Page 1

6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
GPS RECEIVER UNIT
HHGP1
© TOSHIBA Corporation 2001
All Rights Reserved.
( Ver. 1.6 )
Page 2

Page 3

R
Safety Precautions
Before using this product, please read this chapter carefully.
This chapter describes the safety precautions recommended when using the GPS receiver unit
type HHGP1. Before installing and using the equipment, this chapter must be thoroughly read
and understood.
Explanation of symbols used
Signal words such as DANGER, WARNING, and two kinds of CAUTION, will be followed by
important safety information that must be carefully reviewed.
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which will result in death or
DANGE
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which could result in death or
WARNING
serious injury if you do not follow the instructions.
serious injury if you do not follow the instructions.
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
CAUTION Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which if not avoided, may result in
minor injury or moderate injury.
CAUTION Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which if not avoided, may result in
property damage.
1
Page 4

R
DANGE
• Installing arrester
Install a surge arrester between the antenna and the GPS receiver and ground it in accordance
with the guidelines in this manual. Otherwise, it may cause electric shocks, injury or
malfunction.
WARNING
• Exposed terminals
Do not touch the terminals of this equipment while the power is on, as the high voltage generated
is dangerous.
• Residual voltage
Hazardous voltage can be present in the DC circuit just after switching off the DC power supply.
It takes approximately 30 seconds for the voltage to discharge.
• Fibre optic
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
When connecting this equipment via an optical fibre, do not look directly at the optical signal.
CAUTION
• Earth
The earthing terminal of the equipment must be securely earthed.
CAUTION
• Operating environment
The equipment must only used within the range of ambient temperature, humidity and dust
detailed in the specification and in an environment free of abnormal vibration.
• Ratings
Before applying the DC power supply to the equipment, check that they conform to the
equipment ratings.
• Connection cable
Carefully handle the connection cable without applying excessive force.
• Modification
Do not modify this equipment, as this may cause the equipment to malfunction.
• Disposal
When disposing of this equipment, do so in a safe manner according to local regulations.
2
Page 5

Contents
Safety Precautions 1
1. Introduction 5
2. Characteristics 5
3. Configuration 6
3.1 Configuration of GPS Receiver Unit 6
3.2 Outline of GPS Receiver Unit and Function 7
4. Handling 8
4.1 Setting the GPS Receiver Unit 8
4.2 How to Turn on the Power 9
4.3 Checking the 1PPS Signal 9
5. Operation 10
5.1 1PPS Signal Output 10
5.2 Time Data Output 11
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
6. Installation 12
6.1 Receipt of GPS Receiver Unit 12
6.2 Installing GPS Receiver Unit 12
6.3 Installing Antenna 12
6.4 Installing Surge Arrester 15
6.5 Installing Fibre Optics 15
6.6 Connecting the Power Supply and the Earthing Terminal 16
7. Preparation for Installation 17
7.1 Selecting an Antenna and Cables 17
7.2 Selecting Coaxial Cables and Conversion Adapters 17
7.3 Selecting an Antenna Installation Location 18
8. Maintenance 19
8.1 Regular Maintenance 19
8.2 Troubleshooting 19
3
Page 6

6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Appendix A Outline of GPS Rceiver Unit 21
Appendix B Technical Data 23
Appendix C Specification of Recommended Antenna and Arrester 27
Appendix D Supplement 31
The data given in this manual are subject to change without notice. (Ver. 1.6)
4
Page 7

