Page 1

TM
Technology for Innovators
Interface Selection Guide
4Q 2006
Page 2

2
Interface Selection Guide
➔
Table of Contents
Introduction 3
LVDS, xECL, CML . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Multipoint-LVDS (M-LVDS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Digital Isolators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
RS-485/422 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
RS-232 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
UARTs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
CAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
FlatLink™3G . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
SerDes (Serial Gigabit Transceivers and LVDS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
™
DVI/PanelBus
TMDS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
USB Hub Controllers and Peripheral Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
USB Port Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
USB Power Managers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
PCI Express®. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
PCI Bridges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
CardBus Power Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
1394 (FireWire®) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
22
Check inter
face.ti.com
for the latest IBIS Models
and
evaluation modules
GTLP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
VME . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Clock Distribution Circuits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Cross-Reference Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Device Index
Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
(EVMs).
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 3

Interface Selection Guide
3
Introduction
Texas Instruments (TI) provides complete interface solutions that empower you to differentiate your products and accelerate time-to-market.
Our expertise in high-speed, mixed-signal circuits, system-on-a-chip integration and advanced product development processes ensures you will
eceive the silicon, support tools, software and technical documentation to create and deliver the best products on time and at competitive prices.
r
ncluded in this selection guide you will find design considerations, technical overviews, graphic representation of portfolios, parametric tables
I
nd resource information on the following families of devices:
a
LVDS: (p. 4) TIA/EIA-644A specification
d
esigned for differential transmission
delivering signaling rates into the Gbps range
and power in the mW range with low EMI to
the telecommunication and consumer markets.
xECL: (p. 4) Emitter coupled logic (xECL),
high-speed differential interface technology
designed for low jitter and skew.
CML: (p. 4) Current-mode logic (CML), high
speed differential interface technology.
M-LVDS: (p. 8) TIA/EIA-899 specification with
all the benefits of LVDS applicable to multipoint bus architecture in backplanes. Used
often for clock distribution, e.g. AdvancedTCA.
Digital Isolators: (p. 10) The new ISO72x
high-speed digital isolators use state-of-the-art
integrated capacitive coupling and silicondioxide isolation barrier to provide up to
150-Mbps signaling rate with only 1-ns jitter,
best-of-class noise immunity and high reliability.
RS-485/422: (p. 11) Robust TIA/EIA-485 and
TIA/ EIA-422 specifications specially designed
for harsh, industrial environments transmitting
a differential signal up to 50 Mbps or 1.2 km.
RS-232: (p. 13) TIA/EIA-232 specification
defining single-ended interface between data
terminal equipment (DTE) and data circuitterminating equipment (DCE).
UARTs: (p. 16) Universal Asynchronous
Receiver/T
nent of serial communication utilizing RS232,
RS485/422 or LVDS transceivers to transmit or
receive between remote devices performing
parallel
process and serial to parallel conversion in the
receive process.
CAN: (p. 18) Controller Area Network
(ISO11898) specification commonly used in
automotive and industrial applications describes
differential signaling at a rate up to 1 Mbps on
a 40-meter bus with multipoint topology.
ransmitters are the key logic compo
to serial conversion in the transmit
FlatLink™ 3G: (p. 19) A new family of serial-
i
zers and deserializers designed for mobile
phone displays.
SerDes: (p. 20) Serializers and deserializers
in the gigabit range designed to bridge large
numbers of data bits over a small number of
data lines in telecommunication applications.
DVI/PanelBus™: (p. 22) The Digital Visual
Interface Specification, DVI, is an industry
standard developed by the Digital Display
Working Group (DDWG) for high-speed digital
connection to digital displays. DVI uses
transition-minimized DC balanced (TMDS)
data signaling.
TMDS: (p. 24) Transition minimized differential
signaling is the electrical interface used by DVI
and HDMI.
USB Hub Controllers and Peripheral
Devices:
established to make connecting PCs, peripherals and consumer electronics flexible and easy.
The hub controller manages USB port connect/
disconnect activities and a peripheral controller
enables USB connectivity of a peripheral
device to either a host or hub.
USB Port Protection: (p. 26) Transient voltage
suppressor protects USB 1.1 devices from ESD
and electrical noise transients.
USB Power Managers: (p. 27)
like TPS204xA and TPS205xA, are designed to
-
meet all the USB 1.0 and 2.0 requirements for
current-limiting and power switching to reliably
control the power on the voltage bus.
PCI Express®: (p. 29)
flexible and cost-effective I/O interconnect.
PCI Bridges: (p. 33) A peripheral component
interconnect (PCI) bridge provides a highperformance connection path between either
two PCI buses or a PCI component and one or
more DSP devices.
(p. 25) The USB standard was
A robust, scalable,
TI products,
CardBus Power Switches: (p. 34) The
C
ardBus controller uses the card detect and
voltage sense pins to determine a PC card’s
voltage requirements and then directs the
PCMCIA power switch to enable the proper
voltages. Standard PC cards require that V
be switched between ground, 3.3 V, and 5 V,
while VPP is switched between ground, 3.3 V,
5 V, and 12 V. CardBay sockets have the standard requirements for VCC, but require ground,
3.3 V, and 5 V to VPP, and ground, 1.8 V, or 3.3
V to V
simply not need 12 V or VPP while still having
the standard requirements for V
consider the voltage requirements of the
application when selecting a PCMCIA
power switch.
1394: (p. 36) IEEE 1394 (FireWire®) high-speed
interconnection enables simple, low-cost,
high-bandwidth, real-time data connectivity
between computers, peripherals and consumer
electronics.
GTLP: (p. 39) Gunning transceiver logic plus
(GTLP) derived from the JEDEC JESD8-3 GTL
standard is a reduced-voltage-swing
technology designed for high-speed interface
between cards operating at LVTTL logic levels
and backplanes operating at GTLP signal levels.
VME: (p. 41)
64-bit, backplane architecture that is coordinated and controlled by VITA. VME is used
extensively in military
applications.
Clock Distribution Circuits: (p. 42)
TI offers both single-ended and differential
clock buffers that perform from below 200 MHz
up to 3.5 GHz in a variety of fan-out options. In
addition to simple option for customers needing
differential signals (LVPECL) and single-ended
signals (LVTTL/LVCMOS) from the same device.
. Other PC card applications may
CORE
The VMEbus™ is a standardized,
, industrial and aerospace
CC
CC
. Therefore,
➔
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 4

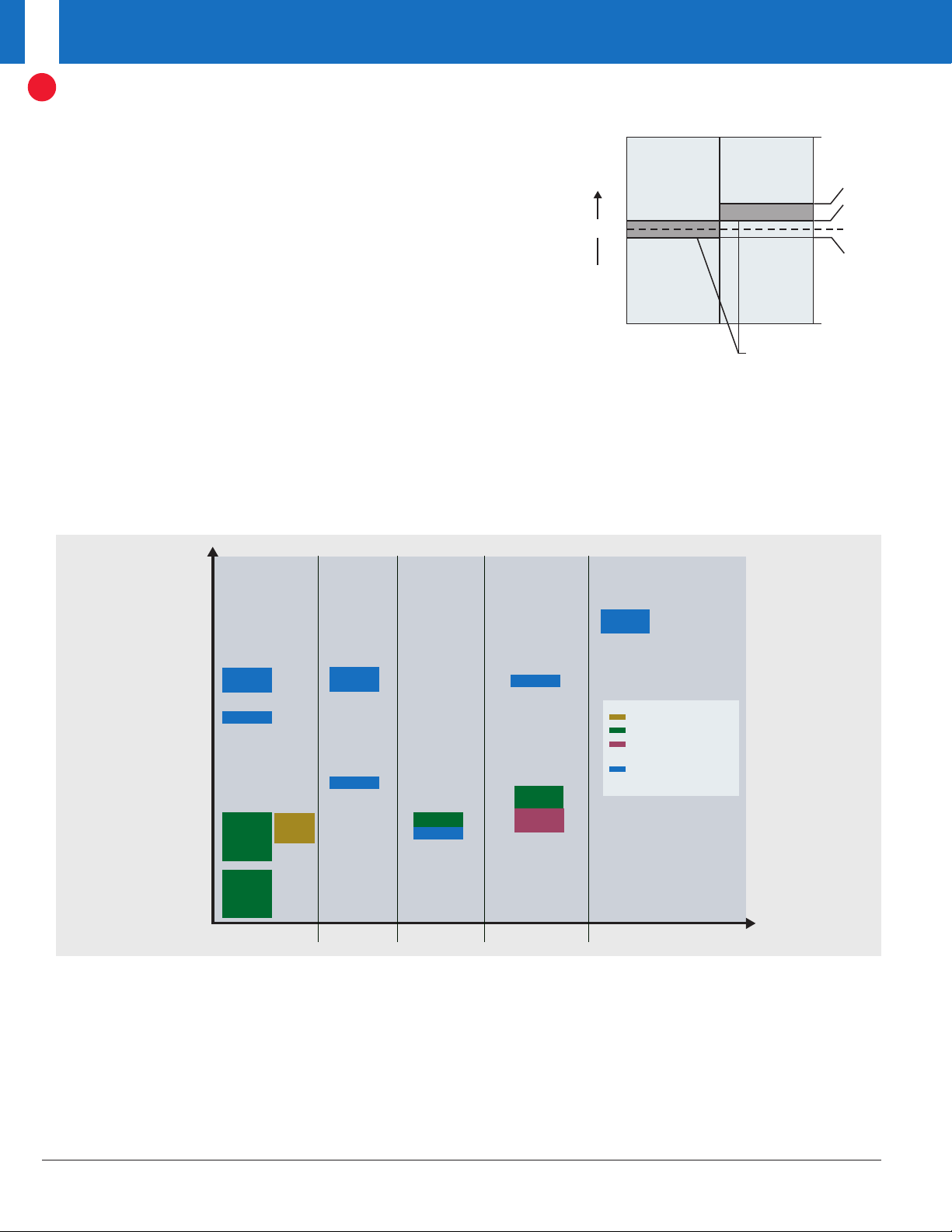
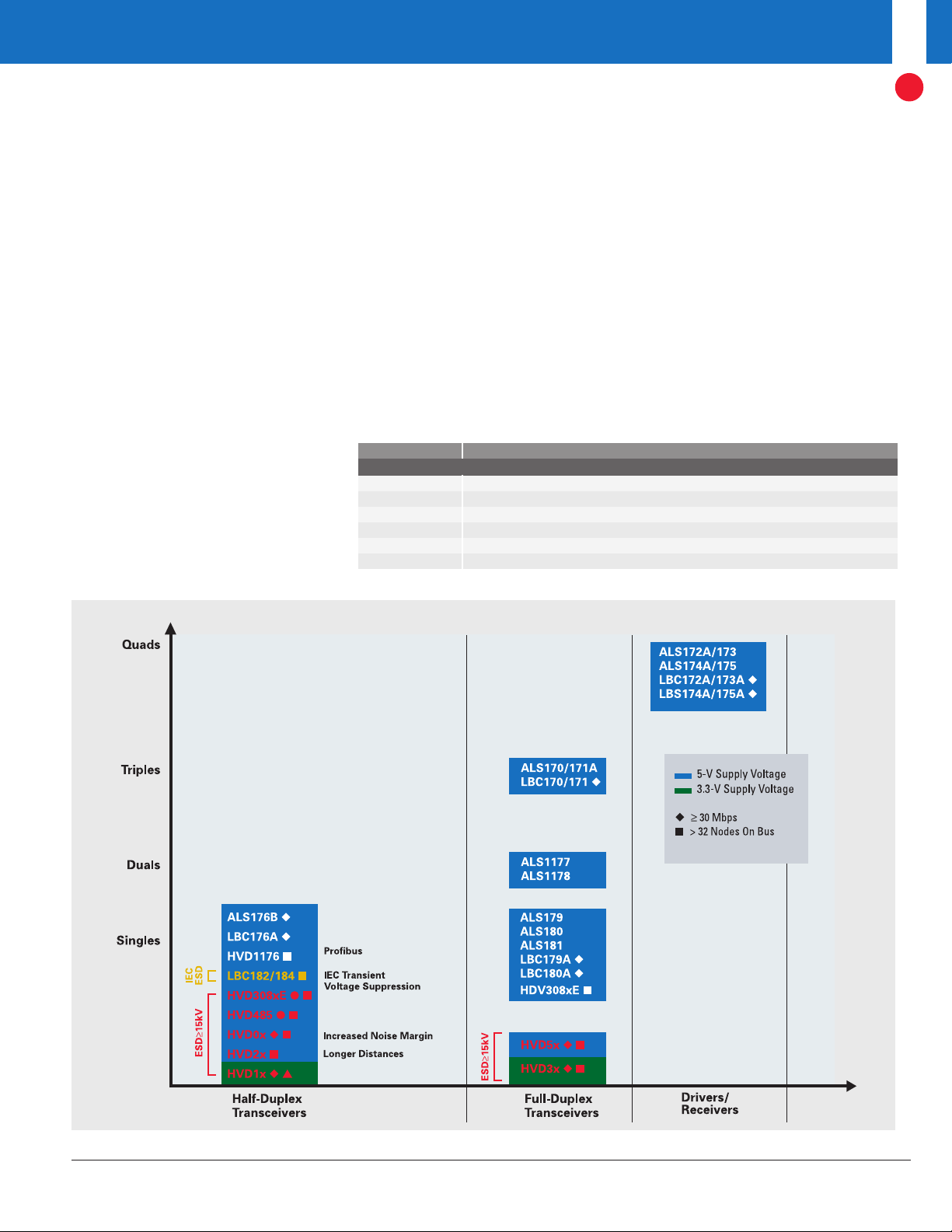
LVDS2
L
VDS9637
LVDS34
Singles
Transmitters Receivers Transceivers Repeaters/
Translators
Crosspoint
Switches
Up to 400 Mbps
Up to 630 Mbps
≥ 1 Gbps
Clock Distribution Devices
(See pg. 42 for table)
LVDS388A
LVDS386
C
DCLVD110
L
VDS108
LVDS104
L
VDS105
L
VDS117
LVDS116
L
VDS9638
LVDS179
LVDS180
L
VDS049
LVDS050
LVDS051
LVDS1050
CML100
LVDS100
LVDS101
LVDS16 LVP16
LVDS17 LVP17
LVDS18 LVP18
LVDS19 LVP19
LVDS20 LVP20
L
VDS22
LVCP22
LVCP23
LVDS122
L
VDS250
Duals
Quads
8 Channels
16 Channels
10 Channels
LVDS109
LVDS1
L
VDS389
LVDS387
LVDS047
LVDS31
LVDS3487
L
VDS391
LVDS048A/348
LVDS32/33
LVDS3486
L
VDS390
4
➔
LVDS, xECL, CML
Design Considerations
ignaling Rate—TI offers repeaters/transla-
S
tors and crosspoint switches with signaling
ates up to 4.0 Gbps.
r
Jitter — Reducing jitter, the deviation of a
signal timing event from its ideal position,
has become a priority for ensuring reliability
in high-speed data buses.
Skew — Excessive skew, the time delta
between the actual and expected arrival
LVDS Family of Products
time of a clock signal, can limit the maximum
bandwidth performance and lead to data
ampling errors. Low skew specifications
s
make high-speed interconnect devices
xcellent for signal buffering.
e
Power Consumption — Low-voltage
differential signaling (LVDS) offers a low-power
alternative to ECL and PECL devices. Currentmode drivers in LVDS produce a constant
current, which allows power consumption to
be relatively independent of frequency. The
constant current driver delivers about 3.5 mA
to a 100-W load.
Technical Information
• LVDS is based on the TIA/EIA-644A
standard conceived to provide a generalpurpose electrical-layer specification for
drivers and receivers connected in a
point-to-point or multidrop interface.
Resources For a complete list of resources (evaluation modules, data sheets and application notes), visit interface.ti.com
Literature
Number
Description
Application Notes
SLLA014A Low-Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS) Design Notes (Rev. A)
SLLA030C Reducing Electromagnetic Interference with LVDS (Rev. C)
SLLA031A Using an LVDS Receiver with TIA/EIA-422 Data (Rev. A)
SLLA034A
SLLA038B
SLLA053B Performance of LVDS with Different Cables (Rev. B)
SLLA054A
SLLA065
SLLA082B Active Fail-Safe in TI's LVDS Receivers (Rev. B)
SLLA100 Increase Current Drive Using LVDS
SLLA101 Interfacing Different Logic with LVDS Receivers
Slew Rate Control of L
Interface Circuits for TIA/EIA-644 (LVDS) (Rev. B)
L
A Comparison of LinBiCMOS and CMOS Process T
VDS Multidrop Connections (Rev
VDS Circuits (Rev
. A)
. A)
echnologies in L
VDS ICs
SLLA103 LVPECL and LVDS Power Comparison
SLLA104 Suggestions for L
VDS Connections
SLLA105 DSP to DSP Link Using LVDS
SLLA107 Live Insertion with Differential Interface Products
SLLA147 Suitable LVDS Architectures
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Literature
Number Description
Application Notes
VDS, HSTL, and CML
SCAA059
SCAA062
Part Number Description Price
Evaluation Modules (EVMs)
SN65LVDS31-32EVM Evaluation Module for LVDS31 and LVDS32 49.00
SN65LVDS31-32BEVM Evaluation Module for LVDS31 and LVDS32B 49.00
SN65LVDS31-33EVM Evaluation Module for LVDS31 and LVDS33 49.00
SN65LVDS386EVM SN65LVDS386 Evaluation Module 49.00
SN65L
SN65LVDS100EVM SN65LVDS100 Evaluation Module 99.00
SN65LVDS20EVM SN65LVDS20 Evaluation Module 49.00
SN65CML20EVM
SN65L
AC-Coupling Between Differential L
DC-Coupling Between Differential LVPECL, LVDS, HSTL, and CML
VDS387 Evaluation Module 49.00
SN65L
VDS387EVM
SN65CML20 Evaluation Module
VCP22 Evaluation Module
VCP22-23EVM
SN65L
VPECL, L
SN65LVDS122EVM SN65LVDS122 Evaluation Module 49.00
SN65LVDS250EVM SN65LVDS250 Evaluation Module 49.00
Note: IBIS models are available at interface.ti.com
*
Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars.
*
49.00
25.00
Page 5

LVDS, xECL, CML
L
VDS/LVPECL/CML Repeaters/Translators and Crosspoints Selection Guide
No. No. Signaling Jitter Part-to- Tx tpd Rx ESD
1
Device
Crosspoint Switch Family
SN65LVCP22 2X2 Crosspoint Switch: 2 2 LVPECL, LVDS 1000 105 100 0.65 0.65 85 5 16SOIC, 2.70
SN65LVCP23 2X2 Crosspoint Switch: 2 2 LVPECL, LVPECL 1300 100 100 0.65 0.65 65 5 16SOIC, 5.20
SN65LVCP40 Dual 1:2 Mux with Equalizer and 6 6 LVPECL, CML 4000 30 500 1 1 254 4 48QFN 17.40
SN65LVDS12222X2 Crosspoint Switch: 2 2 LVPECL, LVDS 1500 65 150 0.9 0.9 100 4 16SOIC, 4.75
SN65LVDS25024X4 Crosspoint Switch: 4 4 LVPECL, LVDS 2000 50 150 0.9 0.9 145 3 TSSOP 7.75
Repeaters/Translators
SN65CML100 LVDS/LVPECL/CML-to-CML 1 1 LVPECL, CML 1500 70 100 0.8 — 12 5 8SOIC, 2.55
VDS100
SN65L
SN65LVDS1012LVDS/LVPECL/CML-to-LVPECL 1 1 LVPECL, LVPECL 2000 65 100 0.9 — 90 5 8SOIC, 2.55
SN65LVDS16/17 2.5-V/3.3-V Oscillator Gain 1 1 LVPECL LVDS 2000 10 130 0.63 — 48 2 8QFN 2.55
SN65LVDS18/19 2.5-V/3.3-V Oscillator Gain 1 1 LVPECL LVDS 1000 10 130 0.63 — 36 2 8QFN 1.95
SN65LVDS20 2.5-V/3.3-V LVDS repeater with enable 1 1 LVPECL LVDS 4000 45 130
SN65LVP16/17 2.5-V/3.3-V Oscillator Gain Stage/Buffer 1 — LVPECL LVPECL 2000 10 130 0.63 — 30 2 8QFN 2.55
SN65LVP18/19
SN65LVP20 2.5-V/3.3-V LVPECL 1 1 LVPECL LVPECL 4000 10 130 0.63 — 45 3 8QFN 4.40
1
Supply voltage for all devices listed above is 3.3 V. 2Integrated termination available (100-Ω)-SN65LVDTxxx. New products are listed in bold red.
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
Description Tx Rx Signal Signal (Mbps) (ps) Skew Max (ns) (ns) Max (mA) (kV) Package(s) Price*
LVDS Outputs LVDS, CML 16TSSOP
LVPECL Outputs LVDS, CML 16TSSOP
Pre-Emphasis LVDS, CML
LVDS Output LVDS, CML 16TSSOP
LVDS Output LVDS, CML
Repeater/Translator LVDS, CML 8VSSOP
2
VDS/LVPECL/CML 1 1 LVPECL, LVDS 2000 65 100 0.8 — 30 5 8SOIC, 2.55
L
to LVDS Repeater/Translator LVDS, CML 8VSSOP
Repeater/Translator LVDS, CML 8VSSOP
Stage/Buffer (single ended/diff inputs)
Stage/Buffer (single ended/diff inputs)
(single ended
2.5-V/3.3-V
(single ended
/diff inputs)
Oscillator Gain Stage/Buffer 1 — LVPECL LVPECL 1000 10 130 0.63 — 20 2 8QFN 1.95
/diff inputs)
of of Input Output Rate Max Part Typ tpd Typ I
0.63 —
LVDS, CML
LVDS, CML
HBM Pin/
CC
45 3 8QFN 3.30
5
➔
PECL Selection Guide
Device
TB5D1M
TB5D2H
TB5R1
TB5R2
TB5R3
TB3R1
TB3R2
TB5T1
VDS33
SN65L
SN65LVDS3481Receiver with –4 V to 5 V
SN65LVDS341Receiver with –4 V to 5 V
SN65LVDS3521Receiver with –4 V to 5 V
1
Integrated Termination Available (100-Ω)-SN65LVDTxxx.
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
Description Tx Rx Signal Signal (Mbps) (ns) (ns) (mA) (kV) (V) Pin/Package(s) Price*
Replacement for Agere BDG1A & BPNGA, 4 — TTL PECL 400 1.2 — 40 3 3.3, 5 16SOIC gull-wing, 7.20
built-in surge protection
Replacement for Agere BDG1A & BDGLA,
power down open circuit o/p
Replacement for Agere BRF1A & BRF2A,
8KΩ Input Impedance
Replacement for Agere BRS2A & BRS2B
Replacement for Agere BRF1A
3.3-V supply alternative to Agere
BRF1A & BRF2A
3.3-V supply alternative to Agere
BRS2A & BRS2B
Dual differential transceiver
Receiver with –4 V to 5
Common-Mode Range, L
Common-Mode Range, L
Common-Mode Range
Common-Mode Range
V — 4 LVDS, LVPECL, LVTTL 400 — 4 23 15 3.3 16SOIC, 16TSSOP 1.60
VDS32 Footprint
VDS48 Footprint
Tx Rx
No. No. Signaling tpd tpd
of of Input Output Rate Typ Typ Max HBM Voltage
—
4
4
—
4
—
4 LVPECL TTL 400 — 2.6 50 3 5 16SOIC gull-wing, 8.65
—
4 LVPECL LVTTL 400 — — 32 3 3.3 16SOIC 8.65
—
4 LVPECL LVTTL 400 — — 32 3 3.3 16SOIC 8.65
—
2 LVPECL, LVPECL, 400 1.2 2.5 35 3 5 8SOIC gull-wing, 7.20
2
4
—
2 LVDS, LVPECL, LVTTL 400 — 4 12 15 3.3 8SOIC 1.15
—
4 LVDS, LVPECL, LVTTL 560 — 6 20 15 3.3 24TSSOP 1.80
—
TTL PECL 400 1.2 — 40 3 3.3, 5 16SOIC gull-wing, 7.20
PECL TTL 400 — 2.5 32 3 5 16SOIC gull-wing, 7.20
PECL TTL 400 — 2.5 32 3 5 16SOIC gull-wing, 7.20
VTTL 8SOIC
VTTL
L
VECL, ECL
PECL, L
LVDS, LVPECL, LVTTL 340 — 6 20 15 3.3 16SOIC, 16TSSOP 1.60
PECL, LVECL, ECL
VECL, ECL
PECL, L
VECL, ECL
PECL, L
L
I
CC
ESD Supply
16SOIC
16SOIC
16SOIC
16SOIC
16SOIC
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 6

