Toshiba MMU-AP0071YH, MMY-MAP0802FT8, MMY-MAP1002FT8 INSTALLATION MANUAL
INSTALLATION MANUAL
Heat Recovery Type (2 Series)
FILE NO. A05-018
R410A
Indoor Unit
<4-way Air Discharge Cassette Type>
MMU-AP0091H, AP0121H, AP0151H,
MMU-AP0181H, AP0241H, AP0271H,
MMU-AP0301H, AP0361H, AP0481H
MMU-AP0561H
<2-way Air Discharge Cassette Type>
MMU-AP0071WH, AP0091WH, AP0121WH,
MMU-AP0151WH, AP0181WH, AP0241WH,
MMU-AP0271WH, AP0301WH, AP0481WH*
* CHINA market only
<1-way Air Discharge Cassette Type>
MMU-AP0071YH, AP0091YH, AP0121YH,
MMU-AP0151SH, AP0181SH, AP0241SH
<Concealed Duct Standard Type>
MMD-AP0071BH, AP0091BH, AP0121BH,
MMD-AP0151BH, AP0181BH, AP0241BH,
MMD-AP0271BH, AP0301BH, AP0361BH,
MMD-AP0481BH, AP0561BH
<Concealed Duct High Static Pressure Type>
MMD-AP0181H, AP0241H, AP0271H,
MMD-AP0361H, AP0481H, AP0721H,
MMD-AP0961H
<Under Ceiling Type>
MMC-AP0151H, AP0181H, AP0241H,
MMC-AP0271H, AP0361H, AP0481H
<High Wall Type>
MMK-AP0071H, AP0091H, AP0121H,
MMK-AP0151H, AP0181H, AP0241H,
MMK-AP0072H*, AP0092H*, AP0122H*
* European market only
<Floor Standing Cabinet Type>
MML-AP0071H, AP0091H, AP0121H,
MML-AP0151H, AP0181H, AP0241H
<Floor Standing Concealed Type>
MML-AP0071BH, AP0091BH, AP0121BH,
MML-AP0151BH, AP0181BH, AP0241BH
<Floor Standing Type>
MMF-AP0151H, AP0181H, AP0241H
MMF-AP0271H, AP0361H, AP0481H
MMF-AP0561H
Outdoor Unit
<Inverter Unit>
MMY-MAP0802FT8
MMY-MAP1002FT8
MMY-MAP1202FT8
FS unit
RBM-Y1122FE
RBM-Y1802FE
RBM-Y2802FE
PRINTED IN JAPAN, 2005
WARNINGS ON REFRIGERANT LEAKAGE
Check of Concentration Limit
The room in which the air conditioner is to be
installed requires a design that in the event of
refrigerant gas leaking out, its concentration will not
exceed a set limit.
The refrigerant R410A which is used in the air
conditioner is safe, without the toxicity or combustibility
of ammonia, and is not restricted by laws to be imposed
which protect the ozone layer. However, since it
contains more than air, it poses the risk of suffocation if
its concentration should rise excessively. Suffocation
from leakage of R410A is almost non-existent. With the
recent increase in the number of high concentration
buildings, however, the installation of multi air
conditioner systems is on the increase because of the
need for effective use of floor space, individual control,
energy conservation by curtailing heat and carrying
power etc.
Most importantly, the multi air conditioner system is able
to replenish a large amount of refrigerant compared
with conventional individual air conditioners. If a single
unit of the multi conditioner system is to be installed in a
small room, select a suitable model and installation
procedure so that if the refrigerant accidentally leaks
out, its concentration does not reach the limit (and in the
event of an emergency, measures can be made before
injury can occur).
In a room where the concentration may exceed the limit,
create an opening with adjacent rooms, or install
mechanical ventilation combined with a gas leak
detection device.
The concentration is as given below.
Total amount of refrigerant (kg)
Min. volume of the indoor unit installed room (m³)
≤ Concentration limit (kg/m³)
The concentration limit of R410A which is used in multi
air conditioners is 0.3kg/m³.
(For details, refer and comply with local regulations.)
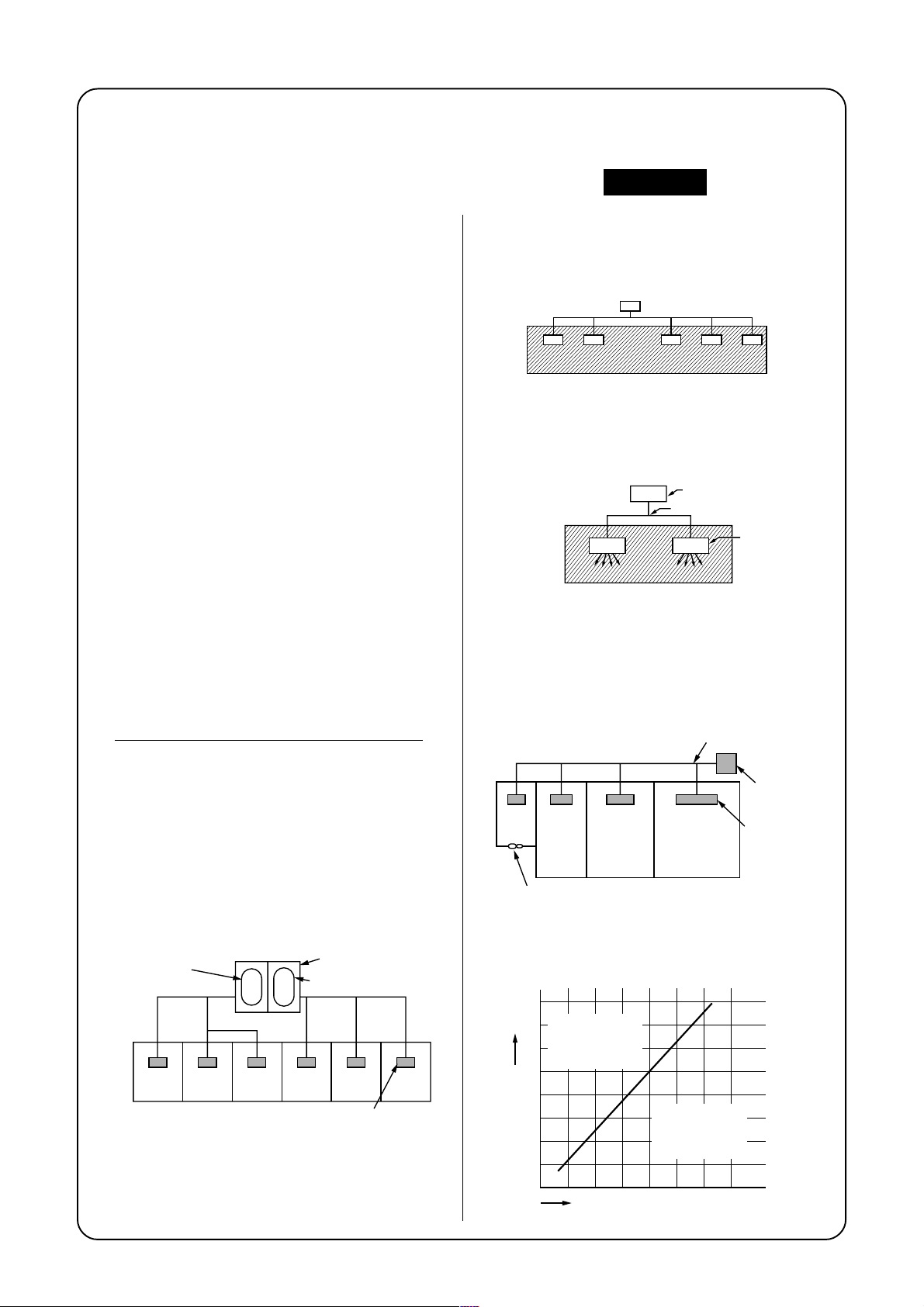
NOTE 1 :
If there are 2 or more refrigerating systems in a single
refrigerating device, the amounts of refrigerant should
be as charged in each independent device.
e.g., charged
amount (10kg)
Room A Room B Room C Room D Room E Room F
For the amount of charge in this example:
The possible amount of leaked refrigerant gas in
rooms A, B and C is 10kg.
The possible amount of leaked refrigerant gas in
rooms D, E and F is 15kg.
Outdoor unit
e.g.,
charged amount (15kg)
Indoor unit
Important
NOTE 2 :
The standards for minimum room volume are as
follows.
(1) No partition (shaded portion)
(2) When there is an effective opening with the
adjacent room for ventilation of leaking refrigerant
gas (opening without a door, or an opening 0.15%
or larger than the respective floor spaces at the top
or bottom of the door).
Outdoor unit
Refrigerant piping
Indoor unit
(3) If an indoor unit is installed in each partitioned room
and the refrigerant piping is interconnected, the
smallest room of course becomes the object. But
when a mechanical ventilation is installed
interlocked with a gas leakage detector in the
smallest room where the density limit is exceeded,
the volume of the next smallest room becomes the
object.
Refrigerant piping
Outdoor unit
Ver y
small
room
Small
room
Mechanical ventilation device - Gas leak detector
Medium
room
Large room
NOTE 3 :
The minimum indoor floor area compared with the
amount of refrigerant is roughly as follows:
(When the ceiling is 2.7m high)
40
Range below the
35
m²
density limit
of 0.3 kg/m³
30
(countermeasures
not needed)
25
20
15
10
5
Min. indoor floor area
0
10 20 30
Total amount of refrigerant
Range above
the density limit
of 0.3 kg/m³
(countermeasures
needed)
Indoor unit
kg

NOTE
A direct current motor is adopted for indoor fan motor in the Concealed Duct Standard Type air conditioner.
Caused from its characteristics, a current limit works on the direct current motor. When replacing the highperformance filter or when opening the service board, be sure to stop the fan. If an above action is executed
during the fan operation, the protective control works to stop the unit operation, and the check code “P12”
may be issued. However it is not a trouble. When the desired operation has finished, be sure to reset the
system to clear “P12” error code using the leak breaker of the indoor unit. Then push the operation stop
button of the remote controller to return to the usual operation.
CONTENTS
1. SELECTING A LOCATION FOR INSTALLATION ................................. 4
2. SAFETY NOTES ...................................................................................... 8
3. CHECK POINTS ...................................................................................... 9
4. KEY POINTS OF AIR CONDITIONER INSTALLATION ...................... 10
5. REFRIGERANT PIPE INSTALLATION ................................................. 11
6. INDOOR UNIT INSTALLATION............................................................. 43
7. FLOW SELECTOR UNIT INSTALLATION ........................................... 82
8. OUTDOOR UNIT INSTALLATION ........................................................ 88
9. ELECTRIC WIRING................................................................................ 95
10. INDOOR UNIT TERMINAL BOARD PLACEMENT AND WIRING..... 111
11. DRAIN PIPE INSTALLATION .............................................................. 117
12. ADJUSTMENT OF AIR DIRECTION .................................................. 126
13. APPLIED CONTROL ........................................................................... 131
14. ADDRESS SETUP ............................................................................... 135
15. TEST OPERATION .............................................................................. 148
16. SUPPORT FUNCTION IN TEST OPERATION ................................... 157
17. TROUBLESHOOTING ......................................................................... 180
18. AIR SPEED CHARACTERISTICS ...................................................... 185
19. FAN CHARACTERISTICS .................................................................. 190
CAUTION New Refrigerant Air Conditioner Installation
• THIS AIR CONDITIONER ADOPTS THE NEW HFC REFRIGERANT (R410A) WHICH DOES
NOT DESTROY OZONE LAYER.
The characteristics of R410A refrigerant are ; easy to absorb water, oxidizing membrane or oil, and its
pressure is approx. 1.6 times higher than that of refrigerant R22. Accompanied with the new refrigerant,
refrigerating oil has also been changed. Therefore, during installation work, be sure that water, dust, former
refrigerant, or refrigerating oil does not enter the refrigerating cycle.
To prevent charging an incorrect refrigerant and refrigerating oil, the sizes of connecting sections of charging
port of the main unit and installation tools are charged from those for the conventional refrigerant.
Accordingly the exclusive tools are required for the new refrigerant (R410A).
For connecting pipes, use new and clean piping designed for R410A, and please care so that water or dust
does not enter. Moreover, do not use the existing piping because there are problems with pressure-resistance
force and impurity in it.
1. SELECTING A LOCATION FOR INSTALLATION
WARNING
Install the air conditioner certainly at a location to sufficiently withstand the weight.
If the strength is insufficient, the unit may fall down resulting in human injury.
Perform a specified installation work to guard against a great wind such as typhoon or an
earth quake.
An incomplete installation can cause accidents by the units failing and dropping.
The following models must be installed at height 2.5m or more from the floor.
(Concealed type duct type and cassette type air conditioners)
If you insert your hands or others directly into the unit while the air conditioner operates, it is dangerous
because you may contact with revolving fan or active electricity.
Installation Location Selection for Outdoor unit
Obtain permission from the customer to install the unit in a location that satisfies the
following requirements :
• A location that permits level installation of the unit.
• A location that provides enough space to service the unit safety
• A location where water draining from the unit will not pose a problem
Avoid installing in the following places.
• Place exposed to air with high salt content (seaside area), or place exposed to large quantities of sulfide
gas (hot spring). (Should the unit be used in these places, special protective measures are needed.)
• Place exposed to oil, vapor, oil smoke or corrosive gas.
• Place where organic solvent is used nearby.
• Place close to a machine generating high frequency.
• Place where the discharged air blows directly into the window of the neighboring house. (For outdoor unit)
• Place where noise of the outdoor unit is easily transmitted.
(When installing the air conditioner on the boundary with the neighbor, pay due attention to the level of noise.)
• Place with poor ventilation.
(Especially in Concealed duct type indoor unit, before air ducting work, check whether value of air volume,
static pressure and duct resistance are correct.)
4
Equipments
1. Outdoor units
Inverter unit
Corresponding HP
8 HP 10 HP 12 HP
Model name
MMY- MAP0802FT8 MAP1002FT8 MAP1202FT8
Cooling capacity (kW) 22.4 28.0 33.5
Heating capacity (kW) 25.0 31.5 35.5
2. Outdoor units (Combination of outdoor units)
Corresponding HP
Combined model
Cooling capacity (kW)
Heating capacity (kW)
Combined outdoor units
No. of connectable indoor units
Corresponding HP
Combined model
Cooling capacity (kW)
Heating capacity (kW)
Combined outdoor units
No. of connectable indoor units
MMY- MAP0802FT8
MMY- AP2002FT8
8HP
22.4
25
8HP
13
20HP
56
63
10HP
10HP
33
10HP
MAP1002FT8
28
31.5
10HP
16
24HP
AP2402FT8
68
76.5
8HP
8HP
8HP
40
12HP
MAP1202FT8
33.5
35.5
12HP
16
26HP
AP2602FT8
73
81.5
10HP
8HP
8HP
43
16HP
AP1602FT8
45
50
8HP
8HP
27
28HP
AP2802FT8
78.5
88
10HP
10HP
8HP
47
Appearance
18HP
AP1802FT8
50.4
56.5
10HP
8HP
30
30HP
AP3002FT8
84
95
10HP
10HP
10HP
48
Allocation standard of model name
MMY– M AP T 8
F
Power supply specifications, 3Ø 380–415 V, 50Hz ....... 8
T : Capacity variable unit
F : Heat recovery
Development series No.
Capacity rank HP x 10
New refrigerant R410A
M : Single module unit, No mark : Combined Model name
Modular Multi
3. FS units (Flow selector units)
Model name Inverter unit Appearance
RBM-Y1122FE
RBM-Y1802FE Total capacity for indoor unit : 11.2 to below 18.0kW
Total capacity for indoor unit : below 11.2kW
RBM-Y2802FE Total capacity for indoor unit : 18.0 to 28.0kW or less
∗ Accessory part : Connection cable kit (RBC-CBK15FE), up to 15m.
