Page 1

Cisco TelePresence
Management Suite
Administration Guide
D13741.12
December 2010
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 1 of 37
Page 2

Table of Contents
Introduction ......................................................................................................................... 5
Zones ................................................................................................................................... 6
ISDN zones ............................................................................................................................................. 6
Area code rules ................................................................................................................................ 7
IP zones ................................................................................................................................................... 8
Gateway resource pool .................................................................................................................... 8
Adding systems ..................................................................................................................10
Automatic system discovery .................................................................................................................. 10
Add systems .......................................................................................................................................... 10
Feedback from Cisco TMS when adding systems, rooms and equipment .................................... 11
Adding a Cisco TelePresence Content Server............................................................................... 11
How pre-registration works .................................................................................................................... 12
Configuring the DHCP server ......................................................................................................... 12
Persistent settings ................................................................................................................................. 12
Swap a system in Cisco TMS ................................................................................................................ 13
Replace system function ................................................................................................................ 13
System tracked by IP address........................................................................................................ 13
System tracked by Host Name ....................................................................................................... 13
System tracked by MAC address ................................................................................................... 14
Support for remote systems ..............................................................................................15
How the communication works .............................................................................................................. 15
Reachable on public Internet.......................................................................................................... 15
Behind firewall ................................................................................................................................ 15
Plugging in at remote location ........................................................................................................ 15
Adding a remote system to Cisco TMS ................................................................................................. 16
A system already added to Cisco TMS .......................................................................................... 16
A system not added to Cisco TMS ................................................................................................. 16
Setting an endpoint in public .......................................................................................................... 16
Booking .................................................................................................................................................. 16
Phonebooks ........................................................................................................................................... 16
Software upgrade .................................................................................................................................. 17
Statistics and monitoring ....................................................................................................................... 17
Cisco TMS configuration ....................................................................................................................... 17
User permissions ...............................................................................................................19
User Administration ............................................................................................................................... 19
User Information and preferences .................................................................................................. 19
Limiting access to Cisco TMS/Locking out a set of users ..................................................................... 20
Groups ................................................................................................................................................... 20
Access to different parts of Cisco TMS .......................................................................................... 21
Users ..................................................................................................................................................... 21
Default Groups ...................................................................................................................................... 22
Default System Access .......................................................................................................................... 22
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 2 of 37
Page 3

Introduction
Phone Books ......................................................................................................................23
Local Directory ....................................................................................................................................... 23
Global Directory ..................................................................................................................................... 23
Corporate Directory ............................................................................................................................... 23
Setting phone books on systems .......................................................................................................... 23
Cisco TMS features ............................................................................................................25
Operator conferences ............................................................................................................................ 25
Operator conference features: ....................................................................................................... 25
How to set up an operator conference ........................................................................................... 25
Provisioning directory ............................................................................................................................ 25
Troubleshooting the Cisco TMS components ..................................................................27
Phonebook (Corporate Directory) errors ............................................................................................... 27
TMSDatabaseScannerService .............................................................................................................. 27
Symptoms....................................................................................................................................... 28
How to fix ........................................................................................................................................ 28
TMSLiveService .................................................................................................................................... 28
Symptoms....................................................................................................................................... 28
How to fix ........................................................................................................................................ 28
TMSPLCMDirectoryService................................................................................................................... 29
Symptoms....................................................................................................................................... 29
How to fix ........................................................................................................................................ 29
TMSSchedulerService ........................................................................................................................... 29
Symptoms....................................................................................................................................... 29
How to fix ........................................................................................................................................ 29
TMSSnmpService (formerly TMSWatchdogServiceStarter.exe) .......................................................... 29
Symptoms....................................................................................................................................... 30
How to fix ........................................................................................................................................ 30
TMSServerDiagnosticsService .............................................................................................................. 30
Symptoms....................................................................................................................................... 30
How to fix ........................................................................................................................................ 30
Cisco TMS Database Management Service (optional) ......................................................................... 31
Symptoms....................................................................................................................................... 31
How to fix ........................................................................................................................................ 31
TMSAgentService .................................................................................................................................. 31
Symptoms....................................................................................................................................... 31
How to fix ........................................................................................................................................ 31
The Web server ..................................................................................................................................... 31
Symptoms....................................................................................................................................... 32
How to fix ........................................................................................................................................ 33
Java Applet – Monitoring ....................................................................................................................... 33
What it does.................................................................................................................................... 33
Symptoms....................................................................................................................................... 33
How to fix ........................................................................................................................................ 33
The database ......................................................................................................................................... 34
Symptoms....................................................................................................................................... 34
How to fix ........................................................................................................................................ 34
Related documents ............................................................................................................36
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 3 of 37
Page 4

