Page 1

TOPFIELD
TF 500 PVRc
User Guide
Digital Cable Receiver
Personal Video Recorder
CONAX
Page 2

Page 3

Contents iii
Contents
1 Introduction 1
1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.2 Controlling the digital receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.2.1 The front panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.2.2 The remote control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.3 What is common interface? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2 Setup 8
2.1 Unpacking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2 Safety precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.3 Rear panel connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.4 Connecting up your digital receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.4.1 Connecting to the broadcasting cable . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.4.2 Connecting to your television . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.4.3 Connecting to your video cassette recorder . . . . . . . 15
2.5 Switching on for the first time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.5.1 Inserting batteries in the remote control . . . . . . . . . 15
2.5.2 Powering on and checking picture . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Page 4

iv Contents
3 Preference Settings 17
3.1 Language settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.2 Video and audio settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.2.1 Television standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.2.2 Colour model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.2.3 Video cassette recorder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.2.4 Television aspect ratio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.2.5 High definition television . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.2.6 Video scaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.2.7 Audio mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.3 Local time setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3.4 Parental control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
3.5 Adjusting the on-screen display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
3.6 To turn on the time shift feature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
4 Service Search 27
4.1 Searching broadcasting services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4.2 Resetting to factory settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4.3 Clearing the services list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
5 Daily Usage 30
5.1 Volume control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
5.2 Watching television . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
5.2.1 The services list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
5.2.2 The favourite services list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
5.2.3 Viewing programme information . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
5.2.4 Selecting audio tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
5.2.5 Selecting subtitle tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
5.2.6 Viewing teletext . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
5.3 Viewing electronic programme guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Page 5

Contents v
5.4 Watching multifeed programme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
5.5 Using time shift . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
5.6 Using picture in picture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6 Listing Services 39
6.1 Editing the favourite list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
6.2 How to use on-screen keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
6.3 Transferring receiver data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
7 Recording and Playing 43
7.1 Recording a programme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
7.1.1 Instant recording . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
7.1.2 Timer recording . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
7.1.3 Scheduling recordings using the programme guide . . 49
7.1.4 Recording a time-shifted programme . . . . . . . . . . 49
7.1.5 Recording a pay service programme . . . . . . . . . . . 50
7.2 File archive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
7.2.1 To delete a recording . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
7.2.2 To sort recordings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
7.2.3 To lock a recording . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
7.2.4 To rename a recording . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
7.2.5 To make a new folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
7.2.6 To move a recording to another folder . . . . . . . . . . 52
7.3 Playing back a recording . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
7.3.1 To navigate using the progress bar . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
7.3.2 To play in slow motion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
7.3.3 To play in fast motion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
7.3.4 To make a bookmark . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
7.3.5 To play back a recording repeatedly . . . . . . . . . . . 55
7.3.6 To play back recordings in sequence . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Page 6

vi Contents
7.3.7 To play back a scrambled recording . . . . . . . . . . . 56
7.4 Copying a recording . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
7.5 MP3 playback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
7.6 Transferring recording files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
7.7 Formatting the hard disk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
8 Topfield Application Program 61
9 Firmware Update 63
9.1 Checking the firmware information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
9.2 From your computer via USB port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
9.3 From your computer via RS-232 port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
9.4 From another digital receiver via RS-232 port . . . . . . . . . . 65
Index 67
Page 7

Chapter 1
Introduction
The TF 500 PVRc digital receiver is fully compliant with the
international Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) standard, and
thus is able to receive digital broadcasts of that standard.
NOTE
In general we equate a channel with a frequency. Unlike analogue broadcasts, however, digital broadcasts are not all assigned to their own frequencies; instead, multiple television
broadcasts are transmitted through a single frequency. The frequency in digital broadcasting is usually called transponder. To
reduce confusion in this manual, the word
used than
broadcast.
channel
as a term to indicate one television or radio
service
is preferably
1
1.1 Features
The TF 500 PVRc digital receiver has the following features:
• Can store up to 2000 television and radio services.
• You can create favourite lists of your favourite services.
Page 8

2 Introduction
•
You can view information about the current television or
radio programme.
•
Has an electronic programme guide that provides an
overview of scheduled programmes.
•
You can update the firmware of the digital receiver to the
latest version which would be provided by the manufacturer.
•
You can record one broadcasting service while you are
currently watching another.
•
The large storage capacity of the built-in hard disk drive
allows you to record up to about 60 hours of television
—in case of 250 gigabytes— in excellent picture and sound
quality.
•
Time shift is a special technical feature available on the TF
500 PVRc. You can pause the programme you are watching and resume it again at a later time. Then you can
quickly go to whatever part of the current programme by
fast foward or backward search.
1.2 Controlling the digital receiver
You can operate the digital receiver with the remote control
and the buttons on the front panel.
NOTE
When the digital receiver is off but plugged into a wall outlet,
we say that it is in standby mode; on the other hand, when it is
on, it is in operation mode. Even when you are not using the
digital receiver, you should keep it plugged into a wall outlet
to be in standby mode so that it can run timer events at any
time.
Page 9
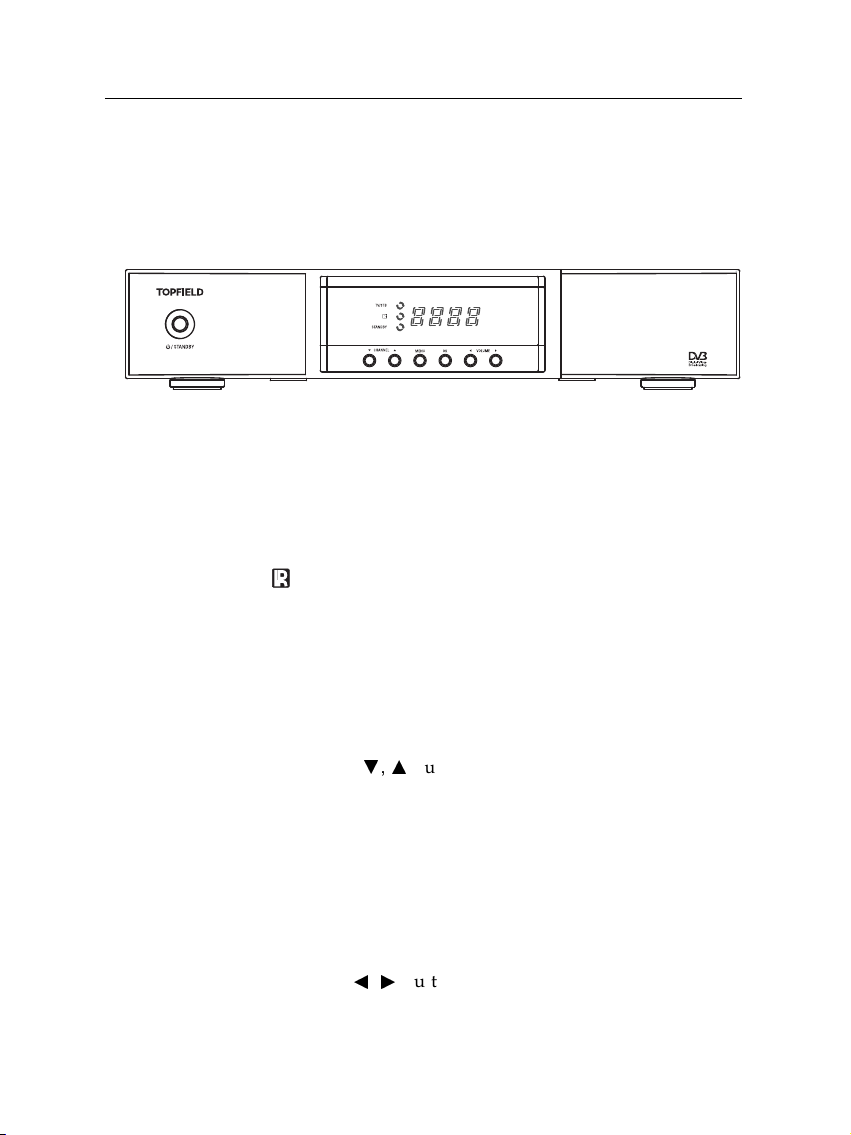
1.2.1 The front panel
The front panel of the digital receiver has buttons to control the
digital receiver, and specific lamps and a display to indicate its
status. The following indicates what they mean.
1.2 Controlling the digital receiver 3
STANDBY
button switches the digital receiver between
standby mode and operation mode.
TV/STB
lamp lights up while your video recorder operates
instead of the digital receiver. See§3.2.3 for more
details.
lamp lights up whenever you press a button on the
remote control.
STANDBY
lamp lights up while the digital receiver is in
standby mode.
Front display
displays the current time in standby mode,
and displays the current service in operation mode.
CHANNELc,abuttons switch to previous or next service.
They are also used to navigate in menus and interactive
screens.
MENU
button displays the main menu. It is also used to
return to the previous menu from a submenu.
OK
button displays the services list. See§5.2.1 for more
details. It is also used to select a menu item.
VOLUMEb,dbuttons decrease or increase the volume.
They are also used to change values for menu options.
Page 10
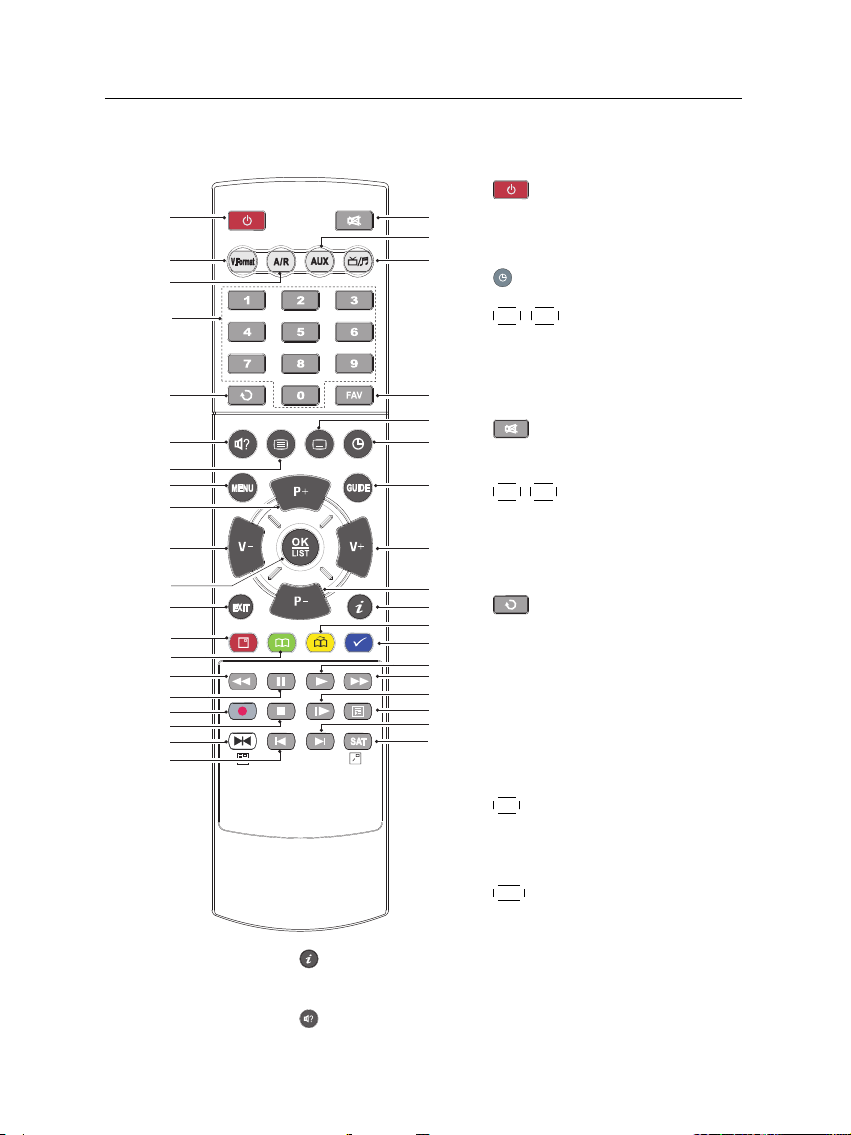
4 Introduction
14
1
4
18
16
9
12
2
17
3
5
10
35
25
28
29
24
19
31
15
7
6
11
13
20
3
8
21
27
26
22
23
36
30
32
34
33
5
1.2.2 The remote control
1
2
3
10
displays the service information box. It is also used to
4
5
6
7
8
9
display more information about a programme.
11
is used to select an audio track and a sound mode, or
button switches the digital
receiver between standby mode
and operation mode.
is used to set a sleep timer.
V−
V+
,
buttons decrease or in-
crease the volume. They are also
used to change values for menu
options.
mutes the sound. Press
again to switch it back on.
P+
P−
,
buttons switch to previ-
ous or next service. They are also
used to navigate in menus and
interactive screens.
switches between the current service and the previously
viewed one.
Numeric buttons are used to enter a service number for service
change or to specify values for
menu options.
OK
displays the services list. See
§
5.2.1 for more details. It is also
used to select a menu item.
FAV
displays the favourite lists.
Page 11
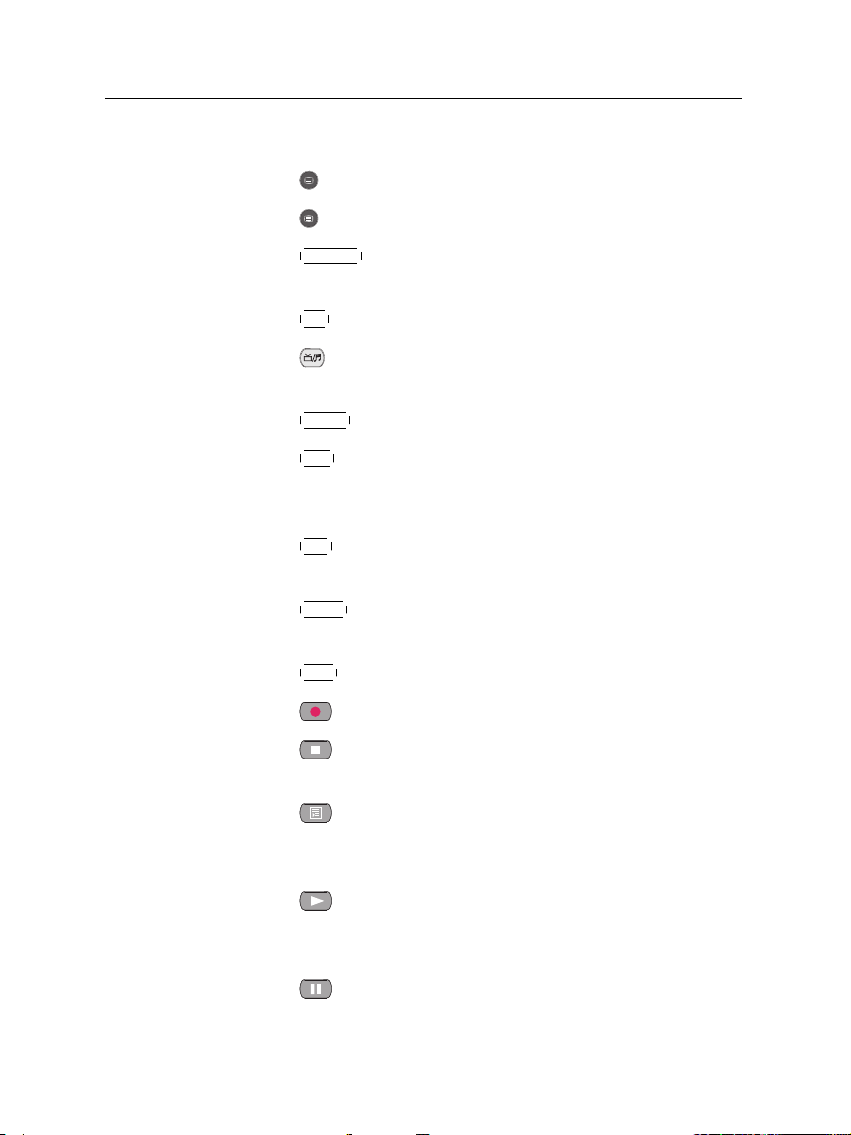
1.2 Controlling the digital receiver 5
a video track of multifeed programme.
12
is used to select a subtitle track.
13
displays teletext.
14
V.Format
changes video resolution. See§3.2.5 for more
details.
15
A/R
changes aspect ratio. See § 3.2.4 for more details.
16
switches between television services and radio ser-
vices.
17
18
GUIDE
displays the electronic programme guide.
AUX
switches the output of the TV SCART socket be-
tween the digital receiver and the device connected to
the VCR SCART socket. See § 3.2.3 for more details.
19
SAT
swaps the sub-picture with the main picture. See
§ 5.6 for more details.
20
MENU
displays the main menu. It is also used to return
to the previous menu from a submenu.
21
EXIT
is used to exit the current screen.
22
23
is used to start recording.
is used to stop playback, to stop recording, or to
jump back to live television from time-shifted television.
24
is used to display the list of recorded programmes
that are stored on the internal hard disk drive. See§7.2
for more details.
25
resumes normal playback speed, or displayes the
progress bar for navigation on playback or time shift. To
play a recorded programme, see button 24.
26
pauses live television or playback of a recorded programme.
Page 12