5
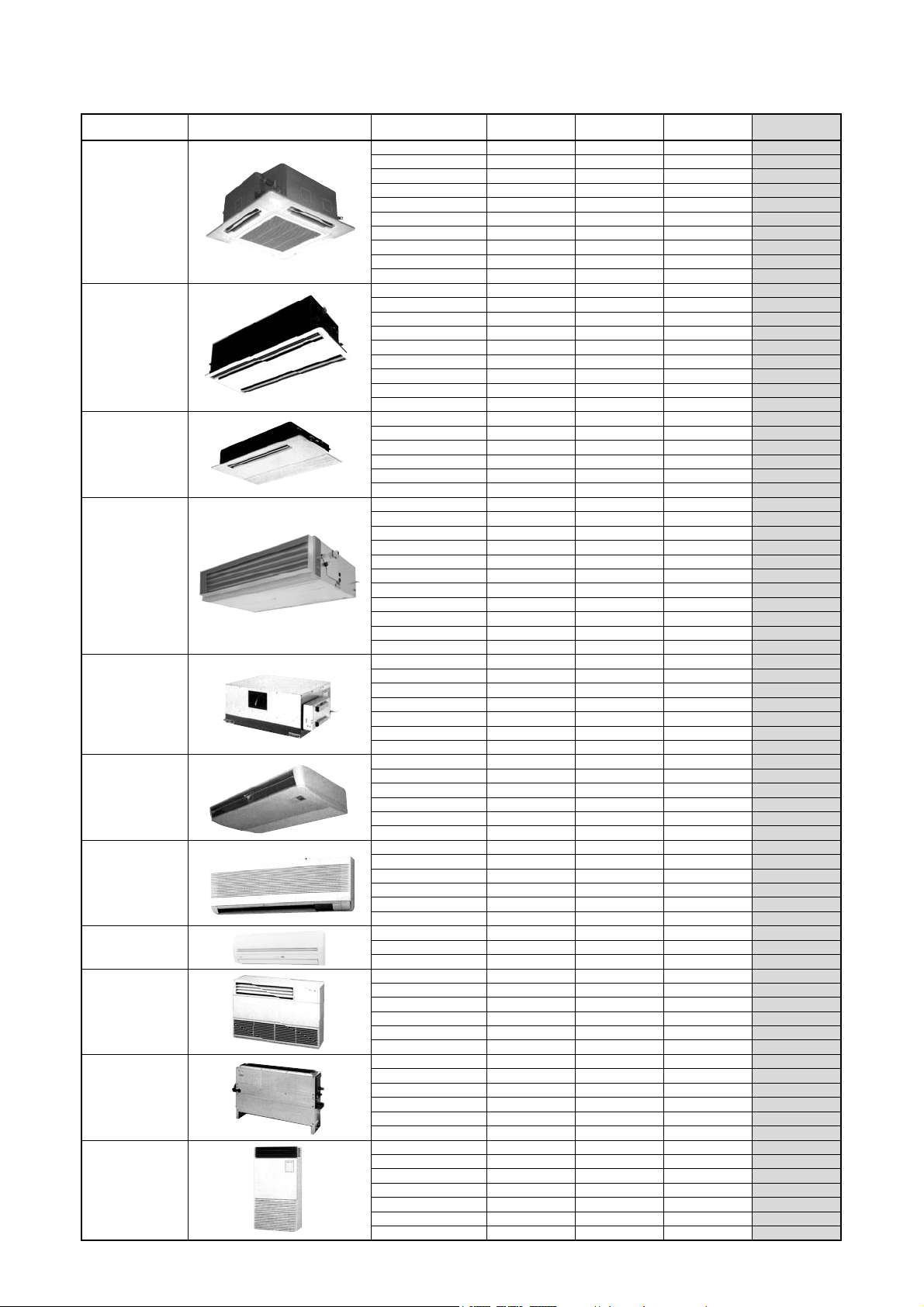
3. Indoor units
Type Appearance Model name Capacity rank Capacity code
MMU-AP0091H 009 type 1 2.8 3.2
4-way Air Discharge
Cassette Type
2-way Air Discharge
Cassette Type
1-way Air Discharge
Cassette Type
Concealed Duct
Standard Type
Concealed Duct
High Static
Pressure Type
Under Ceiling Type
High Wall Type
(1 Series)
High Wall Type
(2 Series)
Floor Standing
Cabinet Type
Floor Standing
Concealed Type
Floor Standing Type
2)
*
MMU-AP0121H
MMU-AP0151H
MMU-AP0181H
MMU-AP0241H
MMU-AP0271H
MMU-AP0301H
MMU-AP0361H
MMU-AP0481H
MMU-AP0561H 056 type 6 16.0
MMU-AP0071WH
MMU-AP0091WH
MMU-AP0121WH
MMU-AP0151WH
MMU-AP0181WH
MMU-AP0241WH
MMU-AP0271WH
MMU-AP0301WH
MMU-AP0481WH*
MMU-AP0071YH
MMU-AP0091YH
MMU-AP0121YH
MMU-AP0151SH
MMU-AP0181SH
MMU-AP0241SH
MMD-AP0071BH
MMD-AP0091BH
MMD-AP0121BH
MMD-AP0151BH
MMD-AP0181BH
MMD-AP0241BH
MMD-AP0271BH
MMD-AP0301BH
MMD-AP0361BH
MMD-AP0481BH
MMD-AP0561BH
MMD-AP0181H
MMD-AP0241H
MMD-AP0271H
MMD-AP0361H
MMD-AP0481H
MMD-AP0721H
MMD-AP0961H
MMC-AP0151H
MMC-AP0181H
MMC-AP0241H
MMC-AP0271H
MMC-AP0361H
MMC-AP0481H
MMK-AP0071H
MMK-AP0091H
MMK-AP0121H
MMK-AP0151H 015 type 1.7 4.5 5.0
MMK-AP0181H
MMK-AP0241H
MMK-AP0072H
MMK-AP0092H
MMK-AP0122H
MML-AP0071H
MML-AP0091H
MML-AP0121H
MML-AP0151H
MML-AP0181H
MML-AP0241H
MML-AP0071BH
MML-AP0091BH
MML-AP0121BH
MML-AP0151BH
MML-AP0181BH
MML-AP0241BH
MMF-AP0151H 015 type 1.7 4.5 5.0
MMF-AP0181H
MMF-AP0241H
MMF-AP0271H
MMF-AP0361H
MMF-AP0481H
MMF-AP0561H
6
012 type 1.25 3.6
015 type 1.7 4.5
018 type 2 5.6
024 type 2.5 7.1
027 type 3 8.0
030 type 3.2 9.0
036 type 4 11.2
048 type 5 14.0
007 type 0.8 2.2
009 type 1 2.8
012 type 1.25 3.6
015 type 1.7 4.5
018 type 2 5.6
024 type 2.5 7.1
027 type 3 8.0
030 type 3.2 9.0
1)
048 type 5 14.0 16.0
007 type 0.8 2.2
009 type 1 2.8
012 type 1.25 3.6
015 type 1.7 4.5
018 type 2 5.6
024 type 2.5 7.1
007 type 0.8 2.2
009 type 1 2.8
012 type 1.25 3.6
015 type 1.7 4.5
018 type 2 5.6
024 type 2.5 7.1
027 type 3 8.0
030 type 3.2 9.0
036 type 4 11.2
048 type 5 14.0
056 type 6 16.0
018 type 2 5.6
024 type 2.5 7.1
027 type 3 8.0
036 type 4 11.2
048 type 5 14.0
072 type 8 22.4
096 type 10 28.0
015 type 1.7 4.5
018 type 2 5.6
024 type 2.5 7.1
027 type 3 8.0
036 type 4 11.2
048 type 5 14.0
007 type 0.8 2.2
009 type 1 2.8
012 type 1.25 3.6
018 type 2 5.6
024 type 2.5 7.1
007 type 0.8 2.2
009 type 1.0 2.8
012 type 1.25 3.6
007 type 0.8 2.2
009 type 1 2.8
012 type 1.25 3.6
015 type 1.7 4.5
018 type 2 5.6
024 type 2.5 7.1
007 type 0.8 2.2
009 type 1 2.8
012 type 1.25 3.6
015 type 1.7 4.5
018 type 2 5.6
024 type 2.5 7.1
018 type 2 5.6
024 type 2.5 7.1
027 type 3 8.0
036 type 4 11.2
048 type 5 14.0
056 type 6 16.0
Cooling
capacity (kW)
*1) China market only *2) European market only
Heating
capacity (kW)
4.0
5.0
6.3
8.0
9.0
10.0
12.5
16.0
18.0
2.5
3.2
4.0
5.0
6.3
8.0
9.0
10.0
2.5
3.2
4.0
5.0
6.3
8.0
2.5
3.2
4.0
5.0
6.3
8.0
9.0
10.0
12.5
16.0
18.0
6.3
8.0
9.0
12.5
16.0
25.0
31.5
5.0
6.3
8.0
9.0
12.5
16.0
2.5
3.2
4.0
6.3
8.0
2.5
3.2
4.0
2.5
3.2
4.0
5.0
6.3
8.0
2.5
3.2
4.0
5.0
6.3
8.0
6.3
8.0
9.0
12.5
16.0
18.0
Tools
Required Tools
The used refrigerating oil is changed, and mixing of oil may cause a trouble such as generation of sludge,
clogging of capillary, etc. Accordingly, the tools to be used are classified into the following three types.
(1) Tools exclusive for R410A (Those which cannot be used for conventional refrigerant (R22))
(2) Tools exclusive for R410A, but can be also used for conventional refrigerant (R22)
(3) Tools commonly used for R410A and for conventional refrigerant (R22)
The table below shows the tools exclusive for R410A and their interchangeability.
Tools exclusive for R410A (The following tools for R410A are required.)
Tools whose specifications are changed for R410A and their interchangeability
Conventional air
conditioner installation
Whether new equipment
can be used with
conventional refrigerant
{
*(Note 1)
×
×
{
{
×
{
×
No.
c
d
e
f
g
h
i
j
k
l
Used tool
Flare tool
Copper pipe gauge for
adjusting projection
margin
Torque wrench
Gauge manifold
Charge hose
Vacuum pump adapter
Electronic balance for
refrigerant charging
Refrigerant cylinder
Leakage detector
Charging cylinder
Usage
Pipe flaring
Flaring by conventional
flare tool
Connection of flare nut
Evacuating, refrigerant
charge, run check, etc.
Vacuum evacuating
Refrigerant charge
Refrigerant charge
Gas leakage check
Refrigerant charge
air conditioner installation
Existence of
new equipment
for R410A
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
(Note 2)
R410A
Whether conventional
equipment can be
used
*(Note 1)
*(Note 1)
×
×
×
Yes
×
×
×
(Note 1) When flaring is carried out for R410A using the conventional flare tools, adjustment of projection
margin is necessary. For this adjustment, a copper pipe gauge, etc. are necessary.
(Note 2) Charging cylinder for R410A is being currently developed.
General tools (Conventional tools can be used.)
In addition to the above exclusive tools, the following equipments which serve also for R22 are necessary
as the general tools.
(1) Vacuum pump
Use vacuum pump by
attaching vacuum pump adapter.
(2) Torque wrench
(3) Pipe cutter
(4) Reamer
(5) Pipe bender
(6) Level vial
(7) Screwdriver (+, –)
(8) Spanner or Monkey wrench
(9) Hole core drill
(10) Hexagon wrench
(Opposite side 4mm)
(11) Tape measure
(12) Metal saw
Also prepare the following equipments for other installation method and run check.
(1) Clamp meter
(2) Thermometer
(3) Insulation resistance tester
(4) Electroscope
7
2. SAFETY NOTES
• Ensure that all Local, National and International regulations are satisfied.
• Read this “SAFETY NOTES” carefully before Installation.
• The precautions described below include the important items regarding safety. Observe them without fail.
• After the installation work, perform a trial operation to check for any problem.
Follow the Owner’s Manual to explain how to use and maintain the unit to the customer.
• Turn off the main power supply switch (or breaker) before the unit maintenance.
• Ask the customer to keep the Installation Manual together with the Owner’s Manual.
WARNING
• Ask an authorized dealer or qualified installation professional to install/maintain the air conditioner.
Inappropriate installation may result in water leakage, electric shock or fire.
• Turn off the main power supply switch or breaker before attempting any electrical work.
Make sure all power switches are off. Failure to do so may cause electric shock.
• Connect the connecting wire correctly.
If the connecting wire is connected in a wrong way, electric parts may be damaged.
• When moving the air conditioner for the installation into another place, be very careful not to enter
any gaseous matter other than the specified refrigerant into the refrigeration cycle.
If air or any other gas is mixed in the refrigerant, the gas pressure in the refrigeration cycle becomes
abnormally high and it as a result causes pipe burst and injuries on persons.
• Do not modify this unit by removing any of the safety guards or by by-passing any of the safety
interlock switches.
• Exposure of unit to water or other moisture before installation may cause a short-circuit of electrical
parts.
Do not store it in a wet basement or expose to rain or water.
• After unpacking the unit, examine it carefully if there are possible damage.
• Do not install in a place that might increase the vibration of the unit.
• To avoid personal injury (with sharp edges), be careful when handling parts.
• Perform installation work properly according to the Installation Manual.
Inappropriate installation may result in water leakage, electric shock or fire.
• When the air conditioner is installed in a small room, provide appropriate measures to ensure that
the concentration of refrigerant leakage occur in the room does not exceed the critical level.
• Install the air conditioner securely in a location where the base can sustain the weight adequately.
• Perform the specified installation work to guard against an earthquake.
If the air conditioner is not installed appropriately, accidents may occur due to the falling unit.
• If refrigerant gas has leaked during the installation work, ventilate the room immediately.
If the leaked refrigerant gas comes in contact with fire, noxious gas may generate.
• After the installation work, confirm that refrigerant gas does not leak.
If refrigerant gas leaks into the room and flows near a fire source, such as a cooking range, noxious gas
might generate.
• Electrical work must be performed by a qualified electrician in accordance with the Installation
Manual. Make sure the air conditioner uses an exclusive power supply.
An insufficient power supply capacity or inappropriate installation may cause fire.
• Use the specified wires for wiring connect the terminals securely fix. To prevent external forces
applied to the terminals from affecting the terminals.
• Conform to the regulations of the local electric company when wiring the power supply.
Inappropriate grounding may cause electric shock.
• Do not install the air conditioner in a location subject to a risk of exposure to a combustible gas.
If a combustible gas leaks, and stays around the unit, a fire may occur.
8
3. CHECK POINTS
Check before operation
• Turn on the main power switch 12 hours or more before starting the operation.
• Check whether earth wire is disconnected or out of place.
• Check that air filter is installed to the indoor unit.
Heating capacity
• For heating operation, a heat pump type which absorbs the outdoor heat and deliver the heat in the room is adopted.
If the outdoor temperature lowers, the heating capacity decreases.
• When the outdoor temperature is low, common use with other heating devices is recommended.
Defrost operation in heating operation
• If frost is found on the outdoor unit during heating operation, the defrost operation starts automatically (for approx. 2 to 10
minutes) so as to increase the heating effect.
• During defrost operation, the fans of both indoor and outdoor units stop.
Protection for 3 minutes
• The outdoor unit does not operate for approx. 3 minutes after air conditioner has been immediately restarted after stop,
or power switch has been turned on. This is to protect the system.
Main power failure
• If a power failure occurs during operation, all operations stop.
• When the power is turned on after power failure, the operation lamp of the remote controller flashes to notify.
• When restarting the operation, push ON/OFF button again.
Fan rotation of stopped unit
• While other indoor units operate, the fan on indoor units on “stand-by” rotates to protect the machine once per approx. 1
hour for several minutes.
Protective device (High pressure switch)
The high pressure switch operate the air conditioner automatically stops when excessive load is applied to the air
conditioner. If the protective device works, the operation lamp keeps lit but the operation stops.
When the protective device works, “CHECK” characters in the remote controller display section flash.
The protective device may work in the following cases.
Cooling
• When air inlet or outlet of the outdoor unit is closed.
• When strong wind blows continuously against air outlet of the outdoor unit.
Heating
• When much dust or dirt is excessively adhered to air filter of the indoor unit.
• When air outlet of the indoor unit is blocked.
NOTE
If the protective device works, turn off the main power switch, remove the cause, and then restart the operation.
Cooling/ heating operation of Multi system air conditioner
• When COOL or HEAT mode is fixed by the manager of the air conditioner, other operation than the set mode is
unavailable. If other operation than the set mode has been performed, [
operation part goes on and the operation stops.
Operating temperature of Super HRM
• When outdoor temperature goes out of specified range, “ or ” mark is indicated on the remote controller display and
required operation will stop. “
[Notice]
• This indication is not failure.
• When outdoor temperature goes back to specified range, “
• Operation stops because concurrent operation can not be kept in the condition of out of specification for Super HRM.
(Outdoor temp. (DB) < –10°C : Cooling, > 21°C : Heating)
• Do not use “Super HRM” for other than personal usage where the ambient temperature may go down below –10°C.
(For example, OA equipment/Electric device/Food/Animals and plants/Art object)
& ” : When heating operation. “ ” : When cooling operation.
or ” disappear and start normal operation.
Characteristics of heating operation
• Air does not blow out immediately after start of the operation. When the indoor heat exchanger has been heated after 3
to 5 minutes passed (differs according to temperature of indoor/outdoor temperature), hot air starts blowing.
• During operation, the outdoor unit may stop when outdoor temperature becomes high.
• When other indoor unit performs heating operation during fan operation, fan operation may be stopped temporarily to
prevent discharge of hot air.
9
PRE-HEAT] or [ Operation ready] on the
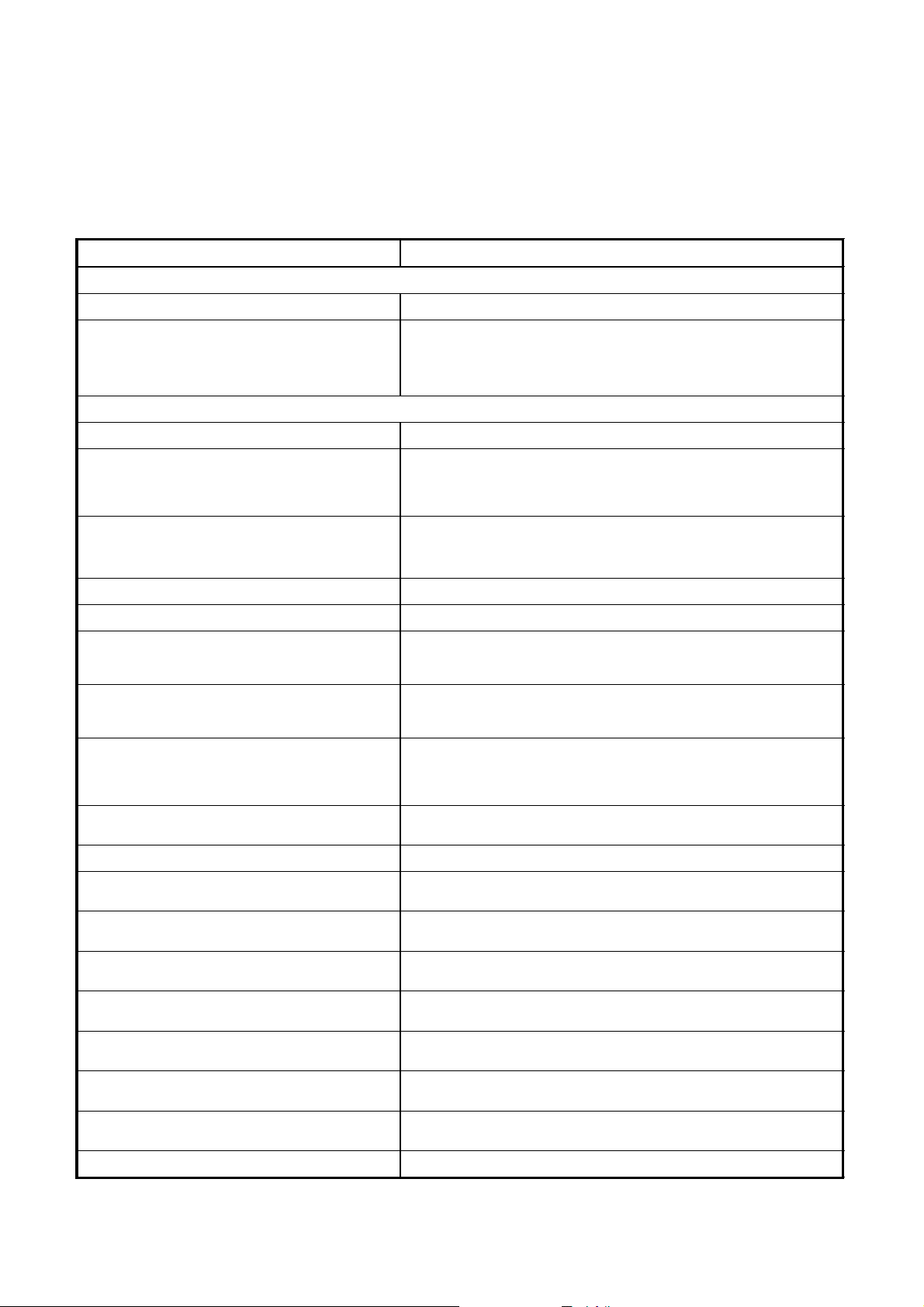
4.
KEY POINTS OF AIR CONDITIONER INSTALLATION
In order to prevent problems before they arise, carefully read (1) the Installation Manual provided with the
equipment, and (2) the Owner’s Manual before installing the air conditioner.
4-1. Flow of Air Conditioner Installation Work
[Step] [Key Points]
(Prior to Installation)
Determination of extent of installation work
Drafting of diagrams
(Installation)
Sleeve/insert installation Pay careful attention to the downward slope of the drain pipe.
Indoor unit and flow selector unit installation
Refrigerant pipe installation
(to outdoor outlet)
Drain pipe installation Pipes should have downward slope (of at least 1/100).
Duct installation
Insulation work
Electrical work
(control wires and power wires)
Various switch settings
Outdoor unit base installation Make sure that the base is level.
Outdoor unit installation
Outside circulation, refrigerant pipe
installation
Gas-leak test
Vacuum suction
Addition of refrigerant
Ceiling panel installation
Test operation and adjustment
Owner’s Manual transfer
Clearly determine the extent of the installation work.
Draft :
• Control wiring system diagram
• Refrigerant line system diagram
• Power wiring system diagram
Be sure to check the name of the model in order to avoid any
installation mistakes. If the model has an installation pattern, attach
the pattern to the ceiling to mark the position of the ceiling openings
and to keep dust away.
Make sure that the pipe system is dry, clean, and airtight.
When brazing pipes, blow out the system with nitrogen gas.
Do not forget the system indications.
Make sure the duct is large enough to carry the desired volume of air.
Be careful not to make any errors in the external static pressure
calculations.
Be especially careful to close off all gaps where connections are
made to the indoor unit, and at joints in the branching kit. Do not
forget the drain pipes.
Use two-core shielded wires for the control wires, and use separate
power supplies for the indoor and outdoor units. For connecting the
flow selector unit, be sure to use the attached cable or connection
cable kit sold separately.
Set the switches correctly, as indicated in the control wiring system
diagram.
Provide for adequate air flow and service space around the outdoor
unit. Indicate the system names clearly.