Introduction
Disclaimers and notices ....................................................................................................37
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 4 of 37
Page 5
Introduction
Introduction
The Cisco TelePresence Management Suite (Cisco TMS) is a portal for managing and monitoring your
video conferencing system from a single structured overview. Cisco TMS provides centralized control
for on-site and remote video systems, and a deployment and scheduling system for your entire video
network.
Cisco TMS can be downloaded from Cisco.com.
Cisco TMS is a powerful tool for maintaining, operating, and increasing the value of your conferencing
network. Cisco TMS adds intelligence, diagnostics, and functionality that enhance your video network
components and the return on your investment.
Cisco TMS automates system configuration for a basic H.323 network, operating ‘right out of the box’.
You can tune Cisco TMS default behavior to suit your organization needs, set up user permissions,
and configure your network model so that all of Cisco TMS call handling functionalities are available.
This document provides information for fresh installs, upgrading an existing version, or configuring the
Cisco TMS version that comes preinstalled on a Cisco TelePresence Management Server. There is
also a guide for uninstalling Cisco TMS.
Along with installation/upgrade processes, you will find guidelines on software and hardware
requirements, integrating Cisco TMS with other applications, and version specific upgrade information.
Further information on Cisco TMS functionality is available online. Cisco also maintains a Cisco TMS
knowledgebase.
Note: For the Cisco TMS user guide, see the online help available via the question mark icon (?) on
the Cisco TMS client.
A list of relevant documents referred to in this guide can be found in the References and related
documents section.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 5 of 37
Page 6
Zones
ISDN Zone Name
Country/Region
Area Code
To access an outsid
e line for
To access an outside line for
Number of digits to use for
Zones
Zones enable Cisco TMS to use the correct international dialing codes when using ISDN between
countries (area codes within the same country), selecting which systems should use IP and which
should use ISDN, and insert the correct prefixes for IP systems when using an ISDN gateway.
Systems in the same IP zone will always connect on IP as default when they are booked via Cisco
TMS. If you always want to use ISDN between systems in a location, they should therefore not be part
of an IP zone. Also, systems that will never connect on ISDN (except through a gateway) should not
be part of an ISDN zone.
ISDN zones
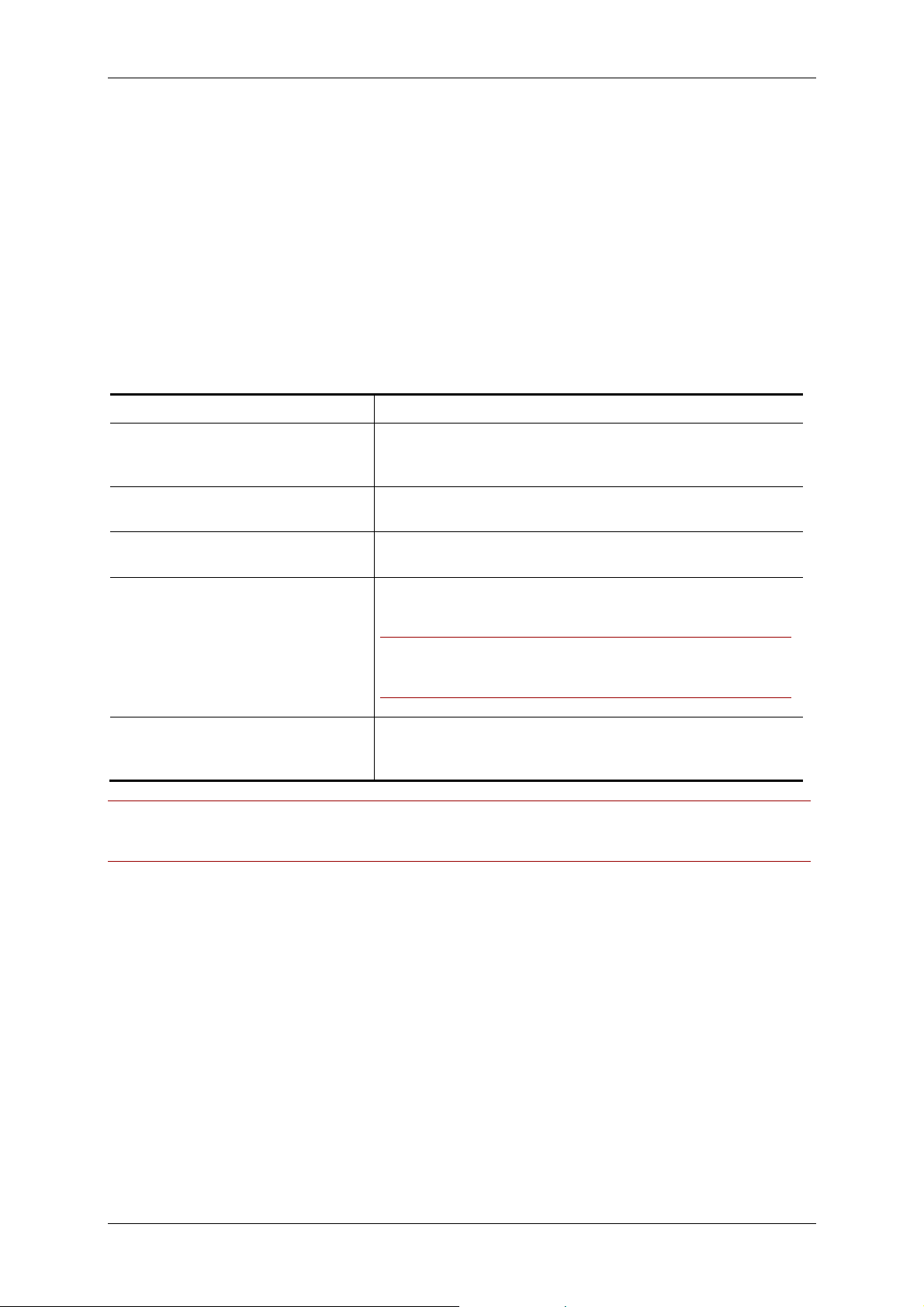
To set up an ISDN zone, go to Administrative Tools > Locations > ISDN Zones, click New and fill in
the following fields:
local calls, dial
long distance calls, dial
internal ISDN calls
Note: If Cisco TMS is generating the wrong numbers to dial when dialing local, domestic or
international calls, you should have a look at the ISDN zone settings and the phone number set on
the system.
Specify the name of the ISDN zone.
Choose the country this zone is situated in. This will let
Cisco TMS choose the correct country code and correct
international dialing prefixes.
Specify the area code this zone is situated in. This will let
Cisco TMS choose the correct area code rules
Insert the prefix needed to gain an outside line in this ISDN
zone
Insert the prefix needed to gain an outside line for long
distance calls in this ISDN zone.
Note: If you use the same prefix to gain an outside line for
both local and long distance calls you should put the same
prefix here as you put in the previous field.
This specifies the number of digits used for internal dialing
within this zone. The leading digits will be stripped from the
number when dialing between systems in this ISDN zone.
Example:
A Swedish phone number in Stockholm would have a number layout like this:
Country code (+46); Area code (08); local number (12345678)
If dialing this number from within Stockholm they would only dial the local number: 12345678
If dialing from Gothenburg (within the country, but outside the area code) they would dial: 08
12345678
If dialing from outside Sweden they would dial: +46 8 12345678
As you see the 0 in front of 8 (in the area code) would have to be removed when dialing this number
from outside the country. This is therefore not looked upon as part of the area code, but rather a prefix
to dial between area codes.
The systems should only be configured with the local ISDN number: 12345678, but with the correct
area and country code in the ISDN Zone. If the system was wrongly configured with the local number
and the area code, Cisco TMS would wrongly configure the following as the international number for
the system: +46 8 0812345678
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 6 of 37
Page 7
Zones
In the ISDN Zone the area code should be stored as just 8, since Cisco TMS will add a 0 in front of it
when dialing between Swedish area codes, and add +46 when dialing from outside Sweden.
There are some exceptions to these rules, but Cisco TMS is aware of these exceptions.
Some countries like Norway do not use area codes; the area code field in the ISDN zones in
these countries should therefore be left empty. An example of a valid number is +47 12345678.
Some other countries like Italy include the leading zero in the area code even when being dialed
into from outside the country. This means that the area codes in the Italian ISDN zones should
include the leading zero. An example of a valid number is +39 02 12345678.
Other countries again such as Switzerland include the area code with the leading zero when
dialing within an area code and when dialing within the country, but remove the leading zero when
being dialed into from outside the country. Cisco TMS knows this, so the area code for ISDN
zones in Switzerland should only include the area code without the leading zero. For example:
+41 33 1234567 and 033 1234567.
Area code rules
Area code rules are typically used in the US to set up 10-digit dialing and area code overlays. Area
code rules determine how ISDN numbers are dialed from one area code (the area code set for the
location) to other area codes.
To add or edit an area code rule for a location, click Area Code Rules inside the ISDN zone. After
clicking the link, a page with an overview of all area code rules for the ISDN zone is displayed.
New rules can be added to the location from this page by clicking New Rule.
You can edit old rules for the location by clicking the Edit links to the right of every rule.
To delete a rule, select it and click Delete.
Note: In a US phone number, for example +1 (123) 456-7890, the area code consists of the digits in
brackets (123), and the prefix consists of the digits 456 (in this example).
Create a new dialing code for the selected location by clicking New Rule.
When adding a new rule for a location, fill in the fields as described below.
When dialing from this area code to the
following area code (Field 1)
This field, combined with the prefix field explained
below, decides the area code that this rule applies to. It
may be set to be the same area code used for the
location.
With the following prefixes (Field 2)
The rule will only apply to the calls made to the area
code in Field 1, with the prefixes listed here. If this field
is left empty, the rule will apply for all calls made to the
area code in Field 1.
Include Area Code
If checked, the area code in Field 1 will be included in
the call. If unchecked, the area code will not be included
in the call. For the US, select this check box to enable
10-digit dialing.
Before dialing, also dial
If the rule applies, as stated in Field 1 and Field 2, the
digit(s) in this field will be dialed first when making a call.
In most cases this field will be empty.
Click Save when you are done defining your new area code for this ISDN zone.
Note: When an Area Code rule is used, prefixes from the ISDN zone are still used, but domestic
dialing behaviors (such as inserting a 1) are ignored by Cisco TMS.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 7 of 37
Page 8
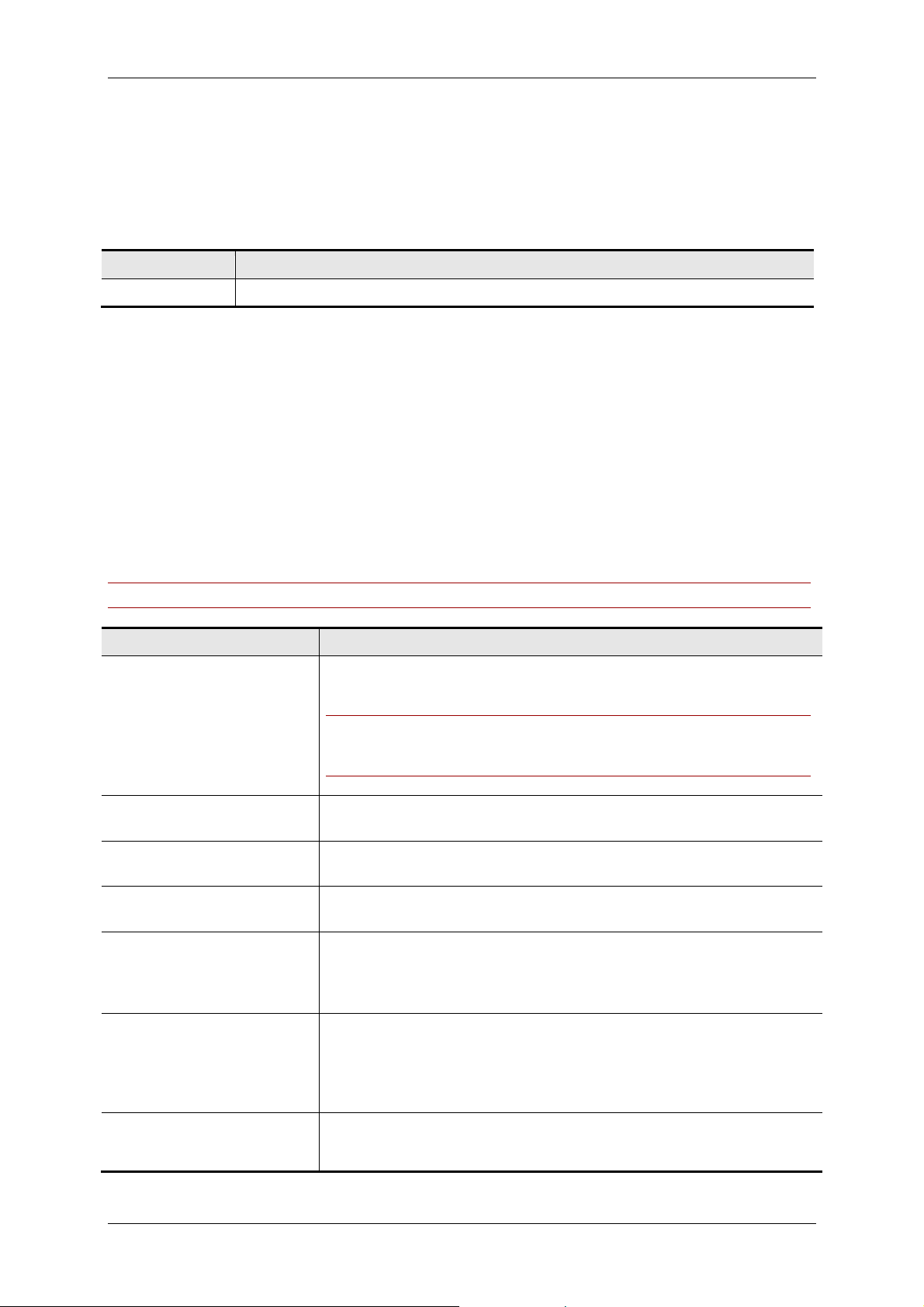
Zones
IP Zone Name
URI Domain Name:
Gateway Auto Prefix:
Gateway Telephone Prefix:
Gateway 3G Prefix:
Dial-in ISDN Number:
Dial-in ISDN Number for
Allow IP
-
ISDN
-
IP:
IP zones
To set up an IP Zone:
1. Go to Administrative Tools > Locations > IP Zones.
2. Click New.
3. Fill in the fields described below.
Field Description
Specify the name of the IP zone
Gateway resource pool
ISDN Zone
By moving IP zones between the two lists at the bottom of an IP zone, you can specify which IP zones
should be dialed using IP, and which IP zones should be dialed using ISDN.
When setting up a conference with participants in different IP zones, Cisco TMS will try to include a
Cisco TelePresence MCU from the IP zone where the majority of the participants are situated.
In the Gateway Resource Pool settings you specify which prefixes to dial in order to use a gateway.
The ISDN Zone dropdown allows you to specify which ISDN Zone’s dialing rules should apply to the
gateway you want to use. The reason you specify the prefix rather than the gateway directly, is that
this allows for more flexibility in Cisco TMS. It means that you can use load-balanced gateways, and
even gateways not supported by Cisco TMS.
Note: This setting must be specified in order for the Gateway Resource Pool to work.
Field Description
Add which domain name Cisco TMS should use for routing H323 calls
to this IP-zone when doing URI dialing.
Note: Cisco TMS will always use URI dialing between two locations
where this setting is filled in, thereby ignoring the IP/ISDN
preferences defined at the bottom of this page.
Specify the prefix to use to get an outside ISDN line through the
gateway for video calls.
Specify the prefix to use to get an outside ISDN line through the
gateway for telephone calls.
Specify the prefix to use to get an outside 3G line through the 3G
gateway for 3G calls.
Specify the TSC4 number that will be used for dialing into endpoints
through a gateway. Cisco TMS will automatically generate the entire
number for a call containing the gateway’s TSC4 number followed by
the star and the endpoint’s E164 alias.
Specify the TSC4 number that will be used for dialing into endpoints or
3G:
Cisco TelePresence MCU through a 3G gateway. Cisco TMS will
automatically generate the entire number for a call containing the
gateway’s TSC4 number followed by the star and the endpoint’s E164
alias.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 8 of 37
Check this option to allow Cisco TMS to schedule calls from an IP only
endpoint out through an IP-ISDN gateway to an IP only endpoint in via
an ISDN-IP gateway. The set-up time for this type of calls can be close
Page 9
Field Description
Prefer IP calls to specific
to a minute.
Systems in the same IP zone will always prefer to dial each other on
IP zones:
IP. This will be the preferred call option when booking via Cisco TMS
booking and the only option when using a different booking interface
like Outlook, Lotus Notes, Microsoft Office Communicator, Lotus
Sametime or Cisco Scheduler. The systems in the same IP zone will
be dialed on E164 alias if all systems in the conference are registered
to one gatekeeper or different neighboring gatekeepers. Participants
that are not reachable through a gatekeeper will be dialed to (or from)
with IP-addresses.
Zones
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 9 of 37
Page 10

