Topcon America 860805 User Manual

(I0ER'A'B
/PERATORlS-ANUAL


POSITIONING SYSTEMS
HiPer Ga/Gb
Operator’s Manual
Part Number 7010-0816
Rev C
©Copyright Topcon Positioning Systems, Inc.
March, 2013
All contents in this manual are copyrighted by Topcon. All rights reserved.
The information contained herein may not be used, accessed, copied, stored,
displayed, sold, modified, published, distributed, or otherwise reproduced
without express written consent from Topcon.


TOC
Table of Contents
Preface .................................................................. v
Introduction .......................................................... 1-1
Principles of Operation .................................................... 1-2
GNSS Overview ........................................................ 1-2
Calculating Absolute Positions ........................... 1-3
Calculating Differential Positions ...................... 1-3
Essential Components for Quality Surveying .... 1-5
Conclusion .......................................................... 1-6
Receiver Overview .................................................... 1-6
Getting Acquainted .......................................................... 1-7
HiPer Ga/Gb Receiver ............................................... 1-8
MINTER ............................................................. 1-8
Data and Power Ports ......................................... 1-14
External Radio Antenna Connector .................... 1-15
Cables ........................................................................ 1-15
Other Accessories ...................................................... 1-16
Optional Accessories ................................................. 1-17
Option Authorization File (OAF) .................................... 1-20
Pre-survey Preparation ........................................ 2-1
Installing Topcon Software .............................................. 2-2
Installing PC-CDU .................................................... 2-2
Installing Modem-TPS .............................................. 2-3
Installing BTCONF ................................................... 2-5
Installing FLoader ..................................................... 2-6
Charging the Internal Batteries ........................................ 2-7
Power Management ......................................................... 2-9
Powering the Receiver with an External Battery ............. 2-13
Turning On/Off the Receiver .................................... 2-14
Connecting the Receiver and a Computer ....................... 2-14
P/N 7010-0816
i

Table of Contents
Establishing a Wireless Connection .......................... 2-15
Establishing an RS232 Cable Connection ................. 2-16
Establishing a USB Connection ................................. 2-17
Bluetooth Module Configuration ..................................... 2-17
Connecting to BTCONF and Setting Security
Parameters .............................................................. 2-18
Collecting Almanacs and Ephemerides ............................ 2-21
HiPer Ga/Gb Configuration ................................. 3-1
Configuring the Radio Modem ........................................ 3-3
Configuring a Digital UHF Radio Modem ..................... 3-3
Configuring the Receiver ................................................. 3-7
Connecting to PC-CDU ............................................. 3-8
MINTER Configuration ................................................... 3-17
HiPer Ga/Gb Receiver Setup and Survey .......... 4-1
Receiver Setup .................................................................. 4-1
Step 1: Setting Up the Receivers ............................... 4-1
Step 2: Measuring Antenna Height ............................ 4-4
Step 3: Collecting Data .............................................. 4-6
MINTER Operation .......................................................... 4-8
Static Surveying for Base Stations ................................... 4-10
Kinematic (Stop & Go) Surveying for Rover Stations .... 4-12
Real Time Kinematic Surveying ...................................... 4-13
Receiver and File Maintenance .......................... 5-1
Downloading Files to a Computer ................................... 5-1
Downloading Files via Topcon Link ......................... 5-2
...Using Windows Explorer ................................. 5-2
...Using Topcon Link .......................................... 5-4
Downloading Files via PC-CDU ............................... 5-6
Deleting Files from the Receiver ..................................... 5-8
Managing Receiver Memory ............................................ 5-9
Managing Receiver Options ............................................. 5-10
Checking the Receiver’s OAF ................................... 5-10
Loading an OAF ........................................................ 5-12
Clearing the NVRAM ...................................................... 5-13
Using the MINTER to Clear the NVRAM ................ 5-13
ii
HiPer Ga/Gb Operator’s Manual

Table of Contents
Using PC-CDU to Clear the NVRAM ...................... 5-14
Changing Receiver Modes ............................................... 5-14
Entering Extended Information Mode ...................... 5-14
Entering Sleep (Off) Mode ........................................ 5-16
Entering Zero Power Mode ....................................... 5-16
Loading New Firmware ................................................... 5-17
Loading Receiver and Power Board Firmware ......... 5-18
Loading Bluetooth Module Firmware ....................... 5-21
Troubleshooting ................................................... 6-1
Check This First! ............................................................. 6-1
Troubleshooting Quick List ............................................. 6-2
Powering Problems .......................................................... 6-3
Receiver Problems ........................................................... 6-4
Bluetooth Problems ......................................................... 6-10
Modem-TPS Problems ..................................................... 6-13
Obtaining Technical Support ........................................... 6-14
Phone ......................................................................... 6-15
E-mail ........................................................................ 6-15
Website ...................................................................... 6-16
Specifications ....................................................... A-1
Receiver Specifications ................................................... A-2
General Details .......................................................... A-2
GPS Board Details .................................................... A-7
Bluetooth Module Details ......................................... A-8
Digital UHF Modem General Specifications ............ A-9
Digital UHF Transmitter Specifications ................... A-10
Digital UHF Receiver Specifications ........................ A-11
Environmental Specifications ................................... A-12
HiPer Ga/Gb Compliance ......................................... A-12
Connector Specifications ................................................. A-13
Radio (Modem) RF Connector .................................. A-13
Power Connector ....................................................... A-13
Serial C-RS232 Connector ........................................ A-14
USB Connector ......................................................... A-15
P/N 7010-0816
iii