From outside outlet to outdoor unit.
In the final test, the system must be pressurized at 3.73MPa
(38kg/cm²G) for 24 hours with no decrease in pressure.
Use a vacuum pump with reverse flaw prevention adaptor with a large
output volume and that can achieve a high level of vacuum.
Record the amount of refrigerant that was added to the system on
both the outdoor unit and on the pre-test operation checklist.
Make sure that the ceiling panel is attached to the ceiling material
tightly, with no gaps.
Operate the indoor units one by one, making sure that all wiring and
pipes are connected correctly, and fill out the checklist.
Explain how to operate the system clearly and concisely.
The procedure described above presents only the general sequence of steps; the sequence of steps may have to
be altered according to the circumstances of any specific installation job.
10
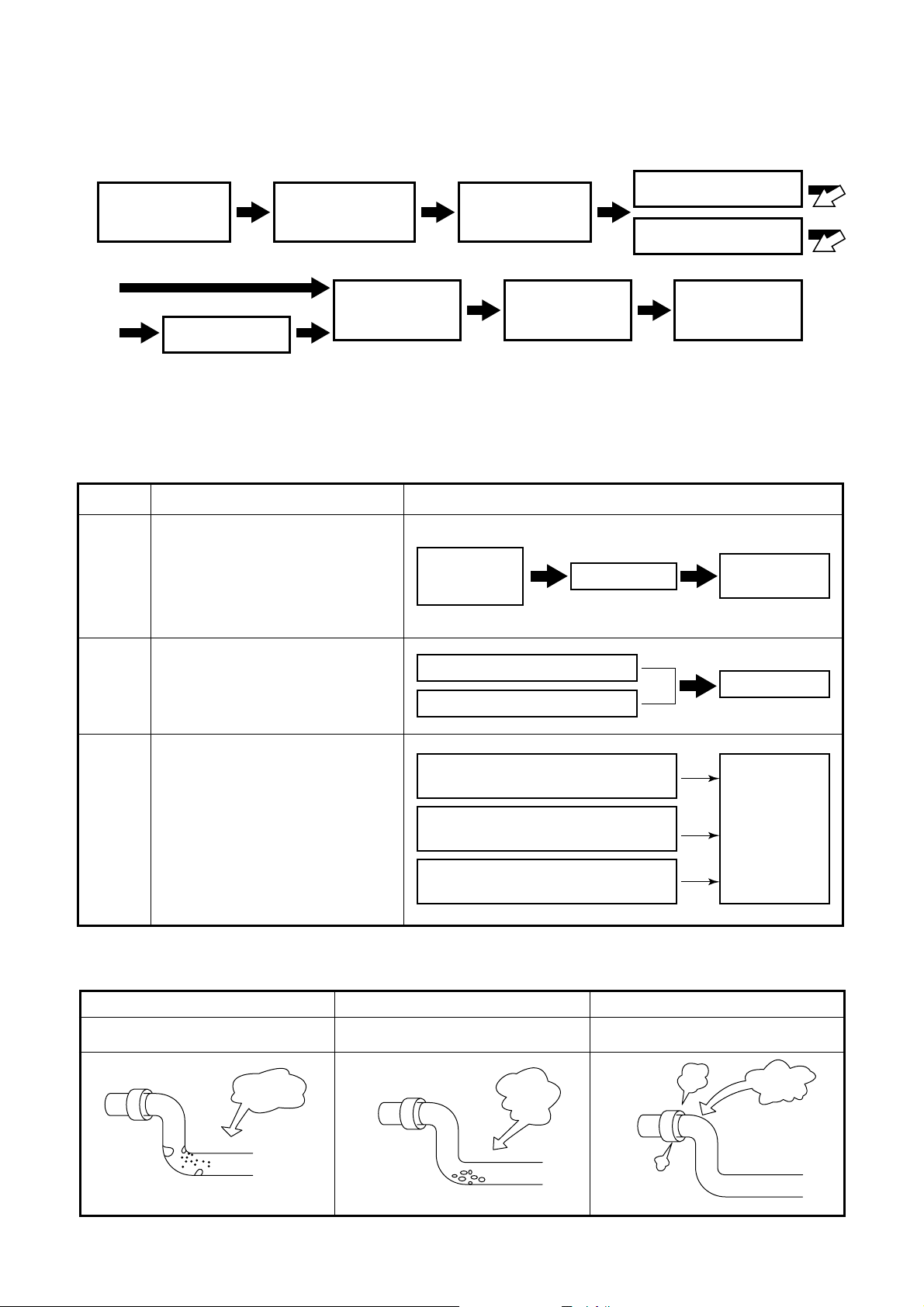
5. REFRIGERANT PIPE INSTALLATION
5-1. Work Procedure
Indoor unit
installation
Sizing
the pipes
Preliminary
installation
Nitrogen gas blow
Flaring
Flushing
Brazing
Leak test
5-2. Three Principles of Refrigerant Pipes
<Observe the three principles of refrigerant pipes>
Causes of Problems Preventing Problems
• Moisture (in the form of
Dry
Clean
rainwater or water used during
installation, for example)
getting inside of the pipes
• Moisture from condensation
forming or seeping into the pipes
• Oxidation inside pipes during
brazing
• Dirt, dust, or foreign matter
getting inside pipes
Careful
handling
of pipes
Nitrogen gas blow
Careful handling of pipes
Flushing
Vacuum
suction
Vacuum
suction
Flushing
Use of suitable materials
(copper pipes, solder, etc.)
Air-
tight
• Poor brazing
• Poor flaring
Perform basic work
of brazing carefully
Perform basic work
of flaring carefully
<Three principles of refrigerant pipes>
Dry
Make sure there is no moisture
inside of the pipes
Moisture
Make sure there is no dirt
Clean Airtight
Make sure the refrigerant
inside of the pipes
Dirt
does not leak
NOT GOOD NOT GOOD NOT GOOD
Leak test
Leak
11
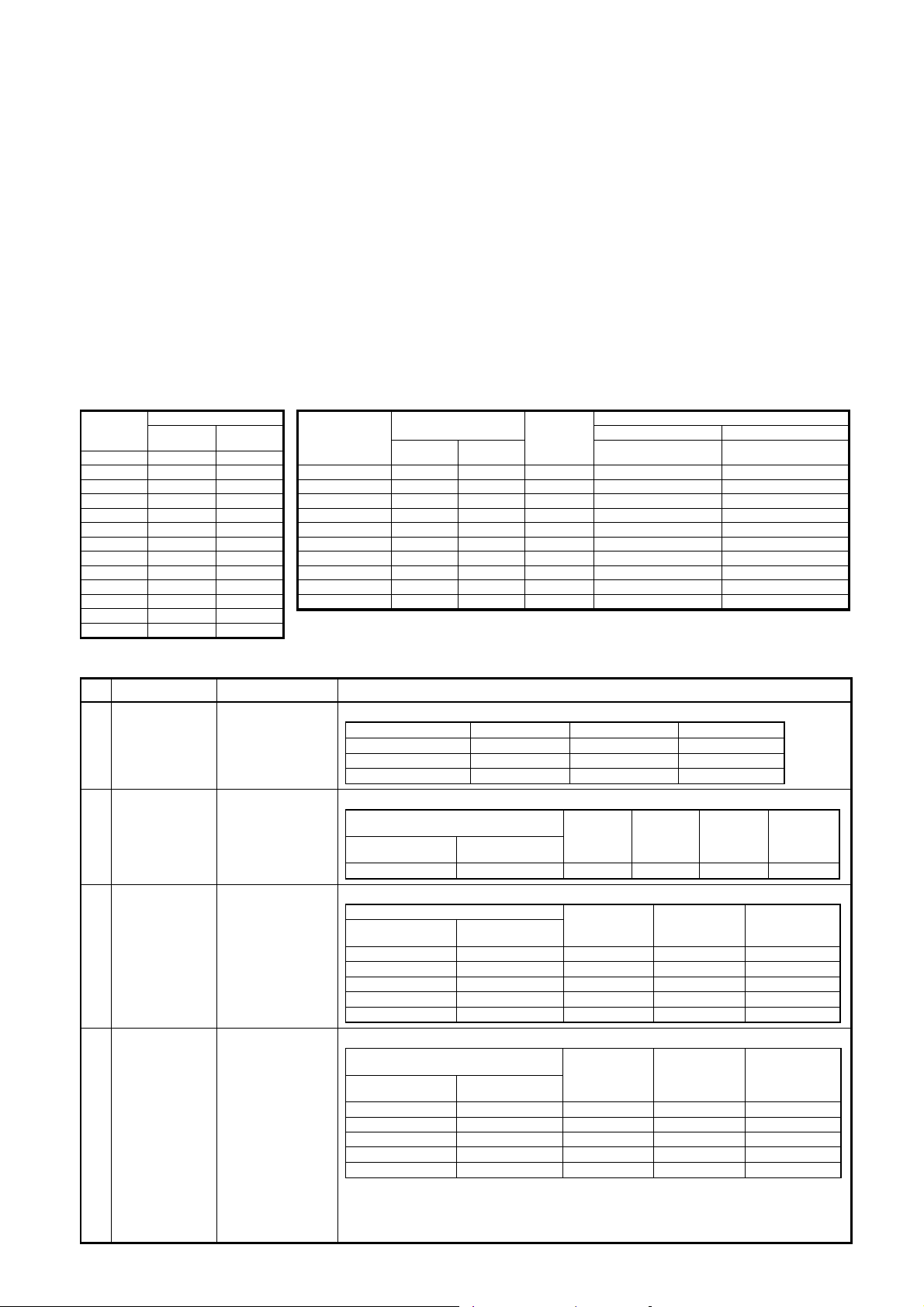
5-3. Selecting the Refrigerant Line Material
• Refrigerant pipes
• Material: Phosphoric deoxidized seam-less pipe
• Capacity code of outdoor unit / indoor unit
• For each indoor unit, the capacity code is determined for every capacity rank.
• For each outdoor unit, the capacity code is determined for every capacity rank. The Max. number of the
connectable indoor units and the total capacity code value of the indoor units are also determined.
Against the capacity code of the outdoor unit, the total capacity codes of the connectable indoor units differ
according to the height difference between indoor units.
• When the height difference between indoor units is 15m or less : Up to 135%* of capacity code of outdoor unit
(* For 12HP system, up to 120%.)
• When the height difference between indoor units is above 15m : Up to 105% of capacity code of outdoor unit
Table 1 Table 2
Indoor unit
capacity rank
007 type 0.8 2.2
009 type 12.8
012 type 1.25 3.6
015 type 1.7 4.5
018 type 25.6
024 type 2.5 7.1
027 type 38
030 type 3.2 9
036 type 4 11.2
048 type 514
056 type 616
072 type 8 22.4
096 type 10 28.0
Capacity code
Equivalent toHPEquivalent to
capacity
Outdoor unit
model name
MMY-MAP0802FT8 8 22.4 13 5.6 10.8
MMY-MAP1002FT8 10 28.0 16 7.0 13.5
MMY-MAP1202FT8 12 33.5 16 8.4 14.4
MMY-AP1602FT8 16 45.0 27 11.2 21.6
MMY-AP1802FT8 18 50.4 30 12.6 24.3
MMY-AP2002FT8 20 56.0 33 14.0 27.0
MMY-AP2402FT8 24 68.0 40 16.8 32.4
MMY-AP2602FT8 26 73.0 43 18.2 35.1
MMY-AP2802FT8 28 78.5 47 19.6 37.8
MMY-AP3002FT8 30 84.0 48 21.0 40.5
Capacity code
Equivalent toHPEquivalent to
capacity
No. of
indoor units
Total capacity code of connectable indoor units
Min Max.
Equivalent to HP Equivalent to HP
Table 3
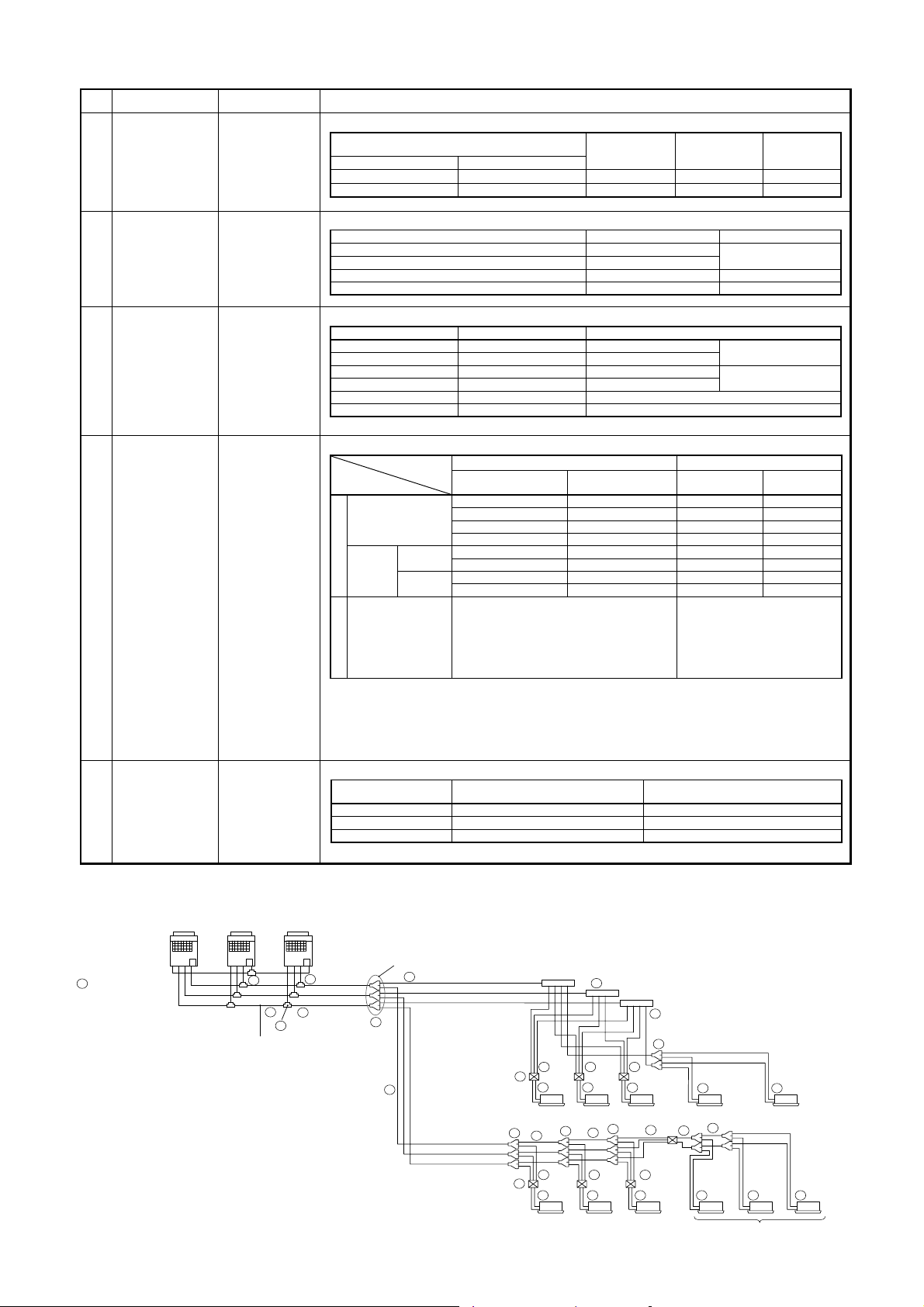
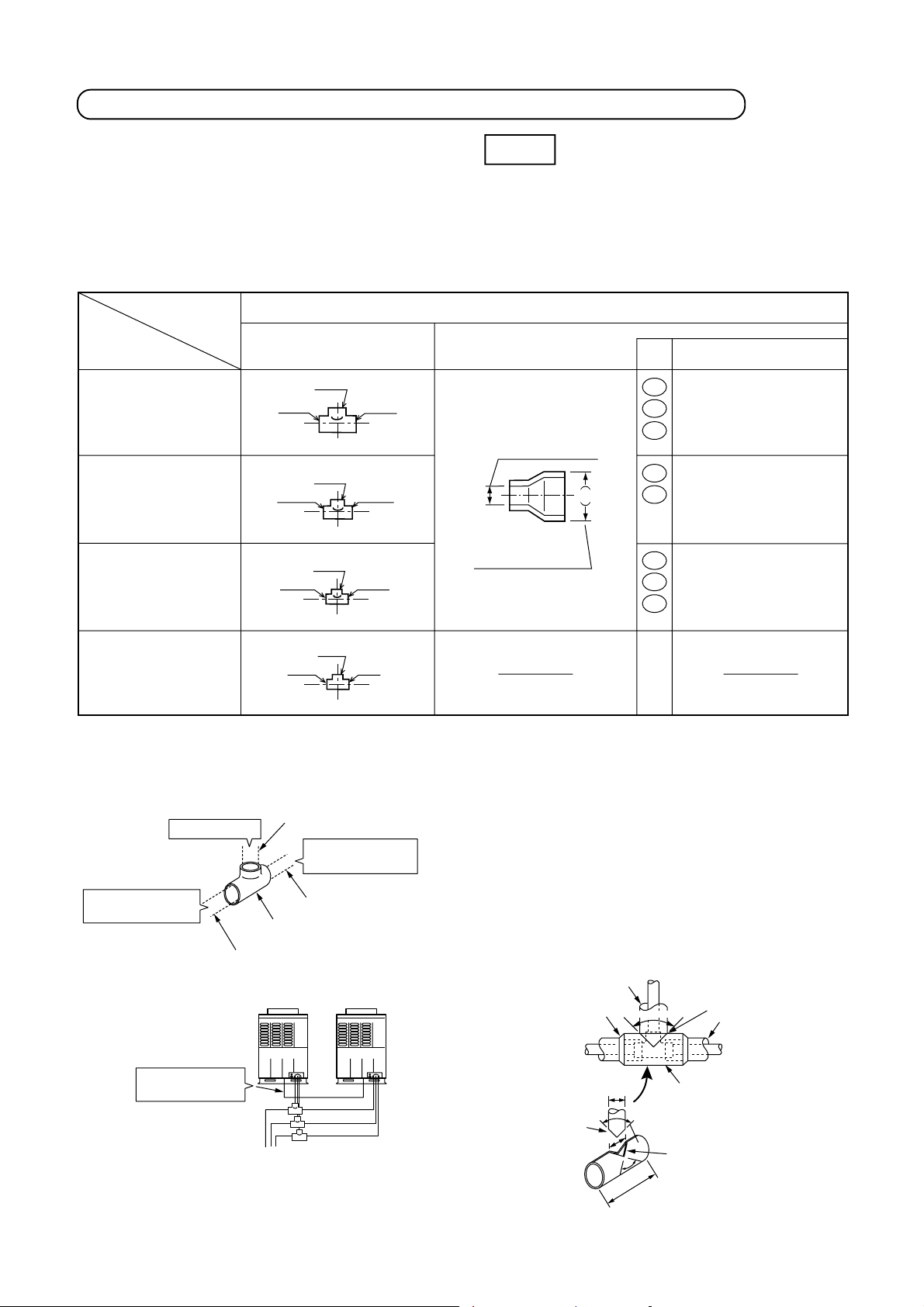
No. Piping parts Name Selection of pipe size
c
Outdoor unit
↓
T-shape
branching joint
d
Between T-shape
branching joints
e
T-shape joint of
header unit
↓
1st branching
section
f
Branching section
↓
Branching section
Connecting pipe of
outdoor unit
Main connecting
piping between of
outdoor units
Balance pipe
Main pipe
Branching pipe
1) Connecting pipe outdoor unit
Model name Suction gas side Discharge gas side Liquid side
MMY-MAP0802FT8 Ø22.2 Ø19.1 Ø12.7
MMY-MAP1002 FT8 Ø22.2 Ø19.1 Ø12.7
MMY-MAP1202 FT8 Ø28.6 Ø19.1 Ø12.7
2) Pipe size for connecting piping between outdoor units
Total capacity codes of outdoor units
at downstream side
Equivalent to
capacity
Below 61.5 Below 22 Ø28.6 Ø22.2 Ø15.9 Ø9.5
Equivalent
to HP
Suction gas
side
3) Size of main pipe
Total capacity codes of all outdoor units
Equivalent to
capacity
Below 33.5 Below 12 Ø22.2 Ø19.1 Ø12.7
33.5 12 Ø28.6 Ø 19.1 Ø12.7
45.0 to below 61.5 16 to below 22 Ø28.6 Ø22.2 Ø19.1
61.5 to below 73.0 22 to below 26 Ø34.9 Ø28.6 Ø19.1
73.0 or more 26 or more Ø34.9 Ø28.6 Ø22.2
Equivalent
to HP
Suction gas
side
4) Pipe size between branching sections
Total capacity codes of indoor units
at downstream side
Equivalent to
capacity
Below 18.0 Below 6.4 Ø15.9 Ø12.7 Ø9.5
18.0 to below 34.0 6.4 to below 12.2 Ø22.2 Ø19.1 Ø12.7
34.0 to below 56.5 12.2 to below 20.2 Ø28.6 Ø22.2 Ø15.9
56.5 to below 70.5 20.2 to below 25.2 Ø34.9 Ø28.6 Ø15.9
70.5 or more 25.2 or more Ø34.9 Ø28.6 Ø19.1
∗
If exceeding the main pipe size, decide the size same to main pipe size.
