Page 1

Online Help
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Application
PHP025510
Adapted from the TDSJIT3 v2 Help,Version 1.0.1 (November, 2004)
www.tektronix.com
Page 2

Copyright © Tektronix, Inc. All rights reserved. Licensed software products are owned by Tektronix or its suppliers
and are protected by United States copyright laws and international treaty provisions.
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph (c)(1)(ii) of
the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFARS 252.227-7013, or subparagraphs (c)(1) and (2)
of the Commercial Computer Software -- Restricted Rights clause at FAR 52.227-19, as applicable.
Tektronix products are covered by U.S. and foreign patents, issued and pending. Information in this documentation
supercedes that in all previously published material. Specifications and price change privileges reserved.
Tektronix, Inc. P.O. Box 500, Beaverton, OR 97077
TEKTRONIX, TEK, and RT-Eye are registered trademarks of Tektronix, Inc.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help, OLH0255, Version 1.0.1
Page 3

Table of Contents
General Safety Summary...................................................................... xi
Preface ..................................................................................................xiii
5-Time Free Trial.............................................................................................. xiii
Related Documentation..................................................................................... xiii
GPIB Information ..............................................................................................xiv
Relevant Web Sites............................................................................................xiv
Application CD Contents...................................................................................xiv
Conventions ........................................................................................................xv
Types of Online Help Information......................................................................xv
Using Online Help .............................................................................................xvi
Find Tab and Searches..................................................................................... xvii
Contacting Tektronix ....................................................................................... xvii
Feedback......................................................................................................... xviii
Getting Started
Operating Basics
Differences between TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced and TDSJIT3 v2 Essentials ...........1
Compatibility ........................................................................................................2
Requirements and Restrictions .............................................................................2
Accessories ...........................................................................................................2
Installation ............................................................................................................2
Connecting to a Device Under Test (DUT) ...................................................3
Deskewing Probes and Channels...................................................................3
General Information..............................................................................................5
Starting the TDSJIT3 v2 Application ............................................................5
Returning to the Application .........................................................................6
Minimizing and Maximizing the Application................................................6
Exiting the Application..................................................................................6
Application Directories and Usage ................................................................6
Tips on the TDSJIT3 v2 User Interface.........................................................8
How to Enter Numeric Values.......................................................................9
Virtual Keypad ..............................................................................................9
Using Basic Oscilloscope Functions............................................................10
File Menus ...................................................................................................10
Navigating the User Interface .............................................................................10
General Steps to Set Up the Application .....................................................11
Jitter Wizard ................................................................................................11
User Interface Information ..........................................................................13
Setting Up the Application for Analysis .............................................................15
Selecting Measurements ..............................................................................15
Configuring a Measurement ........................................................................19
Configuring Sources ....................................................................................36
Measurement Summaries.............................................................................48
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help i
Page 4

Table of Contents
Taking Measurements.........................................................................................48
Localizing Measurements ............................................................................49
About Sequencing........................................................................................49
Acquiring Data ............................................................................................49
New Acquisition Function of the Single Button ..........................................50
Control Panel Functions ..............................................................................50
Clearing Results...........................................................................................51
Results as Statistics .............................................................................................52
Viewing Equivalent Rj/Dj Results (TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced Only) .............52
Results as Plots ...................................................................................................53
Using a Separate Monitor to View Plots .....................................................54
Plot Usage....................................................................................................54
Creating Plots ..............................................................................................56
Configuring Plots.........................................................................................57
Working with Plots .............................................................................................62
Toolbar Functions in Plot Windows ............................................................63
Selecting and Viewing a Plot.......................................................................63
Moving and Resizing a Plot.........................................................................64
Deleting Plots ..............................................................................................64
Using Zoom in a Plot...................................................................................65
Using Cursors in a Plot ................................................................................66
Exporting Plot Files .....................................................................................69
Saving Information to Log Files.........................................................................71
Logging Statistics ........................................................................................71
Logging Measurements ...............................................................................72
Logging Worst Case Waveforms.................................................................73
File Names for Logging Worst Case Waveforms........................................74
Saving and Recalling Setup Files .......................................................................74
Saving a Setup File ......................................................................................74
Recalling a Saved Setup File .......................................................................75
Recalling the Default Setup .........................................................................76
Recalling a Recently Saved or Accessed Setup File....................................76
Recall Recent Files Example .......................................................................77
Recalling a Setup File from a Prior Version of Software ............................77
Docking and Undocking the Jitter Analysis Window..................................78
Acquisition Timeout Utility.........................................................................78
Warnings Utility ..........................................................................................78
Tutorial
ii
Setting Up the Oscilloscope................................................................................79
Starting the Application ...............................................................................79
Waveform Files ...........................................................................................79
Recalling a Waveform File ..........................................................................79
Taking a Clock Period Measurement..................................................................81
Setting Up a Period Measurement ...............................................................81
Taking a Period Measurement and Viewing Statistical Results ..................83
Viewing a Period Measurement as Plots .....................................................84
Ending a Tutorial Lesson ....................................................................................86
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 5

Table of Contents
Taking a Clock-to-Output Time Measurement ...................................................86
Setting Up and Taking a Clock-to-Output Time Measurement ...................86
Logging Statistics to a .CSV File ................................................................89
Logging Data Points as a Measurement Snapshot to a .CSV File ...............92
Logging Worst Case Waveforms to .WFM Files ........................................94
Lessons Learned .................................................................................................97
Application Examples
Recall Default Settings .......................................................................................99
Recall a Waveform and Start the Application ....................................................99
Application Example 1: Spectral Analysis .......................................................100
Set Up and Take Measurements for Example 1.........................................100
Approximate Pattern Length Measured with Cursors................................101
Measuring Rj/Dj and Tj @ BER................................................................102
Using Spectral Analysis to Find Jitter Sources..........................................103
Application Example 2: Trend Analysis...........................................................105
Set Up and Take Measurements for Example 2.........................................105
Using Trend Analysis to Find Jitter Amplitude and Anomalies................106
Algorithms
Oscilloscope Setup Guidelines .........................................................................109
Test Methodology.............................................................................................109
Timing Measurements ......................................................................................110
Rj/Dj Measurement (TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced Only) ..................................110
Spectrum Analysis Based Rj/Dj Separation ..............................................110
Arbitrary Pattern Analysis Based Rj/Dj Separation...................................111
BER and Tj Estimation (TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced Only) ............................112
Effective Rj and Tj Estimation (TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only)..................113
Single Waveform Measurements......................................................................113
Clock Period Measurement........................................................................113
Clock Frequency Measurement .................................................................114
Clock TIE Measurement............................................................................114
Clock PLL TIE Measurement (TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced Only) ..................114
Data Period Measurement..........................................................................115
Data Frequency Measurement ...................................................................115
Data TIE Measurement..............................................................................115
Data PLL TIE Measurement (TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced Only) ....................115
Cycle-to-Cycle Measurement ....................................................................116
N-Cycle Measurement...............................................................................116
Positive and Negative Cycle-to-Cycle Duty Measurements......................116
Positive and Negative Duty Cycle Measurements .....................................117
Rise Time Measurement ............................................................................117
Fall Time Measurement .............................................................................117
Positive and Negative Width Measurements .............................................118
High Time Measurement ...........................................................................118
Low Time Measurement............................................................................118
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
iii
Page 6

Table of Contents
Parameters
Dual Waveform Measurements ........................................................................119
Setup Time Measurement ..........................................................................119
Hold Time Measurement ...........................................................................119
Clock-to-Output Measurement ..................................................................120
Skew Measurement....................................................................................120
Crossover Voltage Measurement (TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced Only) .............120
Statistics............................................................................................................121
Maximum Value ........................................................................................121
Minimum Value.........................................................................................121
Mean Value ...............................................................................................121
Standard Deviation Value..........................................................................121
Maximum Positive and Maximum Negative Difference Values ...............122
Peak-to-Peak Value ...................................................................................122
Population Value .......................................................................................122
File Menus Parameters......................................................................................123
Control Panel Parameters..................................................................................124
Measurements Select ........................................................................................124
Configure Measurements..................................................................................125
Clock Recovery Parameters.......................................................................126
Advanced Clock Recovery Parameters......................................................127
Filters Parameters ......................................................................................127
Advanced Filter Parameters.......................................................................127
TIE: RjDj Analysis Parameters (TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced Only) ................128
Configure Sources ............................................................................................128
Summaries ........................................................................................................130
Results ..............................................................................................................130
Plots ..................................................................................................................130
Logs ..................................................................................................................132
Utilities .............................................................................................................133
Help ..................................................................................................................134
GPIB
Index
iv
Program Example .............................................................................................135
GPIB Reference Materials ................................................................................136
Starting and Setting Up the Application Using GPIB................................136
Variable:Value Command ................................................................................136
Measurements Results Queries .........................................................................142
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 7

Table of Contents
List of Figures
Figure 1: Contents of the application CD-ROM............................................ xiv
Figure 2: Deskew complete example.................................................................. 4
Figure 3: Deskew Summary example................................................................4
Figure 4: Starting the TDSJIT3 v2 application ................................................ 5
Figure 5: Returning to the application ..............................................................6
Figure 6: Directory structure ............................................................................7
Figure 7: On-screen keypad................................................................................ 9
Figure 8: General steps to set up the application........................................... 11
Figure 9: Jitter Wizard when launched........................................................... 12
Figure 10: Menu with user interface items...................................................... 14
Figure 11: Menu navigation tree...................................................................... 14
Figure 12: Measurements Select menu........................................................... 16
Figure 13: Select Source options by measurement category.......................... 16
Figure 14: Clock edge options ..........................................................................21
Figure 15: Active edge options.......................................................................... 21
Figure 16: Clock and Data edge options.......................................................... 22
Figure 17: From Edge and To Edge options ................................................... 22
Figure 18: Main edge options ........................................................................... 23
Figure 19: Meas Range Limits options ............................................................ 23
Figure 20: N-Cycle measurement options .......................................................24
Figure 21: Bathtub Curve and BER versus Decision Time ........................... 26
Figure 22: TIE: RjDj analysis options for Clock TIE and
Clock PLL TIE ...........................................................................................27
Figure 23: TIE: RjDj analysis options for Data TIE and Data PLL TIE.....27
Figure 24: Constant Clock Recovery concept .................................................28
Figure 25: Reference Clock Frequency options.............................................. 29
Figure 26: Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Clock Recovery concept ................... 29
Figure 27: PLL Loop Bandwidth options........................................................ 30
Figure 28: Advanced Clock Recovery options ................................................ 32
Figure 29: Optional filters................................................................................. 32
Figure 30: Filter characteristics ....................................................................... 33
Figure 31: Band Pass filtering ..........................................................................33
Figure 32: Filters options.................................................................................. 34
Figure 33: Advanced Filter options..................................................................35
Figure 34: Effect of the Smoothing window .................................................... 36
Figure 35: Configure Sources Autoset options................................................39
Figure 36: Configure Sources Gating options................................................. 40
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
v
Page 8

Table of Contents
Figure 37: Reference voltage levels diagram...................................................41
Figure 38: Example of Hysteresis on a noisy waveform................................. 42
Figure 39: Autoset Ref Levels options ............................................................. 45
Figure 40: Configure Sources Ref Levels options........................................... 47
Figure 41: Configure Sources Stat pop Limit options.................................... 48
Figure 42: Control Panel options ..................................................................... 51
Figure 43: Plots Create menu........................................................................... 57
Figure 44: Vert/Horiz menu for a Histogram plot.......................................... 58
Figure 45: Vert/Horiz menu for a Time Trend plot ....................................... 59
Figure 46: Vert/Horiz menu for a Spectrum plot........................................... 59
Figure 47: Vert/Horiz menu for a Bathtub plot.............................................. 60
Figure 48: Transfer Function Definition options............................................ 61
Figure 49: Vert/Horiz menu for a Transfer Function plot ............................61
Figure 50: Vert/Horiz menu for a Phase Noise plot........................................ 62
Figure 51: Locate Window At options............................................................. 63
Figure 52: File Save browser ............................................................................ 75
Figure 53: File Recall browser.......................................................................... 76
Figure 54: Recall Recent files example ............................................................ 77
Figure 55: Acquisition Timeout options .......................................................... 78
Figure 56: Oscilloscope Reference Memory options ......................................80
Figure 57: Clock Period measurement selected .............................................. 82
Figure 58: Configuration of a Period measurement....................................... 82
Figure 59: Configure Sources Ref Levels before an autoset.......................... 82
Figure 60: Configure Sources Ref Levels after an autoset............................. 83
Figure 61: Statistical results for a Clock Period measurement..................... 83
Figure 62: Min/Max statistical results for a Clock Period measurement..... 84
Figure 63: Mean/Std. Dev statistical results for a Clock Period
measurement............................................................................................... 84
Figure 64: Create plots of results ..................................................................... 85
Figure 65: Results as a Histogram plot............................................................ 85
Figure 66: Results as a Time Trend plot..........................................................85
Figure 67: Results as a Spectrum plot .............................................................86
Figure 68: Clock-to-Output measurement selected........................................ 87
Figure 69: Configuration of a Clock-to-Output measurement...................... 88
Figure 70: Statistical results for a Clock-to-Output measurement............... 88
Figure 71: Configure Sources Ref Levels for a Clock-to-Output
measurement............................................................................................... 88
Figure 72: Measurements Summary for a Clock-to-Output
measurement............................................................................................... 89
Figure 73: Ref Levels Summary for a Clock-to-Output measurement.........89
vi
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 9

Table of Contents
Figure 74: Log Statistics for a Clock-to-Output measurement ..................... 90
Figure 75: Log File Name dialog ...................................................................... 90
Figure 76: Path to the stats.csv log file............................................................. 91
Figure 77: Viewing statistics in a spreadsheet program.................................91
Figure 78: Log Measurement /configure menu for a Clock-to-Output
measurement............................................................................................... 92
Figure 79: Input Directory Name dialog ......................................................... 93
Figure 80: Save Current Measurements dialog .............................................. 93
Figure 81: Path to the TC01R1R2.csv log file................................................. 94
Figure 82: Viewing a data log file in a spreadsheet program ........................ 94
Figure 83: Log Worst Case Waveforms configuration for a
Clock-to-Output measurement ................................................................. 95
Figure 84: Log Worst Case Waveforms dialog............................................... 96
Figure 85: Path to the worse case .wfm log files .............................................96
Figure 86: Data Period results for example 1................................................101
Figure 87: Pattern Length for example 1 ...................................................... 102
Figure 88: Rj/Dj results for example 1...........................................................103
Figure 89: Spurs for example 1 ......................................................................104
Figure 90: Data Period results for example 2................................................106
Figure 91: Time Trend plot for example 2 .................................................... 107
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
vii
Page 10

Table of Contents
List of Tables
Table 1: Directories and usage .........................................................................7
Table 2: File name extensions............................................................................8
Table 3: Entering numeric values .....................................................................9
Table 4: File menus...........................................................................................10
Table 5: User interface items...........................................................................13
Table 6: Measurement definitions ..................................................................17
Table 7: General measurement definitions ...................................................18
Table 8: File menus...........................................................................................19
Table 9: Configure Measurement menus and applicable
measurements....................................................................................................20
Table 10: N-Cycle measurement configuration .............................................24
Table 11: TIE: RjDj analysis configuration...................................................26
Table 12: Reference Clock Frequency configuration ....................................28
Table 13: PLL Loop Bandwidth configuration..............................................30
Table 14: Advanced Clock Recovery configuration ......................................31
Table 15: Filters configuration........................................................................34
Table 16: Advanced Filter configuration........................................................35
Table 17: Configure Sources menus ...............................................................37
Table 18: Configure Sources Autoset configuration .....................................38
Table 19: Optimize Horizontal For configuration.........................................39
Table 20: Configure Sources Gating configuration.......................................40
viii
Table 21: Configure Sources Qualify configuration......................................40
Table 22: Configure Sources Ref Levels Autoset configuration...................43
Table 23: Configure Sources Ref Levels Autoset configuration...................44
Table 24: Configure Sources Ref Levels configuration.................................46
Table 25: Configure Sources Stat pop Limit configuration..........................47
Table 26: Measurement Summaries menus ...................................................48
Table 27: Control Panel functions...................................................................50
Table 28: Statistics menus................................................................................52
Table 29: Plot types ..........................................................................................53
Table 30: Measurements and available plots .................................................54
Table 31: Plots Create menu options ..............................................................57
Table 32: Vert/Horiz axis options for a Histogram plot................................58
Table 33: Vert/Horiz axis options for a Time Trend plot .............................58
Table 34: Vert/Horiz axis options for a Spectrum plot.................................59
Table 35: Vert/Horiz axis options for a Bathtub plot....................................60
Table 36: Transfer Function Definition configuration..................................60
Table 37: Vert/Horiz axis options for a Transfer Function plot ..................61
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 11

Table of Contents
Table 38: Vert/Horiz axis options for a Phase Noise plot..............................62
Table 39: Log Statistics configuration ............................................................72
Table 40: Log Measurements configuration ..................................................73
Table 41: Log Worst Case Waveforms configuration ...................................74
Table 42: Single waveform measurements...................................................113
Table 43: Dual waveform measurements .....................................................119
Table 44: File menus parameters..................................................................123
Table 45: Select Source area parameters .....................................................124
Table 46: Math Defs area parameters ..........................................................125
Table 47: Waveform Edges parameters .......................................................125
Table 48: Measurement Range Limits parameters .....................................125
Table 49: N-Cycle measurement parameters...............................................126
Table 50: Clock Recovery: Reference Clock Frequency parameters ........126
Table 51: Clock Recovery: Loop BW parameters......................................126
Table 52: Advanced Clock Recovery parameters........................................127
Table 53: Filters parameters..........................................................................127
Table 54: Advanced Filter parameter...........................................................127
Table 55: TIE: RjDj Analysis parameters (TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only).128
Table 56: Configure Sources Autoset parameters.......................................128
Table 57: Configure Sources Gate/Qualify parameters ..............................129
Table 58: Configure Sources Ref Levels parameters ..................................129
Table 59: Configure Stat Pop Limit parameters .........................................129
Table 60; Configure Ref Level Autoset Setup Menu parameters ..............130
Table 61 Histogram Vert/Horiz Axis menu parameters .............................131
Table 62: Time Trend Vert/Horiz Axis menu parameter...........................131
Table 63: Spectrum Vert/Horiz Axis menu parameters .............................131
Table 64: Bathtub Vert/Horiz Axis menu parameters................................131
Table 65: Transfer Function Vert/Horiz Axis menu parameters...............132
Table 66: Phase Noise Vert/Horiz Axis menu parameters..........................132
Table 67: Log Statistics menu parameters ...................................................132
Table 68: Log Measurements Configure menu parameters .......................133
Table 69: Log Worst Case Waveforms Configure menu parameters........133
Table 70: Deskew menu parameters .............................................................134
Table 71: Acq Timeout menu parameters....................................................134
Table 72: Variable:Value JITTER3 command arguments and queries
part 1 ...............................................................................................................135
Table 73: Variable:Value JITTER3 command arguments and queries
part 2................................................................................................................136
Table 74: Variable:Value JITTER3 command arguments and queries
part 3................................................................................................................137
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
ix
Page 12