6
LVDS, xECL, CML
➔
LVDS Selection Guide
Signaling Part-to-Part Tx tpd
No. of No. of Rate Skew Max Typ
Device Description Tx Rx Input Signal Output Signal (Mbps) (ps) (ns)
Single
SN65LVDS1 Driver 1 — LVTTL LVDS 630 — 1.7
SN65LVDS2
SN65LVDS179 Full-Duplex Transceiver, No Enables 1 1 LVDS, LVTTL LVTTL, LVDS 400 — 1.7
SN65LVDS180 Full-Duplex Transceiver, with Enables 1 1 LVDS, LVTTL LVTTL, LVDS 400 — 1.7
Dual
SN65LVDS9638 Driver 2 — LVTTL LVDS 400 800 1.7
SN65LVDS9637 Receiver — 2 LVDS LVTTL 400 1000 —
SN65LVDS049 Transceiver, Driver and Receiver Enable 2 2 LVDS, LVTTL LVTTL, LVDS 400 100 1.3
SN65LVDS050 Transceiver, Driver and Receiver Enable 2 2 LVDS, LVTTL LVDS, LVTTL 400 — 1.7
SN65LVDS051 Transceiver, Driver Enable Only 2 2 LVDS, LVTTL LVDS, LVTTL 400 — 1.7
SN65LVDS1050 Transceiver with 2.7-V Supply 2 2 LVDS, LVTTL LVTTL, LVDS 400 — 1.7
SN65LVDS22 Multiplexed LVDS Repeater 2 2 LVDS LVDS 250 — 4
Quad
SN65LVDS047 Driver with Flow-Through Pinout 4 — LVTTL LVDS 400 1000 1.8
SN65LVDS31 Driver, AM26LS31 Footprint 4 — LVTTL LVDS 400 800 1.7
SN65LVDS3487 Driver, MC34987 Footprint 4 — LVTTL LVDS 400 800 1.7
SN65LVDS391 Driver with Flow-Through Pinout 4 — LVTTL LVDS 630 1500 1.7
SN65LVDS048A Receiver with Flow-Through Pinout — 4 LVDS LVTTL 400 1000 —
SN65LVDS32 Receiver, AM26LS32 Footprint — 4 LVDS LVTTL 400 1000 —
SN65LVDS3486 Receiver, MC3486 Footprint — 4 LVDS LVTTL 400 1000 —
SN65LVDS390
8-Channel
SN65LVDS389 Driver 8 — LVTTL LVDS 630 1500 1.7
SN65LVDS388A
16-Channel
SN65LVDS387 Driver 16 — LVTTL LVDS 630 1500 1.7
SN65LVDS386
1
Integrated termination available (100-Ω) - SN65LVDTx.
1
1
1
1
Receiver — 1 LVDS LVTTL 400 — 1.7
Receiver with Flow-Through Pinout — 4 LVDS LVTTL 630 1000 —
Receiver — 8 LVDS LVTTL 630 1000
Receiver — 16 LVDS LVTTL 630 1000 —
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 7

LVDS, xECL, CML
LVDS Selection Guide
x
R
tpd Typ Max HBM Voltage
Device (ns) (mA) (kV) (V) Pin/Package(s) Price
Single Family
SN65LVDS1 — 8 15 3.3 8SOIC, 5SOP 0.47
SN65LVDS2
SN65LVDS179 3.7 12 12 3.3 8SOIC, 8VSSOP 1.35
SN65LVDS180 3.7 12 12 3.3 14SOIC, 14TSSOP 1.35
Dual Family
SN65LVDS9638 — 13 8 3.3 8HTSSOP, 8SOIC, 8VSSOP 1.15
SN65LVDS9637 2.1 10 8 3.3 8HTSSOP, 8SOIC, 8VSSOP 1.15
SN65LVDS049 1.9 35 10 3.3 16TSSOP 1.00
SN65LVDS050 3.7 20 12 3.3 16SOIC, 16TSSOP 2.00
SN65LVDS051 3.7 20 12 3.3 16SOIC, 16TSSOP 2.00
SN65LVDS1050 3.7 20 12 2.7 16TSSOP 2.00
SN65LVDS22 4 20 12 3.3 16SOIC, 16TSSOP 2.80
Quad Family
SN65LVDS047 — 26 8 3.3 16SOIC, 16TSSOP 1.30
SN65LVDS31 — 35 8 3.3 16SOIC, 16TSSOP, 16SOP 1.50
SN65LVDS3487 — 35 8 3.3 16SOIC 1.50
SN65LVDS391 — 26 15 3.3 16SOIC, 16TSSOP 1.50
SN65LVDS048A 2.4 15 10 3.3 16SOIC, 16TSSOP 1.30
SN65LVDS32 2.1 18 8 3.3 16SOIC, 16TSSOP, 16SOP 1.50
SN65LVDS3486 2.1 18 8 3.3 16SOIC 1.50
SN65LVDS390
8-Channel Family
SN65LVDS389 — 70 15 3.3 38TSSOP 2.90
SN65LVDS388A
16-Channel Family
SN65LVDS387 — 95 15 3.3 64TSSOP 5.55
SN65LVDS386
1
Integrated termination available (100-Ω)-SN65LVDTx
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
1
1
1
1
2.6 7 15 3.3 8SOIC, 5SOP 0.47
2.5 18 15 3.3 16SOIC, 16TSSOP 1.50
2.5 40 15 3.3 38TSSOP 2.90
2.5 70 15 3.3 64TSSOP 5.55
I
CC
SD Supply
E
7
➔
*
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 8
100 Mbps
200 Mbps
300 Mbps
400 Mbps
500 Mbps
600 Mbps
700 Mbps
Single Dual Quad 8-Channel 16-Channel
LVDM179
LVDM180
LVDM176
LVDM050
LVDM051
LVDM1676
LVDM1677
LVDM22
MLVD2
MLVD3
LVDM320
MLVD200A
MLVD202A
MLVD204A
MLVD205A
MLVD201
MLVD203
MLVD206
MLVD207
M-LVDS Transceivers
M-LVDS Clock Distribution
(see p.42 for table)
LVDM: a version of LVDS with
double the output current
M-LVDS Receivers
LVDM31
MLVD047
MLVD129
MLVD080
MLVD082
MLVD128
8
High
T
ype 1
Type 2
2.4 V
150 mV
50 mV
0 mV
–50 mV
High
Low
Transition Region
Low
V
I
D
2.4 V
➔
Multipoint-LVDS (M-LVDS)
M-LVDS Features
• TIA/EIA-899 standard
• Driver output current
11.3 mA vs. 3.5 mA (LVDS)
••
• Receiver thresholds
••
50 mV vs. 100 mV (LVDS)
• Driver edge rate control
••
1 ns min allows ease-of-stub design
• Contention provisions
Driver short circuit limited to 43 mA
••
••
Drivers, receivers and disabled devices
must limit their bus voltage from
0 to 2.4 V
••
Drivers are tested with 32 contending
nodes
Multipoint LVDS
M-LVDS Devices from TI
• TIA/EIA-899 standard compliant
guarantees true multipoint
• Type 1 receivers: 25-mV hysteresis
to prevent oscillation
Type 2 receivers: internal failsafe
•
(no external bias network)
• –1-V to 3.4-V common mode
• 3.3-V supply operation
M-LVDS for ATCA
• Synchronous ATCA clock signals
(8 kHz, 19.22 MHz and user defined
<100 MHz) use M-LVDS.
Receiver types.
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 9

Multipoint-LVDS (M-LVDS)
M-LVDS Selection Guide
Tx
No. No. Half/ Signaling Part-to-
1
Device
SN65MLVD2 — 1 1 — M-LVDS LVTTL 200 — — — — — — ✔ Web
SN65MLVD3 — 1 2 — M-LVDS LVTTL 200 — — — — — — ✔ Web
SN65MLVD200A 1 1 1 Half LVTTL, M-LVDS LVTTL, M-LVDS 100 1000 2.5 3.6 24 8 8SOIC ✔ 1.55
SN65MLVD201 1 1 1 Half LVTTL, M-LVDS LVTTL, M-LVDS 200 1000 1.5 4 24 8 8SOIC ✔ 1.85
SN65MLVD202A 1 1 1 Full LVTTL, M-LVDS LVTTL, M-LVDS 100 1000 2.5 3.6 24 8 14SOIC ✔ 1.55
SN65MLVD203 1 1 1 Full LVTTL, M-LVDS LVTTL, M-LVDS 200 1000 1.5 4 24 8 14SOIC ✔ 1.85
SN65MLVD204A 1 1 2 Half LVTTL, M-LVDS LVTTL, M-LVDS 100 1000 2.5 3.6 24 8 8SOIC ✔ 1.55
SN65MLVD205A 1 1 2 Full LVTTL, M-LVDS LVTTL, M-LVDS 100 1000 2.5 3.6 24 8 14SOIC ✔ 1.55
SN65MLVD206 1 1 2 Half LVTTL, M-LVDS LVTTL, M-LVDS 200 1000 1.5 4 24 8 8SOIC ✔ 1.85
SN65MLVD207 1 1 2 Full LVTTL, M-LVDS LVTTL, M-LVDS 200 1000 1.5 4 24 8 14SOIC ✔ 1.85
SN65MLVD047 4 0 — Half LVTTL M-LVDS 200 1000 1.5 — 60 12 16SOIC, ✔ 1.45
SN65MLVD128 8 1 — — LVTTL M-LVDS 200 800 1.5 1.5 140 8 48TSSOP ✔ 3.80
SN65MLVD129 8 2 — — LVTTL M-LVDS 200 800 1.5 1.5 140 8 48TSSOP ✔ 3.80
SN65MLVD080 8 8 1 Half LVTTL, LVDS LVTTL, M-LVDS 250 1000 2.4 6 180 8 64TSSOP ✔ 4.75
SN65MLVD082 8 8 2 Half LVTTL, LVDS LVTTL, M-LVDS 250 1000 2.4 6 180 8 64TSSOP ✔ 4.75
SN65LVDM179 1 1 — Full LVTTL, LVDM LVTTL, LVDM 500 1000 1.7 3.7 15 12 8SOIC, — 1.70
SN65LVDM05022 2 — Full LVTTL, LVDM LVTTL, LVDM 500 1000 1.7 3.7 27 12 16SOIC, — 2.20
SN65LVDM22 2 2 — — LVDM LVDM 250 — 4 4 27 12 16SOIC, — 2.50
SN65LVDM31 4 0 — — LVCMOS LVDM 150 1000 2.3 — 40 12 16SOIC — 1.55
of of Rx Full Rate Part Skew Typ Typ Max HBM Pin/ Standard
Tx Rx Type Duplex Input Signal Output Signal (Mbps) Max (ps) (ns) (ns) (mA) (kV) Package(s) Compliance Price*
tpd
Rx
tpd
I
ESD TIA/EIA-899
CC
16TSSOP
8VSSOP
16TSSOP
16TSSOP
9
➔
SN65LVDM1676 16 16 — Half LVTTL, LVDM LVTTL, LVDM 630 1000 2.5 3 175 15 64TSSOP — 7.75
1
Supply voltage for all devices listed above is 3.3 V and temperature range is –40 to 85°C. New products are listed in bold red.
2
Automotive version available, temperature range of –40 to 125°C Preview products are listed in bold blue.
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
Resources For a complete list of resources (evaluation modules, data sheets and application notes), visit interface.ti.com
Literature Number Description
Application Notes
SLLA106 TIA/EIA-485 and M-LVDS, Power and Speed Comparison
SLLA088A Transmission at 200 Mbps in VME Card Cage Using LVDM (Rev. A)
SLLA108 Introduction to M-LVDS (TIA/EIA-899)
SLLA121 Interoperability of M-LVDS and BusLVDS
SLLA119 Wired-Logic Signaling with M-LVDS
SLLA127 M-LVDS Signaling Rate Versus Distance
SLLA067A
Part Number Description Price
Evaluation Modules (EVMs)
MLVD20xEVM M-LVDS Evaluation Module 99.00
SN65LVDM31-32BEVM SN65LVDM31-32BEVM Evaluation Module 49.00
Note: IBIS models are available at interface.ti.com
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars.
Comparing Bus Solutions
*
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 10

10
Magnetic Flux Density vs. Frequency
100E-18
100E-12
100E-6
100E+0
100E+6
0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100
MHz
Wb/m
ISO721 Inductive IEC61000-4-9 IEC61000-4-8
2
ISO
721
Isol
ato
rs
➔
Digital Isolators
D
esign Considerations
Reliability — Best-in-class, high voltage
and functional reliability with > 25 years.
agnetic Immunity— Immunity from
M
external magnetic fields to prevent data
corruption is a critical consideration for
industrial applications. 1E6 times higher
magnetic immunity than inductive couplers.
Signaling rate — TI offers digital isolators
with the highest signaling rates of up to
150 Mbps.
Jitter — To ensure signal integrity,
jitter reduction is a priority. ISO72xx products
offer the lowest jitter with 1-ns jitter at
150-Mbps PRBS NRZ data input.
Key Features
• 4000-V
••
UL 1577, IEC 60747-5-2
peak
isolation
(VDE 0884, Rev. 2)
••
IEC 61010-1 and CSA approved
••
50-kV/µs transient immunity
• Signaling rate 0 Mbps to 150 Mbps
••
Low propagation delay
••
Low pulse skew
(pulse-width distortion)
• Low-power sleep mode
• High-electromagnetic immunity
• Low-input current requirement of 10 µA
• Fail-safe output
T
echnical Information
he ISO72xx is a family of digital isolators
T
sing the industry’s first application of digital
u
capacitive isolation technology. Digital buffers
apacitively couple data signals through a
c
silicone-dioxide (SiO2) insulation barrier which
provides galvanic isolation of up to 4000 V.
The device receives digital inputs and provides
clean digital outputs while preventing noise
currents and/or excessive voltages from
entering the local ground.
Recently introduced alternative isolation
techniques that use magnetic coupling may
still share the deficiencies of the older optocoupler solutions such as a restricted operating
temperature along with new concerns such as
he absence of a fail-safe output, an inability to
t
operate with DC-only signals and concerns
associated with susceptibility to external
magnetic fields and operating life under highvoltage conditions. TI isolation solutions are
designed to eliminate such problems.
Digital Isolators Selection Guide
Low-Power Transient
Device Description Rating (UL) Mode (Max) (Min) Voltage Price
ISO721 Single channel (TTL)
ISO721M Single channel (CMOS) 2500 V
ISO722 Single channel OUT EN (TTL) 2500 V
ISO722M Single channel OUT EN (CMOS)
ISO150 Dual channel bi-directional 1500 V
ISO7220A Dual channel uni-directional (TTL) 2500 V
ISO7220C Dual channel uni-directional (TTL)
ISO7220M Dual channel uni-directional (CMOS) 2500 V
ISO7221A Dual channel bi-directional (TTL) 2500 V
ISO7221C Dual channel bi-directional (TTL)
ISO7221M Dual channel bi-directional (CMOS) 2500 V
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Isolation Sleep Data Rate Immunity Supply
µs 3.3 V, 5 V 1.65
2500 V
2500 V
2500 V
2500 V
RMS
RMS
RMS
RMS
RMS
RMS
RMS
RMS
RMS
RMS
RMS
No
Yes 150 Mbps 25 kV/µs 3.3 V, 5 V 1.65
Yes 100 Mbps 25 kV/µs 3.3 V, 5 V 1.75
es
Y
No 80 Mbps 1.6 kV/µs 5 V 8.10
No 1 Mbps 25 kV/µs 3.3 V, 5 V 1.10
No
No 150 Mbps 25 kV/µs 3.3 V, 5 V 2.50
No 1 Mbps 25 kV/µs 3.3 V, 5 V 1.10
No
No 150 Mbps 25 kV/µs 3.3 V, 5 V 2.50
100 Mbps
150 Mbps 25 kV/µs 3.3 V, 5 V 1.75
25 Mbps
25 Mbps
25 kV/
25 kV/µs 3.3 V, 5 V 2.00
25 kV/µs 3.3 V, 5 V 2.00
New products are listed in
Preview products are listed in bold blue.
bold red.
*
Page 11
RS-485/422
11
➔
D
esign Considerations
Interoperability — In general, RS-485 is a
superset of RS-422. Compliance with the
TIA/EIA standard will ensure reliable data
communication in a variety of networks,
including Modbus, INTERBUS, PROFIBUS,
BACnet and a variety of proprietary protocols.
Robustness — RS-485 is a robust interface
standard for use in industrial environments.
It features a wide common mode range of
–7 V to 12 V. Parts from TI are available with
ESD protection up to 30 kV.
Reliability — Integrated fail-safe circuitry
protects the bus from interpreting noise as
valid data when short-circuit, open-circuit or
idle line fault conditions occur.
Speed and Distance — Low noise coupling
of differential signaling with twisted-pair
cabling and wide common-mode voltage
RS-485/422 Family of Products
range allows data exchange at signaling rates
of up to 50 Mbps or to distances of several
20 percent of the characteristic impedance
of the cable and can vary from 90 Ω to 120 Ω.
kilometers at lower rates.
Technical Information
Line Loading — RS-422 is capable of support-
ing one driver and up to 10 receivers on the bus
line. Standard RS-485 is capable of supporting
up to 32 unit loads or nodes on the bus line.
However, there are reduced unit load devices
available that can support up to 256 devices.
Termination — A multipoint bus architecture
requires termination at both ends of the bus
line. The termination resistors must be within
Resources F
Literature Number Description
Application Notes
SLLA036B Interface Circuits for TIA/EIA-485 (RS-485)
SLLA070C 422 and 485 Standards Overview and System Configurations
SLLA112 RS-485 for E-Meter Applications
SLLA177 PROFIBUS Electrical-Layer Solutions
SLLA169 Use Receiver Equalization to Extend RS-485 Data Communications
SLLA143 RS-485 for Digital Motor Control Applications
Note: IBIS models are available at interface.ti.com
or a complete list of resources (evaluation modules, data sheets and application notes), visit interface.ti.com
• The main difference between RS-422 and
RS-485 is the multidrop and multipoint
bus architecture—that is, one driver to
many receivers and many drivers to many
receivers, respectively.
• Typical signaling rates and distances for
these standards are up to 10 Mbps or up
to 1.2 km. TI offers devices capable of
reaching signaling rates of up to 50 Mbps.
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 12

