NTDPJTV04
SERVICETRAINING
"CustomerSatisfactionThroughKnowledge"
SERVICINGTHEN5SS
COLORTELEVISION
CHASSIS/DIGITAL
CONVERGENCE
TOSHIBAAMERICACONSUMERPRODUCTS,INC.
NATIONALSERVICEDIVISION
TRAININGDEPARTMENT
1420-BTOSHIBADRIVE
LEBANON,TENNESSEE37087
PHONE:(615)449-2360
FAX:(615)444-7520

FOREWORD
The material presented in this manual is provided for the technical training of T ACP employees and
qualified service personnel only .
The specific circuit reference designations, pin numbers, etc., are taken from the TP48E50/60 Service
Manual, File Number 020-9508. The diagrams in this manual are simplified for training and should be used
as a reference guide only when servicing the N5SS CTV Chassis. Refer to the applicable service data for
detailed adjustment and servicing procedures.
NTDPJTV04
SERVICING T OSHIBA'S N5SS TELEVISION CHASSIS
©1996
TOSHIBA AMERICA CONSUMER PRODUCTS, INC.
National Service Division
National Training Department
1420 T oshiba Drive
Lebanon, TN 37087
(615) 449-2360
No part of this manual may be reproduced in whole or in part without prior written consent from
Toshiba America Consumer Products, Inc., Service Division.

CONTENTS
SECTION I
OVERALL UNIT CHARACTERISTICS,
BLOCK DIAGRAMS, LABS 1 & 2
1.MAIN FEATURES..................................1-2
2.MERITS OF BUS SYSTEM....................1-2
2-1.Improved Servciceability.................1-2
2-2.Reduction of Parts Count................1-2
2-3.Quality Control.................................1-2
3. COMPARISON/DIFFERENCES TG-1...1-2
4.SPECIFICATIONS..................................1-3
5.FRONT AND REAR CONTROL
VIEWS.....................................................1-4
5-1.Front View........................................1-4
5-2.Rear View.........................................1-5
5-3.Remote Control View.......................1-6
6.'95 PJ-TV CHASSIS LAYOUT...............1-7
7.CONSTRUCTION OF CHASSIS............1-8
8. VIDEO SIGNAL FLOW........................1-9
9.AUDIO SIGNAL FLOW.......................1-11
10.POWER SUPPLY..................................1-12
11.H and V DEFLECTION.........................1-13
12.I2C COMMUNICATIONS.....................1-14
13.DIGITAL CONVERGENCE.................1-15
14.LAB 1.....................................................1-16
15.LAB 2.....................................................1-20
SECTION II
TUNER, IF/MTS/S.PRO MODULE
1.CIRCUIT BLOCK....................................2-2
1-1.Outline..............................................2-2
1-2.Major Features..................................2-2
1-3.Audio Multiplex Demodulation
Circuit...............................................2-3
1-4.A.PRO Section (Audio Processor)...2-4
2.PIP TUNER..............................................2-6
2-1. Outline...............................................2-6
SECTION III
CHANNEL SELECTION CIRCUIT
1.OUTLINE OF CHANNEL
SELECTION CIRCUIT SYSTEM..........3-2
2.OPERATION OF CHANNEL
SELECTION CIRCUIT...........................3-2
3.MICROCOMPUTER...............................3-3
4.MICROCOMPUTER TERMINAL
FUNCTION..............................................3-4
5.EEPROM (QA02)....................................3-6
6.ON SCREEN FUNCTION.......................3-6
7.SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM................3-7
8.LOCAL KEY DETECTION METHOD..3-8
9. ENTERING THE SERVICE MODE.......3-9
10.TEST SIGNAL SELECTION..................3-9
11.SERVICE ADJUSTMENT......................3-9
12.FAILURE DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURE3-10
13.TROUBLE SHOOTING CHARTS.......3-13
SECTION IV
AUDIO OUTPUT CIRCUIT
1.OUTLINE.................................................4-2
2.THEORY OF OPERATION....................4-2
2-1.Operation of TA8256H....................4-2
SECTION V
DSP CIRCUIT
1.ORIGINS OF DOLBY SURROUND......5-2
2.THE DOLBY MP MATRIX....................5-2
3.THE DOLBY SURROUND
DECODER...............................................5-3
4.DSP CIRCUIT..........................................5-3
5.DSP (Digital Surround Processor) IC......5-6
SECTION VI
A/V SWITCHING CIRCUIT
1.OUTLINE.................................................6-2
2.IN/OUT TERMINALS............................6-2
3.CIRCUIT OPERATION..........................6-2
3-1.Composite Video Signal...................6-2
3-2.S-Video Signal.................................6-2
SECTION VII
VIDEO PROCESSING CIRCUIT
1.OUTLINE.................................................7-2
2.SIGNAL FLOW.......................................7-2
3.CIRCUIT OPERATION..........................7-2
SECTION VIII
V/C/D/IC
1.OUTLINE.................................................8-2
2.LARGE SCALE EMPLOYMENT OF
BUS CONTROL OF PARAMETER FOR
PICTURE CONTROLS...........................8-2
3.EMPLOYMENT OF CONTAINING
EACH VIDEO BAND FILTER
INSIDE.....................................................8-2

4. EMPLOYMENT OF CONTAINING
EACH FILTER (FOR S/H) INSIDE ....... 8-2
5. LOW COST OF IC ..................................8-3
SECTION IX
PIP MODULE
1. BOARD LAYOUT...................................9-2
2. SIGNALS .................................................9-2
3. BLOCK DIAGRAM ................................9-3
SECTION X
SYNC SEPARATION, H-AFC,
H-OSCILLATOR CIRCUITS
1. SYNC SEPARATION CIRCUIT .......... 10-2
1-1. Theory of Operation .......................10-2
2. H AFC (Automatic Frequency Control)
CIRCUIT ................................................10-3
3. H OSCILLATOR CIRCUIT ..................10-4
3-1. Outline ............................................10-4
3-2. Theory of Operation .......................10-4
SECTION XI
VERTICAL OUTPUT CIRCUIT
1. OUTLINE...............................................11-2
1-1. Theory of Operation .......................11-2
2. V OUTPUT CIRCUIT ...........................11-3
2-1. Actual Circuit .................................11-3
2-2. Sawtooth Waveform Generation ....11-3
2-3. V Output .........................................11-4
2-4. V Linearity Characteristic
Correction .......................................11-6
3. PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR
V DEFLECTION STOP ........................ 11-7
3-1. +35V Over Current
Protection Circuit ...........................11-8
SECTION XII
HORIZONTAL DEFLECTION CIRCUIT
1. OUTLINE...............................................12-2
2. HORIZONTAL DRIVE CIRCUIT........12-2
2-1. Theory of Operation .......................12-2
3. BASIC OPERATION OF HORIZONTAL
DRIVE....................................................12-3
3-1. Theory of Operation .......................12-3
3-2. Drive System ..................................12-4
3-3. Circuit Description .........................12-5
4. HORIZONTAL OUTPUT CIRCUIT ....12-6
4-1. Theory of Operation .......................12-7
4-2. White Peak Bending
Correction Circuit.........................12-11
4-3. H Blanking ...................................12-12
4-4. 200V Low Voltage Protection......12-13
5. HIGH VOLTAGE GENERATION
CIRCUIT ..............................................12-14
5-1. Theory of Operation .....................12-14
5-2. Operation Theory of the Harmonic
Non-Resonant System and Tuned
Waveforms ...................................12-16
6. HIGH VOLTAGE CIRCUIT ...............12-17
6-1. High Voltage Regulator................12-17
7. X-RAY PROTECTION CIRCUIT ...... 12-20
7-1. Outline ..........................................12-20
7-2. Operation ......................................12-20
8. OVER CURRENT PROTECTION
CIRCUIT ..............................................12-21
8-1. Outline ..........................................12-21
8-2. Operation ......................................12-21
SECTION XIII
DEFLECTION DISTORTION
CORRECTION CIRCUIT (DPC Circuit)
1. DEFLECTION DISTORTION
CORRECTION IC (TA8859P) ..............13-2
1-1. Outline ............................................13-2
1-2. Functions and Features ...................13-2
1-3. Block Diagram ...............................13-2
2. DIODE MODULATOR CIRCUIT ........13-3
3. ACTUAL CIRCUIT...............................13-4
3-1. Basic Operation and Current Path ..13-5
SECTION XIV
CLOSED CAPTION/EDS CIRCUIT
1. OUTLINE...............................................14-2
2. DATA TRANSMISSION FORMAT.....14-2
3. DISPLAY FORMAT ............................. 14-3
4. CIRCUIT OPERATION ........................14-4
SECTION XV
DIGITAL CONVERGENCE CIRCUIT
1. OUTLINE...............................................15-2
2. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION .....................15-2
2-1. Configuration..................................15-2
2-2. Circuit Operation ............................15-2
3. PICTURE ADJUSTMENT ....................15-4
3-1. Change of Memory (E2PROM) ......15-4
3-2. Service Mode ..................................15-4
4. ADJUSTING PICTURE
DIMENSION (Green picture)................15-6
5. KEY FUNCTION OF REMOTE CONTROL
UNIT ......................................................15-7
6. CONVERGENCE OUTPUT
CIRCUIT ................................................15-8
6-1. Outline ............................................15-8

6-2. Circuit Description .........................15-8
7. CONVERGENCE TROUBLESHOOTING
CHART.................................................15-10
8. LAB 3 ...................................................15-11
SECTION XVI
OPTICAL SECTION
1. NECK COMPONENTS .........................16-2
1-1. Outline of Components Around
Neck of The Projection Tube .........16-2
1-2. Theory of Operation........................16-2
1-3. Projection Tube ..............................16-3
2. FUNCTION OF KEY
COMPONENTS .....................................16-4
2-1. Outline ............................................16-4
2-2. Theory of Operation .......................16-4
2-4. Optical Coupling Effect .................16-8
2-5. Lens ................................................16-9
2-6. Focus Adjustment .........................16-10
SECTION XVII
POWER CIRCUIT
1. OVERVIEW...........................................17-3
2. RECTIFYING CIRCUIT AND
STANDBY POWER SUPPLY ..............17-4
3. MAIN SUPPLY CIRCUIT .................... 17-4
4. OUTLINE OF CURRENT RESONANT
TYPE SUPPLY ......................................17-4
5. FUNDAMENTAL THEORY ................17-5
6. ACTUAL CIRCUIT...............................17-6
7. SCAN DERIVED VOLTAGES.............17-8
8. PROTECTOR MODULE (Z801) ..........17-9
9. SUB POWER SUPPLY .......................17-10
10. PROTECT CIRCUITS .........................17-11
11. LAB 4 ...................................................17-15
SECTION XVIII
DYNAMIC FOCUS CIRCUIT
1. OUTLINE...............................................18-2
2. H DYNAMIC FOCUS CIRCUIT ..........18-2
2-1. Theory of Operation .......................18-2
2-2. Circuit Operation ............................18-3
3. V DYNAMIC FOCUS CIRCUIT ..........18-4
3-1. Theory of Operation .......................18-4
3-2. Circuit Operation ............................18-5

