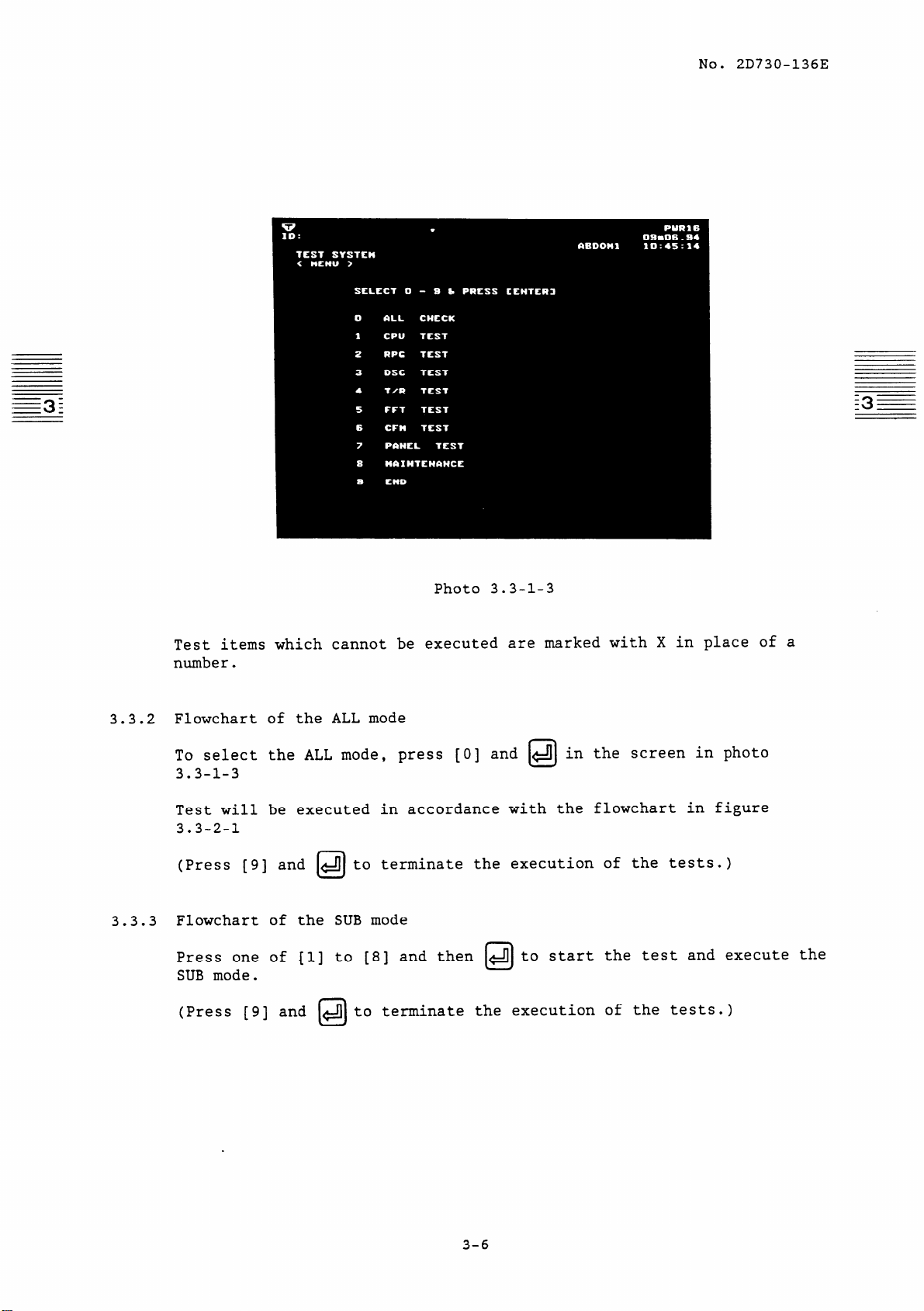
After confirming the above, press &J and the screen in photo 3.3-l-3
will appear.
"Setting of the service mode" of the flowchart shown
0
3-4
Page 23
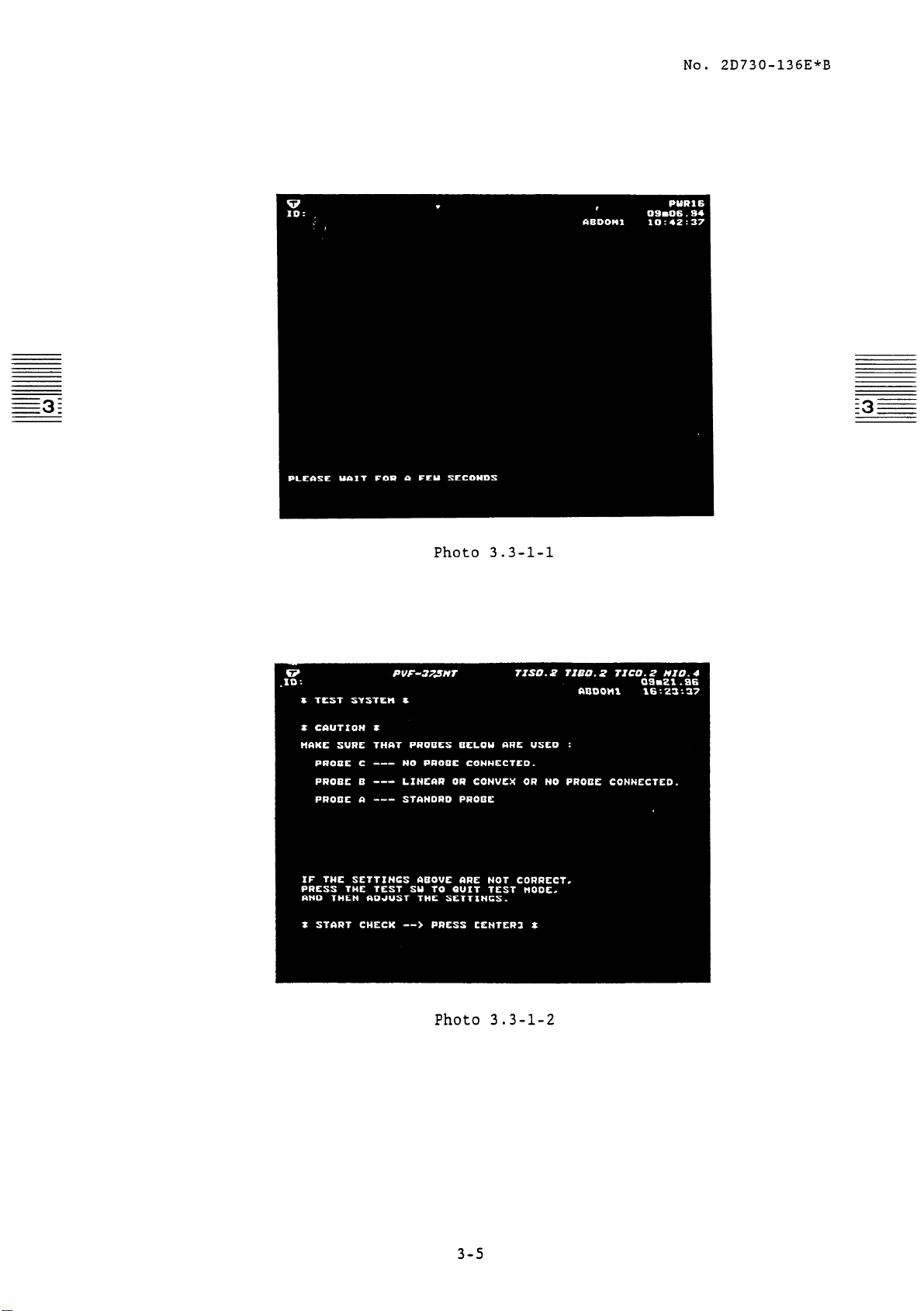
No. 2D730-136E*B
Photo 3.3-l-l
Photo 3.3-l-Z
3-5
Page 24
No. 2D730-136E
Test items which cannot be executed are marked with X in place of a
number.
3.3.2 Flowchart of the ALL mode
To select the ALL mode,
3.3-l-3
Test will be executed in accordance with the flowchart in figure
3.3-2-l
(Press [9] and mto terminate the execution of the tests.)
3.3.3 Flowchart of the SUB mode
Press one of Cl] to [8] and then 4 to start the test and execute the
SUB mode.
(Press [9] and
mto terminate the execution of the tests.)
press [0] and 4 in the screen in photo
Photo 3.3-l-3
0
U
3-6
Page 25
I
1
!!I
ii
0
A
1
_,I!
No. 2D730-136E
Page 26
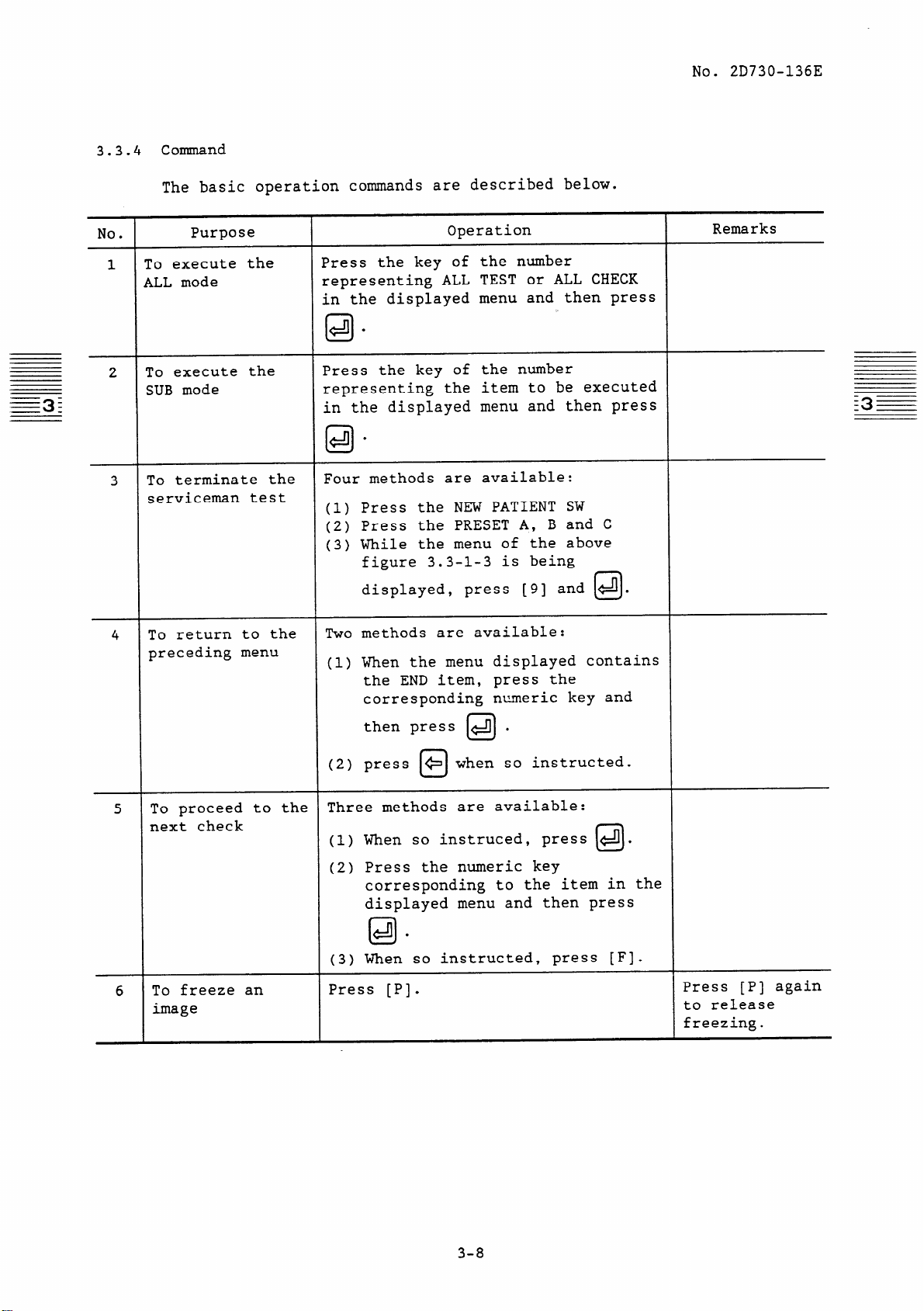
3.3.4 Cormnand
The basic operation commands are described below.
No. 2D730-136E
No.
1
2
3
Purpose
:o execute the
LLL mode
Co execute the
XJB mode
To terminate the
,
serviceman test
To return to the
4
preceding menu
Operation
Press the key of the number
representing ALL TEST or ALL CHECK
in the displayed menu and then press
.
4
IO
Press the key of the number
representing the item to be executed
in the displayed menu and then press
Four methods are available:
(1) Press the NEW PATIENT SW
(2) Press the PRESET A, B and C
(3) While the menu of the above
figure 3.3-l-3 is being
displayed, press [9] and 4.
Two methods are available:
(1) When the menu displayed contains
the END item, press the
corresponding numeric key and
0
Remarks
I
To proceed to the
5
next check
To freeze an
6
image
then press 141 .
(2) press + when so instructed.
Three methods are available:
When so instruced, press 4.
(1)
Press the numeric key
(2)
corresponding to the item in the
displayed menu and then press
@I
When so instructed, press [F].
(3)
Press [PI.
U
0
.
Press [P] again
to release
freezing.
3-8
Page 27

