Page 1
Protocol Solutions Group
3385 Scott Blvd., Santa Clara, CA 95054 Tel: +1/408.727.6600 Fax: +1/408.727.6622
Verification Script Engine
for
LeCroy SATracer /SASTracer
Reference Manual
Manual Version 1.01
For SASTracer/SATracer Software Version 2.60/4.60
February 13, 2006
Page 2

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
Document Disclaimer
The information contained in this document has been carefully checked and is believed to be
reliable. However, no responsibility can be assumed for inaccuracies that may not have been
detected.
LeCroy reserves the right to revise the information presented in this document without
notice or penalty.
Trademarks and Servicemarks
LeCroy, CATC, SASTracer, SATracer, SASTrainer, SATrainer Automation are trademarks of
LeCroy.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows 2000, and Windows XP are registered trademarks of
Microsoft Inc.
All other trademarks are property of their respective companies.
Copyright
Copyright © 2006, LeCroy; All Rights Reserved.
This document may be printed and reproduced without additional permission, but all copies
should contain this copyright notice.
Version
This is version 1.0 the SASTracer/SATracer Verification Script Engine Reference Manual.
This manual applies to SASTracer/SATracer software version 2.60/4.60 and higher.
Page 3

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
Table of Contents
1 INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................................... 1
2 VERIFICATION SCRIPT STRUCTURE ................................................................................... 2
3 INTERACTION BETWEEN SASTRACER/SATRACER AND A VERIFICATION
SCRIPT............................................................................................................................................... 5
4 RUNNING VERIFICATION SCRIPTS FROM THE SASTRACER/SATRACER................ 7
4.1 R
4.2 VSE GUI
UNNING VERIFICATION SCRIPTS .......................................................................................... 9
SETTINGS............................................................................................................ 11
5 VERIFICATION SCRIPT ENGINE INPUT CONTEXT MEMBERS .................................. 12
5.1 TRACE EVENT-INDEPENDENT SET OF MEMBERS................................................................... 12
5.2 T
RACE EVENT-DEPENDENT SET OF MEMBERS ...................................................................... 13
5.2.1 Primitives ..................................................................................................................... 13
5.2.2 OOB.............................................................................................................................. 13
5.2.3 SAS/SATA Generic Frame members........................................................................ 13
5.2.4 SAS Open Address Frame members......................................................................... 14
5.2.5 SAS Identify Address Frame members..................................................................... 14
5.2.6 SAS Broadcast and Short Broadcast Address Frame members ............................ 14
5.2.7 SAS SSP Frame members .......................................................................................... 15
5.2.8 SAS SMP Frame members......................................................................................... 16
5.2.9 SATA/STP Frame Members...................................................................................... 24
6 VERIFICATION SCRIPT ENGINE OUTPUT CONTEXT MEMBERS .............................. 28
7 VERIFICATION SCRIPT ENGINE EVENTS ......................................................................... 29
7.1 F
7.2 C
RAME LEVEL EVENTS ........................................................................................................ 29
OMMAND LEVEL EVENTS .................................................................................................. 29
8 SENDING FUNCTIONS.............................................................................................................. 30
8.1 SENDLEVEL()...................................................................................................................... 30
8.2 S
ENDLEVELONLY() ............................................................................................................ 30
8.3 DONTSENDLEVEL() ............................................................................................................ 31
8.4 S
8.5 S
8.6 D
8.7 S
8.8 S
8.9 D
ENDCHANNEL() ................................................................................................................ 31
ENDCHANNELONLY() ....................................................................................................... 32
ONTSENDCHANNEL () ...................................................................................................... 32
ENDALLCHANNELS()........................................................................................................ 33
ENDTRACEEVENT ().......................................................................................................... 33
ONTSENDTRACEEVENT() ................................................................................................. 33
8.10 SENDTRACEEVENTONLY() ................................................................................................. 33
8.11 S
ENDALLTRACEEVENTS().................................................................................................. 34
9 TIMER FUNCTIONS .................................................................................................................. 35
9.1 VSE TIME OBJECT ............................................................................................................... 35
9.2 S
ETTIMER() ........................................................................................................................ 35
9.3 KILLTIMER()....................................................................................................................... 36
9.4 G
ETTIMERTIME()................................................................................................................ 36
ii
Page 4

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
10 TIME CONSTRUCTION FUNCTIONS.................................................................................. 37
10.1 TIME()................................................................................................................................. 37
11 TIME CALCULATION FUNCTIONS .................................................................................... 38
11.1 ADDTIME() ......................................................................................................................... 38
11.2 SUBTRACTTIME()................................................................................................................ 38
11.3 M
11.4 D
ULTIMEBYINT() .............................................................................................................. 38
IVTIMEBYINT()................................................................................................................ 39
12 TIME LOGICAL FUNCTIONS ............................................................................................... 40
12.1 ISEQUALTIME() .................................................................................................................. 40
12.2 I
12.3 I
SLESSTIME()...................................................................................................................... 40
SGREATERTIME() .............................................................................................................. 40
12.4 ISTIMEININTERVAL().......................................................................................................... 41
13 TIME TEXT FUNCTIONS ....................................................................................................... 42
13.1 T
IMETOTEXT() ................................................................................................................... 42
14 OUTPUT FUNCTIONS .............................................................................................................43
14.1 REPORTTEXT().................................................................................................................... 43
14.2 E
14.3 D
NABLEOUTPUT()............................................................................................................... 43
ISABLEOUTPUT().............................................................................................................. 43
15 INFORMATION FUNCTIONS ................................................................................................ 45
15.1 GETTRACENAME() ............................................................................................................. 45
15.2 G
15.3 G
15.4 G
15.5 G
15.6 G
ETSCRIPTNAME() ............................................................................................................. 45
ETAPPLICATIONFOLDER() ................................................................................................ 45
ETCURRENTTIME()........................................................................................................... 46
ETEVENTSEGNUMBER()................................................................................................... 46
ETTRIGGERPACKETNUMBER()......................................................................................... 46
16 NAVIGATION FUNCTIONS.................................................................................................... 47
16.1 G
16.2 S
OTOEVENT ().................................................................................................................... 47
ETMARKER()..................................................................................................................... 48
17 FILE FUNCTIONS..................................................................................................................... 49
17.1 O
17.2 C
PENFILE()......................................................................................................................... 49
LOSEFILE() ....................................................................................................................... 50
17.3 WRITESTRING() .................................................................................................................. 50
17.4 S
HOWINBROWSER()............................................................................................................ 50
18 COM/AUTOMATION COMMUNICATION FUNCTIONS................................................. 52
18.1 N
OTIFYCLIENT()................................................................................................................. 52
19 USER INPUT FUNCTIONS...................................................................................................... 53
19.1 MSGBOX() .......................................................................................................................... 53
19.2 INPUTBOX() ........................................................................................................................ 55
19.3 G
19.4 S
ETUSERDLGLIMIT()......................................................................................................... 57
ETUSERDLGLIMIT().......................................................................................................... 57
iii
Page 5

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
20 STRING MANIPULATION/FORMATING FUNCTIONS ................................................... 58
20.1 FORMATEX() ...................................................................................................................... 58
21 MISCELLANEOUS FUNCTIONS........................................................................................... 60
21.1 SCRIPTFORDISPLAYONLY()................................................................................................ 60
21.2 SLEEP() ............................................................................................................................... 60
21.3 C
21.4 P
ONVERTTOHTML() ......................................................................................................... 60
AUSE() .............................................................................................................................. 61
22 THE VSE IMPORTANT SCRIPT FILES ............................................................................... 62
22.1 EXAMPLE SCRIPT FILES ....................................................................................................... 62
iv
Page 6

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
1 Introduction
This document contains a description of the LeCroy Verification Script Engine (VSE), a new
utility in the SATracer/SASTracer software that allows users to perform custom analyses of
SAS/SATA traffic, recorded using the new generation of SAS/SATA protocol analyzers.
VSE allows users to ask the SASTracer/SATracer application to send some desired “events”
(currently defined as Primitive/Frame/Transaction/Command) from a trace to a verification script
written using the LeCroy script language. This script then evaluates the sequence of events (timing,
data or both) in accordance with user-defined conditions and performs post-processing tasks; such as
exporting key information to external text-based files or sending special Automation/COM
notifications to user client applications.
VSE was designed to allow users to easily retrieve information about any field in a SAS/SATA
Frame/Transaction/Command, and to make complex timing calculations between different events in a
pre-recorded trace. It also allows filtering-in or filtering-out of data with dynamically changing
filtering conditions, porting of information to a special output window, saving of data to text files and
sending of data to COM clients connected to a SASTracer/SATracer application.
1
Page 7

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
2 Verification Script Structure
Writing a verification script is easy, as long as you follow a few rules and have some
understanding of how the SASTracer/SATracer application interacts with running scripts.
The main script file that contains the text of the verification script should have extension .sasvs,
and be located in the subfolder ..\Scripts\VFScripts of the main SASTracer/SATracer folder. Some
other files might be included in the main script file using directive %include. (see CATC Scripting
Language Reference Manual for details).
The following schema presents a common structure of a verification script (this is similar to the content
of the script template [VSTemplate.pev_] which is included with VSE):
#
#
# VS1.sasvs
#
# Verification script
#
# Brief Description:
# Performs specific verification
#
#############################################################################################
# Module info
#############################################################################################
# Filling of this block is necessary for proper verification script operation...
############################################################################################
set ModuleType = "Verification Script"; # Should be set for all verification scripts
set OutputType = "VS"; # Should be set for all verification scripts that
# output only Report string and Result.
set InputType = "VS";
set DecoderDesc = "<Your Verification Script description>"; # Optional
######################################################################################################
#
# include main Verification Script Engine definitions
#
%include "VSTools.inc" # Should be set for all verification scripts
######################################################################################
# Global Variables and Constants
######################################################################################
# Define your verification script-specific global variables and constant in this section...
# (Optional)
const MY_GLOBAL_CONSTANT = 10;
set g_MyGlobalVariable = 0;
######################################################################################
######################################################################################
# OnStartScript()
######################################################################################
#
# It is a main intialization routine for setting up all necessary
# script parameters before running the script.
#
2
Page 8

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
######################################################################################
OnStartScript()
{
######################################################################################
# Specify in the body of this function the initial values for global variables
# and what kinds of trace events should be passed to the script.
# ( By default, all packet level events from all channels
# will be passed to the script.
#
# For details – how to specify what kind of events should be passed to the script
# please see the topic ‘sending functions’.
#
# OPTIONAL.
######################################################################################
g_MyGlobalVariable = 0;
# Uncomment the line below - if you want to disable output from
# ReportText()-functions.
#
# DisableOutput();
}
######################################################################################
# ProcessEvent()
######################################################################################
#
#
######################################################################################
# It is a main script function called by the application when the next waited event
# occured in the evaluated trace.
#
# !!! REQUIRED !!! – MUST BE IMPLEMENTED IN VERIFICATION SCRIPT
######################################################################################
ProcessEvent()
{
# Write the body of this function depending upon your needs.
# It might require branching on event type:
# select {
# in. TraceEvent == … : …
# in. TraceEvent == … : …
# …
# }
} return Complete();
######################################################################################
# OnFinishScript()
######################################################################################
#
######################################################################################
# It is a main script function called by the application when the script completed
# running. Specify in this function some resetting procedures for a successive run
# of this script.
#
# OPTIONAL.
######################################################################################
OnFinishScript()
{
} return 0;
######################################################################################
3
Page 9

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
######################################################################################
# Additional script functions.
######################################################################################
#
# Write your own script-specific functions here...
#
######################################################################################
MyFunction( arg )
{
if( arg == “My Arg” ) return 1;
return 0;
}
4
Page 10