6 Introduction
27
is used to start reverse playback. Subsequent presses
increase the rewind speed.
28
is used to start fast motion playback. Subsequent
presses increase the playback speed.
29
is used to start slow motion playback. Subsequent
presses change the playback speed.
30
changes the position of sub-picture counterclockwise. It is also used to jump back to beginnng of recording during a playback.
31
changes the position of sub-picture clockwise. It is
also used to jump to end of recording during a playback.
32
is used to display, minify or hide the sub-picture. See
§ 5.6 for information about picture-in-picture.
33
is used to make a bookmark during playback or time
shift.
34
is used to jump to next bookmark position or to jump
forward 30 seconds.
35
is used to jump back 20 seconds for an instant replay.
36
displays the services list for sub-picture. It is also
used to specify a block for editing or for repeated playback.
The , , , and buttons have additional different functions per menu besides their own function. They will
be guided by on-screen help.
Page 13

1.3 What is common interface?
Some broadcasts are scrambled so that only paid
subscribers can enjoy them. Scrambled services
can only be viewed with a Conditional Access
Module (CAM) and a subscription card belonging with the scrambling system.
Common Interface (CI) is the slot on a digitial
receiver into which a conditional access module
may be insterted. The front of the digital receiver
has two common interfaces.
To watch a pay service, you should take the following steps:
1.
Purchase a conditional access module and a subscription
card for the pay service you want to watch.
2.
Insert the subscription card into the conditional access
module.
3.
Insert the conditional access module into a common interface on the front of the digital receiver.
1.3 What is common interface? 7
To view the information about
the module and subscription
card which is inserted into the
digital receiver, select the In-
formation>Common Interface
menu. You should see a screen
like the left figure.
Page 14

8 Setup
2.1 Unpacking
Chapter 2
Setup
Before going any further, check that you have received the
following items with your digital receiver.
• Remote control unit
• Two batteries for the remote control (AAA 1.5 V)
•
One loop cable, to link the first tuner with the second
tuner
• One SCART-to-component cable
• One S-Video cable
• A copy of this user guide
NOTE
Accessories may vary according to your local area.
2.2 Safety precautions
Please read carefully the following safety precautions.
Page 15

2.2 Safety precautions 9
•
The mains power must be 90 to 250 volts. Check it before
connecting the digital receiver to the wall outlet. For
the power consumption of the digital receiver, refer to
Table 2.1.
•
The wall outlet should be near the equipment. Do not
run an extension lead to the unit.
•
Do not expose the digital receiver to any moisture. The
digital receiver is designed for use indoors only. Use dry
cloth when cleaning the digital receiver.
• Place the digital receiver on a firm and level surface.
•
Do not place the digital receiver close to heat emitting
units or in direct sunlight, as this will impair cooling.
Do not lay any objects such as magazines on the digital receiver. When placed in a cabinet, make sure there
is a minimum space of 10 centimetres around it. For
the physical specification of the digital receiver, refer to
Table 2.2.
•
Protect the power cord from being walked on or pinched.
If the cord is damaged, do not use the digital receiver
and get the cord replaced.
•
Never open the digital receiver casing under any circumstances, or the warranty will be void.
• Refer all servicing to a qualified service technician.
Table 2.1: Power specifications
Input voltage 90 to 250 V AC, 50/60Hz
Power consumption 25 W at maximum in operation
8 W in standby
Page 16
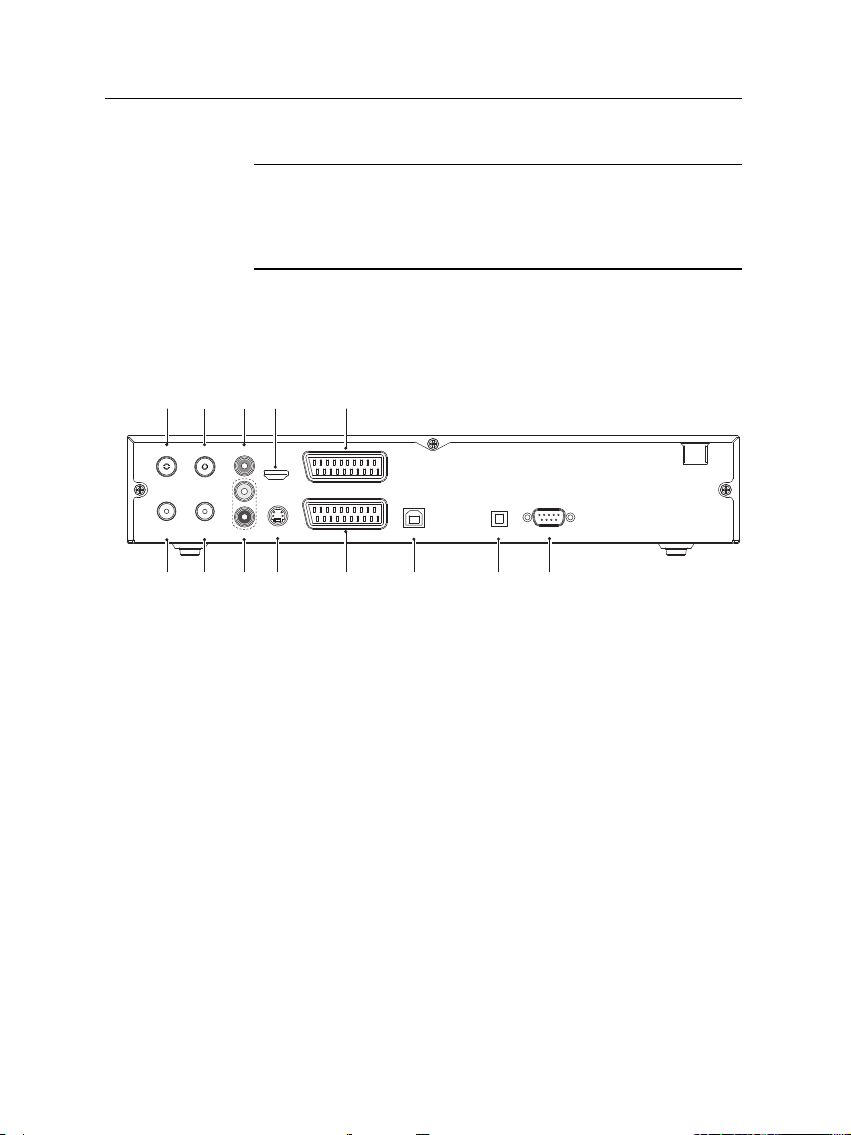
10 Setup
RS-232
S/PDIF
VCR
USB
TV
RF LOOP
1 OUT
CABLE 1 IN
CABLE 2 IN
RF LOOP
2 OUT
VIDEO
S-VIDEO
AUDIO
HDMI
R
L
1234567
8
9
10
11
12
13
Table 2.2: Physical specifications
Size 340× 60× 270 mm
Weight 3.4 kg
Operating temperature 0 to 45°C
Storage relative humidity 5 to 90 %
2.3 Rear panel connections
The TF 500 PVRc has a wide range of connections on the back.
Check what connections your television set has in comparison
with the digital receiver.
1
CABLE 1 IN
the first tuner.
Cable broadcasting signal input socket for
2
RF LOOP 1 OUT
Cable broadcasting signal output
socket through the first tuner.
3
CABLE 2 IN
Cable broadcasting signal input socket for
the second tuner.
4
RF LOOP 2 OUT
Cable broadcasting signal output
socket through the second tuner.
5
VIDEO
6
AUDIO L/R
Composite video output socket for the television
set. (yellow)
Stereo audio output socket for the television
set or the audio system. (white/red)
Page 17
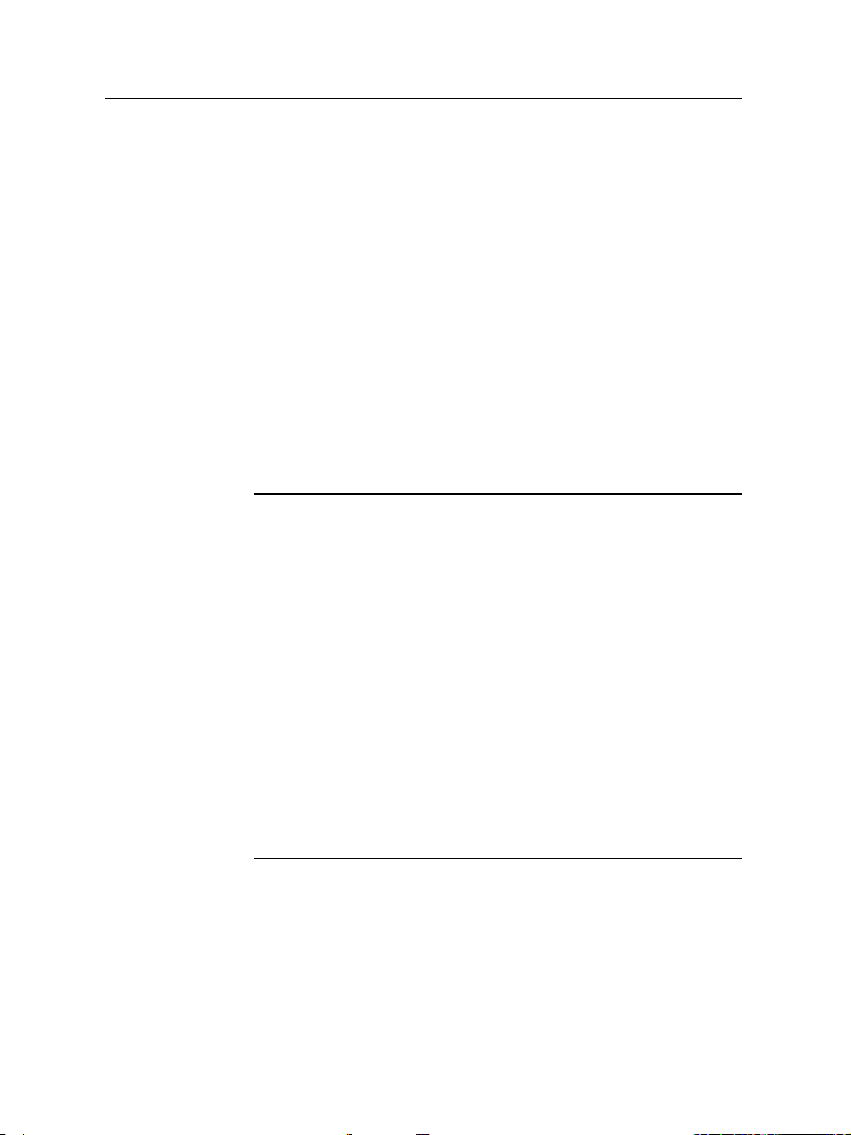
2.4 Connecting up your digital receiver 11
7
HDMI
Audio and video output socket for the high defini-
tion television set.
8
S-VIDEO
Super video output socket for the television
set.
9
TV Audio and video output socket for the television set.
10
VCR
Audio and video input/output socket for the video
cassette recorder or suchlike.
11
USB USB port for firmware update and data transfer.
12
S/PDIF
13
RS-232
Table 2.3: Connectors specifications
HDMI High definition video output
VIDEO Composite video (CVBS) output
AUDIO Left & right audio output
S-VIDEO Super video (S-Video) output
TV CVBS/S-Video/RGB/YUV video output
VCR CVBS video output
S/PDIF Dolby digital audio output
RS-232 115.2 kbps at maximum
USB 2.0 device
Dolby digital output socket for the audio system.
Serial port for firmware update and data transfer.
Left & right audio output
Dolby digital audio output
Left & right audio output
Left & right audio output
CVBS/S-Video/RGB/YUV video input for bypass
Left & right audio input for bypass
2.4 Connecting up your digital receiver
There are several ways to set up the digital receiver. Set up the
digital receiver suitably to your television and other appliances.
If you have any problem with your setup or need help, contact
your dealer.
Page 18