Table of Contents
Safety Warnings ................................................... B-1
General Warnings ............................................................. B-1
Battery Pack Warnings ..................................................... B-2
Usage Warnings ............................................................... B-3
Regulatory Information ....................................... C-1
UHF Radio Usage ............................................................ C-1
FCC Compliance .............................................................. C-2
Community of Europe Compliance .................................. C-3
Canadian Emission Labeling Requirements .................... C-3
WEEE Directive ............................................................... C-3
Industry Canada Compliance ........................................... C-5
RF Radiation Hazard Warning .................................. C-5
Maximum Antenna Gain ........................................... C-5
Industry Canada Notice and Marking ........................ C-6
Warranty Terms ................................................... D-1
iv
HiPer Ga/Gb Operator’s Manual
Preface
NOTICE
Preface
Thank you for purchasing this Topcon product. The materials
available in this Manual (the “Manual”) have been prepared by
Topcon Positioning Systems, Inc. (“TPS”) for owners of Topcon
products, and are designed to assist owners with the use of the
receiver and its use is subject to these terms and conditions (the
“Terms and Conditions”).
Please read these Terms and Conditions carefully.
Terms and Conditions
USE This product is designed to be used by a professional. The user
should have a good knowledge of the safe use of the product and
implement the types of safety procedures recommended by the local
government protection agency for both private use and commercial
job sites.
COPYRIGHT All information contained in this Manual is the
intellectual property of, and copyrighted material of TPS. All rights
are reserved. You may not use, access, copy, store, display, create
derivative works of, sell, modify, publish, distribute, or allow any
third party access to, any graphics, content, information or data in this
Manual without TPS’ express written consent and may only use such
information for the care and operation of your receiver. The
information and data in this Manual are a valuable asset of TPS and
are developed by the expenditure of considerable work, time and
money, and are the result of original selection, coordination and
arrangement by TPS.
HiPer Ga/Gb Operator’s Manual
v

Preface
TRADEMARKS LPS-900™, Pocket-3D™, GR-3™, Topcon Tools™,
Modem-TPS™, Topcon® and Topcon Positioning Systems™ are
trademarks or registered trademarks of TPS. Windows® is a
registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. The Bluetooth® word
mark and logos are owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc. and any use of such
marks by Topcon Positioning Systems, Inc. is used under license.
Other product and company names mentioned herein may be
trademarks of their respective owners.
DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTY EXCEPT FOR ANY
WARRANTIES IN AN APPENDIX OR A WARRANTY CARD
ACCOMPANYING THE PRODUCT, THIS MANUAL AND THE
RECEIVER ARE PROVIDED “AS-IS.” THERE ARE NO OTHER
WARRANTIES. TPS DISCLAIMS ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY
OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR
USE OR PURPOSE. TPS AND ITS DISTRIBUTORS SHALL NOT
BE LIABLE FOR TECHNICAL OR EDITORIAL ERRORS OR
OMISSIONS CONTAINED HEREIN; NOR FOR INCIDENTAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE
FURNISHING, PERFORMANCE OR USE OF THIS MATERIAL
OR THE RECEIVER. SUCH DISCLAIMED DAMAGES
INCLUDE BUT ARE NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF TIME, LOSS
OR DESTRUCTION OF DATA, LOSS OF PROFIT, SAVINGS OR
REVENUE, OR LOSS OF THE PRODUCT’S USE. IN ADDITION
TPS IS NOT RESPONSIBLE OR LIABLE FOR DAMAGES OR
COSTS INCURRED IN CONNECTION WITH OBTAINING
SUBSTITUTE PRODUCTS OR SOFTWARE, CLAIMS BY
OTHERS, INCONVENIENCE, OR ANY OTHER COSTS. IN ANY
EVENT, TPS SHALL HAVE NO LIABILITY FOR DAMAGES OR
OTHERWISE TO YOU OR ANY OTHER PERSON OR ENTITY
IN EXCESS OF THE PURCHASE PRICE FOR THE RECEIVER.
LICENSE AGREEMENT Use of any computer programs or software
supplied by TPS or downloaded from a TPS website (the “Software”)
in connection with the receiver constitutes acceptance of these Terms
and Conditions in this Manual and an agreement to abide by these
Terms and Conditions. The user is granted a personal, non-exclusive,
non-transferable license to use such Software under the terms stated
herein and in any case only with a single receiver or single computer.
vi
HiPer Ga/Gb Operator’s Manual

Terms and Conditions
You may not assign or transfer the Software or this license without
the express written consent of TPS. This license is effective until
terminated. You may terminate the license at any time by destroying
the Software and Manual. TPS may terminate the license if you fail to
comply with any of the Terms or Conditions. You agree to destroy the
Software and manual upon termination of your use of the receiver. All
ownership, copyright and other intellectual property rights in and to
the Software belong to TPS. If these license terms are not acceptable,
return any unused software and manual.
CONFIDENTIALITY This Manual, its contents and the Software
(collectively, the “Confidential Information”) are the confidential and
proprietary information of TPS. You agree to treat TPS’ Confidential
Information with a degree of care no less stringent that the degree of
care you would use in safeguarding your own most valuable trade
secrets. Nothing in this paragraph shall restrict you from disclosing
Confidential Information to your employees as may be necessary or
appropriate to operate or care for the receiver. Such employees must
also keep the Confidentiality Information confidential. In the event you
become legally compelled to disclose any of the Confidential
Information, you shall give TPS immediate notice so that it may seek a
protective order or other appropriate remedy.
WEBSITE; OTHER STATEMENTS No statement contained at the
TPS website (or any other website) or in any other advertisements or
TPS literature or made by an employee or independent contractor of
TPS modifies these Terms and Conditions (including the Software
license, warranty and limitation of liability).
SAFETY Improper use of the receiver can lead to injury to persons or
property and/or malfunction of the product. The receiver should only
be repaired by authorized TPS warranty service centers. Users should
review and heed the safety warnings in an Appendix.
MISCELLANEOUS The above Terms and Conditions may be
amended, modified, superseded, or canceled, at any time by TPS. The
above Terms and Conditions will be governed by, and construed in
accordance with, the laws of the State of California, without reference
to conflict of laws.
P/N 7010-0816
vii
Preface
NOTE
TIP
NOTICE
CAUTION
Manual Conventions
This manual uses the following conventions:
Example Description
FileExit Click the File menu and click Exit.
Connection Indicates the name of a dialog box or screen.
Frequency Indicates a field on a dialog box or screen, or a tab
within a dialog box or screen.
Enter Press or click the button or key labeled Enter.
Further information to note about the configuration,
maintenance, or setup of a system.
Supplementary information that can help you
configure, maintain, or set up a system.
viii
Supplementary information that can have an affect
on system operation, system performance,
measurements, or personal safety.
Notification that an action has the potential to
adversely affect system operation, system
performance, data integrity, or personal health.
HiPer Ga/Gb Operator’s Manual
Manual Conventions
WARNING
DANGER
Notification that an action will result in system
damage, loss of data, loss of warranty, or personal
injury.
Under no circumstances should this action be
performed.
P/N 7010-0816
ix

