Texas Instruments TLC5620IN, TLC5620IDR, TLC5620ID, TLC5620CN, TLC5620CDR Datasheet
...
TLC5620C, TLC5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS081D – NOVEMBER 1994 – REVISED APRIL 1997
D
Four 8-Bit Voltage Output DACs
D
5-V Single-Supply Operation
D
Serial Interface
D
High-Impedance Reference Inputs
D
Programmable 1 or 2 Times Output Range
D
Simultaneous Update Facility
D
Internal Power-On Reset
D
Low-Power Consumption
D
Half-Buffered Output
N OR D PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
GND
REFA
REFB
REFC
REFD
DATA
CLK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
V
DD
LDAC
DACA
DACB
DACC
DACD
LOAD
applications
D
Programmable V oltage Sources
D
Digitally Controlled Amplifiers/Attenuators
D
Mobile Communications
D
Automatic Test Equipment
D
Process Monitoring and Control
D
Signal Synthesis
description
The TLC5620C and TLC5620I are quadruple 8-bit voltage output digital-to-analog converters (DACs) with
buffered reference inputs (high impedance). The DACs produce an output voltage that ranges between either
one or two times the reference voltages and GND, and the DACs are monotonic. The device is simple to use,
running from a single supply of 5 V. A power-on reset function is incorporated to ensure repeatable start-up
conditions.
Digital control of the TLC5620C and TLC5620I are over a simple three-wire serial bus that is CMOS compatible
and easily interfaced to all popular microprocessor and microcontroller devices. The 11-bit command word
comprises eight bits of data, two DAC-select bits, and a range bit, the latter allowing selection between the times
1 or times 2 output range. The DAC registers are double buffered, allowing a complete set of new values to be
written to the device, then all DAC outputs are updated simultaneously through control of LDAC. The digital
inputs feature Schmitt triggers for high noise immunity.
The 14-terminal small-outline (D) package allows digital control of analog functions in space-critical
applications. The TLC5620C is characterized for operation from 0°C to 70°C. The TLC5620I is characterized
for operation from –40°C to 85°C. The TLC5620C and TLC5620I do not require external trimming.
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
PACKAGE
T
A
0°C to 70°C TLC5620CD TLC5620CN
–40°C to 85°C TLC5620ID TLC5620IN
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
SMALL OUTLINE
(D)
PLASTIC DIP
(N)
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Copyright 1997, Texas Instruments Incorporated
1
TLC5620C, TLC5620I
I/O
DESCRIPTION
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS081D – NOVEMBER 1994 – REVISED APRIL 1997
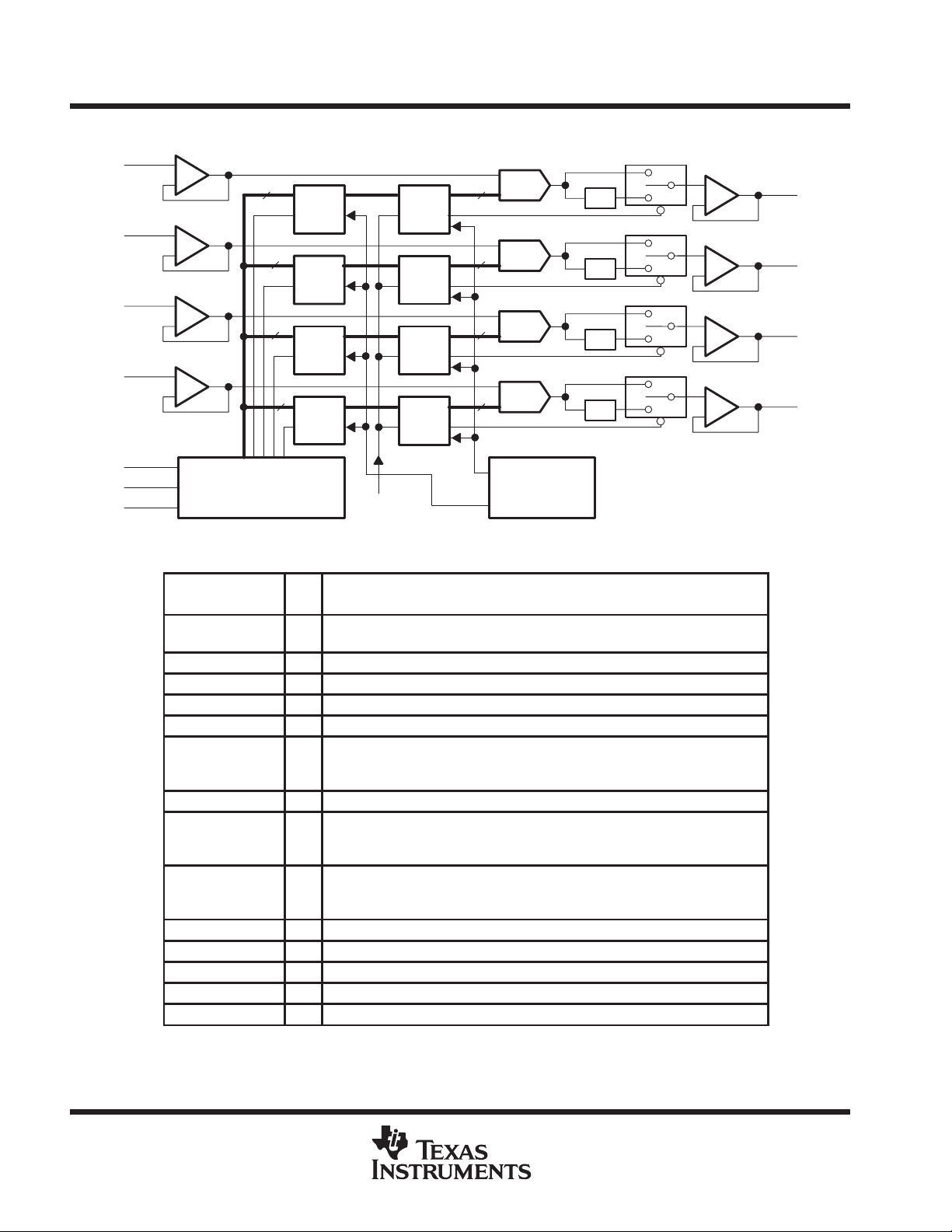
