Page 1

PROGRAMMABLE CONTROLLER
UM-TS03∗∗∗-E032
PROSEC
T3H
USER’S MANUAL
TOSHIBA CORPORATION
Page 2

Important Information
Misuse of this equipment can result in property damage or human injury.
Because controlled system applications vary widely, you should satisfy yourself
as to the acceptability of this equipment for your intended purpose.
In no event will Toshiba Corporation be responsible or liable for either indirect
or consequential damage or injury that may result from the use of this equipment.
No patent liability is assumed by Toshiba Corporation with respect to use of
information, illustrations, circuits, equipment or examples of application in this
publication.
Toshiba Corporation reserves the right to make changes and improvements to this
publication and/or related products at any time without notice. No obligation shall be
incurred other than as noted in this publication.
This publication is copyrighted and contains proprietary material. No part of this book
may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any
means electrical, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise without
obtaining prior written permission from Toshiba Corporation.
© TOSHIBA Corporation 1996. All rights reserved
Ethernet is a registered trademark of Xerox Corporation.
PROSEC and TOSLINE are registered trademarks of TOSHIBA Corporation.
Publication number: UM-TS03
1st edition June 1996
∗∗∗
-E032
Page 3

Safety Precautions
This manual is prepared for users of Toshiba’s Programm able Cont roller T3H.
Read this manual thoroughly before using the T3H. Also, keep this manual and r elat ed manuals
so that you can read them anytime while the T3H is in operation.
General Information
1. The T3H has been designed and manufact ured for use in an industrial environment.
However, the T3H is not intended to be used for systems which may endanger human
life. Consult Toshiba if you intend t o use t he T3H for a special application, such as
transportation machines, medical apparatus, aviation and space systems, nuclear
controls, submarine systems, etc.
2. The T3H has been manufactured under strict quality control. However, to keep safety
of overall automated system, f ail- safe systems should be considered outside the T3H.
3. In installation, wiring, operation and maintenance of the T3H, it is assumed that t he
users have general knowledge of industrial elect r ic cont r ol system s.
If this product is handled or operat ed im properly, electrical shock, fir e or dam age to this
product could result.
4. This manual has been written for users who are familiar with Programmable Controller s
and industrial control equipment. Cont act Toshiba if you have any questions about this
manual.
5. Sample programs and circuits descr ibed in t his manual are provided for explaining the
operations and applications of the T3H. You should t est completely if you use them as
a part of your application system.
Hazard Classifications
In this manual, the following two hazard classifications ar e used t o explain the safety
precautions.
!
WARNING
!
CAUTION
against unsafe practices.
Even a precaution is classified as CAUTION, it m ay cause serious result s depending on
the situation. Observe all the safet y precaut ions descr ibed on t his manual.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could
result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may
result in minor or moderate injur y. I t may also be used to alert
User’s Manual
1
Page 4
Safety Precautions
Installation:
1. Excess temperature, humidity, vibration, shocks, or dusty and corrosive gas
environment can cause electrical shock, f ire or malfunction. Install and use the T3H
and in the environment described in the T3 User’s Manual - Hardware.
2. Improper installation directions or insufficient installation can cause fir e or t he units to
drop. Install the T3H in accordance with the instructions described in the T3 User’s
Manual - Hardware -.
3. Turn off power bef ore installing or removing any units, modules or terminal blocks.
Failure to do so can cause electrical shock or damag e t o the T3H and related
equipment.
4. Entering wire scraps or other for eign debris into to the T3H and related equipment
can cause fire or malfunction. Pay att ent ion to prevent entering them into the T3H
and related equipment during inst allat ion and wiring.
Wiring:
1. Turn off power before wiring to minimize the risk of electrical shock.
2. Exposed conductive parts of wire can cause electrical shock. Use crimp-style
terminals with insulating sheath or insulating tape t o cover the conductive parts. Also
close the terminal covers securely on the terminal block s when wiring has been
completed.
3. Operation without grounding may cause electrical shock or malfunction. Connect the
ground terminal on the T3H t o t he system ground.
4. Applying excess power voltage to the T3H can cause explosion or fire. Apply power
of the specified rating s descr ibed in the T3 User’s Manual - Hardware.
5. Improper wiring can cause fire, electr ical shock or malfunction. Observe local
regulations on wiring and grounding.
Safety Precautions
!
CAUTION
!
CAUTION
PROSEC T3H
2
Page 5
Safety Precautions
Operation:
1. Configure emergency stop and safety interlocking circuits outside the T3H.
Otherwise, malfunction of the T3H can cause injury or serious accidents.
2. Operate the T3H and the related m odules with closing the terminal covers. Keep
hands away from terminals while power on, to avoid the risk of electr ical shock.
3. When you attempt to perform f or c e out puts, RUN/HALT controls, etc. dur ing
operation, carefully check f o r safety.
4. Turn on power to the T3H before turning on power to the loads. Failure to do so may
cause unexpected behavior of the loads.
5. Set operation mode switches of the T3H and I/O modules. Improper switch settings
may cause malfunction of the T 3H and r elat ed equipment.
6. Do not use any modules of the T3H for t he purpose other than specified. This can
cause electrical shock or injury.
7. Configure the external circuit so t hat the external power required for out put modules
and power to the loads are switched on/off simult aneously.
Also, turn off power to t he loads before turning of f power to the T3H.
8. Install fuses appropriate to the load current in the external circuits for the relay output
modules. Failure to do so can cause fire in case of load over- cur r ent.
9. Check for proper connections on wires, connectors and modules. Insufficient contact
can cause malfunction or damage to t he T3H and related equipment.
10.Turn off power imm ediat ely if the T3H is emitting smoke or odor. Operation under
such condition can cause fire or electrical shock.
Also unauthorized repairing will cause fire or serious accidents. Do not at tempt to
repair. Contact Toshiba f or repairing.
!
WARNING
!
CAUTION
User’s Manual
3
Page 6
Maintenance:
1. Do not charge, disassemble, dispose in a fir e nor short-circuit the batteries. It can
2. Turn off power bef or e removing or replacing units, ter m inal blocks or wires. Failure to
3. Replace a blown fuse with a specified one. Failure to do so can cause fire or dam age
4. Perform daily checks, periodical checks and cleaning to maintain the system in
5. Check by referring “T roubleshooting” section of the T3 User’s Manual - Hardware,
6. The contact reliability of the r elays used in the relay output module will reduce if the
7. Replace the battery every 2 years to maintain the T3H’s prog r am and data normally.
8. Do not modify the T3H and related eq uipment in hardware nor software. This can
9. Pay special attention for safet y if you attempt to measure circuit voltage at the T3H’s
10. Turn off power bef or e r eplacing modules. Failure to do so can cause electrical shock
Safety Precautions
!
CAUTION
cause explosion or fire. Observe local regulations for disposal of them.
do so can cause electrical shock or damage to t he T3H and related equipment.
to the T3H.
normal condition and to prevent unnecessary troubles.
when operating improperly. Contact Toshiba for repairing if the T3H or related
equipment is failed. T oshiba will not g uar ant ee proper operation nor safety f or
unauthorized repairing.
switching exceeds the specified life. Replace the module if exceeded.
cause fire, electrical shock or injury.
terminal.
or damage to the T3H and relat ed equipment.
If you attempt to replace an I/O module while power on (by using on-line I/O
replacement function), carefully check for safet y.
PROSEC T3H
4
Page 7
Safety Label
The safety label as shown on the right is
attached to the power terminal of the T3H.
Remove the mount paper before wiring.
Peel off the label f r om the mount paper
and stick it near the power terminals
where it can be readily seen.
Contact Toshiba if the label is damaged.
Safety Precautions
CAUTION
!
Do not touch terminals
while power on.
Hazardous voltage can shock, burn or cause death.
Do not touch terminals while power on.
Read related manual thoroughly for safety.
Stick this seal on unit or near unit.
Take off this sheet before wiring.
User’s Manual
5
Page 8
About This Manual
About This Manual
The T3H is a high speed and large capacity version of the T3. All the hardware
components used for the T3 system, i.e. rack, power supply module, I/O modules, etc.,
are used with the T3H CPU. Regarding software function, the T 3H has all the T3’s
functions and has some expanded functions.
This manual explains the expanded functions of the T 3H and functional differences
between the T3H and the T3. Therefore, for your better understanding of the T3H, r ead
the following T3 manuals at fir st to understand the T3 system, then read t his m anual.
T3 manuals:
T3 User’s Manual − Hardware UM-TS03∗∗∗-E002
T3 User’s Manual − Function UM-TS03∗∗∗-E003
T-series Instruction Set UM-TS03∗∗∗-E004
T-series Computer Link O per at ion Manual UM-TS03∗∗∗-E008
T3 Analog Input Module (AD368) UM-TS03∗∗∗-E016
T3 Analog Output Module (DA364/DA374) UM-TS03∗∗∗-E017
T3 Pulse Input Module (PI312) UM-TS03∗∗∗-E018
T3 ASCII Module (AS311) UM-TS03∗∗∗-E020
Terminology
The following is a list of abbreviations and acronyms used in t his m anual.
µµµµs microsecond
ASCII American Standard Code For Infor m ation Interchange
AWG American Wir e Gage
BCC Block Check Code
CPU Cent r al Processing Unit
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Programmable Read O nly Memory
H hexadecimal (when it appears in front of an alphanumer ic string)
I/O Input/Output
LED Light Emitting Diode
LSB Least Significant Bit
ms millisecond
MSB Most Significant Bit
RAM Random Access Memory
ROM Read Only Memory
SFC Sequential Function Chart
Vac AC voltage
Vdc DC voltage
PROSEC T3H
6
Page 9

Contents
Contents
Safety Precautions .................................................................................. 1
About This Manual ...................................................................................... 6
1. T3H Overview ................................................................................. 9
1.1 Introducing the T3H .......................................................................... 10
1.2 Differences between T3H and T3 .................................................... 11
1.3 T3H components .............................................................................. 12
1.4 Specifications ................................................................................... 20
2. Expanded Functions ..................................................................... 27
2.1 System operation ............................................................................. 28
2.1.1 Auto-RUN / Standby selection ....................................................... 28
2.1.2 Timer interrupt interval ................................................................... 28
2.1.3 Saving the sampling trace condition .............................................. 29
2.2 Expanded registers ........................................................................... 30
2.2.1 External I/O register ...................................................................... 30
2.2.2 Auxiliary register ............................................................................ 30
2.2.3 Timer ............................................................................................. 31
2.2.4 Link register ................................................................................... 31
2.2.5 File register .................................................................................... 34
2.2.6 Special register .............................................................................. 34
2.3 Network support function .................................................................. 38
2.3.1 IC memory card data access through computer link ...................... 38
2.3.2 TOSLINE-S20LP (loop) support .................................................... 41
2.3.3 Ethernet support ........................................................................... 42
2.4 Instructions ....................................................................................... 43
2.4.1 Double-word multiplication and division (D∗/) .............................. 44
2.4.2 Essential PID (PID3) .................................................................... 46
2.4.3 Floating point essential PID (FPID3) ............................................. 51
2.4.4 Expanded data transfer (XFER) .................................................... 56
2.4.5 Network data send (SEND) .......................................................... 62
2.4.6 Network data receive (RECV) ....................................................... 66
User’s Manual
7
Page 10

PROSEC T3H
8
Page 11

Section 1
T3H Overview
1.1 Introducing the T3H, 10
1.2 Differences between T3H and T3, 11
1.3 T3H components, 12
1.4 Specifications, 20
User’s Manual
9
Page 12