12
RS-485/422
➔
RS-485/422 Selection Guide
S
No. of Supply Rate ESD Receiver
Dr/Rx (V) Enables Device1Features (Mbps) (kV) Fail-Safe Nodes Package(s) Price
DE, RE HVD12 3.3V Supply – Low-Speed Slew-Rate Control 1 15 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.75
D
3.3
3 to 5
5 DE, RE HVD3082E Low Power Mode, Optimized for Low-Speed 0.2 15 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC, 8-MSOP 0.90
5
Half-Duplex
1/1
3.3
Full-Duplex
2/2
3/3 Separate DIR LBC170 FAST-20 SCSI, Skew: 3ns 30 12 Open 32 20-SOIC, 16-SSOP 4.10
3/3
4/0 Complementary LBC172 Low Power 10 2 — 32 16-PDIP, 20-SOIC 1.80
4/0
0/4 Complementary LBC173 Low Power 10 2 Open 32 16-PDIP, 16-SOIC 1.15
0/4
1
These devices use the temperature prefixes:
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
5
Triple
Quad-Drivers
Quad-Receivers
E, RE HVD11 3.3V Supply – Low-Speed Slew-Rate Control 10 15 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.80
DE, RE HVD10 3.3V Supply – High-Speed Signaling 25 15 Short, Open, Idle 64 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.85
DE, RE HVD08 Wide Supply Range: 3 to 5.5V 10 15 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.90
D
E, RE HVD3085E Low Power Mode, Optimized for Mid-Speed 1 15 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC, 8-MSOP 0.90
DE, RE HVD3088E Low Power Mode, Optimized for High-Speed 10 15 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC, 8-MSOP 1.00
DE, RE HVD485E Half Duplex Transceiver 10 15 Open 64 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC, 8-MSOP 0.70
DE, RE HVD1176 PROFIBUS Transceiver, EN 50170 40 10 Short, Open, Idle 160 8-SOIC 1.55
DE, RE HVD22 –20V to 25V Common Mode Operation 0.5 16 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.65
DE, RE HVD21 –20V to 25V Common Mode, 5Mbps 5 16 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.65
DE, RE HVD20 –20V to 25V Common Mode, 25Mbps 25 16 Short, Open, Idle 64 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.65
DE, RE HVD23 Receiver Equalization, 160 Meters at 25 Mbps 25 16 Short, Open, Idle 64 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.80
DE, RE HVD24 Receiver Equalization, 500 Meters at 3 Mbps 3 16 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.80
DE, RE HVD07 Strong Driver Outputs – Low Signal Rate 1 16 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.50
DE, RE HVD06 Strong Driver Outputs – Mid Signal Rate 10 16 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.55
DE, RE HVD05 Strong Driver Outputs – Fast Signal Rate 40 16 Short, Open, Idle 64 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.60
DE, RE LBC176 Low Power 10 2 Open 32 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 0.90
DE, RE LBC176A Low Power, Fast Signaling, ESD Protection 30 12 Open 32 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.20
DE, RE LBC184 Transient Protection, IEC Air, Contact, Surge 0.25 30 Open 128 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.30
DE, RE LBC182 IEC ESD Protection, Air and Contact Tests
DE, RE ALS176 Fast Signaling, Skew: 15ns 35 2 Open 32 8-SOIC 1.26
DE, RE 176B Cost Effective 10 2 None 32 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC, 8-SOP 0.44
No HVD30 3.3V Supply, no Enables, 25Mbps 25 15 Short, Open, Idle 64 8-SOIC 1.80
No HVD31 3.3V Supply, no Enables, 5Mbps 5 15 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-SOIC 1.80
No HVD32 3.3V Supply, no Enables, 1Mbps 1 15 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-SOIC 1.80
No HVD379 Balanced Receivers, Ideal for Interbus 25
DE, RE HVD33 3.3V Supply, with Enables, 25Mbps 25 15 Short, Open, Idle 64 14-SOIC 1.85
DE, RE HVD34 3.3V Supply, with Enables, 5Mbps 5 15 Short, Open, Idle 256 14-SOIC 1.85
DE, RE HVD35 3.3V Supply, with Enables, 1Mbps 1 15
No HVD50 Strong Bus Outputs, no Enables, 25Mbps 25 15 Short, Open, Idle 64 8-SOIC 1.70
No HVD51 Strong Bus Outputs, no Enables, 5Mbps 5 15 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-SOIC 1.70
No HVD52 Strong Bus Outputs, no Enables, 1Mbps 1 15 Short, Open, Idle 256 8-SOIC 1.70
No HVD179 Balanced Receivers, Ideal for Interbus 25 15 None 256 8-SOIC 1.85
No LBC179 Low Power, without Enable 10 2 Open 32 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 0.85
No
DE, RE HVD53 Strong Bus Outputs, with Enables, 25Mbps 25 15 Short, Open, Idle 64 14-SOIC 1.60
DE, RE HVD54 Strong Bus Outputs, with Enables, 5Mbps 5 15 Short, Open, Idle 256 14-SOIC 1.60
DE, RE HVD55 Strong Bus Outputs, with Enables, 1Mbps 1 15 Short, Open, Idle 256 14-SOIC 1.60
DE, RE
DE, RE ALS180 High Signaling Rate, with Enables 25 2 Open 32 14-SOIC 1.71
DE, RE ALS1177 Dual full-duplex drivers/receivers 10 2 Open 32 16-PDIP, 16-SOIC 3.24
1DE, 2DE
riple RE
DE, T
Complementary LBC172A High Signaling Rate, High ESD 30 13 — 32 16-PDIP, 16-SOIC, 20-SOIC 2.40
Pairwise LBC174 Low Power 10 2 — 32 16-PDIP, 20-SOIC 1.90
Pairwise
Complementary LBC173A High Signaling Rate, High ESD, Low Power 50 6 Short, Open, Idle 32 16-PDIP, 16-SOIC 1.50
Pairwise LBC175 Low Power 10 2 Open 32 16-PDIP, 16-SOIC 1.10
Pairwise LBC175A High Signaling Rate, High ESD, Low Power 50 6 Short, Open, Idle 32 16-PDIP, 16-SOIC 1.40
Pairwise
LBC179A
LBC180
ALS1178 Dual full-duplex drivers/receivers 10 2 Open 32 16-PDIP, 16-SOIC 3.24
LBC171 FAST-20 SCSI, Skew: 3ns 30 12 Open 32 20-SOIC, 20-SSOP 4.10
LBC174A
175 Standard 10 2 None 32 16-PDIP, 16-SOIC, 16-SOP 2.70
SN55 = military (–55
High Signaling Rate, High ESD w/o Enables
Low Power
High Signaling Rate, High ESD
, with Enables
C to 125° C); SN65 = industrial (–40° C to 85° C); SN75 = commercial (0° C to 70° C).
°
ignaling
0.25
30 10 Open 32 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.10
10
30
15 Open 128 8-PDIP, 8-SOIC 1.05
15 None 256 8-SOIC 1.95
Short, Open, Idle 256 14-SOIC 1.85
2 Open 32 14-PDIP, 14-SOIC, 16-QFN 1.05
13 — 32 16-PDIP, 16-SOIC, 20-SOIC 2.50
*
Interface Selection Guide T
exas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 13
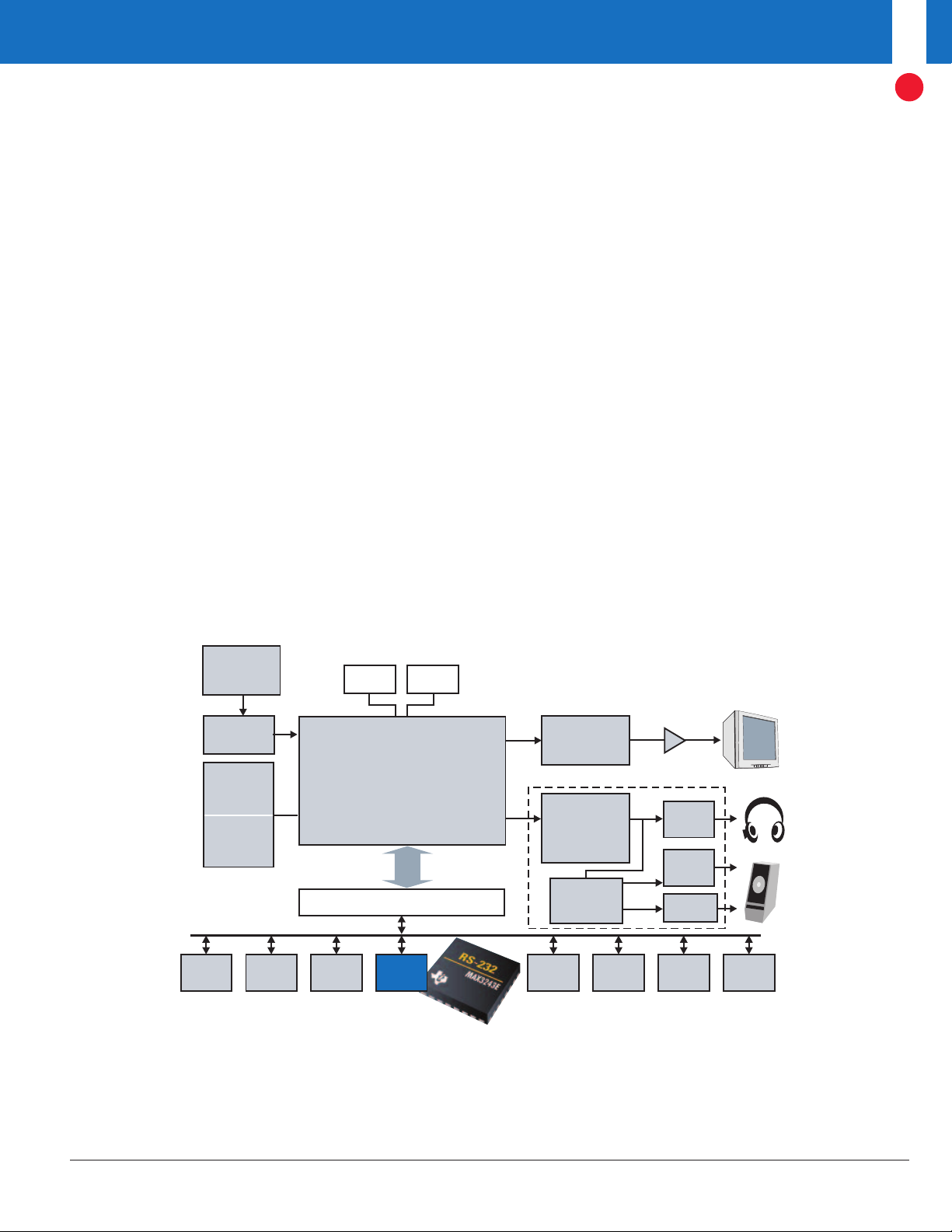
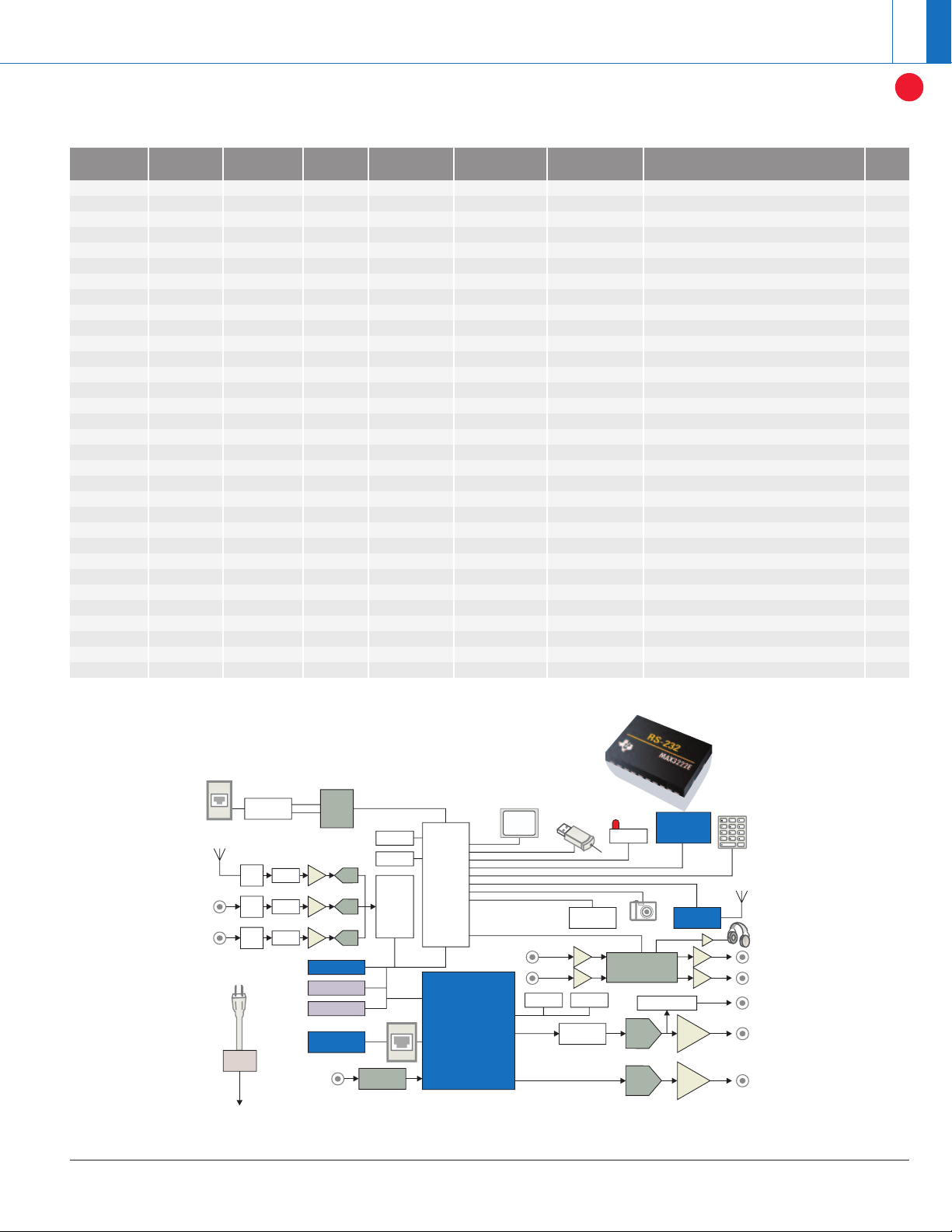
IR
RS-232
Modem
USB
1394
802.11 1284
DV I
TMS320DM64x™
EMIF
Video
Out
Video
In
PCIJTA G
EMAC
SDRAM
TVP5146
TS5V330
TS3V330
Analog MUX
or 5150A
Flash
AMP
forTHS8135 only
Host CPU
Video DAC
THS8200
THS8135
Head-
TS5A23157
Analog
MUX
phone
Volume
Control
Audio DAC
TLV320DAC26
PCI
Bus
McASP
Speaker
ADSL
Cable
Modem
RS-232
13
➔
RS232: IEC6100-4-2 (Level 4)
ESD-Protected Devices
I offers new RS-232 devices with system-
T
level IEC61000-4-2 electrostatic discharge
(ESD) protection. This protection makes the
RS-232 interface immune to damage from
ESD strikes that may occur while the system
is up and running, such as when a connection
to the RS-232 cable is made. These devices
are drop-in replacements and are functionally
identical to the existing industry-standard
solutions, providing a seamless transition in
the qualification process. These devices meet
the requirements for low-power, high-speed
applications such as portable/consumer,
telecom and computing equipment.
TI offers these new devices in the NiPdAu
Pb-Free finish, which eliminates tin whiskers
that might compromise long-term system reliability. TI offers the space-saving QFN package on select devices in addition to its
already extensive RS-232 portfolio.
Key Features
• No external ESD device needed with
these system-level ESD ratings:
– ±15-kV human-body model (HBM)
– ±8-kV IEC61000-4-2, contact
discharge
– ±15-kV IEC61000-4-2, air-gap
discharge
• Improved drop-in replacement of
popular RS-232 devices
• Data rates meet or exceed today’s
high-speed-application requirements
• Flexible power-saving options enable
longer battery life
• Wide portfolio permits selection of the
right form, fit and functionality
• Industry-leading interface product
space with assured source of supply
• NiPdAu Pb-Free solution provides
whisker-free, reliable package options
• Space-saving QFN package options for
portable applications
pplications
A
• The three-driver, five-receiver MAX3243E
is most popular in applications like PCs,
notebooks and servers.
• The MAX3238E/37E offer
complementary five-driver, threereceiver solutions. These two devices
are popular in PC peripheral
applications like data cables, printers,
modems, industrial control, etc.
• The MAX3227E/23E/22E/21E are
popular in portable handheld
applications due to their reduced bit
count, package size and low power
consumption.
• Higher-speed versions like the
SNx5C3232E/23E/22E/21E meet today’s
higher throughput needs through the
serial interface.
• The MAX232E and MAX213 provide a
higher noise margin for more rugged
environments such as industrial control.
Personal video recorder application block diagram.
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 14
14
RS-232
➔
R
S232 Selection Guide
Data Rate ESD Supply I
Device (kbps) Drivers Receivers HBM (kV) Voltage(s) (V) (max) (mA) Pin/Package(s) Price
MAX3223E 500 2 2 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 1 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP, 24QFN 0.84
MAX3222E 500 2 2 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 1 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP, 24QFN 1.00
SN75C3222E 1000 2 2 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 1 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP, 24QFN 2.50
SN65C3222E 1000 2 2 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 1 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP, 24QFN 2.88
SN75C3223E 1000 2 2 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 1 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP, 24QFN 2.11
SN65C3223E 1000 2 2 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 1 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP, 24QFN 2.50
MAX3238E 400 5 3 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 2 28SSOP, 28TSSOP, 32RHB 0.87
MAX3221E 250 1 1 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 1 16SSOP, 16TSSOP 0.88
SN65C3221E 1000 1 1 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 1 16SSOP, 16TSSOP 3.10
SN75C3221E 1000 1 1 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 1 16SSOP, 16TSSOP 2.50
MAX3237E 1000 5 3 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 2 28SSOP, 28TSSOP, 32RHB 0.87
ADM2209E 960 10 6 IEC61000-4-2 Dual 3.3V, 12V 5 38TSSOP TBD
MAX232E 120 2 2 IEC61000-4-2 5 10 38TSSOP, 16PDIP, 16SOIC, 16SSOP 0.39
AX202E
M
MAX207E 120 5 3 IEC61000-4-2 5 20 24SOIC, 24SSOP TBD
MAX208E 120 4 4 IEC61000-4-2 5 20 24PDIP, 24SOIC, 24SSOP TBD
MAX3386E 250 3 2 IEC61000-4-2 VL 1.65V to VCC, 1 20SOIC, 20TSSOP 1.92
SN65C3232E 1000 2 2 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 1 16SOIC, 16SSOP, 16TSSOP 3.92
SN75C3232E 1000 2 2 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 1 16SOIC, 16SSOP, 16TSSOP 3.22
MAX211E 120 4 5 IEC61000-4-2 5 20 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 28SOIC, 28SSOP TBD
MAX3227E 1000 1 1 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 1 16SSOP 1.20
MAX3232E 250 2 2 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 1 16SOIC, 16SSOP, 16TSSOP 0.68
MAX3243E 500 3 5 IEC61000-4-2 3.3, 5 1 28SOIC, 28SSOP, 28TSSOP, 32QFN 0.63
MAX3318E 460 2 2 IEC61000-4-2 2.25, 3 1 20SSOP, 20TSSOP 1.10
MAX213 120 4 5 15KV HBM 5 1 28SOIC, 28SSOP 1.08
MAX202 120 2 2 15KV HBM 5 15 16SOIC, 16TSSOP 0.51
MAX207 120 5 3 15KV HBM 5 20 24SOIC, 24SSOP 0.63
MAX208 120 4 4 15KV HBM 5 20 24PDIP, 24SOIC, 24SSOP 0.96
MAX211 120 4 5 15KV HBM 5 20 28SOIC, 28SSOP 0.63
MAX222 120 2 2 15KV HBM 5 10 18PDIP, 18SOIC 0.74
MAX3221 250 1 1 15KV HBM 3.3, 5 1 16SSOP, 16TSSOP 0.88
MAX3223 250 2 2 15KV HBM 3.3, 5 1 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP 1.12
MAX3232 250 2 2 15KV HBM 3.3, 5 1 16SOIC, 16SSOP, 16TSSOP 0.96
MAX3238 250 5 3 15KV HBM 3.3, 5 2 28SSOP, 28TSSOP 1.20
MAX3243 250 3 5 15KV HBM 3.3, 5 1 28SOIC, 28SSOP, 28TSSOP 0.88
MAX3318 460 2 2 15KV HBM 2.25, 3 2 20SSOP, 20TSSOP 1.58
SN65C23243 250 6 10 15KV HBM 3.3, 5 0.02 48SSOP, 48TSSOP 4.32
SN65C3221
SN65C3223 1000 2 2 15KV HBM 3.3 or 5 1 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP 2.50
SN65C3232 1000 2 2 15KV HBM 3.3 or 5 1 16SOIC, 16SSOP, 16TSSOP 3.02
SN65C3238 1000 5 3 15KV HBM 3.3 or 5 2 28SOIC, 28SSOP, 28TSSOP 3.24
SN65C3243 1000 3 5 15KV HBM 3.3 or 5 1 28SOIC, 28SSOP, 28TSSOP 3.46
SN75C23243 250 6 10 15KV HBM 3.3, 5 0.02 48SSOP, 48TSSOP 3.42
SN75C3221
SN75C3223
SN75C3232 1000 2 2 15KV HBM 3.3 or 5 1 16SOIC, 16SSOP, 16TSSOP 2.79
SN75C3238
SN75C3243 1000 3 5 15KV HBM 3.3 or 5 1 28SOIC, 28SSOP, 28TSSOP 1.51
SN75LP1185 256 3 5 15KV HBM 5, ±12 1 20PDIP, 20SOIC, 20SSOP 1.78
SN75LP196 256 5 3 15KV HBM 5, ±12 1 20PDIP, 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP 1.78
SN75LPE185 256 3 5 15KV HBM 5, ±12 1 24PDIP, 24SOIC, 24SSOP, 24TSSOP 1.89
SN75185 120 3 5 10KV HBM ±12, 5 30 20PDIP, 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP 0.45
SN75196
SN75LV4737A 128 3 5 4KV HBM 3 or 5 20.7 28SSOP 2.61
MAX232 120 2 2 2KV HBM 5 10 16PDIP, 16SO, 16SOIC 0.48
SN75150 120
SN75155 120
SN75188 120 4 2KV HBM –9 25 14PDIP, 14SO, 14SOIC 0.22
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000. New products are listed in bold red.
20 2 2 IEC61000-4-2 5 15 16SOIC, 16TSSOP TBD
1
VCC3V to 5.5V
1000
1000
1000 2 2 15KV HBM 3.5 or 5 1 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP 2.38
1000
120
1
1
5
5
2
1
1
1
3
3 10KV HBM ±12, 5 20 20PDIP, 20SOIC 0.68
1
15KV HBM
15KV HBM 3.3 or 5 1 16SOIC, 16SSOP, 16TSSOP 1.94
15KV HBM
2KV HBM
2KV HBM –12 14 8PDIP, 8SOIC 0.72
3.3 or 5 1 16SOIC, 16SSOP, 16TSSOP 2.38
3.3 or 5
–12
C
C
2
22
28SOIC, 28SSOP, 28TSSOP 2.81
8PDIP, 8SOIC 0.72
Preview products are listed in bold blue.
*
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 15
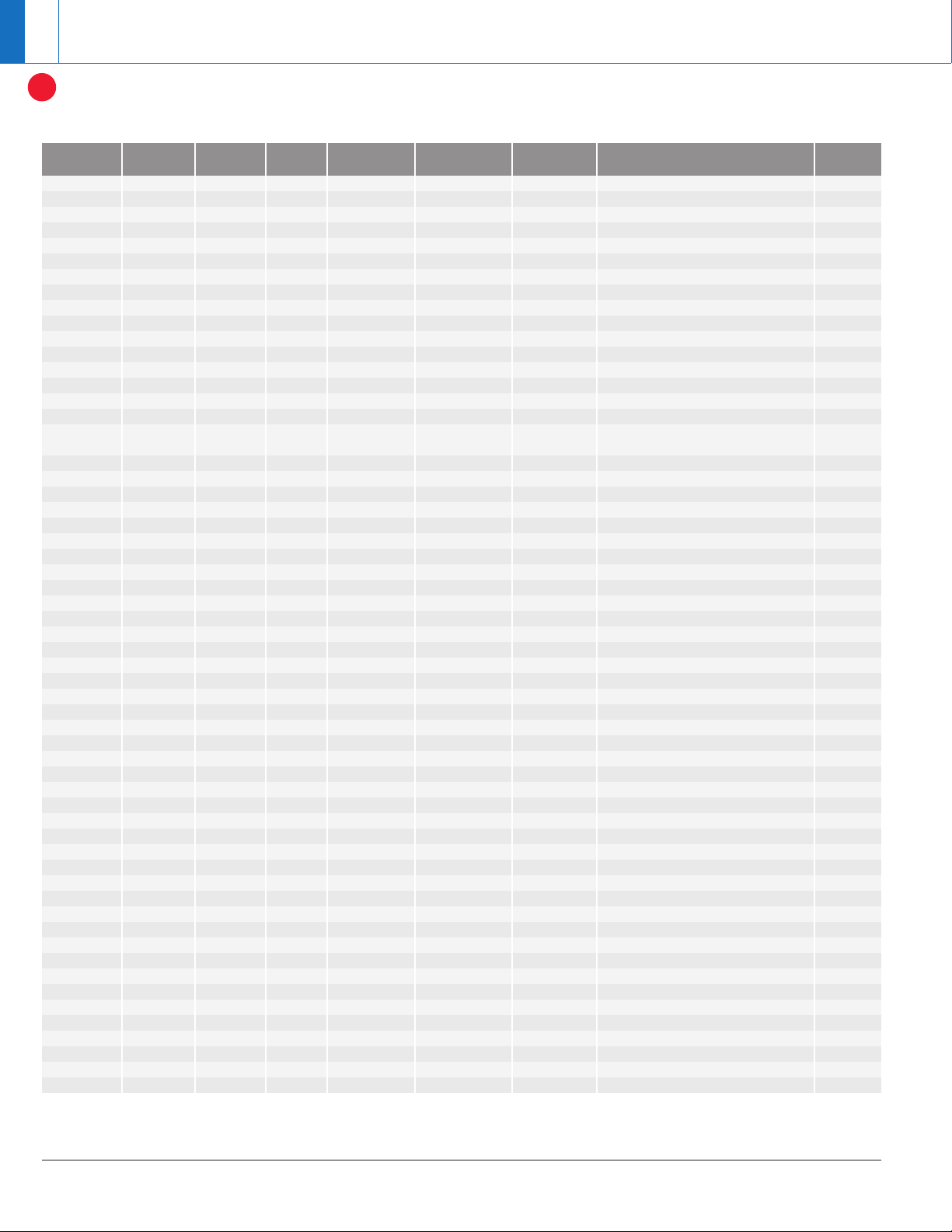
Smart Card
MMC SD
LAN
Port
Stereo Audio Line In
L
L
R
R
LED
Analog
Phone Line
Antenna
Plug
Satellite
Video Input
CATV
RF
FE
RF
FE
RF
FE
LCD
Display
USB Plug
Keypad
Camera
Video Processor
PCI
/
IF
EMAC
Video Port
Video Port
Video Port
EMIF
Bluetooth
®
Controller
ADSL
/
Cable MODEM
803.11
RS-232
1394 PHY
DVI
/
TMDS
Video
Decoder
3-Ch
DAC
3-Ch
DAC
Stereo Audio
CODEC
Voice
CODEX
ADC
ADC
ADC
3-Ch
Amp
3-Ch
Amp
Tuner
Tuner
Tuner
SDRAM
OFDM
QAM
QPSK
DEMOD
FLASH
CPU
PCI
Interface
IrDA
Video
Encoder
SDRAM FLASH
TV CH3-4 MOD
2-to-4 Wire
Interface
2-to-4 Wire
Interface
AC
Adapter
RS-232
RS-232 Selection Guide (Continued)
Device (kbps) Drivers Receivers HBM (kV) Voltage(s) (V) (max) (mA) Pin/Package Price
Data Rate ESD Supply I
SN75C1406 120 3 3 2KV HBM ± 12, 5 0.45 16PDIP, 16SO, 16SOIC 0.86
SN75C185 120 3 5 2KV HBM ± 12, 5 0.75 20PDIP, 20SOIC 1.08
SN75C188 120 4 — 2KV HBM –12 0.16 14PDIP, 14SO, 14SOIC, 14SSOP 0.31
TL145406 120 3 3 2KV HBM ± 12, 5 20 16PDIP, 16SOIC 0.94
GD65232 120 3 5 — ±9, 5 38 20PDIP, 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP 0.29
GD75232 120 3 5 — ±9, 5 30 20PDIP, 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP 0.27
GD75323 120 5 3 — ± 12, 5 32 20SOIC 0.41
LT1030 120 4 — — –5 1 14PDIP, 14SOIC 1.44
MAX3222 120 2 2 — 3.3, 5 1 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP 1.36
MC1488 120 4 — — –9 25 14PDIP 0.20
MC1489 120 — 4 — 5 26 14PDIP 0.25
MC1489A 120 — 4 — 5 26 14PDIP 0.29
SN65C1154 120 4 4 — — — 20PDIP 3.42
SN65C1406 120 3 3 — ± 12, 5 — 16SOIC 1.80
SN65C3222 120 2 2 — 3.3 or 5 1 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP 3.24
SN75154 120 4 4 — 5 or 12 35 16PDIP, 16SO, 16SOIC 0.72
SN751701 120 1 1 — ± 5, 9, 12 11.9 8SO 1.30
SN75186 120 1 1 — ± 12, 5 — 24SOIC 1.80
SN75189 120 — 4 — 5 26 14PDIP, 14SO, 14SOIC 0.22
SN75189A 120 — 4 — 5 26 14PDIP, 14SO, 14SOIC 0.22
SN752232 120 6 10 — 5 +/-50 48SSOP, 48TSSOP 0.90
SN75C1154 120 4 4 — ± 12, 5 — 20PDIP, 20SO, 20SOIC 0.76
SN75C189 120 — 4 — 5 0.7 14PDIP, 14SO, 14SOIC 0.31
SN75C189A 120 — 4 — 5 0.7 14PDIP, 14SO, 14SOIC, 14SSOP 0.31
SN75C198 120 4 — — –12 0.32 14PDIP, 14SOIC 2.25
SN75C3222 120 2 2 — 3.3 or 5 1 20SOIC, 20SSOP, 20TSSOP 2.81
SN75LBC187 120 3 5 — 5 30 28SSOP 3.60
SN75LBC241 120 4 5 — 5 8 28SOIC 2.16
UA9636A 120 2 — — –12 36 8PDIP, 8SOIC 0.36
UC5170C 120 — — — — — 28PLCC 3.15
UC5180C 120 — 8 — 4.75 to 5.25 35 28PLCC 3.00
UC5181C 120 — 8 — 4.75 to 5.25 35 28PLCC 3.15
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
CC
15
➔
*
PDA interface application block diagram.
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 16

TL16C451
TL16C452
TL16C752B
TL16C2752
TL16C750
TL16PIR552A
TIR1000
TL16PC564B
TL16C754B
T
L16C554A
TL16C2550
TL16C2552
TL16C552A
TL16C550D
TL16C550C
TL16C450
1
2
4
No FIFO 16-Byte 64-Byte Special
Functions
FIFO Memory Size
Channels
16
➔
UARTs (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitters)
Design Considerations
The UART is a key component of an
asynchronous serial communications system.
For example, all internal modems have their
own UARTs. In this application, parallel data
within the computer is converted by the
UART to serial data before being transferred
to the modem. In addition to PC/peripheral
communication, UARTs can be used for
chip-to-chip communications.
As data transfer speeds have increased to
support applications such as telecommunication base stations, cell phones, PCs, fax
servers and rack modems, the transmission
rate of the UART has become critical to
Key Features
• Single-, dual- and quad-channel devices
• 16- and 64-byte FIFOs available
• 5-, 3.3-, 2.5- and 1.8-V supply
• Clock rates up to 24/20/16-MHz for
1.5/1.25/1.0-Mbps data transfer rates
• Hardware and software autoflow control
• Programmable sleep mode and
low-power mode
• Industrial temperature characterization
preventing system bottlenecks. When a fast
xternal modem is used, designers should be
e
ure the computer’s UART can handle the
s
odem’s maximum transmission rate. For
m
xample, the TL16C550D UART contains a
e
16-byte buffer, enabling it to support higher
sustained transmission rates than the older
8250 UART. To reduce software buffering
and data overruns, TI has added its patented
hardware autoflow control to all new
designs and most existing UARTs. Most
UARTs allow the divisor to be programmed
from 1 to 65,535 and sometimes with an
added predivisor factor of 1, 4, 16 or 64.
UART Family of Products
To accommodate the requirements of diverse
pplications, TI offers a wide portfolio of
a
arallel-to-serial and serial-to-parallel UARTs
p
n highly integrated, space-saving configura-
i
ions that allow designers to increase system
t
performance while decreasing space
requirements.
As one of the world’s leading high-volume
semiconductor manufacturers, TI offers
designers and OEMs the satisfaction of
knowing they are backed by a supplier with
the resources to meet their needs. These
include a dedicated marketing and technical
support team to assist with any issues.
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 17