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
3 Interaction Between SASTracer/SATracer and a Verification
Script
When a user runs a script against a pre-recorded trace, the following sequence occurs:
1. Prior to sending information to the script's main processing function ProcessEvent(), VSE looks
for the function OnStartScript() and calls it if it is found. In this function, setup actions are
defined, such as specifying the kind of trace events that should be passed to the script and
setting up initial values for script-specific global variables.
2. Next, the VSE parses the recorded trace to verify that the current packet or other event meets
specific criteria—if it does, VSE calls the script’s main processing function ProcessEvent(),
placing information about the current event in the script’s input context variables.
(Please refer to the topic Input context variables later in this document for a full description of
verification script input context variables )
3. ProcessEvent() is the main verification routine for processing incoming trace events. This
function must be present in all verification scripts. When the verification program consists of a
few stages, the ProcessEvent() function processes the event sent to the script, verifies that
information contained in the event is appropriate for the current stage, and decides if VSE
should continue running the script or, if the whole result is clear on the current stage, tell VSE
to complete execution of the script.
The completion of the test before the entire trace has been evaluated is usually done by
setting the output context variable in this manner: out.Result = _VERIFICATION_PASSED or
_VERIFICATION_FAILED.
(Please refer to the topic Output context variables later in this document for a full description of
verification script output context variables)
NOTE: Not only does a verification script evaluate recorded traces against some criteria—but it can also extract
information of interest and post-process it later by some third-party applications (there is a set of script functions
allowing you to save extracted data in text files, or send it to other applications, via COM/Automation interfaces).
4. When the script has completed running, VSE looks for the function OnFinishScript() and calls
it if found. In this function, some resetting procedures can be done.
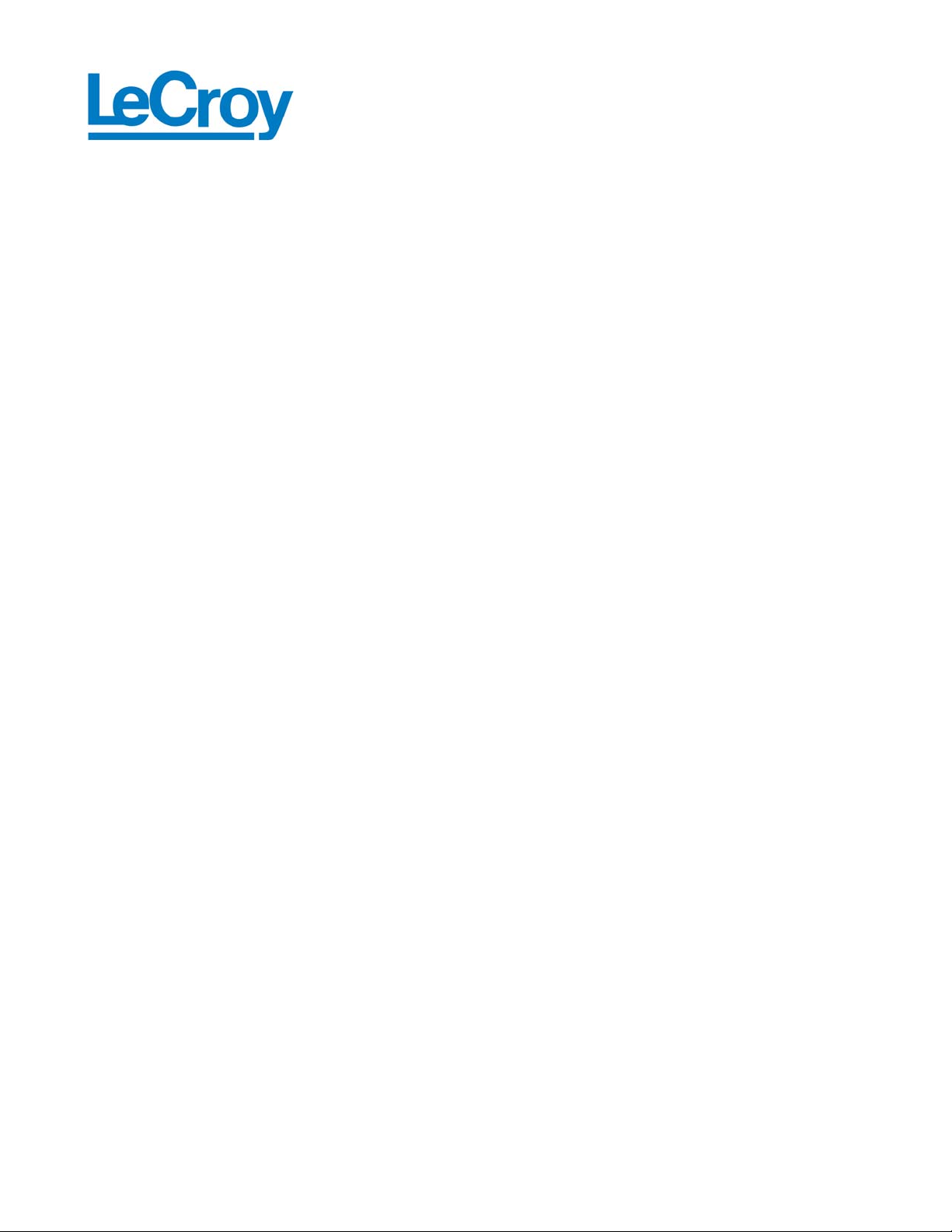
The following figure illustrates the interaction between the SASTracer/SATracer application and a
running verification script:
5
Page 11
LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
V
_
_
V
erification Script
OnStartScript()
ProcessEvent()
ProcessEvent()
ProcessEvent()
ProcessEvent()
(If expected event )
(If expected event )
(If expected event )
(If expected event )
Data…
Text
File
COM
Client
Call..
Call
..
Call
..
Call..
Call
..
SASTracer Application
(Run verification script)
Starting VSE running …
ProcessEvent()
Set out.Result =
VERIFICATION_PASSED
or
VERIFICATION_FAILED
will complete the script run.
OnFinishScript()
PASSED
erification Script results
FAILED
Call
..
(If expected
event )
Call..
DONE
Finishing VSE running … …
The Verification script result "DONE" occurs when the script has been configured to extract and display some information about
the trace, but not to display PASSED/FAILED results. To configure a script so that it only displays information—place a call
somewhere in your script to the function ScriptForDisplayOnly()in OnStartScript(), for example.
6
Page 12
LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
