TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
1
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
D
2.7-V Operation
D
Two Differential Microphone Inputs, One
Differential Earphone Output, and One
Single-Ended Earphone Output
D
Programmable Gain Amplifiers for
Transmit, Receive, Sidetone, and Volume
Control
D
Earphone Mute and Microphone Mute
D
On-chip I2C-Bus, Which Provides a Simple,
Standard, Two-Wire Serial Interface With
Digital ICs
D
Programmable for 15-Bit Linear Data or
8-Bit Companded (µ-Law or A-Law) Data
D
Available in a 32-Terminal TQFP Package
D
Designed for Analog and Digital Wireless
Handsets and Telecommunications
Applications
D
Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF) and
Single Tone Generator
D
Pulse Density Modulated (PDM) Buzzer
Output
description
The voice-band audio processor (VBAP) is designed to perform the transmit encoding analog/digital (A/D)
conversion and receive decoding digital/analog (D/A) conversion, together with transmit and receive filtering
for voice-band communications systems. The device operates in either the 15-bit linear or 8-bit companded
(µ-law or A-Law) mode, which is selectable through the I
2
C interface. From a 2.048-MHz master clock input,
the VBAP generates its own internal clocks.
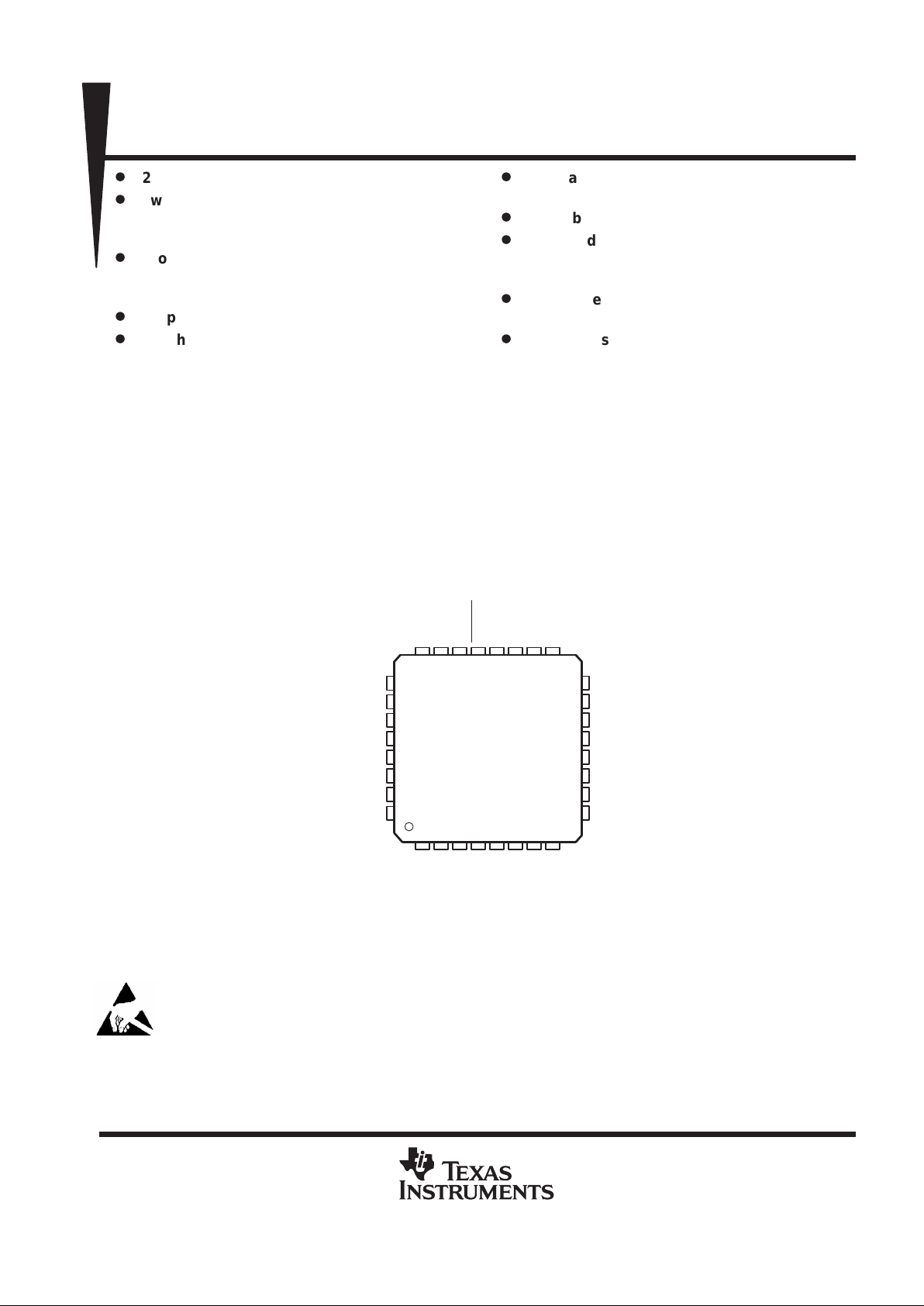
PBS PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
31
30
29
28
27
9
10
PCMO
PCMI
DV
SS
DV
DD
SCL
SDA
NC
NC
PLLV
DD
EARV
SS
EAR1ON
EARV
DD
EAR1OP
EARV
SS
EAR2O
AV
DD
32
26
11
12
13
14
15
MBIAS
MIC1P
MIC1N
MIC2P
NC
16
25
1234567 8
24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17
MIC2N
REXT
AV
SS
MCLK
PLLV
SS
V
SS
RESET
PWRUPSEL
BUZZCON
PCMSYN
PCMCLK
NC – No internal connection
This device contains circuits to protect its inputs and outputs against damage due to high static voltages or electrostatic fields. These
circuits have been qualified to protect this device against electrostatic discharges (ESD) of up to 2 kV according to MIL-STD-883C,
Method 3015; however, it is advised that precautions be taken to avoid application of any voltage higher than maximum-rated
voltages to these high-impedance circuits. During storage or handling, the device leads should be shorted together or the device
should be placed in conductive foam. In a circuit, unused inputs should always be connected to an appropriated logic voltage level,
preferably either VCC or ground. Specific guidelines for handling devices of this type are contained in the publication
Guidelines for
Handling Electrostatic-Discharge-Sensitive (ESDS) Devices and Assemblies
available from Texas Instruments.
Copyright 1999, Texas Instruments Incorporated
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
VBAP is a trademark of Texas Instruments Incorporated.
TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
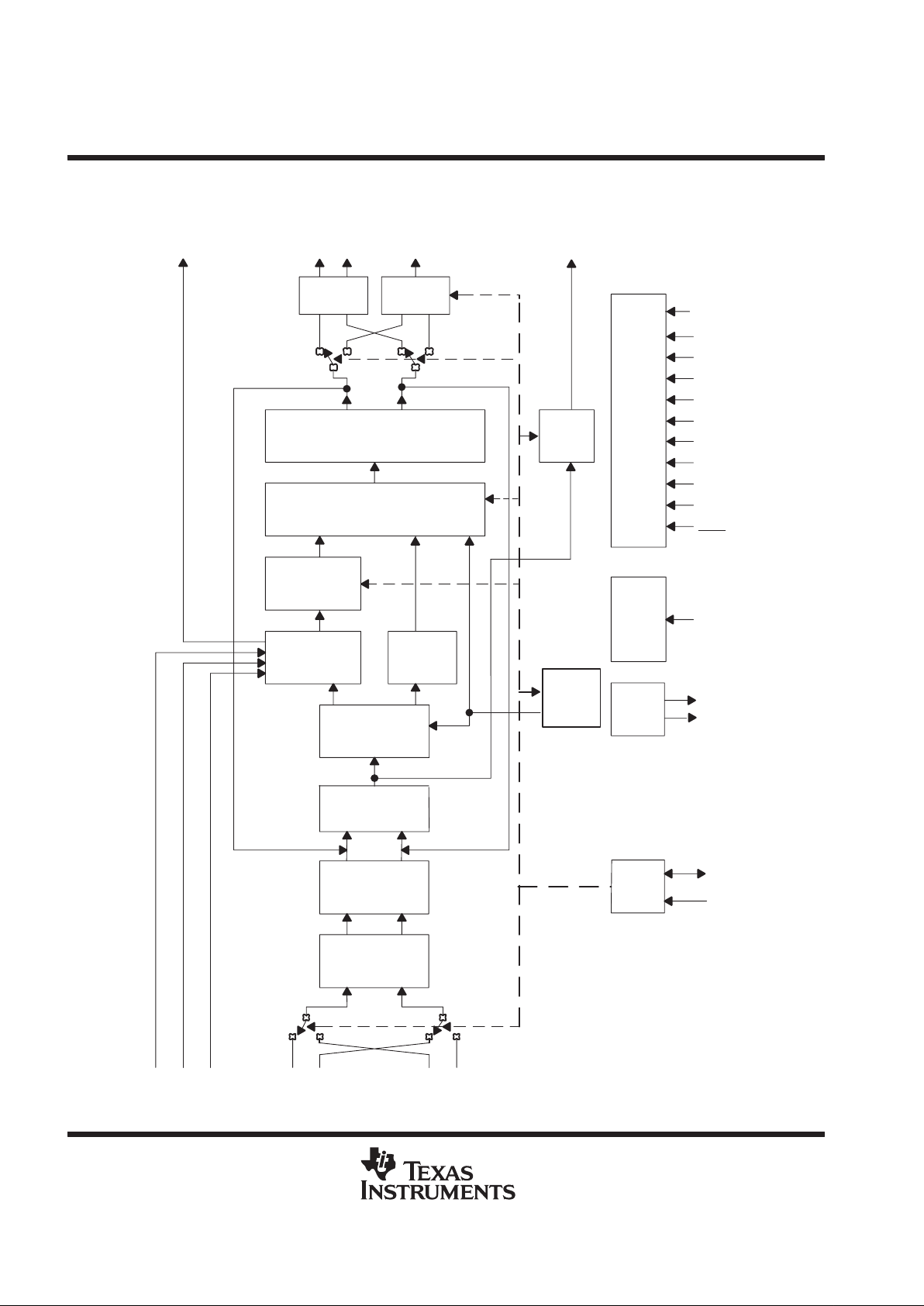
functional block diagram
PCMIN
PCMSYN
PCMCLK
MIC1P
MIC1N
MIC2P
MIC2N
MIC
Amplifier
1
g =
23.5 dB
MIC
Amplifier
2
g = 12 dB
or
0 dB
Analog
Modulator
TX Filter
and PGA
g = –10 dB
to
0 dB
PCM
Interface
Sidetone
g = –24 dB
to
–12 dB
RX Vol
Control
g = –18 dB
to
0 dB
RX Filter
and PGA
g = –6 dB
to
+6 dB
Digital
Modulaor
and Filter
Ear
Amp1
Ear
Amp2
DTMF
Generator
Control Bus
I
2
C
I/F
REF PLL
Buzzer
Control
Power and RESET
SCLK
SDATA
MBIAS
REXT
MCLK
RESET
SS
EARV
DD
EARV
SS
PLLV
DD
PLLV
SS
DV
DD
DV
SS
AV
DD
AV
SS
V
PWRUPSEL
PCMOUT
EAR1OP
EAR1ON
EAR2O
BUZZCON