1. Introduction
The GPS (Global Positioning System) receiver unit is a device that receives the information from
satellites and outputs time signals synchronous to UTC (Universal Coordinated Time) to external
devices. The GPS receiver unit provides multiple outputs with optical signals for noise
immunity.
2. Characteristics
■ Highly accurate time signal output
Realizes a precision with respect to ±2µs for UTC (UTC: Universal Coordinated Time)
(excluding the propagation delay time on the cable).
■ Reduced cabling work
Adopting the signal superimposition method, the unit can be connected to an external device
with a single optical fibre only.
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
■ Application to a large system
Equipped with eight ports for output, the time distribution can be made to multiple devices
separated from each other by a maximum of 1 km.
■ High reliability
Aimed at reducing the number of parts through high-integration circuits and high-density
mounting technology, thus securing high reliability.
5
Page 8
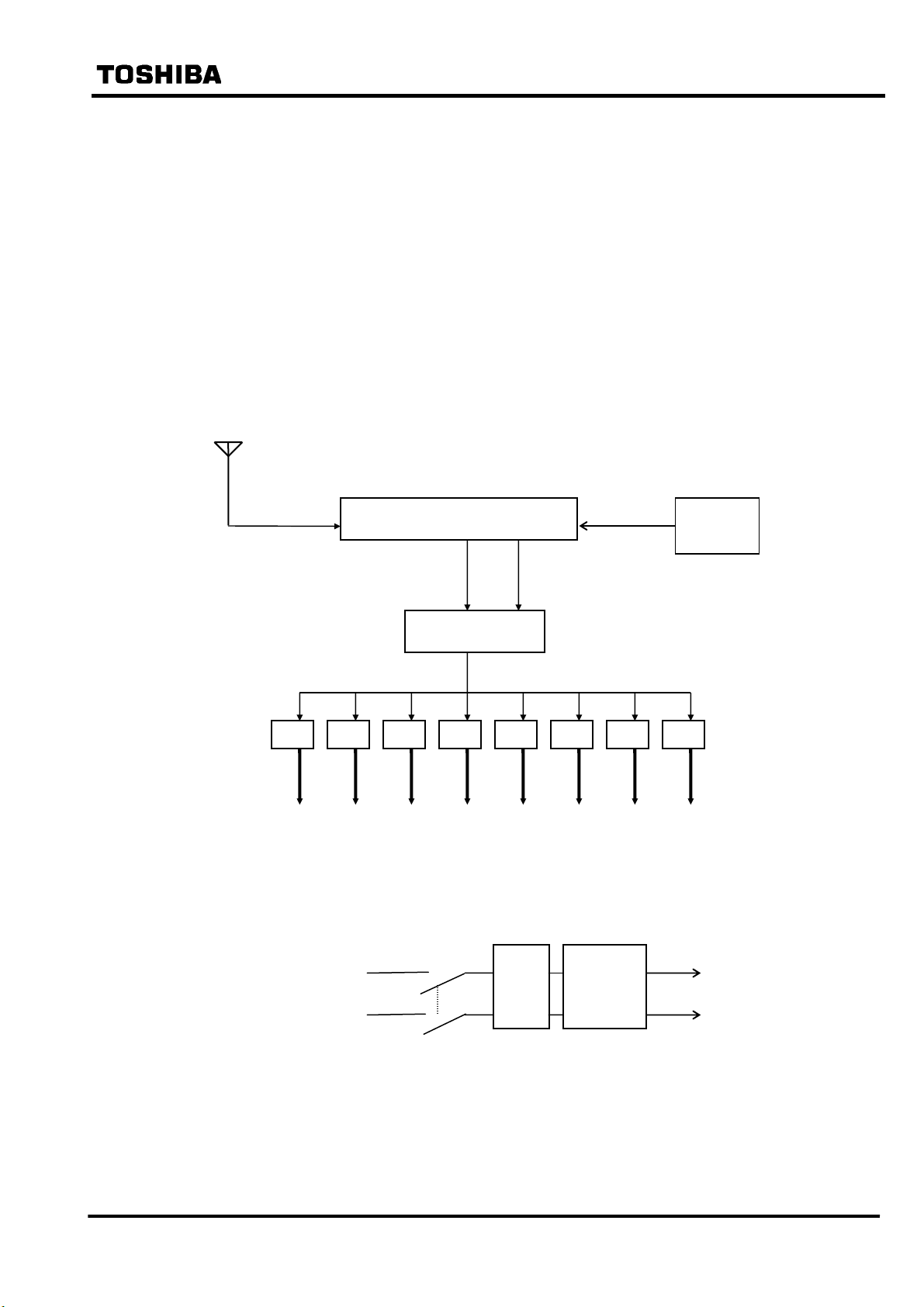
3. Configuration
3.1 Configuration of GPS Receiver Unit
Figure 3.1.1 shows the configuration of the GPS receiver unit.
The GPS receiver unit receives electromagnetic signals from satellites through an antenna and
outputs time data to external devices. Through an internal receiver, the unit generates serial time
data and 1-second pulses (1PPS signals), based on the received electromagnetic signal. Each
1PPS signal occurs at the instant in time given by its accompanying frame of serial data.
To reduce the number of cables to external devices, time data and 1PPS signals are superimposed
through a mixing circuit before being output to the optical fibre.
Antenna
Receiver
Time data
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Backup
Capacitor
1 Pulse per second
(1PPS)
Mixing Circuit
E/O
E/O E/O E/O
E/O E/O E/O E/O
Electrical-to-optical
Converter
Fibre-optic Cable
Power supply
+48V
0V
Noise
Filter
DC/DC
+5V
Converter
0V
Figure 3.1.1 Configuration of GPS Receiver Unit
6
Page 9
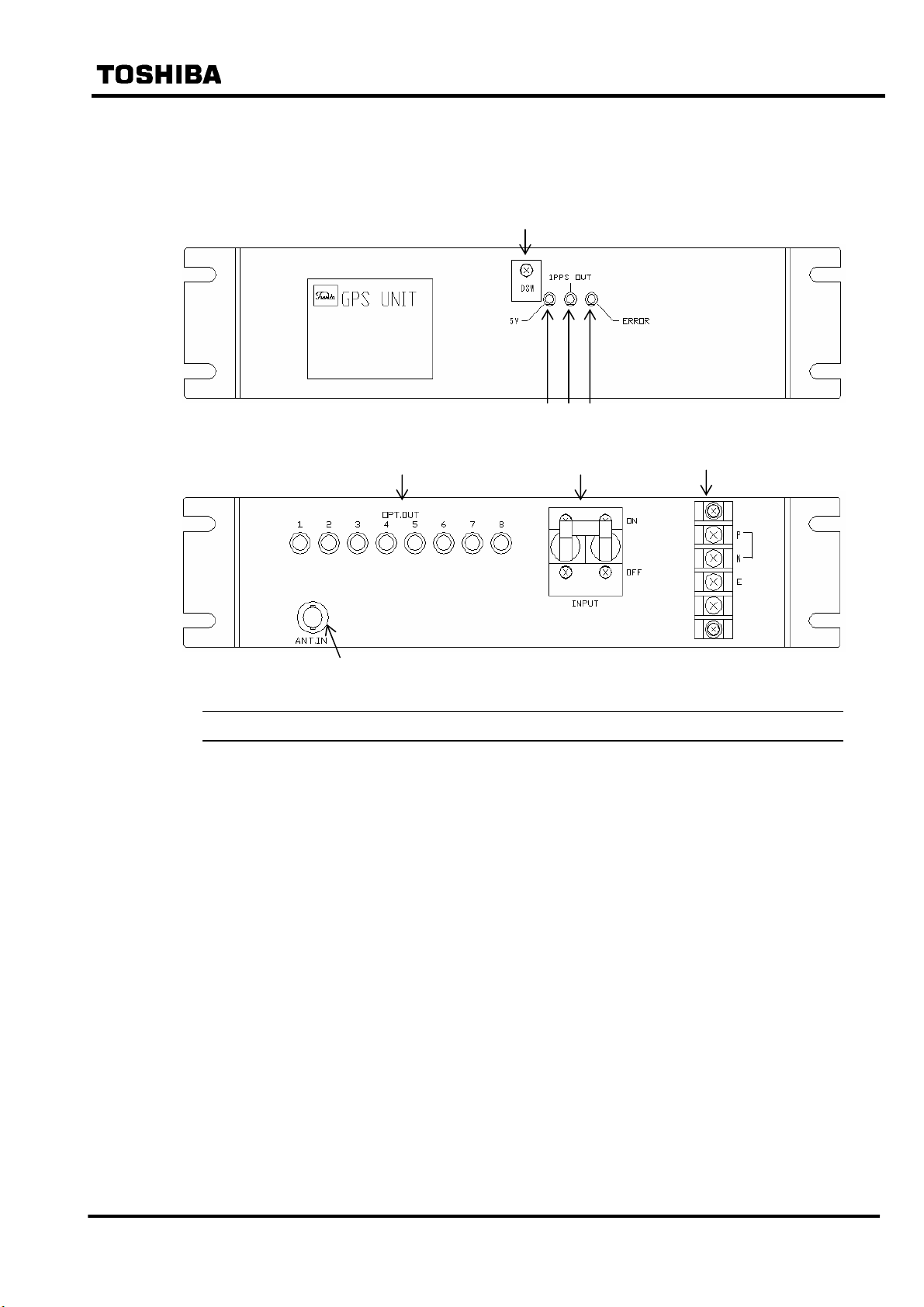
3.2 Outline of GPS Receiver Unit and Function
Figure 3.2.1 shows outline and functions of GPS receiver unit.
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
FRONT VIEW
REAR VIEW
⑧
⑤
④
②①③
⑥
⑦
48V
No. Device Indication Functions
Yellow LED 5 V Turns on when the power (5Vdc) is supplied.
①
Yellow LED 1PPS OUT Blinks when 1PPS signals are output synchronously with UTC.
②
Red LED ERROR Turns on when the internal crystal oscillator stops.
③
DIP switches DSW Set the GPS receiver unit settings. During operation, these DIP
④
switches are covered to prevent erroneous operations.
Signal output ports OPT.OUT Outputs time signals. The optical fibre is connected here.
⑤
Power supply switch INPUT Turns on or off the power of the GPS receiver unit.
⑥
Terminal block __ The 48V dc power is applied and the earth cable is connected.
⑦
P: 48Vdc, N: 0Vdc, E: earth
Antenna terminal ANT.IN The antenna cable is connected.
⑧
Figure 3.2.1 Outline and Functions of GPS Receiver Unit
7
Page 10
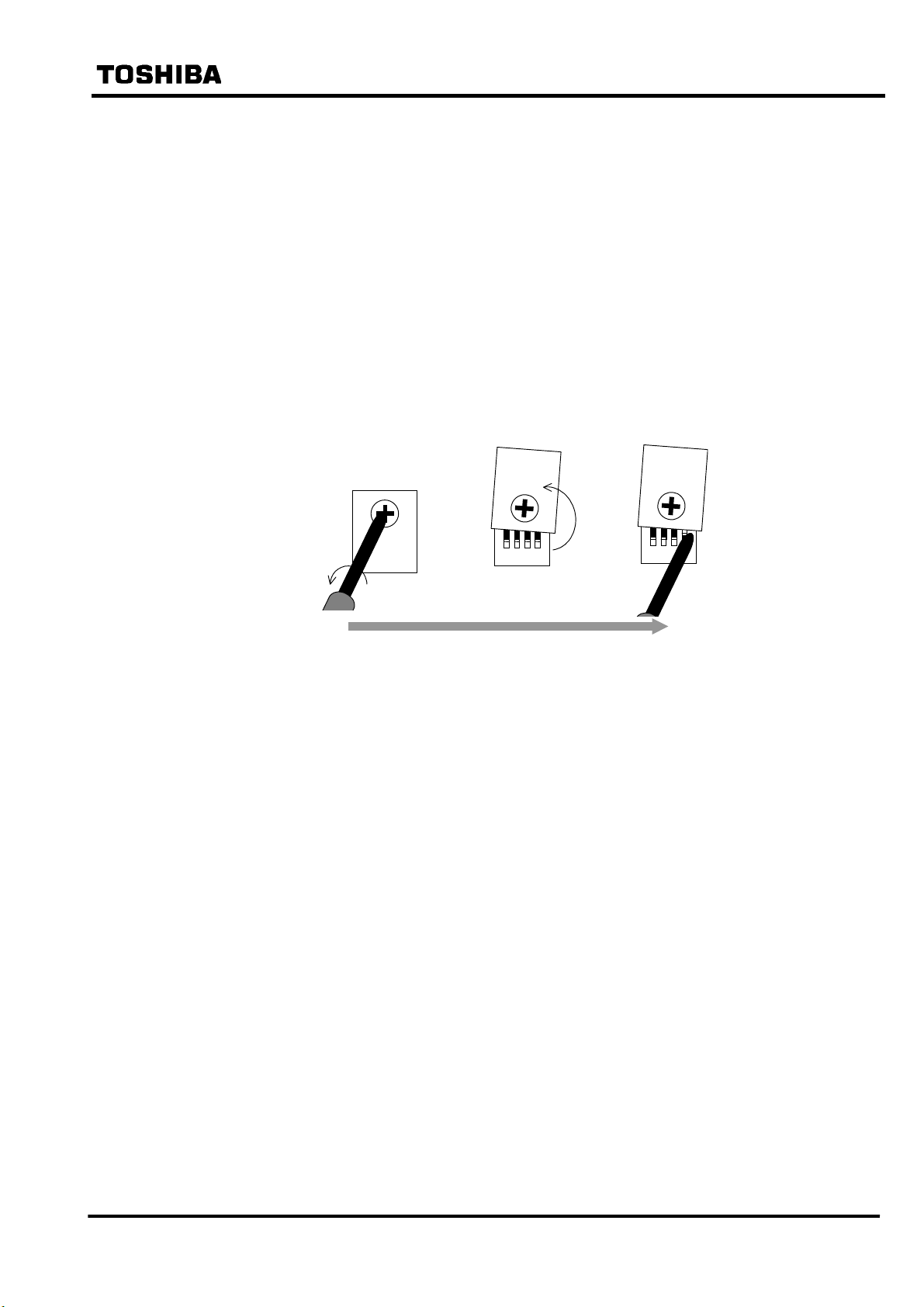
4. Handling
4.1 Setting the GPS Receiver Unit
The GPS receiver unit is set in accordance with the requirements of the system by using the DIP
switches located on the front panel of the unit.
To prevent erroneous operations, the DIP switches are protected with a cover. As shown in
Figure 4.1.1, when the cover is rotated after loosening the cover screw with a screwdriver, the
switches are exposed thus making it possible to handle them. Switches are handled with a
sharp-pointed object such as a screwdriver and set to “ON” or “OFF” by pushing them up or
down respectively. After accessing the switches, tighten the cover screw to its original state.
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
DSW
Figure 4.1.1 Switch Operation Method
Four switches are numbered 1 to 4 from left to right. (The numbers are indicated on their
respective switches.)
Table 4.1 shows the function and setting of each switch. (All the switches are set to “OFF” for
default setting.)
1234
8
Page 11

