Page 1

ЦЦЦЦЦ"2533%,3ЦЦЦ(!../6%2ЦЦЦ"!2#%,/.!ÖÖÖ4/+9/ÖÖÖ-),!.ÖÖÖ!-34%2$!-ЦЦЦ3).'!0/2%ЦЦЦЦЦЦЦЦЦ,/.$/.ÖÖÖ0!2)3ÖÖÖ.%7Ö9/2+ÖÖÖ,/3Ö!.'%,%3ÖÖÖ4/2/.4/ÖÖÖ(/.'Ö+/.'ÖÖÖ39$.%9
BRUSSELS HANNOVER BARCELONA TOKYO MILAN AMSTERDAM SINGAPORE LONDON PARIS NEW YORK LOS ANGELES TORONTO HONG KONG SYDNEY
Targus WiFi
Scanner
USER’S GUIDE
Making Your Mobile Life Easier.
®
Making Your Mobile Life Easier.
®
Visit our Web site at: www.targus.com
Features and specifications are subject to change without notice.
© 2005 Targus Group International, Inc. and Targus Inc.
ACW20US / 400-0204-001A
Page 2
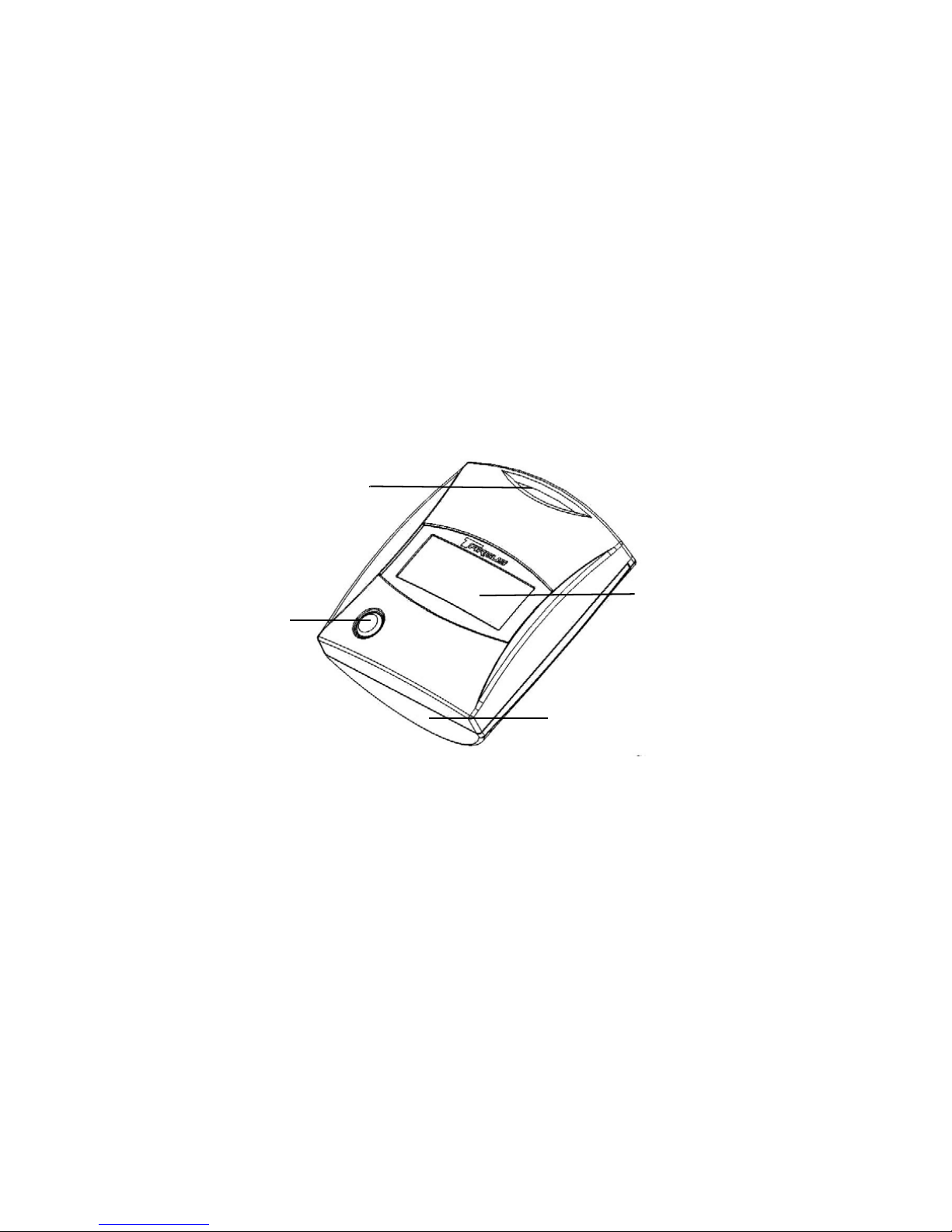
TARGUS WIFI SCANNER
Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the Targus WiFi Scanner. The
Targus scanner quickly identifies all access points in the
area. It detects 2.4Ghz WiFi signals (802.11b/g) from
access points within 200 feet (61 m) outdoors and 60 feet
(18 m) indoors. It also features an LCD display of SSID,
Signal Strength, Secure/Open, and Channel Number.
Keychain loop
Activation
button
Installing the Batteries
1 Slide the battery door toward the top of the housing.
2 Insert two AAA batteries as indicated.
The Targus scanner features a battery strength indicator
that will display when battery power is low and an automatic
shut-off to maximize battery life.
LCD
Battery
compartment
Operating the WiFi Scanner
1 Push the activation button.
2 The WiFi® Scanner will begin scanning channels.
2
Page 3

