Telefunken TV-CR210-C Service Manual

SERVICE MANUAL
Sec. 1: Main Section
I Specifications
I Preparation for Servicing
I Adjustment Procedures
I Schematic Diagrams
I CBA’s
I Exploded views
I Parts List
Sec. 2: Deck Mechanism Section
I Standard Maintenance
I Alignment for Mechanism
I Disassembly/Assembly of Mechanism
I Alignment Procedures of Mechanism
I Deck Exploded Views
I Deck Parts List
VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER
TVCR-210(C)
TVCR-610(C)
PAL
MAIN SECTION
VIDEO CASSETTE RECORDER
TVCR-210(C)/TVCR-610(C)
Sec. 1: Main Section
I Specifications
I Preparation for Servicing
I Adjustment Procedures
I Schematic Diagrams
I CBA’s
I Exploded Views
I Parts List
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1-1
Important Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2-1
Standard Notes for Servicing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3-1
Preparation for Servicing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4-1
Cabinet Disassembly Instructions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5-1
Electrical Adjustment Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6-1
Block Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7-1
Function Indicator Symbols. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7-7
Schematic Diagrams / CBA’s and Test Points. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8-1
Waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-9-1
Wiring Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-10-1
IC Pin Function Descriptions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-11-1
Lead Identifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-12-1
Exploded Views. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-13-1
Mechanical Parts List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-14-1
Electrical Parts List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-15-1
SPECIFICATIONS
Description Unit Minimum Nominal Maximum Remark
1. Video
1-1. Video Output (PB) Vp-p 0.8 1.0 1.2 FL6A
1-2. Video Output (R/P) Vp-p 0.8 1.0 1.2
1-3. Video S/N Y (R/P) dB 40 45
1-4. Video Color S/N AM (R/P) dB 37 41 SP Mode
1-5. Video Color S/N PM (R/P) dB 30 36 SP Mode
1-6. Resolution (PB) Line 230 245 SP Mode
2. Servo
2-1. Jitter Low µsec 0.07 0.12 SP Mode
2-2. Wow & Flutter % 0.3 0.5 SP Mode
3. Normal Audio
3-1. Output (PB) dBV -9 -6 -3 SP Mode
3-2. Output (R/P) dBV -9 -6 -1.5 SP Mode
3-3. S/N (R/P) dB 36 41 SP Mode
3-4. Distortion (R/P) % 1.0 4.0 SP Mode
3-5. Freq. resp (R/P) at 200Hz dB -7 -4 SP Mode
(-20dB ref. 1kHz) at 6kHz dB -10 -4 SP Mode
SP Mode,
W/O Burst
4. Tuner
4-1. Video output Vp-p 0.8 1.0 1.2 E-E Mode
4-2. Video S/N dB 39 42 E-E Mode
4-3. Audio output dB -10 -6 -2 E-E Mode
4-4. Audio S/N dB 40 46 E-E Mode
5. Hi-Fi Audio [ TVCR-610(C) ]
5-1. Output dBV -12 -8 -4 SP Mode
5-2. Dynamic Range dB 70 85 SP Mode
5-3. Freq. resp (6dB B.W) Hz 20 ~ 20K SP Mode
Note: Nominal specs represent the design specs. All units should be able to approximate these – some will exceed
and some may drop slightly below these specs. Limit specs represent the absolute worst condition that still might
be considered acceptable; In no case should a unit fail to meet limit specs.
1-1-1 HG2E0SP

IMPORTANT SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Product Safety Notice
Some electrical and mechanical parts have special
safety-related characteristics which are often not evident from visual inspection, nor can the protection they
give necessarily be obtained by replacing them with
components rated for higher voltage, wattage, etc.
Parts that have special safety characteristics are identified by a ! on schematics and in parts lists. Use of a
substitute replacement that does not have the same
safety characteristics as the recommended replacement part might create shock, fire, and/or other hazards. The Product’s Safety is under review
continuously and new instructions are issued whenever appropriate. Prior to shipment from the factory,
our products are carefully inspected to confirm with
the recognized product safety and electrical codes of
the countries in which they are to be sold. However, in
order to maintain such compliance, it is equally important to implement the following precautions when a set
is being serviced.
Precautions during Servicing
A. Parts identified by the ! symbol are critical for
safety. Replace only with part number specified.
B. In addition to safety, other parts and assemblies
are specified for conformance with regulations
applying to spurious radiation. These must also be
replaced only with specified replacements.
Examples: RF converters, RF cables, noise blocking capacitors, and noise blocking filters, etc.
C. Use specified internal wiring. Note especially:
1)Wires covered with PVC tubing
2)Double insulated wires
3)High voltage leads
D. Use specified insulating materials for hazardous
live parts. Note especially:
1)Insulation tape
2)PVC tubing
3)Spacers
4)Insulators for transistors
E. When replacing AC primary side components
(transformers, power cord, etc.), wrap ends of
wires securely about the terminals before soldering.
F. Observe that the wires do not contact heat produc-
ing parts (heatsinks, oxide metal film resistors, fusible resistors, etc.).
G. Check that replaced wires do not contact sharp
edges or pointed parts.
H. When a power cord has been replaced, check that
5 - 6 kg of force in any direction will not loosen it.
I. Also check areas surrounding repaired locations.
J. Be careful that foreign objects (screws, solder
droplets, etc.) do not remain inside the set.
K. Crimp type wire connector
The power transformer uses crimp type connectors
which connect the power cord and the primary side
of the transformer. When replacing the transformer,
follow these steps carefully and precisely to prevent
shock hazards.
Replacement procedure
1)Remove the old connector by cutting the wires at a
point close to the connector.
Important: Do not re-use a connector. (Discard it.)
2)Strip about 15 mm of the insulation from the ends
of the wires. If the wires are stranded, twist the
strands to avoid frayed conductors.
3)Align the lengths of the wires to be connected.
Insert the wires fully into the connector.
4)Use a crimping tool to crimp the metal sleeve at its
center. Be sure to crimp fully to the complete closure of the tool.
L. When connecting or disconnecting the internal
connectors, first, disconnect the AC plug from the
AC outlet.
1-2-1 U29PSFP
Safety Check after Servicing
Examine the area surrounding the repaired location for
damage or deterioration. Observe that screws, parts,
and wires have been returned to their original positions. Afterwards, do the following tests and confirm
the specified values to verify compliance with safety
standards.
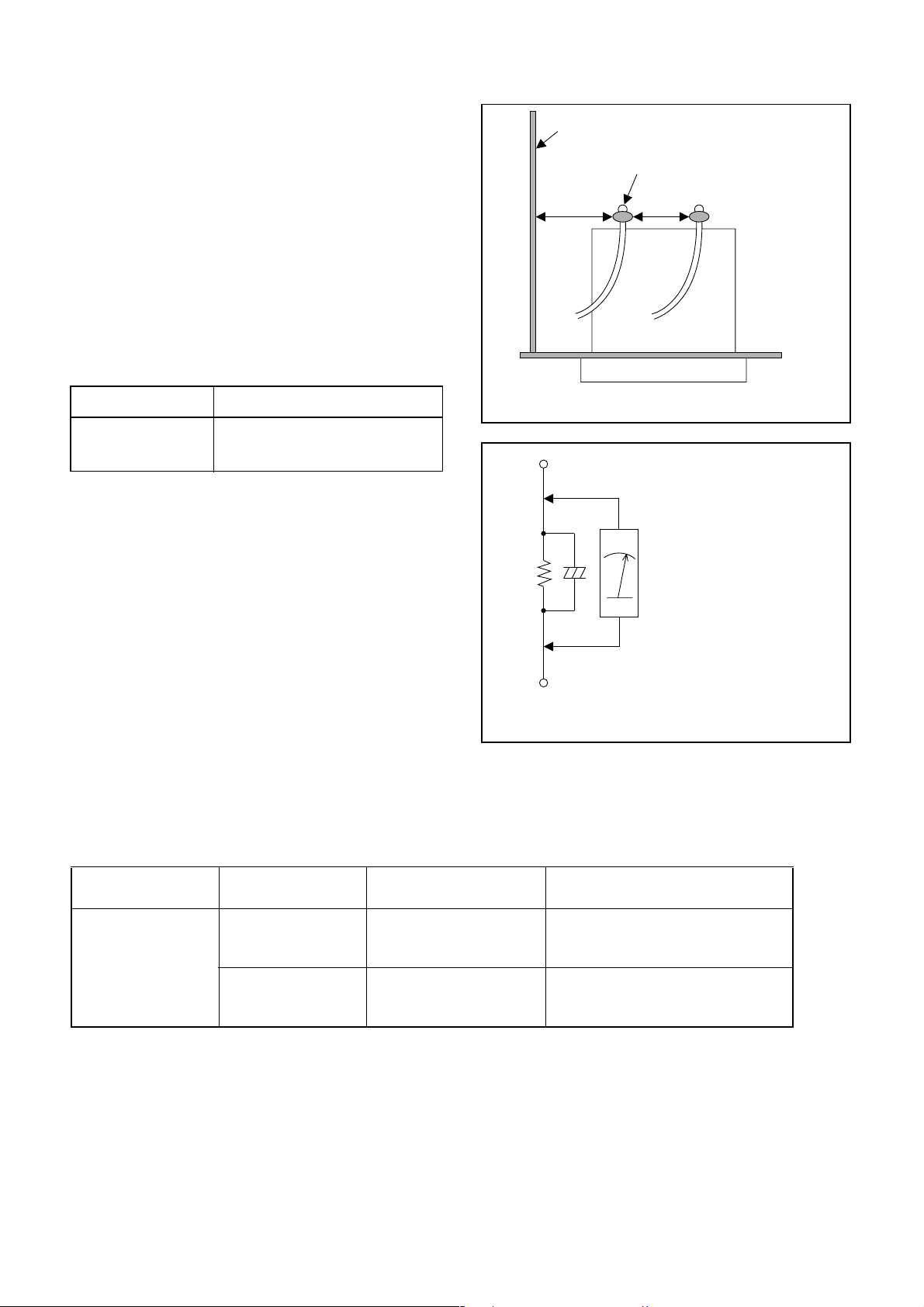
1. Clearance Distance
When replacing primary circuit components, confirm
specified clearance distance (d) and (d’) between soldered terminals, and between terminals and surrounding metallic parts. (See Fig. 1)
Table 1 : Ratings for selected area
AC Line Voltage Clearance Distance (d), (d’)
220 to 240 V
Note: This table is unofficial and for reference only.
Be sure to confirm the precise values.
≥ 3mm(d)
≥ 6 mm(d’)
2. Leakage Current Test
Confirm the specified (or lower) leakage current
between B (earth ground, power cord plug prongs)
and externally exposed accessible parts (RF terminals, antenna terminals, video and audio input and
output terminals, microphone jacks, earphone jacks,
etc.) is lower than or equal to the specified value in the
table below.
Measuring Method (Power ON) :
Insert load Z between B (earth ground, power cord
plug prongs) and exposed accessible parts. Use an
AC voltmeter to measure across the terminals of load
Z. See Fig. 2 and the following table.
Chassis or Secondary Conductor
Primary Circuit Terminals
dd'
Exposed Accessible Part
Z
One side of
B
Power Cord Plug Prongs
AC Voltmeter
(High Impedance)
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Table 2: Leakage current ratings for selected areas
AC Line Voltage Load Z Leakage Current (i)
2kΩ RES.
Connected in
parallel
220 to 240 V
50kΩ RES.