Table 4.1 Setting the Switches
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Switch
No.
1 Location mode
2 Reliability/TRAIM
3 Optical level test Continuous light emission Normal light emission
4 Clock range
Function
ON OFF (default)
Location fixing mode Location estimation mode
change
Normal/TRAIM OFF High-reliability/TRAIM ON
mode change
2020 – 2039 (Year) 2001 – 2019 (Year)
change
Setting
Note: Settings can be changed when the power is ON, but changes are not valid until the
power has been switched OFF and ON again, except in the case of switch 3 for optical
level testing, which is valid immediately.
- In the case of location mode, the location estimation mode (OFF) should be used.
- In the case of reliability/TRAIM, the High-reliability/Train ON mode (SW-OFF)
should be used.
- In high-reliability mode, the unit outputs the 1PPS signal only when no failed
satellites are detected. In the case of two or more failed satellites, correct
operation of the unit cannot be assured.
- In the case of clock range change, the switch should be OFF before 2019 and ON
after 2020.
For the details, see the Appendix D.
4.2 How to Turn on the Power
Turn on the power switch. Power ON is confirmed by the illumination of the "5V" LED on the
front panel of the unit.
4.3 Checking the 1PPS Signal
After the power is turned on, check that 1PPS signals are output. If 1PPS signals are not output, it
is impossible to use the time signals that are output from the GPS receiver unit. Output of 1PPS
signals is confirmed by the blinking of the "1PPS OUT" LED on the front panel of the unit.
9
Page 12

