Page 1

Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas Instruments
www.ti.com
µ
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
FEATURES
D Single Channel Codec
D Noise Shaped Delta Sigma ADC and DAC
Technology
D Low Supply Voltage and Current:
− 1.3-V Typical Power Supply
− 350-µA Typical Supply Current Drain
D Power Supply Up Monitor and Low Battery
Monitor That Also Automatically Shuts Off
H-Bridge Output When Battery Decays Below
1.05 V in a Nontransient Manner
D Typical 2.4-µVrms Input Referred Noise With
0.01% Total Harmonic Distortion for Front
End and 108-dB Dynamic Range
D ADC Has 87-dB Dynamic Range With 73-dB
Total Harmonic Distortion 100 Hz−10 kHz,
40-kHz Sampling Rate
D Typical 55-dB PSRR 100 Hz to 10 kHz for
Analog Front End
D Low Noise Programmable Gain
Amplifier/Compressor Front End With
Programmable Fast and Slow Attack and
Decay Rates With Dual or Single Attack and
Decay Rate Option
D Typical Output Noise of 12 µVrms With 0.05%
Total Harmonic Distortion for Delta Sigma
DAC and H-Bridge Output Driver
D Low Jitter Oscillator That Generates all
Internal Clocks and Generates 5-MHz Output
DSP/µC Clock
D Regulated Bandgap Voltage Reference
D Programmable Functionality via Digital Serial
Interface
− McBSP Interface, DSP Protocol
− TI TMS320VC54x, TMS320VC55x DSPs
− SPI Interface, Microcontroller Protocol
− TI MSP430xx
D External Chip Power Down and Reset
D Available in:
− 32-Pin QFN 5×5-mm Plastic Package
− 32-Pad Bumped Die in Waffle Pack (wafer
scale packaging), or Tape and Reel,
(Preview, Available 3rd Quarter 2003)
APPLICATIONS
D Hearing Instruments
D Personal Medical Devices
D Hearing Protection
D Aural Processing
D Low-Power Headsets
DESCRIPTION
The AIC111 IC design specification serves to provide
product development teams with a guideline for how the
AIC1 11 IC is specified and programmable options that are
available. The document outlines a top-level block
description of the IC along with system specifications and
functions. Individual block descriptions and target
specifications are also outlined.
The Texas Instruments AIC111 is a TI µPower DSP
compatible, or microcontroller compatible audio codec
product, or analog interface circuit. The AIC111 is part of
a comprehensive family of DSP/µC based highperformance analog interface solutions. The AIC111 is
targeted primarily at personal medical devices, such as
hearing instruments, aural preprocessing applications,
and low-power headset applications. The AIC111 is used
in any design requiring a programmable time constant
PGA/compressor interface, high dynamic range
analog-to-digital converter, an external DSP/µC
handling signal processing, or a low distortion
digital-to-analog converter with a balanced H-Bridge
speaker driver. It supports a CMOS digital interface
tailored for TI DSPs with the McBSP protocol such as
TMS320VC54x DSP family and SPI-based controllers
such as TI MSP430x family of microcontrollers. The
AIC111 also has an external microphone or sensor supply
and bias and power supply up low-battery monitor
indicator.
semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
!" !"#! !$#"! ! %" ! "#! ! %# $
&'%!" "#" $ # & !#" ! " %#()* %$+!( "
'"#' ##""
Copyright 2003, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 2
H-bridge amplifier output
DAC full scale output differential
V
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
These devices have limited built-in ESD protection. The leads should be shorted together or the device placed in conductive foam during
storage or handling to prevent electrostatic damage to the MOS gates.
www.ti.com
The AIC1 11 comes in a 32-pin QFN 5×5-mm package. A 32-pad solder ball bumped flip chip die that comes in waffle
packs or tape and reel is in preview and will be available 3rd quarter 2003.
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
PART NUMBER PACKAGE
AIC111RHB 32-pin QFN (5 mm x 5 mm), in tube.
AIC111RHBR 32-pin QFN (5 mm x 5 mm), tape and reel
AIC111YE
AIC111YER
32-pad waffle scale chip package, bumped die in waffle pack (contact the factory for availability) − Preview,
available 3rd quarter 2003
