Teledyne GFC-7000E Instruction Manual

INSTRUCTION MANUAL
MODEL GFC7000E
CARBON DIOXIDE ANALYZER
© TELEDYNE ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTS
16830 Chestnut St.
City of Industry, Ca. 91748
USA
Phone:
626-961-9221
Phone:
626-934-1500
Fax:
626-961-2538
Fax:
626-934-1651
04584
REV. A1
Copyright 2003 Teledyne Instruments Incorporated
02-August-2004


Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual GFC7000E Documentation
04584 Rev A1 i
SAFETY MESSAGES
Your safety and the safety of others is very important. We have provided many important safety
messages in this manual. Please read these messages carefully.
A safety message alerts you to potential hazards that could hurt you or others. Each safety
message is associated with a safety alert symbol. These symbols are found in the manual and
inside the instrument. The definition of these symbols is described below:
GENERAL SAFETY HAZARD: Refer to the instructions for
details on the specific hazard.
CAUTION: Hot Surface Warning
CAUTION: Electrical Shock Hazard
TECHNICIAN SYMBOL: All operations marked with this
symbol are to be performed by qualified maintenance
personnel only.
CAUTION
The analyzer should only be used for the purpose and in the manner described in this
manual. If you use the analyzer in a manner other than that for which it was intended,
unpredictable behavior could ensue with possible hazardous consequences.

NGFC7000E Documentation Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SAFETY MESSAGES .................................................................................................................................I
TABLE OF CONTENTS............................................................................................................................ II
LIST OF APPENDICES .........................................................................................................................VII
LIST OF FIGURES ...............................................................................................................................VII
LIST OF TABLES................................................................................................................................ VIII
1. MGFC7000E DOCUMENTATION.......................................................................................................... 1
1.1. Using This Manual.......................................................................................................................... 1
2. SPECIFICATIONS, APPROVALS AND WARRANTY.............................................................................. 5
2.1. Specifications ................................................................................................................................ 5
2.2. CE Mark Compliance ...................................................................................................................... 6
2.3. Warranty ...................................................................................................................................... 6
3. GETTING STARTED ............................................................................................................................ 9
3.1. Unpacking and Initial Set Up........................................................................................................... 9
3.1.1. Electrical Connections.............................................................................................................11
3.1.2. Pneumatic Connections: .........................................................................................................15
3.1.2.1. Basic Pneumatic Connections............................................................................................15
3.1.2.2. Connections with Internal Valve Options Installed ..............................................................19
3.2. Initial Operation ...........................................................................................................................21
3.2.1. Startup .................................................................................................................................22
3.2.2. Warm Up...............................................................................................................................23
3.2.3. Warning Messages .................................................................................................................24
3.2.4. Functional Check....................................................................................................................25
3.3. Initial Calibration Procedure...........................................................................................................26
4. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ................................................................................................... 31
4.1. FAQ’s...........................................................................................................................................31
4.2. Glossary ......................................................................................................................................32
5. OPTIONAL HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE......................................................................................... 35
5.1. Rack Mount Kits (Options 20a, 20b & 21)........................................................................................35
5.2. Current Loop Analog Outputs (Option 41) .......................................................................................35
5.3. Expendable Kits (Options 42C, 42D and 43)....................................................................................36
5.4. Calibration Valves Options .............................................................................................................36
5.4.1. Zero/Span/Shutoff Valve (Option 50).......................................................................................36
5.4.2. Zero/Span/Shutoff with External CO2 Scrubber (Option 51) ......................................................38
5.4.3. Zero/Span Valve (Option 52) ..................................................................................................38
5.4.4. Zero/Span Valve with External CO2 Scrubber (Option 53) ..........................................................39
5.5. Communication Options ................................................................................................................39
5.5.1. RS232 Modem Cable (Option 60).............................................................................................39
5.5.2. RS-232 Multidrop (Option 62) .................................................................................................40
5.5.3. Ethernet (Option 63) ..............................................................................................................40
5.6. Additional Manuals........................................................................................................................40
5.6.1. Printed Manuals (Option 70) ...................................................................................................40
5.6.2. Manual on CD (Part number 045840200) .................................................................................41
5.7. Extended Warranty (Options 92 & 93) ............................................................................................41
5.8. Dilution Ratio Option (Option ??)....................................................................................................41
5.9. Maintenance Mode Switch (Option ??) ............................................................................................41
5.10. Second Language Switch (Option ??) ............................................................................................42
6. OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS ........................................................................................................... 43
6.1. Overview of Operating modes ........................................................................................................43
6.2. Sample Mode ...............................................................................................................................44
6.2.1. Test Functions .......................................................................................................................44
6.2.2. Warning Messages .................................................................................................................46
6.3. Calibration Mode...........................................................................................................................48
6.3.1. SETUP – PASS: Calibration Password Security ..........................................................................48
6.4. SETUP Mode.................................................................................................................................50
6.4.1. SETUP Mode Password Security...............................................................................................51
6.5. SETUP – CFG: Viewing the Analyzer’s Configuration Information .......................................................51
6.6. SETUP – CLK: Setting the Internal Time-of-Day Clock ......................................................................52

Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual GFC7000E Documentation
04584 Rev A1 iii
6.7. SETUP – RNGE: Analog Output Reporting Range Configuration .........................................................54
6.7.1. Physical Range versus Analog Output Reporting Ranges ............................................................54
6.7.2. Reporting Range Modes ..........................................................................................................55
6.7.3. Single Range mode (SNGL).....................................................................................................56
6.7.4. Dual Range Mode (DUAL) .......................................................................................................58
6.7.5. Auto Range Mode (AUTO) .......................................................................................................59
6.7.6. Range Units...........................................................................................................................60
6.7.7. Dilution Ratio.........................................................................................................................61
6.8. SETUP – VARS: Using the Internal Variables ...................................................................................62
6.9. SETUP – DIAG: Using the Diagnostics Functions ..............................................................................64
6.9.1. Accessing the Diagnostic Features ...........................................................................................65
6.9.2. Signal I/O .............................................................................................................................65
6.9.3. Analog Output Step Test.........................................................................................................66
6.9.4. Analog I/O Configuration ........................................................................................................67
6.9.4.1. Analog Output Signal Type and Range Span Selection ........................................................69
6.9.4.2. Analog Output Calibration Mode........................................................................................69
6.9.4.3. Manual Analog Output Calibration and Voltage Adjustment..................................................71
6.9.4.4. Current Loop Output Adjustment ......................................................................................73
6.9.4.5. AIN Calibration................................................................................................................75
6.9.5. Electric Test...........................................................................................................................75
6.9.6. Dark Calibration Test..............................................................................................................76
6.9.7. Pressure Calibration ...............................................................................................................76
6.9.8. Flow Calibration .....................................................................................................................78
6.9.9. Test Channel Output ..............................................................................................................79
6.10. SETUP – COMM: Using the Analyser’s Communication Ports............................................................80
6.10.1. Analyzer ID Code .................................................................................................................80
6.10.2. COMM Port Default Settings ..................................................................................................81
6.10.3. COMM Port Cable Connections ...............................................................................................82
6.10.4. RS-485 Configuration of COM2 ..............................................................................................82
6.10.5. DTE and DCE Communication................................................................................................83
6.10.6. COMM Port Communication Modes .........................................................................................83
6.10.7. COM Port Baud Rate .............................................................................................................86
6.10.8. COM Port Testing .................................................................................................................87
6.10.9. Ethernet Card Configuration ..................................................................................................87
6.10.9.1. Ethernet Card COM2 Communication Modes and Baud Rate...............................................88
6.10.9.2. Configuring the Ethernet Interface Option using DHCP ......................................................88
6.10.9.3. Manually Configuring the Network IP Addresses ...............................................................90
6.10.9.4. Changing the Analyzer’s HOSTNAME ...............................................................................92
6.11. SETUP – ALRM: Using the Gas Concentration Alarms......................................................................93
6.12. SETUP – DAS: Using the Data Acquisition System (iDAS) ...............................................................94
6.12.1. iDAS Structure.....................................................................................................................94
6.12.1.1. iDAS Channels...............................................................................................................95
6.12.1.2. iDAS Parameters ...........................................................................................................96
6.12.1.3. iDAS Triggering Events ..................................................................................................96
6.12.2. Default iDAS Channels..........................................................................................................97
6.12.2.1. Viewing iDAS Data and Settings....................................................................................101
6.12.2.2. Editing iDAS Data Channels ..........................................................................................102
6.12.2.3. Trigger Events.............................................................................................................103
6.12.2.4. Editing iDAS Parameters ..............................................................................................104
6.12.2.5. Sample Period and Report Period ..................................................................................105
6.12.2.6. Number of Records ......................................................................................................107
6.12.2.7. RS-232 Report Function ...............................................................................................108
6.12.2.8. Compact Report ..........................................................................................................109
6.12.2.9. Starting Date ..............................................................................................................109
6.12.2.10. Disabling/Enabling Data Channels ...............................................................................109
6.12.2.11. HOLDOFF Feature ......................................................................................................110
6.12.3. Remote iDAS Configuration .................................................................................................111
6.13. Remote Operation of the Analyzer ..............................................................................................113
6.13.1. Remote Operation Using the External Digital I/O...................................................................113
6.13.1.1. Status Outputs ............................................................................................................113