Adding systems
Adding systems
Systems in Cisco TMS include Endpoints, Gateways, Gatekeepers, Cisco TelePresence MCU,
Equipment and Rooms. Every system can be represented in multiple folders, but these
representations will all have the same entry in the database – which means that changes done to the
system will be reflected in all of its representations.
Automatic system discovery
From Cisco TMS 11.5 a new feature called Automatic system discovery was added. This feature
can be turned on during installation or after installation by going to Administrative Tools >
Configuration > Network Settings. When this feature is enabled, Cisco TMS will scan the network
for systems. If a system not yet known to Cisco TMS responds, this system will automatically be
added to a default folder and given a default template. This template will include an IP Zone and a
Cisco TMS Phonebook containing all the endpoints in Cisco TMS. The folder and template can be
changed under Administrative Tools > Configuration > Network Settings.
Add systems
To add systems, go to Systems > Navigator > select folder to add system to > click Add System.
This page contains four different tabs where you can add systems to the selected folder in Cisco TMS.
Each of them allows different ways of adding systems and rooms/equipment:
Add Systems tab
On this page you can either enter a start IP address and an end IP address for a range of systems to
be added, or you can enter a comma-separated list of IP addresses and host addresses for those
systems you want to add to the Cisco TMS. The following example will add two systems, one by DNS
name and one by IP address, and scan ten systems in a range: “user.tms.int, 10.0.0.1, 10.1.1.0 -
10.1.1.10”
This page is also where you specify the correct locations for the systems and the time zone.
In the Advanced Setting pane you can:
Enter Username, Password and/or an Admin Password if the systems require it in order to be
added.
Select a template to be set as persistent settings on the systems.
Set Discovery Options. For example which SNMP names to use when searching for systems
and if you want to search for non-SNMP systems and whether or not to add discovered systems
although they are not supported by Cisco TMS (for example PC’s and network infrastructure
devices). The list of SNMP community names is pulled from Administrative Tools >
Configuration > Network Settings > SNMP Community Names. If you know the community
names of the system you want to add, you may edit this field to speed up the adding process. Any
changes here will NOT affect the settings under Administrative Tools.
The Usage Type field specifies the usage of the system that is added. The options are: Meeting
Room, Personal Home System, Personal Office System or a Roll About system.
From List tab
On this page you can add systems that have already been added to Cisco TMS but are not already in
the current folder or have been automatically discovered by the Cisco TMS Network Scanner.
To select the systems you want to add to the folder, select the check box to the left of the
systems.
Specify the locations and the time zone you want the systems to have in the Enter Location
Settings pane.
For systems that require authentication data, this is entered in the Advanced pane.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 10 of 37
Page 11