Connected in
parallel
Note: This table is unofficial and for reference only. Be sure to confirm the precise values.
i≤0.7mA AC Peak
i≤2mA DC
i≤0.7mA AC Peak
i≤2mA DC
1-2-2 U29PSFP
One side of power cord plug
prongs (B) to:
RF or
Antenna terminals
A/V Input, Output
STANDARD NOTES FOR SERVICING
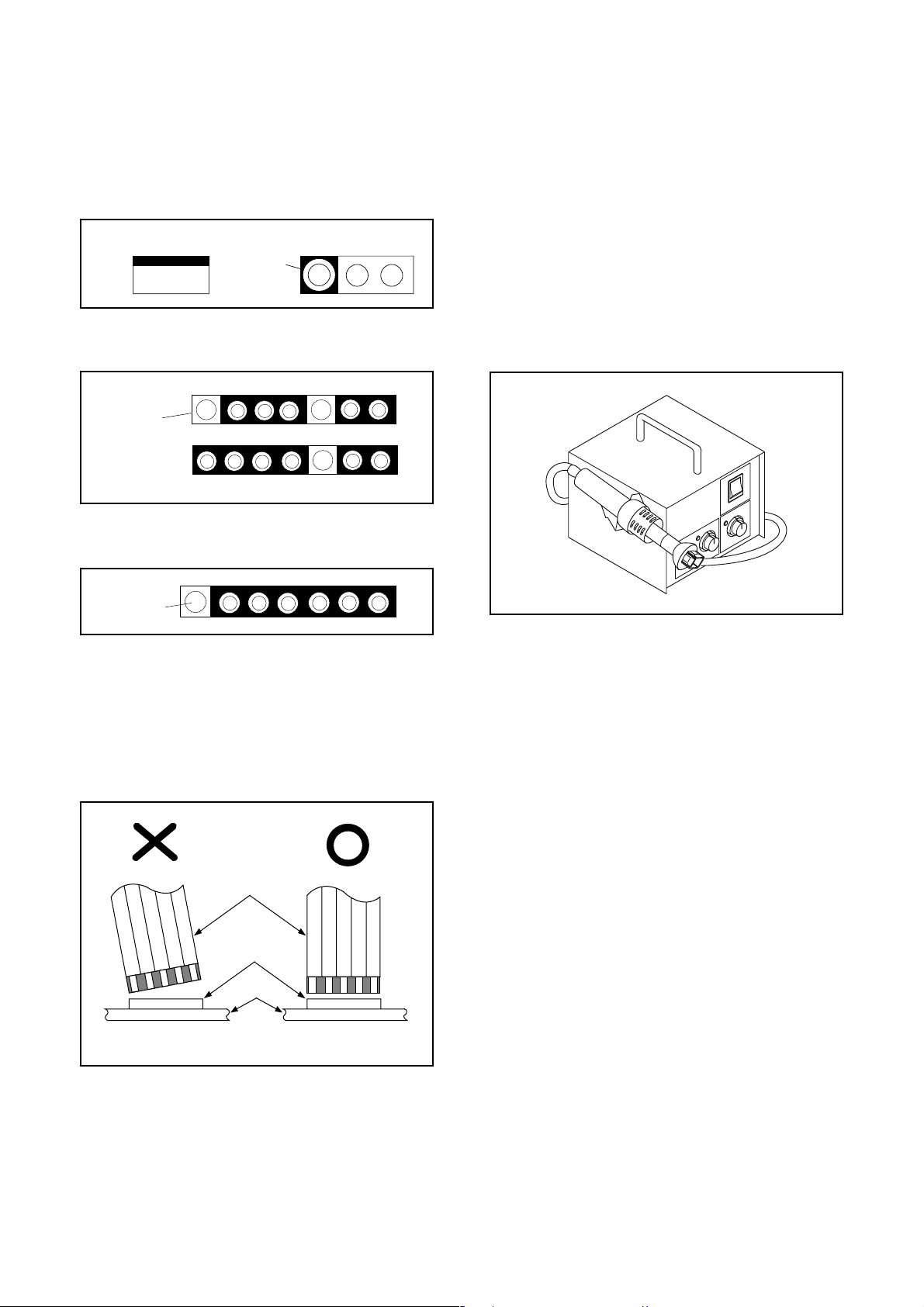
Circuit Board Indications
a. The output pin of the 3 pin Regulator ICs is indi-
cated as shown.
Top View
Out
b. For other ICs, pin 1 and every fifth pin are indicated
as shown.
Pin 1
c. The 1st pin of every male connector is indicated as
shown.
Input
In
Bottom View
5
10
Pb (Lead) Free Solder
When soldering, be sure to use the Pb free solder.
How to Remove / Install Flat Pack-IC
1. Removal
With Hot-Air Flat Pack-IC Desoldering Machine:.
(1) Prepare the hot-air flat pack-IC desoldering
machine, then apply hot air to the Flat Pack-IC
(about 5 to 6 seconds). (Fig. S-1-1)
Pin 1
Instructions for Connectors
1. When you connect or disconnect the FFC (Flexible
Foil Connector) cable, be sure to first disconnect
the AC cord.
2. FFC (Flexible Foil Connector) cable should be
inserted parallel into the connector, not at an angle.
FFC Cable
Connector
CBA
* Be careful to avoid a short circuit.
Fig. S-1-1
(2) Remove the flat pack-IC with tweezers while apply-
ing the hot air.
(3) Bottom of the flat pack-IC is fixed with glue to the
CBA; when removing entire flat pack-IC, first apply
soldering iron to center of the flat pack-IC and heat
up. Then remove (glue will be melted). (Fig. S-1-6)
(4) Release the flat pack-IC from the CBA using twee-
zers. (Fig. S-1-6)
Caution:
1. The Flat Pack-IC shape may differ by models. Use
an appropriate hot-air flat pack-IC desoldering
machine, whose shape matches that of the Flat
Pack-IC.
2. Do not supply hot air to the chip parts around the
flat pack-IC for over 6 seconds because damage to
the chip parts may occur. Put masking tape around
the flat pack-IC to protect other parts from damage.
(Fig. S-1-2)
1-3-1 NOTE_1
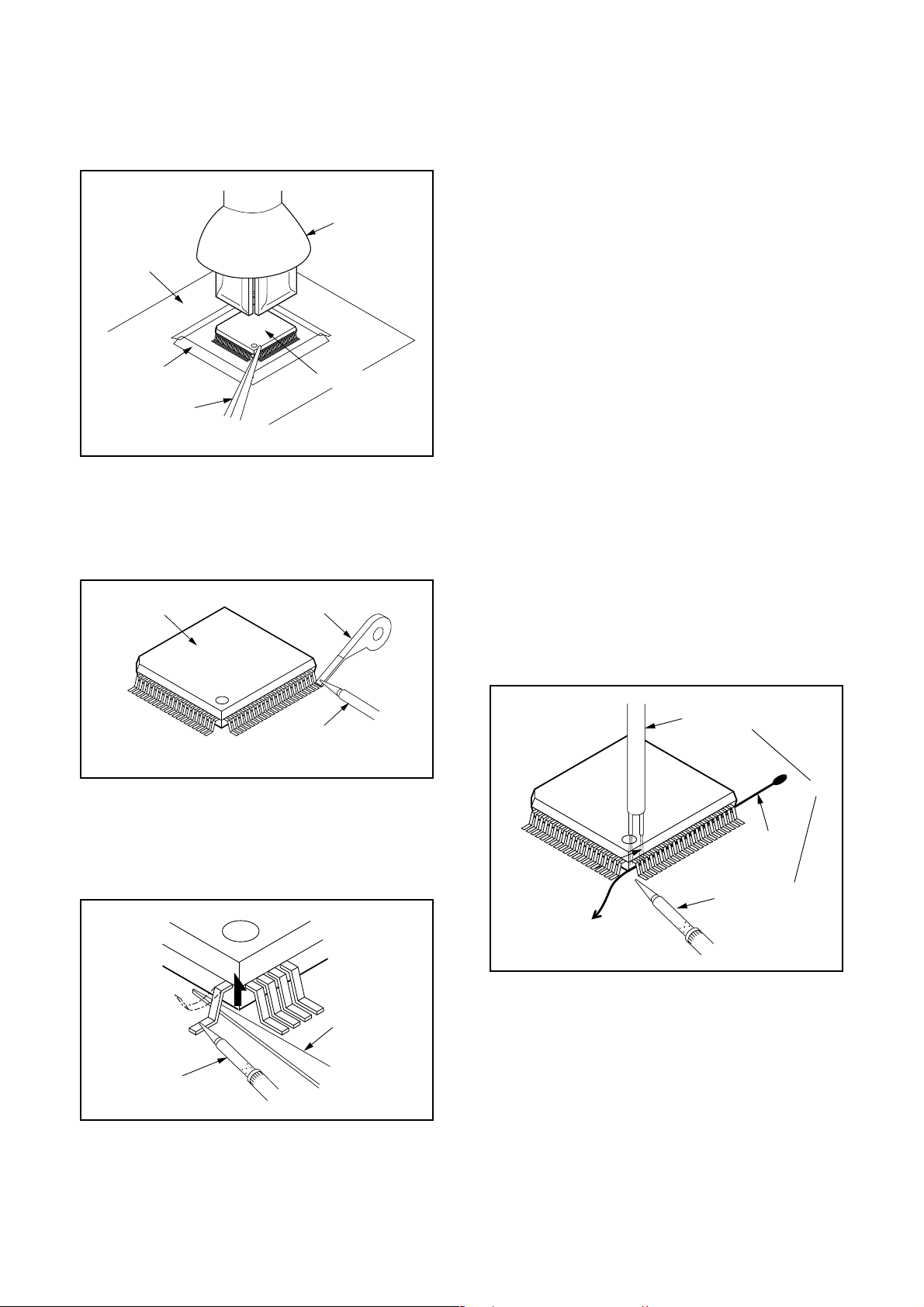
3. The flat pack-IC on the CBA is affixed with glue, so
be careful not to break or damage the foil of each
pin or the solder lands under the IC when removing
it.
Hot-air
Flat Pack-IC
Desoldering
CBA
Masking
Tape
Machine
Flat Pack-IC
Tweezers
Fig. S-1-2
With Soldering Iron:
(1) Using desoldering braid, remove the solder from all
pins of the flat pack-IC. When you use solder flux
which is applied to all pins of the flat pack-IC, you
can remove it easily. (Fig. S-1-3)
Flat Pack-IC
Desoldering Braid
(3) Bottom of the flat pack-IC is fixed with glue to the
CBA; when removing entire flat pack-IC, first apply
soldering iron to center of the flat pack-IC and heat
up. Then remove (glue will be melted). (Fig. S-1-6)
(4) Release the flat pack-IC from the CBA using twee-
zers. (Fig. S-1-6)
With Iron Wire:
(1) Using desoldering braid, remove the solder from all
pins of the flat pack-IC. When you use solder flux
which is applied to all pins of the flat pack-IC, you
can remove it easily. (Fig. S-1-3)
(2) Affix the wire to a workbench or solid mounting
point, as shown in Fig. S-1-5.
(3) While heating the pins using a fine tip soldering
iron or hot air blower, pull up the wire as the solder
melts so as to lift the IC leads from the CBA contact
pads as shown in Fig. S-1-5
(4) Bottom of the flat pack-IC is fixed with glue to the
CBA; when removing entire flat pack-IC, first apply
soldering iron to center of the flat pack-IC and heat
up. Then remove (glue will be melted). (Fig. S-1-6)
(5) Release the flat pack-IC from the CBA using twee-
zers. (Fig. S-1-6)
Note:
When using a soldering iron, care must be taken
to ensure that the flat pack-IC is not being held by
glue. When the flat pack-IC is removed from the
CBA, handle it gently because it may be damaged
if force is applied.
Soldering Iron
Fig. S-1-3
(2) Lift each lead of the flat pack-IC upward one by
one, using a sharp pin or wire to which solder will
not adhere (iron wire). When heating the pins, use
a fine tip soldering iron or a hot air desoldering
machine. (Fig. S-1-4)
Sharp
Pin
Fine Tip
Soldering Iron
Fig. S-1-4
Hot Air Blower
or
Iron Wire
Soldering Iron
To Solid
Mounting Point
Fig. S-1-5
1-3-2 NOTE_1
Instructions for Handling
Semi-conductors
CBA
Tweezers
Fine Tip
Soldering Iron
Flat Pack-IC
Fig. S-1-6
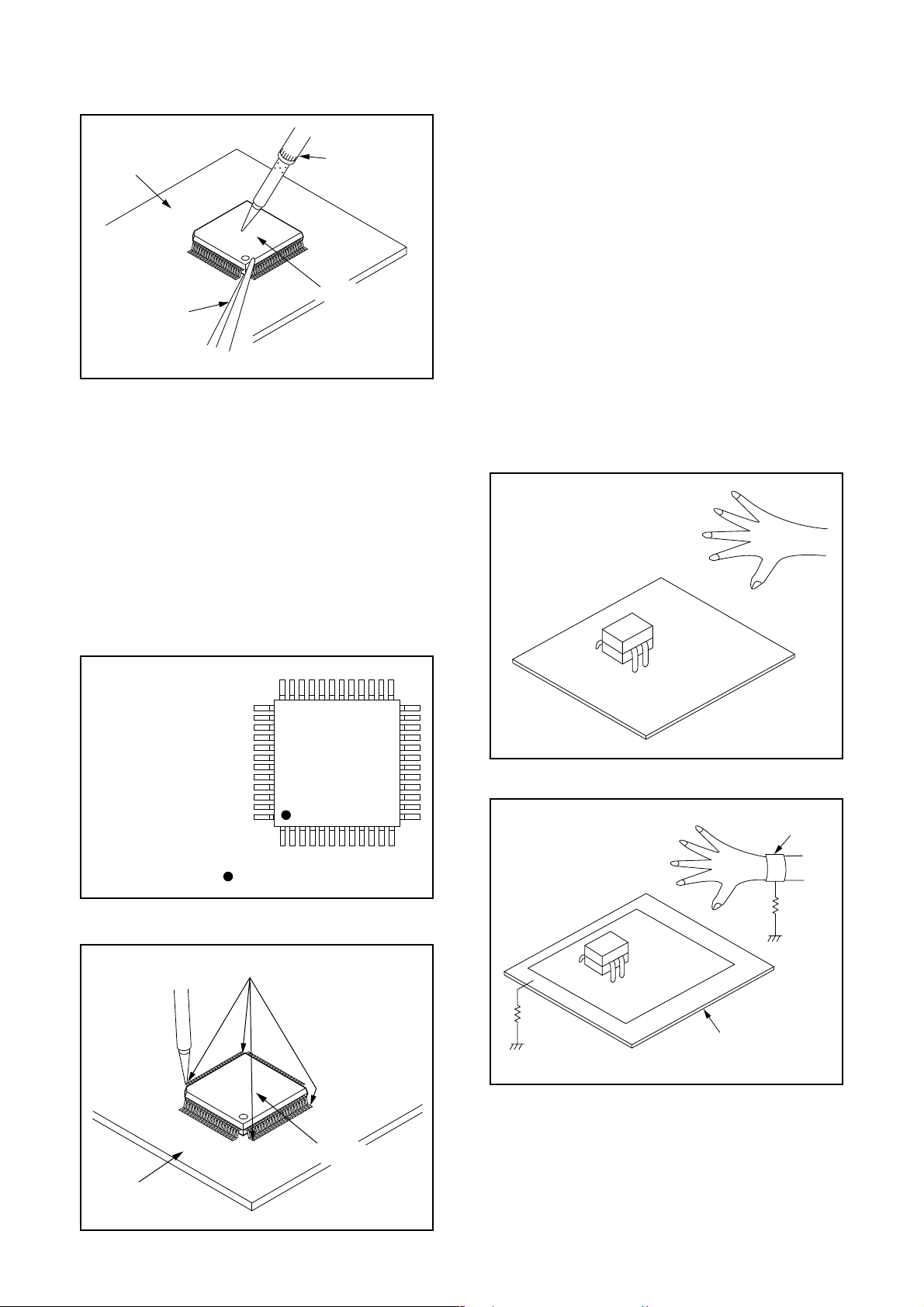
2. Installation
(1) Using desoldering braid, remove the solder from
the foil of each pin of the flat pack-IC on the CBA so
you can install a replacement flat pack-IC more
easily.