Table of Contents
Table 75: Variable:Value JITTER3 command arguments and queries
part 4................................................................................................................138
Table 76: Variable:Value JITTER3 command arguments and queries
part 5................................................................................................................141
Table 77: Measurement result queries..........................................................144
Table 78: Measurement names and keys......................................................144
Table 79: Source names and key..................................................................144
Table 80: Plot names and key ........................................................................144
Table 81: Error codes....................................................................................145
x
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 13

General Safety Summary
Review the following safety precautions to avoid injury and prevent damage to
this product or any products connected to it. To avoid potential hazards, use this
product only as specified.
Only qualified personnel should perform service procedures.
While using this product, you may need to access other parts of the system. Read
the General Safety Summary in other system manuals for warnings and cautions
related to operating the system.
To Avoid Fire or Personal Injury:
Connect and Disconnect Properly: Do not connect or disconnect probes or test
leads while they are connected to a voltage source.
Observe All Terminal Ratings: To avoid fire or shock hazard, observe all
ratings and markings on the product. Consult the product manual for further
ratings information before making connections to the product.
Do Not Operate With Suspected Failures: If you suspect there is damage to
this product, have it inspected by qualified service personnel.
Symbols and Terms: The following terms and symbols may appear in the online
help.
WARNING: Warning statements identify conditions or practices that could
result in injury or loss of life.
CAUTION: Caution statements identify conditions or practices that could
result in damage to this product or other property.
Terms on the Product: The following terms may appear on the product:
DANGER indicates an injury hazard immediately accessible as you read the
marking.
WARNING indicates an injury hazard not immediately accessible as you read
the marking.
CAUTION indicates a hazard to property including the product.
Symbols on the Product: The following symbol may appear in the product:
CAUTION Refer to Help
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help xi
Page 14

General Safety Summary
xii
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 15

Preface
5-Time Free Trial
The TDSJIT3 v2 application consists of two products: Jitter Analysis Advanced
and Jitter Analysis Essentials. These products are applications that enhance basic
capabilities of some Windows-based oscilloscopes from Tektronix. These jitter
analysis applications include the following features:
• Select and configure multiple measurements on more than one waveform
• Display statistical results for up to six measurements
• Perform random and deterministic jitter analysis including BER estimation
(TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only)
• Show results as plots
• Save statistical results to a data log file
• Save individual data points to a measurement results file
• Save the worst case waveforms to .wfm files
A 5-time free trial is available for all applications in the "Applications on this CD
and Compatible Oscilloscope" table found in the Optional Applications Software
on a Windows Based Oscilloscope Installation Manual (accessible as a PDF file.)
You can start and exit an application up to five times to help you evaluate
Tektronix software solutions.
If an application becomes available after you receive your oscilloscope, you can
download the application as described in the installation manual to try the free
trial.
Related Documentation
Refer to the Optional Applications Software on a Windows-Based Oscilloscope
Installation Manual for the following information:
• Software warranty
• Software license agreement
• List of all available applications, compatible oscilloscopes, and relevant
• How to use the 5-time free trial
• Installation procedures
• How to enable an application
• How to download files from the Tektronix web site
software and firmware version numbers
Note: You can view PDF files of the reference guide and the installation manual
from the CD Installation Browser and from the Documents directory on the
Optional Applications Software on a Windows-Based Oscilloscope CD-ROM.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help xiii
Page 16
Preface
GPIB Information
Relevant Web Sites
For information on how to operate the oscilloscope and use the applicationspecific GPIB commands, refer to the following items:
• The user manual for your oscilloscope provides general information on how to
operate the oscilloscope.
• The online help for your oscilloscope can provide details on how to use GPIB
commands to control the oscilloscope if you install the GPIB Programmer
guide (and code examples) from the oscilloscope CD-ROM.
• The example directory for programming examples of how to remotely control
the application. The default location for the example files is
C:\TekApplications\TDSJIT3v2\Examples\GPIB-Examples.
The Tektronix web site offers the following information:
• Understanding and Characterizing Jitter Primer, part number 55W-16146-0
• Jitter analysis details on the www.tektronix.com/jitter web page
You can also find useful information in the Fibre Channel - Methodologies for
Jitter and Signal Quality Specification – MJSQ on the www.t11.org web site.
Application CD Contents
The Optional Applications Software on a Windows Based Oscilloscope CD-ROM
includes files for the following types of documentation:
• Printable file of the TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis online help formatted to
• Reference guides
• Optional Applications Installation manual
resemble a user manual
xiv
Figure 1: Contents of the application CD-ROM
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 17

Preface
You can use the following methods to view most PDF files associated with this
application:
• Access a file in the Documents directory on the Optional Applications
Software on a Windows-Based Oscilloscope CD-ROM from any PC
• Access a file from the CD Installation Browser
• Select a file (except Reference guides) from the Start menu in the oscilloscope
task bar; you may need to minimize the oscilloscope and minimize the
application
• Use the Manuals Finder from the www.tektronix.com web site.
You can also use this additional method to view only the PDF file of the online
help:
• Select the shortcut on the desktop of the oscilloscope after you minimize the
oscilloscope
Note: If you do not have an Acrobat reader to view a PDF file, you can get a free
copy of the reader from the www.adobe.com/products/acrobat web page.
Conventions
Online help topics use the following conventions:
• The terms "TDSJIT3 v2 application" or "application" refer to the TDSJIT3 v2
Advanced or TDSJIT3 v2 Essentials Jitter Analysis Application (except when
noted as Advanced only)
• The term "oscilloscope" refers to any product on which this application runs.
• The term "select" is a generic term that applies to the two mechanical methods
of choosing an option: with a mouse or with the Touch Screen.
• The term "DUT" is an abbreviation for Device Under Test.
• User interface screen graphics are from a TDS7000 series oscilloscope; there
may be minor differences in the displays on other types of oscilloscopes.
• When steps require a sequence of selections using the application interface,
the ">" delimiter marks each transition between a menu and an option. For
example, one of the steps to recall a setup file would appear as File> Recall.
Types of Online Help Information
The online help contains the following types of information:
• A Getting Started group of topics briefly describes the application, contains
connection procedures, and includes a deskew procedure.
• An Operating Basics group of topics covers basic operating principles of the
application, including the Jitter Wizard. The sequence of topics reflects the
steps you perform to operate the application and includes definitions for all
menus and options.
• A Tutorial group of topics teaches you how to set up the application to acquire
a waveform, take a measurement, view the results, view a plot, and save data
to a file.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
xv
Page 18

Preface
Using Online Help
• An Application Examples group of topics demonstrates how to use jitter
measurements to identify a problem with a waveform. This should give you
ideas on how to solve your own measurement problems.
• A Reference group of topics specifies the minimum, maximum, incremental,
or list of choices, and the default values for all adjustable parameters.
• A Measurement Algorithms group of topics includes measurement guidelines
and information on how the application calculates each measurement.
• A GPIB Command Syntax group of topics contains a list of arguments and
values that you can use with the remote commands and their associated
parameters. The application includes simple remote interface programs to
show you how to operate the application using GPIB commands.
The application installs a desktop shortcut to access a PDF file of the help topics.
The file is printable and is formatted to resemble a user manual.
Online help has many advantages over a printed manual because of advanced
search capabilities. You can select Help> Topics on the right side of the
application menu bar to display the Help file.
The main (opening) Help screen shows a series of book icons and three tabs
along the top menu, each of which offers a unique mode of assistance:
• Table of Contents (TOC) tab - organizes the Help into book-like sections.
Select a book icon to open a section; select any of the topics listed under the
book.
• Index tab - enables you to scroll a list of alphabetical keywords. Select the
topic of interest to display the corresponding help page.
• Find tab - allows a text-based search. Follow these steps:
1. Type the word or phrase you wish to find in the search box.
If the word or phrase is not found, try the Index tab.
2. Select some matching words in the next box to narrow your search.
3. Choose a topic in the lower box, and then select the Display button.
Note: The Find tab function does not include words found in graphics. Refer to
the Find Tab and Searches topic for more information.
A Note: in the topic text indicates important information.
When you use a mouse, you can tell when the cursor is over an active
hyperlink because the arrow cursor changes to a small pointing hand cursor.
The light bulb icon and word Tip in the graphic above indicates additional
information to help you operate the application more efficiently.
xvi
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 19

Preface
Find Tab and Searches
Many online help topics only contain tables. To retain vertical and horizontal
lines, the tables are graphical objects. The Find tab in the online help does not
recognize words in these tables.
The online help is extensively indexed with the proper names of all menus and
options as they appear in the application and in the left column of graphical
tables.
Note: If you conduct a Find tab search with no results, try the Index tab instead.
Contacting Tektronix
Phone
Address
Web site
Sales support
Service support
Technical support
* This Telephone number is toll free in North America. After office hours, please leave
a voice mail message.
Outside North America, contact a Tektronix sales office or distributor; See the
Tektronix web site for a list of offices.
1-800-833-9200*
Tektronix, Inc.
Department or name (if known)
14200 SW Karl Braun Drive
P.O. Box 500
Beaverton, OR 97077
USA
www.Tektronix.com
1-800-833-9200, select option 1*
1-800-833–9200, select option 2*
www.tektronix.com/support
1-800-833-9200, select option 3*
6:00 a.m. - 5:00 p.m. Pacific time
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
xvii
Page 20

Preface
Feedback
Tektronix values your feedback on our products. To help us serve you better,
please send us suggestions, ideas, or other comments you may have about your
application or oscilloscope.
You can email your feedback to techsupport@tektronix.com, FAX at (503) 6275695, or by phone. Please be as specific as possible and include the following
information:
General Information
• Oscilloscope model number and hardware options, if any
• Probes used
• Serial data standard
• Signaling rate
• Your name, company, mailing address, phone number, FAX number
Note: Please indicate if you would like to be contacted by Tektronix regarding
your suggestion or comments.
Application-Specific Information
• Software version number
• Description of the problem such that technical support can duplicate the
problem
• If possible, save the oscilloscope waveform file as a .wfm file
• If possible, save the oscilloscope and application setup files from the
application to obtain both the oscilloscope .set file and the application .ini file.
Refer to Saving a Setup File.
Once you have gathered this information, you can contact technical support by
phone or through e-mail. If using e-mail, be sure to enter "TDSJIT3 v2 Problem"
in the subject line, and attach the .set, .ini, and .wfm files.
To include screen shots, from the oscilloscope menu bar, select File>
Export. In the Export dialog box, enter a file name with a .bmp extension and
select Save. The file is saved in the C:\TekScope\Images directory. You can then
attach the file to your email (depending on the capabilities of your email editor).
xviii
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 21

Getting Started
The TDSJIT3 v2 application consists of two products: Jitter Analysis Advanced
and Jitter Analysis Essentials. These products are applications that enhance basic
capabilities of some Windows-based oscilloscopes from Tektronix. The
application includes a Wizard to help you quickly set up measurements and
obtain measurement results.
You can use this application to do the following tasks:
• Select and configure multiple measurements on one or more waveforms
• Display statistical results for up to six measurements
• Perform random and deterministic jitter analysis including BER estimation
(TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only)
• Apply high pass and low pass filters to the measurements (TDSJIT3 v2
Advanced only)
• Display the results as Histogram, Time Trend, Cycle Trend, and Spectrum
plots; for TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only, also display the results as Bathtub,
Transfer Function, and Phase Noise plots
• Export plots
• Log statistical results to a file
• Log individual data points to a measurement results file
• Log worst case waveforms to files
Note: There are no standard accessories for this product.
Differences between TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced and TDSJIT3 v2 Essentials
The TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced application provides the following features that are
not included in the TDSJIT3 v2 Essentials application:
• PLL-Based Clock Recovery
• Crossover Voltage Analysis
• Jitter separation (Rj/Dj analysis)
• Bit error rate estimation (BER)
• Filters
• Bathtub, Transfer Function, and Phase Noise plots
Features that are only available with the TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced application are
indicated as "TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only."
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help 1
Page 22

Getting Started
Compatibility
For information on oscilloscope compatibility, refer to the product data sheet (use
the Search tool on the www.tektronix.com web site).
The setup files for TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced and TDSJIT3 v2 Essentials are
compatible with each other.
The TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced application will recall setup files made with previous
versions of TDSJIT3 and TDSJIT3E. To convert an existing setup file, recall it
and then save it again. If you wish to retain a copy of the original setup file, use a
different filename when saving. Note that setup files from previous versions may
include directory paths such as "C:\TekApplications\TDSJIT3\...", whereas the
v2 application defaults to "C:\TekApplications\TDSJIT3v2\...". If you would like
your converted setup files to use the TDSJITv2 directory, recall the existing
setup file, use the Graphical User Interface to change any file paths to use the
new directory structure, and then save the setup.
Requirements and Restrictions
The Sun Java Run-Time Environment (JRE) V1.4.2 must be installed on the
oscilloscope to operate the TDSJIT3 v2 application. When you install the
application, the InstallShield Wizard automatically installs the proper version of
the JRE. If the JRE is deleted, install TDSJIT3 v2 application again.
Accessories
Installation
Memory. A minimum of 512 MB PC memory is required and 1 GB PC memory
is highly recommended.
Keyboard. You will need to use a keyboard to enter new names for some file
save operations.
There are no standard accessories for this product. However, you can refer to the
product datasheet available on the Tektronix web site for information on optional
accessories relevant to your application.
Refer to the Optional Applications Software on a Windows-Based Oscilloscope
Installation Manual for the following information:
• List of available applications, compatible oscilloscopes, and version numbers
• How to use the 5-time free trials
• How to apply a new authorized Option Installation key label
• Installation procedures
• How to enable an application
• How to download updates from the Tektronix web site
2
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 23