4 Running Verification Scripts from the SASTracer/SATracer
In order to run a verification script over a trace—you need to open the SASTracer/SATracer
main menu item Report\Run verification scripts… or push the icon on the main toolbar if it is not
hidden.
7
Page 13
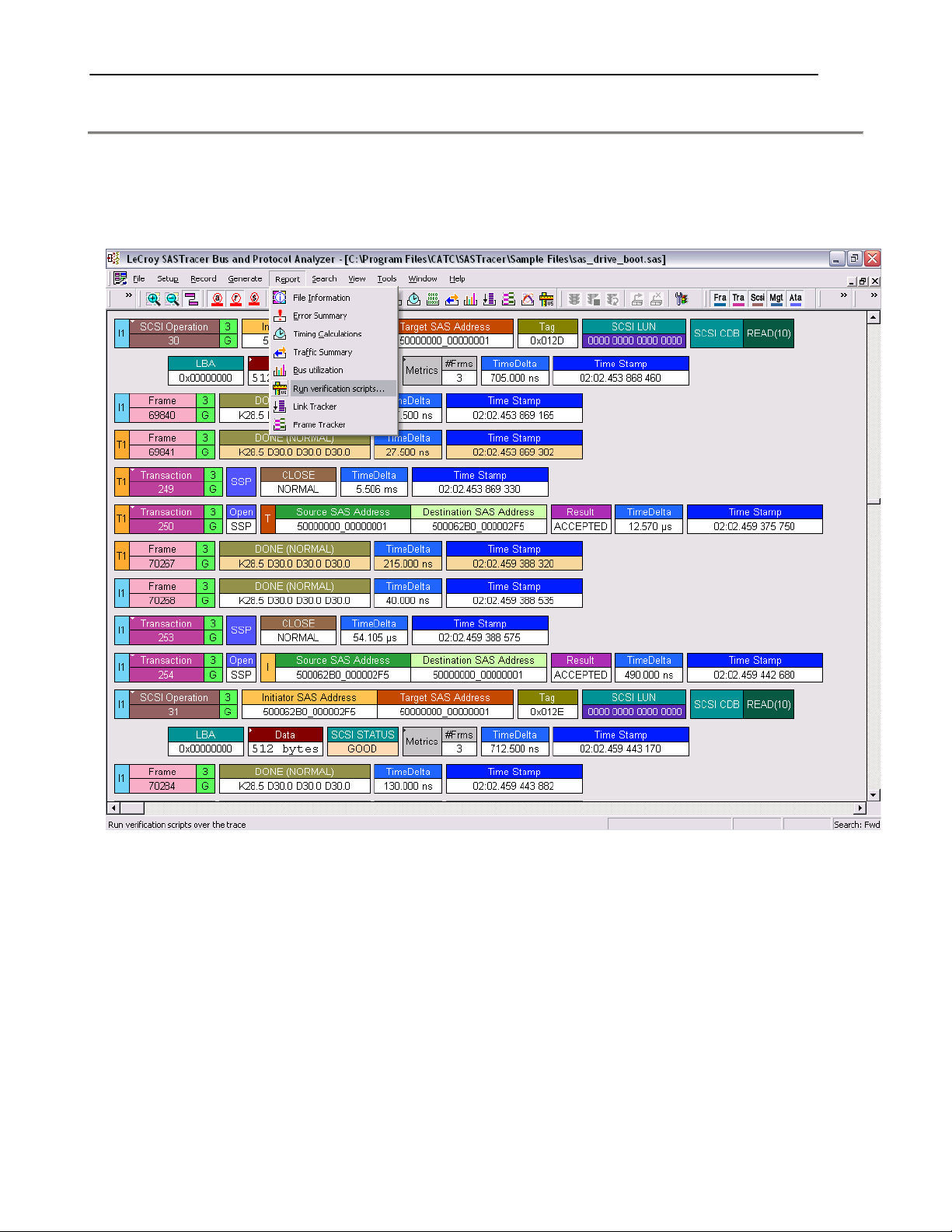
LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
V
V
A
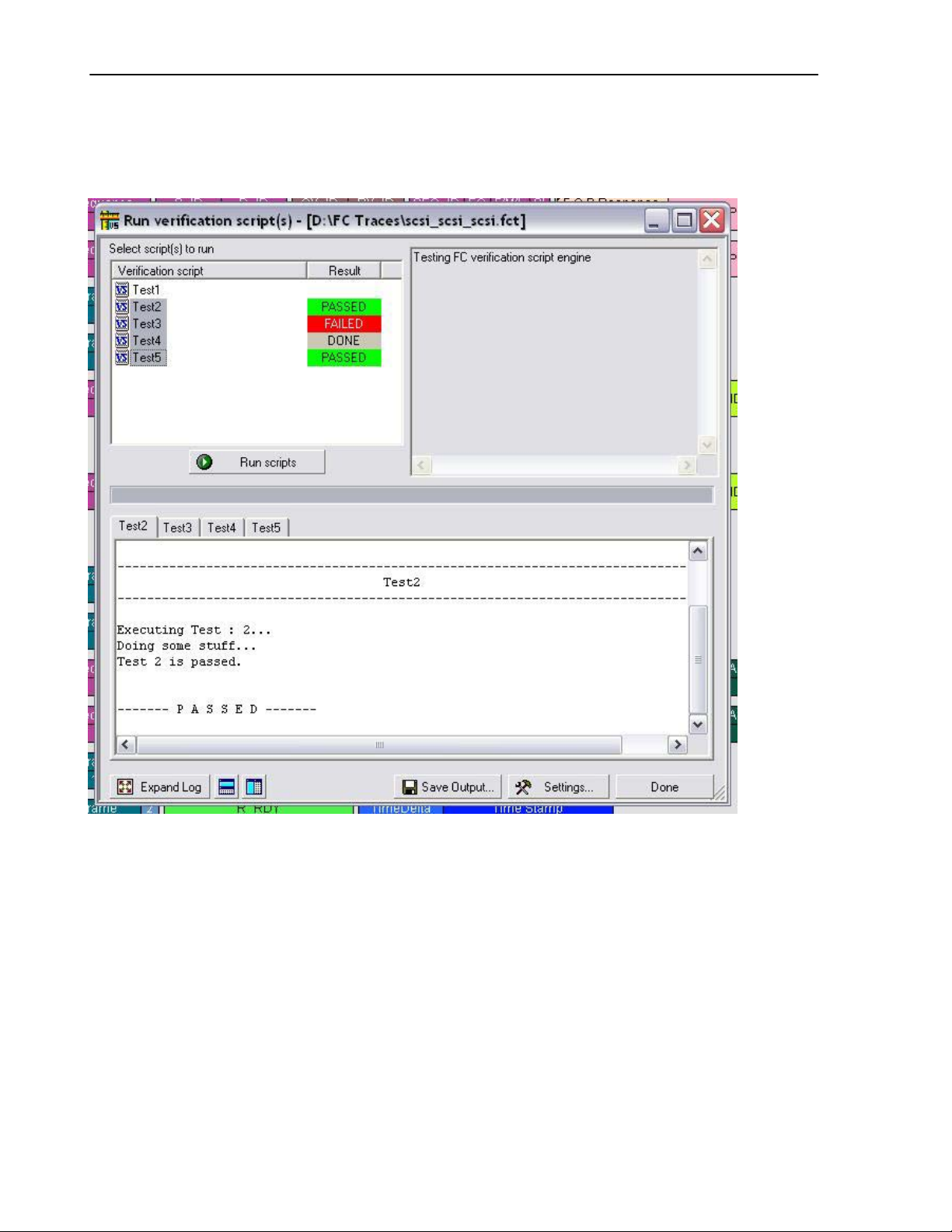
The special dialog will open displaying a list of verifications scripts. You can select one script to run,
or several scripts from the list to run in parallel:
output windows
erification Script List
Name for scripts are file names
without extension.
Finds a view related to the
verified trace and place this
window under it.
.
Starts running selected
verification scripts
Finds a view related to the
verified trace and place this
window by the right side of it.
erification Script description
Descriptions for scripts are defined in
set DecoderDesc="MyDescription";
.
Expands. ( Shortcut key : F11.
Shift+F11 also maximizes
dialog. )
Tabbed output
windows for selected
verification scripts.
Saves contents of
output windows in
text files.
llows to set
different settings.
8
Page 14
LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
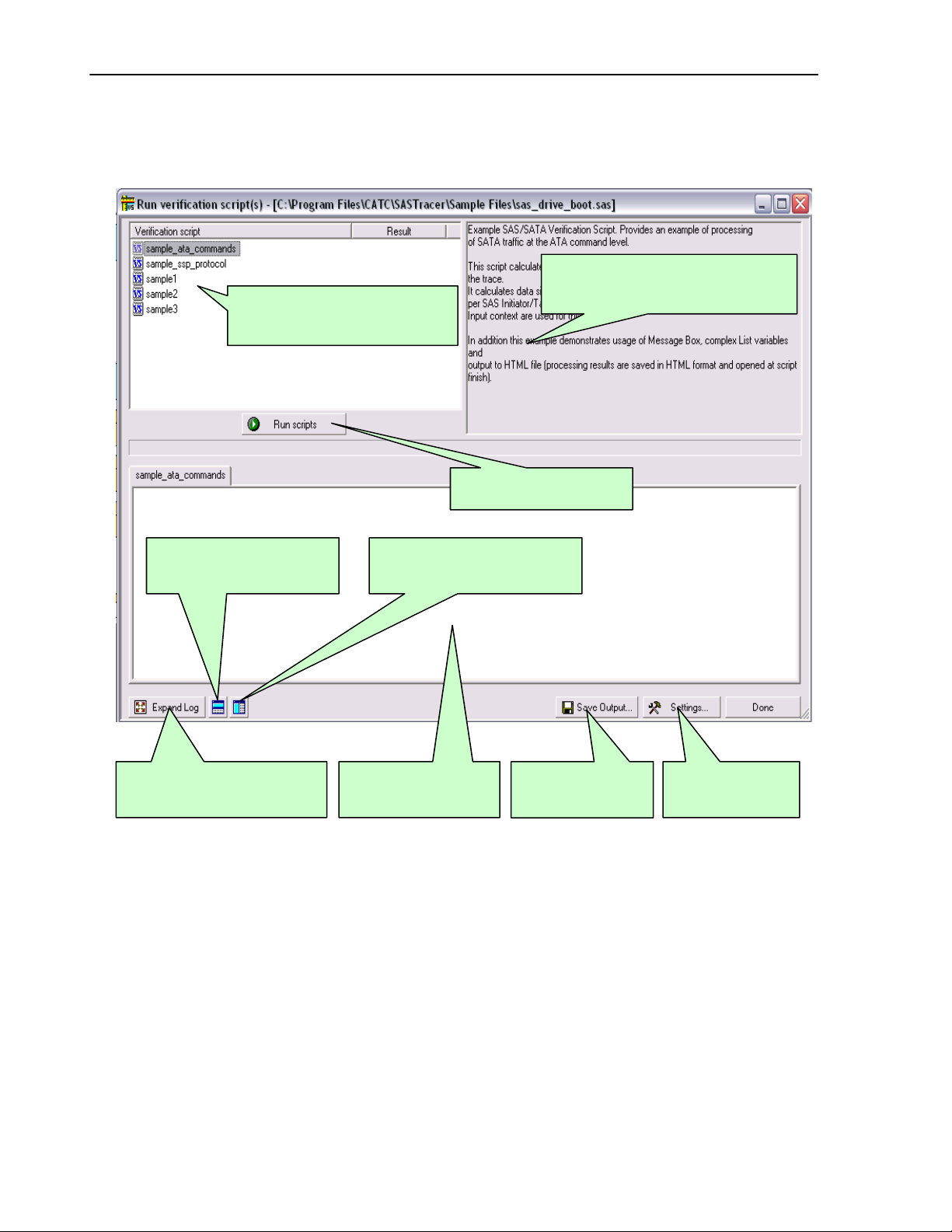
4.1 Running verification scripts
Push the button Run scripts after you selected the desired script(s) to run. VSE will start
running the selected verification script(s), show script report information in the output windows,
and present results of verifications in the script list:
9
Page 15
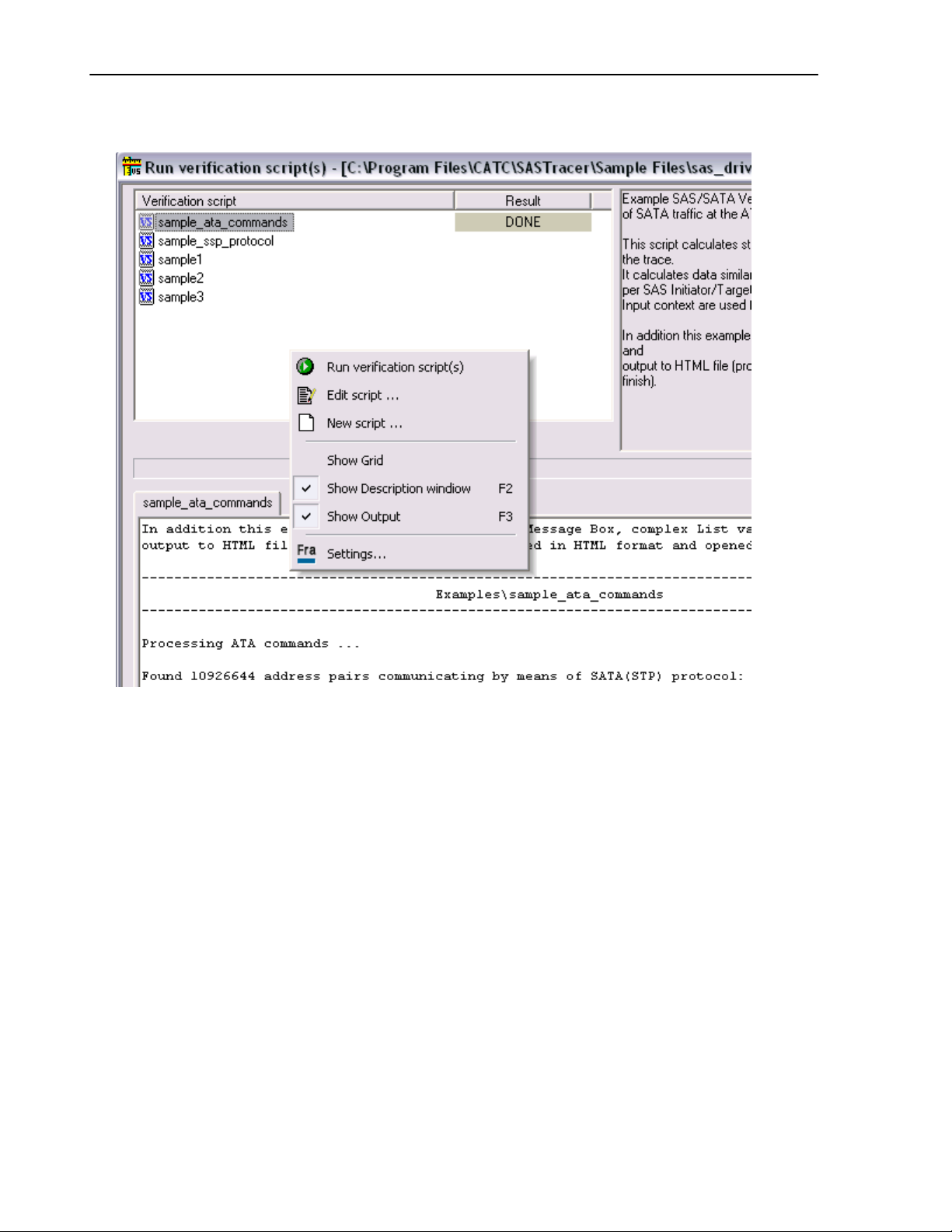
LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
Right-click in script list opens a pop-up menu with options for performing additional operations on
the selected scripts:
-
Run verification script(s) – starts running selected script(s)
-
Edit script – allows editing of the selected script(s) using whatever editor was specified in Editor
settings
- New script – creates a new script file using the template specified in Editor settings.
-
Show Grid – shows/hides a grid in the verification script list.
- Show Description window – shows/hides the script description window. (Shortcut key : F2)
-
Show Output - shows/hides the script output windows. (Shortcut key : F3)
-
Settings – opens a special Setting dialog which allows you to specify different settings for VSE.
10
Page 16
LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
p
g
p
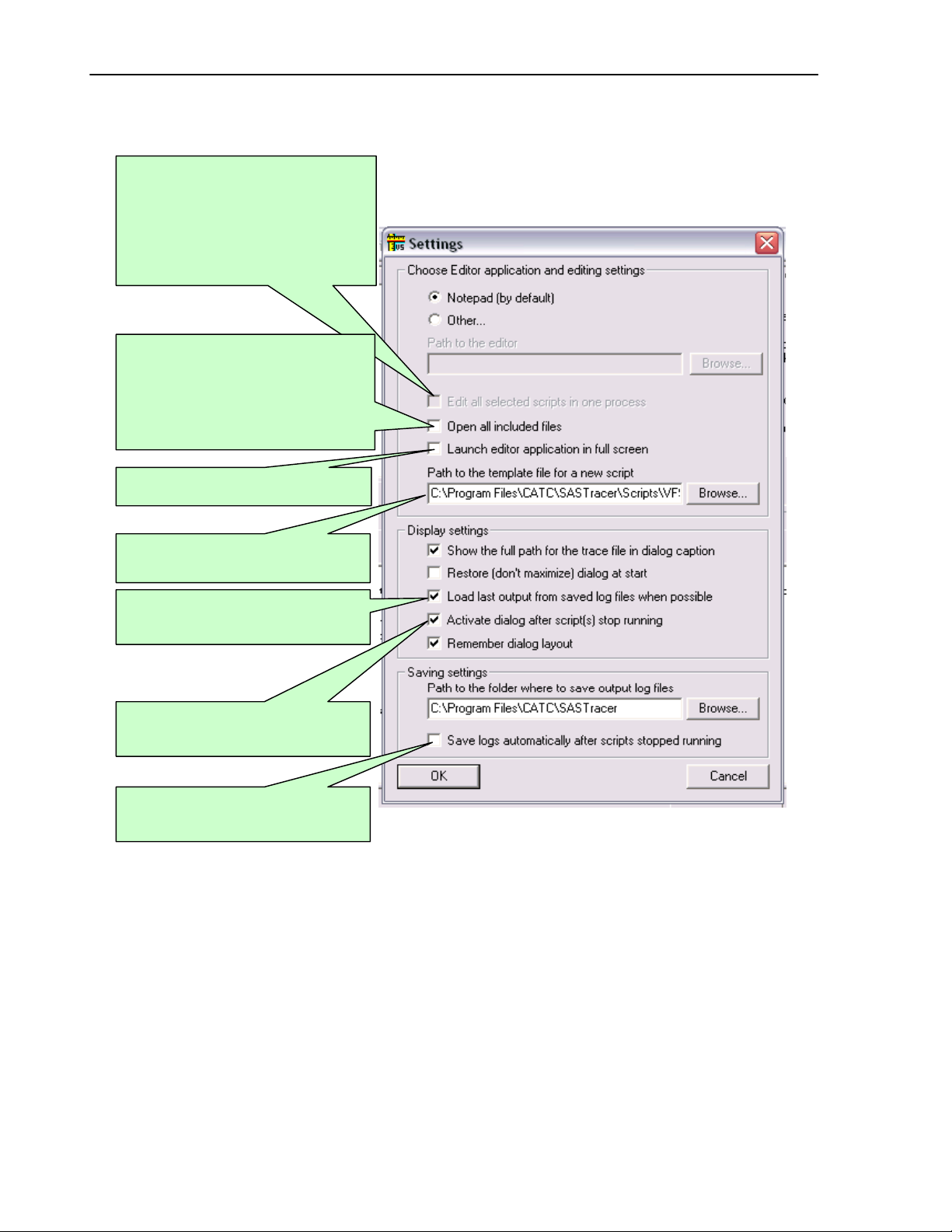
4.2 VSE GUI settings.
After choosing Settings, the following dialog will appear:
This option (if set) allows editor
applications supporting multi-document
interface (MDI) to edit all script files
related to the selected scripts in one
application instance.
Otherwise, a new application instance will
be launched for each script file.
This option (if set) allows editor
applications to edit all included files
(extension : *.inc) along with main
verification script files (extension : *.vse )
Otherwise, only main verification script
files will be opened for editing.
Launches editor application in full screen
mode.
Full path to the file to be used as a
template for a new script.
This setting (if set) specifies that the last
saved output for selected scripts should
be loaded into the out
This setting (if set) brings Run VS dialog
to foreground when scripts stopped
.
runnin
This setting (if set) forces the application
to save output automatically when the
ts stopped running.
scri
ut windows.
See screen pop-up tooltips for
explanation of other settings…
11
Page 17