(2) The “ I ” mark on the flat pack-IC indicates pin 1.
(See Fig. S-1-7.) Be sure this mark matches the 1
on the PCB when positioning for installation. Then
presolder the four corners of the flat pack-IC. (See
Fig. S-1-8.)
(3) Solder all pins of the flat pack-IC. Be sure that none
of the pins have solder bridges.
Electrostatic breakdown of the semi-conductors may
occur due to a potential difference caused by electrostatic charge during unpacking or repair work.
1. Ground for Human Body
Be sure to wear a grounding band (1MΩ) that is properly grounded to remove any static electricity that may
be charged on the body.
2. Ground for Workbench
Be sure to place a conductive sheet or copper plate
with proper grounding (1MΩ) on the workbench or
other surface, where the semi-conductors are to be
placed. Because the static electricity charge on clothing will not escape through the body grounding band,
be careful to avoid contacting semi-conductors with
your clothing.
<Incorrect>
CBA
Example :
Pin 1 of the Flat Pack-IC
is indicated by a " " mark.
Presolder
Fig. S-1-7
<Correct>
1MΩ
Grounding Band
1MΩ
CBA
Conductive Sheet or
Copper Plate
CBA
Flat Pack-IC
Fig. S-1-8
1-3-3 NOTE_1
PREPARATION FOR SERVICING
How to Enter the Service Mode
About Optical Sensors
Caution:
An optical sensor system is used for the Tape Start
and End Sensors on this equipment. Carefully read
and follow the instructions below. Otherwise the unit
may operate erratically.
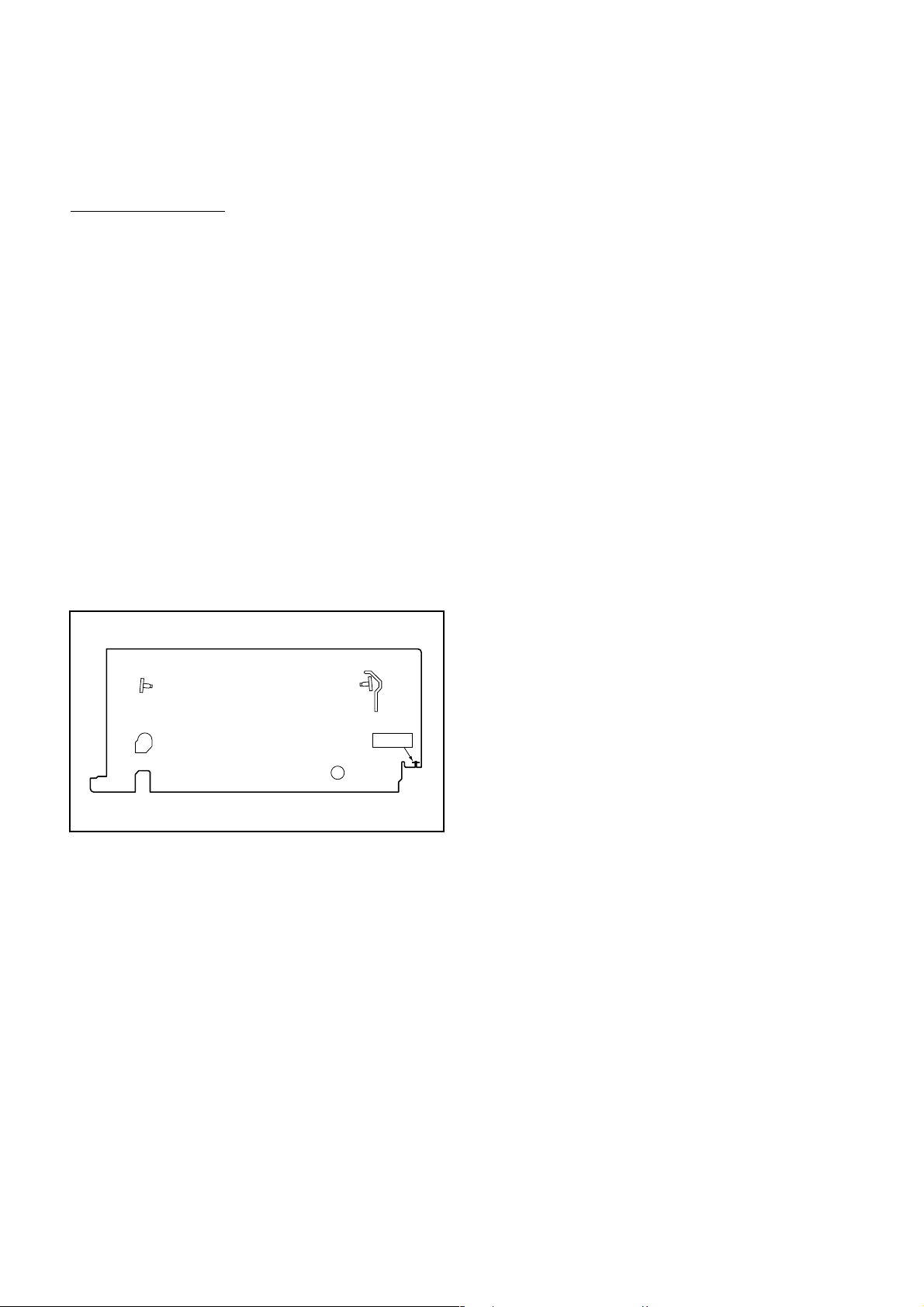
What to do for preparation
Insert a tape into the Deck Mechanism Assembly and
press the PLAY button. The tape will be loaded into
the Deck Mechanism Assembly. Make sure the power
is on, connect TP507 (S-INH) to GND. This will stop
the function of Tape Start Sensor, Tape End Sensor
and Reel Sensors. (If these TPs are connected before
plugging in the unit, the function of the sensors will
stay valid.) See Fig. 1.
Note: Because the Tape End Sensors are inactive, do
not run a tape all the way to the start or the end of the
tape to avoid tape damage.
Q505
Q504
TP507
S-INH
Fig. 1
1-4-1 HG240PFS
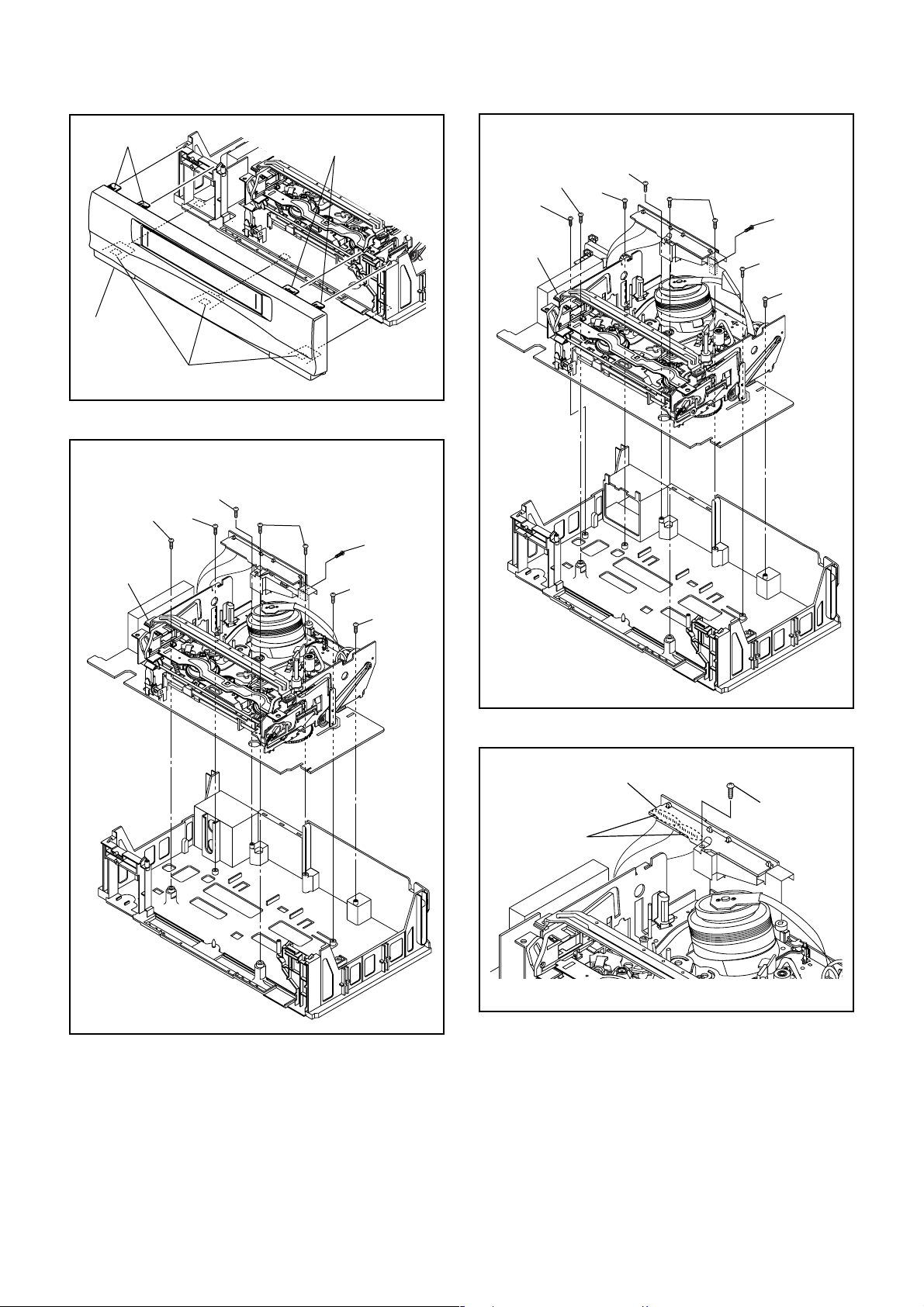
CABINET DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
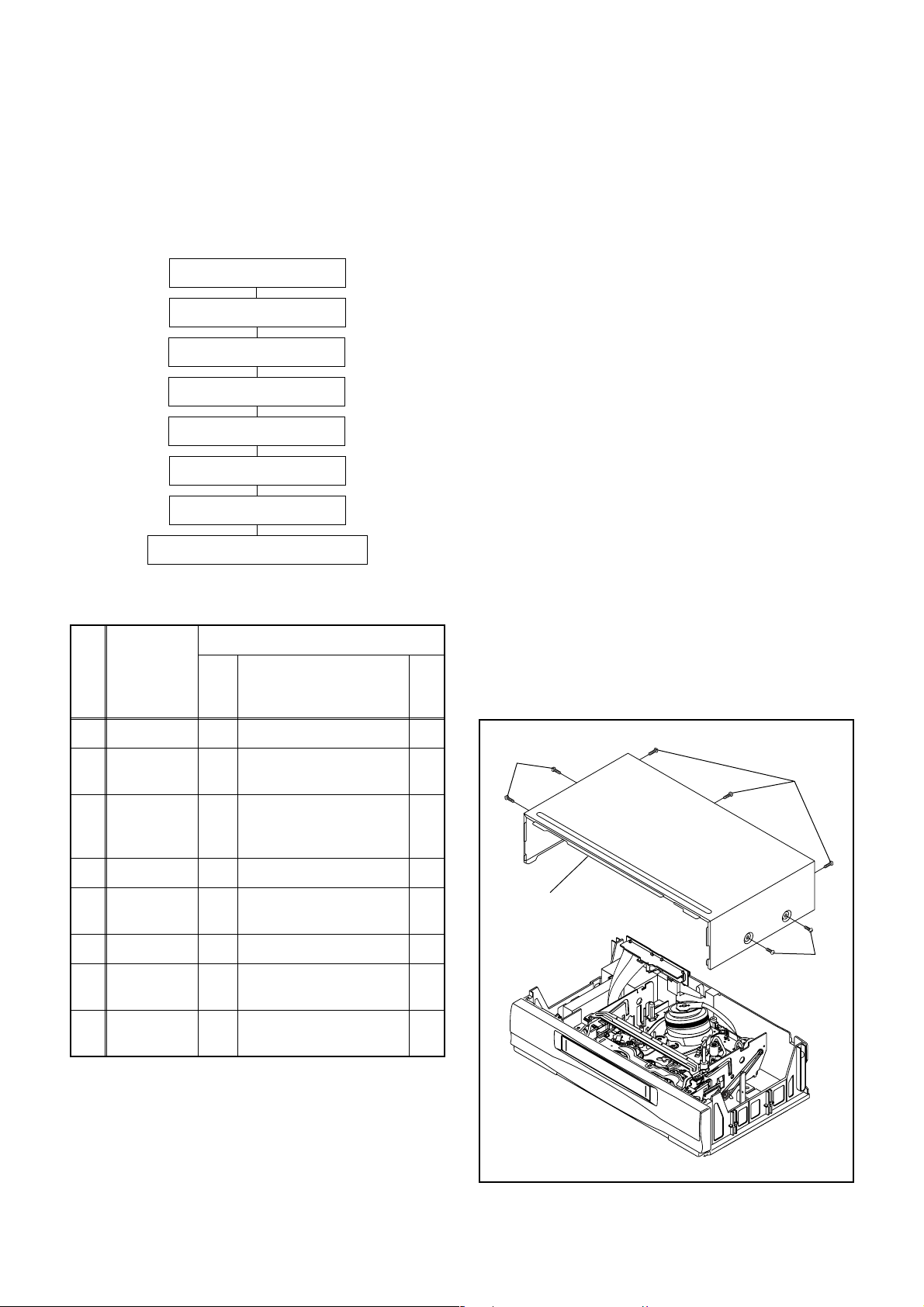
1. Disassembly Flowchart
This flowchart indicates the disassembly steps to gain
access to item(s) to be serviced. When reassembling,
follow the steps in reverse order. Bend, route, and
dress the cables as they were originally.