Getting Started
Connecting to a Device Under Test (DUT)
You can use any compatible probes or cable interface to connect between your
DUT and oscilloscope. One connection is sufficient for most signals.
The Clock-to-Output, Skew, and Crossover Voltage (TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced
only) measurements require two input channels, two reference, or two Math
waveforms.
Warning: To avoid electric shock, remove power from the DUT before
attaching probes. Do not touch exposed conductors except with the properly rated
probe tips. Refer to the probe manual for proper use.
Refer to the General Safety Summary in your oscilloscope manual.
Deskewing Probes and Channels
To ensure accurate results for two-channel measurements, it is important to first
deskew the probes and oscilloscope channels before you take measurements from
your DUT.
The application includes an automated deskew utility that you can use to deskew
any pair of oscilloscope channels.
Note: To produce the best deskew results, you should connect the probes to the
fastest signal in your DUT.
Deskewing on Oscilloscopes with Bandwidth Extension
Some Tektronix oscilloscopes feature software-based bandwidth extension. The
bandwidth extension may be enabled on a per-channel basis.
Enabling or disabling bandwidth extension on any channel affects the skew on
that channel. Thus, you should deskew probes and channels after you make such
configuration changes.
Steps to Deskew Probes and Channels
To deskew a pair of probes and oscilloscope channels, follow these steps:
1. Refer to Connecting to a Device Under Test before starting the procedure.
2. Connect both probes to the fastest signal in your DUT.
Set up the oscilloscope as follows:
1. Use the Horizontal Scale knob to set the oscilloscope to an acquisition rate so
that there are two or more samples on the deskew edge.
2. Use the Vertical Scale and Position knobs to adjust the signals to fill the
display without missing any part of the signals.
3. Set the Record Length so that there are more than 100 edges in the
acquisition.
4. Start the TDSJIT3 v2 application.
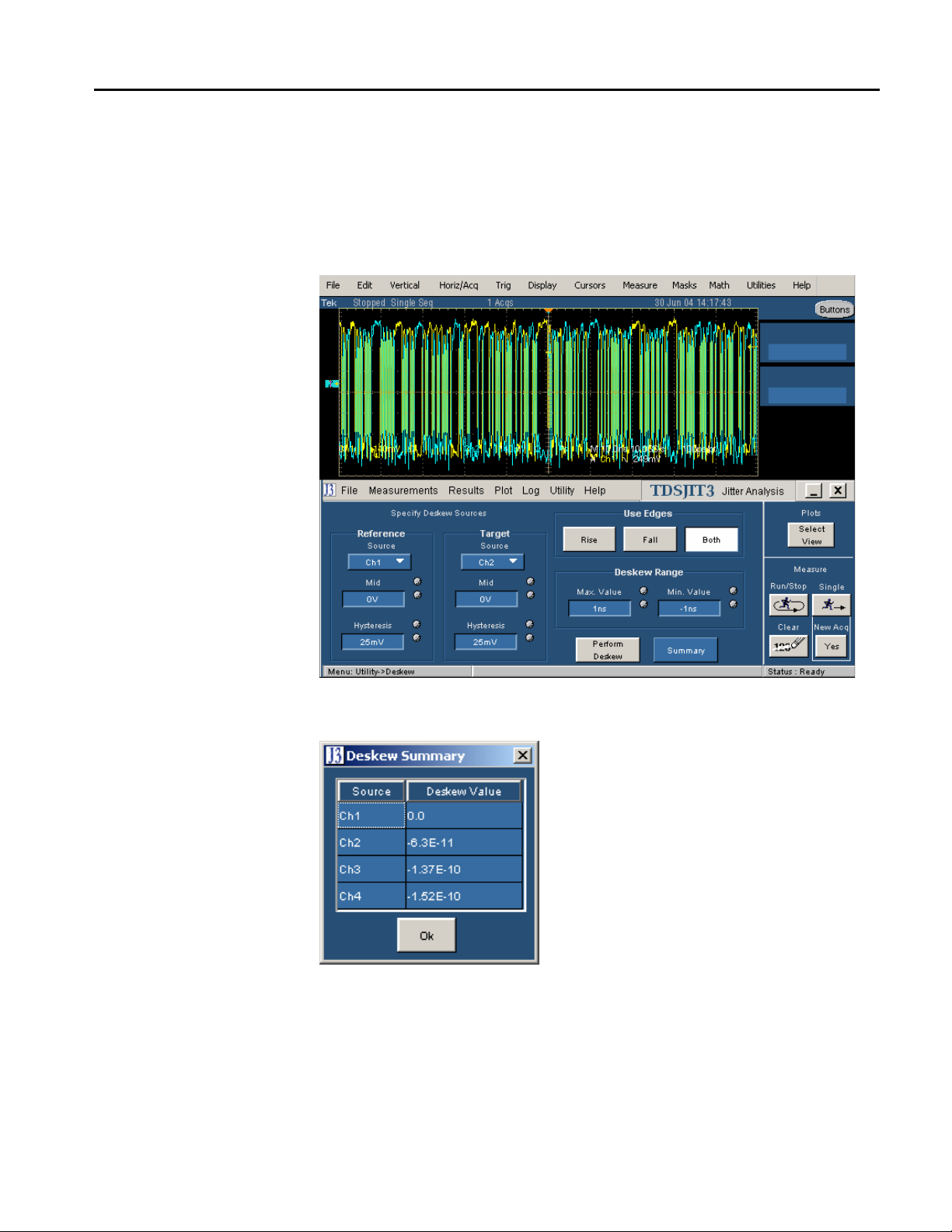
5. Select Utilities> Deskew. The Deskew Utility menu appears.
6. Set the Reference Source option to Ch1. The Source waveform is the
reference point used to deskew the remaining channels.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
3
Page 24
Getting Started
7. Set the Target Source option to Ch2. This is the channel that will be
deskewed.
8. To start the utility, select the Perform Deskew command button, and then
select Yes.
9. Repeat steps 7 and 8 for Ch3, and then for Ch4 to deskew those channels.
10. To view the deskew values, select the Summary button.
Figure 2: Deskew complete example
Figure 3: Deskew Summary example
4
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 25
Operating Basics
The topics in the Operating Basics book cover the following definitions and
tasks:
• General information, such as on navigating the user interface
• Setting up the application
• Taking measurements
• Viewing the measurement results as statistics or as plots
• Using the plot window zoom and cursors functions
• Exporting Plot Files
• Logging statistical results to a file
• Logging individual data points to a file
• Logging worst case waveforms to files
• Saving and recalling set up files
General Information
Starting the TDSJIT3 v2 Application
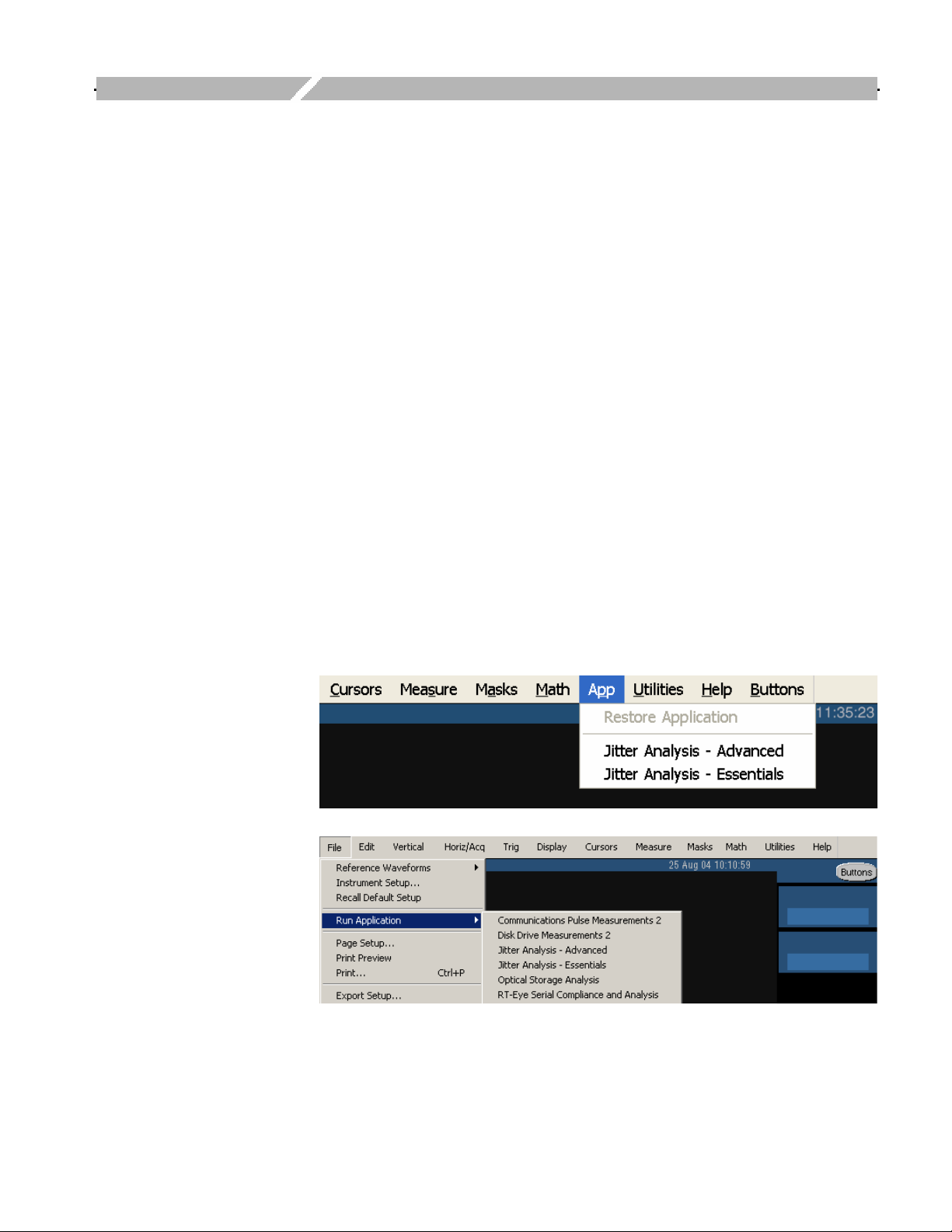
The way you start the application depends on the oscilloscope model. On the
oscilloscope menu bar, select App> Jitter Analysis - Advanced or select File>
Run Application> Jitter Analysis - Advanced. If you are using the TDSJIT3 v2
Essentials application, select Jitter Analysis - Essentials.
Figure 4: Starting the TDSJIT3 v2 application
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help 5
Page 26

Operating Basics
Returning to the Application
The way you return to the application depends on the oscilloscope model.
Figure 5: Returning to the application
Minimizing and Maximizing the Application
To minimize the application, select File> Minimize or the command button
in the application menu bar. When you minimize the application, the oscilloscope
fills the display.
To maximize the application, select
Exiting the Application
To exit the application, select File> Exit or the command button in the
application menu bar. When you exit the application, you can choose to keep the
oscilloscope setup currently in use with the application or to restore the
oscilloscope setup that was present before you started the application.
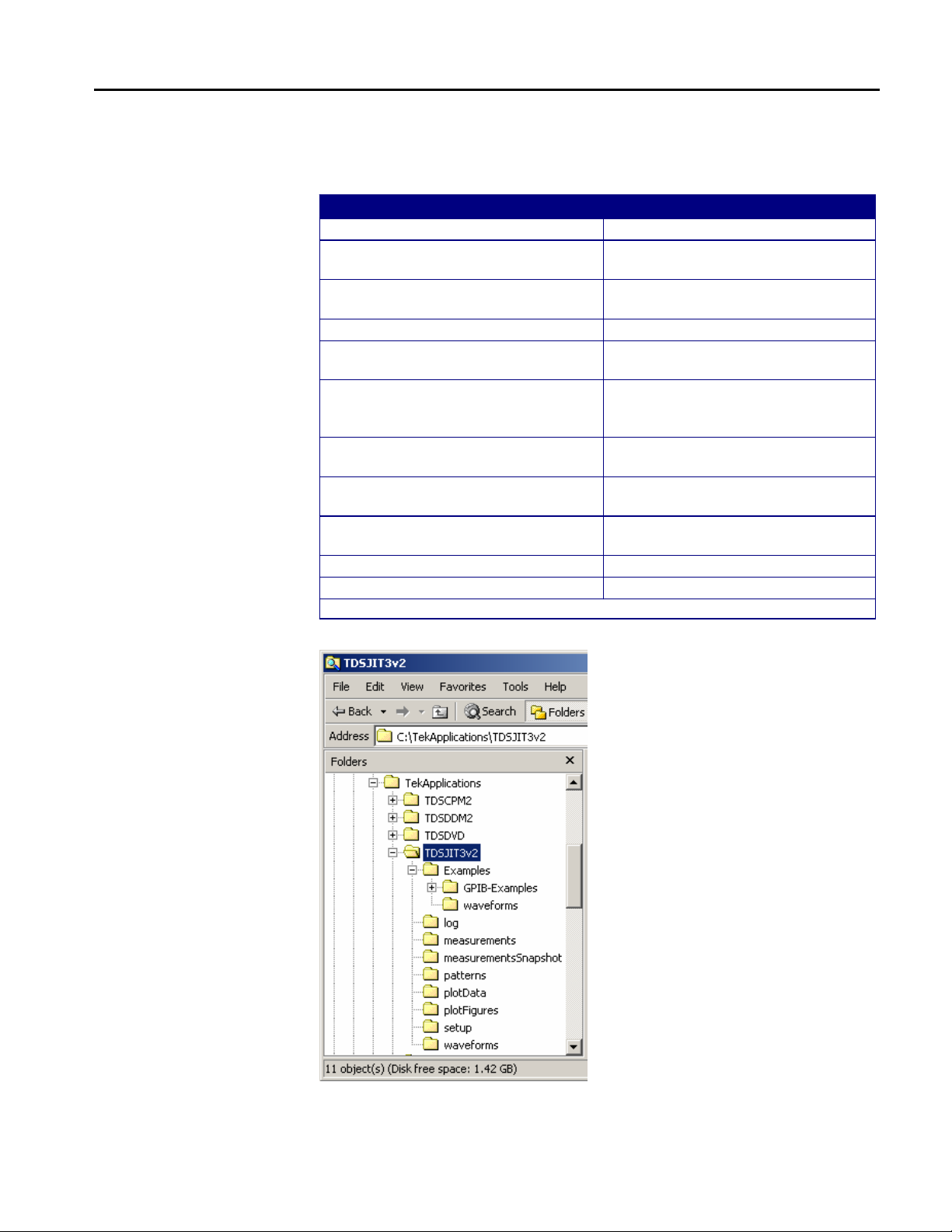
Application Directories and Usage
During installation, the application sets up directories for various functions, such
as to save setup files, and uses extensions appended to file names to identify the
file types.
in the oscilloscope task bar.
6
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 27
Operating Basic
Table 1: Directories and usage
Default directory names*
\TDSJIT3v2 Home location
\TDSJIT3v2\Examples\GPIB-Examples Examples of remote control programs
\TDSJIT3v2\Examples\waveforms Waveform files used in the tutorial
\TDSJIT3v2\log Statistics log files
\TDSJIT3v2\measurements Log files of data points for each
\TDSJIT3v2\measurementsSnapshot Measurement log files for the Save
\TDSJIT3v2\patterns Pattern files for the Advanced Clock
\TDSJIT3v2\plotData Data exported from measurement
\TDSJIT3v2\plotFigures Image files exported from
\TDSJIT3v2\setup Setup files
\TDSJIT3v2\waveforms Worst case waveforms files
* All subdirectories are located in the C:\TekApplications directory.
Directory use
that use GPIB commands
and application examples
selected measurement
Current Measurements option (Log
Measurements)
Recovery configuration
plots
measurement plots
Figure 6: Directory structure
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
7
Page 28

Operating Basics
Table 2: File name extensions
Extension Description
.bmp File that uses a “bitmap” format
.csv File that uses a "comma separated value" format
.ini TDSJIT3 application setup file
.jpg File that uses a “joint photographic experts group” format
.mat File that uses native MATLAB binary format
.png File that uses a “portable network graphics” format
.set Oscilloscope setup file that is recalled with an application .ini file;
.txt File that uses an ASCII format
.wfm Waveform file; can be recalled into Reference memory
Tips on the TDSJIT3 v2 User Interface
Here are some tips to help you with the application user interface:
• Use the Jitter Wizard to set up and take one measurement from a set of
commonly used measurements
both files will have the same name
• Select a Source before selecting each measurement
• Select any waveform source and any measurement multiple times to use
different configuration options
• Use the Single run button
to obtain a single set of measurements from
a single run; push the button again to interrupt the acquisition
• Use the Run/Stop button
to acquire measurements from continuous
runs; push the button again to interrupt the current acquisition, or push the
Single button to stop sequencing when the current acquisition and
measurement cycle is complete
8
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 29
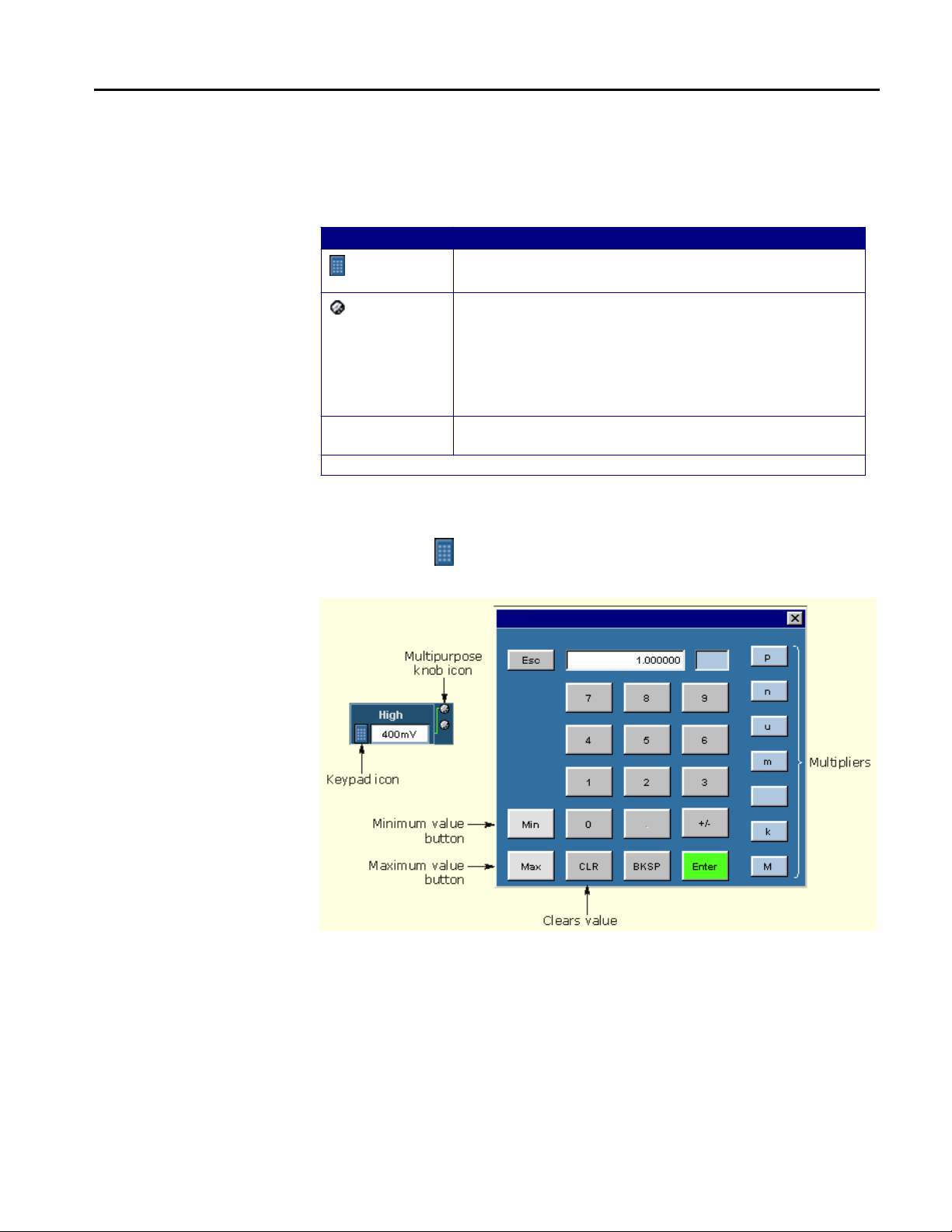
Operating Basic
How to Enter Numeric Values
Table 3: Entering numeric values
Method Description
Virtual Keypad
Keypad
Multipurpose
knob*
Edit box*
* When selected twice, the Keypad appears.
Displays the virtual keypad (looks similar to a calculator);
use to enter a value
Displays a line between the icon and the option box to
indicate that either the upper or lower multipurpose knob
on the front panel of the oscilloscope is active; turn the
knob to select a value
Press the FINE button on the oscilloscope to enter or
select the smallest values or units
Type in a value from the physical keyboard and press the
Enter key
Note: Select the icon, and then use the virtual keypad to enter information,
such as reference voltage levels.
Figure 7: On-screen keypad
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
9
Page 30

Operating Basics
Using Basic Oscilloscope Functions
You can use oscilloscope controls and functions while the application is running.
To do so, select a menu from the oscilloscope Menu bar (or Toolbar) and access
menus, or use the front-panel knobs and buttons. You can also use the
oscilloscope Help menu to access information about the oscilloscope and how to
use it.
When you access some oscilloscope controls, the oscilloscope fills the display.
File Menus
You can use the File menus to save and recall different application setups and
recently accessed files.
Do not edit a setup file or recall a file not generated by the application.
Table 4: File menus
Menu/function Description or function
Default Setup Recalls most default (startup) parameters
Recall*
Save*
Recent Files Select from a list of the four most recently accessed setup
Dock Positions and locks the TDSJIT3 v2 application in the lower
Undock Unlocks and allows you to move the TDSJIT3 v2 application
Minimize Minimizes the application
Exit Exits the application; you can choose to retain the current
*Save or Recall functions also save or recall the associated oscilloscope setup
file (.set); an oscilloscope file is recalled if the application finds a .set file with a
matching name.
Browse to select an application setup (.ini) file to recall;
restores the application to the values saved in the setup file
Saves the current application settings in a .ini file
files (saved or recalled) and recall that setup
half of the oscilloscope display and the oscilloscope
application in the upper half of the display
to another position in the oscilloscope display or to a second
monitor; the oscilloscope display returns to full size
oscilloscope settings or restore the oscilloscope to settings
prior to starting the application
Navigating the User Interface
The application provides you with several methods to set up the application:
• The Jitter Wizard
• The Measurement Setup Sequence buttons
• The menus available in the menu bar
10
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 31