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
functional description
power-on/reset
The power for the various digital and analog circuits is separated to improve the noise performance of the
device. An external reset must be applied to the active low RESET terminal to guarantee reset upon power on.
After the initial power-on sequence the TWL1103 can be functionally powered up and down by writing to the
power control register through the I
2
C interface. There is a hardwired terminal selectable power up in default
mode option. The PWRUPSEL function allows the VBAP to power up in the default mode and allows use without
a microcontroller.
reference
A precision band gap reference voltage is generated internally and supplies all required voltage references to
operate the transmit and receive channels. The reference system also supplies bias voltage for use with an
electret microphone at terminal MBIAS. An external precision resistor is required for reference current setting
at terminal REXT.
control interface
The I
2
C interface is a two-wire bidirectional serial interface that controls the VBAP by writing data to six control
registers: 1) power control, 2) mode control, 3) transmit PGA and sidetone control, 4) receive PGA gain and
volume control, 5) DTMF high tone, 6) DTMF low tone.
There are two power-up modes which may be selected at the PWRUPSEL terminal: 1) The PWRUPSEL state
(Vdd at terminal 20) causes the device to power up in the default mode when power is applied. In the default
mode the I
2
C interface is not required and the device may be used without an I2C interface. The programmable
functions will be fixed at the default modes. 2) The PWRUPSEL state (ground at terminal 20) causes the device
to go to a power-down state when power is applied. In this mode an I2C interface is required to power up the
device.
phase-locked loop
The internal digital filters and modulators require a 10.24-MHz clock that is generated by phase locking to the
2.048-MHz master clock input.
PCM interface
The PCM interface transmits and receives data at the PCMO and PCMI terminals respectively. The data is
transmitted or received at the PCMCLK speed once every PCMSYN cycle. The PCMCLK may be tied directly
to the 2.048-MHz master clock (MCLK). The PCMSYN can be driven by an external source or derived from the
master clock and used as an interrupt to the host controller.
microphone amplifiers
The microphone input is a switchable interface for two differential microphone inputs. The first stage is a low
noise differential amplifier that provides a gain of 23.5 dB. The second stage amplifier has a selectable gain of
0 dB or 12 dB.
analog modulator
The transmit channel modulator is a third-order sigma-delta design.
transmit filter and PGA
The transmit filter is a digital filter designed to meet CCITT G.714 requirements. The device operates in either
the 15-bit linear or 8-bit companded µ-law or A-law mode that is selectable through the I
2
C interface. The
transmit PGA defaults to 0 dB.