No. 2D730-136E
No.
7
Purpose
To change the
frequency of test
execution
To terminate the
8
test when the
test execution
frequency is
unlimited.
To correct a
9
value entered
incorrectly.
To stop the
10
display of an
error message at
the time of
memory check
Note:
Operation
Refer to section 3.3.5.
Press [DEL].
Press [DEL] and enter the correct
value.
Press [C] when so instructed.
For the RS-232C Centronix check,
immediately.
I
Remarks
This can be
performed even
when the test
frequency is
not unlimited.
I
the [DEL] key does not work
3-9
Page 28
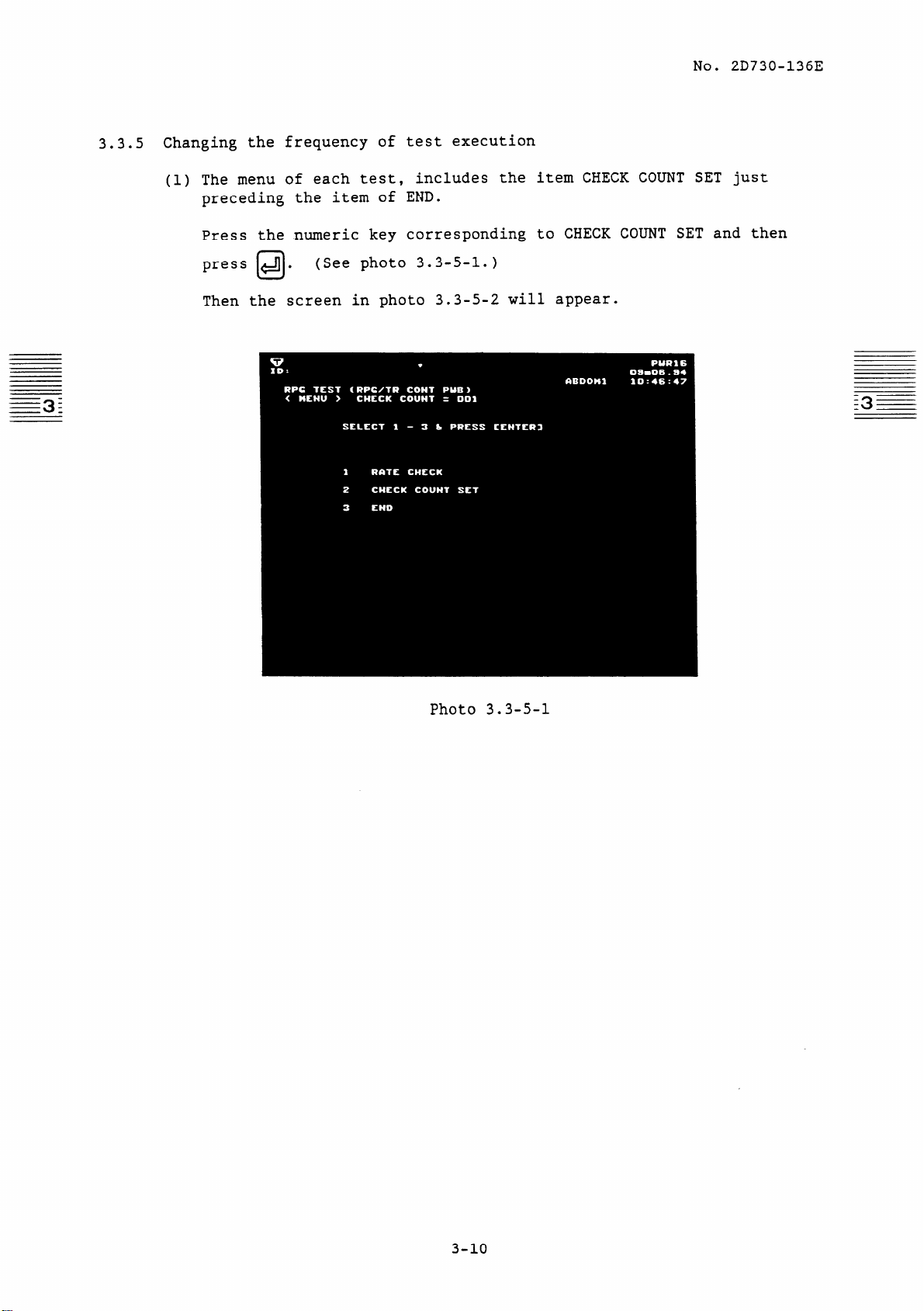
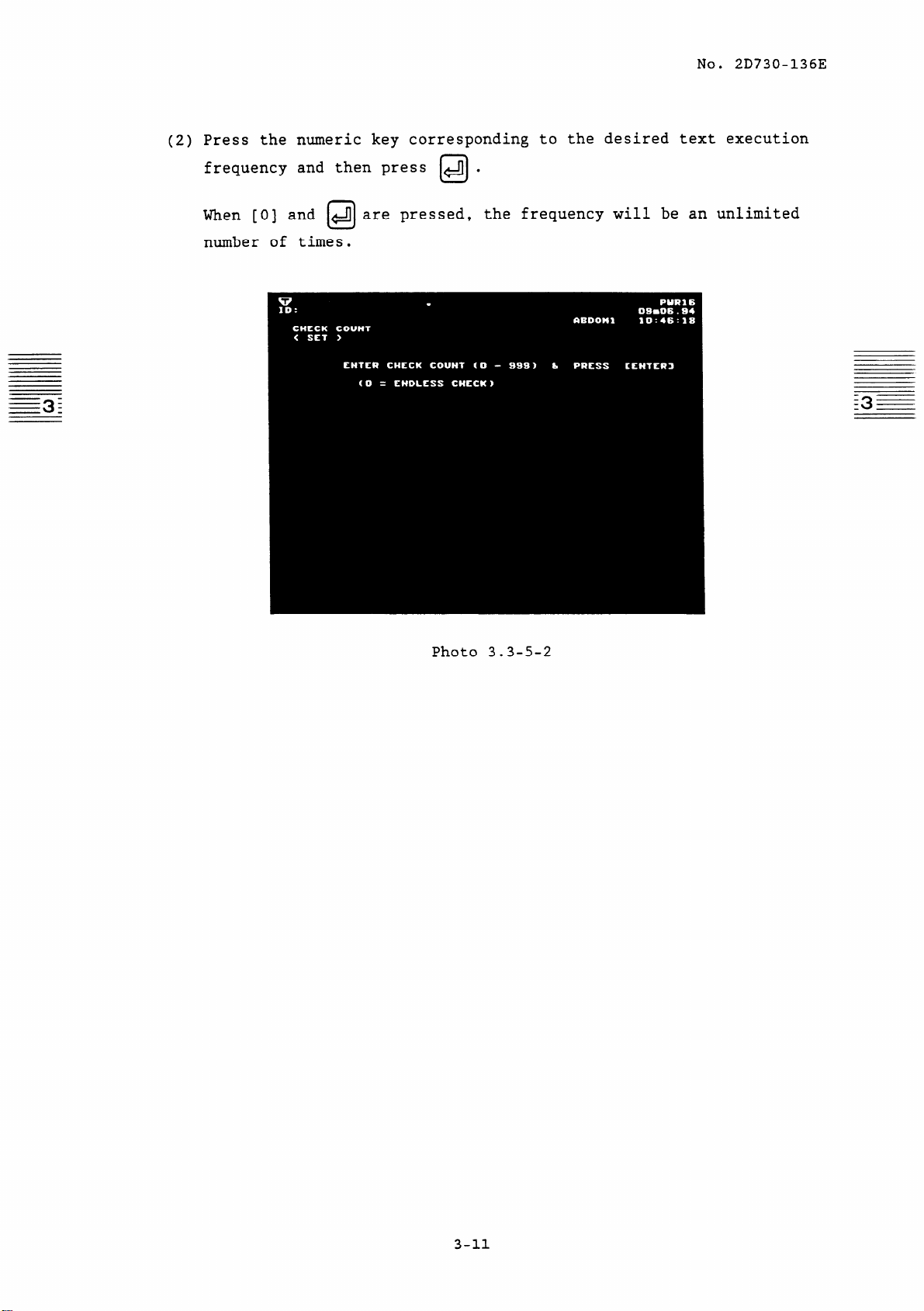
3.3.5 Changing the frequency of test execution
No. 20730-136E
(1) The menu of each test,
preceding the item of END.
Press the numeric key corresponding to CHECK COUNT SET and then
press +Jj.
Then the screen in photo 3.3-5-2 will appear.
0
(See photo 3.3-5-l.)
includes the item CHECK COUNT SET just
Photo 3.3-5-l
3-10
Page 29
No. 2D730-136E
(2) Press the numeric key corresponding to the desired text execution
frequency and then press 4 .
When [0] and
number of times.
141 are pressed,
U
the frequency will be an unlimited
Photo 3.3-5-2
3-11
Page 30

