
Document Number: 58682-003
Date: March, 2011
H9
LOCAL/
REMOTE
TOSHIBA
H9 Adjustable Speed Drive
Installation and Operation Manual
H9 ASD

Document Number: 58682-003
Date: March, 2011
H9 ASD Installation and Operation
Manual

Introduction
Congratulations on the purchase of the new H9 Adjustable Speed Drive!
The H9 Adjustable Speed Drive (ASD) is a solid-state AC drive that features Toshiba International
Corporation’s (TIC) Vector Control Algorithm enables the motor to develop high starting torque and
provide compensation for motor slip, which results in smooth, quick starts and highly efficient operation.
The H9 ASD uses digitally-controlled pulse width modulation. The programmable functions may be
accessed via the easy-to-use menu or via the Direct Access Numbers (see page 76). This feature,
combined with TIC’s high-performance software, delivers unparalleled motor control and reliability.
The H9 ASD is a very powerful tool, yet surprisingly simple to operate. The user-friendly Electronic
Operator Interface (EOI) of the H9 ASD has an easy-to-read LCD screen. There is also a read-only LED
screen with enhanced visibility that can be read from a greater distance. The EOI provides easy access to
the many monitoring and programming features of the H9 ASD.
The motor control software is menu-driven, which allows for easy access to the motor control parameters
and quick changes when required.
To maximize the abilities of your new H9 ASD, a working familiarity with this manual will be required.
This manual has been prepared for the ASD installer, user, and maintenance personnel. This manual may
also be used as a reference guide or for training. With this in mind, use this manual to develop a system
familiarity before attempting to install or operate the device.
Important Notice
The instructions contained in this manual are not intended to cover all details or variations in equipment
types, nor may it provide contingency concerning the installation, operations, or maintenance of this
equipment. Should additional information be required contact your TIC Sales Representative.
The contents of this manual shall not become a part of or modify any prior or existing agreement,
commitment, or relationship. The sales contract contains the entire obligation of Toshiba International
Corporation. The warranty contained in the contract between the parties is the sole warranty of Toshiba
International Corporation and any statements contained herein do not create new warranties or modify the
existing warranty.
Any electrical or mechanical modifications to this equipment without prior written consent of
Toshiba International Corporation may void all warranties and may void the UL/CSA listing or
other safety certifications. Unauthorized modifications may also result in a safety hazard or
equipment damage.
Misuse of this equipment could result in injury and equipment damage. In no event will Toshiba
International Corporation be responsible or liable for direct, indirect, special, or consequential
damage or injury that may result from the misuse of this equipment.

About This Manual
This manual was written by the TIC Technical Publications Group. This group is tasked with providing
technical documentation for the H9 Adjustable Speed Drive. Every effort has been made to provide
accurate and concise information to you, our customer.
At Toshiba International Corporation we are continuously striving for better ways to meet the constantly
changing needs of our customers. E-mail your comments, questions, or concerns about this publication
to Technical-Publications-Dept@tic.toshiba.com.
Manual’s Purpose and Scope
This manual provides information on how to safely install, operate, maintain, and dispose of your
H9 Adjustable Speed Drive. The information provided in this manual is applicable to the
H9 Adjustable Speed Drive only.
This manual provides information on the various features and functions of this powerful cost-saving
device, including
• Installation,
• System operation,
• Configuration and menu options, and
• Mechanical and electrical specifications.
Included is a section on general safety instructions that describe the warning labels and symbols that are
used throughout the manual. Read the manual completely before installing, operating, performing
maintenance, or disposing of this equipment.
This manual and the accompanying drawings should be considered a permanent part of the equipment
and should be readily available for reference and review. Dimensions shown in the manual are in metric
and/or the English equivalent.
Because of our commitment to continuous improvement, Toshiba International Corporation reserves the
right, without prior notice, to update information, make product changes, or to discontinue any product
or service identified in this publication.
Toshiba International Corporation (TIC) shall not be liable for direct, indirect, special, or
consequential damages resulting from the use of the information contained within this manual.
This manual is copyrighted. No part of this manual may be photocopied or reproduced in any form
without the prior written consent of Toshiba International Corporation.
© Copyright 2011 Toshiba International Corporation.
TOSHIBA® is a registered trademark of Toshiba Corporation. All other product or trade references
appearing in this manual are registered trademarks of their respective owners.
All rights reserved.
Printed in the U.S.A.

Contacting TIC’s Customer Support
TOSHIBA INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
H9 Adjustable Speed Drive
Please complete the Warranty Card supplied with the H9 ASD and return it to Toshiba International Corporation
by prepaid mail. This will activate the 12 month warranty from the date of installation; but, shall not exceed 18
months from the shipping date.
Complete the following information and retain for your records.
Model Number: ______________________________________________________________________
Serial Number: ______________________________________________________________________
Project Number (if applicable): __________________________________________________________
Date of Installation: __________________________________________________________________
Inspected By: ______________________________________________________________________
Name of Application: ______________________________________________________________
Center
TIC’s Customer Support Center can be contacted to obtain help in resolving any Adjustable Speed
Drive system problem that you may experience or to provide application information.
The Support Center is open from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. (CST), Monday through Friday. The Center’s toll free
number is US (800) 231-1412/Fax (713) 937-9349 CAN (800) 872-2192 MEX 01 (800) 527-1204.
For after-hours support follow the directions in the outgoing message when calling.
You may also contact Toshiba International Corporation by writing to:
Toshiba International Corporation
13131 West Little York Road
Houston, Texas 77041-9990
Attn: ASD Product Manager.
For further information on TIC’s products and services, please visit our website at www.toshiba.com/
ind/.

Table of Contents
General Safety Information ....................................................................................................1
Safety Alert Symbol ...........................................................................................................1
Signal Words ......................................................................................................................1
Special Symbols .................................................................................................................2
Equipment Warning Labels ................................................................................................2
Qualified Personnel ............................................................................................................2
Equipment Inspection .........................................................................................................3
Handling and Storage .........................................................................................................3
Disposal ..............................................................................................................................3
Installation Precautions ...........................................................................................................4
Location and Ambient Requirements .................................................................................4
Mounting Requirements .....................................................................................................4
Conductor Routing and Grounding ....................................................................................5
Power Connections .............................................................................................................6
Protection ............................................................................................................................6
System Integration Precautions ..............................................................................................7
Personnel Protection ...........................................................................................................7
System Setup Requirements ...............................................................................................8
Operational and Maintenance Precautions ...........................................................................9
Motor Characteristics ............................................................................................................10
Motor Autotuning .............................................................................................................10
Pulse Width Modulation Operation ..................................................................................10
Low-Speed Operation .......................................................................................................10
Overload Protection Adjustment ......................................................................................10
Operation Above 60 Hz ....................................................................................................10
Power Factor Correction ...................................................................................................11
Light Load Conditions ......................................................................................................11
Motor/Load Combinations ...............................................................................................11
Load-Produced Negative Torque ......................................................................................12
Motor Braking ..................................................................................................................12
ASD Characteristics ..............................................................................................................13
Over-Current Protection ...................................................................................................13
ASD Capacity ...................................................................................................................13
Using Vector Control ........................................................................................................13
Installation and Connections ................................................................................................14
Installation Notes ..............................................................................................................14
Mounting the ASD ............................................................................................................15
H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual i

Connecting the ASD .........................................................................................................16
Lead Length Specifications ..............................................................................................20
I/O and Control .................................................................................................................21
Electronic Operator Interface ..............................................................................................28
EOI Operation ...................................................................................................................28
Battery Backup .................................................................................................................28
EOI Remote Mounting .....................................................................................................29
EOI Features .....................................................................................................................30
EOI Remote Mounting .....................................................................................................33
Command Mode and Frequency Mode Control .................................................................36
Command Control (F003) ................................................................................................36
Frequency Control (F004) ................................................................................................37
Override Operation ...........................................................................................................38
System Configuration and Menu Options ...........................................................................41
Root Menus .......................................................................................................................41
System Operation ...................................................................................................................70
Initial Setup .......................................................................................................................70
Startup Wizard Parameters ...............................................................................................70
Operation (Local) ..............................................................................................................73
Default Setting Changes ...................................................................................................74
Save User Settings ............................................................................................................75
Direct Access Parameter Information .................................................................................76
Direct Access Parameters/Numbers .................................................................................76
Alarms, Trips, and Troubleshooting ..................................................................................244
Alarms and Trips ............................................................................................................244
User Notification Codes .................................................................................................245
Alarms .............................................................................................................................246
Trips/Faults .....................................................................................................................248
Enclosure and Conduit Plate Dimensions .........................................................................254
Enclosure Dimensions ....................................................................................................254
Conduit Plate Dimensions ..............................................................................................259
Current/Voltage Specifications ...........................................................................................262
Cable/Terminal/Torque Specifications ..............................................................................264
Dynamic Braking System Specifications ...........................................................................266
Short Circuit Protection Recommendations .....................................................................268
H9 ASD Optional Devices ...................................................................................................269
ii H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual

General Safety Information
DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
CAUTION
DO NOT attempt to install, operate, maintain, or dispose of this equipment until you have read and
understood all of the product safety information and directions that are contained in this manual.
Safety Alert Symbol
The Safety Alert Symbol is comprised of an equilateral triangle enclosing an exclamation mark. This
indicates that a potential personal injury hazard exists.
Signal Words
Listed below are the signal words that are used throughout this manual followed by their descriptions
and associated symbols. When the words DANGER, WARNING, and CAUTION are used in this
manual they will be followed by important safety information that must be carefully followed.
The word DANGER preceded by the safety alert symbol indicates that an imminently hazardous
situation exists that, if not avoided or if instructions are not followed precisely, will result in serious
injury to personnel or loss of life.
The word WARNING preceded by the safety alert symbol indicates that a potentially hazardous
situation exists that, if not avoided or if instructions are not followed precisely, could result in serious
injury to personnel or loss of life.
The word CAUTION preceded by the safety alert symbol indicates that a potentially hazardous
situation exists that, if not avoided or if instructions are not followed precisely, may result in minor or
moderate injury.
The word CAUTION without the safety alert symbol indicates a potentially hazardous situation exists
that, if not avoided or if instructions are not followed precisely, may result in equipment and property
damage.
H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual 1

Special Symbols
To identify special hazards, other symbols may appear in conjunction with the DANGER, WARNING,
and CAUTION signal words. These symbols indicate areas that require special and/or strict adherence
to the procedures to prevent serious injury to personnel or loss of life.
Electrical Hazard Symbol
A symbol that is comprised of an equilateral triangle enclosing
a lightning bolt indicates a hazard of injury from electrical
shock or burn.
Explosion Hazard Symbol
A symbol that is comprised of an equilateral triangle enclosing
an explosion indicates a hazard of injury from exploding parts.
Equipment Warning Labels
DO NOT attempt to install, operate, perform maintenance, or dispose of this equipment until you have
read and understood all of the product labels and user directions that are contained in this manual.
Warning labels that are attached to the equipment will include the exclamation mark within a triangle.
DO NOT remove or cover any of these labels. If the labels are damaged or if additional labels are
required, contact your TIC Sales Representative.
Labels attached to the equipment are there to provide useful information or to indicate an imminently
hazardous situation that may result in serious injury, severe property and equipment damage, or loss of
life if safe procedures or methods are not followed as outlined in this manual.
Qualified Personnel
Installation, operation, and maintenance shall be performed by Qualified Personnel Only. A Qualified
Person is one that has the skills and knowledge relating to the construction, installation, operation, and
maintenance of the electrical equipment and has received safety training on the hazards involved (Refer
to the latest edition of NFPA 70E for additional safety requirements).
Qualified Personnel shall:
• Have carefully read the entire manual.
• Be familiar with the construction and function of the ASD, the equipment being driven, and the
hazards involved.
• Be able to recognize and properly address hazards associated with the application of motor-driven
equipment.
• Be trained and authorized to safely energize, de-energize, ground, lock out/tag out circuits and
equipment, and clear faults in accordance with established safety practices.
• Be trained in the proper care and use of protective equipment such as safety shoes, rubber gloves,
hard hats, safety glasses, face shields, flash clothing, etc., in accordance with established safety
practices.
For further information on workplace safety visit www.osha.gov.
2 H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual

Equipment Inspection
• Upon receipt of the equipment inspect the packaging and equipment for shipping damage.
• Carefully unpack the equipment and check for parts that may have been damaged during shipping,
missing parts, or concealed damage. If any discrepancies are discovered, it should be noted with the
carrier prior to accepting the shipment, if possible. File a claim with the carrier if necessary and
immediately notify your TIC Sales Representative.
• DO NOT install the ASD if it is damaged or if it is missing any component(s).
• Ensure that the rated capacity and the model number specified on the nameplate conform to the
order specifications.
• Modification of this equipment is dangerous and is to be performed by factory trained personnel.
When modifications are required contact your TIC Sales Representative.
• Inspections may be required after moving equipment.
• Contact your TIC Sales Representative to report discrepancies or for assistance if required.
Handling and Storage
• Use proper lifting techniques when moving the ASD; including properly sizing up the load, getting
assistance, and using a forklift if required.
• Store in a well-ventilated location and preferably in the original carton if the equipment will not be
used upon receipt.
• Store in a cool, clean, and dry location. Avoid storage locations with extreme temperatures, rapid
temperature changes, high humidity, moisture, dust, corrosive gases, or metal particles.
• The storage temperature range of the H9 ASD is -13° to 149° F (-25° to 65° C).
• Do not store the unit in places that are exposed to outside weather conditions (i.e., wind, rain, snow,
etc.).
• Store in an upright position.
Disposal
Never dispose of electrical components via incineration. Contact your state environmental agency for
details on disposal of electrical components and packaging in your area.
H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual 3

Installation Precautions
Location and Ambient Requirements
• The TIC ASD is intended for permanent installations only.
• Installation should conform to the National Electrical Code — Article 110 (Requirements For
Electrical Installations), all regulations of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration,
and any other applicable national, regional, or industry codes and standards.
Note: For ALL references to the National Electrical Code (NEC), see the latest release of
the National Electrical Code.
• Select a mounting location that is easily accessible, has adequate personnel working space, and
adequate illumination for adjustment, inspection, and maintenance of the equipment (refer to NEC
Article 110-13).
• DO NOT mount the ASD in a location that would produce catastrophic results if it were to fall
from its mounting location (equipment damage or injury).
• DO NOT mount the ASD in a location that would allow it to be exposed to flammable chemicals or
gases, water, solvents, or other fluids.
• Avoid installation in areas where vibration, heat, humidity, dust, fibers, metal particles, explosive/
corrosive mists or gases, or sources of electrical noise are present.
• The installation location shall not be exposed to direct sunlight.
• Allow proper clearance spaces for installation. Do not obstruct the ventilation openings. Refer to
the section titled Installation and Connections on pg. 14 for further information on ventilation
requirements.
• The ambient operating temperature range of the H9 ASD is 14° to 104° F (-10 to 40° C).
Mounting Requirements
•Only Qualified Personnel should install this equipment.
• Install the unit in a secure and upright position in a well-ventilated area.
• As a minimum, the installation of the equipment should conform to the NEC — Article 110,
OSHA, as well as any other applicable national, regional, or industry codes and standards.
• Installation practices should conform to the latest revision of NFPA 70E Electrical Safety
Requirements for Employee Workplaces.
• It is the responsibility of the ASD installer/maintenance personnel to ensure that the unit is installed
into an enclosure that will protect personnel against electric shock.
4 H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual
Conductor Routing and Grounding
WARNING
• Use separate metal conduits for routing the input power, output power, and control circuits.
• A separate ground cable should be run inside the conduit with the input power, output power, and
control circuits.
• DO NOT connect CC to earth ground.
•Use IICC terminal as the return for the V/I input.
• Always ground the unit to prevent electrical shock and to help reduce electrical noise.
• It is the responsibility of the ASD installer/maintenance personnel to provide proper grounding and
branch circuit protection in accordance with the NEC and any applicable local codes.
— The Metal Of Conduit Is Not An Acceptable Ground —
Grounding Capacitor Switch
The ASD is equipped with noise reduction capacitors which are used to reduce the EMI leakage via the
3-phase power-input circuit and for compliance with the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive
(EMC).
The effective value of the capacitor may be increased, reduced, or removed entirely via the Selector
Switch, Switching Bar, or the Switching Screw — the type used is typeform-specific.
The Grounding Capacitor Switch allows the user to quickly change the value of the capacitance of the
3-phase input circuit without the use of tools.
See the section titled System Grounding on pg. 18 for more on the Grounding Capacitor.
See figures 4, 5, 6, and 7 on pg. 19 for an electrical depiction of the leakage-reduction functionality of
the Grounding Capacitor and the methods used to set the capacitance value.
H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual 5

Power Connections
DANGER
Contact With Energized Wiring Will Cause Severe
Injury Or Loss Of Life.
• Turn off, lock out, and tag out all power sources before proceeding to connect the power wiring to
the equipment.
• After ensuring that all power sources are turned off and isolated in accordance with established
lock out/tag out procedures, connect the 3-phase power source wiring of the correct voltage to the
correct input terminals and connect the output terminals to a motor of the correct voltage and type
for the application (refer to the NEC Article 300 – Wiring Methods and Article 310 – Conductors
For General Wiring). Size the branch circuit conductors in accordance with the NEC Table 310.16.
• Ensure that the 3-phase input power is NOT connected to the output of the ASD. This will damage
the ASD and may cause injury to personnel.
• DO NOT connect resistors across terminals PA – PC or PO – PC. This may cause a fire.
• Ensure the correct phase sequence and the desired direction of motor rotation in the Bypass mode
(if applicable).
Protection
• Ensure that primary protection exists for the input wiring to the equipment. This protection must be
able to interrupt the available fault current from the power line. The equipment may or may not be
equipped with an input disconnect (option).
• All cable entry openings must be sealed to reduce the risk of entry by vermin and to allow for
maximum cooling efficiency.
• External dynamic braking resistors must be thermally protected.
• It is the responsibility of the ASD installer/maintenance personnel to setup the Emergency Off
braking system of the ASD. The function of the Emergency Off braking function is to remove
output power from the drive in the event of an emergency. A supplemental braking system may also
be engaged in the event of an emergency. For further information on braking systems, see
parameters F250 and F304.
Note: A supplemental emergency stopping system should be used with the ASD. Emergency
stopping should not be a task of the ASD alone.
• Follow all warnings and precautions and do not exceed equipment ratings.
6 H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual

System Integration Precautions
WARNING
The following precautions are provided as general guidelines for the setup of the ASD within the
system.
• The TIC ASD is a general-purpose product. It is a system component only and the system design
should take this into consideration. Please contact your TIC Sales Representative for application-
specific information or for training support.
• The TIC ASD is part of a larger system and the safe operation of the ASD will depend upon
observing certain precautions and performing proper system integration.
• Improperly designed or improperly installed system interlocks may render the motor unable to start
or stop on command.
• The failure of external or ancillary components may cause intermittent system operation (i.e., the
system may start the motor without warning).
• A detailed system analysis and job safety analysis should be performed by the systems designer
and/or systems integrator before the installation of the ASD component. Contact your TIC Sales
Representative for options availability and for application-specific system integration information
if required.
Personnel Protection
• Installation, operation, and maintenance shall be performed by Qualified Personnel Only.
• A thorough understanding of the ASD will be required before the installation, operation, or
maintenance of the ASD.
• Rotating machinery and live conductors can be hazardous and shall not come into contact with
personnel. Personnel should be protected from all rotating machinery and electrical hazards at all
times.
• Insulators, machine guards, and electrical safeguards may fail or be defeated by the purposeful or
inadvertent actions of workers. Insulators, machine guards, and electrical safeguards are to be
inspected (and tested where possible) at installation and periodically after installation for potential
hazardous conditions.
• DO NOT allow personnel near rotating machinery. Warning signs to this effect shall be posted at or
near the machinery.
• DO NOT allow personnel near electrical conductors. Contact with electrical conductors can be
fatal. Warning signs to this effect shall be posted at or near the hazard.
• Personal protection equipment shall be provided and used to protect employees from any hazards
inherent to system operation.
H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual 7

System Setup Requirements
CAUTION
• When using the ASD as an integral part of a larger system, it is the responsibility of the ASD
installer/maintenance personnel to ensure that there is a fail-safe in place (i.e., an arrangement
designed to switch the system to a safe condition if there is a fault or failure).
• Power factor improvement capacitors or surge absorbers MUST NOT be installed on the output of
the ASD.
• Use of the built-in system protective features is highly recommended (i.e., E-Off, Overload
Protection, etc.).
• The operating controls and system status indicators should be clearly readable and positioned
where the operator can see them without obstruction.
• Additional warnings and notifications shall be posted at the equipment installation location as
deemed required by Qualified Personnel.
• System safety features should be employed and designed into the integrated system in a manner
such that system operation, even in the event of system failure, will not cause harm or result in
system damage or injury to personnel (i.e., E-Off, Auto-Restart settings, System Interlocks, etc.).
• The programming setup and system configuration of the ASD may allow it to start the motor
unexpectedly. A familiarity with the Auto-Restart (F301) settings are a requirement to use this
product.
• There may be thermal or physical properties, or ancillary devices integrated into the overall system
that may allow for the ASD to start the motor without warning. Signs to this effect must be posted
at the equipment installation location.
• If a secondary magnetic contactor (MC) or an ASD output disconnect is used between the ASD and
the load, it should be interlocked to halt the ASD before the secondary contact opens. If the output
contactor is used for bypass operation, it must be interlocked such that commercial power is never
applied to the ASD output terminals (U, V, or W).
• When using an ASD output disconnect, the ASD and the motor must be stopped before the
disconnect is either opened or closed. Closing the output disconnect while the 3-phase output of the
ASD is active may result in equipment damage or injury to personnel.
8 H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual

Operational and Maintenance
WARNING
Precautions
• Turn off, lock out, and tag out the main power, the control power, and instrumentation connections
before inspecting or servicing the drive, opening the door of the enclosure, or connecting/
disconnecting the power wiring to the equipment.
• The capacitors of the ASD maintain a residual charge for a period of time after turning the ASD off.
The required time for each ASD typeform is indicated with a cabinet label and a Charge LED
(shown for smaller ASDs in Figure 2 on pg. 16; LED is located on the front panel of larger ASDs).
Wait at least the minimum time indicated on the enclosure-mounted label and ensure that the
Charge LED has gone out before opening the door of the ASD once the ASD power has been
turned off.
• Turn the power on only after attaching (or closing) the front cover and DO NOT remove or open
the front cover of the ASD when the power is on.
• DO NOT attempt to disassemble, modify, or repair the ASD. Call your TIC Sales Representative
for repair information.
• DO NOT place any objects inside of the ASD.
• If the ASD should emit smoke, or an unusual odor or sound, turn the power off immediately.
• The heat sink and other components may become extremely hot to the touch. Allow the unit to cool
before coming in contact with these items.
•The Auto-Restart (F301) programmable functions of the ASD may allow for the system to start or
stop unexpectedly. Signs to this effect are to be clearly posted at the installation location.
• Remove power from the ASD during extended periods of non-use.
• The system should be inspected periodically for damaged or improperly functioning parts,
cleanliness, and to ensure that the connectors are tightened securely.
H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual 9

Motor Characteristics
Listed below are some variable speed AC motor control concepts with which the user of the
ASD should become familiar.
Motor Autotuning
Motor production methods may cause minor differences in the motor operation. The negative effects of
these differences may be minimized by using the Autotune feature of the ASD. Autotuning is a function
of the ASD that measures several parameters of the connected motor and places these readings in a stored
table. The software uses the information in the table to help optimize the response of the ASD to
application-specific load and operational requirements. The Autotuning function may be enabled for
automatic tuning, configured manually at F400, or disabled.
The measured parameters include the rotor resistance, the stator resistance, the required excitation
inductance, rotational inertia values, and leakage inductance values.
Pulse Width Modulation Operation
The ASD uses sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) control. The output current waveform
generated by the ASD approaches that of a perfect sine wave; however, the output waveform is slightly
distorted. For this reason, the motor may produce more heat, noise, and vibration when operated by an
ASD, rather than directly from commercial power.
Low-Speed Operation
Operating a general-purpose motor at lower speeds may cause a decrease in the cooling ability of the
motor. Reducing the torque requirement of the motor at lower speeds will decrease the generated heat at
lower speeds.
When the motor is to be operated at low speed (less than 50% of full speed) and at the rated torque
continuously, a TIC VF motor (designed for use in conjunction with an ASD) is recommended.
Overload Protection Adjustment
The ASD software monitors the output current of the system and determines when an overload condition
occurs. The overload current level is a percentage of the rating of the motor. This function protects the
motor from overload.
The default setting for the overload detection circuit is set to the maximum rated current of the ASD at the
factory. This setting will have to be adjusted to match the rating of the motor with which the ASD is to be
used. To change the overload reference level, see Motor Overload Protection Level 1 on pg. 182.
Operation Above 60 Hz
A motor produces more noise and vibration when it is operated at frequencies above 60 Hz. Also, when
operating a motor above 60 Hz, the rated limit of the motor or its bearings may be exceeded; this may void
the motor warranty.
Contact the motor manufacturer for additional information before operating the motor above 60 Hz.
10 H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual

Power Factor Correction
DO NOT connect a power factor correction capacitor or surge absorber to the output of the ASD.
If the ASD is used with a motor that is equipped with a capacitor for power factor correction, remove the
capacitor from the motor.
Connecting either of these devices to the output of the ASD may cause the ASD to malfunction and trip,
or the output device may cause an over-current condition resulting in damage to the device or the ASD.
Light Load Conditions
When a motor is operated under a continuous light load (i.e., at a load of less than 50% of its rated
capacity) or it drives a load which produces a very small amount of inertia, it may become unstable and
produce abnormal vibration or trips because of an over-current condition. In such a case, the carrier
frequency may be lowered to compensate for this undesirable condition (see Program Special
Carrier Frequency PWM Carrier Frequency).
Note: When operating in the Vector Control mode the carrier frequency should be set to
2.2 kHz or above.
Motor/Load Combinations
When the ASD is used in combination with one of the following motors or loads, it may result in unstable
operation.
• A motor with a rated capacity that exceeds the motor capacity recommended for the ASD.
• An explosion-proof motor.
When using the ASD with an explosion-proof motor or other special motor types, lower the carrier
frequency to stabilize the operation. DO NOT set the carrier frequency below 2.2 kHz if operating the
system in the vector control mode.
Note: When operating in the Vector Control mode the carrier frequency should be set to
2.2 kHz or above.
If the motor being used is coupled to a load that has a large backlash or if coupled to a reciprocating load,
use one of the following procedures to stabilize motor operation.
• Adjust the S-pattern acceleration/deceleration setting,
• If operating in the Vector control mode, adjust the response time, or
•Switch to the Constant Torque control mode.
H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual 11