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
functional description (continued)
sidetone
A portion of the transmitted audio is attenuated and fed back to the receive channel through the sidetone path.
The sidetone path defaults to –12 dB. The sidetone path can be enabled by writing to the power control register.
receive volume control
The receive volume control block acts as an attenuator with a range of –18 dB to 0 dB in 2 dB steps for control
of the receive channel volume. The receive volume control gain defaults to 0 dB.
receive filter and PGA
The receive filter is a digital filter that meets CCITT G.714 requirements with a high-pass filter that is selectable
through the I
2
C interface. The device operates in either the 15-bit linear or 8-bit µ-law or A-law companded
mode, which is selectable through the I2C interface. The gain defaults to –1 dB representing a 3 dBm0 level
for a 32 Ω
load impedance and the corresponding digital full scale PCMI code. The gain may be set to –2 dB
for the respective 3 dBm0 level for a 16 Ω load impedance.
digital modulator and filter
The second-order digital modulator and filter convert the received digital PCM data to the analog output required
by the earphone interface.
earphone amplifiers
The analog signal can be routed to either of two earphone amplifiers, one with differential output (EAR1ON and
EAR1OP) and one with single-ended output (EAR2O). Clicks and pops are suppressed for EAR1 differential
output only.
tone generator
The tone generator provides generation of standard DTMF tones and single tone frequencies which are output
to the following: 1) The buzzer driver, as a pulse density modulation (PDM) signal. 2) The receive path
digital/analog converter (D/A), for outputting through the earphone. There are 255 possible single tones. The
tone integer value is determined by the following formula Round (Tone Freq (Hz)/7.8135 Hz). The value is
loaded into one of two 8-bit registers, the high tone register [04}or the low tone register {05}. The tone output
is 2 dB higher when applied to the high tone register {04}. When generating DTMF tones the high DTMF tone
must be applied to the high tone register, and the low frequency tone to the low tone register.
TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
5
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
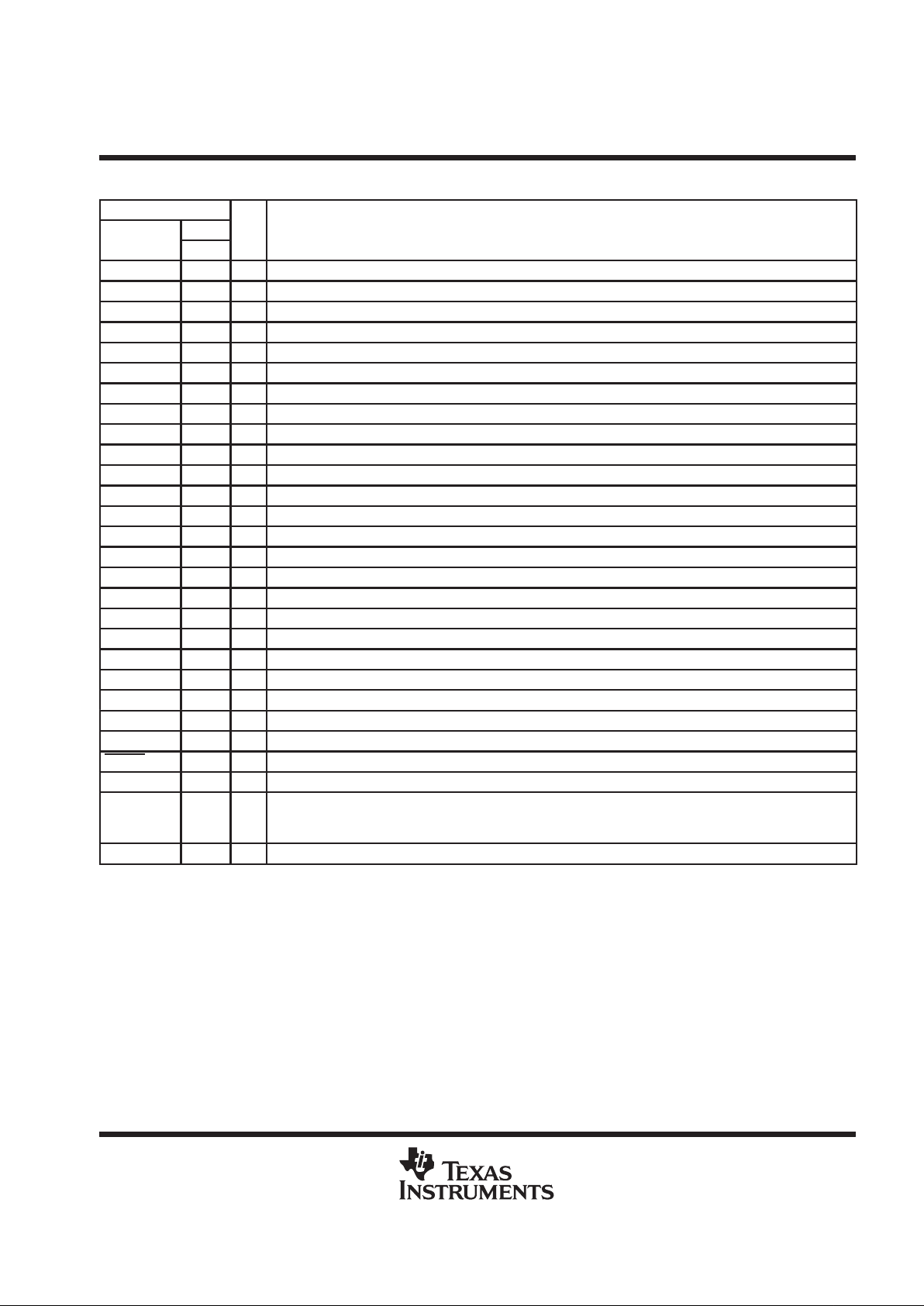
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NO.
I/O DESCRIPTION
NAME
PFB
AV
DD
32 I Analog positive power supply
AV
SS
8 I Analog negative power supply
BUZZCON 19 O Buzzer output, a pulse-density modulated signal to apply to external buzzer driver
DV
DD
13 I Digital positive power supply
DV
SS
14 I Digital negative power supply
EAR1ON 27 O Earphone 1 amplifier output (–)
EAR1OP 29 O Earphone 1 amplifier output (+)
EAR2O 31 O Earphone 2 amplifier output
EARV
DD
28 I Analog positive power supply for the earphone amplifiers
EARV
SS
30, 26 I Analog negative power supply for the earphone amplifiers
MBIAS 1 O Microphone bias supply output, no decoupling capacitors
MCLK 22 I Master system clock input (2.048 MHz) (digital)
MIC1P 2 I MIC1 input (+)
MIC1N 3 I MIC1 input (–)
MIC2P 4 I MIC2 input (+)
MIC2N 5 I MIC2 input (–)
PCMI 15 I Receive PCM input
PCMO 16 O Transmit PCM output
PCMSYN 18 I PCM frame sync
PCMCLK 17 I PCM data clock
PLLV
SS
24 I PLL negative power supply
PLLV
DD
25 I PLL digital power supply
PWRUPSEL 20 I Selects the power-up default mode
REXT 6 I/O Internal reference current setting terminal – use precision 100-kΩ resistor and no filtering capacitors
RESET 21 I Active low reset
SCL 12 I I2C-bus serial clock – this input is used to synchronize the data transfer from and to the VBAP
SDA 11 I/O I2C-bus serial address/data input/output – this is a bidirectional terminal used to transfer register control
addresses and data into and out of the CODEC. It is an open
-drain terminal and therefore requires a pull-up
resistor to VDD (typical 10 kΩ for 100 kHz)
V
SS
23 I Ground return for bandgap internal reference
TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
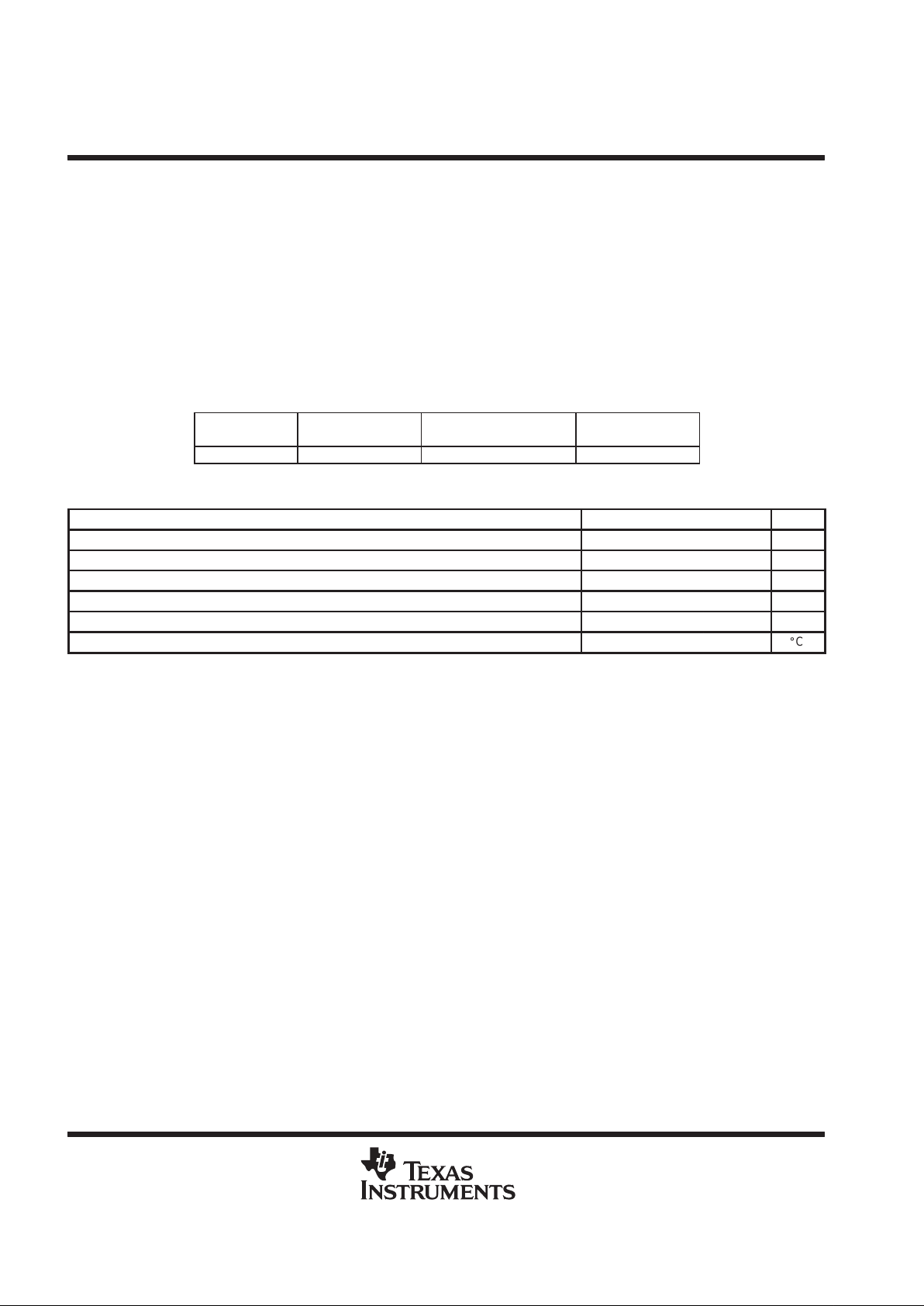
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
†
Supply voltage range –0.5 V to 4 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output voltage range –0.5 V to 4 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input voltage range –0.5 V to 4 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continuous total power dissipation See Dissipation Rating Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating free air temperature range (industrial temperature) –40°C to 85°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range, testing –65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lead temperature 1,6 mm from case for 10 seconds 260°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
DISSIPATION RATING TABLE
PACKAGE
TA ≤ 25°C
POWER RATING
DERATING FACTOR
ABOVE TA = 25°C
TA = 85°C
POWER RATING
PBS 680 mW 6.8 mW/°C 270 mW
recommended operating conditions (see Notes 1 and 2)
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Supply voltage, AVDD, DVDD, PLLVDD, EARV
DD
2.7 3.3 V
High-level input voltage (V
IHMIN
) 0.7 x V
DD
V
Low-level input voltage (V
ILMAX
) 0.3 x V
DD
V
Load impedance between EAR1OP and EAR1ON-R
L
16 to 32 Ω
Load impedance for EAR2OP-R
L
32 Ω
Operating free-air temperature, T
A
–40 85
_
C
NOTES: 1. To avoid possible damage and resulting reliability problems to these CMOS devices, the power-on initialization paragraph should
be followed, described in the Principles of Operations.
2. Voltages are with respect to AVSS, DV
SS,
PLLVSS
and
EARV
SS.
TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
7
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
electrical characteristics at 2.7 V and 25° C (unless otherwise noted)
supply current
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Operating, EAR1 selected, MicBias disabled 6 7 mA
Operating, EAR2 selected, MicBias disabled 5.4 6 mA
I Supply current from V
DD
Power down, Reg 2 bit 7 = 1, MClk not present
(see Note 3)
0.5 10 µA
Power down, Reg 2 bit 7 = 0, MClk not present
(see Note 3)
25 40 µA
t
on(i)
Power-up time from power down 5 10 ms
NOTE 3: V
IHMIN
= VDD, V
ILMAX
= V
SS
digital interface
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
V
OH
High-level output voltage PCMO and BuzzCon IOH = –3.2 mA, VDD = 3 V DV
DD
V
V
OL
Low-level output voltage PCMO and BuzzCon IOL = 3.2 mA, VDD = 3 V 0 V
I
IH
High-level input current, any digital input VI = V
DD
10 µA
I
IL
Low-level input current, any digital input VI = V
SS
10 µA
C
I
Input capacitance 10 pF
C
o
Output capacitance 20 pF
R
L
Load impedance (BuzzCon) 5 kΩ
microphone interface
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
V
IO
Input offset voltage at MIC1N, MIC2N See Note 4 –5 5 mV
I
IB
Input bias current at MIC1N, MIC2N –200 200 nA
C
i
Input capacitance at MIC1N, MIC2N 5 pF
V
n
Microphone input referred noise, psophometric weighted,
(C-message weighted is similar)
Micamp 1 gain = 23.5 dB
Micamp 2 gain = 0 dB
3.0 7.7 µV
rms
IOmax Output source current – MBIAS 1 1.2 mA
V(
mbias)
Microphone bias supply voltage (see Note 5) 2.4 2.5 2.55 V
MICMUTE –80 dB
Input impedance Fully differential 35 60 100 kΩ
NOTES: 4. Measured while MIC1P and MIC1N are connected together. Less than 5 mV offset results in 0 value code on PCMOUT .
5. Not a JEDEC symbol.
speaker interface
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
p
p
p
VDD = 2.7 V , fully differential, 16-Ω load,
3-dBm0 output, RGXPA = –2 dB
120.9 151.1 mW
Earphone AMP1 output power ( See Note 6)
VDD = 2.7 V , fully differential, 32-Ω load,
3-dBm0 output, RGXPA = –1 dB
76.1 95.1 mW
Earphone AMP2 output power ( See Note 6)
VDD = 2.7 V, single ended, 32-Ω load,
3-dBm0 output
10 12.5 mW
V
OO
Output offset voltage at EAR1 Fully differential ± 5 ±30 mV
p
3-dBm0 input, 16-Ω load 86.9 108.6
IOmax
Maximum output current for EAR1(rms)
3-dBm0 input, 32-Ω load 48.7 60.8
mA
Maximum output current for EAR2 (rms) 3-dBm0 input 17.7 22.1
EARMUTE –80 dB
NOTE 6: Maximum power is with a load impedance of –25%.
TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
electrical characteristics at 2.7 V and 25° C (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
transmit gain and dynamic range, companded mode (µ-law or A-law) or linear mode selected, transmit slope
filter bypassed (see Notes 7 and 8)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Transmit reference-signal level (0dB) Differential 175 mV
pp
Differential, normal mode 248 mV
pp
Overload-signal level (3 dBm0)
Differential, extended mode 63 mV
pp
Absolute gain error 0 dBm0 input signal, VDD = 2.7 V (minimum) –1 1 dB
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at 3 dBm0 to –30 dBm0 –0.5 0.5
Gain error with input level relative to gain at
–
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –31 dBm0 to –45 dBm0 –1 1
dB
–10
dBm0 MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –46 dBm0 to –55 dBm0 –1.2 1.2
NOTES: 7. Unless otherwise noted, the analog input is 0 dB, 1020-Hz sine wave, where 0 dB is defined as the zero-reference point of the channel
under test.
8. The reference signal level, which is input to the transmit channel, is defined as a value 3 dB below the full-scale value of 88-mV
rms
.
transmit gain and dynamic range, companded mode (µ-law or A-law) or linear mode selected, transmit slope
filter enabled (see Notes 9 and 10)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Transmit reference-signal level (0dB) Differential 175 mV
pp
Differential, normal mode 248 mV
pp
Overload-signal level (3 dBm0)
Differential, extended mode 63 mV
pp
Absolute gain error 0 dBm0 input signal, VDD = 2.7 V (minimum) –1 1 dB
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at 3 dBm0 to –30 dBm0 –0.5 0.5
Gain error with input level relative to gain at
–
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –31 dBm0 to –45 dBm0 –1 1
dB
–10
dBm0 MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –46 dBm0 to –55 dBm0 –1.2 1.2
NOTES: 9. Unless otherwise noted, the analog input is 0 dB, 1020-Hz sine wave, where 0 dB is defined as the zero-reference point of the channel
under test.
10. The reference signal level, which is input to the transmit channel, is defined as a value 3 dB below the full-scale value of 88-mV
rms
.
transmit filter transfer, companded mode (µ-law or A-law) or linear mode selected, transmit slope filter
bypassed, external high pass filter bypassed (MCLK = 2.048 MHz)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
<100 Hz –0.5 0.5
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 200 Hz –0.5 0.5
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 300 Hz to 3 kHz –0.5 0.5
Gain relative to input signal gain at 1020 Hz, internal high-pass
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 3.4 kHz –1.5 0
dB
filter disabled
.
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 4 kHz –14
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 4.6 kHz –35
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 8 k Hz –47
Gain relative to input signal gain at 1020 Hz, internal high-pass
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
<100 Hz –15
gg , g
filter enabled.
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 200 Hz –5
dB
TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
9
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
electrical characteristics at 2.7 V and 25° C (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
transmit filter transfer, companded mode (µ-law or A-law) or linear mode selected, transmit slope filter
selected (MCLK = 2.048 MHz) (see Note 11)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
=100 Hz –27 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 200 Hz –8 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 250 Hz –4 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 300 Hz –1.80 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 400 Hz –1.50 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 500 Hz –1.30 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 600 Hz –1.1 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 700 Hz –0.8 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 800 Hz –0.57 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 900 Hz –0.25 dB
p
p
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 1000 Hz 0 dB
Gain relative to input signal gain at 1000 H
z, w
ith slope filter selected
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 1500 Hz 1.8 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 2000 Hz 4.0 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 2500 Hz 6.5 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 3000 Hz 7.6 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 3100 Hz 7.7 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 3300 Hz 8.0 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 3500 Hz 6.48 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 4000 Hz –13 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 4500 Hz –35 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 5000 Hz –45 dB
f
MIC1
or f
MIC2
= 8000 Hz –50 dB
NOTE 11: The pass-band tolerance is ± 0.25 dB from 300 Hz to 3500 Hz.
transmit idle channel noise and distortion, companded mode (µ-law or A-law) selected, slope filter bypassed
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Transmit idle channel noise, psophometrically
weighted
TXPGA gain= 0 dB, micamp 1 gain = 23.5 dB,
micamp 2 gain = 0 dB
–86.6 –78 dBm0
p
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at 3 dBm0 27
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at 0 dBm0 30
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –5 dBm0 33
Transmit signal-to-distortion ratio with
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –10 dBm0 36
g
1020-Hz sine-wave input
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –20 dBm0 35
dB
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –30 dBm0 26
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –40 dBm0 24
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –45 dBm0 19
Intermodulation distortion, 2-tone CCITT method,
CCITT G.712 (7.1), R2 49
,,
composite power level, –13 dBm0
CCITT G.712 (7.2), R2 51
dB