Functional block diagram ( for PT and PFB packages)
I
nternal
Data Bus
Autoflow
Control
(AFE)
8
7
S
IN
R
CLK
R
TS
B
AUDOUT
SOUT
CTS
INTRPT
OUT2
OUT1
RI
DCD
DSR
DTR
5
3
2
12
4
–2
47–43
28
A0
A
1
A
2
CS0
C
S1
CS2
ADS
MR
RD1
RD2
WR2
WR1
DDIS
TXRDY
XIN
XOUT
RXRDY
V
CC
V
SS
27
2
6
9
10
11
24
3
5
19
20
16
17
22
23
14
15
29
42
18
D
(7–0)
8
8
38
33
39
40
41
34
31
30
88
8
8
8
8
Power
Supply
S
elect
and
Control
Logic
Receiver
F
IFO
Receiver
S
hift
Register
Receiver
T
iming and
Control
Transmitter
T
iming and
Control
Transmitter
Shift
Register
R
eceiver
Buffer
R
egister
D
ata
Bus
B
uffer
S
e
l
e
c
t
S
e
l
e
c
t
Line
Control
R
egister
Line
S
tatus
Register
Transmitter
Holding
Register
Modem
Control
Register
Modem
Status
Register
Modem
Control
Logic
Interrupt
Enable
Register
Interrupt
Control
Logic
Interrupt
Identification
Register
FIFO
Control
Register
Divisor
L
atch (MS)
Divisor
L
atch (LS)
B
aud
Generator
Transmitter
FIFO
UARTs (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitters)
UART Selection Guide
Voltage Characterized
Device Channel(s) FIFOs (V) Temp. (°C) Package(s) Description Price
Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitters (UARTs)
TL16C2550 2 16-Byte 1.8/2.5/3.3/5 –40 to 85 32 QFN, 44 PLCC, Dual UART with Programmable Auto-RTS and Auto-CTS 2.80
48 TQFP
TL16C2552 2 16-Byte 1.8/2.5/3.3/5 –40 to 85 32 QFN, 44 PLCC Dual UART with Programmable Auto-RTS and Auto-CTS 3.00
TL16C2752 2 64-Byte 1.8/2.5/3.3/5 — 44 PLCC Dual UART with Customizable Trigger Levels Call
TL16C450 1 None 5 0 to 70 40 DIP, 44 PLCC Single UART 1.50
TL16C451 1 None 5 0 to 70 68 PLCC Single UART with Parallel Port 2.50
TL16C452 2 None 5 0 to 70 68 PLCC Dual UART with Parallel Port 2.55
TL16C550C 1 16-Byte 3.3/5 –40 to 85 40 DIP, 44 PLCC, Single UART with Hardware Autoflow Control 1.75
48 LQFP, 48 TQFP
TL16C550D 1 16-Byte 2.5/3.3/5 –40 to 85 32 QFN Single UART with Hardware Autoflow Control 1.75
48 LQFP, 48 TQFP
TL16C552A 2 16-Byte 5 –40 to 85 68 PLCC, 80 TQFP Dual UART with Parallel Port 3.85
TL16C554A 4 16-Byte 5 –40 to 85 68 PLCC, 80 LQFP Quad UART with Hardware Autoflow Control 6.00
TL16C750 1 16/64-Byte 5 –40 to 85 44 PLCC, 64 LQFP Single UART with Hardware Autoflow Control, Low-Power Modes 3.70
TL16C752B 2 64-Byte 3.3 –40 to 85 48 LQFP, 48 TQFP Dual UART with Hardware Autoflow Control, Low-Power Modes 3.10
TL16C754B 4 64-Byte 3.3/5 –40 to 85 68 PLCC, 80 LQFP Dual UART with Hardware Autoflow Control, Low-Power Modes 8.35
TL16PC564B/BLV 1 16/64-Byte 3.3/5 0 to 70 100 BGA, 100 LQFP Single UART with PCMCIA Interface 5.90/6.10
TL16PIR552 2 16-Byte 5 0 to 70 80 QFP Dual UART with Selectable IR & 1284 Modes 6.10
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
17
➔
*
TL16C550D Asynchronous Communications Element
Get samples, datasheets, EVMs and reports at: www.ti.com/sc/device/TL16C550D
Asynchronous Communications Element
with Autoflow Control
The TL16C550D is a performance-enhanced
version of TI’s industry-standard TL16C550C
single-channel UART with 16-byte FIFO. The
TL16C550D can support voltages of down to
2.5 V and data transfer rates of up to 1.5
Mbps. Combining these features with an
ultra-small 32-pin QFN package, the
TL16C550D is ideal for a variety of portable
applications.
Key Features
Expanded voltage and package options
•
ideal for small form factors
Lower voltage
•
TL16C550C
• Pin-for-pin replacement for TL16C550C
• Programmable auto-RTS and auto-CTS
(autoflow)
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
and higher frequency than
• Up to 24/20/16-MHz clock rates for
up to 1.5/1.25/1-Mbps operation
• Programmable baud-rate generator
allows division to generate internal
16x clock
• Independent clock input receiver
Fully programmable serial interface
•
characteristics
• Available packages: DIP, PLCC,
TQFP and QFN
Applications
• PDAs
• MP3 players
• Gaming systems
• Modems
• Serial ports
elecom
T
•
Functional block diagram.
Page 18

18
➔
CAN (3.3-V and 5-V High-Speed CAN Transceivers)
D
esign Considerations
Bus Protection — Features such as
short-circuit protection, thermal shutdown
protection, glitch-free power-up and powerdown protection, high-ESD protection,
wide common-mode range that provides for
common-mode noise rejection, and currentlimiting circuitry to protect the transceivers
and system from damage during a fault
condition have been incorporated into
these devices.
Electromagnetic Compatibility — An
mportant requirement for products intended
i
for networking applications is that they
behave in a way that does not interfere with
the operation of other nearby components or
systems. TI offers specially designed and
tested transceivers for EM compatibility
without malfunction or degradation of
performance in rugged EM environments.
Compatibility in this definition means both
immunity to external EM fields, and the
limited strength of generated EM fields.
Supply Voltage — In addition to 5-V
transceivers, TI offers 3.3-V transceivers
that accomplish the same tasks with less
than half the power and save on the cost of
an additional voltage regulator in 3.3-V
powered applications.
Technical Information
• ISO11898 specifies the physical-layer
implementation of CAN.
• This specification describes a twisted
wire pair bus with 120-W characteristic
impedance (Zo) and differential signaling
rate of up to 1 Mbps on a 40-meter bus
with multi-drop topology.
CAN Transceiver Selection Guide
Supply I
Voltage Device Description Max (mA) (kV) Protection (V) Temp Range Price*
5.0 SN65HVD251 Improved Drop-In Replacement for the PCA82C250 and PCA82C251 65 ±14 ±36 –40 to 125° C 0.90
5.0
SN65HVD1050 Improved Drop-In Replacement for the TJA1050 with Better ESD 70 ±8 –27 to 40 –40 to 125° C 0.55
3.3 SN65HVD230 3.3-V CAN Bus Transceiver, Standby Mode 67 ±16 –4 to 16 –40 to 85° C 1.35
SN65HVD231 3.3-V CAN Bus Transceiver, Sleep Mode 67 ±16 –4 to 16 –40 to 85° C 1.35
SN65HVD232 3.3-V CAN Bus Transceiver, Cost Effective 67 ±16 –4 to 16 –40 to 85° C 1.30
3.3
SN65HVD233 3.3-V CAN Bus Transceiver, Standby Mode, Diagnostic Loop-back 56 ±16 ±36 –40 to 125° C 1.50
SN65HVD234 3.3-V CAN Bus Transceiver, Standby Mode, Sleep Mode 56 ±16 ±36 –40 to 125° C 1.45
SN65HVD235 3.3-V CAN Bus Transceiver, Standby Mode, Autobaud Loop-back 56 ±16 ±36 –40 to 125° C 1.50
All devices have a signaling rate of 1 Mbps. New products are listed in bold red.
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
CC
ESD Bus Fault Operating
Selection Guide
Device
DSPs with CAN Controllers (3.3-V Supply Voltage)
TMS320LF2403A TMS320F2802-60 TMS320LC2403A TMS320F2806 TMS320LF2406A TMS320F2808 TMS320LC2406A TMS320F2809
TMS320LF2407A TMS320F2810 TMS320LF2407A TMS320C2810 TMS320F2801 TMS320F2811 TMS320F2801-100 TMS320R2811
TMS320F2801-60 TMS320C2811 TMS320F28016 TMS320F2812 TMS320C2802 TMS320C2812 TMS320F2802-100 TMS320R2812
ARM7 Microprocessors with CAN Controllers (3.3-V Supply Voltage)
TMS470R1A64 TMS470R1A384 TMS470R1A128 TMS470R1B512 TMS470R1A256 TMS470R1B768 TMS470R1A288 TMS470R1B1M
Standard Compliant Protocols
CAN is a serial communications bus for robust
real-time control applications that is rapidly
gaining the attention of industrial process,
test, measurement and control engineers
worldwide. It has excellent error detection
and confinement capabilities, and has the
flexibility to operate either as a primary
backbone data communications network, as a
secondary local embedded system, or as both.
The engineering community is just now
exploring the limits of what this bus can do
when coupled with newly developed intelligent
sensing technologies.
Besides CAN’s high reliability, another of the
main advantages of CAN when compared to
alternative networks, is the availability of
higher layer protocols (HLPs). There are many
CAN-related system development packages
prepared for these HLPs – hardware interface
cards and easy-to-use software packages that
provide system designers with a wide range of
design and diagnostic tools. These compo
nents provide for the rapid development of
complex control applications without building
each node of a system network from scratch.
The HLP relieves a developer from the burden
of dealing with CAN-specific details such as
bit-timing and implementation functions. It
provides standardized communication objects
for real-time data with Process Data Objects
(PDOs) and Service Data Objects (SDOs), and
provides special functions such as a time
stamp, a sync message, and emergency
shut-down procedures as well as network
management, boot-up commands, and error
management.
Among the most popular HLPs are CANopen,
CANkingdom and DeviceNet with applications
ranging from medical equipment to process
control and assembly line coordination.
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 19

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
*
0
#
L
CD
Driver
L
VDS302
L
VDS301
CLK DATA
Application
P
rocessor
with
RGB
Video
Interface
Flatlink™ 3G
XGA
SVGA
VGA
HVGA
QVGA
Tx
LVDS301
Rx
LVDS302
Tx
LVDS303
Rx
LVDS304
Tx
LVDS305
Rx
LVDS306
QVGA 240 320
640 200
CIF+ 352 416
352 440
HVGA 320 480
800250
640 320
VGA 480 640
1024 320
WVGA 480 800
SVGA 800600
XGA 1024 768
Resolution (W x H)
XGA
SVGA
VGA
HVGA
QVGA
Tx
LVDS301
Rx
LVDS302
Tx
LVDS303
Rx
LVDS304
Tx
LVDS305
Rx
LVDS306
3-Ch 2-Ch 1-Ch
Flatlink
™
3G
19
➔
FlatLinkTM3G – Display SerDes
for Mobile Phones
FlatLink 3G uses low EMI subLVDS to carry
24-bit color RGB data from applications
processors, such as OMAP™ from TI, to the
LCD Driver. It caters to screen resolutions
from QVGA to XGA.
FPC cabling typically interconnects the
erializer-Transmitter with the display.
S
Compared to parallel signaling, FlatLink 3G
utputs significantly reducing the EMI of the
o
interconnect by over 20 dB. The electromag-
etic emission of the device itself is very low
n
and meets the SAE J1752/3 ‘M’-specification.
FlatLink™ 3G Selection Guide
Device
SN65LVDS301 QVGA-XGA Serializer Transmitter — 27 1755 4-65 — 3 2.10
SN65L
VDS302
SN65LVDS303 QVGA-VGA Serializer Transmitter — 27 810 4-30 — 2 Web
SN65LVDS304 QVGA-VGA Deserializer Receiver 27 — 810 4-30 2 — Web
SN65LVDS305 QVGA-HVGA Serializer Transmitter — 27 405 4-15 — 1 Web
SN65LVDS306 QVGA-HVGA Deserializer Receiver 27 — 405 4-15 1 — Web
*
Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000. New products are listed in bold red.
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Description
QVGA-XGA Deserializer Receiver
Number of Number of Data Serial Data Serial Data
Parallel
Outputs Inputs (MB/s) (MHz) Channels Channels Price
Parallel
Throughout
PLL Frequency
Receiver
Transmitter
27 — 1755 4-65 3 — 2.10
Preview products are listed in bold blue.
*
Page 20

Line Module
Reference
Clock
DSP
Controller
Photo-
diode
Laser
Diode
TIA*
MAC
Framer/
Mapper
PLL Multiplier
NPU/
ASICs
Clock
Buffer
Backplane
SerDes
Frontplane
SerDes
Clock
Buffer
Memory
PA*
LD*
Power
Management
*TIA, PA and LD are in development and not currrently available.
L
VDS
SN65LVDS93/94
S
N65LVDS95/96
SN65LV1023A/1224B
S
N75
L
V
DT1422
S
N75LVDS82/83
10 Gigabit
E
thernet
S
erDes
P
ortfolio
Gigabit
E
thernet/FC
EPON
TLK3114SC
T
LK3104SA
T
LK3104SC
TLK3118
TLK10021
TLK1201AI
T
NETE2201
T
LK2208B
TLK2226
T
LK2201BI
TLK2201AJR
TLK1211
G
eneral
Purpose
TLK3101
T
LK2711
T
LK2701
TLK2501
T
LK1501
TLK4015
T
LK2521
TLK1521
TLK4120
T
LK4250
S
N75LVDS84A/86
20
SerDes (Serial Gigabit Transceivers and LVDS)
➔
The serial gigabit transceiver family of
devices from TI provides low power dissipation while enabling multigigabit transmission
over copper backplanes, cable and optical
links. The transceivers can be used in a
variety of applications, including Gigabit
Ethernet, 10-Gigabit Ethernet modules,
synchronous optical network (SONET) OC-48
and OC-192 based equipment, wireless
infrastructure backplanes and general-purpose
backplane applications.
SerDes Solutions—Frontplane/Backplane
TLK1201AI/TLK2226/TLK2208B
Low-Power 1 GbE Transceiver
1 to 1.6 Gbps
(Backplane/Frontplane)
TLK3114SC
TLK2208B—8-Channel Gigabit Ethernet Xcvr (8 x 1-1.3-Gbps)
—10-Gigabit Ethernet Backplane Device XAUI (4 x 3.125 Gbps)
TLK2226—6-Channel Gigabit Ethernet Xcvr (6 x 1-1.3 Gbps)
TLK1201AI—1- to 1.6-Gbps Gigabit Ethernet-Compliant SerDes
TLK3101/TLK2501/TLK1501—600-Mbps to 3.2-Gbps General-Purpose Backplane SerDes
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
SN65LV1023A/1224B—100 to 660 Mbps—10:1 LVDS SerDes
Page 21

SerDes (Serial Gigabit Transceivers and LVDS)
SerDes (Serial Gigabit Transceivers) Selection Guide
Device Function Data Rate Serial I/F
General Purpose
TLK1501 Single-Ch. 16:1 SerDes 0.6-1.5 Gbps 1 CML 16 LVTTL 200 mW Built-In Testability 8.40
TLK2501 Single-Ch. 16:1 SerDes 1.6-2.5 Gbps 1 CML 16 LVTTL 300 mW Built-In Testability 12.60
TLK2701 Single-Ch. 1.6-2.5 Gbps 1 CML 16 LVTTL 300 mW Built-In Testability 12.60
16:1 SerDes and K Character Control
TLK2711 Single-Ch. 1.6-2.5 Gbps 1 VML 16 LVTTL 350 mW MicroStar Junior™BGA 10.50
TLK3101 Single-Ch. 16:1 SerDes 2.5-3.125 Gbps 1 VML 16 LVTTL 350 mW Built-In Testability 16.85
TLK2521 Single-Ch. 1.0-2.5 Gbps 1 VML 18 LVTTL <550 mW Low Power and 12.60
TLK1521 Single-Ch. 0.6-1.3 Gbps 1 VML 18 LVTTL <350 mW Low Power and 10.50
TLK4120 Four-Ch. 18:1 Serdes 0.5-1.3 Gbps 4 VML 18 LVTTL <350 mW
TLK4250 Four-Ch. 18:1 Serdes 1.0-2.5 Gbps 4 VML 18 LVTTL <550 mW
TLK4015 Four-Ch. of 16:1 Xcvr 0.6-1.5 Gbps/Ch. 4X CML 16 LVTTL/Ch. 1 W Four-Channel Version of TLK1501 29.40
EPON
TLK1211 Single-Ch. 10:1 Gigabit Ethernet 0.6-1.3 Gbps 1 LVPECL 10 LVTTL 200 mW Fast Relock for PON Web
Gigabit Ethernet/FibreChannel
TLK1201AI Single-Ch. 10:1 Gigabit 0.6-1.3 1 LVPECL 10 LVTTL 200 mW Industrial Temperature 4.85
TLK2201BI Single-Ch. 1.2-1.6 Gbps 1 LVPECL 10 LVTTL 200 mW JTAG; 5-Bit DDR Mode, 4.65
TLK2201AJR Single-Ch. 1.0-1.6 Gbps 1 LVPECL 10 LVTTL 200 mW MicroStar Junior 4.25
TLK2208B Eight-Ch. of 10:1 Gigabit 1.0-1.3 Gbps 8 VML 4/5-Bit/Ch. (Nibble 1 W JTAG, MDIO Supported 31.50
TLK2226 Six-Ch. 16:1 Gigabit 1.0-1.3 Gbps 6 VML 4/5-Bit RTBI or RGMII <1.5 W MDIO Supported 19.65
10 Gigabit (XAUI) Ethernet
TLK3104SA Four-Ch. of 2.5-3.125 Gbps 4X 3.125 Gbps 4X 10/8-Bit 700 mW/Ch. JTAG; Programmable 69.30
TLK3104SC Four-Ch. of 3.0-3.125 Gbps 4X 20X622 700 mW/Ch. JTAG, 8b/10b On/Off 126.00
TLK3114SC Four-Ch. of 2.5-3.125 Gbps 4X 3.125 Gbps 4X 10/8-Bit 600 mW/Ch. IEEE 802.3ae 57.75
TLK3118 Four-Ch. 10/8:1 Xcvr w/ 2.5-3.125 Gbps/Ch. 4X 3.125 8/10 HSTLx4 <2 W Full Redundancy for 80.00
TLK10021 Four XAUI to XFI 10 Gbps 1 XFI 4 XAUI 800 mW Built-In Testability Web
LVDS Serdes
SN65LVDS93/94 Four-Ch. 28:4 TX/RX 140-455 Mbps/Ch. 5 LVDS 28 LVTTL 250 mW/Chip Supports Up to 1.82 Gbps 3.45
SN65LVDS95/96 Three-Ch. 21:3 TX/RX 140-455 Mbps/Ch. 4 LVDS 28 LVTTL 250 mW/Chip Supports Up to 1.82 Gbps 3.45
SN65LV1023A/1224B Single-Ch. 10:1 TX/RX 100-660 Mbps 1 LVDS 10 LVTTL <400 mW Low Power Solution 4.60
VDT1422 14:1 Xcvr SerDes 140 Mbps-1.4 Gbps 1 LVDS 14-Bit LVTTL <300 mW Supports Spread Spectrum 3.70
SN75L
SN75LVDS82/83 Four-Ch. 28:4 TX/RX Chipset 0.651-1.428 Gbps 4 LVDS 28 LVTTL 250 mW/Chip Commercial Temp 2.25
VDS84A/86
SN75L
1
CML = Current Mode Logic; VML = Voltage Mode Logic. New products are listed in bold red.
*
Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000. Preview products are listed in bold blue.
16:1 SerDes Packaging
18:1 SerDes Built-In Equalization
18:1 SerDes Built-In Equalization
Ethernet Xcvr Gbps
10:1 Gigabit Industrial Temperature
Ethernet Xcvr Qualified
10:1 Gigabit 5 mm x 5 mm LGA
Ethernet Xcvr
Ethernet Xcvr DDR Mode), 8/10-Bit/Ch.
Ethernet Xcvr 100-FX mode support
10/8:1 Xcvr LVPECL (XAUI) SSTL/HSTL Pre-Emphasis and XAUI I/F
4.1: Xcvr LVPECL LVDS Lines
10/8:1: Xcvr LVPECL (XAUI) SSTL/HSTL Backplane Transceiver
(XAUI) Full Redundancy LVPECL (XAUI) (XGMII) Four Channels (XAUI)
Chipset
Chipset Throughout
Chipset
Three-Ch. 21:3 TX/RX Chipset
0.42-1.428 Gbps
1
3 LVDS 21 LVTTL 250 mW/Chip Commercial Temp 2.10
Parallel I/F Power Special Features Price
Four-Channel Version of TLK1521
Four-Channel Version of TLK2521
(Multiplex Ch. Mode)
(XGMII) Compliant
Throughout
Clocking
24.00
32.00
21
➔
*
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 22

TX
Keys
TMDS
Decode
TMDS
Decode
DVI LinkContent
DVI TX
(PC’s D VI Output)
DVI RX
(Displays DVI Input)
Application
Program
S
W
Driver
EDID
PROM
Controller
I
2
C Master
Content
I
2
C
I
2
C
Slave IF
HDCP
Encrypt
HDCP
Encrypt
I
2
C
Slave IF
I
2
C
RX
Keys
22
DVI/PanelBus
™
➔
D
esign Considerations
The Digital Visual Interface (DVI)
Specification, is an industry standard developed by the Digital Display Working Group
DDWG) for high-speed digital connection to
(
digital displays. DVI uses Transition-minimized
DC balanced (TMDS) data signaling. Single
link supports up to 165Mpixels/s – UXGA
FPDs, SXGA DCRTs, 720p and 1080i HDTVs.
High Bandwidth Digital Content
Protection (HDCP)
• Content protection for video sent over DVI
• Implementation of HDCP requires a
license from the Digital Content
Protection Licensing, L.L.C.
(www.digital-cp.com)
HDCP Elements
• Authentication is a process for verifying
that a device is authorized (e.g. licensed)
DVI-HDCP implementation.
to handle protected content.
• Encryption prevents eavesdropping of
protected content.
• Renewability enables revocation of
compromised devices.
PanelBus™ (DVI) Transmitters and Receivers
Voltage Recvr./Trans. Parallel Data Speed I
Device (V) Channels Outputs (Mbps) (mA) Package Description Price
TFP401 3.3 3 48 495 400 100 HTQFP DVI receiver, 165 MHz 4.00
TFP401A
TFP403 3.3 3 48 495 400 100 HTQFP DVI receiver 5.45
TFP410 3.3 3 6 495 250 64 HTQFP DVI transmitter, 165 MHz 3.00
TFP501 3.3 3 48 495 400 100 HTQFP DVI receiver, 165 MHz plus HDCP Call
TFP503
TFP510
TFP513 3.3 3 6 495 250 64 HTQFP DVI transmitter, 165 MHz plus HDCP and embedded HDCP keys Call
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
3.3
3.3
3.3
3
3 48 495 400 100 HTQFP DVI receiver, 165 MHz plus HDCP and embedded HDCP keys Call
3
48
6
495
495 250 64 HTQFP DVI transmitter, 165 MHz plus HDCP Call
CC
400 100 HTQFP DVI receiver, 165 MHz, HSYNC jitter immunity 4.00
*
Interface Selection Guide T
exas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 23

T.M.D.S. Transmitter
TX2
TX1
TX0
TXC
TFADJ
IDCK
DATA[23:0]
DE
VSYNC
HSYNC
EDGE/
HTPLG
MSEN
BSEL/SCL
DSEL/SDA
V
REF
MDA/DK2
MCL/DK1
ISEL/RST
PD
Serializer
Serializer
Serializer
Control
Encoder
Encoder
Encoder
IC Slave I/F
2
For DDC
1.8-V Regulators
with Bypass
Capacitors
PLL
for EEPROM
IC Master I/F
2
Universal Input
HDCP
Encryption
12-/24-Bit
I/F
Data
Format
HDCP
Cipher
DVI/PanelBus
™
23
➔
PanelBus™ HDCP Digital Receiver
FP501, TFP503
T
Get datasheets at: www.ti.com/TFP501 or www.ti.com/TFP503
The TFP501 and TFP503 are TI PanelBus flat panel display products,
part of a comprehensive family of end-to-end DVI 1.0-compliant
solutions. The TFP501/TFP503 support display resolutions up to UXGA,
including the standard HDTV formats, in 24-bit true-color pixel format.
The TFP501/TFP503 offer design flexibility to drive one or two pixels
per clock, support TFT or DSTN panels and provide an option for
time-staggered pixel outputs for reduced ground-bounce.
Key Features
• Supports UXGA resolution (output pixel rates up to 165 MHz)
• Digital visual interface (DVI) and high-bandwidth digital content
protection (HDCP) specification compliant
Encrypted external HDCP device key storage for exceptional security
•
and ease of implementation
• True color, 24 bits/pixel, 48-bit dual-pixel output mode;
16.7/M colors at one or two pixels per clock
• 4x oversampling for reduced bit-error rates and better performance
over longer cables
• Embedded HDCP keys (TFP503 only)
• Supports hot-plug detection
• Packaging: 100-pin TQFP PowerPAD™
Applications
• Desktop LCD monitors
• DLP®and LCD projectors
• Digital TVs
TI PanelBus™ Digital Transmitters
FP510, TFP513
T
Get the datasheets and app reports at: www.ti.com/sc/device/TFP510 or
www.ti.com/sc/device/TFP513
The TFP510 and TFP513 provide a universal interface allowing a glueless connection to most commonly available graphics controllers. Some
of the advantages of this universal interface include selectable bus
widths, adjustable signal levels and differential and single-ended
clocking. The DVI interface supports flat panel display resolutions up
to UXGA at 165 MHz in 24-bit true color pixel format.
Key Features
• Digital visual interface (DVI) compliant
• Supports resolutions from VGA to UXGA
(25-MHz to 165-MHz pixel rates)
• Universal graphics controller interface
12-bit, dual-edge and 24-bit, single-edge input modes
••
••
Adjustable 1.1-V to 1.8-V and standard 3.3-V CMOS input signal
levels
Fully differential and single-ended input clocking modes
••
••
Standard Intel®12-bit digital video port compatible as on Intel
81x chipsets
• Programmable using I2C serial interface
• Monitor detection through hot-plug and receiver detection
• Embedded HDCP keys (TFP513 only)
• Packaging: 64-pin TQFP PowerPAD™
Applications
• Set-top boxes
• DVD recorders/players
TFP510 block diagram.
TFP501 block diagram.
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 24