No. 29733-136Z
(3) When a is pressed at (2),
screen with the new frequency displayed as "CHECK COUNT = XXX"
(photo 3.3-5-3).
steps from (1) again.
If the wrong frequency is entered, perform the
the screen returns to the preceding
Photo 3.3-5-3
3-12
Page 31

3.4 Error Code Table
The error codes for visual check are described below.
No. 20730-136E
Error
code
CPU 00 CPU
CPU 01 CPU
PNL 00 PANEL
DSC 01 PC DSC
DSC02
DSC 03 B & W DSC
(--
DSC 04 ADC/LB/CAL
DSC 05 Ditto
DSC 06 CFM DSC and the
DSC 07 ADC/LB/CAL
PWB error
has occurred
CPU
I
RPG/TR CONT
B b W DSC
CFM DSC
RGB CONVERTER
subsequent PWBs
CFM DSC
RGB CONVERTER
Detail of the error
Graphic memory abnormal
Centronics abnormal
I
Sampling address abnormal
Raster address abnormal
FM-OUT GA abnormal or abnormal
/ between FM-OUT GA and GAMMARAM 1 No* 4 Of 4*4*3
RIP abnormal, etc.
WIP abnormal, etc.
FM-IN SC abnormal, etc.
FM-OUT GA abnormal, etc.
Reference
No. 3 of 4.1.3
No. 6 of 4.1.3
I
4.2.3
No. 2 of 4.4.3
No. 3 of 4.4.3
No. 6 of 4.4.3
No. 7 of 4.4.3
No. 8 of 4.4.3
No. 9 of 4.4.3
.
T/R 00
T/R 02 )
T/R 03
FFT 01 PHASE DETECTOR
FFT UNIT
FFT 02 FFT/CONT/AUDIO
FFT 03 FFT AUDIO &
L/M FFT CONT
FFT 04 FFT AUDIO &
L/M FFT CONT
Reception system abnormal
Reception system abnormal
I
Transmission system abnormal
I
Delay-line system abnormal
I
Analog system abnormal
(PHASE DETECTOR FFT I/O)
Digital system abnormal
FFT/CONT/AUDIO
Digital system abnormal (FFT)
Digital system abnormal (FFT)
4.5
4.5
I
4.5
I
4.5
I
4.6.2
4.6.2
4.6.2
4.6.2
3-13
Page 32

No. 2D730-136E
E3;
Error
code
CFMOl
to
cFMo3
cFMo4
to
CFMOS
CFM06
CFMll
to
cFM13
cFM14
to
cFM15
CFM16
PWB error
has occurred
CAL section on the
ADC/LB/CAL PWB
(BDF)
CAL section on the
ADC/LB/CAL PWB
(MDF)
CAL section on the
ADC/LB/CAL PWB
(BDF/MDF)
ADC/LB/PWB and
FIL/CORR PWB (BDF)
ADC/LB/CAL PWB and
FIL/CORR PWB (MDF)
ADC/LB/CAL PWB and
FIL/CORR PWB
(BDF/MDF)
Detail of the error
Abnormal ROM table and control
system in the BDF channel
system.
Abnormal ROM table and control
system in the MDF channel
system.
Abnormal ROM table and control
system in the BDF/MDF channel
system.
Abnormal control system and.
memory channel in the BDF
channel system
Abnormal control system and
memory channel in the MDF
channel system.
Abnormal control system and
memory channel in the BDF/MDF
channel system.
Reference
No. 5 to 7 of
4.7.3
No. 8 to 9 of
4.7.3
No. 10 of
4.7.3
No. 11 to 13
of 4.7.3
No. 14 to 15
of 4.7.3
No. 16 of
4.7.3
3-14
Page 33

FLOWCHARTS FOR IDENTIFYING MALFUNCTIONS
4.
4.1 Identifying Faults in the CPU Unit
4.1.1 Preparatory work
The following preparatory work is required before carrying out the
tests for the CPU which are listed below:
(1) When the RS-232C interface is checked
(a) The power to the ultrasonic diagnostic equipment is switched
OFF.
(b) Connect the loopback connector to the PS-232C connector on the
bottom of the main panel of the diagnostic ultrasound
equipment.
No. 2D730-136E
For the loopback connector,
use the connector to which the
following pins have been connected in the shell of the
DSUB-25s connector.
I) SD (pin 2) - RD (pin 3)
(c) The power to the ultrasonic diagnostic equipment is switched
ON, and the CPU test is selected.
4.1.2 Flowchart for identifying malfunctions
The flow of processing of the CPU test system is shown as a flowchart.
Figure 4.1-1 shows the processing flow of the entire CPU test system.
Since actual processing will proceed according to this flowchart when
the test system is operated,
it is recommended that the fault be
diagnosed while confirming the processing currently being performed
with respect to the entire test system by referring to this flowchart.
4-l
Page 34

4-2
No. 2D730-136E
f
Page 35

4.1.3 Decision criteria
This section shows decision criteria (normal or abnormal) for results
of the tests performed according to the flowchart in section 4.1.2,
depending on the messages
Items which do not match the normal data shown here are faults as test
results and faulty portions.
No. 2D730-136E
resulting from images obtained.
4-3
Page 36

No. 2D730-136E
Photo 4.1-l
[No. 0]
CPU test menu
Application:
Selection of CPU test menu
(Refer to photo 4.1-l)
Outline:
To perform selected CPU
tests by function
0 ALL CHECK
To perform RAM'CHECR, ROM
4
CHECK, GRAPHIC MEMORY
CHECK, RS-232C CHl CHECK,
RS-232C CH2 CHECK,
CENTRONICS CHECK
sequentially.
RAM CHECK
1
To check RAM operation.
+
ROM CHECK
2
To check ROM operation.
+
GRAPHIC MEMORY CHECK
3
To check graphic memory
-+
operation.
RS-232C CHl CHECK (For the
4
160A/270A/250A and 140A
CPUS)
To check RS-232C interface
+
CHl operation.
RS-232C CH2 CHECK
X
To check RS-232C interface
+
CH2 operation.
CENTRONICS CHECK
X
To check CENTRONICS
+
interface operation.
4-4
Page 37

No. 2D730-136E
7 CHECK COUNT
+ To set the frequency of the
CPU test.
(This is preset
at a frequency of one
normally.)
8 END
+ To complete the CPU test
and return to the main
menu.
Procedure:
+ To input the No. of the
test which is to be
performed
Example . . . . . ROM CHECK
Input 123
H in that
order.
Note:
Before performing a check,
including the RS-232C CHl
CHECK, RS-232C CH2 CHECK,
and CENTRONICS CHECK, refer
to 4.1.1 Preparatory work.
4-5
Page 38