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
electrical characteristics at 2.7 V and 25° C (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
transmit idle channel noise and distortion, companded mode (µ-law or A-law) selected, slope filter enabled
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Transmit idle channel noise, psophometrically
weighted
TXPGA gain= 0 dB, micamp 1 gain = 23.5 dB,
micamp 2 gain = 0.0 dB
–86.6 –78 dBm0
p
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at 3 dBm0 27
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at 0 dBm0 30
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –5 dBm0 33
Transmit signal-to-total distortion ratio with 1020-Hz
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –10 dBm0 36
g
sine-wave input
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –20 dBm0 35
dB
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –30 dBm0 26
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –40 dBm0 24
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –45 dBm0 19
Intermodulation distortion, 2-tone CCITT method,
CCITT G.712 (7.1), R2 49
,,
composite power level, –13 dBm0
CCITT G.712 (7.2), R2 51
dB
transmit idle channel noise and distortion, linear mode selected, slope filter bypassed
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Transmit idle channel noise
TXPGA gain = 0 dB, micamp 1 gain = 23.5 dB,
micamp 2 gain = 0.0 dB
–86.6 –78 dBm0
p
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at 3 dBm0 40 50
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at 0 dBm0 50 65
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –5 dBm0 60 68
Transmit signal-to-total distortion ratio with 1020-Hz
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –10 dBm0 55 70
g
sine-wave input
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –20 dBm0 58 65
dB
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –30 dBm0 50 60
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –40 dBm0 38 50
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –45 dBm0 30 45
transmit idle channel noise and distortion, linear mode selected, slope filter enabled
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Transmit idle channel noise
TXPGA gain = 0 dB, micamp 1 gain = 23.5 dB,
micamp 2 gain = 0.0 dB
–86.6 –78 dBm0
p
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at 3 dBm0 40 50
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at 0 dBm0 50 65
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –5 dBm0 60 68
Transmit signal-to-total distortion ratio with 1020-Hz
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –10 dBm0 55 70
g
sine-wave input
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –20 dBm0 58 65
dB
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –30 dBm0 50 60
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –40 dBm0 38 50
MIC1N, MIC1P to PCMO at –45 dBm0 30 45