Preface
Notes:
x
HiPer Ga/Gb Operator’s Manual
Chapter 1
Introduction
The HiPer Ga/Gb receiver is a dual-frequency, GPS+ receiver built to
be the most advanced and compact receiver for the surveying market.
The receiver is a multi-function, multi-purpose receiver intended for
precision markets. Precision markets means markets for equipment,
subsystems, components and software for surveying, construction,
commercial mapping, civil engineering, precision agriculture and
land-based construction and agriculture machine control,
photogrammetry mapping, hydrographic and any use reasonably
related to the foregoing.
The HiPer Ga/Gb can receive and process the latest GPS and
GLONASS signal types, improving the accuracy and reliability of the
survey points and positions, especially under difficult jobsite
conditions, and reducing cost.
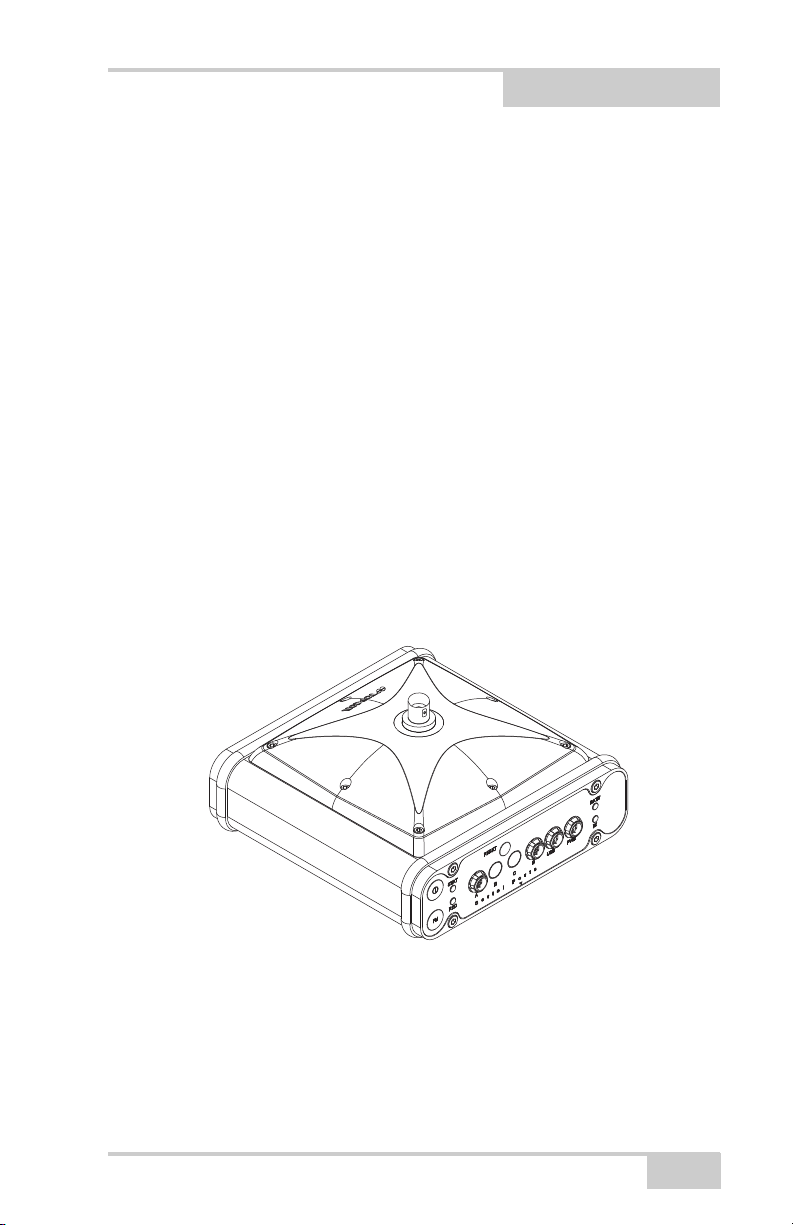
Figure 1-1. HiPer Ga/Gb Receiver
The dual-frequency and GPS+ features of the receiver combine to
provide a positioning system accurate for any survey. Several other
features, including multipath mitigation, provide under-canopy and
low signal strength reception. The receiver provides the functionality,
P/N 7010-0816
1-1

Introduction
accuracy, availability, and integrity needed for fast and easy data
collection.
Principles of Operation
Surveying with the right GPS receiver offers users accurate and
precise positioning, a requirement for any surveying project.
This section gives an overview of existing and proposed Global
Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) and receiver functions so basic
operating principles can be applied.
GNSS Overview
Currently, the following three global navigation satellite systems
(GNSS) offer line-of-site radio navigation and positioning, velocity,
and time services on a global, all-weather scale to any user equipped
with a GNSS tracking receiver on or near the Earth’s surface:
• GPS – the Global Positioning System maintained and operated by
the United States Department of Defense. For information on the
status of this system, visit the US Naval Observatory website
(http://tycho.usno.navy.mil/) or the US Coast Guard website
(http://www.navcen.uscg.gov/).
• GLONASS – the Global Navigation Satellite System maintained
and operated by the Russian Federation Ministry of Defense. For
information on the status of this system, visit the Coordinational
Scientific Information Center website (http://www.glonassianc.rsa.ru/).
• GALILEO – an upcoming global positioning system maintained
and operated by European Satellite Navigation Industries, a joint
venture of several European space agencies/companies working
closely with the European Space Agency. Unlike GPS and
GLONASS, this is a civil endeavor and is currently in the
development and validation stage. For information on the status
of this system, visit the European Satellite Navigation Industries
website (http://www.european-satellite-navigationindustries.net).
1-2
HiPer Ga/Gb Operator’s Manual

Principles of Operation
Despite numerous technical differences in the implementation of
these systems, satellite positioning systems have three essential
components:
• Space – GPS, GLONASS, and GALILEO satellites orbit
approximately 12,000 nautical miles above Earth and are
equipped with a clock and radio. These satellites broadcast
ranging signals and various digital information (ephemerides,
almanacs, time and frequency corrections, and so forth).
• Control – Ground stations located around the Earth that monitor
the satellites and upload data, including clock corrections and
new ephemerides (satellite positions as a function of time), to
ensure the satellites transmit data properly.
• User – The community and military that use GNSS receivers to
calculate positions.
Calculating Absolute Positions
When calculating an absolute position, a stationary or moving
receiver determines its three-dimensional position with respect to the
origin of an Earth-Center Earth-Fixed coordinate system. To calculate
this position, the receiver measures the distance (called pseudoranges) between it and at least four satellites. The measured pseudoranges are corrected for clock differences (receiver and satellites) and
signal propagation delays due to atmospheric effects. The positions of
the satellites are computed from the ephemeris data transmitted to the
receiver in navigation messages. When using a single satellite system,
the minimum number of satellites needed to compute a position is
four. In a mixed satellite scenario (GPS, GLONASS, GALILEO), the
receiver must lock onto five or more satellites to account for the
different time scales used in these systems and to obtain an absolute
position.
Calculating Differential Positions
DGPS, or Differential GPS, is a relative positioning technique where
the measurements from two or more remote receivers are combined
and processed using sophisticated algorithms to calculate the
receivers’ relative coordinates with high accuracy.
P/N 7010-0816
1-3