1. T3H Overview
1.1 Introducing the T3H
The T3H is a high perfor mance large scale programmable cont r oller.
Program memory capacity:
The T3H is available in two CPU types, PU325H and PU326H. Each type has the
following user program mem or y capacity.
PU325H: 32 k steps
PU326H: 64 k steps
I/O points:
The T3H can handle up to 76 I/O modules in its local configuration. And the T3H has
512 words of external I/O register (data memory).
If all the I/O modules are discrete I/Os, the T3H can control up to 4864 points.
(64 points × 76 = 4864 points)
If all the I/O modules are analog I/Os, the T3H can control up to 512 channels of
analog signals.
High speed processing:
A standard 16-bit micro processor and a special designed language processor are
used in the T3H CPU. This dual-processor ar chit ecture provides high speed
processing.
0.09 µs/contact 0.18 µs/coil
0.54 µs/16-bit transf er 0.90 µs/16-bit addition
Multitasking:
The T3H supports the multitask processing. By using this function, suitable control
interval for a target applicat ion can be obt ained.
1 × internal timer int errupt (interval setting: 1 t o 1000 m s , 1 m s unit s )
8 × I/O interrupts (activated by external events)
1 × main program (core of the user progr am )
4 × sub-programs ( activated from other tasks and executed as back-ground job)
Multiple programming languages:
The T3H supports two types of prog ramming languages, i. e. ladder diagram and SFC
(Sequential Function Chart). T he ladder diagram is suited for logic control, and the
SFC is suited for sequential contr ol. These languages can be used in mixture.
High performance software:
The T3H supports 24 basic ladder instruct ions and 204 function instructions. Floating
points data processing is also available. The T3H can be applied to complex control
applications.
Network support:
The T3H can be connected to work-stations/ per sonal- c om put ers through Ethernet.
Peer-to-peer communications between two T3H’s via Ethernet is also available.
For high-speed control-data linkage, TOSLINE-S20/F10 can be used.
PROSEC T3H
10
Page 13
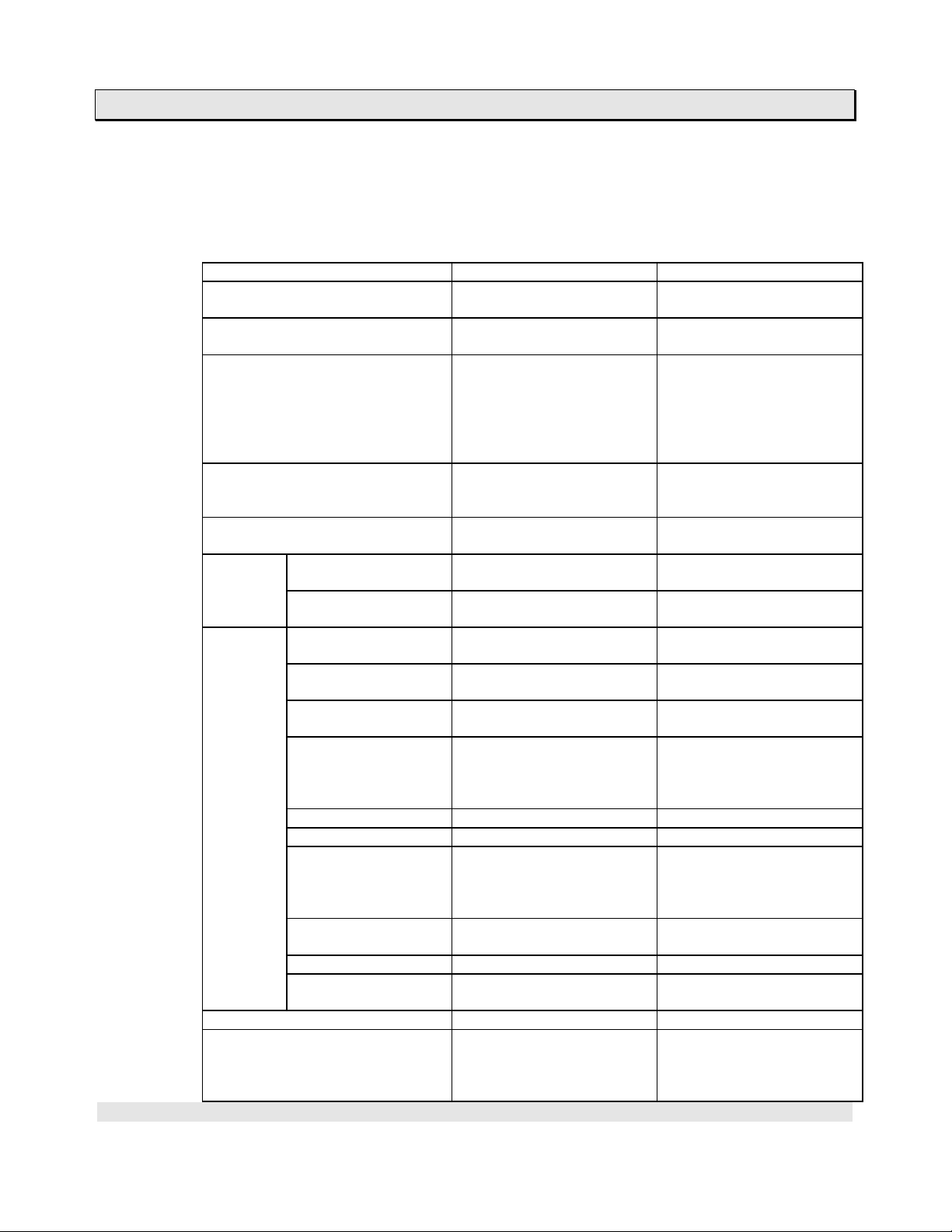
1.2 Differences between T3H and T3
The table below summarizes the differences between the T3H and T3. All other
functions supported by the T3 can also be supported by the T3H as same.
Item T3H T3
Program memory capacity 32 k steps (PU325H)
Built-in EEPROM Yes
Programming instructions All T3’s instructions plus
Execution speed (µs)
Max. number of I/O modules
supported in local
System
operation
Auto-RUN / standby
User data External I/O
Auxiliary register
Special register
Timer (T./T) 1000 points
Counter (C./C) 512 points Same as left
Data register (D) 8192 words Same as left
Link register (Z/W)
Link register (L/LW)
File register (F) 32768 words 8192 words
Index register
Programming tool T-PDS T-PDS and HP911
Networking Ethernet,
Timer interrupt interval
setting
selection
(X/XW, Y/YW)
(R/RW)
(S/SW)
(for TOSLINE-S20)
(for TOSLINE-F10)
(I, J, K)
1. T3H Overview
32 k steps
64 k steps (PU326H)
(PU325H and PU326H)
FUN042 D∗/
FUN156 PID3
FUN232 FPID3
FUN239 SEND
FUN240 RECV
0.09 / contact
0.18 / coil
0.9 / addition
76 modules
(when IF321 is used)
1 to 1000 ms, 1 ms units 2 to 1000 ms, 1 ms units
Software setting
(system information)
8192 points / 512 words 4096 points / 256 words
16000 points /
1000 words
4096 points / 256 words Same as left
(proportion of 0.1s and
0.01s timer is user
definable)
16000 points /
2048 words
(bit access available for
leading 1000 words)
4096 points / 256 words Same as left
3 words Same as left
TOSLINE-S20,
TOSLINE-F10,
RS-485 computer link
(PU315 and PU325)
No (PU315)
Yes (PU325)
−
0.15 / contact
0.3 / coil
1.5 / addition
43 modules
Hardware switch
(RAM/ROM switch)
8192 points / 512 words
512 points
(T000 - T063: 0.1s)
(T064 - T511: 0.01s)
8192 points /
1024 words
(bit access available for
leading 512 words)
TOSLINE-S20,
TOSLINE-F10,
RS-485 computer link
User’s Manual
11
Page 14
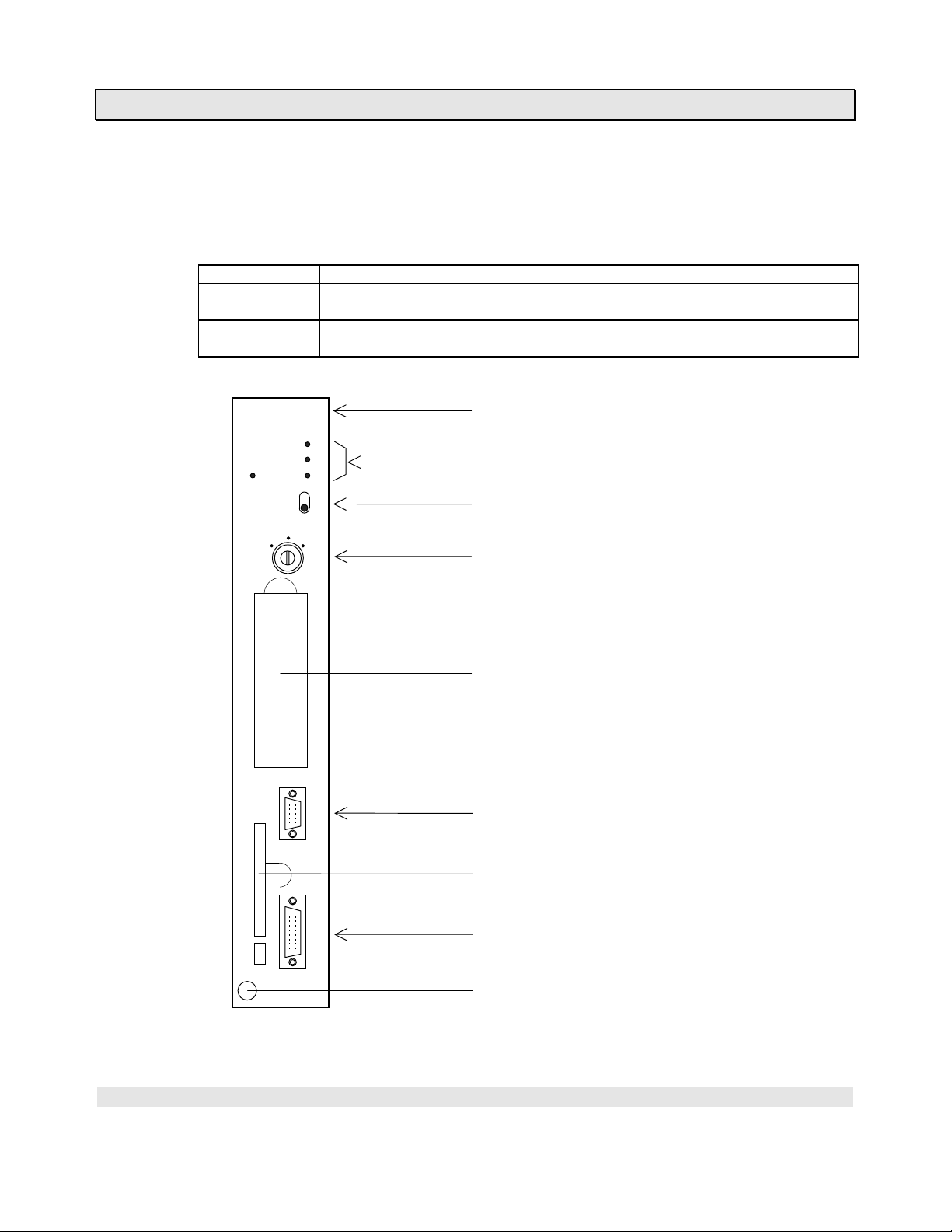
1. T3H Overview
1.3 T3H components (1) CPU module
Two types of T3H CPU modules are available.
Type Description
PU325H EEPROM + RAM (battery backed), User program 32 k steps,
PU326H EEPROM + RAM (battery backed), User program 64 k steps,
PU325H
RUN
FAULT
BATT
I/O
RAM
ROM
RUN
HALT P-RUN
Ladder diagram and SFC
Ladder diagram and SFC
Product identification
Status LEDs
RAM/ROM switch
Mode control switch (HALT/RUN/P-RUN)
BATTERY
Battery cover
PROG
CARD
Programmer port
(RS-232C, D-Sub 9-pin female connect or)
IC memory card slot
LINK
Computer link port
(RS-485, D-Sub 15-pin female connect or )
EJECT
Module fixing screw
The external feature of the T3H CPU is the same as the T3 CPU except for the
product identification.
PROSEC T3H
12
Page 15
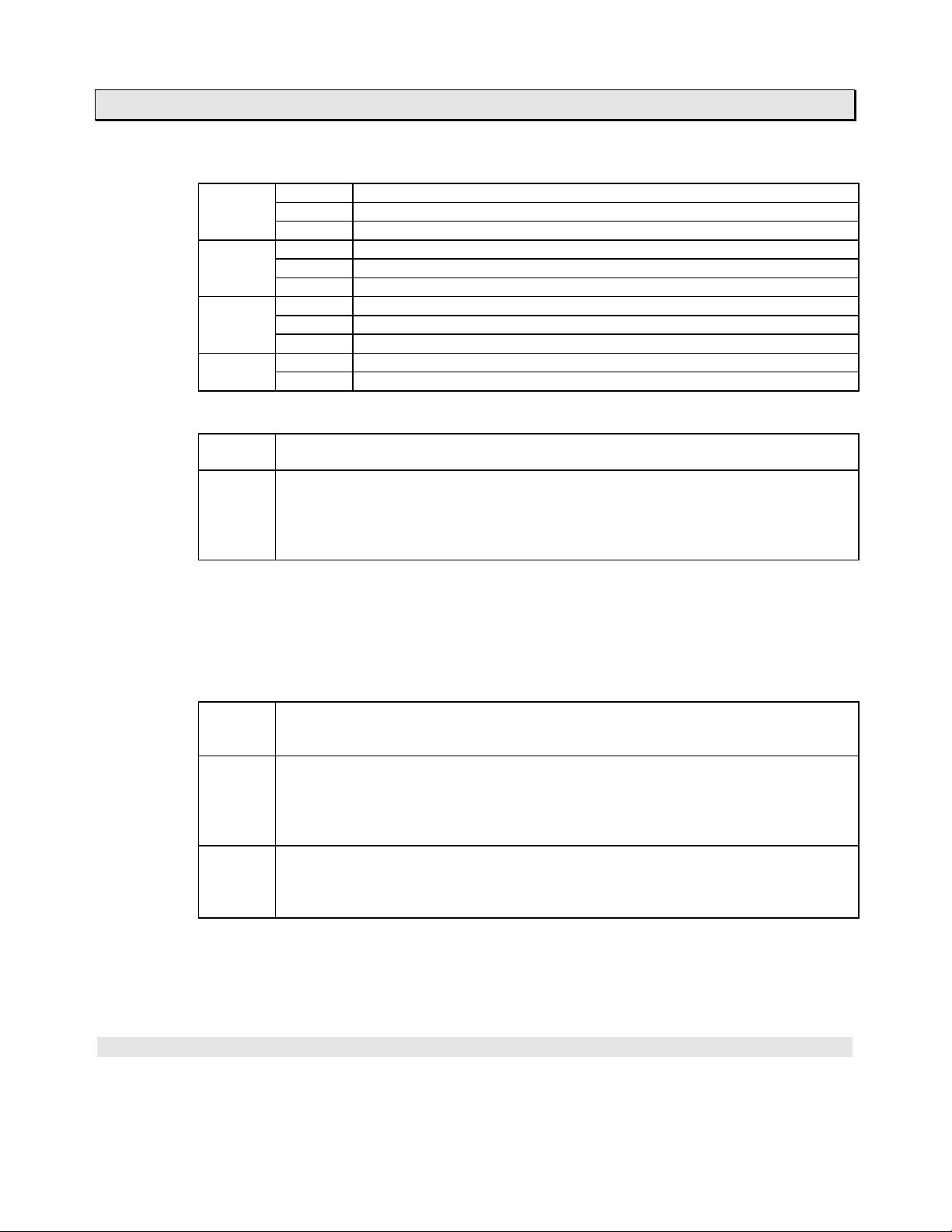
1. T3H Overview
Status LEDs:
RUN Lit User program is being executed (RUN mode)
(green) Blink User program execution is stopped (HOLD mode)
Not lit User program execution is stopped (HALT or ERROR mode)
FAULT Lit CPU or program error
(red) Blink Hardware initialization error
Not lit Normal
I/O Lit I/O error
(red) Blink Hardware initialization error
Not lit Normal
BATT Lit Battery voltage is normal
(green) Not lit Battery voltage is low (battery replacement is required)
RAM/ROM switch:
RAM User program stored in RAM is used.
(Program transfer from EEPROM to RAM is not executed)
ROM At the beginning of RUN mode, user program stored in EEPROM is transferred to
RAM. (It is called Initial load)
If an IC memory card which contains user program has been installed, the IC
memory card becomes transfer source.
(If mode control switch is in P-RUN, the initial load is not executed)
Note) In case of T3, the RAM/ROM switch has the function of auto-RUN/standby
selection in addition to the initial load selection.
However, in case of T3H, the RAM/ROM switch only has the function of initial
load selection as mentioned above.
Mode control switch:
HALT User program execution is stopped. (HALT mode)
Normally, programming is performed in the HALT mode.
T3H operation mode control by programmer is not allowed.
RUN T3H executes user program cyclically. (RUN mode)
It is the normal switch position under operation.
Even in the RUN mode, program changes are possible. However, saving into the
EEPROM is available only in the HALT mode.
T3H operation mode control by programmer is possible.
P-RUN T3H executes user program cyclically. (RUN mode)
User program and the leading 4 k words of D register (D0000 to D4095) are writeprotected.
T3H operation mode control by programmer is possible.
Note) In case of T3, even in P-RUN, data writing into D0000 to D4095 by instruction
is allowed except for some instructions.
However, in case of T3H, data writing into D0000 t o D4095 by instr uction is
inhibited if in P-RUN.
User’s Manual
13
Page 16