∗
When two pipes are used for the circuits exclusive to cooling, use pipes at liquid and suction
gas sides.
∗
2 pipes from FS unit to branching section shall be used with liquid pipe and suction gas pipe.
Equivalent
to HP
Suction gas side
Discharge
gas side
Discharge gas
Discharge gas
Liquid side
side
side
Balance
pipe
Liquid side
Liquid side
12
No. Piping parts Name Selection of pipe size
g
End branching
section
↓
Flow selector unit
Connecting pipe
of flow selector
unit
5) Pipe size between end branching section and flow selector unit
Total capacity codes of indoor units
Equivalent to capacity Equivalent to HP
at downstream side
Below 18.0 Below 6.4 Ø15.9 Ø12.7 Ø9.5
18.0 or more 6.4 or more Ø22.2 Ø19.1 Ø12.7
Suction
gas side
Discharge
gas side
Liquid side
h
Branching section
or flow selector
Connecting pipe
of indoor unit
unit
↓
Indoor unit
i
Branching section
Piping of cooling
only indoor unit
(Between
branching and
indoor unit)
j
Branching section Branching
k
header
Y-shape
branching joint
T shape
branching joint
l
Branching Flow selector unit
6) Connecting pipe size of indoor unit
Capacity rank Gas side Liquid side
007 to 012 type Ø9.5
015 to 018 type Ø12.7
024 to 056 type Ø15.9 Ø9.5
072 to 096 type Ø22.2 Ø12.7
Ø6.4
7) Connecting pipe size of cooling only indoor unit
Gas side Liquid side Capacity rank of indoor unit
Ø9.5 Ø6.4 15m or less
Ø12.7 Ø9.5 above 15m
Ø12.7 Ø6.4 15m or less
Ø15.9 Ø9.5 above 15m
Ø15.9 Ø9.5 024 to 056 Type
Ø22.2 Ø12.7 072, 096 Type
∗
2 pipes for cooling only indoor unit shall be used with liquid pipe and suction gas pipe.
007 to 012 Type
015 to 018 Type
8, 9) Selection of branching joint/header
Total capacity codes of indoor units Model name
Equivalent to
capacity
Below 18.0 Below 6.4
Y-Shape branching
joint *1 *2
j
Branching
Header
*1, *2, *3
T-Shape branching
k
joint (For connecting
outdoor unit)
∗
1 Branching pipe on the 1st branch should be selected according to the capacity code for
outdoor unit.
∗
2 In case total capacity code for indoor units shall be exceeded to capacity code for outdoor
unit, the pipe size should be selected with capacity code for outdoor unit.
∗
3 For 1 line after header branching, indoor units with a maximum of 6.0 capacity code in total
can be connected.
For 4
Branching
For 8
Branching
18.0 to below 40.0 6.4 to below 14.2
40.0 to below 70.5 14.2 to below 25.2
70.5 or more 25.2 or more
Below 40.0 Below 14.2
40.0 to below 70.5 14.2 to below 25.2
Below 40.0 Below 14.2
40.0 to below 70.5 14.2 to below 25.2
1 set of 4 types of T-shape joint pipes as
described below : The rewired quantity is
arranged and combined at the site.
- Balance pipe (Ø 9.52) X 1
- Piping at liquid side (Ø 12.7 to Ø 22.2) X 1
-
Piping at discharge gas side (Ø 19.1 to Ø 28.6) X 1
-
Piping at suction gas side (Ø 22.2 to Ø 38.1) X 1
Equivalent to HP For 3 piping For 2 piping
RBM-BY53FE RBM-BY53E
RBM-BY103FE RBM-BY103E
RBM-BY203FE RBM-BY203E
RBM-BY303FE RBM-BY303E
RBM-HY1043FE RBM-HY1043E
RBM-HY2043FE RBM-HY2043E
RBM-HY1083FE RBM-HY1083E
RBM-HY2083FE RBM-HY2083E
RBM-BT13FE
10) Selection of flow selector unit
Model name Total capacity rank of connectable
RBM-Y1122FE below 11.2 kW 5
RBM-Y1802FE 11.2 to below 18.0kW 8
RBM-Y2802FE 18.0 below 28.0kW or less 8
∗
Confirm also Installation Manual of flow selector unit.
indoor unit
Max. No. of connected
indoor units
Outdoor unit
Outdoor unit
1
connecting piping
Follower UnitCFollower UnitBHeader Unit
Main connecting piping
between outdoor units
1
A
2
9
T-shape
branching joint
Balance pipe
1
Main piping
3
1st branching section
4
Discharge gas pipe
Suction gas pipe
8
4
Discharge gas pipe
Suction gas pipe
Liquid pipe
Liquid pipe
13
5 5 5
10
FS unit
6
4
5
FS unit
6
Indoor unit
8
8
10
Y-Shape branching joint
8
4
6 6
8
4
5 5
4
6 6 6 6 6
Y-Shape branching joint8
7 7
< Cooling only >
4
4
< Cooling only >
Group control
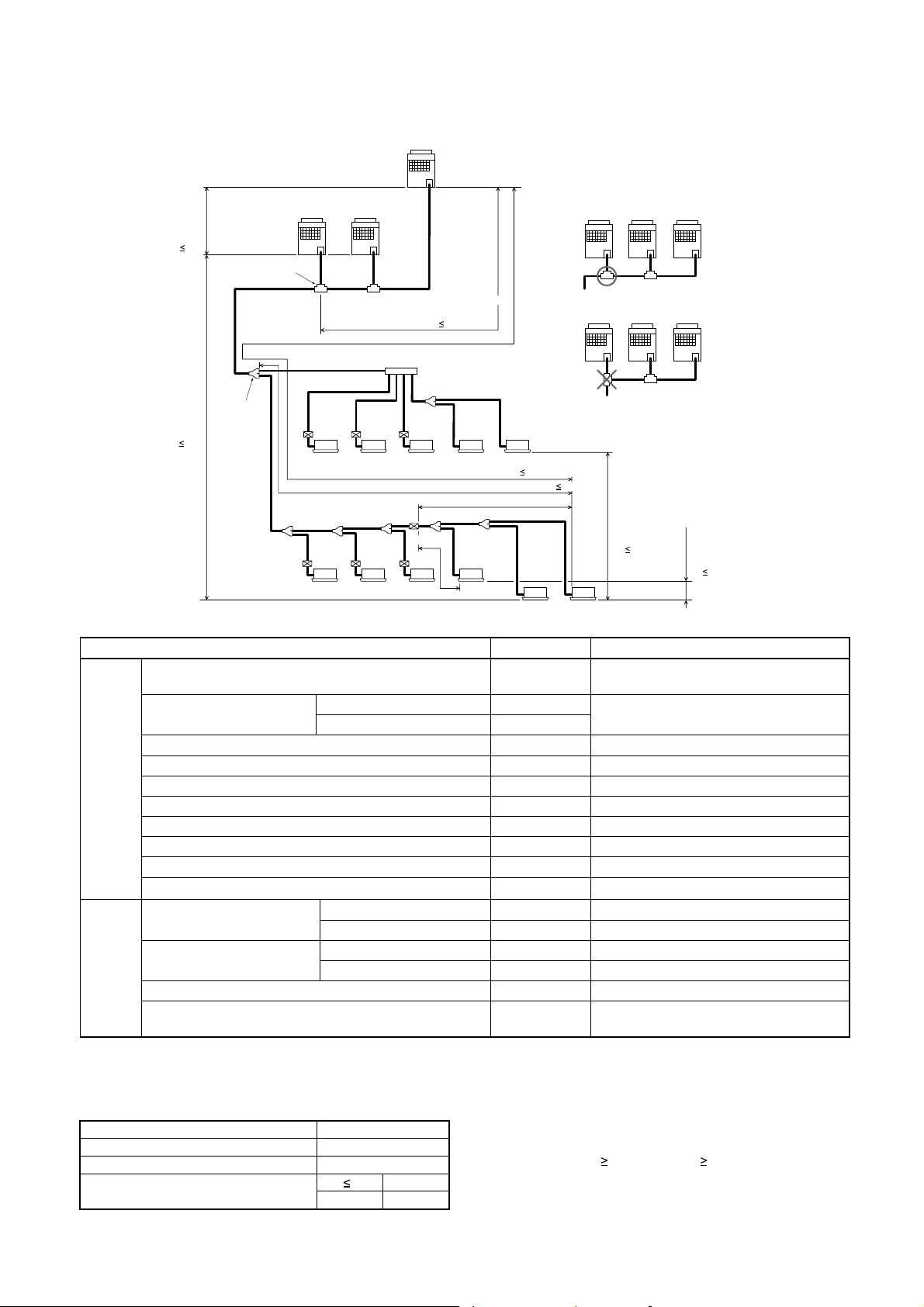
5-4. Allowable Length/Height Difference of Refrigerant Piping
Height
difference
between
outdoor
units
H3 5m
Height
difference
between
outdoor
and indoor
units
H1 50m
Outdoor Unit
T-shape
branching
Main piping
L1
1st branching
section
Follower Unit
C
Header Unit
Connecting piping of
indoor unit
L3
Equivalent length corresponded to farthest piping after 1st branching Li 50m
FS unit
Follower Unit
A
Branching piping
a
ghi j
Indoor unit
Equivalent length corresponded to farthest piping L 150m
L4 L5 L6 L7LhL8
def
lmn
Indoor unit
B
La Lb Lc
LA
Main connecting piping between outdoor units
Length corresponded to farthest piping
between outdoor units LO 25m
Branching
header
L2
L9
bc
FS unit
< Cooling only >
FS unit
o
(Header)
k
Note:
In case of connecting method <Ex.2>, a large
amount of refrigerant and refrigerant oil may
return to the head unit. Therefore, set the T-shape
joint so that oil does not enter directly.
<Ex.1>
Header UnitAFollower UnitBFollower Unit
<Ex.2>
Header UnitAFollower UnitBFollower Unit
< Cooling only >
(q)
Height difference
between
indoor
units
H2 35m
(Upper outdoor unit)
Lj
pq
C
C
Height difference
between indoor units
in group control by
one FS unit
H4 0.5 m
* Allowable length and height difference of refrigerant piping
Allowable value Piping section
Total extension of pipe (Liquid pipe, real length) 300 m
Farthest piping length L (*1)
Real length 125 m
Equivalent length 150 m
Max. equivalent length of main piping 85 m L1
Equivalent length of farthest piping from 1st branching Li (*1) 50 m L3+L4+L5+L6+L7+L8+q
Pipe
Length
Max. real length of indoor unit connecting piping 30 m a+g, b+h, c+i, d+l, e+m, f+n, j, k
Max. real length between FS unit and indoor unit (*2) 15 m g, h, i, l, m, n, L7+o, L7+L8+p, L7+L8+q
Max. Equivalent length of outdoor unit connecting piping LO (*1) 25 m LA+Lc (LA+Lb)
Max. real length of outdoor unit connecting piping 10 m La, Lb, Lc
30 m
15 m
50 m
Height
Difference
Max. equivalent length between FS unit and indoor unit Lj
Max. real length between FS unit and header indoor unit Lh (
Height between indoor
and outdoor units H1
Height between indoor units H2
Upper outdoor unit
Lower outdoor unit 30 m ——
Upper outdoor unit 35 m ——
Lower outdoor unit 15 m ——
2)
*
Height between outdoor units H3 5 m ——
Height difference between indoor units in group control by one FS
unit H4
1 : The farthest outdoor unit from 1st branch to be named C, and farthest indoor unit from 1st branch to be named (q).
*
2 : Attached connection cable can be used up to 5 m in pipe length between indoor and FS unit. When the pipe length
*
between indoor and FS unit exceeds 5 m, be sure to use the connection cable kit (RBC-CBK15FE).
* System restrictions
Max. No. of combined outdoor units
Max. capacity of combined outdoor units
Max. No. of connected indoor units
Max. capacity of combined indoor units
1 : MMY-MAP1201HT8 : UP to 120 %
*
3 units
84.0 kW
48 units
H2 15m
H2
>
15m
135% (*1)
105%
Note 1) Combination of outdoor units : Header unit (1 unit) +
Note 2) Install the outdoor units in order of capacity.
Note 3) Refer to outdoor unit combination table in page.6.
Note 4) Piping to indoor units shall be perpendicular to piping to
0.5 m ——
Follower unit (0 to 2 units). Header unit is outdoor unit
nearest to the connected indoor units
(Header unit Follower unit 1 Follower unit 2)
the head outdoor unit as <Ex.1>.
Do not connect piping to indoor units in the same
direction of head outdoor unit as <Ex.2>.
14
LA+La+Lb+Lc+L1+L2+L3+L4+L5+L6+L7+L8+9
+a+b+c+d+e+f+g+h+i+j+k+l+m+n+o+p+q
LA+Lc+L1+L3+L4+L5+L6+L7+L8+q
L7+L8+q, L7+L8+p
L7+o
——
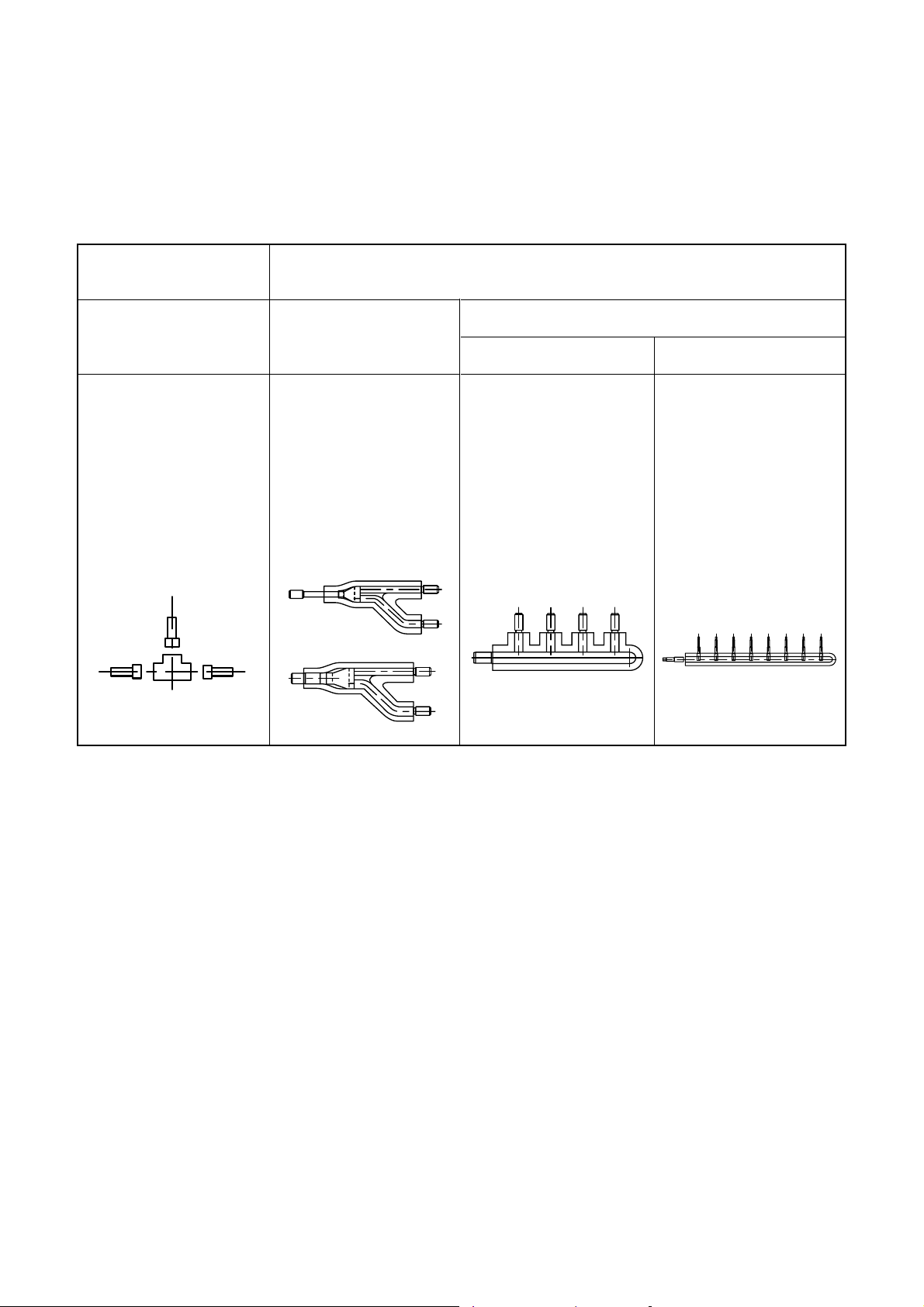
• Brazed couplings and special branches
• Use suitable parts for typical elbow couplings and socket couplings.
(Consider the size, material, thickness, etc.)
• Special branches
Use deoxidized parts sold separately.
Branching at
outdoor unit side
T-shape branching
joint
RBM-BT13FE
Branching joint
RBM-BY53E
RBM-BY103E
RBM-BY203E
RBM-BY303E
RBM-BY53FE
RBM-BY103FE
RBM-BY203FE
RBM-BY303FE
Branching at indoor unit side
Branch header
4 branching 8 branching
RBM-HY1043E RBM-HY1083E
RBM-HY2043E RBM-HY2083E
RBM-HY1043FE RBM-HY1083FE
RBM-HY2043FE RBM-HY2083FE
• Solder
Because only “copper-to-copper” connections are made in the multi type air conditioning system, use the hard
solder “phosphor copper solder.”