[1] Top Case
[2] Front Assembly
[3] VCR Chassis Unit
[4] Jack CBA
[5] Deck Assembly
[6] Main CBA
[7] Cylinder Shield
[8] Jack Board [ TVCR-610(C) ]
2. Disassembly Method
REMOVAL
ID/
LOC
.No.
PA RT
REMOVE/*UNHOOK/
Fig.
UNLOCK/RELEASE/
No.
UNPLUG/DESOLDER
Note
(1): Identification (location) No. of parts in the figures
(2): Name of the part
(3): Figure Number for reference
(4): Identification of parts to be removed, unhooked,
unlocked, released, unplugged, unclamped, or
desoldered.
P=Spring, L=Locking Tab, S=Screw,
CN=Connector
*=Unhook, Unlock, Release, Unplug, or Desolder
e.g. 2(S-2) = two Screws (S-2),
2(L-2) = two Locking Tabs (L-2)
(5): Refer to “Reference Notes.”
Reference Notes
CAUTION: Locking Tabs (L-1) and (L-2) are fragile.
Be careful not to break them.
1. Remove five Screws (S-2), two Screws (S-3):
TVCR-210(C), three Screws (S-3): TVCR-610(C),
and Screw (S-4). Then, slowly lift the VCR Chassis
Unit (Deck Assembly, Jack CBA and Main CBA) up.
2. When reassembling, solder wire jumpers as shown
in Fig. D5.
3. Before installing the Deck Assembly, be sure to
place the pin of LD-SW on Main CBA as shown in
Fig. D6. Then, install the Deck Assembly while
aligning the hole of Cam Gear with the pin of LDSW, the shaft of Cam Gear with the hole of LD-SW
as shown in Fig. D6.
[1] Top Case D1 7(S-1) -
Front
[2]
Assembly
VCR Chassis
[3]
Unit
[4] Jack CBA D4 Desolder, (S-5) -
Deck
[5]
Assembly
[6] Main CBA D5 *(L-3) --- [ TVCR-610(C) ] -
Cylinder
[7]
Shield
Jack Board
[8]
[ TVCR-610(C) ]
↓
(1)
↓
(2)
D2 *3(L-1),*4(L-2) -
5(S-2), (S-4),
D3-1
2(S-3) --- [ TVCR-210(C) ]
D3-2
3(S-3) --- [ TVCR-610(C) ]
D5
2(S-6), Desolder 2,3
D6
D5 (S-7) -
D5 ---------- -
↓
(3)
↓
(4)
(S-1)
(S-1)
1
[1] Top Case
(S-1)
↓
(5)
Fig. D1
1-5-1 HG2E0DC
(L-2)
[2] Front
Assembly
(L-2)
[ TVCR-610(C) ]
(S-2)
(S-2)
(S-3)
(S-3)
[3]VCR
Chassis
Unit
(S-2)
(S-4)
(S-3)
(S-2)
(L-1)
[ TVCR-210(C) ]
(S-2)
(S-2)
[3] VCR
Chassis
Unit
(S-3)
Fig. D2
(S-2)
(S-4)
(S-3)
(S-2)
Fig. D3-2
[4] Jack CBA
(S-5)
Fig. D3-1
Desolder
Fig. D4
1-5-2 HG2E0DC
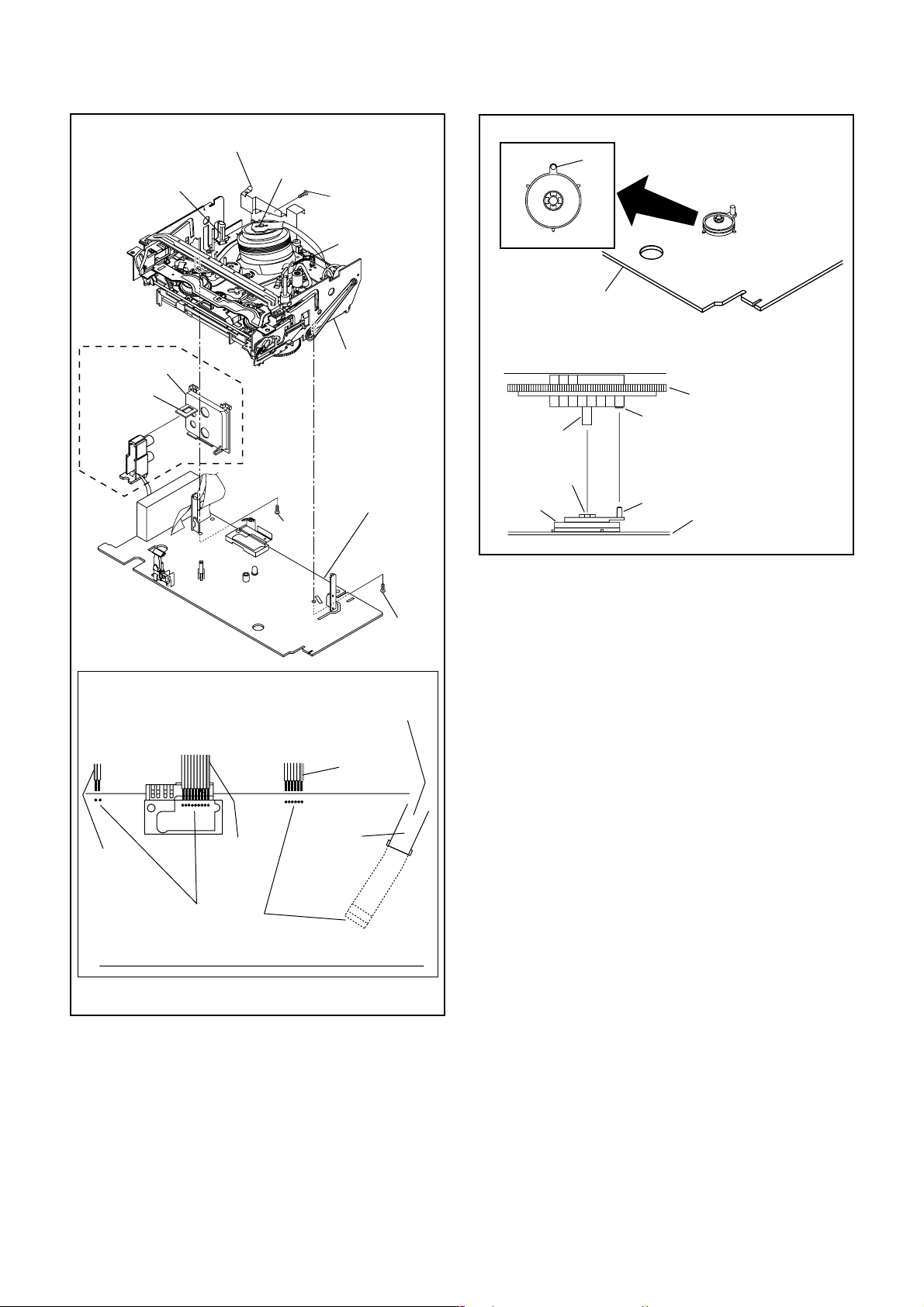
[7] Cylinder Shield
FE Head
[ TVCR-610(C) ]
Cylinder Assembly
(S-7)
ACE Head
Assembly
Pin
SW507
LD-SW
[6] Main CBA
[8] Jack Board
(L-3)
From
From
FE Head
Cylinder
Assembly
(S-6)
TOP VIEW
From
ACE Head
Assembly
[5] Deck
Assembly
[6] Main CBA
(S-6)
From
Capstan Motor
Assembly
Lead with
blue stripe
[5] Deck Assembly
Shaft
Hole
LD-SW
Cam Gear
Hole
Pin
[6] Main CBA
Fig. D6
Printing
Lead with
white stripe
Lead connections of Deck Assembly and Main CBA
Lead with
blue stripe
Desolder
from bottom
side
Fig. D5
1-5-3 HG2E0DC
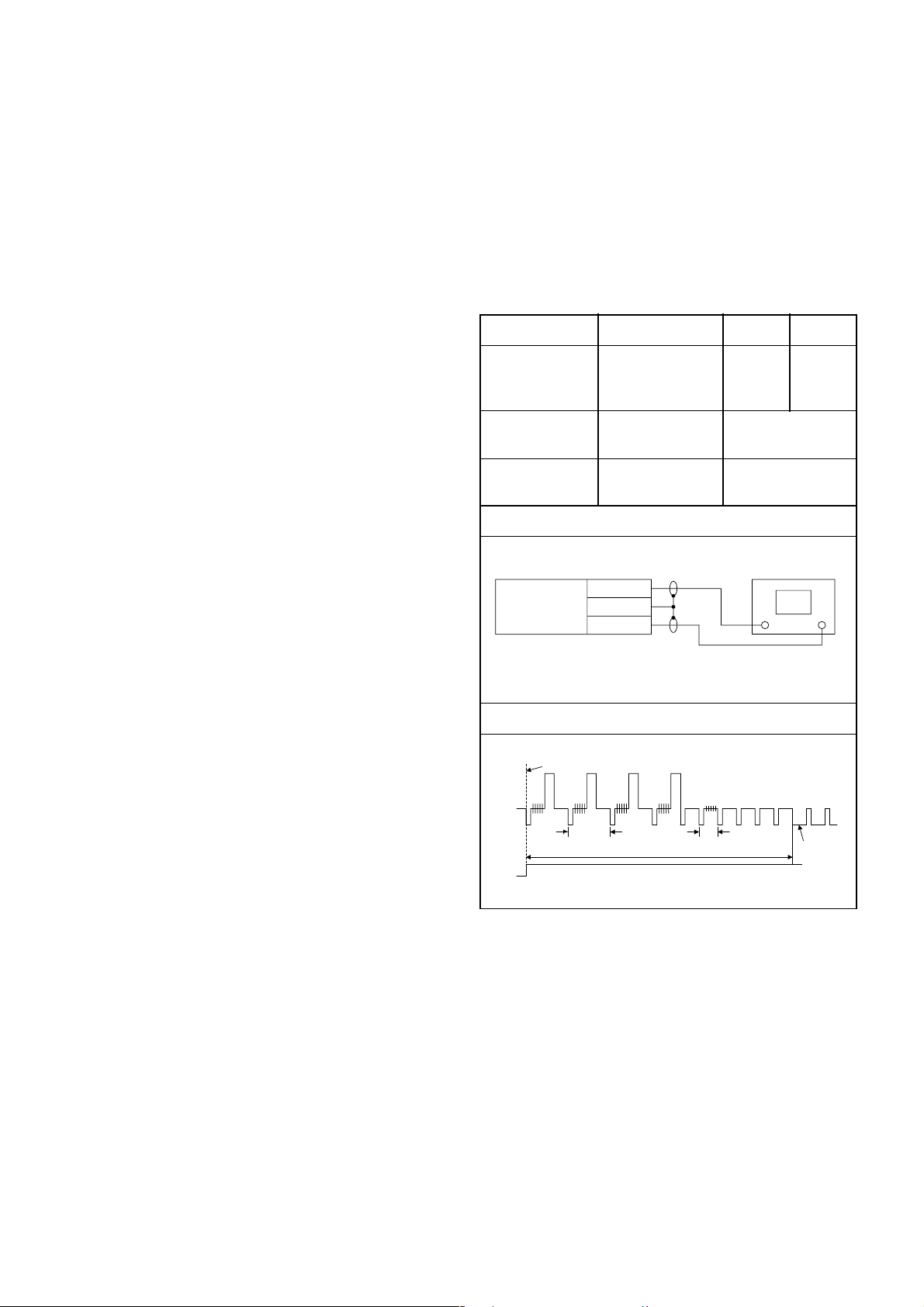
ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENT INSTRUCTIONS
General Note: "CBA" is an abbreviation for
"Circuit Board Assembly."