No. 2D730-136E
Photo 4.1-Z
[No. 13
Application:
Operation check of RAM for
the CPU program
Outline:
After data is written into
RAM, data is read, then
compared with the written
data. If they do not match,
non-matching addresses are
indicated.
Procedure:
The CPU carries out the
test automatically and
displays the message in 1):
**Jr CPU RAM CHECK Jr**
1)
Results are displayed
2)
unit.
CPU RAM CHECK
sequentially in the RAM
i4E
When test results are
3)
normal:
The displayed image is as
shown in photo 4.1-2.
The system advances to the
next CHECK (CPU ROM CHECK)
when
The CPU test menu is
displayed when + is
pressed.
is pressed.
+JJ
n
0
4-6
Page 39

No. 2D730-136E
4) When test results are
abnormal:
Based on the results of
comparison, abnormal
addresses are displayed.
Bits set to "1" indicate
bits with abnormal RAM.
If [F] is pressed, advances
to the next address.
If [C] is pressed,
completes the present MM
check, and performs the
next RAM check.
Operation upon completion
of all addresses is the
same as in 3) above.
RAM showing abnormal
addresses in the above
tests are faulty.
Replace the CPU PWB.
;4=
4-7
Page 40

z:.
IIt CPU ROM CHECK tf*
* CPU PUB
13Y (X08)
12Y (X10)
1DY (X18) 665E OK
12v (X30)
1DV (X38)
12T (X40)
1DT (X48)
12R (X50)
1DR (X59)
END
llF7 OK
FPZF OK
1645 OK
6763 OK
5161 OK
F674 OK
BDPl OK
DD25 OK
RBDOMl
PUR16
llml7.94
20:!56:55
No. 2D730-136E
[No. 21 CPU ROM CHECK
Application:
Operation check of ROM for
the CPU program
Outline:
Checksum is performed by
reading the contents of ROM,
then comparison is made with
the previous checksum
results,
and IC locations and
checksum results (OK =
normal) are indicated.
Procedure:
Photo 4.1-3
The CPU carries out the test
automatically, and displays
the message in 1):
1) *** CPU ROM CHECK ***
2) Results are displayed
sequentially for each ROM
unit.
3) When test results are normal:
The displayed image is as
shown in photo 4.1-3.
With Isl) ON, the system
advances to the next CHECK
(GRAPHIC MEMORY).
With u ON,
the CPU test
menu is displayed.
4) When test results are
abnormal:
:4=
4-8
The location of abnormal ROM
is displayed.
Operations upon completion of
all ROM CHECKS are the same
as those in 3) above.
Abnormal ROM is identified
from the above results.
Faulty ROM should be
replaced.
Page 41

No. 2D730-136E
Photo 4.1-4
[No. 31
Application:
Operation check of CPU
GRAPHIC MEMORY
Outline:
"1" and "0" are written on 6
planes of GRAPHIC MEMORY.
The CRT screen will appear
black and white.
(With the color display, the
CRT screen will appear green
and blue.)
Procedure:
Check visually that the CRT
screen displays a normal
black and white pattern.
*Jr* GRAPHIC MEMORY CHECK *Jr*
(Refer to photo 4.1-4)
GRAPHIC MEMORY CHECK
Photo 4.1-5
The test starts when 4 is
2)
pressed.
When test results are
3)
normal:
The CRT screen becomes
"white"
4.1-5.
pressed,
becomes "black" as shown in
photo 4.1-6, permitting
visual check.
If [F] is pressed, the next
GRAPHIC MEMORY CHECK is
performed.
After checking 6 planes of
GRAPHIC MEMORY, the system
advances to the next CHECK
when 4 is pressed.
(RS-232C CHl CHECK).
as shown in photo
Then, when [F] is
the CRT screen
U
0
4-9
The CPU test menu is
displayed when + is
pressed.
0
Page 42

Page 43

No. 2D730-136E
[No. 41 RS-232C (CHl) CHECK
Application:
Transmission and reception
check for the CPU RS-232C
interface CHl
Outline:
The contents of
transmission from the
equipment and reception
from the return connector
are compared, and-if the
two do not agree, an error
is indicated.
Procedure:
Photo 4.1-8
The CPU carries out the
test automatically and
displays the message in 1):
1) **Jr RS-232C (CHl) CHECK ***
2) When test results are
normal:
The displayed image is as
shown in photo 4.1-8.
The system advances to the
next CHECK when 4 is
pressed.
(RS-232C CH2 CHECK).
The CPU test menu is
displayed when + is
pressed.
3) When test results are
abnormal:
0
0
Photo 4.1-9
An error message is
displayed as shown in photo
4.1-9.
Types and meanings of error
messages are given in table
4.1-1.
Operations after display of
an error message are the
same as in 2) above.
4-11
Page 44

No. 2D730-136E
Note:
Before performing this
CHECK, refer to 4.1.1
Preparatory work.
If the return connector is
not connected, a NO ANSWER
BACK occurs.
-4i
No.
5
6
Error message
FRAMING ERROR
OVERRUN ERROR
PARITY ERROR
TIME OUT ERROR
NO ANSWER BACK
COMPARE ERROR
Table 4.1-1
Error messages
Meaning
Format of 1 character received is not correct.
Before 1 character received is processed, the next
character is received.
A parity error has occurred within 1 character
received.
Transmission could not be performed within one minute
upon completion of preparation.
Text could not be received.
Transmitted and received text do not agree.
4-12
Page 45

4.1.4 Supplement
No. 2D730-136E
The checksum value must be registered prior to the CPU ROM check.
different registration methods are available.
(1) Refer to subsection 4.8.
(2) This method clears the preset data,
preset data.
Turn on No. 3 of the DIP SW on the CPU PWB.
(a)
Turn on the power.
(b)
When the following message is displayed, key-in Y:
w
INITIALIZE PRESET DATA
ARE YOU SURE?
After the initial screen displaying a B mode image appears,
(d)
turn off No.
Note:
4.2 Identifying Faults in the PANEL Unit
The above procedure has been already performed before
shipment from the factory.
3 of the DIP SW.
Two
and requires resetting of the
4.2.1 Preparatory work
No preparatory work is required.
4.2.2 Flowchart
for identifying faults
START
cr’
The LED on the panel
blinks at intervals of
approx. 1 second.
Figure 4.2-l
4-13
Page 46

4.2.3 Criteria
(Purpose) To identify faults in the PANEL unit.
(Outline) Turns the LEDs of the switches
No. 2D730-136E”B
indicated by
of approximately one second.
in figure 4.2-2 ON/OFF at intervals
Not all LEDs on the PANEL are turned
OFF/ON at intervals of about 1 s
(Some LEDs may be always on, always
off, or going OFF/ON at intervals other
than 1 s).
I
(1) Either the LEDs of switches not on
. _
the full keyboard are abnormal
(2) Ke LEDs of switches on the
keyboard are abnormal.
It is highly probable that the
PANEL is faulty.
1
No
I
Both groups
(1) and (2) are abnormal.
l
I
.
It is highly probable that the CPU
PWB or the cable between the
CPU and the PANEL is faulty. .
(If the panel data bus is faulty,
LEDs in both groups (1) and (2)
will be abnormal, regardless of the
panel’s condition.)
Note : The above is based on the assumption that the D & D MOTHER PWB
is normal.
4-14
Page 47