Load-Produced Negative Torque
CAUTION
When the ASD is used with a load that produces negative torque (an overhauling load), the over-voltage
or over-current protective functions of the ASD may cause nuisance tripping.
To minimize the undesirable effects of negative torque the dynamic braking system may be used. The
dynamic braking system converts the regenerated energy into heat that is dissipated using a braking
resistor. The braking resistor must be suitably matched to the load. Dynamic braking is very effective in
reducing the DC bus voltage during a momentary over-voltage condition.
If under extreme conditions the dynamic braking system or a component of this system were to fail, the
dynamic braking resistor may experience an extended over-current condition. The DBR circuit was
designed to dissipate excessive amounts of heat and if the extended over-current condition were allowed
to exceed the circuit parameters, this condition could result in a fire hazard.
To combat this condition, the 3-phase input may be connected using contactors that are configured to open
in the event of an extended DBR over-current condition or an internal circuit failure. Using a thermal
sensor and/or overload protection as the 3-phase input contactor drive signal, the contactors will open and
remove the 3-phase input power in the event of an extended DBR over-current or system over-voltage
condition. See Dynamic Braking System Specifications on pg. 266 for more information on using
Dynamic Braking with the H9 ASD.
Motor Braking
The motor may continue to rotate and coast to a stop after being shut off due to the inertia of the load. If an
immediate stop is required, a braking system should be used. The two most common types of motor
braking systems used with the ASD are DC Injection Braking and Dynamic Braking.
For further information on braking systems, see DC Injection Braking on pg. 124 and Dynamic Braking
on pg. 136.
12 H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual

ASD Characteristics
Over-Current Protection
Each ASD model is designed for a specified operating power range. The ASD will incur a trip if the
design specifications are exceeded.
However, the ASD may be operated at 100% of the specified output-current range continuously or at
120% for a limited amount of time as indicated in the section titled Current/Voltage Specifications on pg.
262. Also, the Stall Prevention Level may be adjusted to help with nuisance over-current trips (see F601).
When using the ASD for an application to control a motor that is rated significantly less than the
maximum current rating of the ASD, the over-current limit (Thermal Overload Protection) setting will
have to be changed to match the FLA of the motor. For further information on this parameter, see Motor
Overload Protection Level 1 on pg. 182.
ASD Capacity
The ASD must not be used with a motor that has a larger capacity than the ASD, even if the motor is
operated under a small load. An ASD being used in this way will be susceptible to a high-output peak
current which may result in nuisance tripping.
Do not apply a level of input voltage to an ASD that is beyond that which the ASD is rated. The input
voltage may be stepped down when required with the use of a step-down transformer or some other type
of voltage-reduction system.
Using Vector Control
Using Vector Control enables the system to produce very high torque over the entire operating range
even at extremely low speeds. Vector Control may be used with or without feedback. However, using
feedback increases the speed accuracy for applications requiring precise speed control.
See F015 on pg. 81 for further information on using Vector Control.
H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual 13