Rx1
Rx1
PC
STB
DVD
Allows Distant Connection
to Connector Socket
Rx
Rx2
Main Picture
Picture
in
Picture
TV
TV
TV
Game
Console
STB
DVD
PC
24
➔
TMDS
TMDS (for HDMI and DVI)
ransition Minimized Differential Signaling
T
TMDS) is the electrical level standard used
(
to transmit Digital Visual Interface (DVI) and
High-Definition Multimedia Interface
(HDMI) data.
Design Considerations
Intra-Pair Skew – The time difference
between the true and complementary signals
of a given differential pair should be kept as
small as possible.
Residual Jitter – The difference in the
amount of measured jitter between the test
point and the signal source. It is the allowable
maximum residual jitter is equivalent to the
minimum jitter budget between transmitter
and receiver.
ESD – External connectors being exposed
to the outside world are especially susceptible
to electrostatic discharge. A higher ESD
rating provides improved protection.
TMDS341A 3-to-1 Mux.
TMDS442 4-to-2 Mux.
TMDS141 HDMI Hider.
Device Description Inputs Outputs (max) (max) (ps) (max) (ps) (max) (ps) (mA) (kV) Package Price*
TMDS141 HDMI Hider 1 1 50 100 30 — 150 5 40QFN Web
TMDS341A 3-to-1 DVI/HDMI Switch 3 1 50 100 30 50 230 5 80TQFP 3.50
TMDS442 4-to-2 DVI/HDMI Switch 4 2 50 100 30 — 550 5 128TQFP Web
TS3DV416 4-to-1 Analog Switch 4 1 — — — — — 2 48TSSOP, 2.00
for DVI/HMDI 48TVSOP
TS3DV520 4-to-1 Analog Switch 5 1 — — — — — 2 56QFN 2.97
for DVI/HMDI
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000. New products are listed in bold red.
No. of No. of Skew Skew Jitter Jitter ICC (max) ESD HBM Pin/
Intra-Pair (ps) Inter-Pair Clock P-P Data P-P
Preview products are listed in bold blue.
Interface Selection Guide T
exas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 25

Universal Serial Bus (USB)
In
Out
S
IN
S
OUT
USB
Legacy
Serial
Peripheral
Host
(PC or OTG DRD)
TUSB3410
he USB standard defines a bus product that
T
equires a host controller and enables plug-
r
nd-play connectivity. The most recently
a
eleased final specification, USB 2.0, defines
r
high speed and allows complete backward
compatibility with USB 1.1.
USB products fall into three categories: hubs,
host controllers and peripherals. USB 1.1 supported speeds of up to 12 Mbps and cables
up to 5 meters long for these devices. USB
2.0 extends the connection speed to 480
Mbps to support next-generation peripherals
of higher-performance PCs and applications.
USB 2.0 officially defines three speeds: low
(1.5 Mbps), full (12 Mbps) and high (480
Mbps). The lowest speed is ideal for human
interface devices such as a mouse, game pad
or keyboard; while full speed is well suited
for “data dumps” to the PC via digital still
cameras, PDA cradles and flash-card readers.
Modems, printers, scanners and storage
drives are just a few of the items that can
take advantage of USB’s highest speed
specification.
USB Hub Controllers and Peripheral Devices
he USB On-The-Go (OTG) supplement to USB
T
.0 specifies a new class of devices aimed at
2
he portable market. USB OTG defines devices
t
hat can operate as standard USB peripherals
t
when connected to a standard USB host
controller.
However, these same devices can operate
as reduced-function host controllers to
support selected USB OTG peripheral
devices. End-equipment manufacturers
can specify what type of peripherals their
devices will support when in OTG host
mode. This new specification allows easy
sharing of contact information between
USB OTG PDAs and cell phones or printing
of photographs directly from an OTGenabled digital still camera without a PC.
Technical Information
Speed
• The USB 2.0 standard defines three
speeds: low speed (LS) 1.5 Mbps, full
speed (FS) 12 Mbps and high speed (HS)
480 Mbps. It requires full backward and
forward compatibility for devices and
cables. All three modes offer both asyn-
hronous and isochronous (real-time) data
c
transmission over a simple and inexpensive
4-wire cable to meet requirements of
peripherals including keyboards, mice,
printers, speakers, scanners, external
storage devices and digital still cameras.
Transfer Type
• USB 2.0 defines four types of transfers:
bulk, control, interrupt and isochronous.
Bulk transfer is intended for applications
such as printers, scanners and mass
storage, where latency isn’t critical but
accuracy is. All devices must include
control transfers for configuration.
Interrupt transfer is for devices such as
mice, keyboards and game pads that must
receive the host’s or device’s attention
periodically. Isochronous transfer offers
guaranteed delivery time but no errorchecking or automatic retransmission of
data received with errors, making it the
better choice for audio or video applications.
25
➔
RS232/IrDA Serial-to-USB Converter
TUSB3410
Get samples, datasheets, EVMs and app reports at: www.ti.com/sc/device/TUSB3410
USB-to-Serial Bridge
The TUSB3410 provides an easy way to move a
serial-based legacy device to a fast, flexible
USB interface by
and an enhanced UART serial port. The
TUSB3410 contains all the necessary logic to
communicate
USB bus.
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
bridging
between a USB port
with the host computer using the
TUSB3410 data flow
.
Key Features
• USB full-speed-compliant: data rate of
12 Mbps
• 8052 microcontroller with 16 Kbytes of
RAM that can be loaded from the host
or from external onboard memory via an
2
C bus
I
• Integrated, enhanced UART features
including:
••
Programmable software/hardware flow
control
Automatic RS-485 bus transceiver
••
control, with and without echo
Software-selectable baud rate from
••
50 to 921.6 kbaud
••
Built-in, two-channel DMA
controller for USB/UART bulk I/O
• Evaluation module to jump-start USB
development or for use as a complete
USB-to-RS-232 converter
Applications
• Handheld meters
• Health metrics/monitors
• Any legacy serial device that needs
to be upgraded to USB
Page 26

U
SB Hub Controllers
U
SB Peripherals
USB Devices
TUSB2036
TUSB2046B
TUSB2077A
TUSB2136
T
USB5052
TUSB3210
TUSB3410
TUSB6250
U
SB OTG
TUSB6020
TUSB1105
TUSB1106
T
USB2551
U
SB PHY
26
USB Hub Controllers and Peripheral Devices
➔
USB Family of Products
Selection Guide
Voltage
Device Speed Ports I2C (V) Package Description Price
USB Hub Controllers
TUSB2036 Full (1.1) 2/3 No 3.3 32 LQFP 2/3-port hub for USB with optional serial EEPROM interface 1.15
TUSB2046B Full (1.1) 4 No 3.3 32 LQFP 4-port hub for USB with optional serial EEPROM interface 1.20
TUSB2077A Full (1.1) 7 No 3.3 48 LQFP 7-port USB hub with optional serial EEPROM interface 1.95
TUSB2136 Full (1.1) 1/2 Yes 3.3 64 LQFP 2-port hub with integrated general-purpose function controller 3.25
TUSB5052 Full (1.1) 1-5 Yes 3.3 100 LQFP 5-port hub with integrated bridge to two serial ports 5.10
*
Voltage Remote
Device Speed (V) Wakeup Package Description Price
USB Peripherals
TUSB3210 Full 3.3 Yes 64 LQFP USB full-speed general-purpose device controller 2.50
TUSB3410 Full 3.3 Yes 32 LQFP USB-to-serial converter (RS-232, RS-485) 2.25
TUSB6250 Full, High 3.3 Yes 80 TQFP USB 2.0 high-speed, low-power ATA/ATAPI bridge solution 2.80
Voltage Local Bus
Device Speed (V) Package Interface Description Price
USB On-The-Go (OTG)
TUSB6020 High 1.5, 1.8, 3.3 80 QFP VLYNQ™ USB 2.0 High-Speed On-The-Go to Local Bus Interface Controller Call
Voltage Single ended
Device
Speed (V) Package Input Description Price
USB Transceivers
TUSB1105 Full, Low 1.6, 3.6 16RTZ, 16RGT Yes USB Transceivers Call
TUSB1106 Full, Low 1.6, 3.6 16RTZ, 16PW No USB Transceivers Call
TUSB2551 Full, Low 1.6, 3.6 14PW, 16RGT No USB Transceivers Call
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000. Preview products are listed in bold blue.
USB Port Protection—Transient voltage suppressor protects USB 1.1
devices from ESD and electrical noise transients.
Temp Range
Device Description °C Price
USB Transceivers
SN65220 Single suppressor –40 to 85 0.33
SN65240 Dual suppressor –40 to 85 0.41
SN75240 Dual suppressor 0 to 70 0.38
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
Interface Selection Guide T
*
Resources For a complete list of resources
(evaluation modules, data sheets and application notes), visit
Literature Number Description
Application Notes
SLLA122
SLLA154 VIDs, PIDs and Firmware:
SLLU043 TUSB3410 UART Evaluation Board
SLLA170B USB/Serial Applications Using
SLLAA276 MSP430 USB Connectivity Using
Selection and Specification of
Crystals for Texas Instruments
USB 2.0 Devices
Design Decisions When Using
TI USB Device Controllers
TUSB3410/5052 and the VCP
Software
TUSB3410
exas Instruments 4Q 2006
*
*
*
interface.ti.com
Page 27

VIN/SW1
LDO_EN
EN1
SW2
EN2
GND
LDO_OUT
LDO_ADJ
OC1
OUT1
OUT2
OC2
TPS2145/55
TSSOP-14
LDO
VIN/SW1
EN1
SW2
EN2
GND
LDO_OUT
OC1
OUT1
OUT2
OC2
TPS2147/57
MSOP-10
LDO
VIN/SW1
LDO_EN
EN1
EN2
GND
LDO_OUT
OUT1
OUT2
TPS2148/58
MSOP-8
LDO
VIN
EN1
EN2
GND
LDO_OUT
OUT1
OC
OUT2
TPS2149/59
MSOP-8
LDO
D
esign Considerations
USB High-Power Peripheral Switch With
Dual Current Limit + LDO
Universal Serial Bus (USB) Power Managers
4-Port USB Hub Power Controllers
Power Distribution Switches
27
➔
TPS2140/41/50/51—The TPS2140/41/50/51
target high-power USB peripherals such as
ADSL modems. The devices contain a power
switch and an LDO. The dual-current-limiting
switch allows the use of high-value capacitance to stabilize the voltage from the USB bus.
Dual Power Switch + LDO for USB
Bus-Powered Peripherals and Hubs
TPS2148/49—TPS2148 is a complete power
management solution for USB bus-powered
peripherals such as zip drives, while TPS2149 is
for USB bus-powered hubs, such as keyboards
with integrated hubs. TPS2148/9 each combine
a 3.3-V LDO and dual power switch in a single
MSOP package. The TPS2148 switch configuration allows power and board capacitance
segmentation to meet USB system current
requirements. The TPS2149 switches manage
two independent or four ganged USB ports.
TPS207x—The TPS207x family provides the
complete power solution for 4-port selfpowered, bus-powered or hybrid USB hubs by
incorporating current-limited switches for four
ports, a 3.3-V 100-mA LDO, a 5-V LDO
controller for self power (TPS2070, TPS2071)
and a DP0 line control to signal an attach to
the host.
Ease of Use—USB allows simplified installa-
tion and improved performance for peripheral
devices by eliminating the need to repeatedly
load new drivers and establish individual settings. USB combines a multitude of existing
interfaces into a single easy-to-use connector,
greatly reducing system complexity and offering manufacturers the ability to develop highly
integrated products.
TPS204xB/5xB—The TPS204xB/5xB families
of 80-mΩ current-limiting power switches
meet all the USB power management
requirements for controlling downstream
ports, and include additional features to
improve the design reliability. For example,
when an over-current condition exists, the
device intelligently shuts down only the port
that sees the fault.
TPS202x/3x/6x—The TPS202x/3x/6x families
of low on-resistance current-limiting power
switches allow ganging of multiple ports to
a single switch, as described in Application
Note SLVA049. Though ganging can be costeffective, all ports are affected by a fault.
USB Power Managers Family of Products
Current Limit (min) (A)
0.22 0.3 0.66 0.7 1.1 1.5 1.65 2.2
USB Power Distribution Switches
Quad — TPS2048A/58A — TPS2044B/54B — — — —
Triple — TPS2047B/57A — TPS2043B/53B TPS2063/67 — — —
Dual — TPS2046B/56A — TPS2042B/52B TPS2062/66 TPS2060/64 — —
Single TPS2020/30 TPS2045A/55A TPS2021/31 TPS2041B/51B TPS2022/32/61/65 — TPS2023/33 TPS2024/34
Dual Power Switch +
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
LDO for USB
Bus-Powered Peripherals and Hubs
Device Controller Indicator Pins Package
4-Port USB Hub Power Controllers
TPS2070 Yes Active Low 32 HTSSOP
TPS2071 Yes Active High 32 HTSSOP
TPS2074 No Active Low 24 SSOP
TPS2075 No Active High 24 SSOP
5-V LDO Mode
Bus Power
Page 28

D
ual
Threshold
I
LIMIT
LDO_IN
LDO_EN
L
DO_OUT
A
DJ
LDO_PG
S
W_OUT
S
W_PG
T
PS2140/41/50/51
T
SSOP-14
L
DO
S
W_IN
S
W_EN
G
ND
28
Universal Serial Bus (USB) Power Managers
➔
USB Power Managers Family of Products (Continued)
USB High-Power Peripheral Bus Switch + LDO
Device Switch Voltage Description
TPS2140 3.3 V 3.3-V, 500-mA switch with active-low enable, 250-mA LDO
TPS2141 5.0 V 5.0-V, 500-mA switch with active-low enable, 250-mA LDO
TPS2150 3.3 V 3.3-V, 500-mA switch with active-high enable, 250-mA LDO
TPS2151 5.0 V 5.0-V, 500-mA switch with active-high enable, 250-mA LDO
USB Power Managers Selection Guide
Number I
OS
Device of FETs (min) (A) (mΩ) (V) (µA) Output Output Enable Predecessor Price
USB Power Distribution Switches
TPS2020/30 1 0.22 33 2.7 to 5.5 73 Yes Yes L/H
TPS2021/31 1 0.66 33 2.7 to 5.5 73 Yes Yes L/H TPS2014 1.05
TPS2022/32 1 1.1 33 2.7 to 5.5 73 Yes Yes L/H TPS2015 1.05
TPS2023/33 1 1.65 33 2.7 to 5.5 73 Yes Yes L/H
TPS2024/34 1 2.2 33 2.7 to 5.5 73 Yes Yes L/H
TPS2041B/51B 1 0.7 70 2.7 to 5.5 40 Yes Yes L/H TPS2041/51/41A/51A 0.50
TPS2042B/52B 2 0.7 70 2.7 to 5.5 53 Each Yes L/H TPS2042/52/42A/52A 0.70
TPS2043B/53B 3 0.7 70 2.7 to 5.5 65 Each Yes L/H TPS2043/53/43A/53A 0.90
TPS2044B/54B 4 0.7 70 2.7 to 5.5 75 Each Yes L/H TPS2044/54/44A/54A 1.00
TPS2045A/55A 1 0.3 80 2.7 to 5.5 80 Yes Yes L/H TPS2045/55 0.60
TPS2046B/56A 2 0.3 80 2.7 to 5.5 80 Each Yes L/H TPS2046/46A/56 0.65
TPS2047B/57A 3 0.3 80 2.7 to 5.5 160 Each Yes L/H TPS2047/47A/57 0.90
TPS2048A/58A 4 0.3 80 2.7 to 5.5 160 Each Yes L/H TPS2048/58 1.20
TPS2060/4 2 1.5 70 2.7 to 5.5 50 Each Yes L/H — 1.20
TPS2061/5 1 1.1 70 2.7 to 5.5 43 Yes Yes L/H — 0.60
TPS2062/6 2 1.1 70 2.7 to 5.5 50 Each Yes L/H — 0.75
TPS2063/7 3 1.1 70 2.7 to 5.5 65 Each Yes L/H — 0.90
r
DS(on)
VINRange Supply Current OC Logic OT Logic
—
—
—
*
1.05
1.05
1.05
Bus Powered Self Powered
Number Bus Power V
Switch
of
Indicator (min) (max) per FET Limit per FET Limit Controller
IN
r
DS(on)
Current r
DS(on)
Current LDO
Device Application FETs Enable (BPMODE) (V) ( V) (typ) (mΩ) (min) (A) (typ) (mΩ) (min) (A) (A) LDO Price
USB Power Controllers
TPS2070 USB 4-port hub 8 L 1L 4.5 5.5 560 0.12 107 0.6 5 V, 3 A 3.3 V, 100 mA 2.55
TPS2071 USB 4-port hub 8 L 1H 4.5 5.5 560 0.12 107 0.6 5 V, 3 A 3.3 V, 100 mA 2.55
TPS2074
USB 4-port hub 8 L 1L 4.5 5.5 500 0.12 100 0.6 — 3.3 V, 100 mA 2.55
TPS2075 USB 4-port hub 8 L 1H 4.5 5.5 500 0.12 100 0.6 — 3.3 V, 100 mA 2.55
TPS2140 USB peripheral 1 L — 2.7 5.5 70 0.1 & 1.2 — — — Adj. 0.9 to 3.3 V, 250 mA 1.10
TPS2141 USB peripheral 1 L — 4 5.5 70 0.1 & 1.2 — — — Adj. 0.9 to 3.3 V, 250 mA 1.10
TPS2150 USB peripheral 1 H — 2.7 5.5 70 0.1 & 1.2 — — — Adj. 0.9 to 3.3 V, 250 mA 1.10
TPS2151 USB peripheral 1 H — 4 5.5 70 0.1 & 1.2 — — — Adj. 0.9 to 3.3 V, 250 mA 1.10
TPS2145
DSP
, PDA
L
2
— 2.9 5.5 340 0.2 — — — 3.3 V, 200 mA 1.15
TPS2147 DSP, PDA 2 L — 2.9 5.5 340 0.2 — — — 3.3 V, 200 mA 1.10
TPS2148 USB peripheral 2 L — 2.9 5.5 340 0.2 — — — 3.3 V, 200 mA 0.99
TPS2149 USB 2-port hub 2 L — 2.9 5.5 340 0.2 — — — 3.3 V, 200 mA 0.95
TPS2155 DSP, PDA
TPS2157 DSP, PDA 2 H — 2.9 5.5 340 0.2 — — — 3.3 V, 200 mA 1.10
TPS2158 USB peripheral 2 H — 2.9 5.5 340 0.2 — — — 3.3 V, 200 mA 0.99
TPS2159 USB 2-port hub
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000. Please check www
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
5.5 340 0.2 — — — 3.3 V, 200 mA 1.15
H
2
H — 2.9 5.5 340 0.2 — — — 3.3 V, 200 mA 0.95
2
—
2.9
.ti.com
for the most current pricing information.
*
Page 29

Design Considerations
Device A Device C
Device BDevice
PCI Express
®
Reference ClockReference Clock
Device B
PCI Express
PCI Express
PCI/PCI-X
PCI
Express
PCI
Express
PCI
Express
PCI
Express
Legacy
Endpoint
Legacy
Endpoint
PCI Express
Endpoint
PCI Express
Endpoint
PCI Express-PCI
Bridge
PCI Express
Memory
PCI Express
Endpoint
CPU
Root
Complex
Switch
PCI Express
Bridge
XIO2000A XIO3130 XIO2200A XIO1100
PCI Express
Switch
PCI Express
Portfolio
PCI Express
Endpoint
PCI Express
PHY
PCI Express®takes the best features and
ideas behind PCI and combines them with
more than 10 years of industry “lessons
learned.” The result is a robust, scalable,
flexible, cost-effective I/O interconnect that
will serve the industry for the next 10-15 years.
Key Features
• PCI Express architecture is an industry
standard high-performance, generalpurpose serial I/O interconnect designed
for use in enterprise, desktop, mobile,
communications and embedded platforms.
• It is PCI-compatible by using the established PCI software programming models.
PCI Express facilitates a smooth transition
to new hardware and allows software to
evolve and leverage the advantages of
PCI Express features.
• Gen I has a scalable bandwidth of 16
Gigabytes-per-second at its initial signaling rate of 2.5GHz. In the future, Gen II
promises much higher transfer rates using
higher frequency signaling technologies.
• Supports multiple interconnect widths via
1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 16 and 32 lane configurations aggregated to match application
bandwidth needs.
• Serves new and innovative, hot-plug/
hot-swap add-in card and module devices.
• Delivers unique, advanced features such
as Power Management, Quality of Service
and other native functions not available in
other I/O architectures.
PCI Express®topology.
PCI Express
Device
Classifications
• Root Complex
• Switch
• PCI/PCI-X
• Bridge
• Legacy Endpoint
• Endpoint
®
29
➔
Current TI PCI Express
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
®
portfolio.
Page 30

PCI Express
Transmitter
Power
Mgmt
Clock
Generator
Reset
Controller
Configuration and
Memory Register
PCI Bus Interface
PCI Express
Receiver
GPIO
Serial
EEPROM
Serial IRQ
Upstream
PCI Express
Device
Vaux
Auxilliary
Power
Serial
EEPROM
Miscellaneous
PCI Bus functions:
CLR_RUN, PWR_OVRD,
LOCK, M6 6EN,
PME, External Arbiter
PCI Express
Link
PCI Bus—32 bit, 33/66 MHz
System Side
PCI
Express
Reference
Clock
GPIO
Serial
Interrupt
Controller
XIO2000A
30
PCI Express
®
➔
PCI Express®Bridge Chip
XIO2000A
et samples, datasheets, EVMs and app reports at: www.ti.com/sc/device/XIO2000A
G
TI’s PCI Express bridge chip, the XIO2000A, is
an industry first. It is designed for seamless
migration from the legacy PCI to the PCI
Express interface. It bridges an x1 PCI Express
bus to a 32-bit, 33/66-MHz PCI bus capable of
supporting up to six PCI devices downstream.
The XIO2000A fully supports PCI Express rates
of 2.5 Gbps. Its architecture supports the PCI
2.3 interface. The chip’s design enables PC
and I/O add-on card manufacturers to begin
transitioning to native PCI Express technology
while preserving compatibility with existing
PCI system software and firmware.
Key Features
• Compliant with PCI Express to PCI/PCI-X
Bridge Specification Revision 1.0
• Compliant with PCI Express Base
Specification 1.0a
• Compliant with PCI Local Bus Specification
rev 2.3
• Utilizes 100 MHz differential PCI Express
Common Reference Clock or 125 MHz
Single-Ended Reference Clock
• Full PCI Local Bus 66 MHz/32-bit Throughput
• Wake/Beacon Event Support
• Robust Architecture to Minimize Latency
ey Benefits
K
• Built-in adaptive receiver equalizer
••
Improves jitter tolerance thereby
reliably increasing PCB trace, or cable
length, supported by the XIO2000
• Seven buffered PCI clock outputs
(33 MHz or 66 MHz)
••
Reduces external components, costs
and premium board space
• 32-bit secondary PCI bus with 33-MHz or
66-MHz clocking option
••
Customizes to meet the needs of highperformance or low-power applications
• Proven compatibility with various PCI
Express chipsets and PCI add-in cards
Rigorous field testing with major root
••
complex device and numerous PCI
add-in cards
• Compact footprint
••
Allows placement in ExpressCard and
mini-PCI cards in limited board space
• Advanced power management
features
••
Software programmable and hardware
autonomous power management
features for low-power applications
such as ExpressCard
XIO2000A functional block diagram.
Target Markets
The XIO2000A meets the needs of multiple
market segments, including desktop and
mobile PC, server, storage, PC add-in cards
and embedded systems.
Typical system implementation.
Interface Selection Guide T
exas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 31

2.5Gbps XMT 2.5Gbps
Internal PCI Bus
PHY Port 0 PHY Port
PCI to 1394a Core
x1 PCI Express Upstream PHY Interface
Digital Link Layer
Transaction Layer:
PCI Bridge Core (32 Bit, 66 MHz)
2.5Gbps 2.5Gbps
PHY Port 0 PHY Port 1
PHY Port 2
Port Logic Port Logic Port Logic
x1 PCI Express Upstream PHY Interface
Digital Link Layer
Transaction Layer:
Crossbar Switch & Packet Control
x1 PCI Express 2.5 Gbps
1394a
1394a
South Bridge XIO2200A
PCI Express
®
31
➔
x1 PCI Express®to 1394a OHCI Bridge
XIO2200A
Get samples, datasheets, EVMs and app reports at:
ww.ti.com/sc/device/XIO2200A
w
Key Features
• x1 PCI Express Primary Interface
• Supports two 1394a ports
• Fully-Compliant with 1394 Open Host Controller Interface
Specification, Revision 1.1
• ExpressCard Reference Design supports two 1394a ports
• Internal dedicated PCI bus operates at 32-bit, 66 MHz
• Compact Footprint, 176-Ball, GGW MicroStar™ BGA or Lead-Free
176-Ball, ZGW MicroStar BGA
Key Benefits
• One-chip solution for 1394a ExpressCards
• Advanced power management features
• Software-programmable and hardware-autonomous power
management
• Supports low-power applications such as ExpressCard
• Compact footprint, 176-ball MicroStar BGA
• EEPROM configuration allows a global unique ID for the 1394
fabric to load
Target Market
• ExpressCards
• PC Add-In Cards
• PC Motherboards
4-Lane, 4-Port PCI Express Switch
XIO3130
www.ti.com/sc/pcl-e *
TI’s XIO3130 is an integrated PCI Express fan-out switch solution
with one upstream x1 port and three downstream x1 ports. This highperformance, integrated solution provides the latest in PCI Express
switch technology. It features cut-through architecture and integrated
reference clock buffers for downstream ports. The XIO3130 is fullycompliant with the PCI Express Base Specification Rev. 1.1. It supports
Advanced Error Reporting as defined in the PCI Express base specifications and is backwards-compatible with the PCI Local Bus
Specification, Rev. 2.3.
Key Features
• PCI Express fan-out switch with x1 upstream port and three x1
downstream ports
• Fully compliant with PCI Express Base Specification, Rev. 1.1
• Cut-through architecture
• Built-in Adaptive Equalizer in each of the four ports
• Wake-event and Beacon support
• Support for D1, D2, D3hot, and D3cold
• Active State Power Management (ASPM)
• Uses both L0s and L1
• Low power PCI Express transmitter mode (pre-emphasis disabled)
• Integrated AUX Power Switch drains VAUX power only when main
power is “off”
• Integrated Hot-Plug Support
• Integrated REFCLK Buffers for Switch Downstream Ports
• Advanced Error Reporting to assist with System Debug Tools
• 3.3V Multifunction I/O pins (e.g. for Hot-Plug status-and-control, or
General Purpose I/Os)
• Listed in PCI-SIG Compliance List
Expected release 1Q 2007
Target Market
The primary purpose of the XIO3130 as a fan-out device is efficiently
expanding the chipset’s computing resources to multiple I/O ports and
enhancing system functionality and flexibility. Target applications for the
XIO3130 include PCs, servers, storage, industrial control and backplane.
ExpressCard reference design.
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 32