NOTE:
1.Electrical adjustments are required after replacing
circuit components and certain mechanical parts.
It is important to do these adjustments only after
all repairs and replacements have been completed. Also, do not attempt these adjustments
unless the proper equipment is available.
2.To perform these alignment / confirmation procedures, make sure that the tracking control is set in
the center position: Press either "L5??" or "K" button
on the remote control unit first, then the "PLAY"
button (Front Panel only).
Test Equipment Required
1.Oscilloscope: Dual-trace with 10:1 probe,
V-Range: 0.001~50V/Div.,
F-Range: DC~AC-20MHz
2.Alignment Tape (FL6A)
Head Switching Position Adjustment
Purpose:
To determine the Head Switching position during
playback.
Symptom of Misadjustment:
May cause Head Switching noise or vertical jitter
in the picture.
Test point Adj.Point Mode Input
J23(V-OUT)
TP502(RF-SW)
GND
Tape
FL6A Oscilloscope
Connections of Measurement Equipment
Main CBA
VR501
(Switching Point)
(MAIN CBA)
Measurement
Equipment
J23
GND
TP502
PLAY
(SP)
6.5H±1H
(416µs±64µs)
Oscilloscope
-----
Spec.
CH1 CH2
Trig. (+)
Figure 1
EXT. Syncronize Trigger Point
CH1
CH2
Reference Notes:
Playback the Alignment tape and adjust VR501 so that
the V-sync front edge of the CH1 video output waveform is at the 6.5H±1H (416µs±64µs) delayed position
from the rising edge of the CH2 head switching pulse
waveform.
1.0H
6.5H+/-1H (416µs+/-64µs)
Switching Pulse
0.5H
V-Syn c
1-6-1 HG240EA

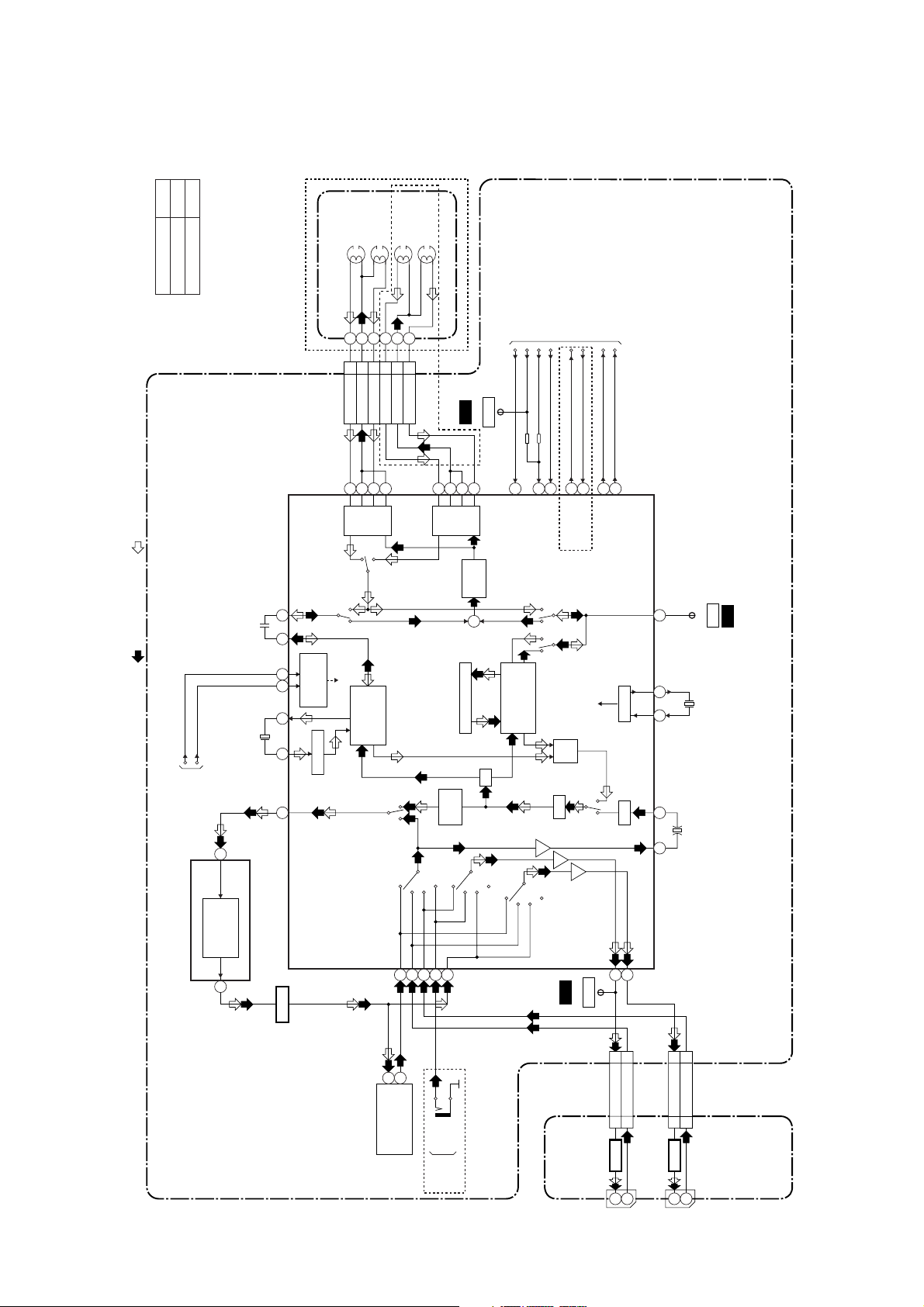
BLOCK DIAGRAMS
Servo/System Control Block Diagram
TO
AUDIO BLOCK
TO
Hi-Fi AUDIO
BLOCK
TO
VIDEO BLOCK
FP562
TP507
SENS-INH
KEY
SWITCH
KEY
SWITCH
8
7
KEY- 2
KEY- 1
REMOCON-IN
CTL(+)
CTL(-)
REMOTE
RS501
14
SENSOR
D502
S-LED
LD-SW9
94
957610480
IC501
(SERVO/SYSTEM CONTROL)
AL+5V
LED DISPLAY
232221
2011161413e12
17
DRV-STB
2
DRV-STB
S-REEL79
T-REEL
a
D4
DRV-CLK
1
DRV-CLK
RESET
34
Q501
RESET
D1D2D3
DRV-DATA
IC561A(LED DISPLAY)
28
686970
DRV-DATA
B
ST-S
END-S
bcd
TP501
CTL
+5V
TU701(TUNER UNIT)
7
f
A
CTL AMP OUT
97
Q562
SDA
SDA
SCL
3
5
12
j
CAS-LED
POWER-LED
24
23
Q563
SCL
IC503 (MEMORY)
11
TIMER-LED
REC-LED
26
25
Q564
SDA
5
SCL
6
Q565
AUDIO-SW-2
AUDIO-SW-1
IIC-BUS SDA
30
29
AUDIO-SW-2
AUDIO-SW-1
AL+5V
A-MUTE-H
IIC-BUS SCL
IIC-BUS SDA
83
A-MUTE-H
REC-SAF-SW
PG-DELAY
2
31
AL+5V
A-MODE
Hi-Fi-H-SW
IIC-BUS SCL
32
19
A-MODE
Hi-Fi-H-SW
B
SW506
REC-SAFETY
P-ON+15V
AL+12V
LINE-MUTE
IIC-BUS SCL
IIC-BUS SDA
72
28
LINE-MUTE
IIC-BUS SDA
LM-FWD/REV
D-CONT77
D-PFG
90
RF-SW
D-REC-H
71
18
33
RF-SW
D-REC-H
IIC-BUS SCL
C-CONT
81
C-ROTA
D-V-SYNC
13
15
C-ROTA
D-V-SYNC
C-F/R
C-FG
78
87
H-A-SW
H-A-COMP
17
16
H-A-SW
H-A-COMP
B
AL+12V/+20.5V
P-ON+5V
V-ENV
C-SYNC
6
58
V-ENV
C-SYNC
C-POW-SW
66
P-ON-H
C-POW-SW
P-ON-H
P-DOWN-L
67
86
P-DOWN-L
LD-SW
SW507
MAIN CBA
A
B
Model Mark
TVCR-210(C)
Comparison Chart of
TVCR-610(C)
Models & Marks
AL+5V
Q504
ST-S
SENSOR CBA
PS503
Q503
TP506
END-S
TIMER+5V
D561 STAND-BY
S-REEL
T-REEL
END-S
Q505
D562 POWER
D563 CAS
SENSOR CBA
D564 TIMER
D565 REC
CN504
2 CTL(+)
1 CTL(-)
CONTROL
HEAD
(DECK ASSEMBLY)
VR501
SW-POINT
CN502
CAPSTAN MOTOR
AC HEAD ASSEMBLY
CYLINDER ASSEMBLY
AL+12V(2)
12 P-ON+15V
11
10 GND
PG
SENSOR
D-PFG8D-CONT7LM-FWD/REV
GND5C-CONT4C-F/R3C-FG2P-ON+5V1AL+12V/+20.5V
6
9
M
CAPSTAN
MOTOR
M
DRUM
MOTOR
M
LOADING
MOTOR
TO POWER
SUPPLY BLOCK
1-7-1
HG2E0BLS
Video Block Diagram
A
B
Model Mark
TVCR-210(C)
Comparison Chart of
TVCR-610(C)
Models & Marks
VIDEO (L)-1
HEAD
VIDEO (R)-1
HEAD
CYLINDER ASSEMBLY
(DECK ASSEMBLY)
123
456
V(L)-2
V(R)-1
V-COM
V(L)-2
CN253
VIDEO (R)-2
VIDEO (L)-2
HEAD
V(R)-2
V-COM
HEAD
WF1
TP502
RF-SW
B
RF-SW
D-REC-H
C-ROTA
D-V-SYNC
H-A-SW
TO SERVO/SYSTEM
CONTROL BLOCK
V-ENV
C-SYNC
H-A-COMP
969593
94
SP
HEAD
AMP
EP
SP
SERIAL
DECORDER
Y. DELAY
P
R
LUMINANCE
SIGNAL
PROCESS
7978
REC-VIDEO SIGNAL PB-VIDEO SIGNAL MODE: SP/REC
69684643
IIC-BUS SDA
IIC-BUS SCL
65
TO
SERVO/SYSTEM
CONTROL BLOCK
50
AGC
BYPASS
IN1
TUNER
908988
87
80
EP
HEAD
AMP
Y
CCD 1H DELAY
CHARA.
INS.