When a WiFi access point is located, the scanner's LCD
will display:
› the access point's SSID (service set identifier);
› a set of one to four bars indicating signal strength (one
bar equals weak signal and four bars equals strong
signal) ;
› the words "Secure" or "Open" to indicate the network's
encryption status;
› the channel that the access point is broadcasting will
be displayed (number 1 to 13).
3 After the device has located an access point, you may
push the activation button again to scan for additional
access points. If no access point is present, the scanner
will display "No AP Found".
4 The device will display any located access points for
approximately 30 seconds. After such time, the device
will power down automatically. The device does not
continuously scan. You must press the Activate button
each time you want updated information on local access
points.
5 If the device displays "Low Battery", the batteries should
be replaced.
Using the WiFi Scanner
The following are some of the many uses
for the WiFi Scanner:
Finding usable networks - Travelers, students and other
roaming WiFi users can use the scanner to find available
networks (please check your local law before using an open
network without prior permission). The scanner only detects
3
Page 4

802.11b and 802.11g access points. It will not detect
802.11a signals.
Site survey - Use the scanner to determine where your
home or office coverage extends, and where the optimal
locations for use of the network are.
Security - The scanner can be used to determine whether
your home or office network is "leaky". The device can
detect whether your access point's signal extends beyond
your walls, and whether it is secured. The scanner can also
help you detect "rogue" access points.
About WiFi Networks
The scanner provides the following information about a
WiFi network: SSID, signal strength, encryption status and
channel.
SSID
The SSID is the name given a network by a network
operator to distinguish the network from other networks. An
SSID may be distinctive enough that it will allow you to
distinguish a public network from a network that is intended
for public use. Public WiFi service providers often configure
their networks to display an SSID that is similar to the
service provider's name.
For example, if the scanner shows a network with a
"wayport_access" SSID or a "t-mobile" SSID, you are likely
to be able to access a commercial WiFi hotspot, as these
SSIDs are commonly used by Wayport and T-Mobile, two
commercial hotspot providers.
By contrast, a "default" SSID or an SSID that contains the
name of an access point manufacturer may indicate that a
network is operated by a home user that has not specifically
configured the SSID of his or her network.
With most access points, it is possible to disable the
broadcast of an SSID. If the scanner detects an access
4
Page 5