Adding systems
Pre Register Systems tab
If you are planning to deploy a large number of endpoints, pre-registering them allows Cisco TMS to
configure the systems the first time they come online. When you pre-register, you must supply a name
for the system and an identifier. You must first select what to use as primary identifier; MAC address,
IP or Serial Number for the systems.
Note: Currently only the Cisco TelePresence System MXP series and Polycom HDX support using
serial number as the identifier. Cisco recommends using MAC address as the unique identifier for
systems.
If you want a list of settings to be applied to the system when it comes online, you can select a
pre-created template from the list in the Set templates pane. This template can be modified at
any time using the template pages. A persistent template for the system can also be
preconfigured here, together with the option of setting persistent E164 Alias, H323Id, SIP URI and
the endpoint name. The templates and persistent settings require that the system supports
templates in Cisco TMS.
Specify the locations and the time zone you want the systems to have in the Enter Location
Settings pane.
To learn more, see How pre-registration works.
Add Rooms/Equipment tab
Here you choose whether you want to enter a room or a type of equipment.
Start by entering the name of the room or equipment you want to add to the Cisco TMS.
If you select to add a room, you can specify more settings in the advanced area. In the advanced area
you may enter information about IP, ISDN, Gatekeeper, SIP and location settings.
Feedback from Cisco TMS when adding systems, rooms and equipment
When adding systems and rooms/equipment, Cisco TMS will analyze the systems configurations
using the ticketing service to ensure that when a system is added its settings are verified.
If Cisco TMS finds any faulty configurations, it will present the system in the table with the header
saying “NOTE: Systems Discovered with Incorrect Settings, Not Yet Added to Folder:” with a
description in the table row saying what is wrong.
You may change/correct the settings by clicking Edit in the table row where the system is presented.
Change the settings for the system in the pop-up window. Have the user guides for the systems
available.
If there are no incorrect system settings, the system will be added to the folder and will be shown in
the table saying “Systems Discovered and Successfully Added to Folder:”
If the system is already added to the folder, you will get a message saying that it already is in the
folder. The system will be added to the table saying “Systems Discovered and Successfully Added
to Folder:”
If the system couldn’t be added because the SNMP Community Name is not added to the list in Cisco
TMS, or Cisco TMS couldn’t get in contact with the system or the system is of a type that TMS does
not support, it will be added to the table saying “NOTE: Systems That Could Not Be Added:”.
Adding a Cisco TelePresence Content Server
TMS 11 and versions onwards support adding the Cisco TelePresence Content Server for booking
and management purposes.
To add the Content Server to Cisco TMS follow the procedures in the Add Systems tab
description.
Select the Discover Non-SNMP Systems. WARNING: Will significantly increase time
required for discovery check box in the Advanced Settings pane of the tab.
Note: You need to add the Content Server’ API user and password when adding the system to Cisco
TMS.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 11 of 37
Page 12
Adding systems
How pre-registration works
When pre-registering a system, you can select whether you want the system to be identified on MAC
Address, IP/Hostname or Serial Number.
Note that only the Cisco TelePresence System MXP series and Polycom HDX endpoints can preregister based on serial number. Also keep in mind that only systems supporting SNMP can be preregistered by serial number and MAC-address if they are using static IP addresses. Cisco
TelePresence System MXP endpoints are using HTTP traps rather than SNMP traps to communicate
with the Cisco TMS server for most information. They are therefore dependent on having their
External Manager’s IP address configured. This is done automatically when the endpoint contacts the
DHCP server to retrieve an IP address, but only if the option 242 on the DHCP server is configured to
point to the Cisco TMS server.
Configuring the DHCP server
If you are using a Windows 2000/2003 DHCP server, add the following settings in the
DHCP Manager
You can create the 242 option by redefining an existing global option. To do this, highlight the global
option in the “Unused” list and click Add in the DHCP manager. Once you have defined a vendorspecific option, you can select it for use by the vendor class by moving the option to the “Configured”
list, and defining its value which should be the IP or the DNS name of the Cisco TMS server.
If you are using ISC’s DHCP-server, put the following statements in dhcpd.conf.
1. Define option 242:
option local-tms-ip code 242 = ip-address;
2. Define the value in the subnet of pool section:
option local-tms-ip < IP address>;
If the systems are not using DHCP, they need to be able to respond to the SNMP broadcast
messages that Cisco TMS will send out on set intervals. This interval is configurable in
Administrative Tools > Configuration > Network Settings > TMS Services >SNMP Broadcast
Interval (in minutes).
Note: The Cisco 150 MXP with L1.1 and L1.2 is configured to request the DHCP for option 173. It is
therefore advised to either upgrade the endpoints to newer software, or to configure both the option
242 and 173 on the DHCP server until the endpoints are upgraded.
Persistent settings
Persistent settings allow the administrator to enforce settings on systems throughout the network.
These persistent settings can be specified during pre-registration or after the system has been added
to Cisco TMS (via the Persistent settings tab in Navigator).
The persistent settings will be set on the endpoint every time Cisco TMS receives a boot event from
the endpoint; either via SNMP or HTTP. The Persistent setting template is also set on the system at
the same time every day. This time is based on the first time the template was set on the system and
is configurable when editing the template in the Systems > Provisioning > Configuration
Templates page.
To view a log of the daily updates go to Systems > Provisioning Activity Status. You will see that
there are 2 types of entries; the first will be when the template has been set on the system and this will
have no recurrence set. As the second entry you will see the template again but the recurrence will be
set to every day. If you click on this description, you will see a log of all transactions for this template.
There are four persistent settings, and three of them allow you to set a persistent System Name,
H323 Id, E164 Alias and SIP URI. The last setting gives you the option to pick a predefined template
that will be set on the endpoint after every system boot. The template can typically include settings like
Auto answer on, Microphone off and Volume 7.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 12 of 37
Page 13