5. Operation
5.1 1PPS Signal Output
The GPS receiver unit outputs 1PPS signals with each pulse defining the instant of time
described by the preceding frame of serial data. (For the time signal transmission format, refer to
Appendix D.)
Following power-up, the GPS receiver begins outputting 1PPS signals after the acquisition of the
almanac data and the estimation of the receiver location (or the antenna location to be more
exact) are completed.
Almanac data received from the satellites include satellites outline orbit information and UTC
time correction parameters. It takes about 12 to 30 minutes to acquire the data.
The almanac data is backed up temporarily following power-down. If power is removed for 16
hours or more, then the data back-up may be lost and will have to be re-acquired on power-up.
If the almanac data back-up is valid on power-up, acquisition of almanac data is unnecessary.
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
To estimate the location, signals from four or more satellites are required in the case of normal
mode; and five or more are required in the case of high-reliability mode.
Note: If the antenna is positioned in the shade of buildings, or in other locations where it is difficult to
receive satellite signals, then location estimation may take a longer time or may even be
impossible.
If satellites are closely aligned in relation to the receiver, then it may not be possible to achieve
a location estimate, even when the necessary numbers of signals are received. The reason for
this is that, as the angle between received signals becomes small, the error in location
estimation becomes large.
Accordingly, installing an antenna in a location of narrow visual field such as between tall
buildings may make the location estimation impossible. When using the high-reliability mode
and/or TRAIM function, the alignment of satellites has even stricter limits.
The location estimation may take more than an hour depending on constellation of satellites in
case of the high-reliability mode.
The location estimation is required each time the power is turned on.
After the location estimation is completed, the 1PPS signal is output in normal mode if signals
from one or more satellites are received; and two or more in high-reliability mode.
The initialization time for the 1PPS signal at power-up varies as shown in Table 5.1.1, depending
on the state of the almanac data back-up.
Table 5.1.1 1PPS Output Start Time
Back up of almanac data Initial time needed for 1PPS signal output from power on
Lost 30 seconds to 1 hours (*1)
Available 10 seconds to 1 hours (*1)
(*1) It may take further time depending on constellation of satellites and antenna position.
10
Page 13