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
11
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
electrical characteristics at 2.7 V and 25° C (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
receive gain and dynamic range, EAR1 selected, linear or companded (µ-law or A-law) mode selected (see
Note 12)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
16 Ω load RXPGA = -2.0 dB 3.93
Overload-signal level (3.0 dB)
32 Ω load RXPGA = -1.0 dB (default gain) 4.41
V
pp
Absolute gain error 0 dBm0 input signal, VDD = 2.7 V (minimum) –1 1 dB
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at 3 dBm0 to –40 dBm0 –0.5 0.5
Gain error with output level relative to gain
–
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at –41 dBm0 to –50 dBm0 –1 1
dB
at –10 dBm0
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at –51 dBm0 to –55 dBm0 –1.2 1.2
NOTE 12: RXPGA = -1 dB for 32 Ω default mode or RXPGA = -2 dB for 16 Ω, RXVOL = 0 dB, 1020 Hz input signal at PCMI, output measured
differentially between EAR1ON and EAR1OP
receive gain and dynamic range, EAR2 selected, linear or companded (µ-law or A-law) mode selected (see
Note 13)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Receive reference-signal level (0 dB) 0 dBm0 PCM input signal 1.1 V
pp
Overload-signal level (3 dB) 1.6 V
pp
Absolute gain error 0 dBm0 input signal, VDD = 2.7 V (minimum) –1 1 dB
PCMIN to EAR2O at 3 dBm0 to –40 dBm0 –0.5 0.5
Gain error with output level relative to gain at
–
PCMIN to EAR2O at –41 dBm0 to –50 dBm0 –1 1
dB
–10
dBm0
PCMIN to EAR2O at –51 dBm0 to –55 dBm0 –1.2 1.2
NOTE 13: RXPGA = -1 dB, RXVOL = 0 dB
receive filter transfer, companded mode (µ-law or A-law) or linear mode selected (MCLK = 2.048 MHz) (see
Note 13)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
f
EAR1
or f
EAR2
<100 Hz –0.5 0.5
f
EAR1
or f
EAR2
= 200 Hz –0.5 0.5
f
EAR1
or f
EAR2
= 300 Hz to 3 kHz –0.5 0.5
Gain relative to input signal gain at 1020 Hz, internal
-p
f
EAR1
or f
EAR2
= 3.4 kHz –1.5 0
dB
high-ass filter disabled
.
f
EAR1
or f
EAR2
= 4 kHz –14
f
EAR1
or f
EAR2
= 4.6 kHz –35
f
EAR1
or f
EAR2
= 8 kHz –47
Gain relative to input signal gain at 1020 Hz, internal
f
EAR1
or f
EAR2
<100 Hz –15
gg ,
high-pass filter enabled.
f
EAR1
or f
EAR2
= 200 Hz –5
dB
NOTE 13. RXPGA = -1 dB, RXVOL = 0 dB

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
electrical characteristics at 2.7 V and 25° C (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
receive idle channel noise and distortion, EAR1 selected, companded mode (µ-law or A-law) selected (see
Note 14)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Receive noise, psophometrically weighted PCMIN = 11010101 (Α–law) –89 –86 dBm0
p
Receive noise, C-message weighted PCMIN = 11111111 (µ–law) 36 50 µV
rms
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at 3 dBm0 21
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at 0 dBm0 25
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at –5 dBm0 36
Receive signal-to-distortion ratio with 1020-Hz
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at –10 dBm0 43
g
sine-wave input
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at –20 dBm0 40
dB
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at –30 dBm0 38
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at –40 dBm0 28
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at –45 dBm0 23
NOTE 14: 10. RXPGA = -1 dB for 32 Ω default mode or RXPGA = -2 dB for 16 Ω, RXVOL = 0 dB, 1020 Hz input signal at PCMI, output measured
differentially between EAR1ON and EAR1OP.
receive idle channel noise and distortion, EAR1 selected, linear mode selected (see Note 14)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Receive noise, (20 Hz to 20 kHz brickwall window) PCMIN = 0000000000000 –86 –83 dBm0
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at 3 dBm0 65 78
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at 0 dBm0 73 80
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at –5 dBm0 72 78
Receive signal-to-distortion ratio with 1020 Hz
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at –10 dBm0 70 78
g
sine-wave input
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at –20 dBm0 60 76
dB
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at –30 dBm0 50 67
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at –40 dBm0 40 60
PCMIN to EAR1ON, EAR1OP at –45 dBm0 35 55
Intermodulation distortion, 2-tone CCITT method,
CCITT G.712 (7.1), R2 50
,,
composite power level, –13 dBm0
CCITT G.712 (7.2), R2 54
dB
NOTE 14. RXPGA = -1 dB for 32 Ω default mode or RXPGA = -2 dB for 16 Ω, RXVOL = 0 dB, 1020 Hz input signal at PCMI, output measured
differentially between EAR1ON and EAR1OP.
receive idle channel noise and distortion, EAR2 selected, companded mode (µ-law or A-law) selected (see
Note 13)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Receive noise, psophometrically weighted PCMIN = 11010101 (Α–law) –81 –78 dBmo
p
Receive noise, C-message weighted PCMIN = 11111111 (µ–law) 36 50 µV
rms
PCMIN to EAR2O at 3 dBm0 21
PCMIN to EAR2O at 0 dBm0 25
PCMIN to EAR2O at –5 dBm0 36
Receive signal-to-distortion ratio with 1020-Hz
PCMIN to EAR2O at –10 dBm0 43
Receive signal to distortion ratio with 1020 Hz
sine-wave input
PCMIN to EAR2O at –20 dBm0 40
dB
PCMIN to EAR2O at –30 dBm0 38
PCMIN to EAR2O at –40 dBm0 28
PCMIN to EAR2O at –45 dBm0 23
NOTE 13. RXPGA = -1 dB, RXVOL = 0 dB