1. T3H Overview
Battery cover:
A battery has been installed inside this cover at the factory shipment. The battery
keeps the RAM contents (user program and user dat a) , and supports the clockcalendar operation during power off .
The same battery as the T3’s is used.
Programmer port:
The programmer (T-PDS) is connected to the T3H thr ough this port.
The same connection cable as the T3’s is used.
Computer link port:
The T3H CPU module has the computer link function as standard. This por t is used to
connect between T3H and a computer.
The T-series computer link pr ot ocol is supported by T3H.
IC memory card slot:
Optional IC memory card (type: ME914) can be used with the T3H.
By using the IC memory card, user progr am saving/ loading or user data expansion is
available.
NOTE
For details of the operation mode and functions, refer to t he T3 User’s
Manual.
PROSEC T3H
14
Page 17
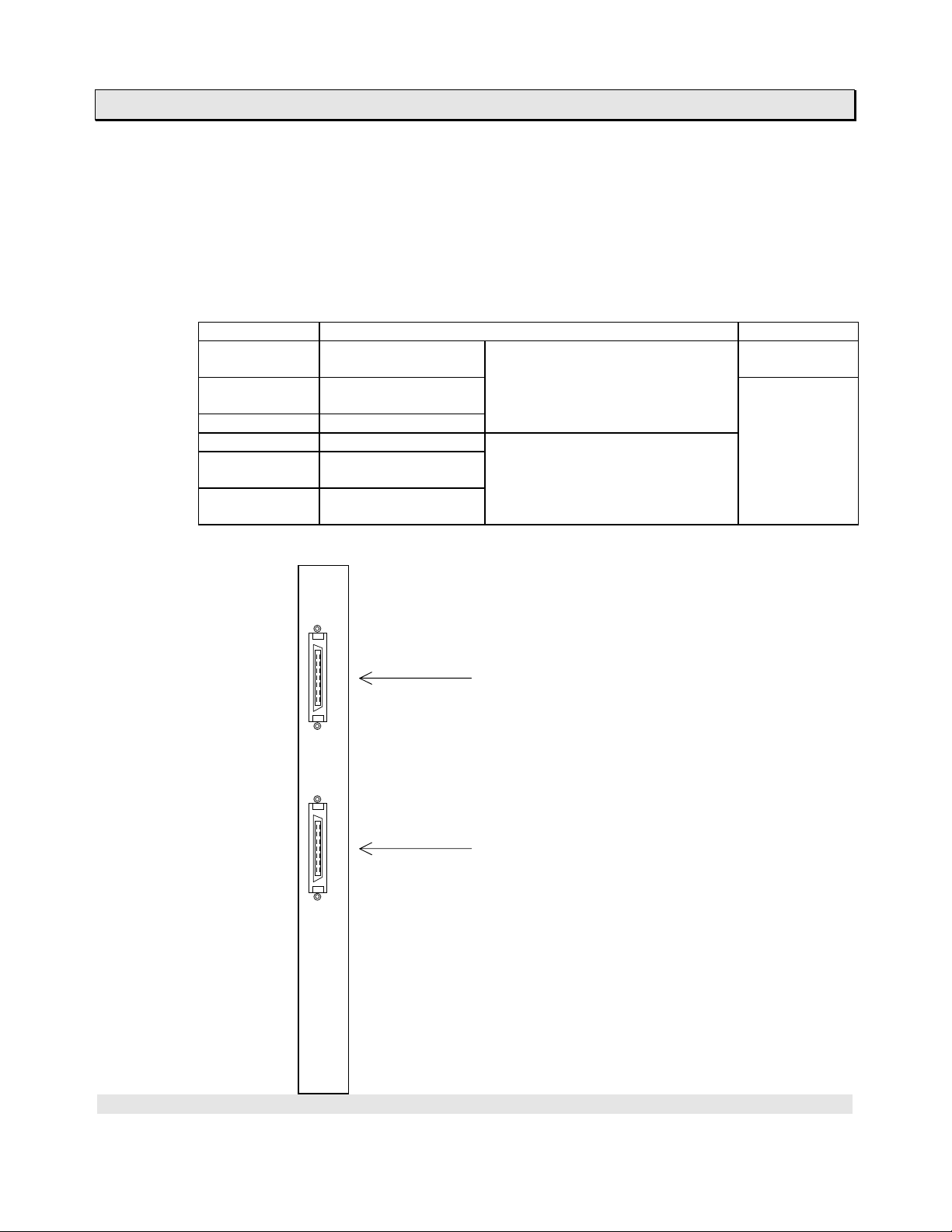
1. T3H Overview
(2) Expansion interface module
The expansion interface modules for t he T3, i.e. IF311, IF351, I F312, I F352 and
IF353, are also used with the T3H. When the IF311 or IF312 is used with the T3H, up
to three expansion units can be connected, as same as the T3.
On the other hand, the IF321 is a dedicated expansion interface module for the T3H.
When the IF321 is used instead of the IF311, up to 6 expansion units can be
connected. In the maximum configuration, the T3H can control up to 76 I/O modules.
Type Description Remarks
IF321 For basic unit
(2 channels)
IF311 For basic unit
(1 channel)
IF351 For expansion unit
IF312 For basic unit Long-distance expansion type.
IF352 For middle expansion
unit
IF353 For end expansion
unit
IF321
Standard expansion type.
2 m max. between units, 6 m
max. in total cable length for each
channel.
40 m max. in cable length.
(one channel only)
Only for T3H
T3/T3H
common
Channel 2 expansion
(connected to the expansion #4)
CH2
Channel 1 expansion
(connected to the expansion #1)
CH1
User’s Manual
15
Page 18
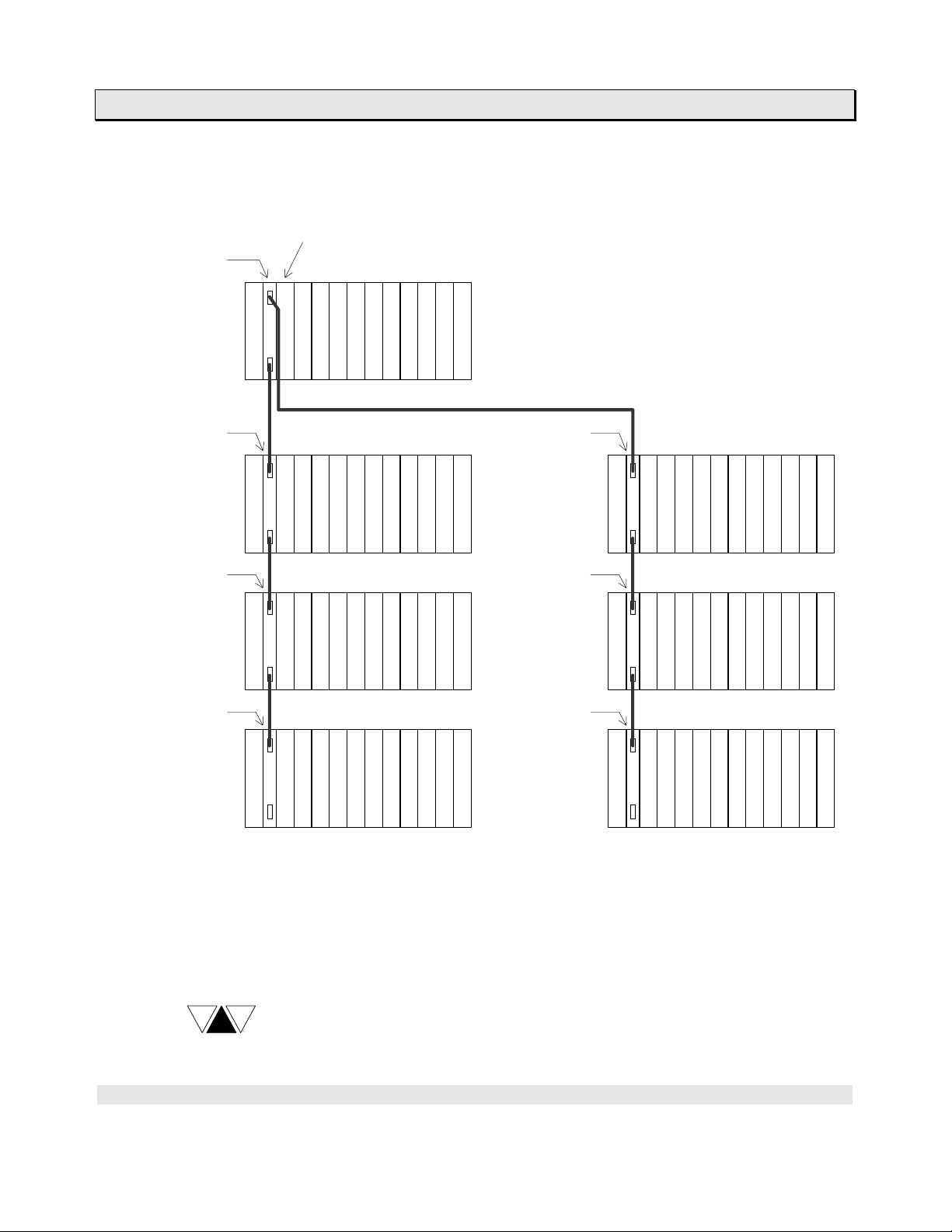
1. T3H Overview
The figure below shows the T3H’s maximum expansion configuration.
T3H CPU
IF321
IF351
IF351
CH1
Basic unit
P
C
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
S
P
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
I
U
O
O
O
O
O
O
F
O
/
O
O
O
IF: Expansion interface module
CPU: CPU module
I/O: I/O module or
data transmission module
CH2
PS: Power supply module
Expansion unit #1
P
S
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
I
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
F
O
/
O
O
O
Expansion unit #2
P
S
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
I
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
F
O
/
O
O
O
IF351
IF351
Expansion unit #4
P
S
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
I
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
F
O
/
O
O
O
Expansion unit #5
P
S
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
I
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
F
O
/
O
O
O
IF351
P
S
I
F
Expansion unit #3
I
I
I
I
/
/
/
/
O
O
O
O
O
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
O
O
O
O
O
O
IF351
Expansion unit #6
P
S
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
I
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
F
O
/
O
O
O
In this configuration, the T3H can handle up to 76 I/O modules. If 64 points I/O
modules are mounted on all the I/O slots (76 slots), the T3H can control up to 4864
points of discrete I/O.
NOTE
The unit configuration using other expansion interface modules are t he
same as that of T3. Refer to the T3 User’s Manual.
PROSEC T3H
16
Page 19
1. T3H Overview
(3) Power supply module
The power supply module for the T3 is also used with the T3H. The following two
types are available depending on power voltage.
Type Rated voltage Frequency
PS361 100 - 120 Vac/200 - 240 Vac (selectable) 50/60 Hz
PS332 24 Vdc
NOTE
For details, refer to the T3 User’s Manual.
(4) Rack
The rack (base board) f or the T3 is also used with the T3H. The f ollowing four types
are available.
Type Number of slot Use
BU31A 1 for PS, 1 for IF, 1 for CPU, 10 for I/O’s For basic unit
BU315 1 for PS, 1 for IF, 1 for CPU, 5 for I/O’s
BU35B 1 for PS, 1 for IF, 11 for I/O’s For expansion
BU356 1 for PS, 1 for IF, 6 for I/O’s unit
NOTE
For details, refer to the T3 User’s Manual.
(5) Expansion cable
The following types of the expansion cables are available.
Type Cable length Remarks
CS3R5 0.5 m For standard expansion.
CS301 1 m With both-end connectors (50-pin)
CS302 2 m
CL3R5 0.5 m For long-distance expansion.
CL301 1 m With both-end connectors (68-pin)
CL305 5 m
CL310 10 m
CL320 20 m
CL340 40 m
NOTE
For details, refer to the T3 User’s Manual.
−
User’s Manual
17
Page 20
1. T3H Overview
(6) I/O module
The following types of I/O modules are available.
Type Description
DI334 DC input 32 points input (8 points/common), 12 to 24 Vdc,
DI334H 32 points input (8 points/common), 12 to 24 Vdc,
DI335 64 points input (8 points/common), 24 Vdc, 5 mA/point
DI335H 64 points input (8 points/common), 24 Vdc, 5 mA/point,
IN354 AC input 32 points input (8 points/common), 100 to 120 Vac,
IN364 32 points input (8 points/common), 200 to 240 Vac,
DO333 DC output 16 points output (8 points/common), 12 to 24 Vdc,
DO334 32 points output (16 points/common), 12 to 24 Vdc,
DO335 64 points output (8 points/common), 5 to 24 Vdc,
AC363 AC output 16 points output (8 points/common), 100 to 240 Vac,
AC364 32 points output (16 points/common), 100 to 240 Vac,
RO364 Relay
RO363S 16 points output (isolated contact), 240 Vac/24 Vdc,
AD368 Analog
DA364
DA374 4 channels analog output, 0 - 20 mA or 4 - 20 mA,
PI312 Special
AS311 Communication interface, 2 port of RS-232C/RS-422,
CD332 Change detect DC input, 8 points input, 12 to 24 Vdc,
NOTE
10 mA/point
10 mA/point, high-speed response
(connector type)
high-speed response (connector type)
10 mA/point
10 mA/point
2 A/point, 5 A/common
0.5 A/point, 5 A/common
0.1 A/point (connector type)
2 A/point, 5 A/common
0.5 A/point, 3.2 A/common, 5 A/module
32 points output (8 points/common), 240 Vac/24 Vdc,
output
I/O
I/O
2 A/point, 5 A/common
2 A/point
8 channels analog input, ±5 V, ±10 V, 0 - 5 V, 0 - 10 V,
1 - 5 V, ±20 mA, 0 - 20 mA, or 4 - 20 mA, 12-bit resolution
4 channels analog output, ±5 V, ±10 V, 0 - 5 V, 0 - 10 V, or
1 - 5 V, 12-bit resolution
12-bit resolution
2 channel pulse input, 5/12 V, 50 kHz (max.), 24-bit counter,
interrupt function
full-duplex, ASCII code, no protocol, 300 / 600 / 1200 / 2400 /
4800 / 9600 / 19200 bps
10 mA/point, interrupt function
For detailed specifications, refer to the T3 User’s Manual.
PROSEC T3H
18
Page 21
1. T3H Overview
(7) Data transmission module
The following types of data transmission modules are available.
Type Description Remarks
EN311 Ethernet 10BASE5 or 10BASE2, 10 Mbps,
computer link, T3H to T3H, and socket
service
SN321 TOSLINE-S20 High-speed Co-axial T3/T3H
SN322 control data Optical common
SN323 link, 2 Mbps Co-axial/optical
SN325 TOSLINE-S20LP High-speed control data link, 2 Mbps,
4 k words scan memory, optical loop
MS311 TOSLINE-F10 Field network, Master station T3/T3H
RS311 750 k bps Remote station common
NOTE
(1) Maximum number of modules available on one T3H is as follows.
Ether net : 4
TOSLINE-S20 and S20LP total: 2
TOSLINE-F10: 8
(2) Ethernet module and T O SLINE-S20LP are under development.
(8) Module internal current consumption
The table below shows the internal 5 Vdc current consumption (max. value) of each
T3H module. Use this data to check the power capacity.
Type Internal 5 Vdc
consumption
CPU PU325H 1.5 A AC output AC363 530 mA
PU326H 1.5 A AC364 800 mA
Expansion I/F IF321 40 mA Relay output RO364 170 mA
IF311 20 mA RO363S 100 mA
IF351 20 mA Analog input AD368 450 mA
IF312 800 mA Analog output DA364 180 mA
IF352 700 mA DA374 180 mA
IF353 700 mA Pulse input PI312 800 mA
DC input DI334 100 mA ASCII AS311 1.0 A
DI334H 100 mA Change detect CD332 300 mA
DI335 170 mA Ethernet EN311 700 mA
DI335H 170 mA TOSLINE-S20 SN321 800 mA
AC input IN354 120 mA SN322 800 mA
IN364 120 mA SN323 800 mA
DC output DO333 320 mA TOSLINE-S20LP SN325 800 mA
DO334 210 mA TOSLINE-F10 MS311 600 mA
DO335 400 mA RS311 600 mA
Type Internal 5 Vdc
Only for T3H
Only for T3H
consumption
User’s Manual
19
Page 22
1. T3H Overview
1.4 Specifications Functional specifications
Type PU325H PU326H
Control method Stored program, cyclic scan system
Scan system Floating scan or constant scan (10 - 200 ms, 10 ms units)
I/O update Batch I/O refresh (direct I/O instruction available)
Program memory Main memory: RAM (battery backed)
Program capacity 32 k steps 64 k steps
Programming language Ladder diagram with function block,
Instructions Ladder Basic instructions: 24 types,
SFC Step, transition, sequence selection, simultaneous
Execution speed
Multitasking 1 Main program
I/O capacity 2432 points (using 32 points I/O modules)
User data Auxiliary relay 16000 points / 1000 words (R/RW)
Special relay 4096 points / 256 words (S/SW)
Timer 1000 points (T./T)
Counter 512 points (C./C)
Data register 8192 words (D)
Link register 16000 points / 2048 words (Z/W) (for TOSLINE-S20)
Link relay 4096 points / 256 words (L/LW) (for TOSLINE-F10)
File register 32768 words (F)
Index register 3 words (I, J, K)
Retentive memory F register and user defined ranges of RW, T, C, D
RAS Self-diagnosis Power interruption, main/expansion power failure,
Monitoring Event history record, scan time measurement, others
Debugging On-line trace monitor, force, sampling trace, status latch,
RAM data back-up
Auxiliary memory: EEPROM (built-in), IC card (option)
SFC (sequential function chart)
Function instructions: 206 types
sequences, jump, etc.
0.09 µs/contact, 0.18 µs/coil,
0.54 µs/transfer, 0.90 µs/addition
4 Sub-program
1 Timer interrupt (1 - 1000 ms, 1 ms units)
8 I/O interrupt (task switch 500 µs or less)
256 Subroutine
4864 points (using 64 points I/O modules)
Local I/O space: 8192 points / 512 words
(X/XW and Y/YW: batch I/O)
(I/IW and O/OW: direct I/O)
(proportion of 0.01s and 0.1s timer is user definable)
(leading 4096 words are stored in EEPROM)
CPU/RAM/ROM check, I/O response, I/O bus check, I/O
registration, I/O parity, battery level, watch dog timer,
program check, others
single step/N scan execution, break point, others
Lithium battery (type: TBT911∗AS)
Recommended replacement: every 2 years
PROSEC T3H
20
Page 23