Operating Basic
The Jitter Wizard allows you to set up, configure, and launch a single
measurement without requiring any knowledge of the control menus. However, it
does not provide access to many of the advanced features.
The Measurement Setup Sequence buttons show the logical order you would
follow to set up the application if you do not use the Jitter Wizard.
The menus from the menu bar allow the same full control as the Measurement
Setup Sequence buttons, but are accessible at all times.
General Steps to Set Up the Application
Jitter Wizard
Figure 8: General steps to set up the application.
The Jitter Wizard provides a quick and easy graphical interface that guides you
through a short series of menus so you can take measurements in the fewest steps
possible. The wizard lets you pick one measurement from a subset of
measurements, and then take a single measurement only. (The application can
take six measurements simultaneously.)
The selections you make in each wizard menu determine the subsequent choices
the wizard offers in the next selection menu. You can use several methods to
configure the wizard: by preference selections, by default selections, or a
combination of both.
Note: You can set the Jitter Wizard menu to always appear when you start the
application.
To quickly take measurements, follow these steps:
1. Select Measurements> Wizard or select Help> Wizard to launch the Jitter
Wizard.
2. Select a measurement category.
3. Select the
default settings.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
button in each subsequent menu to use all the
11
Page 32

Operating Basics
4. Select the
The wizard closes, the application takes the measurement, and displays
statistical results.
Note: The statistical results when you use the wizard are identical to the results
when you do not use the wizard if the measurement and setup are the same.
When you are through setting up a measurement and plots with the wizard, select
the Run button. The application takes the measurement and displays the results,
including selected plots. To obtain new measurement results, select the
Single Run button.
If you select the Cancel button, the wizard exits and discards all of the selections.
Note: After you use the wizard, you may decide to refine some options, such as
the calculated values for reference voltage levels, to suit your analysis situation.
Note: The application does not launch the Jitter Wizard when you start the
application if you clear the Show This Wizard At Startup option.
button.
12
Figure 9: Jitter Wizard when launched
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 33

Operating Basic
User Interface Information
The application uses a Microsoft Windows based user interface. Display the
definitions of the application user interface items, or view a menu labeled with
the user interface items.
Note: The oscilloscope application shrinks to half size and appears in the top half
of the screen when the application is running.
Table 5: User interface items
Item Description
Area Visual frame that encloses a set of related options
Box Use to define an option; enter a value with the Keypad or
a Multipurpose knob
Browse Displays a window where you can look through a list of
directories and files
Button Use to define an option; not a command button
Check box Use to select or clear an option
Command button Initiates an immediate action, such as the Start command
button in the Control panel
Control panel Located to the right of the application; contains command
buttons that you use often, such as to Start sequencing
Keypad On-screen keypad that you can use to enter numeric
values
List box Use to select an option from a list
Menu All options in the application window (except the Control
panel) that display when you select a menu bar item
Menu bar Located along the top of the application display and
contains application menus
Multipurpose
knob
Option Any named button (other than a command button) or any
Status bar Line located at the bottom of the application display that
Tab Short cut to a menu in the menu bar or a category of
Virtual keyboard On-screen keyboard that you can use to enter
Scroll bar Vertical or horizontal bar at the side or bottom of a
Icon that indicates when you can use one of the
multipurpose knobs on the oscilloscope front panel to
adjust a value
named box that defines a control or task
shows the name of the current menu (location) and the
latest Warning or Error message
menu options; most tabs are short cuts
alphanumeric strings, such as for file names
display area that you use to move around in that area
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
13
Page 34

Operating Basics
Figure 10: Menu with user interface items
14
Figure 11: Menu navigation tree
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 35

Operating Basic
Setting Up the Application for Analysis
The Jitter Wizard allows you to set up, configure, and launch a single
measurement without requiring any knowledge of the control menus. However, it
does not provide access to many of the advanced features.
The Measurement Setup Sequence buttons show the logical order you would
follow to set up the application if you do not use the Jitter Wizard. The menus
from the menu bar allow the same full control as the Measurement Setup
Sequence buttons, but are accessible at all times.
When you use the Measurement Setup Sequence buttons or the menus, you may
need to perform some or all of the following tasks:
• Select up to six measurements
• Configure measurement options
• Configure waveform sources, such as the Source Autoset function
• Create and configure up to four plots
• Log statistics, measurements, or worst case waveforms
• Take measurements and display the results
Selecting Measurements
After setting up the application, you can select the
button to take measurements. The application displays the results as statistics,
and as plots if you set up the Plot Create menu.
After taking measurements, you can do any of the following tasks:
• View the results as statistics
• View the results graphically
You can use the Measurements Select menu to select up to six measurements.
You can always access the menu by selecting Measurements> Select in the menu
bar. In addition, you can use the
the Measurements Select menus.
To select a measurement, always choose the Source (or sources) first, and then
select a measurement. To select a measurement, follow these steps:
1. Select the Source in the Select Source area.
2. Select a measurement in the Add Measurement area.
3. For some advanced configurations, use the options in the Math Defs area in
conjunction with the Source Select area.
You can select the same measurement type multiple times using different
sources. To do so, select a source first, and then select a measurement. You can
also create two or more measurement entries that use the same measurement type
and source, and then configure each measurement differently.
button (when visible) as a short cut to
or command
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
15
Page 36

Operating Basics
You can view the configured measurements, sources, and any associated values
in various Measurement Summary menus.
Figure 12: Measurements Select menu
Select Source Area
The application takes measurements from waveforms specified as sources (also
called input sources). You can select a live channel (CH1, CH2, CH3, or CH4), a
reference (Ref1, Ref2, Ref3, or Ref4), or a math (Math1, Math2, Math3, or
Math4) waveform as a source.
The titles above the Select Source option list boxes vary depending on the
measurement category.
Note: Most measurements require one source. The Setup, Hold, Clock-to-Output,
Skew, and Crossover Voltage (TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only) measurements
require two sources.
Option names (in the Select Source area) vary with the category of
measurements.
Clock Data Clk-Data General
Figure 13: Select Source options by measurement category
16
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 37

Operating Basic
Table 6: Measurement definitions
Area Option Description
Clock Period Elapsed time between consecutive crossings of the mid
reference voltage level by the waveform in the specific
direction; see the Common Cycle Start Edge option
Frequency Inverse of the period for each clock cycle
TIE Difference in time between each edge of a designated
polarity on a sampled clock waveform to the
corresponding edge on a calculated clock waveform with
a constant frequency (zero jitter)
PLL TIE Measurement errors relative to a timing reference that is
recovered from a data stream by a phase locked loop
(PLL); for TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only
Cycle-Cycle Difference in period measurements from one cycle to the
next
N-Cycle Difference in elapsed time between two consecutive
groups of N-Cycles where N is a configuration object that
you can set
Positive Cy-Cy
Duty
Negative Cy-Cy
Duty
Positive Duty
Cycle
Negative Duty
Cycle
Data Period Elapsed time between when a waveform crosses specific
Frequency Inverse of the period for each data cycle
TIE Difference in time between the data edges on an
PLL TIE Measurement errors relative to a timing reference that is
Clk-Data Setup Elapsed time between when a data waveform crosses a
Hold Elapsed time between when the clock waveform crosses
Clk-Out Elapsed time between when the clock waveform crosses
Difference between two consecutive positive widths
Difference between two consecutive negative widths
Ratio of the positive portion of the cycle relative to the
period
Ratio of the negative portion of the cycle relative to the
period
reference voltage levels in the opposite direction once
acquired data waveform to the data edges on a
recovered data waveform with a constant rate (zero jitter)
recovered from a data stream by a phase locked loop
(PLL); for TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only
voltage reference level followed by the clock signal
crossing its own voltage level
a voltage reference level followed by a data waveform
crossing its own voltage level
a voltage reference level followed by an output waveform
crossing its own voltage level
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
17
Page 38

Operating Basics
Table 7: General measurement definitions
Area Option Description
General Rise Time Time difference between when the Lo reference level is
crossed and the Hi reference level is crossed on the
rising edge of the waveform
Fall Time Time difference between when the Hi reference level is
crossed and the Lo reference level is crossed o n the
falling edge of the waveform
Positive Width Amount of time the waveform remains above the mid
reference voltage level
Negative Width Amount of time the waveform remains below the mid
reference voltage level
High Time Amount of time the waveform remains above the high
reference voltage level
Low Time Amount of time the waveform remains below the high
reference voltage level
Skew Difference in time between two similar edges on two
waveforms with the assumption that every edge in one
waveform has a corresponding edge (either the same or
opposite polarity) in the other waveform; edge locations
are referenced to the mid reference voltage level
Crossover
Voltage
Edge timing derived from the crossover (voltage) of
differential clock or data measurements; for TDSJIT3 v2
Advanced only
Math Definitions
The application includes four preset math operations and an option to use any
other math operation as defined in the oscilloscope. You can assign each math
waveform (Math1, Math2, Math3, or Math4) to any of these five operations.
The Math Defs area includes the following preset math operations:
• Ch1-Ch3
• Ch2-Ch4
• Ref1-Ref2
• Ref3-Ref4
You can select Scope User if you want to use a math waveform based on a userdefined math operation. To define your own math operation, use the oscilloscope
math equation editor.
18
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 39

Operating Basic
Clearing Measurements
You can remove individual or all selected measurements through the
Measurements Select menu. To remove an individual measurement, follow these
steps:
1. Select the measurement to be removed in the table on the right side of the
Measurements Select menu.
Configuring a Measurement
2. Select the
3. To remove all selected measurements, select the
button.
button.
Most measurements offer configuration options. The options available in each
Configure Measurement menu are specific to the selected measurement.
You can always access the menus by selecting Measurements> Configure in the
menu bar. In addition, you can use the
button (when visible) as a short
cut to the Configure Measurements menus.
The application includes the following Configure Measurement menus:
• General
• Clock Recovery
• Filters (TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only)
Configure Measurement Menus Definitions
Table 8: File menus
Menu name Description
General Define waveform edges; define range limits for some
measurements
Clock Recovery Define reference clock frequency or PLL loop bandwidth for
some measurements; advanced functions
Filters*
* TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only.
Define high pass, low pass, or band pass filters; advanced
functions
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
19
Page 40

Operating Basics
Table 9: Configure Measurement menus and applicable measurements
Measurements General Clock recovery Filters*
Clock TIE
Clock PLL TIE*
Data TIE
Data PLL TIE*
Clock Period
Clock Frequency
Data Period
Data Fre quency
Cycle-Cycle
N-Cycle
Positive Duty Cycle
Negative Duty Cycle
Setup
Hold
Clk-Out
Skew
Crossover Voltage*
Positive Cy-Cy Duty
Negative Cy-Cy Duty
Rise Time
Fall Time
Positive Width
Negative Width
High Time
Low Time
* TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced on ly.
** TIE: RjDj configure options are for TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only.
† No configuration options are available for these measurements.
Yes** Yes Yes
Yes** Yes Yes
Yes - - - Yes
- - - Yes Yes
Yes - - - - - -
None†
20
General
You can select which waveform edge the application will use to take
measurements. The name of the edge option depends on the measurement being
configured.
Edge options appear in the General Configure Measurement menu. Some
measurements include two edge options because they require two waveforms.
Note: Data measurements do not include Waveform Edge options.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 41

Operating Basic
Clock Edge Options
The Clock Edge option defines which edge of the clock input is used to calculate
the statistics of clock based measurements.
Figure 14: Clock edge options
Active Edge Options
The Active Edge option defines which edge of the source waveform is used to
take measurements.
Figure 15: Active edge options
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
21
Page 42

Operating Basics
Clock and Data Edge Options
The Clock Edge option defines which edge of the clock input is used to calculate
the statistics of clock based measurements. The Data Edge defines which edge of
the data input is used to calculate the statistics on clock-data based
measurements.
Figure 16: Clock and Data edge options
From Edge and To Edge Options
The From Edge option defines which edge on the first waveform is used to take
the measurement. The To Edge option defines which edge on the second
waveform is used to take the measurement, the same edge or the opposite edge as
the first waveform.
Figure 17: From Edge and To Edge options
22
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 43

Operating Basic
Main Edge Options
The Main Edge option defines which edge on the Main waveform is used to take
the measurement.
Figure 18: Main edge options
Measurement Range Limits Configuration
For two-channel measurements, you can specify the minimum and maximum
range of valid measurement values. Individual measurements falling outside the
selected range are discarded.
The default values for the Meas Range Limits options vary by measurement.
Figure 19: Meas Range Limits options
N-Cycle Measurement Configuration
You can define a Clock Edge and some unique General Configuration options for
the N-Cycle measurement.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
23
Page 44

Operating Basics
Table 10: N-Cycle measurement configuration
Option Description
Clock Edge Waveform edge used to calculate statistics
N= Number of cycles in an N-cycle group
1st Meas: Start @ Edge Number of cycles skipped prior to starting the
measurement
Edge Increment
1
N
N-Cycle Measurement Options
Specifies how consecutive measurements (each
spanning 2 N-cycles) jump forward
By one cycle in the waveform
By N cycles in the waveform
Figure 20: N-Cycle measurement options
TIE Rj/Dj
Rj/Dj analysis refers to the process of separating jitter into the major categories
of Random Jitter (Rj) and Deterministic Jitter (Dj), and further separating Dj into
specific subcomponents based on observable properties of the jitter. This can
help you understand and reduce the jitter in your circuit. For serial data signals
with embedded clocks, it also allows you to accurately predict the eye opening
and total jitter at very low bit error rates, in a few seconds. By contrast, direct
measurement of these quantities can take hours for a single eye-opening
measurement.
For data signals, there are two methods of Rj/Dj analysis provided in the
application. The Rj/Dj Analysis of Repeating Patterns Using a Spectral
Approach, which requires a data signal with a cyclically repeating data pattern, is
a method of analysis with wide industry acceptance. The Rj/Dj Analysis of
Arbitrary Patterns method uses a technique that allows jitter separation and
analysis even if the data pattern is random or unknown.
Each method has advantages and limitations. For clock signals, the spectral
analysis approach is automatically used.
24
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 45

Operating Basic
Once an Rj/Dj analysis has been done, the results may be plotted in the form of a
Bathtub Plot.
Rj/Dj Analysis of Repeating Patterns Using a Spectral Approach
This method of Rj/Dj analysis uses a Fourier transform of the time-interval error
signal to identify and separate jitter components. It is described in the Fibre
Channel -- Methodologies for Jitter and Signal Quality Specification (MJSQ),
and was the analysis method originally introduced with the TDSJIT3 application.
This method requires that the data signal be composed of a pattern of N bits that
are repeated over and over. The pattern length (N) must be known, although it is
not necessary to know the specific bits that make up the pattern.
When the data pattern is not repeating, or is unknown, a second method of Rj/Dj
analysis may be used. (It may also be used if the pattern is repeating, and
correlates well with the Spectral method in this case.) This method assumes that
the effects of Intersymbol Interference (ISI) only last for a few bits. For example,
in a band-limited link where a string of ones follows a string of zeros, the signal
may require three or four bit periods to fully settle to the "high" state.
In this method, an analysis window with a width of K bits is slid along the
waveform. For each position of the window, the time interval error of the rightmost bit in the window is stored, along with the K-1 bit pattern that preceded it.
After the window has been slid across all positions, it is possible to calculate the
component of the jitter that is correlated with each observed K-1 bit pattern, by
averaging together all the observed errors associated with that specific pattern.
In the configuration menu for the arbitrary-pattern method, the Window Length
field allows you to select how many bits are included in the sliding window. The
window should include enough bits to encompass the impulse response of the
system under test, usually 5 to 10 bits. A good practical test is to check whether
increasing the window length causes any appreciable change in the jitter results;
if not, the window length is effectively capturing all the ISI effects. The
disadvantage of increasing the window length is that it uses more memory and
slows the processing.
The configuration menu also includes a field for selecting what population of
each K-1 bit pattern must be accumulated before the TIE associated with that
pattern is considered accurate. Using a larger population means that more
observations are averaged together, so that the variance of the measurement is
reduced. Specifying a larger population has the disadvantage of requiring a
longer measurement period before results can be calculated.
It may be necessary to sequence the instrument several times before enough
statistics are accumulated to provide results. A vertical gauge on the TIE:RjDj
results screen provides an indication of how the accumulation is progressing.
The arbitrary-pattern approach to measuring jitter may not be appropriate if there
are very-long-duration memory effects in your data link. An example would be if
there is impedance mismatch reflections that arrive long enough after the initial
edge to fall outside the analysis window.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
25
Page 46

Operating Basics
Bathtub Curve and BER Versus Decision Time
The Bathtub Curve plot shows the eye opening and total jitter values as functions
of the BER level. The plot is obtained from the Rj/Dj separation.
Figure 21: Bathtub Curve and BER versus Decision Time
Table 11: TIE: RjDj analysis configuration
Option Description
Separation Enables or disables Rj/Dj separation analysis
Total Jitter
BER=1E- ? Sets the BER level for the eye opening and total jitter
Dat a Patt ern*
T ype* Selects a Repeating or an Arbitrary data pattern
Pattern Length* When the Type option is set to Repeating, sets the
pattern length of the repetitive pattern data; use for
spectrum analysis Rj/Dj separation
Window Length* When the Type option is set to Arbitrary, sets the pattern
window length used for arbitrary pattern Rj/Dj separation
Population* When the Type option is set to Arbitrary, sets the
minimum population limit for each pattern to be qualified
for arbitrary pattern Rj/Dj separation
* Available only for Data TIE and Data PLL TIE measurements.
26
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 47

Operating Basic
Figure 22: TIE: RjDj analysis options for Clock TIE and Clock PLL TIE
Figure 23: TIE: RjDj analysis options for Data TIE and Data PLL TIE
Clock Recovery Configuration
For waveforms that are synchronized to a nominal clock frequency, TIE
measurements offer a choice of clock recovery methods. Clock recovery is
defined as the way in which the TDSJIT3 v2 application determines the
theoretically jitter-free clock to which the waveform will be compared.
Constant (straight line) clock recovery is implicitly chosen by selecting a Clock
TIE or Data TIE measurement. Phase-Locked Loop clock recovery is chosen by
selecting a Clock PLL TIE or Data PLL TIE measurement.
For Data measurements (Data Period, Data Frequency, Data TIE, and Data PLL
TIE) on signals with extremely high jitter, advanced clock recovery support is
offered. This support is not needed or recommended for most signals. It allows
you to provide extra guidance to the clock recovery algorithm with respect to
how many unit intervals are represented by each pair of clock edges. This is most
useful in cases where the total jitter on a data signal exceeds 0.5 unit intervals.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
27
Page 48