Introduction
DGPS accommodates various implementation techniques that can be
classified according to the following criteria:
• The type of GNSS measurements used, either code-phase or
carrier-phase differential measurements
• If real-time or post-mission results are required. Real-time
applications can be further divided according to the source of
differential data and the communication link used.
With DGPS in its most traditional approach, one receiver is placed at
a known surveyed location and is referred to as the reference receiver
or base station. Another receiver is placed at an unknown location and
is referred to as the remote receiver or rover. The reference station
collects the code-phase and carrier-phase measurements from each
GNSS satellite in view.
• For real-time applications, these measurements and the reference
station coordinates are then built up to the industry standard
RTCM—or various proprietary standards established for
transmitting differential data—and broadcast to the remote
receiver(s) using a data communication link. The remote receiver
applies the transmitted measurement information to its observed
measurements of the same satellites.
• For post-mission applications, the simultaneous measurements
from reference and rover stations are normally recorded to the
receiver’s internal memory (not sent over communication link).
Later, the data are downloaded to computer, combined, and
processed.
Using this technique, the spatially correlated errors—such as
satellite orbital errors, ionospheric errors, and tropospheric
errors—can be significantly reduced, thus improving the position
solution accuracy.
A number of differential positioning implementations exist, including
post-processing surveying, real-time kinematic surveying, maritime
radio beacons, geostationary satellites (as with the OmniSTAR
service), and satellite based augmentation systems (WAAS, EGNOS,
MSAS).
1-4
HiPer Ga/Gb Operator’s Manual

Principles of Operation
The real-time kinematic (RTK) method is the most precise method of
real-time surveying. RTK requires at least two receivers collecting
navigation data and communication data link between the receivers.
One of the receivers is usually at a known location (Base) and the
other is at an unknown location (Rover). The Base receiver collects
carrier phase measurements, generates RTK corrections, and sends
this data to the Rover receiver. The Rover processes this transmitted
data with its own carrier phase observations to compute its relative
position with high accuracy, achieving an RTK accuracy of up to 1 cm
horizontal and 1.5 cm vertical.
Essential Components for Quality Surveying
Achieving quality position results requires the following elements:
• Accuracy – The accuracy of a position primarily depends upon
the satellite geometry (Geometric Dilution of Precision, or
GDOP) and the measurement (ranging) errors.
– Differential positioning (DGPS and RTK) strongly mitigates
atmospheric and orbital errors, and counteracts Selective
Availability (SA) signals the US Department of Defense
transmits with GPS signals.
– The more satellites in view, the stronger the signal, the lower
the DOP number, the higher positioning accuracy.
• Availability – The availability of satellites affects the calculation
of valid positions. The more visible satellites available, the more
valid and accurate the position. Natural and man-made objects
can block, interrupt, and distort signals, lowering the number of
available satellites and adversely affecting signal reception.
• Integrity – Fault tolerance allows a position to have greater
integrity, increasing accuracy. Several factors combine to provide
fault tolerance, including:
– Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM) detects
faulty GNSS satellites and removes them from the position
calculation.
– Five or more visible satellites for only GPS or only
GLONASS; six or more satellites for mixed scenarios.
P/N 7010-0816
1-5

Introduction
– Satellite Based Augmentation Systems (WAAS, EGNOS, and
so on) creates and transmit, along with DGPS corrections,
data integrity information (for example, satellite health
warnings).
– Current ephemerides and almanacs.
Conclusion
This overview simply outlines the basics of satellite positioning. For
more detailed information, visit the TPS website at
www.topconpositioning.com.
Receiver Overview
When power is turned on and the receiver self-test completes, the
receiver’s 40 channels initialize and begin tracking visible satellites.
Each of the receiver’s channels can be used to track any one of the
GPS and GLONASS signals. The number of channels available
allows the receiver to track all visible global positioning satellites at
any time and location.
An internal GPS+ antenna equipped with a low noise amplifier (LNA)
and the receiver’s radio frequency (RF) device are connected with a
coaxial cable. The wide-band signal received is down-converted,
filtered, digitized, and assigned to different channels. The receiver
processor controls the process of signal tracking.
Once the signal is locked in the channel, it is demodulated and
necessary signal parameters (carrier and code phases) are measured.
Also, broadcast navigation data are retrieved from the navigation
frame.
After the receiver locks on to four or more satellites, its absolute
position in WGS-84 and the time offset between the receiver clock
and GPS time are computed. This information and the measurement
data are stored in the receiver’s internal memory and can be
downloaded later onto a computer, then processed using a postprocessing software package. When the receiver operates in RTK
mode, raw data measurements can also be recorded into the receiver’s
1-6
HiPer Ga/Gb Operator’s Manual