No. 2D730-136E*B
a
” . . . . . . . . . . .
” . . . . . & . . . . . M
” .r... . . . . . M
“z+
” . . . . . . . . . . w
“WM
Figure 4.2-2
Panel of the SSA-340A
4-15
Page 48

4.2.4 Supplement
No. 2D730-136E
CPU
I=-
AA
Data bus
Address bus
Figure 4.2-3
a
Trackball, STC VR data 1 D&D MOTHER
INITIAL
Peripheral control signal path
1 I
b .
*
I
Cable
1
PAN-EL
4-16
Page 49

Page 50

4.3 Identifying Faults in RPG
4.3.1 Preparatory work
None
4.3.2 Troubleshooting flowchart
Troubleshooting procedures for RPG faults are shown in the flowchart.
<RPG CHECK>
START
cr’
Checking of various enable
signals, raster addresses, OF,
generated in the RFG
No. 2D730-136E
4-18
Page 51

Signal names and functions which can be checked using this test program and PWB names which utilize these signals
are shown in the table below.
c-
Signal name
(between
boards)
BSAENO
MlSAENO
MZSAENO
DSAENO
FFTCMDO
BDFSAENO
MDFSAENO
DFINTO
Function
Signal showing B mode echo
sampling rate
k
Signal showing Ml mode echo
sampling rate
Signal showing M2 mode echo
sampling rate
Signal showing D mode echo o
sampling rate
Signal showing MDF mode
echo sampling rate
Signal showing initial CFM
operation sampling rate
PWB utilizing the signal
B & W DSC CFM DSC IMAGE MEMORY FFT/CONT/AUDIO MIT CONT ECG/NON FADE
CPU
o
o
0
0
0
0 0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
DFA*O
(3 bit)
TRAST*O
(12 bit)
DRAST*O
(12 bit)
ID signal showing position
of transmission focus
Raster address for 0
transmission and reception
Raster address for
indication
o
0
0
0
0
0
0
Page 52

4.3.3 Decision tree
From the test results, normal (OK) or abnormal (NG) is determined for
each signal as shown below.
No. 2D730-136E
If NG is indicated,
and the PWB should be replaced.
it is highly likely that the RPG PWB is faulty,
4-20
Page 53

4.3.4 Supplement
The RPG test program is activated when the host CPU sets test scan
mode with respect to the RPG.
[Specification of test scan mode]
(1) Each enable signal is set to the enable condition sequentially for
each rate,
(2) Focus
B : FO, F3, F4, F5, F6, F7 (6 step CF)
Ml : Fl
M2 : F2
(3) Number of B mode raster lines : 240
The raster address ranges from 0 to 239 in the upper 8 bits.
as shown in the attached timing chart.
_.
No. 2D730-136E
(4) M-mode position
Ml : 55 (H)
M2 : AA (H)
[Functions of the Host CPU]
Sets test scan mode in the I/O port of the RPG.
(1)
By setting data 0 --> 1
(2)
--> 0 in the I/O port #70/19 TSTSYNCl bit,
the leading edge of this signal serves as a trigger for generating
the rate once.
Each time the rate is generated once,
(3)
#7O/lC, lD,
and it is checked whether such data agrees with the
data is read from I/O port
data shown in the attachment.
For NG, the NG decision is made with respect to the signal in the
(4)
specific bit,
By generating the rate 8 x 240 = 1920 times, one frame is
(5)
completed and DOFO is generated,
with respect to the CPU.
and the signal name is indicated.
thereby causing OF interruption
The CPU completes the test upon
confirmation of this interruption.
4-21
Page 54

s
_L
1 eqep alod 30 sanTaA anzLl
1
__
,-- .
_-----
3IIOL #
r
C
___
._.
I:
c
c
_-a
.
-me
.-_
1T
.
L
I:
C
we_
_
._ _
me-
-r
__ _-_--.
a----_
(H) T 0 0
‘Ioz
ZOT
80C
0 9 9
oz5
OT 9
CMOqlZ 66 EUlIt?S
08L
_-----.
ahoqo St? aumS
-----.
ahoqe se sues
(H) 0
aI/of i
0 00
0
00
0
vv
25
05s
OT 0
ovv
010
ozo
055
ovv
ozo
No. 2D730-136E
Page 55

4.4 Identifying Faults in the DSC Unit
4.4.1 Preparations
No preparations are required to test the DSC.
4.4.2 Troubleshooting flowchart
Figure 4-11 shows a flowchart for DSC unit test system processing.
This flowchart shows the actual processing flow.
When operating the test system, perform troubleshooting by checking
the current processing on the flowchart.
No. 2D730-136E
4-23
Page 56

<DSC TEST>
0: ALL
CHECK
B/W FMAO-I, FMBO-1
B/W DSC test pattern
Ckk
I
Color FMAO-2, FMBOR/W check
I
cola crJcul8ta tcu
paean check
I
I
Cola LIP test Pattun
ChCCk
I
B/W FMAl
R/W check
I
B/W FMBO
R/W check
B/W FMBl
R/W check
RETURN
I
I
I I I
1: B/WFM 2: BIWTEST 3: B/WTEST
CPuR/w
I
I
I
I
PATTERN PA-lTERN
(SYNC)
(ASYNC)
c
B/W
P&k
4: R/wLrP
TEST FJMRAM PATIERN
PAlTERN R/W
5: COLOR 6: CALTEST
Cola FMBO
R/W check
I
I
(RI
7: CALTEST
PATI-ERN PRIP TEST
(THETA)
8: COLOR
PATTERN
9: COLOR
LIP TEST
PATTERN
lo: END
Figure 4-l 1
Page 57

4.4.3 Criteria
This section describes the criteria for normality or abnormality,
based on the messages displayed on the screen, for the results of
tests performed according to the flowchart.
If any test item does not meet the requirements, it is rejected.
No. 2D730-136E
4-25
Page 58

NO
No. 2D730-136E
Frame memory error.
Faulty PWB:
B&WDSC
(CPV)
I
Faulty PWB: CPU B & W DSC
4
NG
OK
Raster address or transmission
stage count error.
Faulty PWB:
B&WDSC
RPG/IR CONT
Figure 4-12
4-26
No error in LIP and
subsequent units
I
Page 59

No. 2D730-136E
NO
Faulty PWB: CPU B_& W DSC
,
Frame memory ermr.
Faulty PWB:
CFMDSC .
(CPv)
I
Sampling address error.
Faulty PWB:
CFM DSC
NG
NG
END
OK
OK
The DSC unit is normal.
No signal is sent from the CFM unit.
Raster address error
Faulty PWB:
CFM DSC
RPGIrR CONT
A
b
4-27
Page 60

OK
No. 2D730-136E
No error in RIP and
END
A
Figure 4-13
No error in LIP and
subsequent units
I
4-28
Page 61

No. 2D730-136E
Note:
If the gradation is abnormal, proceed to the test of the next
item.
If the gradation becomes normal at item "n", it shows
that the path of the signal at item "n-l" not included in the
signal of item "n" is abnormal.
Abnormal Normal
Item "n" Item "n-l"
2
3
{ I
4
4 B & W DSC
___
8
8
9
B & W DSC
CFM unit, CFM DSC
CFM DSC
Faulty PWB
yr---- 1 CFM DSC, RGB CONVERTER
4-29
Page 62