IN2
FRT
IN2
FRT
REC FM
AGC
+
C
1/2
MUTE
PB/EE
D-REC-H
RPRP
CHROMINANCE
SIGNAL
PROCESS
IN1
TUNER
PB/EE
83
62
70
71
H-A-SW
H-A-COMP
D-V-SYNC
B
C-ROTA/RF-SW
Y/C
MIX
FBC
MUTE
PR
84
67
V-ENV
C-SYNC
AGC VXO
21
2928
58 59
WF2
C-PB
TP301
X301
4.433619MHz
IC501 (OSD)
MAIN CBA
OSD
CHARACTER
MIX
52
IC301
(Y/C SIGNAL PROCESS)
BUFFER
Q351
485052
54
6
24
VIDEO-IN
VIDEO-OUT
TU701(TUNER UNIT)
56
JK756
V-IN
FRONT
1-7-2
61
63
WF3
J23
V-OUT
CN151
B
CN101
Q101
JACK CBA
JK101
CN152
1
V-OUT1
V-IN1
33
1
BUFFER
19
20
V-OUT1
V-IN1
CN102
Q102
JK102
1
V-OUT2
V-IN2 3
3
1
BUFFER
19
20
V-OUT2
V-IN2
HG2E0BLV
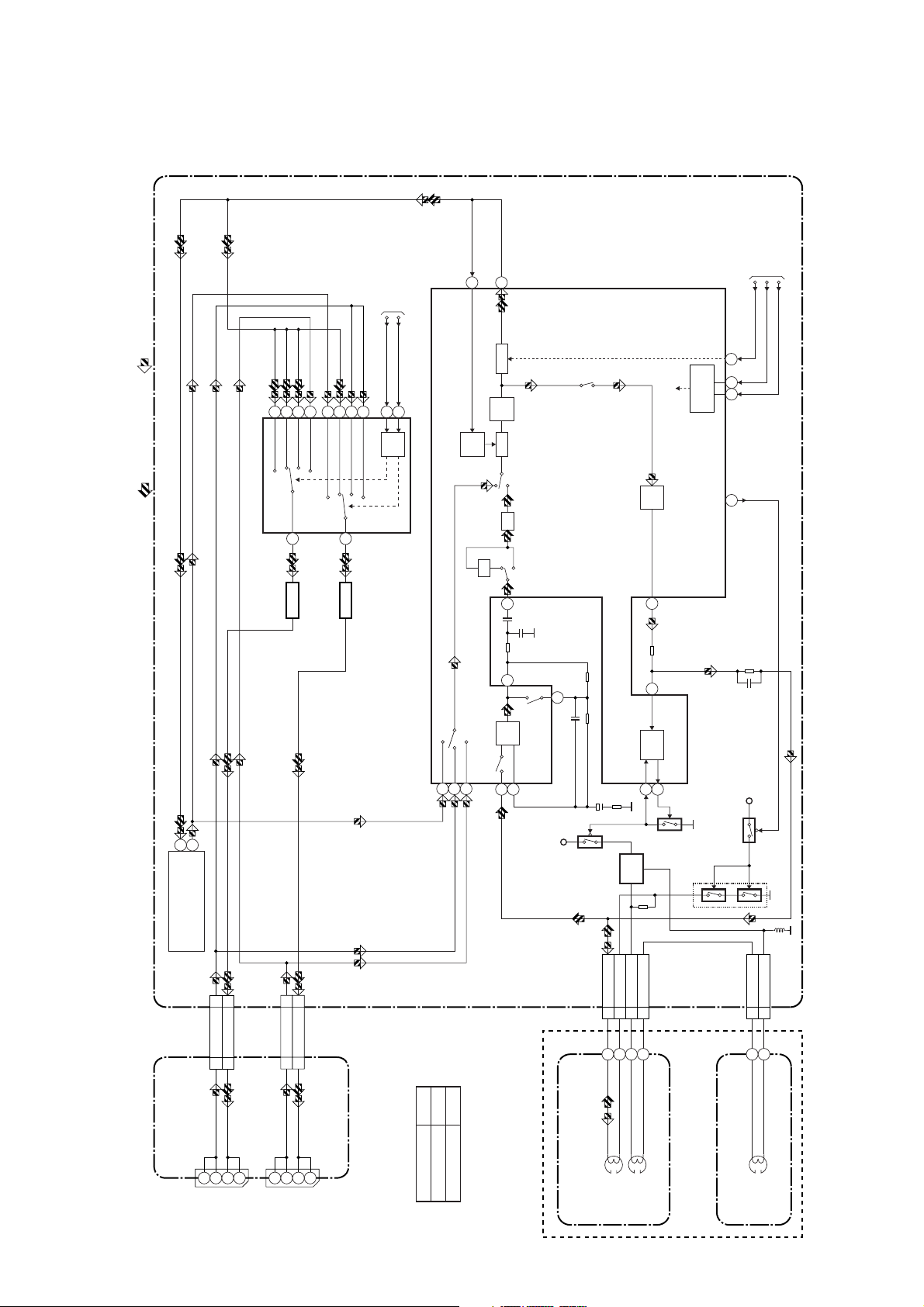
Audio Block Diagram ( A )
Mode : SP/REC
152
4
1214151110
PB/EE
PB/EE
PB/EE
PB/EE
TUNER
PB-AUDIO SIGNAL REC-AUDIO SIGNAL
MAIN CBA
IC151 (SWITCHING)
IN2
3
IN1
13
IN1
TO SERVO/SYSTEM
CONTROL BLOCK
AUDIO-SW-1
AUDIO-SW-2
9
SW
CTL
ALC
TO SERVO/SYSTEM
71
68 69
16
CONTROL BLOCK
A-MUTE-H
IIC-BUS SCL
IIC-BUS SDA
11
12
MUTE
SERIAL
DECODER
AUDIO HD-SW
CONTROL
DET
LINE
ALC
R
AMP
ATT
REC-ON
P
REC
AMP
2
21
AUDIO
TU-AUDIO
TU701(TUNER UNIT)
CN151
5
7
Q151
CN152
8
BUFFER
6
Q152
BUFFER
TUNER
IC301 (AUDIO SIGNAL PROCESS)
IN1
IN2
151317
INV
PB-ON
98
7
EQ
AMP
SP/LP-ON
5
6
+5V
Q401
CN504
BIAS
Q402
3 A-PB/REC
4 A-COM
6 AE-H
100
3
AUTO
BIAS
1
OSC
5 AE-H/FE-H
2
Q406
+5V
Q403
(SWITCHING)
CN501
2 FE-H
Q405
(PB=ON)
1 FE-H-GND
JACK CBA
JK101
A-IN1(L)
7
CN101
261
A-IN1
A-IN1
A-OUT1(R)
5
3
A-OUT1
A-OUT1
JK102
A-IN2(L)
8
CN102
261
A-IN2
A-IN2
A-OUT2(R)
6
3
A-OUT2
A-OUT2
A
B
Model Mark
TVCR-210(C)
Comparison Chart of
TVCR-610(C)
Models & Marks
AC HEAD ASSEMBLY
AUDIO
HEAD
(DECK ASSEMBLY)
AUDIO
ERASE
HEAD
FE HEAD
FULL
ERASE
HG2E0BLA1-7-3
HEAD
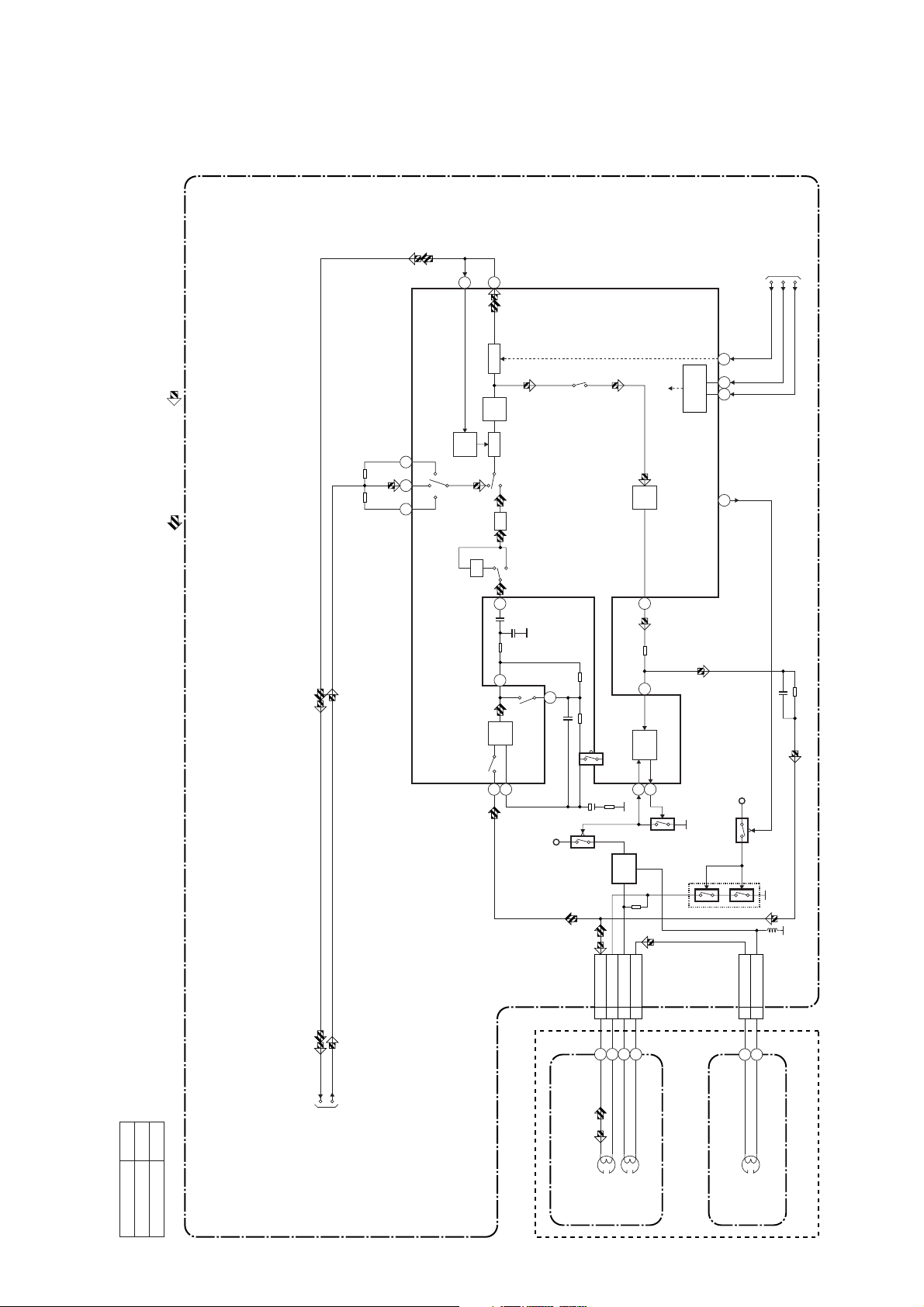
Audio Block Diagram ( B )
Mode : SP/REC
PB-AUDIO SIGNAL REC-AUDIO SIGNAL
TO SERVO/SYSTEM
11
12
SERIAL
DECODER
AUDIO HD-SW
CONTROL
71
68 69
16
MUTE
LINE
AMP
ALC
ALC
DET
IN1
1513 17
TUNER IN2
INV
P
R
ATT
98
REC-ON
REC
AMP
100
7
3
CONTROL BLOCK
A-MUTE-H
IIC-BUS SCL
IIC-BUS SDA
MAIN CBA
IC301
(AUDIO SIGNAL PROCESS)
N-A-PB
N-A-REC
A
B
TO Hi-Fi
AUDIO BLOCK
EQ
PB-ON
5
AMP
6
SP/LP-ON
+5V
Q401
CN504
BIAS
Q402
3 A-PB/REC
4 A-COM
6 AE-H
AUTO
BIAS
1
OSC
5 AE-H/FE-H
2
Q406
Q403
CN501
+5V
Q405
2 FE-H
(PB=ON)
1 FE-H-GND
FE HEAD
Model Mark
TVCR-210(C)
Comparison Chart of
TVCR-610(C)
Models & Marks
1-7-4
AC HEAD ASSEMBLY
AUDIO
HEAD
(DECK ASSEMBLY)
AUDIO
ERASE
HEAD
FULL
ERASE
HEAD
HG459BLA
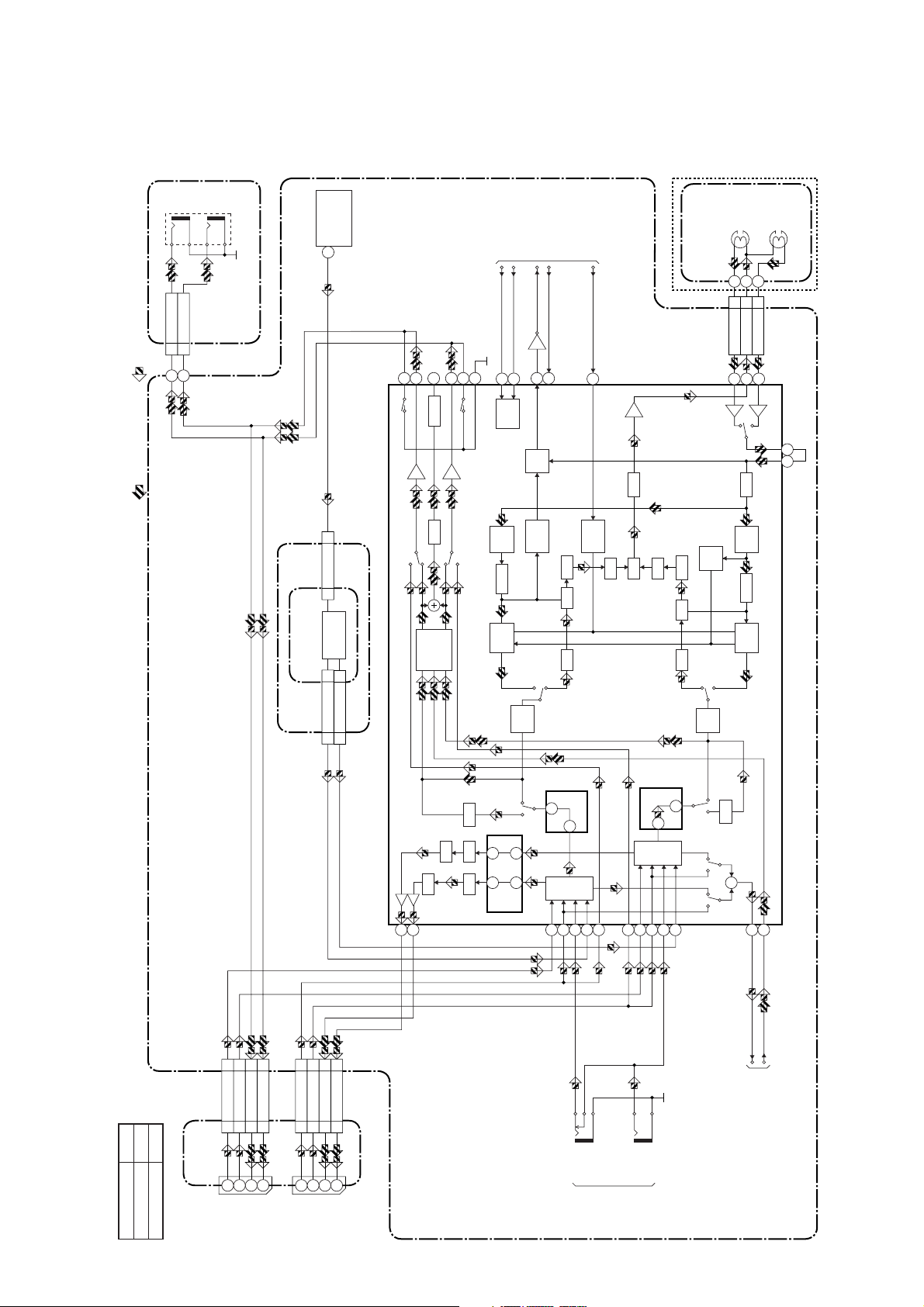
Hi-Fi Audio Block Diagram ( B )
A-OUT
(L)
A-OUT
(R)
TU701
JK751
SIF OUT
(TUNER UNIT)
22
TO
SERVO/SYSTEM
CONTROL BLOCK
Hi-Fi
CYLINDER
ASSEMBLY
AUDIO
(R) HEAD
Hi-Fi
AUDIO
(L) HEAD
CN509
A-OUT1(L)2A-OUT1(R)
1
REC-AUDIO SIGNALPB-AUDIO SIGNAL Mode : SP/REC
MAIN CBA
SUB JACK CBA
AFV CBA
2
CN701
SIF
2
CN1
4
TU-AUDIO(R)
4
CN701 CN 1
IF SIGNAL
PROCESS
5
TU-AUDIO(L)
5
7374727677
MUTE-ON
VCO MUTE
OUTPUT
SELECT
75
MUTE-ON
A-MODE
IIC-BUS SCL
IIC-BUS SDA
Q451
37
38
LOGIC
ENV
R-CH
BPF
NOISE
COMP
SW
NOISE
PPR
R-CH
PNR
LINE-MUTE
21
53
MUTE
DET
DET
VCO
LIM DEV
Hi-Fi-H-SW
39
HOLD
PULSE
LPF
(DECK ASSEMBLY)
MIX V/I
LPF
VCO
LIM DEV
R
DO
L-CH
DET
PNR
CN253
Hi-Fi-A(R) 7
242627
R
Hi-Fi-COM 8
LIM
L-CH
COMP
SW
Hi-Fi-A(L) 9