Getting Acquainted
internal memory. This allows the operator to double check real-time
results obtained in the field.
Depending on your options, capabilities of the receiver include:
• Co-op tracking
• Multipath reduction
• Satellite based augmentation systems (WAAS, EGNOS, and so
forth).
• Adjustable phase locked loop (PLL) and delay lock loop (DLL)
parameters
• Dual-frequency modes, including static, kinematic, real-time
kinematic (RTK), and differential GPS (DGPS) survey modes
(DGPS modes include static, kinematic, and RTK)
• Auto data logging
• Setting different mask angles
• Setting different survey parameters
• Static or dynamic modes
Getting Acquainted
The HiPer Ga/Gb comes in a real-time kinematic (RTK) package with
two receivers, one as a Base Station and the other as a Rover Station
(also, refer to the packaging instruction card). Each receiver casing
allocates space for two non-removable, rechargeable batteries, a
Bluetooth wireless technology module, a dual-system receiver board,
and radio modem communications board.
The embedded radio board is configured with a Digital UHF
transceiver that has a 410 to 470 MHz frequency range and 12.5 kHz
channel spacing. The board provides 29 dBm (0.79 W) power output
for data transmission.
The HiPer Ga/Gb Base and Rover receivers are shipped with the most
commonly used settings for the radio modem. The Rover settings are
configured to match the Base settings.
P/N 7010-0816
1-7
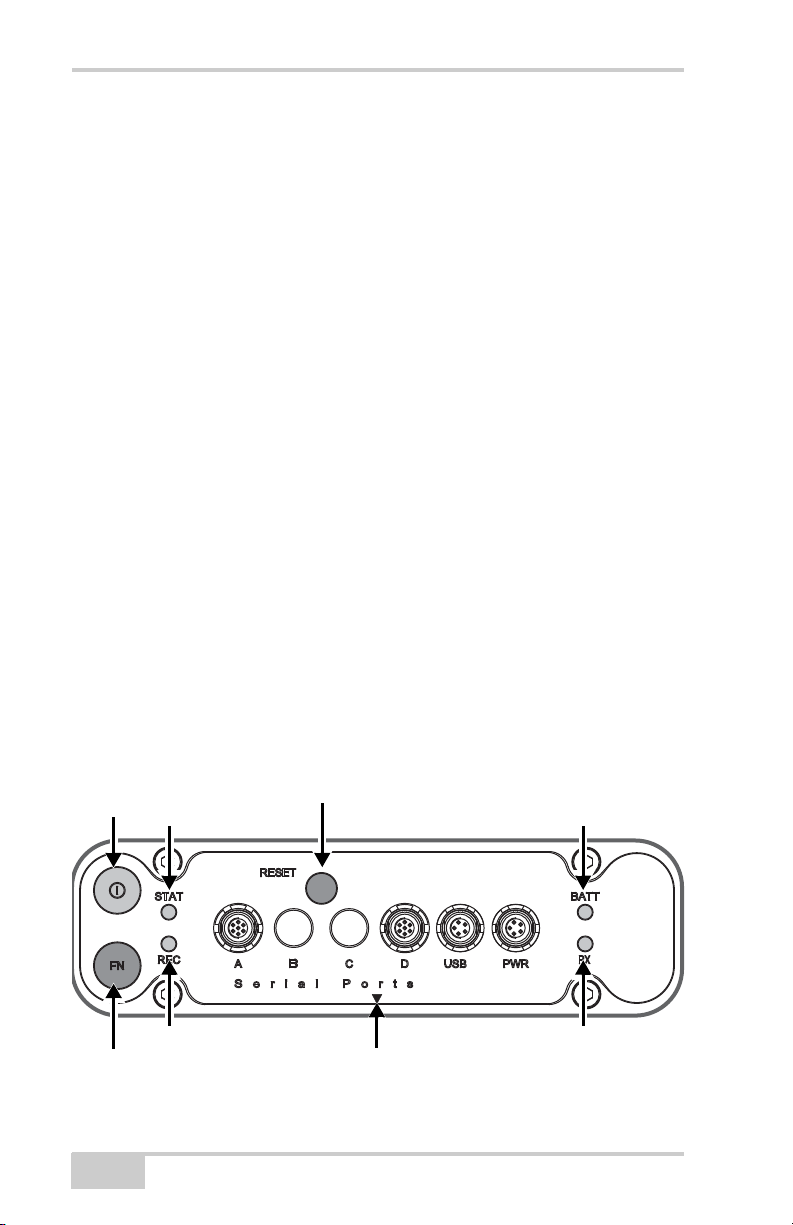
Introduction
Record LED
Slant Height Measure Mark
Modem Status LED
FN Button
Power
Button
Status LED
Reset Button
Battery LED
The frequency range of the modem depends on the country in which
the receiver is used: for North America, the frequency range is
410 to 470; for all other countries, contact your local distributor.
Other features include serial and USB data ports, a power port, and a
MINTER for viewing status and controlling data input/output. These
features are described on the following pages.
HiPer Ga/Gb Receiver
The HiPer Ga/Gb receiver’s advanced design reduces the number of
cables required for operation, allowing for more reliable and efficient
surveying. The casing allocates space for a Bluetooth
technology module, a multi-system receiver board, and a radio
modem communications board.
The HiPer Ga/Gb comes with a Digital UHF TX/RX radio modem.
Other features include three data ports, a power port, and a MINTER
for viewing status and controlling data input/output.
MINTER
®
wireless
The MINTER is the receiver’s minimum interface used to display and
control data input and output (Figure 1-2). The slant height measure
mark (SHMM) is used when measuring the height offset of the
receiver.
Figure 1-2. HiPer Ga/Gb MINTER
1-8
HiPer Ga/Gb Operator’s Manual
Getting Acquainted
The Reset button causes a hard reset of the receiver and causes the
receiver to leave Zero Power Mode and return to Normal Mode.
Only use this procedure if the receiver does not
NOTICE
respond to commands or does not charge the
internal batteries (is in Zero Power Mode).
The Power button turns the receiver on and off.
The Battery LEDs display the power status for each battery:
• Green – indicates greater than 85% charge.
• Orange – indicates an intermediate charge.
• Red – indicates less than 15% charge.
When the internal batteries have completely
NOTICE
discharged and no external power is connected, the
receiver goes into Zero Power Mode to prevent the
batteries from over discharging.
The pattern of blinks also indicates the source of power:
• Solid light – an external power supply is used, and the batteries
are not being charged.
• Blinking once a second – the batteries are being charged.
• Blinking once every five seconds – the receiver uses the internal
batteries for power.
• Not blinking – the receiver is in Zero Power Mode or the internal
batteries are discharged, and no external power is connected.
The STAT LED displays the status of tracked satellites.
• Red blink – receiver is on but is not tracking satellites or does not
have a solution.
• Green blink – receiver is on and tracking satellites; one blink per
tracked GPS satellite.
• Orange blink – receiver is on and tracking satellites; one blink per
tracked GLONASS satellite.
P/N 7010-0816
1-9