Installation and Connections
CAUTION
The H9 Adjustable Speed Drive may be set up initially by performing a few simple configuration
settings. To operate properly, the ASD must be securely mounted and connected to a power source
(3-phase AC input at the R/L1, S/L2, and T/L3 terminals). The control terminals of the ASD may be
used by connecting the terminals of the Terminal Board to the proper sensors or signal input sources
(see the section titled I/O and Control on pg. 21
System performance may be further enhanced by assigning a function to the output terminals of the
Terminal Board and connecting the terminals to the proper indicators or actuators (LEDs, relays,
contactors, etc.).
Note: The optional ASD interface boards may be used to expand the I/O functionality of the
ASD.
Installation Notes
When a brake-equipped motor is connected to the ASD, it is possible that the brake may not release at
startup because of insufficient voltage. To avoid this, DO NOT connect the brake or the brake contactor
to the output of the ASD.
If an output contactor is used for bypass operation, it must be interlocked such that commercial power is
never applied to the output terminals of the ASD (U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3).
and
Figure 9 on pg. 24).
DO NOT apply commercial power to the ASD output terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3.
If a secondary magnetic contactor (MC) is used between the output of the ASD and the motor, it should
be interlocked such that the ST – CC connection is disconnected before the output contactor is opened.
DO NOT open and then close a secondary magnetic contactor between the ASD and the motor unless
the ASD is off and the motor is not rotating.
Note: Re-application of power via a secondary contact while the ASD is on or while the
motor is still turning may cause ASD damage.
The ASD input voltage should remain within 10% of the specified input voltage range. Input voltages
approaching the upper or lower-limit settings may require that the over-voltage and under-voltage stall
protection level parameters be adjusted. Voltages outside of the permissible tolerance should be
avoided.
The frequency of the input power should be ±2 Hz of the specified input frequency.
DO NOT use an ASD with a motor that has a current rating higher than the rated current of the ASD.
The H9 ASD is designed to operate NEMA B motors. Consult with your TIC Sales Representative
before using the ASD for special applications such as with an explosion-proof motor or applications
with a piston load.
Disconnect the ASD from the motor before megging or applying a bypass voltage to the motor.
Interface problems may occur when an ASD is used in conjunction with some types of process
controllers. Signal isolation may be required to prevent controller and/or ASD malfunction (contact
your TIC Sales Representative or the process controller manufacturer for additional information about
compatibility and signal isolation).
Use caution when setting the output frequency. Over speeding a motor decreases its ability to deliver
torque and may result in damage to the motor and/or the driven equipment.
14 H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual
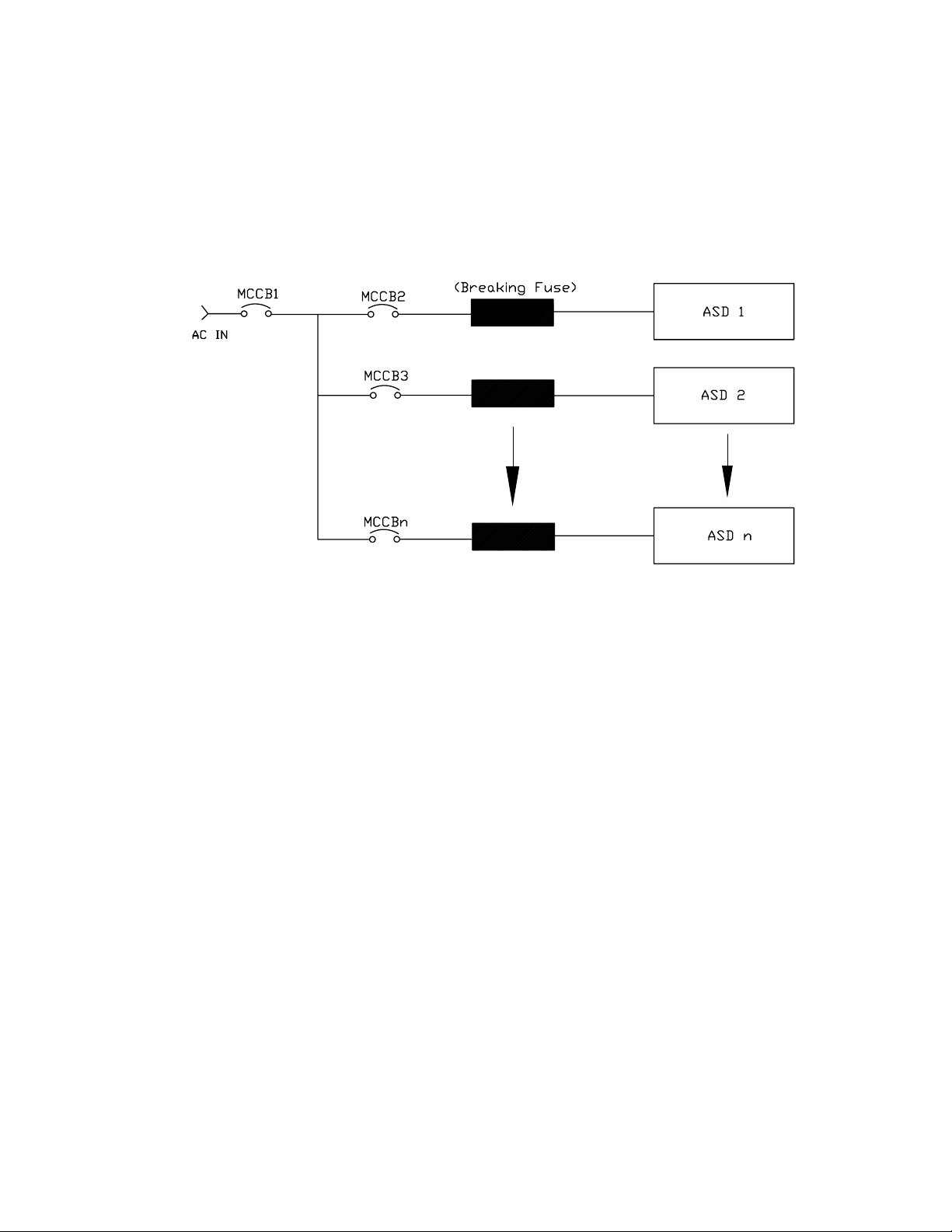
Not all H9 ASDs are equipped with internal primary power input fuses (HP dependent). When
Figure 1. Typical Circuit Breaker Configuration.
CAUTION
connecting two or more drives that have no internal fuse to the same power line as shown in Figure 1,
select a circuit-breaking configuration that will ensure that if a short circuit occurs in ASD 1, only
MCCB2 trips, not MCCB1. If it is not feasible to use this configuration, insert a fuse between MCCB2
and ASD 1.
Mounting the ASD
— The following thermal specifications apply to the 230-volt and 460-volt ASDs ONLY —
Install the unit securely in a well ventilated area that is out of direct sunlight.
The process of converting AC to DC, and then back to AC produces heat. During normal ASD
operation, up to 5% of the input energy to the ASD may be dissipated as heat. If installing the ASD in a
cabinet, ensure that there is adequate ventilation.
DO NOT operate the ASD with the enclosure door open.
The ambient operating temperature rating of the 3.0 to 20 HP H9 ASD is 14° to 104° F (-10° to 40° C).
When installing adjacent ASDs horizontally TIC recommends at least 5 cm of space between adjacent
units. However, horizontally mounted ASDs may be installed side-by-side with no space in between the
adjacent units — side-by-side installations require that the top cover be removed from each ASD.
For 150 HP and above ASDs, a minimum of 50 cm of space is required above and below adjacent units
and any obstruction.This space is the recommended minimum space requirement for the ASD and
ensures that adequate ventilation is provided for each unit. More space will provide a better
environment for cooling (see the section titled Enclosure and Conduit Plate Dimensions on pg. 254 for
additional information on mounting space requirements).
Note: Ensure that the ventilation openings are not obstructed.
H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual 15
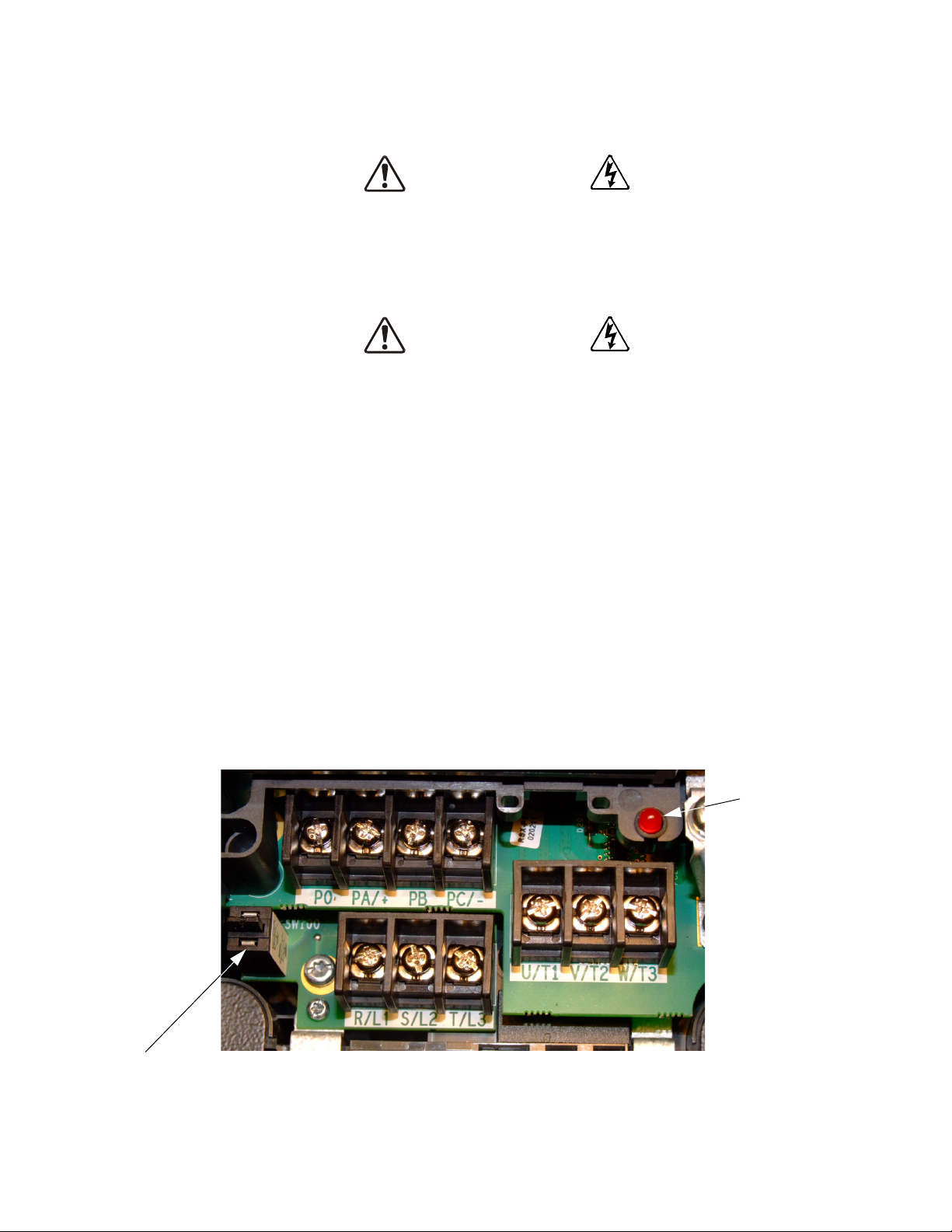
Connecting the ASD
DANGER
DANGER
Charge LED
Grounding Capacitor Switch — Pull for Small capacitance/push for Large capacitance.
Refer to the section titled Installation Precautions on pg. 4 and the section titled Lead Length
Specifications on pg. 20 before attempting to connect the ASD and the motor to electrical power.
Power Connections
Contact With 3-Phase Input/Output Terminals May Cause An
Electrical Shock Resulting In Injury Or Loss Of Life.
See the Typical Connection Diagram on pg. 26 for a system I/O connectivity schematic.
An inductor (DCL) may be connected across the PO and PA/+ terminals to provide additional filtering.
When not used, a jumper must be connected across these terminals (see Typical Connection Diagram on
pg. 26).
PA/+ and PB are used for the DBR connection if using a braking resistor.
PC/- is the negative terminal of the DC bus.
R/L1, S/L2, and T/L3 are the 3-phase input supply terminals for the ASD.
U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3 are the output terminals of the ASD that connect to the motor.
The location of the Charge LED for the smaller typeform ASD is provided in Figure 2. The Charge
LED is located on the front door of the enclosure of the larger ASDs.
Figure 2. Typical H9 ASD Input/output Terminals and the Grounding Capacitor Switch.
16 H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual
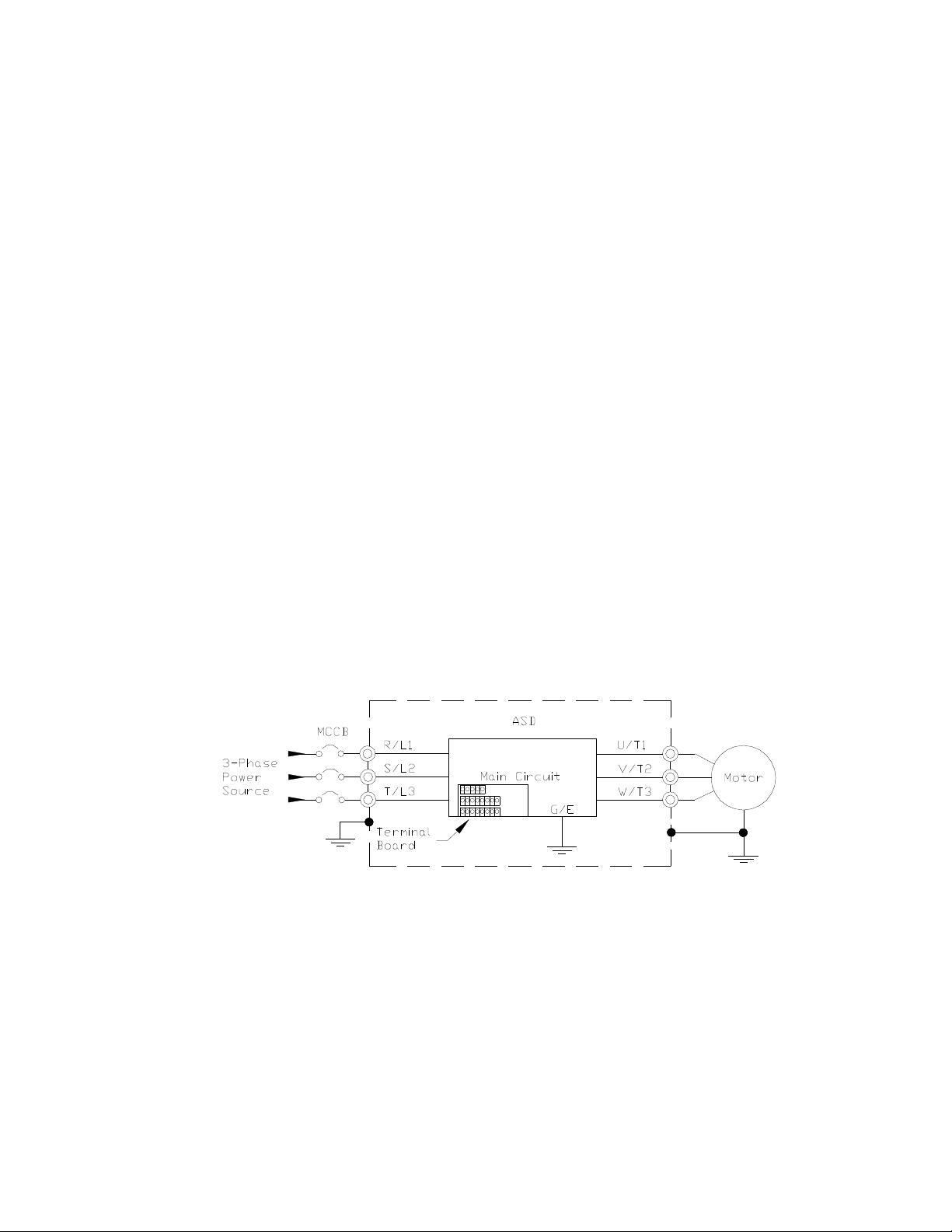
Power Connection Requirements
Connect the 3-phase input power to the input terminals of the ASD at R/L1, S/L2, and T/L3 (see Figure
3 for the typical electrical connection scheme). Connect the output of the ASD to the motor from the
ASD terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3. The input and output conductors and terminal lugs used shall be
in accordance with the requirements listed in the section titled Current/Voltage Specifications on pg.
262.
If multiple conductors are used in parallel for the input or output power and it is necessary to use
separate conduits, each parallel set shall have its own conduit and not share its conduit with other
parallel sets (i.e., place U1, V1, W1, and a ground wire in one conduit and U2, V2, W2 and a ground
wire in another; refer to the NEC Article 300.20 and Article 310.4). National and local electrical codes
should be referenced if three or more power conductors are run in the same conduit (refer to the NEC
Article 310 adjustment factors).
Note: National and local codes should be referenced when running more than three
conductors in the same conduit.
Install a molded case circuit breaker (MCCB) or fuse between the 3-phase power source and the ASD in
accordance with the fault current setting of the ASD and the NEC Article 430.
The ASD is designed and tested to comply with UL Standard 508C. Modifications to the ASD system
or failure to comply with the short circuit protection requirements outlined in this manual may
disqualify the UL rating. See Table 22 on pg. 268 for typeform-specific short circuit protection
recommendations.
As a minimum, the installation of the ASD shall conform to the NEC Article 110, the Occupational
Safety and Health Administration requirements, and to any other local and regional industry codes
and standards.
Note: In the event that the motor rotates in the wrong direction when powered up, reverse
any two of the three ASD output power leads (U, V, or W) connected to the motor.
Figure 3. H9 ASD/Motor Typical Connection Diagram.
H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual 17