functional block diagram
REFA
REFB
REFC
REFD
CLK
DATA
LOAD
2
3
4
5
7
6
8
+
–
8
Latch Latch
+
–
8
+
–
8
+
–
8
Latch
Serial
Interface
LatchLatch
LatchLatch
Latch
13
LDAC
8
8
8
8
DAC
× 2
DAC
× 2
DAC
× 2
DAC
× 2
Power-On
Reset
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
CLK 7 I Serial interface clock. The input digital data is shifted into the serial interface
register on the falling edge of the clock applied to the CLK terminal.
DACA 12 O DAC A analog output
DACB 11 O DAC B analog output
DACC 10 O DAC C analog output
DACD 9 O DAC D analog output
DATA 6 I Serial interface digital data input. The digital code for the DAC is clocked into the
serial interface register serially. Each data bit is clocked into the register on the
falling edge of the clock signal.
GND 1 I Ground return and reference terminal
LDAC 13 I Load DAC. When the LDAC signal is high, no DAC output updates occur when
the input digital data is read into the serial interface. The DAC outputs are only
updated when LDAC is taken from high to low.
LOAD 8 I Serial Interface load control. When LDAC is low, the falling edge of the LOAD
signal latches the digital data into the output latch and immediately produces the
analog voltage at the DAC output terminal.
REFA 2 I Reference voltage input to DAC A. This voltage defines the output analog range.
REFB 3 I Reference voltage input to DAC B. This voltage defines the output analog range.
REFC 4 I Reference voltage input to DAC C. This voltage defines the output analog range.
REFD 5 I Reference voltage input to DAC D. This voltage defines the output analog range.
V
DD
14 I Positive supply voltage
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
12
11
10
9
DACA
DACB
DACC
DACD
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TLC5620C, TLC5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS081D – NOVEMBER 1994 – REVISED APRIL 1997
detailed description
The TLC5620 is implemented using four resistor-string DACs. The core of each DAC is a single resistor with
256 taps, corresponding to the 256 possible codes listed in T able 1. One end of each resistor string is connected
to the GND terminal and the other end is fed from the output of the reference input buffer. Monotonicity is
maintained by use of the resistor strings. Linearity depends upon the matching of the resistor elements and upon
the performance of the output buffer . Since the inputs are buffered, the DACs always present a high-impedance
load to the reference source.
Each DAC output is buffered by a configurable-gain output amplifier that can be programmed to times 1 or times
2 gain.
On power up, the DACs are reset to CODE 0.