Operating Basics
In Constant Clock Recovery, the clock is assumed to be of the form A*sin(2 ft
+ ), where the frequency (f) and phase ( ) are treated as unknown constants.
Once a source waveform has been acquired and the edges extracted, f and are
chosen using linear regression, so that the recovered clock minimizes the meansquared sum of the Time Interval Error (TIE) for that waveform.
Figure 24: Constant Clock Recovery concept
Constant Clock Recovery Setup
The Ref Clock Frequency control area provides three options that control how
the clock recovery is performed.
Selecting Autocalc Every Acq will allow the clock-recovery algorithm to choose
a new best-fit clock frequency and phase for each new oscilloscope acquisition.
Selecting Autocalc 1st Acq will allow the clock-recovery algorithm to choose a
new best-fit clock frequency and phase only on the first acquisition. Subsequent
acquisitions will choose a best fit on clock phase but retain the clock frequency
found on the first acquisition. Clearing the measurements by choosing Clear on
the control panel will reset the clock recovery so that both frequency and phase
are optimized on the subsequent acquisition.
Selecting Custom allows you to specify an exact clock frequency, so that
absolutely no clock frequency optimization is performed. A best fit of the clock
phase is still performed on every acquisition.
Table 12: Reference Clock Frequency configuration
Option Description
Autocalc 1st Acq Calc ulates the best fit of the initial acquisition or the
first acquisition after clearing results, and then uses the
value until yo u clear the results
Autocalc Every Acq Calculates the best fit for each acquisition (default)
Custom: Value Uses the exact frequency you enter
28
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 49

Operating Basic
Figure 25: Reference Clock Frequency options
Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Clock Recovery
In PLL Clock Recovery, the application simulates the behavior of a hardware
phase-locked loop clock recovery circuit. This is a feedback loop in which a
voltage-controlled oscillator is used to track, or follow, slow variations in the bit
rate of the input waveform. Such loops are frequently used to recover the clock in
communications links that do not transmit the clock as a separate signal. The
PLL parameters in the application may be adjusted to mimic the behavior of a
receiver in such a link, within certain guidelines.
Figure 26: Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Clock Recovery concept
PLL Clock Recovery Setup
The PLL control area provides control over the phase-locked loop used for clock
recovery. You can choose the loop bandwidth and the loop order, and if a
second-order loop is chosen, you can specify the damping factor.
The loop bandwidth can be selected implicitly by specifying a data
communications standard, or it can be set explicitly.
To use a standards-based setup, select the Standard Frequency button. From the
Standard: Speed (Gb/s) list box, choose the standard that matches your data link.
For example, choose "FC2125: 2.125" to test a 2.125 Gbit/second Fibre Channel
link. The PLL bandwidth will be set to 1/1667 of the baud rate.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
29
Page 50

Operating Basics
To manually control the loop bandwidth, choose the User button and use the
Value option to select the 3 dB bandwidth of the loop, in Hertz.
You can use the PLL Order list box to choose between a first-order or secondorder loop. More correctly, this is the loop type, where a type 1 loop has a
transfer function that approaches zero frequency with a slope of 1/s and a type 2
2
1 s
loop approaches zero frequency with a
slope. The term Order is used in the
application as a concession to popular usage. For a more thorough treatment of
loop type and order, see Frequency Synthesis by Phase Lock, by William Egan.
If you choose a second-order loop, the Damping option becomes enabled. (The
Damping Factor does not apply to first-order loops.)
Note: Although it is possible to configure a second-order PLL with a bandwidth
up to 1/10 of the baud rate, such a loop will have poor dynamic performance.
This is because second-order loops have less phase margin than first-order loops.
A preferred alternative to using a second-order PLL with a high bandwidth is to
use a second-order high-pass measurement filter to emulate the effects of the
PLL.
Table 13: PLL Loop Bandwidth configuration
Option Description
Standard
Frequency
Custom: Value Sets the 3 dB bandwidth of the Phase Locked Loop (PLL)
PLL Order Sets the or der of the PLL
Damping Sets the damping ratio of the PLL
Advanced*
* Available only for Data PLL TIE measurements.
Loop BW Options
Select a standard:
FC133:0.1328, FC266:0.2656, FC531:1.0625,
FC1063:11.063,: FC2125:2.125, IB2500:2.5, SerATAG1:1.5,
SerATAG2:3, SerATAG3:6, USB_FS:0.12, USB_H S:0.48,
1394b_S400b:0.4915, 1394b_S800b:0.983,
1394b_S1600b:1.966, GB_Ethernet:1.25, 100BaseT:0.125,
OC1:0.0518, OC3:0.155, OC12:0.622, OC48:2.488
30
Figure 27: PLL Loop Bandwidth options
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 51

Operating Basic
Advanced Clock Recovery Setup
For Data Period, Data Frequency, Data TIE and Data PLL TIE measurements,
you may use several types of advanced clock recovery if needed. The advanced
clock recovery tools can be helpful if your signal has jitter excursions that exceed
0.5 unit intervals, by guiding the application in choosing the number of unit
intervals that correspond to each pair of edges. Advanced clock recovery is
seldom required, and is not recommended for general analysis.
When Advanced Clock Recovery is enabled for a given source, it applies to all
Data measurements using that source. For example, if you have Data Period and
Data TIE measurements on Channel 1, enabling advanced clock recovery for one
measurement will cause it to be enabled for the other as well.
Two types of advanced clock recovery are available. In the first, you can provide
the nominal data rate to the clock recovery algorithm. Normally, the application
analyzes your data and determines the nominal data rate automatically. If you
know the data rate or unit interval to an accuracy of +/- 3%, you can provide this
information as a clue to the algorithm.
You can also provide clock recovery guidance in the form of a known data
pattern. The pattern is specified by using an ASCII text file containing the
characters 1 and 0. The file may contain other characters, spaces and tabs for
formatting purposes, but they will be ignored. Several files for commonly-used
patterns are included with the application, and you may use these as examples if
you wish to create your own pattern files. The default location for pattern files is
C:\TekApplications\TDSJIT3v2\patterns.
If you use pattern file guidance, the clock recovery algorithm will perform a best
fit of the selected data pattern against the acquired edge sequence. It will then use
the pattern file to determine the number of unit intervals that fall between each
set of edges.
Note: Clock recovery using pattern match will provide erroneous results if your
data has missing edges or extra edges at the defined edge threshold.
Table 14: Advanced Clock Recovery configuration
Area/option Description
Nominal Data Rate
On Off Enables or disables advanced clock recovery through
rate guidance
Unit Interval Defines the nominal data r ate by UI in time
Bit Rate Defines the nominal data rate by the bit rate in
frequency
Known Data Pattern
On Off Enables or disables advanced clock recovery through a
known data pattern
Pattern File Name Selects a file to use for the data pattern
OK button Accepts changes and closes
Cancel button Discards changes and closes
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
31
Page 52

Operating Basics
Figure 28: Advanced Clock Recovery options
Filters
For some measurements (Clock Period, Clock Frequency, Clock TIE, Clock PLL
TIE, Data Period, Data Frequency, Data TIE, and Data PLL TIE), the
measurements-versus-time waveform (time trend) that is derived from the
original oscilloscope waveform can be filtered before it is passed to the statistics
and plotting subsystems.
Figure 29: Optional filters
You can modify the time trend by applying filters that block specific frequency
bands. You can configure a High Pass filter to block out the low frequency band
or a Low Pass filter to block out the high frequency band.
32
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 53

Operating Basic
Figure 30: Filter characteristics
Band Pass Filtering
You can create a band pass filter by enabling both the High Pass and Low Pass
filters on a measurement. The cutoff frequency for the Low Pass filter must be
greater than or equal to the cutoff frequency for the High Pass filter.
You should be aware that setting the cutoff frequencies close to each other may
effectively filter out all of the time trend, or all but a small amount of noise. This
diagram shows the spectrum of the time trend passed to the statistics and plotting
subsystems when you use both the High Pass and the Low Pass filters.
Figure 31: Band Pass filtering
Influence of High Pass Filters on Period and Frequency Statistics
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
33
Page 54

Operating Basics
High-pass filters attenuate low frequencies, and filter out DC values entirely.
When a high-pass filter is added to a period or frequency measurement, the mean
value of the filtered measurement goes to zero. This can be seen by creating a
Time Trend plot of a high-pass-filtered period or frequency measurement.
Although this is the correct theoretical behavior for the filtered measurement, it
isn't very useful if the Results panel reports that the mean period or frequency is
zero. For this reason, the mean values that appear in the results panels for Period
and Frequency measurements are the values prior to the filter.
Table 15: Filters configuration
Option Description
High Pass
Filter Spec When enabled, blocks the low frequency band and
passes on only the high frequency band of the
waveform; defined as 1st order, 2nd order, or 3rd order
Butterworth
Freq (F1)* High Pass filter cutoff frequency; frequency at which
the filter magnitude has dropped by 3 dB
Low Pass
Filter Spec When enabled, blocks the high frequency band and
passes on only the low frequency band of the
waveform; defined as 1st order, 2nd order, or 3rd order
Butterworth
Freq (F2)* Low Pass filter cutoff frequency; frequency at which the
filter magnitude has dropped by 3 dB
* Includes a 3 dB attenuation.
These options are also available for Data measurements.
34
Figure 32: Filters options
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 55

Operating Basic
Advanced Filter Configuration
The measurement filters are implemented using infinite impulse response (IIR)
designs. As with any causal filter, a transient may occur at the filter’s output in
response to the arrival of the input signal. It is usually desirable to exclude this
transient from the measurement results.
In the TDSJIT3 v2 application, the filter transient is managed by specifying a
settling time, Td. A smoothing window ramps the filter input from 0 to 1 during
this settling time. The output of the filter during the settling time is excluded
from the measurement results. The smoothing window has a raised-cosine profile
which is described by:
1
)(
2
where the settling time of the filter (Td) is configurable. The operation of the
smoothing window is shown graphically in the Effect of the Smoothing Window
topic.
By default, the settling time is set to 2/Fc, where Fc is the lowest filter cut-off
frequency applied to the measurement.
Note: Setting the settling time to less than 1/Fc increases the chance that the
measurement results will include effects that are due to the filter transient. The
user interface will warn you if you configure the measurement this way.
Table 16: Advanced Filter configuration
Option Description
Duration D efines the amount of time excluded from the measurement
OK button Accepts changes and closes
−=
cos1
results to allow the filter to settle
⋅
ttWπ
T
d
for
Tt <≤0
d
Figure 33: Advanced Filter options
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
35
Page 56

Operating Basics
Configuring Sources
Figure 34: Effect of the Smoothing window
You may configure the sources associated with your measurements, which can be
as simple as using the Autoset features that automatically calculate the scale or
the reference voltage levels.
You can always access the menus by selecting Measurements> Source in the
menu bar. In addition, you can use the
cut to the Configure Measurements menus.
The application includes the following Configure Source menus:
• Autoset
• Gate/Qualify
• Ref Levels
• Stat Pop Limit
button (when visible) as a short
36
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 57

Operating Basic
Table 17: Configure Sources menus
Menu name Description
Sources Autoset*
Gate/Qualify*
Ref Levels Specifies reference voltage levels for each measurement
Stat Pop Limit**
* All sources must have the same Horizontal Sample Rate, Record Length, and
Position to assure that measurements function properly.
** In Free Run mode, sequencing stops when all the population limits are met.
Automatically changes the vertical scale or horizontal
resolution of the measurement source waveforms
Autoset acts on all active (Ch1, Ch2, Ch3, Ch4) sources
used by measurements directly or contained in a math
source definition
Accurate measurement results require sufficient vertical
and horizontal resolution
Gating limits measurements to an area of the source
waveform bounded on the left and right by vertical cursors
or by the lowest zoom that is on
Qualify limits measurements to the one or more areas of
the waveform where a qualifier waveform is active
source; separate reference levels apply to rising and falling
edges
Sets the maximum population of all measurements; Free
Run sequencing mode will stop when all measurements
have attained this limit
Autosetting Sources for Live (Channel) Waveforms
In most situations, you can improve accuracy on channel or math waveform by
using the Source Autoset options to optimize the vertical scale or horizontal
resolution settings of the oscilloscope.
The Vertical Scale option automatically checks the Peak-to-Peak level of live
sources. The vertical scale and offset of all signals with a Peak-to-Peak less than
6 divisions is adjusted so the Peak-to-Peak will be 8 divisions. If the maximum or
minimum value of a signal is "clipped," the vertical scale and offset is adjusted so
the Peak-to-Peak will be 8 divisions.
The Horizontal Resolution option automatically checks the number of
samples/edge on the rising and falling transitions (Rise Time/Resolution and Fall
Time/Resolution) of all live channels. The oscilloscope horizontal resolution is
set to the largest value that does not cause the samples/edge of the fastest edge to
fall below the specified target. The target is 5 samples per edge when optimized
for edge resolution, and 2.5 samples per edge when optimized for edge count.
Horizontal Resolution sets the acquisition sampling mode to Interpolated Real
Time for signals with very high edge speeds. The default record length is 500 k
points.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
37
Page 58

Operating Basics
To automatically define both the vertical and horizontal settings for all channel
sources, select the All button. The All option also applies an oscilloscope Autoset
on each channel prior to performing the vertical scale and horizontal resolution
autoset.
To automatically define the vertical or horizontal settings for active sources,
follow these steps:
1. Ensure that any channel waveform that you want to autoset is visible on the
oscilloscope.
2. If you intend to select the All or Horizontal Resolution button, configure the
Optimize Horizontal For option to one of the following:
• Edge Resolution: results in 5 samples per edge or more, giving you better
edge timing and measurement accuracy.
• High Edge Count: results in as few as 2.5 samples per edge. Some edge
timing accuracy is sacrificed for more edges in a given record length. High
edge count is desirable for RjDj analysis in oscilloscopes without extended
record lengths.
3. Select one of the following options:
• All button to Autoset both vertical and horizontal setting
• Vertical Scale button to Autoset oscilloscope vertical settings only
• Horizontal Resolution button to Autoset oscilloscope horizontal settings
only
Optionally, select the Undo button to return the oscilloscope to its state prior to
autoset.
Note: At rise times less than 100 ps, the application may have only two actual
sample points per edge to work with. The application will set up a suitable level
of oscilloscope acquisition interpolation to increase the point count per edge to
around 5 points.
Table 18: Configure Sources Autoset configuration
Option Description
All Performs a sequence: oscilloscope AUTOSET, Vertical
Scale, and Horizontal Resolution
Vertical Scale If a channel waveform does not exceed six vertical
divisions, decreases the scale so the waveform
occupies about 8 divisions
Horizontal Resolution Sets the horizontal resolution so that the number of
samples on the fastest transition (edge) exceeds a
specified target; see Optimize Horizontal For option
Undo Returns to the settings present before an Autoset was
performed; disabled after measurements are taken until
you perform another Source Autoset
38
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 59

Operating Basic
Table 19: Optimize Horizontal For configuration
Area/option Description
Optimize Horizontal For
Edge Resolution Sets the horizontal scale to ? 5 samples per
transition; edge timing accuracy does not improve
significantly at higher resolution
Edge timing accuracy will not significantly improve
at higher resolution (default)
Max Edge Count Sets the horizontal scale to ? 2.5 samples per
transition; Rj/Dj analysis requires a larger data set
If the oscilloscope does not have a long acquisition
memory, it may be necessary to trade some Edge
timing accuracy for a larger data set
Figure 35: Configure Sources Autoset options
Gate/Qualify
Gating allows you to limit the analysis to a specific area of the waveform
bounded by cursors or zoom limits, thereby excluding unnecessary information.
To access the Gating menu, select Measurements> Configure Source> Source
Gate/Qualify. View the Configure Sources Gate/Qualify menu.
You can set up a gated region in one of the following ways:
• Zoom
• Cursors (vertical)
Qualifiers allow you to limit the application to more narrowly defined conditions
before taking measurements. This is another way to exclude unnecessary
information. All sources for the measurements and Qualify input must have the
same Horizontal Sample Rate, Record Length, and Position to ensure that
measurements function properly. For TIE and PLL TIE measurements, only the
first qualified region will be measured even if multiple qualified regions are
present.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
39
Page 60

Operating Basics
Table 20: Configure Sources Gating configuration
Option Description
Off No gating occurs; application takes measurements over the entire
waveform
Zoom Zoom to a specified region of the source waveform and take
measurements within the selected area
Cursors Use oscilloscope cursors to define a specific part of the waveform
and take measurements within the selected area
Configure Sources Gate/Qualify Menu
Figure 36: Configure Sources Gating options
Table 21: Configure Sources Qualify configuration
Option Description
Source*
Mid Shows the vertical reference level of the qualifier waveform
Hysteresis Shows the vertical reference margin of the qualifier waveform
Active
Off Disables the use of the qualify waveform
High
Low
* Measurement and Qualify sources must have the same Horizontal Sample Rate,
Record Length, and Position to ensure that measurements function properly.
** For TIE and PLL TIE measurements, only the first qualified region will be
measured even if multiple qualified regions are present.
Selects a waveform to qualify the signal or clock source used
for the measurement
Enables measurements in regions** where the qualifier
waveform exceeds the mid reference level
Enables measurements in regions** where the qualifier
waveform falls below the mid reference level
40
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 61

Operating Basic
Ref Levels
Timing measurements are based on state transition times. By definition, edges
occur when a waveform crosses specified reference voltage levels. Reference
voltage levels must be set so that the application can identify state transitions on
a waveform. By default, the application automatically chooses reference voltage
levels when necessary.
The TDSJIT3 v2 application uses three basic reference levels: High, Mid and
Low. In addition, a hysteresis value defines a voltage band that prevents a noisy
waveform from producing spurious edges. The reference levels and hysteresis are
independently set for each source waveform, and are specified separately for
rising versus falling transitions.
There are two ways to set the reference voltage levels: automatically or
manually.
High, Mid and Low Reference Voltage Levels
The application uses three reference voltage levels: High, Mid, and Low.
• For most measurements, the application only uses the Mid reference voltage
level. The Mid reference level defines when the waveform state transition
occurs at a given threshold.
• For Rise Time and Fall Time measurements, the High and Low reference
voltage levels define when the waveform is fully high or low.
Figure 37: Reference voltage levels diagram
Rising Versus Falling Thresholds
You can specify thresholds for each of the reference voltage levels: High, Mid,
and Low. The application uses the thresholds to determine the following events:
• A Low/Mid/High rising event, which occurs when the waveform passes
through the corresponding Rise threshold in the positive direction.
• A Low/Mid/High falling event, which occurs when the waveform passes
through the corresponding Fall threshold in the negative direction.
For a given logical reference level (such as Low, Mid, or High), rising and falling
events alternate as time progresses.
Note: In many cases, the rising and falling thresholds for a given reference
voltage level are set to the same value. In those cases, a hysteresis value helps
prevent spurious edges produced by small amounts of noise in a waveform.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
41
Page 62