NGFC7000E Documentation Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual
6.13.1.2. Control Inputs.............................................................................................................114
6.13.2. Remote Operation Using the External Serial I/O....................................................................115
6.13.2.1. Terminal Operating Modes............................................................................................115
6.13.2.2. Help Commands in Terminal Mode ................................................................................116
6.13.2.3. Command Syntax ........................................................................................................116
6.13.2.4. Data Types .................................................................................................................117
6.13.2.5. Status Reporting .........................................................................................................118
6.13.2.6. Remote Access by Modem ............................................................................................118
6.13.2.7. COM Port Password Security.........................................................................................120
6.13.2.8. APICOM Remote Control Program .................................................................................120
6.13.3. Additional Communications Documentation ..........................................................................121
6.13.4. Using the MGFC7000E with a Hessen Protocol Network..........................................................121
6.13.4.1. General Overview of Hessen Protocol ............................................................................121
6.13.4.2. Hessen COMM Port Configuration ..................................................................................122
6.13.4.3. Activating Hessen Protocol ...........................................................................................122
6.13.4.4. Selecting a Hessen Protocol Type ..................................................................................123
6.13.4.5. Setting The Hessen Protocol Response Mode ..................................................................124
6.13.4.6. Hessen Protocol Gas ID................................................................................................124
6.13.4.7. Setting Hessen Protocol Status Flags.............................................................................125
6.13.4.8. Instrument ID Code.....................................................................................................126
7. CALIBRATION PROCEDURES ......................................................................................................... 129
7.1. Before Calibration .......................................................................................................................129
7.1.1. Zero Air and Span Gas .........................................................................................................129
7.1.2. Calibration Gas Traceability...................................................................................................130
7.1.3. Data Recording Devices ........................................................................................................130
7.2. Manual Calibration without Zero/Span Valves ................................................................................130
7.3. Manual Calibration Checks...........................................................................................................133
7.4. Manual Calibration with Zero/Span Valves.....................................................................................133
7.5. Manual Calibration Checks with Zero/Span Valves .........................................................................137
7.5.1. Zero/Span Calibration on Auto Range or Dual Ranges .............................................................137
7.5.2. Use of Zero/Span Valves with Remote Contact Closure............................................................138
7.6. Automatic Zero/Span Cal/Check (AutoCal) ....................................................................................139
7.6.1. AutoCal with Auto or Dual Reporting Ranges Modes Selected ...................................................142
7.7. Calibration Quality ......................................................................................................................142
8. EPA PROTOCOL CALIBRATION ...................................................................................................... 145
9. MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE & PROCEDURES................................................................................... 147
9.1. Maintenance Schedule.................................................................................................................147
9.2. Predicting Failures Using the Test Functions ..................................................................................150
9.3. Maintenance Procedures..............................................................................................................150
9.3.1. Replacing the Sample Particulate Filter ..................................................................................151
9.3.2. Rebuilding the Sample Pump.................................................................................................152
9.3.3. Performing Leak Checks .......................................................................................................152
9.3.3.1. Vacuum Leak Check and Pump Check .............................................................................152
9.3.3.2. Pressure Leak Check......................................................................................................152
9.3.4. Performing a Sample Flow Check...........................................................................................153
9.3.5. Cleaning the Optical Bench ...................................................................................................153
9.3.6. Cleaning Exterior Surfaces of the MGFC7000E ........................................................................153
10. THEORY OF OPERATION.............................................................................................................. 155
10.1. Measurement Method ................................................................................................................155
10.1.1. Beer’s Law.........................................................................................................................155
10.1.2. Measurement Fundamentals................................................................................................156
10.1.3. Gas Filter Correlation..........................................................................................................156
10.1.4. Ambient CO2 Interference Rejection.....................................................................................160
10.2. Pneumatic Operation.................................................................................................................160
10.2.1. Sample Gas Flow................................................................................................................161
10.2.1.1. Critical Flow Orifice ......................................................................................................161
10.2.1.2. Sample Pressure Sensor...............................................................................................162
10.2.1.3. Sample Flow Sensor ....................................................................................................162
10.2.1.4. Valve Options..............................................................................................................163
10.2.2. Purge Gas Pressure and Flow Control ...................................................................................163
10.3. Electronic Operation..................................................................................................................163

Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual GFC7000E Documentation
04584 Rev A1 v
10.3.1. Overview...........................................................................................................................163
10.3.2. CPU ..................................................................................................................................165
10.3.3. Optical Bench & GFC Wheel.................................................................................................165
10.3.3.1. Sample Gas and GFC Temperature Control ....................................................................165
10.3.3.2. IR Source ...................................................................................................................166
10.3.3.3. GFC Wheel..................................................................................................................166
10.3.3.4. IR Photo-Detector........................................................................................................167
10.3.4. Synchronous Demodulator (Sync/Demod) Assembly..............................................................167
10.3.4.1. Overview ....................................................................................................................167
10.3.4.2. Signal Synchronization and Demodulation......................................................................168
10.3.4.3. Phase Lock Warning.....................................................................................................169
10.3.4.4. Sync/Demod Status LED’s ............................................................................................169
10.3.4.5. Photo-Detector Temperature Control .............................................................................170
10.3.4.6. Dark Calibration Switch................................................................................................170
10.3.4.7. Electric Test Switch......................................................................................................170
10.3.5. Relay Board.......................................................................................................................170
10.3.5.1. Status LED’s ...............................................................................................................171
10.3.5.2. I
2
C Watch Dog Circuitry ..............................................................................................172
10.3.6. Mother Board.....................................................................................................................172
10.3.6.1. A to D Conversion........................................................................................................172
10.3.6.2. Sensor Inputs .............................................................................................................173
10.3.6.3. Thermistor Interface ....................................................................................................173
10.3.6.4. Analog Outputs ...........................................................................................................174
10.3.6.5. Internal Digital I/O ......................................................................................................174
10.3.6.6. External Digital I/O......................................................................................................175
10.3.7. I2C Data Bus......................................................................................................................175
10.3.8. Power Supply/ Circuit Breaker .............................................................................................175
10.4. Interface..................................................................................................................................176
10.4.1. Front Panel Interface ..........................................................................................................177
10.4.1.1. Analyzer Status LED’s ..................................................................................................178
10.4.1.2. Keyboard....................................................................................................................178
10.4.1.3. Display .......................................................................................................................178
10.4.1.4. Keyboard/Display Interface Electronics..........................................................................179
10.5. Software Operation ...................................................................................................................180
10.5.1. Adaptive Filter ...................................................................................................................181
10.5.2. Calibration - Slope and Offset..............................................................................................181
10.5.3. Measurement Algorithm......................................................................................................182
10.5.4. Temperature and Pressure Compensation.............................................................................182
10.5.5. Internal Data Acquisition System (iDAS) ..............................................................................182
11. TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR PROCEDURES............................................................................. 185
11.1. General Troubleshooting Hints ...................................................................................................185
11.1.1. Interpreting WARNING Messages.........................................................................................186
11.1.2. Fault Diagnosis with TEST Functions ....................................................................................188
11.1.3. Using the Diagnostic Signal I/O Function ..............................................................................190
11.1.4. Internal Electronic Status LED’s...........................................................................................191
11.1.4.1. CPU Status Indicator....................................................................................................191
11.1.4.2. Sync Demodulator Status LED’s ....................................................................................192
11.1.4.3. Relay Board Status LED’s .............................................................................................193
11.1.5. Gas Flow Problems .............................................................................................................194
11.1.6. Typical Sample Gas Flow Problems ......................................................................................195
11.1.6.1. Flow is Zero ................................................................................................................195
11.1.6.2. Low Flow ....................................................................................................................195
11.1.6.3. High Flow ...................................................................................................................196
11.1.6.4. Displayed Flow = “XXXX” .............................................................................................196
11.1.6.5. Actual Flow Does Not Match Displayed Flow ...................................................................196
11.1.6.6. Sample Pump..............................................................................................................196
11.1.7. Poor or Stopped Flow of Purge Gas ......................................................................................196
11.2. Calibration Problems .................................................................................................................197
11.2.1. Miss-Calibrated ..................................................................................................................197
11.2.2. Non-Repeatable Zero and Span ...........................................................................................197

NGFC7000E Documentation Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual
11.2.3. Inability to Span – No SPAN Key..........................................................................................198
11.2.4. Inability to Zero – No ZERO Key ..........................................................................................198
11.3. Other Performance Problems......................................................................................................198
11.3.1. Temperature Problems........................................................................................................199
11.3.1.1. Box or Sample Temperature .........................................................................................199
11.3.1.2. Bench Temperature .....................................................................................................199
11.3.1.3. GFC Wheel Temperature ..............................................................................................200
11.3.1.4. IR Photo-Detector TEC Temperature..............................................................................200
11.3.2. Excessive Noise..................................................................................................................200
11.4. Subsystem Checkout.................................................................................................................201
11.4.1. AC Mains Configuration.......................................................................................................201
11.4.2. DC Power Supply ...............................................................................................................202
11.4.3. I2C Bus .............................................................................................................................202
11.4.4. Keyboard/Display Interface .................................................................................................203
11.4.5. Relay Board.......................................................................................................................203
11.4.6. Sensor Assembly................................................................................................................204
11.4.6.1. Sync/Demodulator Assembly ........................................................................................204
11.4.6.2. Opto Pickup Assembly..................................................................................................204
11.4.6.3. GFC Wheel Drive .........................................................................................................205
11.4.6.4. IR Source ...................................................................................................................205
11.4.6.5. Pressure/Flow Sensor Assembly....................................................................................205
11.4.7. Motherboard ......................................................................................................................206
11.4.7.1. A/D Functions .............................................................................................................206
11.4.7.2. Analog Outputs: Voltage ..............................................................................................206
11.4.7.3. Analog Outputs: Current Loop ......................................................................................207
11.4.7.4. Status Outputs ............................................................................................................207
11.4.7.5. Control Inputs – Remote Zero, Span .............................................................................208
11.4.8. CPU ..................................................................................................................................208
11.4.9. RS-232 Communications.....................................................................................................208
11.4.9.1. General RS-232 Troubleshooting...................................................................................208
11.4.9.2. Troubleshooting Analyzer/Modem or Terminal Operation .................................................209
11.5. Repair Procedures.....................................................................................................................209
11.5.1. Repairing Sample Flow Control Assembly .............................................................................209
11.5.2. Removing/Replacing the GFC Wheel.....................................................................................211
11.5.3. Disk-On-Chip Replacement Procedure ..................................................................................212
12. A PRIMER ON ELECTRO-STATIC DISCHARGE .............................................................................. 215
12.1. How Static Charges are Created .................................................................................................215
12.2. How Electro-Static Charges Cause Damage .................................................................................216
12.3. Common Myths About ESD Damage ...........................................................................................217
12.4. Basic Principles of Static Control.................................................................................................218
12.4.1. General Rules ....................................................................................................................218
12.4.2. Basic anti-ESD Procedures for Analyzer Repair and Maintenance.............................................220
12.4.2.1. Working at the Instrument Rack ...................................................................................220
12.4.2.2. Working at a Anti-ESD Work Bench. ..............................................................................220
12.4.2.3. Transferring Components from Rack To Bench and Back .................................................221
12.4.2.4. Opening Shipments from and Packing Components for Return to Teledyne Instruments
Customer Service. .....................................................................................................................222

Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual GFC7000E Documentation
04584 Rev A1 vii
LIST OF APPENDICES
APPENDIX A - VERSION SPECIFIC SOFTWARE DOCUMENTATION
APPENDIX A-1: MGFC7000E Software Menu Trees, Revision E.0
APPENDIX A-2: Setup Variables For Serial I/O, Revision E.0
APPENDIX A-3: Warnings and Test Functions, Revision E.0
APPENDIX A-4: MGFC7000E Signal I/O Definitions, Revision E.0
APPENDIX A-5: MGFC7000E iDAS Functions, Revision E.0
APPENDIX A-6: Terminal Command Designators, Revision E.0
APPENDIX B - GFC7000E SPARE PARTS LIST
APPENDIX C - REPAIR QUESTIONNAIRE - MGFC7000E
APPENDIX D - ELECTRONIC SCHEMATICS
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 3-1: Removal of Shipping Screws ............................................................................10
Figure 3-2: Rear Panel Layout...........................................................................................12
Figure 3-3: Pneumatic Connections–Basic Configuration–Using Bottled Span Gas .....................16
Figure 3-4: Pneumatic Connections–Basic Configuration–Using Gas Dilution Calibrator..............17
Figure 3-5: Pneumatic Connections–MGFC7000E with Zero/Span/Shutoff Valves (OPT 50).........19
Figure 3-6 Pneumatic Connections–MGFC7000E with Zero/Span/Shutoff Valves and External
Zero Air Scrubber (OPT 51) ............................................................................19
Figure 3-7: Pneumatic Connections–MGFC7000E with Zero/Span Valves (OPT 52)....................20
Figure 3-8: Pneumatic Connections–MGFC7000E with Zero/Span Valves with External Zero air
Scrubber (OPT 53) ........................................................................................20
Figure 3-9: Example of Pneumatic Set up for Multipoint Calibration of M360 ............................21
Figure 3-10: Front Panel Layout ..........................................................................................23
Figure 3-11: Assembly Layout ............................................................................................29
Figure 3-12: Optical Bench Layout.......................................................................................30
Figure 3-13: Internal Pneumatic Flow – Basic Configuration ....................................................30
Figure 5-1: Current Loop Option Installed on the Motherboard...............................................35
Figure 5-2: Internal Pneumatic Flow – Zero/Span/Shutoff Valves OPT 50 & 51.........................37
Figure 5-3: Internal Pneumatic Flow – Zero/Span OPT 52 & 53..............................................39
Figure 5-4: GFC7000E Ethernet Card and rear panel With Ethernet Installed ...........................40
Figure 6-1: Front Panel Display .........................................................................................43
Figure 6-2 Viewing MGFC7000E TEST Functions..................................................................46
Figure 6-3 Viewing and Clearing MGFC7000E WARNING Messages ........................................48
Figure 6-4: Analog Output Connector Pin Out......................................................................54
Figure 6-5: Setup for Calibrating Analog Voltage Outputs......................................................72
Figure 6-6: Setup for Calibrating Current Outputs................................................................73
Figure 6-7: Default iDAS Channels Setup............................................................................99
Figure 6-8: APICOM user interface for configuring the iDAS................................................. 111
Figure 6-9: iDAS Configuration Through a Terminal Emulation Program. ...............................112
Figure 6-10: Status Output Connector................................................................................ 113
Figure 6-11: Control Inputs ..............................................................................................115
Figure 6-12: APICOM Remote Control Program Interface ...................................................... 121
Figure 7-1: Pneumatic Connections–Basic Configuration–Using Bottled Span Gas ................... 130
Figure 7-2: Pneumatic Connections–Basic Configuration–Using Gas Dilution Calibrator............ 131
Figure 7-3: Pneumatic Connections–MGFC7000E with Zero/Span/Shutoff Valves (OPT 50)....... 134
Figure 7-4 Pneumatic Connections–MGFC7000E with Zero/Span/Shutoff Valves and External
Zero Air Scrubber (OPT 51) .......................................................................... 134

NGFC7000E Documentation Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual
Figure 7-5: Pneumatic Connections–MGFC7000E with Zero/Span Valves (OPT 52)..................134
Figure 7-6: Pneumatic Connections–MGFC7000E with Zero/Span Valves with External Zero air
Scrubber (OPT 53) ...................................................................................... 135
Figure 9-1: Sample Particulate Filter Assembly..................................................................151
Figure 10-1: Measurement Fundamentals........................................................................... 156
Figure 10-2: GFC Wheel................................................................................................... 157
Figure 10-3: Measurement Fundamentals with GFC Wheel ....................................................157
Figure 10-4: Affect of CO2 in the Sample on CO2 MEAS & CO2 REF ........................................ 158
Figure 10-5: Effects of Interfering Gas on CO2 MEAS & CO2 REF ........................................... 159
Figure 10-6: Chopped IR Signal ........................................................................................ 159
Figure 10-7: Internal Pneumatic Flow – Basic Configuration ..................................................161
Figure 10-8: Flow Control Assembly & Critical Flow Orifice ....................................................162
Figure 10-9: GFC7000E Electronic Block Diagram ................................................................ 164
Figure 10-10: GFC Light Mask............................................................................................. 166
Figure 10-11: Segment Sensor and M/R Sensor Output..........................................................167
Figure 10-12: GFC7000E Sync / Demod Block Diagram ..........................................................168
Figure 10-13: Sample & Hold Timing ...................................................................................169
Figure 10-14: Location of relay board Status LED’s ................................................................ 172
Figure 10-15: Power Distribution Block Diagram....................................................................176
Figure 10-16: Interface Block Diagram................................................................................. 177
Figure 10-17: MGFC7000E Front Panel Layout....................................................................... 177
Figure 10-18: Keyboard and Display Interface Block Diagram.................................................. 179
Figure 10-19: Basic Software Operation ............................................................................... 181
Figure 11-1: Viewing and Clearing Warning Messages .......................................................... 186
Figure 11-2: Example of Signal I/O Function....................................................................... 191
Figure 11-3: CPU Status Indicator ..................................................................................... 192
Figure 11-4: Sync/Demod Board Status LED Locations .........................................................193
Figure 11-5: Relay Board Status LEDs................................................................................ 193
Figure 11-6: Critical Flow Restrictor Assembly Disassembly................................................... 210
Figure 11-7: Opening the GFC Wheel Housing ..................................................................... 211
Figure 11-8: Removing the GFC Wheel................................................................................ 212
Figure 12-1: Triboelectric Charging.................................................................................... 215
Figure 12-2: Basic anti-ESD Work Station........................................................................... 218
Figure A-1: Basic Sample Display Menu.............................................................................225
Figure A-2: Sample Display Menu - Units with Z/S Valve or IZS Option installed ..................... 226
Figure A-3: Primary Setup Menu (Except iDAS) .................................................................. 227
Figure A-4: Primary Setup Menu (iDAS)............................................................................ 228
Figure A-5: Secondary Setup Menu (COMM & VARS) ........................................................... 229
Figure A-6: Secondary Setup Menu (COMM Menu with Ethernet Card) ...................................230
Figure A-7: Secondary Setup Menu (COMM Menu with HESSEN) ........................................... 231
Figure A-8: Secondary Setup Menu (DIAG) ........................................................................ 232
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2-1: Model GFC7000E Basic Unit Specifications ............................................................ 5
Table 3-1: GFC7000E Analog Output Pin Outs .....................................................................13
Table 3-2: GFC7000E Status Output Pin Outs......................................................................14
Table 3-3: GFC7000E Control Input Pin Outs.......................................................................15
Table 3-4: Model GFC7000E Rear Panel Pneumatic Connections.............................................16
Table 3-5: Front Panel Display During System Warm-Up.......................................................23
Table 3-6: Possible Warning Messages at Start-Up...............................................................24
Table 5-1: Zero/Span Valve Operating States for Options 50 & 51 .........................................36
Table 5-2: Zero/Span Valve Operating States for Options 52 & 53 .........................................38

Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual GFC7000E Documentation
04584 Rev A1 ix
Table 6-1: Analyzer Operating modes ................................................................................44
Table 6-2: Test Functions Defined .....................................................................................45
Table 6-3: List of Warning Messages..................................................................................47
Table 6-4: Primary Setup Mode Features and Functions........................................................50
Table 6-5: Secondary Setup Mode Features and Functions ....................................................50
Table 6-6: Variable Names (VARS) Revision B.3 ..................................................................62
Table 6-7: GFC7000E Diagnostic (DIAG) Functions ..............................................................64
Table 6-8: DIAG - Analog I/O Functions .............................................................................67
Table 6-9: Analog Output Voltage Ranges...........................................................................67
Table 6-10: Analog Output Current Loop Range.....................................................................68
Table 6-11: Analog Output Pin Assignments..........................................................................68
Table 6-12: Voltage Tolerances for Analog Output Calibration..................................................71
Table 6-13: Current Loop Output Calibration with Resistor ......................................................74
Table 6-14: Test Parameters Available for Analog Output A3 ...................................................79
Table 6-15: COM1 and COM2 DB-9 Pin Assignments ..............................................................83
Table 6-16: COMM Port Communication modes .....................................................................84
Table 6-17: Ethernet Status Indicators.................................................................................87
Table 6-18: LAN/Internet Configuration Properties.................................................................88
Table 6-19: Internet Configuration Keypad Functions .............................................................92
Table 6-20: CO2 Concentration Alarm Default Settings ...........................................................93
Table 6-21: Front Panel LED Status Indicators for iDAS ..........................................................94
Table 6-22: iDAS Data Channel Properties ............................................................................95
Table 6-23: iDAS Data Parameter Functions..........................................................................96
Table 6-24: Status Output Pin Assignments ........................................................................ 114
Table 6-25: Control Input Pin Assignments .........................................................................114
Table 6-26: Terminal Mode Software Commands ................................................................. 116
Table 6-27: Command Types ............................................................................................ 117
Table 6-28: Serial Interface Documents ............................................................................. 121
Table 6-29: RS-232 Communication Parameters for Hessen Protocol ...................................... 122
Table 6-30: Teledyne Instruments Hessen Protocol Response Modes ...................................... 124
Table 6-31: Default Hessen Status Bit Assignments ............................................................. 125
Table 7-1: AUTOCAL Modes ............................................................................................139
Table 7-2: AutoCal ATTRIBUTE Setup Parameters ..............................................................139
Table 7-3: Calibration Data Quality Evaluation...................................................................142
Table 9-1: GFC7000E Maintenance Schedule..................................................................... 148
Table 9-2: GFC7000E Test Function Record....................................................................... 149
Table 9-3: Predictive uses for Test Functions..................................................................... 150
Table 10-1: Sync/Demod Status LED Activity ...................................................................... 170
Table 10-2: Relay Board Status LED’s ................................................................................171
Table 10-3: Front Panel Status LED’s ................................................................................. 178
Table 11-1: Warning Messages - Indicated Failures.............................................................. 187
Table 11-2: Test Functions - Indicated Failures ...................................................................189
Table 11-3: Sync/Demod Board Status Failure Indications ....................................................192
Table 11-4: I
2
C Status LED Failure Indications .................................................................... 193
Table 11-5: Relay Board Status LED Failure Indications ........................................................ 194
Table 11-6: DC Power Test Point and Wiring Color Codes...................................................... 202
Table 11-7: DC Power Supply Acceptable Levels..................................................................202
Table 11-8: Relay Board Control Devices............................................................................ 203
Table 11-9: Opto Pickup Board Nominal Output Frequencies .................................................204
Table 11-10: Analog Output Test Function - Nominal Values Voltage Outputs ............................206
Table 11-11: Analog Output Test Function - Nominal Values Current Outputs ............................ 207
Table 11-12: Status Outputs Check ..................................................................................... 207
Table 12-1: Static Generation Voltages for Typical Activities.................................................. 216
Table 12-2: Sensitivity of Electronic Devices to Damage by ESD ............................................ 216