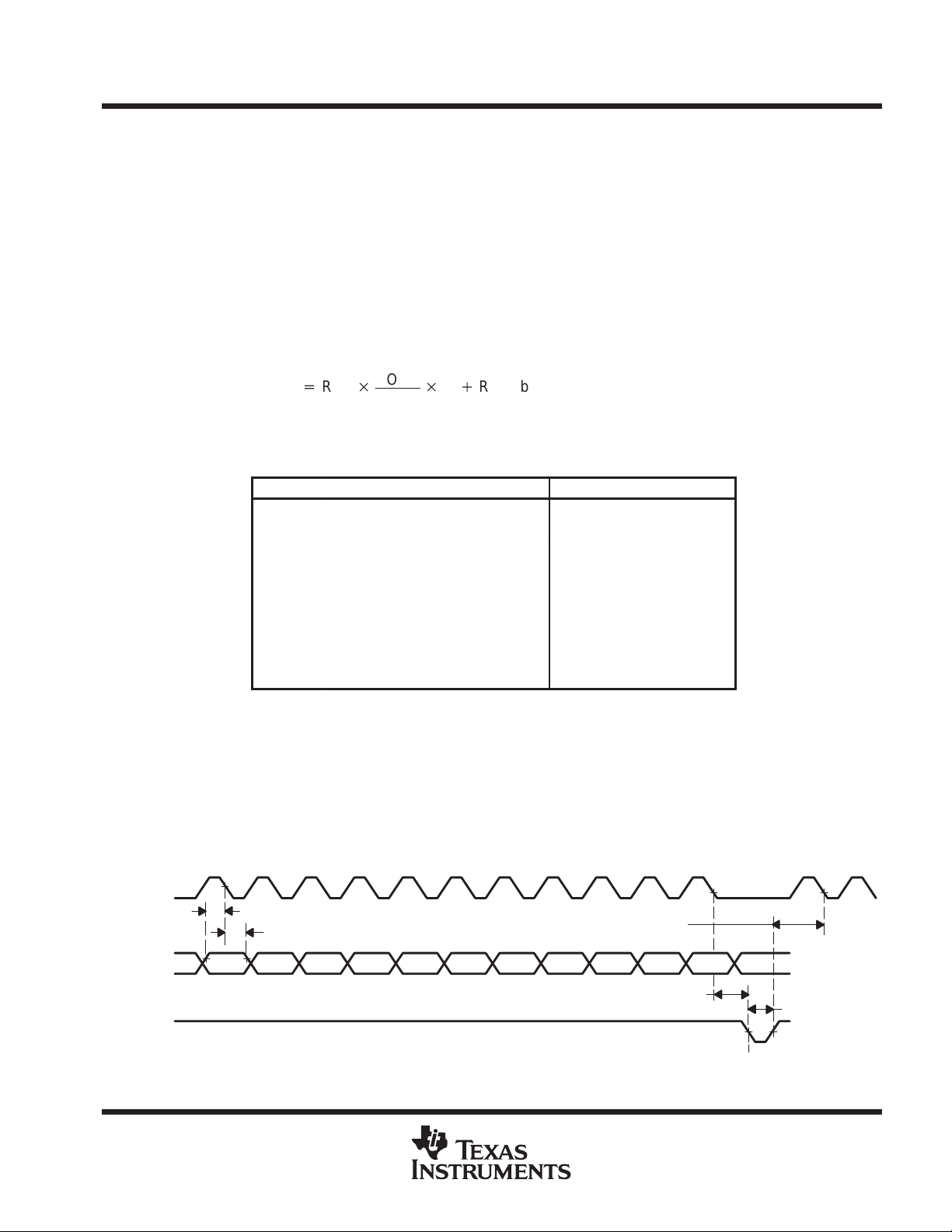
Each output voltage is given by:
VO(DACA|B|C|D)+REF
where CODE is in the range 0 to 255 and the range (RNG) bit is 0 or 1 within the serial control word.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 OUTPUT VOLTAGE
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 GND
0 0000001 (1/256) × REF (1+RNG)
• ••••••• •
• ••••••• •
0 1111111 (127/256) × REF (1+RNG)
1 0000000 (128/256) × REF (1+RNG)
• ••••••• •
• ••••••• •
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 (255/256) × REF (1+RNG)
CODE
256
(1)
RNG bit value)
Table 1. Ideal Output Transfer
data interface
With LOAD high, data is clocked into the DATA terminal on each falling edge of CLK. Once all data bits have
been clocked in, LOAD is pulsed low to transfer the data from the serial input register to the selected DAC as
shown in Figure 1. When LDAC is low, the selected DAC output voltage is updated when LOAD goes low . When
LDAC is high during serial programming, the new value is stored within the device and can be transferred to
the DAC output at a later time by pulsing LDAC low as shown in Figure 2. Data is entered most significant bit
(MSB) first. Data transfers using two 8-clock cycle periods are shown in Figures 3 and 4.