A
e
e
Numb er of recei vabl e
satellite signals
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Power ON
Four receivabl
satellite signals
Five receivable
satellite signals
1PPS output
Two receivable
satellite signals
One receivabl
satellite signal
Stop
1PPS output
(In the case of normal mode)
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Time
lmanac data reception
(12 to 30 minutes)
Figure 5.1.1 Receiving Satellite Signals and 1PPS Output Status
5.2 Time Data Output
On power-up, time data (serial data consisting of year-month-date and hour:minute:second) is
output from the receiver's internal RTC (real time clock).
If satellite signals are received, then time data transmitted by the satellite (i.e., GPS time) is
output until acquisition of the almanac data is completed. The GPS time deviates from UTC time
by an accumulated number of leap seconds.
When reception of the almanac data is completed, then UTC time is output.
Any device receiving this output data can distinguish between the RTC, GPS and UTC time data,
since this is indicated in the data itself.
1PPS stop 1PPS output 1PPS output
(In the case of hi ghreliability mode)
11
Page 14

A
A
R
6. Installation
6.1 Receipt of GPS Receiver Unit
When GPS receiver units are received, carry out the acceptance inspection immediately. In
particular, check for damage during transportation, and if any is found, contact the vendor.
Always store the GPS receiver units in a clean, dry environment.
6.2 Installing GPS Receiver Unit
CAUTION
Do not remove flanges from the main unit, as this may cause a failure.
The flanges attached to both sides of the unit are used to fix the main unit to a rack or plain table
installed in a stable location.
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
6.3 Installing Antenna
DANGE
A surge arrester must be installed between the antenna and the GPS receiver unit. It must be
grounded according to the methods specified in section 6.4 so as to prevent injury or
malfunction.
Install the antenna in the specified location in the method shown in the diagrams below.
CAUTION
An improper antenna installation location may cause malfunctions.
Locate the antenna as far as possible from other antennas. If the antenna is located within one
meter from other antennas, it may not be possible to receive the GPS signal correctly.
Locate over the top of fence.
ntenna
nother antenna
More than 1 meter
Locate over the top of fence.
12
Page 15

A
A
A
f
j
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Don’t locate in shade of obstructing objects (Box, antenna, etc.).
Don’t locate in shade of
obstructing objects
(Box, antenna, etc.)
Next, connect the antenna to the arrestor with a coaxial cable.
The following antennas are recommended: GPA-014B or GPA-017S manufactured by Furuno
Electric Co., Ltd. The specifications for and dimensions of these antennas are described in
Appendix C.
The antenna should be fixed to a support pole with Debe clamps and U bolts. An example
installation of the Furuno Electric antenna, using the accompanying clamps, is shown in Figures
6.3.1, 6.3.2 and 6.3.3.
Wind the tape to cover the whole o
unction and U-shaped gap.
Pipe
Leave the connector slightly loose so
that no excessive force is applied.
Connector junction.
Insulation prevention measure
(Autofusion tape, vinyl tape or water-proof cap)
ntenna
Parker clamp
uxiliary mounting
bracket
Support pole (φ25 to 70)
Convex
ntenna cable
Figure 6.3.1 An Example of Installation, Using GPA-017S for Antenna
13
Page 16

A
A
A
A
Fix the cable to the support
cable by making a circle
while making sure the cable
is long enough.
Debe clamp
ntenna
Connector junction
Insulation treatment
(Autofusion tape, vinyl tape or
water-proof cap)
Coaxial cable
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Support pole (φ38 to 64
)
Figure 6.3.2 An Example of Installation, Using GPA-014B for Antenna (A)
ntenna
Parker clamp
Leave the connector slightly loose so
that no excessive force is applied.
Connector junction.
Insulation prevention measure
(Autofusion tape, vinyl tape or water-proof cap)
Support pole (φ27 to 90)
ntenna cable
uxiliary mounting
bracket
Tape
Figure 6.3.3 An Example of Installation, Using GPA-014B for Antenna (B)
14
Page 17

6.4 Installing Surge Arrester
The GPS antenna must be installed outdoors, so a surge arrestor is required as a measure against
induced surges due to lightening. (This is not effective against a direct lightening strike.)
The arrestor should be installed at the point where the coaxial cable from the antenna enters the
building. A recommended arrestor is CA-23RS made by Daiichi Denpa Kogyo. The
specifications for and the appearance diagram of the arrestor are described in Appendix C. The
surge arrestor is not water-proof and should be installed in a box. Connect the coaxial cable to the
arrestor by an N-type connector.
Stitch or solder a copper earth wire, 2.5 to 3.2 mm in diameter, to the earthing terminal on the
arrestor. Connect the other end of the wire to the arrestor’s own earthing point. Make the
connection distance between the arrester and the earthing point as short as possible and protect
the earth cable with an insulation pipe.
The surge arrestor must have its own direct connection to earth and must not share an earth
connection with other equipment. Failure to comply with this requirement will result in risk of
electric shock at time of lightening strike.
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
6.5 Installing Fibre Optics
For the fibre optic connection, multi-mode GI fibre (62.5/125 µm) is used. When laying fibre
optic lines, ensure a minimum curvature radius of 50 mm.
CAUTION
Do not bend the fibre optic cable sharply, as this may damage it and may cause malfunctions.
Ensure that fibre optic connectors are fixed securely.
15
Page 18

6.6 Connecting the Power Supply and the Earthing Terminal
Connect the 48Vdc power cable and the earth cable to the terminal block with M4 crimped
terminals. For safety purposes, make sure that the earth connection is reliable.
CAUTION
The earthing terminal must be securely earthed. The failure to ground may cause
malfunctions, electric shocks or injury.
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Adapter
Co - axial cable
Fibre optic cable to relay
Arrester
Earth
(Earth the arrester only.)
P
48V
N
E
Earth
Co - axial cable
Antenna
Adapter
Figure 6.6.1 External Connection of GPS Receiver Unit
16
Page 19