12 Setup
2.4.1 Connecting to the broadcasting cable
Whatever sort of connection you have between the digital receiver and the television,
you need to connect the digital receiver to
the broadcasting cable so that it can receive
digital television services.
Connect the broadcasting cable to the CABLE
1 IN connector on the back panel of the digital
receiver.
Also, you must ensure that there is a connection to both the CABLE 1 IN and CABLE 2
IN connectors on your digital receiver, so that
both tuners work properly.
Normally you do that by using a loop cable to link from the RF
LOOP 1 OUT connector to the CABLE 2 IN connector.
If you have another digital receiver, you may link it from the
RF LOOP 2 OUT connector.
2.4.2 Connecting to your television
Between all the following connectors of the digital receiver, we
recommend you to use the first connector to get best picture
quality. If your television does not have the matching connector,
then use the next connector in the following order for better
picture quality.
1. HDMI connector (HDMI)
2. SCART connector (TV)
3. S-Video connector (S-VIDEO)
4. Composite connector (VIDEO)
You should configure audio and video settings after connecting
up the digital receiver. See § 3.2 for detailed description.
Page 19
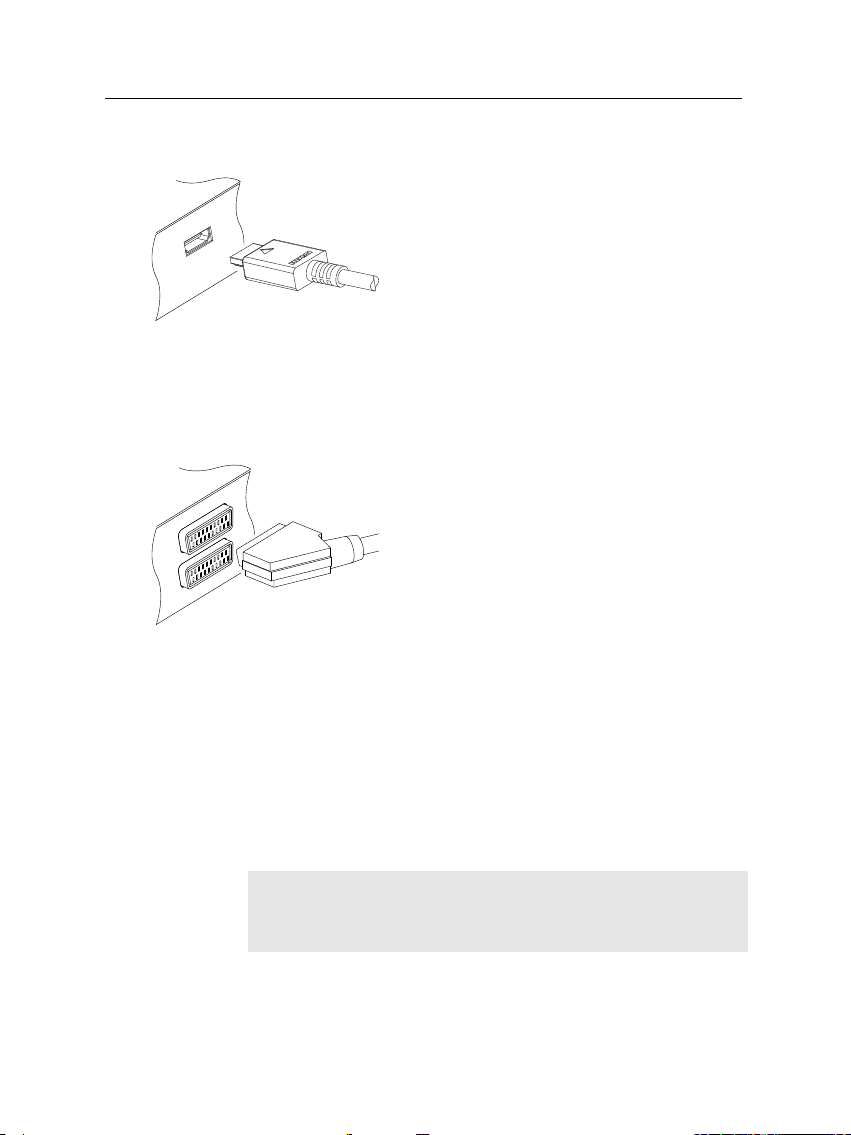
To use the HDMI connector
To use the SCART connector
If you have such a television, use an appropriate conversion cable to link the TV socket on the digital receiver to the matching
socket on your television.
If you connect with a standard SCART cable, you do not have
to make audio connections because the SCART connector can
output stereo audio. But if you use a conversion cable, such as
SCART-to-Component, you have to make audio connections.
2.4 Connecting up your digital receiver 13
If you have a high definition television set,
you should use a HDMI cable for best results. Plug one end of the cable into the HDMI
socket on the digital receiver, and the other
end into the matching socket on your television. In this case, you do not have to make
audio connections because the HDMI connector can output stereo audio or Dolby digital
audio.
For best results with a standard television set,
you should use a SCART cable, plugging one
end into the TV socket on the digital receiver
and the other end into a free SCART socket
on your television.
Some televisions have inputs via Component
connector or S-Video connector rather than
SCART.
NOTE
You cannot view high definition video with the SCART connector.
Page 20
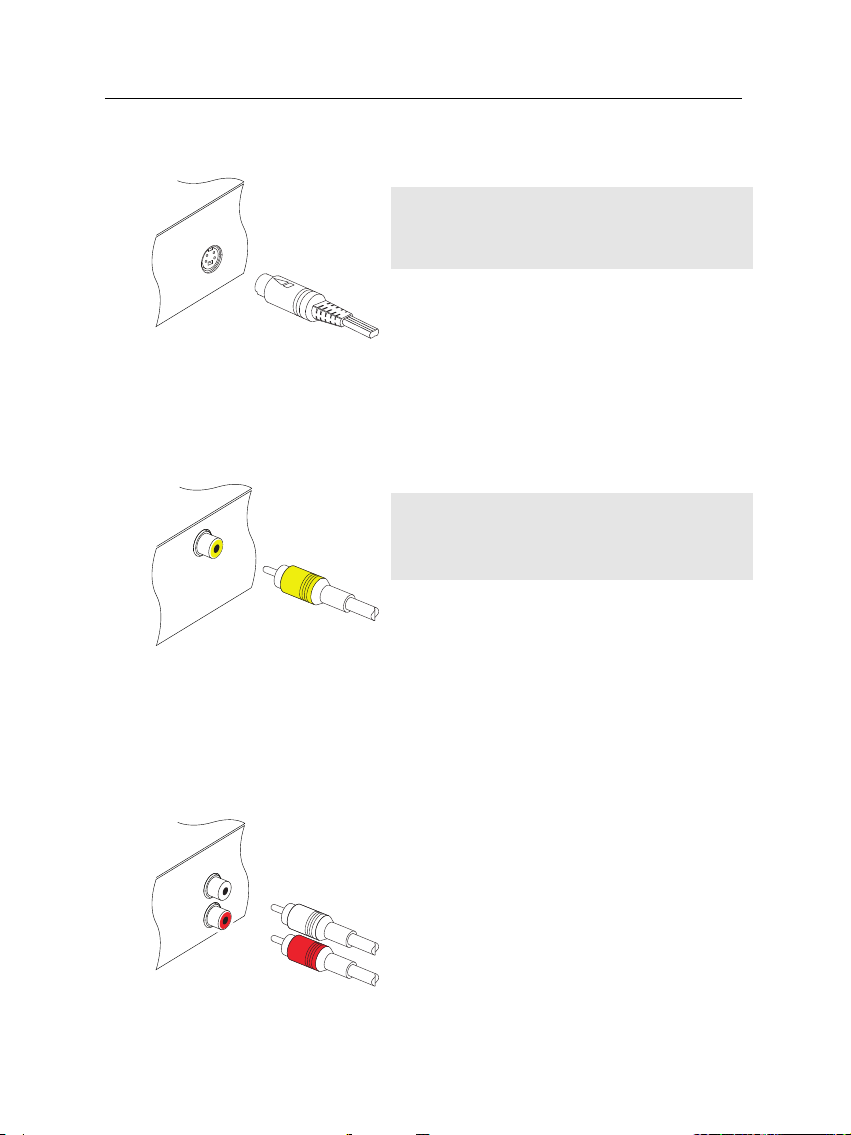
14 Setup
To use the S-Video connector
To use the composite video connector
NOTE
You cannot view high definition video with
the S-Video connector.
You will need to obtain a S-Video cable to use
the S-Video connector. Plug one end of the
cable into the S-VIDEO socket on the digital
receiver, and the other end into the matching
socket on your television.
NOTE
You cannot view high definition video with
the composite video connector.
You will need to obtain a composite video
cable (RCA cable) to use the composite video
connector. Plug one end of the cable into the
VIDEO (yellow) socket on the digital receiver,
and the other end into the matching socket
on your television.
To connect the audio connectors
You will need to obtain an audio cable (RCA
cable) to connect the audio connectors. Plug
one end of the cable into the AUDIO L (white)
and AUDIO R (red) sockets on the digital receiver, and the other end into the matching
sockets on your television or audio system.
Page 21
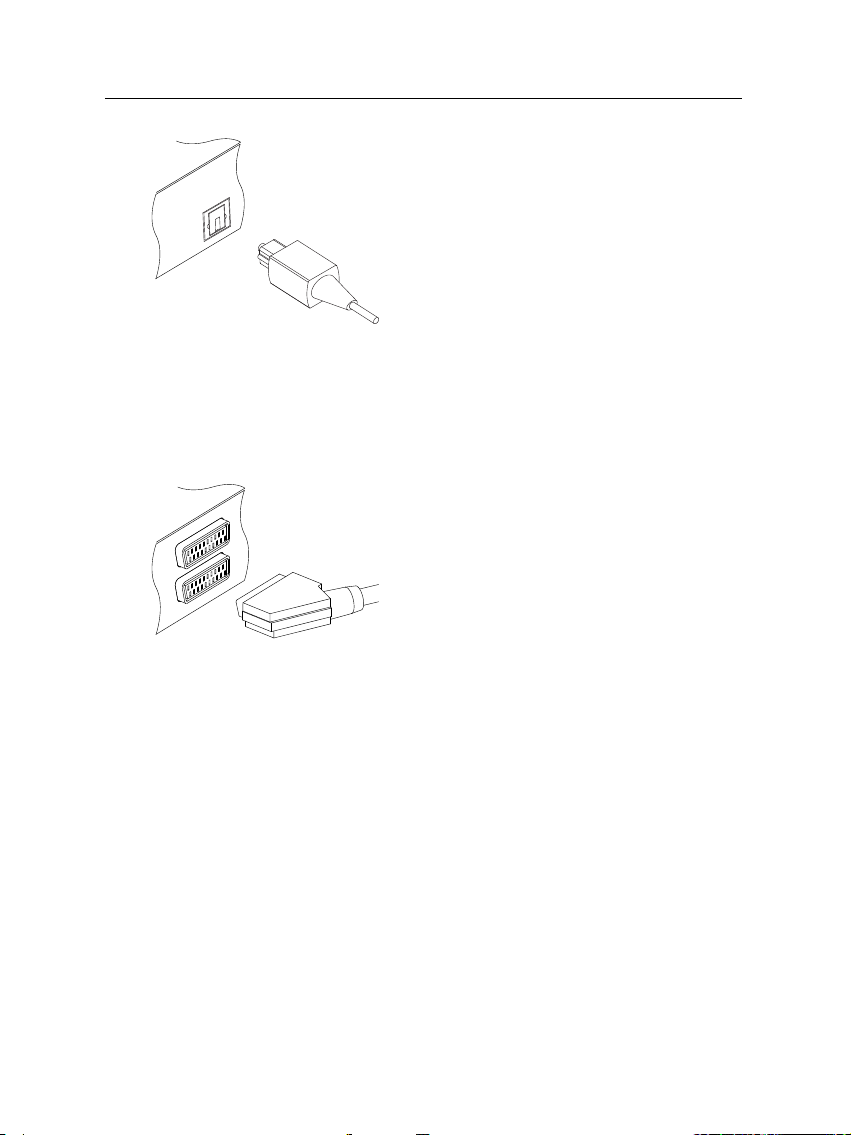
2.5 Switching on for the first time 15
To enjoy Dolby digital audio, your television or audio system must be able to decode
Dolby digital audio, and you will need to obtain a S/PDIF cable. Plug one end of the
cable into the S/PIDF socket on the digital
receiver, and the other end into the matching
socket on your audio system.
2.4.3 Connecting to your video cassette recorder
The digital receiver can also output video to another appliance
such as a video cassette recorder or video receiver through an
auxiliary SCART connector.
You will need to obtain a SCART cable to use
the auxiliary SCART connector. Plug one end
of the cable into the VCR socket on the digital
receiver, and the other end into the matching socket on your video cassette recorder or
suchlike.
2.5 Switching on for the first time
Now that you have your digital receiver connected, you should
plug it in to a mains socket. Ensure that your television set is
turned on, so that you will be able to see the display from the
digital receiver.
2.5.1 Inserting batteries in the remote control
To insert the batteries, open the battery compartment by removing the lid, and then insert the batteries observing the polarity,
which is marked on the base of the battery compartment.
If the digital receiver no longer reacts properly to remote control commands, the batteries may be flat. Be sure to remove
Page 22