Introduction
The REC LED displays the data recording status. See “The FN
(FUNCTION) button” on page 1-11 for more information on REC
LED behavior when using the FN button.
• Green blinks – each blink indicates that data is being written to
the SD/MMC card.
• Solid Orange – indicates the receiver is changing modes.
• Orange blinks – indicates that the receiver is checking its internal
file system (after clearing the NVRAM or loading new firmware).
During this operation, the file system is not accessible for CDU
(control display unit) applications or for data recording. This
operation may require from fractions of a second to several
minutes, depending on the circumstances and the amount of
internal memory.
• Solid Red – indicates a fault condition with the receiver (no more
memory, no SD/MMC card inserted, a hardware problem, or an
improper OAF).
Table 1-2 on page 1-12 describes the REC LED status when using the
FN button.
The RX TX LED displays the status of the modem. Table 1-1
describes the LED colors and patterns for the different modems
available for the HiPer Ga/Gb receiver.
1-10
HiPer Ga/Gb Operator’s Manual
Getting Acquainted
Table 1-1. RX TX LED Indications
• No light – modem is turned off.
• Solid Red – the modem is in transmitter mode; the modem is
transmitting data.
• Orange flashes – the modem is in command mode. This mode
allows the operator to send/query commands to/from the
modem.
UHF Modem
• Flashing Green – the modem is in receiver mode
• Solid Green – a radio link has been established; the modem is
ready to receive data
• Solid Green with Orange flashes – the modem is receiving data.
• Red flashes – a fault condition has been detected. Check the
condition of the radio modem’s antenna to ensure it is
undamaged, and is connected properly and securely. Also make
sure that there is nothing to interrupt the signal.
The BT LED indicates the level of activity at the Bluetooth wireless
technology communication link:
• Blue flashes – the Bluetooth module is on but no connection is
established.
• Solid blue light – the Bluetooth module is on and a connection
has been established.
• No light – the Bluetooth module is off.
The power button turns the receiver on and off.
The FN (FUNCTION) button switches the receiver between
information modes and post-processing modes, starts/stops data
recording, and changes the baud rate of the serial port to 9600. See
“MINTER Operation” on page 4-7 for more information. Table 1-2