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
13
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
electrical characteristics at 2.7 V and 25° C (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
receive idle channel noise and distortion, EAR2 selected, linear mode selected (see Note 13)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Receive noise, (20 Hz to 20 kHz brickwall window) PCMIN = 0000000000000 –86 –83 dBm0
PCMIN to EAR2O at 3 dBm0 45 60
PCMIN to EAR2O at 0 dBm0 60 65
PCMIN to EAR2O at –5 dBm0 58 62
Receive signal-to-distortion ratio with 1020-Hz sine-wave input
PCMIN to EAR2O at –10 dBm0 55 60
g
PCMIN to EAR2O at –20 dBm0 53 60
dB
PCMIN to EAR2O at –30 dBm0 52 58
PCMIN to EAR2O at –40 dBm0 50 57
PCMIN to EAR2O at –45 dBm0 45 52
Intermodulation distortion, 2-tone CCITT method, composite power
CCITT G.712 (7.1), R2 50
,,
level, –13 dBm0
CCITT G.712 (7.2), R2 54
dB
NOTE 13. RXPGA = -1 dB, RXVOL = 0 dB
power supply rejection and crosstalk attenuation
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Supply voltage rejection, transmit channel
MIC1N, MIC1P =0 V ,
VDD = 2.7 Vdc + 100 mV
peak to peak
, f = 0 to 50 kHz
–80 –45 dB
Supply voltage rejection, receive channel,
EAR1 selected (differential)
PCM code = positive zero,
VDD = 2.7 Vdc + 100 mV
peak to peak
, f = 0 to 50 kHz
–90 –45 dB
Crosstalk attenuation, transmit-to-receive
(differential)
MIC1N, MIC1P = 0 dB, f = 300 to 3400 Hz measured
differentially between EAR1ON and EAR1OP
70 dB
Crosstalk attenuation, receive-to-transmit
PCMIN = 0 dBm0, f = 300 to 3400 Hz measured at
PCMO, EAR1 amplifier
70 dB
switching characteristics
clock timing requirements
PARAMETER MIN NOM MAX UNIT
t
t
Transition time, MCLK 10 ns
MCLK frequency 2.048 MHz
MCLK jitter 37%
Number of PCMCLK clock cycles per PCMSYN frame 256 256
t
c(PCMCLK)
PCMCLK clock period 156 488 512 ns
Duty cycle, PCMCLK 45% 50% 68%
transmit timing requirements (see Figure 6)
PARAMETER MIN MAX UNIT
t
su(PCMSYN)
Setup time, PCMSYN high before falling edge of PCMCLK 20 t
c(PCMCLK)
–20
t
h(PCMSYN)
Hold time, PCMSYN high after falling edge of PCMCLK 20 t
c(PCMCLK)
–20
ns

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
14
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
switching characteristics (continued)
receive timing requirements (see Figure 7)
PARAMETER MIN MAX UNIT
t
su(PCSYN)
Setup time, PCMSYN high before falling edge of PCMCLK 20 t
c(PCMCLK)
–20 ns
t
h(PCSYN)
Hold time, PCMSYN high after falling edge of PCMCLK 20 t
c(PCMCLK)
–20 ns
t
su(PCMI)
Setup time, PCMI high or low before falling edge of PCMCLK 20 ns
t
h(PCMI)
Hold time, PCMI high or low after falling edge of PCMCLK 20 ns
propagation delay times, C
Lmax
= 10 pF (see Figure 6)
PARAMETER MIN MAX UNIT
t
pd1
From PCMCLK bit 1 high to PCMO bit 1 valid 35 ns
t
pd2
From PCMCLK high to PCMO valid, bits 2 to n 35 ns
t
pd3
From PCMCLK bit n low to PCMO bit n Hi-Z 30 ns
I2C bus timing requirements (see Figure 8)
PARAMETER MIN MAX UNIT
SCL Clock frequency 400 kHz
t
HIGH
Clock high time 600 ns
t
LOW
Clock low time 1300 ns
t
R
SDA and SCL rise time 300 ns
t
F
SDA and SCL fall time 300 ns
t
HD:STA
Hold time (repeated) ST ART condition. After this period the first clock pulse is generated. 600 ns
t
SU:STA
Setup time for repeated STAR T condition 600 ns
t
HD:DAT
Data input hold time 0 ns
t
SU:DAT
Data input setup time 100 ns
t
SU:STO
STOP condition setup time 600 ns
t
BUF
Bus free time 1300 ns
DTMF generator characteristics
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
DTMF high to low tone relative amplitude
(pre-emphasis)
1.5 2 2.5 dB
Tone frequency accuracy –1.5 % 1.5 %
Harmonic distortion Measured from lower tone group to highest parasitic –20 dB
MICBIAS characteristics
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Load impedance 5 kΩ

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
15
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
NOTE: SLAVE = VBAP
A6 A5 A4 A0 R/W0ACK
0
R7 R6 R5 R0 ACK
0
D7 D6 D5 D0 ACK
0
Stop
Slave Address Register Address Data
SCL
SDA
Start
Figure 1. I2C-Bus Write to VBAP
NOTE: SLAVE = VBAP
Master
Drives
ACK and Stop
A6 A5 A0 R/W ACK
00
R7 R6 R0 ACK A6 A0 R/W ACK
10
D7 D6 D0 ACK
Slave Address Register Address Slave Address
Slave Drives
The Data
Repeated
Start
SCL
SDA
Start Stop
Figure 2. I2C Read From VBAP: Protocol A
NOTE: SLAVE = VBAP
A6 A5 A0 R/W ACK R7
00
R6 R0 ACK A6 A5 A0
R/W ACK
D7 D0
ACK
Master
Drives
ACK and Stop
Slave Address Register Address Slave Address
Slave Drives
The Data
Stop
Stop Start
SCL
SDA
Start
Figure 3. I2C Read From VBAP: Protocol B

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
16
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
register map addressing
REG 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
Power control 00 Sidetone
En
TXEn RXEn MICSEL BIASEn RXEn EAROUT
Sel
PWRUP
Mode control 01 Comp Sel TMEn PCMLB Comp En BUZZEn RXFLTREnTXFLTREnTXSLOPE
En
TXPGA 02 PD0 TP3 TP2 TP1 TP0 ST2 ST1 ST0
RXPGA 03 RP3 RP2 RP1 RP0 RV3 RV2 RV1 RV0
High DTMF 04 HIFREQ
Sel7
HIFREQ
Sel6
HIFREQ
Sel5
HIFREQ
Sel4
HIFREQ
Sel3
HIFREQ
Sel2
HIFREQ
Sel1
HIFREQ
Sel0
Low DTMF 05 LOFREQ
Sel7
LOFREQ
Sel6
LOFREQ
Sel5
LOFREQ
Sel4
LOFREQ
Sel3
LOFREQ
Sel2
LOFREQ
Sel1
LOFREQ
Sel0
register power-up defaults
REG 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
Power control (1) 00 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0
Power control (2) 00 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1
Mode control 01 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
TXPGA 02 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
RXPGA 03 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0
High DTMF 04 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Low DTMF 05 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1. Value when PWRUPSEL = 0
2. Value when PWRUPSEL = 1

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
17
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
register map
T able 1. Power Control Register: Address {00} HEX
BIT NUMBER
7 65 43210
DEFINITIONS
1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 Default setting PWRUPSEL = 0
1 00 11011Default setting PWRUPSEL = 1
X X X X X X X 0 Reference system, power down
X X X X X X X 1 Reference system, power up
X X X X X X 1 X EAR AMP1 selected, EAR AMP2 power down
X X X X X X 0 X EAR AMP2 selected, EAR AMP1 power down
X X X X X 0 X X Receive channel enabled
X X 0 X X 1 X X Receive channel muted
X X 1 X X 1 X 0 Receive channel, power down
X X X X 1 X X X MICBIAS selected
X X X X 0 X X X MICBIAS power down
X X X 1XXXXMIC1 selected
X X X 0XXXXMIC2 selected
X 0X XXXXXTransmit channel enabled
X 1 0XXXXXTransmit channel muted
X 1 1XXXXXTransmit channel power down
0 XXXXXXXSidetone enabled
1 X X X X X X X Sidetone muted
Table 2. Mode Control Register: Address {01} HEX
BIT NUMBER
7 6543210
DEFINITIONS
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 Default setting
X X X X X X 0 0 TX channel high-pass filter enabled and slope filter enabled
X X X X X X 0 1 TX channel high-pass filter enabled and slope filter disabled
X X X X X X 1 0 TX channel high-pass filter disabled and slope filter enabled
X X X X X X 1 1 TX channel high-pass filter disabled and slope filter disabled
X X X X X 0 X X RX channel high-pass filter disabled (low pass only)
X X X X X 1 X X RX channel high-pass filter enabled
X X X X 0 X X X BUZZCON disabled
X X X X 1 X X X BUZZCON enabled
X X X 0 X X X X Linear mode selected
1 X X 1 X X X X A-law companding mode selected
0 XX1XXXXµ-law companding mode selected
X X 0 X X X X X TX and RX channels normal mode
X X 1 X X X X X PCM loopback mode
X 0 X X X X X X T one mode disabled
X 1 X X X X X X T one mode enabled