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
5 Verification Script Engine Input Context Members
All verification scripts have input contexts – some special structures whose members are filled by
the application and can be used inside of the scripts (for more details about input contexts – please refer
to the CATC Script Language(CSL) Manual). The verification script input contexts have two sets of
members:
- Trace event-independent set of members.
- Trace event -dependent set of members.
5.1 Trace event-independent set of members
This set of members is defined and can be used for any event passed to script:
in.Level - transaction level of the trace event (0 = frames, 1= sequences )
in.Index - Index of the event in the trace file (frame number for frames, sequence number
for sequences)
in.Time - time of the event (type: list, having the format: 2 sec 125 ns -> [2 , 125].
(See 9.1 VSE time object for details)
in.Channel - channel where the event occured. (may be
in.TraceEvent - type of trace event (application predefined constants are used. See the list of possible
events, below)
in.Notification - type of notification (application predefined constants are used.
Currently, no notifications are defined)
_CHANNEL_2 (2) indicating which direction of the SAS/SATA link the event occurred)
_CHANNEL_1 (1) or
12
Page 18

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
5.2 Trace event-dependent set of members
This set of members is defined and can be used only for a specific events or after calling some
functions filling out some of the variables:
5.2.1 Primitives
in.Primitive – 4-byte value of the Primitive
in.Count – Primitive count
5.2.2 OOB
in.OOBType – OOB Types are defind as:
SAS_OOB_UNDETERMINED = 0
SAS_OOB_COMWAKE = 1
SAS_OOB_COMRESET = 2
SAS_OOB_COMSAS = 3
in.OOBBurstIdleList – list of pairs (<burst_or_idle>, <count>), where <burst_or_idle> is 0 for
idle and 1 for burst. Example:
oob_burst_idle_list = in.OOBBurstIdleList;
for ( i = 0; i < sizeof( oob_burst_idle_list ); i++ )
{
oob_burst_idle = oob_burst_idle_list[ i ];
report += repIndent;
select
{
oob_burst_idle[ 0 ] == SAS_OOB_ELEMENTTYPE_IDLE :
oob_burst_idle[ 0 ] == SAS_OOB_ELEMENTTYPE_BURST :
};
}
report += Format( "OOBIdle : %ld oobi\n", i, oob_burst_idle[ 1 ] );
report += Format( "OOBBurst : %ld oobi\n", i, oob_burst_idle[ 1 ] );
5.2.3 SAS/SATA Generic Frame members
in.Payload - bit source of the frame/sequence payload (you can extract any necessary
information using GetNBits(), NextNBits() or PeekNBits() functions—please refer to the CSL Manual
for details about these functions)
in.PayloadLength - the length (in bytes of the retrieved payload)
in.SOF,
in.StartOfFrame – 4-byte value of Start of frame primitive
in.EOF,
in.EndOfFrame – 4-byte value of End of frame primitive
in.CRC – CRC value as transmitted
13
Page 19

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
in.CalculatedCRC – CRC value as calculated
5.2.4 SAS Open Address Frame members
Note: All members return the content of the matching field name (in.xyz returns the value of field
“xyz”) based on the SAS specification.
in.Protocol
in.InitiatorPort
in.SourceAddress
in.SourceAddressHi
in.SourceAddressLo
in.DestinationAddress
in.DestinationAddressHi
in.DestinationAddressLo
in.ConnectionRate
in.InitiatorConnectionTag
in.AccessZoneManagement
in. SourceZoneGroup
in.PathwayBlockedCount
in.ArbitrationWaitTime
5.2.5 SAS Identify Address Frame members
Note: All members return the content of the matching field name (in.xyz returns the value of field
“xyz”) based on the SAS specification.
in.DeviceType
in.PhyIdentifier
in.SSPInitiatorPort
in.STPInitiatorPort
in.SMPInitiatorPort
in.SSPTargetPort
in.STPTargetPort
in.SMPTargetPort
in.SASAddress
in.SASAddressHi
in.SASAddressLo
in. ZoneDevice
in. ZoneBroadcastMethod
5.2.6 SAS Broadcast and Short Broadcast Address Frame members
in.BroadcastType
in.SourceZoneGroup
14
Page 20

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
5.2.7 SAS SSP Frame members
Note: All members return the content of the matching field name (in.xyz returns the value of field xyz)
based on the SAS specification.
in.FrameType
in. RetryDataFrames
in.Retransmit
in.ChangingDataPointer
in.FillBytes
in.Tag
in.TargetPortTransferTag
in.DataOffset
in.HashedDestinationAddress
in.HashedSourceAddress
5.2.7.1 COMMAND SSP Frame
in.FrameType is SSP_FRAME_TYPE_COMMAND (0x06)
in.SspCommandScsiOpcode
in.SspCommandHasScsiLBA
in.SspCommandScsiLBA
in.SspCommandLUNHi
in.SspCommandLUNLo
in.SspCommandTaskAttribute
in.SspCommandAdditionalCDBLen
5.2.7.2 XFER_RDY SSP Frame
in.FrameType is SSP_FRAME_TYPE_ XFER_RDY (0x05)
in.SspXferRdyRequestedOffset
in.SspXferRdyWriteDatalength
5.2.7.3 RESPONSE SSP Frame
in.FrameType is SSP_FRAME_TYPE_RESPONSE (0x07)
in.SspResponseDATAPRE
in.SspResponseStatus
in.SspResponseSenseDataLength
in.SspResponseResponseDataLength
15
Page 21

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
5.2.7.4 TASK SSP Frame
in.FrameType is SSP_FRAME_TYPE_TASK (0x16)
in.SspTaskLUNHi
in.SspTaskLUNLo
in.SspTaskTaskMGMTFunc
in.SspTaskTAG
5.2.8 SAS SMP Frame members
Note: All members return the content of the matching field name (in.xyz returns the value of field xyz)
based on the SAS specification.
5.2.8.1 Common SMP Frame members
in.FrameType
in.Function
5.2.8.2 SMP Request Frame members
5.2.8.2.1 Report General Frame members
5.2.8.2.2 Report Manufacturer Info Frame members
5.2.8.2.3 Discover Frame members
in.Ignored_1A
in.Ignored_2A
in.PhyIdentifier
in.Reserved_2A
in.Reserved_2B
in.NoZoneMask
5.2.8.2.4 Report Phy Error Log Frame members
in.Ignored_1A
in.Ignored_2A
in.PhyIdentifier
in.Reserved_2A
in.Reserved_2B
16
Page 22

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
5.2.8.2.5 Report Phy SATA Frame members
in.Ignored_1A
in.Ignored_2A
in.PhyIdentifier
in.Reserved_2A
in. Reserved_2B
5.2.8.2.6 Report Route Info Frame members
in.ExpanderRouteIndex
in.Reserved_1A
in.Reserved_2B
in.Ignored_2A
in.PhyIdentifier
in.Reserved_2A
5.2.8.2.7 Configure Route Info Frame members
in.ExpanderRouteIndex
in.Reserved_1A
in.Reserved_2B
in.PhyIdentifier
in.Reserved_2A
in.Ignored_3B
in.Ignored_3A
in.DisableExpanderRou
in.RoutedSASAddress
in.RoutedSASAddressHi
in.RoutedSASAddressLo
in.Ignored_6A
in.Ignored_7A
in.Ignored_8A
in.Reserved _9A
5.2.8.2.8 Phy Control Frame members
in.UpdatePartialPathwayTimeout
in.PartialPathwayTimeout
in.PhyOperation
in.PhyIdentifier
in.ProgrammedMaxPhysLinkRate
in.ProgrammedMinPhysLinkRate
in.Ignored_1A
in.Reserved_2A
in.Reserved_2B
in.Ignored_3A
in.Ignored_4A
17
Page 23