on page 1-12 describes the REC LED status when using the FN
button.
P/N 7010-0816
1-11
Introduction
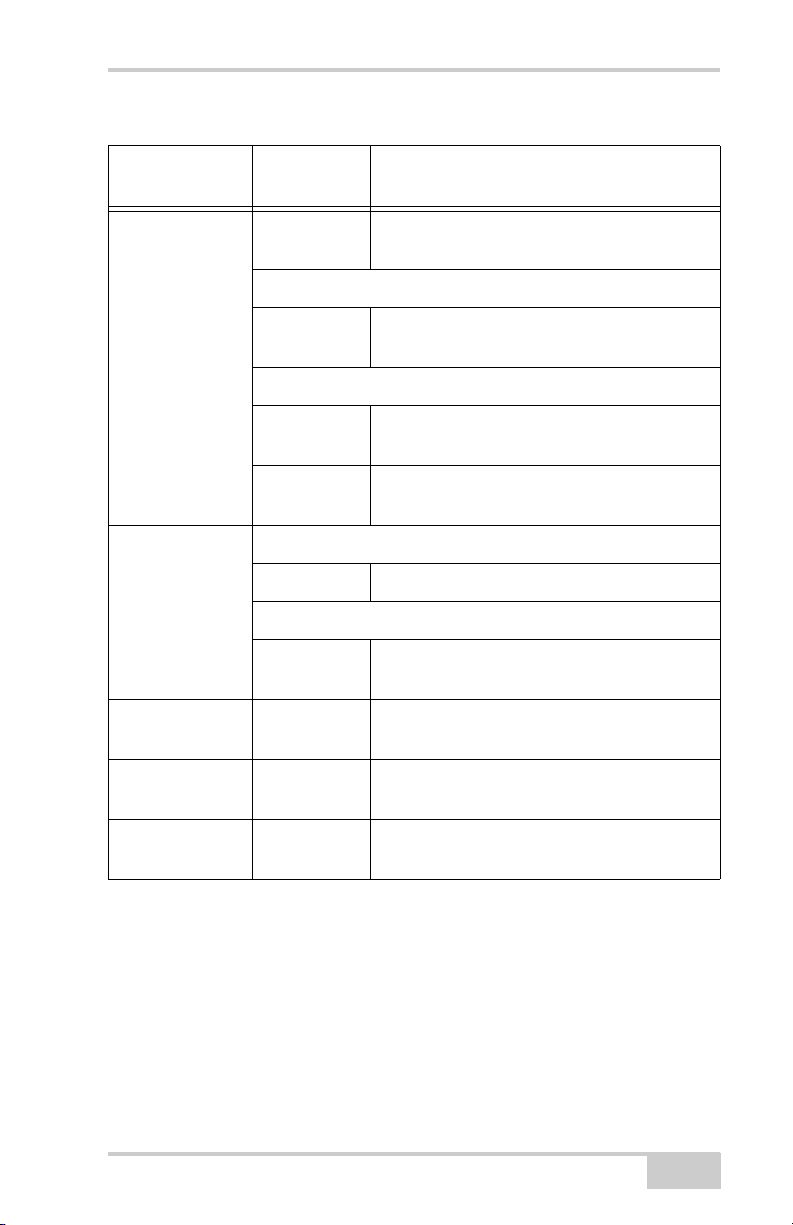
Table 1-2. FN (FUNCTION) key operations and REC LED Status
FN Key
REC LED Status
When data recording is off, and the FN key is...
No light No data recording.
Not pressed
Orange blink Internal file system test in progress.
Red No free memory; hardware problem with
data recording.
If FN key mode is “LED blink mode switch”
Pressed for < 1
second
Orange Release to change information mode.
If FN key mode is “Occupation mode switch”
Orange No function.
If FN key mode is “LED blink mode switch”
Pressed for 1–5
seconds
Green Release to start data recording (post-
processing occupation mode undefined).
If FN key mode is “Occupation mode switch”
Green Release to start recording (Kinematic or
Static post-processing occupation mode).
Pressed for 5–8
seconds
Pressed for > 8
Red Release to turn serial port A baud rate to
9600 bps.
No light No function.
seconds
When data recording is on, and the FN key is...
1-12
HiPer Ga/Gb Operator’s Manual
Getting Acquainted
Table 1-2. FN (FUNCTION) key operations and REC LED Status (Continued)
FN Key
Not pressed
Pressed for < 1
second
Pressed for 1–5
seconds
REC LED Status
Red No free memory; hardware problem with
data recording.
If FN key mode is “LED blink mode switch”
Green Data recording started (post-processing
occupation mode undefined).
If FN key mode is “Occupation mode switch”
Green Data recording started (Kinematic post-
processing occupation mode).
Orange Data recording started (Static post-
processing occupation mode).
If FN key mode is “LED blink mode switch”
Orange Release to change information mode.
If FN key mode is “Occupation mode switch”
Orange Release to toggle between Static and
Kinematic post-processing modes.
No light Release to stop data recording.
Pressed for 5–8
seconds
Pressed for > 8
seconds
P/N 7010-0816
Red Release to turn serial port A baud rate to
9600 bps.
No light No function (data recording still on).
1-13
Introduction
Slant Height Measure Mark
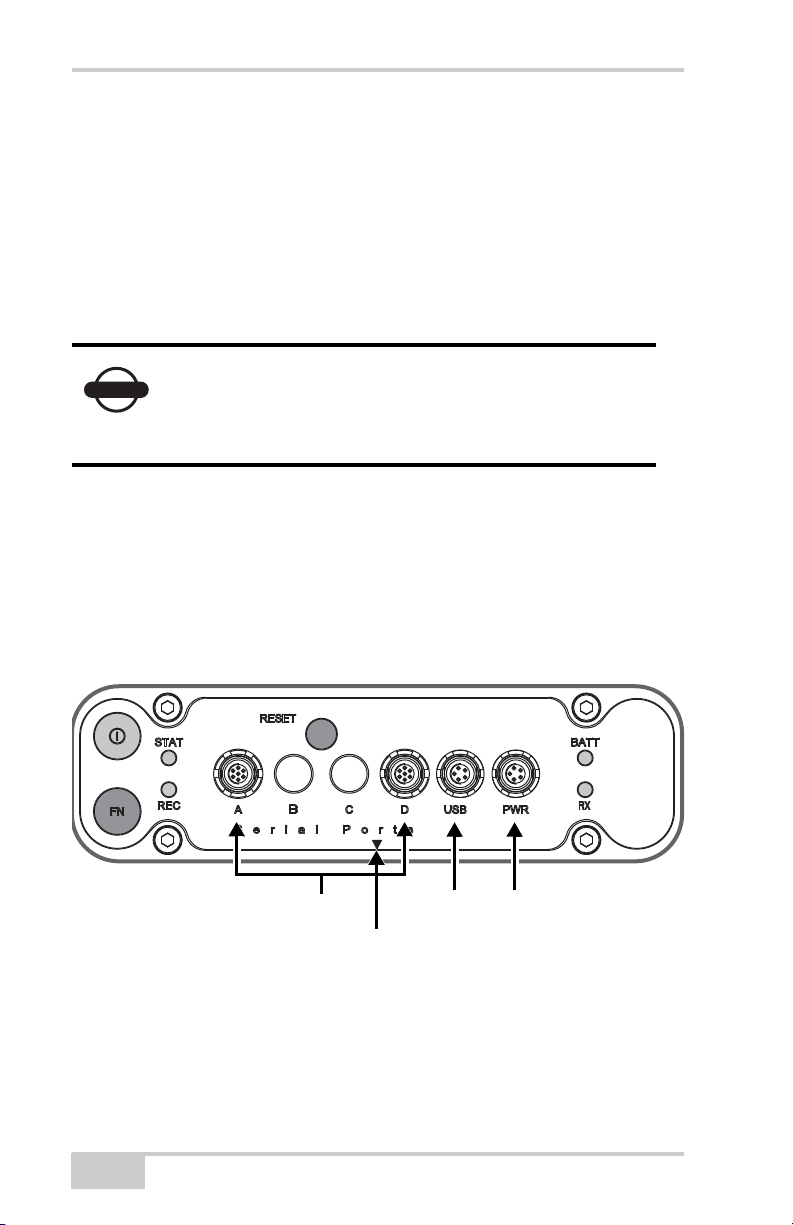
Serial Ports A–D USB Power
Data and Power Ports
The receiver has the following ports (Figure 1-3 on page 1-14):
• Two serial ports:
– Port A used for communication between HiPer Ga/Gb and a
controller or any other external device.
– Port B used internally to connect the receiver board with the
optional Bluetooth module.