TX Block
PLL
REFCLK±
TXP/TXN
RXP/RXN
TX_DATA 16/8
TX_CLK
TX_DATAK [1:0]
RX_DATAK [1:0]
STATUS
COMMAND
RX_DATA 16/8
RX_CLK
RX Block
FPGA
PCIe x1 IP Core
User
Application
Layer
Transaction
Layer
Data Link
Layer
MAC
Enhanced
PIPE
TI XIO1100
2.5
Gbps
2.5
Gbps
REF CLK
PCS PMA
32
PCI Express
®
➔
PCI Express PHY
XIO1100
et samples, datasheets, EVMs and app reports at: www.ti.com/sc/device/XIO1100
G
The XIO1100 is a PCI Express PHY, compliant with the PCI Express Base
Specification Revision 1.1 that interfaces the PCI Express Media Access
Layer (MAC) to a PCI Express serial link. It uses a modified version of
the “PHY Interface for the PCI Express” (PIPE) interface also referred to
as a TI-PIPE interface. The TI-PIPE interface is a pin-configurable
interface that can be configured as either a 16-bit or an 8-bit interface.
• The 16-bit TI-PIPE interface is a 125 MHz 16-bit parallel interface,
a 16 bits output bus (RXDATA) being clocked by the RXCLK output
clock, and a 16-bits Input bus (TXDATA) being clocked by the TXCLK
input clock. Both buses are clocked using Single Data Rate (SDR)
clocking in which the data transitions are on the rising-edge of the
associated clock.
• The 8-bit TI-PIPE interface is a 250 MHz 8-bit parallel interface, an
8-bit output bus (RXDATA) being clocked by the RXCLK output clock,
and an 8-bit input bus (TXDATA) being clocked by the TXCLK input
clock. Both buses are clocked using Double Data Rate (DDR) clocking
where the data transitions on both the clock’s rising-edge and
falling-edge.
The XIO1100 PHY interfaces to a 2.5Gbps PCI Express serial link with a
transmit differential pair (TXP and TXN) and a receive differential pair
(RXP and RXN). Incoming data at the XIO1100 PHY receive differential
pair (RXP and RXN) is forwarded to the MAC on the RXDATA output
bus. Data received from the MAC on the TXDATA input bus is forwarded
to the XIO1100 PHY transfer differential pair (TXP and TXN).
Key Benefits
• XIO1100 is TI’s Third-Generation PHY
Passed PCI SIG Workshop #49
••
• v1.0a and v1.1 compliant
••
Proven PCI Express Compatibility and Interoperability
• Source-Synchronous (SS) Clocking
••
Without SS clocking and running at 125 MHz the interface
must be tuned to the center capture window
• Painful and not robust
• XIO1100 is SS in BOTH RX and TX directions which makes
positioning I/O capture window easy to identify and robust
• SS approach works great from design without need for
experimental tuning
• Flexible MAC Interface
Selectable 8-bit or 16-bit Parallel Interface
••
• 16-bit: 125MHz rising-edge clocked
• Can use low-cost FPGAs
• 8-bit: 125MHz rising-and-falling edge clocked (DDR)
• No need for extra clock buffer needed to generate 250MHz
• Flexible Digital I/O Power Supply
1.5V or 1.8V
••
••
Only two supply voltages needed: 3.3V and 1.5V
• Support for two PCI Express Reference Clocks
100 MHz differential for normal system clock designs
••
••
125 MHz single-ended for asynchronous clocking designs
The XIO1100 is also responsible for handling the 8B/10B encoding/
decoding of the outgoing data. In addition, XIO1100 can recover/
interpolate the clock on the receiver side based on the transitions
guaranteed by the use of the 8B/10B mechanism and supply this to
the receive side of the data link layer logic. In addition to the TI-PIPE
Interface, the XIO1100 has some TI proprietary side-band signals some
customers may wish to use to take advantage of additional low-power
state features (for example, disabling the PLL during the L1 power
state) of the XIO1100.
Low-cost FPGA-based PCI Express
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
®
solution.
XIO1100 functional block diagram.
Page 33

Design Considerations
PCI Bridges
PCI2040
PCI2050B
PCI2250
PCI2060
PCI Option Card
CPU
M
emory
Host
Bridge
PCI2050B
P
CI Bus 0
PCI Bus 1
Host Bus
PCI Option Slot
PCI2050B
PCI
Device
PCI
Device
PCI
Device
PCI
Device
PCI Bus 2
(Option)
PCI Option Card
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) is
an interconnection system between a microprocessor and attached devices in which
expansion slots are spaced closely for highspeed operation. A PCI-to-PCI bridge is a
high-performance connection path between
two PCI buses that allows bridge transactions
to occur concurrently on both buses. Burstmode transfers maximize data throughput
while the two bus traffic paths through the
bridge act independently. In future systems,
many PCI bus structures will be replaced by
he new serial PCI Express architecture. TI is
t
actively developing a portfolio of PCI Express
roducts to address this new market.
p
Key Features
• Two 32-bit, 33- or 66-MHz buses
• Configurable for PCI power-management
interface specification
• CompactPCI hot-swap functionality
• 3.3-V core logic with 3.3- to 5-V PCI
signaling compatibility
• Intel®bridge compatibility
• Transparent bridging
PCI Bridges
T
echnical Information
apabilities
C
• TI’s PCI2050B is a 32-bit, 66-MHz bridge
ith internal two-tier arbitration for up to
w
9 secondary bus masters and support for
an external secondary bus. There are
independent read/write buffers for each
direction and 10 secondary PCI clock outputs.
Functionality
• The PCI2250 is a 33-MHz bridge similar to
the PCI2050B but supports 4 secondary bus
masters and 5 secondary PCI clock outputs.
33
➔
PCI bridge family of products.
Typical PCI-to-PCI bridge system application.
Selection Guide
Intel-Compatible Speed Expansion MicroStar BGA™ Voltage
Device Part No. (MHz) Interface (bits) Hot-Swap Packaging (V) Package(s) Description Price
PCI Bridges
PCI2040 — 33 — — Yes 3.3, 5 144 BGA, PCI-to-DSP bridge controller, compliant with 10.55
144 LQFP Compact PCI Hot-Swap Specification 1.00
PCI2050B 21150bc 66 32 Yes Yes 3.3, 5 208 LQFP, 32-bit, 66-MHz, 9-master PCI-to-PCI bridge 9.50
208 QFP, 257 BGA
PCI2250 21152ab 33 32 Friendly No 3.3, 5 176 LQFP, 32-bit, 33-MHz PCI-to-PCI bridge, Compact 6.10
160 QFP PCI hot-swap friendly, 4-master
PCI2060 — 66 32 Yes Yes 3.3, 5 257 BGA 32-bit, 66-MHz, 9-master, asynchronous 9.50
1
Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
Resources For a complete list of resources (evaluation modules, data sheets and application notes), visit interface.ti.com
Literature Number
Application Notes
SCPA029A Adding Debounce Logic to /HSSwitch Terminal
SLLA067 Comparing Bus Solutions
SCPA027 Connecting ENUM Terminal to an External Open-Drain Buffer
SCPA030
SPRA679 Texas Instruments TMS320VC5409/5421 DSP to PCI Bus
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Description
Interfacing the PCI2040 to the TMS320VC5420 DSP
PCI-to-PCI bridge
*
Page 34

A
VCC
AVCC
AVCC
AVPP
VCCD0
V
CCD1
VPPD0
VPPD1
OC
SHDNGND
0.1 µF
0.
1
µ
F
V
C
C1
V
CC2
V
pp1
V
pp2
PC Card
Connector
PCMCIA
Controller
VCC_EN0
VCC_EN1
VPP_EN0
V
PP_EN1
C
S
To CPU
T
PS2211A
1
2 V
5 V
5
V
0.1 µF
5
V
3.3 V
3.3 V
0
.1 µF
3.3 V
Shutdown Signal From CPU
12 V
+
+
0
.1 µF
+
34
CardBus Power Switches
➔
PS2211A
Design Considerations
ExpressCard Power Switches
he TPS2231 and TPS2236 ExpressCard
T
power interface switches provide the total
power management solution required by the
ExpressCard specification. The TPS2231 and
TPS2236 ExpressCard power interface
switches distribute 3.3 V, AUX and 1.5 V to
the ExpressCard socket. Each voltage rail is
protected with integrated current-limiting
circuitry. The TPS2231 supports systems with
single-slot ExpressCardj34 or ExpressCardj54
sockets. The TPS2236 supports systems with
dual-slot ExpressCard sockets.
PCMCIA/CardBus Power Switches
Standard PC cards require that VCCbe
switched between ground, 3.3 V and 5 V,
while V
5 V and 12 V. CardBay sockets have the
standard requirements for VCC, but require
ground, 3.3 V and 5 V to VPP, and ground,
1.8 V or 3.3 V to V
applications may simply not need 12 V or V
while still having the standard requirements
for VCC. Therefore, consider the voltage
requirements of the application when selecting a PCMCIA power switch.
Current-Limiting Power Switches
Power switches are used to intelligently
turn power on and off, while providing fault
protection. They are useful anywhere controlled
allocation of power is needed to circuit
blocks, modules, add-in cards or cabled
connections. They are ideal for power
sequencing or segmentation.
To minimize voltage drop, select devices
with the lowest r
on-resistance.
Power MUX ICs
Power MUX ICs are designed to transition
from a main power supply to an auxiliary
source when the main supply shuts down
(e.g. switching from battery operation to a
wall adapter).
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
is switched between ground, 3.3 V,
PP
. Other PC card
CORE
or Drain to Source
DS(on)
PP
T
• Fully integrated V
and V
s
switching for
P
P
ingle-slot PC card
C
C
interface
• Low r
•
DS(on)
3.3-V low-voltage
mode
• Short-circuit and
hermal protection
t
• Compatible with
3.3-V, 5-V and 12-V
PC cards
ypical PC card power-distribution application.
T
Power Distribution Devices Family of Products
Current-Limiting Power Switch ICs
Current Limit (min) (A)
0.22 0.3 0.345 0.66 0.7 1.1 1.65 2.2
Fault Reporting
Quad — TPS2048A/58A TPS2048/581— TPS2044/54
TPS2044A/54A — — —
TPS2095/6/7 TPS2044B/54B
TPS2085/6/7
Triple — TPS2047B/57A TPS2047/571— TPS2043/53
TPS2043A/53A
TPS2043B/53B
Dual — TPS2046B/56A TPS2046/561— TPS2042/52
TPS2090/1/2 TPS2042A/52A
TPS2042B/52B
TPS2080/1/2
Single TPS2020/301TPS2045A/55A TPS2045/551TPS2021/311TPS2041/512TPS2022/32 TPS2023/33 TPS2024/34
TPS2041A/51A
TPS2041B/51B
No Fault Reporting
Single TPS2010A — — TPS2011A — TPS2012A TPS2013A —
1
Nemko recognized. 2UL and Nemko recognized.
PCMCIA/CardBus Power Switch Matrix ICs
Current Limit (min) (A)
0.3 0.7 1.0 2.5
3.3 V, 5 V, 12 V, V
Dual — — TPS2224(A), TPS2226(A), TPS2204A, TPS2206A, TPS2205 —
PP
Single TPS2212 — TPS2204A, TPS2210A, TPS2211(A), TPS2220A, TPS2220B TPS2231
No 12 V
Dual — — TPS2223A TPS2236
Single — TPS2044B/54B — —
No V
Dual
PP
—
TPS2044B/54B
—
Power MUX ICs
I
Configuration
IN1
IN2
Device (mA) Transition Comments
TPS2100/1
TPS2102/3
TPS2104/5
TPS2110A Adj. 310 to 750 Auto/Manual TSSOP
TPS2111A Adj. 630 to 1250 Auto/Manual TSSOP
TPS2112A
TPS2113A
OUT
IN1: 500, IN2: 10 Manual SOT-23, 0 to 70°C
IN1: 500, IN2: 100 Manual SOT-23, 0 to 70°C
IN1: 500, IN2: 100 Manual SOT-23, –40 to 85°C
Adj. 310 to 750 Auto TSSOP, Status pin
Adj. 630 to 1250 Auto TSSOP, Status pin
TPS2114A Adj. 310 to 750 Auto/Manual TSSOP, Status pin
TPS2115A Adj. 630 to 1250 Auto/Manual TSSOP, Status pin
ExpressCard Power Switch ICs
Device Ports 3V rDS(on) (mΩ) Interface Current Limit (Min) (A)
TPS2231 1 45 Parallel 2.5
TPS2236 2 45 Parallel 2.5
2
2
———
2
———
—
Page 35

Power Distribution (
PCMCIA/CardBus Power Switches, Current-Limiting Power Switches and Power MUX ICs)
Selection Guide
Number I
O
S
Device of FETs (min) (A) (mΩ) (V) (µA) Output Output Enable Predecessor Price
Current-Limiting Power Switch ICs
TPS2010A 1 0.22 30 2.7 to 5.5 73 No No L TPS2010 0.75
TPS2011A 1 0.66 30 2.7 to 5.5 73 No No L TPS2011 0.75
TPS2012A 1 1.1 30 2.7 to 5.5 73 No No L TPS2012 0.75
TPS2013A 1 1.65 30 2.7 to 5.5 73 No No L TPS2013 0.75
TPS2020/30 1 0.22 33 2.7 to 5.5 73 Yes Yes L/H — 1.05
TPS2021/31 1 0.66 33 2.7 to 5.5 73 Yes Yes L/H TPS2014 1.05
TPS2022/32 1 1.1 33 2.7 to 5.5 73 Yes Yes L/H TPS2015 1.05
TPS2023/33 1 1.65 33 2.7 to 5.5 73 Yes Yes L/H — 1.05
TPS2024/34 1 2.2 33 2.7 to 5.5 73 Yes Yes L/H — 1.05
TPS2041B/51B 1 0.7 70 2.7 to 5.5 43 Yes Yes L/H TPS2041/51/41A/51A 0.50
TPS2042B/52B 2 0.7 ea 70 2.7 to 5.5 50 Each Yes L/H TPS2042/52/42A/52A 0.70
TPS2043B/53B 3 0.7 ea 70 2.7 to 5.5 65 Each Yes L/H TPS2043/53/43A/53A 0.90
TPS2044B/54B 4 0.7 ea 70 2.7 to 5.5 75 Each Yes L/H TPS2044/54/44A/54A 1.00
TPS2045A/55A 1 0.3 80 2.7 to 5.5 80 Yes Yes L/H TPS2045/55 0.60
TPS2046B/56A 2 0.3 ea 80 2.7 to 5.5 80 Each Yes L/H TPS2046/46A/56 0.65
TPS2047B/57A 3 0.3 ea 80 2.7 to 5.5 160 Each Yes L/H TPS2047/47A/57 0.90
TPS2060/4 2 1.5 ea 70 2.7 to 5.5 50 Each Yes L/H — 1.20
TPS2061/5 1 1.1 70 2.7 to 5.5 43 Yes Yes L/H — 0.60
TPS2062/6 2 1.1 ea 70 2.7 to 5.5 50 Each Yes L/H — 0.75
TPS2063/7 3 1.1 ea 70 2.7 to 5.5 65 Each Yes L/H — 0.90
TPS2048A/58A 4 0.3 ea 80 2.7 to 5.5 160 Each Yes L/H TPS2048/58 1.20
TPS2080/1/2
TPS2085/6/7
TPS2090/1/2
TPS2095/6/7
1
2 0.7 ea 80 2.7 to 5.5 85 Yes Yes 2H, 1L/1H, 2L — 0.65
1
4 0.7 ea 80 2.7 to 5.5 85 Yes Yes 4H, 2L/2H, 4L — 1.05
1
2 0.3 ea 80 2.7 to 5.5 85 Yes Yes 2H, 1L/1H, 2L — 0.65
1
4 0.3 ea 80 2.7 to 5.5 85 Yes Yes 4H, 2L/2H, 4L — 1.05
Device Interface of Ports (typ) (mΩ) (typ) (mΩ) (min) (A) Predecessor Price
PCMCIA/CardBus Switch Matrix ICs
TPS2210A 3-line Serial 1 85 95 1 — 0.85
TPS2204A 3-line Serial 2 85 95 1 TPS2214/14A 1.95
TPS2220B 3-line Serial 1 85 95 1 TPS2220A 0.85
TPS2223A 3-line Serial 2 85 95 1 — 1.80
TPS2224A 3-line Serial 2 85 95 1 TPS2214/14A 1.95
TPS2226A 3-line Serial 2 85 95 1 TPS2206, TPS2216/16A 2.10
TPS2206A 3-line Serial
TPS2205 8-line Parallel 2 70 100 1 TPS2201 2.90
TPS2211A 4-line Parallel 1 70 57 1 TPS2211 0.75
TPS2212
4-line Parallel 1 160 160 0.3 — 1.45
TPS2231 4-line Parallel 1 68 — 2.5 — 1.00
TPS2044B or 54B Parallel 1 or 2 80 80 0.7 TPS2044/44A, TPS2054/54A 1.00
TPS2221
Interface Parallel 1 72 97 1 — 1.85
TPS2228 Interface Serial 2 72 97 1 — 3.10
Number
IN1 IN2 IN1 Output IN2 Output IN1 Supply IN2 Supply Transition Time
of r
DS(
)
on
Device Inputs (mΩ)(mΩ) (mA) (mA) (µA) (µA) Range (V) (µs) (µs) Transition Price
Power MUX ICs
TPPM0301/2
3
TPPM0303 3 — — 250 250 2500 250 3 to 5.5 — — Autoswitch 1.07
TPS2100/1 2 250 1300 500 10 10 0.75 2.7 to 4.0 4 900 L/H enable 0.59
TPS2102/3
2
TPS2104/5 2 250 1300 500 100 18 0.75 2.7 to 5.5 3 700 L/H enable 0.85
TPS2110A/2A/4A
TPS2111A/3A/5A
1
Can be configured as power MUX ICs.
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
2
2
—
250
120
84 84 625 to 1250 625 to 1250 85 85 2.8 to 5.5 40 40 Autoswitch 0.70
r
D
S(on)
r
)
on
DS(
V
Range Supply Current OC Logic OT Logic
I
N
Number 3.3-V r
2
DS(on)
85
5.0-V r
95
DS(on)
I
OS
1 TPS2206, TPS2216/16A 2.10
Current Current Current Current Input Voltage IN1 to IN2 IN2 to IN1
— 400 400 2500 250 3 to 5.5 — — Autoswitch 1.60
1300 500 100 14 0.75 2.7 to 4.0 3 700 L/H enable 0.69
120
312 to 750
312 to 750
85 85 2.8 to 5.5 40 40 Autoswitch 0.70
New products are listed in
bold red.
35
➔
*
*
*
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 36

36
1394 (FireWire®)
➔
O
verview
IEEE 1394 high-speed interconnection enables simple, low-cost, high-bandwidth real-time data connectivity between many types of electronic equip-
ent. As a multimedia network standard, 1394 is ideally suited for consumer electronics, computers and peripherals. It is also ideal for situations that
m
benefit from true peer-to-peer operation and maximum flexibility. 1394 is self-configuring, has strong power management/distribution capabilities and
obust error-detection that make it a leading choice in control applications, especially those that also need to accommodate streaming multimedia.
r
The new 1394b technology enables higher performance (up to 3.2 Gbps), longer distance (up to 100 meters) and a variety of cable media to fit any
application (STP, UTP, POF and GOF), making it ideal for home networking and high-speed data transfer applications. For example, in long-haul applications such as home networking, 1394b is capable of 100 Mbps over 100 meters of unshielded twisted pair Category 5 cable (called CAT5 or UTP5).
For high-speed applications, TI offers a 1394b chip set that enable speeds up to 800 Mbps for applications such as video-on-demand or backing up a
RAID array. TI 1394b is backward compatible to 1394a.
Design Considerations
Physical-Layer Selection Issues
• The 1394 PHY layer should support the
minimum number of nodes or ports
required by the end product. Having two
ports permits spanning to other devices
on the bus through daisy-chaining. Three
or more nodes enable branching or hub
capabilities.
• Will the end product need DC isolation at
the 1394 interface? The cable doesn’t
provide a DC-isolated path from node to
node. In cases where there’s a possibility
for the various equipment connected
across 1394 to be at different ground
potentials or different power domains,
the grounds may need to be isolated from
each other to prevent excessive currents
and noise. However, the ground signal on
the 1394 cable must not be DC-isolated
from the PHY power-distribution ground
plane. Thus when DC isolation between
units is required at the 1394 interface, it
is frequently performed at the PHY- and
link-layer interfaces—often through the
use of special I/O cells that allow for
capacitive coupling of the PHY-link signals.
• While the EIA-775 specification requires
a minimum speed of 200 Mbps at the
1394 interface, using 400-Mbps PHYs is
recommended. Slower nodes present on
the bus can be a source of speed traps.
Almost all 1394 silicon available today is
already 400-Mbps capable.
• The suspend/resume feature of the PHY
layer lets two currently inactive ports
achieve low-power states while maintain
ing their connection status. It also permits
them to quickly resume operation as soon
as they detect an applied port bias voltage.
Link-Layer Selection Issues
• What kind of data needs to be transferred?
Some link controllers are designed to
implement specific data protocols over
1394, such as the serial bus protocol
2 (SBP-2) for mass storage or IEC 61883-4
for MPEG-2 transport, and some are
designed as general purpose.
• What is being interfaced to 1394? If the
system has PCI, consider one of the
PCI/OHCI links. Applications involving
streaming compressed audio/video most
likely need a link from the iceLynx family.
Other TI links have interfaces for external
processors/memory or are dedicated for a
peripheral function (camera/storage).
• For audio/visual (A/V) applications,
different types of A/V data require different
formatting and transmission methods on
1394. Specifically identifying which types
of A/V to be supported is fundamental to
choosing the right 1394 chip set for the
digital set-top box (DSTB) or digital TV
(DTV) design. Standards define how to
carry MPEG-2 transport streams in both
digital video broadcasting (DVB) format
and in DirecTV format, which have different
packetization schemes.
• Another aspect of the link layer that
should be considered is the amount of
data-buffer memory supported. Typically,
the more bandwidth an application
requires, or the more simultaneous
isochronous/asynchronous traffic that
needs to be supported, the larger the
buffer memories must be.
-
• As the number of simultaneous isochronous channels present goes up, or the bit
rate of an individual stream increases, the
receive buffer needs to be larger.
Technical Information
• 1394-1995 is an IEEE designation for a
high-performance serial bus. A revision to
this standard has been published as IEEE
1394a-2000, and clarifies and adds to
portions of the IEEE 1394-1995 standard.
The 1394b standard increases the speed
of 1394 to 800, 1600 and 3200 Mbps, as
well as providing new connection options
such as plastic optical fiber (POF), glass
optical fiber (GOF) and UTP-5. This serial
bus defines both a backplane (for example, VME, FB+) physical layer and a pointto-point, cable-connected virtual bus. The
backplane version operates at 12.5, 25 or
50 Mbps, whereas the cable version
supports data rates of 100, 200, 400, 800
and 1,600 Mbps across the cable medium
supported in the current standard. Both
versions are totally compatible at the link
layer and above. The interface standard
defines transmission method, media and
protocol.
• Applications of the cable version are the
integration of I/O connectivity of personal
computers, peripherals, and consumer
electronics using a low-cost, scalable,
high-speed serial interface. The 1394
standard provides services such as
real-time I/O and live connect/disconnect
capability for devices including storage
(HDD, CD-ROM, CDRW, MO, ZIP, RAID,
SAN, etc.), printers, scanners, cameras,
set-top boxes, HDTVs and camcorders.
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 37

1394 (FireWire®)
37
➔
Technical Information
(Continued)
Applications of the cable version are the
•
integration of I/O connectivity of personal
computers, peripherals, and consumer
electronics using a low-cost, scalable,
high-speed serial interface. The 1394
standard provides services such as realtime I/O and live connect/disconnect
capability for devices including storage
(HDD, CD-ROM, CDRW, MO, ZIP, RAID,
Key Features
• Real-time streaming of audio and video
• High-speed: up to 400 Mbps with IEEE
1394-1995 and 1394a-2000, up to 1, 2
and 4 Gbps with 1394b
• Plug-and-play hot pluggable
• Peer-to-peer communication
• Small, durable and flexible cable and
connectors
• Memory-mapped architecture
• Seamless I/O interconnect
1
394b Advantages
• Faster: speeds from 800 Mbps to
3200 Mbps
• Longer distances: 100 meters with GOF
and CAT5; 50 meters with POF
• TI1394b is bi-lingual: communicates in
1394a and 1394b modes
• More cabling options: STP, CAT5, POF, GOF
• More efficient: BOSS arbitration
• More user-friendly: loop-free build allows
any topology and redundancy
SAN, etc.), printers, scanners, cameras,
set-top boxes, HDTVs and camcorders.
Selection Guide
Voltage Data Rate
Device Ports (V) (Mbps) Package(s) Description Price
1394 Physical Layer Controllers
TSB14AA1A 1 3.3 up to 100 48 TQFP IEEE 1394-1995, 3.3-V, 1-port, 50/100-Mbps, backplane PHY controller 5.90
TSB41AB1 1 3.3 up to 400 48/64 HTQFP, IEEE 1394a 1-port cable transceiver/arbiter 1.50
TSB41AB2 2 3.3 up to 400 64 HTQFP
TSB41AB3 3 3.3 up to 400 80 HTQFP IEEE 1394a 3-port cable transceiver/arbiter 3.00
TSB41BA3B 3 3.3 up to 400 80 TQFP 1394b-2002 3-port physical layer device 6.50
TSB41LV04A 4 3.3 up to 400
TSB41LV06A 6 3.3 up to 400 100 HTQFP IEEE 1394a 6-port cable transceiver/arbiter 6.40
TSB81BA3D 3 1.8, 3.3 up to 800 80 HTQFP High-performance 1394b s800 3-port cable transceiver/arbiter 5.55
*
Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
80 HTQFP IEEE 1394a 4-port cable transceiver/arbiter 6.50
IEEE 1394a 2-port cable transceiver/arbiter 1.85
*
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 38