Operating Basics
Using the Hysteresis Option
The hysteresis option can prevent small amounts of noise in a waveform from
producing multiple threshold crossings. You can use a hysteresis when the rising
and falling thresholds for a given reference voltage level are set to the same
value.
The reference voltage level the hysteresis value defines a voltage range that
must be fully crossed by the waveform for an edge event to occur. If the decision
threshold is crossed more than once before the waveform exits the hysteresis
band, the mean value of the first and last crossing are used as the edge event
time.
For example, if the waveform rises through the Threshold - Hysteresis, then rises
through the Threshold, then falls through the Threshold, then rises through both
the Threshold and the Threshold + Hysteresis, a single edge event occurs at the
mean value of the two rising crossings.
Example of Hysteresis on a Noisy Waveform
42
Figure 38: Example of Hysteresis on a noisy waveform
Automatic Versus Manual Reference Voltage Levels
Each measurement source may be configured to automatically choose voltage
reference levels (default), or to lock the reference voltages to levels of your
choosing.
In the Ref Levels configuration panel, a table at the left edge contains all of the
currently active measurement sources. An Autoset checkbox appears beside each
source. To enable or disable Autoset for a given source, choose the source button
in the left column and select the corresponding checkbox to toggle its state.
To learn more about automatically or manually setting voltage reference levels,
refer to Understanding When Ref Level Autoset will Occur and Understanding
How Ref Level Autoset Chooses Voltages.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 63

Operating Basic
Table 22: Configure Sources Ref Levels Autoset configuration
Option/button Description
Autoset Identifies which sources on which to perform an autoset; you
can set or clear the option for each source
Update* Immediately calculates and displays the reference voltage
levels for all sources where the Autoset option is set
according to the Autoset Ref Level Setup menu
Setup Specifies the Base-Top method and relative percent to be
used for all reference voltage levels when an autoset occurs
*If you do not select this button, the applic ation updates the reference levels (if
needed) when you select the Single or Run/Stop button to take measurements.
Understanding When Ref Level Autoset will Occur
When Autoset is enabled for a given source, the individual reference levels are
displayed but you may not manually adjust them. Instead, the reference levels are
automatically recalculated whenever one of the following events occurs:
• A measurement sequence is initiated for the first time after a source has
become active
• A measurement sequence is initiated for the first time after all results have
been cleared
• The "Update" button at the right edge of the panel is pressed
The Update button is provided as a convenience, but it is never required. Autoset
will always be run (if enabled) before an uninitialized source is used for a
measurement.
An "Armed" indicator appears in the upper right corner of the panel whenever a
new source has been added or measurement results have been cleared. This lets
you know that the reference levels will be recalculated the next time either the
Single or Run/Stop button is selected. If the "Armed" indicator is not visible, the
displayed reference levels will be retained if a measurement sequence is
performed with no further configuration changes. Of course, you can cause the
reference levels to be recalculated at any time by simply selecting the Update
button.
Understanding How Ref Level Autoset Chooses Voltages
Once triggered, the Reference Level Autoset function uses the following logic to
determine actual voltage levels.
For each applicable source, the Top (high logic level) and Base (low logic level)
are first determined. Then, the High, Mid and Low levels are calculated as
percentages of the Top-Base difference. For example, if the Top and Base were
2.8 volts and 0.4 volts respectively and the High percentage level was 90%, this
threshold would be calculated as:
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
56.2)4.08.2(9.04.0)( =−⋅+=−⋅+= BaseToptHighPercenBaseHighThresh
43
Page 64

Operating Basics
You can select the method used for calculating the Top and Base of the
waveform, as well as the percentages used for the High, Mid and Low thresholds,
for each source. To do so, see the Configure Source Ref Levels Autoset Options
topic.
Table 23: Configure Sources Ref Levels Autoset configuration
Area/option Description
Base-Top Method
Min-Max Uses the minimum and maximum values in the
waveform to determine the base-top amplitude
Useful on a waveform with low noise and free from
excessive overshoot
Low-High (Histogram) Uses a histogram approach to determine the base-
top amplitude
Creates a histogram of the amplitudes of the
waveform; the histogram should have a peak at the
nominal high level, and another peak at the nominal
low level
Auto Automatically determines the best Base-Top Method
to use
Set Ref Level %
Relative to Base-Top*
Rise High Sets the high threshold level for the rising edge of
the source
Rise Mid Sets the middle threshold level for the rising edge of
the source
Rise Low Sets the low threshold level for the rising edge of the
source
Fall High Sets the high threshold level for the falling edge of
the source
Fall Mid Sets the middle threshold level for the falling edge of
the source
Fall Low Sets the low threshold level for the falling edge of
the source
Hysteresis Sets the threshold margin to the reference level
which the voltage must cross to be recognized as
changing; the margin is the relative reference level
plus or minus half the hysteresis; use to filter out
spurious events
* Default settings are 90% (High), 50% (Mid), 10% (Low), and 3% (Hysteresis).
44
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 65

Operating Basic
Figure 39: Autoset Ref Levels options
Manually Adjusting the Reference Voltage Levels
Whether or not you use the application to automatically calculate the initial
reference voltage levels, you may need to manually change the values. To set the
reference levels manually, follow these steps:
1. Select Measurements> Configure Sources> Ref Levels.
2. Select the desired source from the Source column.
Note: You cannot select sources that are not currently active.
3. Clear the Autoset option for the source you wish to set manually.
4. Select the reference levels or hysteresis options and manually adjust the
values. The values will not change when you select the Update button or take
measurements.
Once an active source has been set to Manual, the reference levels for that source
will not change when you select the Update button or take measurements.
Note: A source will become inactive if all measurements on that source are
removed. If a new measurement is then added on that source, the source once
again becomes active, and defaults to Autoset. If you clear all measurement on a
source that was set to Manual, you must re-select the Manual state (if desired)
when the source is again added.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
45
Page 66

Operating Basics
Table 24: Configure Sources Ref Levels configuration
Area/option Description
Autoset (Source)
Set (enabled) Allows the application to automatically calculate
reference voltage levels when necessary
The calculation occurs when you select the Single or the
Run/Stop button to start sequencing after a change to the
configuration or when you select the Update b utton
Clear (disabled) Prevents the application from changing the reference
voltage levels from the values you set
Autoset
Armed Visible only when an Autoset will occur on the next
measurement sequence
Update* Immediately calculates and displays the reference
voltage levels for all sources where the Autoset option is
set
Setup Displays the Autoset Ref Level menu where you can
adjust the relative percent values or select a Base-Top
method
Reference Level**
Rise High Sets the high threshold level on the slope in volts for the
rising edge of the sour ce
Rise Mid Sets th e middle threshold level on the slope in volts for
the rising edge of the source
Rise Low Sets the low threshold level on the slope in volts for the
rising edge of the sour ce
Fall High Sets the high threshold level on the slope in volts for the
falling edge of the source
Fall Mid Sets the middle threshold level on the slope in volts for
the falling edge of the source
Fall Low Sets the low threshold level on the slope in volts for the
falling edge of the source
Hyst eresis Sets the threshold margin relative to the reference level
which the voltage must cross to be recognized as
changing; the margin is the reference voltage level plus
or minus half the hysteresis; use to filter out spurious
events
*If you do not select this button, the application update s the reference levels (if
needed) when you select the Single or Run/Stop button to take measurements.
** Default settings are 90% (High), 50% (Mid), 10% (Low), and 3% (Hysteresis)
46
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 67

Operating Basic
Figure 40: Configure Sources Ref Levels options
Stat Pop Limit
The Population control allows you to limit the amount of waveform data that is
analyzed. You can use the Configure Source Stat Pop Limit menu to set a limit
on a maximum population to obtain for all selected measurements. View the
Configure Source Statistics Population Limit menu.
To define the maximum population for measurements, follow these steps:
1. Select Measurements> Configure Source> Stat Pop Limit > On.
2. Specify a value for the Size option from one to one million.
If you use a population limit, statistics individually accumulate for each
measurement until the population limit is reached. A Free Run stops sequencing
when all active measurements reach the population limit. A Single Run stops
sequencing when the limit is less than the normal population for that Single Run.
Note: Statistics stop accumulating for an individual measurement when it reaches
an internal limit of two billion. The application stops sequencing when all
selected measurements have reached this internal limit.
Table 25: Configure Sources Stat pop Limit configuration
Option Description
On
Off
Size Specifies the maximum population to obtain for each active
Enables or disables the application from using a population limit
while taking measurements
measurement
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
47
Page 68

Operating Basics
Measurement Summaries
Figure 41: Configure Sources Stat pop Limit options
You can view various summary menus that show measurement settings.
Table 26: Measurement Summaries menus
Menu name Description
Measurement Shows the names of each selected measurement, the
waveform sources for each measurement, and the
configuration parameters for each measurement
Source Ref
Levels
Miscellaneous Shows if Gating, Qualify, and Stat Pop Limit functions are
Shows the reference voltage levels for the high, mid, and
low thresholds for the rising edge and for the falling edge of
each active source, plus the hystersis
enabled; if enabled, also shows the Source for qualification
the Size for population, and various other configuration
choices.
Taking Measurements
48
If you want to change trigger settings or localize the measurement, you should do
so before you take any measurements.
Note: If an error message displays because there are not enough cycles from
which to take a measurement, adjust the Horizontal setting on the oscilloscope to
increase cycles.
Note: If you select a reference waveform as the source, you need to recall and
display the waveform on the oscilloscope before the application can take a
measurement. To do so, refer to recalling a waveform file.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 69

Operating Basic
Localizing Measurements
By specifying the trigger position, the starting point, and the length of the
waveform, you can effectively exclude information that is not useful to analyze
before taking a measurement.
To limit the application measurement to a part of the waveform, you can use the
Configure Source Gate/Qualify menu. You can also adjust the Record Length,
Scale, or pre-trigger information in the oscilloscope Horizontal menu, or the
Trigger Level and Slope in the oscilloscope Trigger menu.
About Sequencing
You use the Control Panel to start or stop the sequence of processes for the
application and oscilloscope to acquire information from a waveform. The
application then determines if the algorithm for the selected measurement can be
applied to the waveform information. Sequencing is the steps to acquire
waveform information, determine if the information is usable for the
measurement, take the measurement, and display the results (and plots if
selected).
Acquiring Data
To acquire data from waveforms and take measurements, follow these steps:
1.If the Control Panel is not displayed, select the
menu from the Results drop down list.
2.Select the
the Free Run mode.
Select the
displays the results when the sequencing is complete.
Note: If none of the selected measurements is a live source (or a Math
expression which includes a live source), Free Run mode will stop after a
single sequence since there is no point in repeatedly analyzing the same data.
To stop sequencing, do one of the following:
1. If you wish to stop a Single measurement sequence before it is complete,
select the Single button a second time. This may be useful if you have started
a sequence on a long waveform and then realize you would like to change the
configuration.
2. If you wish to interrupt a Free Run as quickly as possible, select Run/Stop a
second time. Sequencing will be halted as quickly as practical but the final
measurement cycle may include results from only part of a waveform.
3. If you wish to halt a Free Run cleanly, select the Single button. This will
convert the Free Run mode to Single mode, so that the sequencer stops when
the latest measurement cycle is complete. This is the preferred method since
all accumulated measurement results will include the same number of
complete measurement cycles.
Run/Stop button for continuous acquisitions. This is called
Single button for a single acquisition. The application
button or select any
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
49
Page 70

Operating Basics
Note: The status bar at the bottom of the Control Panel indicates the current
sequencer state. It displays Sequencing when either Single or Free Run
measurements are in process. The status bar indicates Ready when the
sequencing is complete. It may also indicate Stopping when a measurement cycle
has been interrupted, prior to indicating Ready.
Use the command button to delete all measurement results.
New Acquisition Function of the Single Button
You may wish to perform additional measurements on the current waveform(s)
rather than acquiring new waveforms. For example, you may wish to make more
than six measurements on a single waveform. Or you may decide after
performing a measurement cycle that you would like to perform a slightly
different measurement on the same data. To do this, follow these steps:
Control Panel Functions
1. Take the first measurements using the
2. Select the
button to change the New Acq setting from Yes to No.
Single button.
3. Select and configure the next set of measurements and press the Single button
again.
4. When you are ready to acquire new data, select the New Acq button again to
change the setting to Yes.
Note: If Run/Stop is selected while the New Acq button is set to No, the
application will change the button to Yes and Free Run will proceed.
Table 27: Control Panel functions
Command
button Description
Run/Stop
(Free Run)*
Single Acquires a new waveform if the source is Ch1, Ch2, Ch3, or
New Acq = No Without acquiring new data, calculates the statistical results
Clear Clears all previous information in the Results menus and Plot
*Stops when the sequencing reaches the population limit; plots also display (if
selected) when you select Stop.
Continuously acquires waveforms and sequences until you
select the Run/Stop or Single command button again
Ch4; for all sources, the application sequences until complete
and displays the results (and plots if selected)
for the selected measurements and displays the results (and
plots if selected)
windows; data saved to files remains intact (.csv, .wfm, etc.)
50
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 71

Operating Basic
Figure 42: Control Panel options
There are two ways to view the results after an analysis is complete: as statistical
values or as graphical plots.
If you set up plots before taking measurements, the application shows the
selected plots in a separate window in the oscilloscope part of the display. The
application shows statistics in the application part of the display. Each selected
plot appears in its own window, which initially occupies the upper half of the
display in front of the oscilloscope waveform.
Clearing Results
You can also log the measurement data and measurement statistics to .csv files
for viewing in a spreadsheet, database, text editor or data analysis program.
Before taking more measurements, you may want to clear the results. To do so,
select the
does not clear log files.
Note: Measurement log files will be overwritten with new data and results the
next time you select the Run/Stop or Single buttons to take measurements.
command button in the Control Panel. Clearing the results
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
51
Page 72

Operating Basics
Results as Statistics
Table 28: Statistics menus
Statistics menu Description
All For each individually selected measurement, shows
numeric values for the population, mean, standard
deviation, maximum, minimum, peak-to-peak, positive
deviation, and negative deviation characteristics; two sets
of values display results for the current acquisition and for
all acquisitions
Min/Max For all selected measurements, shows the sources and
numeric values for the population, maximum, minimum,
positive deviation, and negative deviation characteristics;
you can display values for the current acquisition or for all
acquisitions
Mean/Std Dev For all selected measurements, shows the sources and
numeric values for the population, mean, and standard
deviation characteristics; you can display values for the
current acquisition or for all acquisitions
TIE: RjDj – BER*
Equivalent RjDj***
* TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only.
** To enable, see the Viewing Equivalent RjDj Results topic.
For selected TIE measurements, shows the jitter
decomposition and the eye opening at the selected BER;
two sets of values display results for the current
acquisition and for all acquisitions
For selected TIE measurements, shows the jitter values
according to the equivalent jitter model as defined in the
Fibre Channel - Methodologies for Jitter and Signal
Quality Specification - MJSQ document; two sets of values
display results for the current acquisition and for all
acquisitions
Viewing Equivalent Rj/Dj Results (TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced Only)
Some standards require that timing jitter be separated into deterministic and
random categories using a prescribed method called Equivalent Rj/Dj or
Effective Rj/Dj, This method is described in Section 8 of the Fibre Channel -
Methodologies for Jitter and Signal Quality Analysis - MJSQ document. This
analysis makes some simplifying assumptions about the jitter characteristics, in
an attempt to yield results that are consistent between different types of
measurement instrumentation. It is known that the assumptions required for this
analysis method generally result in conservative (overstated) Rj amounts.
By default, the Equivalent Rj/Dj tab is not enabled in the TDSJIT3 v2 user
interface, although the measurement is always active and the results are always
reported via GPIB. To enable the Equivalent Rj/Dj tab in the user interface,
follow these steps:
1. Exit the TDSJIT3 v2 application if it is running.
52
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 73

Operating Basic
2. Use a text editor (such as Notepad) to open the "jit3option.ini" file, which
resides in the C:\Program Files\TekApplications\TDSJIT3v2 directory.
3. Locate the line that says "equivalentRjDj=false" and change it to
"equivalentRjDj=true". If you cannot find the line, add it.
4. Save the file.
5. Restart the TDSJIT3 v2 application and take measurements. The application
displays the Equivalent Rj/Dj tab in the Results menu for TIE measurements.
Results as Plots
The application can display the results as 2-dimensional plots for easier analysis.
Before or after you take measurements, you can select and configure up to four
plots. The last plot selected displays when the application completes sequencing.
If you set up plots after sequencing, the application displays the plot based on the
current measurement and result.
Note: When taking measurements in the Free Run mode, you must stop the
sequencing before you can use some plot features.
Table 29: Plot types
Plot type Description
Histogram Represents measurements sorted by value as a distribution of
measurement values versus the number of times the value
occurred
Time Trend Represents the measurement values versus the time location
Cycle Trend Represents the measurement values versus the index number
of the measurement
Spectrum Represents the frequency content computed using the FFT of
the Time Trend plot
Bathtub*
Transfer
Function*
Phase Noise*
* TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only.
Represents the Bit Error Rate versus the horizontal eye
opening for TIE or PLL TIE measurements that include Rj/Dj
analysis
Represents the magnitude ratio of two spectrums; the plot
requires two measurements from the following set: Clock
Period, Clock Frequency, Clock TIE, Clock PLL TIE, Data
Period, Data Frequency, Data TIE, Data PLL TIE
For Clock TIE measurements only, represents the phase noise
of a clock signal and is plotted in the frequency domain
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
53
Page 74