7. Preparation for Installation
The following issues should be considered prior to commencing installation of the system.
7.1 Selecting an Antenna and Cables
The choice of antenna and cable types should be made based on the distance from the antenna
installation site to the GPS receiver unit installation site, and also on the cabling conditions.
Coaxial cables of characteristic impedance 50 ohms are required. The signal frequency is
1.57GHz.
The antennas may be selected according to the distance between the sites. In the case of areas
where snow is prevalent, the use of pole-shaped antennas is advisable.
The maximum extension lengths of cables based on the combinations of antennas and cables are
shown in Table 7.1.1. It shows the lengths from the antenna to the GPS receiver unit.
Table 7.1.1 Maximum Extension Lengths of Cables Based on Combinations of
Antennas and Cables
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Coaxial Cable Type
RG213 Fujikura 5D-FB Belden 9913 Westflex 103 Fujikura 8D-FB
GPA-017S antenna
GPA-014B antenna
16m 25m 35m 35m 35m
33m 50m 75m 75m 75m
7.2 Selecting Coaxial Cables and Conversion Adapters
N-type (NP) connectors are installed on both ends of the coaxial cables. Conversion adapters are
required, since different types of connector are fitted on the antenna, surge arrestor and GPS
receiver.
Required conversion adapters are as shown in Table 7.2.1.
Table 7.2.1 List of Conversion Adapters
Part Required conversion adapter Remark
Connector conversion
from coaxial cable to
antenna
Connector conversion
from the coaxial cable to
the GPS receiver unit
NJ-BNCP adapter or NJ-TNCP
conversion cable (within 1 m)
NJ-BNCP adapter
The 5D-FB and RG213 cables can
be fitted with a BNC-P connector,
in which case, no conversion
adapter is needed for connection
to the BNC-fitted antenna and
GPS receiver unit.
17
Page 20

A
7.3 Selecting an Antenna Installation Location
CAUTION
If antenna is not located in the method described below, it may not be possible to receive the
GPS signal correctly.
Obstructing object is not
allowed in this area.
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
15°(maximum)
Neighbouring
building
Support pole
(
fix to fence etc.)
ntenna
Roof of building
The antenna is installed outdoors to receive satellite transmissions. It should be installed in a
location that offers an unobstructed view of the sky with an elevation angle of 15 degrees to
horizontal. This is imperative for operation in high-reliability mode with operation of the
TRAIM function, since it is necessary to received signals from satellites which are widely
spaced. These restrictions can be relaxed for normal mode operation.
Since the alignment of satellites varies during the course of a day, it is necessary to test that the
installation is adequate to allow immediate location estimation and continuous 1PPS output for
an entire one day period.
On sites where installation conditions are not ideal then it may be necessary to conduct a survey
to establish whether reception quality is adequate. This may include situations where the antenna
must be mounted on a wall, or if the visual field is narrow or if the site is close to structures which
reflect electromagnetic waves.
18
Page 21

8. Maintenance
8.1 Regular Maintenance
Surge arrestors are degraded by lightening induced voltages, resulting in changes to their
discharge breakdown voltage. They require periodic checks and should be replaced if necessary.
They can be checked by removing the internal components from the arrestor cabinet. The glass
pipe part should be inspected and if it has turned black then replacement is required.
CAUTION
The surge arrestor must be periodically maintained to prevent malfunction.
8.2 Troubleshooting
In the event of failure or unexpected behaviour of the unit, the following items should be
checked.
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Symptom Possible cause and / or remedy
"5V" LED is off. Check that power connections to the unit are made correctly and that the power supply switch on
the front panel is ON. If so, then a failure of the internal power supply unit is a possible cause.
"ERROR" LED is on. The GPS receiver unit is failed. The internal circuit clock has stopped oscillating.
"1PPS OUT" LED does not
start to blink after power ON.
It takes a long time until
"1PPS OUT" LED starts
blinking after power ON.
During operation, the 1PPS
output is interrupted.
Data cannot be detected on
the receiving device.
The 1PPS signal or the time
data is irregular.
"1PPS OUT" LED does not
turn on.
Check the antenna location and connection.
Check that the DIP switches are set to proper positions.
In cases where the power has been turned off for 16 hours or more, internal back-up data may
be lost and it may take about 30 minutes before the unit is ready to output the 1PPS signal. This
case is not an error.
However, if 1PPS is not output after about 30 minutes, check that the antenna is installed in a
satisfactory location.
Check to make sure that the antenna is installed in a satisfactory location.
Check that the optical fibre is connected securely and that it is not damaged or severely bent
(minimum bend radius is 50mm).
Possible failure of the internal receiver.
Check that the DIP switches are set to proper positions.
If a failure continues, stop using the GPS receiver unit and contact the vendor.
19
Page 22

6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
20
Page 23

6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Appendix A
Outline of GPS Receiver Unit
21
Page 24

6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Outline
162.5
140.0
2.3
260.0
12.5
4-R3.5
7.0
7.0
45.0
12.5
70.0
290.0
308.0
Panel cutout
45
15
4-φ7 hole
266
15
45
72
22
Page 25

6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Appendix B
Technical Data
23
Page 26