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
in.Ignored_5A
in.Ignored_6A
in.Ignored_7A
in.Ignored_8A
in.Ignored_8B
in.Ignored_8C
in.Reserved_2B
in.Reserved _9A
5.2.8.2.9 Phy Test Function Frame members
in.Ignored_1A
in.PhyTestPattern
in.PhyTestFunction
in.PhyIdentifier
in.Reserved_2A
in.PhyTestPatternPhysLinkRate
in.Reserved_3B
in.Reserved_3A
in.Reserved_4A
in.Reserved_5A
in.Reserved_6A
in.Reserved_7A
in.Reserved_8A
in.Reserved_9A
5.2.8.2.10 Configure Phy Zone Frame members
in.Reserved_1A
in.UpdateComplete
in.StartPhyIndex
in.NumberOfZonePhyEntries
in.ZoneParticipatingList
in.ZoneSupervisingPriorityList
in.ZoneGroupList
5.2.8.2.11 Configure Zone Permission Frame members
in.Reserved_1A
in.Reserved_1B
in.SourceZoneGroup
in.GroupPermission
in.TargetZoneGroup
in.Reserved_2A
in.ZoneSupervisingPriority
18
Page 24

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
in.Reserved_2B
in.UpdatePriority
in.Batch
in.UpdateComplete
in.Reserved_2C
in.StartZoneEntryIndex
in.NumberOfZonePermissionEntries
in.ZonePermList
5.2.8.2.12 Report Zone Permission Frame members
in.Reserved_1A
in.Reserved_1B
in.StartZoneEntryIndex
in.NumberOfZonePermissionEntries
5.2.8.2.13 Report Zone Route Table Frame members
in.NumberOfZoneRouteTableEntries
in.PhyIdentifier
in.StartPhyRouteIndex
in.Reserved_2A
5.2.8.3 SMP Response Frames members
in.FunctionResult
5.2.8.3.1 Report General Frame members
in.ExpanderRouteIndexes
in.ExpanderChangeCount
in.ActiveZoneSupervisorPriority
in.ZoneSupervisingPriority
in.ConfigurableRouteTable
in.Configuring
in.Reserved_2B
in.NumPhys
in.Reserved_2A
in.EnclosureLogicalID
in.EnclosureLogicalIDHi
in.EnclosureLogicalIDLo
in.ActiveZoneSupervisorSASAddress
in.ActiveZoneSupervisorSASAddressHi
in.ActiveZoneSupervisorSASAddressLo
19
Page 25

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
5.2.8.3.2 Report Manufacturer Info Frame members
in.Ignored_1A
in.Reserved_2B
in.Ignored_2A
in.Reserved_2A
in.Sas11Format
in.VendorID
in.VendorIDHi
in.VendorIDLo
in.ProductID
in.ProductIDHiHi
in.ProductIDHiLo
in.ProductIDLoHi
in.ProductIDLoLo
in.ProductRevisionLevel
in.ProductRevisionLevelDword
when in.Sas11Format is 0:
in.VendorSpecific
in.VendorSpecificDword0
in.VendorSpecificDword1
in.VendorSpecificDword2
in.VendorSpecificDword3
in.VendorSpecificDword4
when in.Sas11Format is 1:
in.ComponentVendorID
in.ComponentVendorIDHi
in.ComponentVendorIDLo
in.ComponentID
in.ComponentRevisionID
in.Reserved_12A
in.VendorSpecific
in.VendorSpecificDword0
in.VendorSpecificDword1
5.2.8.3.3 Discover Frame members
in.Reserved_1A
in.Ignored_1A
in.Reserved_2B
in.Ignored_2A
in.PhyIdentifier
in.Reserved_2A
in.AttachedSataDevice
20
Page 26

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
in.AttachedSMPTarget
in.AttachedSTPTarget
in.AttachedSSPTarget
in.AttachedSataPortSelector
in.Reserved_3C
in.AttachedSataHost
in.AttachedSMPInitiator
in.AttachedSTPInitiator
in.AttachedSSPInitiator
in.Reserved_3B
in.NegPhysLinkRate
in.Reserved_3A
in.Ignored_3A
in.AttachedDevType
in.Ignored_3B
in.SASAddress
in.SASAddressHi
in.SASAddressLo
in.AttachedSASAddress
in.AttachedSASAddressHi
in.AttachedSASAddressLo
in.Reserved_8A
in.AttachedPhyIdentifier
in.AttachedZoneDevice
in.AttachedZoneBroadcastMethod
in.Reserved_8B
in.Reserved_9A
in.PartialPathwayTimeout
in.Reserved_10A
in.VirtualPhy
in.PhyChangeCount
in.HardwareMaxPhysLinkRate
in.ProgrammedMaxPhysLinkRate
in.HardwareMinPhysLinkRate
in.ProgrammedMinPhysLinkRate
in.Reserved_11B
in.RoutingAttribute
in.ConnectorType
in.ConnectorElementIndex
in.ConnectorPhysicalLink
in.Reserved_11A
in.VendorSpecific
in.Reserved_12A
in.ZoneViolation
in.ZoneParticipating
in.ZoneSupervisingPriority
in.Reserved_12B
in.ZoneGroup
21
Page 27

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
5.2.8.3.4 Report Phy Error Log Frame members
in.Ignored_1A
in.Reserved_2B
in.Ignored_2A
in.PhyIdentifier
in.Reserved_2A
in.InvalidDwordCount
in.RDCount
in.LossOfDWordSyncCount
in.PhyResetProblemCount
5.2.8.3.5 Report Phy SATA Frame members
in.Ignored_1A
in.Reserved_2B
in.Reserved_2A
in.Ignored_2A
in.Reserved_3A
in.Reserved_11A
in.AffiliationValid
in.AffiliationsSupported
in.PhyIdentifier
in.STPSasAddress
in.STPSasAddressHi
in.STPSasAddressLo
in.RegisterDevToHostFIS
in.RegisterDevToHostFISDword0
in.RegisterDevToHostFISDword1
in.RegisterDevToHostFISDword2
in.RegisterDevToHostFISDword3
in.RegisterDevToHostFISDword4
in.AffiliatedSTPInitiatorSasAddress
in.AffiliatedSTPInitiatorSasAddressHi
in.AffiliatedSTPInitiatorSasAddressLo
5.2.8.3.6 Report Route Info Frame members
in.ExpanderRouteIndex
in.Reserved_1A
in.Reserved_2B
in.Ignored_2A
in.PhyIdentifier
22
Page 28

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
in.Reserved_2A
in.Ignored_3B
in.Ignored_3A
in.ExpanderRouteEntryDisabled
in.RoutedSasAddress
in.RoutedSasAddressHi
in.RoutedSasAddressLo
in.Ignored_6A
in.Ignored_7A
in.Ignored_8A
in.Reserved_9A
5.2.8.3.7 Configure Route Info Frame members
5.2.8.3.8 Phy Control Frame members
5.2.8.3.9 Phy Test Function Frame members
5.2.8.3.10 Configure Phy Zone Frame members
5.2.8.3.11 Configure Zone Permission Frame members
5.2.8.3.12 Report Zone Permission Frame members
in.Reserved_1A
in.Reserved_1B
in.StartZoneEntryIndex
in.NumberOfZonePermissionEntries
5.2.8.3.13 Report Zone Route Table Frame members
in.NumberOfZoneRouteTableEntries
in.PhyIdentifier
in.StartPhyRouteIndex
in.EndOfEntries
in.Reserved_2A
in.ZoneRouteTableList
in.DisableExpanderRouteEntryList
in.AttachedDeviceTypeList
in.ZoneParticipatingList
23
Page 29

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
in.ZoneSupervisingPriorityList
in.ZoneGroupList
in.RoutedSASAddressList
5.2.9 SATA/STP Frame Members
Note: All members return the content of the matching field name (in.xyz returns the value of field xyz)
based on the SATA specification.
5.2.9.1 Common SATA/STP Frame Members
in.FrameType
STP_FRAME_TYPE_XMT_FRAME (1)
STP_FRAME_TYPE_RCV_FRAME (2)
in.FisType
in.Port
in.TotalPrimitives
Primitives:
in.PrimSataSof
in.PrimSataEof
in.PrimSataCont
in.PrimSataDmat
in.PrimSataHold
in.PrimSataHoldA
in.PrimSataRErr
in.PrimSataRUp
in.PrimSataROk
in.PrimSataRRdy
in.PrimSataSync
in.PrimSataWtrm
in.PrimSataXRdy
in.PrimSataError
in.PrimSataAlignment
in.PrimIntermixDwordFiltered
in.PrimIntermixDwordTruncated
For each in.Prim… the list of four elements is received:
( <TotalNumberSent>, <TimesThisPrimitiveSent>, <TimesContSent>, <TimesXxxxSent> )
5.2.9.2 Register Host To Device Frame Members
in.Features
in.Command
24
Page 30

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
in.DevHead
in.CylHigh
in.CylLow
in.SectorNumber
in.SectorNumberExp
in.FeaturesExp
in.CylHighExp
in.CylLowExp
in.UpdateType
in.Control
in.SectorCount
in.SectorCountExp
in.Res1
in.Res2
in.Res3
5.2.9.3 Register Device To Host Frame Members
in.DevHead
in.CylHigh
in.CylLow
in.SectorNumber
in.CylHighExp
in.CylLowExp
in.SectorNumberExp
in.SectorCount
in.SectorCountExp
in.Error
in.Status
in.Interrupt
in.Res1
in.Res2
in.Res3
in.Res4
in.Res5
5.2.9.4 Set Device Bits Frame Members
in.Error
in.StatusLo
in.StatusHi
in.Interrupt
in.SActive
in.Res1
in.Res2
in.Res3
in.Res4
25
Page 31

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
5.2.9.5 DMA Activate Frame Members
in.Res1
in.Res2
5.2.9.6 DMA Setup Frame Members
in.Direction
in.Interrupt
in.DMABufferIDLow
in.DMABufferIDHi
in.DMABufferOffset
in.DMATransferCount
in.Res1
in.Res2
in.Res3
in.Res4
in.Res5
5.2.9.7 Bist Activate Frame Members
in.Pattern
in.Pattern_V
in.Pattern_R
in.Pattern_P
in.Pattern_F
in.Pattern_L
in.Pattern_S
in.Pattern_A
in.Pattern_T
in.BISTData
in.BISTDataHi
in.BISTDataLo
in.Res1
in.Res2
5.2.9.8 PIO Setup Frame Members
in.Error
in.Status
in.Direction
in.Interrupt
in.DevHead
in.CylHigh
in.CylLow
in.SectorNumber
in.SectorNumberExp
in.CylHighExp
26
Page 32

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
in.CylLowExp
in.SectorCount
in.SectorCountExp
in.E_Status
in.TransferCount
in.Res1
in.Res2
in.Res3
in.Res4
in.Res5
5.2.9.9 DATA Frame Members
27
Page 33