NGFC7000E Documentation Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual
Table A-1: GFC7000E Setup Variables, Revision E.0 ........................................................... 233
Table A-2: GFC7000E Warning Messages, Revision E.0 .......................................................240
Table A-3: GFC7000E Test Functions, Revision E.0............................................................. 241
Table A-4: GFC7000E Signal I/O Definitions, Revision E.0 ................................................... 242
Table A-5: GFC7000E DAS Trigger Events, Revision E.0...................................................... 245
Table A-6: GFC7000E iDAS Functions, Revision E.0............................................................246
Table A-7: Terminal Command Designators, Revision E.0 ...................................................247
Table D-1: List of Included Electronic Schematics .............................................................. 255
User Notes

Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual MGFC7000E Documentation
04584 Rev A1 1
1. MGFC7000E DOCUMENTATION
Thank you for purchasing the Model GFC7000E Gas Filter Correlation Carbon Dioxide Analyzer!
The documentation for this instrument is available in several different formats:
• Printed format, part number 045840100
• Electronic format on a CD-ROM, part number 045840200
The electronic manual is in Adobe® Systems Inc. “Portable Document Format”. The Adobe
®
Acrobat Reader® software, which is necessary to view these files, can be downloaded for free from
the internet at http://www.adobe.com/.
The electronic version of the manual has many advantages:
• Keyword and phrase search feature
• Figures, tables and internet addresses are linked so that clicking on the item will display
the associated feature or open the website.
• A list of chapters and sections as well as thumbnails of each page are displayed to the left
of the text.
• Entries in the table of contents are linked to the corresponding locations in the manual.
• Ability to print sections (or all) of the manual
Additional documentation for the Model GFC7000E CO2 Analyzer is available from Teledyne
Analytical Instruments’ website at http://www.teledyne-ai.com/manuals/
• APICOM software manual, part number 03945
• Multi-drop manual, part number 01842
• DAS Manual, part number 02837.
1.1. Using This Manual
This manual has the following data structures:
1.0 Table of Contents:
Outlines the contents of the manual in the order the information is presented. This is a good
overview of the topics covered in the manual. There is also a list of tables, a list of figures and a
list of appendices. In the electronic version of the manual, clicking on a any of these table entries
automatically views that section.

MGFC7000E Documentation Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual
2.0 Specifications and Warranty
This section contains a list of the analyzer’s performance specifications, a description of the
conditions and configuration under which EPA equivalency was approved and Teledyne
Instruments Incorporated’s warranty statement.
3.0 Getting Started:
A concise set of instructions for setting up, installing and running your analyzer for the first time.
4.0 FAQ:
Answers to the most frequently asked questions about operating the analyzer.
5.0 Optional Hardware & Software
A description of optional equipment to add functionality to your analyzer.
6.0 Operation Instructions
This section includes step by step instructions for operating the analyzer and using its various
features and functions.
7.0 Calibration Procedures
General information and step by step instructions for calibrating your analyzer.
8.0 EPA Protocol Calibration
Because CO2 is not declared a criteria air pollutant by the US EPA, EPA equivalency is not required
for this type of analyzer. Therefore no special calibration methods are needed to satisfy EPA
requirements.
9.0 Instrument Maintenance
Description of certain preventative maintenance procedures that should be regularly performed on
you instrument to keep it in good operating condition. This section also includes information on
using the iDAS to record diagnostic functions useful in predicting possible component failures
before they happen.
10.0 Theory of Operation
An in-depth look at the various principals by which your analyzer operates as well as a description
of how the various electronic, mechanical and pneumatic components of the instrument work and
interact with each other. A close reading of this section is invaluable for understanding the
instrument’s operation.
11.0 Troubleshooting Section:
This section includes pointers and instructions for diagnosing problems with the instrument, such
as excessive noise or drift, as well as instructions on performing repairs of the instrument’s major
subsystems.
Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual MGFC7000E Documentation
04584 Rev A1 3
Appendices:
For easier access and better updating, some information has been separated out of the manual
and placed in a series of appendices at the end of this manual. These include: software menu
trees, warning messages, definitions of iDAS & serial I/O variables, spare parts list, repair
questionnaire, interconnect listing and drawings, and electronic schematics.
NOTE
Throughout this manual, words printed in capital, bold letters, such as SETUP or ENTR
represent messages as they appear on the analyzer’s front panel display.
NOTE
The flowcharts in this manual contain typical representations of the analyzer’s display
during the various operations being described. These representations are not intended
to be exact and may differ slightly from the actual display of your instrument.
User Notes

Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual Specifications, Approvals and Warranty
04584 Rev A1 5
2. SPECIFICATIONS, APPROVALS AND
WARRANTY
2.1. Specifications
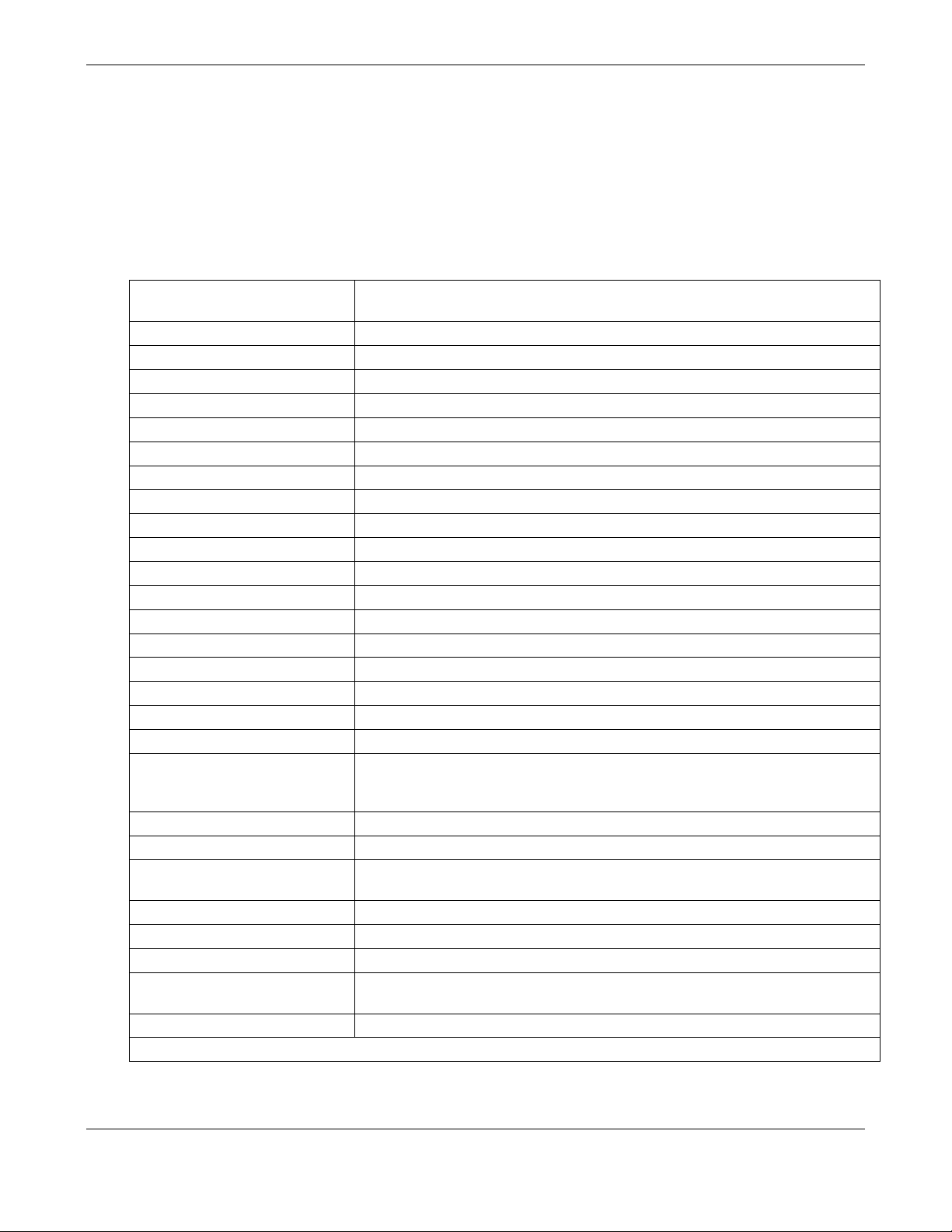
Table 2-1: Model GFC7000E Basic Unit Specifications
Min/Max Range
(Physical Analog Output)
In 1ppb increments from 50ppb to 2 000ppm, dual ranges or auto
ranging
Measurement Units
ppb, ppm, µg/m3, mg/m3, %(user selectable)
Zero Noise
< 0.1 ppm (RMS)
Span Noise
< 1% of reading (RMS)
Lower Detectable Limit1
< 0.2 ppm
1
Zero Drift (24 hours)
<0.25 ppm
1
Zero Drift (7 days)
<0.5 ppm
1
Span Drift (7 Days)
1% of reading above 50 PPM
1
Linearity
1% of full scale
Precision
0.5% of reading
Temperature Coefficient
< 0.1% of Full Scale per oC
Voltage Coefficient
< 0.05% of Full Scale per V
Lag Time
10 sec
Rise/Fall Time
95% in <60 sec
Sample Flow Rate
800cm3/min. ±10%
Temperature Range
5-40oC
Humidity Range
0 - 95% RH, non-condensing
Dimensions H x W x D
7" x 17" x 23.5" (178 mm x 432 mm x 597 mm)
Weight, Analyzer
38 lbs. (17 kg); add 1 lbs (0.5 kg) for IZS
AC Power Rating
100 V, 50/60 Hz (3.25A);
115 V, 60 Hz (3.0 A);
220 – 240 V, 50/60 Hz (2.5 A)
Environmental
Installation category (over-voltage category) II; Pollution degree 2
Analog Outputs
Three (3) Outputs
Analog Output Ranges
0.1V, 1 V, 5 V, 10 V, 2-20 or 4-20 mA isolated current loop.
All Ranges with 5% Under/Over Range
Analog Output Resolution
1 part in 4096 of selected full-scale voltage
Status Outputs
8 Status outputs - opto-isolated; including 2 alarm outputs
Control Inputs
6 Control Inputs, 3 defined, 3 spare
Serial I/O
One (1) RS-232; One (1) RS-485
Baud Rate : 300 – 115200: Optional Ethernet Interface
Certifications
CE: EN61010-1:90 + A1:92 + A2:95, EN61326 - Class A
1
At constant temperature and voltage.