Adding systems
Swap a system in Cisco TMS
Systems get an id (Cisco TMS System Id) when they are first added to Cisco TMS. This id is used as
the reference for the systems in booking, reporting, event, permissions etc. It is therefore important to
retain the id, even if a system gets swapped (because of theft, upgrade, hardware failure etc). A
system should therefore never be purged from Cisco TMS. It may be deleted from a folder since the
data for the system will still be in the database, but it should not be purged unless you are 100%
confident that a new system should take over this system’s roles.
If a system in Cisco TMS is out of order, or awaiting a swap, it can be set to Not Allow Bookings. This
is done in the Connection tab in Systems > Navigator. By doing this you can avoid anyone booking
the system while it is unavailable.
Replace system function
From Cisco TMS 11.5 a feature called ‘Replace system’ was introduced. This feature makes it much
easier to replace systems in Cisco TMS. Cisco recommends using this feature when replacing
systems in Cisco TMS.
To replace a system:
1. Go to Systems > Navigator > select the system you wish to replace
2. Click the Connection tab.
3. Click Replace Systems. Here you choose whether to change the system’s network address to an
IP or DNS address of a system on the network, or choosing an existing system in Cisco TMS by
clicking Select system….
4. Click Next… You will then be shown a summary page where you choose whether you would like
to keep the system name, keep call configuration, apply last configuration backup and keep all
logs of the system. You can also choose to purge the system that you are replacing from Cisco
TMS.
5. Click OK and the switch will be completed.
System tracked by IP address
When a system is tracked by IP address and the system is swapped, the easiest way is to give the
new system the same IP address and connect it to the network. If a Configuration Backup was done of
the previous system, a Configuration Restore can now be done to restore all previous settings and
phonebooks.
If the new system is configured with a new IP address,
1. Insert the new IP address in the Connection tab for that system in Systems > Navigator in
Cisco TMS
2. Click Save/Try.
Note: Verify that the SNMP community name is correct, or else this will not work.
System tracked by Host Name
When a system is tracked by the Host Name and the system is swapped, the new system should be
configured with the same host name. If a Configuration Backup was done of the previous system, a
Configuration Restore can now be done to restore all previous settings and phonebooks.
If the new system is configured with a new Host Name,
1. Insert the new Host Name in the Connection tab for that system in Systems > Navigator in
Cisco TMS
2. Click Save/Try.
Note: Verify that the SNMP community name is correct, or else this will not work.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 13 of 37
Page 14