SECTION I
OVERALL UNIT
CHARACTERISTICS
BLOCK DIAGRAMS
LABS 1 & 2
1-1
SECTION I
OVERALL UNIT
CHARACTERISTICS
1. MAIN FEATURES
The main feature of Toshiba's projection television model
TP48E60, is the use of the N5SS (TG-1C) chassis. This
chassis utilizes a bus control system, developed by PHILIPS
Corporation, called the I2C (or IIC) bus. IIC stands for InterIntegrated Circuit control. This bus co-ordinates the transfer
of data and control between ICs inside the Television. It is a
bi-directional serial bus consisting of two lines, namely SDA
(Serial DATA), and SCL (Serial CLOCK).
Digital data which is passed along the bus is received by
individual devices and can be either command or data.
Digital-to analog converters are also found within some of
the ICs, allowing them to be addressed and controlled by
strings of digital instructions, replacing those functions
which were previously implemented by external
potentiometers.
2. MERITS OF THE BUS SYSTEM
2-1. Improved Serviceability
Most of the adjustments previously made by resetting variable
resistors and/or capacitors can be made on the new chassis
by operating the remote control and seeing the results on the
television screen. This allows adjustments to be made without
removing covers on the unit thus increasing servicing speed
and efficiency.
2-2. Reduction of Parts Count
The use of digital-to-analog converters built into the ICs,
allowing them to be controlled by software, has eliminated
or reduced the requirement for many discrete parts such as
potentiometers and trimmers, etc.
2-3. Quality Control
The central control of adjustment data makes it easier to
understand, analyze, and review the data, thus improving
the quality of the product.
3. COMPARISON/DIFFERENCES OF TG-1 CHASSIS
Toshiba's concept for the TG-1 chassis was to create a sort
of universal chassis which, with minimal changes, could be
used as a standard throughout the entire Toshiba color
television lineup starting in 1995. TG-1 stands for "Toshiba
Global 1". The TG-1 chassis can be found in several
different models and varies in both complexity and features.
Ro ot TG-1 Typical Pic ture and
Chassis Chassis Sizes Features
N5E A1 13, 19 Less
N5ES A2 20, 32
N5S A2 - LEM 20, 32
N5S B 27, 32
N5SS C 27 thru 35 More
Typical Chassis Ex am ples
Model TG-1
CF13E22,23 A1
CF19E22 A1
CF20E30 A1
CF20E40 A1
CN27E55 A 2
CF30E50 A2
CF32E50 A2
CF32E55 A2
CX32E60 B
CX32E60 B
CN27E90 C
CX32E70 C
CN32E90 C
CN35E15 C
TP48E50,51 C
TP48E60,61 C
TP55E50,51 C
TP55E80.81 C
TP61E80 C
TP48E90 C
1-2
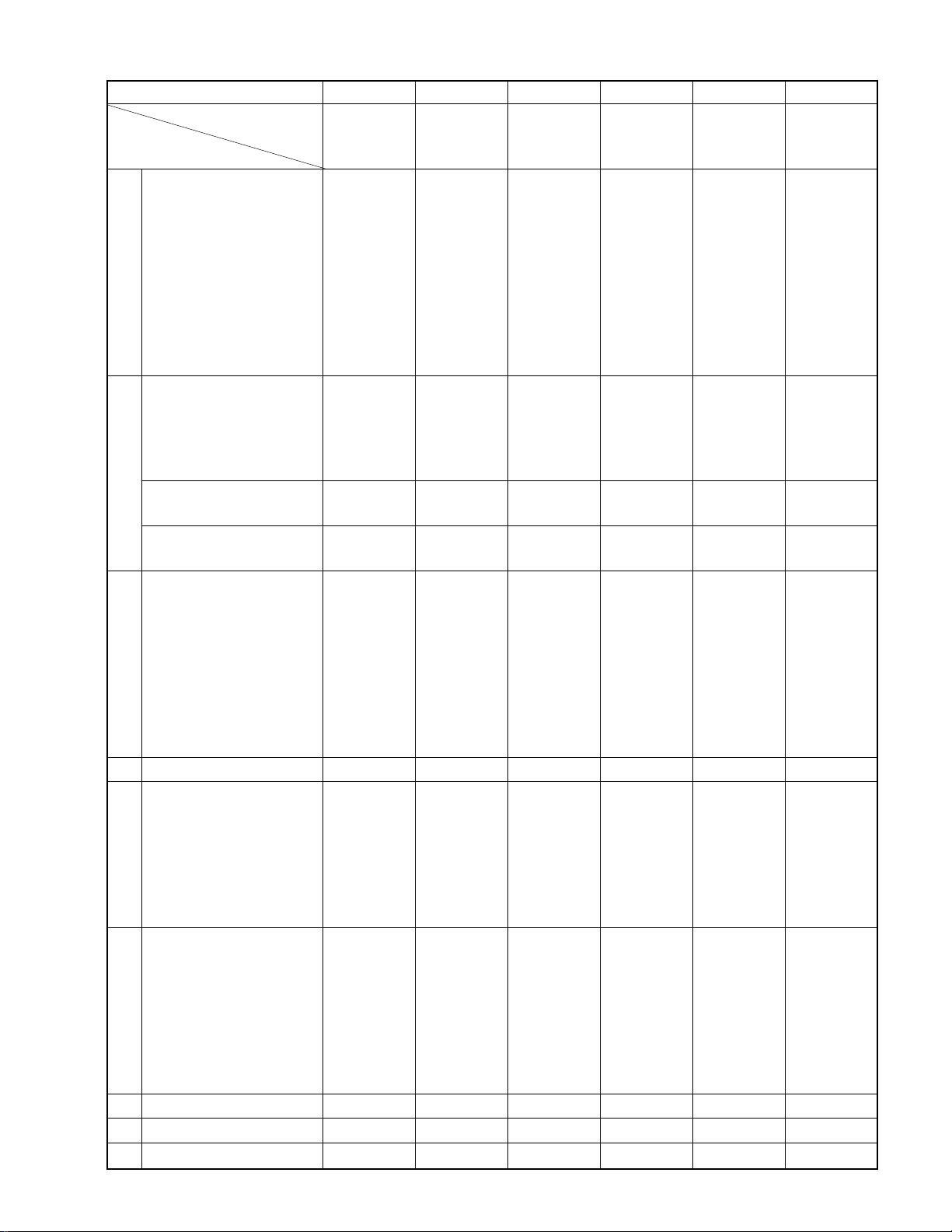
4. SPECIFICATIONS
CHASSIS CCCCCC
MODEL Nbr TP48E50 TP48E60 TP48E90 TP55E50 TP55E80 TP61E80
TP48E51 TP48E61 TP55E51 TP55E81 STEP-UP
SPECIFICATION
1 Picture Size# 48"-D/S 48"-D/S 48"-D/S 55"-D/S 55"-D/S 61"-D/S
2 Channel Capacity 181ch 181ch 181ch 181ch 181ch 181ch
*
3 C. Caption ●●●●●●
G
4 MTS with dbx ●●●●●●
E
N
5 Bass, Tre/Balance ●●●●●●
E
6 Sub-Audio-Program ●●●●●●
R
7 Remote Control *A-Uni (42k A-Uni (42k *Intelig+EZ A-Univ (42k A-Univ (43k A-Univ (43k
A
8 Picture-in-Picture * ●
L
9 LED Indicator (RED) ● (P) ● (P) ● (P) ● (P) ● (P) ● (P)
10 Local Key 8key 8key 8key 8key 8key 8key
11 Dolby Surround — — ●(Prolo) — ●●
12 Dig-Sound Processor — — ● (DSP4ch) — ● (DSP4ch) ● (DSP4ch)
*
13 Front Surround ●●—●——
S
14 Cyclone ABX ——————
O
15 Sub-Bass-System ●●●●●●
U
16 Audio Output 14Wx2 14Wx2
N
D
17 Speaker Size & Nbr 160Rx2 160Rx2 160Rx2 160Rx2 160Rx2 160Rx2
18 Comb Filter ●
*
19 Dynamic Focus # ●●●●●●
P
20 Scan Velocity Modu ●
I
21 Vert Contour Corre ——————
C
22 Black Level Expand ●●●●●●
T
23 Flesh Tone Correct ●●●●●●
U
R
24 Dynamic Noise Reduc ●●●●●●
E
25 Picture Preference ●●●●●●
26 Digital-Convergence ●●●●●●
27 Horiz Resolution 800 800 800 800 800 800