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
6 Verification Script Engine Output Context Members
All verification scripts have output contexts – some special structures whose members are filled
by the script and can be used inside of the application (for more details about output contexts – please
refer to the CATC Script Language(CSL) Manual). The verification script output contexts have only
one member:
out.Result - the result of the whole verification program defined in the verification script.
This member is supposed to have 3 values:
_VERIFICATION_PROGRESS,( is set by default when script starts running )
_VERIFICATION_PASSED, and _VERIFICATION_FAILED
The last two values should be set if you decide that recorded trace does (or does not) satisfy the
imposed verification conditions. In both cases, the verification script will stop running.
If you don't specify any of those values - the result of script execution will be set as
_VERIFICATION_FAILED at exit.
NOTE: If you don’t care about the results of the script that’s running, please call function
ScriptForDisplayOnly() one time before stopping the script – then the results will be DONE.
28
Page 34

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
7 Verification Script Engine Events
VSE defines a large group of trace “events”—on packet, link and split transaction levels—that
can be passed to a verification script for evaluation or retrieving and displaying some contained
information. The information about the type of event can be seen in in.TraceEvent. Please refer to the
topic Sending functions in this manual for details about how to specify transaction levels and which
events should be sent to verification scripts.
7.1 Frame level events
The table below describes the current list of Frame level events (transaction level: 0) and value of
in.TraceEvent:
Types of Frames in.TraceEvent
Primitive only _FRM_PRIMITIVE
OOB Signal Frame _FRM_OOB_SIGNAL
Connect Frame _FRM_CONNECT
Disconnect Frame _FRM_DISCONNECT
Open Address Frame _FRM_AF_OPEN
Identify Address Frame _FRM_AF_IDENTIFY
SSP Frame _FRM_SSP
SMP Frame _FRM_SMP
STP Frame _FRM_STP
7.2 Command level events
No command level events defined yet.
29
Page 35

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
8 Sending Functions
This topic contains information about the special group of VSE functions designed to specify
which events the verification script should expect to receive.
8.1 SendLevel()
This function specifies that events of the specified transaction level should be sent to the script.
Format : SendLevel( level )
Parameters: level – This parameter can be one of following values:
_ATA – ( value 4 ) send ATA Command level events
Note: only Packet and Link Transaction level events are available in release 4.4 of PETracer software.
Example:
SendLevel( _LINK); # - send Link level events
…
Remark:
If no level was specified – events of packet level will be sent to the script by default.
8.2 SendLevelOnly()
This function specifies that ONLY events of the specified transaction level should be sent to the
script.
Format : SendLevelOnly( level )
Parameters: level – This parameter can be one of following values:
_ATA – ( value 4 ) send ATA Command level events
Example:
SendLevelOnly( _LINK ); # - send ONLY Link level events
…
_LINK – ( value 0 ) send Link level events
_LINK – ( value 0 ) send Link level events
30
Page 36

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
8.3 DontSendLevel()
This function specifies that events of the specified transaction level should NOT be sent to the
script.
Format : DontSendLevel( level )
Parameters: level – This parameter can be one of following values:
_LINK – ( value 0 ) do not send Link level events
_ATA – ( value 4 ) do not send ATA Command level events
Example:
DontSendLevel( _LINK ); # - DO NOT send Link level events
…
8.4 SendChannel()
This function specifies that events that have occurred on the specified channel should be sent to
script.
Format : SendChannel( channel )
Parameters: channel – This parameter can be one of following values:
_CHANNEL_2 ( = 2 ) – send events from Channel T1
_CHANNEL_3 ( = 3 ) – send events from Channel I2
_CHANNEL_4 ( = 4 ) – send events from Channel T2
_CHANNEL_5 ( = 5 ) – send events from Channel I3
_CHANNEL_6 ( = 6 ) – send events from Channel T3
_CHANNEL_7 ( = 7 ) – send events from Channel I4
_CHANNEL_8 ( = 8 ) – send events from Channel T4
Example:
SendChannel(_CHANNEL_1); # - send events from Channel I1
…
_CHANNEL_1 ( = 1 ) – send events from Channel I1
31
Page 37

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
8.5 SendChannelOnly()
This function specifies that ONLY events that have occurred on the specified channel should be
sent to the script.
Format : SendChannelOnly( channel )
Parameters: channel – This parameter can be one of following values:
_CHANNEL_1 ( = 1 ) – send events from Channel I1
_CHANNEL_2 ( = 2 ) – send events from Channel T1
_CHANNEL_3 ( = 3 ) – send events from Channel I2
_CHANNEL_4 ( = 4 ) – send events from Channel T2
_CHANNEL_5 ( = 5 ) – send events from Channel I3
_CHANNEL_6 ( = 6 ) – send events from Channel T3
_CHANNEL_7 ( = 7 ) – send events from Channel I4
_CHANNEL_8 ( = 8 ) – send events from Channel T4
Example:
SendChannelOnly( _CHANNEL_1 ); # - send ONLY events from Channel I1
…
8.6 DontSendChannel ()
This function specifies that events that have occurred on the specified channel should NOT be
sent to the script.
Format : DontSendChannel ( channel )
Parameters: channel – This parameter can be one of following values:
_CHANNEL_2 ( = 2 ) – send events from Channel T1
_CHANNEL_3 ( = 3 ) – send events from Channel I2
_CHANNEL_4 ( = 4 ) – send events from Channel T2
_CHANNEL_5 ( = 5 ) – send events from Channel I3
_CHANNEL_6 ( = 6 ) – send events from Channel T3
_CHANNEL_7 ( = 7 ) – send events from Channel I4
_CHANNEL_8 ( = 8 ) – send events from Channel T4
Example:
DontSendChannel ( _CHANNEL_1 ); # - DO NOT send events from Channel I1
…
_CHANNEL_1 ( = 1 ) – send events from Channel I1
32
Page 38

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
8.7 SendAllChannels()
This function specifies that events that have occurred on ALL channels should be sent to the
script.
Format : SendAllChannels ()
Example:
…
SendAllChannels (); # - send events from ALL channels
8.8 SendTraceEvent ()
This function specifies the events to be sent to the script.
Format : SendTraceEvent( event )
Parameters: event – See Verification Script Engine Events
for all possible values.
Example:
…
SendTraceEvent( _FRM_AF_OPEN
…
);
8.9 DontSendTraceEvent()
This function specifies that the event specified in this function should not be sent to script.
Format : DontSendTraceEvent ( event )
Parameters: event – See Verification Script Engine Events for all possible values.
Example:
…
if( SomeCondition )
{
DontSendTraceEvent( _FRM_AF_OPEN
}
);
8.10 SendTraceEventOnly()
This function specifies that ONLY the event specified in this function will be sent to the script.
Format : SendTraceEventOnly( event )
Parameters: event – See Verification Script Engine Events
for all possible values.
33
Page 39

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
Remark: This function may be useful when many events are to be sent, yet you need to send
only one kind of event and turn off the rest.
Example:
…
if( SomeCondition )
{
SendTraceEventOnly (_FRM_AF_OPEN );
}
8.11 SendAllTraceEvents()
This function specifies that ALL trace events relevant for the selected transaction level will be
sent to the script.
Format : SendAllTraceEvents ()
Example:
…
SendLevel( _LINK ); # Send link level events
SendAllTraceEvents ( );
34
Page 40

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
9 Timer Functions
This group of functions covers VSE capability to work with timers –-- internal routines that
repeatedly measures a timing intervals between different events.
9.1 VSE time object
A VSE time object is a special object that presents time intervals in verification scripts.
From point of view of the CSL, the verification script time object is a “list”-object of two elements.
( Please see the CSL Manual for more details about CSL types )
[seconds, nanoseconds]
NOTE: The best way to construct VSE time object is to use Time() function (see below ).
9.2 SetTimer()
Starts timing calculation from the event where this function was called.
Format : SendTimer( timer_id = 0)
Parameters:
timer_id – a unique timer identifier.
Example:
SetTimer(23); # - start timing for timer with id = 23;
Remark :
If this function is called a second time for the same timer id, it resets the timer and starts timing
calculations again from the point where it was called.
SetTimer(); # - start timing for timer with id = 0;
35
Page 41

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
9.3 KillTimer()
Stops timing calculation for a specific timer and frees related resources.
Format : KillTimer( timer_id = 0)
Parameters:
timer_id – a unique timer identifier.
Example:
KillTimer(23); # - stop timing for timer with id = 23;
KillTimer(); # - stop timing for timer with id = 0;
9.4 GetTimerTime()
Retrieve the timing interval from the specific timer
Format : GetTimerTime ( timer_id = 0)
Parameters:
timer_id – a unique timer identifier.
Return values:
Returns VSE time object from timer with id = timer_id.
Example:
GetTimerTime (23); # - Retrieve timing interval for timer with id = 23;
Remark :
This function, when called, does not reset the timer.
GetTimerTime (); # - Retrieve timing interval for timer with id = 0;
36
Page 42

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
10 Time Construction Functions
This group of functions are used to construct VSE time objects.
10.1 Time()
Constructs a verification script time object.
Format : Time(nanoseconds)
Time(seconds, nanoseconds)
Return values:
First function returns [0, nanoseconds], second one returns [seconds, nanoseconds]
Parameters:
nanoseconds – number of nanoseconds in specified time
seconds – number of seconds in specified time
Example:
Time (3, 100); # - create time object of 3 seconds and 100
nanoseconds
Time( 3 * MICRO_SECS ); # - create time object of 3 microseconds
Time( 4 * MILLI_SECS ); # - create time object of 4 milliseconds
NOTE: MICRO_SECS and MILLI_SECS are constants defined in VS_constants.inc.
Time ( 50 * 1000 ); # - create time object of 50 microseconds
37
Page 43

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
11 Time Calculation Functions
This group of functions covers VSE capability to work with “time” —VSE time objects.
11.1 AddTime()
Adds two VSE time objects
Format : AddTime(time1, time2)
Return values:
Returns VSE time object representing the time interval equal to the sum of time_1 and time_2
Parameters:
time_1 - VSE time object representing the first time interval
time_2 - VSE time object representing the second time interval
Example:
t2 = Time(2, 200);
t3 = AddTime( t1, t2 ) # - returns VSE time object = 2 sec 300 ns.
11.2 SubtractTime()
Format : SubtractTime (time1, time2)
Return values:
and time_2
Parameters:
Example:
t2 = Time(2, 200);
t3 = SubtractTime ( t2, t1 ) # - returns VSE time object = 2 sec 100 ns.
11.3 MulTimeByInt()
t1 = Time(100);
Subtract two VSE time objects
Returns VSE time object representing the time interval equal to the difference between time_1
time_1 - VSE time object representing the first time interval
time_2 - VSE time object representing the second time interval
t1 = Time(100);
Multiplies VSE time object by integer value
38
Page 44

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
Format : MulTimeByInt (time, mult)
Return values:
Returns VSE time object representing the time interval equal to the product of time * mult
Parameters:
time - VSE time object
mult - multiplier, integer value
Example:
t1 = MulTimeByInt ( t, 2 ) # - returns VSE time object = 4 sec 400 ns.
t = Time(2, 200);
11.4 DivTimeByInt()
Divides VSE time object by integer value
Format : DivTimeByInt (time, div)
Return values:
Returns VSE time object representing the time interval equal to the quotient of time / div
Parameters:
time - VSE time object
div - divisor, integer value
Example:
t1 = DivTimeByInt ( t, 2 ) # - returns VSE time object = 1 sec 100 ns.
t = Time(2, 200);
39
Page 45