L
34 33
BPF
NOISE
A
B
Model Mark
TVCR-210(C)
Comparison Chart of
TVCR-610(C)
Models & Marks
CN151
9
A-IN1(R)
9
CN101
JACK CBA
JK101
2
A-IN1(R)
5
A-OUT1(R)
A-IN1(L) 7
7
5
6
1
A-OUT1(R)
A-IN1(L)
CN152
A-OUT1(L) 11
11
CN102
JK102
3
A-OUT1(L)
9
A-IN2(R)
A-IN2(L) 8
8
9
2
6
A-IN2(R)
A-IN2(L)
6
A-OUT2(R)
A-OUT2(L) 11
6
11
1
3
A-OUT2(R)
A-OUT2(L)
(Hi-Fi AUDIO SIGNAL PROCESS)
IC451
6108
JK757
A-IN(L)
14
L-CH
INSEL
15
4
ALC
+
78
N-A-REC
80
N-A-PB
TO AUDIO BLOCK
61 71
47
48
R-CH
INSEL
5256545060
JK758
A-IN(R)
2
FRONT
ALC
70
SW
ALC
62
ALC
SW
67
65
1-7-5
HG459BLH
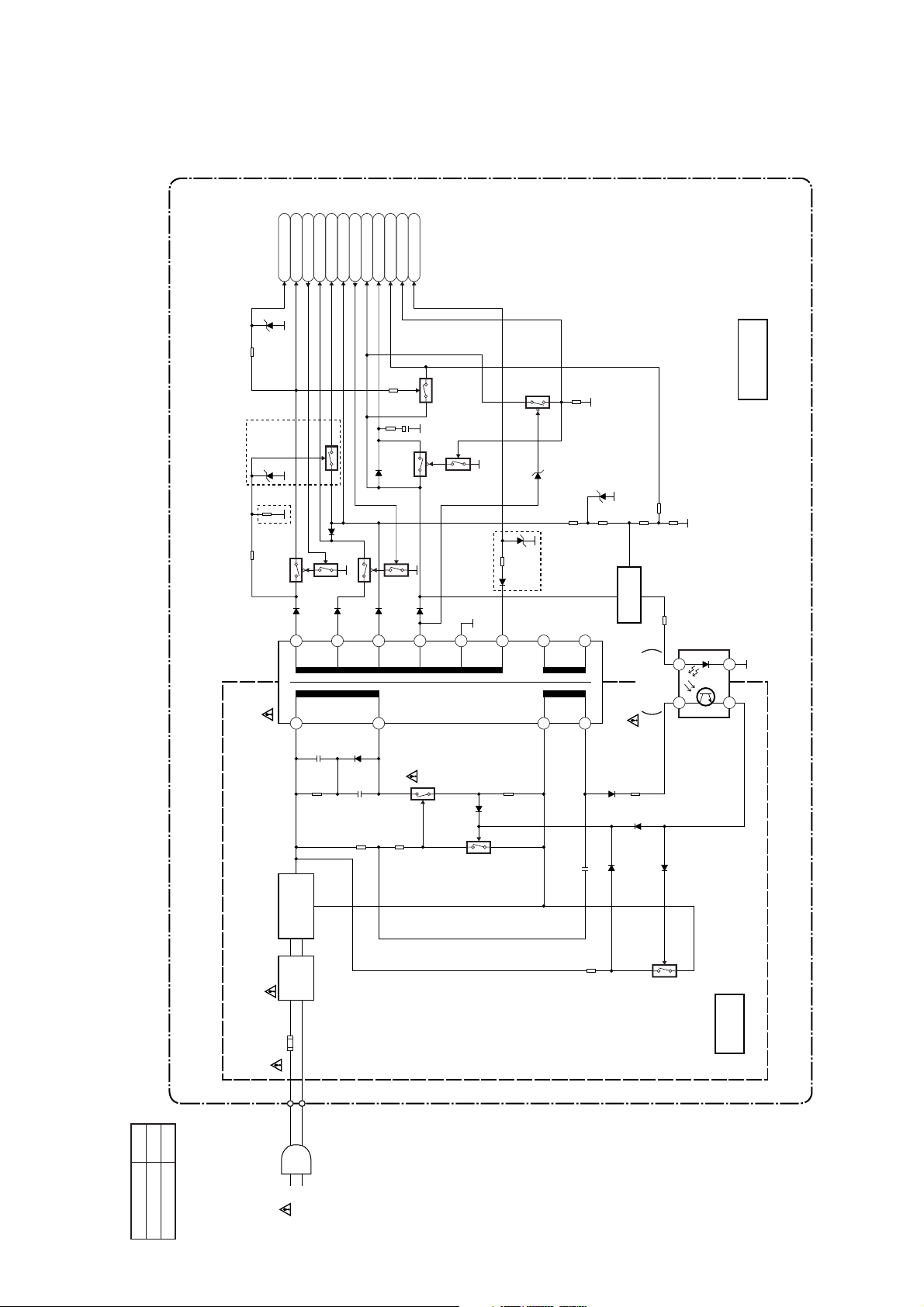
Power Supply Block Diagram
P-ON+44V
P-ON+15V12P-ON-H
AL+12V/+20.5V
AL+9V
AL+12V
C-POW-SW
AL+5V
TIMER+5V
P-ON+5V
P-DOWN-L
AL-5V
Q053
MAIN CBA
CAUTION !
Fixed voltage (or Auto voltage selectable ) power supply circuit is used in this unit.
If Main Fuse (F001) is blown, check to see that all components in the power supply
circuit are not defective before you connect the AC plug to the AC power supply.
Otherwise it may cause some components in the power supply circuit to fail.
CAUTION
FOR CONTINUED PROTECTION AGAINST FIRE HAZARD,
REPLACE ONLY WITH THE SAME TYPE T1.6AL/250V FUSE.
B
A
Q051
T001
2
Q052
Q057
13
14
4
Q058
Q055
15
Q001
Q054
Q059
16
Q056
A
SHUNT
REGULATOR
Q004
11
17
18
1
4
IC001
ERROR
6
7
VOLTAGE DET
COLD
23
D001 - D004
F001 L003
NOTE :
The voltage for parts in hot circuit is measured using
hot GND as a common terminal.
A
HOT CIRCUIT. BE CAREFUL.
B
Model Mark
TVCR-210(C)
Comparison Chart of
TVCR-610(C)
Models & Marks
BRIDGE
RECTIFIER
LINE
FILTER
T1.6A L 250V
AC001
1-7-6
Q002
Q003
HOT
HG2E0BLP
FUNCTION INDICATOR SYMBOLS
Note:
The following symbols will appear on the indicator panel to indicate the current mode or operation of the VCR.
On-screen modes will also be momentarily displayed on the tv screen when you press the operation buttons.
Display panel
[ TVCR-210(C) ]
TAPE IN TIMER RECFUNCTIONSTANDBY
" H "= LED Light on, " L "= LED Light off
MODE INDICATOR ACTIVE
STANDBY Always " H " during electricity
FUNCTION Power on = " H "
Power off = " L "
TAPE IN Cassette in = " H "
Cassette out = " L "
TIMER Timer stand by = " H "
One touch recording = " H "
Timer recording = " H "
General mode = " L "
REC REC mode = " H "
REC pause
General mode = " L "
When reel or capstan mechanism is not
functioning correctly
When tape loading mechanism is not functioning correctly
When cassette loading mechanism is not
functioning correctly
When the drum is not working properly
P-ON Power safety detection
“A R” is displayed on a TV screen. (Refer to Fig. 1.)
“A T” is displayed on a TV screen. (Refer to Fig. 2.)
“A C” is displayed on a TV screen. (Refer to Fig. 3.)
“A D” is displayed on a TV screen. (Refer to Fig. 4.)
“A P” is displayed on a TV screen. (Refer to Fig. 5.)
Blinks at 0.8Hz interval
1-7-7 HG2E0FIS
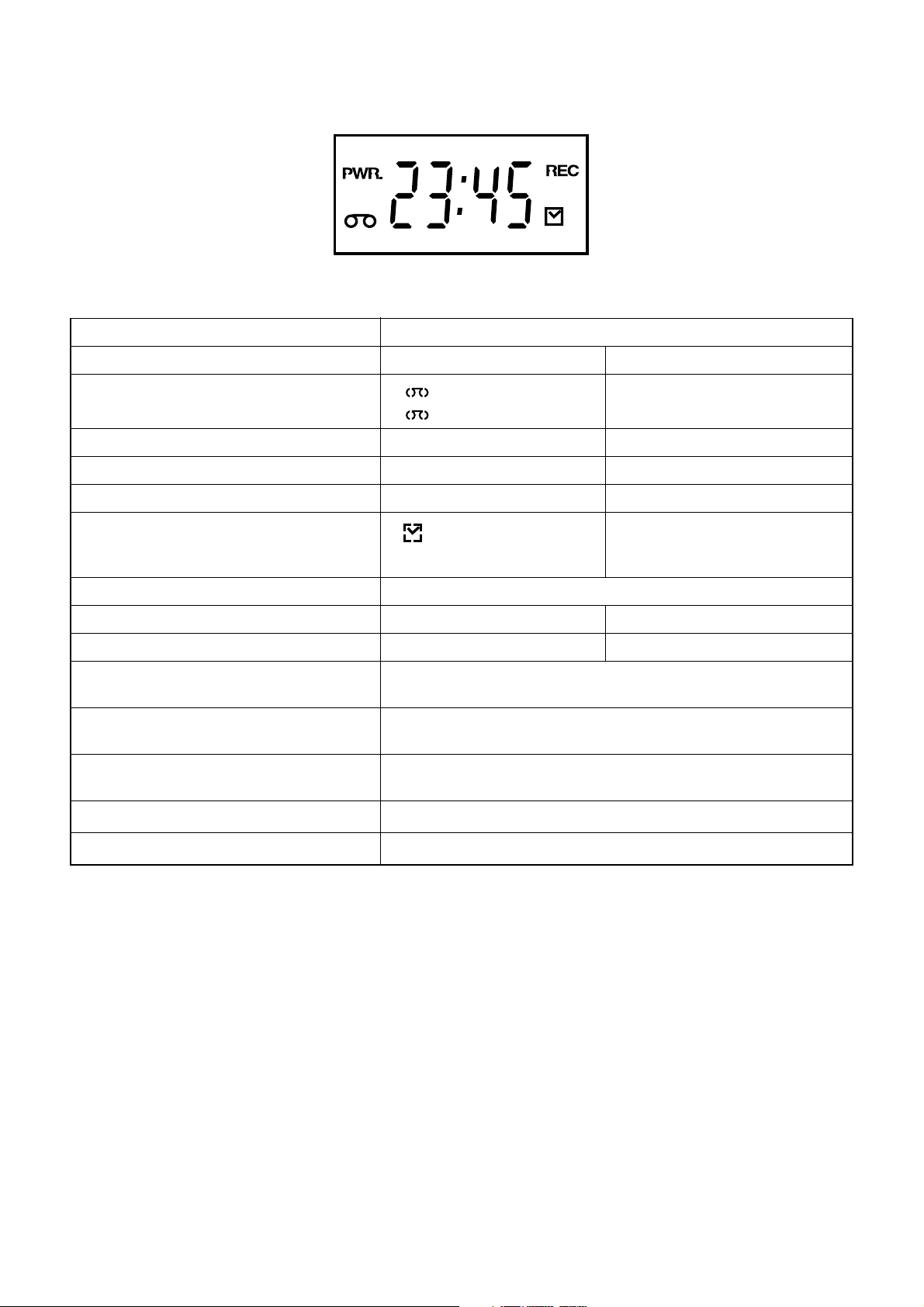
[ TVCR-610(C) ]
MODE INDICATOR ACTIVE
POWER ON " PWR." ON
CASSETTE "IN"
CASSETTE "OUT"
CLOCK " 88:88 " ON
REC " REC " ON
REC PAUSE " REC " Blinks at 0.8Hz interval
T- R E C , O T R
RF OUT RF out channel number is displayed on the indicator panel.