Specifications, Approvals and Warranty Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual
2.2. CE Mark Compliance
Emissions Compliance
The Teledyne Instruments Model GFC7000E Gas Filter Correlation CO2 Analyzer was tested and
found to be fully compliant with:
EN61326 (1997 w/A1: 98) Class A, FCC Part 15 Subpart B Section 15.107 Class A, ICES-003
Class A (ANSI C63.4 1992) & AS/NZS 3548 (w/A1 & A2; 97) Class A.
Tested on 11-29-2001 at CKC Laboratories, Inc., Report Number CE01-249.
Safety Compliance
The Teledyne Instruments Model GFC7000E Gas Filter Correlation CO2 Analyzer was tested and
found to be fully compliant with:
IEC 61010-1:90 + A1:92 + A2:95,
Tested on 02-06-2002 at Nemko, Report Number 2002-012219.
2.3. Warranty
Warranty Policy (02024)
Prior to shipment, Teledyne Instruments Incorporated equipment is thoroughly inspected and
tested. Should equipment failure occur, Teledyne Instruments Incorporated assures its customers
that prompt service and support will be available.
Coverage
After the warranty period and throughout the equipment lifetime, Teledyne Instruments
Incorporated stands ready to provide on-site or in-plant service at reasonable rates similar to
those of other manufacturers in the industry. All maintenance and the first level of field
troubleshooting is to be performed by the customer.
Non-API Manufactured Equipment
Equipment provided but not manufactured by Teledyne Instruments Incorporated is warranted
and will be repaired to the extent and according to the current terms and conditions of the
respective equipment manufacturers warranty.
General
Teledyne Instruments Incorporated warrants each product manufactured by Teledyne Instruments
Incorporated to be free from defects in material and workmanship under normal use and service
for a period of one year from the date of delivery. All replacement parts and repairs are warranted
for 90 days after the purchase.
If a product fails to conform to its specifications within the warranty period, Teledyne Instruments
Incorporated shall correct such defect by, in Teledyne Instruments Incorporated’s discretion,
repairing or replacing such defective product or refunding the purchase price of such product.

Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual Specifications, Approvals and Warranty
04584 Rev A1 7
The warranties set forth in this section shall be of no force or effect with respect to any product:
(i) that has been altered or subjected to misuse, negligence or accident, or (ii) that has been used
in any manner other than in accordance with the instruction provided by TELEDYNE ANALYTICAL
INSTRUMENTS or (iii) not properly maintained.
THE WARRANTIES SET FORTH IN THIS SECTION AND THE REMEDIES THEREFORE ARE
EXCLUSIVE AND IN LIEU OF ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR OTHER WARRANTY OF QUALITY, WHETHER
EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED. THE REMEDIES SET FORTH IN THIS SECTION ARE THE
EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES FOR BREACH OF ANY WARRANTY CONTAINED HEREIN. Teledyne
Instruments Incorporated SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF OR RELATED TO THIS AGREEMENT OF
TELEDYNE INSTRUMENTS INCORPORATED’S PERFORMANCE HEREUNDER, WHETHER
FOR BREACH OF WARRANTY OR OTHERWISE.
Terms and Conditions
All units or components returned to Teledyne Amnalytical Instruments should be properly packed
for handling and returned freight prepaid to the nearest designated Service Center. After the
repair, the equipment will be returned, freight prepaid.
User Notes


Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual Getting Started
04584 Rev A1 9
3. GETTING STARTED
3.1. Unpacking and Initial Set Up
CAUTION
To avoid personal injury, always use two persons to lift and carry the
Model GFC7000E.
1. Verify that there is no apparent external shipping damage. If damage has occurred, please
advise the shipper first, then Teledyne Analytical Instruments.
2. Included with your analyzer is a printed record of the final performance characterization
performed on your instrument at the factory. This record, titled Final Test and Validation Data
Sheet (part number 04307) is an important quality assurance and calibration record for this
instrument. It should be placed in the quality records file for this instrument.
3. Carefully remove the top cover of the analyzer and check for internal shipping damage.
• Remove the set screw located in the top, center of the rear panel.
• Remove the four screws fastening the top cover to the unit (two per side).
• Lift the cover straight up. Do not slide backwards.
NOTE
Some versions of the GFC7000E CO2 Analyzer may have a spring loaded fastener at the
top center of the rear panel and as many as eight screws (four per side) fastening the
top cover to the chassis.
NOTE
Static sensitive parts are present on PCA (Printed Circuit Assemblies). Before touching
PCAs, touch a bare metal part of the chassis to discharge any electrostatic potentials or
connect a grounding strap to your wrist.
CAUTION
Never disconnect PCAs, wiring harnesses or electronic subassemblies
while under power.
Getting Started Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual
4. Inspect the interior of the instrument to make sure all circuit boards and other components
are in good shape and properly seated.
5. Check the connectors of the various internal wiring harnesses and pneumatic hoses to make
sure they are firmly and properly seated.
6. Verify that all of the optional hardware ordered with the unit has been installed. These are
listed on the paperwork accompanying the analyzer.
7. Once you have determined that no shipping damage exists, and the unit includes all expected
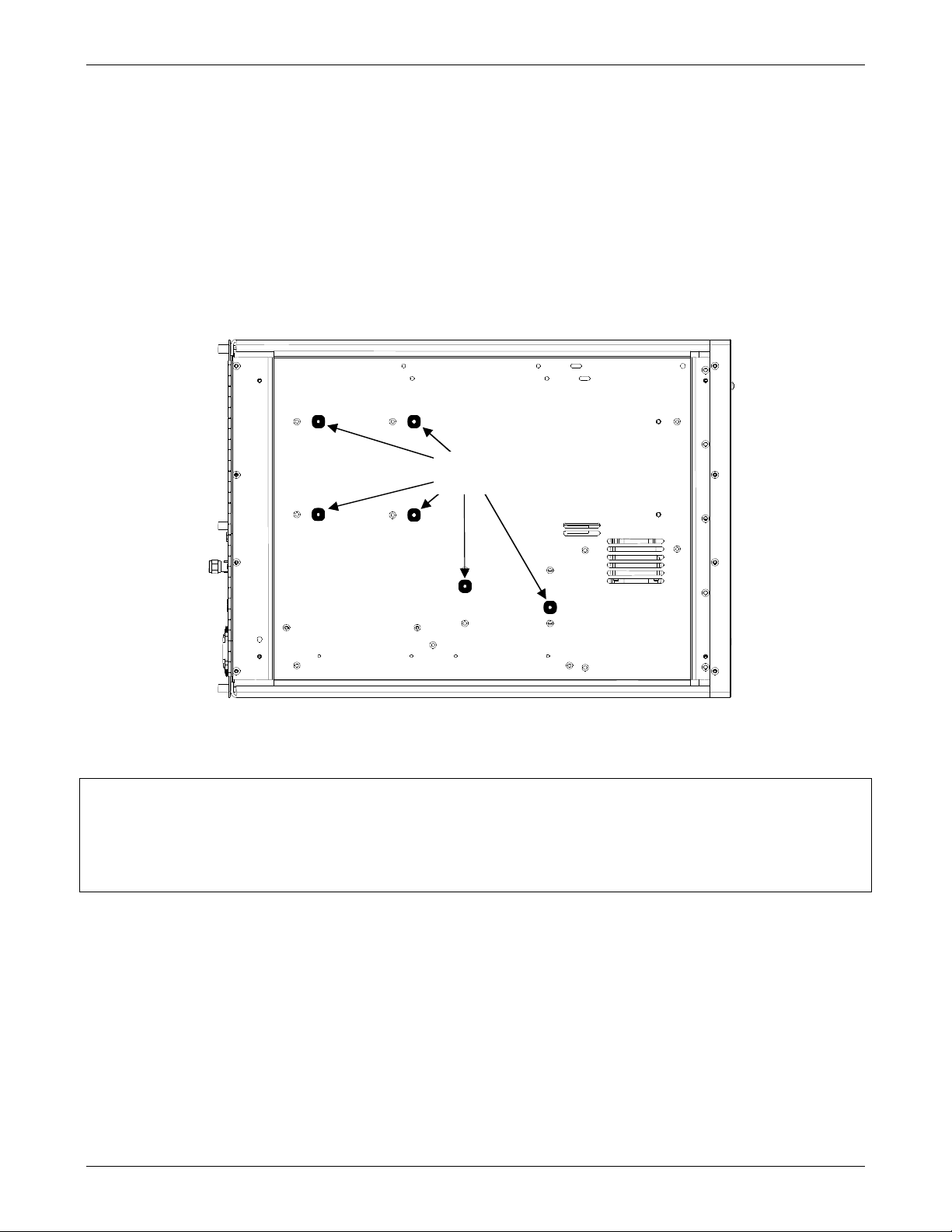
hardware options, remove all red colored shipping screws from the bottom of the chassis as
shown in Figure 3-1.
Shipping
Screws
Figure 3-1: Removal of Shipping Screws
NOTE
Save these shipping screws and re-install them whenever the unit is shipped to another
location.
Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual Getting Started
04584 Rev A1 11
8. VENTILATION CLEARANCE: Whether the analyzer is set up on a bench or installed into an
instrument rack, be sure to leave sufficient ventilation clearance.
AREA
MINIMUM REQUIRED CLEARANCE
Back of the instrument
4 in.
Sides of the instrument
1 in.
Above and below the instrument
1 in.
• Various rack mount kits are available for this analyzer. See Section 5.1 of this manual
for more information.
3.1.1. Electrical Connections
CAUTION
Check the voltage and frequency label on the rear panel of the
instrument (See Figure 3-2) for compatibility with the local
power before plugging the MGFC7000E into line power.
Do not plug in the power cord if the voltage or
frequency is incorrect.
CAUTION
Power connection must have functioning ground connection.
Do not defeat the ground wire on power plug.
CAUTION
Turn off analyzer power before disconnecting or
connecting electrical subassemblies.
Do not operate with cover off.
Getting Started Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual
Figure 3-2: Rear Panel Layout
9. Attach a strip chart recorder and/or data-logger to the appropriate analog output connections
on the rear panel of the analyzer.
ANALOG
A1 A2 A3 A4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
When the instrument is in its default configuration, the A1 and A2 channels output a signal
that is proportional to the CO2 concentration of the sample gas. Either can be used for
connecting the analog output signal to a chart recorder or for interfacing with a datalogger.
The third analog output, labeled A3 is special. It can be set by the user (see Section
6.9.9) to output any one of the parameters accessible through the <TST TST> keys of the
units sample display.
The standard configuration for these outputs is mVDC. An optional current loop output is
available for each.
Output A4 is not used on the Model 306E.
Pin-outs for the analog output connector at the rear panel of the instrument are:
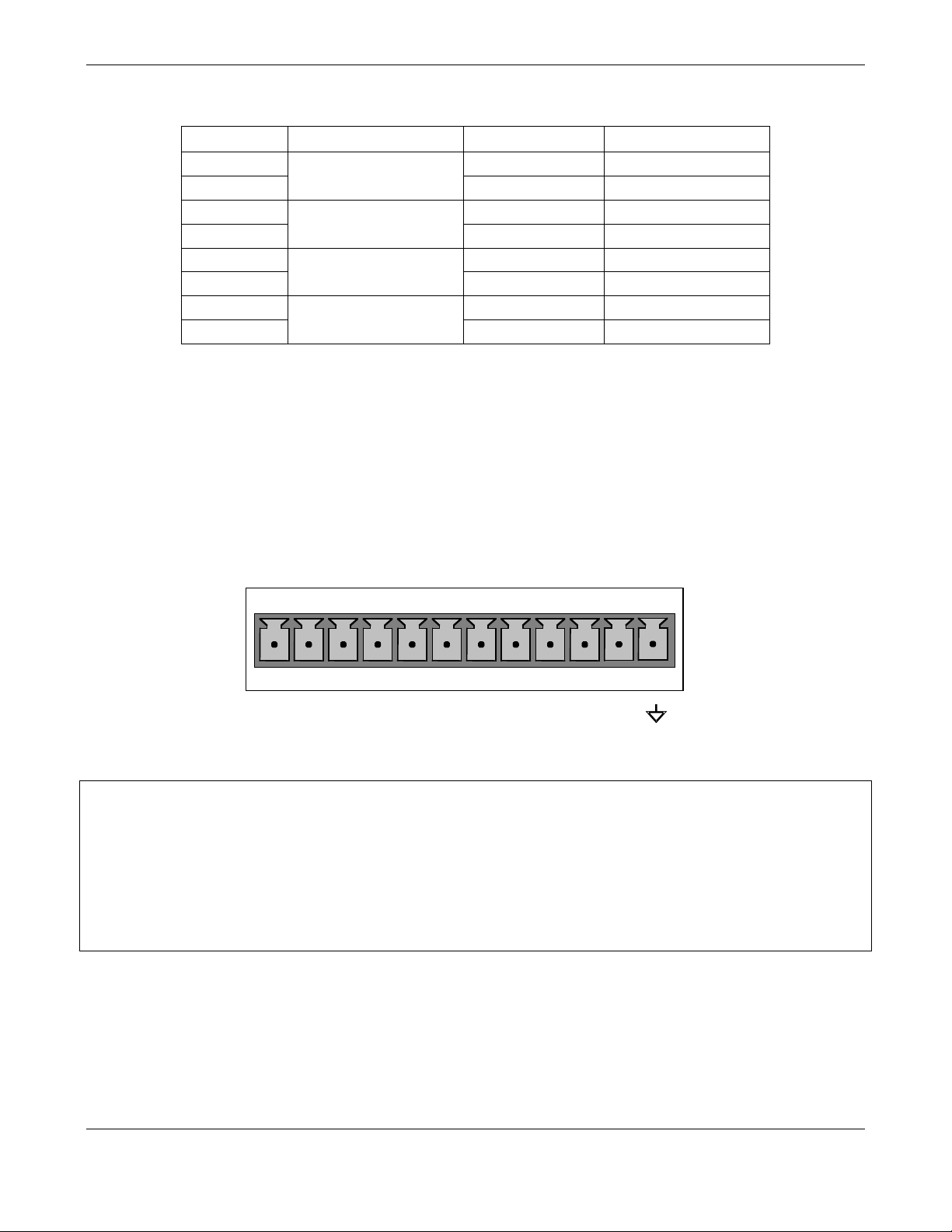
Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual Getting Started
04584 Rev A1 13
Table 3-1: GFC7000E Analog Output Pin Outs
Pin
Analog Output
VDC Signal
mADC Signal
1
V Out
I Out +
2A1Ground
I Out -
3
V Out
I Out +
4A2Ground
I Out -
5
V Out
I Out +
6A3Ground
I Out -
7
V Out
Not Available
8
A4 (Spare)
Ground
Not Available
• The default analog output voltage setting of the GFC7000E CO2 Analyzer is 0 – 5 VDC
with a range of 0 – 500 ppm.
• TO change these settings, see Sections 6.9.4 and 6.7 respectively.
10. If you wish utilize the analyzer’s status outputs to interface with a device that accepts logic-
level digital inputs, such as programmable logic controllers (PLC’s) they are accessed via a 12pin connector on the analyzer’s rear panel labeled STATUS.
STATUS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 D +
NOTE
Most PLC’s have internal provisions for limiting the current that the input will draw from
an external device. When connecting to a unit that does not have this feature, an
external dropping resistor must be used to limit the current through the transistor
output to less than 50mA. At 50mA, the transistor will drop approximately 1.2V from its
collector to emitter.
Getting Started Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual
The pin assignments for the status outputs can be found in the table below:
Table 3-2: GFC7000E Status Output Pin Outs
Output #
Status
Definition
Condition
1
SYSTEM OK
On if no faults are present.