32-pad (WSCP) bumped die in tape and reel (contact the factory for availability) − Preview, available 3rd
quarter 2003
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
over operating free-air temperature range unless otherwise noted
Input voltage AI or DI pins −0.3 V to 4 V
Power supply VDD, power pins −0.3 V to 4.5 V
Latch-up tolerance JEDEC latch-up (EIA/JEDS78) 100 mA
Operating free-air temperature range, T
Functional temperature range −15°C to 85°C
Reflow temperature range (flip chip) 220°C to 230°C
Storage temperature range, T
Storage humidity 65% R.H.
(1)
Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only , a n d
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied.
Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2)
Specifications are assured operating at maximum device limits for QFN package only, unless otherwise specified.
stg
A
(1)(2)
UNIT
0°C to 70°C
−40°C to 125°C
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
INPUT/OUTPUT, OPERATING TEMPERATURE AT 2 5 °C
PARAMETER TEST CONDITION MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Digital interface (see Notes 1 and 2) BUF_DVDD (see Note 1) 3.6 V
VIH High-level input voltage BUF_DVDD−0.2 V
VIL Low-level input voltage BUF_DVSS+0.2 V
VOH High-level output voltage BUF_DVDD V
VOL Low-level output voltage BUF_DVSS V
Maximum allowed input voltage (AVIN) Differential 450 mVpk
Input impedance (AVIN) (see Note 3) Nominal gain = 50x 20 kΩ
Input capacitance (AVIN) 5 pF
Microphone bias voltage (MIC_VSUP) 20-µA maximum 0.87 0.94 0.99 V
Microphone bias resistor (MIC_BIAS) 27 29.1 31 kΩ
Fixed Q 3/4 HB_VDD
Adaptive Q HB_VDD
Output resistance Differential, HB − VDD = 1.3 V 20 or 40 Ω
(1)
DVDD, VDD_OSC, and AVDD should be within 50 mV, preferably connected together.
AVSS1, 2, DVSS, and VSS_OSC should be within 50 mV, preferably connected together.
(2)
Maximum (0.9 V , DVDD −0.5 V) ≤ BUF_DVDD ≤3.6 V
(3)
Driving single-ended: Rin = R × [(1+A)/(2+A)], A = PGAC Gain (linear), R = 20.4 kΩ for A ≥ 4 or 20.4 kΩ × (4/A) for A<4.
Rin(min) = 1 7 k Ω (A=4), Rin(max) = 59.89 kΩ (A = 0.89), Rin(nom) = 20 kΩ (A = 50).
PP
2
Page 3
www.ti.com
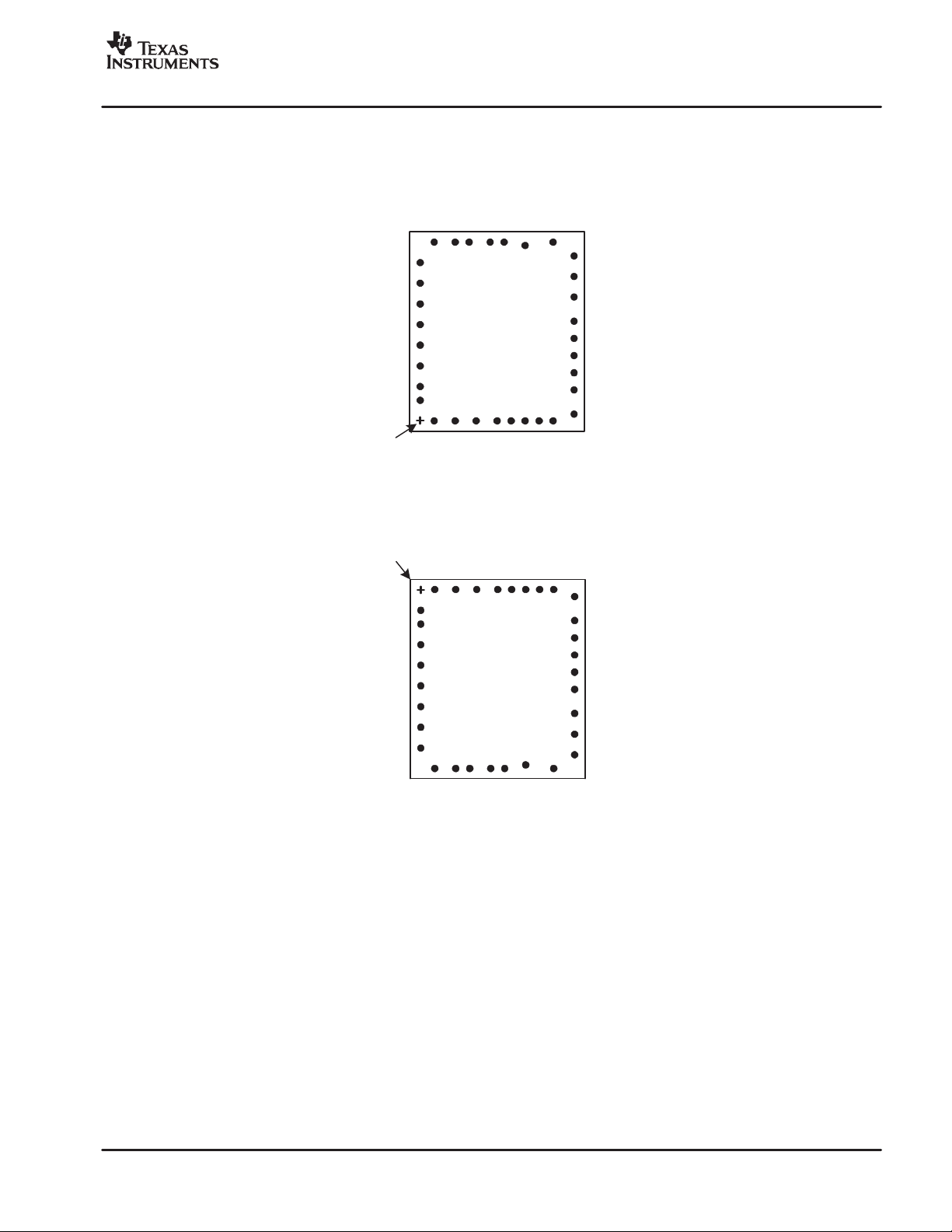
TERMINAL ASSIGNMENTS
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
AVSS1
AVSS2
AVINP
AVINM
VMID_FILT
MIC_BIAS
VREF
MIC_VSUP
Alignment
Marker
(0,0)
MIC_VSUP
VREF
MIC_BIAS
VMID_FILT
AVINM
AVINP
AVSS2
AVSS1
AVSS_REF
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
91011121314
SUB_VSS
SUB_VSS
91011121314
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
AVSS_REF
VRFILT
AVDD
3132
AIC111
Bumped Side
VDD_OSC
VDD_OSC
VSS_OSC
Back Side
AIC111
3132
VRFILT
AVDD
EXT_RST/PWDN
RST/LBM
28
2930
27
VOUT_P
VSS_OSC
HB_VSS_P
HB_VSS_P
HB_VDD
VOUT_P
27
28
2930
DVSS2
RST/LBM
EXT_RST/PWDN
DVSS2
26
16
15
HB_VDD
VOUT_M
HB_VSS_M
VOUT_M
16
15
26
SCLK
SCLK
FRAME
25
24
SDIN
SDOUT
23
22
BUF_DVSS
21
BUF_DVDD
20
DVDD
DVSS1
19
18
MCLK
17
IMODE
Bumped View
HB_VSS_M
For exact bump
location see Spec.
IMODE
17
18
MCLK
19
DVSS1
20
DVDD
21
BUF_DVDD
22
BUF_DVSS
23
SDOUT
24
SDIN
25
FRAME
PCB View
Section 2.2
Figure 1. AIC111YE Bumped View and PCB Flipped Pin Placements
3
Page 4
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
www.ti.com
AVSS1
AVSS2
AVINP
AVINM
VMID_FILT
MIC_BIAS
VREF_BG
MIC_VSUP
AVSS_REF
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 10111213141516
VRFILT
AVDD
DVSS
29303132
RST/LBM
28
DVSS
SCLK
AIC111RHB
FRAME
252627
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
SDIN
SDOUT
BUF_DVSS
BUF_DVDD
DVDD
DVSS
MCLK
IMODE
SUB_VSS
VDD_OSC
VSS_OSC
HB_VSS_P
VOUT_P
HB_VDD
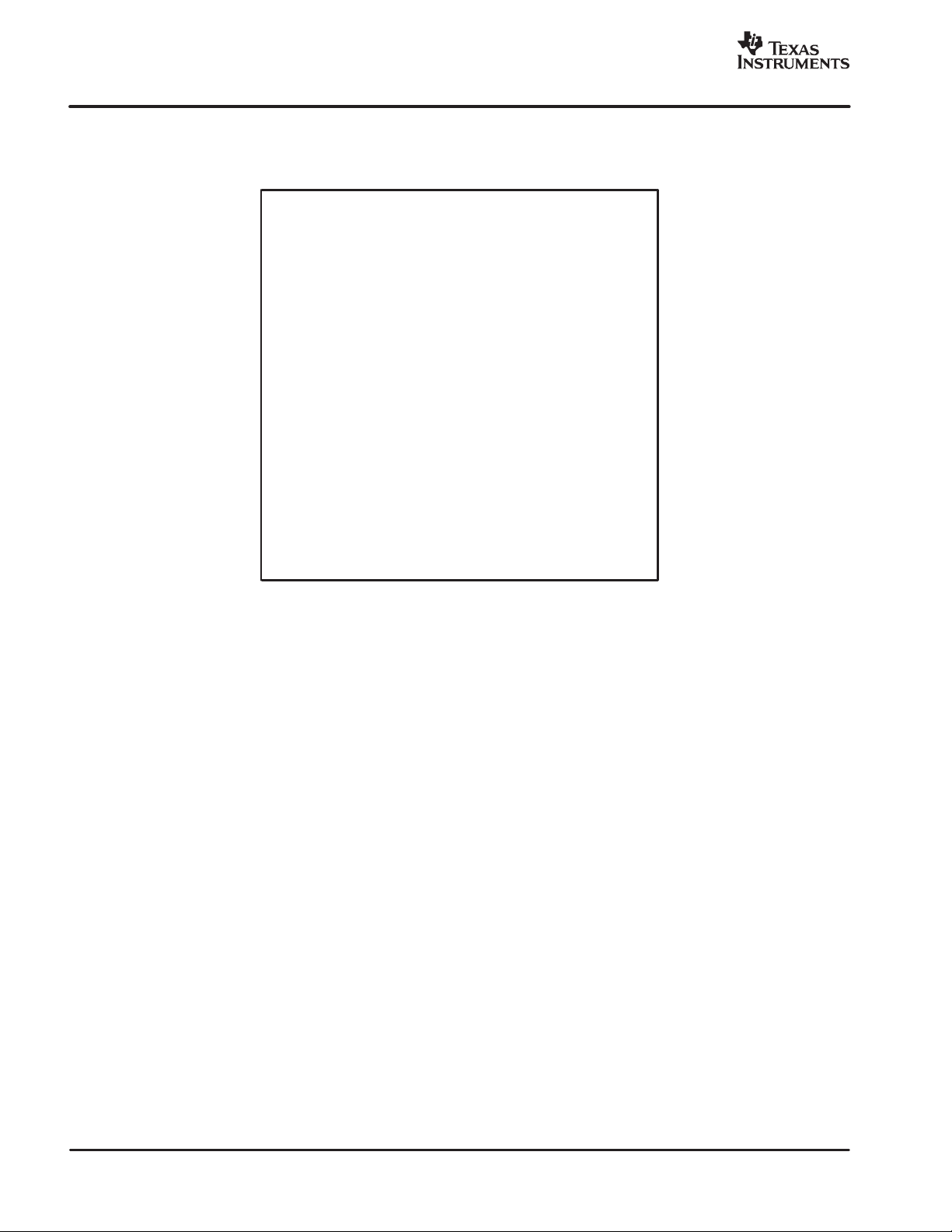
Figure 2. AIC111RHB 32-Pin QFN Pinout
VOUT_M
HB_VSS_M
4
Page 5
www.ti.com
TYPE
DESCRIPTION
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NO. NAME
1 AVSS1 GND Ground return for ADC analog circuits
2 AVSS2 GND Ground return for PGAC and MIC power analog circuits
3 AVINP AI Noninverting differential analog input coupled through an external 1-µF capacitor to external microphone
output
4 AVINM AI Inverting d i fferential analog signal input coupled through an external 1-µF capacitor to ground
5 VMID_FILT AO Midsupply ac ground reference filter pin bypassed by a 1-µF capacitor connected to ground