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
18
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
Transmit PGA and sidetone control register: Address {02}HEX
Bit definitions :
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 DEFINITION
PDO TP3 TP2 TP1 TP0 ST2 ST1 ST0 See Table 2 and Table 4
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 Default setting
Receive volume control register: Address {03}HEX
Bit definitions :
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 DEFINITION
RP3 RP2 RP1 RP0 RV3 RV2 RV1 RV0 See Table 3 and Table 5
0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 Default setting
High tone selection control register: Address {04}HEX
Bit definitions :
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 DEFINITION
X X X X X X X X DTMF (see Table 7)
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Default setting
Low tone selection control register: Address {05}HEX
Bit definitions :
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 DEFINITION
X X X X X X X X DTMF (see Table 7)
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Default setting
0 1 2 3 4 N–2 N–1 N N+1
Transmit T ime Slot
1 2 3 4 N–2 N–1 N
80%
20%
t
su(PCMSYN)
t
h(PCMSYN)
See Note A
See Note C
See Note B
t
pd2
t
pd1
See Note D
t
su(PCMO)
t
pd3
80%
20%
PCMCLK
PCMSYN
PCMO
NOTES: A. This window is allowed for PCMSYN high.
B. This window is allowed for PCMSYN low (t
h(PCMSYN)
max determined by data collision considerations).
C. Transitions are measured at 50%.
D. Bit 1 = MSB, Bit N = LSB
Figure 4. Transmit Timing Diagram

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
19
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
80%
20%
See Note C
PCMI
PCMSYN
PCMCLK
0 1 2 3 4 N –2 N –1 N N +1
20%
80%
1 2 3 4 N –2 N –1 N
See Note D
t
h(PCMSYN)
t
su(PCMSYN)
See Note A
t
su(PCMI)
t
h(PCMI)
See Note B
Receive Time Slot
A. This window is allowed for PCMSYN high.
B. This window is allowed for PCMSYN low.
C. Transitions are measured at 50%.
D. Bit 1 = MSB, Bit N = LSB
Figure 5. Receive Timing Diagram
t
BUF
t
hd(STA)
t
LOW
t
r
t
f
t
hd(DAT)
t
HIGH
t
su(DAT)
t
su(STA)
t
hd(STA)
t
su(STO)
STO STA STA STO
SDA
SCL
Figure 6. I2C-Bus Timing Diagram

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
20
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
power-on initialization
An external reset with a minimum pulse width of 500 ns must be applied to the active low RESET terminal to
guarantee reset upon power on. All registers are set with default values upon external reset initialization.
The desired selection for all programmable functions can be initialized prior to a power-up command using the
I2C interface.
Table 3. Power-Up and Power-Down Procedures (V
DD
= 2.7 V, Earphone amplifier unloaded)
DEVICE STATUS PROCEDURE
MAXIMUM POWER
CONSUMPTION
p
Set bit 1 = 1 in power control register, EAR1 enabled 16.2 mW
Power-up
Set bit 1 = 0 in power control register, EAR2 enabled 14.6 mW
Set bit 7 = 1 in TXPGA control register and bit 0 = 0 1.35 µW
Power-down
Set bit 7 = 0 in TXPGA control register and bit 0 = 0 67.5 µW
In addition to resetting the power-down bit in the power control register, loss of MCLK (no transition detected)
automatically enters the device into a power-down state with PCMO in the high impedance state. If during a
pulse code modulation (PCM) data transmit cycle an asynchronous power down occurs, the PCM interface
remains powered up until the PCM data is completely transferred.
An additional powerdown mode overrides the MCLK detection function. This allows the device to enter the
powerdown state without regard to MCLK. Setting bit 7 of the TX filter and PGA sidetone register to logic high
enables this function.
conversion laws
The device can be programmed either for a 15-bit linear or 8-bit (µ-law or A-law) companding mode. The
companding operation approximates the CCITT G.711 recommendation. The linear mode operation uses a
15-bit twos-complement format.
transmit operation
microphone input
The microphone input stage is a low noise differential amplifier that provides a preamplifier gain of 23.5 dB. A
microphone can be capacitively connected to the MIC1N and MIC1P inputs, while the MIC2N and MIC2P inputs
can be used to capacitively connect a second microphone or an auxiliary audio circuit.

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
21
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
transmit operation (continued)
_
+
_
+
V
ref
510 kΩ
510 kΩ
34 kΩ
34 kΩ
Ci MIC1N
Ci MIC1P
M
I
C
R
mic
R
mic
MBIAS
Figure 7. Typical Microphone Interface
microphone mute function
Transmit channel muting provides 80-dB attenuation of input microphone signal. The MICMUTE function can
be selected by setting bit 6 of the power control register through the I2C interface.
transmit channel gain control
The values in the transmit PGA control registers control control the gain in the transmit path. The total TX
channel gain can vary from 35.5 dB to 13.5 dB. The default total TX channel gain is 23.5 dB
Table 4. Transmit Gain Control
BIT NAME MIC AMP1 MIC AMP2 TX PGA
GAIN
MODE
TOTAL TX GAIN
TP3 TP2 TP1 TP0 GAIN GAIN GAIN MIN TYP MAX UNIT
0 0 0 0 23.5 12 0 Extended 35.3 35.5 35.7 dB
0 0 0 1 23.5 12 –2 Extended 33.3 33.5 33.7 dB
0 0 1 0 23.5 12 –4 Extended 31.3 31.5 31.7 dB
0 0 1 1 23.5 12 –6 Extended 29.3 29.5 29.7 dB
0 1 0 0 23.5 12 –8 Extended 27.3 27.5 27.7 dB
0 1 0 1 23.5 12 –10 Extended 25.3 25.5 25.7 dB
1 0 0 0 23.5 0 0 Normal 23.3 23.5 23.7 dB
1 0 0 1 23.5 0 –2 Normal 21.3 21.5 21.7 dB
1 0 1 0 23.5 0 –4 Normal 19.3 19.5 19.7 dB
1 0 1 1 23.5 0 –6 Normal 17.3 17.5 17.7 dB
1 1 0 0 23.5 0 –8 Normal 15.3 17.5 17.7 dB
1 1 0 1 23.5 0 –10 Normal 13.3 13.5 13.7 dB

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
22
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
receive operation
receive channel gain control
The values in the receive PGA control registers control the gain in the receive path. PGA gain is set from –6
to 6 dB dB in 1 dB steps through the I2C interface. The default receive channel gain is –1 dB.
Table 5. Receive PGA Gain Control
BIT NAME RELATIVE GAIN
RP3 RP2 RP1 RP0 MIN TYP MAX UNIT
0 0 0 0 5.8 6 6.2 dB
0 0 0 1 4.8 5 5.2 dB
0 0 1 0 3.8 4 4.2 dB
0 0 1 1 2.8 3 3.2 dB
0 1 0 0 1.8 2 2.2 dB
0 1 0 1 0.8 1 1.2 dB
0 1 1 0 –0.2 0 0.2 dB
0 1 1 1 –1.2 –1 –0.8 dB
1 0 0 0 –2.2 –2 –1.8 dB
1 0 0 1 –3.2 –3 –2.8 dB
1 0 1 0 –4.2 –4 –3.8 dB
1 0 1 1 –5.2 –5 –4.8 dB
1 1 0 0 –6.2 –6 –5.8 dB
sidetone gain control
The values in the sidetone PGA control registers control the sidetone gain. Sidetone gain is set from –12 dB
to –24 dB in 2-dB steps through the I2C interface. Sidetone can be muted by setting bit 7 of the power control
register. The default sidetone gain is –12 dB.
Table 6. Sidetone Gain Control
BIT NAME RELATIVE GAIN
ST2 ST1 ST0 MIN TYP MAX UNIT
0 0 0 –12.2 –12 –11.8 dB
0 0 1 –14.2 –14 –13.8 dB
0 1 0 –16.2 –16 –15.8 dB
0 1 1 –18.2 –18 –17.8 dB
1 0 0 –20.2 –20 –19.8 dB
1 0 1 –22.2 –22 –21.8 dB
1 1 0 –24.2 –24 –23.8 dB