2
CONC VALID
On if CO2 concentration measurement is valid.
If the CO2 concentration measurement is invalid, this bit is OFF.
3
HIGH RANGE
On if unit is in high range of DUAL or AUTO range modes.
4
ZERO CAL
On whenever the instruments ZERO point is being calibrated.
5
SPAN CAL
On whenever the instruments SPAN point is being calibrated.
6
DIAG MODE
On whenever the instrument is in DIAGNOSTIC mode.
7
ALARM1
On whenever the measured CO2 concentration is above the set
point for ALM1
8
ALARM2
On whenever the measured CO2 concentration is above the set
point for ALM2
D
EMITTER BUSS
The emitters of the transistors on pins 1-8 are bussed together.
+
DC POWER
+ 5 VDC
Digital Ground
The ground level from the analyzer’s internal DC power supplies.
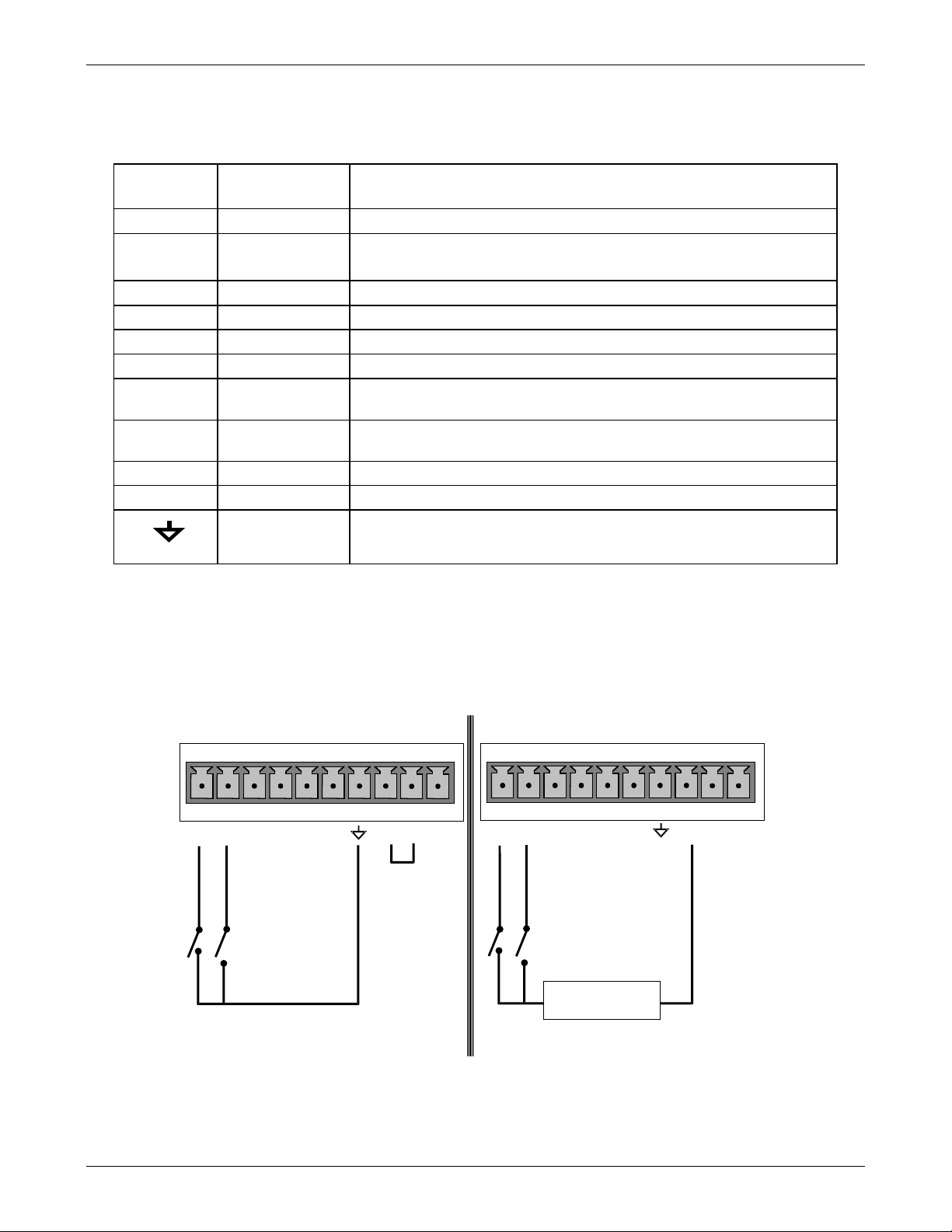
11. If you wish to use the analyzer’s to remotely activate the zero and span calibration modes,
several digital control inputs are provided via a 10-pin connector labeled CONTROL IN on the
analyzer’s rear panel. Two methods for energizing the inputs are provided below; the first
using the internal +5V available on the CONTROL IN connector and the second, if an external,
isolated supply is employed.
CONTROL IN
A B C D E F U +
S
P
A
N
Z
E
R
O
CONTROL IN
A B C D E F U +
-
+
5 VDC Power
Supply
S
P
A
N
Z
E
R
O
Local Power Connections
External Power Connections
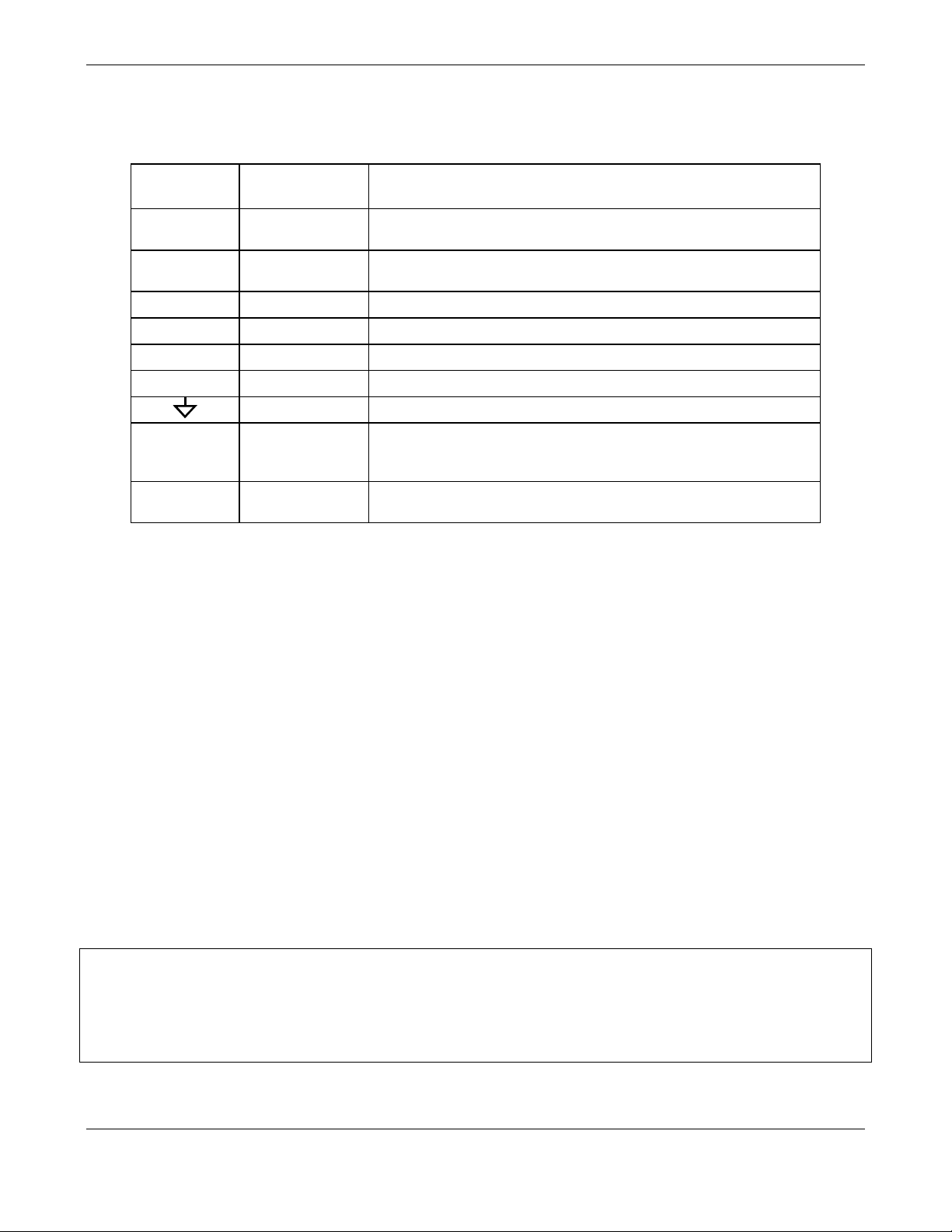
Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual Getting Started
04584 Rev A1 15
The pin assignments for the digital control inputs can be found in the table below:
Table 3-3: GFC7000E Control Input Pin Outs
Input #
Status
Definition
On Condition
A
REMOTE ZERO
CAL
The Analyzer is placed in Zero Calibration mode. The mode
field of the display will read ZERO CAL R.
B
REMOTE
SPAN CAL
The Analyzer is placed in Span Calibration mode. The mode
field of the display will read SPAN CAL R.
C
SPARE
D
SPARE
E
SPARE
F
SPARE
Digital Ground
May be connected to the ground of the datalogger/recorder.
U
Pullup supply
for inputs
Input pin for +5 VDC required to activate pins A – F. This
can be from an external source or from the “+” pin of the
instruments STATUS connector.
+
Internal +5V
Supply
Internal source of +5V which can be used to actuate control
inputs when connected to the U pin.
12. If you wish to utilize either of the analyzer’s two serial interface COMM ports, refer to Section
6.10 of this manual for instructions on their configuration and usage.
13. If your unit has a Teledyne Instruments Ethernet card (Option 63), plug one end into the 7’
CAT5 cable supplied with the option into the appropriate place on the back of the analyzer
(see Figure 5-4 in Section 5.5.3) and the other end into any nearby Ethernet access port.
3.1.2. Pneumatic Connections:
3.1.2.1. Basic Pneumatic Connections
Figures 3-3 and 3-4 illustrate the most common configurations for gas supply and exhaust lines to
the Model GFC7000E Analyzer. Figure 3-13 illustrates the internal gas flow of the instrument in
its basic configuration.
Please refer to Figure 3-2 for pneumatic connections at the rear panel and Table 3-4 for
nomenclature.
NOTE
Sample and calibration gases should only come into contact with PTFE (Teflon), FEP,
glass, stainless steel or brass. CAUTION
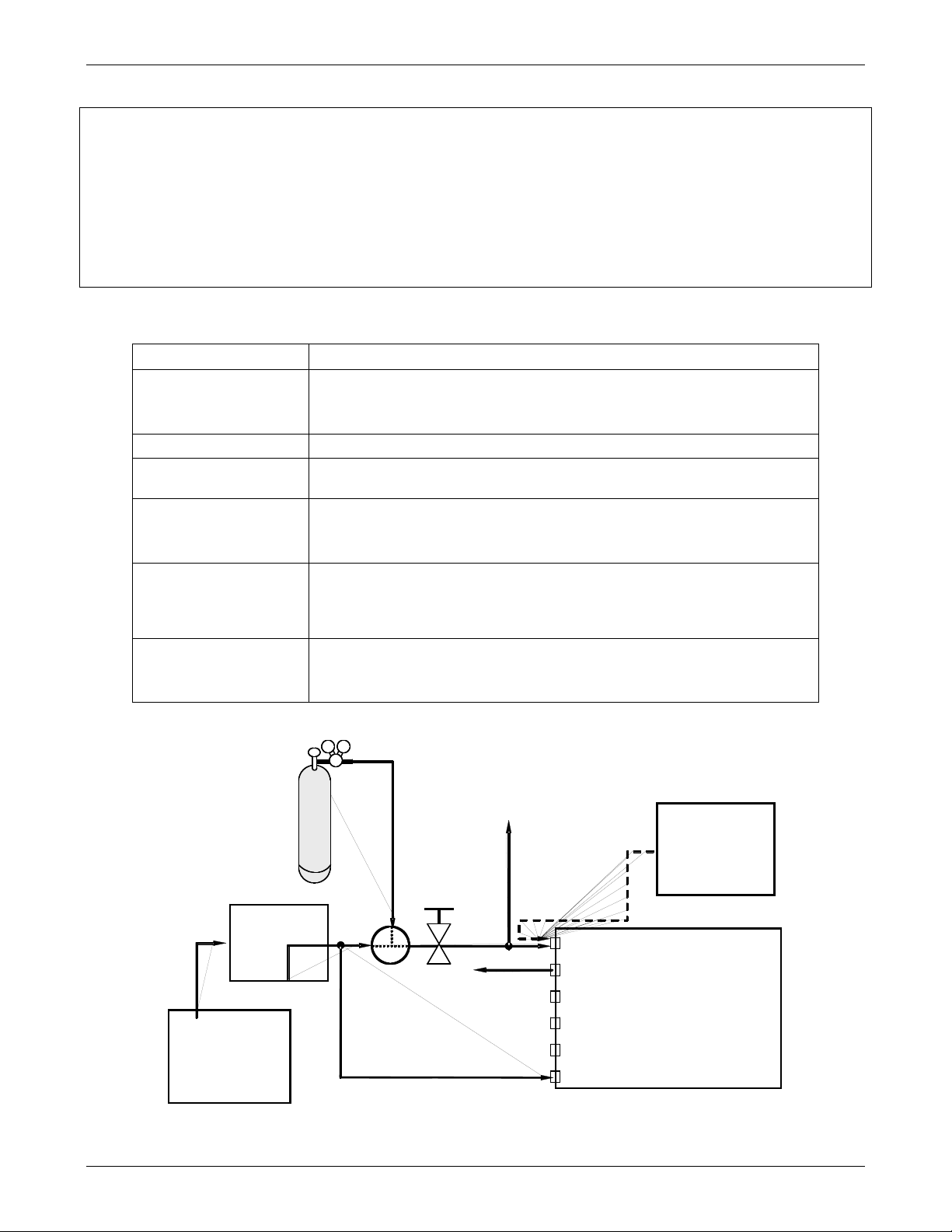
Getting Started Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual
CAUTION
In order to prevent dust from getting into the gas flow channels of your analyzer, it was
shipped with small plugs inserted into each of the pneumatic fittings on the back panel.
Make sure that all of these dust plugs are removed before attaching
exhaust and supply gas lines.
Table 3-4: Model GFC7000E Rear Panel Pneumatic Connections
Rear Panel Label
Function
SAMPLE
Connect a gas line from the source of sample gas here.
Calibration gasses are also inlet here on units without
zero/span/shutoff valve or IZS options installed.
EXHAUST
Connect an exhaust gas line of not more than 10 meters long here.
PRESSURE SPAN
On units with zero/span/shutoff valve options installed, connect a
gas line to the source of calibrated span gas here.
VENT SPAN
Span gas vent outlet for units with zero/span/shutoff valve options
installed.
Connect an exhaust gas line of not more than 10 meters long here.
IZS
Internal zero air scrubber.
on units with zero/span/shutoff valve options installed but NO
internal zero air scrubber, attach a gas line to the source of zero air
here.
PURGE IN
This inlet supplies purge air to the GFC wheel housing (see section
10.2.2)
Connect a source of dried air that has been scrubbed of CO2.
VENT
Calibrated CO2
gas at desired
span gas
concentration
Source of
SAMPLE Gas
Removed
during
Calibration
Valve
Needle
valve to
control
flow
MODEL
GFC7000E
Sample
IZS
Exhaust
Vent Span
Pressure Span
Purge In
Indicating
soda-lime
MODEL 701
Zero Air
Generator
Figure 3-3: Pneumatic Connections–Basic Configuration–Using Bottled Span Gas
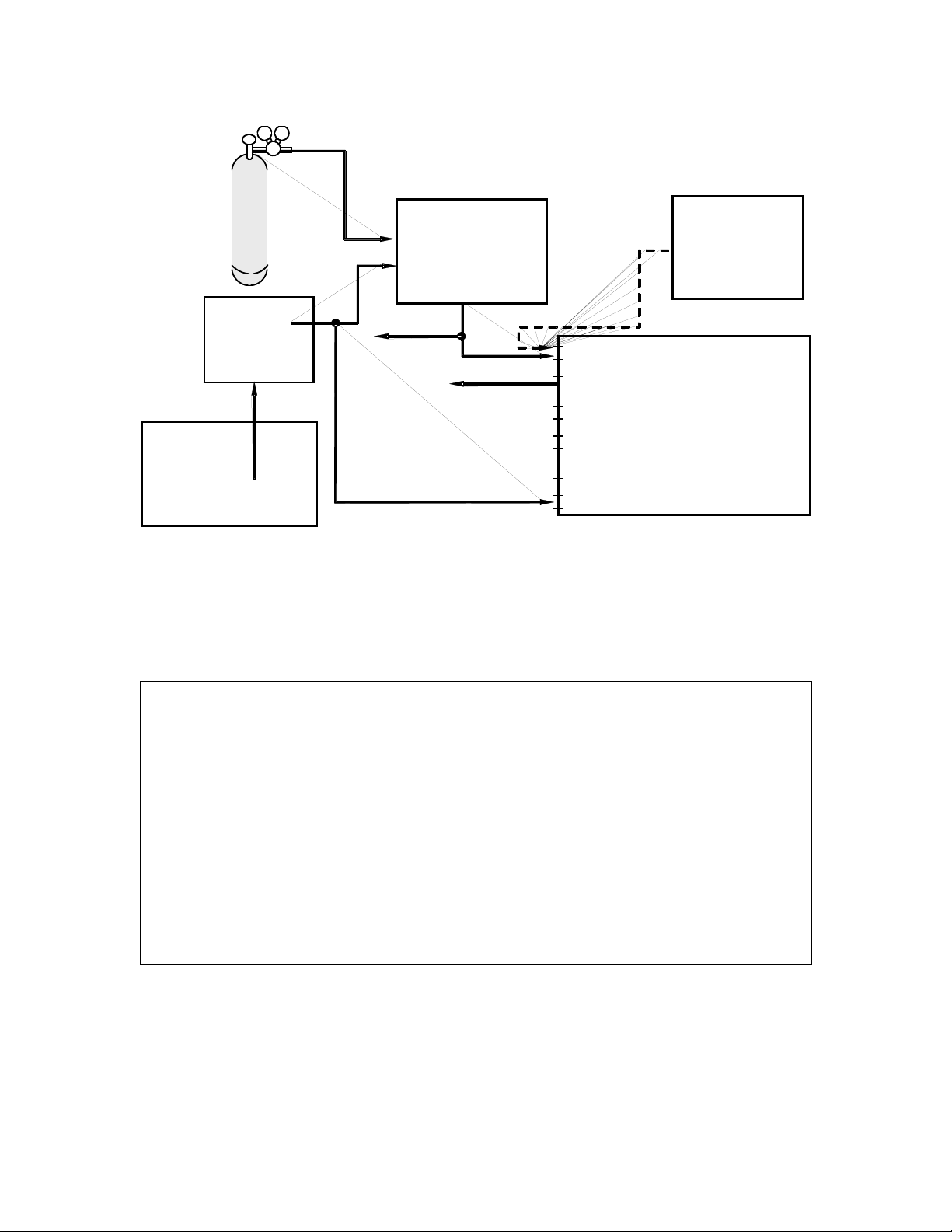
Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual Getting Started
04584 Rev A1 17
MODEL 700
Gas Dilution
Calibrator
VENT
Calibrated
CO2 Gas
Source of
SAMPLE Gas
Removed
during
Calibration
MODEL
GFC7000E
Sample
IZS
Exhaust
Vent Span
Pressure Span
Purge In
MODEL 701
Zero Air Generator
Indicating
soda-lime
Figure 3-4: Pneumatic Connections–Basic Configuration–Using Gas Dilution Calibrator
1. Attach a sample inlet line to the sample inlet port. The SAMPLE input line should not be more
than 2 meters long.
NOTE
Ideally, the pressure of the sample gas should be at ambient pressure (0
psig). Maximum pressure of sample gas should not exceed 1.5 in-Hg over
ambient.
In applications where the sample gas is received from a pressurized
manifold, a vent must be placed as shown to equalize the sample gas with
ambient atmospheric pressure before it enters the analyzer.
This vent line must be:
• At least 0.2m long
• No more than 2m long and vented outside the shelter or immediate
area surrounding the instrument.