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
12 Time Logical Functions
This group of functions covers VSE capability to compare VSE time objects
12.1 IsEqualTime()
Verifies that one VSE time object is equal to the other VSE time object
Format : IsEqualTime (time1, time2)
Return values:
Returns 1 if time_1 is equal to time_2, returns 0 otherwise
Parameters:
time_1 - VSE time object representing the first time interval
time_2 - VSE time object representing the second time interval
Example:
If( IsEqualTime( t1, t2 ) ) DoSomething();
12.2 IsLessTime()
Format : IsLessTime (time1, time2)
Return values:
Parameters:
Example:
If( IsLessTime ( t1, t2 ) ) DoSomething();
12.3 IsGreaterTime()
Format : IsGreaterTime (time1, time2)
t1 = Time(100); t2 = Time(500);
Verifies that one VSE time object is less than the other VSE time object
Returns 1 if time_1 is less than time_2, returns 0 otherwise
time_1 - VSE time object representing the first time interval
time_2 - VSE time object representing the second time interval
t1 = Time(100); t2 = Time(500);
Verifies that one VSE time object is greater than the other VSE time object
40
Page 46

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
Return values:
Returns 1 if time_1 is greater than time_2, returns 0 otherwise
Parameters:
time_1 - VSE time object representing the first time interval
time_2 - VSE time object representing the second time interval
Example:
If( IsGreaterTime ( t1, t2 ) ) DoSomething();
t1 = Time(100); t2 = Time(500);
12.4 IsTimeInInterval()
Verifies that a VSE time object is greater than some VSE time object and less than the other
VSE time object
Format : IsTimeInInterval( min_time, time, max_time )
Return values:
Returns 1 if min_time <= time <= max_time, returns 0 otherwise
Parameters:
time_1 - VSE time object representing the first time interval
time_2 - VSE time object representing the second time interval
Example:
t = Time(400);
If( IsTimeInInterval ( t1, t, t2 ) ) DoSomething();
t1 = Time(100);
t2 = Time(500);
41
Page 47

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
13 Time Text Functions
This group of functions covers VSE capability to convert VSE time objects into text strings.
13.1 TimeToText()
Converts a VSE time object into text.
Format : TimeToText (time)
Return values:
Returns a text representation of VSE time object
Parameters:
time - VSE time object
Example:
ReportText( TimeToText( t ) ); # see below details for ReportText() function
t = Time(100);
42
Page 48

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
14 Output Functions
This group of functions covers VSE capability to present information in the output window.
14.1 ReportText()
Outputs text in the output window related to the verification script
Format : ReportText (text)
Parameters:
text - text variable,constant or literal
Example:
…
ReportText ( “Some text” );
…
t = “Some text”
ReportText ( t );
…
num_of_frames = in.NumOfFrames;
text = Format( “Number of frames : %d”, num_of_frames );
ReportText ( text );
…
x = 0xAAAA;
y = 0xBBBB;
text = FormatEx( “x = 0x%04X, y = 0x%04X”, x, y );
ReportText( “Text : ” + text );
…
14.2 EnableOutput()
Enables showing information in the output window and sending COM reporting notifications to
COM clients.
Format : EnableOutput ()
Example:
EnableOutput ( );
14.3 DisableOutput()
Disables showing information in the output window and sending COM reporting notifications
to COM clients.
43
Page 49

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
Format : DisableOutput ()
Example:
DisableOutput ();
44
Page 50

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
15 Information Functions
15.1 GetTraceName()
This function returns the filename of the trace file being processed by VSE.
If the script is being run over a multi-segmented trace, this function will return the path to the
segment being processed.
Format : GetTraceName( filepath_compatible )
Parameters:
filepath_compatible - if this parameter is present and not equal to 0, the returned value may be
used as part of the filename.
Example:
…
File = OpenFile( "C:\\My Files\\" + GetTraceName(1) + "_log.log" );
# For trace file with path - D:\Some SAS Traces\Data.sas
# GetTraceName(1) will return – "D_Some SAS Traces_Data.sas"
15.2 GetScriptName()
Format : GetScriptName()
Example:
15.3 GetApplicationFolder()
started.
Format : GetApplicationFolder()
Example:
ReportText( “Trace name : ” + GetTraceName() );
This function returns the name of the verification script where this function is called.
ReportText( “Current script : ” + GetScriptName() );
This function returns the full path of the folder where the SASTracer/SATracer application was
ReportText( “SASTracer folder : ” + GetApplicationFolder () );
45
Page 51

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
15.4 GetCurrentTime()
This function returns the string representation of the current system time.
Format : GetCurrentTime()
Example:
ReportText( GetCurrentTime() ); # will yield “February 10, 2006 5:49 PM”
15.5 GetEventSegNumber()
In case if a multi-segmented trace is being processed, this function returns the index of the
segment for the current event.
NOTE: When a multi-segmented trace file (extension *.smt or *.smat) is processed by VSE – different trace events in
different segments of the same trace file may have the same indexes (value stored in in.Index input context members)
– but they will have different segment numbers.
Format : GetEventSegNumber()
Example:
ReportText( Format( “Current segment = %d”, GetEventSegNumber() ) );
15.6 GetTriggerPacketNumber()
This function returns the number of the trigger packet in the trace. In case no trigger event was
recorded in the trace, a value of 0xFFFFFFFF is returned.
Format : GetTriggerPacketNumber()
Example:
ReportText( FormatEx( “Trigger packet # : %i”, GetTriggerPacketNumber() );
46
Page 52

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
16 Navigation Functions
16.1 GotoEvent ()
This function forces the application to jump to some trace event and show it in the main trace
view.
Format : GotoEvent( level, index, segment )
GotoEvent()
Parameters:
level - the transaction level of the event to jump to (possible values: _LINK, _ATA)
index - the transaction index of the event to jump to
segment - the segment index of the event to jump to. If omitted, the current segment index will
be used.
Remarks:
If no parameters were specified, the application will jump to the current event being processed
by VSE. The segment parameter is used only when the verification script is running over a multisegmented trace (extensions: *.smt, *.samt). For regular traces it is ignored.
If wrong parameters were specified (like an index exceeding the maximum index for the
specified transaction level), the function will do nothing and an error message will be sent to the output
window.
Example:
if( Something == interesting ) GotoEvent(); # go to the current event
…
if( SomeCondition )
…
{
interesting_segment = GetEventSegNumber();
interesting_level = in.Level;
interesting_index = in.Index;
}
…
OnFinishScript()
{
…
# go to the interesting event…
GotoEvent( interesting_level, interesting_index, interesting_segment );
}
47
Page 53

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
16.2 SetMarker()
This function sets a marker for some trace event.
Format : SetMarker( marker_text )
SetMarker( marker_text, level, index, segment )
Parameters:
marker_text - the text of the marker
level - the transaction level of the event to jump to (possible values: _LINK, _ATA)
index - the transaction index of the event to jump to
segment - the segment index of the event to jump to. If omitted, the current segment index will
be used.
Remarks:
If no parameters were specified, other than marker_text, the application will set a marker to the
current event being processed by VSE. The segment parameter is used only when a verification script
is running over a multi-segmented trace (extensions: *.smt, *.samt). For regular traces it is ignored.
If wrong parameters were specified (like an index exceeding the maximum index for a specified
transaction level), the function will do nothing and an error message will be sent to the output window.
Example:
# set marker to the current event
if( Something == interesting ) SetMarker( "!!! Something cool !!!" );
…
if( SomeCondition )
interesting_index,
…
{
interesting_segment = GetEventSegNumber();
interesting_level = in.Level;
interesting_index = in.Index;
}
…
OnFinishScript()
{
…
# set marker to the interesting event…
SetMarker( " !!! Cool Marker !!! ", interesting_level,
interesting_segment );
# go to the interesting event…
GotoEvent( interesting_level, interesting_index, interesting_segment );
}
48
Page 54

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
17 File Functions
This group of functions covers VSE capabilities to work with the external files.
17.1 OpenFile()
This function opens a file for writing.
Format : OpenFile( file_path, append )
Parameters:
file_path - the full path to the file to open. ( For ‘\’ use ‘\\’ )
append - this parameter (if present and not equal to 0) specifies that VSE should append to the
contents of the file – otherwise, the contents of the file will be overwritten.
Return Values:
The “handle” to the file to be used in other file functions.
Example:
set file_handle = 0;
…
file_handle = OpenFile( “D:\\Log.txt” ); # opens file, the previous
contents will be
…
…
CloseFile( file_handle ); # closes file
…
the file.
file_handle = OpenFile( GetApplicationFolder() + “Log.txt”, _APPEND );
…
# erased.
WriteString( file_handle, “Some Text1” ); # write text string to file
WriteString( file_handle, “Some Text2” ); # write text string to file
# opens file, the following file operations will append to the contents of
49
Page 55

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
17.2 CloseFile()
This function closes an opened file.
Format : CloseFile( file_handle )
Parameters:
file_handle - the file “handle”.
Example:
set file_handle = 0;
file_handle = OpenFile( “D:\\Log.txt” ); # opens file, the previous contents will
be
…
…
CloseFile( file_handle ); # closes file
…
…
…
# erased.
WriteString( file_handle, “Some Text1” ); # write text string to file
WriteString( file_handle, “Some Text2” ); # write text string to file
17.3 WriteString()
This function writes a text string to the file.
Format : WriteString( file_handle, text_string )
Parameters:
file_handle - the file “handle”.
text_string - the text string”.
Example:
set file_handle = 0;
file_handle = OpenFile( “D:\\Log.txt” ); # opens file, the previous
contents will be
…
…
CloseFile( file_handle ); # closes file
…
…
# erased.
WriteString( file_handle, “Some Text1” ); # write text string to file
WriteString( file_handle, “Some Text2” ); # write text string to file
…
17.4 ShowInBrowser()
This function allows you to open a file in the Windows Explorer. If the extension of the file has
the application registered to open files with such extensions – it will be launched. For instance, if
50
Page 56

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
Internet Explorer is registered to open files with extensions *.htm and the file handle passed to
ShowInBrowser() function belongs to a file with such an extension,this file will be opened in the
Internet Explorer.
Format : ShowInBrowser ( file_handle )
Parameters:
file_handle - the file “handle”.
Example:
…
set html_file = 0;
…
html_file = OpenFile( “D:\\Log.htm” );
…
WriteString( html_file, “<html><head><title>LOG</title></head>” );
WriteString( html_file, “<body>” );
…
WriteString( html_file, “</body></html>” );
ShowInBrowser( html_file ); # opens the file in Internet Explorer
CloseFile( html_file );
…
51
Page 57

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
18 COM/Automation Communication Functions
This group of functions covers VSE capabilities to communicate with COM/Automation clients
connected to the SASTracer/SATracer application. (Please refer to the SASTracer/SATracer
Automation manual for the details on how to connect to the SASTracer/SATracer application and
VSE).
18.1 NotifyClient()
This function allows you to send information to COM/Automation client applications in a
custom format. The client application will receive a VARIANT object which it is supposed to parse.
Format : NotifyClient( event_id, param_list )
Parameters:
event_id - event identifier
param_list - the list of parameters to be sent to the client application. Each parameter might be
an integer, string or list.
(See CSL Manual for details about data types available in CSL ).
Because the list itself may contain integers, strings, or other lists it is possible
to send complicated messages.
(lists should be treated as arrays of VARIANTs)
Example:
if( SomeCondition() )
{
NotifyClient( 2, [ in.Index, in.Level,
TimeToText( in.Time )] );
}
…
# Here we sent 2 parameters to clients applications :
Remark:
See an example of handling this notification by client applications and parsing code in the
SASTracer/SATracer Automation document.
…
# 2 ( integer ),
# [ in.Index, in.Level, TimeToText( in.Time )] ( list )
52
Page 58