Adding systems
System tracked by MAC address
When a system is tracked by MAC address, Cisco TMS relies on traps from the endpoint containing
the (new) IP address of the system and the MAC address. If the IP address has changed (which
happens when using DHCP), Cisco TMS will update the IP address in the database to the new IP
address. Cisco TMS will then be able to contact the system.
When swapping a system with a new system, the MAC address will change. If Cisco TMS is tracking
the system by the MAC address, the MAC address in Cisco TMS therefore needs to be updated.
This can be done in two ways:
1. Update the MAC address field in the Connection tab for the system with the new system’s MAC
address, click Save/Try, and reboot the system via the remote control or telnet. This will make the
endpoint send a trap to Cisco TMS with its MAC address and IP address, resulting in Cisco TMS
recognizing the MAC address and updating the IP address in Cisco TMS.
2. Set Track system on network by to IP Address and update the IP address to the new IP
address of the system. Click Save/Try to allow Cisco TMS to read the new MAC address, and set
Track system on network by back to MAC Address.
If a Configuration Backup was done of the previous system, a Configuration Restore can now be done
to restore all previous settings and phonebooks.
Note: Verify that the SNMP community name is correct or else this will not work.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 14 of 37
Page 15

Support for remote systems
Support for remote systems
From Cisco TMS 11.5, remote systems are supported for booking, getting software upgrades,
receiving phonebook and being part of the statistics created in Cisco TMS. The following section
describes how this feature works and answers some frequently asked questions.
Cisco recommends that the remote system is on a DNS compatible network to ensure proper
communication between Cisco TMS and the remote system.
Before you can use a system as a remote system in Cisco TMS, you must be sure to have set a public
DNS address on the Cisco TMS server. This can be done in Administrative Tools > Configuration >
Network Settings in the pane Advanced Network Settings for Systems on Public Internet/Behind
Firewall. Make sure that this address is reachable from the remote system, if you enter a fully
qualified host name the remote system needs to have its DNS settings in order.
How the communication works
A remote system can either be located publically on the Internet or behind a firewall. The way Cisco
TMS communicates with these two differs slightly.
Reachable on public Internet
Having the system set to Reachable on Public Internet as System Connectivity will make Cisco TMS
communicate with the system in the same way as it does with the systems internally. (To set System
Connectivity, go to on the system in System Navigator > Connection Tab.) However, since the
system cannot contact TMS on TMS’s internal DNS name or IP address, TMS will set a different
address for the phonebook service and feedback on the endpoint. The address used is the one listed
under Administrative Tools > Configuration > Network Settings > Advanced Network Settings
for Systems on Public Internet/Behind Firewall, the field TMS Server Address (Fully Qualified
Host Name or IPv4 Address).
When the system is reachable on the public Internet, you can have TMS communicate with the system
on both HTTPS (port 443) and HTTP (port 80).
Behind firewall
Setting Behind firewall as System Connectivity will make TMS communicate with the endpoint in
much the same way as Reachable on Public Internet, except TMS will not be able to tell the endpoint
to dial and must therefore set up a route where for example a Cisco TelePresence MCU is calling to
the endpoint. All communication between the system and TMS will be HTTP over port 80 or HTTPS
over port 443.
Cisco TMS will automatically detect that a system is a SOHO system when the IP address the
endpoint reports in status.xml is different from the IP address the HTTP packets are coming from, and
the HTTP (port 80) and HTTPS (port 443) ports are closed. Cisco TMS will then set System
Connectivity to Behind Firewall.
Plugging in at remote location
When a system is plugged in at a remote location, it will contact Cisco TMS either with a register event
or a boot event depending on whether the system is already in Cisco TMS. For information on how to
add a remote system to Cisco TMS, see the section Adding a remote system to Cisco TMS.
When Cisco TMS gets this event, it will reply with an acknowledgement and ask to get three files from
the endpoint: ‘status.xml’, ‘history.xml’ and ‘configuration.xml’. It will also check whether any software
upgrade has been scheduled for the endpoint, and if so, perform this.
After 60 seconds, the system will communicate with Cisco TMS, which will set the feedback
expression on the system enabling it to send events.
Cisco TMS will also set the endpoint to contact the Cisco TMS server every 15 minutes.
This will be the heartbeat that allows for communication between the Cisco TMS server and the
remote system, and any change that is done on the remote system or in Cisco TMS will be
synchronized through this heartbeat.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 15 of 37
Page 16