1. T3H Overview
Instruction execution speed
FUN
No.
NO contact
NC contact
Transitional contact
(rising) Subtraction
Transitional contact
(falling) Multiplication
Coil -( )┤ 0.18 34 Double-word D/ 9.85
Forced coil
Inverter
Invert coil -( I )┤ 0.18 36 Subtraction with −C 6.29
Positive pulse
contact 37 Double-word D+C 7.21
Negative pulse
contact 38 Double-word D−C 7.21
Positive pulse coil -( P )┤ 0.36 subtraction with
Negative pulse coil -( N )┤ 0.36 carry
Jump control set JCS 0.09 39 Unsigned U∗ 7.37
Jump control reset JCR 0.09 multiplication
End END
ON-delay timer TON 0.18 41 Unsigned double/ DIV 8.67
OFF-delay timer TOF 0.18 single division
Single-shot timer SS 0.18 42 Double-word D∗/ 61.07
Counter CNT 0.18 multiplication and
Master control set MCS 0.09 division
Master control reset MCR 0.09 43 Increment +1 3.23
18 Data transfer MOV 0.54 44 Double-word D+1 4.11
19 Double-word data DMOV 4.14 increment
transfer 45 Decrement
20 Invert transfer NOT 3.6 46 Double-word D−1 4.11
21 Double-word invert DNOT 4.32 decrement
transfer 48 AND AND 4.84
22 Data exchange XCHG 6.12 49 Double-word AND DAND 5.92
23 Double-word data DXCH 7.56 50 OR OR 4.84
exchange 51 Double-word OR DOR 5.92
24 Table initialization TINZ
+0.37n 53 Double-word DEOR 5.92
25 Table transfer TMOV 24.32 Exclusive OR
+0.49n 54 Not exclusive OR ENR 4.84
26 Table invert transfer TNOT 24.44 55 Double-word DENR 5.92
+0.58n Not exclusive OR
27 Addition + 0.9 57 Table AND TAND 23.31
28 Subtraction
29 Multiplication
30 Division / 4.59 +0.72n
Name Symbol Execution
time (µs)
┤ ├
0.09 31 Double-word D+ 6.1
┤/├
0.09 addition
┤↑├
0.36 32 Double-word D− 6.1
┤↓├
0.36 33 Double-word D∗ 6.22
×
-( )┤ 0.09 division
┤I├
0.09 35 Addition with carry +C 6.29
┤P├
0.36 carry
┤N├
0.36 addition with carry
−
15.5
−
0.9 +0.72n
∗
2.61 58 Table OR TOR 23.31
FUN
No.
40 Unsigned division U/ 7.77
52 Exclusive OR EOR 4.84
Name Symbol Execution
time (µs)
−
1 3.23
User’s Manual
21
Page 24

1. T3H Overview
Instruction execution speed (continued)
FUN
No.
59 Table Exclusive OR TEOR 23.31 83 m bit file n bit rotate TRTL (Word)
+0.72n left 16.21
60 Table Not exclusive TENR 23.31 +0.46n
OR +0.72n +0.45m
64 Bit test TEST 3.76 (Bit)
65 Double-word bit test DTST 4.68 23.15
66 Bit file bit test TTST 8.98 +0.12n
68 1 bit shift right SHR1 4.12 +0.06m
69 1 bit shift left SHL1 4.68 84 1 bit rotate right with RRC1 4.69
70 n bit shift right SHR 4.77 carry
+0.27n 85 1 bit rotate left with RLC1 4.15
71 n bit shift left SHL 5.33 carry
+0.27n 86 n bit rotate right with RRC 4.59
72 m bit file n bit shift TSHR (Word) carry +0.81n
right 14.59 87 n bit rotate left with RLC 5.44
-0.08n carry +0.72n
+0.45m 88 m bit file n bit rotate TRRC (Word)
(Bit) right with carry 16.24
21.3 +0.43n
-0.02n +0.45m
+0.06m (Bit)
73 m bit file n bit shift TSHL (Word) 25.49
left 14.96 +0.12n
-0.09n +0.05m
+0.45m 89 m bit file n bit rotate TRLC (Word)
(Bit) left with carry 16.21
21.44 +0.46n
-0.04n +0.45m
+0.06m (Bit)
74 Shift register SR 16.21 28.55
+0.11n +0.07n
75 Bi-directional shift DSR 16.42 +0.05m
register +0.14n 90 Multiplexer MPX 9.74
76 Device shift SFT 12.82 91 Demultiplexer DPX 8.86
78 1 bit rotate right RTR1 4.31 92 Table bit transfer TBM 12.44
79 1 bit rotate left RTL1 4.15 93 Bit table transfer BTM 11.54
80 n bit rotate right RTR 5.49 95 Bit file compare TCMP 18.03
+0.1n 96 Greater than > 3.76
81 n bit rotate left RTL 5.11 97 Greater than or >= 3.76
+0.1n equal
82 m bit file n bit rotate TRTR (Word) 98 Equal = 3.76
right 16.23 99 Not equal <> 3.76
+0.45n 100 Less than < 3.76
+0.45m 101 Less than or equal <= 3.76
(Bit) 102 Double-word greater D> 4.84
23.1 than
+0.12n 103 Double-word greater D>= 4.48
+0.06m than or equal
Name Symbol Execution
time (µs)
FUN
No.
Name Symbol Execution
time (µs)
PROSEC T3H
22
Page 25

1. T3H Overview
Instruction execution speed (continued)
FUN
No.
104 Double-word equal D= 4.48 134 Master control set n MCSn 4.9
105 Double-word not D<> 4.48 135 Master control reset MCRn
equal n
106 Double-word less D< 4.84 136 Jump label LBL
than 137 Subroutine entry SUBR 0.18
107 Double-word less D<= 4.48 140 Enable interrupt EI 53.28
than or equal 141 Disable interrupt DI 52.88
108 Unsigned greater U> 3.76 142 Interrupt return IRET
than 143 Watch dog timer WDT 62.78
109 Unsigned greater U>= 3.76 reset
than or equal 144 Step sequence STIZ 5.0
110 Unsigned equal U= 3.76 initialize +0.02n
111 Unsigned not equal U<> 3.76 145 Step sequence input STIN 3.22
112 Unsigned less than U< 3.76 146 Step sequence STOT 5.67
113 Unsigned less than U<= 3.76 output +2.44n
or equal 147 Flip-flop F/F 3.78
114 Device/register set SET (Device) 148 Timer trigger TRG 2.89
3.6 149 Up/down counter U/D 2.26
(Register) 150 Diagnostic display DIAG 10.98
2.32 +0.02n
115 Device/register RST (Device) 151 Diagnostic reset DIAR 6.41
reset 3.6 +1.31n
(Register) 152 Status latch set STLS 320.48
2.52 +12.94n
116 Table bit set TSET 9.42 153 Status latch reset STLR 47.18
117 Table bit reset TRST 9.62 154 Set calendar CLND 201.98
118 Set carry SETC 1.26 155 Calendar operation CLDS 382.48
119 Reset carry RSTC 1.26 156 Essential PID PID3
120 Encode ENC 19.55 158 Drum sequencer DRUM 16.46
+2.91n +0.02m
121 Decode DEC 10.68 159 Cam sequencer CAM 9.88
+2.48n +4.62n
122 Bit count BC 10.56 160 Upper limit UL 5.04
123 Double-word bit DBC 18.16 161 Lower limit LL 5.04
count 162 Maximum value MAX 8.89
124 Data search SCH 12.47 +0.72n
+0.9n 163 Minimum value MIN 8.89
125 Push PUSH 9.99 +0.81n
+0.47n 164 Average value AVE 9.79
126 Pop last POPL 10.9 +1.03n
+0.46n 165 Function generator FG 10.09
127 Pop first POPF 11.46 +1.14n
128 Subroutine call CALL 9.24 166 Dead band DB 6.12
129 Subroutine return RET 167 Square root RT 80.26
130 Jump JUMP 3.24 168 Integral INTG 17.64
132 Loop FOR FOR 6.17
133 Loop NEXT NEXT +2.71n 170 PID PID 17.78
Name Symbol Execution
time (µs)
FUN
No.
169 Ramp function RAMP 12.24
Name Symbol Execution
time (µs)
−
−
User’s Manual
23
Page 26

1. T3H Overview
Instruction execution speed (continued)
FUN
No.
171 Deviation square PID2 25.28 203 Double-word BCD DB−C 48.12
PID subtraction with
172 Sine function SIN 14.94 carry
173 Cosine function COS 15.44 204 Floating point FLT 5.03
174 Tangent function TAN 4.24 conversion
175 Arc-sine function ASIN 4.64 205 Fixed point FIX 5.03
176 Arc-cosine function ACOS 5.04 conversion
177 Arc-tangent function ATAN 192.28 206 Floating point FABS 4.5
178 Exponential function EXP 169.28 absolute value
179 Logarithm LOG 217.28 207 Floating point sign FNEG 4.68
180 Absolute value ABS 3.76 inversion
181 Double-word DABS 4.32 208 Floating point F+ 14.44
absolute value addition
182 2’s complement NEG 3.6 209 Floating point F− 14.82
183 Double-word 2’s DNEG 4.68 subtraction
complement 210 Floating point F∗ 12.08
184 Double-word DW 4.12 multiplication
conversion 211 Floating point F/ 12.06
185 7-segment decode 7SEG 3.76 division
186 ASCII conversion ASC 9.29 212 Floating point F> 7.2
+0.33n greater than
188 Binary conversion BIN 13.86 213 Floating point F>= 7.2
189 Double-word binary DBIN 32.58 greater than or
conversion equal
190 BCD conversion BCD 13.86 214 Floating point equal F= 6.31
191 Double-word BCD DBCD 13.52 215 Floating point not F<> 6.31
conversion equal
192 BCD addition B+ 25.26 216 Floating point less F< 7.22
193 BCD subtraction B− 25.26 than
194 BCD multiplication B∗ 39.66 217 Floating point less F<= 7.18
195 BCD division B/ 34.86 than or equal
196 Double-word BCD DB+ 48.86 218 Floating point upper FUL 8.46
addition limit
197 Double-word BCD DB− 46.86 219 Floating point lower FLL 8.5
subtraction limit
198 Double-word BCD DB∗ 106.88 220 Floating point dead FDB 20.68
multiplication band
199 Double-word BCD DB/ 86.12 221 Floating point FRT 54.3
division square root
200 BCD addition with B+C 25.92 222 Floating point PID FPID 201.98
carry 223 Floating point FPID2 217.48
201 BCD subtraction B−C 26.12 deviation square
with carry PID
202 Double-word BCD DB+C 47.32 224 Floating point sine FSIN 129.08
addition with carry 225 Floating point FCOS 148.48
Name Symbol Execution
time (µs)
FUN
No.
cosine
Name Symbol Execution
time (µs)
PROSEC T3H
24
Page 27

1. T3H Overview
Instruction execution speed (cont’d)
FUN
No.
226 Floating point FTAN 259.48 SFC initialize 197.48
tangent SFC initial step 3.15
227 Floating point arc- FASIN 213.98 SFC step 1.2
sine SFC end step 1.26
228 Floating point arc-
cosine SFC wait step 3.81
229 Floating point arc- FATAN 189.98 SFC alarm step 4.32
tangent SFC transition 2.24
230 Floating point FEXP 141.08 SFC end 2.61
exponential SFC jump 3.21
231 Floating point FLOG 206.98 SFC macro end 2.61
logarithm SFC label 4.4
232 Floating point FPID3 SFC macro entry 1.2
essential PID SFC sequence selection 2.58
235 Direct I/O I/O *1 Divergence (I)
236 Expanded data XFER *2 SFC sequence selection 2.58
transfer Divergence (II)
237 Special module data READ *3 SFC sequence selection 2.31
read Divergence (III)
238 Special module data WRITE *4 SFC sequence selection 0.09
write Convergence
239 Network data send SEND SFC simultaneous 0.09
240 Network data RECV sequences Divergence
receive SFC simultaneous 2.07
241 SFC initialize SFIZ 6.95 sequences Convergence (I)
+0.05n SFC simultaneous 3.52
sequences Convergence (II)
*1 I/O: 6.8+3.05n (Basic unit)
6.45+7.93n (Expansion unit)
*2 XFER: 286.48+4.5n (register → S20 on basic unit)
302.46+9.02n (register → S20 on expansion unit)
394.69+7.49n (S20 on basic unit → register)
417.97+9.51n (S20 on expansion unit → register)
252.44+1.54n (register → EEPROM)
185.88+1.58n (EEPROM → register)
186.75+1.53n (register → IC card)
185.3+1.58n (IC card → register)
179.99+1.09n (register → register)
*3 READ: 261.01+9.97n (Basic unit)
280.62+12.86n (Expansion unit)
*4 WRITE: 252.04+9.93n (Basic unit)
278.57+12.91n (Expansion unit)
Name Symbol Execution
time (µs)
FACOS
221.98 SFC macro step 3.96
FUN
No.
Name Execution
time (µs)
User’s Manual
25
Page 28

1. T3H Overview
NOTE
When index modification, digit designation or direct I/O register (IW/OW) is
used for an operand, the additional time is r equired per one operand as
shown below.
operand modification (µs)
Index modification 5.4 6.7 6.7
Digit designation 6.0 10.0 11+3.0(n+1)
Direct I/O Basic unit 4.3 7.2 3+3.5n
Expansion unit 8.8 16.2 3+8.0n
Direct I/O with Basic unit 14.6 22.3 14+6.26(n+1)
digit designation Expansion unit 23.6 35.8 14+10.76(n+1)
Additional time by Operand format
Single Double Table
PROSEC T3H
26
Page 29

Section 2
Expanded Functions
2.1 System operation, 28
2.2 Expanded registers, 30
2.3 Network support function, 38
2.4 Instructions, 43
User’s Manual
27
Page 30

2. Expanded Functions
2.1 System operation
2.1.1 Auto-RUN / Standby selection
The initial operation mode (HALT or RUN) just after power on is determined by the
user-setting status of the Auto-RUN / Standby selection.
When the setting status is;
Auto-RUN: The T3H’s initial operation mode is determined by the mode cont rol
switch (HALT / RUN / P-RUN) . When this switch is in RUN or P- RUN,
the T3H moves into RUN mode aut om atically.
Standby: The T3H stays in HALT mode regardless of the mode control switch
(HALT / RUN / P-RUN) after power on. Then the operation m ode can be
changed manually, i.e. by progr am m er command or by changing the
mode control switch.
The Auto-RUN / Standby selection is included in the system information memory, and
the selection is made by using the programm er .
NOTE
(1) The default set ting is Standby.
(2) Differ ent from the T3H, in case of the T3, this selection is made by the
har dware switch (RAM/ROM switch).
2.1.2 Timer interrupt interval
In the T3H, the timer int e r r upt program is available with the interval setting of 1 to
1000 ms in 1 ms increments.
(In case of the T3, it is 2 t o 1000 m s in 1 m s incr ements)
NOTE
In case of the T3H, SFC (Sequential Function Chart) can also be program m ed on the
interrupt program, as well as Ladder diag r am.
If you use the timer interrupt with 1 ms interval, consider to minimize the
execution time of the timer inter r upt program. If t he interrupt task requir es
long time, the T3H cannot assig n enough time for main program execution.
As the result, scan time over error will occur.
PROSEC T3H
28
Page 31

2.1.3 Saving the sampling trace condition
The sampling trace function is available on the T3H as well as the T3. In addition to
all the sampling trace funct ions on the T3, the T3H can save the sampling tr ace
condition into the IC memory card. By using this function, the sampling trace dat a
which is collected and saved in the IC memory card on one T3H can be displayed
using other T3H via the IC memory card.
This function is used as follows.
T3H which performs sampling (data collection):
• Install the IC memory card in the T3H CPU module.
• Set MMR for the PU slot in the I/O allocation in order to use an IC memory card for
sampling data storage.
• Set the special device S0620 to ON.
• Edit the sampling trace condition. The edited condition is also saved into the IC
memory card.
• Execute the sampling trace. The sampling data is saved into the IC memory card.
• Remove the IC memory card.
T3H which is used to display the sampling data stored in the IC mem ory card:
• Install the IC memory card in which the sampling trace data is stored.
• Set MMR for the PU slot in the I/O allocation in order to use an IC memory card for
sampling trace function.
• Monitor the sampling trace condition. T he condit ion st or ed in the IC memory card
is displayed.
• Display the sampling trace data. The sampling data stored in the IC memor y card
is displayed.
NOTE
To copy the sampling data stored in the T 3H’s file register to an IC mem or y
card, set the special device S0620 to ON and display the sampling trace
condition. By this operation, the sampling t r ace condit ion and t he sam pling
data stored in file register ar e copied into the IC memory card.
2. Expanded Functions
User’s Manual
29
Page 32