6 MIC_BIAS AO Source connection of external microphone source follower preamp. (Provides 29.1 kΩ to AVSS2)
7 VREF AO Bandgap reference output bypassed by external 1-µF VREF filter capacitor
8 MIC_VSUP AO Supply voltage for external microphone source follower preamp bypassed with an external 0.1-µF capacitor
9 SUB_VSS GND Isolated substrate VSS for analog circuits
10 VDD_OSC VDD Power pin for internal oscillator
11 VSS_OSC GND Ground return for internal oscillator
12 HB_VSS_P GND Ground return for noninverting stack of H-bridge amplifier
13 VOUT_P AO Noninverting H-bridge output voltage
14 HB_VDD VDD Power pin for H-bridge amplifier
15 VOUT_M AO Inverting H-bridge output voltage
16 HB_VSS_M GND Ground return for inverting stack of H-bridge amplifier
17 IMODE DI Digital interface format selection pin
18 MCLK DO 5-MHz output clock for external DSP/µC
19 DVSS1 GND Ground return for digital circuits
20 DVDD VDD Power pin for digital circuits
21 BUF_DVDD VDD Power pin for interface digital I/O circuits
22 BUF_DVSS GND Ground return for interface digital I/O circuits
23 SDOUT DO Digital interface serial data output pin
24 SDIN DI Digital interface serial data input pin
25 FRAME DO Digital interface serial data framer
26 SCLK DO Digital interface serial shift clock
27 DVSS2 GND Ground return for digital circuits
28 RST/LBM DO Provides external reset and low battery monitor
29 EXT_RST/PWDN DI Powers down all analog blocks and holds digital outputs low until internal system is up
30 AVDD VDD VDD power pin for analog circuits
31 VRFILT AO Positive ADC reference pin bypassed with 1-µF capacitor to AVSS_REF
32 AVSS_REF GND Ground for ADC voltage reference
5
Page 6
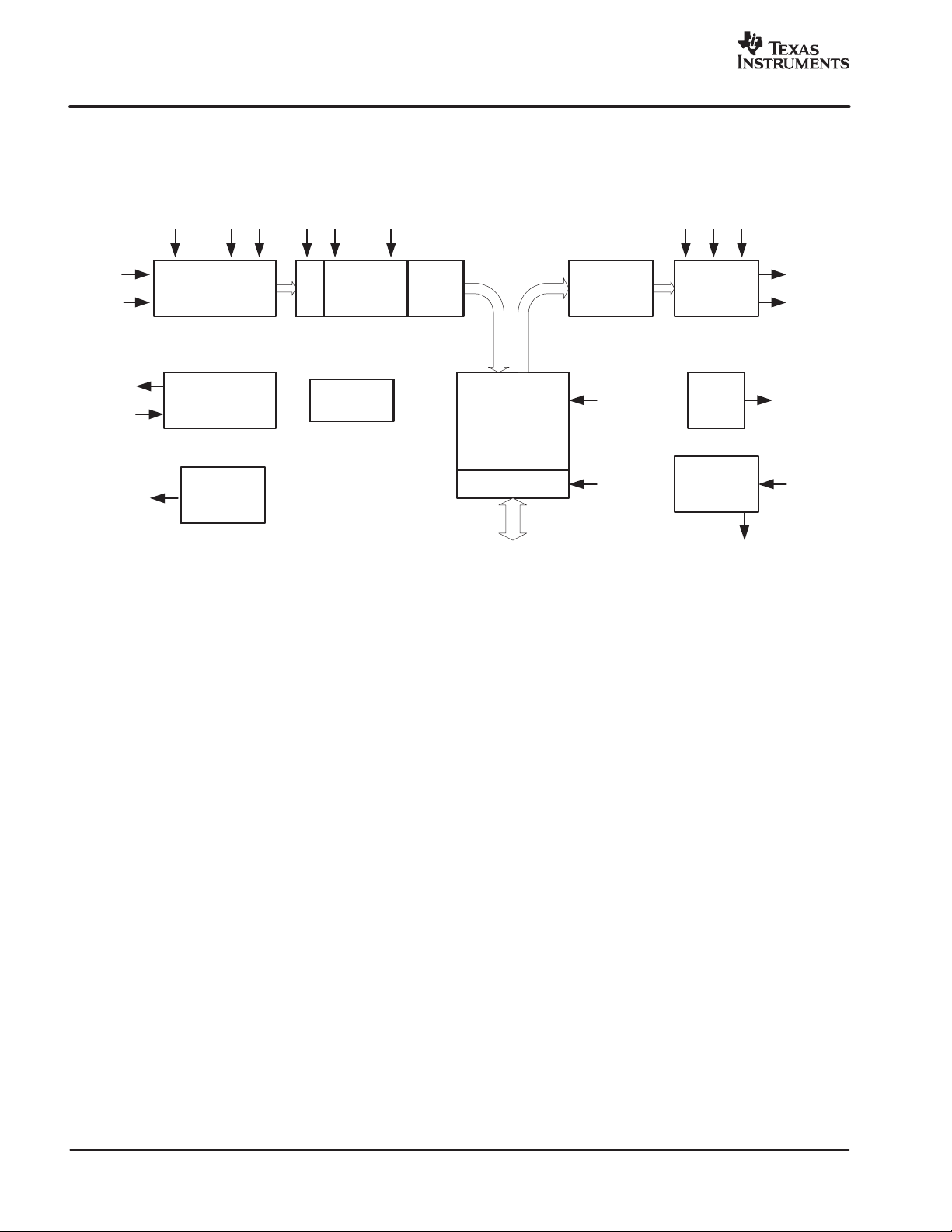
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
www.ti.com
AVINP
AVINM
VREF
VMID_FILT
PGA/Compressor
SUB_VSS
MIC/Sensor
Power and
Bias
Bandgap
Reference
AVDD
VRFILT
AVSS_REF
RC
Flt
Biases
Generator
Delta
Sigma
ADC
AVSS
Dec.
Filter
&
HPF
Output Buffers
IMODE
EXT_RST/PWDN
Digital
Interface
SCLK
SDOUT
FRAME
Delta
Sigma
DAC
DVDDMIC_VSUP
DVSSMIC_BIAS
BUF_DVDD
BUF_DVSS
SDIN
HB_VDD
HB_VSS_P
H−Bridge
Speaker
Driver
POR
Oscillator
HB_VSS_M
VOUT_P
VOUT_M
RST/LBM
VDD_OSC
VSS_OSC
MCLK
6
Page 7
www.ti.com
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
OPERATION
The power source may be a zinc-air battery operating at a typical voltage of 1.3 V. A single external de-coupling
capacitor of 1 µF is recommended on the main power supply.
VOLTAGE and CURRENT, OPERATING TEMPERATURE AT 25°C
PARAMETER TEST CONDITION MIN TYP MAX UNIT
AVDD, DVDD (All pins of type AVDD, DVDD in
pin-out table)
IS (supply current)
Steady-state battery supply
S Unloaded: H-Bridge output open
S Microphone resistor model connected (see Figure 6)
S Power supplies = 1.3 V
S No receiver attached
1.1 1.3 1.5 V
350 µA
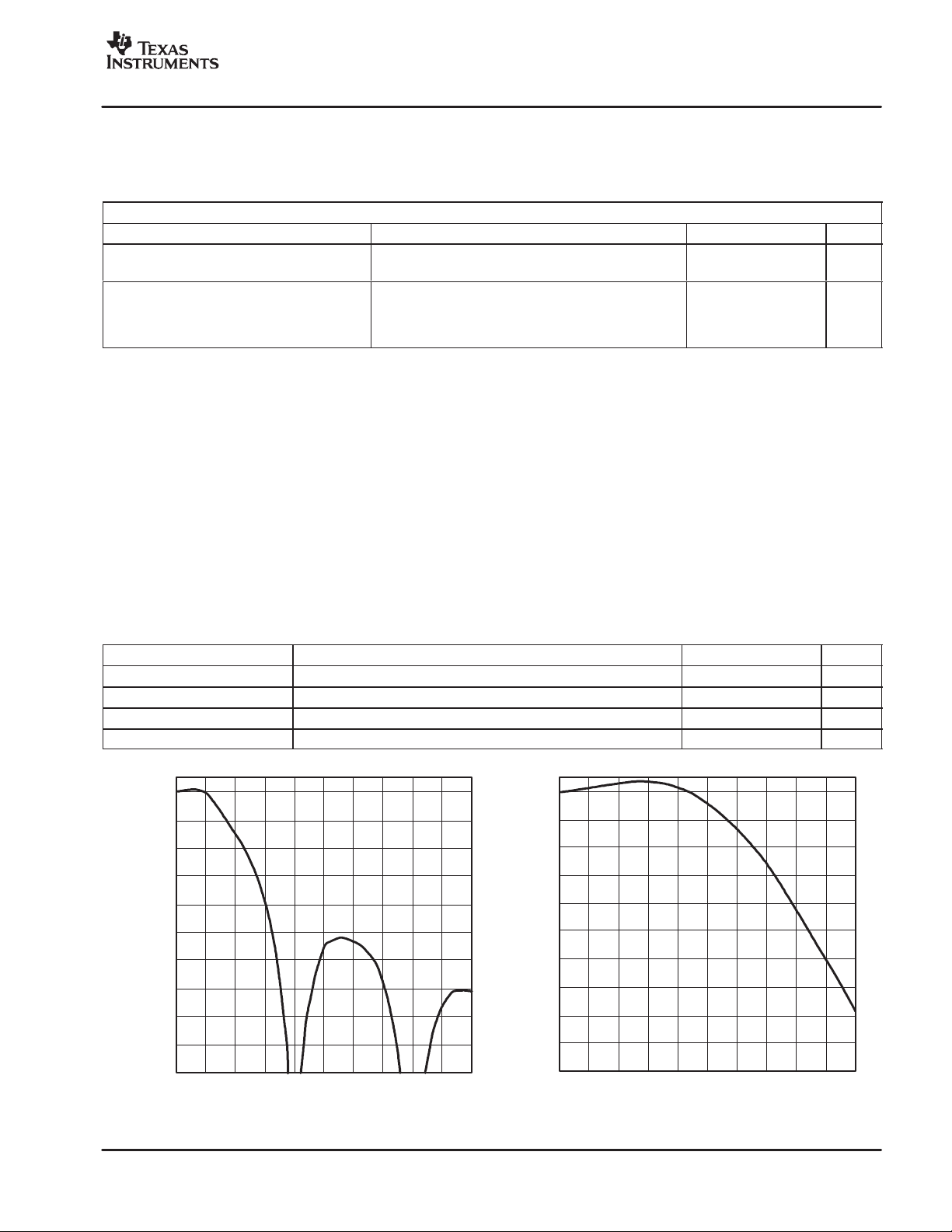
FUNCTIONAL INPUT CHANNEL PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENTS
The front end is defined as the differential signal path from the PGA/compressor inputs, AVINP, and A VINM through
the delta-sigma ADC and decimation filter.
Typical Conditions; deviations are noted in table.
D Operating Temperature Range: 0°C to 70°C. All specification are at 25°C and 1.3 V unless otherwise noted.
D AVDD, DVDD range: 1.1 V to 1.5 V
D AVINP, AVINM inputs: AC coupled, Frequency ranging from 100 Hz–10 kHz
D Measurement Bandwidth: 100 Hz–10 kHz A-weighted.
D Idle channel definition: AVINP and AVINM are both ac-coupled to AVSS.
D Typical PGAC gain range is −1 dB to 40 dB.
D Maximum input voltage: 450 mVpk.
PARAMETER TEST CONDITION MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Broad-band noise Input referred idle channel 2.4 µV RMS
THD (low level) AVIN≤ PGAC threshold (see Note 1) 0.01 0.2%
DC Offset Idle channel −5 0 5 mV
Droop at 10 kHz Referenced to amplitude at 1 kHz 1.2 dB
(1)
PGAC threshold = PGAC threshold voltage/maximum gain of PGAC.
0
−10
−20
−30
−40
−50
Gain − dB
−60
−70
−80
−90
−100
0 102030405060708090100
f − Frequency − kHz
0
−2
−4
−6
−8
−10
Gain − dB
−12
−14
−16
−18
−20
0 2 4 6 8 101214161820
f − Frequency − kHz
Figure 3. Input Channel Frequency Response With HPF Bypassed
7
Page 8

SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
www.ti.com
Analog-to-Digital Converter Filtered Input Voltage Reference
Function – Filters analog supply AVDD for DS-ADC reference. With a recommended 0.1-µF external capacitor
between pins VRFILT and AVSS_REF, the pole is set at approximately 72 Hz, with 1 µF, the pole is set at
approximately 7 Hz.
Programmable Gain Amplifier and Compressor
Function: The programmable gain amplifier and compressor (PGAC) amplifies the microphone or sensor output
signal, provides an appropriate impedance to the microphone buffer or sensor , and provides input gain compression
limiting depending on the input signal level if one is not using the fixed gain mode, where the PGAC gain is set by
selected register bits. Input compression limiting is discrete automatic gain correction (AGC) based on detecting the
peak input signal level using a peak detector circuit that has programmable time responses to provide AGC control,
and is intended to prevent a steady state input level up to the defined PGAC limit from being clipped. The
attack/release times of the PGAC are programmable by internal clock selection inside the PGAC digital level circuitry
that affects the rate of gain changes.
The PGAC has four modes of operation: automatic dual-rate (default), automatic single-rate, fixed single-rate, and
fixed immediate. Mode selection is controlled by bits 3 and 2 of the PDCREG register.
Automatic dual-rate mode (00, default):
In this mode of operation, the PGAC has two attack (gain decrease) rates and two release (gain increase) rates, which
may be selected by programming the FASTARREG and FORMAT4 registers. Internally, two counters are used to
control the compressor gain. The fast rate counter responds at the fast attack and release rates, and it counts down
at the attack rate to decrease the PGAC gain if the output of the PGAC is instantaneously larger than a preset
threshold (PGAC_THRES = 400-mV peak), or it counts up to increase the gain, up to the maximum allowed gain
as set by the PGACREG register, if the output of the PGAC falls below a second threshold, which is 3 dB lower
(283-mV peak), which provides hysteresis. Before the gain is allowed to increase, the signal at the output of the
PGAC must be below the lower threshold for a period of time which is controlled by bit 4 of PDCREG, and can be
50 ms (0, default) or 25 ms (1). The slow-rate counter responds at the slow attack and release rates, and it attempts
to track the state of the fast rate counter. The PGAC gain is determined by whichever counter is smaller. In this way,
the PGAC can respond and recover rapidly to short signal bursts while responding more slowly to the signal average.
Automatic single-rate mode (01):
In this mode of operation, the PGAC has one attack rate and one release rate, which may be selected by
programming the FASTARREG register. The operation of the PGAC is similar to the dual-rate mode, except that
the slow-rate counter is disabled and the PGAC gain is solely determined by the fast-rate counter.
Fixed single-rate mode (10):
In this mode of operation, the PGAC gain tracks the value specified in the PGACREG register regardless of the signal
amplitude, and changes in PGACREG cause the gain to decrease or increase at the corresponding fast attack or
release rate specified in the FASTARREG register.
Fixed immediate mode (11):
In this mode of operation, the PGAC gain tracks the value specified in the PGACREG register regardless of the signal
amplitude, and changes in PGACREG cause the gain to change immediately to the desired gain without stepping
through the intermediate gain states.
Bit 7 of the PGACREG register controls the PGAC gain read mode. While this bit is low (default), reading PGACREG
returns the contents of PGACREG. However, if this bit is set high, then any subsequent read(s) of PGACREG returns
the actual, instantaneous PGAC gain. This information may be useful, for example, for dynamic range expansion,
effectively undoing the compression effect in the automatic modes of operation.
Characteristics: Compression limits the PCAG output. PGACREG is a programmable register.
8
Page 9
www.ti.com
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
Specifications at 25°C, AVDD = 1.3 V
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Input Signal Parameters
Maximum signal swing Gain = −1 dB 900 mV
Block Parameters
Gain size step 0.3 0.5 0.7 dB
(1)
Based on a system clock of 1.280 MHz.
(2)
For fixed gain mode the rate is 80 KdB/s to new programmed value of gain. All intermediate 0.5 dB gain steps are passed through to reach new
gain.
PP
Delta Sigma A/D Converter/Anti-alias Filter
Function: Converts the PGAC differential output to a digital word with an equivalent dynamic range of approximately
14 bits.
Characteristics: The delta sigma ADC has a 64 oversampling ratio, a 1.28-MHz master clock, and a 40-kHz output
data rate. Digital coding is 2s complement. Tones are at least 12 dB below broadband noise level. Full-scale signal
range corresponds to +215 –1, −2
15
Specifications at 25°C, AVDD = 1.3 V
PARAMETER
Block parameters
Dynamic range −3 dB rel. to reference 87 dB
Input sample rate 1.28 MHz
Output sample rate 40 kHz
THD BW: 100 Hz−10 kHz 85 dB
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Digital High-Pass Filter
Function: Provide a high-pass filter in ADC signal path. The high-pass filter (HPF first order) removes dc offsets
introduced into the channel. FORMAT1 register selections for a 50 Hz, 100 Hz, or bypass are available.
Characteristics: Programmable selections for a 50 Hz, 100 Hz, or bypass are available. The default HPF pole is
50 Hz.
Specifications
PARAMETER
HPF corner frequency −3 dB nom mode 50 Hz
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Delta Sigma DAC
Function: Generates an over-sampled bit string to drive the H-bridge output amplifier such that when filtered
reproduces the desired analog waveform.
Characteristics: A 32 times over-sampled modulator multi-bit design.
Specifications
fd
(input_data)
f
clk
PARAMETER
Signal; BW = 10 kHz 40 kHz
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
640 kHz
9
Page 10
H-Bridge Load Switching
AVSS
Idle channel, measured at output of channel,
Broadband noise
Idle channel, measured at output of channel,
Vrms
Maximum output swing
V
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
www.ti.com
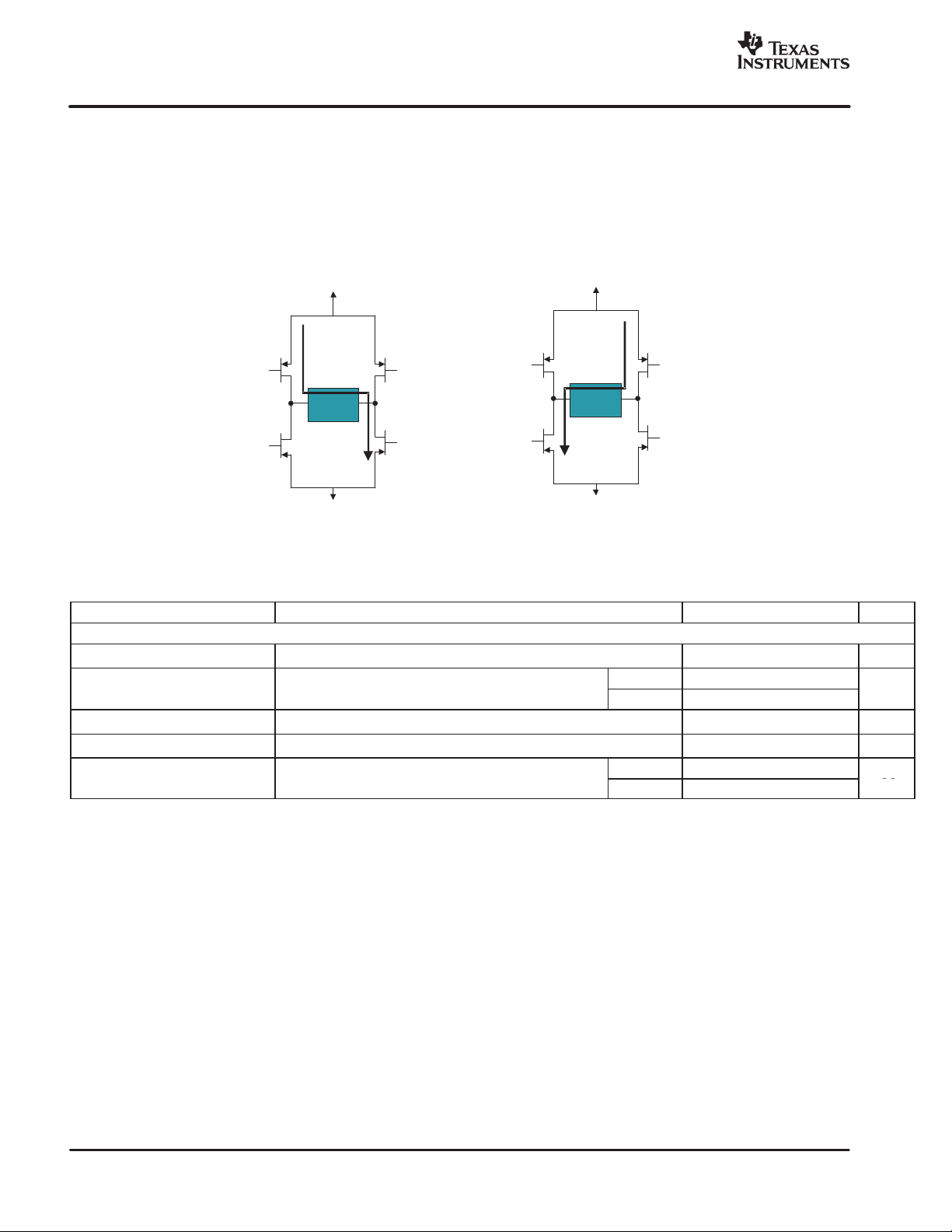
H-bridge Output Driver
Function: An H-bridge output driver efficiently converts the delta sigma DAC modulator output signals. The external
load provides the low-pass filtering that recovers the differential analog signal from the H-bridge.
Characteristics: Standard H-bridge configuration with transistors sized to differentially drive the load impedance.
The load impedance is complex and a function of frequency.
Inverting Phase
VDD ( vbat)
OUTMM
OUTP OUTM
Receiver
Load
AVSS
OUTPP
NOTE:
Noninverting Phase
VDD (vbat)
OUTPM
OUTP OUTM
OUTMP
VDD does not necessarily have to be connected to the same potential as AVDD, it could be connected to a higher potential than A VDD, equal
to A V DD, but not less than AVDD.
Receiver
Load
OUTMM
OUTPP
OUTPM
OUTMP
Figure 4. Definition of Phase and Output Switching Current Polarity
Specifications at 25°C, HB_VDD = 1.3 V
PARAMETER
Block Parameters
DC offset Idle channel; Differential across VOUT_P and VOUT_M −5 0 5 mV
BW = 100 Hz−10 kHz, HB_VDD = 1.3 V , A-weighted
THD BW = 100 Hz−10 kHz 0.03%
Switching frequency 640 kHz
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Fixed Q 33
Adaptive Q 12
Fixed Q 3/4 HB_VDD
Adaptive Q HB_VDD
µ
PP
10
Page 11
www.ti.com
V
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
Microphone Power Supply
Function: The microphone power supply circuit provides a constant power supply voltage and bias current for the
microphone preamp or sensor bias, provides a low-noise voltage reference (ac ground) for the PGAC, provides
regulated PGAC comparator threshold levels, provides bandgap regulated POR comparator trip voltage levels, and
provides a bandgap regulated current for the biases generator circuit.
Characteristics: The low-dropout regulator configuration or single stage, single-pole amplifier drives an external
0.1-µF capacitor. The regulator does not oscillate under no-load or loaded conditions. The circuit supplies up to 50-µA
of continuous current.
Specifications at 25°C, AVDD = 1.3 V
PARAMETER
MIC_VSUP IL = 20 µA 0.87 0.94 0.97 V
VMID_FILT 0.59 × A VDD 0.78 V
PSRR 0.1-µF external bypass cap from MIC_VSUP to AVSS2. 55 dB
Output impedance 1.5 kΩ
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
MCLK Output
Function: Provides a clock signal for external use.
Specifications at 25°C, VDD_OSC, DVDD, BUF_DVDD = 1.3 V
PARAMETER
Frequency 4.7 5.12 5.5 MHz
Jitter RMS jitter 150 ps
Duty cycle 50%
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Power-On Reset
Function: Provides a reset signal upon power up (stable voltage reference) that initializes the digital interface. It also
provides a gating signal to the delta-sigma DAC modulator to prevent audible pops and clicks from erroneous data
sent to the H-bridge circuit at power up and during periods when battery voltage has degraded below 1.05 V for an
extended period of time (typically greater than 44 µs). The reset signal is asynchronous to MCLK. Digital interface
does not start operating until after t
_valid has transpired.
(VDD)
POR has to:
D Deal with system’s on/off switch bounce lasting 100 ms or less.
D Detect when the power supply AVDD is ≥1.1 V to enable the H-bridge output.
D Provide kick-start to oscillator.
D Detect when VDD degrades below 1.05 V for a period of time that is nontransient, and gate H-bridge output.
Specifications at 25°C, AVDD = 1.3 V
PARAMETER
t
_valid:
(VDD)
Time VDD considered valid at powerup after switch bounce has settled.
Allowed transient spike below 1.05 V before H-bridge output and digital interface
are not asserted.
POR on 1.1
POR off 1.05
TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
VDD > 1.1 V 100 ms
VDD < 1.05 V 44 µs
11
Page 12

SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
www.ti.com
DIGITAL INTERFACE
Function: The digital interface can be selected (IMODE=LOW) as a serial audio/control interface (SACI), which is
the McBSP DSP-codec protocol, or (IMODE=HIGH), a serial peripheral interface (SPI). Either SACI or SPI sends
out a 16-bit audio stream from the ∆−Σ ADC and receives a 20-bit audio stream going to the ∆−Σ DAC/H-Bridge.
Several control functions, READ/WRITE to user registers, are also included totaling five 8-bit registers. Four pins,
SCLK, FRAME, SDIN and SDOUT, are employed in SACI or SPI. An internal register map exists that contains
read/write program registers for a variety of FORMA T (user) settings. The register bits that are designated not used
will always read back zero or voltage level VSS regardless of what is written to them.
DIG INTERFACE PIN I/O DESCRIPTION
SCLK Output Bit shift clock. SCLK has an internal pull down.
FRAME Output Data frame sync: controls the separation of audio channels and provides a reset/synchronization
to the interface’s internal state machine. FRAME has an internal pull down.
SDIN Input Serial audio/control data input pin.
SDOUT Input Serial audio/control data output pin.
IMODE Input Interface protocol selection pin. LOW=SACI, HIGH=SPI.
MCLK Output Clock output pin.
MASTER
AIC111
NOTE A: The dotted line indicates the connection is not essential for communication to work.
SDOUT
FRAME FSX
SDIN DX
SCLK
MCLK
(See Note A)
DR
FSR
CLKR
CLKS
CLKX
CLKIN
SLAVE
C54x
Figure 5. AIC111 McBSP DSP-Codec Interface
McBSP DSP-Codec (SACI) Protocol
Use this protocol when interfacing to TI DSPs.
D The SACI works in a master mode.
D SCLK = 1.28 MHz. FRAME (= 40 kHz) has a 50% duty cycle. FRAME is an output.
D 32-bit control/audio data, written on the SDIN pin, consist of a 20-bit audio word going to the ∆−Σ DAC, and a
12-bit control word.
D DAC input has two modes of operation, a 20-bit mode, and a 16-bit mode.
D The 12-bit control word consists of: a R/W bit, 3 address bits, and 8-bits of control register content. Note that
the R/W bit is defined as 0=READ, and 1=WRITE.
D When the 3 address bits are all zeros, the control function of the SACI is disabled.
D 24-bit audio/control data, read from the SDOUT pin, consist of one 16-bit output from the ∆−Σ ADC followed by
an 8-bit control word.
D All data/control words are formatted as the MSB first.
12
Page 13