28 Parental-Ch Lock ●●●●●●
*
29 Channel Label (32ch) ●●●●●●
O
30 3-Language Display ●●●●●●
T
31 Clock/Off-Timer ● / ●●/●●/●●/●●/●●/●
H
32 Favorite Channel ●●●●●●
E
R
33 Extended-Data-Servi ●●●●●●
34 Star-Sight-Decoder ——————
35 S-Video In-Term ●
36 Audio, Video-In/Out 1+2/1 1+2/1 1+2/1 1+2/1 1+2/1 1+2/1
*
37 Front AV Jack ●●●●●●
T
E
38 Variable Audio Out ●●●●●●
R
39 2-RF Input *— ●●—●●
M
40 Ext Speaker Term ●●●●●
S
41 PIP Audio Out Jack — — ● ———
42 Center-Ch-Aud-Input ————●●
43 Speaker-Box — — ● (SS-SR94 — ● (SS-SR94 ● (SS-SR94
AC
*Cabinet NEW NEW NEW NEW NEW NEW
PARTS SUPPLY (ISO) ——————
(1TN)
(DIG)
(RGB)
(1+1)
●
●
●
●
(2TN)
(DIG)
(RGB)
(1+1)
●
(2TN)
14Wx2, 10Wx2
& 10Wx2
& REAR SPK & REAR SPK & REAR SPK
●
(DIG)
●
(RGB)
●
(1+1)
●
(1TN)
14Wx2 14Wx2 14Wx2
●
(DIG)
●
(RGB)
●
(1+1)
●
(2TN)
& 10Wx2 & 10Wx2
●
(DIG)● (3D-Y/C)
●
(RGB)
●
(1+1)
●
●
●
(2TN)
(RGB)
(1+1)
1-3
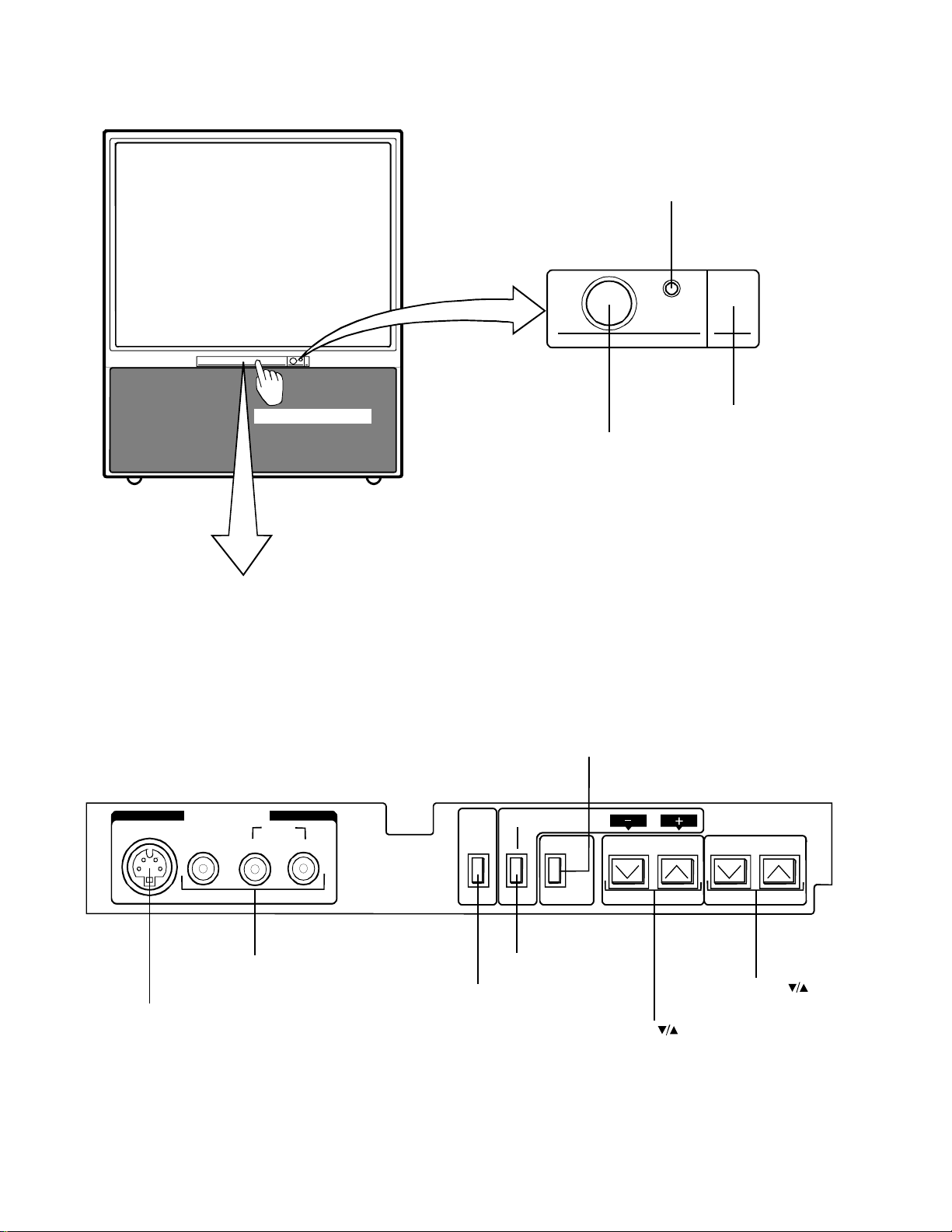
5. FRONT AND REAR CONTROL VIEWS
5-1. Front View
POWER indicator
POWER
S-VIDEO
Press to open the door.
Behind the door
IN-VIDEO 3
VIDEO
L/MONO R
AUDIO
Fig. 1-1
DEMO
POWER button
ANT/VIDEO button*
ADV butto n
MENU-ADV
ANT/VIDEO
VOLUME
Remote se ns or loca tio n
CHANNEL
VIDEO/AUDIO INPUT
jacks
S-VIDEO INPUT jack
* These buttons have dual functions.
MENU buttom
DEMO button
Fig. 1-2
1-4
VOLUME buttons*
butto ns
−/+
CHANNEL
butttons
1-5
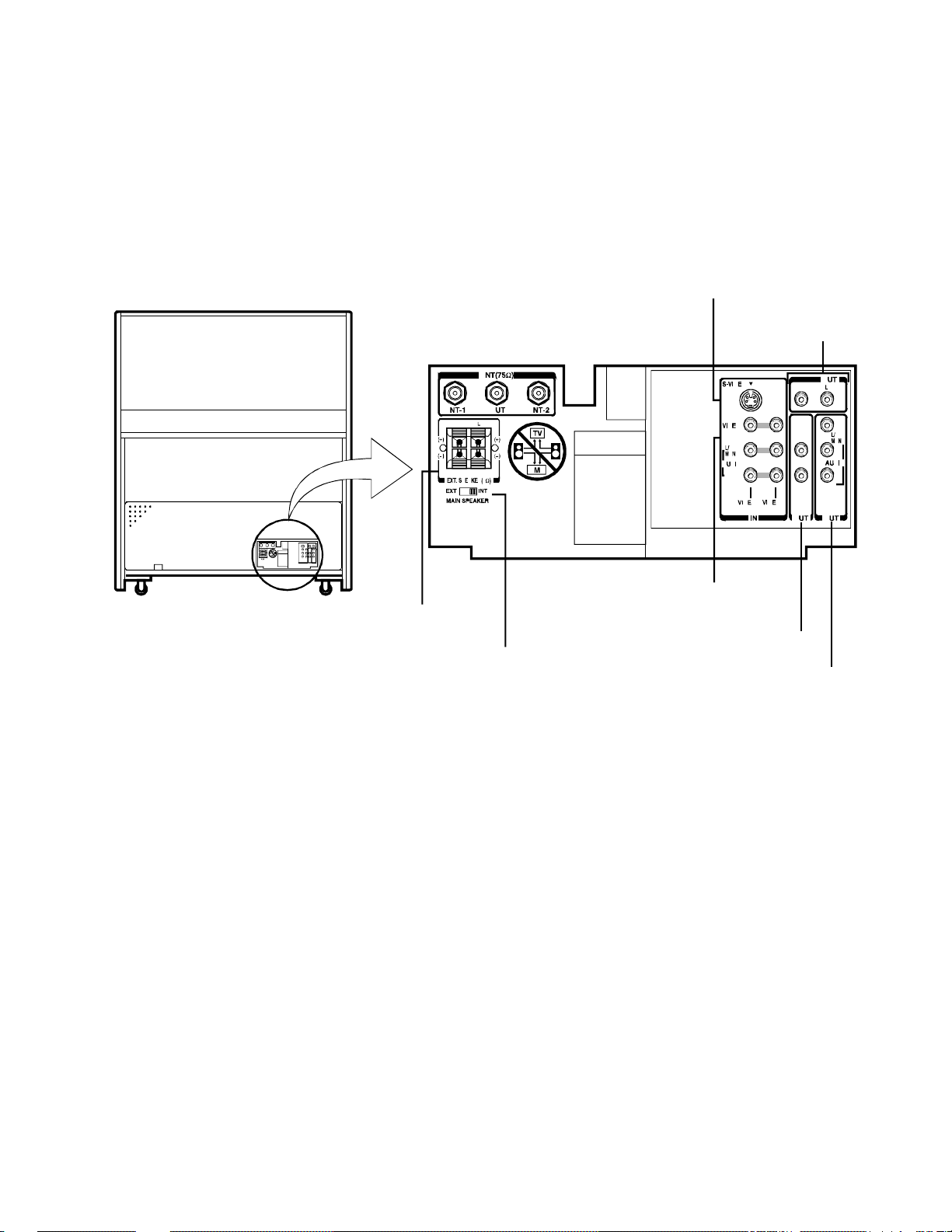
5-2. Rear View
OUTPUT jacks
TV rear
EXTERNAL
SPEAKER
terminals
A
A AO
R
A RP 8
MAIN
SPEAKER
switch
A P
S-VIDEO INPUT jack
D
O
D O
O O
D OA
R
O1 D O2
D
VIDEO 1 INPUT
jacks
VIDEO 2 INPUT
jacks
VARIABLE AUDIO
OUTPUT jacks
O
VAR
R
AUDIO
VIDEO
O O
L/MONO
AUDIO
O
D
R
R
PIP
OO
VIDEO/AUDIO
Fig. 1-3
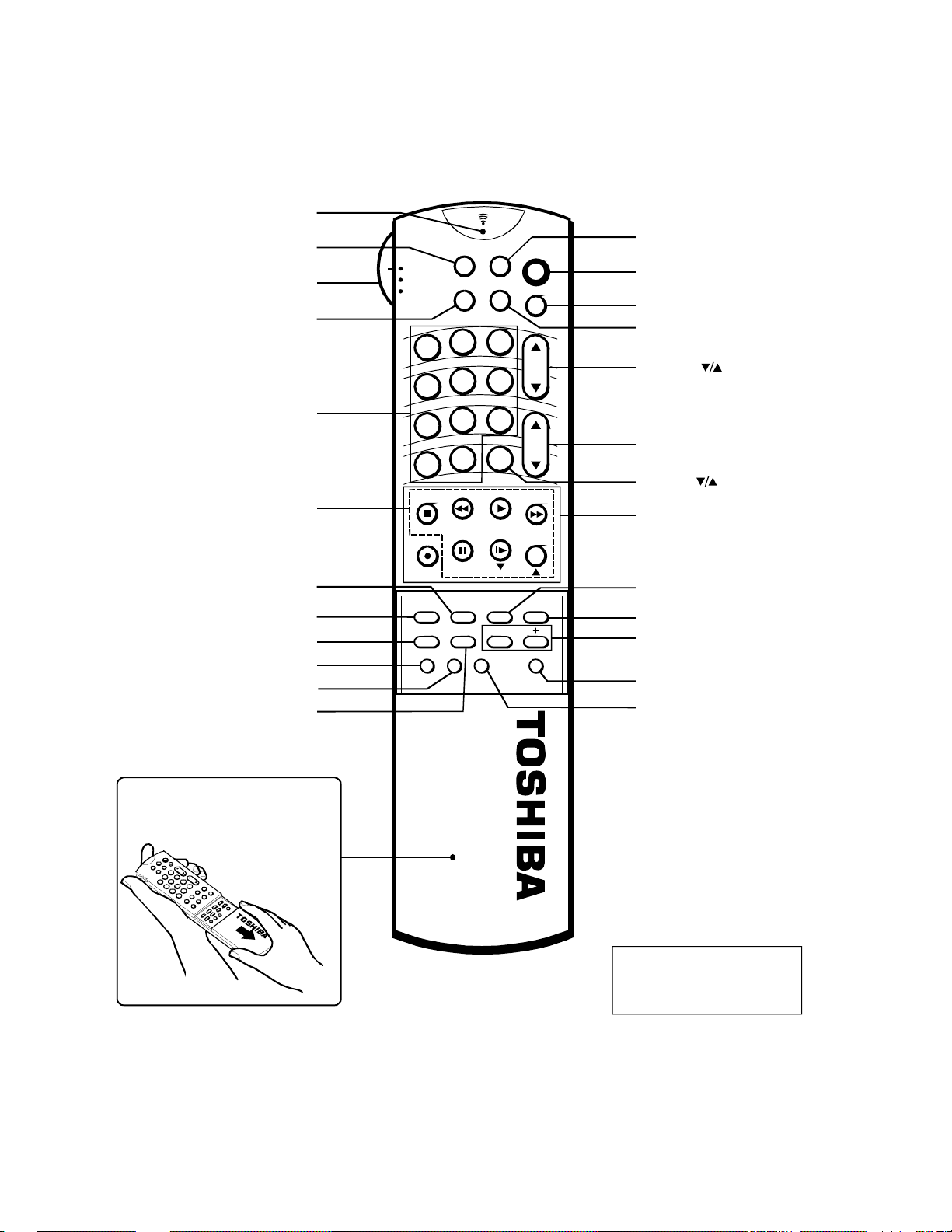
5-3. Remote Control View
y
y
y
Transmit indicator
TV/CABLE/VCR switch
Channel Number*
EDS*
TV/VIDEO*
PIP function*
AUDio*
PICture*
RESET*
C. CAPT*
ANT1/2*
EXIT*
S
D
E
V
T
E
L
B
A
C
R
C
V
1
4
7
100
STOP
LOCATE
REC
PIC.
RESETEXIT
C.CAPTANT1/ 2CYC/ SBS DSP/SUR
O
E
D
I
V
/
V
T
2
5
8
0
REW
SW APSOURCE
PAUSE/ STI LL
SLOW
STILL
AUD.SET UP
R
R
E
C
A
3
6
9
ENT
RTN
PLAY
FAV
O
W
L
L
M
U
T
E
CH
VOL
FF
PIP
TV/VC R
PIP
CH
OPTION
E
P
M
I
T
E
TIMER/Clock*
R
POWER
RECALL*
MUTE*
CHANNEL
RTN*
VOLUME
VCR function*
SET UP*
OPTION*
−/+
FAV −/+*
DSP/SUR*
SYC/SBS*
To operate buttons inside the cover,
slide the cover down and toward
ou.
*
These functions do not have
duplicate locations on the TV.
can be controlled only b
The
the Remote Control.
Fig. 1-4
1-6
6. PJTV CHASSIS LAYOUT
3
1-7
Fig. 1-5
:DIGITAL CONVER
8
-1:CRT-D(R)
5
5
REAR
AMP 2CH
-5:SVH
-4:CRT-D(G)
5
-4:FRONT
5
FOCUS PACK
-4:CRT-D(B)
5
:CONV/POW2
CENTER
AMP 2CH
to FOCUS
PACK
F.B.T
-4:DYNAMIC FOCUS
4
to CRT
J-BOX
3:DPC
−
3
1. AUDIO
7A
7B
2. COMB FILTER
:DEF/POWER
1
FEATURE
FRONT SURROUND
TP48E50/51/60/61
TP55E50/51
* SPK. TREM. 1pcs
* REAR.CENTER AMP W/O
:DSP4CH
TP55E80/81
TP61E80
* SPK TERM. 2pcs
* REAR. AMP W/
* CENTER. AMP W/O
* CENTER INPUT W/
:DOLBY PRO
9
TP48E90
* SPK. TERM. 2pcs
* REAR. CENTER AMP W/
:DIGITAL COMB
6A
TP48E50/51/60/61/90
TP55E50/51
:3D Y/C TP61E80
6B
3. TUNER
* TP48E50/51
* TP55E50/51ONLY
1 TUNER
OTHER 2 TUNER
FRONT
AMP 2CH
-2:SPEAKER
4
2
:MAIN
-1:FRONT SURRO UND
7A
-1:DSP 4CH
7B
:DOLBY PRO
9
:DIGITAL COMB
6A
:3D Y/C
6B
PIP(HOKURIKU)
-1:A/V
4
-2:EDS.CC
7A
-2:EDS.CC
7B
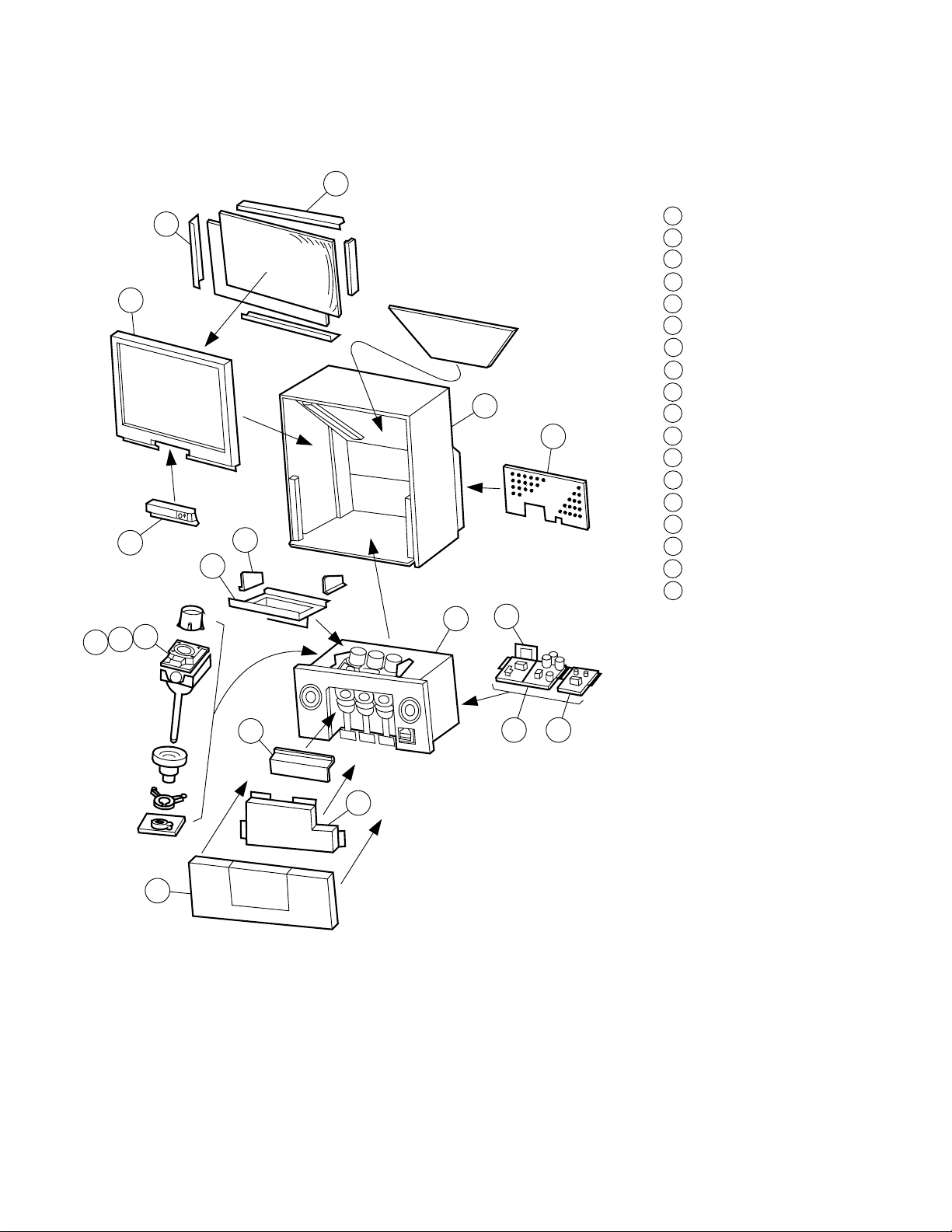
7. CONSTRUCTION OF CHASSIS
9
10
8
7
5
13
14
11
15
WOOD CABINET
1
LIGHT BOX
2
SPEAKER GRILLE
3
FRONT COVER
4
CRT MOUNTING
5
SHIELD FRONT
6
SHIELD SIDE
7
SCREEN BEZEL
8
SCREEN BRACKET L
1
12
2
18
9
SCREEN BRACKET S
10
CONTROL PANEL
11
BACK BOARD
12
COUPLING R
13
COUPLING G
14
COUPLING B
15
CHASSIS FRAME MAIN
16
CHASSIS FRAME POWER
17
AV TERMINAL BOARD
18
6
4
3
16 17
Fig. 1-6
1-8