TPA2+
TPA2−
TPB2+
TPB2−
TPA1+
TPA1−
TPB1+
TPB1−
TPB0+
TPB0−
Bilingual
Cable Port 0
Bilingual
Cable Port 1
Bilingual
Cable Port 2
CPS
LPS
CNA
PINT
LCLK
LREQ
CTL0
CTL1
D0
D5
D1
D2
D3
D4
D6
D7
RESETz
LKON/DS2
PD
BMODE
Received Data
D
ecoder/Retimer
Arbitration
and Control
State Machine
Logic
Transmit
Data
Encoder
Crystal Oscillator,
PLL System,
and Transmit
Clock Generator
PCLK
PC0
PC1
PC2
SE
SM
DS0
DS1
TESTM
TESTW
Voltage
Regulator
XI
TPA0+
TPA0−
Bias Voltage
a
nd
C
urrent
Generator
R0
R1
TPBIAS0
TPBIAS1
TPBIAS2
Link
Interface
I/O
38
1394 (FireWire®)
➔
IEEE 1394b 3-Port Cable Transceiver/Arbiter
TSB81BA3D
Get samples, datasheets and app reports at: www.ti.com/sc/device/TSB81BA3D
Key Features
• Compliant with IEEE 1394b-2002, IEEE
1394a-2000 and 1394-1995 standards
• 3 Bilingual 1394 Ports
1394b (Beta) Mode at s400 and s800
••
•• 1394a (Data Strobe -DS) Mode at s100,
s200 and s400
• Interoperable with link layer controllers using
3.3-V supplies and other 1394 PHYs using
1.8-V, 3.3-V and 5-V supplies
Applications
• Storage devices
• Consumer electronics
• 1394B PC ports
TSB81BA3D block diagram.
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 39

Conn. Conn. Conn. Conn. Conn. Conn.
Rcvr Rcvr Rcvr Rcvr Rcvr
Rcvr
22 Ω 22 Ω
V
TT
V
TT
0.25" 0.25".94".94".94".94"
Z
0
†
Z
0
¥
† Unloaded backplane trace natural impedance (Z0) is 45 Ω to 60 Ω, with 60 Ω being ideal.
¥ Card stub natural impedance (Z
0
) is 60 Ω.
1" 1" 1" 1" 1" 1"
Slot 1 Slot 2 Slot 3 Slot 18 Slot 19 Slot 20
TI
Competitor A
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
1.98E-08 4.48E-08
Time
6.98E-08
Vol ts
Design Considerations
rimary
P
Speed — The speed of the GTLP family in
arallel backplanes is 4x that of traditional
p
logic. Optimized output edge-rate control
(OEC™) circuitry allows clock frequencies in
excess of 100 MHz in high-performance
system backplane applications.
Voltage Range — The GTLP family operates
at 3.3 V and with 5-V tolerant LVTTL inputs/
outputs and can operate in a mixed-voltage
environment. GTLP acts as LVTTL-to-GTLP
bi-directional translators with 5 V tolerance
on the LVTTL port.
Drive — The GTLP family provides ±24-mA
drive on the A-Port (LVTTL side) and the
choice of medium (50 mA) or high (100 mA)
drive on the B-Port (GTLP side). This offers
flexibility in matching the device to backplane
length, slot spacing and termination resistance.
GTLP (Gunning Transceiver Logic Plus)
ignal Integrity–TI-OPC
S
tection circuitry was designed specifically for
he GTLP family and incorporated into the
t
GTLP outputs. TI-OPC actively clamps any
overshoots that are caused by improperly
terminated backplanes, unevenly distributed
cards or empty slots. OEC on the rising and
falling edge of the GTLP outputs reduces line
reflections and extra EMI, improving overall
signal integrity.
True Live Insertion — GTLP backplane drivers
allow for Level 3 isolation and true liveinsertion capability. Level 1 isolation, partial
power-down: I
O
prevents damage by limiting the current
flowing from an energized bus when the
device V
goes to zero. Level 2 isolation,
CC
hot insertion: both I
(PU3S) circuitry allow insertion or removal of
a board into a backplane without powering
™
Overshoot pro-
—
circuitry within the device
FF
and power-up 3-state
OFF
down the host system and without suspending
signaling. Level 3 isolation, live insertion: for
ive insertion both I
l
nd PU3S circuitry are
a
FF
O
needed and the board I/Os must be precharged
to mid-swing levels prior to connector insertion/
removal.
Secondary
Compatibility — GTLP provides an easy
migration path from traditional backplane logic
like ABT, FCT, LVT, ALVT, LVC and FB+.
Portfolio — TI offers the broadest GTLP
portfolio in the industry, with both high-drive
(100 mA) and medium-drive (50 mA) devices.
Packaging — TI offers GTLP in a low-profile,
fine-pitch BGA package (LFBGA) and in a quad
flat no-lead package (QFN) for higher
performance and the ultimate reduction in
board-space requirements.
39
➔
Single Bit Representation of a Multipoint Parallel Backplane
Signal Integrity: TI vs Competition
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 40

40
GTLP (Gunning Transceiver Logic Plus)
➔
GTLP Selection Guide
Device Description Price*
SN74GTLP1394 2-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Adjustable-Edge-Rate Bus Xcvr w/ Split LVTTL Port, Feedback Path and Selectable Polarity 2.09
SN74GTLP1395 Two 1-Bit LVTTL/GTLP Adjustable-Edge-Rate Bus Xcvrs w/ Split LVTTL Port, Feedback Path and Selectable Polarity 2.09
SN74GTLP2033 8-Bit LVTTL-GTLP Adjustable-Edge-Rate Registered Transceiver w/ Split LVTTL Port and Feedback Path 5.17
SN74GTLP2034 8-Bit LVTTL-GTLP Adjustable-Edge-Rate Registered Transceiver w/ Split LVTTL Port and Feedback Path 5.17
SN74GTLP21395 Two 1-Bit LVTTL/GTLP Adjustable-Edge-Rate Bus Xcvrs w/ Split LVTTL Port, Feedback Path and Selectable Polarity 2.09
SN74GTLP22033 8-Bit LVTTL-GTLP Adjustable-Edge-Rate Registered Transceiver w/ Split LVTTL Port and Feedback Path 5.17
SN74GTLP22034 8-Bit LVTTL-GTLP Adjustable-Edge-Rate Registered Transceiver with Split LVTTL Port and Feedback Path 5.17
SN74GTLP817 GTLP-to-LVTTL 1-to-6 Fanout Driver 1.95
SN74GTLPH1612 18-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Adjustable-Edge-Rate Universal Bus Transceiver 5.25
SN74GTLPH1616 17-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Adjustable-Edge-Rate Universal Bus Transceiver w/ Buffered Clock Outputs 5.25
SN74GTLPH1627 18-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Bus Xcvr w/Source Synchronous Clock Outputs 5.63
SN74GTLPH1645 16-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Adjustable-Edge-Rate Bus Transceiver 3.30
SN74GTLPH1655 16-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Adjustable-Edge-Rate Universal Bus Transceiver 5.25
SN74GTLPH16612 18-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Universal Bus Transceiver 4.58
SN74GTLPH16912 18-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Universal Bus Transceiver 4.88
SN74GTLPH16916 17-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Universal Bus Transceiver w/ Buffered Clock Outputs 4.88
SN74GTLPH16927 18-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Bus Transceiver w/Source Synchronous Clock Outputs 7.70
SN74GTLPH16945 16-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Bus Transceiver 2.75
SN74GTLPH306 8-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Bus Transceiver 2.42
SN74GTLPH3245 32-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Adjustable-Edge-Rate Bus Transceiver 5.83
SN74GTLPH32912 36-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Universal Bus Transceiver 7.50
SN74GTLPH32916 34-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Universal Bus Transceiver w/ Buffered Clock Outputs 7.50
SN74GTLPH32945 32-Bit LVTTL-to-GTLP Bus Transceiver 4.29
*Suggested resale price in U.S. dollars in quantities of 1,000.
Resources For a complete list of resources (evaluation modules, data sheets and application notes), visit interface.ti.com
Literature Number Description
Application Notes
SCEA017 GTLP in BTL Applications
SCEA019 Texas Instruments GTLP Frequently Asked Questions
SCEA026 Logic in Live-Insertion Applications With a Focus on GTLP
SCEA022 Achieving Maximum Speed on Parallel Buses With Gunning Transceiver Logic
SCBA015A Fast GTLP Backplanes With the GTLPH1655
Other Literature
SCYT126 Advanced Bus Interface Logic Selection Guide
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 41

VME
41
➔
Design Considerations
Backward compatibility — The VMEH22501/A
improves the performance up to 8X of the
VMEbus™ without making changes to
existing hardware.
Standard Specification — The VMEH22501/A
are referenced by the 2eSST VITA 1.5 spec
as a device that provides excellent signaling
at 40-Mbps data rate.
Increased Noise Immunity — The ±50-mV input
threshold allows the VMEH22501/A to provide
clean signaling under harsh environments.
Full Live Insertion—This device is fully
pecified for live-insertion applications using
s
power-up 3-state and BIAS V
I
,
FF
O
Speed/Signal Integrity—High-speed
backplane operation is a direct result of the
improved OEC circuitry that has been tested
on the standard VME backplane. Furthermore,
signal integrity is not compromised with
higher speed operation.
VME Parametric Table
Parameter Name SN74VMEH22501 SN74VMEH2501A
Voltage Nodes (V) 3.3 3.3
VCCRange (V) 3.15 to 3.45 3.15 to 3.45
Input Level LVTTL LVTTL
Output Level LVTTL LVTTL
Output Drive (mA) –48/64 –48/64
No. of Outputs 10 10
Logic True True
Static Current (mA) 30 30
tpdmax (ns) 8.9 8.9
T
A
0° C to 85° C –40° C to 85° C
Technical Information
• TI’s SN74VMEH22501/A are specifically
designed for the VMEbus technology. The
.
C
C
device is an 8-bit universal bus transceiver
(UBT) with two bus transceivers. It
provides incident switching on the 21-slot
VMEbus backplane, thus providing data
signaling rates of up to 40 Mbps-—an 8X
improvement over the VME64 standard.
Highlights
• Ability to transmit data on the VMEbus
up to 2eSST protocol speed is an
improvement over VME64.
• Incident wave switching allows for higher
performance on the VMEbus compared to
conventional logic that depends on
reflective wave switching.
Resources For a complete list of resources (evaluation modules, data sheets and application notes), visit interface.ti.com
Literature Number Description
Application Notes
SCEA028 VMEH22501 in 2eSST and Conventional VME Backplane Applications
Other Literature
SCYB009 VME Application Clip
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 42

42
➔
Clock Distribution Circuits
Clock Selection by Speed and Signaling Type
Clock Selection by Number of Outputs and Signaling Type
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 43

he following products have similar functionality:
T
Cross-Reference Guide
43
➔
Part Number TI Replacement
AGERE
BDG1A TB5D1M
DG1A TB5D2H
B
DGLA TB5D2H
B
PNGA TB5D1M
B
RF1A TB5R1
B
RF2A TB5R1
B
RS2A TB5R2
B
BRS2B TB5R2
BTF1A TB5T1
AGILENT
HDMP1636/1646 TNETE2201B
ALLEGRO
A2525 TPS2051A
A2526 TPS2052A
A2535 TPS2041A
A2536 TPS2042A
ANALOG DEVICES (ADI)
ADM1485 SN75LBC176A*
ADM1486 SN65HVD1176*
ADM3485E SN75HVD10*
ADM483E SN65HVD3082E
ADM483E SN75LBC176A*
ADM485 SN65HVD3085E*
ADM485 SN65HVD485E*
ADM485 SN75LBC176A*
ADM485 SN75176B*
ADM488 SN75LBC179A*
ADM489 SN75LBC180A*
CMP
CMPWR025 TPS210x
CYPRESS
AN-213x TUSB3410
EUREKA
EP600 TL16C550C
EXAR
ST16C2450 TL16C452
ST16C2550 TL16C552A
ST16C2550 TL16C752B*
ST16C2552 TL16C552A*
ST16C450
ST16C452 TL16C452*
ST16C550
ST16C550 TL16C550C
ST16C552 TL16C552
ST16C552 TL16C552A
ST16C552A TL16C552
ST16C552A
ST16C554 TL16C554A
ST16C554D TL16C554
ST16C554D TL16C554A
ST16C580
TL16C450*
TL16C550B
TL16C552A
TL16C550C
Part Number TI Replacement
EXAR (cont.)
ST16C654 TL16C754B
T16C654D TL16C754B
S
T68C554 TL16C554A
S
R16L2750 TL16C752B
X
R16L2751 TL16C752B
X
R16L2752 TL16C752B
X
R16L651 TL16C750
X
XR16L784 TL16C754B
FAIRCHILD SEMICONDUCTOR
FIN1001 SN65LVDS1*
FIN1002 SN65LVDS2*
FIN1017 SN65LVDS1*
FIN1018 SN65LVDS2*
FIN1019 SN65LVDS180
FIN1022 SN65LVCP22*
FIN1025 SN65LVDS9638
FIN1026 SN65LVDS9637
FIN1027 SN65LVDS9638*
FIN1028 SN65LVDS9637*
FIN1031 SN65LVDS31*
FIN1032 SN65LVDS32*
FIN1047 SN65LVDS047*
FIN1048 SN65LVDS048A*
FIN1049 SN65LVDS049
FIN1101 SN65LVDS100
FIN1102 SN65LVCP22
FIN1104 SN65LVDS125
GTLP1616 SN74GTLPH1616
GTLP16612 SN74GTLPH1612
GTLP16612 SN74GTLPH16612
GTLP16T1655 SN74GTLPH1655
GTLP18T612 SN74GTLPH16912
GTLP6C817 SN74GTLP817
GTLP8T306
FTDI
FT232BM TUSB3410
GOLDSTAR
GM16C550
GM16C550 TL16C550C*
HYNIX (LG)
GD75232 GD75232*
IMP
Ei16C450
Ei16C550 TL16C550C
Ei16C552
Ei16C552 TL16C552A
Ei16C554
Ei16C554
SN74GTLPH306
TL16C550B*
TL16C450
TL16C552
TL16C554
TL16C554A
Part Number TI Replacement
IMPX
IMP2525 TPS2051A
MP2525A TPS2051A
I
MP2526 TPS2052A
I
INFINEON
LE6250 SN65HVD251
T
TLE6250 SN65HVD1050
INTEL
21150AB/AC PCI2050*
21150BC PCI2050B*
21152 PCI2250*
INTERSIL
HIN211 SN75LBC241
HIN211E SN75LBC241
HIN232 MAX232*
HIN232E MAX232
HIN241 SN75LBC241
HIN241E SN75LBC241
ICL232 MAX232*
ICL3221 MAX3221*
ICL3221E MAX3221
ICL3222 MAX3222*
ICL3222E MAX3222
ICL3223 MAX3223*
ICL3223E MAX3223
ICL3232 MAX3232*
ICL3232E MAX3232
ICL3238 MAX3238*
ICL3238E MAX3238
ICL3243 MAX3243*
ICL3243E MAX3243
ISL1483 SN65HVD3082E*
ISL1483 SN65LBC184*
ISL1487 SN65HVD06*
ISL1487 SN65HVD21*
ISL1487E SN65HVD06*
ISL1487E SN65HVD21*
ISL1487L SN65HVD3082E*
ISL1487L
ISL8483 SN65HVD3082E*
ISL8485 SN65HVD06*
ISL8485 SN65HVD21*
ISL8488 SN65LBC179A*
ISL8489 SN65LBC180A*
ISL8490 SN65LBC179A*
ISL8491 SN65LBC180A*
Part Number TI Replacement
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY CORP. (LTC)
LT1030 LT1030
T1081
L
T1181A
L
LT1381 MAX232
Part Number
* Drop-in, pin-compatible devices
SN65LBC184*
MAX232
MAX232
TI Replacement
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 44

44
Cross-Reference Guide
➔
The following products have similar functionality:
art Number TI Replacement
P
LINEAR TECHNOLOGY CORP. (LTC) (cont.)
LT1785 SN75LBC184*
LTC1472 TPS2211A
LTC1480 SN75HVD11*
LTC1481 SN75LBC176A*
LTC1482 SN75LBC176A*
LTC1483 SN75LBC176A*
LTC1484 SN75LBC176A*
LTC1485 SN65LBC176A*
LTC1487 SN65HVD3082E*
LTC1487 SN75HVD07*
LTC1518 SN75LBC173A*
LTC1519 SN75LBC175A*
LTC1685 SN65HVD1176*
LTC1686 SN75LBC179A*
LTC1687 SN75LBC180A*
LTC1688 SN75LBC172A*
LTC1689 SN75LBC174A*
LTC1690 SN75LBC179A*
LTC1796 SN65HVD251*
LTC485 SN65HVD3085E*
LTC485 SN65HVD485E*
LTC485 SN75LBC176A*
LTC485 SN75176B*
LTC486 SN75172*
LTC486 SN75ALS172A*
LTC486 SN75LBC172A*
LTC487 SN75174*
LTC487 SN75ALS174A*
LTC487 SN75LBC174A*
LTC488 SN75173*
LTC488 SN75ALS173*
LTC488 SN75LBC173A*
LTC489 SN75175*
LTC489 SN75ALS175*
LTC489 SN75LBC175A*
TC490 SN75LBC179A*
L
LTC491 SN75LBC180A*
MAXIM
MAX1487 SN65HVD3082E*
MAX1487 SN75HVD06*
MAX1487E SN65HVD3082E*
MAX1487E SN75HVD06*
MAX1600/MAX1603 TPS2205
MAX1601/MAX1604 TPS2205
MAX1602 TPS2211A
MAX1607
MAX202 MAX202*
MAX211 MAX211*
MAX232 MAX232*
MAX241 SN75LBC241
MAX3040
MAX3041 SN75LBC174A*
MAX3042B
MAX3043 SN75LBC172A*
TPS2041A
SN75LBC174A*
SN75LBC174A*
art Number TI Replacement
P
MAXIM (cont.)
MAX3044 SN75LBC172A*
MAX3045B SN75LBC172A*
MAX3050 SN65HVD251*
MAX3053 SN65HVD251
MAX3053 SN65HVD251*
MAX3057 SN65HVD251*
MAX3082 SN65HVD3082E*
MAX3082E SN65HVD3082E*
MAX3085 SN65HVD3085E*
MAX3085E SN65HVD3085E*
MAX3088 SN65HVD3088E*
MAX3088E
MAX3093E SN75LBC173A*
MAX3095E SN75LBC175A*
MAX3221 MAX3221*
MAX3221E MAX3221
MAX3222 MAX3222*
MAX3222E MAX3222
MAX3223 MAX3223*
MAX3223E MAX3223
MAX3232 MAX3232*
MAX3232E MAX3232
MAX3238 MAX3238*
MAX3238E MAX3238
MAX3243 MAX3243*
MAX3243E MAX3243
MAX3362 SN75HVD10*
MAX3443E SN75LBC184*
MAX3463 SN65HVD1176*
MAX3464 SN65HVD3082E*
MAX3464 SN75HVD05*
MAX3483 SN75HVD12*
MAX3483E SN75HVD12*
MAX3485
MAX3485E SN75HVD11*
MAX3486 SN75HVD12*
MAX3486E SN75HVD12*
MAX481/E
MAX481 SN75LBC176*
MAX481E SN75LBC176A*
MAX483/E
MAX483 SN75LBC176*
MAX483E
MAX485/E SN65HVD3085E*
MAX485 SN75LBC176*
MAX485E SN75LBC176A*
MAX487 SN75HVD07*
MAX487 SN75LBC182*
MAX487E SN65HVD3082E*
MAX488 SN75LBC179*
MAX488E SN75LBC179A*
MAX489
MAX489E SN75LBC180A*
MAX490
MAX490E SN75LBC179A*
SN65HVD3088E*
SN75HVD11*
SN65HVD3088E*
SN65HVD3082E*
SN75LBC176A*
SN75LBC180*
SN75LBC179*
art Number TI Replacement
P
MAXIM (cont.)
MAX491 SN75LBC180*
MAX491E SN75LBC180A*
MAX625 TPS2044A/54A
MAX780 TPS2205
MAX869L TPS2024/34
MAX890L TPS2022/32
MAX9110 SN65LVDS1*
MAX9111 SN65LVDS2*
MAX9112 SN65LVDS9638*
MAX9113 SN65LVDS9637*
MAX9115 SN65LVDS2
MAX9121 SN65LVDS048A*
MAX9122 SN65LVDT048A*
MAX9123 SN65LVDS047*
MAX9124 SN65LVDS31*
MAX9125 SN65LVDS32*
MAX9126 SN65LVDT32*
MAX9130 SN65LVDS2
MAX9152 SN65LVCP22
MAX9155 SN65LVDS100
MAX9156 SN65LVDS100
MAX9159 SN65LVDS9637*
MAX9163 SN65MLVD201
MAX9164 SN65LVDS180
MAX9169 SN65LVDS104*
MAX9170 SN65LVDS105*
MAX9171 SN65LVDS2*
MAX9172 SN65LVDS9637
MAX9173 SN65LVDS048A
MAX9174 SN65LVDS122
MAX9175 SN65LVDS122
MAX9177 SN65LVCP22
MAX9178 SN65LVDS047*
MAX9179 SN65LVDS348*
MAX9180 SN65L
MAX9181 SN65LVDS100
MAX9205 SN65LV1023*
MAX9206 SN65L
MAX9207 SN65LV1224*
MAX9208
MAX9320
MAX9320A NS65LVCP23
MAX9321B SN65LVDS101
MAX9374 SN65LVDS100
MAX9374A SN65LVDS100
MAX9375 SN65LVDS101
MICROCHIP
MCP2551
MCP2120 TIR1000
* Drop-in, pin-compatible devices
VDS100
V1021*
V1212*
SN65L
SN65LVCP23
SN65HVD251*
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 45

The following products have similar functionality:
Cross-Reference Guide
45
➔
Part Number TI Replacement
MICREL
MIC2505 TPS2024/34
MIC2506 TPS2042A/52A
MIC2507 TPS2044A/54A
MIC2514 TPS210x
MIC2524 TPS2044A/54A
MIC2525 TPS2041A/51A
MIC2526 TPS2042A/52A
MIC2527 TPS2044A/54A
MIC2563A TPS2205
MIC2564A TPS2216A
NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR
DS14185 SN75185*
DS14196 SN75196
DS1487 SN75HVD06*
DS1488 SN75188
DS1489 SN75189
DS14C232 MAX232
DS14C88 SN75C188
DS14C89A SN75C189A
DS36276 SN75HVD05*
DS3695 SN65HVD3088E*
DS3695 SN75LBC176A*
DS3695 SN75ALS176*
DS3695 SN75176B*
DS3697 SN75179*
DS3697 SN75ALS179*
DS3697 SN75LBC179*
DS36C278 SN75HVD06*
DS36C279 SN75HVD06*
DS36C280 SN75HVD06*
DS36F95 SN75LBC176*
DS485 SN65HVD3088E*
DS485 SN75LBC176A*
DS485 SN75ALS176*
DS485 SN75176B*
DS75176B SN75LBC176A*
DS75176B SN75ALS176*
DS75176B SN75176B*
DS90CP04 SN65LVDS250
DS90CP22 SN65L
DS90CR215 SN65LVDS95*
DS90CR216
DS90CR283 SN65LVDS93*
DS90CR284 SN65LVDS94*
DS90LT012A
DS90LV001 SN65LVDS100*
DS90LV0101A SN65MLVD201
DS90LV011A SN65LVDS1*
DS90LV012A SN65LVDS2*
DS90LV017 SN65LVDS1*
DS90LV017A
DS90LV018A SN65LVDS2*
DS90LV018A
DS90LV019 SN65LVDS179
DS90LV027A SN65LVDS9638*
VCP22*
SN65LVDS96*
SN65LVDT2*
VDS1*
SN65L
VDT2*
SN65L
Part Number TI Replacement
NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR (cont.)
DS90LV028A SN65LVDS9637*
DS90LV031 SN65LVDM31*
DS90LV031 SN65LVDS31*
DS90LV031A SN65LVDM31*
DS90LV031A SN65LVDS31*
DS90LV031B SN65LVDM31*
DS90LV031B SN65LVDS31*
DS90LV032 SN65LVDS32*
DS90LV032A SN65LVDS32*
DS90LV047 SN65LVDS047*
DS90LV047A SN65LVDS047*
DS90LV048 SN65LVDS048A*
DS90LV048A SN65LVDS048A*
DS90LV049 SN65LVDS049*
DS90LV1021 SN65LV1021*
DS90LV1023 SN65LV1023*
DS90LV1023 SN65LV1023A*
DS90LV1212A SN65LV1212*
DS90LV1224 SN65LV1224A*
DS92LV010A SN65MLVD200*
DS92LV010A SN65MLVD201*
DS92LV010A SN65MLVD204*
DS92LV010A SN65MLVD206*
DS92LV090 SN65LVDM976
DS92LV090 SN65LVDM977
DS92LV090A SN65LVDM976
DS92LV090A SN65LVDM977
DS92LV1010 SN65MLVD201
DS92LV1021 SN65LV1021*
DS92LV1021 SN65LV1023A*
DS92LV1021 SN65LVDS151
DS92LV1023 SN65LV1023A*
DS92LV1212A SN65LV1212*
DS92LV1224 SN65LV1224B*
V16 TLK2521
DS92L
DS92LV18 TLK2521
V222
DS92L
V222 SN65LVDM22
DS92L
DS92LV222A SN65LVCP22
DS92LV222A SN65LVDM22
DS96173 SN75173*
DS96173 SN75ALS173*
DS96173 SN75LBC173A*
DS96174 SN75174*
DS96174 SN75ALS174A*
DS96174 SN75LBC174A*
DS96175 SN75LBC175A*
DS96175
DS96175
DS96176
DS96176 SN75LBC176A*
DS96176 SN75ALS176*
DS96176 SN75176B*
DS9636 DS9636
SN65LVCP22
SN75ALS175*
SN75175*
SN65HVD3088E*
Part Number TI Replacement
NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR (cont.)
DS96F174C SN75174*
DS96F174C SN75ALS174A*
DS96F174C SN75LBC174A*
DS96F175C SN75175*
DS96F175C SN75ALS175*
DS96F175C SN75LBC175A*
PC16550D TL16C550B
PC16550D TL16C550C*
PC16552D TL16C552A
SC28L194 TL16C554A*
SC28L92 TL16C552A*
SC68C562C1A TL16C552A*
ON SEMI
MC100EP16 SN65LVDS100
MC100EP16 SN65LVDS101
MC1488 SN75188*
MC1489 SN75189*
MC1489A SN75189A*
MC14C89AB SN75C189A
MC3488A UA9636A
OXFORD
OXCF950 TL16PC564B
PERICOM
PI7C8150A PCI2050*
PI7C8150A PCI2050B*
PI7C8152A PCI2250*
PI90LV001 SN65LVDS1*
PI90LV019 SN65LVDS180
PI90LV02 SN65LVDS2*
PI190LV03 SN65LVDS100
PI90LV051 SN65LVDS051*
PI90LV179 SN65LVDS179*
PI90LV180
PI90LV3486 SN65LVDS3486*
PI90LV3487
PI90LV3487
PI90LV9637 SN65LVDS9637*
V9638 SN65LVDS9638*
PI90L
PI90LVB001 SN65LVDS1
PI90LVB010 SN65MLVD201
PI90LVB03 SN65LVDS100
PI90LVB047A SN65LVDS047
PI90LVB180 SN65LVDM180*
PI90LVB387
PI90LVB9638 SN65LVDS9638
PI90LVT02 SN65LVDS2*
VT02
PI90L
PI90LVT048A SN65LVDT348
VT3486
PI90L
PI90LVT3486 SN65LVDT3486B*
PI90LVT386 SN65LVDT386*
PI90LVT9637 SN65LVDT9637*
* Drop-in, pin-compatible devices
SN65LVDS180*
VDS3487
SN65L
SN65LVDS3487*
SN65LVDS387
SN65LVDT2*
SN65LVDT3486*
Texas Instruments 4Q 2006 Interface Selection Guide
Page 46