www.ti.com
20-Bit Mode
D/A Input
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
D19 − D0
AIC111 Input
16-Bit Mode
D/A Input
AIC111 Input
D19 D19 D19 D19
D19 − D0
D19 D19 D19
D19 D19
D19
NOTE B: For 5-bit left shift, digital word is limited to 15 bits with sataration.
Figure 6. AIC111 Data Output
D19 − D0
D19 − D4
D19 − D4
D19 − D4
D19 − D4
D19 − D4
D18 − D4
0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
See Note B
0
Shift = 0
Shift = 1
Shift = 2
Shift = 3
Shift = 4
Shift = 5
13
Page 14

F
S
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
www.ti.com
C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0 D19 D18
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0 D15 D14
D6
14
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
D18D19 D17 D16 W/R A2 A1 A0
RAME
SCLK
1 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 166
SDIN
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DOUT
Figure 7. AIC111 DSP-Codec (SACI) Signals (Read = 0, Write = 1)
Page 15

www.ti.com
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
SLAVE
MSP430x
MASTER
AIC111
GPIO
FRAME STE
SDOUT
SDIN SOMI
SCLK
MCLK
SIMO
UCLK
MCLK
Figure 8. AIC111 SPI I/O Diagram
SPI Protocol
D AIC111 can also implement a master SPI protocol.
D SCLK supplies a bit shift clock of 1.28 MHz to the SPI port of a slave device.
D FRAME must be in the active low state prior to data transaction and must stay low for the duration of data
transaction. Before communication, there are eight silent cycles on SCLK. During this period FRAME also sends
a pulse to reset the slave device.
D When the control function is not required, the AIC111 transmits a 16-bit audio word to and receives a 20-bit audio
word from the slave device in every FRAME cycle.
D A WRITE/READ of an 8-bit user register (address 0x01 to 0x07) takes two FRAME cycles.
D All data/control words are formatted as the MSB first.
15
Page 16

SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
www.ti.com
A2D0 W/R A1 A0
D1
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 321 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 101112131415166
3231
D18
D19 D17 D16 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
Don’t Care
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D0
NOTE:
16
FRAME
SCLK
SDIN
SDOUT
If A2, A1, and A0 = 0, one gets audio data only and W/R is a don’t care. If in the previous frame A2, A1, and A0 = 0, then one gets both audio
and control data depending on the W/R bit defined as Read = 0 and Write = 1.
Figure 9. AIC111 SPI Signals
Page 17

www.ti.com
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
C2C4 C3 C1 C0
C7 C6 C5 C2C4 C3 C1 C0
D1
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 321 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 101112131415166
3231
D18
D19 D17 D16 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 C7 C6 C5
Don’t Care
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D0
FRAME
NOTE:
SDIN shows writing to A2, A1, and A0 specified from the previous frame. SDOUT shows reading from A2, A1, and A0 specified from a
SCLK
SDIN
SDOUT
different previous frame.
Figure 10. AIC111 SPI Signals
17
Page 18

SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
www.ti.com
Digital Interface Timing
PARAMETER
F_sclk SCLK frequency 1.28 MHz
F_frame FRAME frequency F-sclk/32 MHz
MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Digital Interface Block Diagram
PGA/Compressor
SCLK
FRAME
SDIN
SDOUT
IMODE
MCLK
McBSP/SPI
Register Map and Register Bit Definitions
ADDRESS REGISTER NAME DETAILED DESCRIPTION
0x00 Reserved Reserved for future use
0x01 PGACREG PGAC gain register
0x02 HPFSFTREG HPF and shift control register
0x03 PDCREG Power-down control register
0x04 FASTARREG Fast attack/release rate control register
0x05 SLOWARREG Slow attack/release rate control register
0x06−07 Reserved Reserved for future use
NOTE:
Do not write to the reserved registers.
CONTROL REGISTERS
CONTROL LOGIC
DATA BLOCK
ADC
DAC/H−Bridge
Oscillator
Power−on Reset
Mic Power/VREF
18
Page 19

www.ti.com
PGACREG
BIT NAME FUNCTION DEFAULT=0x46
HPFSFTREG
BIT NAME FUNCTION DEFAULT=0x11
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
7 PGAC_READ_MODE Select register contents or actual gain to read
0: Read FORMAT0 register contents (default)
1: Read actual PGAC gain
6:0 PGAC_GAIN [6:0] PGAC gain adjustment (0.5 dB steps). A full table is found in the
Appendix Section of this data sheet.
0x52 = +40.0 dB
0x51 = +39.5 dB
0x50 = +39.0 dB
…
0x46 =+34.0 dB (default)
….
0x01 = −0.5 dB
0x00 = −1.0 dB
7 DBUFF_EN Enable weak (1/2 strength) dig I/O buffer
6:5 HPF_CTL [1:0] Control bits for high-pass filter
00: normal mode
01: HPF bypass
10: 100 Hz corner frequency
11: Not used
4:2 SHIFT [2:0] Select shift bits when ADC 16-b output is used as DAC 20-b input.
000: no shift −24 db gain
001: 1b left shift −18 dB gain
010: 2b left shift −12 dB gain
011: 3b left shift −6 dB gain
100: 4b left shift (default) 0 dB gain
101: 5b left shift +6 dB gain
11X: 5b left shift
1:0 DAC_MODE Select DAC mode of operation.
00: DAC off, powered down
01: 16-bit input goes through shifter (default)
10: 20-bit input bypasses shifter
11: ADC→DAC digital loopback
PDCREG
BIT NAME FUNCTION DEFAULT=0x00
7 DAC_ADAPTIVE_Q 0 = fixed quantization, 1 = adaptive quantization
6 HB_OUT_EN H-bridge output enable
5 HB_DRIVE H-bridge drive strength, 0 = 40 Ω, 1 = 20 Ω
4 HIST_TIMEOUT_SEL PGAC hysteresis timeout select
0: 50 ms (default)
1: 25 ms
3:2 PGAC_GAIN_MODE Set gain mode of PGAC
00: Automatic, dual rate (default)
01: Automatic, single rate
10: Fixed, single rate
11: Fixed, immediate
1 MIC_VSUP_PD Power down MIC_VSUP
0 FRONTEND_PD Power down PGAC+ADC
19
Page 20

SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
FASTARREG PGAC Fast Rates
BIT NAME FUNCTION DEFAULT=0xF7
7:4 ATTACK<7:4> 1111: Attack rate = 80000 dB/s
1110: Attack rate = 40000 dB/s
1101: Attack rate = 20000 dB/s
1100: Attack rate = 10000 dB/s
1011: Attack rate = 5000 dB/s
1010: Attack rate = 2500 dB/s
1001: Attack rate = 1250 dB/s
1000: Attack rate = 625 dB/s
0111: Attack rate = 312.5 dB/s
0110: Attack rate = 156.25 dB/s
0101: Attack rate = 78.13 dB/s
0100: Attack rate = 39.1 dB/s
0011: Attack rate = 19.53 dB/s
0010: Attack rate = 9.77 dB/s
0001: Attack rate = 4.88 dB/s
0000: Attack rate = 2.44 dB/s
3:0 RELEASE<3:0> 1111: Release rate = 80000 dB/s
1110: Release rate = 40000 dB/s
…
0001: Release rate = 4.88 dB/s
0000: Release rate = 2.44 dB/s
SLOWARREG PGAC Slow Rates (Dual Rate Mode Only)
BIT NAME FUNCTION DEFAULT=0x42
7:4 ATTACK<7:4> 1111: Attack rate = 80000 dB/s
1110: Attack rate = 40000 dB/s
…
0001: Attack rate = 4.88 dB/s
0000: Attack rate = 2.44 dB/s
3:0 RELEASE<3:0> 1111: Release rate = 80000 dB/s
1110: Release rate = 40000 dB/s
…
0001: Release rate = 4.88 dB/s
0000: Release rate = 2.44 dB/s
www.ti.com
20
Page 21

www.ti.com
PGAC
PGAC_GAIN<6:0>
PGAC
PGAC_GAIN<6:0>
PGAC GAIN
APPENDIX
PGAC GAIN VALUES
BUS NAME HEX VALUE BINARY GAIN (DB)
PGAC PGAC_GAIN<6:0>
PGAC PGAC_GAIN<6:0>
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
0x52 1010010 40
0x51 1010001 39.5
0x50 1010000 39
0x4F 1001111 38.5
0x4E 1001110 38
0x4D 1001101 37.5
0x4C 1001100 37
0x4B 1001011 36.5
0x4A 1001010 36
0x49 1001001 35.5
0x48 1001000 35
0x47 1000111 34.5
0x46 1000110 34
0x45 1000101 33.5
0x44 1000100 33
0x43 1000011 32.5
0x42 1000010 32
0x41 1000001 31.5
0x40 1000000 31
0x3F 0111111 30.5
0x3E 0111110 30
0x3D 0111101 29.5
0x3C 0111100 29
0x3B 0111011 28.5
0x3A 0111010 28
0x39 0111001 27.5
0x38 0111000 27
0x37 0110111 26.5
0x36 0110110 26
0x35 0110101 25.5
0x34 0110100 25
0x33 0110011 24.5
0x32 0110010 24
0x31 0110001 23.5
0x30 0110000 23
0x2F 0101111 22.5
0x2E 0101110 22
0x2D 0101101 21.5
0x2C 0101100 21
0x2B 0101011 20.5
0x2A 0101010 20
0x29 0101001 19.5
0x28 0101000 19
0x27 0100111 18.5
0x26 0100110 18
0x25 0100101 17.5
0x24 0100100 17
0x23 0100011 16.5
21
Page 22

PGAC (Continued)
PGAC_GAIN<6:0>
PGAC
PGAC_GAIN<6:0>
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
PGAC GAIN VALUES
BUS NAME HEX VALUE BINARY GAIN (DB)
PGAC (Continued) PGAC_GAIN<6:0>
PGAC PGAC_GAIN<6:0>
Default 0x00 0000000 −1
www.ti.com
0x22 0100010 16
0x21 0100001 15.5
0x20 0100000 15
0x1F 0011111 14.5
0x1E 0011110 14
0x1D 0011101 13.5
0x1C 0011100 13
0x1B 0011011 12.5
0x1A 0011010 12
0x19 0011001 11.5
0x18 0011000 11
0x17 0010111 10.5
0x16 0010110 10
0x15 0010101 9.5
0x14 0010100 9
0x13 0010011 8.5
0x12 0010010 8
0x11 0010001 7.5
0x10 0010000 7
0x0F 0001111 6.5
0x0E 0001110 6
0x0D 0001101 5.5
0x0C 0001100 5
0x0B 0001011 4.5
0x0A 0001010 4
0x09 0001001 3.5
0x08 0001000 3
0x07 0000111 2.5
0x06 0000110 2
0x05 0000101 1.5
0x04 0000100 1
0x03 0000011 0.5
0x02 0000010 0
0x01 0000001 −0.5
22
Page 23

www.ti.com
TI TMS320C54xx APPLICATION CIRCUIT
AVDD
DVDD
BUF_DVDDBUF_DVSS
ZINC AIR
BATTERY
1.3V
VCC
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
VSS
MIC_VSUP
MIC_BIAS
Microphone
1.3V
HB_VDD
HB_VSS
Speaker
AIC111
H
B
R
I
D
G
E
SDIN
SDOUT
I/O
B
U
FRAME
F
F
E
RST/LBM
R
S
MCLK
EXT_RST/PWDN
SCLK
DX
DR
RST
CLKIN
CLKR
CLKS
CLKX
M
c
B
S
P
FSX
FSR
’C54x
AVSS
DVSS
LBM = Low Battery Monitor
Figure 11. Interfacing to the TMS320C54xx for a Hearing Aid Application
Required external capacitors:
D 1-µF coupling capacitor on AVINP, AVINM
D 1-µF from VMID_FILT to analog ground
D 1-µF from VREF to analog ground
D 0.1-µF from MIC_VSUP to analog ground
D At least 0.1-µF from VRFILT to analog ground. 1-µF from VRFILT to analog ground is recommended.
23
Page 24

SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
TI MSP430F12x APPLICATION CIRCUIT
1.3 V
www.ti.com
Microphone
Speaker
MIC_VSUP
MIC_BIAS
AVDD
AIC111
DVDD
BUF_DVDD
SCLK
SDIN
I/O
SDOUT
B
U
F
FRAME
F
E
R
S
RST/LBM
MCLK
2.8 V
(See Note A)
RST/NMI
P2.5
INCLK
SOMI
SIMO
STE
XIN
VSS
VCC
MSP430F12x
AVSS
DVSS
BUF_DVSS
LBM = Low Battery Monitor ’430 Can Also Use
EXT_RST/PWDN to Reset or Power Down the AIC111
Note A: P2.5 enables the MSP430F12x to shut down the AIC111 when desired.
Figure 12. Interfacing to the MSP430F12x for a Hearing Aid Application
24
Page 25

www.ti.com
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
MECHANICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL
Packaging
The AIC111 is available in a 32-pin quad QFN 5x5-mm package. The AIC111 will be available 3rd quarter 2003 as
bare solder ball bumped die intended for direct PCB mounting (also known as wafer scale packaging).
D For QFN packaged part in tubes order: AIC111RHB.
D For QFN packaged part in tape and reel order: AIC111RHBR.
D For ball bumped die (in waffle pack) order: AIC111YE (Preview, available 3rd quarter 2003).
D For ball bumped die (in tape and reel) order: AIC111YER (Preview, available 3rd quarter 2003).
BOND PAD PITCH AND DIE AREA
Die dimensions X = 2737.62 µ, Y = 3175.02 µ,
Maximum die area (includes scribe area) 13.47kmil2 (8.69mm2)
Minimum bond pad pitch 202.95 µ or 7.99 mil
Nearest PITCH
PAD (#) PAD (#) (micron) (mil)
7
30
12
14
16
28
18
20
21
22
25
9
10
23
1
32
4
27
17
6
2
3
31
13
15
15
29
19
19
20
21
26
10
11
24
32
28
16
8
1
5
7
1
2
202.950
202.950
237.690
237.690
237.690
241.200
256.410
256.410
256.410
256.410
287.651
295.470
295.470
306.360
327.147
327.147
356.940
357.034
359.453
369.450
371.520
380.700
(107.78 mil, 125.0 mil)
(2,74 mm, 3,18 mm)
(7.990)
(7.990)
(9.358)
(9.358)
(9.358)
(9.496)
(10.095)
(10.095)
(10.095)
(10.095)
(11.325)
(11.633)
(11.633)
(12.061)
(12.880)
(12.880)
(14.053)
(14.056)
(14.152)
(14.545)
(14.627)
(14.988)
25
Page 26
Bump height
SLAS382 − JUNE 2003
Number of pins 32
Pad locations: Bond Pad Coordinates Bond Pad Dimensions
Units: microns Pad # Xcenter Ycenter Diameter
Dimensions: X = 2737.62 Y = 3175
Bond pad origin: X = 0.000 Y = 0.000
Bond pad offset: X = 0.000 Y = 0.000
(X,Y) = (0,0) is located at the left bottom of the die by pads 8 and 9.
See section 1.6, Figure 1−1.
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
154.080
154.080
154.080
154.080
154.080
154.080
154.080
154.080
410.310
705.780
1001.250
1327.860
1565.550
1803.240
2040.930
2278.620
2574.990
2574.990
2574.990
2574.990
2574.990
2574.990
2574.990
2574.990
2574.990
2371.590
1910.430
1553.850
1312.650
955.530
752.580
410.310
2808.990
2437.470
2056.770
1676.070
1319.130
938.430
568.980
366.030
162.630
162.630
162.630
162.630
162.630
162.630
162.630
162.630
366.030
782.550
1038.960
1295.370
1551.780
1808.190
2188.890
2495.250
2808.990
3012.390
2994.390
3012.390
3012.390
3012.390
3012.390
3012.390
www.ti.com
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
70.020
DIE THICKNESS
TYPICAL TOLERANCE
Final die thickness Z (without solder bump) 29.59 mil or 725 µm ±0.79 mil or 20 µm
SOLDER BUMP
D Bump metal composition: 37% Pb (lead)/63% Sn (tin)
D Type: Spherical
BUMP SPEC. TYPICAL TOLERANCE NOTE
100 µm +8 µm Tolerance across a single die.
+16 µm Tolerance across any wafer.
Re-flow temperature 183°C
WAFFLE SCALE PACKAGE DISCLAIMERS FOR AIC11YE AND AIC11YER
D The AIC111’s die bond pads, their peripheral placement, passivation opening, and layout are in accordance with
ASE’s Bumping Design Guide revision D, June, 2001.
D The final application is assumed to use plastic overmolding where the die is hermetically sealed, and the
maximum ratings apply only to the QFN package and not to the WSCP.
26
Page 27

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
9-Oct-2007
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
AIC111RHB ACTIVE QFN RHB 32 73 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
AIC111RHBG4 ACTIVE QFN RHB 32 73 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
AIC111RHBR ACTIVE QFN RHB 32 3000 Green(RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
AIC111RHBRG4 ACTIVE QFN RHB 32 3000 Green(RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
AIC111YE ACTIVE DIESALE YE 32 39 TBD Call TI Call TI
AIC111YER ACTIVE DIESALE YE 32 1000 TBD Call TI Call TI
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in
a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS), Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt), or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check
http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements
for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered
at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt): This component has a RoHS exemption for either 1) lead-based flip-chip solder bumps used between the die and
package, or 2) lead-based die adhesive used between the die and leadframe. The component is otherwise considered Pb-Free (RoHS
compatible) as defined above.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame
retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous material)
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
Call TI Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
Call TI Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
Call TI Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
Call TI Level-2-260C-1 YEAR
(3)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder
temperature.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is
provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the
accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take
reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on
incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited
information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI
to Customer on an annual basis.
Addendum-Page 1
Page 28

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com
TAPE AND REEL INFORMATION
19-Mar-2008
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package
Type
AIC111RHBR QFN RHB 32 3000 330.0 12.4 5.3 5.3 1.5 8.0 12.0 Q2
Package
Drawing
Pins SPQ Reel
Diameter
(mm)
Reel
Width
W1 (mm)
A0 (mm) B0 (mm) K0 (mm) P1
(mm)W(mm)
Pin1
Quadrant
Pack Materials-Page 1
Page 29

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com
19-Mar-2008
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package Type Package Drawing Pins SPQ Length (mm) Width (mm) Height (mm)
AIC111RHBR QFN RHB 32 3000 340.5 333.0 20.6
Pack Materials-Page 2
Page 30

Page 31

Page 32

Page 33

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements,
and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should
obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are
sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard
warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where
mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products and applications, customers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask work right,
or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a
warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual
property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied
by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive
business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional
restrictions.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all
express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not
responsible or liable for any such statements.
TI products are not authorized for use in safety-critical applications (such as life support) where a failure of the TI product would reasonably
be expected to cause severe personal injury or death, unless officers of the parties have executed an agreement specifically governing
such use. Buyers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their applications, and
acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning their products
and any use of TI products in such safety-critical applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support that may be
provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in
such safety-critical applications.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI products are
specifically designated by TI as military-grade or "enhanced plastic." Only products designated by TI as military-grade meet military
specifications. Buyers acknowledge and agree that any such use of TI products which TI has not designated as military-grade is solely at
the Buyer's risk, and that they are solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in automotive applications or environments unless the specific TI products are
designated by TI as compliant with ISO/TS 16949 requirements. Buyers acknowledge and agree that, if they use any non-designated
products in automotive applications, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet such requirements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Interface interface.ti.com Medical www.ti.com/medical
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
RFID www.ti-rfid.com Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
RF/IF and ZigBee® Solutions www.ti.com/lprf Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
 Loading...
Loading...