15
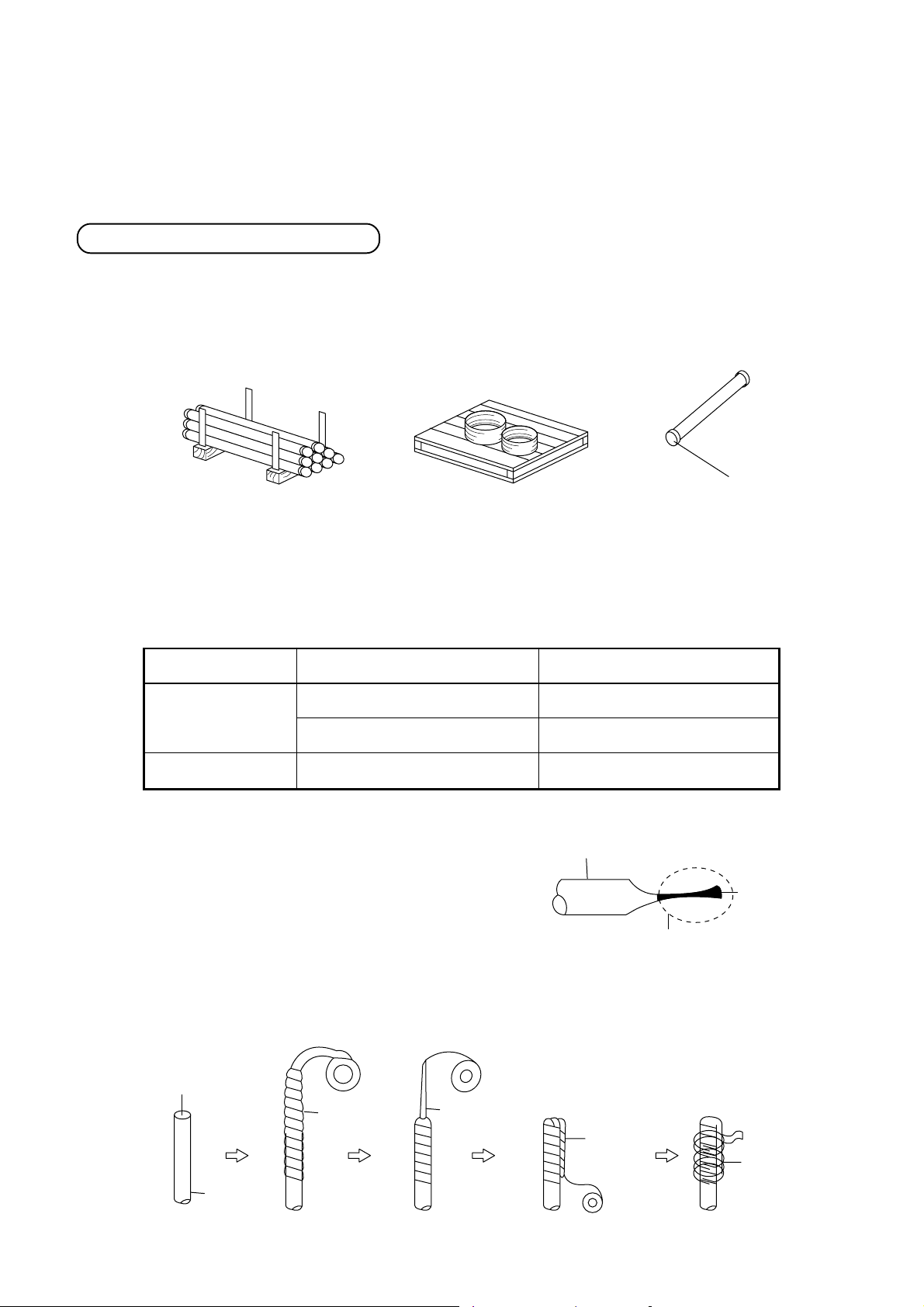
5-5. Careful Handling
Careful handling is the most important step in preventing moisture, dirt, and dust from getting inside of the pipes.
Moisture in pipes has caused major problems in numerous instances in the past. Therefore, it is important to be
as careful as possible in order to prevent problems before they occur.
Pipe delivery and storage
When pipes are delivered, care should be taken to prevent it from becoming bent or deformed, and the ends of the
pipes should be capped in order to prevent dirt, mud, rain, etc., from getting inside. Build a wooden frame to hold
the pipes securely, and store the pipes in the specified location.
Delivery of copper pipes without caps to a work site is not acceptable.
Cap
Frame for careful handling
and to prevent rolling
Careful handling on a pallet
Pipe caps
The ends of all pipes must be sealed. The most reliable method is the “pinch method,” but the taping method can
be selected in some circumstances.
Location
Outdoors
Indoors
Pinch method
Pinch the end of the copper pipe closed,
and braze any opening closed.
Taping method
Cover the end of the copper pipe with vinyl tape.
Time for installation
One month or more
Less than one month
Does not matter
Careful handling method
Pinch method
Pinch or taping method
Pinch or taping method
Copper pipe
Solder
Braze here
[Taping method]
Opening
Copper
pipe
Vinyl tape
Flatten
Fold over
Tape again
16
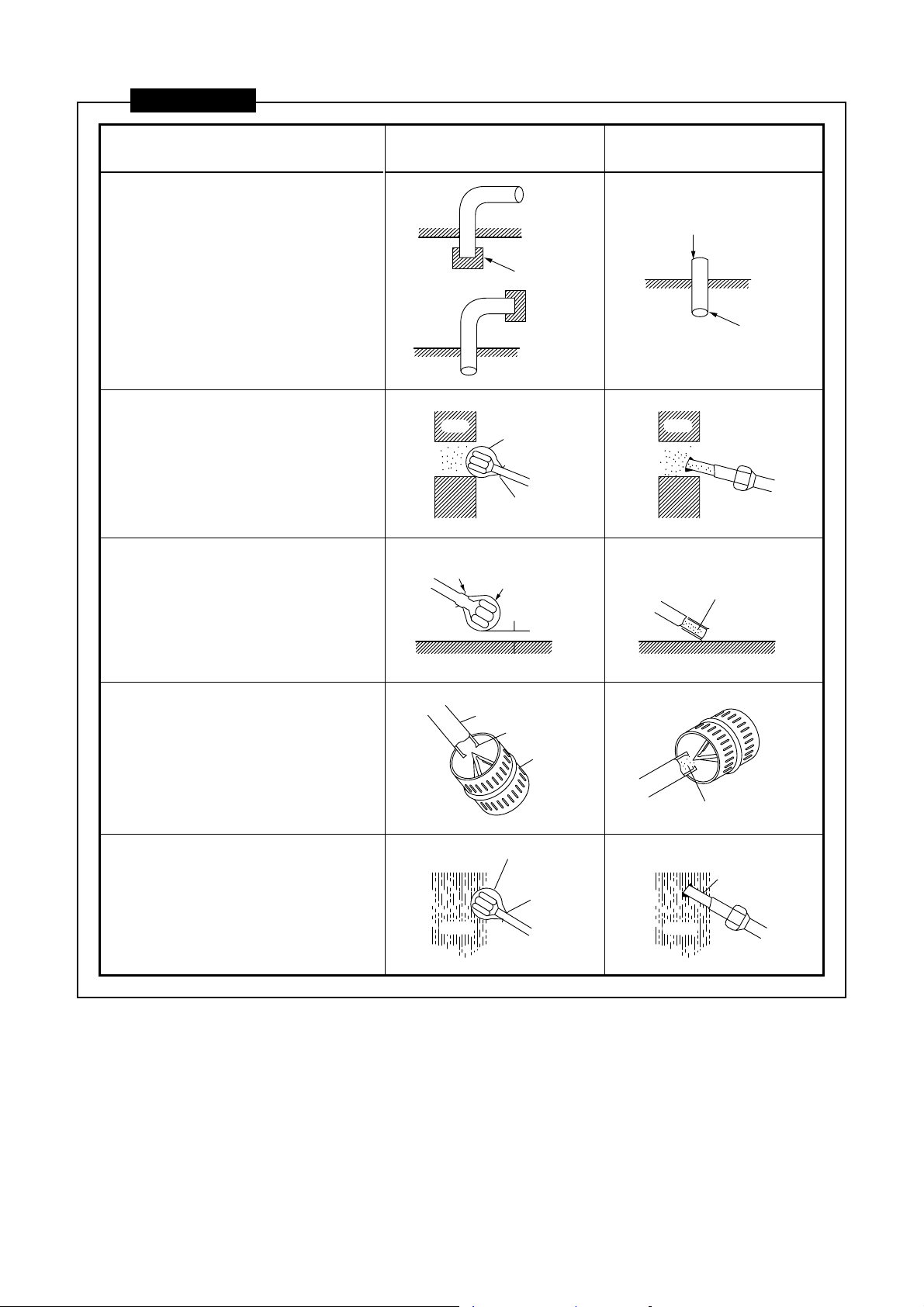
CAUTIONS
1) Do not allow dirt or moisture
inside of the pipes.
• Keep the open ends of all pipes
capped until all pipes have been
connected.
• Pipe openings should face
horizontally or downwards if at all
possible.
GOOD NOT GOOD
Dirt and moisture get inside
Cap
Pipe
2) When passing a pipe through an
opening in a wall, always keep
the end of the pipe capped.
3) Do not place pipes directly on
the ground. Do not scrape pipes
on the ground.
4) When deflashing (removing
burrs from) a pipe, point the
opening downwards so that no
scraps fall inside of the pipe.
5) When installing pipes on a rainy
day, always keep the ends of the
pipes capped.
Cap or
Wall
plastic bag
Rubber band
Rubber
Cap or
band
plastic bag
Do not allow
pipe to touch
ground
Ground Ground
Pipe
Burrs
Deflasher
Cap or
plastic bag
Rubber
band
Rain
Wall
Dirt gets inside of pipe
Scraps get inside of pipe
Rain
Particles of
the wall get
inside the pipe
Rain gets
inside of pipe
17
socket
projection
Diameter of the
connecting pipe
1pc
Ø31.8
1pc
RBM-HY2083E
Ø15.9
Ø9.5
Ø15.9
1pc each
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 7pcs
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 7pcs
06
09
No.
Ø28.6 x (Ø31.8) 1pc
Ø34.9 x (Ø31.8) 1pc
27
59
No.
(Ø 9.5) 3pcs
(Ø15.9) 3pcs
(Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø 6.4 x (Ø 9.5) 7pcs
01
1pc
Ø19.1
Ø38.1
Ø38.1
RBM-BY303E
Ø22.2
Ø38.1
Ø19.1
1pc
1pc each
Ø 9.5 x (Ø38.1) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø38.1) 1pc
77767574737161
No.
No.
Ø15.9 x (Ø38.1) 1pc
Ø19.1 x (Ø38.1) 1pc
Ø22.2 x (Ø38.1) 1pc
Ø 6.4 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø28.6 x (Ø38.1) 2pcs
Ø34.9 x (Ø38.1) 1pc
Ø41.3 x (Ø38.1) 1pc
0407101352
62
Ø15.9 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
14
Ø 9.5 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø19.1) 1ps
Ø15.9 x (Ø19.1) 2pcs
Ø22.2 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø19.1 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
18
1pc
Ø31.8
RBM-HY2043E
Ø15.9
indicates diameter of the indicated position, and others indicate
diameter of the connecting pipe.
( 51 , 52 , 54 , 58 , 59 , 61 , 62 , 70 , 89 : without projection)
Ø9.5
1pc
Ø15.9
1pc each
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 2pcs
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 2pcs
06
09
No.
Ø28.6 x (Ø31.8) 1pc
Ø34.9 x (Ø31.8) 1pc
27
59
No.
Ø 6.4 x (Ø 9.5) 4pcs
01
2. Please connect pipe to the side with a projection of the socket.
1pc
NOTE : 1. All dimensions are in millimeters. In the following tables, ( )
Ø22.2
RBM-HY1083ERBM-HY1043E
Ø15.9
Ø9.5
1pc
Ø15.9
1pc each
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 8pcs
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 8pcs
06
09
No.
Ø15.9 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
Ø19.1 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
Ø28.6 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
141870
No.
Ø 6.4 x (Ø 9.5) 8pcs
01
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 1ps
06
(Ø 9.5) 1pc
(Ø15.9) 1pc
(Ø15.9) 1pc
(Ø 9.5) 3pcs
(Ø15.9) 3pcs
(Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 1ps
09
1pc
Ø15.9
Ø28.6
RBM-BY203E
Ø19.1
RBM-BY103E
Ø28.6
Ø15.9
Ø31.8
1pc
Ø12.7
Ø19.1
Ø22.2
Ø15.9
Ø15.9
Ø12.7
1pc
1pc
1pc each
Ø 9.5 x (Ø28.6) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø28.6) 1pc
4849162043
No.
Ø28.6 x (Ø31.8) 1pc
Ø34.9 x (Ø31.8) 1pc
27
59
No.
1pc each
Ø 9.5 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
0710135289
No.
Ø19.1 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
Ø28.6 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
18
70
No.
Ø 6.4 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø15.9 x (Ø28.6) 1pc
Ø19.1 x (Ø28.6) 1pc
Ø22.2 x (Ø28.6) 2pcs
Ø15.9 x (Ø19.1) 2pcs
Ø22.2 x (Ø19.1) 2pcs
Ø28.6 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø34.9 x (Ø28.6) 1pc
030609
58
Ø 6.4 x (Ø12.7) 1pc
Ø 9.5 x (Ø12.7) 2pcs
020554
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
06
09
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 2pcs
Ø15.9 x (Ø12.7) 1pc
1pc
Ø22.2
Ø15.9
Ø9.5
1pc
Ø15.9
1pc each
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 4pcs
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 4pcs
06
09
No.
Ø15.9 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
Ø19.1 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
Ø28.6 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
141870
No.
Ø 6.4 x (Ø 9.5) 4pcs
01
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
06
09
( )
MODEL
diameter of the
connected pipe
external diameter
of socket
side
side
Gas
NAME
Branching header
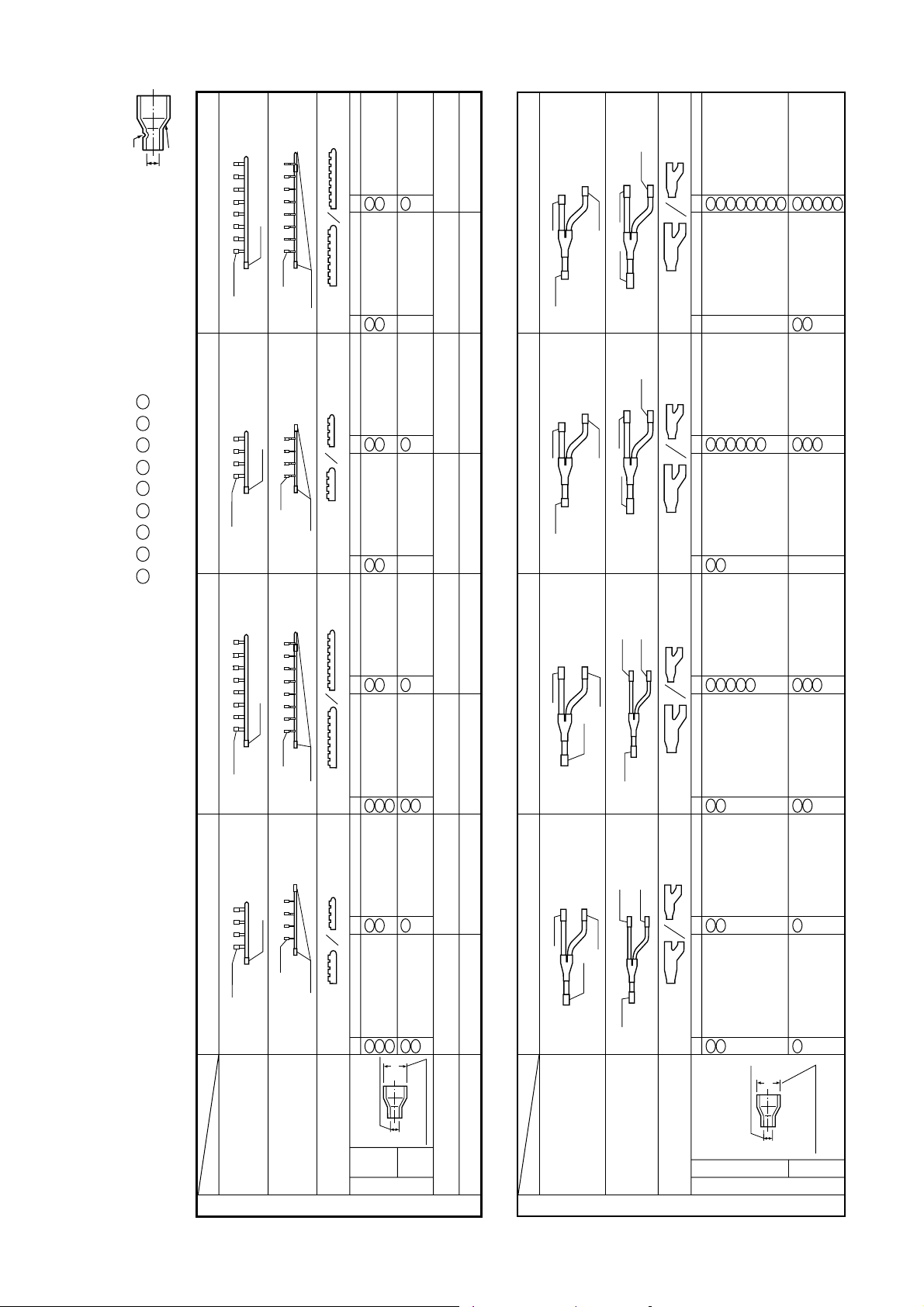
5-6. Parts of Branching Header/Joint
Branching Header : RBM-HY1043E / HY1083E / HY2043E / HY2083E
Branching Joint : RBM-BY53E / BY103E / BY203E / BY303E
• Check the following parts in the package.
• For piping material and size of the refrigerant pipes, refer to the Installation Manual of the Air Conditioner.
gas side
Branching header
liquid side
Heat insulator
(gas side/liquid side)
Socket
Branching Header
(Ø 9.5) 1pc
(Ø15.9) 1pc
(Ø15.9) 1pc
MODEL
Liquid
Outlet sealed pipe at gas side
Header sealed pipe at liquid side
Outlet sealed pipe at liquid side
18
1pc
Ø12.7
Ø12.7
RBM-BY53E
NAME
Ø15.9
Branching joint
gas side
1pc
Ø9.5
Ø9.5
Ø12.7
Branching joint
liquid side
1pc each
Ø 9.5 x (Ø12.7) 2pcs
Ø15.9 x (Ø12.7) 2pcs
05
54
No.