Support for remote systems
Adding a remote system to Cisco TMS
A system already added to Cisco TMS
The easiest way to add a remote system to Cisco TMS is to first have the system registered in Cisco
TMS before you bring it home. Before you unplug it, go to Edit Settings in the Settings tab for the
system and click Enforce Management Settings. If the system will be behind a firewall that is not
open or doesn’t have HTTP or HTTPS ports opened up, you also have to go to the Connection tab on
that endpoint and change System Connectivity to Behind Firewall. Cisco TMS will then set the
management address on that system to Cisco TMS external management address. When the system
is plugged in at home, the system will then send a boot event to Cisco TMS and from then on the
system will be available from Cisco TMS.
A system not added to Cisco TMS
If you want to use an endpoint that has not been added to Cisco TMS before it is plugged in at the
remote location, you will need to set the external management address of Cisco TMS on the endpoint.
This can be automatically done by the DHCP server (see section Configuring the DHCP server) or
manually on the endpoint. With F5.x and L4.1 this must be done using telnet, while F6.x and L4.2 (and
newer) have this in the endpoint’s menu:
1. In Windows, go to Start > Run.
2. Type telnet <ip-address of the endpoint> (This can be displayed on the endpoint by
pressing the Up arrow and then the Left arrow.)
3. Type password if needed
4. Type xConfiguration ExternalManager Address: “<dns name of the TMS
server>”. If you are using a proxy, type the dns name of the proxy server instead.
5. This configuration is correct by default, but if it has changed, type ‘xConfiguration
ExternalManager Path: “tms/public/external/management/systemmanagementservice.asmx”’
6. Type bye
When this has been set, the endpoint will send a register event to Cisco TMS, and when Cisco TMS
receives this and notices that the system is not already in Cisco TMS, it will add it to a list. One must
then add the system to Cisco TMS afterwards. However, if Automatic System Discovery Mode for
SoHo has been enabled, the system will be added in the default folder specified in the Administrative
Tools > Configuration > Network Settings.
Setting an endpoint in public
If your system is in public, not behind a firewall or behind a firewall that has opened up the HTTP or
HTTPS ports, it is advised to change the system connectivity on the system to Reachable on Public
Internet. This way it will also be possible for Cisco TMS to set up calls where the endpoint is calling
out, and not only being called to.
Booking
A booking in Cisco TMS including remote systems can be done like any other booking. However, as
Cisco TMS is not able to communicate directly to a remote system that is behind a firewall, it is not
possible for Cisco TMS to ask the endpoint to initiate a call. The endpoint must therefore be dialed
into. If two or more systems that are behind a firewall would like to call each other, then an internal
system with multisite must be included in the call.
Phonebooks
The phonebook will work in the same way as if the system was located on a LAN. When the endpoint
is requesting the phonebook, it will send the request to the Cisco TMS server where Cisco TMS
creates the .xml file and sends it back to the endpoint as the response.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 16 of 37
Page 17

Support for remote systems
Software upgrade
Software upgrade on remote systems is set up in the same way as software upgrade on internal
systems. However, the mechanism used to upgrade the system is different. When you have
scheduled the upgrade, Cisco TMS will say that the upgrade went successfully. What has happened is
that Cisco TMS has put the upgrade on hold until it gets a boot event from the system. When Cisco
TMS gets this boot event, it will see that an upgrade has been scheduled for that system. On the reply
to the boot event, Cisco TMS will send the endpoint a URL where it can get the software package.
This URL is defined in Administrative Tools > Network > General Network Settings. It is
recommended that the directory is left to the default (tms/public/data/software) as this is where Cisco
TMS populates its list of packages from (Systems > System Upgrade > Software Manager). In other
words, if you provide a different URL, you might end up scheduling an upgrade with a package found
in the list that is not found in the URL specified.
Statistics and monitoring
The statistics and monitoring of the remote systems will be made up the same way as systems that
are on the LAN, by sending event traps to Cisco TMS. As for retrieving status and detailed call
information (‘status.xml’ and ‘history.xml’), these are sent every 15 minutes. The configuration of the
system (‘configuration.xml’) will be sent on demand (Clicking Force Refresh in Cisco TMS) or when
doing changes in Cisco TMS.
Ad hoc calls will not be shown for systems behind a firewall as the TMSLiveService service is not able
to contact the system to get information about the call.
Cisco TMS configuration
To allow for the remote systems to communicate with the Cisco TMS server, Cisco TMS needs to be
reachable from the remote system. There are several ways that this can be done:
Alternative: Description
Put the Cisco TMS in
public
Put the Cisco TMS in
DMZ
Use a proxy This option provides the best security without having to have two separate
Have two Cisco TMS
servers, one on the
inside and one in DMZ
talking to the same
database
This option provides less security, and makes the Cisco TMS vulnerable for
attacks directly over the Internet.
This option provides a bit more security. Port 80 (HTTP) needs to be open in
the firewall to allow for incoming traffic.
Cisco TMS servers, and is set up by having the proxy forward to the Cisco
TMS server requests that are made to the management address path of the
Cisco TMS server.
• /tms/public/external/management/systemmanagementservice.asmx
• /tms/public/feedback/code.aspx
• /tms/public/external/phonebook/phonebookservice.asmx
• /tms/public/feedback/postdocument.aspx
This will allow you to add and manage the internal and external systems
seamlessly, but requires some extra configuration of firewalls and the
external Cisco TMS server.
The Cisco TMS server in the DMZ should only be accessible on port 80 from
the Internet, and can also be limited to only respond to connections, but not
open any new connections. The Cisco TMS in the DMZ must be able to talk
to the SQL server on the inside of the network, but this can be limited to one
port only. It is recommended to use a limited user with only read/write
permissions to the tmsng database for this (doing upgrades of the Cisco
TMS server will require db_owner permissions to the tmsng database), and
to disable the XP_CMD_SHELL command on the SQL server for security
reasons.
All Cisco TMS services on the Cisco TMS server in the DMZ must be
disabled to prevent the Cisco TMS server in the DMZ from trying to contact
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 17 of 37
Page 18