16 Setup
used batteries. The manufacturer accepts no liability for the
damage resulting from leaking batteries.
NOTE
Batteries, including those which contain no heavy metals, may
not be disposed of with household waste. Please dispose of
used batteries in an environmentally sound manner. Find out
about the legal regulations which apply in your area.
2.5.2 Powering on and checking picture
Now, press the button in top left corner on the remote
control.
If you do not see a picture, check that the television is set to the
correct input.
If the picture is good, you can skip to§4.1 to search for the
available television and radio services. Otherwise, you may
need to temporarily connect the composite video connector
(VIDEO) to your television set so that you can see the on-screen
menus in order to configure the video settings.
Page 23
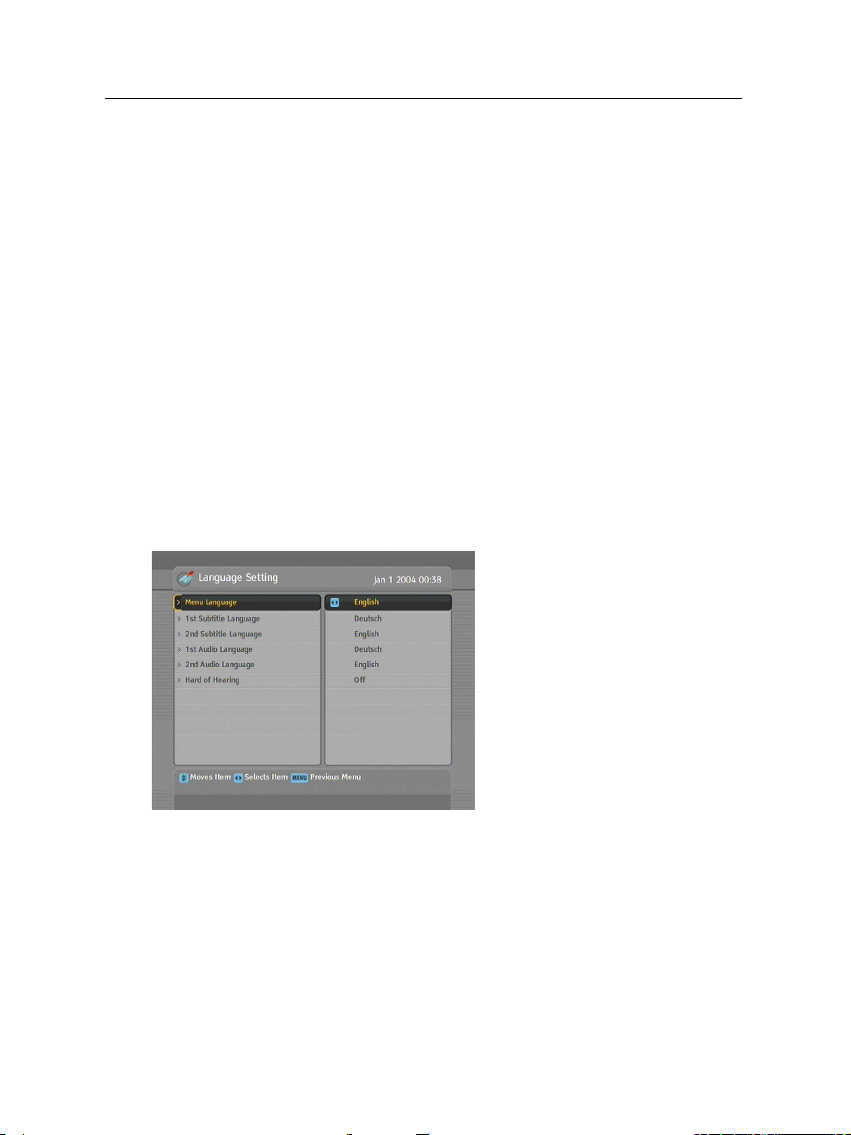
3.1 Language settings
17
Chapter 3
Preference Settings
You can select the language in
which the menu would be displayed. In addition to that, you
can select which language of audio track and of subtitle track
should be output.
Select the System Setting>Language Setting menu. You should
see a screen like the left figure.
Menu language
The digital receiver supports many menu languages: Dutch,
English, German, French, Italian, Russian, Turkish and so forth.
Set the Menu Language option to your desired language. Once
you select a language, the menu will be immediately displayed
in the selected language.
Page 24

18 Preference Settings
Subtitle language
Set the 1st Subtitle Language option and the 2nd Subtitle Language option to your desired languages. When you watch a
programme, if the programme has a subtitle track of the language that is designated for the 1st Subtitle Language, it will be
displayed. If the first language is not available but the second
language is available, the subtitle of the second language will
be displayed. If there is not any available language, no subtitle
will be displayed.
Apart from this setting, you can select a subtitle track with the
Some broadcaster may send a subtitle track dedicated to persons who have difficulty in hearing. Even when one or more
subtitle tracks are available, that subtitle track will be displayed
prior to those you have designated for the 1st Subtitle Lan-
guage and the 2nd Subtitle Language options if the Hard of
hearing option is set to On.
Audio language
Set the 1st Audio Language option and the 2nd Audio Language option to your desired languages. When you watch a
programme, if the programme has an audio track of the language that is designated for the 1st Audio Language, it will
be output. If the first language is not available but the second
language is available, the audio of the second language will be
output.
Apart from this setting, you can select an audio track with the
button. See § 5.2.5 for detailed description.
button. See § 5.2.4 for detailed description.
Page 25

3.2 Video and audio settings
3.2.1 Television standard
The digital receiver supports two television standards. One
is PAL standard, and the other is NTSC standard. PAL was
adopted in European countries while NTSC is adopted in USA,
Canada, Mexico and so forth.
If you have a PAL television, you have to set the TV Type
option to PAL. In that case, if you switch to a service of the
NTSC standard, the digital receiver will presents the pictures
converting into the PAL standard. However, it is inevitable to
lose a little picture quality. Likewise, the contrary case brings
about the same result.
The best thing is to watch PAL services with a PAL television
and to watch NTSC services with a NTSC television. However,
a multi television set is able to process both of them. So if
you have a multi television set, you had better set the TV Type
option to Multi. Then the digital receiver will present pictures
without standard conversion.
3.2 Video and audio settings 19
You have to configure the video
and audio settings appropriately
to your television set and other
appliances.
Select the System Setting
A/V Output Setting menu. You
should see a screen like the left
figure.
>
3.2.2 Colour model
Through the TV SCART connector, the digital receiver is able
to output video in various colour models. If you have the
Page 26