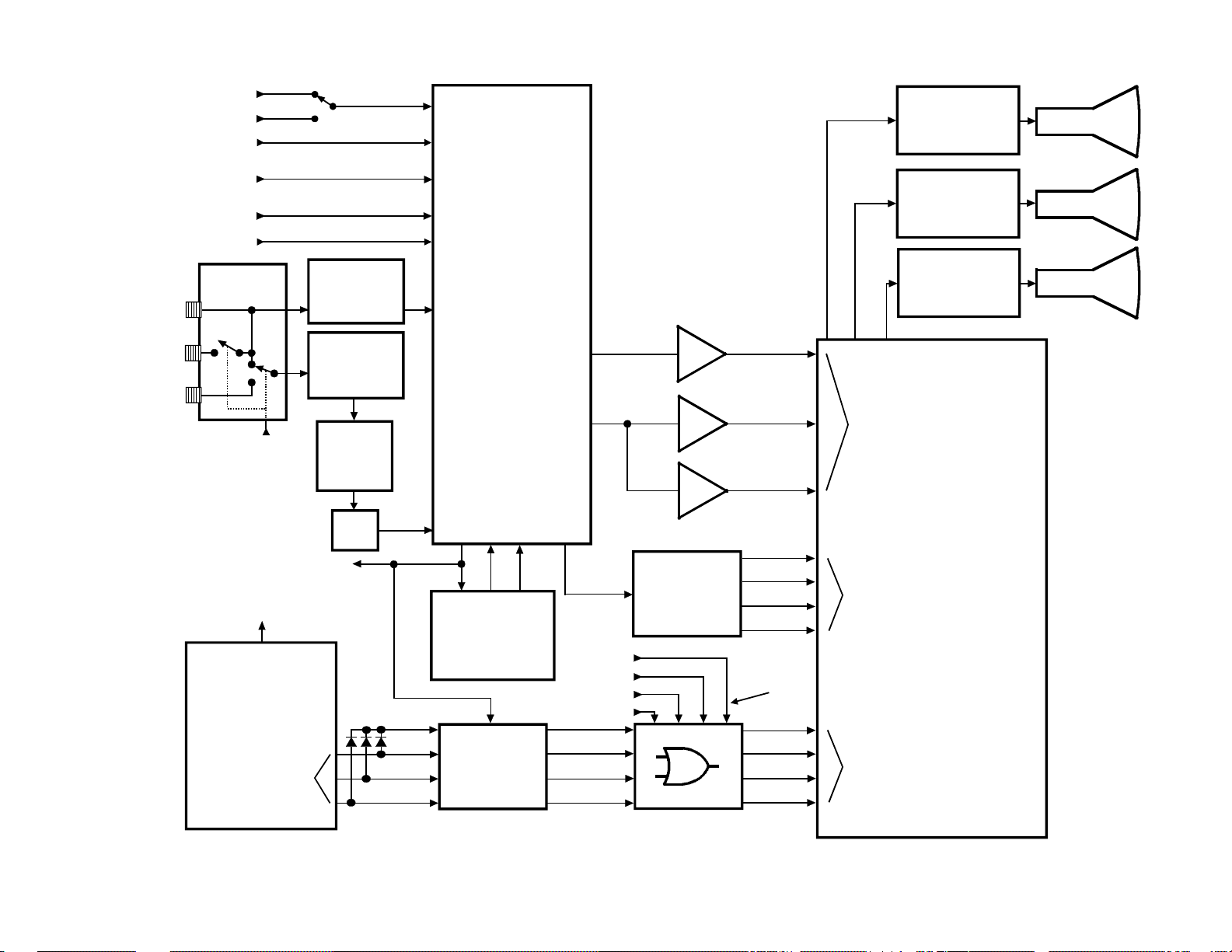
8. VIDEO SIGNAL FLOW BLOCK DIAGRAM
Basic Circuit Operation
The basic operation of the TG-1 chassis is illustrated in the
block diagrams, figures 1-7 through 1-12. Although these
diagrams focus on the TP48E60, the video and audio signal
flow diagrams can be applied to any TG-1 chassis with
minor modifications.
Video Signal Flow
Figure 1-7 illustrates the video signal flow through the TG1 chassis. The Antenna 1 (ANT 1) and Antenna 2 (ANT
2) inputs allow two separate RF signals to be connected to
the RF switcher. When the switch, which is controlled by
the microcomputer, QA01, is in the up position the ANT 1
signal is connected to the HY01 PIP Tuner/IF and the H001
Main Tuner. Moving the switch down connects the ANT
2 signal to the H001 Tuner. Due to the RF Switch the ANT
2 signal can’t be used as the PIP source, but when ANT 2
is selected the ANT 1 signal is available at RF OUT. The
PIP Tuner/IF produces a composite video (CV) signal and
sends it to the AV Switcher, QV01. An IF signal produced
by the Main Tuner is sent to H002, which produces a
composite video signal and sends it to the AV Switcher.
Three video inputs, video 1 through 3, are applied to the AV
Switcher. The video 1 input can be composite video, Y/C
video, or the test signal from QA01. Video 2 is composite
video only, and video 3 is either composite video or Y/C
video. A mechanical switch on the video 1 input defaults
to the test signal, so a video connector must not be plugged
into the video 1 input jack when the internal test signals are
used.
The selected video signal is output as composite video and
applied to the video output jack, the EDS/CC/RGB SW.,
and the Digital Comb Filter or the 3D - Y/C circuit. After
processing the video signal is sent back to the AV Switcher
as separate luminance (Y) and chrominance (C) signals.
The Y and C signals are then sent to Q501 the Video
Chroma Deflection Processing IC. A sync signal is tapped
off the Y signal and applied to Q501. Q501 processes the
video signal and sends separate R, G, and B signals to the
CRT drives and the CRTs.
If the PIP feature is selected, composite video from AV
Switcher is sent to the PIP circuit, ZY01. After processing,
the PIP signal is sent to Q501 as R, G, B, and YS where it
is mixed with the main video.
On screen display (OSD) R, G, and B signals produced by
the Microcomputer, QA01, are mixed with the Extended
Data Service (EDS) and Closed Caption (CC) data in
UM01. These new signals are applied to an OR gate,
QB91, and combined with the convergence signals from
the digital convergence circuit. The convergence signals
can be either the customer convergence cross hairs, or the
service cross hatch pattern. All of these signals are sent to
Q501 where they are mixed with the main video signal.
1-9
1-10
TEST
VIDEO 1
VIDEO 2
VIDEO 3
Figure 1-7 Video Signal Flow Block Diagram
ANT 1
RF
OUT
ANT 2
CV/Y
C
CV
CV/Y
C
RF
SWITC H
CONTROL
FROM
QA01
HY01 PIP
TUNER/IF
H001
MAIN
TUNER
IF
2
H002
IF/MTS
A. PRO
7
EQ
CV TO VIDEO
OUT JAC K
TEST SIGNAL
TO VIDEO 1
QA01
MICRO
COMPUTER
OSD
DATA
22
23
24
12
14
QV01
16
SWITCHING
18
15
CV
28
7
CV
38 30 32
CV
6
DIGITAL
COMB
FILTER
OR, 3D - Y/C
YS
R
G
B
18
19
20
21
9
UM01
EDS/CC
RGB SW.
AV
Y
2
CV
E031Z
9
RED CRT
RED CRT
DRIVE
E032Z
3
GREEN CRT
GRN CRT
DRIVE
E033Z
9
BLUE CRT
B
G
R
42 41
C
34
YY
36
Q503
Q202
SYNC
Q204
43
C
13
MAIN VIDEO
15
17
INPUT
VIDE O CHROMA
DRIVE
Q501
BLUE CRT
DEFLECTION
42
C
4
CV
ZY01
8
PIP
YS
R
G
B
10 13
YS
6
1
5
2
2
R
12
G
5
B
9
4
OR
QB91
1
4
R
5
G
B
6
FROM
DIGITAL
CONV.
1
3
11
6
8
YS
G
B
35
34
33
36
R
39
38
37
32
YS
PROCESSING
PIP VIDEO
INPUT
OSD, EDS, CC, &
CONVERGENCE
VIDEO INPUT
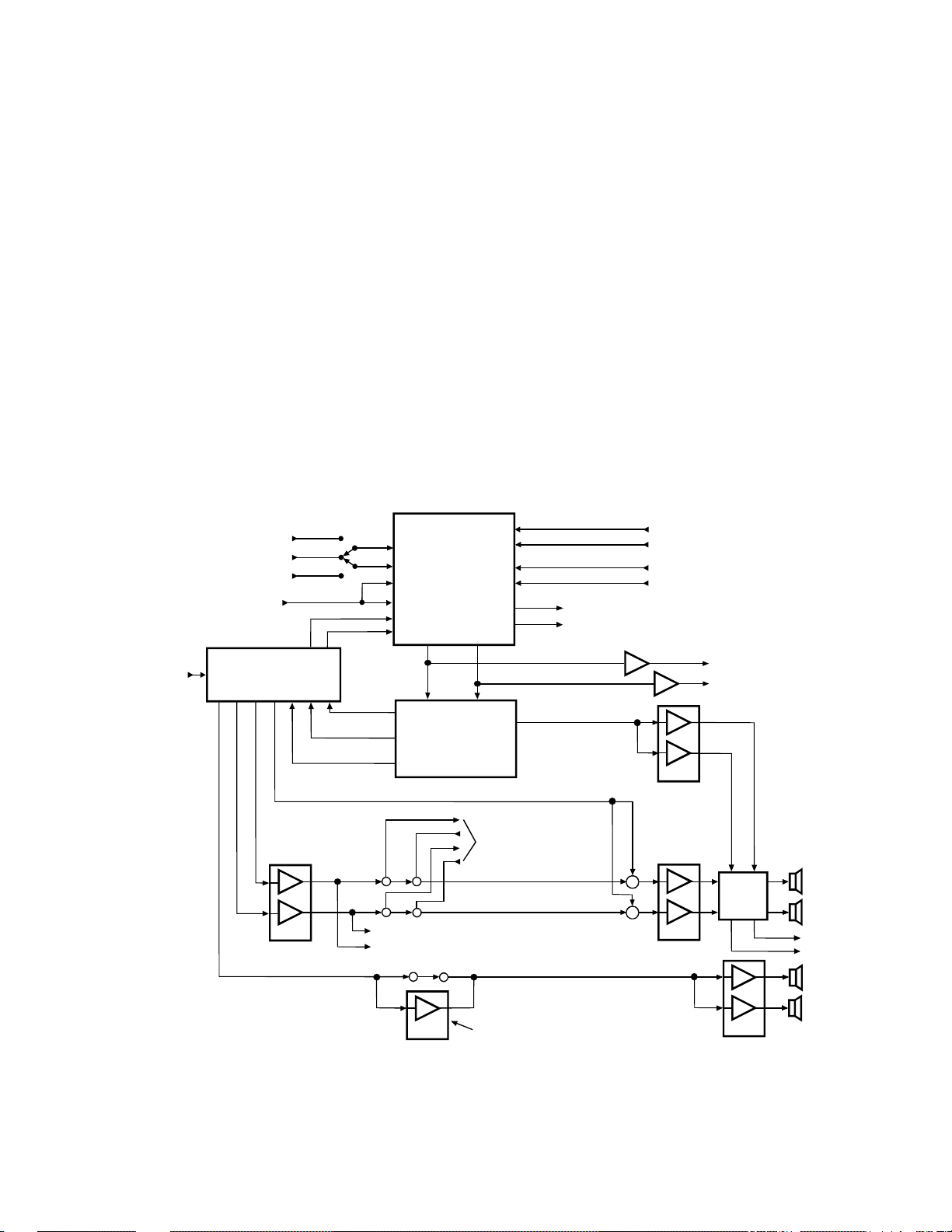
9. AUDIO SIGNAL FLOW BLOCK DIAGRAM
Audio Signal Flow
Audio signals are applied to the AV Switcher from the
three video jacks, H002, and the PIP Tuner, as shown in
Figure 1-8. Like the video signal, there must not be a
connector in the video 1 jack for the audio test signal to be
applied to the AV Switcher. In the TP48E90, PIP audio is
applied to the PIP output jack. The main audio signals are
applied to the audio output jacks and to the Front Surround
circuit, the DSP/Dolby circuit, or the Dolby Pro Logic
circuit. Afterprocessing, the left and right audio signals
are applied to the audio processor in H002 where the
volume, balance, treble, and bass are controlled. Next, the
audio signals are amplified by QS101 and applied to the
variable output jacks, and Q601. If the sub bass system
(SBS) is selected, a signal is mixed with the left and right
signals just before Q601 to increase the signals bass
response. In TP55E80/81 and TP61E80 models, the
jumper is removed so a center signal can be switched in to
replace the main left and right signals. The amplified left
and right audio signals are applied to the internal/external
speaker switch and routed to the desired speakers.
Sets equipped with Dolby or Dolby Pro Logic have a
surround audio signal that is sent to the audio processor in
H002 from the Dolby circuit. The surround signal is then
sent to the rear amplifier, Q641, amplified, and applied to
the rear speakers. In the TP48E90 the surround signal is
routed through an amplifier in Q690 before it is applied to
Q641. Also, the TP48E90 is equipped with Dolby Pro
Logic, and has a center channel. The center channel is
amplified by the Center Amplifier, Q621, and applied to
the front speakers through the internal/external speaker
switch.
VIDEO 1
IF
FROM H001
MAIN TUNE R
SURROUND
TP48E90
TP55E80/81
TP61E80
TEST SIGNAL
FROM QA01
MONO AUDIO
FROM HY01
PIP TUNER
L
R
H002
IF/MTS/A. PRO
2326242217 16 18
L
R
5
L
3
R
QS101
11
13
29
31
L
5
6
R
L
6
R
SURROUND OUT
SBS (SUB BASS SYSTEM)
7
1
5
10
R
TO VARIABLE AUDIO
L
QV01
AV
SWITCHING
37 35
3
DSP/DOLBY,
OR
1
Q690
R
2
TO &FROM CEN TER
INPUT SWITCH & JACK
TP55E80/81 & TP61E80
TP48E90
ONLY
L
FRONT SURROUND,
DOLBY PRO LOGIC
OUT JACK
3
8
9
15
17
1
2
11
CENTER OUT
ONLY
L
TO PIP OUT JACK
(TP48E90 ONLY)
R
QS04
L
R
L
R
QV14
2
4
Q621
CENTER AMP
TP48E90 ONLY
5
+
2
+
Q601
VIDEO 2
VIDEO 3
L
R
12
7
7
INT/EXT
L
SWITCH
11
R
2
4
REAR AMP
TO AUDIO
OUT JACK
RL
Q641
12
7
FRONT OR
CENTER
SPEAKERS
EXTERNAL
REAR
SPEAKERS
Figure 1-8 Audio Signal Flow Block Diagram
1-11
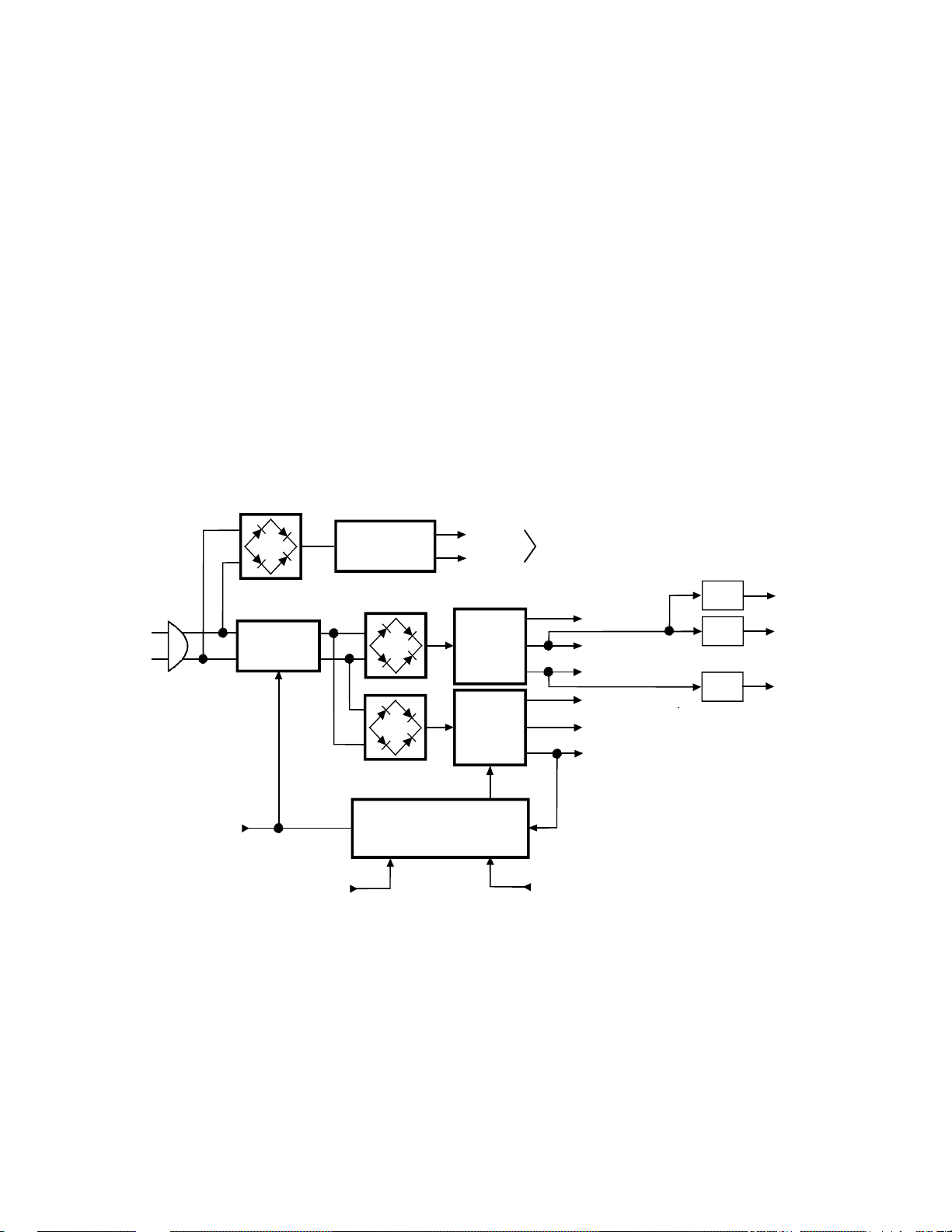
10. POWER SUPPLY AND PROTECTION BLOCK DIAGRAM
The E model PTVs actually have three separate power
supplies as shown in Figure 1-9. These supplies consist of