System Grounding
Proper grounding helps to prevent electrical shock and to reduce electrical noise. The ASD is designed
to be grounded in accordance with Article 250 of the NEC or Section 10/Part One of the Canadian
Electrical Code (CEC).
The grounding conductor shall be sized in accordance with Article 250-122 of the NEC or Part One-
Tab le 6 of the CEC.
— The Metal Of Conduit Is Not An Acceptable Ground —
The input, output, and control lines of the system shall be run in separate metal conduits and each shall
have its own ground conductor.
ASDs produce high-frequency noise — take steps to avoid the negative effects of noise. Listed below
are some examples of measures that will help to combat noise problems.
• DO NOT install the input power and output power wires in the same duct or in parallel with each
other, and do not bind them together.
• DO NOT install the input/output power wires and the wires of the control circuit in the same duct
or in parallel with each other, and do not bind them together.
• Use shielded wires or twisted wires for the control circuits.
• Ensure that the grounding terminals (G/E) of the ASD are securely connected to ground.
• Connect a surge suppressor to every electromagnetic contactor and every relay installed near the
ASD.
• Install noise filters as required.
Grounding Capacitor
The Grounding Capacitor plays a role in minimizing the effects of leakage current through the ASD
system and through ground paths to other systems. Leakage current may cause the improper operation
of earth-leakage current breakers, leakage-current relays, ground relays, fire alarms, and other sensors
— and it may cause superimposed noise on CRT screens.
The Grounding Capacitor Switch allows the user to quickly change the value of the leakage-reduction
capacitance of the 3-phase input circuit. See figures 4, 5, 6, and 7 on pg. 19 for an electrical depiction of
the leakage-reduction functionality and the methods used to change the capacitance value. The method
used is typeform-specific.
If using a 460-volt 5 HP ASD or a 460-volt ASD that is in the range of 7.5 HP to 25 HP, and the U/T1,
V/T2, and W/T3 connections to the motor are 100 meters or more in length, the ASD Carrier
Frequency must be set to 4 kHz or less when activating or deactivating the Grounding Capacitor
Switch. ASD overheating may occur if the Carrier Frequency is set above 4 kHz when activating or
deactivating the Grounding Capacitor Switch.
See pg. 5 for more information on the Grounding Capacitor Switch and pg. 16 for the location.
18 H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual
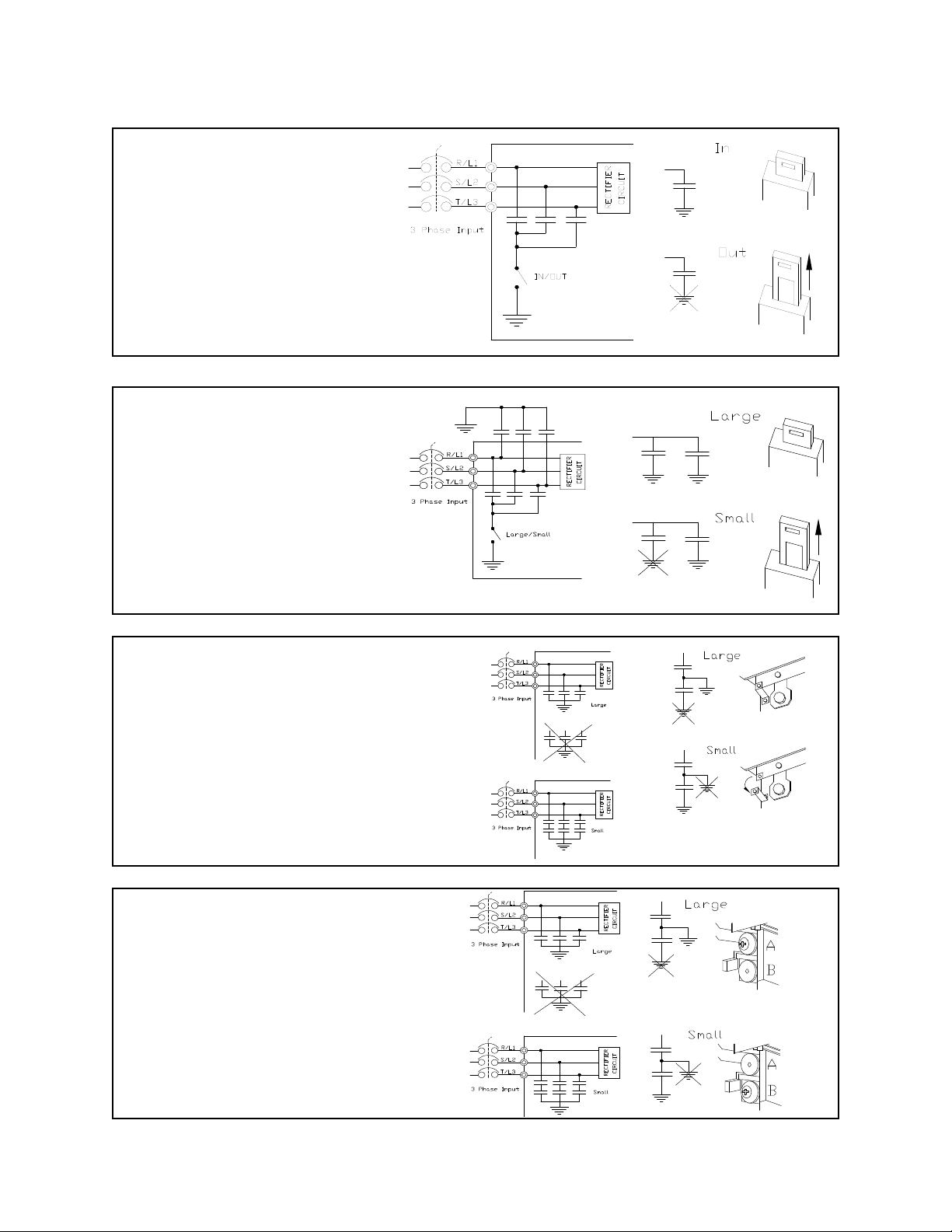
Figure 4. The Grounding Capacitor
Switch is used on typeforms 230-
volt 0.75 HP to 10 HP and the 25
and 30 HP/460-volt 1.0 HP to 25 HP.
The value may be set to Maximum
(default setting) or to Zero by
pushing or pulling the switch
actuator, respectively.
Figure 5. The Grounding Capacitor
Switch is used on typeforms 230-
volt 15 HP to 20 HP and the 40 HP to
60 HP/460-volt 30 HP to 100 HP.
The value may be set to Large
(default setting) or Small by pushing
or pulling the switch actuator,
respectively.
Figure 6. The Grounding Capacitor
Bar is used on typeforms 230-volt
75 HP and the 100 HP/460-volt 125
HP and the 150 HP.
The value may be set to Large or
Small (default setting) by connecting
or disconnecting the switching bar,
respectively.
Figure 7. The Grounding Capacitor
Screw is used on typeforms 460-volt
200 HP and above.
The value may be set to Large or
Small (default setting) by placing the
screw in the A position or by placing
the screw in the B position,
respectively.
H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual 19
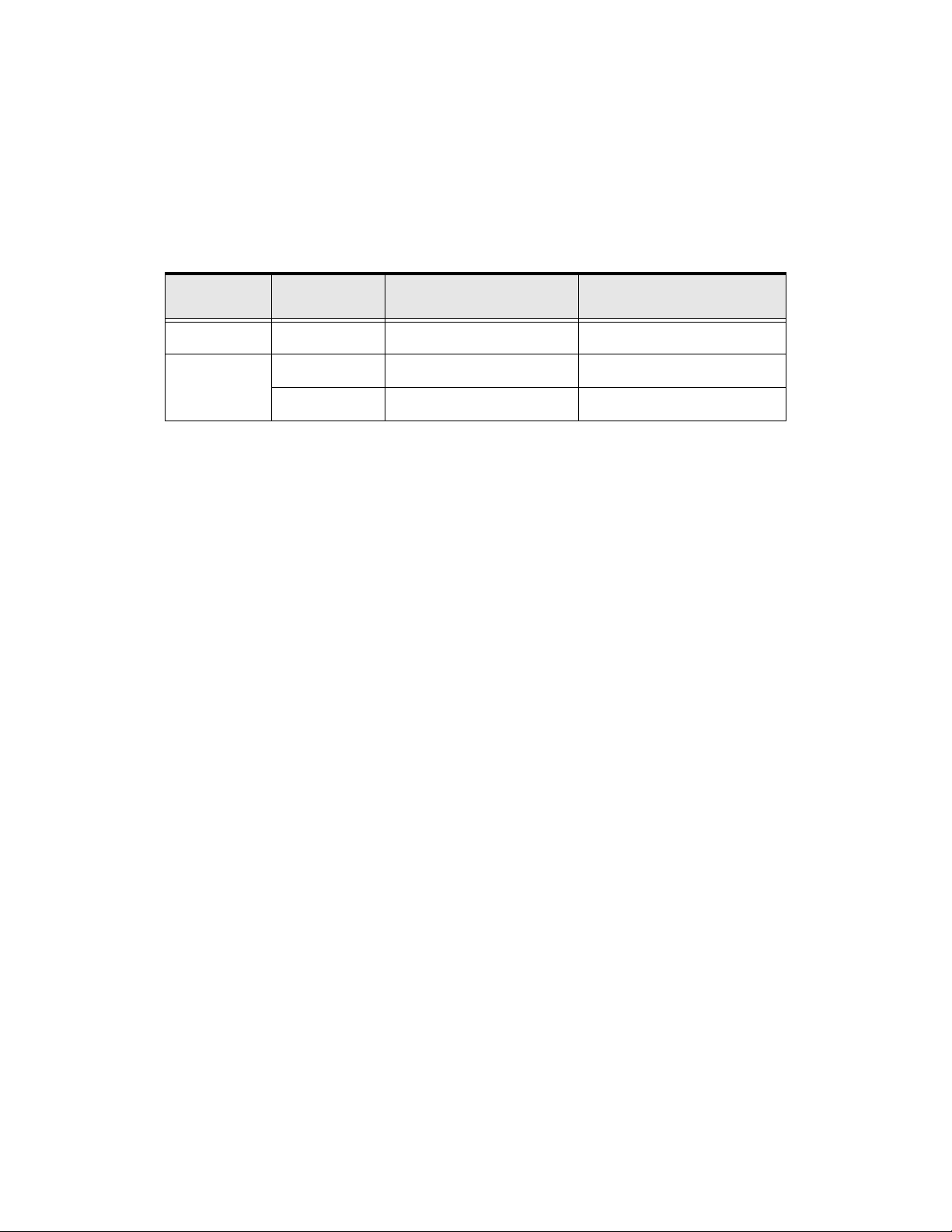
Lead Length Specifications
Adhere to the NEC and any local codes during the installation of ASD/motor systems. Excessive lead
lengths may adversely effect the performance of the motor. Special cables are not required. Lead lengths
from the ASD to the motor in excess of those listed in Table 1 may require filters to be added to the output
of the ASD. Table 1 lists the suggested maximum lead lengths for the listed motor voltages.
Table 1. Lead Length Recommendations.
Model
230-Volt All 1000 feet 450 feet
460-Volt
Note: Contact the TIC Customer Support Center for application assistance when using lead
PWM Carrier
Frequency
< 5 kHz 600 feet 200 feet
5 kHz 300 feet 100 feet
lengths in excess of those listed.
Exceeding the peak voltage rating or the allowable thermal rise time of the motor
insulation will reduce the life expectancy of the motor.
When operating in the Vector Control mode the carrier frequency should be set to
2.2 kHz or above.
NEMA MG1 Part 31
Compliant Motors
NEMA MG1 Part 30
Compliant Motors
20 H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual
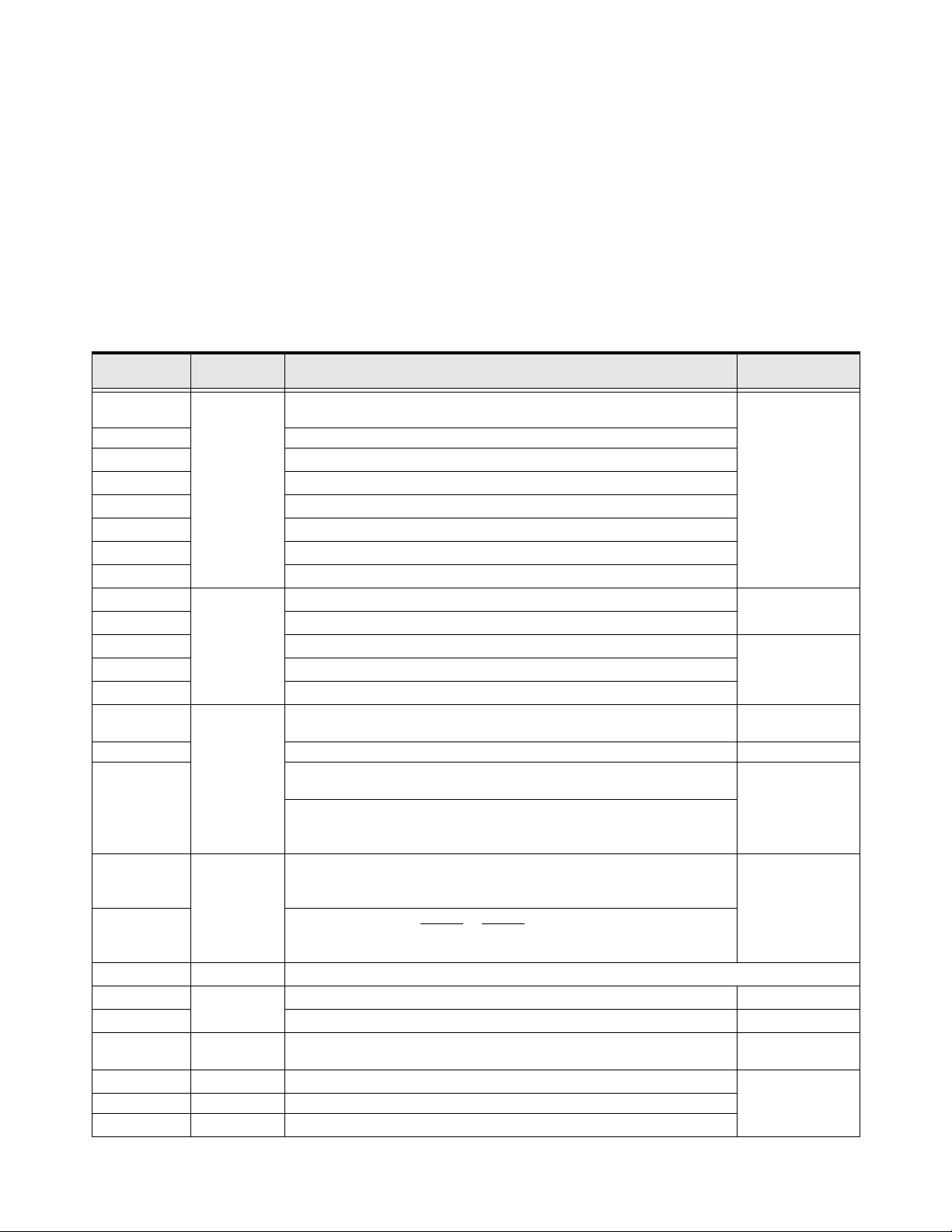
I/O and Control
The H9 ASD can be controlled by several input types and combinations thereof, as well as operate within
a wide range of output frequency and voltage levels. This section discusses the ASD control methods and
supported I/O functions.
The Terminal Board supports discrete and analog I/O functions and is shown in Figure 9 on pg. 24.
Table 2 lists the names, functions, and settings (default settings of programmable terminals) of the input
and output terminals of the Terminal Board.
Note: To use the input lines of the Te rmi n al Boa r d to provide Run commands the Command
Mode setting must be set to Ter m i nal B l ock .
Typical Connection Diagram on pg. 26 shows the typical connection diagram for the H9 ASD system.
Table 2. Terminal Board Terminal Names and Functions.
Term inal
Name
ST
RES Reset — Multifunctional programmable discrete input. Resets ASD.
F
R
S1
S2
S3
S4
O1A/B (OUT1)
O2A/B (OUT2)
FLA
FLB
FLC
RR
RX Multifunctional programmable analog input (-10 to +10 VDC input). Figure 12 on pg. 25.
V/I
(Select V or I
via SW301)
AM
FM
SU+
P24
PP
FP Pulsed Output
IICC
CCA — Return for the RR, RX, P24, and the PP terminals.
CC
H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual 21
Input/Output
Standby — Multifunctional programmable discrete input. Activation required
for normal ASD operation.
Discrete Input
Connect to CC
to activate
(Sink mode).
Switched
Output
Analog Input
Analog Output
DC Input Externally-supplied 24 VDC backup control power (1.1 A min.).
DC Output
— Return for the V/I input terminal. (see IICC on pg. 105).
— Return for the AM, FM, SU+, and the discrete input terminals.
Forward — Multifunctional programmable discrete input.
Reverse — Multifunctional programmable discrete input.
Preset Speed 1 — Multifunctional programmable discrete input.
Preset Speed 2 — Multifunctional programmable discrete input.
Preset Speed 3 — Multifunctional programmable discrete input.
Preset Speed 4 — Multifunctional programmable discrete input.
Low Speed — Multifunctional programmable discrete output.
Reach Frequency — Multifunctional programmable discrete output.
Fault relay (N.O.).
Fault relay (N.C.).
Fault relay (common).
Frequency Mode 1 — Multifunction programmable analog input. (0.0 to 10
VDC input — 0 Hz to Maximum Frequency).
Unassigned — V — Multifunctional programmable isolated analog voltage
input (0 to 10 VDC input)
Frequency Mode 2 (default SW301 setting) — I — Multifunctional
programmable isolated analog current input (4 [0] to 20 mADC input — 0 Hz
to Maximum Frequency).
Output Current — Current output that is proportional to the output current of
the ASD or to the magnitude of the function assigned to this terminal (see
Table 8 on pg. 239 for assignment listing).
Output Frequency — Current
output frequency of the ASD or to the magnitude of the function assigned to
this terminal (see Table 8 on pg. 239). Select Current or Vo lt ag e at F681.
24 VDC output (200 mA max.). Figure 14 on pg. 25.
10.0 VDC/10 mA voltage source for an external potentiometer. Figure 15 on pg. 25.
Frequency Pulse — Multifunctional programmable output pulse train of a
frequency based on the output frequency of the ASD (see Table 6 on pg. 237).
Function (Default Setting If Programmable)
(See Terminal Descriptions on pg. 22)
or Voltage output that is proportional to the
Circuit Config.
Figure 10 on pg. 25.
Figure 16 on pg. 25.
Figure 19 on pg. 25.
Figure 11 on pg. 25.
Figure 13 on pg. 25.
Figure 18 on pg. 25
Figure 17 on pg. 25.
DO NOT connect to
Earth Gnd or to
each other.