20 Preference Settings
digital receiver linked to your television via this connector, you
should set the SCART Output option to your desired colour
model. If you have connected via the RCA connector labeled
VIDEO on the back panel, you do not have to set this option
because the digital receiver outputs CVBS video through the
RCA connector independent of the SCART connector.
However, if you have connected via the S-VIDEO connector,
you have to set this option to S-Video because the output
through S-Video connector comes from the SCART interface.
It is known in general that the RGB colour model provides the
best video quality with little difference from the YUV colour
model but the CVBS colour model does the least. So RGB
would be most desirable for this option.
3.2.3 Video cassette recorder
You can have the digital receiver linked to your video cassette
recorder or such an appliance via the VCR SCART connector. In
that case, the digital receiver will operate differently depending
on the setting of the VCR Scart Type option. If the option is
set to Standard, the digital receiver will pass the video from
the video cassette recorder to your television when it starts
playback. But if the option is set to External A/V, the digital
receiver will not pass the video automatically. To pass it, you
have to press the
AUX
button.
NOTE
It is impossible for the digital receiver to record the video that
the video recorder plays back because the digital receiver is
just a bypass for the video recorder.
3.2.4 Television aspect ratio
If you have a wide-screen television, set the TV Aspect Ratio
option to 16:9.
Page 27

3.2 Video and audio settings 21
You can enjoy well both wide-screen programmes and normalscreen programmes with your wide-screen television as the
above figures show. To watch normal-screen programmes in
full screen like the left figure, set the 4:3 Display Format option
to Full. Normal-screen pictures then will be inflated to fit to
the width of the wide screen. Otherwise, to watch them in the
original ratio like the right figure, set it to Center.
Otherwise, if you have a normal-screen television, set the TV
Aspect Ratio option to 4:3.
You cannot fully enjoy wide-screen programmes with your
normal-screen television as the above figures show. The left
figure shows a normal picture displayed in the normal screen.
To watch wide-screen programmes in the shape like the centre
figure, set the 16:9 Display Format option to Letter Box. Wide-
screen pictures then will be reduced to fit to the width of the
normal screen. Otherwise, to watch them in the shape like the
right figure, set it to Center extract. Wide-screen pictures then
will be cut out on the left and right sides equally to fit to the
width of the normal screen.
Page 28

22 Preference Settings
3.2.5 High definition television
The digital receiver supports various video resolutions from
576 to 1080. In general a resolution of 720 or more is considered
high definition. The higher the resolution is, the better quality
you can enjoy. However, if your television set does not support high definition, you cannot enjoy high definition quality
picture.
Set the HDMI Output option as you desire. The available values
for this option are changed according to the TV Type option.
If you set this option to 576P, the digital receiver will present
even high definition programmes in resolution of 576. On the
contrary, if you set it to 1080I, the digital receiver will present
even standard definition programmes in resolution of 1080.
NOTE
You can enjoy only standard definition video with the following
connectors:
• Composite video connector (VIDEO)
• S-Video connector (S-VIDEO)
• SCART connector (TV)
3.2.6 Video scaling
By adjusting the Video Output Scaling option, you can inflate
or shrink pictures from−20 to+20 percent so that they could
fit tight to the frame of your television without black space.
3.2.7 Audio mode
Basically, there are two audio sources as you can find two audio
sockets on the back panel of the digital receiver. You can enjoy
only one source or both of them in either stereo or mono. Set
the Sound Mode option as you desire.
Apart from this setting, you can change the sound mode with
the button. See § 5.2.4 for detailed description.
Page 29

3.3 Local time setting
You should set your local time for timer events.
1.
Set the Mode option to Auto; then the Time Offset option
becomes enabled.
2.
Set the Time Offset option to the time difference between
your time zone and GMT referring to Table 3.1.
3.
Make sure that your local time is correctly displayed on
the Local Time option.
3.3 Local time setting 23
Select the System Setting>Time
Setting menu. You should see a
screen like the left figure.
You can set the clock manually
or use the time signal, Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), carried
as part of the digital television
broadcast.
To use Greenwich Mean Time,
take the following steps:
To set the local time yourself, set the Mode option to Manual and
enter your local time to the Local Time option with the numeric
buttons. The time format is day/month/year 24-hour:minute.
If daylight saving time is observed in your state at the moment,
set the Daylight Saving Time option to On.
NOTE
Daylight saving time adds one hour to the time when the option is set to On. When setting the time offset from Greenwich
Mean Time, make sure that time offset does not include daylight saving time.
Page 30

24 Preference Settings
Table 3.1: Time offset table
Time offset City
GMT − 12:00 Eniwetok, Kwajalein
GMT − 11:00 Midway Island, Samoa
GMT − 10:00 Hawaii
GMT − 09:00 Alaska
GMT − 08:00 Pacific Time US, Canada
GMT − 07:00 Mountain Time US, Canada
GMT − 06:00 Central Time US, Canada, Mexico City
GMT − 05:00 Eastern Time US, Canada, Bogota, Lima
GMT − 04:00 Atlantic Time Canada, La Paz
GMT − 03:30 Newfoundland
GMT − 03:00 Brazil, Georgetown, Buenos Aries
GMT − 02:00 Mid-Atlantic
GMT − 01:00 Azores, Cape Verde Islands
GMT London, Lisbon, Casablanca
GMT + 1:00 Paris, Brussels, Copenhagen, Madrid
GMT + 2:00 South Africa, Kaliningrad
GMT + 3:00 Baghdad, Riyadh, Moscow, St. Petersburg
GMT + 3:30 Tehran
GMT + 4:00 Abu Dhabi, Muscat, Baku, Tbilisi
GMT + 4:30 Kabul
GMT + 5:00 Ekaterinburg, Islamabad, Karachi, Tashkent
GMT + 5:30 Bombay, Calcutta, Madras, New Delhi
GMT + 6:00 Almaty, Dhaka, Colombo
GMT + 7:00 Bangkok, Hanoi, Jakarta
GMT + 8:00 Beijing, Perth, Singapore, Hong Kong
GMT + 9:00 Tokyo, Seoul, Osaka, Sapporo, Yakutsk
GMT + 9:30 Adelaide, Darwin
GMT + 10:00 Eastern Australia, Guam, Vladivostok
GMT + 11:00 Magadan, Solomon Islands, New Caledonia
GMT + 12:00 Fiji, Auckland, Wellington, Kamchatka
3.4 Parental control
In general, television programmes are classified according to
the level of violence, nudity and language of their content.
When you are watching a programme, you can check its programme classification on the information box. For the information box, see § 5.2.3.
You can prevent your children from watching specific programmes by specifying a programme classification.
Page 31

3.4 Parental control 25
Select the System Setting
Parental Control menu. You
should see a screen like the
left figure, and you will be
asked your Personal Identification Number (PIN). The number
is initially set to ‘0000’.
If you wish to block 15 or above rated programmes, set the
Censorship option to 15 (age). Setting it to No block blocks no
programme; on the other hand, setting it to Total block blocks
every programme.
NOTE
If a programme does not have any programme classification
information, your censorship setting will not take effect.
If anyone is trying to watch a programme that is of or above
the censorship setting, the person has to enter the personal
identification number to override.
To change the number, select the Change PIN Code menu; then
an input box appears. You have to enter a desired number
twice for confirmation.
You can also restrict uses of some menus. Selecting the Access
Control menu displays a list of menus that you can lock. If the
Time Setting item is set to Locked, you have to enter the per-
sonal identification number when accessing the Time Setting
menu. If you enter a wrong number, you cannot use the menu.
To release a shut item, set it to Unlocked.
>
Page 32

26 Preference Settings
3.5 Adjusting the on-screen display
You can adjust the transparency level of the on-screen display.
Select the System Setting menu and set the OSD Transparency
option as you desire. Its available range is from 0 to 50 percent.
You can adjust the display time of the information box. For
the information box, see§5.2.3. To adjust its display time,
select the System Setting menu and set the Info Box Display
Time option as you desire. Its available range is from 1 to 30
seconds. If you set this option to No Info Box, the information
box will not be displayed when you switch services. However,
pressing the button will display the information box. If you
set this option to Never Hide, the information box will always
be displayed.
In addition, you can raise or lower the position of the information box. Select the System Setting menu and set the Info Box
Position option as you desire. Its available range is from−10
to+3 lines. The more high you set the option, the more low
the information box will be positioned.
3.6 To turn on the time shift feature
Time shift means that the most recent hour of the television service you are watching gets saved temporarily on the hard disk
of the digital receiver. When this feature is enabled, you can
reverse and pause live television as if playing back a recording.
To enable this feature, select the System Setting menu and then
set the Time Shifting option to Enable. See§5.5 for how to use
this feature.
Page 33

After connecting up the digital receiver, you will need to perform a service search.
4.1 Searching broadcasting services
27
Chapter 4
Service Search
To perform service search, select
the Installation>Service Search
menu. You should see a screen
like the left figure.
You should set the Search Mode option to Auto at the first
service search after installing the digital receiver. The digital
receiver will search all available services with the automatic
search mode within the frequency range from the frequency
of the Start Frequency option to the frequency of the End Fre-
Page 34

28 Service Search
quency option. Symbol Rate stands for data transfer rate, and
QAM is a form of modulation used in digital broadcasting.
Broadcasting operators send their services in a symbol rate by
a modulation method. Perhaps you do not have to specify the
Symbol Rate and QAM Mode options since they are seldom
changed. However, you should set the QAM Mode option to
Auto for more certainty. You can specify the Start Frequency,
End Frequency and Symbol Rate options with the numeric
buttons if you want to change them.
If the digital receiver have failed to find every service you want
in a service search, you should set the Search Mode option to
Network. With this option, the digital receiver will check up
the up-to-date channel information as searching services, but it
takes rather longer time.
To search only one frequency, set the Search Mode option to
Manual and specify your desired frequency at the Frequency
option with the numeric buttons. In this case, you had better
set the Network Search option to On.
It is most recommended that you should set the Search Mode
option to Quick Scan. With this option, you can search every
service rather quickly.
You can search pay services as well as free services as follows:
•
To searchonly free services, set the FTA/Scrambled option
to FTA only.
• To search only pay services, set it to CAS only.
•
To search both free services and pay services, set it to FTA
+ CAS.
To start service search, select the Start Search item; then a list
box appears, in which found services will be listed. When it has
completed, press the
at any time or to exit without saving, press the
OK
button to save found services. To stop
EXIT
button.
Page 35

4.2 Resetting to factory settings
The digital receiver maintains the following data:
• Services list
• Favourite list
• Timer list
• Preference settings
You can reset all data of the digital receiver. To do that, select
the Installation>Factory Setting menu, and then you are asked
for confirmation. If you select Yes, service entries, favourite
entries and timer events will all be deleted, and preference
options will be reset to the manufacturer’s factory settings.
NOTE
A factory reset will not delete any recorded programmes.
4.3 Clearing the services list
If you want to delete all services, select Installation>Reset
Service List; then you are asked for confirmation. If you select
Yes, the services list will be cleared.
4.2 Resetting to factory settings 29
NOTE
You cannot undo the services list but you have to perform
service search again.
Page 36

30 Daily Usage
5.1 Volume control
Use the
fortable level. You may need to adjust the volume on your
television set too. To temporarily switch off the sound, press
the button. Press it again to restore the sound to previous
level.
V−
and
Chapter 5
Daily Usage
V+
buttons to alter the volume to a com-
5.2 Watching television
To change services, press the
button switches to the previously viewed service. In
addition, you can switch to your desired service by entering its
service number with the numeric buttons. You can also select a
service to watch in the services list.
5.2.1 The services list
To view the services list, press the
P+
or
OK
P−
button. Pressing the
button.
Page 37