TECHNICAL DATA
Ratings
DC power supply: 48Vdc-10W
AC ripple on dc supply IEC 60255-11: maximum 12%
DC supply interruption IEC 60255-11: less than 10ms at 48Vdc
Permitted duration of dc supply voltage
interruption to maintain normal operation
Mechanical design
Weight: 2.7kg
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
(Operative range: 38.4 to 57.6Vdc)
Installation: Flush mounting
Receiving function
Number of receiving satellites: Eight satellites received in parallel
Receive signals: L1 C/A code
Receive frequency: 1575.42 MHz
Time transfer accuracy
Within±2µs with respect to UTC(When the receiver is tracking GPS Satellites)
Data backup
Data life: more than 16 hours
Communication Interface
Connection: ST connector
Cable type: GI multimode optical fibre (62.5/125µm or
50/125µm)
Wavelength: 820nm
Cable Length: 0 to 1km (3dB/km)
GPS antenna interface
Preamp power supply for Antenna Min 4.5V(at 20mA), Min 4.0V(at 40mA)
Connection: BNC connector
Cable type: 50 ohm coaxial cable
GPS antenna
NF: Max 3dB
Gain: 10 to 35dB(Antenna + Amp + Cable)
24
Page 27

Environmental Performance Claims for GPS Receiver
Test Standards Details
Atmospheric Environment
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Temperature IEC60068-2-1/2
Humidity IEC60068-2-3
Mechanical Environment
Vibration IEC60255-21-1 Response - Class 1
Shock and Bump IEC60255-21-2 Shock Response Class 1
Seismic IEC60255-21-3 Class 1
High Voltage Environment
Dielectric Withstand IEC60255-5 2kVrms for 1 minute between PSU terminals and earth.
High Voltage Impulse IEC60255-5 Three positive and three negative impulses of 5kV(peak),
Electromagnetic Environment
High Frequency
Disturbance /
IEC60255-22-1 Class 3
Operating range: -10°C to +55°C.
Storage / Transit: -25°C to +70°C.
56 days at 40°C and 93% relative humidity.
Endurance - Class 1
Shock Withstand Class 1
Bump Class 1
1.2/50µs, 0.5J between all terminals and between PSU
terminals and earth.
1MHz 2.5kV applied to PSU terminals in common mode.
1MHz 1.0kV applied to PSU terminals in differential mode.
Damped Oscillatory
Wave
Electrostatic
Discharge
Radiated RF
Electromagnetic
Disturbance
Fast Transient
Disturbance
Conducted RF
Electromagnetic
Disturbance
Conducted
Disturbance over
Freq. Range 15Hz to
150kHz
Power Frequency
Disturbance
IEC61000-4-12,
EN61000-4-12 Class 3
IEC60255-22-2 Class 4 8kV contact discharge.
IEC60255-22-3 Class 3
IEC60255-22-4 Class 4 4kV, 2.5kHz, 5/50ns applied to PSU terminals in common
IEC60255-22-6 Class 3 10Vrms applied over frequency range 150kHz to 100MHz.
IEC61000-4-16,
EN61000-4-16, Class 3
IEC60255-22-7 300V 50Hz for 10s applied to PSU terminals in common mode.
0.1MHz 2.5kV applied to PSU terminals in common mode.
0.1MHz 1.0kV applied to PSU terminals in differential mode.
15kV air discharge.
Field strength 10V/m for frequency sweeps of 80MHz to 1GHz
and 1.7GHz to 2.2GHz. Additional spot tests at 80, 160, 450,
900 and 1890MHz.
mode.
Additional spot tests at 27 and 68MHz.
Varying voltages applied in common mode as follows:
15Hz to 150Hz: 10V → 1Vrms (20dB/decade)
150Hz to 1.5kHz: 1Vrms
1.5kHz to 15kHz: 1 → 10Vrms (20dB/decade)
15kHz to 150kHz: 10Vrms
25
Page 28

6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Surge Immunity IEC61000-4-5,
EN61000-4-5
Conducted and
Radiated Emissions
Power Frequency
Magnetic Field
Pulsed Magnetic Field IEC61000-4-9,
Damped Oscillatory
Magnetic Field
European Commission Directives
EN55022 Class A Conducted emissions:
IEC61000-4-8,
EN61000-4-8, Class 4
EN61000-4-9, Class 5
IEC61000-4-10,
EN61000-4-10, Class 5
89/336/EEC
73/23/EEC
1.2/50µs surge applied to PSU terminals in common/differential
modes: 2kV/1kV (peak)
0.15 to 0.50MHz: <79dB (peak) or <66dB (mean)
0.50 to 30MHz: <73dB (peak) or <60dB (mean)
Radiated emissions:
30 to 230MHz: <30dB
230 to 1000MHz: <37dB
Field applied at 50Hz with strengths of:
30A/m continuously,
300A/m for 1 second.
6.4/16µs magnetic pulses (positive and negative) applied with
magnitude 1000A/m.
Oscillation frequencies of 0.1MHz and 1MHz applied with
magnitude 100A/m.
Compliance with the European Commission Electromagnetic
Compatibility Directive is demonstrated according to generic
EMC standards EN50081-2 and EN50082-2.
Compliance with the European Commission Low Voltage
Directive is demonstrated according to generic safety
standards EN61010-1 and EN60950.
26
Page 29

6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Appendix C
Specification of Recommended
Antenna and Arrester
27
Page 30

6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Recommended Antenna
Type GPA-014B GPA-017S
Manufacturer FURUNO Electric Co.,Ltd. FURUNO Electric Co.,Ltd.
Operating connector BNC-J TNC-J
Applicable connector BNC-P TNC-P
Gain 29 to 35dB 22 to 33dB
Preamplifier noise index No more than 2.1dB No more than 1.6dB
Supply voltage 4 to 13V 4.0 to 5.5V
Current consumption 25 to 30mA No more than 25mA
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
Weight Approx. 300g
- 30 to + 80℃ - 25 to + 65℃
- 40 to + 85℃ - 35 to + 75℃
Approx. 123 ± 30g
200
52
φ42.2
φ
69
24
290
3D-XV
BNC-J
85.5
200
3D-2V
TNC-J
GPA-014B
GPA-017S
Outline of Antenna
28
Page 31