the Standby Supply, the Main Switch Mode Supply, and
the Sub Switch Mode Supply. The Standby Supply provides
the 5 VDC needed to run the microcomputer and the
customer interface controls, such as the key pad and the IR
receiver. When the set is turned on, the switch closes to
activate the two switch mode supplies and provide the
numerous DC voltages needed to operate the set.
STANDBY
REGULATOR
The Control/Protection circuit, Z801, has two functions.
The first is to regulate the Main Switch Mode Supply, and
the second is to monitor over current, over voltage, and
under voltage sensors throughout the set. If any one of
these sensors activates the protection circuit, Z801 turns
off the switch powering the two switch mode supplies thus
turning off the set. If this occurs, a red LED on the front
panel flashes at half second intervals, and the set must be
unplugged to reset Z801.
+5VDC
RESET
TO MICROCO MPUTER
120VAC
POWER
ON/OFF FROM
MICROCOMPUTER
SWITCH
POWER
OFF
X-RAY SENSING
Figure 1-9 Power Supply/Protection Block Diagram
SWITCH
SWITCH
FEEDBAC K
Z801
16
CONTROL/PRO TEC TION
13
MODE
(SUB)
MODE
(MAIN)
3
14
+30VDC
+15VDC
-15VDC
+12VDC
+38VDC
+125VDC
1
OVERCURRENT,
OVERVOLT A GE, &
UNDER VOLTAGE
SENSING
REG
REG
REG
+5VDC
+15VDC
-9VDC
1-12
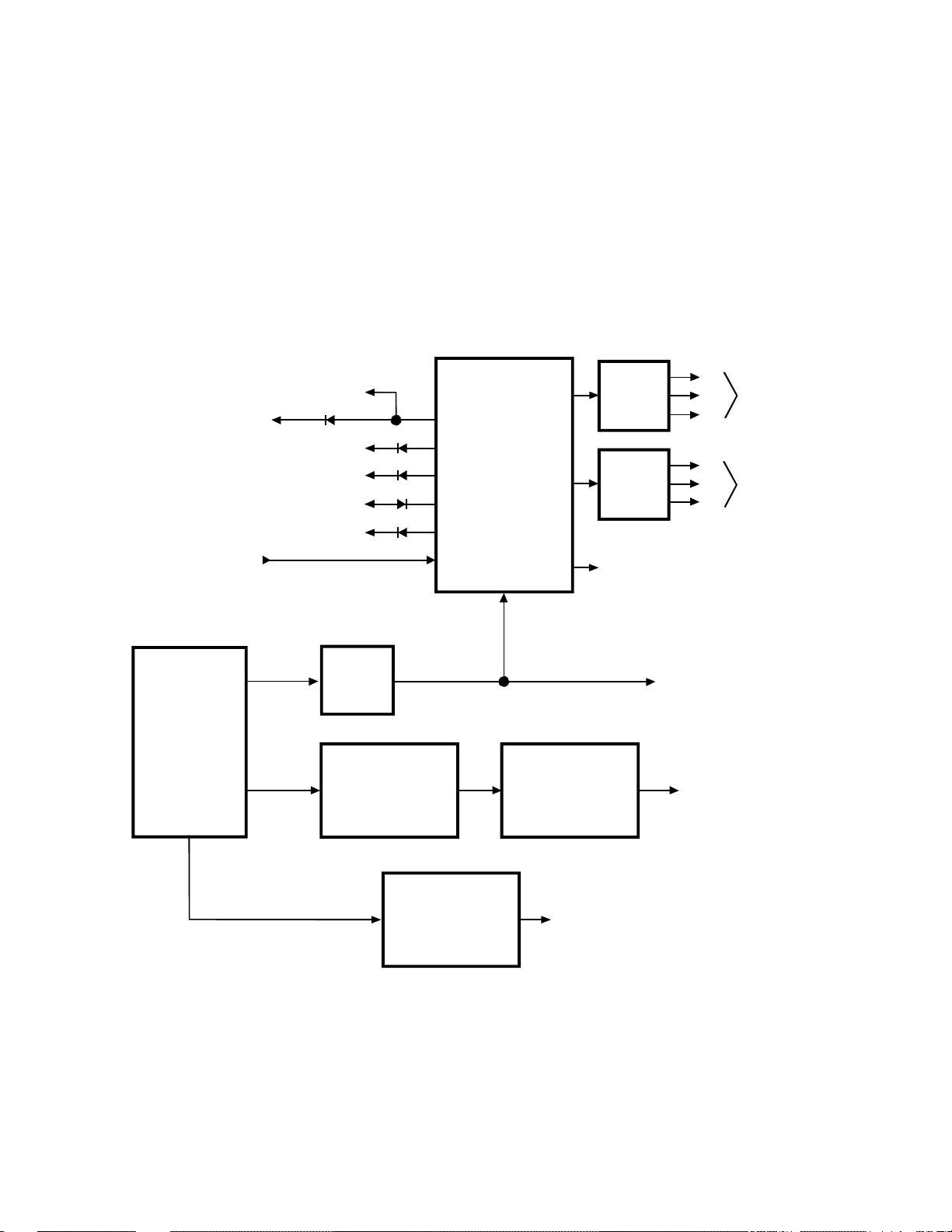
11. HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL DEFLECTION
Deflection circuitry in the E model PTV’s is rather straight
forward as show in Figure 1-10. The horizontal pulse from
Q501 drives the horizontal drive circuitry, which in turn
drives the Horizontal Yokes and the Flyback Transformer,
T461. Numerous low voltage DC supplies are produced by
the Flyback, as well as the high voltages for the anode,
focus, and screen drives. To prevent excessive high
voltages, a sample X-Ray protection voltage is monitored
by the over voltage protection circuits.
AC TO HEATERS
+23VDC TO X-RAY
PROTECT
+12VDC
+35VDC
-27VDC
+200VDC
+125VDC FROM
MAIN POWER
9
TRANSFORMER
7
6
5
3
2
Vertical drive (VD) is applied to the DPC circuit, U421, to
correct any distortions before it’s sent to the Vertical Drive
circuit, Q301. Then the vertical drive circuit supplies the
signals required by the yokes for deflection.
To enhance horizontal transitions between dark and light
areas of the picture, a Velocity Scan Modulation (VSM)
signal is produced by Q501. This signal is sent to the SVM
circuit, E036Z, which in turn drives the SVM coils on the
CRTs.
R
T461
HV
HV
DIST
BLOCK
G
B
30.7KV
TO CRT
ANODES
FLYBACK
2
8
FOCUS
BLOCK
TO ABL
R
G
B
FOCUS &
SCREEN DRIVE
TO CRTs
CIRCUIT
Q501
VIDEO
CHROMA
DEFLECTION
PROCESSING
48
VSM
1
HORIZ
DRIVE
H-OUT
23
VD
31
4
HORIZ
DRIVE
U421
DPC
CIRCUIT
2
6
EO36Z
SVM
4
Q301
VERTICAL
DRIVE
1
TO SVM
COILS
CIRCUIT
Figure 1-10 Horizontal and Vertical Deflection Block Diagram
TO HORIZ
YOKES
TO VERT
2
YOKES
1-13
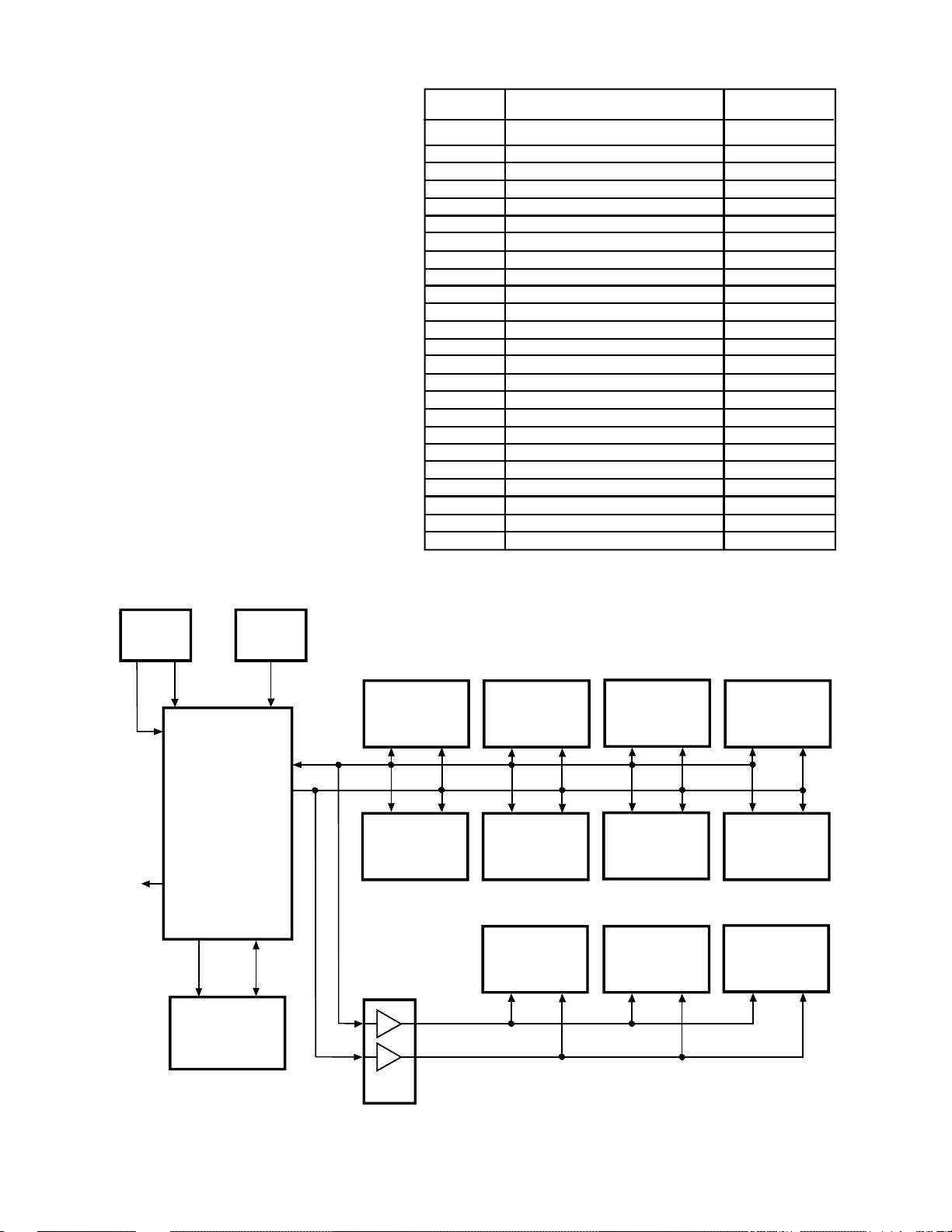
12. I2C Communications
REG
ADJUSTMENT
PRESET
The TG-1 chassis uses I2C data communications to
control all customer features and most of the service
adjustments that where previously done with discrete
devices, refer to Figure 1-11. All communications
are controlled by the Microcomputer, QA01 through
serial data lines (SDA) and serial clock lines (SCL).
Memory settings for customer controls and service
adjustments (except convergence data) are stored in
the E2PROM Memory, QA02, and communicated
to QA01 by the SCL0 and SDA0 lines. Data and
clock lines SDA1 and SCL1 communicate with
most of the circuits in the set. However, there are
three plug in circuits where the data and clock
signals are buffered by QB90 to provide isolation.
All customer functions and most services
adjustments are implemented through the Key Pad
and the Remote Sensor. The RMT OUT signal on
the microcomputer drives the IR Transmitter on the
front panel, but it’s only used in the manufacturing
process. Figure 1-12 shows the Service Registers
and their default values used for making adjustments
in the set.
RCUT RED CUTOFF 40
G C U T G R E E N C U T O F F 4 0
B C U T B L U E C U T O F F 4 0
R D R V R E D D R I V E 4 0
B D R V B L U E D R I V E 4 0
C N T X S U B - C O N T R A S T M A X 7 F
B R T C S U B - B R I G H T C E N T E R 8 0
COLC SUB-COLOR CENTER 50
TNTC SUB-TINT CENTER 40
SCOL SAP-COLOR 15
SCNT SUB-CONTRAST 15
HPOS HORIZ. POSITION 16
VPOS VERTICAL POSITION 00
HIT VERTICAL HEIGHT D1
GMPS GMPS 00
VLIN VERTICAL LINEARITY 12
VSC A-S CORRECTION 08
V P S V E R T I C A L S H I F T 1 5
VCP V-COMPENSATION 03
WID PICTURE WIDTH 25
TRAP TRAPEZIUM 10
HCP H-COMPENSATION 02
VFC V-F CORRECTION 0F
STRH HORIZ. START POSITION 82
Figure 1-12 Service Register Default Values
KEY A
TO IR
LED
TRANS
KEY
PAD
KEY B
18 35
17
REMOTE
SENSOR
QA01
MICRO-
COMPUTER
RMT OUT
3
12
SCL0 SDA0
11
65
QA02
EEPROM
MEMORY
38
SDA1
SCL1
37
IC501
V/C/D
PROCESSING
27 28 21
910
COMB FILTER
OR
3D-Y/C
3
2
QB90
SDA2
5
SCL2
6
H002
IF/MTS/A.PRO
20
25
QAV01
SWITCHING
F. SURR.,
DSP/DOLBY,
D. PRO LOGIC
14 15 14 13
24 44
AV
DPC CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT
H001
TUNER
U421
ZY01
PIP
21
HY01
TUNER/IF
34
43
Q701
CONV.
PROCESSOR
UM01
EDS/CC
RGB SW.
14 13
Figure 1-11 I2C Communication Block Diagram
1-14
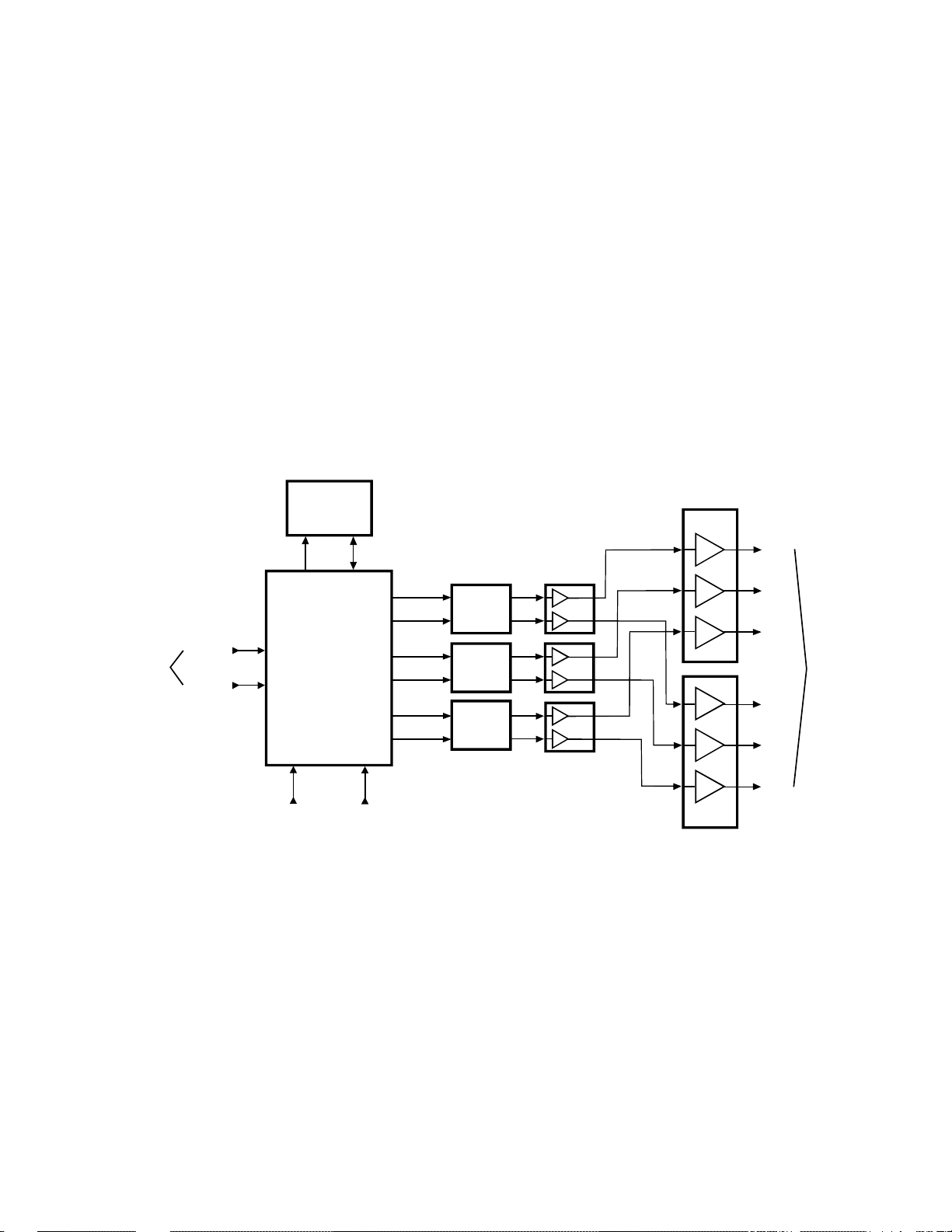
13. Digital Convergence
The TG-1 model PTV’s are equipped with a new digital
convergence circuit shown in Figure 1-13. This circuit
allows servicers to set the convergence with the remote
control. Q701, the Digital Convergence Processor aligns
the convergence from data received from the remote, and
saves the settings in the E2PROM, Q713. The digital
convergence signals are converted to analog by the D/A
Converters Q703, Q704, and Q705. Then they are amplified
Q713
EEPROM
FROM
QAO1
CLK
DATA
65
CLK
45
Q701
43
DIGITAL
CONVERGENCE
44
PROCESSOR
31 32
HD
FROM
IC501
46
VD
FROM
Q301
DATA
7
RH
86
6
RV
87
GH
89
GV
90
BH
96
BV
97
7
6
7
6
CONV.
CONV.
CONV.
by the pre amps (Q715, Q717, & Q719) and power amps
(Q751 & Q751) before being applied to the convergence
yokes. The Power Amps Q752 and Q751 dissipate allot of
heat because of their current draw, so the supplies to these
amps have a number of sensors for over current conditions.
Most of the convergence circuit is on a shielded board, but
the power amps are easily accessible for service.
Q752
18
11
9
18
11
9
Q703
D/A
Q704
D/A
Q705
D/A
15
20
Q715
Q717
Q719
1
7
1
7
7
1
3
1
5
20
3
1
5
20
5
1
3
14
6
15
14
6
Q751
RH
GH
BH
TO
CONV.
YOKES
RV
GV
BV
Figure 1-13 Convergence Block Diagram
1-15