5.2 Watching television 31
On the services list, you can see
the service information:
• Service number and name
• Transponder information
A dollar sign ($) may be marked on some entries, indicating
pay service. To watch pay services, you need the subscription
card.
To select a desired service, put the highlight bar on its entry
with the
P+
P−
or
button and press the
OK
button; then it will
be presented.
V−
Pressing the
V+
or
button skips over 10 entries up or down.
Entering a service number with the numeric buttons puts the
highlight bar on its entry.
You can switch between the television services list and the
radio services list by pressing the button.
Pressing the button displays the additional options, with
which you can do the following:
•
By setting the Show Provider option to On, you can view
service entries by groups of broadcasters.
•
To change the name of the highlighted service, select the
Rename option; then the on-screen keyboard appears,
with which you can enter a new name. See§6.2 for how
to use the on-screen keyboard.
•
You can prevent other family members from watching the
highlighted service by setting the Lock option to Locked.
Page 38

32 Daily Usage
You have to enter your personal identification number to
watch or unlock it.
•
To add the highlighted service into a favourite group,
select the Add to Fav option; then the favourite groups
will be displayed. Put the highlight bar on a desired
group and press the
5.2.2 The favourite services list
You can select a service to watch on a favourite list as well as
on the services list.
OK
button.
To display the favourite lists,
press the
FAV
button. You
should see a screen like the left
figure. As you move the highlight bar up or down on the
favourite group list at the left
box, favourite services belonging to the highlighted group are
listed on the right box.
For how to edit the favourite lists, refer to § 6.1.
To select a favourite service, put the hightlight bar on a desired
group and press the
favourite services list. Once you select a desired service with
OK
the
button, it will be presented. Otherwise, to select other
group, press the
After you have selected a favourite service, if you then switch
to another service using the
V−
V+
button; a highlight bar appears on its
button.
P+
P−
or
button, it will be also
another favourite service of the selected group. The digital
receiver will remind you what group you have selected by
displaying its name at the top right of the screen whenever you
switch services. If you wish to get out of the current group,
select the All services group on the favourite group list.
Page 39

Besides that, you can add or delete a favourite group or service.
To add the service you are currently watching into a favourite
group, put the highlight bar on a desired group and press the
button. To create a new group, press the button; then
the on-screen keyboard appears. Enter your desired name and
save it. See§6.2 for how to use the on-screen keyboard. To
delete a group or a service, press the button; then you get
asked for confirmation. If you select Yes, it will be deleted.
5.2.3 Viewing programme information
Pressing the button displays the information box, on which
you can see all of the following:
5.2 Watching television 33
• Service number and name
• Signal level and quality
• Programme name
• Programme classification symbol
• Programme summary
• Broadcasting time
• Current time
In addition, you might see the following symbols:
•
Subtitle symbol ( ) if subtitle tracks are provided on the
current programme.
•
Teletext symbol ( ) if teletext pages are provided on the
current service.
• Dollar symbol ($) if the current service is a pay service.
•
Multifeed symbol ( ) if the current programme is provided as a multifeed programme. To use this feature,
refer to § 5.4.
Page 40

34 Daily Usage
If the electronic programme guide is provided on the current
service, you can see the information about the current and next
programmes with the
volume in this case, hold down the
sound bar appears and reaches your desired level.
Pressing the button once more displays detailed information
about the current programme. To hide the information box,
press the
EXIT
5.2.4 Selecting audio tracks
Some programmes are provided with audio tacks in one or
more languages. Pressing the button displays available audio tracks. Once you select an audio track, it will be sounded.
In addition, you can enjoy audio tracks in four sound modes:
Stereo, Mono, Left or Right. However, if a multifeed programme is provided at the moment, video tracks will be displayed. In this case, you have to press the button once more
to select an audio track.
5.2.5 Selecting subtitle tracks
button.
V−
V+
or
button. To adjust the sound
V−
V+
or
button until the
Some programmes are provided with subtitle tracks in one or
more languages. If the current programme provides subtitle
tracks, the subtitle symbol ( ) will be marked on the information box. Pressing the button displays available subtitle
tracks. Once you select a subtitle track, it will be displayed.
5.2.6 Viewing teletext
On some services, such information as weather reports, news
or stock quotations is provided by means of teletext. If the
current service provides teletext, the teletext symbol ( ) will
be displayed on the information box. Press the button to
view teletext pages.
Select a desired page to view by entering its page number with
the numeric buttons. You can zoom into a teletext page with
Page 41

5.3 Viewing electronic programme guide 35
the button, and adjust its transparency level with the
button. To hide the teletext screen, press the
5.3 Viewing electronic programme guide
The Electronic Programme Guide shows the current and scheduled programmes that are or will be available on each service
with a short summary for each programme.
Pressing the
plays the electronic programme
guide, on which you can see the
following:
• Scheduled programmes
• programme summary
• Broadcasting date
• Broadcasting time
To see detailed information of a desired programme, put the
highlight bar on your choice with the
press the button. To switch to another service, press the
V+
or
button. You can travel over previous days with the
button, and can travel over next days with the button.
To see the programme guide for radio broadcasts, press the
button. To switch it back, press the button again.
Pressing the button displays the programme guide in the
form of a spreadsheet. To switch it back, press the button
again.
You can make a timer recording on the electronic programme
guide. See § 7.1.3 for detailed description.
P+
or
EXIT
GUIDE
P−
button.
button dis-
button and
V−
Page 42

36 Daily Usage
5.4 Watching multifeed programme
Some broadcasts such as sports channels can provide a variety
of perspectives on a programme at a same time. We call it a
multifeed programme. You can select and watch a perspective
you prefer.
If a multifeed programme is provided on the current service,
the multifeed symbol ( ) will be marked on the information
box. Press the button, then available video tracks will be
listed. Once you select one, it will be presented. At this time,
you have to press the button once more to select audio
tracks.
5.5 Using time shift
You can pause and resume a live television programme, and
even rewind and replay it. When you are watching a programme and you miss something, you can rewind and replay
it. Or when your attention is needed elsewhere, you can pause
it and resume it a short time later without losing any of it.
When you do this, you are no
longer watching the live programme, instead you are watching a delayed presentation of it.
This is called time shifted television. Then, you can skip commercials until you catch up to the
live broadcast.
In order to use the time shift
feature, the Time Shifting option
must be set to Enable. See§3.6.
When enabled, the digital receiver will keep as much as one
hour recording buffer of current service by utilizing the hard
disk drive storage. The buffer will reset each time you change
to another service.
Page 43

5.5 Using time shift 37
With time shift enabled, the following operations are possible:
•
To go back in time, hold down the button; to go
forward, hold down the button. The progress bar is
displayed momentarily with a preview window.
• You can navigate using the progress bar, refer to § 7.3.1.
•
You can jump forward 30 seconds at a time by pressing
the button.
•
You can jump backward 20 seconds at a time by pressing
the button.
•
You can change playback speed. For slow motion see
§ 7.3.2. For fast motion see § 7.3.3.
•
To check your current position in time shift, press the
button. The time difference compared to live programme is displayed momentarily in top right corner of
screen. A value of−02:00 means two minutes behind
live programme.
• To make a recording of what is in time shift, see § 7.1.4.
•
To end time shift, press the button. The live programme will be presented.
When time shift option is disabled and pause is kept for more
than 10 seconds, the time shift feature will be switched on to
stop you loosing part of the programme. In such case it will
remain enabled until you change services.
Page 44

38 Daily Usage
5.6 Using picture in picture
1.
Press the button to display a sub-picture, on which
another service will be presented.
2.
Pressing the button once more minifies the subpicture, and pressing it once again hides the sub-picture.
3.
To display the services list for the sub-picture, press the
button.
You can watch two services
at the same time with one of
them presented in a sub-picture.
We call this feature picture-in-
picture.
The instructions on how to use
the picture-in-picture feature are
as follows:
NOTE
When a recording is in progress, the available services in
the services list may be limited.
4.
Pressing the button moves the sub-picture counterclockwise, and pressing the button moves it clock-
wise.
5.
Pressing the
sub-picture. Even when you play back a recording, you
can watch a live programme in the sub-picture. However,
you cannot swap the pictures in that case.
6.
If both pictures are pay services, only the main-picture
will be presented.
SAT
button swaps the main picture with the
Page 45

6.1 Editing the favourite list
You can make your own favourite services list. In fact, you can
define multiple favourite services lists, each being a ‘group’ of
chosen services.
39
Chapter 6
Listing Services
Select the Organizing Favorites
menu. You should see a screen
like the left figure.
There are three columns:
• Group list (left)
• Favourite list (centre)
• Services list (right)
The services list contains all available services, whereas the
favourite list contains only chosen services that have been
added to the highlighted group. As you move the highlight
bar up or down on the group list, favourite services belonging
to the highlighted group get shown in the favourite list.
Page 46

40 Listing Services
You can add up to 30 groups. To add a group, select the NEW
option in the group list; then the on-screen keyboard appears.
See § 6.2 for how to use the on-screen keyboard.
To rename a group, put the highlight bar on the group entry you
want and press the button; then the on-screen keyboard
appears. See § 6.2 for how to use the on-screen keyboard.
To delete a group, put the highlight bar on the group entry you
want and press the button; then a message box appears
asking you for confirmation. If you select Yes, it will be deleted.
You can add a favourite service to a group by taking the following steps:
1.
Put the highlight bar on a desired group entry in the
group list and press the
OK
button to select it. The high-
light bar then moves to the services list.
2.
To add a service to the selected group, put the highlight
bar on a desired service entry and press the
OK
button.
The selected service entry gets added to the favourite list.
Repeat this step to add more entries.
3. Press the button and the highlight bar get moved to
the favourite list. You can delete a favourite entry with
OK
the
button.
4.
To select another group, press the button again. By
pressing the button, the highlight bar gets moved to
each column.
To add radio services, press the button; then radio service
entries get listed in the services list. To recall the television
services list after adding radio services, press the button
again.
With your favourite services list, you can select your favourite
services more easily. Refer to § 5.2.2 for detailed description.
Page 47

6.2 How to use on-screen keyboard
6.2 How to use on-screen keyboard 41
To delete a letter, put the cursor to the right of the desired letter
on the input line and then select the Del key. You must select
the Save key to complete naming; otherwise, if you press the
EXIT
button, it will not be named.
6.3 Transferring receiver data
The digital receiver retains the following data:
• Services list
• Favourite lists
• Preference settings
You can move the highlight key
horizontally with the
V+
buttons and vertically with
P+
the
ing the
ters its letter in the input line. To
type a space, select the Space
key. To type lower case letters or
numerals, select the Other key.
P−
and
OK
button on a key en-
V−
and
buttons. Press-
It is possible to transfer the receiver data from the digital receiver to another same digital receiver by connecting them with
a RS-232 cable. To have the receiver data transferred, perform
the following steps:
Page 48

42 Listing Services
1.
Plug one end of a RS-232 cable (9 pin Dsub cable) into the RS-232 port on the digital receiver, and the other end into the
matching port on the other digital receiver.
2. Turn on the source digital receiver.
3.
Select the Installation>Transfer Firmware
>
Transfer Data to Other IRD menu, then
you get asked for confirmation; select Yes.
4.
To start the data transfer, turn on the target
digital receiver.
5.
A progress bar appears showing the
progress of the data transfer.
6.
Restart the target digital receiver when the
data transfer is complete.
Page 49

43
Chapter 7
Recording and Playing
You can record two different services while watching another if
two of the services are provided through the same transponder
The TF 500 PVRc digital receiver has two tuners so that you can
enjoy the following:
•
While playing a recording back, you can watch a service
in the sub-picture using the picture-in-picture feature.
•
You can record two different services while playing back
a previously recorded programme.
•
You can record two different services while watching one
of them using the time shift feature. See§5.5 for the time
shift feature.
•
You can even record two different services while watching two other different services—only if two or more
services are provided in a same transponder and the
other services are provided in another same transponder.
In this case you can watch two services at the same time
using the picture-in-picture feature. See§5.6 for the
picture-in-picture feature.
Page 50

44 Recording and Playing
7.1 Recording a programme
Once recording has started, a symbol like the left
figure will be displayed at the top right of the screen
for a few seconds. When you are watching a service different
from the service being recorded, you can view a number on
the centre of the symbol, which indicates the order that the
recording is started.
To record two programs simultaneously, two tuners are allocated for the recording. Therefore, you can only change to a
limited number of services while the two programs are being
recorded.
CAUTION
Do not move the digital receiver nor pull out the plug while
it is running. It may cause damage to recorded programmes.
Note that Topfield is not responsible for damages inflicted
on files that are stored on the hard disk drive.
NOTE
When a recording is complete, it might not be saved if its
recording duration is less than one minute.
7.1.1 Instant recording
To instantly record the programme you are watching at present,
press the button. Pressing the button will not pause
the current recording like it does with a video cassette recorder.
Page 51