2. Expanded Functions
2.2 Expanded registers
The T3H has the same types of reg ister s as the T3. However, the address ranges of
some registers are expanded in the T3H.
This section explains the expanded registers and the notes.
NOTE
For details of functions of each register/device, refer to the T3 User’s
Manual.
2.2.1 External I/O register
The T3H can handle up to 76 I/O modules. Accordingly, the T3H has 512 words of
external I/O register.
Function type Type
Input register X W XW280
Output register YW 000 - 511 Total 512 words YW412
Direct input register IW IW280
Direct output register OW OW412
Input device X X280A
Output device Y 0000 - 511F Total 8192 points Y4128
Direct input device I I2809
Direct output device O O412C
Regarding the I/O allocation, the channel 1 of the IF321 is assigned to Unit 1 to 3,
and the channel 2 of the IF321 is assigned to Unit 4 t o 6. The XW/YW r egisters are
assigned in the sequence of Unit 0 → 1 → ... → 6.
2.2.2 Auxiliary register
The T3H has 1000 words of auxiliary register.
Function type Type
Auxiliary register RW 000 - 999 1000 words RW725
Auxiliary device R 000 - 999F 16000 points R725B
code
code
Address range Quantity Expression
example
Address range Quantity Expression
example
PROSEC T3H
30
Page 33

2.2.3 Timer
The T3H has 1000 points of timer .
Function type Type
Timer register T 000 - 999 1000 words T670
Timer device T. 000 - 999 1000 point s T.670
The proportion of the 0.01 s base and t he 0. 1 s base timers within this 1000 points
can be specified by user. This setting information is stored in the system inf or mation.
10 ms Timer Range Setting :
T000 - T [ ] User setting (max. 999)
NOTE
T3H internally, the register r anges T000 to T511 and T512 to T 999 are
handled separately. Therefore, index modification or table designation
across these ranges are not allowed.
For example)
├─
[ T450 TMOV (100) D1000 ]- Not allowed
├─
[ T450 TMOV (62) D1000 ]- Allowed
│
├─
[ T512 TMOV (38) D1062 ]-
2.2.4 Link register
The T3H has 2048 words of link reg ist er . This link register is prepared for the
TOSLINE-S20 (here called S20).
Function type Type
Link register W 0000 - 2047 2048 words W1500
Link device Z 0000 - 999F 16000 points Z847E
The link device Z corresponds to a bit in a link register W . The bit access as Z device
is available for the leading 1000 words of W register.
2. Expanded Functions
Address range Quantity Expression
code
Address range Quantity Expression
code
example
example
User’s Manual
31
Page 34

2. Expanded Functions
Regarding the network assignment, the W register is divided into 32 blocks.
(64 words per one block)
The S20 has 1024 words of scan memory. In case of the T3H, even if two S20’s are
used, the scan memory of each S20 can be fully mapped t o t he W regist er . Channel
1 S20 is allocated to the blocks 1 to 16, and channel 2 S20 is allocated t o the blocks
17 to 32.
The allocation example below shows the case of all the blocks are set as “LINK”.
T3H’s link register Block Setting CH1 S20 CH2 S20
W CH1 CH2 sca n memory scan memory
W0000 - W0063 1 LINK 0000 - 0063
W0064 - W0127 2 LINK 0064 - 0127
W0128 - W0191 3 LINK 0128 - 0191
W0192 - W0255 4 LINK 0192 - 0255
W0256 - W0319 5 LINK 0256 - 0319
W0320 - W0383 6 LINK 0320 - 0383
W0384 - W0447 7 LINK 0384 - 0447
W0448 - W0511 8 LINK 0448 - 0511
W0512 - W0575 9 LINK 0512 - 0575
W0576 - W0639 10 LINK 0576 - 0639
W0640 - W0703 11 LINK 0640 - 0703
W0704 - W0767 12 LINK 0704 - 0767
W0768 - W0831 13 LINK 0768 - 0831
W0832 - W0895 14 LINK 0832 - 0895
W0896 - W0959 15 LINK 0896 - 0959
W0960 - W1023 16 LINK 0960 - 1023
W1024 - W1087 17 LINK 0000 - 0063
W1088 - W1151 18 LINK 0064 - 0127
W1152 - W1215 19 LINK 0128 - 0191
W1216 - W1279 20 LINK 0192 - 0255
W1280 - W1343 21 LINK 0256 - 0319
W1344 - W1407 22 LINK 0320 - 0383
W1408 - W1471 23 LINK 0384 - 0447
W1472 - W1535 24 LINK
W1536 - W1599 25 LINK 0512 - 0575
W1600 - W1663 26 LINK 0576 - 0639
W1664 - W1727 27 LINK 0640 - 0703
W1728 - W1791 28 LINK 0704 - 0767
W1792 - W1855 29 LINK 0768 - 0831
W1856 - W1919 30 LINK 0832 - 0895
W1920 - W1983 31 LINK 0896 - 0959
W1984 - W2047 32 LINK 0960 - 1023
-
-
0448 - 0511
PROSEC T3H
32
Page 35

2. Expanded Functions
When “GLOBAL” setting is used, the link r egisters of “GLOBAL” set ting block are
assigned to both CH1 and CH2 S20’s.
T3H’s link register Block Setting CH1 S20 CH2 S20
W CH1 CH2 sca n memory scan memory
-
W0192 - W0255 4 LINK 0192 - 0255
W0256 - W0319 5 GLOBAL 0256 - 0319 0256 - 0319
W0320 - W0383 6 GLOBAL 0320 - 0383 0320 - 0383
W0384 - W0447 7 GLOBAL 0384 - 0447 0384 - 0447
W0448 - W0511 8 GLOBAL 0448 - 0511 0448 - 0511
W0512 - W0575 9 LINK 0512 - 0575
W1216 - W1279 20 LINK 0192 - 0255
W1280 - W1343 21
-
W1344 - W1407 22
W1408 - W1471 23
W1472 - W1535 24
W1536 - W1599 25 LINK 0512 - 0575
• The blocks 1 - 16 are dedicated to the CH1 S20, and the blocks 17 - 32 are
dedicated to the CH2 S20.
It is not allowed to assign the blocks 1 - 16 t o CH2, and blocks 17 - 32 to CH1.
• For the blocks set as “LINK” or “GLOBAL”, the T3H performs data read fr om S20
(for data receive area) and data write to S20 ( for data send area).
The data transfer dir ect ion (read or write) is automatically decided by the T3H
according to the S20’s receive/send setting.
• For the blocks set as “GLO BAL” , the data transfer is as f ollows.
1) If CH1 is receive and CH2 is send;
CH1 receive data is read and written into both W register and CH2.
2) If CH1 is send and CH2 is receive;
CH2 receive data is read and written into both W register and CH1.
3) If both CH1 and CH2 are send;
W register data is written into both CH1 and CH2.
4) If both CH1 and CH2 are receive;
The receive data of “GLOBAL” set ting channel is read and stored in W register.
NOTE
In case of TOSLINE-S20LP, it has 4096 words of scan memory. The
leading 2048 words can be assigned straight to W register . The following
2048 words can be accessed by using XFER instruction.
-
-
User’s Manual
33
Page 36
2. Expanded Functions
2.2.5 File register
The T3H has 32768 words of file register in the CPU module.
Function type Type
File register F 0000 - 9999
For the address range F0000 to F9999, normal direct addressing is available as
follows.
─
[ D1000 MOV F9999 ]─
However, for the addresses F10000 and after, dir ect addr essing is not possible.
To use this address range with an instruction, the index modification must be used.
I
─
[ D1000 MOV F0000 ]─ If I=30000, D1000 data is transferred to F30000.
2.2.6 Special register
The T3H has 256 words of special register as sam e as the T3. However, within the
address range, some functions are added accor ding to function expansion of the
T3H.
The table below shows the added functions on the special register. They are not used
with the T3.
Special
device
S0500 I/O error map #4-0 ON when I/O error detected in unit 4 - slot 0
S0501 I/O error map #4-1 ON when I/O error detected in unit 4 - slot 1
S0502 I/O error map #4-2 ON when I/O error detected in unit 4 - slot 2
S0503 I/O error map #4-3 ON when I/O error detected in unit 4 - slot 3
S0504 I/O error map #4-4 ON when I/O error detected in unit 4 - slot 4
S0505 I/O error map #4-5 ON when I/O error detected in unit 4 - slot 5
S0506 I/O error map #4-6 ON when I/O error detected in unit 4 - slot 6
S0507 I/O error map #4-7 ON when I/O error detected in unit 4 - slot 7
S0508 I/O error map #4-8 ON when I/O error detected in unit 4 - slot 8
S0509 I/O error map #4-9 ON when I/O error detected in unit 4 - slot 9
S050A I/O error map #4-10 ON when I/O error detected in unit 4 - slot 10
S050B
S050C
S050D Reserve (for future use)
S050E
S050F
Address range Quantity Expression
code
example
32768 words F9000
(10000 - 32767)
Name Function
PROSEC T3H
34
Page 37

2. Expanded Functions
Special
device
S0510 I/O error map #5-0 ON when I/O error detected in unit 5 - slot 0
S0511 I/O error map #5-1 ON when I/O error detected in unit 5 - slot 1
S0512 I/O error map #5-2 ON when I/O error detected in unit 5 - slot 2
S0513 I/O error map #5-3 ON when I/O error detected in unit 5 - slot 3
S0514 I/O error map #5-4 ON when I/O error detected in unit 5 - slot 4
S0515 I/O error map #5-5 ON when I/O error detected in unit 5 - slot 5
S0516 I/O error map #5-6 ON when I/O error detected in unit 5 - slot 6
S0517 I/O error map #5-7 ON when I/O error detected in unit 5 - slot 7
S0518 I/O error map #5-8 ON when I/O error detected in unit 5 - slot 8
S0519 I/O error map #5-9 ON when I/O error detected in unit 5 - slot 9
S051A I/O error map #5-10 ON when I/O error detected in unit 5 - slot 10
S051B
S051C
S051D Reserve (for future use)
S051E
S051F
S0520 I/O error map #6-0 ON when I/O error detected in unit 6 - slot 0
S0521 I/O error map #6-1 ON when I/O error detected in unit 6 - slot 1
S0522 I/O error map #6-2 ON when I/O error detected in unit 6 - slot 2
S0523 I/O error map #6-3 ON when I/O error detected in unit 6 - slot 3
S0524 I/O error map #6-4 ON when I/O error detected in unit 6 - slot 4
S0525 I/O error map #6-5 ON when I/O error detected in unit 6 - slot 5
S0526 I/O error map #6-6 ON when I/O error detected in unit 6 - slot 6
S0527 I/O error map #6-7 ON when I/O error detected in unit 6 - slot 7
S0528 I/O error map #6-8 ON when I/O error detected in unit 6 - slot 8
S0529 I/O error map #6-9 ON when I/O error detected in unit 6 - slot 9
S052A I/O error map #6-10 ON when I/O error detected in unit 6 - slot 10
S052B
S052C
S052D Reserve (for future use)
S052E
S052F
Special
device
S0620 Sampling trace copy Used for saving sampling trace data (ON for active)
S0621
Reserve (for future use)
S062F
Special
register
SW067 Write protect for
SEND/RECV
Name Function
Name Function
Name Function
Used for setting write protect against SEND and
RECV instructions
User’s Manual
35
Page 38

2. Expanded Functions
Special
register
SW192 W1024 - W1039
SW193 W1040 - W1055 the W register is updated normally.
SW194 W1056 - W1071
SW195 W1072 - W1087
SW196 W1088 - W1103 corresponds to bit 0 in the SW
SW197 W1104 - W1119 register, and in the order.
SW198 W1120 - W1135
SW199 W1136 - W1151
SW200 W1152 - W1167
SW201 W1168 - W1183
SW202 W1184 - W1199
SW203 W1200 - W1215
SW204 TOSLINE-S20 W1216 - W1231
SW205 scan healthy map W1232 - W1247
SW206 W1248 - W1263
SW207 W1264 - W1279
SW208 W1280 - W1295
SW209 W1296 - W1311
SW210 W1312 - W1327
SW211 W1328 - W1343
SW212 W1344 - W1359
SW213 W1360 - W1375
SW214 W1376 - W1391
SW215 W1392 - W1407
SW216 W1408 - W1423
SW217 W1424 - W1439
SW218 W1440 - W1455
SW219 W1456 - W1471
SW220 W1472 - W1487
SW221 W1488 - W1503
SW222 W1504 - W1519
SW223 W1520 - W1535
NOTE
In case of TOSLINE-S20LP, it does not have the scan healthy map.
Therefore these SW registers ar e not effective for the TOSLINE-S20LP.
Name
•
The corresponding bit is ON when
•
The lowest address of W register
Function
PROSEC T3H
36
Page 39

2. Expanded Functions
Special
register
SW224 W1536 - W1551
SW225 W1552 - W1567 the W register is updated normally.
SW226 W1568 - W1583
SW227 W1584 - W1599
SW228 W1600 - W1615 corresponds to bit 0 in the SW
SW229 W1616 - W1631 register, and in the order.
SW230 W1632 - W1647
SW231 W1648 - W1663
SW232 W1664 - W1679
SW233 W1680 - W1695
SW234 W1696 - W1711
SW235 W1712 - W1727
SW236 TOSLINE-S20 W1728 - W1743
SW237 scan healthy map W1744 - W1759
SW238 W1760 - W1775
SW239 W1776 - W1791
SW240 W1792 - W1807
SW241 W1808 - W1823
SW242 W1824 - W1839
SW243 W1840 - W1855
SW244 W1856 - W1871
SW245 W1872 - W1887
SW246 W1888 - W1903
SW247 W1904 - W1919
SW248 W1920 - W1935
SW249 W1936 - W1951
SW250 W1952 - W1967
SW251 W1968 - W1983
SW252 W1984 - W1999
SW253 W2000 - W2015
SW254 W2016 - W2031
SW255 W2032 - W2047
NOTE
In case of TOSLINE-S20LP, it does not have the scan healthy map.
Therefore these SW registers ar e not effective for the TOSLINE-S20LP.
Name
•
The corresponding bit is ON when
•
The lowest address of W register
Function
User’s Manual
37
Page 40

2. Expanded Functions
2.3 Netw ork support function
2.3.1 IC memory card data access through computer link
The expanded file register data stor ed in the IC memory card can be read/written
through RS-485 computer link .
There are two types of data storage format for the I C m em or y card. They are 8 k
words per bank and 64 k words per bank. (Refer to XFER instruction)
Note that the computer link com m and for these format s ar e slightly different.
Expanded file register data read [MR]
Request message format (Host → T3H):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
( A
ADR
M R
Can be shortened Can be omitted
ADR:
Station address ... 01 to 32
Starting register:
For 8 k words per bank ..... F0000 to F8191
For 64 k words per bank ... f0000 to f65535 (bank 1)
f0000 to f57343 (bank 2)
Bank:
For 8 k words per bank ..... 1 to 15
For 64 k words per bank ... 1 to 2
N:
Number of registers to be read ... 1 to 61 (61 words max.)
Sum:
Check sum
Response message format (T3H → Host):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
( A
ADR
M R
n-5 n-4 n-3 n-2 n-1 n
Data:
Dat a in hexadecimal
Starting register
Data #1 Data #2
,
Data #N-1 Data #N
Bank
,
N
Sum
&
Upper case F
Lower case f
Sum
&
CR
)
CR
)
PROSEC T3H
38
Page 41