S-INH condition All modes Blinks at 0.8Hz interval
All lighting mode All characters ON
When reel or capstan mechanism is not
functioning correctly
When tape loading mechanism is not functioning correctly
When cassette loading mechanism is not
functioning correctly
When the drum is not working properly
" "
" "
" "
“A R” is displayed on a TV screen. (Refer to Fig. 1.)
“A T” is displayed on a TV screen. (Refer to Fig. 2.)
“A C” is displayed on a TV screen. (Refer to Fig. 3.)
“A D” is displayed on a TV screen. (Refer to Fig. 4.)
ON
OFF
ON
(T-REC OFF,T-REC incomplete
Blinks at 0.8Hz interval)
P-ON Power safety detection
“A P” is displayed on a TV screen. (Refer to Fig. 5.)
1-7-8 HG2E0FIS
TV screen
Note:
OSD for mechanical error will be displayed for 5 sec. after the mechanical error occurs.
When reel or capstan mechanism is not functioning
correctly
A
R
Fig. 1
When tape loading mechanism is not functioning correctly
A
T
Fig. 2
When cassette loading mechanism is not functioning
correctly
When the drum is not working properly
A
D
P-ON Power safety detection
A
P
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
A
C
Fig. 3
1-7-9 HG2E0FIS
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS / CBA’S AND TEST POINTS
Standard Notes
WARNING
Many electrical and mechanical parts in this chassis
have special characteristics. These characteristics
often pass unnoticed and the protection afforded by
them cannot necessarily be obtained by using replacement components rated for higher voltage, wattage,
etc. Replacement parts that have these special safety
characteristics are identified in this manual and its
supplements; electrical components having such features are identified by the mark " ! " in the schematic
diagram and the parts list. Before replacing any of
these components, read the parts list in this manual
carefully. The use of substitute replacement parts that
do not have the same safety characteristics as specified in the parts list may create shock, fire, or other
hazards.
Capacitor Temperature Markings
Mark
Capacity
change rate
Standard
temperature
Temperature
range
Notes:
1. Do not use the part number shown on these drawings for ordering. The correct part number is shown
in the parts list, and may be slightly different or
amended since these drawings were prepared.
2. All resistance values are indicated in ohms
3
(K=10
3. Resistor wattages are 1/4W or 1/6W unless otherwise specified.
4. All capacitance values are indicated in µF
(P=10
5. All voltages are DC voltages unless otherwise
specified.
6. Electrical parts such as capacitors, connectors,
diodes, IC’s, transistors, resistors, switches, and
fuses are identified by four digits. The first two digits are not shown for each component. In each
block of the diagram, there is a note such as shown
below to indicate these abbreviated two digits.
, M=106).
-6
µF).
(B)
(F) +30 - 80% 20°C -25~+85°C
(SR)
(Z) +30 - 80% 20°C -10~+70°C
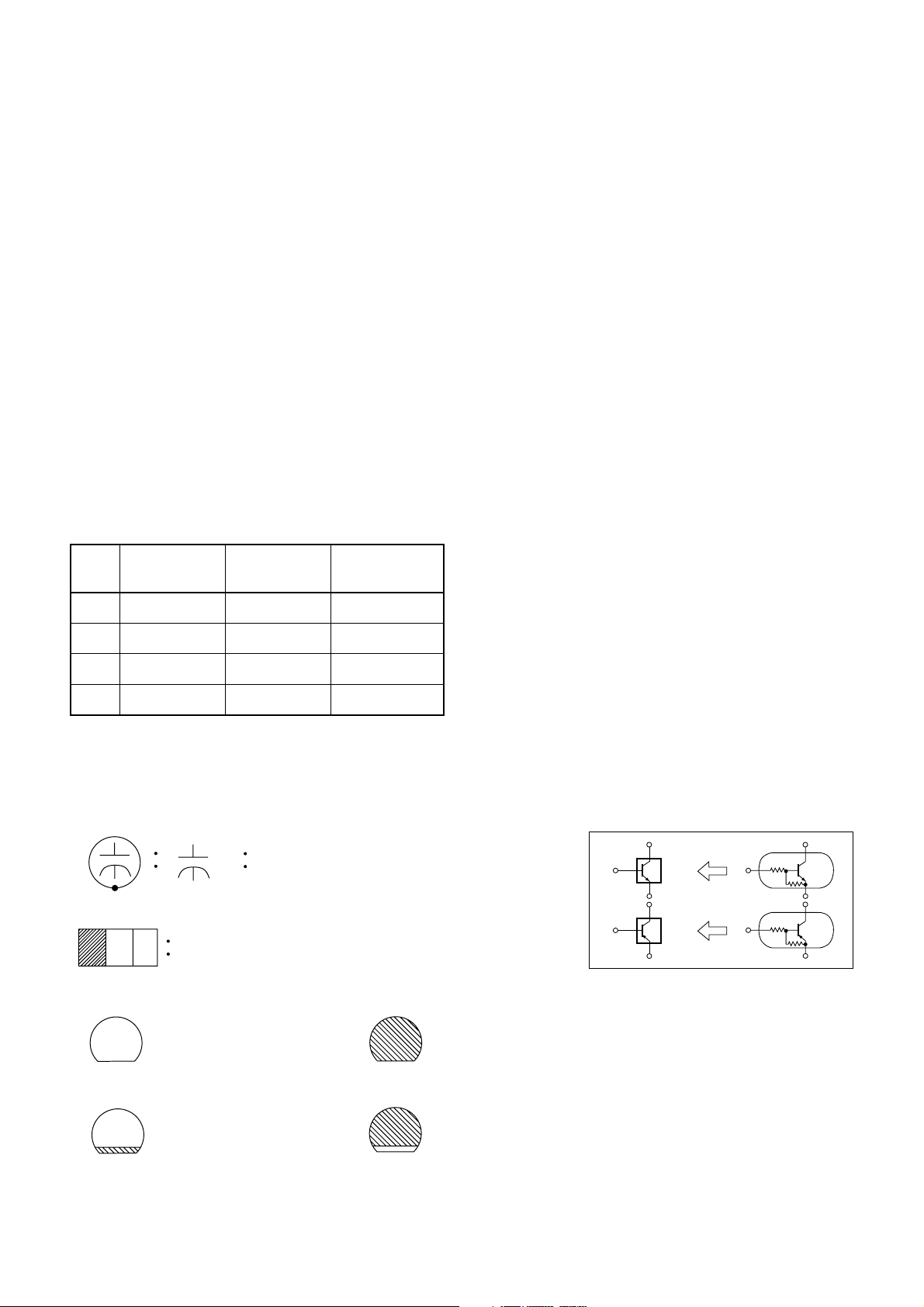
Capacitors and transistors are represented by the following symbols.
±10%
±15%
20°C -25~+85°C
20°C -25~+85°C
CBA Symbols
(Top View) (Bottom View)
+
Electrolytic Capacitor
(Bottom View)
Transistor or Digital Transistor
E C B
(Top View)
NPN Transistor
(Top View)
PNP Transistor
Schematic Diagram Symbols
Digital Transistor
E C B
(Top View)
E C B
NPN Digital Transistor
E C B
(Top View)
PNP Digital
Transistor
E C B
1-8-1 SCPA1
LIST OF CAUTION, NOTES, AND SYMBOLS USED IN THE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS ON THE FOLLOWING
PAG ES :
1. CAUTION:
FOR CONTINUED PROTECTION AGAINST FIRE HAZARD, REPLACE ONLY WITH THE SAME TYPE FUSE.
2. CAUTION:
Fixed Voltage (or Auto voltage selectable) power supply circuit is used in this unit.
If Main Fuse (F001) is blown, first check to see that all components in the power supply circuit are not defective
before you connect the AC plug to the AC power supply. Otherwise it may cause some components in the power
supply circuit to fail.
3. Note:
(1) Do not use the part number shown on the drawings for ordering. The correct part number is shown in the parts
list, and may be slightly different or amended since the drawings were prepared.
(2) To maintain original function and reliability of repaired units, use only original replacement parts which are
listed with their part numbers in the parts list section of the service manual.
4. Mode: SP/REC
5. Voltage indications for PLAY and REC modes on the schematics are as shown below:
Unit: Volts
The same voltage for
both PLAY & REC modes
6. How to read converged lines
1-D3
Distinction Area
Line Number
(1 to 3 digits)
Examples:
1. "1-D3" means that line number "1" goes to area "D3".
2. "1-B1" means that line number "1" goes to area "B1".
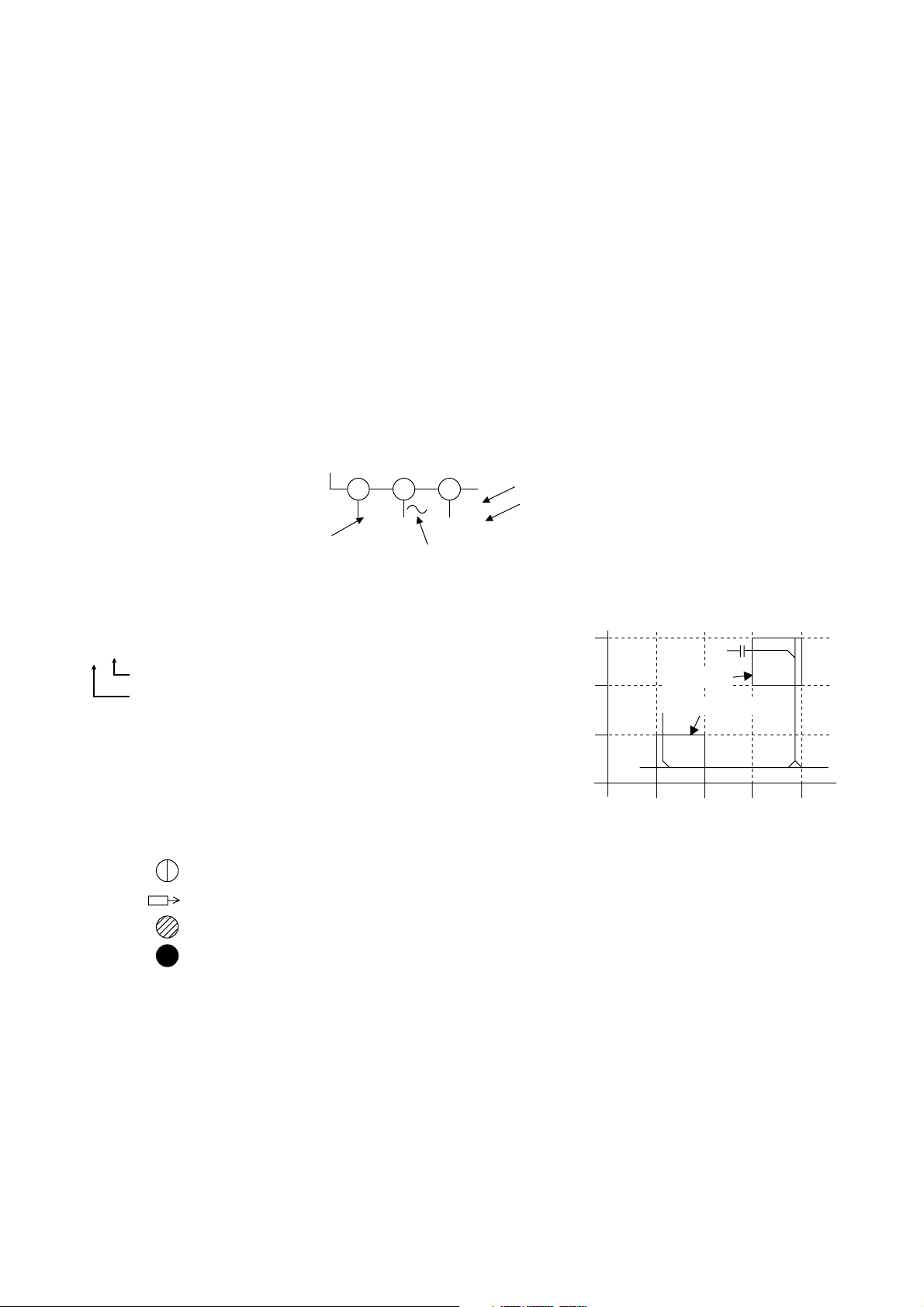
7. Test Point Information
: Indicates a test point with a jumper wire across a hole in the PCB.
: Used to indicate a test point with a component lead on foil side.
: Used to indicate a test point with no test pin.
5.0
231
5.0
PLAY mode
REC mode
(2.5)
Indicates that the voltage
is not consistent here.
3
AREA D3
2
1
AREA B1
1-D3
ABCD
1-B1
: Used to indicate a test point with a test pin.
1-8-2 SCRK05
 Loading...
Loading...