CLK
t
DATA
LOAD
su(DATA-CLK)
t
v(DATA-CLK)
RNGA1 A0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 1. LOAD-Controlled Update (LDAC = Low)
t
su(LOAD-CLK)
t
su(CLK-LOAD)
DAC Update
t
w(LOAD)
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
3
TLC5620C, TLC5620I
QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
SLAS081D – NOVEMBER 1994 – REVISED APRIL 1997
CLK
t
su(DATA-CLK)
t
v(DATA-CLK)
DATA
LOAD
LDAC
CLK
A1 A0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
RNG
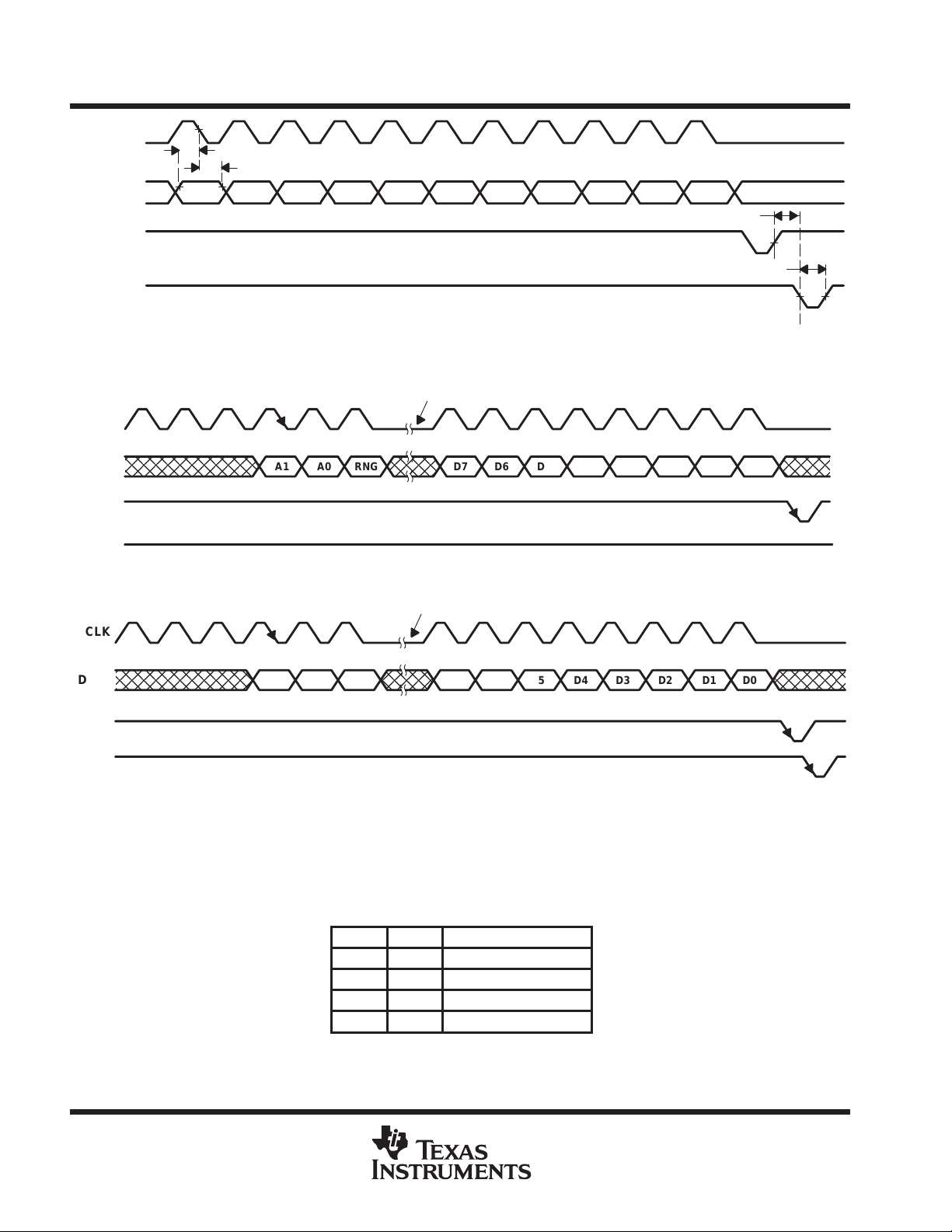
Figure 2. LDAC-Controlled Update
CLK Low
t
su(LOAD-LDAC)
t
w(LDAC)
DAC Update
DATA
LOAD
LDAC
A1 A0 RNG D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 3. Load-Controlled Update Using 8-Bit Serial Word (LDAC = Low)
CLK Low
CLK
DATA
LOAD
LDAC
A1 A0 RNG D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 4. LDAC-Controlled Update Using 8-Bit Serial Word
Table 2 lists the A1 and A0 bits and the selection of the updated DACs. The RNG bit controls the DAC output
range. When RNG = low, the output range is between the applied reference voltage and GND, and when
RNG = high, the range is between twice the applied reference voltage and GND.
Table 2. Serial Input Decode
A1 A0 DAC UPDATED
0 0 DACA
0 1 DACB
1 0 DACC
1 1 DACD
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
 Loading...
Loading...