Image mode at the time of DSC test
No. 2D730-136E
No. 2
B/W TEST PATTERN (SYNC)
No. 3
B/W TEST PATTERN (ASYNC)
No. 4
B/W LIP TEST PATTERN
TV display
I
Display mode
!4tB
B-Dual
FMA
FMB
I
TV1
TV2
B-Dual
No. 6
CAL TEST PATTERN (R)
No. 7
CAL TEST PATTERN (THETA)
No. 8
COLOR RIP TEST PATTERN
No. 9
COLOR LIP TEST PATTERN
TV?
FMA
TV?
FMA FMB
,
TV?
TV2
FMB
TV2
TV2
MtB
B-Dual
I
B-Dual
B-Dual
4-30
Page 63

No. 2D730-136E
Photo 4.4-l
[No. 0]
CPU test menu
Application:
The DSC test mode is
selected.
(See photo 4.4-l)
Outline:
The DSC function test is
selected.
0 ALL CHECK
The following checks are
sequentially performed:
B/W FM CPU R/W, B/W TEST
PATTERN (SYNC), B/W TEST
PATTERN (ASYNC), B/W LIP
TEST PATTERN, COLOR FM CPU
R/W, CAL TEST PATTERN (R),
CAL TEST PATTERN (THETA),
COLOR RIP TEST PATTERN,
COLOR LIP TEST PATTERN
1 B/W FM CPU R/W
+ B/W FMA, FMB are checked.
2 B/W TEST PATTERN (SYNC)
-+ The sampling address is
checked by the rate
synchronization test
pattern.
3 B/W TEST PATTERN (ASYNC)
+ The raster address is
checked by the rate asyn-
chronization test pattern.
4 B/W LIP TEST PATTERN
+ Determining whether the
error position is in the
system preceding the B/W
DSC unit or in the system
following the B/W DSC unit.
4-31
5 COLOR FM CPU R/W
+ COLOR FMAO to 2, FMBO to 2
R/W is checked.
Page 64

No. 2D730-136E
6 CAL TEST PATTERN (R)
The sampling address and
+
r-direction thresholds are
checked.
7
CAL TEST PATTERN (THETA)
The raster address and
+
r-direction and e-direction
thresholds are checked.
COLOR RIP TEST PATTERN
0
The RIP test pattern is
-+
checked.
COLOR LIP TEST PATTERN
9
Determining whether the
+
error position is in the
system preceding the color
DSC unit or in the system
following the color DSC
unit.
11
-LA END
+ The DSC tests are
completed,
and the screen
returns to the main menu.
Procedure:
Enter the test number.
Example . . .
B/W TEST PATTERN (SYNC)
Input [2] @ in that
order.
Caution:
Characters should be
displayed on the screen.
If no characters are
displayed,
either the CPU,
B&W DSC, or CPM DSC PWB is
abnormal.
4-32
Page 65

No. 20730-1363
Photo 4.4-2
[No. l]
Application:
FM memory IC operation is
checked.
Outline:
Data is written into RAM,
then read.
data does not match the
written data, the address
is displayed.
Procedure:
The CPU carries out the
test automatically, and
displays the message in 1):
**** B/W FM RAM CHECK ***Jr
1)
The result is displayed
2)
sequentially for each RAM.
B/W FM CPU R/W
If the read
i4E
When F'MAO is completed,
3)
FMAl and FMBO are checked
in that order.
When the test results are
4)
normal,
photo 4.4-2 is displayed.
When 4 is pressed, it
proceeds to the next check
(B/W TEST PATTERN (SYNC)).
When * is pressed, the
DSC test menu is displayed.
The error address and the
comparison result are
displayed.
set to 1 is an error bit in
the RAM.
the image shown in
0
0
A bit which is
4-33
Page 66

No. 2D730-136E
If the [F] key is pressed,
the next address is tested.
When [C] is pressed, this
check is terminated.
The operations when all
addresses have been tested
are the same as the
operations described in 4).
4-34
Page 67

Page 68

4-36
4
3
ml
X
a
+-
No. 2D730-136E
Page 69

Page 70

No. 2D730-136E
3) When +!I is pressed, the
When + is pressed, the
Note:
0
operation proceeds to the
next check (B/W LIP TEST
PATTERN).
U
DSC test menu is displayed.
When both check results,
B/W TEST PATTERN (ASYNC)
and B/W TEST PATTERN
(SYNC).
unit is normal.
is sent from the Receiver.
are normal, the DSC
No signal
4-38
Page 71

4-39
u4
0
No. 2D730-136E
Page 72

Page 73

No. 2D730-136E
Note:
If the check result is
normal and no pattern is
displayed when B/W TEST
PATTERN (SYNC) or B/W TEST
PATTERN (ASYNC) is checked,
the error is in the system
from the FM-IN SC to the
FM- OUT.
4-41
Page 74

BaW DSC
Flow chart of B/W LIP TEST PATTERN signal
ENC/
DEL
I
Character
t
I
CONTROL
,
.
BLOCK
66000
BLOCK
7
0 RPG
*
o HOST
CPU
Page 75

Photo 4.4-6
No. 2D730-136E
[No. 51 COLOR FM CPU R/W
Application:
EM memory IC operation is
checked.
Outline:
Data is written into RAM,
then read.
data does not match the
written data, the address
at which the discrepancy
has occurred is displayed.
Procedure:
The CPU carries out the
test automatically, and
displays the message in 1):
If the read
**** CF'M FM RAM CHECK ****
1)
The result is displayed
2)
sequentially for each RAM.
When FMAO is completed,
3)
F'MAl and F'MA3 are checked
in that order.
When the test result is
4)
normal,
photo 4.4-6 is displayed.
When 4 is pressed, the
operation proceeds to the
next check (CAL TEST
PATTERN (R)).
When m
DSC test menu is displayed.
If COLOR FM CPU R/W is
selected,
is displayed when the &/
key is pressed.
the image shown in
U
is pressed, the
the DSC test menu
0
4-43
The error address and the
5)
comparison result are
displayed.
set to 1 is an error bit in
the MM.
A bit which is
Page 76

No. 2D730-136E
l If the [F] key is
pressed,
is tested.
When [C] is pressed, this
check is terminated.
The operations when all
the addresses have been
tested are the same as
the operations in 4).
the next address
4-44
Page 77

Page 78

No. 2D730-136E
l If the pattern is
otherwise abnormal, the
error is in the
CALCULATOR PWB or CPM DSC
PWB.
l If no pattern is
displayed, the error is
in the CALCULATOR PWB,
CPM DSC PWB, or RGB CONV
PWB.
3) When m is pressed, the
system proceeds to the next
check (CAL TEST PATTERN
(THETA)).
When + is pressed, the
Note:
U
DSC test menu is displayed.
If both check results, CAL
TEST PATTERN (R) and CAL
TEST PATTERN (THETA), are
normal,
normal. No signal is sent
from the CPM unit.
the DSC unit is
4-46
Page 79

4-47
No. 2D730-136E
Page 80

Page 81

No. 2D730-136E
l If the pattern is
otherwise abnormal the
error is in the
CALCULATOR PWB or CPM DSC
PWB.
0 If no pattern is
displayed,
in the CALCULATOR PWB,
CF'M DSC PWB or RGB CONV.
the error is
3) When +lJ is pressed, the
- (COLOR RIP TEST PATTERN).
Note:
0
proceeds to the next check
When + is pressed, the
U
DSC test menu is displayed.
If both check results, CAL
TEST PATTERN (THETA) and
CAL TEST PATTERN (R) are
normal,
normal.
from the CPM unit.
the DSC unit is
No signal is sent
4-49
Page 82