Operating Basics
Table 30: Measurements and available plots
Histogram
All All All All TIE
* TIE: RjDj analysis options are available in the Configure Meas General menu.
** TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced only.
Note: TIE and PLL TIE measurements refer to Clock TIE, Clock PLL TIE, Data
TIE, and Data PLL TIE measurements unless specified.
Using a Separate Monitor to View Plots
If your oscilloscope setup includes a second monitor that extends the Windows
desktop, you can select and drag the title bar of a plot window to position it in the
second monitor. This allows you to simultaneously display a waveform on the
oscilloscope, the TDSJIT3 v2 measurement results, and the plot for easy viewing.
Note: When setting your oscilloscope to include a second monitor, the Number
of Colors setting for the second monitor must be the same number of colors as
your oscilloscope.
Plot Usage
Time
Trend
Cycle
Trend Spectrum Bathtub*
PLL TIE
Transfer
Function*** Phase Noise***
Period,
Frequency
TIE
PLL TIE
Clock TIE
Clock PLL TIE
Histogram Plot Usage
Histogram plots display the results such that the horizontal axis represents the
measurement value ranges and the vertical axis represents the number of times
that the range of values occurred. Unlike most other plots, a histogram plot
accumulates measurements over multiple acquisitions, up to a total population
size of 2.0 billion.
Histograms are particularly useful in analyzing jitter. A histogram of the Time
Interval Error (TIE) represents the basis of jitter analysis using a histogram
approach. In a histogram, Deterministic Jitter (Dj) is bounded and shows up as a
non-gaussian distribution. Random Jitter (Rj) is unbounded and the amplitude
along the horizontal axis will continue to grow as more population is acquired.
The TIE histogram is an excellent way to quickly assess jitter visually.
The vertical scaling (log versus linear) can be changed at any time without losing
the accumulated statistics. The number of bins can also be changed at any time,
since 2500 bins are always used for the actual computation. Autoset sets the
Center and Span appropriately based on the currently accumulated results.
54
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 75

Operating Basic
Note: Changing any of the horizontal scale controls (Center, Span, Refresh,
Autoset) will cause the histogram plot to reset so that only the results from the
most recent acquisition are displayed. This is because the bin size must be
recalculated. If you change the Center or Span options, you can select the
Refresh button, or the Run/Stop or Single buttons (to acquire data) to update the
plot display.
Time Trend Plot Usage
A Time Trend plot is a waveform trace of a measurement versus time. This is
useful, for example, in determining if the embedded clock in a serial bit stream is
modulated outside the capabilities of your receiver to recover the clock. If the
TIE time trend plot starts to take an unexpected periodic shape, then this could
indicate that you have uncorrelated periodic jitter from crosstalk or from power
supply coupling.
Cycle Trend Plot Usage
A Cycle Trend plot shows measurement values versus measurement index, where
the indexes are always equally spaced along the horizontal axis. In contrast, the
measurement values on a Time Trend plot are not equally spaced along the
horizontal time axis.
Spectrum Plot Usage
A Spectrum plot is obtained from the Fast Fourier Transform of a Time Trend
plot. This plot is useful in identifying frequency components that contribute to
timing errors, such as modulation of the measurements.
When the signal has a repetitive data pattern, an analysis on the TIE Spectrum of
the signal can be used to separate Random Jitter (Rj) from Deterministic Jitter
(Dj) as well as separate Dj components of Periodic Jitter (PJ) and other Dj
components such as ISI and DCD. The frequency of periodic jitter spikes that do
not correlate to frequencies contained in the data pattern can be a clue that you
should look at frequencies of different components in your design as possible
sources of jitter.
Bathtub Plot Usage (TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced Only)
The Bathtub curve plot is a convenient way to visualize how the jitter eye
opening varies for different bit error rate assumptions. Many communications
standards call for Total Jitter to be measured at 10-12 BER. The eye opening
represented by the Bathtub Curve is what is left of the unit interval after the total
jitter measurement is subtracted.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
55
Page 76

Operating Basics
Transfer Function Plot Usage (TDSJIT3 v2_Advanced Only)
A Transfer Function plot shows the magnitude ratio of the spectrums of two
measurements. In the next equation, X(t) is a jitter measurement at the input of a
device, and Y(t) is a jitter time trend at the output of the device. The Transfer
Function plot can be used to show the following function, where X(f) is the
Fourier Transform of x(t):
|)(|
)(
fH =
The horizontal axis of the Transfer Function plot goes up to the nyquist
frequency of X or Y, whichever is lower. These plots work best if averaged
across multiple acquisitions to reduce the effects of measurement noise.
Phase Noise Plot Usage (TDSJIT3 v2_Advanced Only)
The Phase Noise plot shows a frequency domain view of the jitter noise on a
waveform normalized in an industry-standard way. The vertical axis is
logarithmic and uses the units of dBc/Hz, which means "decibels (relative to the
carrier) per Hertz." The horizontal axis is logarithmic. In addition to showing the
phase noise curve, this plot allows the integrated noise between two userselectable frequencies to be displayed.
fY
|)(|
fX
Creating Plots
Before or after you take measurements, you can set up plots in the Plots Create
menu. To create a plot, follow these steps:
1. Select Plots> Create. View the Plots Create menu.
2. Select a measurement from the list of available measurements and sources
shown on the left side.
3. Select a plot format from the Add Plot buttons. The selected measurement and
plot type appears in the list of Plots shown on the right side. If results are
available, the application displays the plot; otherwise the plot will appear after
a measurement sequence is complete.
4. Add another plot format for the current measurement, or select a different
measurement and add plots.
Note: The Phase Noise plot and Bathtub plot (both in TDSJIT3 v2 Advanced
only) are only enabled when a TIE-type measurement is chosen. The Bathtub
plot also requires that the RjDj analysis be enabled in the Configure Meas TIE:
RjDj menu.
56
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 77

Operating Basic
Table 31: Plots Create menu options
Option Description
List of active
measurements
Add Plot buttons Selects the type of plot
Plots Lists up to four selected plots; use this list to clear plots
Clear button Clears the selected plot
Clear All button Clears all plots
Selects the measurement to plot
Configuring Plots
Figure 43: Plots Create menu
After you create the plots, you can further configure the axes for each
measurement and plot combination (except for a Cycle Trend plot). To configure
a plot, follow these steps:
1. Select Plot> Vert/Horiz Axis or the Vert/Horiz Axis tab.
2. Select a measurement in the Plots list of measurements and plot types on the
left side. This causes the area to the right of the table to display options
relevant to the selected measurement and plot type.
3. Configure the plot. The application displays the reconfigured plot.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
57
Page 78

Operating Basics
Table 32: Vert/Horiz axis options for a Histogram plot
Area/option Description
Vertical Scale
Log Depicts the vertical axis in a logarithmic scale
Linear Depicts the vertical axis in a linear scale (default)
No of Bins Defines resolution by the number of bins into which Span is
divided: 25, 50, 100, 250 (default), or 500
Horizontal Scale
Center Numerical value for the horizontal center position of the
Histogram after Refresh
Span Numerical value for the total horizontal range of the
Histogram after Refresh
Autoset*
Refresh*
* Changing the Horizontal Scale causes any accumulated results across multiple
acquisitions to be lost, and only the results of the most recent acquisition will be
displayed.
Uses the latest results to determine the logical values for
the Center and Span options if the population of the
measurement is three or more, and then redraws the plot
Updates the plot with the latest Center and Span values
entered
58
Figure 44: Vert/Horiz menu for a Histogram plot
Table 33: Vert/Horiz axis options for a Time Trend plot
Option Description
Vector Measurement points connect with straight lines (default)
Bar Places a vertical bar at the horizontal position of each
measurement with a height (positive or negative) that represents
the value of that measurement; a horizontal baseline represents
the mean value of the Time Trend
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 79

Operating Basic
Figure 45: Vert/Horiz menu for a Time Trend plot
Table 34: Vert/Horiz axis options for a Spectrum plot
Area/option Description
Vertical Scale
Log Depicts the vertical axis in a logarithmic scale
Linear Depicts the vertical axis in a linear scale (default)
Baseline Numeric value (expressed as a base-10 exponent) at the
bottom of a logarithmic vertical scale
Horizontal Scale
Log Depicts the horizontal axis in a logarithmic scale
Linear Depicts the horizontal axis in a linear scale (default)
Mode Selects whether the plot shows only the most recent
spectrum, the uniform average of all spectrums since the
last time the results were cleared, or the peak of the
envelope of all spectrums since the last time the results
were cleared
Normal updates the plot with current values (default)
Average averages the magnitude values at each frequency
Peak Hold keeps the maximum value at each frequency
Figure 46: Vert/Horiz menu for a Spectrum plot
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
59
Page 80

Operating Basics
Table 35: Vert/Horiz axis options for a Bathtub plot
Option Description
Linear Depicts the vertical axis in a linear scale
Log Depicts the vertical axis in a logarithmic scale (default)
Minimum Displayed
BER=1E-?
Numeric value (expressed as the negative of a base-10
exponent) at the bottom of the logarithmic vertical scale;
default = 12, representing 10
-12
Figure 47: Vert/Horiz menu for a Bathtub plot
Transfer Function Definition Options
The Transfer Function plot requires two measurements from the following set:
Clock Period, Clock Frequency, Clock TIE, Clock PLL TIE, Data Period, Data
Frequency, Data TIE, and Data PLL TIE.
Table 36: Transfer Function Definition configuration
Option Description
Numerator Measurement for which the magnitude spectrum is used as a
reference
Denominator Measurement for which the magnitude spectrum is used to
normalize the numerator
Invert Swaps the measurements used as the Numerator and as the
Denominator
OK Accepts changes and closes
Cancel Discards changes and closes
60
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 81

Operating Basic
Transfer Function Definition Menu
Figure 48: Transfer Function Definition options
Table 37: Vert/Horiz axis options for a Transfer Function plot
Area/option Description
Vertical Scale
Log Depicts the vertical axis in a logarithmic scale (default)
Linear Depicts the vertical axis in a linear scale
Horizontal Scale
Log Depicts the horizontal axis in a logarithmic scale (default)
Linear Depicts the horizontal axis in a linear scale
Mode Selects whether the plot shows only the most recent
spectrum, or the uniform average of all spectrums since the
last time the results were cleared (default)
Normal updates the plot with current values
Average averages the magnitude values at each frequency
Function Def
Invert
Swaps the measurements used as the Numerator and as
the Denominator; resets any averaging to include only the
most recent acquisition
Figure 49: Vert/Horiz menu for a Transfer Function plot
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
61
Page 82

Operating Basics
Table 38: Vert/Horiz axis options for a Phase Noise plot
Area/option Description
Vertical Position
Baseline Numeric value at the bottom of a logarithmic vertical scale
Integrated Noise
Lower Limit Sets the lower frequency limit over which noise will be
integrated
Upper Limit Sets the upper frequency limit over which noise will be
integrated
RMS Displays the RMS value of integrated noise between the
lower and upper limits.
Working with Plots
Figure 50: Vert/Horiz menu for a Phase Noise plot
You can create and configure up to four plots. By default, all four plot windows
are overlayed on the upper half of the display, but each window can be moved,
resized, or dragged to a second monitor. The application includes tools to help
you select which plots to view, to size and position the plot windows, to save plot
information, to use the zoom function, and to use the cursors functions.
If your Windows desktop is extended to a second monitor, you can drag the plots
window to the second monitor.
Note: When sequencing is complete, the plot window displays with the last plot
selected. The plot window also updates whenever you reconfigure a plot.
62
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 83

Operating Basic
Toolbar Functions in Plot Windows
Each plot window includes the following tool groups:
Selecting and Viewing a Plot
•
reference memory location on the oscilloscope
•
the window is displayed on the oscilloscope
•
positions
•
•
•
To select and view an existing plot, follow these steps:
1. Select the
to save the plot contents to a file (data or image) or to export to a
to position the plot window in default positions and sizes when
to place a selected plot in the foreground in one of the two default
to select between the Zoom tools or the Cursors tools
to use the Zoom tools
to use the Cursor tools
button. The Locate Window At dialog appears.
Figure 51: Locate Window At options
The Select View button appears on the Control Panel and in the toolbar of
every plot window.
2. To view the first plot in the Active Plots Summary table on the top half of the
display, select the Plot1 button from the Top column. To view this plot on the
bottom half of the display, select Plot1 from the Bottom column.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
63
Page 84

Operating Basics
You can place the other defined plots on the top or bottom of the display by
similar steps. Select the Scope button to bring the oscilloscope interface to the
top of the display. Select the App button to bring the TDSJIT3 v2 main
window to the bottom.
Moving and Resizing a Plot
Deleting Plots
3. Select Close or
be dismissed before the TDSJIT3 v2 windows will respond to any other
commands.
If you have a keyboard, you can use the alt-tab Window shortcut to quickly
select a window for viewing.
If you have a second monitor, you can select and drag the title bar of a plot
window to position it in the other monitor.
You can move and resize plot windows the same way you would move and resize
any window.
The plot position tools can move a plot to the upper or lower half of the
oscilloscope display. The tools also return the plot to the original size. To
position a plot quickly on the oscilloscope, select one of the following tools in
the plot window:
•
•
positions the plot in the upper half
positions the plot in the lower half
to dismiss the Locate Window At dialog. This dialog must
64
You can remove individual or all selected plots. To remove an individual plot,
follow these steps:
1. Select Plots> Create or the Create tab.
2. Select the plot to be removed in the list of Plots on the right side.
3. Select the
To remove all selected plots, select the
The plot window updates and removes the deselected plot from the display.
button.
button.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 85

Operating Basic
Using Zoom in a Plot
Once you have created a plot, you can use the Zoom tools to examine the data at
various scales. You can use the buttons in the Zoom toolbar to do the following
tasks:
•
•
•
•
you can activate the Touch Screen on the oscilloscope provided the model you
are using has this feature.
Zooming In
To examine a portion of the waveform in greater detail, follow these steps:
1. In the
2. In the Zoom toolbar, select the
3. To zoom the horizontal scale by a factor of two without affecting the vertical
4. To zoom in by an arbitrary amount both horizontally and vertically, use a
to examine a small portion of a waveform in greater detail
see the a larger portion of the waveform
to see the entire available waveform
for Time Trend plots, to synchronize the zoom window of the
oscilloscope with the zoom window of the TDSJIT3 v2 application
If you prefer to use the zoom functions in a plot window with your finger,
Control tools, select the button. This step is
not necessary if the Zoom toolbar is already visible.
button.
scale, click-and-release on a point of interest in the waveform.
click-drag-release action with the mouse. After you click and begin dragging,
a bounding box will appear to show what part of the waveform will be
expanded upon release.
The two zoom methods may be repeated in any order until the maximum zoom is
reached.
Zooming Out
To reduce the scale of a plotted waveform so that more of the waveform can be
seen, follow these steps:
1. In the
not necessary if the Zoom toolbar is already visible.
2. To zoom out partially, select the
click anywhere on the waveform. The view is restored to the zoom values that
existed before the most recent zoom-in. Clicking multiple times will restore
successively earlier views
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Control tools, select the button. This step is
button in the Zoom toolbar and then
65
Page 86

Operating Basics
3. To zoom out completely, select the
its initial zoom settings, in which the entire waveform can be seen.
Using Zoom Sync (Time Trend Only)
By using the Zoom Sync function, you can synchronize the zoom window of the
oscilloscope with the current horizontal axis limits of a Time Trend plot. To do
so, follow these steps:
1. Create, configure, and display a Time Trend plot.
2. In the
not necessary if the Zoom toolbar is already visible.
3. Use the zoom tools until the desired portion of the Time Trend waveform is
visible.
4. Select the
adjusts the horizontal zoom scale and position to correspond closely with
those of the Time Trend plot.
Note: Selecting the Sync button will not bring the oscilloscope user interface to
the foreground if it is obscured by a plot window. To make the oscilloscope
visible, use the Select View button or the Windows alt-tab shortcut.
Since the zoom window of the oscilloscope has a limited number of valid scale
factors, the time scale synchronization is not necessarily an exact match.
button. This turns on the zoom mode on the oscilloscope, and
Control tools, select the button. This step is
button. The view will be restored to
Using Cursors in a Plot
Cursors allow you to view numerical values associated with a plot based on
cursor locations. There are two cursor modes: Vertical-paired and Horizontalpaired. Each mode displays two cursors in a plot.
Note: You can only use one mode at a time; vertical or horizontal-paired but not
both.
You can use the buttons in the Cursor toolbar to do the following tasks:
•
•
•
•
•
to display the horizontal coordinate where each cursor touches the plot
and the difference (delta) between the cursors
to display the vertical coordinate where each cursor touches the plot and
the difference (delta) between the cursors
to position cursors on minimum and maximum values
for Time Trend plots, to synchronize the oscilloscope cursors with the
position of the plot cursors
to remove cursors from the display
66
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 87

Operating Basic
The most precise way to move the cursors in a plot window is with the
Multipurpose knobs of the oscilloscope provided the cursors are associated with
the Multipurpose knobs (focused).
Focusing Cursors
The cursors do not always become focused (associated with the Multipurpose
knob) when you select a plot window. Sometimes the application can lose focus
of the cursors if you switch windows, switch cursors when using both, use the
Min/Max button, or use the Sync cursors between a Time Trend plot and the
oscilloscope and then move the oscilloscope cursors.
To focus the cursors, select the cursor in the plot window.
Using Vertical Cursors in a Plot
Vertical cursors appear as two vertical lines in a plot window. They enable you to
read the horizontal coordinates where each line touches the plot and also view the
horizontal difference (delta) between the two cursors.
In addition, a red cross appears where each cursor intersects the plotted
waveform. The vertical value at each of these crosses (as well as the vertical
delta) is shown in the plot window.
To use Vertical cursors while viewing a plot, follow these steps:
1. In the Control tools, select the
2. In the Cursor tools, select the
3. Select and drag either cursor line, or use the Multipurpose knobs on the
oscilloscope to move the cursor to the part of the plot desired.
The cursor readout changes value to reflect the cursor position.
If you prefer to move the cursors in the plot window with your finger, you
can activate the Touch Screen on the oscilloscope provided the model you are
using has this feature.
Note: You can drag cursors only when the Zoom functions are disabled.
The most precise way to move the cursors in the plot window is with the
Multipurpose knobs of the oscilloscope provided the cursors are associated with
the Multipurpose knobs (focused).
Use the button to place the Vertical cursors at the levels
corresponding to the minimum and maximum values within the currently
displayed horizontal extent of the plot.
button.
button.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
67
Page 88