6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Recommended Arrester
Type CA-23RS
Manufacturer DAI-ICHI DENPA KOGYO CO., LTD.
Frequency range DC – 2500MHz
VSWR No more than 1.1
Loss No more than 0.2dB
Withstand power 200W PEP
Discharge breakdown voltage
DC 230V ±15%
Impulse wave discharge voltage 1,000V
Impulse wave current endurance 6,000A
Impulse wave repetitive discharge endurance
Insulation resistance at 100Vdc
(1×40) µs, 500A, at least 500 times
At least 10,000MΩ
Connector N-J / N-J
Dimensions
78(W)×48(H)×20(D)mm
Weight 113g
N-J CONNECTOR
48
30
EARTH CABLE
φ
2.5 – φ3.2
19
78
CA-23RS
19
Outline of Arrester
29
20
Page 32

6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
30
Page 33

6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Appendix D
Supplement
31
Page 34

1. Time Signal Transmission Format
The time signal format is shown below, consisting of 4,800bps serial data indicating the time,
and 1PPS timing signal indicating the instant of time corresponding to the serial data.
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Serial data
4800bps
Signal code format: ASCII codes based on NMEA-0183 data
Output data: GPtps data (time and 1PPS flag)
GPtst data (self-test result)
2. Date Rollover
1PPS timing signal
Signal for next second
The GPS week number sent from the satellite returns to 0 (i.e., rollover) every 19.6 years;
therefore, the GPS receiver unit cannot output the date data correctly. This is the rollover
problem. To solve this problem, the GPS receiver unit provides a DIP switch.
- When the DIP switch 4 is set to OFF and the power is ON, the GPS receiver unit starts
outputting the date and time from any date between April in 2001 and September in
2020.
- When the DIP switch 4 is set to ON and the power is ON, the GPS receiver unit starts
outputting the date and time from any date between October in 2019 and March in 2039.
The default setting of the DIP switch 4 is OFF. After 2020, the DIP switch 4 should be set ON so
that the GPS unit outputs the date data correctly.
Note 1: The date and time data from the GPS receiver unit are used for the recording data of
GRL100 relay and do not influence the function of GRL100 relay. The 1 PPS signal is
output independently of the switch 4 setting.
Note 2: For one year from October, 2019 to September, 2020, any setting of the DIP switch 4 is
allowed. So, in this term, the changing of the DIP switch 4 is recommended.
3 High-reliability Mode and TRAIM Function
TRAIM (Time Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring) is a function which allows the unit to
detect an error in the signal from a satellite. For operation of this function, it is necessary to
receive one additional signal to the minimum number normally required for output of the 1PPS
32
Page 35

pulse. If the necessary number of satellites are available then the unit carries out error detection
and removal of erroneous signals. In the event of two or more satellites in error, the operation is
not assured.
In high-reliability mode, the receiver will only output the 1PPS signal when no TRAIM alarm
occurs. If any satellite is in error then it must be excluded, and so two or more satellites are
required for the purpose of outputting 1PPS.
Satellite alignment is subject to strict limits for operation of the TRAIM function. The antenna
must be located with a wide field of view.
4. Conditions for Receiving Electric Waves from Satellites
Signals from satellites at an elevation angle of less than 5 degrees are too weak to be received.
In terms of the impact of weather, satellite signals can be received correctly while it is raining or
lightly snowing, or while a small amount of snow is piled on the antenna; however, during
lightening or heavy snow, the receive status may deteriorate temporarily.
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
33
Page 36

Version-up Records
6 F 2 S 0 7 3 8
Version
No.
0.0 May. 23, 2001 -- First issue.
1.0 Jun. 22, 2001 3.2
1.1 Jul. 19, 2001 --
1.2 Jul. 25, 2001 6.3 Corrected Type of GPS antenna.
1.3 Sep. 10, 2001 3.1
Date Revised Section Contents
Modified Figure 3.2.1.
5.1
6.6
7.1
Appendices
4.1
Appendix D
3.2
4
5.1
6.6
8.2
Appendices
Modified Figure 5.1.1
Modified Figure 6.6.1.
Modified descriptions in Section 7.1.
Modified Appendices B, C, I and K.
Corrected Type of GPS unit. (HHGP3 →HHGP1)
Modified descriptions in Section 4.1.
Modified descriptions 0f “2. Date rollover” in Appendix D.
(GPA-01T→GPA-016, GPA-14B→GPA-016B)
Modified Figure 3.1.1.
Modified Figure 3.2.1.
Modified descriptions in Chapter 4 and Section 4.1.
Modified descriptions in Section 5.1.
Modified Figure 6.6.1.
Modified descriptions in Section 8.2.
Modified Appendices A, B, C and D.
1.4 Jul. 30, 2002 Appendix B Modified the description in Conducted and Radiated Emissions.
1.5
1.6 May.30, 2003 4.1
Mar. 28, 2003 6.3
7.1
Appendix C
6.3
7.3
Changed Type of GPS antenna and Figure 6.3.1. (GPA-016→GPA-017S)
Added Figure 6.3.3.
Modified Table 7.1.1.
Changed specification and outline of antenna. (GPA-016→GPA-017S)
Added the description in Note of Table 4.1.
Added the description in Caution.
Added Caution.
34
Page 37

 Loading...
Loading...