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
23
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
receive operation (continued)
receive volume control
The values in the volume control PGA control registers provide volume control into the earphone. Volume
control gain is set from 0 dB to –18 dB in 2-dB steps through the I2C interface. The default RX volume control
gain is 0 dB.
Table 7. rx Volume Control
BIT NAME RELATIVE GAIN
RV3 RV2 RV1 RV0 MIN TYP MAX UNIT
0 0 0 0 –0.2 0 0.2 dB
0 0 0 1 –2.2 –2 –1.8 dB
0 0 1 0 –4.2 –4 –3.8 dB
0 0 1 1 –6.2 –6 –5.8 dB
0 1 0 0 –8.2 –8 –7.8 dB
0 1 0 1 –10.2 –10 –9.8 dB
0 1 1 0 –12.2 –12 –11.8 dB
0 1 1 1 –14.2 –14 –13.8 dB
1 0 0 0 –16.2 –16 –15.8 dB
1 0 0 1 –18.2 –18 –17.8 dB
earphone amplifier
The analog signal can be routed to one of two earphone amplifiers: one with differential output (EAR1ON and
EAR1OP) capable of driving a 16 Ω load, or one with single-ended output (EAR2O) capable of driving a 32 Ω
load.
earphone mute function
Muting can be selected by setting bit 3 of the power control register through the I
2
C interface.
receive PCM data format
D
Companded mode: 8 bits are received, the most significant (MSB) first.
D
Linear mode: 15 bits are received, MSB first.

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
24
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
receive operation (continued)
Table 8. Receive-Data Bit Definitions
BIT NO. COMPANDED
MODE
LINEAR
MODE
1 CD7 LD14
2 CD6 LD13
3 CD5 LD12
4 CD4 LD11
5 CD3 LD10
6 CD2 LD9
7 CD1 LD8
8 CD0 LD7
9 – LD6
10 – LD5
11 – LD4
12 – LD3
13 – LD2
14 – LD1
15 – LD0
16 – ––
Transmit channel gain control bits always follow the PCM data in time:
CD7–CD0 = data word in companded mode
LD14–LD0 = data word in linear mode
DTMF generator operation and interface
The dual-tone multifrequency generator (DTMF) circuit generates the summed DTMF tones for push button
dialing and provides the PDM output for the BUZZCON user-alert tone. There are 255 possible single tones.
The tone integer value is determined by the formula round (tone frequency (Hz)/7.8125 Hz). The integer value
is loaded into either one of two 8-bit registers, high tone register (04) or low tone register (05). The tone output
is 2 dB higher when applied to the high tone register (04). When generating DTMF tones, the high frequency
value must be applied to the high tone register (04) and the low DTMF value to the low tone register.

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
25
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
DTMF generator operation and interface (continued)
Table 9. Typical DTMF and Single Tone Control
DT7 DT6 DT5 DT4 DT3 DT2 DT1 DT0
INTEGER
VALUE
TONE
FUNCTION
TONE/HZ
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 OFF 0
0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 45 F 349
0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 47 F# 370
0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 50 G 392
0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 53 G# 415
0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 56 A 440
0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 60 A# 466
0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 63 B 494
0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 67 C 523
0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 71 C# 554
0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 75 D 587
0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 80 D# 622
0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 84 E 659
0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 89 F 698
0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 95 F# 740
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 100 G 784
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 106 G# 831
0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 113 A 880
0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 119 A# 932
0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 126 B 988
1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 134 C 1047
1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 142 C# 1109
1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 150 D 1175
1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 159 D# 1245
1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 169 E 1319
1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 179 F 1397
1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 189 F# 1480
1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 201 G 1568
1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 213 G# 1661
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 225 A 1760
1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 239 A# 1865
1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 253 B 1976
0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 89 DTMF Low 697
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 99 DTMF Low 770
0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 109 DTMF Low 852
0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 120 DTMF Low 941
1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 155 DTMF HIgh 1209
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 171 DTMF HIgh 1336
1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 189 DTMF HIgh 1477
1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 209 DTMF HIgh 1633

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
26
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
DTMF generator operation and interface (continued)
T ones from the DTMF generator block are present at all outputs and are controlled by enabling or disabling the
individual output ports. The values that determine the tone frequency are loaded into the tone registers (high
and Lo) as two separate values.
The values loaded into the tone registers initiate an iterative table look-up function, placing a 6-bit or 7-bit in 2s
complement value into the the tone registers. There is a 2 dB difference in the resulting output of the two
registers, the high tone register having the greater result.
The resulting range of a tone set into the low register value is +31 {1F}HEX to –32 {20}HEX for a range of six
bits and is in 2s complement format. The resulting range of a tone set into the high register value is +39 {27}HEX
to –40 {D8}HEX in twos-complement format, as well.
The maximum range is six bits having a maximum value of {31}HEX. The value {31} is represented as 01 1111.
Two zeros are added to the leading side of the value and then the value is padded with seven LSB zeros to create
a value of 000 1 11 1 1000 0000. As the maximum full scale value is 000 1 11 1 1000 0000, then the resulting output
magnitude is 20 log (input value/maximum value) or 20 log (3968/16783) or –12.31 dB below full scale. This
is the result when all gains are set at default.
buzzer logic section
The single-ended output BUZZCON is a PDM signal intended to drive a buzzer through an external driver
transistor. The PDM begins as a selected tone, generated and passed through the receive D/A channel, and
fed back to the transmit channel analog modulator, where a PDM signal is generated and routed to the
BUZZCON output.
support section
The clock generator and control circuit uses the master clock input (MCLK) to generate internal clocks to drive
internal counters, filters, and convertors. Register control data is written into and read back from the VBAP
registers via the control interface.
I2C–bus protocols
The VBAP serial interface is designed to be I2C-bus compatible and operates in the slave mode. This interface
consists of the following terminals:
SCL: I2C-bus serial clock – This input synchronizes the control data transfer from and to the CODEC.
SDA: I
2
C-bus serial address/data input/output – This is a bidirectional terminal that transfers register
control addresses and data into and out of the codec. It is an open drain terminal and therefore
requires a pullup resistor to V
CC
(typical 10 kΩ for 100 kHz).
TWL1103 has a fixed device select address of {E2}HEX for write mode and {E3}HEX for read mode.
For normal data transfer, SDA is allowed to change only when SCL is low. Changes when SCL is high are
reserved for indicating the start and stop conditions.
Data transfer may be initiated only when the bus is not busy. During data transfer, the data line must remain
stable whenever the clock line is at high. Changes in the data line while the clock line is at high are interpreted
as a start or stop condition.

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
27
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
Table 10. I2C-Bus Conditions
CONDITION STATUS DESCRIPTION
A Bus not busy Both data and clock lines remain at high
B Start data transfer
A high to low transition of the SDA line while the clock (SCL) is high determines a start condition.
All commands must proceed from a start condition.
C Stop data transfer
A low to high transition of the SDA line while the clock (SCL) is high determines a stop condition.
All operations must end with a stop condition.
D Data valid
The state of the data line represents valid data when, after a start condition, the data line is stable
for the duration of the high period of the clock signal.
I2C bus protocols
The data on the line must be changed during the low period of the clock signal. There is one clock pulse per
bit of data.
Each data transfer is initiated with a start condition and terminated with a stop condition.
When addressed, the VBAP generates an acknowledge after the reception of each byte. The master device
(microprocessor) must generate an extra clock pulse that is associated with this acknowledge bit.
The VBAP must pull down the SDA line during the acknowledge clock pulse so that the SDA line is at stable
low state during the high period of the acknowledge related clock pulse. Setup and hold times must be taken
into account. During read operations, a master must signal an end of data to the slave by not generating an
acknowledge bit on the last byte that was clocked out of the slave. In this case, the slave (VBAP) must leave
the data line high to enable the master to generate the stop condition.
clock frequencies and sample rates
A fixed PCMSYN rate of 8 kHz determines the sampling rate.

TWL1103
VOICE-BAND AUDIO PROCESSOR (VBAP)
SLVS259 – NOVEMBER 1999
28
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
MECHANICAL DATA
PBS (S-PQFP-G32) PLASTIC QUAD FLATPACK
Gage Plane
16
9
0,13 NOM
0,25
0,40
0,70
Seating Plane
0,10 MIN
4087735/A 11/95
17
0,17
0,23
8
5,05
4,95
SQ
3,50 TYP
24
25
1
32
6,90
7,10
SQ
1,05
0,95
1,20 MAX
0,08
0,50
M
0,08
0°–7°
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERT AIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MA Y INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS”). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICA TIONS IS UNDERSTOOD T O
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 1999, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...