Operating Basics
Additional Ways to Use Vertical Cursors
You can also use the Vertical Cursors in the following ways
• Use the
to the minimum and maximum vertical values within the plot. If the plot
display has been zoomed, the minimum and maximum values within the
current horizontal limits of the zoom are used.
• For Time Trend only, you can use the
oscilloscope cursors with the plot cursors’ positions.
• Min/Max is most useful for Trend Plots. The Max (half of the feature) is
useful for Spectrum plots.
Using Horizontal Cursors in a Plot
Horizontal cursors appear as two horizontal lines in a plot window. They enable
you to read the vertical coordinates where each line touches the plot and also
view the horizontal difference (delta) between the two cursors.
To use Horizontal cursors while viewing a plot, follow these steps:
1. In the Control tools, select the
2. In the Cursor tools, select the
3. Select and drag either cursor line, or use the Multipurpose knobs on the
oscilloscope to move the cursor to the part of the plot desired.
The cursor readout changes value to reflect the cursor position.
button to place the two cursors at the positions corresponding
button to synchronize the
button.
button.
68
If you prefer to move the cursors in the plot window with your finger, you
can activate the Touch Screen on the oscilloscope provided the model you are
using has this feature.
Note: You can drag cursors only when the Zoom functions are disabled.
The most precise way to move the cursors in the plot window is with the
Multipurpose knobs of the oscilloscope provided the cursors are associated with
the Multipurpose knobs (focused).
Use the button to place the Horizontal cursors at the levels
corresponding to the minimum and maximum values of the visible portion of the
plot.
Using Cursors Sync (Time Trend Only)
You can select the Sync button to synchronize the oscilloscope cursors with those
in a Time Trend plot.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 89

Operating Basic
Using Min/Max Cursors
You can select the Min/Max button to position cursors to the maximum and
minimum values as appropriate horizontally or vertically.
Min/Max cursors are most useful for Time Trend plots. The Max (half of the
feature) is useful for Spectrum plots.
Exporting Plot Files
There are several ways you can export plot information from the TDSJIT3 v2
application for use in other applications:
• You can export the mathematical data that is represented in the plot figure.
This may be useful if you wish to perform additional processing on the data.
• You can create an image file that captures the current plot view. This may be a
useful way to document your results.
• You can export a plot to a reference memory location in the oscilloscope. This
may be useful if you want to use math expressions in the oscilloscope to
further process the measured data.
The
down list:
• Data saves the numerical values from the plot window in text or MATLAB
format
• Fig saves the contents of the plot window as an image file
• Ref saves the plot in an oscilloscope reference memory location (Ref1, Ref2,
Ref3, or Ref4)
Note: Export plot functions are disabled whenever the application is actively
sequencing.
Exporting Raw Plot Data
The waveform image in each plot is typically only 500 by 160 pixels, but the data
that it represents may be several million samples of double-precision floatingpoint information. Exporting this data allows you to perform addition processing
or derive custom measurements.
Note: The TDSJIT3 v2 application can produce files that are too large for most
spreadsheet programs to load completely. However, you can still use a text editor
to view the entire file.
To export the mathematical data that was used to create a plot, follow these steps:
1. Select Data as the Export tool in the upper left corner of the plot window. A
file chooser window appears.
By default, the chooser provides a filename derived from the current date and
time, and offers to place the data in a folder called "plotData" in the TDSJIT3
v2 file area. The default data type is ASCII text.
2. Use the controls at the top of the file chooser to select the directory where you
would like to save the data.
tool offers the following choices from the Save drop-
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
69
Page 90

Operating Basics
3. If ASCII text is not the desired data format, use the drop-down list labeled
"Files of type:" to select another file type. The choices are:
• ASCII Text (.txt) – ASCII text that is readable by an editor such as
Wordpad
• Comma Separated Values (.csv) – ASCII text that can be loaded into a
spreadsheet
• MATLAB (.mat) – Binary data in the native MATLAB 5.0 format
•
• If you have a keyboard, you can change the filename.
• Select Save to save the data.
Note: Files with .txt and .csv extensions are identical except for the extension.
Exporting Plot Images
You can save the exact waveform that you see in the plot window, including any
cursors. This may be convenient for reports, engineering records, or sharing
interesting results with your peers.
To create an image file from your plot, follow these steps:
1. Adjust the zoom and/or cursors to get the view you wish to save.
2. Select Fig as the Export tool in the upper left corner of the plot window. A file
chooser window appears.
By default, the chooser provides a filename derived from the current date and
time, and offers to place the image file in a folder called "plotFigure" in the
TDSJIT3 v2 file area. The default image format is Portable Network Graphics
(.png).
3. Use the controls at the top of the file chooser to select the directory where you
would like to save the image.
4. If PNG is not the desired image format, use the drop-down list labeled "Files
of type:" to select another format. The choices are:
Binary files typically use about 40% as much disk space as text files.
70
• Windows Bitmap (.bmp) – Uncompressed pixel map in the standard
Windows format
• JPEG File Interchange Format (.jpg) – A lossy, compressed format
• Portable Network Graphics (.png) – A lossless, compressed format that
offers good portability
5. If you have a keyboard, you can change the filename.
6. Select Save to save the data.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 91

Operating Basic
Exporting a Plot to a Reference Memory Location
You can transfer the plot to a reference memory location on the oscilloscope, and
then save it as a .wfm file. To do so, follow these steps:
1. Select Ref as the Export tool in the upper left corner of the plot window.
2. Select the desired Ref and then OK.
3. Use the export function of the oscilloscope to save the plot in the reference
memory location to the hard disk as a .wfm file.
Saving Information to Log Files
The application includes the following Log menus:
• Statistics
• Measurements
• Worst Case Waveforms
Logging Statistics
The application can continuously log (save to file) the calculated statistics, or
save a snapshot of the current statistics. You can save the statistics to a "comma
separated value" (.csv) file to import into a text editor, a spreadsheet, or an
analysis tool.
Note: The TDSJIT3 v2 application can produce .csv files that are too large for
most spreadsheet programs to load completely. However, you can still use a text
editor to view the entire file.
By default, all actual measurements are selected. You can select individual
measurements by selecting the measurement number or row in the table on the
left side of the menu.
To log statistics to a file, follow these steps:
1. Select Log> Statistics. The Log Statistics menu appears.
2. Select measurements that you want to log in the table on the left of the menu
or choose the "Yes to All" button. You can also choose "No to All" to clear
the current selection list.
3. To log statistics continuously, select the
menu appears. The default directory is C:\TekApplications\TDSJIT3v2\log.
4. Select an existing file or a new file to contain the saved statistics for all
selected measurements.
5. Select the
6. To stop logging, select the Off button or the Delete button to delete the current
statistics file.
button. The file name menu closes.
button. The Log File Name
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
71
Page 92

Operating Basics
To save a snapshot of current statistics (as shown in the Results menu), under
Save Current Statistics, select the Save button to save the current statistics to a
statsSnapshot.csv file. The default directory is
C:\TekApplications\TDSJIT3v2\log.
Note: For either type of logging, you can use the Delete button to browse and
delete files.
Table 39: Log Statistics configuration
Option/button Description
Log Statistics Enables the application to continuously save the statistical
results for all selected measurements
On button Browse to select or enter a file name and enable logging
Off button Disable continuous logging
Delete button Browse to select and delete .csv files
Save Current
Statistics
Save button Browse to select a file name and save a Snapshot of
Delete button Browse to select and delete .csv files
Saves a snapshot of the current statistics for the current
acquisition and accumulated acquisitions for selected
measurements
statistics
Logging Measurements
You can log the actual data points as measurement files. You can log data points
continuously or save the data points for the current acquisition. You can save the
data points to a "comma separated value" (.csv) file to import into a text editor, a
spreadsheet, or an analysis tool.
Note: The TDSJIT3 v2 application can produce .csv files that are too large for
most spreadsheet programs to load completely. However, you can still use a text
editor to view the entire file.
To log measurements, follow these steps:
1. Select Log> Measurements> Configure. The Log Measurements menu
appears.
2. Select measurements that you want to log or choose the "Yes to All" button.
(You can also choose "No to All" to clear the current selection list.)
3. To log measurements continuously, select the
button. The Choose
Log Measurement Directory menu appears.
4. Select a directory to contain the saved measurement files (one file for each
measurement).
5. Select the OK button. The Choose Log Measurement Directory menu closes.
6. To stop logging, select the Off button.
72
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 93

Operating Basic
To save current data points in measurement log files, under Save Current
Measurements, select the Save button to browse for a directory and to save a
snapshot of the data points to a file for each selected measurement.
Note: For either type of logging, you can use the Delete button to browse and
delete individual measurement files. Using either log measurement feature
provides a directory browser to navigate or create new folders.
Table 40: Log Measurements configuration
Option/button Description
Log Measurements Enables the application to save all selected
measurements
On button Browse to select or enter a directory name and turn on
logging
Off button Turn off continuous logging
Delete button Browse to select and delete .csv files
Save Current
Measurements
Save button Save current and accumulated measurements
Delete button Browse to select and delete .csv files
Saves a snapshot of the current measurements for the
current acquisition and accumulated acquisitions for
selected measurements
File Names for Logging Measurement Files
The application automatically names the files for you based on a combination of
the measurement name and source used. You can select the File Names tab to see
the file names created by the application.
You can also choose a directory for measurement log files.
Logging Worst Case Waveforms
You can use the Log Worst Case menus to save the acquired waveforms
whenever a selected measurement exceeds the highest or lowest prior value.
When enabled, the waveforms are saved to a set of .wfm files including the
qualify waveform if active.
To log worst case waveforms, follow these steps:
1. Select Log> Worst Case> Configure.
2. Select measurements for which you want to log the worst case waveforms, or
3. To log worse case waveforms continuously, select the
4. Select a directory to contain the saved waveforms.
choose the "Yes to All" button. (You can also choose "No to All" to clear the
current selection list.)
button. The
Log Worst Case Waveforms menu appears.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
73
Page 94

Operating Basics
5. Select the OK button. The Log Worst Case Waveforms menu closes.
6. To stop logging, select the Off button.
Note: Use the Delete button to delete all the .wfm files in the selected directory.
Table 41: Log Worst Case Waveforms configuration
Option/button Description
Log Worst Case
Waveforms
On button Browse to select or enter a directory name and turn on
Off button Turn off continuous logging
Delete button Browse to select and delete .wfm files
File Names for Logging Worst Case Waveforms
The application automatically names the files for you based on a combination of
the following information:
Enables the application to save worst case waveforms for
all selected measurements
logging
• Measurement name
• Source of the waveform, such as Ch1
• Whether the file is a maximum or minimum value waveform
You can select the File Names tab to see the file names created by the
application.
If a qualify waveform is saved, the file name will include the following
information:
• QUAL to identify it as a qualify waveform if active
• Source of the waveform, such as Ch2
Saving and Recalling Setup Files
You can use the File menus to save and recall different application setups and
recently accessed files.
Do not edit a setup file or recall a file not generated by the application.
Saving a Setup File
To save the application and oscilloscope settings to a setup file, follow these
steps:
1. Select File> Save. The Save dialog box appears. View the Save browser.
2. In the file browser, select the directory in which to save the setup file or use
the current directory.
3. To view details about existing files, such as size, type, and date modified,
select the Details tool.
4. Use the keyboard to enter a new file name.
74
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 95

Operating Basic
The application appends an ".ini" extension to the name of the application
setup file.
5. Select the
exists, a confirmation dialog appears that allows you to cancel the operation.
Note: The application also saves the oscilloscope setup to a ".set" file when you
save an application setup. Both the application .ini file and oscilloscope .set file
have the same file name.
To view details, such as file size, type, and date modified, select the
tool.
command button. If the selected filename already
Details
Figure 52: File Save browser
Recalling a Saved Setup File
To recall the application and oscilloscope settings from saved setup files, follow
these steps:
1. Select File> Recall. The Recall dialog box appears. View the Recall browser.
2. In the Recall dialog box, select the directory from which to recall the setup
file.
To view details about the files in the directory, such as size, type, and date
modified, select the Details tool.
3. Select a setup file name, and then select Open.
Note: The application recalls the .ini setup file and the associated oscilloscope
setup if the application can find a .set file with a matching name.
Do not edit setup files. If you try to recall a setup file that has been edited,
the recall operation fails.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
75
Page 96

Operating Basics
If a matching .set file is not found or if the .set file does not recall correctly
to the oscilloscope, then a warning appears that says the oscilloscope recall failed
while the TDSJIT3 v2 application recall succeeded.
To view details, such as file size, type, and date modified, select the
tool.
Figure 53: File Recall browser
Details
Recalling the Default Setup
To recall the default application settings, select File> Default Setup. Most of the
menu options are set to the same values or selections as when you launch the
application.
Recalling a Recently Saved or Accessed Setup File
To recall a recently saved or accessed setup file, select File> Recent Files and
then the file from the drop down list of setup file names.
Note: The application also recalls the associated oscilloscope setup if the
application can find a .set file with a matching name.
Do not edit setup files. If you try to recall a setup file that has been edited,
the recall operation fails.
If a matching .set file is not found or if the .set file does not recall correctly
to the oscilloscope, then a warning appears that says the oscilloscope recall failed
while the TDSJIT3 v2 application recall succeeded.
76
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 97

Operating Basic
Recall Recent Files Example
Figure 54: Recall Recent files example
Recalling a Setup File from a Prior Version of Software
Setup files that were saved using a prior version of the TDSJIT3 application may
be recalled. For those features that were not present in the prior version,
reasonable default settings are used. You may wish to verify that settings not
specified by the old file are acceptable.
Note: Setup files from previous versions may include directory paths such as
"C:\TekApplications\TDSJIT3\...", whereas the v2 application defaults to
"C:\TekApplications\TDSJIT3v2\...". If you would like your converted setup
files to use the TDSJITv2 directory, recall the existing setup file, use the
Graphical User Interface to change any file paths to use the new directory
structure, and then save the setup.
After you recall the setup file, you may save the setup again to create a setup file
with the latest format. Use a different filename if you wish to retain the old setup
file.
Vertical reference levels receive special attention during setup file conversion. If
all of the reference levels for an active source are the default values (where High
is set to 1.0 V, Mid is set to 0.0 V, Low is set to -1.0 V, and the Hysteresis is set
to 0.03 V), then that source shall be configured for Automatic reference levels.
Otherwise, the source shall be configured for Manual reference level and the
reference levels in the setup shall be used exactly as they are. For more
information, see the Automatic Versus Manual Reference Voltage Levels topic.
Some prior versions of the TDSJIT3 application used a configuration file
("jit3option.ini") to establish the order of the phase-locked loop used for clock
recovery in PLL TIE measurements. The current TDSJIT3 application includes
these controls and ignores the loop-order settings in the older configuration file.
You can set these values manually, if necessary, and save a new setup file. After
this, you can use the new setup file to ensure that the PLL settings are properly
set.
Note: Setup files from the TDSJIT2 application are not supported.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
77
Page 98

Operating Basics
Docking and Undocking the Jitter Analysis Window
The Dock function positions and locks the TDSJIT3 v2 application in the lower
half of the oscilloscope display and the oscilloscope application in the upper half
of the display.
The Undock function unlocks the window and allows you to move the
application to another position in the oscilloscope display or drag it to a second
monitor; the oscilloscope display returns to full size.
The Dock and Undock functions are available under the File menus in the menu
bar.
Acquisition Timeout Utility
The Acq Timeout utility sets the delay (in seconds) that the application allows
between an acquisition start and when a waveform is expected.
• Auto allows the application to adjust the delay according to the record length
and measurement complexity
• User allows you to set the appropriate delay value from 30 seconds to 24
hours (86400 seconds) in 30 second increments
Warnings Utility
78
Figure 55: Acquisition Timeout options
The Warnings utility lists errors that have occurred and a brief description of
each. To clear the contents from the file, select the Clear button.
Warnings are also designated with a yellow
icon in the status bar along the bottom of the TDSJIT3 v2 application window.
Once a message appears in the status bar, you can dismiss it by selecting the
View Log button in the status bar, or by selecting the Clear results button.
Neither action removes the message from the warnings log file.
icon and errors with a red
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
Page 99

Tutorial
The purpose of this tutorial is to familiarize you with the basic functions of the
TDSJIT3 v2 application and menus. This tutorial teaches you how to do the
following basic tasks:
• Set up the application
• Take two types of measurements
• View the results as statistics and as plots
Before you begin the tutorial, you must do the following tasks:
• Set up the oscilloscope
• Start the application
• Recall the tutorial waveform
Note: The screen captures shown are from a TDS7000 oscilloscope; there may
be minor differences in the screens from other oscilloscope models.
Setting Up the Oscilloscope
Starting the Application
Waveform Files
Recalling a Waveform File
To set up the oscilloscope, follow these steps:
1. In the oscilloscope menu bar, select File> Recall Default Setup to set the
oscilloscope to the default factory settings.
2. Press the individual CH1, CH2, CH3, and CH4 buttons as needed to remove
active waveforms from the display.
The way you start the application depends on the oscilloscope model. On the
oscilloscope menu bar, select App> Jitter Analysis - Advanced or select File>
Run Application> Jitter Analysis - Advanced. View how to start the application.
If you are using the TDSJIT3 v2 Essentials application, select Jitter Analysis Essentials.
If the Jitter Wizard displays, select the Cancel button.
The application includes two waveform files to use with this tutorial:
• j3clk1.wfm (clock signal)
• j3dat1.wfm (data signal)
The way you recall a waveform to reference memory depends on the oscilloscope
model.
To recall a waveform file on most oscilloscopes, follow these steps:
1. In the oscilloscope menu bar, select File> Reference Waveforms> Reference
Setup. If the oscilloscope is in the Button mode, select the Ref button.
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help 79
Page 100

Tutorial
Ref1 is the default memory location to recall a waveform file. View the
Oscilloscope Reference Memory Setup menu.
2. Select the
3. Navigate to the C:\TekApplications\TDSJIT3v2\Examples\waveforms
directory.
4. Select the j3clk1.wfm file, and then the
The oscilloscope recalls the waveform file to reference memory and displays
the waveform when the recall is complete.
5. The way you return to the application depends on the oscilloscope model. To
return to the application, in the oscilloscope menu bar, select App> Restore
Application or select the
application.
To recall a waveform file on TDS5000B oscilloscopes, follow these steps:
1. Select File> Recall. The Recall dialog appears.
2. In the left side of the dialog, select the Waveform icon.
3. Select Ref1, Ref2, Ref3, or Ref4 as the Destination option.
4. Browse to select the waveform to recall.
5. Select the Recall button. The oscilloscope recalls and activates the Reference
Waveform control window.
6. Select On to display the waveform.
7. Return to the application.
button for Recall Ref1 from File.
button.
button. View how to return to the
Note: The screen capture is from a TDS7000 oscilloscope. There are differences
in the menu on other oscilloscope models.
Figure 56: Oscilloscope Reference Memory options
80
TDSJIT3 v2 Jitter Analysis Online Help
 Loading...
Loading...