Terminal Descriptions
Note: The programmable terminal assignments may be accessed and changed from the
default settings as mapped on pg. 46 or via the Direct Access method: Program
Direct Access Applicable Parameter Number. See the section titled Program
Mode Menu Navigation on pg. 46 for the applicable Direct Access parameter
numbers. For further information on terminal assignments and default setting
changes, see the sections titled Terminal on pg. 47 and Default Setting Changes on
pg. 74.
Note: See the section titled Cable/Terminal/Torque Specifications on pg. 264 for the ASD
conductor and terminal electrical specifications.
ST — The default setting for this terminal is the Standby mode controller. As the default setting, this
terminal must be activated for normal system operation. The ST terminal is activated by connecting CC
to this terminal (Sink mode). When deactivated, OFF is flashed on the LED screen and the Not-Ready-
to-Run icon is displayed on the LCD screen as shown in Figure 22 on pg. 32. This input terminal may
be programmed to any of the functions listed in Table 5 on pg. 234 (see F113).
RES — The default setting for this terminal is Reset. The RES terminal is activated by connecting CC
to this terminal (Sink mode). A momentary connection to CC resets the ASD and any fault indications
from the display. Reset is effective when faulted only. This input terminal may be programmed to any
of the functions listed in Table 5 on pg. 234 (see F114).
F — The default setting for this terminal is the Forward run command. The F terminal is activated by
connecting CC to this terminal (Sink mode). This input terminal may be programmed to any of the
functions listed in Table 5 on pg. 234 (see F111).
R — The default setting for this terminal is the Reverse run command. The R terminal is activated by
connecting CC to this terminal (Sink mode). This input terminal may be programmed to any of the
functions listed in Table 5 on pg. 234 (see F112).
S1
— The default setting for this terminal is the Preset Speed 1 (see Preset Speed 1 on pg. 83). The S1
terminal is activated by connecting CC to this terminal (Sink mode). This input terminal may be
programmed to any of the functions listed in Table 5 on pg. 234 (see F115).
S2 — The default setting for this terminal is the Preset Speed 2 (see Preset Speed 2 on pg. 83). The S2
terminal is activated by connecting CC to this terminal (Sink mode). This input terminal may be
programmed to any of the functions listed in Table 5 on pg. 234 (see F116).
S3 — The default setting for this terminal is the Preset Speed 3 (see Preset Speed 3 on pg. 84). The S3
terminal is activated by connecting CC to this terminal (Sink mode). This input terminal may be
programmed to any of the functions listed in Table 5 on pg. 234 (see F117).
S4 — The default setting for this terminal is the Preset Speed 4 (see Preset Speed 4 on pg. 84). The S4
terminal is activated by connecting CC to this terminal (Sink mode). This input terminal may be
programmed to any of the functions listed in Table 5 on pg. 234 (see F118).
RR — The default function assigned to this terminal is Frequency Mode 1. The RR terminal accepts a
0 – 10 VDC input signal that is used to control the function assigned to this terminal. This input terminal
may be programmed to control the speed or torque of the motor via an amplitude setting or regulate by
setting a limit. The gain and bias of this terminal may be adjusted for application-specific suitability
(see F210 – F215). See pg. 26 for an electrical depiction of the RR terminal.
RX — The default function assigned to this terminal is Tor q u e Com m an d. The RX terminal accepts a
±10 VDC input signal that is used to control the function assigned to this terminal. This input terminal
may be programmed to raise or lower the speed or torque of the motor via an amplitude setting or this
terminal may be used to regulate the speed or torque of a motor by setting a limit. The gain and bias of
this terminal may be adjusted for application-specific suitability (see F216 –
F221).
22 H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual

V/I — The V/I terminal has the dual function of being able to receive an input voltage or current. The
function as a voltage input is to receive a 0 – 10 VDC input signal. The function as a current input is to
receive a 0 – 20 mA input signal. Using either input type, the function is to control the 0.0 – Maximum
Frequency output or the 0.0 to 250% torque output of the ASD. This is an isolated input terminal. This
terminal may be programmed to control the speed or torque of the motor and cannot process both input
types simultaneously. SW301 must be set to V or I to receive a voltage or current, respectively (see
Figure 9 on pg. 24). Terminal scaling and the selection of speed or torque control is accomplished via
parameters F201 – F206. The gain and bias of this terminal may be adjusted for application-specific
suitability (see F470 and F471).
SU+ — Control Power Supply Backup input terminal. This terminal accepts the user-supplied
24 VDC backup power to the control circuits (only). Backup power is used in the event of an open
MCCB or during a momentary loss of the 3-phase input power. Parameter settings, real-time clock
information, and trip history information are retained with the use of the SU+ backup power. See the
section titled Battery Backup on pg. 28 for more information on system backup features.
4
P24 — +24 VDC at 200 mA power supply for customer use.
PP — The function of output PP is to provide a 10 VDC/10 mADC (max.) output that may be divided
using a potentiometer. The tapped voltage is applied to the RR input to provide manual control of the
RR programmed function.
O1A/B (OUT1A/B) — The default function assigned to this terminal is Output Low-Speed. This
output may be programmed to provide an indication (open or closed) that any of the functions listed in
Table 8 on pg. 239 has occurred or is active. This function may be used to signal external equipment
(e.g., activate the brake) (see F130). The OUT1 terminal is rated at 2 A/120 VAC and 2 A/30 VDC.
O2A/B (OUT2A/B) — The default function assigned to this terminal is ACC/DEC Complete. This
output may be programmed to provide an indication (open or closed) that any of the functions listed in
Table 8 on pg. 239 has occurred or is active. This function may be used to signal external equipment
(e.g., activate the brake) (see F131). The OUT2 terminal is rated at 2A/120 VAC and 2A/30 VDC.
FP — The default function of this output terminal is to output a series of pulses at a rate that is a
function of the ASD output frequency (50 mA max. at 1.0 kHz to 43.3 kHz). As the output frequency of
the ASD goes up so does the FP output pulse rate. This terminal may be programmed to provide an
output pulse rate that is proportional to the magnitude of the user-selected item from Table 6 on pg. 237.
For further information on this terminal see F676 on pg. 193.
AM — This output terminal produces an output current that is proportional to the output frequency of
the ASD or of the magnitude of the function assigned to this terminal. The available assignments for
this output terminal are listed in Table 6 on pg. 237. For further information on this terminal see F670
on pg. 192.
FM — This output terminal produces an output current or voltage that is proportional to the output
frequency of the ASD or of the magnitude of the function assigned to this terminal. The available
assignments for this output terminal are listed in Table 6 on pg. 237. For further information on this
terminal see F005 on pg. 78. The Voltage/Current output selection is performed at F681.
FLA — One of two normally open contacts that, under user-defined conditions, connect to FLC.
FLB — One of two normally closed contacts that, under user-defined conditions, connect to FLC.
C
FLC — FLC is the common leg of a single-pole double-throw form C relay. The FL relay is the Fault
Relay by default, but may be programmed to any of the selections of Table 8 on pg. 239. For further
information on this terminal see F132 and Figure 8.
Note: The FLA, FLB, and FLC contacts are rated at 2A/120 VAC and 2A/30 VDC.
H9 ASD Installation and Operation Manual 23
 Loading...
Loading...