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø19.1 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
09
51
No.
diameter of the
connected pipe
Heat insulator
(gas side/liquid side)
Branching Joint
Ø 6.4 x (Ø 9.5) 2pcs
01
Ø 9.5 x (Ø12.7) 1pc
05
( )
external diameter
Gas side
Socket
of socket
Liquid side
socket
projection
Diameter of the
connecting pipe
Ø15.9
Ø15.9
Ø9.5
Ø15.9
RBM-HY2083FERBM-HY2043FE
Ø22.2
Ø15.9
1pc 1pc
Ø15.9
1pc 1pc
Ø15.9
Ø9.5
Ø31.8
1pc 1pc
Ø15.9
1pc each
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 8pcs
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 7pcs
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 7pcs
060909
Ø34.9 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
Ø28.6 x (Ø31.8) 1pc
Ø34.9 x (Ø31.8) 1pc
275970
1pc each
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 4pcs
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 2pcs
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 2pcs
060909
(Ø 9.5) 3pcs
(Ø15.9) 3pcs
(Ø15.9) 7pcs
Ø 6.4 x (Ø 9.5) 7pcs
01
(Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø19.1 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
51
(Ø 9.5) 1pc
(Ø15.9) 3pcs
(Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø 6.4 x (Ø 9.5) 4pcs
01
(Ø15.9) 1pc
38.1
38.1
28.6
28.6
Ø
Ø
Ø
Ø
RBM-BY303FERBM-BY203FE
38.1
31.8
Ø
Ø
28.6
Ø
1pc 1pc
28.6
Ø
19.1
Ø
1pc 1pc
19.1
Ø
19.1
19.1
Ø
Ø
22.2
Ø
12.7Ø12.7
Ø
1pc 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø28.6) 1pc
Ø 9.5 x (Ø38.1) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø38.1) 1pc
Ø15.9 x (Ø38.1) 1pc
Ø22.2 x (Ø38.1) 1pc
77767573715149204304071013
Ø34.9 x (Ø38.1) 1pc
61
Ø19.1 x (Ø28.6) 1pc
Ø28.6 x (Ø38.1) 2pcs
Ø34.9 x (Ø38.1) 2pcs
Ø28.6 x (Ø31.8) 1pc
27
1pc each 1pc each
Ø12.7 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø 9.5 x (Ø28.6) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø28.6) 1pc
Ø15.9 x (Ø28.6) 1pc
4849164358105289020554
Ø22.2 x (Ø19.1) 2pcs
Ø22.2 x (Ø28.6) 2pcs
Ø34.9 x (Ø28.6) 1pc
x (Ø28.6) 1pc
Ø 6.4 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø 9.5 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø22.2 x (Ø28.6) 2pcs
Sealed pipe
Ø15.9 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø19.1 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
18
x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø 6.4 x (Ø12.7) 1pc
Ø 9.5 x (Ø12.7) 1pc
Ø28.6 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø15.9 x (Ø12.7) 2pcs
Sealed pipe
Ø31.8
Ø22.2
Ø15.9
51 , 52 , 54 , 58 , 59 , 70 , 89 : without projection)
the indicated position, and others indicate diameter of the connecting pipe.
(
2. Please connect pipe to the side with a projection of the socket.
Ø15.9
Ø15.9
Ø15.9
Ø9.5
NOTE : 1. All dimensions are in millimeters. In the following tables, ( ) indicates diameter of
Ø28.6 x (Ø31.8) 1pc
275970
No. No. No. No.
1pc each
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 7pcs
0609060901
RBM-HY1083FE
Ø22.2
1pc 1pc
Ø22.2
1pc 1pc
Ø15.9
1pc 1pc
Ø15.9 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
1470851806
Ø19.1 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø28.6 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
Ø34.9 x (Ø31.8) 1pc
51
(Ø15.9) 3pcs
(Ø15.9) 7pcs
Ø 6.4 x (Ø 9.5) 8pcs
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 8pcs
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 8pcs
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 8pcs
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
Ø19.1 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
Ø28.6 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
09
(Ø 9.5) 3pcs
(Ø15.9) 1pc
RBM-BY103FERBM-BY53FE
1pc each
Ø15.9
Ø15.9
Ø9.5
Ø15.9
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 4pcs
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 4pcs
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 3pcs
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 4pcs
0609060901
(Ø15.9) 3pcs
(Ø 9.5) 1pc
(Ø15.9) 1pc
(Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø 6.4 x (Ø 9.5) 4pcs
31.8
Ø
19.1
Ø
22.2
Ø
12.7
Ø
19.1
Ø
1pc 1pc
12.7
Ø
22.2
Ø
19.1
Ø
22.2
Ø
12.7
Ø
19.1
Ø
1pc 1pc
12.7
Ø
15.9
Ø
12.7
Ø
15.9
Ø
9.5Ø9.5
Ø
12.7
Ø
1pc 1pc
Ø28.6 x (Ø31.8) 1pc
27
No. No. No. No.
Ø 9.5 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø15.9 x (Ø19.1) 2pcs
07101352891052
Ø28.6 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
70
1pc each 1pc each
Ø 9.5 x (Ø12.7) 2pcs
Ø15.9 x (Ø12.7) 2pcs
05
54
Ø28.6 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
70
Ø19.1 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
51
x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø 6.4 x (Ø12.7) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø19.1) 2pcs
Ø22.2 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø22.2 x (Ø19.1) 2pcs
Ø28.6 x (Ø19.1) 1pc
Ø19.1 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
18
Ø 9.5 x (Ø12.7) 2pcs
Sealed pipe
020554
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
09
x (Ø12.7) 1pc
Ø 9.5 x (Ø12.7) 2pcs
05
Ø 6.4 x (Ø 9.5) 2pcs
Ø15.9 x (Ø12.7) 1pc
Sealed pipe
54
01
Ø15.9 x (Ø12.7) 1pc
RBM-HY1043FE
Ø22.2
Ø22.2
MODEL
Suction gas side
NAME
of the Air Conditioner.
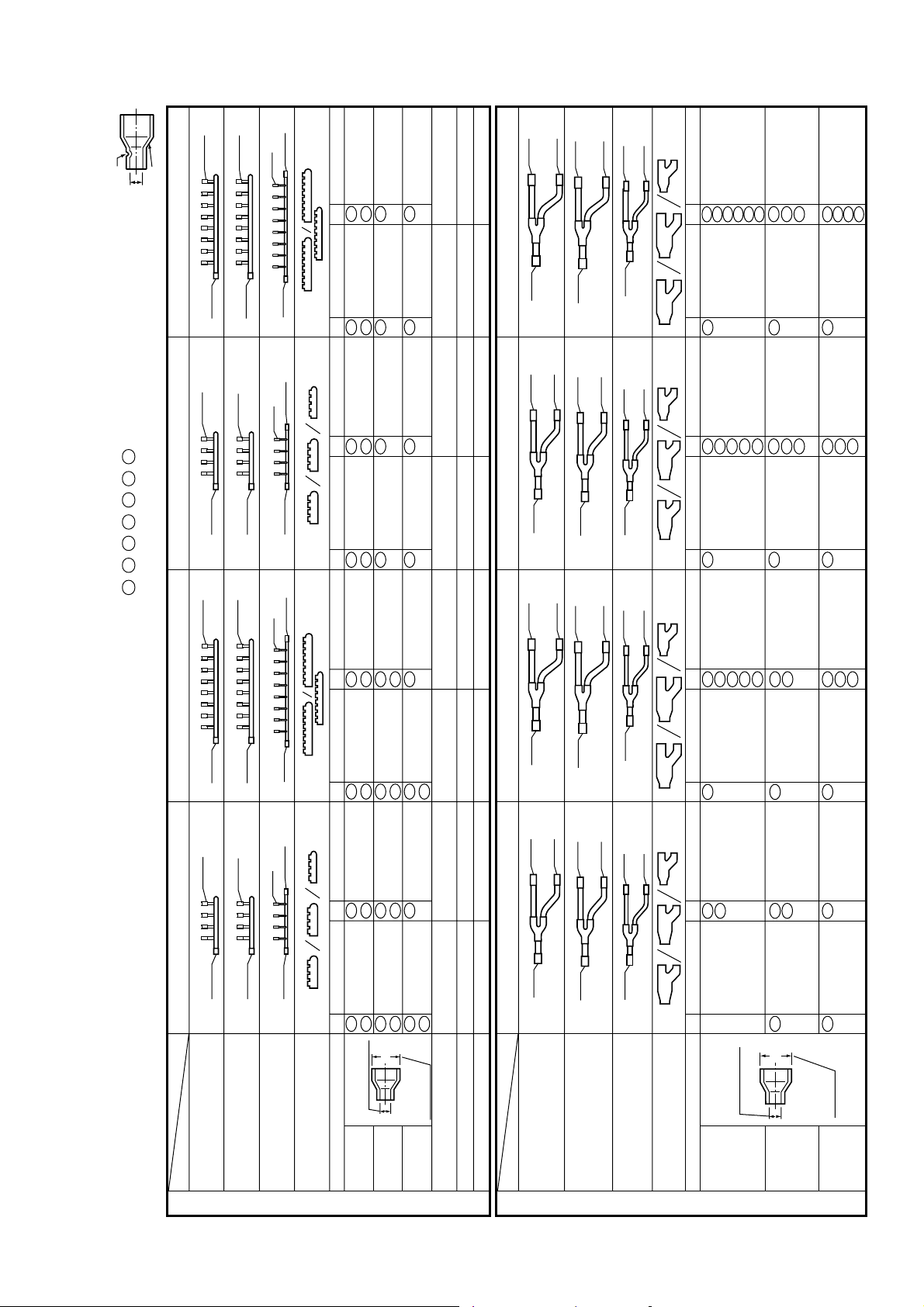
Branching Header : RBM-HY1043FE / HY1083FE / HY2043FE / HY2083FE
Branching Joint : RBM-BY53FE / BY103FE / BY203FE / BY303FE
• Check the following parts in the package.
• For piping material and size of the refrigerant pipes, refer to the Installation Manual
Ø15.9
No. No. No. No.
Socket
Liquid side
Discharge gas side
Heat insulator (suction gas side/
discharge gas side/liquid side)
Ø 9.5 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
Ø12.7 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
Ø19.1 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
Ø15.9 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
Ø28.6 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
1470851806
diameter of the
connected pipe
Suction
gas side
09
( )
external
diameter
of socket
Liquid
side
Discharge
gas side
Branching Header
Outlet sealed pipe at suction gas side
Outlet sealed pipe at discharge gas side
Outlet sealed pipe at liquid side
15.9
Ø
15.9
Ø
MODEL
Suction gas side
Header sealed pipe at liquid side
NAME
Discharge gas side
19
12.7
Ø
Liquid side
Ø 9.5 x (Ø12.7) 1pc
05
external
diameter
of socket
No. No. No. No.
diameter of the
connected pipe
Ø12.7 x (Ø15.9) 1pc
09
( )
Socket
Heat insulator
(suction gas side/discharge gas side/liquid side)
Suction
gas side
Branching Joint
Discharge
gas side
Liquid
side
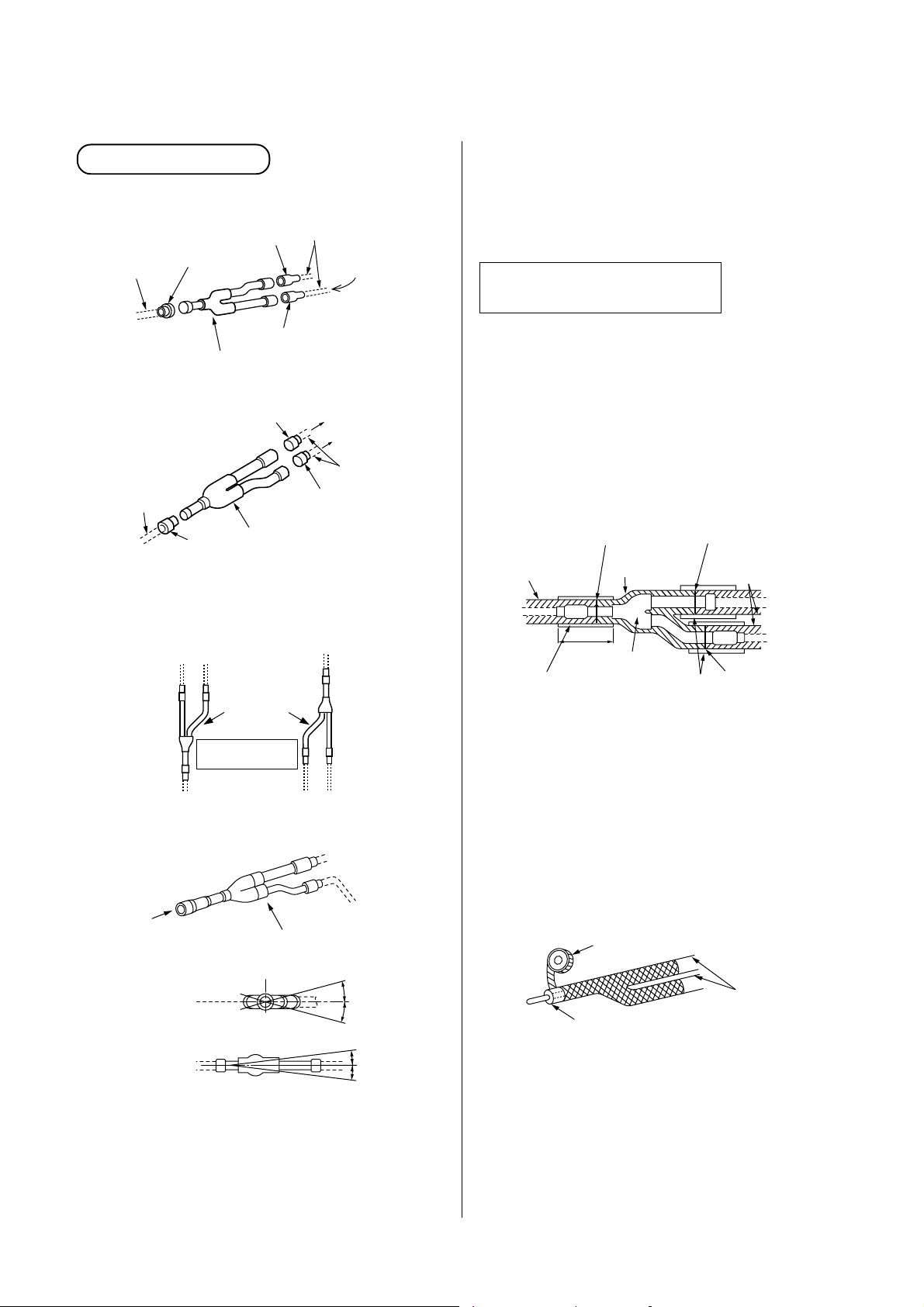
5-7. Branching Kit Connection Method
[1] Branch joint
<Suction gas/Discharge gas side>
Socket
Pipe in use
on the site
Inlet
To outdoor unit
Socket
Gas side branch joint
Outlet (2)
Outlet (1)
<Liquid side>
Socket
Outlet (1)
Pipe in use
on the site
Inlet
To outdoor unit
Socket
• Installation direction of branch pipe
Install the branching pipes so that it branch either
vertically or horizontally.
Outlet (2)
Gas/Liquid side branch joint
Both directions
are possible.
Pipe in use on the site
To other branching
pipe or indoor unit
Socket
To other branching pipe or indoor
unit
Pipe in use
on the site
Socket
NOTE :
Install the branch pipes horizontally or vertically so
that they branch evenly.
Install the branching joint within ± 15 degrees.
Heat insulating for pipes
(Branching Joint)
• In order to prevent dripping at the place where the
insulation provided with the branching kit meets the
insulating material obtained on the site, butt the two
types of insulation up against each other, and then
wrap the seam between the two types of insulation
in at least 10mm of the insulating material (in use on
the site).
<Suction gas/Discharge gas/Liquid side>
Heat insulator
for piping
(in use on the site)
Heat insulator (in use on the site)
by 10mm or more thickness.
Butt together
150
Branching joint
Heat insulator
in package
Butt together
Heat insulator for piping
(in use on the site)
Butt together
In case of vertical
installation
<Suction gas/Discharge gas/Liquid side>
A
B
(Horizontal line)
(A view)
(Horizontal line)
(B view)
<In case of horizontal installation>
NOTE :
• Install the branch pipes horizontally or vertically so
that they are branched evenly.
• Install the branching joint within ±15 degrees.
Within
± 15
Within
± 15
degrees
degrees
• On the gas-side pipe, use insulation that can
withstand heat of 120°C or higher. For the branch
pipe, either use a commercially available coupling
cover (for T-shape) that is at least 10mm thick, or
else insulate the pipe as shown in the figure at
below.
• After applying insulation as outlined above, tape the
insulation in place.
Taping (in use on the site)
Heat insulator
Heat insulator
(in use on the site)
(in use on the site)
20
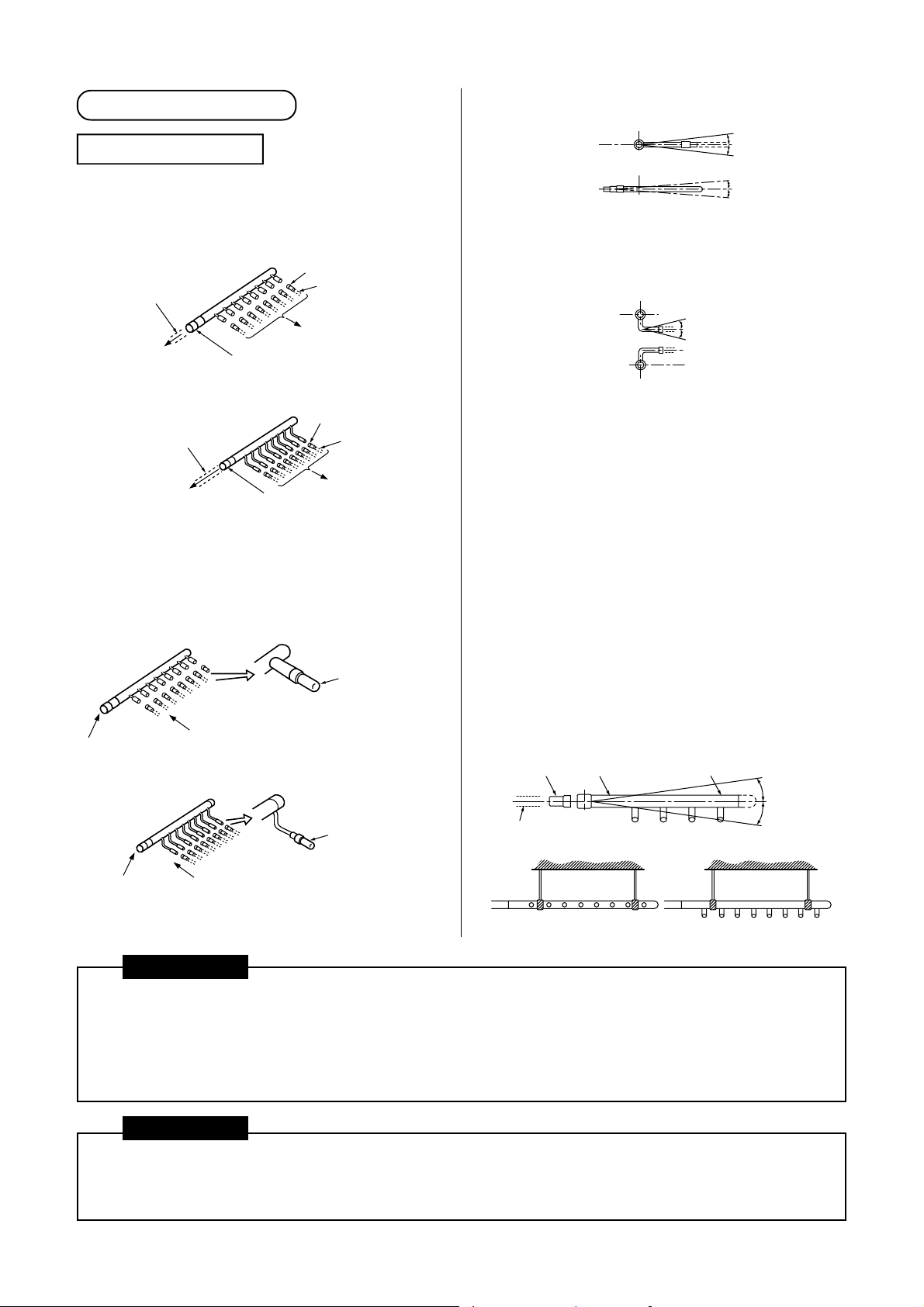
[2] Branch header
<Suction gas/Discharge gas side>
Branching Header
Select and install the socket that matches the
diameter of a pipe to be connected to the indoor unit.