%
3
3
Y
d
%
’ a
El
E
x
3
. 1
I
.
I I
5
L
4-50
% (
z
L
I
4
1
8s~
9
L
No. 2D730-136E
Page 83

Page 84

4-52
f
v
:
I-
No. 2D730-136E
Page 85

Page 86

No. 2D730-136E
When the test results are
3)
abnormal:
0 When interpolation is not
performed normally, the
error is in the FM-OUT
GA.
0 When no pattern is
displayed or the color
tone is incorrect, the
error is in the CPM DSC
PWB or RGB CONVERTER PWB
subsequent to the FM-OUT
GA.
If ALL CHECK or COLOR LIP
4)
TEST PATTERN is selected,
the DSC test menu is
displayed when the + key
is pressed.
0
.
g4E
4-54
Page 87

P-l
k’
l-l
No. 2D730-136E
Page 88

4.5 Identifying Faults in the T/R Unit
4.5.1 Preparations
Ultrasonic jelly is required in the items listed below:
No. 2D730-136E
(1) T/R test item No.
(2) T/R test item No.
4.5.2 Fault diagnosis flow chart
Figure 4.5-l shows the processing for the T/R test.
4 R-channel check (CONVEX)
5 T-channel check (CONVEX)
4-56
Page 89

<T/R TEST>
Tut mode sclactim
0: ALL
CHECK
Command RAM R/w
I
ChCCk I
Rccqxion chumcl chat
(=W
I
1
2 DLCONT
RAM
CHJXK
I
I
( RETURN )
Figure 4.5 1
l’hcT/Rtcstis
complctcd 8nd Ihc.
main mu is
displayed once again
I
1
Page 90

Troubleshooting procedure
No. 2D730-136E
[Suspcctcd PM’B 1
,
IOK
NG
NG
NG
NG
NG
* RPG/l-R CONT PWB
* RPG/T’R CONT PWB
PROBE SELECTOR PWB
R-DELAY PWB
*
w PROBE SELECTOR
r
* R-DELAY PWB
PULSER PWB *
*
PULSER PWB
‘*
1 END ]
* The RAM check function (command RAM,
of RPGjTR CONT PWB.
There is a slight chance that RPG/TR CONT is defective, in addition
to the PWBs with Jr.
Notes: 1.
If more than one PWB, identify the dcfcctive PWB by
checking the patterns of test results.
BRI RAM) does not check whole
Prior to replacing PWBs,
check that cables are connected
correctly and are not cut off.
2.
The DVAF/RECEIVER cannot be checked using the test program.
These PWBs must be checked separately.
4-58
Page 91

4.5.3 Criteria
No. 2D730-136E
[No. 13 T&R TEST MENU
Purpose:
T&R test menu selection
Outline:
Select the test for each
block.
0 ALL CHECK
The following tests are
executed sequentially.
1 T&R CONT RAM CHECK
Photo 4.5-l
The RAM for T/R CONTl and
delay time data is checked
for read and write.
2 DELAY CONT RAM CHECK
The RAM for DELAY CONT
delay time data is checked
for read and write.
x R-CHANNEL CHECK (RESERVE)
4 R-CHANNEL CHECK (CONVEX)
Each channel of the convex
reception system is
checked.
5 T-CHANNEL CHECK (CONVEX)
Each channel of the sector
transmission system is
checked.
6 DELAY TIME CHECK (CONVEX)
2
4-59
The sector transmission -
reception delay time is
checked.
7 CHECK COUNT SET
Page 92

No. 2D730-136E
8 END
The T&R test is completed.
The [No. l] menu is
displayed.
Procedure:
_ Enter the number of the
test to be executed.
Example . . . . . R-CHANNEL
CHECK (CONVEX)
Press the [4] and
in that order.
@J keys
4-60
Page 93

No. 2D730-136E
Photo 4.5-2
[No. 21
Purpose:
Operation check for T/R
delay time RAM
Outline:
Data is written into the
MM.
compared with the written
data.
each other,
data are displayed.
Procedure:
The CPU executes the test
automatically and displays
the message below:
1) "***T/R CONT RAM CHECK***"
is displayed.
T/R CONT RAM CHECK
The data is read and
If they do not match
the address and
2) The result is displayed for
each RAM.
3) When the test result is
normal,
photo 4.5-2 is displayed.
When the 4 key is
pressed,
executed.
When the + key is
pressed,
displayed.
4) When the test result is
abnormal,
address and the results of
comparison are displayed.
the message in
0
the next check is
0
menu [No. l] is
the abnormal
4-61
Page 94

No. 20730-1363
When the [F] key is
pressed,
is checked.
When the [C] key is
pressed,
check is terminated.
After all the addresses are
checked:
the next address
the current RAM
When the 4 key is
pressed,
executed.
When the + key is
pressed, the [No. l] menu
is displayed.
The RAM containing the error
address is faulty.
the RPG/TR CONT PWB.
0
the next check is
0
Replace
4-62
Page 95

No. 2D730-136E
Photo 4.5-3
[No. 31
Purpose:
BRI RAM operation check
Outline:
Data is written into the
MM, then the data is read
and compared with the
written data.
not match each other, the
address and data are
displayed.
Procedure:
The CPU automatically
executes the test and
displays the message below:
1) "***DL CONT RAM CHECK***"
is displayed.
DELAY CONT MM CHECK
If they do
2) The result is displayed for
each RAM.
3) When the test result is
normal:
a) The message in photo
4.5-3 is displayed
When the 4 key is
pressed,
is executed.
When the C=, key is
pressed,
displayed.
0
the next check
U
menu [No. l] is
4-63
Page 96

No. 2D730-136E
4) When the test result is
abnormal, the abnormal
address and the result of
comparison are displayed.
When the [F] key is
pressed, the next address
is checked.
When the [C] key is
pressed,
check is terminated.
After all the addresses are
checked:
the current RAM
When the 4 key is
pressed, the next check is
executed.
When the + key is
pressed, the menu [No. l]
is displayed.
The RAM containing the error
address is faulty. Replace
the RPG/TR CONT PWB.
0
n
;4---
4-64
Page 97

Page 98

No. 2D730-136E
When the + key is
pressed,
u
menu [No. l] is
displayed.
When the [SPACE] key is
pressed,
the first half and
the second half of the
channels are switched.
(See the figure below.)
If the values of the STC
controls are set too high,
the brightness of the line
of a faulty channel
increases, making it
difficult to detect faulty
channels.
CH64
t
m129
cH5
@WI
I
Examples:
Photo 4.5-4 shows an
example of a normal result
for channels 5 to 64.
Photo 4.5-S shows an
example of a normal result
for channels 65 to 124.
For abnormal results, the
defective ch is black.
4-66
Page 99

Page 100

No. 2D730-136E
Example
Photo 4.5.6 shows an
example of normal 5 to 64
ch and photo 4.5.7 shows
an example of normal 64 to
124 ch.
The marker on the raster
is displayed every 10
channels.
If the channel for the
transmission system is
defective,
the raster
corresponding to the
channel is black.
The gain dial has no
effect,
so adjust the STC
to clarify the black area.
;4=
4-68
 Loading...
Loading...