7.1 Recording a programme 45
Pressing the button will
pause the live show and begin
time shifting within the current
recording even with the Time
Shifting option disabled. However, it is still possible to pause
a recording. After a recording
is started, pressing the button displays a menu like the left
figure, in which you can set the
recording duration.
To specify an arbitrary recording duration, set the Duration
option as you desire with the
OK
the
button; the recording will end at the specified time.
V−
and
V+
buttons and press
If the information about the next programme is provided by
the electronic programme guide, the After this program and
After next program options will be available. Once the After
this program option is selected, the current recording will stop
when the current programme is scheduled to end. Likewise,
once the After next program option is selected, the current
recording will stop when the next programme is scheduled to
end.
Selecting the Record pause option pauses recording. When
you press the button again, you will see this option is
changed to Record continue. To resume recording, select it.
Page 52

46 Recording and Playing
To additionally record another service, switch to the service
you want to record, and press the button.
Once a recording is started, it is put on the recorded programme
list even though it is not finished yet. The recording file is
named after its service name with a suffix of a number. To
view the recorded programme list, press the button or
alternatively select the File List menu. See§7.2 for detailed
description about the recorded programme list.
7.1.2 Timer recording
To stop recording, press the
button; then a box like
the left figure appears, which
shows programmes currently being recorded. If you select one,
its recording will stop.
While a recording is going on,
you can watch or record another
service.
You can set a service to be recorded at a specific time. Even
if the digital receiver is in standby mode, it will switch into
operation mode and start recording at a specified time. When
the recording comes to the end, the digital receiver will switch
back into standby mode again in one minute. However, if
you press any button on the remote control or on the front
panel even just one time, the digital receiver will not switch
into standby mode.
Page 53

7.1 Recording a programme 47
To input a timer recording, select
the Timer Setting menu; then the
timer list will be displayed.
To add a new timer event, press
the button, and a box like
the left figure appears. Take the
following steps:
1.
Set the Record option to On to make a recording. If this
option is set to Off, the digital receiver will turn on at the
specified time but not record; instead, you may record
with your video cassette recorder or suchlike in this case.
2.
If you want a radio programme, set the Type option to
Radio; otherwise, set it to TV.
3.
Set the Service option to the service which provides the
programme you want. Pressing the
OK
button on this
option displays a services list, from which you can select
your desired service.
4. There are five timer modes:
One Time means literally ‘one time’.
Every Day means literally ‘every day’.
Every Weekend
means ‘Saturday and Sunday every
week’.
Weekly means ‘one day every week’.
Every Weekday
means ‘from Monday to Friday every
week’.
If your favourite programme is broadcasted at weekends
and you wish to record every episode of the programme,
set the Mode option to Every Weekend.
Page 54

48 Recording and Playing
5.
6.
7.
8.
You can also edit or delete timer events in the timer list.
To edit a timer entry, put the highlight bar on the entry you
want and press
can change its settings in the same manner as making a new
one.
To delete a timer event, put the highlight bar on the entry you
want to remove and press the button; then you are asked
for confirmation. If you select Yes, it will be deleted.
Set the Date option to a desired date, on which the digital
receiver will turn on. The date format is day/month/year-
day of the week.
Set the Start Time option to a desired time, at which the
recording will be started. The time format is hour:minute.
Set the Duration option to a desired time, in which the
recording will be finished.
Pressing the
OK
button on the File Name option displays
the on-screen keyboard, with which you can specify a
file name for the timer recording. If you do not specify
anything, it will be named after the service name. See
§ 6.2 for how to use the on-screen keyboard.
To set a timer recording with the above settings, select
the OK option; otherwise, it will not be saved and will
not occur.
OK
button; then appears a box in which you
Page 55

7.1 Recording a programme 49
7.1.3 Scheduling recordings using the programme guide
If the electronic programme
guide is properly provided, you
can make timer events on it. The
instructions on how to make
timer recordings using the electronic programme guide are as
follows:
buttons.
GUIDE
button to display the electronic pro-
1.
Press the
gramme guide.
2.
Select a service you want to record with the
buttons.
3.
Select a programme you want to record with the
P−
4.
To make a timer event without recording, press the
button; the letterPis displayed. To make a timer event
with recording, press it once more or alternatively press
the button; then the letter R is displayed.
V−
and
P+
and
V+
OK
5.
This timer event is placed on the timer list. To change
its settings, press the button to show a box in which
you can edit. Refer to § 7.1.2 for detailed description.
6. Pressing the
OK
button once more will cancel the timer.
7.1.4 Recording a time-shifted programme
See§5.5 for detailed description about the time shift feature.
While watching a programme with time shift, you can record it
by performing the following steps:
Page 56

50 Recording and Playing
1. Press the button to display the progress bar.
2.
To move to the beginning of the desired scene, hold down
the or button until it is reached.
3.
Press the button to start recording. The time shift
buffer from that position onwards will now be recorded.
4. Press the button to stop time shift.
5. Press the button once more to stop recording.
7.1.5 Recording a pay service programme
You can record a pay service programme without the subscription card. However, you need the subscription card to play
it back because it has not been descrambled. So it is recommended to record pay service programmes with the subscription card so that they can be recorded in descrambled form. In
that case you can enjoy them without the subscription card like
free service ones.
To record a programme of a pay service in descrambled form,
perform the following steps:
1. Select a programme of a pay service you want to record.
2.
Make sure that the subscription card is inserted in the
slot on the front of the digital receiver.
3. Start recording.
4.
Do not switch to other service nor use time shift until it
is finished.
NOTE
If you switch to other service or use time shift in the middle
of recording a pay programme, it will be recorded without
descrambling from that moment. Even if the recording is only
partially descrambled, you need the subscription card to play
it back.
Page 57

7.2 File archive
When a programme is recorded, it is stored as a file on the
built-in hard disk drive of the digital receiver. You can select a
recording to play back from the recorded programme list.
You can play, move, delete, rename and lock a recording file.
You can also sort the recording files by file name, playing duration or file size. In addition, you can make a new folder.
7.2.1 To delete a recording
7.2 File archive 51
Select the File List menu or alternatively press the button to
display the recorded programme
list. The file information is comprised of the following elements:
file number, file name, recording
time, playing duration, file size
and so on.
To delete a recording, put the highlight bar on it and press the
button; then you are asked for confirmation. If you select
Yes, it will be deleted.
7.2.2 To sort recordings
To sort the recordings, perform the following steps:
1. Press the button to display the additional options.
2.
Set the Sorting option to Alphabetic, Time or Size as you
want.
3. Press the
4. They are sorted by the specified option.
EXIT
button.
Page 58

52 Recording and Playing
7.2.3 To lock a recording
To lock a recording so that other people cannot play it, perform
the following steps:
1. Put the highlight bar on a desired recording.
2. Press the button to display the additional options.
3. Set the Lock option to Locked.
4. Press the
5. The lock symbol ( ) is displayed on it.
If you select a locked recording to play it back, you will be
asked for your personal identification number.
7.2.4 To rename a recording
To change the name of a recording, perform the following steps:
1. Put the highlight bar on a desired recording.
2. Press the button to display the additional options.
EXIT
button.
3.
Select the Rename option, and the on-screen keyboard
appears. Change the name and save it. See§6.2 for how
to use the on-screen keyboard.
7.2.5 To make a new folder
To make a new folder, press the button; then a new folder
named GROUP # is created. You can change its name in the
same manner as renaming a recording. See above.
7.2.6 To move a recording to another folder
To move a recording to another folder, put the highlight bar on
a desired recording and press the button; then the folders
are listed. Once you choose a folder, the recording is moved to
it.
Page 59

7.3 Playing back a recording
When a programme is recorded, its additional contents such as
audio tracks or teletext are also recorded together. So you can
enjoy them while playing back a recording.
The instructions on how to play a recording are as follows:
1.
Select the File List menu or alternatively press the
button to display the list of recorded programmes.
2. Put the highlight bar on a desired recording.
3. Press the
4. To stop playback, press the button.
During a playback, you can enjoy the following tricks:
•
To see the detailed information about the currently played
recording, press the button; then the information box
appears and shows its file name, playing duration, programme information, and so on.
•
To pause playback, press the button. To resume it,
press the button.
OK
7.3 Playing back a recording 53
button to start playback.
•
To go forward, hold down the button; to go back-
ward, hold down the button.
•
To display the progress bar, press the button; to hide
it, press the button again.
•
when the progress bar is hidden, you can move to a desired scene by entering the percentage with the numeric
buttons
7.3.1 To navigate using the progress bar
First press the button to display the progress bar, then:
Page 60

54 Recording and Playing
•
To go forward, hold down the button; to go back-
ward, hold down the button.
• To bookmark a position, refer to § 7.3.4.
•
If there are no bookmarks, you can jump forward 30
seconds at a time by pressing the button.
•
To jump back to beginning of recording, press the
button.
• To jump to end of recording, press the button.
• To hide the progress bar, press the button again.
7.3.2 To play in slow motion
To watch in slow motion during a playback, press the
button. If you press it repeatedly, the playback speed changes
in 3 steps: 1/2, 1/4 and 1/8 times. To resume normal speed,
press the button.
7.3.3 To play in fast motion
To watch in fast motion during a playback, press the button. If you press it repeatedly, the playback speed changes in 3
steps: 2, 4 and 6 times. To resume normal speed, press the
button.
You can play not only forward but also backward in fast motion. To play backward, press the button. If you press it
repeatedly, the playback speed changes in 3 steps: 1, 2 and 3
times. To resume normal speed, press the button.
Page 61

7.3.4 To make a bookmark
1. Press the button to display the progress bar.
2.
To add a bookmark, press the button at a desired
scene; then you will see a small dot appear above the
progress bar like in the picture above.
3.
To jump forward to next bookmark, press the button.
4.
To jump to first bookmark, press the button then the
button.
7.3 Playing back a recording 55
You can mark favourite parts
of a recording by creating bookmarks, and then jump to them.
You can have up to 64 bookmarks. Bookmarks are stored
with the recording so that you
can use them again afterwards.
To make bookmarks, perform
the following steps during playback:
5.
To delete a bookmark, jump to it and then press the
button.
7.3.5 To play back a recording repeatedly
You can play back a recording repeatedly both in whole and in
part.
To play back in whole, press the button when the progress
bar is hidden; then the repetition symbol ( ) is displayed on
the information box. To cancel it, press the button again.
To play back in part, perform the following steps:
1. Press the button to display the progress bar.
Page 62

56 Recording and Playing
2.
Move to the beginning scene of the part you want to play
repeatedly by holding down the or button.
3. Press the button, then the pointer starts to blink.
4. Move to the end scene; the part is marked in purple.
5.
Press the button again, then the part turns green,
and repeated playback starts.
6. To cancel it, press the button when the progress bar
is displayed.
7.3.6 To play back recordings in sequence
You can play several recordings continuously in sequence by
performing the following steps:
1.
Press the button or alternatively select the File List
menu to display the list of recorded programmes.
2.
Select each desired recording with the button. once
a recording is selected, it gets numbered.
3. Press the
OK
button to start playback.
4.
The selected recordings are played in the sequence that
they are numbered.
5.
To jump to start of next selected recording, press the
button to display the progress bar, then press the
button.
7.3.7 To play back a scrambled recording
If you have recorded a programme of a pay service with the
subscription card, you can play it as freely like one of a free
service. Otherwise you need the subscription card to play
it, because it has been recorded without unscrambling even
though it may have been partially descrambled.
Page 63

On the recorded programme list, a purely green$indicates the
recording has been wholly descrambled; on the other hand, a
yellowish green$indicates it has been partially descrambled,
and a purely yellow$indicates it has not been descrambled at
all.
Refer to § 7.1.5 for how to record a pay service programme.
7.4 Copying a recording
You can copy a recording file in whole or in part during a
playback by performing the following steps:
1. Start playback of a recording you want.
2.
Move to a scene from which you want to start copy by
holding down the or button.
3. Press the button, then it will be copied in a new file
which is named after the original recording with a suffix
of ‘COPY’ and a number.
4. To stop copy, press the button.
NOTE
You can make a copy of a long recording more quickly by starting to play the original recording, then pressing button
until the speed has increased to six times, then pressing the
button. The copy will be done at six times normal speed.
7.4 Copying a recording 57
7.5 MP3 playback
You can enjoy music or audio books in MP3 format with the
digital receiver. For how to transfer MP3 files to the digital
receiver from your computer, refer to § 7.6.
To play a MP3 file, perform the following steps:
1.
Press the button and then the or button to
display the MP3 list.
Page 64