<Suction gas/Discharge gas side branch
header>
Pipe in use on the site
To outdoor unit
Socket
Socket
Pipe in use on the site
To indoor unit
<Liquid-side branch header>
Socket
Pipe in use on the site
To outdoor unit
Socket
Pipe in use
on the site
To indoor unit
• If the number of indoor units to be connected is
fewer than the maximum number of units that can
be connected to the branch header, attach a sealed
pipe to the unused connectors.
<Suction gas/Discharge gas side branch
header>
Outlet sealed pipe
(Provided with
branch header)
A
B
<Liquid-side branch header>
Outlet sealed pipe
(Provided with
branch header)
C
• Install the branch header so that it branches
horizontally. It cannot be used in a vertical position.
D
(Horizontal line)
(Horizontal line)
(A view)
(B view)
Within
± 15
Within
± 10
degrees
degrees
<Liquid-side>
(Horizontal line)
NOT GOOD
(C view)
When arranging the branching header at the liquid
side, attach a header sealed pipe on the sealing side
of the header as shown in the fiqure at below.
Be sure to install the branch pipe downward.
Horizontal viewed from D point should be within ± 10
degrees same as view B.
• Supporting branching header
After applying the insulation, set the hanging metals
as support. (in use on the site).
NOTE :
1. Install the branching header so that it branches
horizontally. It cannot be used in a vertical
position.
2. Do not use T-type pipe for the branching section.
Inlet socket
Pipe in use
on the site
Branching Header
(D view) Sealing side
Within
± 15
degrees
Header sealed pipe
Within
± 10
degrees
CAUTION
1. On the inlet side of a Y-type branch joint or branch header, allow for at least 300mm of straight pipe.
2. A Y-type branch joint can be installed so that it branches either vertically or horizontally; if branching
horizontally, it should be within an angle of ± 15°.
3. A branch header should be installed so that it branches horizontally.
4. Do not use T-type branch joints.
CAUTION
In the multi air conditioning system, because the refrigerant pipes congregate at the rooftop pipeshaft outlet in
the vertical pipeshaft, it is necessary to attach “labels” to each pipe in order to make clear to which system a
given pipe belongs so as to prevent pipes from being connected incorrectly.
21
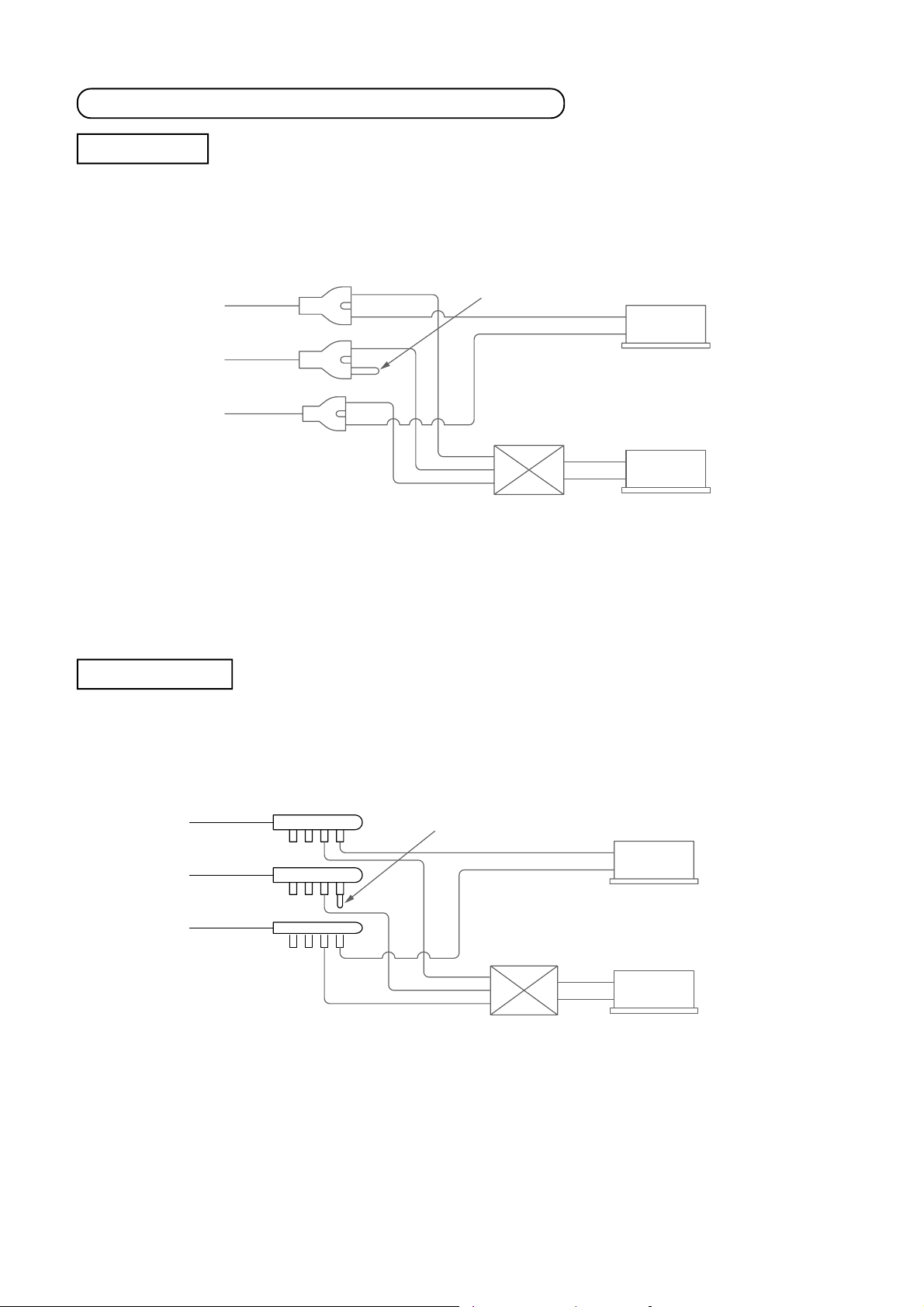
How to connect “Cooling Only” indoor unit
Branch joint
• When connecting a Cooling Only indoor unit, attach a sealed pipe to the unused connectors of the branching
pipe of discharge gas side.
Suction gas side
* Discharge gas side
Liquid side
∗ Refer to above. There is the method of connecting without using branching joint pipe of discharge gas side.
For details, refer to the Installation Manual of the Air Conditioner.
Connect sealed pipe.
Flow selector unit
Indoor unit
Cooling only
Indoor unit
Heating and Cooling
Branch header
• When connecting a Cooling Only indoor unit, attach a sealed pipe to the unused connectors of the branching
pipe of discharge gas side.
Suction gas side
Connect sealed pipe.
Discharge gas side
Liquid side
Flow selector unit
Indoor unit
Cooling only
Indoor unit
Heating and Cooling
[NOTE]
For cooling only indoor unit in Super-HRM system, item code (DN) setting from the wired remote controller is
necessary. (Refer to the section “13-1.”)
22
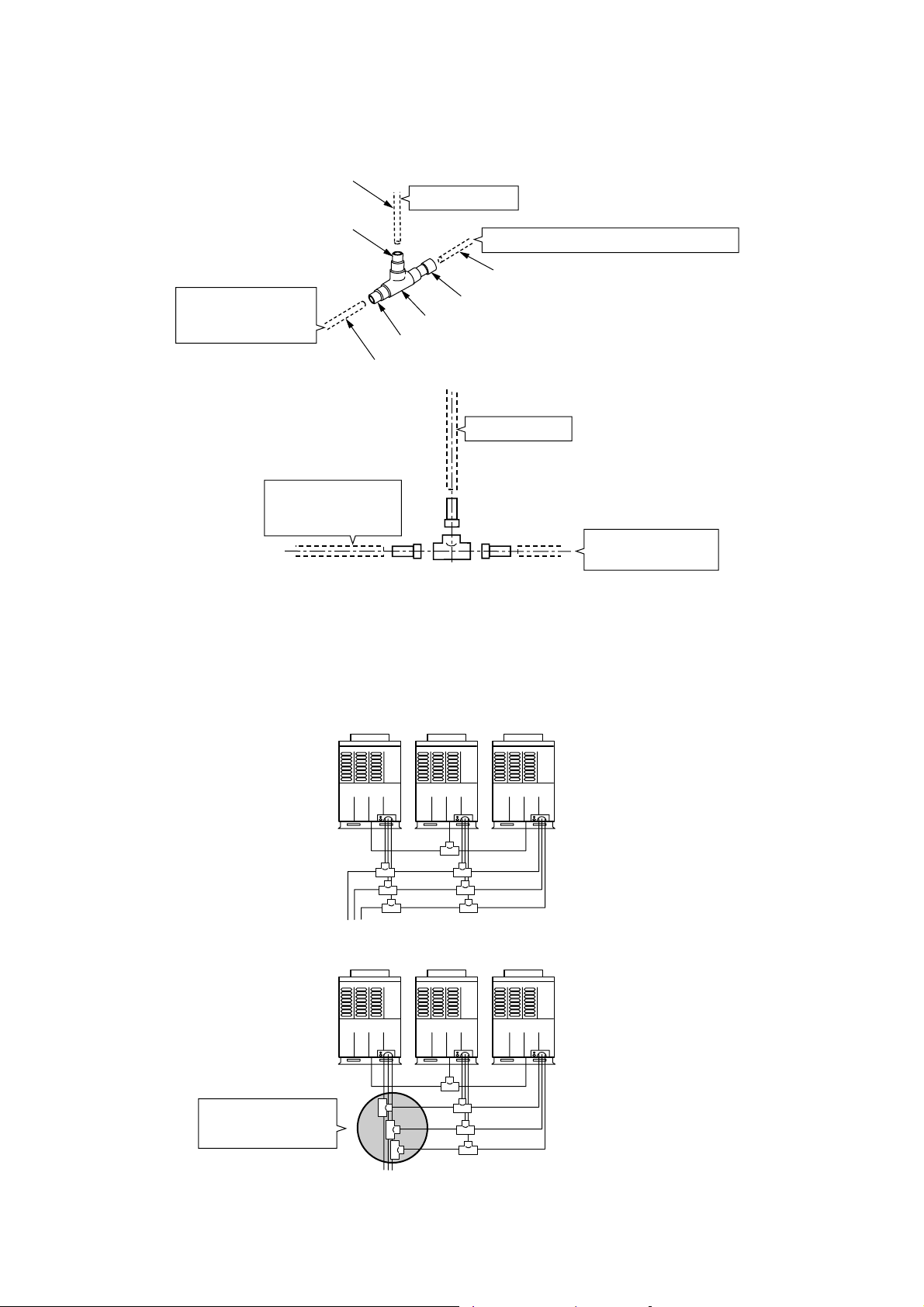
[3] T-shape branching joint (For connection of outdoor unit)
RBM-BT13FE
Please read "Safety Cautions" described in the
Installation Manual of the Air Conditioner.
• Check the following parts in the package.
• For piping material and size of the refrigerant pipes,
refer to the Installation Manual of the Air
Conditioner.
RBM-BT13E (T-shape branching joint)
Branching joint Socket
Ø38.1
Suction
Ø38.1
Ø38.1
Gas side
1 pc
Ø28.6
Discharge gas side
Liquid side
Ø28.6
Ø22.2
Ø28.6
1 pc
Ø22.2
Ø22.2
1 pc
Parts
NOTE :
All dimentions are in millimeters.
In the following tables, ( ) indicates diameter of the
indicated position, and others indicate diameter of the
connected pipe.
DiameterNo.
Ø34.9 x (Ø38.1) 1pc
61
Ø28.6 x (Ø38.1) 3pcs
71
Ø22.2 x (Ø38.1) 2pcs
Diameter of the
connected pipe
(external diameter
of soket)
73
Ø19.1 x (Ø28.6) 2pcs
20
Ø22.2 x (Ø28.6) 2pcs
43
Ø15.9 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
14
Ø19.1 x (Ø22.2) 1pc
18
Ø12.7 x (Ø22.2) 2pcs
85
Ø9.5
For balancing pipe
Ø9.5
Ø9.5
<Branching pipe for balancing pipe>
To outdoor unit
To other branching
pipe or outdoor unit
Pipe in use on the site
• When combining two units,
connect directly between
outdoor units.
Connect balancing
pipe directly.
Pipe in use on the site
To other branching
pipe or outdoor unit
Pipe in use on the site
Branching pipe for
balancing pipe (Provided)
Follower unitHeader unit
1 pc
<Heat insulating for pipe (In use of the site)>
• Be sure to perform heat insulating at liquid side and
gas side, and balancing pipes separately.
(Heat insulator for balancing is not provided.)
• Use heat-resisting heat insulator (120°C or more)
for pipes at gas side.
• To insulate heat of the branching pipes, use a joint
cover (For T-shape) available on the market that is
with 10mm or more thickness, or one applied with
machining as shown in the figure.
• Seal the branching piping completely without
clearance to prevent dewing or falling of water
drops.
Heat insulating
pipe for piping
Seal with vinyl tape
Cut the heat
insulator at the
right angle
ØD
90 degrees
ØD
90 degrees
Seal the joint with urethane
foaming agent, etc.
Heat insulating
pipe for piping
Heat insulator
Cut the heat insulator
at the right angle
23
90 degrees
more then 100mm
<Branching pipes at suction gas side/discharge gas side/liquid side>
Pipe in use on the site
To outdoor unit
Socket at suction gas/
discharge gas/liquid side
(Provided)
To other branching
pipe or branching
section of main pipe
Pipe in use on the site
Use the attached socket at suction gas/
*
discharge gas/liquid sides along with
the selected pipe size.
(Figure shows a connecting example.)
To other branching
pipe or branching
section of main pipe
Branching pipe at suction gas/discharge gas/liquid side (Provided)
Socket at suction gas/discharge gas/liquid side (Provided)
To other branching pipe or outdoor unit
Pipe in use on the site
Socket at suction gas/discharge gas/liquid side (Provided)
To outdoor unit
• Installation of branching pipes to suction gas/discharge gas/liquid sides.
To other branching
pipe or outdoor unit
GOOD
NOT GOOD
Do not install branch
pipe in this direction
Header
outdoor unit
Header
outdoor unit
Follower
outdoor unit
Follower
outdoor unit
24
5-8. External Dimensions of Branch Connectors
(Outline drawings are shown on the following pages.)
Branching joints and headers
Model name Appearance
RBM-BY53FE
Y-shape
branching
joint (*3)
4-branching
header (*4) (*5)
8-branching
header (*4) (*5)
T-shape
branching
joint (For
connection
of outdoor
units)
1 “Capacity code” can be obtained from page 6. (Capacity code is not actual capacity.)
*
2 If total capacity code value of indoor unit exceeds that of outdoor unit, apply capacity code of outdoor unit.
*
3 When using Y-shape branching joint for 1st branching, select according to capacity code of outdoor unit.
*
4 Max. 6.0 capacity code in total can be connected.
*
5 If the capacity code of outdoor unit is 26 or more, it is not used for 1st branching.
*
6 This is used for branching to “cooling only” indoor unit.
*
7 Model names for outdoor and indoor units described in this guide are shortened because of the space constraint.
*
RBM-BY203FE
RBM-BY303FE
RBM-BY53E
RBM-BY103E
RBM-BY203E
RBM-BY303E
RBM-HY1043FE
RBM-HY2043FE
RBM-HY1043E
RBM-HY2043E
RBM-HY1083FE
RBM-HY2083FE
RBM-HY1083E
RBM-HY2083E
RBM-BT13FE
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total below 6.4
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total 6.4 or more and below 14.2RBM-BY103FE
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total 14.2 or more and below 25.2
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total 25.2 or more
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total below 6.4
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total 6.4 or more and below 14.2
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total 14.2 or more and below 25.2
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total 25.2 or more
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total below 14.2
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total 14.2 or more and below 25.2
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total below 14.2
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total 14.2 or more and below 25.2
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total below 14.2
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total 14.2 or more and below 25.2
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total below 14.2
Indoor unit capacity code (*1) : Total 14.2 or more and below 25.2
1 set 4 types T-shape joint pipes as described below:
The required quantity is arranged and they are combined on site.
Connection piping Corresponded dia. (mm) Q'ty
Balance pipe
Piping at liquid side
Piping at discharge gas side
Piping at suction gas side
Usage
Ø12.7 to Ø22.2
Ø19.1 to Ø28.6
Ø22.2 to Ø38.1
For 3
piping
For 2
piping (*6)
For 3
piping
For 2
piping (*6)
For 3
piping
For 2
piping (*6)
Ø 9.5 1
1
1
1
5-9. Nitrogen Gas Blow Method (During Brazing)
• If nitrogen gas is not passed through the pipes during brazing, a film of oxidized material will form on the inner
surfaces of the pipes. The presence of a such a film in the system will adversely affect the operation of the
valves and compressor in the refrigerant system, and will prevent the system from operating normally.
• In order to prevent this from occurring, nitrogen gas is passed through the pipes while brazing is in progress.
This process of replacing the air in the pipes with nitrogen is called the “nitrogen gas blow.”
This is the basic method that is used for brazing work.
CAUTION
1. Nitrogen gas must be used. (Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and fluorocarbons cannot be used.)
2. Always be sure to use a pressure-reducing valve.
Piping
Valve
Hose
Reducing
valve
Nitrogen
gas bomb
Piping at site
Brazing
position
Copper pipe Ø6.4
Valve
Taping
Reducing valve
Pressure
tight hose
Outside
Nitrogen
gas bomb
25
5-10. Brazing Work
1. Brazing work should be performed downwards or
(Recommended brazing)
sideways. Avoid brazing upwards (in order to
avoid incomplete brazing). (Recommendation)
2. Always used the specified piping materials for
liquid pipes and gas pipes, and make sure that
GOOD NOT GOOD
Brazing material
they are installed in the proper direction and at
the proper angle.
3. The “nitrogen gas blow” method should be used
when brazing.
(Direction downward) (Direction upward)
Lateral direction
Brazing
material
Brazing
material
CAUTIONS
1. Pay attention to fire prevention concerns. (Take preventative measures in the area where brazing work is
to be performed, such as keeping a fire extinguisher or water handy.)
2. Be careful not to burn yourself.
3. Make sure that any gaps between pipes and couplings are appropriate. (Do not miss brazing any joints.)
4. Make sure that pipes are adequately supported.
• The following table provides basic guidelines for the interval between supports for horizontal copper pipe.
Coupling size of brazed pipe
Connected section
External size Internal size
K
ØC
G
ØF
Interval between supports for copper pipe
Nominal dia.
Max. interval (m)
• Avoid securing copper pipes with metal brackets
directly.
20 or less 25 to 40
1.0 1.5
(Unit: mm)
Connected section
Standard outer dia. of
connected copper pipe
6.35
9.52
12.70
15.88
19.05
22.22
28.58
34.92
External size Internal size
Standard outer dia. (Allowable difference)
CF
6.35 (±0.03) 6.45 ( )
9.52 (±0.03) 9.62 ( )
12.70 (±0.03) 12.81 ( )
15.88 (±0.03) 16.00 ( )
19.05 (±0.03) 19.19 ( )
22.22 (±0.03) 22.36 ( )
28.58 (±0.04) 28.75 ( )
34.90 (±0.04) 35.11 ( )
+0.04
–0.02
+0.04
–0.02
+0.04
–0.02
+0.04
–0.02
+0.03
–0.03
+0.03
–0.03
+0.06
–0.02
+0.04
–0.04
Min. depth
of insertion
KG
76
87
98
98
11 10
11 10
13 12
14 13
Oval value
0.06 or less
0.08 or less
0.10 or less
0.13 or less
0.15 or less
0.16 or less
0.20 or less
0.25 or less
Min. thickness
of coupling
0.50
0.60
0.70
0.80
0.80
0.82
1.00
1.20
∗ Gas brazing of refrigerant pipes must be performed by personnel qualified to do so under local ordinances.