Changing the receiver’s Port B default settings will
NOTICE
• PWR – The power input port to which an external power source
(+6 to +28 V DC) is connected and where the unit is charged.
• USB – Used for high-speed data transfer and communication
between the receiver and an external device.
• Slant height measure mark (SHMM).
affect the Bluetooth link. The default settings for
Port B are: 115200 bps, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no
parity, and no handshaking.
1-14
Figure 1-3. HiPer Ga/Gb Ports
HiPer Ga/Gb Operator’s Manual
Getting Acquainted
External
Antenna
Connector
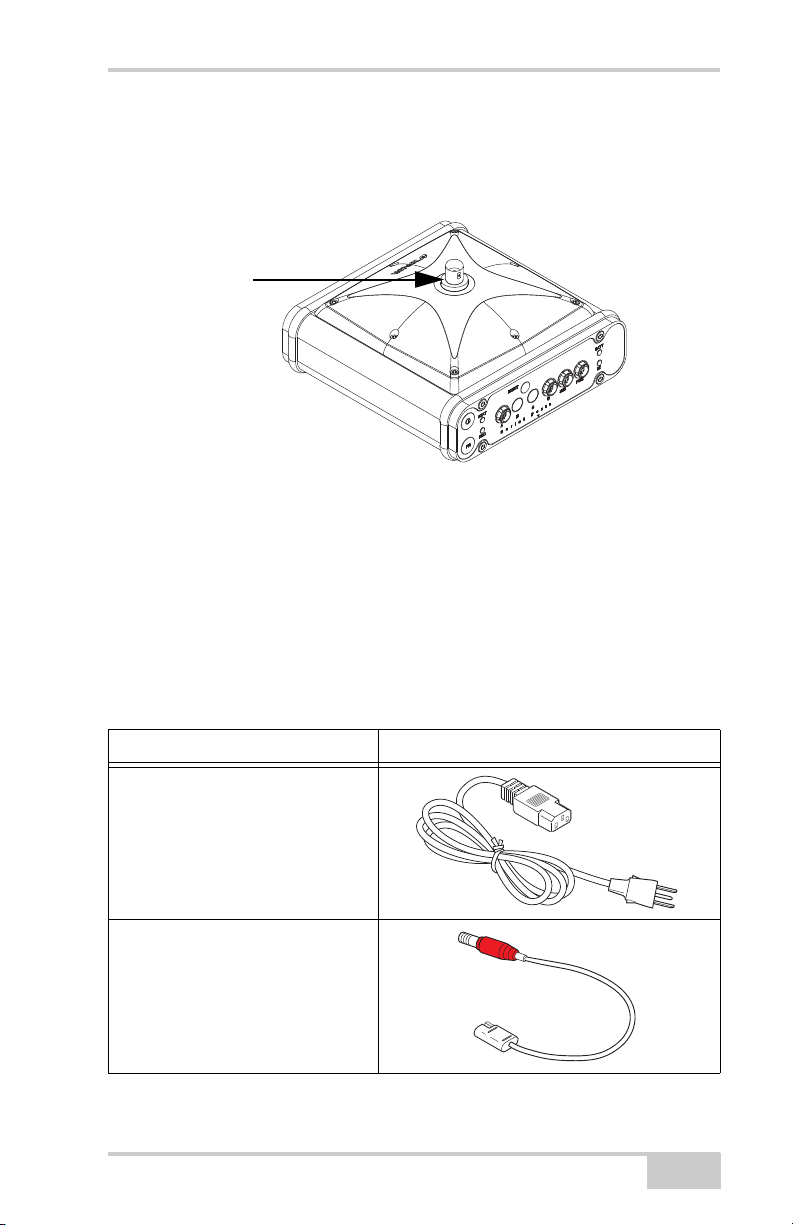
External Radio Antenna Connector
The antenna connector on the receiver’s radome is a BNC connection
(Figure 1-4).
Figure 1-4. Receiver Radome and External Antenna Connector
Cables
The HiPer Ga/Gb package includes standard communication and
power cables for configuring the receiver and providing a power
source to the receiver. Table 1-3 lists the cables included in the HiPer
Ga/Gb package.
Table 1-3. Package Cables
Cable Description Cable Illustration
Power cable
Connects the power supply unit to a
grounded outlet.
U.S. p/n 14-008052-01
Europe p/n 14-008054-01
Australia p/n 14-008074-01
Receiver power cable
Connects the receiver and the
power supply unit via SAE
connectors.
p/n 14-008016-03
P/N 7010-0816
1-15
Introduction
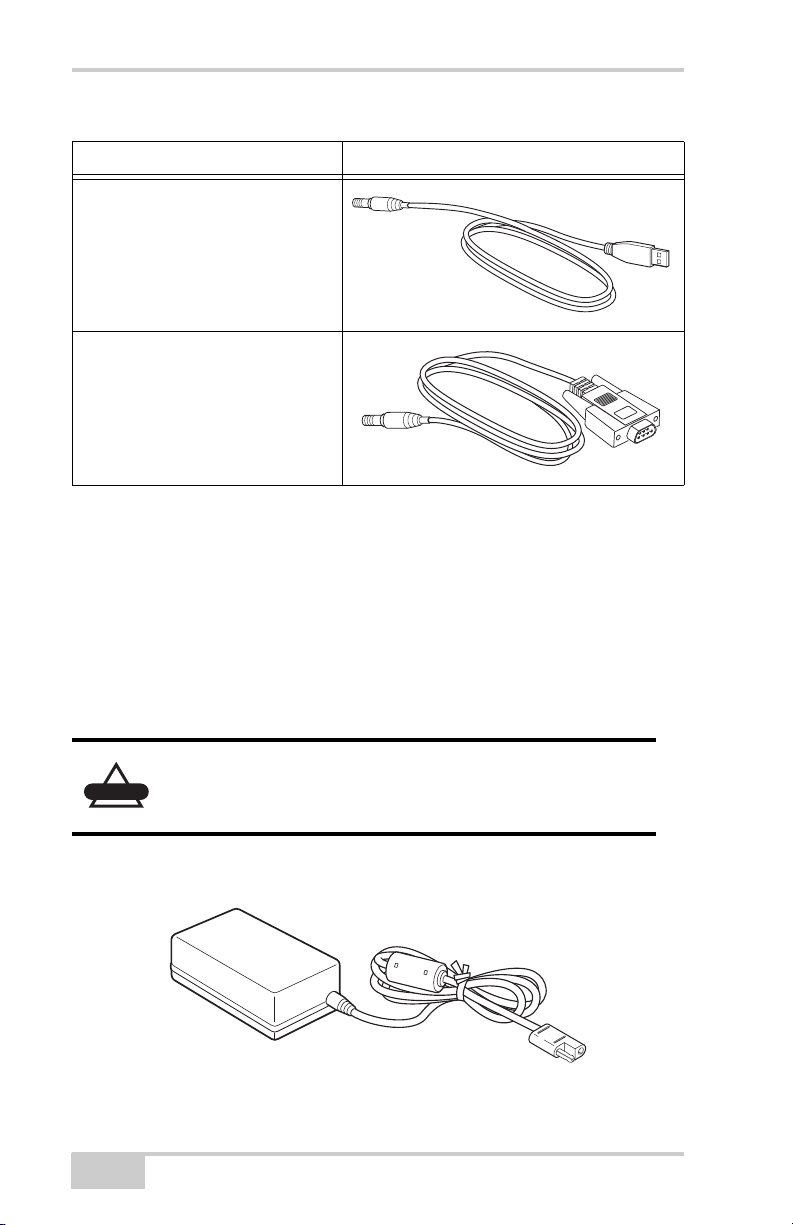
Table 1-3. Package Cables (Continued)
Cable Description Cable Illustration
USB cable
Connects the receiver to an external
device (controller or computer) for
high-speed data transfer and
receiver configuration.
p/n 14-008031-01
Serial cable
Connects the receiver to an external
device (controller or computer) for
data transfer and receiver
configuration.
p/n 14-008005-03
Other Accessories
This package can include the following accessories.
The power supply unit (p/n 22-034101-01) charges the internal
batteries when connected to a grounded outlet (Figure 1-5). This unit
converts the alternating current (AC) normally supplied from an
electrical outlet to a direct current (DC) used to charge the batteries
and/or power the receiver.
The power supply unit should only be used for
CAUTION
charging the batteries. Do not use as a power source
during surveying.
The power supply unit connects directly to the receiver. For details,
see the power related sections on page 2-13.
Figure 1-5. Power Supply Unit
1-16
HiPer Ga/Gb Operator’s Manual
 Loading...
Loading...