58 Recording and Playing
2.
Put the highlight bar on a desired file; if you want to play
several files, select them with the button.
3. Press the
4. To stop playback, press the button.
To play all MP3 files in a subfolder, put the highlight bar on a
desired folder, and press the button.
OK
button to start playback.
7.6 Transferring recording files
You can transfer files between the digital receiver and your
computer via USB connection with Altair, which is a program
used to transfer files. You can download it from the Topfield
website, http://www.i-topfield.com.
To transfer files, take the following steps:
1.
2. Install them on your computer.
3.
Download the Altair programme and the
USB driver from the Topfield website.
Plug one end of a USB cable into the USB
port on the digital receiver, and the other
end into the matching port on your computer.
4. Turn on the digital receiver.
5.
Run Altair, then its screen will appear like
the figure below.
Page 65

7.6 Transferring recording files 59
The instructions on how to use Altair are as follows:
1.
Select files to transfer. The left panel shows files and
folders that are on the digital receiver, while the right
panel shows files and folders that are on your computer.
2.
To transfer files from the digital receiver to your computer, press the right arrow button (→).
3.
To transfer files from your computer to the digital receiver, press the left arrow button (←).
At the top of the panel, you will see a message that says Turbo
Off. Turbo mode is a way of speeding up the transfer of files to
and from the digital receiver. You can click the circle to the left
of the message to turn turbo mode on or off.
Turbo mode makes transferring files faster, but the digital receiver stops responding to commands from the remote control.
If you want to use the digital receiver while transferring, or if
any scheduled recordings are due to start, you should not use
turbo mode.
NOTE
You cannot play back the recordings with a regular MPEG
player on your computer because they are formatted differently from the standard MPEG format.
Page 66

60 Recording and Playing
Visit
http://www.videolan.orgorhttp://www.elecard.com
where you can find a MPEG player able to play them back.
If you wish to author DVDs with them, visit
haenlein-software.com
program able to process them.
7.7 Formatting the hard disk
You can delete all contents stored in the hard disk drive by
formatting it. If you wish to do that, select the Installation
Format Hard Disk menu, then you are asked for confirmation.
If you select Yes, formatting will start.
CAUTION
Formatting the hard disk will delete all files permanently.
NOTE
If a new hard disk drive is installed, it must be formatted
because the file system of the digital receiver is different from
any of the personal computer. You can neither record nor use
time shift with an unformatted hard disk.
http://www.
where you can find a DVD authoring
>
Page 67

61
Chapter 8
Topfield Application Program
If you are good at programming with C++ language, you
can make a program executable to run on the digital receiver.
We call this a Topfield Application program (TAP). In making a TAP, it is recommended to use Diab compiler of Wind
River, whose website address is
Some variants of GCC compiler also might be available as
a compiler for TAPs. You can get the Application program
Interface (API) libraries for TAPs from the Topfield website,
http://www.i-topfield.com.
http://www.windriver.com
.
Your TAPs will be run under the following conditions:
•
Their extension name is tap. If they have any other extension name, they will be ignored.
•
They are in the Program Files folder. If they are in other
folders, they will be ignored.
For how to transfer your program to the digital receiver, refer
to § 7.6.
Page 68

62 Topfield Application Program
To run a TAP in the digital receiver, perform the following
steps:
1.
Press the button and then the or button to
display the program file list.
2. Place the highlight bar on a file entry you want to run.
3. Press the
4. To exit the program, press the
In the program file list, you can use a variety of file control
functions including: renaming, sorting, deleting and so on. For
detailed descriptions about the file control functions, refer to
§ 7.2.
If you want a program to run automatically when the digital
receiver starts up, move the program to the Auto Start folder.
Press the
0
run.
OK
button to start the program.
EXIT
button.
The figure on the left is a running screen of a TAP, Image
Viewer, which displays image
files of BMP, GIF and JPG format. This TAP is available
from the website,
http://www.
i-topfield.com.
button at start-up if you want the program not to
Page 69

Firmware Update
The digital receiver has a stable and convenient firmware to
use. However, a new firmware may be released to improve
the digital receiver. You can get the latest firmware and an
update utility which runs on most versions of Windows from
the Topfield website, http://www.i-topfield.com.
9.1 Checking the firmware information
63
Chapter 9
You have to check the firmware
information of your digital receiver before downloading a
new firmware. Select the Infor-
mation>IRD Status menu. You
should see a screen like the left
figure.
Remember the System ID, and download a firmware with the
same system identification.
Page 70

64 Firmware Update
NOTE
You can only update with firmwares of which system identification is identical to that of yours. Otherwise you will fail in
firmware update.
9.2 From your computer via USB port
You can transfer a new firmware to the digital receiver from
your computer by connecting them with a USB cable. You
need TFDN USB, a firmware transfer utility for this, which is
available from the website, http://www.i-topfield.com.
To update the firmware with this method, perform the following steps:
1.
Download a new firmware applicable to
your digital receiver from the Topfield
website.
2.
Plug one end of a USB cable into the USB
port on the digital receiver, and the other
end into the matching port on your computer.
3. Turn on the digital receiver.
4. Run TFDN USB.
The instructions on how to use TFDN USB are as follows:
1.
Press the Find button to select the
new firmware file.
2.
Press the download button, and then
restart thedigital receiver to start the
file transfer.
3.
A countdown will be displayed on
screen
4.
Restart the digital receiver once
more when the file transfer is complete.
Page 71

9.3 From your computer via RS-232 port 65
9.3 From your computer via RS-232 port
It is possible to transfer a new firmware to the digital receiver
from your computer by connecting them with a RS-232 cable.
You need TFD-Down, a firmware transfer utility for this, which
is available from the website, http://www.i-topfield.com.
To update the firmware with this method, perform the following steps:
1.
Download a new firmware applicable to
your digital receiver from the Topfield
website.
2. Turn off the digital receiver.
3.
Plug one end of a RS-232 cable (9 pin Dsub cable) into the RS-232 port on the digital receiver, and the other end into the
matching port on your computer.
4. Run TFD-Down.
The instructions on how to use TFD-Down are as follows:
1.
Press the Find button to select the new
firmware file.
2.
Press the download button, and then turn
on the digital receiver to start the file transfer.
3. A countdown will be displayed on screen
4.
Restart the digital receiver when the file
transfer is complete.
9.4 From another digital receiver via RS-232 port
It is possible to transfer the firmware from the digital receiver
to another same digital receiver by connecting them with a RS232 cable. To update the firmware with this method, perform
the following steps:
Page 72

66 Firmware Update
1. Turn off the target digital receiver.
2.
Plug one end of a RS-232 cable (9 pin Dsub cable) into the RS-232 port on the digital receiver, and the other end into the
matching port on the other digital receiver.
3.
Turn on the source digital receiver if not
already on.
4.
Select the Installation>Transfer Firmware
>
Transfer Firmware to Other IRD menu,
then you get asked for confirmation; select
Yes.
5.
Turn on the target digital receiver to start
the firmware transfer.
6.
A progress bar appears showing the
progress of the firmware transfer.
7.
Restart the target digital receiver when the
firmware transfer is complete.
Page 73

Index
67
16:9, 20
16:9 Display Format, 21
1st Audio Language, 18
1st Subtitle Language, 18
2nd Audio Language, 18
2nd Subtitle Language, 18
4:3, 21
4:3 Display Format, 21
A/V Output Setting, 19
Access Control, 25
Add to Fav, 32
After next program, 45
After this program, 45
Alphabetic, 51
Altair, 58, 59
AUDIO L, 14
AUDIO L/R, 10
AUDIO R, 14
Auto, 27, 28
Auto Start, 62
Button, 4
CABLE 1 IN, 10
CABLE 1 IN, 12
CABLE 2 IN, 10
CABLE 2 IN, 12
CAM, 7
CAS only, 28
Censorship, 25
Center, 21
Center extract, 21
Change PIN Code, 25
CI, 7
Common Interface, 7
Common Interface, 7
Date, 48
Daylight Saving Time, 23
Diab, 61
download, 64, 65
Duration, 45, 48
DVB, 1
Electronic Programme Guide, 35
End Frequency, 28
Every Day, 47
Every Weekday, 47
Every Weekend, 47
Factory Setting, 29
File List, 46, 51, 53, 56
File Name, 48
Find, 64, 65
Format Hard Disk, 60
Frequency, 28
FTA + CAS, 28
FTA only, 28
FTA/Scrambled, 28
Full, 21
GCC, 61
Page 74

68 INDEX
Hard of hearing, 18
HDMI, 11
HDMI, 13
HDMI Output, 22
high definition, 22
Info Box Display Time, 26
Info Box Position, 26
information box, 33
IRD Status, 63
keyboard, 41
Language Setting, 17
Letter Box, 21
Local Time, 23
Lock, 31, 52
Locked, 52
Manual, 28
Menu Language, 17
Mode, 23, 47
mono, 22
multifeed, 36
Network, 28
Network Search, 28
NEW, 40
No block, 25
normal-screen television, 21
NTSC, 19
One Time, 47
Organizing Favorites, 39
OSD Transparency, 26
PAL, 19
Parental Control, 25
picture-in-picture, 38
PIN, 25
program file list, 62
Program Files, 61
progress bar, 50
QAM, 28
QAM Mode, 28
Quick Scan, 28
Radio, 47
Record, 47
Record continue, 45
Record pause, 45
recorded programme list, 51
Rename, 31, 52
Reset Service List, 29
RF LOOP 1 OUT, 10
RF LOOP 1 OUT, 12
RF LOOP 2 OUT, 10
RF LOOP 2 OUT, 12
RS-232, 11
RS-232, 42, 65, 66
S-VIDEO, 11
S-VIDEO, 14, 22
S/PDIF, 11
S/PIDF, 15
SCART Output, 20
Search Mode, 27, 28
Service, 47
Service Search, 27
services list, 30
Show Provider, 31
Size, 51
Sorting, 51
Sound Mode, 22
Space, 41
specifications, 9–11
Start Frequency, 27, 28
Start Search, 28
Start Time, 48
stereo, 22
subtitle, 34
Symbol Rate, 28
Symbol Rate, 28
System ID, 63
System Setting, 26
TAP, 61
tap, 61
teletext, 34
Page 75

TFD-Down, 65
TFDN USB, 64
Time, 51
time format, 23
Time Offset, 23
Time Setting, 23, 25
Time Shifting, 26, 36, 45
timer list, 47
Timer Setting, 47
Total block, 25
Transfer Data to Other IRD, 42
Transfer Firmware to Other IRD, 66
transponder, 1
Turbo Off, 59
TV, 11
TV, 13, 22, 47
TV Aspect Ratio, 20, 21
TV Type, 19, 22
Type, 47
USB, 11
USB, 58, 64
VCR, 11
VCR, 15
VCR Scart Type, 20
VIDEO, 10
VIDEO, 12, 14, 22
Video Output Scaling, 22
69
Weekly, 47
wide-screen television, 20
Wind River, 61
Page 76

Page 77

Page 78

Correct disposal of this product
This marking shown on the product or its literature indicates that it should
not be disposed with other household wastes at the end of its working life. To
prevent possible harm tothe environment or human health from uncontrolled
waste disposal, please separate this from other types of wastes and recycle it
responsibly to promote the sustainable reuse of material resources.
Household users should contact either the retailer where they purchased this
product or their local government office for details of where and how they
can dispose this product for environmentally safe recycling.
Business users should contact their supplier and check the terms and condi-
tions of the purchase contract. This product should not be mixed with other
commercial wastes for disposal.
Topfield continues to improve the digital receiver which this guide explains. So some expla-
nations and illustrations in this guide could be different from the actual digital receiver.
Copyright © 2007, Topfield Co., Ltd. English version
http://www.i-topfield.com 110T-S3059-201-0
 Loading...
Loading...