point on which the SSID broadcast has been disabled, it
will typically display "Cloaked" instead of an SSID.
Signal Strength
The scanner displays an image of one to four vertical bars,
indicating the relative strength of the signals detected by
the scanner. By scanning repeatedly, you may be able to
determine whether you are moving closer to or farther from
a network access point by watching the increase or
decrease in the relative signal strength.
Encryption
Any WiFi certified access point is capable of encrypting
WiFi signals using the Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
standard or Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA™). WEPencrypted network requires that a user input an encryption
key before the network can be accessed. The scanner
displays "Secure" when a given network is encrypted, and
"Open" when the network is not encrypted.
Network operators use WEP to prohibit roaming WiFi users
from accessing a network. A network operator who has
enabled WEP is sending a clear signal to a roaming user
that the network is not intended to be accessed by
outsiders.
You can use the scanner to verify that your home or office
network is properly secured, or to detect "rogue" access
points. IT managers may wish to scan their office premises
to detect unexpected access points, and to find any access
points that are unintentionally unencrypted.
Channel
The scanner scans 13 channels. While only 11 channels
are used in the U.S., 13 channels are used for WiFi in
Europe.
Because WiFi channels overlap on adjacent channels,
channel information can be useful in detecting potential
reasons for interference.
5
Page 6

You may wish to use the scanner when configuring your
home or office network to determine what channels are
least likely to experience interference.
Troubleshooting
I am seeing strange symbols in the SSID readings/
the LCD display is faint/ the WiFi Scanner is inconsistent in detecting networks.
• These are all possible symptoms of a low battery.
I am receiving inconsistent signal strength indications.
• The scanner determines signal strength based on a very
small sample. Radio frequency signals are, by their
nature, variable in strength and coverage. By scanning a
few times, you may be able to get a better sense of the
strength of signal available to you.
The WiFi Scanner seems to be "sticking" on a single
SSID.
• In some WiFi implementations that use multiple access
points on the same network, with the same SSID, the
scanner may bounce from one access point to another
with the same SSID. This appears to the user as though
the scanner is "stuck" on a single network. This problem
will correct itself as you move around within a coverage
area.
My home network is on, but the WiFi Scanner
doesn't detect it.
• First, check your battery. The scanner sometimes fails to
detect networks if its batteries are low. In addition,
access points are occasionally configured in a way that
the scanner cannot detect. If the scanner does not detect
your home network you may want to try any of the
6
Page 7

following: (i) check your SSID for non-alphanumeric
characters; (ii) temporarily lower your default data rate; or
(iii) enable the broadcast of your SSID. The scanner
detects most, but not all access points that have been
configured to disable the broadcasting of their SSIDs.
Technical Support
For technical questions, please visit:
http://www.targus.com/support.asp
Product Registration
Targus recommends that you register your Targus accessory shortly
after purchasing it. To register your Targus accessory, go to:
http://www.targus.com/registration.asp
You will need to provide your full name, email address, phone
number, and company information (if applicable).
Warranty
Targus warrants this product to be free from defects in materials and
workmanship for one year. If your Targus accessory is found to be
defective within that time, we will promptly repair or replace it. This
warranty does not cover accidental damage, wear and tear, or
consequential or incidental loss. Under no conditions is Targus liable
for loss of, or damage to a computer; nor loss of, or damage to,
programs, records, or data; nor any consequential or incidental
damages, even if Targus has been informed of their possibility. This
warranty does not affect your statutory rights.
Regulatory Compliance
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is
subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not
cause harmful interference, and (2) This device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
7
Page 8

FCC Statement
Tested to Comply
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
of a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna;
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver;
• Move the computer away from the receiver;
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
All trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their
respective owners. Features and specifications subject to change without
notice. © 2005, Targus Group International, Inc. and Targus, Inc., Anaheim, CA
92806 USA.
8
 Loading...
Loading...