Minmum wall thickness for R410A application
Soft (Coil)
OK
OK
OK
OK
NG
NG
NG
NG
Hard or Half hard
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OD (Inch)
1/4
3/8
1/2
5/8
3/4
7/8
1.1/8
1.3/8
OD (mm)
6.35
9.52
12.70
15.88
19.05
22.20
28.58
34.92
Minium wall thickness
0.80
0.80
0.80
1.00
1.00
1.00
1.00
1.10
26

5-11. Flare Processing
Flare processing procedure
Parts and material : Copper pipe, flare nut. Flare nut shallbe of attached on the indoor unit or R410A exclusive.
Tools : Flare tool (“Rigid” type), reamer, pipe cutter
Work procedure
Straighten the coiled copper pipe.
Cut the pipe with the pipe cutter.
Use the reamer to remove burrs
from the cut surface of the pipe.
Pipe
Burr
Deburring
Key point
Uncoil the pipe.
1. Position the blade of the cutter
so that it will cut the pipe at a
perpendicular angle.
2. Rotate the pipe cutter to the
left to cut the pipe.
3. Move the pipe cutter slowly.
1 . Keep the opening of the pipe
facing downwards.
2. Be careful not to scratch the
inner surface of the pipe.
(Reason)
• It is difficult to cut the coiled
pipe correctly, which increases
the chance of failure.
• The cut surface will be at an
angle.
• The cutter will bite too tightly.
• The copper pipe will be
deformed.
• Scraps will get inside of the
pipe.
• A gas leak could result.
Clear out the inside of the pipe by
tapping on the end with a
screwdriver.
Insert the flare nut.
Make sure that all scraps of metal
are out of the tube by lightly
tapping on the tube while the
opening is pointing down.
Be certain to insert the flare nut
before beginning the flare process.
27
• Metal scraps in the tube can
damage the compressor.
• If the scraps adhere to the flared
region, a gas leak may result.
• The flare nut will not fit inside
the copper pipe after the flare
process.
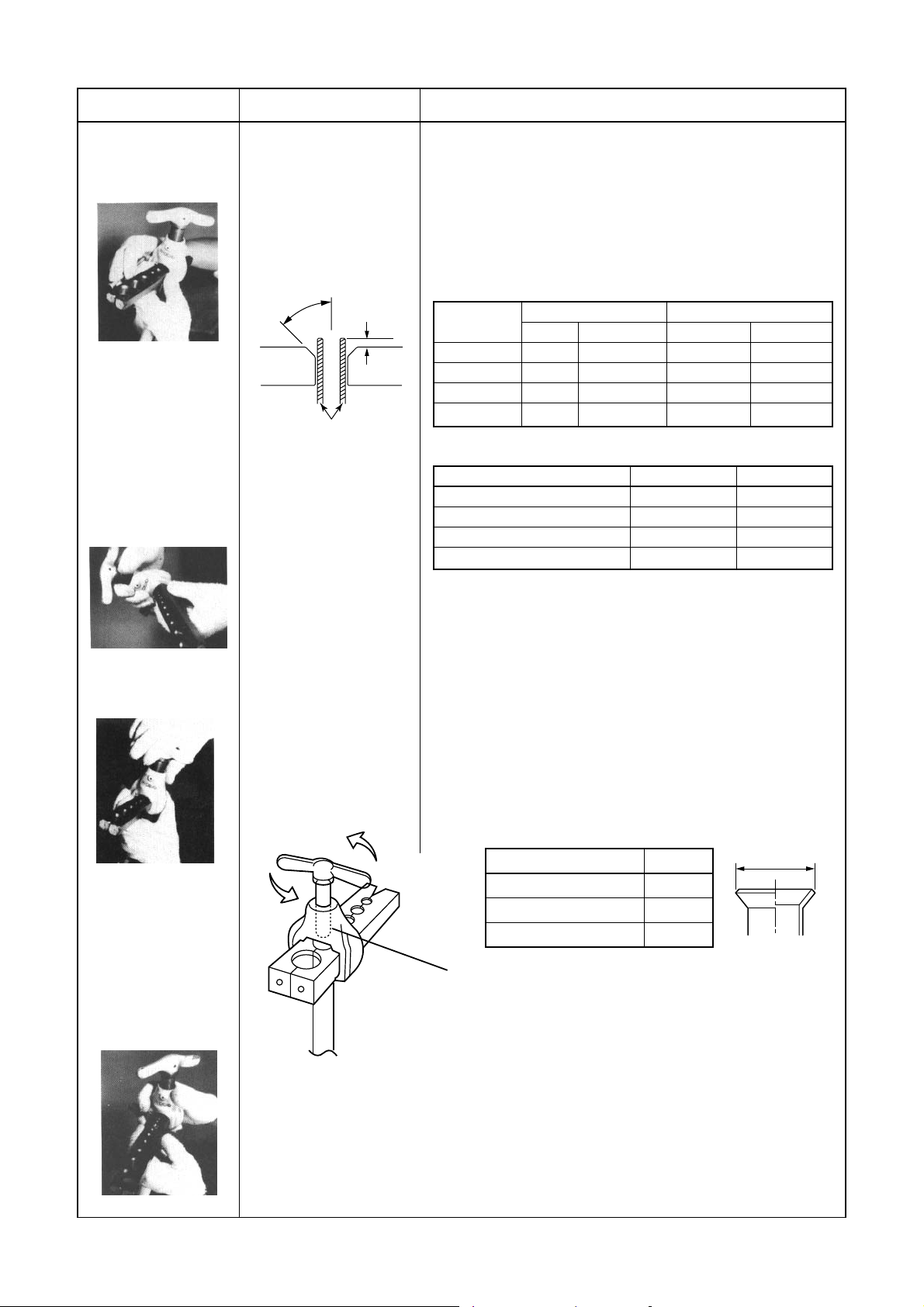
Work procedure
Key point
(Reason)
Attach the (“Rigid”)
flare tool to the
copper pipe.
Align the punch.
(Align the arrow with
the line adjacent to
the next hole.)
1. Make sure that the
inner surfaces of the
flare tool are clean.
2. Determine the
dimensions of the
copper pipe in
accordance with the
flare tool.
45˚
A
Flare tool
Copper pipe
Align the arrow on the
punch with the
prescribed position on
the flare tool.
• The copper pipe will slip out while the flaring process is in
progress.
• The flared dimensions vary.
Dimensions to end of copper tube when flared with one tool
surface
• Projection margin in flaring : A (Unit : mm)
Rigid (Clutch type)
Outer dia. of
copper pipe
6.4
9.5
12.7
15.9
R410A tool used
R410A R22
0 to 0.5 (Same as left)
0 to 0.5 (Same as left)
0 to 0.5 (Same as left)
0 to 0.5 (Same as left)
Conventional tool used
R410A R22
1.0 to 1.5 0.5 to 1.0
1.0 to 1.5 0.5 to 1.0
1.0 to 1.5 0.5 to 1.0
1.0 to 1.5 0.5 to 1.0
Imperial (Wing nut type)
Outer dia. of copper pipe
6.4
9.5
12.7
15.9
R410A R22
1.5 to 2.0 1.0 to 1.5
1.5 to 2.0 1.0 to 1.5
2.0 to 2.5 1.5 to 2.0
2.0 to 2.5 1.5 to 2.0
Flare the pipe.
Remove the flare tool
and check the flared
surface.
Slowly and carefully turn
the flare tool handle
while it clicks, until it
turns freely. Turn the
handle to the left and
raise it to the top.
If the handle is not raised to the
top, the flare tool will scratch the
extended portion of the pipe
(the cone-shaped portion).
• If the “A” dimension is small, the flared contact surface is
smaller and a gas leak becomes more likely.
• The pipe will not be flared fully.
• The extended portion of the pipe (the cone-shaped portion)
will be scratched.
• Extruding margin of copper pipe
with flare machining : A (Unit: mm)
Copper pipe outer dia.
9.5
12.7
15.9
A
13.2
16.6
19.7
+0.0
–0.4
A
Check list :
• Is the inner surface of the flared portion equal in width and shiny?
• Is the thickness of the flared portion equal?
• Is the flared portion of a suitable size?
28
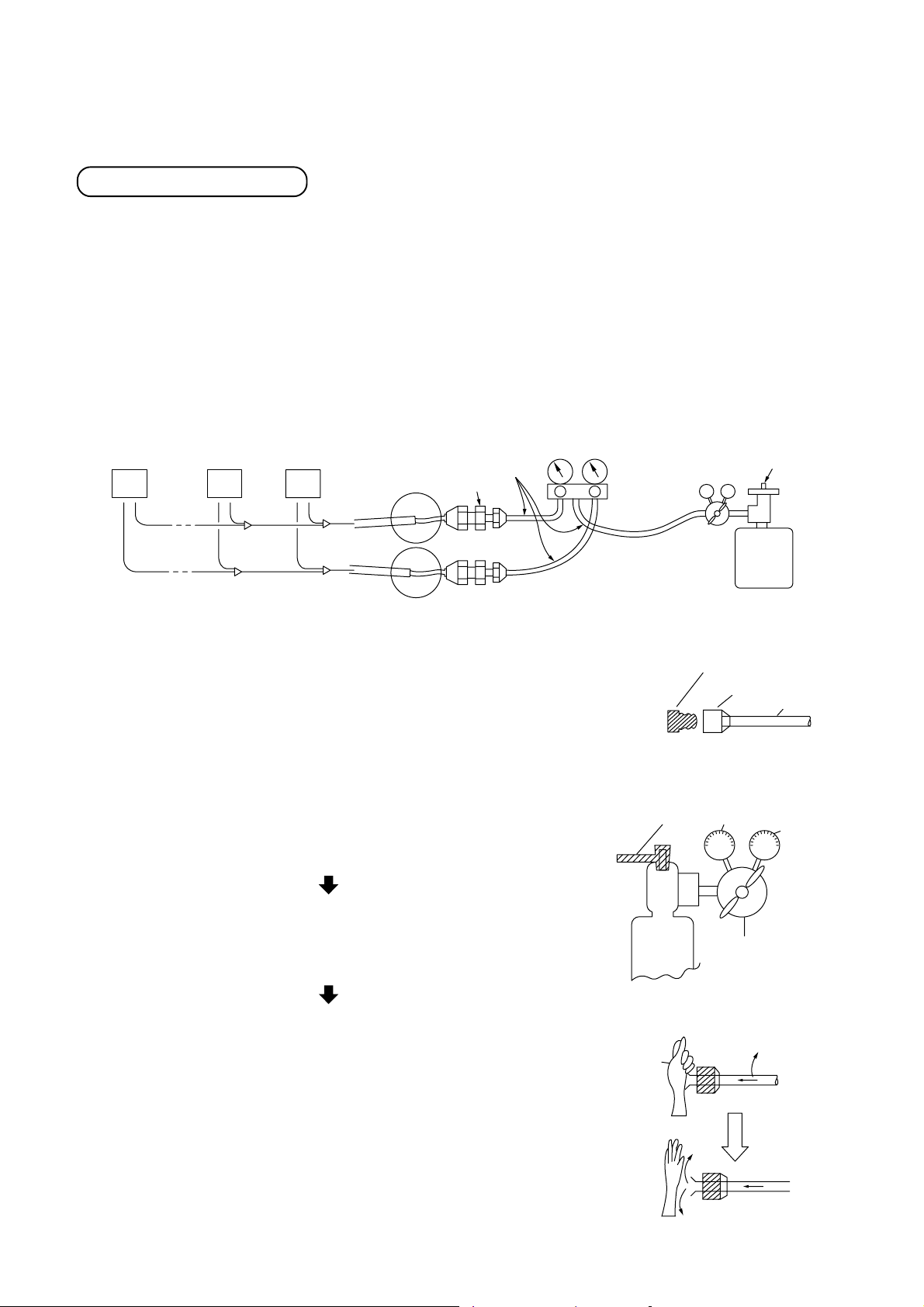
5-12. Flushing
The flushing process uses gas pressure to remove foreign matter from the inside of pipes.
Three major effects
(1) Removes oxidation that formed inside of the pipe during brazing as a result of an inadequate “nitrogen gas
blow” procedure.
(2) Removes foreign matter and moisture that has gotten inside of pipes due to improper handling.
(3) Checks the connections in the pipe system between the indoor unit and the outdoor unit.
[Example work procedure]
1. Install a pressure reducing valve on a nitrogen cylinder. (Fluorocarbon gases and carbon dioxide carry a risk
of promoting condensation, while oxygen causes explosion.)
2. Connect the pressure reducing valve to a gauge manifold and then to the gas-side pipe and the liquid-side pipe
on the outdoor unit.
Indoor unit
Ø6.4 copper pipe
N21
Diff. size union
3. On the indoor unit side, plug all gas-side pipes except those for the
indoor units that are to be flushed.
4. Open the source valve on the nitrogen cylinder and increase the
pressure on the secondary side of the pressure reducing valve until it
reaches 0.5MPa (5kg/cm2G), and then open the valve on the gauge
manifold connected to the gas-side pipe.
5. Flushing
Press down on the end of the indoor-side gas pipe with your palm.
VLV
H
Gauge
manifold
valve
Source
valve
Reducing
valve
Nitrogen gas bomb
Plug (Brass)
1st side
Source valve
Flare nut
Copper pipe
2nd side
0.5MPa
(5kg/cm²G)
When the pressure becomes so great that you can no longer hold it
against the end of the pipe, remove your hand from the pipe. (This is
the first flush.) Press down against the end with your hand again.
Flush the pipe a second time.
(When flushing, place a piece of gauze, etc., on the end of the pipe,
and then check the gauze for debris or moisture. Repeat the flushing
process until nothing more comes out of the pipe.)
6. Close the gauge manifold valve, and repeat the above process for next
indoor unit (No. 2 to No. N). Close the gauge manifold valve, open the
valve on the gauge manifold that is connected to the liquid-side pipe to
allow the nitrogen to flow, and flush that liquid-side pipe.
29
Nitrogen
Hand
gas
Reducing valve
Pressure
0.5MPa (5kg/cm²G)
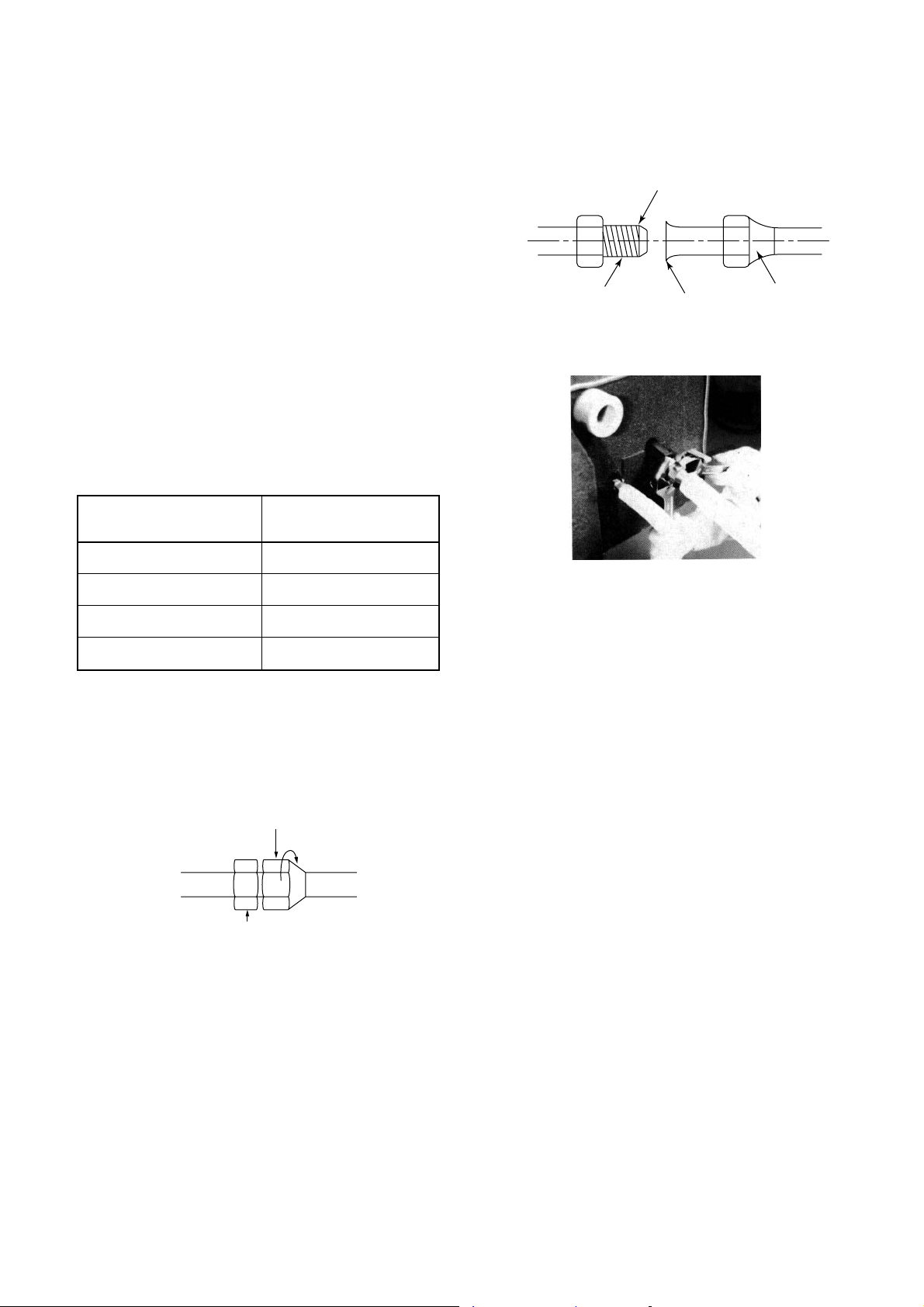
5-13. Pipe Connections to the Indoor Unit
1. Once you remove the flare nut from the pipe on
the indoor unit (always use a torque wrench), a
small amount of gas will escape, but this is
simply nitrogen gas with atmospheric pressure
that was sealed inside to prevent corrosion, and
does not indicate a problem.
2. Flare the pipe according to the procedure
described previously.
3. Centering
Center the pipes be seating the tapered portion of
the half union in the flared portion of the pipe.
4. Tightening the flare nut
First hand-tighten the flare nut as much as
possible, and then use a torque wrench to tighten
the nut completely.
<Indoor unit> <Pipe>
Center
Brazing union
(half union)
Tapered portion
Flared portion
Flare nut
Connecting pipe outer dia.
(mm)
Ø6.4
Ø9.5
Ø12.7∗
Ø15.9∗
Tightening torque
(N•m)
14 to 18 (1.4 to 1.8 kgf•m)
34 to 42 (3.4 to 4.2 kgf•m)
50 to 62 (5.0 to 6.2 kgf•m)
68 to 82 (6.8 to 8.2 kgf•m)
∗ : R410A torque wrench required.
<Two spanners>
Turn flare nut with a wrench
<Indoor unit> <Pipe>
Secure half union in place with a wrench
Tightening the flare nut with a torque wrench
* Avoid initially tightening the nut with a wrench.
* When tightening a 6.4mm-diameter pipe, tighten the nut lightly with a wrench, and then tighten the nut about 90°
to 120° (1.5 to 2 corners of the nut) with a torque wrench.
30
 Loading...
Loading...