LAB 1
BASIC OPERATION AND UNIT UNDERSTANDING
As a servicer, it is important now, more than ever, to fully understand the operation and functions of
a television set before proceeding with a repair. This is because many of the problems encountered by
a customer today can be caused by an incorrect menu selection or improper setup.
Therefore, the purpose of this lab is to familiarize you with menus and features of the television from
the customer’s point of view.
SECTION ONE
BASIC OPERATION
1. Verify that the unit is connected to an AC supply, and that a signal is connected to the ANT 1
input. While verifying signal connections, take time to examine all of the inputs on the rear and
front (behind door) of the unit.
2. Turn on the set with the remote control and tune to an active channel. Refer to page 9 of the
service manual provided and familiarize yourself with all of the keys on the remote paying,
particular attention to the following keys:
o EDS
o TIMER
o PIP Functions
Open the bottom door on the remote control by sliding it down. Try each key starting with the upper
row. Each of these buttons brings up another menu and/or sub-menus.
3. In the Picture Menu, What is Color Temperature?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
4. In the Audio Menu, Where can the speakers be turned off by the user?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
5. In the Setup Menu, What is Favorite Channel?, What is Channel Lock?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
1-16

6. Refer to page 16 of the Service Manual and perform the User Convergence Adjustments. How
is this different from previous Toshiba PJTVs?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
7. In the Option Menu , How many different languages are there? What are they used for? What is
Channel Label Used for?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
NOTES:
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
SECTION TWO
DISASSEMBLY & SERVICE POSITION
Follow the procedure listed below to gain access to the tubes and circuit boards.
1. Remove the speaker grill by holding the sides and pulling straight out.
2. Take out the four screws holding the plastic shield in place. Then remove the shield.
3. Remove the control wires from the holder on the metal shield in front of the CRTs.
4. Remove the 4 screws holding the metal shield in place. The shield is notched, so slide it to the
right then down to remove it.
5. Remove the two screws holding the front control panel. Then release the tabs on either side and
let it hang down out of the way.
6. Remove the 4 screws holding the bottom of the screen. Then lift up on the top of the screen and
pull it away from the cabinet.
1-17