2. Expanded Functions
Expanded file register data Write [MW]
Request message format (Host → T3H):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
( A
ADR
M W
Can be shortened
n-5 n-4 n-3 n-2 n-1 n
,
Can be shortened Can be omitted
ADR:
Station address ... 01 to 32
Starting register:
For 8 k words per bank ..... F0000 to F8191
For 64 k words per bank ... f0000 to f65535 (bank 1)
f0000 to f57343 (bank 2)
Bank:
For 8 k words per bank ..... 1 to 15
For 64 k words per bank ... 1 to 2
N:
Number of registers to be written ... 1 to 46 (see Note)
Data:
Dat a in hexadecimal
Sum:
Check sum
Response message format (T3H → Host):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
( A
ADR
S T
Status:
T3H operation st at us
Starting register
Data #N-1 , Data #N & Sum
Status
&
Sum
,
Bank
CR
)
N
,
,
Data #1
)
CR
Upper case F
Lower case f
User’s Manual
39
Page 42

2. Expanded Functions
NOTE
(1) The maximum message text length is limited to 255 bytes.
(2) Shortening expression for starting register, bank, number and data
(MW only) are available. E.g. F9 for F00009.
When shortening expression is used, the maximum number of MW
com mand can be increased more than 46 words. In this case, it is
lim ited by the maximum message text length (255 bytes) .
(3) When an error has occurred, error response CE or EE is returned.
⋅ If designated register or bank is out of t he effective range, EE115
(register no./size error) is returned.
⋅ If IC memory card is not installed or MMR setting for PU slot is not
made, EE128 (No IC card error) is retur ned.
⋅ If IC memory card is used for program storag e, EE132 ( IC card type
error) is returned.
⋅ If IC memory card is set as write- pr otect, EE134 (IC card write protect error) is returned.
(4) For general inf or m ation of computer link function, refer to T - ser ies
Com puter Link Operation Manual.
PROSEC T3H
40
Page 43

2.3.2 TOSLINE-S20LP (loop) support
In addition to the standard bus connection type TOSLI NE-S20 (here called S20), the
optical loop connection type TOSLINE-S20LP (here called S20LP) can be used with
the T3H. (SN325: T3H station module of S20LP)
By using the S20LP, high speed control-data linkage is available as same as the S20.
Furthermore, peer-to- peer com munication between T3H’s becomes available via
S20LP.
• Up to two S20LP can be installed on a T3H. (S20LP and S20 total)
• The S20LP has 4 k words of scan transmission capacit y.
The leading 2 k words of the scan mem or y can be assig ned t o T3H’s link register
(W). And the following 2 k words can be read/written by using XFER inst ruction.
• The S20LP does not have the scan healthy map. Therefore, SW128 to SW255 ar e
not used for the S20LP.
• The S20LP has the loop map which indicates loop connection status of each
station. This loop map can be read by using READ instruct ion.
• By using SEND and RECV instructions, any register dat a of a T3H can be sent to
other T3H, and any register data of other T3H can be read into a T 3H, via S20LP.
(peer-to-peer communication)
NOTE
(1) The S20LP is under development.
(2) For details of the S20LP, refer to the separat e m anual for S20LP.
2. Expanded Functions
User’s Manual
41
Page 44

2. Expanded Functions
2.3.3 Ethernet support
The Ethernet module (EN311) is available fo r t he T3H. By using the EN311, the T3H
can be connected to Ethernet network.
Using the Ethernet module, the T3H supports the following communication functions.
• Computer link function:
Host computer on the Ethernet can perform data read/write, T3H st atus read,
program up-load/down-load, etc. for the T3H, by using the T-series computer link
command.
• Peer-to-peer communication:
By using SEND and RECV instructions, any register data of a T3H can be sent to
other T3H, and any register data of other T3H can be read into a T3H, via
Ethernet.
• Socket service:
Communication between a computer and a T3H user prog r am is available by using
SEND and RECV instructions. Maximum 8 ports of sock et are available. The
protocol can be selected either TCP/IP or UDP/ IP for each port.
Up to four EN311’s can be installed on a T3H.
To activate the EN311, SEND instruction is required to set parameters (I P addr ess,
UDP port number) and to send commands (communication start, etc.)
NOTE
(1) The Ethernet module (EN311) is under development.
(2) For details of t he EN311, r efer to the separate manual for EN311.
PROSEC T3H
42
Page 45

2.4 Instructions
This section explains the specifications of t he following instructions.
Double-word multi pl i cation and division (FUN042 D∗∗∗∗////)
Combination instruction of multiplication and division f or double-word data.
This inst r uction is not available on the T3.
Essential PID (FUN156 PID3)
PID (Pr opor tional, Integral, Derivative) contr ol instruction which has the following
features.
⋅ Incom plete derivative action expanding stable application range
⋅ Essential digital algorithm succeeding t o benefits of analog PID
This inst r uction is not available on the T3.
Floating point essential PI D ( FUN232 FPID3)
Essential PID instruction for f loat ing point data.
This inst r uction is not available on the T3.
Expanded data transfer (FUN236 XFER)
Data tr ansfer instruction between special objects, i.e. expanded file register in IC
memory card, data in EEPROM, TOSLINE-S20 scan memory, etc.
Some functions are added to this instruction for the T3H.
Network data send (FUN239 SEND)
Used to peer- to-peer communication via TOSLINE-S20LP or Et her net. This
instruct ion is also used for Ethernet module (EN311) cont rol.
This inst r uction is not available on the T3.
Network data receive (FUN240 RECV)
Used to peer- to-peer communication via TOSLINE-S20LP or Et her net. This
instruct ion is also used for Ethernet module (EN311) cont rol.
This inst r uction is not available on the T3.
2. Expanded Functions
User’s Manual
43
Page 46

2. Expanded Functions
2.4.1 Double-word multiplication and division (D
∗∗∗∗////
)
FUN 042
D∗/
Double-word multiplication and division
Expression
⋅
Input ─[
A+1
A
D∗/
B+1⋅B
→
C+1⋅C
]─ Output
Function
⋅
A+1
When the input is ON, the data of
⋅
B+3
B+2
, then the quotient is stored in
The data range is -2147483648 to 2147483647. If the result (quotient) is out of the data range, the following
limit value is stored.
Positive overflow: quotient = 2147483647, remainder = 0
Negative overflow: quotient = -2147483647, remainder = 0
A
is multiplied by the data of
C+1⋅C
and the remainder in
B+1⋅B
, and the product is divided by
C+3⋅C+2.
Execution condition
Input Operation Output ERF
OFF No execution OFF
ON
B+3
B+3
B+3
⋅
B+2
≠ 0, no overflow
⋅
B+2
≠ 0, overflow
⋅
B+2
= 0
Normal execution ON
Limit ON ON
No execution OFF ON
−
−
Operand
Name Device Register Con- Index
X Y S L R Z T. C. I O X W Y W S W L W R W W T C D F I W O W I J K
stant
A
Operation
data
B
Multiplier,
divisor
C
Result
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
Example
When R0200 is ON, the double-word data of D0351⋅D0350 is multiplied by the data of D0262⋅D0261,
and the product is divided by the data of D0264⋅D0263, then the quotient is stored in D0401⋅D0400 and
the remainder in D0403⋅D0402.
√
√
√
√
PROSEC T3H
44
Page 47

2. Expanded Functions
If the data of D0351⋅D0350 is 23437688, D0262⋅D0261 is 1876509, and D0264⋅D0263 is 113487, the
quotient (387542471) is stored in D0401⋅D0400 and the remainder (64815) is stored in D0403⋅D0402.
D0351⋅D0350 23437688
D0401⋅D0400 387542471
×
D0403⋅D0402 64815
D0262⋅D0261 1876509
D0264⋅D0263
÷
113487
Note
•
Edge execution modifier is also available for this instruction.
User’s Manual
45
Page 48

2. Expanded Functions
2.4.2 Essential PID (PID3)
FUN 156 PID3 Essential PID
Expression
Input ─[ A PID3 B → C ]─ Output
Function
Performs PID (Proportional, Integral, Derivative) control which is a fundamental method of feed-back control.
(Pre-derivative real PID algorithm)
This PID3 instruction has the following features.
•
For derivative action, incomplete derivative is used to suppress interference of high-frequency noise and to
expand the stable application range,
•
Controllability and stability are enhanced in case of limit operation for MV, by using digital PID algorithm
succeeding to benefits of analog PID.
•
Auto, cascade and manual modes are supported in this instruction.
•
Digital filter is available for PV.
•
Direct / reverse operation is selectable.
Execution condition
Input Operation Output
OFF Initialization OFF
ON Execute PID every setting interval ON when
execution
Operand
Name Device Register Con- Index
X Y S L R Z T. C. I O X W Y W S W L W R W W T C D F I W O W I J K
stant
A
Top of input
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
data
B
Top of
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
parameter
C
Top of
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
output data
Input data Control parameter Output data
A
Process input value
A+1
A-mode set value
A+2
C-mode set value
A+3
M-mode MV input
A+4
MV tracking input
A+5
Mode setting
A-mode: Auto mode
C-mode: Cascade mode
M-mode: Manual mode
PROSEC T3H
46
PVC
ASV
CSV
MMV
TMV
MODE
B
Proportional gain
B+1
Integral time
B+2
Derivative time
B+3
Dead-band
B+4
A-mode initial SV
B+5
Input filter constant
B+6
ASV differential limit
B+7
MMV differential limit
B+8
Initial status
B+9
MV upper limit
B+10
MV lower limit
B+11
MV differential limit
B+12
Control interval setting
K
T
GP
ISV
FT
DSV
DMMV
STS
MH
ML
DMV
P
T
I
D
n
C
Manipulation value
C+1
Last error
C+2
Last derivative value
C+3
Last PV
C+4
Last SV
C+5
Integral remainder
C+6
Derivative remainder
C+7
Internal MV
C+8
Internal counter
C+9
Control interval
√
√
√
PV
SV
MV
MV
e
D
Dr
n-1
n-1
n-1
n-1
∆∆∆∆
Ir
n
C
t
Page 49

Control block diagram
Auto
DSV
mode
Cascade
mode
SV
+
n
PV
ASV
Differential
CSV
Integral
1
⋅
s
T
I
Proportional
e
n
Gap K
-
n
1
Derivative
⋅
s
T
D
1+η⋅T
D
(η = 0.1)
⋅
s
Integral
control
∆
I
n
∆
P
n
∆
D
n
2. Expanded Functions
MV
n
+
+
-
∆
MV
n
P
MVS H/L DMV
MMV
Differential limit
DMMV
MVC
n
MV
Manual
mode
1
1+T⋅s
Digtal filter
PVC
MVS: Velocity → Position
MVn = MV
H/L: Upper / lower limit
DMV: Differential limit
n-1
± ∆MV
n
Integral action control:
When MV is limited (H/L, DMV) and the integral value has same sign as limit over, integral action
is stopped.
Velocity → Position conversion:
In Direct mode, MV increases when PV is increased.
In Reverse mode, MV decreases when PV is increased.
→
→
MV
MV
= MV
n
= MV
n
- ∆MVn
n-1
+ ∆MVn
n-1
Gap (dead-band) operation:
Error e
SV - PV
GP (%) GP (%)
Algorithm
Digital filter:
nn
=− ⋅ + ⋅ −
PV FT PVC FT PV
()1
Here,
0 000 0 999..
≤≤
FT
1
User’s Manual
47
Page 50

2. Expanded Functions
PID algorithm:
MV K P I D
nn n
=±
MV MV MV
()
1
−
∆
P
nnnn
=⋅ ++
∆∆∆∆
Here,
nnn
=−
∆
Pee
nnn
=−
eSVPV
1
−
(If GP ≠ 0, Gap is applied)
n
∆
=
I
etIr
I
T
(If TI = 0, ∆In = 0)
n
∆
⋅+
D
⋅−−⋅+
TPV PV tD Dr
n
∆
=
D
nn n
DD D
η
1
−
=+
(Fixed)
=
01
.
11
nn n
−−
()
∆
tT
+⋅
η
∆
D
∆
Parameter details
A Process input value PVC (0.00 to 100.00 %) Data range: 0 to 10000
A+1
A+2
A+3
A+4
A+5
Operation mode
00 : Manual mode
01 : Auto mode
10 : Cascade mode
11 : (Reserve)
Tracking designation
0 : No
1 : Yes
B Proportional gain K
B+1
B+2
B+3
B+4
B+5
B+6
B+7
Auto mode set value ASV (0.00 to 100.00 %) Data range: 0 to 10000
Cascade mode set value CSV (0.00 to 100.00 %) Data range: 0 to 10000
Manual mode MV MMV (-25.00 to 125.00 %) Data range: -2500 to 12500
MV tracking input TMV (-25.00 to 125.00 %) Data range: -2500 to 12500
Mode setting MODE
F C 8 4 0
(0.00 to 327.67) Data range: 0 to 32767
P
Integral time T
Derivative time T
(0.000 to 32.767 min., stop if T
I
(0.000 to 32.767 min.) Data range: 0 to 32767
D
= 0) Data range: 0 to 32767
I
Gap (dead-band) GP (0.00 to 10.00 %) Data range: 0 to 1000
Auto mode initial set value ISV (0.00 to 100.00 %) Data range: 0 to 10000
Input filter constant FT (0.000 to 0.999) Data range: 0 to 999
ASV differential limit DSV (0.00 to 100.00 %/∆t) Data range: 0 to 10000
MMV differential limit DMMV (0.00 to 100.00 %/∆t) Data range: 0 to 10000
PROSEC T3H
48
Page 51

2. Expanded Functions
B+8
Initial operation mode
00 : Manual mode
01 : Auto mode
10 : Cascade mode
11 : (Reserve)
Direct / reverse selectio n
0 : Direct
1 : Reverse
Executes PID every n scan. Therefore, control interval ∆t = n × constant scan interval
(It is treated as n = 1 when n ≤ 0)
: Internal work area
Operation
1. When the instruction input is OFF:
2. When the instruction input is ON:
•
Initial status STS
F C 8 4 0
B+9
MV upper limit MH (-25.00 to 125.00 %) Data range: -2500 to 12500
B+10
MV lower limit ML (-25.00 to 125.00 %) Data range: -2500 to 12500
B+11
MV differential limit DMV (0.00 to 100.00 %/∆t) Data range: 0 to 10000
B+12
Control interval setting n (1 to 32767 times) Data range: 1 to 32767
C
Manipulation value MV (-25.00 to 125.00 %) Data range: -2500 to 12500
C+1
C+9
Initializes the PID3 instruction.
Operation mode is set as specified by
Auto mode SV is set as specified by
Manual mode MV is set as current MV. MMV ← MV
Internal calculation data is initialized.
MV remains unchanged.
Executes PID calculation every n scan which is specified by
available according to the setting of
Auto mode
This is a normal PID control mode with ASV as set value.
Set value differential limit DSV, manipulation value upper/lower limit MH/ML and differential limit DMV
are effective.
Bump-less changing from auto mode to manual mode is available. (Manual mode manipulation value
MMV is over-written by current MV automatically. MMV ← MV)
A+5
B+8
.
B+4
. ASV
.
A+5
bit 0, 1 ←
←
ISV
B+12
. The following operation modes are
B+8
bit 0, 1
User’s Manual
49
Page 52