46
Cross-Reference Guide
➔
The following products have similar functionality:
Part Number TI Replacement
ERICOM (cont.)
P
PI90LVT9637 SN65LVDT9637B*
PI90LV017A SN65LVDS1*
PI90LV018A SN65LVDS2*
PI90LV019 SN65MLVD200*
PI90LV019 SN65MLVD201*
PI90LV019 SN65MLVD204*
I90LV019 SN65MLVD206*
P
I90LV022 SN65LVCP22
P
PI90LV022 SN65LVDS122
PI90LV027A SN65LVDS9638*
PI90LV028A SN65LVDS9637*
PI90LV031A SN65LVDS31*
PI90LV032A SN65LVDS32*
PI90LV047A SN65LVDS047*
PI90LV048A SN65LVDS048*
PI90LV050 SN65LVDS050*
PI90LV386 SN65LVDS386*
PI90LV387 SN65LVDS387*
PI90LVB022 SN65LVDM22
PI90LVB047A SN65LVDM31
PI90LVB050 SN65LVDM050*
PI90LVB051 SN65LVDM051*
PI90LVB179 SN65LVDM179*
PI90LVB180 SN65MLVD202*
PI90LVB180 SN65MLVD203*
PI90LVB180 SN65MLVD205*
PI90LVB180 SN65MLVD207*
PHILIPS
PCA82C250 SN65HVD251*
PCA82C251 SN65HVD251*
SC16C550 TL16C55C*
SC16C554 TL16C554*
SC16C554 TL16C554A*
SC16C650A TL16C550
SC16C652 TL16C752
SC16C654 TL16C754
SC16C752 TL16C752B*
SC16C2550
SC16C2552 TL16C752B
SC28L194 TL16C554A
SC28L91 TL16C550C
SC28L92 TL16C552A
SC68C562C1A
SCC2691 TL16C450
SCC2692 TL16C452*
SCC68692 TL16C452*
TL16C752B
TL16C552A
Part Number TI Replacement
PHILIPS (cont.)
SCN2681 TL16C452*
TJA1040 SN65HVD1040*
TJA1050 SN65HVD1050*
PLX
PCI6150 PCI2050*
PCI6150 PCI12050B*
PCI6140 PCI2250*
PROLIFIC
PL-2303 TUSB3410
SEMTECH
SC5825 TPS2041A/51A
SC5826 TPS2042A/52A
SILICON LABORATORIES
CP2101 TUSB3410
CP2102 TUSB3410
SILICONIX/VISHAY
Si9711 TPS2211A
Si9712
SILICON SYSTEM
73M550 TL16C550C*
SIPEX
SP211 SN75LBC241
SP232A MAX232
SP3222E MAX3222
SP3222EB MAX3222
SP3222EU SNx5C3222
SP3223E MAX3223
SP3223EB MAX3223
SP3223EU SNx5C3223
SP3232E MAX3232
SP3232EB
SP3232EU SNx5C3232
SP3238E MAX3238
SP3243E MAX3243
SP3243EB MAX3243
SP3243EU SNx5C3243
SP3481 SN75HVD11*
SP3483 SN75HVD12*
SP3485 SN75HVD11*
SP3494
SP481 SN65HVD3088E*
SP481 SN75LBC176*
SP481 SN75ALS176*
SP481
SP481E SN65HVD3088E*
TPS2211A
MAX3232
SN75HVD10*
SN75176B*
Part Number TI Replacement
SIPEX (cont.)
SP481E SN75LBC176A*
SP481R SN65HVD3088E*
SP483 SN65HVD3082E*
P483 SN75LBC176*
S
P483 SN75ALS176*
S
P483 SN75176B*
S
P483E SN65HVD3085E*
S
SP483E SN65HVD485E*
SP485 SN65HVD3088E*
SP485 SN75LBC176*
SP485 SN75ALS176*
SP485 SN75176B*
SP485E SN65HVD3088E*
SP485E SN75LBC176A*
SP486 SN75LBC172*
SP486E SN75LBC172A*
SP487 SN75LBC174*
SP487E SN75LBC174A*
SP488 SN75LBC173*
SP488A SN75LBC173A*
SP488E SN75LBC173A*
SP489 SN75LBC175*
SP489A SN75LBC175A*
SP489E SN75LBC175A*
SP490 SN75LBC179*
SP490E SN75LBC179A*
SP491 SN75LBC180*
SP491E SN75LBC180A*
Part Number TI Replacement
STM
ST232 MAX232*
ST3222 MAX3222*
ST3222E MAX3222
ST3232 MAX3232*
ST3232E MAX3232
ST3243 MAX3243*
ST3243E MAX3243
ST75185 SN75185
ST75C185
SN75C185*
* Drop-in, pin-compatible devices
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 47

Device Index
Device Page Device Page Device Page Device Page Device Page Device Page
75 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9, 12, 42
1
76B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
1
DM2209E . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
A
ALS1177 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LS1178 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
A
LS176 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
A
LS180 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
A
CDC208 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
DC2351 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
C
DC2536 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
C
DC2582 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
C
CDC2586 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDC286 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
DC318A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
C
DC319 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
C
CDC328A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDC329A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
DC337 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
C
DC339 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
C
CDC340 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDC341 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
DC351 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
C
DC391 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
C
CDC536 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDC5801A . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
DC5806 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
C
DC582 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
C
CDC586 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDC7005
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDC930
DC950 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
C
CDC960 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCD5704 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCD5804 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCE706 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCE906 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCF5801A . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCFR83A . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCL6010 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCLVD110 . . . . . . . . . . .4, 42
CDCLVP110 . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCM1802 . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCM1804 . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCM7005 . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCP1802 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCP1803 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCR61A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCR83A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCU2A877 . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCU855 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCU877A
CDCUA855 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCUA877 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCV304 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCV850 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCV855 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCV857B
CDCV877/A . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCVF111
CDCVF2310 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CDCVF2505 . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCVF25081 . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCVF25084 . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCVF2509A . . . . . . . . . . . .42
CDCVF2510A . . . . . . . . . . . .42
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CDCVF857
EPON . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
GD65232 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GD75232
GD75323 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
HVD05 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
HVD06 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
HVD07 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
HVD08 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
HVD10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
HVD11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
HVD1176 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
HVD12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
HVD179 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
HVD20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
HVD21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
HVD22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
VD23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
H
VD24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
H
VD30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
H
HVD3082E . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
VD3085E . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
H
VD3088E . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
H
VD31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
H
HVD32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
VD33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
H
VD34 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
H
VD35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
H
HVD379 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
HVD485E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
VD50 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
H
VD51 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
H
HVD52 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
HVD53 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
VD54 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
H
VD55 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
H
ISO150 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
ISO721 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
SO721M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
I
SO722 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
I
ISO7220A . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
ISO7220C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
SO7220M . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
I
SO7221A . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
I
ISO7221C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
ISO7221M
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
ISO722M
BC170 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
L
LBC171 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC172 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC172A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC173 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC173A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC174 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC174A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC175 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC175A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC176 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC176A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC179 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC179A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC180 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC182 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LBC184 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
LT1030 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
MAX202 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX202E . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX207
MAX207E . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX208 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX208E . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX211 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX211E . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . . . . . .13-14
MAX213
MAX222 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX232
42
MAX232E . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAX3221 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX3221E . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX3222 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
MAX3222E . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX3223 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
42
MAX3223E
MAX3227E . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX3232 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
15
MAX3232E
MAX3237E . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX3238 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX3238E . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX3243 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . . . .
MAX3243E
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAX3318
MAX3318E . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
MAX3386E . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MC1488
MC1489 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
MC1489A . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
MLVD128 . . . . . . . . . . . . .8, 42
MLVD129 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
13-14
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
13-14
CI2040 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
P
CI2050B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
P
CI2060 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
P
PCI2250 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
N65220 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
S
N65240 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
S
N65C1154 . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
S
SN65C1406 . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
N65C23243 . . . . . . . . . . . .14
S
N65C3221 . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
S
N65C3221E . . . . . . . . . . . .14
S
SN65C3222 . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
SN65C3222E . . . . . . . . . . . .14
N65C3223 . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
S
N65C3223E . . . . . . . . . . . .14
S
SN65C3232 . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SN65C3232E . . . . . . . . . . . .14
N65C3238 . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
S
N65C3243 . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
S
SN65CML100 . . . . . . . .4-5, 42
SN65HVD1050 . . . . . . . . . .18
N65HVD230 . . . . . . . . . . .18
S
N65HVD231 . . . . . . . . . . .18
S
SN65HVD232 . . . . . . . . . . .18
SN65HVD233 . . . . . . . . . . .18
N65HVD234 . . . . . . . . . . .18
S
N65HVD235 . . . . . . . . . . .18
S
SN65HVD251 . . . . . . . . . . .18
1023A/1024B . . . . .2
SN65LV
CP22 . . . . . . . . . . .4-5
SN65LV
N65LVCP23 . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
S
SN65LVCP40 . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
SN65LVDM050 . . . . . . . . . . .9
SN65LVDM1676 . . . . . . . . . .9
SN65LVDM179 . . . . . . . . . . .9
SN65LVDM22 . . . . . . . . . . . .9
SN65LVDM31 . . . . . . . . . . . .9
SN65LVDS047 . . . . . . . . . .6-7
SN65LVDS048A . . . . . . . . .6-7
SN65LVDS049 . . . . . . . . . .6-7
SN65LVDS050 . . . . . . . . . .6-7
SN65LVDS051 . . . . . . . . . .6-7
SN65LVDS1 . . . . . . . . . . . .6-7
SN65LVDS100 . . . . . . . . . .4-5
SN65LVDS101 . . . . . . . . . .4-5
SN65LVDS104 . . . . . . . . . . .42
SN65LVDS105 . . . . . . . . . . .42
SN65LVDS1050 . . . . . . . . .6-7
SN65LVDS108 . . . . . . . . . . .42
SN65LVDS109 . . . . . . . . . . .42
VDS116 . . . . . . . . . . .42
SN65L
SN65LVDS117 . . . . . . . . . . .42
SN65LVDS122 . . . . . . . . . .4-5
SN65LVDS16/17 . . . . . . . . . .5
SN65LVDS179 . . . . . . . . . .6-7
SN65LVDS18/19 . . . . . . . . . .5
VDS180 . . . . . . . . . .6-7
SN65L
SN65LVDS2 . . . . . . . . . . . .6-7
VDS20 . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
SN65L
SN65LVDS22
SN65LVDS250 . . . . . . . . .5, 42
SN65LVDS301 . . . . . . . . . . .19
SN65LVDS302 . . . . . . . . . . .19
SN65LVDS303 . . . . . . . . . . .19
SN65LVDS304 . . . . . . . . . . .19
14
14
14
15
VDS305
SN65L
SN65LVDS306 . . . . . . . . . . .19
SN65LVDS31 . . . . . . . . . . .6-7
VDS32
SN65L
SN65LVDS33 . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
SN65LVDS34 . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
SN65LVDS348 . . . . . . . . . . . .5
SN65LVDS3486 . . . . . . . . .6-7
VDS3487
SN65L
VDS352
SN65L
SN65LVDS386 . . . . . . . .4, 6-7
SN65LVDS387 . . . . . . . .4, 6-7
VDS388A
SN65L
SN65LVDS389 . . . . . . . . . .6-7
SN65LVDS390 . . . . . . . . . .6-7
SN65LVDS391 . . . . . . . . . .6-7
SN65LVDS93/94 . . . . . .20-21
. . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . .6-7
N65LVDS95/96 . . . . . .20-21
S
N65LVDS9637 . . . . . . . . .6-7
S
N65LVDS9638 . . . . . . . . .6-7
S
SN65LVP16/17 . . . . . . . . . . .5
N65LVP18/19 . . . . . . . . . . .5
S
N65LVP20 . . . . . . . . . . .5, 42
S
N65MLVD047 . . . . . . . . . . .9
S
SN65MLVD080 . . . . . . . . . . .9
N65MLVD082 . . . . . . . . . . .9
S
N65MLVD128 . . . . . . . . . . .9
S
N65MLVD129 . . . . . . . . . . .9
S
SN65MLVD2 . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
SN65MLVD200A . . . . . . . . . .9
N65MLVD201 . . . . . . . .9, 42
S
N65MLVD202A . . . . . . . . . .9
S
SN65MLVD203 . . . . . . . . . . .9
SN65MLVD204A . . . . . . . . . .9
N65MLVD205A . . . . . . . . . .9
S
N65MLVD206 . . . . . . . . . . .9
S
SN65MLVD207 . . . . . . . . . . .9
SN65MLVD3 . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
N65MLVDS201 . . . . . . . . .42
S
N74GTLP1394 . . . . . . . . . .40
S
SN74GTLP1395 . . . . . . . . . .40
SN74GTLP2033 . . . . . . . . . .40
N74GTLP2034 . . . . . . . . . .40
S
N74GTLP21395 . . . . . . . . .40
S
SN74GTLP22033 . . . . . . . . .40
1
SN74GTLP22034
SN74GTLP817
N74GTLPH1612 . . . . . . . . .40
S
SN74GTLPH1616 . . . . . . . . .40
SN74GTLPH1627 . . . . . . . . .40
SN74GTLPH1645 . . . . . . . . .40
SN74GTLPH1655 . . . . . . . . .40
SN74GTLPH16612 . . . . . . . .40
SN74GTLPH16912 . . . . . . . .40
SN74GTLPH16916 . . . . . . . .40
SN74GTLPH16927 . . . . . . . .40
SN74GTLPH16945 . . . . . . . .40
SN74GTLPH306 . . . . . . . . . .40
SN74GTLPH3245 . . . . . . . . .40
SN74GTLPH32912 . . . . . . . .40
SN74GTLPH32916 . . . . . . . .40
SN74GTLPH32945 . . . . . . . .40
SN74VMEH22501 . . . . . . . .41
SN75150 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SN75154 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
SN75155 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SN751701 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SN75185
SN75186 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
SN75188 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SN75189 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
SN75189A . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
SN75196 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SN752232
SN75240 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
SN75C1154
6-7
SN75C1406 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SN75C185 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
SN75C188 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
SN75C189 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
SN75C189A . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
SN75C198 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
19
SN75C23243
SN75C3221 . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SN75C3221E . . . . . . . . . . . .14
6-7
SN75C3222
SN75C3222E . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SN75C3223 . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SN75C3223E . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SN75C3232 . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
6-7
SN75C3232E
5
SN75C3238
SN75C3243 . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SN75LBC187 . . . . . . . . . . . .15
SN75LBC241
SN75LP1185 . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SN75LP196 . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SN75LPE185 . . . . . . . . . . . .14
SN75LV4737A . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . .40
. . . . . . . . . . .40
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
. . . . . . . . . . . . .15
. . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . .
N75LVDS82/83 . . . . . .20-21
S
N75LVDS84A/86 . . . . .20-21
S
N75LVDT1422 . . . . . . .20-21
S
TB3R1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
B3R2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
T
B5D1M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
T
B5D2H . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
T
TB5R1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
B5R2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
T
B5R3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
T
B5T1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
T
TFP401 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
TFP401A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
FP403 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
T
FP410 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
T
TFP501 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22-23
TFP503 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22-23
FP510 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22-23
T
FP513 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22-23
T
TL145406 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
TL16C2550 . . . . . . . . . . .16-17
L16C2552 . . . . . . . . . . .16-17
T
L16C2752 . . . . . . . . . . .16-17
T
TL16C450 . . . . . . . . . . . .16-17
TL16C451 . . . . . . . . . . . .16-17
L16C452 . . . . . . . . . . . .16-17
T
L16C550C . . . . . . . . . . .16-17
T
TL16C552A . . . . . . . . . . .16-17
TL16C554A
TL16C550D
T
TL16C752B . . . . . . . . . . .16-17
TL16C754B . . . . . . . . . . .16-17
TL16PC564B/BLV . . . . . . . . .17
TL16PIR552 . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
TLK10021 . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK1201AI . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK1211 . . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK1501 . . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK1521 . . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK2201AJR . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK2201BI . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK2208B . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK2226 . . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK2501 . . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK2521 . . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK2701 . . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK2711 . . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK3101 . . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK3104SA . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK3104SC
TLK3114SC . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK3118 . . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK4015 . . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK4120 . . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TLK4250 . . . . . . . . . . . . .20-21
TMDS141
TMDS341A . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
TMDS442
15
TPPM0301/2 . . . . . . . . . . . .
TPPM0303 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
TPS2010A . . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
TPS2011A . . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
TPS2012A . . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
TPS2013A . . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
14
TPS2020/30
TPS2021/31 . . . .27-28, 34-35
TPS2022/32 . . . . . . . . . .28, 35
15
TPS2022/32/61/65
TPS2023/33 . . . .27-28, 34-35
TPS2024/34 . . . . . . .27-28, 35
TPS2041B/51B . . . . .27-28, 35
TPS2042B/52B . .27-28, 34-35
14
TPS2043B/53B
14
TPS2044B/54B
TPS2045A/55A . .27-28, 34-35
TPS2046B/56A . .27-28, 34-35
15
TPS2047B/57A
TPS2048A/58A . .27-28, 34-35
TPS2060/4 . . . . . . . . . . .28, 35
TPS2061/5 . . . . . . . . . . .28, 35
TPS2062/6 . . . . . . . . . . .28, 35
. . . . . . . . . . .16-17
L16C750 . . . . . . . . . . . .16-17
. . . . . . . . . . .20-21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
. . . . . . . . . . . . .17
27-28, 34-35
. . . .
. . . . . . .
27-28, 35
. . . . .
27-28, 34-35
. .
27-28, 34-35
. .
PS2063/7 . . . . . . . . . . .28, 35
T
PS2070 . . . . . . . . . . . . .27-28
T
PS2071 . . . . . . . . . . . . .27-28
T
TPS2074 . . . . . . . . . . . . .27-28
PS2075 . . . . . . . . . . . . .27-28
T
PS2080/1/2 . . . . . . . . .34-35
T
PS2085/6/7 . . . . . . . . .34-35
T
TPS2090/1/2 . . . . . . . . .34-35
PS2095/6/7 . . . . . . . . .34-35
T
PS2100/1 . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
T
PS2102/3 . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
T
TPS2104/5 . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
TPS2110A/2A/4A . . . . . . . .35
PS2111A/3A/5A . . . . . . . .35
T
PS2140 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
T
TPS2141 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
TPS2145 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
PS2147 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
T
PS2148 . . . . . . . . . . . . .27-28
T
TPS2149 . . . . . . . . . . . . .27-28
TPS2150 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
PS2151 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
T
PS2155 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
T
TPS2157 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
TPS2158 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
PS2159 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
T
PS2204A . . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
T
TPS2205 . . . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
. . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
TPS2206A
. . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
TPS2210A
PS2211A . . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
T
TPS2212 . . . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
TPS2220B . . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
TPS2221 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
TPS2223A . . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
TPS2224A . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
TPS2226A . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
TPS2228 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
TPS2231 . . . . . . . . . . . . .34-35
TS3DV416 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
TS3DV520 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
TSB14AA1A . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
TSB41AB1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
TSB41AB2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
TSB41AB3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
TSB41BA3B . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
TSB41LV04A . . . . . . . . . . . .37
TSB41LV06A . . . . . . . . . . . .37
TSB81BA3D . . . . . . . . . .37-38
TUSB1105 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
TUSB1106
TUSB2036 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
TUSB2046B . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
TUSB2077A . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
TUSB2136 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
TUSB2551 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
TUSB3210
TUSB3410 . . . . . . . . . . .25-26
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
TUSB5052
35
TUSB6020 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TUSB6250 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
UA9636A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
UC5170C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
UC5180C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
UC5181C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
XIO1100
XIO2000A . . . . . . . . . . . .29-30
XIO2200A . . . . . . . . . . .29, 31
27
XIO3130
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
29, 32
29, 31
47
➔
26
Interface Selection Guide Texas Instruments 4Q 2006
Page 48

Technology for Innovators
M
T
TI Worldwide Technical Support
Internet
I Semiconductor Product Information Center
T
Home Page
support.ti.com
TI Semiconductor KnowledgeBase Home Page
support.ti.com/sc/knowledgebase
Product Information Centers
Americas
Phone +1(972) 644-5580
Fax +1(972)927-6377
Internet support.ti.com/sc/pic/americas.htm
Europe, Middle East, and Africa
Phone
Belgium (English) +32 (0) 27 45 54 32
Finland (English) +358 (0) 9 25173948
France +33 (0) 1 30 70 11 64
Germany +49 (0) 8161 80 33 11
Israel (English) 180 949 0107
Italy 800 79 11 37
Netherlands (English) +31 (0) 546 87 95 45
Russia +7 (4) 95 98 10 701
Spain +34 902 35 40 28
Sweden (English) +46 (0) 8587 555 22
United Kingdom +44 (0) 1604 66 33 99
Fax +49 (0) 8161 80 2045
Internet support.ti.com/sc/pic/euro.htm
Japan
Fax
International +81-3-3344-5317
Domestic 0120-81-0036
Internet
International support.ti.com/sc/pic/japan.htm
Domestic www.tij.co.jp/pic
Asia
Phone
International +886-2-23786800
Domestic T
oll Free Number
Australia 1-800-999-084
China 800-820-8682
Hong Kong 800-96-5941
India +91-80-41381665 (Toll)
Indonesia 001-803-8861-1006
Korea 080-551-2804
Malaysia 1-800-80-3973
New Zealand 0800-446-934
Philippines 1-800-765-7404
Singapore 800-886-1028
Taiwan 0800-006800
Thailand 001-800-886-0010
Fax +886-2-2378-6808
Email tiasia@ti.com or ti-china@ti.com
Internet support.ti.com/sc/pic/asia.htm
D062706
Safe Harbor Statement
This publication may contain forward-looking statements that
involve a number of risks and uncertainties. These “forward-
looking statements” are intended to qualify for the safe harbor from
liability established by the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act
of 1995. These forward-looking statements generally can be
identified by phrases such as TI or its management “believes,”
“expects,” “anticipates,” “foresees,” “forecasts,” “estimates” or
other words or phrases of similar import. Similarly, su ch state-
ments herein that describe the company’s products, business
s
trategy, outlook, objectives, plans, intentions or goals also are
f
orward-looking statements. All such forward-looking state-
m
ents are subject to certain risks and uncertainties that could
c
ause actual results to differ materially from those in forward-
l
ooking statements. Please refer to TI’s most recent Form 10-K for
more information on the risks and uncertainties that could materi-
ally affect future results of operations. We disclaim any intention
or obligation to update any forward-looking statements as a result
of developments occurring after the date of this publication.
Important Notice: The products and services of Texas
Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries described herein
are sold subject to TI’s standard terms and conditions of sale.
Customers are advised to obtain the most current and complete
information about TI products and services before placing orders.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance, customer’s
applications or product designs, software performance, or
infringement of patents. The publication of information regarding
any other company’s products or services does not constitute TI’s
approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Technology for Innovators, the black/red banner, PanelBus,
FlatLink, MicroStar Junior, PowerPAD, DLP, MicroStar, OEC and
TI-OPC are trademarks of Texas Instruments. All other trademarks
are the property of their respective owners.
© 2006 Texas Instruments Incorporated
Printed in U.S.A. by (Printer, City, State), on recycled paper
Texas Instruments Incorporated
AA Blvd.
14950 F
Fort Worth, TX 76155-9950
Address service requested
PRSRT STD
U.S. POSTAGE
PAID
DALLAS, TEXAS
PERMIT NO. 2758
SSZT009C
Page 49

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications,
enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue
any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing
orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s terms
and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI
deems necessary to support this warranty . Except where mandated by government requirements, testing of all
parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for
their products and applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products
and applications, customers should provide adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right,
copyright, mask work right, or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process
in which TI products or services are used. Information published by TI regarding third-party products or services
does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof.
Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property
of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without
alteration and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction
of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for
such altered documentation.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that
product or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and
is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application
solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Interface interface.ti.com Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Low Power Wireless www.ti.com/lpw Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments
Post Office Box 655303 Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright 2006, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...