Getting Started Model GFC7000E Instruction Manual
2. Attach sources of zero air and span gas (see Figures 3-3 through 3-8 inclusive).
• Span Gas is a gas specifically mixed to match the chemical composition of the type of gas
being measured at near full scale of the desired measurement range.
In the case of CO2 measurements made with the Teledyne Analytical Instruments Model
GFC7000E Analyzer it is recommended that you use a gas calibrated to have a CO2 content
equaling 80% of the range of compositions being measured.
EXAMPLE: If the application is to measure between 0 ppm and 500 ppm, an appropriate
Span Gas would be 400 ppm. If the application is to measure between 0 ppm and 100
ppm, an appropriate Span Gas would be 80 ppm.
• Span Gas can be purchased in pressurized canisters or created using Dynamic Dilution
Calibrator such as the Teledyne Analytical Instruments Model 700 and a source of dried
air scrubbed of CO2 such as a Teledyne Analytical Instruments Model 701 Zero Air
Generator in combination with a canister of indicating soda-lime.
• Zero Air is similar in chemical composition to the earths atmosphere but scrubbed of all
components that might affect the analyzer’s readings.
In the case of CO2 measurements this means CO2 less than 0.1 ppm of CO2 and Water
Vapor. Zero Air can be purchased in pressurized canisters or created using a Teledyne
Instruments Model 701 Zero Air Generator in combination with a canister of indicating
soda-lime.
3. Attach an exhaust line to the exhaust outlet port.
• The exhaust from the pump and vent lines should be vented to atmospheric pressure using
maximum of 10 meters of _” PTEF tubing.
CAUTION
Venting should be outside the shelter or immediate area surrounding the
instrument.
4. Attach a source of dried air scrubbed of CO2 to the purge inlet port
NOTE
The source of purge air should be at 20-25 psig and capable of maintaining a flow of at
least 0.5 liters/min.
Purge source air pressure should not exceed 35 pisg
5. Once the appropriate pneumatic connections have been made, check all pneumatic fittings for
leaks using a procedure similar to that defined in Section 9.3.3.
 Loading...
Loading...