2. Expanded Functions
•
Manual mode
In this mode, the manipulation value MV can be directly controlled by the input value of MMV.
MV differential limit for manual mode DMMV is effective. MH/ML and DMV are not effective.
When mode is changed from manual to auto or cascade, the operation is started from the current MV.
•
Cascade mode
This is a mode for PID cascade connection. PID is executed with CSV as set value.
Different from the auto mode, set value differential limit is not effective. Manipulation value upper/lower
limit MH/ML and differential limit DMV are effective.
Bump-less changing from cascade mode to manual mode is available. (Manual mode manipulation
value MMV is over-written by current MV automatically. MMV ← MV)
And, bump-less changing from cascade mode to auto mode is available. (Auto mode set value ASV is
over-written by current CSV automatically. ASV ← CSV)
•
MV tracking
This function is available in auto and cascade modes. When the tracking designation (
tracking input TMV is directly output as MV.
Manipulation value upper/lower limit MH/ML is effective, but differential limit DMV is not effective.
When the tracking designation is changed to OFF, the operation is started from the current MV.
A+5
bit 2) is ON,
Note
•
PID3 instruction is only usable on the main-program.
•
PID3 instruction must be used under the constant scan mode. The constant scan interval can be selected
in the range of 10 to 200 ms, 10 ms increments.
•
The data handled by the PID3 instruction are % units. Therefore, process input value PVC, manipulation
value MV, etc., should be converted to % units (scaling), before and/or after the PID3 instruction. For this
purpose, the function generator instruction (FUN165 FG) is convenient.
PROSEC T3H
50
Page 53

2. Expanded Functions
V
V
V
V
E
2.4.3 Floating point essential PID (FPID3)
FUN 232 FPID3 Floating point essential PID
Expression
⋅
A+1
Input ─[
A
FPID3
Function
Performs PID (Proportional, Integral, Derivative) control which is a fundamental method of feed-back control.
(Pre-derivative real PID algorithm)
The operation of this FPID3 instruction is the same as the PID3 (FUN156) instruction except for dealing data
as floating point data.
Execution condition
Input Operation Output
OFF Initialization OFF
ON Execute PID every setting interval ON when
Operand
Name Device Register Con- Index
X Y S L R Z T. C. I O X W Y W S W L W R W W T C D F I W O W I J K
B+1
⋅
B →
⋅
C+1
C ]─ Output
execution
stant
A
Top of input
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
data
B
Top of
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
parameter
C
Top of
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
output data
Input data Control parameter Output data
A+1
Process input value
⋅
A
A-mode set value
C-mode set value
M-mode MV input
MV tracking input
Mode setting
A-mode: Auto mode
C-mode: Cascade mode
M-mode: Manual mode
PVC
AS
CS
MM
TM
MOD
B+1
Proportional gain
⋅
B
Integral time
Derivative time
Dead-band
A-mode initial SV
Input filter constant
ASV differential limit
MMV differential limit
Initial status
MV upper limit
MV lower limit
MV differential limit
Control interval setting
K
T
T
GP
ISV
FT
DSV
DMMV
STS
MH
ML
DMV
C+1
P
I
D
n
Manipulation value
⋅
C
Last error
Last derivative value
Last PV
Last SV
Integral remainder
Derivative remainder
Internal MV
Internal counter
Control interval
√
√
√
PV
SV
MV
e
D
MV
n-1
n-1
n-1
n-1
Dr
∆∆∆∆
Ir
n
C
t
User’s Manual
51
Page 54

2. Expanded Functions
Control block diagram
Auto
DSV
mode
Cascade
mode
SV
+
n
PV
Gap K
-
n
ASV
Differential
CSV
e
n
Integral
1
⋅
s
T
I
Proportional
1
Derivative
⋅
s
T
D
⋅
1+η⋅T
s
D
(η = 0.1)
Integral
control
∆
I
n
∆
P
n
∆
D
n
MV
n
+
+
-
∆
MV
n
P
MVS H/L DMV
MMV
Differential limit
DMMV
MVC
n
MV
Manual
mode
1
1+T⋅s
Digtal filter
PVC
MVS: Velocity → Position
MVn = MV
H/L: Upper / lower limit
DMV: Differential limit
n-1
± ∆MV
n
Integral action control:
When MV is limited (H/L, DMV) and the integral value has same sign as limit over, integral action
is stopped.
Velocity → Position conversion:
In Direct mode, MV increases when PV is increased.
In Reverse mode, MV decreases when PV is increased.
→
→
MV
MV
= MV
n
= MV
n
- ∆MVn
n-1
+ ∆MVn
n-1
Gap (dead-band) operation:
Error e
SV - PV
GP (%) GP (%)
Algorithm
Digital filter:
nn
=− ⋅ + ⋅ −
PV FT PVC FT PV
()1
Here,
01
≤<
FT
1
PROSEC T3H
52
Page 55

2. Expanded Functions
PID algorithm:
MV K P I D
nn n
=±
MV MV MV
()
1
−
∆
P
nnnn
=⋅ ++
∆∆∆∆
Here,
nnn
=−
∆
Pee
nnn
=−
eSVPV
1
−
(If GP ≠ 0, Gap is applied)
n
∆
=
I
etIr
I
T
(If TI = 0, ∆In = 0)
n
∆
⋅+
D
⋅−−⋅+
TPV PV tD Dr
n
∆
=
D
nn n
DD D
η
1
−
=+
(Fixed)
=
01
.
11
nn n
−−
()
∆
tT
+⋅
η
∆
D
∆
Parameter details
⋅
A
A+1
A+3
A+5
A+7
A+9
A+11
F 0 F C 8 4 0
Operation mode
00 : Manual mode
01 : Auto mode
10 : Cascade mode
11 : (Reserve)
Tracking designation
0 : No
1 : Yes
B+3
B+5
B+7
B+9
B+11
B+13
B+15
Process input value PVC (0 to 100 %) Data range: 0.0 to 100.0
⋅
A+2
⋅
A+4
⋅
A+6
⋅
A+8
⋅
A+10
B+1
⋅
B+2
⋅
B+4
⋅
B+6
⋅
B+8
⋅
B+10
⋅
B+12
⋅
B+14
Auto mode set value ASV (0 to 100 %) Data range: 0.0 to 100.0
Cascade mode set value CSV (0 to 100 %) Data range: 0.0 to 100.0
Manual mode MV MMV (-25 to 125 %) Data range: -25.0 to 125.0
MV tracking input TMV (-25 to 125 %) Data range: -25.0 to 125.0
Mode setting MODE
A+11 A+10
⋅
B
Proportional gain KP (0 to 327.67) Data range: 0.0 to 327.67
Integral time TI (0 to 32.767 min., stop if TI = 0) Data range: 0.0 to 32.767
Derivative time TD (0 to 32.767 min.) Data range: 0.0 to 32.767
Gap (dead-band) GP (0 to 10 %) Data range: 0.0 to 10.0
Auto mode initial set value ISV (0 to 100 %) Data range: 0.0 to 100.0
Input filter constant FT (0 to less than 1) Data range: 0.0 to less than 1.0
ASV differential limit DSV (0 to 100 %/∆t) Data range: 0.0 to 100.0
MMV differential limit DMMV (0 to 100 %/∆t) Data range: 0.0 to 100.0
User’s Manual
53
Page 56

2. Expanded Functions
⋅
B+17
B+16
F 0 F C 8 4 0
Initial operation mode
00 : Manual mode
01 : Auto mode
10 : Cascade mode
11 : (Reserve)
Direct / reverse selectio n
0 : Direct
1 : Reverse
B+19
B+21
B+23
B+25
Executes PID every n scan. Therefore, control interval ∆t = n × constant scan interval
(It is treated as n = 1 when n ≤ 0)
C+3
: Internal work area
C+15
Initial status STS
B+17 B+16
⋅
B+18
MV upper limit MH (-25 to 125 %) Data range: -25.0 to 125.0
⋅
B+20
MV lower limit ML (-25 to 125 %) Data range: -25.0 to 125.0
⋅
B+22
MV differential limit DMV (0 to 100 %/∆t) Data range: 0.0 to 100.0
⋅
B+24
Control interval setting n (1 to 32767 times) Data range: 1.0 to 32767.0
⋅
C
C+1
Manipulation value MV (-25 to 125 %) Data range: -25.0 to 125.0
⋅
C+2
⋅
C+14
Operation
1. When the instruction input is OFF:
Initializes the FPID3 instruction.
⋅
B+16
Operation mode is set as specified by
Auto mode SV is set as specified by
Manual mode MV is set as current MV. MMV ← MV
Internal calculation data is initialized.
MV remains unchanged.
2. When the instruction input is ON:
Executes PID calculation every n scan which is specified by
are available according to the setting of
•
Auto mode
This is a normal PID control mode with ASV as set value.
Set value differential limit DSV, manipulation value upper/lower limit MH/ML and differential limit DMV
are effective.
Bump-less changing from auto mode to manual mode is available. (Manual mode manipulation value
MMV is over-written by current MV automatically. MMV ← MV)
B+17
B+9
A+11
⋅
B+8
⋅
A+10
.
. ASV
.
A+10
B+25
bit 0, 1 ←
←
ISV
⋅
B+24
B+16
bit 0, 1
. The following operation modes
PROSEC T3H
54
Page 57

2. Expanded Functions
•
Manual mode
In this mode, the manipulation value MV can be directly controlled by the input value of MMV.
MV differential limit for manual mode DMMV is effective. MH/ML and DMV are not effective.
When mode is changed from manual to auto or cascade, the operation is started from the current MV.
•
Cascade mode
This is a mode for PID cascade connection. PID is executed with CSV as set value.
Different from the auto mode, set value differential limit is not effective. Manipulation value upper/lower
limit MH/ML and differential limit DMV are effective.
Bump-less changing from cascade mode to manual mode is available. (Manual mode manipulation
value MMV is over-written by current MV automatically. MMV ← MV)
And, bump-less changing from cascade mode to auto mode is available. (Auto mode set value ASV is
over-written by current CSV automatically. ASV ← CSV)
•
MV tracking
This function is available in auto and cascade modes. When the tracking designation (
tracking input TMV is directly output as MV.
Manipulation value upper/lower limit MH/ML is effective, but differential limit DMV is not effective.
When the tracking designation is changed to OFF, the operation is started from the current MV.
A+10
bit 2) is ON,
Note
•
FPID3 instruction is only usable on the main-program.
•
FPID3 instruction must be used under the constant scan mode. The constant scan interval can be
selected in the range of 10 to 200 ms, 10 ms increments.
•
The data handled by the FPID3 instruction are % units. Therefore, process input value PVC, manipulation
value MV, etc., should be converted to % units (scaling), before and/or after the FPID3 instruction.
User’s Manual
55
Page 58

2. Expanded Functions
2.4.4 Expanded data transfer (XFER)
FUN 236 XFER Expanded data transf er
Expression
Input ─[ A XFER B → C ]─ Output
Function
When the input is ON, data block transfer is performed between the source which is indirectly designated by
A
A+1
and
words) is designated by B.
The transfer size is 1 to 256 words. (except for writing into EEPROM)
Data transfer between the following objects are available.
•
CPU register ↔ CPU register
•
CPU register ↔ Expanded F register (IC memory card)
•
CPU register ↔ TOSLINE-S20 or TOSLINE-S20LP (here called S20 or S20LP)
•
CPU register ↔ EEPROM (D register)
and the destination which is indirectly designated by C and
Execution condition
Input Operation Output ERF
OFF No execution OFF
ON Normal execution ON
When error is occurred (see Note) ON Set
Operand
Name Device Register Con- Index
X Y S L R Z T. C. I O X W Y W S W L W R W W T C D F I W O W I J K
C+1
. The transfer size (number of
−
−
stant
A
Source
parameter
B
Transfer
size
C
Destination
parameter
Source parameter Transfer size and status Destination parameter
A
Bank / CH Type
A+1
•
Refer to the following table for contents of each designation.
•
The status flag is created only when the transfer from S20 to Register.
PROSEC T3H
56
B
Leading address
B+1
B+16
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
Transfer size
Status flag
(Scan healthy map)
Max. 16 words
C
Bank / CH Type
C+1
Leading address
√
√
√
Page 59

2. Expanded Functions
Transfer parameter table
Transfer object Bank / CH TYPE Leading address Transfer size Status
flag
XW/YW register 0 H00 0 to 511 (T3H)
0 to 255 (T3)
0 to 63 (T2)
W register 0 H01 0 to 2047 (T3H)
0 to 1023 (T3/T2)
LW register 0 H02 0 to 255 (T3H/T3/T2) 1 to 256 None
RW register 0 H03 0 to 999 (T3H)
0 to 511 (T3)
0 to 127 (T2)
D register 0 H04 0 to 8191 (T3H/T3)
0 to 4095 (T2)
F register 0 H05 0 to 32767 (T3H)
0 to 8191 (T3)
0 to 1023 (T2)
Expanded F register 1 to 15 H05 0 to 8191 (T3H/T3/T2) 1 to 256 None
(IC memory card) *1 1 or 2 H06 0 to 65535 (bank 1) (T3H)
0 to 57343 (bank 2) (T3H)
S20 scan memory 1 or 2 *2 H10 0 to 1023 (T3H/T3/T2) 1 to 256 Yes *3
S20LP scan memory *4 1 or 2 H10 0 to 4095 (T3H) 1 to 256 None
EEPROM (D register) 0 H20 0 to 8191 (T3H/T3)
0 to 4095 (T2)
Destination (write)
*1) Two format types of the IC memory card is available. They are 8 k words/bank (type: H05) and 64 k
words/bank (type: H06). Type H06 is available only in the T3H.
*2) Channel 1 (CH1) only for the T2.
*3) The status flag is created only when S20 is designated as transfer source.
*4) S20LP is available only with the T3H. The S20LP does not have the scan healthy map. Therefore
status flag is not created for S20LP.
1 to 256 None
1 to 256 None
1 to 256 None
1 to 256 None
1 to 256 None
1 to 256 None
Source (read)
1 to 256
1 to 128 (T3H)
1 to 64 (T3)
1 to 32 (T2)
None
User’s Manual
57
Page 60

2. Expanded Functions
CPU register ↔↔↔↔ Expanded F register (IC memory card)
Expanded F register configuration:
< Type H05 > <Type H06 >
F0000
F8191
F0000
F8191
F0000
F8191
F0000
F8191
Example:
Bank 1
Bank 2
Bank 3
F00000
Bank 15
F00000
Bank 1
F65535
Bank 2
F57343
Source designation Transfer size Destination designation
RW000 H00 H04 RW002 00045 RW010 H01 H05
RW001 00000 RW011 00000
D0000 (CPU register) 45 words transfer Bank 1 F0000 (Expanded F register)
When R0000 is ON, 45 words data starting with D0000 is transferred to Bank 1 F0000 and after in
the IC memory card.
Remarks:
•
When the IC memory card is used for expanded F register, MMR setting on the PU slot is necessary
by I/O allocation.
•
In case of the T2, the capacity of F register in CPU is 1024 words. However, the T2 can access
8192 words × 15 banks (= 122880 words) of expanded F register in the IC memory card.
•
When type H06 is used in the T3H, the expanded F register can be accessed as F00000 to F65535
(bank 1) and F00000 to F57343 (bank 2).
PROSEC T3H
58
Page 61

CPU register ↔↔↔↔ S20/S20LP scan memory
Example:
2. Expanded Functions
Source designation Transfer size Destination designation
RW000 H00 H01 RW002 00010 RW010 H01 H10
RW001 00000 RW011 00000
W0000 (CPU register) 10 words transfer Channel 1 S20/S20LP
scan memory address 00000
When R0000 is ON, 10 words data starting with W0000 is transferred to scan memory address
00000 and after of channel 1 S20/S20LP.
Remarks:
•
When writing data into S20/S20LP scan memory, confirm that the address range is S20/S20LP’s data
send block.
•
If S20/S20LP scan memory is accessed only by this XFER instruction, the network assignment, i.e.
“LINK” or “GLOBAL” setting, is not necessary.
•
When S20 is designated as source, the status flag (scan healthy map) for the read-out data is stored
in operand
For example, when 99 words data is read from S20 with using RW030 as transfer size designation,
RW031 to RW037 (7 words) are used to store the scan healthy map.
RW030 99
RW031 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
RW032 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 29 18 17
RW036 96 95 94 93 92 91 90 89 88 87 86 85 84 83 82 81
RW037 99 98 97
0 is stored in the excess bits
B+1
and after. (Status flag is not created for S20LP)
F C 8 4 0
Transfer size (99 words)
Status flag
(scan healthy map)
1: Scan normal
0: Not normal
User’s Manual
59
Page 62