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
19 User Input Functions
19.1 MsgBox()
Displays a message in a dialog box, waits for the user to click a button and returns an Integer
indicating which button the user clicked.
Format : MsgBox( prompt, type, title )
Parameters:
prompt - Required. String expression displayed as the message in the dialog box.
type - Optional. Numeric expression that is the sum of values specifying the number
and type of buttons to display, the icon style to use, the identity of the default
button, and the modality of the message box. If omitted, the default value for
buttons is _MB_OK. (See the list of possible values in the table below)
title - Optional. String expression displayed in the title bar of the dialog box. If you omit
the title, the script name is placed in the title bar.
The type argument values are:
Constant Description
_MB_OKONLY Display OK button only ( by Default ).
_MB_OKCANCEL Display OK and Cancel buttons.
_MB_RETRYCANCEL Display Retry and Cancel buttons.
_MB_YESNO Display Yes and No buttons.
_MB_YESNOCANCEL Display Yes, No, and Cancel buttons.
_MB_ABORTRETRYIGNORE Display Abort, Retry, and Ignore buttons.
_MB_EXCLAMATION Display Warning Message icon.
_MB_INFORMATION Display Information Message icon.
_MB_QUESTION Display Warning Query icon.
_MB_STOP Display Critical Message icon.
_MB_DEFBUTTON1 First button is default.
_MB_DEFBUTTON2 Second button is default.
_MB_DEFBUTTON3 Third button is default.
_MB_DEFBUTTON4 Fourth button is default.
Return Values:
This function returns an integer value indicating which button the user clicked.
53
Page 59

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
Constant Description
_MB_OK OK button was clicked.
_MB_CANCEL Cancel button was clicked.
_MB_YES Yes button was clicked.
_MB_NO No button was clicked.
_MB_RETRY Retry button was clicked.
_MB_IGNORE Ignore button was clicked.
_MB_ABORT Abort button was clicked.
Remark:
This function works only for VS Engines controlled via the GUI. For VSEs controlled by
COM/Automation clients, it does nothing.
This function "locks" the SASTracer/SATracer application, which means that there is no access to
other application features until the dialog box is closed. In order to prevent too many MsgBox calls—in
the case of a script not written correctly—VSE keeps track of all function calls demanding user
interaction and doesn't show dialog boxes if a customizable limit was exceeded (returns _MB_OK in
this case).
Example:
…
if( Something )
{
…
str = "Something happened!!!\nShould we continue?"
result = MsgBox( str ,
_ MB_YESNOCANCEL | _MB_EXCLAMATION,
"Some Title" );
if( result != _MB_YES )
ScriptDone();
… # Go on…
}
54
Page 60

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
19.2 InputBox()
Displays a prompt in a dialog box, waits for the user to input text or click a button, and returns a
CSL list object (see the CSL manual for details about list objects) or a string containing the contents of
the text box.
Format : InputBox( prompt, title, default_text, return_type )
Parameters:
prompt - Required. String expression displayed as the message in the dialog box.
title - Optional. String expression displayed in the title bar of the dialog box. If you omit
title, the script name is placed in the title bar.
default_text - Optional. String expression displayed in the text box as the default
response if no other input is provided. If you omit default_text, the text box is
displayed empty.
return_type – Optional. It specifies the contents of the return object.
The return_type argument values are:
Constant Value Description
_IB_LIST 0 CSL list object will be returned ( by Default ).
_IB_STRING 1 String input as it was typed in the text box
Return Values:
Depending upon the return_type argument, this function returns either a CSL list object or the
text typed in the text box as it is.
In case of return_type = _IB_LIST (by default), the text in the text box is considered as a set of list
items delimited by ',' (only hexadecimal, decimal, and string items are currently supported).
Text example:
Will produce a CSL list object of5 items:
NOTE: Although the dialog box input text parser tries to determine a type of list item automatically, a text enclosed
in quote signs "" is always considered as a string.
Hello world !!!, 12, Something, 0xAA, 10, "1221"
list = [ "Hello world !!!", 12, "Something", 0xAA, 10, "1221" ];
list [0] = "Hello world !!!"
list [1] = 12
list [2] = "Something"
list [3] = 0xAA
list [4] = 10
list [5] = "1212"
55
Page 61

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
Remark:
This function works only for VS Engines controlled via the GUI. For VSEs controlled by
COM/Automation clients, it does nothing.
This function "locks" the SASTracer/SATracer application, which means that there is no access to
other application features until the dialog box is closed. In order to prevent too many InputBox calls—
in the case of a script not written correctly—VSE keeps track of all function calls demanding user
interaction and doesn't show dialog boxes if a customizable limit was exceeded (returns null object in
that case).
Example:
…
if( Something )
{
…
v = InputBox( "Enter the list", "Some stuff", "Hello world !!!, 0x12AAA,
Some, 34" );
ReportText ( FormatEx( "input = %s, 0x%X, %s, %d", v[0],v[1],v[2],v[3]
) );
… # Go on…
str = InputBox( "Enter the string", "Some stuff", "<your string>",
_IB_STRING );
ReportText( str );
}
56
Page 62

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
19.3 GetUserDlgLimit()
This function returns the current limit of user dialogs allowed in the verification script. If the
script reaches this limit, no user dialogs will be shown and the script will not stop. By default this limit
is set to 20.
Format : GetUserDlgLimit()
Example:
…
result = MsgBox( Format( "UserDlgLimit = %d", GetUserDlgLimit() ),
_MB_OKCANCEL | _MB_EXCLAMATION, "Some Title !!!" );
SetUserDlgLimit( 2 ); # set the limit to 2
…
19.4 SetUserDlgLimit()
This function sets the current limit of user dialogs allowed in the verification script. If the script
reaches this limit, no user dialogs will be shown and script will not stop. By default this limit is set to
20.
Format : SetUserDlgLimit()
Example:
…
result = MsgBox( Format( "UserDlgLimit = %d", GetUserDlgLimit() ),
_MB_OKCANCEL | _MB_EXCLAMATION, "Some Title !!!" );
SetUserDlgLimit( 2 ); # set the limit to 2
…
57
Page 63

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
20 String Manipulation/formating Functions
20.1 FormatEx()
Write formatted data to a string. FormatEx() is used to control the way that arguments will print out. The format string may contain conversion specifications that affect the way in which the arguments in the value string are returned. Format conversion characters, flag characters and field width modifiers are used to define the conversion specifications.
Format : FormatEx ( format_string, argument_list )
Parameters:
format_string - Format-control string
argument_list- Optional list of arguments to fill in the format string
Return Values:
Formatted string .
Format conversion characters:
Code Type Output
c Integer Character
d Integer Signed decimal integer
i Integer Signed decimal integer
o Integer Unsigned octal integer
u Integer Unsigned decimal integer
x Integer Unsigned hexadecimal integer, using "abcdef."
X Integer Unsigned hexadecimal integer, using "ABCDEF."
s String String
Remark:
A conversion specification begins with a percent sign (%) and ends with a conversion character.
The following optional items can be included, in order, between the % and the conversion character to
further control argument formatting:
• Flag characters are used to further specify the formatting. There are five flag characters: A minus sign (-) will
cause an argument to be left-aligned in its field. Without the minus sign, the default position of the argument is
right-aligned.
• A plus sign (+) will insert a plus sign before a positive signed integer. This only works with the conversion
characters d and i.
58
Page 64

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
• A space will insert a space before a positive signed integer. This only works with the conversion characters d and
i. If both a space and a plus sign are used, the space flag will be ignored.
• A hash mark (
#) will prepend a 0 to an octal number when used with the conversion character o. If # is used with
x or X, it will prepend 0x or 0X to a hexadecimal number.
• A zero (
• Field width specification is a positive integer that defines the field width, in spaces, of the converted argument. If
the number of characters in the argument is smaller than the field width, then the field is padded with spaces. If the
argument has more characters than the field width has spaces, then the field will expand to accommodate the
argument.
0) will pad the field with zeros instead of with spaces.
Example:
str = "String";
i = 12;
hex_i = 0xAABBCCDD;
…
formatted_str = FormatEx( "%s, %d, 0x%08X", str, i, hex_i );
# formatted_str = "String, 12, 0xAABBCCDD"
59
Page 65

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
21 Miscellaneous Functions
21.1 ScriptForDisplayOnly()
Specifies that the script is designed for displaying information only and that its author doesn’t
care about verification script result. Such a script will have a result of DONE after execution.
Format : ScriptForDisplayOnly ()
Example:
ScriptForDisplayOnly();
21.2 Sleep()
Asks VSE not to send any events to a script until the timestamp of the next event is greater than
the timestamp of the current event plus sleeping time.
Format : Sleep( time )
Parameters:
time - VSE time object specifying sleep time
Example:
current event
21.3 ConvertToHTML()
string.
Format : ConvertToHTML( text_string )
Parameters:
Example:
str += “How are you today?”;
html_str = ConvertToHTML ( str );
# html_string =
“Hello world !!!<br>How are you today?”
NOTE : Some other useful miscellaneous functions can be found in the file VSTools.inc
Sleep ( Time(1000) ); # Don’t send any event occurred during 1 ms from the
This function replaces spaces with “ ” and carriage return symbols with “<br>” in a text
text_string - text string
str = “Hello world !!!\n”;
60
Page 66

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
21.4 Pause()
Pauses a running script. Later, script execution can be resumed or cancelled.
Format : Pause()
Example:
…
If( Something_Interesting() )
{
GotoEvent(); # Jump to the trace view
Pause(); # Pause script execution
}
…
Remark:
This function works only for VS Engine controlled via a GUI. For VSEs controlled by
COM/Automation clients, it does nothing.
When script execution is paused, the Run Verification Script window will look like:
Click right mouse button and
select 'Stop verification
script(s)' menu item to
cancel script execution.
Click this button to resume
script running.
61
Page 67

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
22 The VSE Important Script Files
The VSE working files are located in the ..\Scripts\VFScripts subfolder of the main
SASTracer/SATracer folder. The current version of VSE includes the following files:
File Description
VSTools.inc
VS_constants.inc
VSTemplate.sasv_
VSUser_globals.inc
VS_OOB.inc
VS_Primitives.inc
VS_SMPFrames.inc
VS_SSPFrames.inc
VS_STPFrames.inc
VS_AddressFrames.inc
VS_ATACommands.inc
22.1 Example script files
The VSE example files are located in the ..\Scripts\VFScripts\Samples subfolder of the main
SASTracer/SATracer folder. The current version of VSE includes the following files:
File Description
sample1.sasvs
sample2.sasvs
sample3.sasvs
sample_ata_commands.sasvs
sample_ssp_protocol.sasvs
main VSE file containing definitions of some generic and SAS/SATAspecific VSE script functions provided by LeCroy (must be included in
every script)
file containing definitions of some important generic and SAS/SATAspecific VSE global constants
template file for new verification scripts.
file of user global variable and constant definitions (In this file, it is useful
to enter definitions of constants, variables, and functions to be used in many
scripts you write.)
OOB definitions and utilities
Primitives definitions and utilities
SMP Frames definitions and utilities
SSP Frames definitions and utilities
STP Frames definitions and utilities
Address Frames definitions and utilities
ATA Commands definitions and utilities
Sample script that outputs all frames
Sample script that outputs all data payloads
Sample script that outputs all ATA Commands
Sample script that outputs all frames
Sample script that outputs all frames
62
Page 68

LeCroy Corporation Verification Script Engine Reference Manual Version 1.01
How to Contact LeCroy
Type of Service Contract
Call for technical support… US and Canada: 1 (800) 909-2282
Worldwide: 1 (408) 727-6600
Fax your questions… Worldwide: 1 (408) 727-6622
Write a letter … LeCroy Corporation
Customer Support
3385 Scott Blvd.
Santa Clara, CA 95054
Send e-mail… support@lecroy.com
Visit LeCroy web site… http://www.lecroy.com/
63
 Loading...
Loading...