7. Remove the 5 screws holding the back panel. Then remove the back panel.
8. Reattach the control panel to the light box.
9. Remove the six screws on the front of the light box.
10. Remove the three screws on the back of the cabinet.
11. Remove the one screw holding the back of the light box to the cabinet.
12. From the front of the set, lift the light box up just a little, and pull it towards you.
13. Pull the light box all the way out of the cabinet and turn it on its side.
CAUTION: the light box weighs about 85 pounds, so get help if you need it.
SECTION THREE
IDENTIFICATION
1. Identify each of the board assemblies and note their locations. Use Figure 1-5 to help you
identify the various boards.
o Convergence/Output/Power Board
o Deflection/Power Board
o Main PCB
o Front Surround Board
o Digital Comb Filter Board
o PIP Board
o EDS/CC Board
2. Is there a convergence board in this unit?
If so, where?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
3. How does this convergence setup differ from previous models?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
4. Examine the Flyback and HV lead assemblies. What is different about this area from earlier
models?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
1-18

5. Is it possible for one technician to perform a service call on this type of unit?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
6. Put the lightbox in the cabinet, but don't screw it in. Then replace the screen and control panel.
Use a few screws to hold the screen and control panel in place.
SUMMARY
In this lab, the operation and function of the unit was determined, and the unit was set up for service
on the bench. Common user type problems in addition to overall serviceability was also discussed.
END OF LAB 1
1-19