2. Expanded Functions
CPU register ↔↔↔↔ EEPROM (D register)
EEPROM D register configuration:
< T3H > <T3 > < T2 >
D0000
D0127
D0128
D0255
D0256
D0383
D7936
D8191
128 words/page, 64 pages 64 words/page, 128 pages 32 words/page, 128 pages
Total 8192 words Total 8192 words Total 4096 words
Example:
Page 1
Page 2
Page 3
Page 64
D0000
D0063
D0064
D0127
D0128
D0191
D8128
D8191
Page 1
Page 2
Page 3
Page 128
D0000
D0031
D0032
D0063
D0064
D0095
D4064
D4095
Page 1
Page 2
Page 3
Page 128
Source designation Transfer size Destination designation
RW000 H00 H04 RW002 00032 RW010 H00 H20
RW001 00100 RW011 00064
D0100 (CPU register) 32 words transfer D0064 (EEPROM)
When R0000 is ON, 32 words data starting with D0100 is transferred to D0064 and after in the
EEPROM. (Data write into EEPROM)
Remarks:
•
EEPROM is internally divided by page.
•
Writing data into the EEPROM is available within one page at a time.
•
For data reading from the EEPROM, there is no need to consider the pages.
•
The EEPROM has a life limit for data writing into an address. It is 100,000 times. Pay attention not to
exceed the limit. (EEPROM alarm flag = S0007 is not updated by executing this instruction)
•
Once data writing into the EEPROM is executed, EEPROM access (read/write) is prohibited for the
duration of 10 ms. Therefore, minimum 10 ms interval is necessary for data writing.
PROSEC T3H
60
Page 63

2. Expanded Functions
Note
•
Edge execution modifier is also available for this instruction.
•
The XFER instruction is not executed as error in the following cases. (ERF = S0051 is set to ON)
Transfer Error cause
Between CPU
registers
CPU register to
expanded F register
CPU register to
S20/S20LP
CPU register to
EEPROM
Others 1) When source/destination designation is invalid.
1) When the transfer size is 0 or more than 256.
2) When the source/destination table of transfer is out of the valid range.
1) When the transfer size is 0 or more than 256.
2) When the source/destination table of transfer is out of the valid range.
3) When IC memory card is not installed or MMR setting is not made.
4) When the IC memory card is write-protect state. (for data writing)
5) When program is stored in the IC memory card. (detected only T3H)
1) When the transfer size is 0 or more than 256.
2) When the source/destination table of transfer is out of the valid range.
3) When channel designation is other than 1 or 2. (other than 1 for T2)
4) When S20/S20LP is not installed or not allocated.
5) When status flag area is not sufficient.
6) When an odd address is designated as the leading address in the case of
S20/S20LP is set as double-word access.
7) When the transfer size is odd address in the case of S20/S20LP is set as
double-word access.
8) When the S20/S20LP module is not normal.
1) When the transfer size is 0 or more than 256.
2) When the source/destination table of transfer is out of the valid range.
3) When the data writing address range exceeds page boundary.
4) When this instruction is executed during EEPROM access inhibited (10 ms).
5) When the CPU does not have EEPROM.
2) When an invalid transfer combination is designated.
3) When the index modification is used for an operand and register boundary
error is occurred as the result of the index modification. (in this case, the
instruction output comes OFF)
User’s Manual
61
Page 64

2. Expanded Functions
2.4.5 Network data send (SEND)
FUN 239 SEND Network dat a send
Expression
Input ─[ A SEND B ]─ Output
Function
This instruction sends the designated range of register data to another T3H through the network.
(Network: TOSLINE-S20LP or Ethernet)
The transfer source register (self-station) is designated by
The transfer destination register (target-station) is designated by
The transfer size (number of words) is designated by
or 485 words (Ethernet).
The designation method of the target-station is different between S20LP and Ethernet.
This instruction is also used for other functions of the Ethernet module. Refer to the Ethernet module (EN311)
manual for detailed functions used for the EN311.
A+3
A+2
. The maximum transfer size is 128 words (S20LP),
Execution condition
Input Operation Output ERF
OFF No execution OFF
ON During execution OFF
Normal complete ON
When error is occurred (see Note) ON Set
Operand
Name Device Register Con- Index
X Y S L R Z T. C. I O X W Y W S W L W R W W T C D F I W O W I J K
and
A+5
A+4
and
.
A+6
.
−
−
−
stant
A
Transfer
parameter
B
Status √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
< In case of S20LP > < In case of Ethernet >
Note) Parameters for the Ethernet varies depending on the request command. Above figure shows the
parameters for the register read/write command (H0021). Refer to the EN311 manual.
62
F C B 8 7 0
A
A+1
A+2
A+3
A+4
A+5
A+6
A+7
PROSEC T3H
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
F C B 8 7 0
MID CH Target station No.
0 (fixed)
Transfer size
Register type (self-station)
Leading address (self-station)
Register type (target-station)
Leading address (target-station)
Response time limit
A
A+1
A+2
A+3
A+4
A+5
A+6
A+7
A+8
A+9
A+10
MID CH 0 (fixed)
Request command
Transfer size
Register type (self-station)
Leading address (self-station)
Register type (target-station)
Leading address (target-station)
Response time limit
Target-station IP address
Target-station UDP port No.
Page 65

2. Expanded Functions
B
B+1
Inside the parameter:
F E D C B 8 7 0
Abn Busy Status 0 TermSTS
Transmission error information (if TermSTS is H0B)
Transfer parameter S20LP Ethernet
MID (network type) 2 3
CH (channel of self-station) 1 or 2 (max. two S20LP’s on T3H) 1 to 4 (max. four EN311’s on T3H)
Target station No. 1 to 64 0 (fixed)
Request command 0 (fixed) H0021: Register read/write
(for other commands, refer to EN311
manual)
Transfer size
(number of words)
Register type H0000: XW/YW register
Leading address Designates the leading register address to be transferred
Response time limit Specifies the time limit of the response from target-station. (0.1 s units)
Target-station IP address N/A Designates the IP address of the
Target-station UDP port No. N/A Designates the UDP port No. of the
1 to 128
(max. 84 words for T or C register)
(designation across T511 and T512 is
not allowed)
H0001: W register
H0002: LW register
H0003: RW register
H0004: D register
H0005: F register (CPU)
H∗∗05: Expanded F register
(IC card, 8k words/bank, ∗∗ is bank No. 01 - 0F)
H∗∗06: Expanded F register
(IC card, 64k words/bank, ∗∗ is bank No. 01 - 02)
H0007: T register
H0008: C register
H0009: SW register
When the bit F is set to ON, the following default value is used.
S20LP ...... 4.1 s
Ethernet ... 30 s
1 to 485
(max. 323 words for T or C register)
(designation across T511 and T512 is
not allowed)
target-station
target-station
User’s Manual
63
Page 66

2. Expanded Functions
Inside the parameter (cont’d):
Status S20LP Ethernet
Abn 0: Normal complete
1: Error complete
Busy 0: Initial state
1: Transmission port busy
Status 0: Initial state
1: While send requesting
2: While waiting response
3: Complete
TermSTS H00: Normal complete
H01: Register designation error
H02: Response time-out
H03: Parameter error
H04: Register write protect
H05: (Reserve)
H06: Module error (send time-out)
H07: No send channel
H08: Invalid station No.
H09: Transfer size error
H0A: Boundary error
H0B: Transmission error Bit 7 indicates the error is occurred
H0C: I/O no answer error whether self-station or target-station.
H0D: IC card designation error 0: Self-station
H0E: (Reserve) 1: Target-station
H0F: (Reserve)
Transmission error
information
When TermSTS is H0B, the error information is stored. (0 for other cases)
For detailed information, refer to the S20LP or EN311 manual.
Example
RW010 2 1 3 S20LP, channel 1, target station No. is 3
RW011 0
RW012 128 Transfer size: 128 words
RW013 3 Self-station RW register
RW014 100 Leading address: RW100
RW015 4 Target-station D register
RW016 1000 Leading address: D1000
RW017 10 Response time limit: 1 second
Send requesting
RW050 0 0 1 0 0
RW051 0
PROSEC T3H
64
Page 67

2. Expanded Functions
TOSLINE-S20LP
Station No. 3
T3H T3H
(self-station) (target-station)
RW100 D1000
RW101 D1001
RW227 D1127
When R0020 is ON, 128 words data starting with RW100 is transferred to D1000 and after of the T3H on
which station No. 3 S20LP is installed.
When the operation is completed, the status is set in RW050 and instruction output comes ON.
Note
•
Keep the input ON until the output comes ON.
•
This instruction becomes error complete in the following cases. (ERF = S0051 is set to ON)
(1) Target station No. is invalid. (for S20LP)
(2) Invalid register designation. (In case of T and C registers, T → T and C → C is only possible)
(3) Source/destination register address range is out of valid range.
(4) Destination register is write-protected.
(5) Response time-out is occurred.
(6) If expanded F register is designated;
- when MMR setting is not made.
- when IC card is not installed.
- when IC card is used to store program.
- when IC card is write-protected. (for destination)
•
By using SW067, register write-protect is available against SEND instruction of other T3H.
F 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SW067 SW C T F D RW LW W YW
0: Write enable
1: Write protect
•
Resetting the status register (operand B) is necessary at the first scan.
•
When using the TOSLINE-S20LP or Ethernet module (EN311), read the manual for these network
modules.
Both F register in CPU and
expanded F register in IC card
User’s Manual
65
Page 68

2. Expanded Functions
2.4.6 Network data receive (RECV)
FUN 240 RECV Network data receive
Expression
Input ─[ A RECV B ]─ Output
Function
This instruction reads the designated range of register data from another T3H through the network.
(Network: TOSLINE-S20LP or Ethernet)
The transfer source register (target-station) is designated by
The transfer destination register (self-station) is designated by
The transfer size (number of words) is designated by
or 485 words (Ethernet).
The designation method of the target-station is different between S20LP and Ethernet.
This instruction is also used for other functions of the Ethernet module. Refer to the Ethernet module (EN311)
manual for detailed functions used for the EN311.
A+2
A+5
A+3
. The maximum transfer size is 128 words (S20LP),
Execution condition
Input Operation Output ERF
OFF No execution OFF
ON During execution OFF
Normal complete ON
When error is occurred (see Note) ON Set
Operand
Name Device Register Con- Index
X Y S L R Z T. C. I O X W Y W S W L W R W W T C D F I W O W I J K
and
and
A+6
A+4
.
.
−
−
−
stant
A
Transfer
parameter
B
Status √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
< In case of S20LP > < In case of Ethernet >
Note) Parameters for the Ethernet varies depending on the request command. Above figure shows the
parameters for the register read/write command (H0021). Refer to the EN311 manual.
66
F C B 8 7 0
A
A+1
A+2
A+3
A+4
A+5
A+6
A+7
PROSEC T3H
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
F C B 8 7 0
MID CH Target station No.
0 (fixed)
Transfer size
Register type (self-station)
Leading address (self-station)
Register type (target-station)
Leading address (target-station)
Response time limit
A
A+1
A+2
A+3
A+4
A+5
A+6
A+7
A+8
A+9
A+10
MID CH 0 (fixed)
Request command
Transfer size
Register type (self-station)
Leading address (self-station)
Register type (target-station)
Leading address (target-station)
Response time limit
Target-station IP address
Target-station UDP port No.
Page 69

2. Expanded Functions
B
B+1
Inside the parameter:
F E D C B 8 7 0
Abn Busy Status 0 TermSTS
Transmission error information (if TermSTS is H0B)
Transfer parameter S20LP Ethernet
MID (network type) 2 3
CH (channel of self-station) 1 or 2 (max. two S20LP’s on T3H) 1 to 4 (max. four EN311’s on T3H)
Target station No. 1 to 64 0 (fixed)
Request command 0 (fixed) H0021: Register read/write
(for other commands, refer to EN311
manual)
Transfer size
(number of words)
Register type H0000: XW/YW register
Leading address Designates the leading register address to be transferred
Response time limit Specifies the time limit of the response from target-station. (0.1 s units)
Target-station IP address N/A Designates the IP address of the
Target-station UDP port No. N/A Designates the UDP port No. of the
1 to 128
(max. 84 words for T or C register)
(designation across T511 and T512 is
not allowed)
H0001: W register
H0002: LW register
H0003: RW register
H0004: D register
H0005: F register (CPU)
H∗∗05: Expanded F register
(IC card, 8k words/bank, ∗∗ is bank No. 01 - 0F)
H∗∗06: Expanded F register
(IC card, 64k words/bank, ∗∗ is bank No. 01 - 02)
H0007: T register
H0008: C register
H0009: SW register
When the bit F is set to ON, the following default value is used.
S20LP ...... 4.1 s
Ethernet ... 30 s
1 to 485
(max. 323 words for T or C register)
(designation across T511 and T512 is
not allowed)
target-station
target-station
User’s Manual
67
Page 70

2. Expanded Functions
Inside the parameter (cont’d):
Status S20LP Ethernet
Abn 0: Normal complete
1: Error complete
Busy 0: Initial state
1: Transmission port busy
Status 0: Initial state
1: While send requesting
2: While waiting response
3: Complete
TermSTS H00: Normal complete
H01: Register designation error
H02: Response time-out
H03: Parameter error
H04: Register write protect
H05: (Reserve)
H06: Module error (send time-out)
H07: No send channel
H08: Invalid station No.
H09: Transfer size error
H0A: Boundary error
H0B: Transmission error Bit 7 indicates the error is occurred
H0C: I/O no answer error whether self-station or target-station.
H0D: IC card designation error 0: Self-station
H0E: (Reserve) 1: Target-station
H0F: (Reserve)
Transmission error
information
When TermSTS is H0B, the error information is stored. (0 for other cases)
For detailed information, refer to the S20LP or EN311 manual.
Example
RW030 3 1 0 Ethernet, channel 1
RW031 33 (H21) Request command H21: Register read/write
RW032 200 Transfer size: 200 words
RW033 5 Self-station F register
RW034 5000 Leading address: F5000
RW035 4 Target-station D register
RW036 4000 Leading address: D4000
RW037 50 Response time limit: 5 second
RW038 H71 H85 Target-station IP address:
RW039 H0A H62 133.113.98.10 = H85.H71.H62.H0A
RW040 1024 Target-station UDP port No.: 1024
Send requesting
RW060 0 0 1 0 0
RW061 0
PROSEC T3H
68
Page 71

2. Expanded Functions
Ethernet
IP address = 133.113.98.10
T3H T3H
(self-station) (target-station)
F5000 D4000
F5001 D4001
F5199 D4199
When R0030 is ON, 200 words data starting with D4000 of the T3H on which EN311 (IP address =
133.113.98.10) is installed, is read and stored in F5000 and after.
When the operation is completed, the status is set in RW060 and instruction output comes ON.
Note
•
Keep the input ON until the output comes ON.
•
This instruction becomes error complete in the following cases. (ERF = S0051 is set to ON)
(1) Target station No. is invalid. (for S20LP)
(2) Invalid register designation. (In case of T and C registers, T → T and C → C is only possible)
(3) Source/destination register address range is out of valid range.
(4) Destination register is write-protected.
(5) Response time-out is occurred.
(6) If expanded F register is designated;
- when MMR setting is not made.
- when IC card is not installed.
- when IC card is used to store program.
- when IC card is write-protected. (for destination)
•
By using SW067, self-station’s register write-protect is available.
F 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SW067 SW C T F D RW LW W YW
0: Write enable
1: Write protect
•
Resetting the status register (operand B) is necessary at the first scan.
•
When using the TOSLINE-S20LP or Ethernet module (EN311), read the manual for these network
modules.
Both F register in CPU and
expanded F register in IC card
User’s Manual
69
Page 72

PROSEC T3H
70
Page 73

TOSHIBA CORPORATION
Industrial Equipment Department
1-1, Shibaura 1-chome, Minato-ku
Tokyo 105-8001, JAPAN
Tel: 03-3457-4900 Fax: 03-5444-9268
 Loading...
Loading...