LAB 2
TEST SIGNALS, SELF DIAGNOSTICS, & SERVICE REGISTERS
OBJECTIVES: After completing this lab you will be able to:
1. Enter and exit the set’s internal video and audio test signals.
2. Use the test signals for troubleshooting.
3. Use the set’s self diagnostic feature.
4. Make adjustments in the set with the service registers via the remote control.
SECTION ONE
VIDEO TEST SIGNALS
1. Verify that the unit is connected to an AC supply, and that a signal is connected to the ANT 1
input.
2. Enter the service mode by pressing mute on the remote. Press and hold mute a second time
while pressing menu on the control panel. An S appears in the upper right corner of the screen
indicating that the set is in the service mode. Press menu and the RCUT register appears in the
upper left corner of the screen.
3. Push the TV/VIDEO button on the remote once to enter the internal test pattern mode. The
screen should be red.
4. Slowly cycle through the test signals with the TV/VIDEO button until the white cross hairs on
a black background appear. (If the TV/VIDEO button is pushed in rapid succession, the set will
jump out of the test signal mode to one of the inputs - ANT 1, VIDEO 1, VIDEO 2, or VIDEO
3. The set is still in the service mode, so if this occurs, push the menu button then the TV/
VIDEO button to get back into the test signal mode.)
5. Plug a video cable into the VIDEO 1 input jack (make sure the other end of the cable is not
plugged into a video source)
6. What happened to the cross hairs?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
7. If something did happen to the cross hairs, why did it happen?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
1-20

8. Is there video on the screen?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
9. If there is video on the screen, where does it come from?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
10. Unplug the video cable.
SECTION TWO
AUDIO TEST SIGNALS
1. Push the 8 button on the remote to activate the audio test signal. (NOTE: The internal test
pattern mode must be activated for this feature to work.)
2. Push the mute button twice. Now you can control the volume of the signal.
3. Select AUD on the remote control.
4. Select BALANCE and adjust it from left to right with the + and - buttons.
5. Select SPEAKERS and turn them off then on. (NOTE: The speakers are turned off at Q601,
refer to Figure 1-8, while the volume, bass, treble, and balance are controlled in H002. This
means you can troubleshoot most of the audio system with the speakers off.)
6. Plug an audio cable into the left AUDIO 1 input jack (make sure the other end of the cable is
not plugged into an audio source)
7. What happened to audio?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
8. If something did happen to the audio, why did it happen?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
9. Push the 8 button to turn off the audio test signal.
10. Cycle the video test signals back to the ANT 1 signal with the TV/VIDEO button.
1-21

SECTION THREE
SELF DIAGNOSTICS
1. Push the 9 button to activate the self diagnostic feature.
2. What does POWER indicate?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
3. What does BUS LINE indicate?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
4. What does BUS CONT indicate?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
5. What does BLOCK indicate?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
6. Push the EXIT button to exit the self diagnostic feature.
7. Select the VIDEO 1 input with the TV/VIDEO button. (Make sure there is no signal applied to
VIDEO 1)
8. Push MENU on the control panel to display the registers.
9. Push 9 to activate the self diagnostic feature.
10. Is the display different from the previous display. ______
11. If it is, explain why.
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
12. Push the EXIT button to exit the self diagnostic feature.
13. Push MENU on the control panel to display the registers.
1-22
SECTION FOUR
SERVICE REGISTERS
NOTE: In each of the following exercises write down the register’s value before adjusting it. Then
restore the register to its original value before proceeding to the next exercise.
1. Enter the internal test pattern mode and select the test signal that has a white window in the
upper center of a black background as shown below.
2. Increase the RCUT register value and describe its effect on the picture.
RCUT______
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
3. Change the test signal to the white on black cross hatch pattern as shown below.
4. Select the HPOS register and vary its value between 00 and 1F. Describe its effect on the
picture. What happens if you increase the register to 20?
HPOS______
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
5. Select the VPOS register and vary its value between 00 and 07. Describe its effect on the
picture. What happens if you increase the register to 08?
VPOS______
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
1-23

6. Select the HIT register and vary its value 5 steps above and below the recorded value.
Describe its effect on the picture.
HIT______
___________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
7. Select the VLIN register and vary its value 8 steps above and below the recorded value.
Describe its effect on the picture.
VLIN______
___________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
8. Select the WID register and vary its value 8 steps above and below the recorded value.
Describe its effect on the picture.
WID______
___________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
9. Select the STRH register and vary its value 8 steps above and below the recorded value.
Describe its effect on the picture.
STRH______
___________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
SUMMARY
Now that you have completed Lab 2, you should be able to use the internal video and audio test
signals, the self diagnostic feature, and the service registers for making adjustments.
END OF LAB 2
1-24

SECTION II
TUNER, IF/MTS/S.PRO MODULE
2-1
 Loading...
Loading...