Alternative: Description
systems on the inside.
Support for remote systems
Have two Cisco TMS
servers, one for
internal and one for
public systems
This is the most secure option, but will remove some of the features as well
as complicate the usage. The booking will be limited since internal and
external systems are now in two different databases. The two databases will
also cause a problem for statistics as the remote systems will have its
statistics stored on the public Cisco TMS and the internal systems will have
its statistics stored on the internal Cisco TMS. System upgrades will need to
be scheduled separately, and software packages must be put on the two
servers. Phonebooks can however be centralized using an LDAP server that
is available for the two servers. For more information, see the chapter Cisco
TMS features.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 18 of 37
Page 19

User permissions
User permissions
User Administration
User Administration controls which users have permissions to which parts of Cisco TMS. Permissions
are controlled on a group level (for example, you assign permissions to a group). The total permission
level for an end user will then be the sum of all the permissions assigns to all the groups that the end
user is a member of.
Note: An end user can be (and in most cases is) a member of several groups.
There are three pre-defined groups in Cisco TMS:
Site Administrator
The Site Administrator group has full access to all functions, folders and systems in Cisco TMS. Only
people who could be made responsible for Cisco TMS functioning properly should be members of this
group. Only the site administrator has the rights to edit the Configuration pages under
Administration Tools. For example, only site administrators can change the IP address of the server
and alter the option keys.
Video Unit Administrator
The Video Unit Administrator (VUA) group has full administrative rights to all video conferencing
systems (including gateways, gatekeepers and Cisco TelePresence MCU) in your network. Typically,
the technical engineers are members of this group. Video unit administrators do not have the rights to
edit the Configuration page;otherwise, they have the same rights as the Site Administrator.
Users
All users automatically become members of the Users group. It is recommended that the access
rights assigned to this group represents the lowest level you want any person in your organization to
have. This applies both to what Cisco TMS functions you want them to see and to which systems they
are allowed to use.
Note: You are not allowed to change any of the permission rights for the Site Administrator group.
Also, you cannot add or remove users belonging to the Users group, as all users by default are
members of this group.
User Information and preferences
The first time a user accesses Cisco TMS, the Windows Username of the user is automatically
detected, if configured in Administrative Tools > Configuration > Network Settings. A new Cisco
TMS user is then added automatically. Cisco TMS will also try to detect new user information such as
email address, first and last name through Active Directory lookup. If the information is not available,
the user will be prompted to fill in user information and user preferences in a popup window, as listed
in the table below. First name, last name and email address must be filled in at first logon to the Cisco
TMS server.
User Information Preferences
Windows Username
First Name
Last Name
E-mail Address
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 19 of 37
Your username on the Cisco TMS server. This is automatically detected
by the Internet Information Server. This information can only be
changed by an administrator.
The user’s first name.
The user’s last name.
The email address that meeting bookings and event notifications should
be sent to.
Page 20

User Information Preferences
The format must be xxx@yyy.zz.
User permissions
Language
Office Telephone
Mobile Telephone
Primary System
Web Conference
Username
Web Conference
Password
SIP URI:
Time Zone
IP Zone
This setting lets the users select between 20 different languages in
Cisco Scheduler, where six of the languages also affect the rest of
Cisco TMS (English, Simplified Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Russian
and French.) English is the default language for Cisco TMS so that
users who select, for example, Swedish as the language, they will get
the Scheduler presented in Swedish and the rest of Cisco TMS in
English.
The user’s office telephone number
The user’s mobile telephone number
The user’s preferred video system.
The username for accessing the web conference account
The password for accessing the web conference account
This is the user’s SIP URI. This field is used by the Cisco LCS
integration. The SIP URI is automatically retrieved from AD if the AD
lookup is properly configured in Cisco TMS.
This setting is used to present the correct time and date information for
the users in Cisco Scheduler (if the client is on a different location than
the Cisco TMS server).
This field allows users to select an IP zone where they are situated.
This IP zone is used when a user books a meeting with only dial-in
participants, to ensure that the Cisco TelePresence MCU that is closest
to the user is picked.
Number of last used
systems listed
First page for New
Conference in Scheduler
This option lets the user choose how many of the previously used
systems should be shown when booking a meeting in Cisco TMS.
Lets the user choose whether to start with the “default page”, the
“choose conference room page” or the “choose time page” when
opening Scheduler.
List your meetings when
opening Cisco Scheduler
Lets the user choose whether all of their meetings should be listed
when accessing Cisco Scheduler
Limiting access to Cisco TMS/Locking out a set of users
Cisco TMS is running on top of Microsoft Internet Information Server and is therefore also utilizing the
Windows user structure for authentication. If the Cisco TMS server is part of a domain, Cisco TMS will
look up any new and existing users in the Active Directory or the local users to see if the users have
the proper permissions to access the Cisco TMS server. If the user has access to the server, they will
also get access to Cisco TMS, and automatically become members of the user groups defined in
Default Groups. When Cisco TMS is installed the first time, all new users will become members of the
Site Administrator group. This should be changed as soon as possible. By setting Default Groups to
Users and limiting the access of the group Users, you can deny access to Cisco TMS to all new
users, even if they are allowed to access the server through the user permissions. A Video Unit
Administrator can then grant each new user the proper permissions by adding them to a new custom
defined group.
Groups
Go to Administrative Tools > User Administration > Groups. This is where you view, edit and set
permissions for Cisco TMS user groups.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 20 of 37
Page 21

User permissions
To add a new group,
1. Click New.
2. Fill in the name of the group.
3. Fill in a description for this new group.
Cisco TMS supports using Active Directory groups where the group memberships for users are
managed through Active Directory (AD)
To enable AD groups:
1. Go to Administrative Tools > Configuration > Network Settings > Active Directory,
2. Configure the AD lookup information with a Domain user.
3. AD groups can then be imported to Cisco TMS and given permissions as a normal Cisco TMS
group.
Cisco TMS will do a lookup towards AD during login for every user to see which AD groups they
belong to, and give them the respective permissions in Cisco TMS.
1. Continue with selecting which users should be part of the group if it is not an AD group.
2. Click Save.
To set the permissions for a group, click Set Permissions. A page with multiple check boxes will load.
1. Select check boxes according to your specifications.
2. Click Save.
Access to different parts of Cisco TMS
When setting up permissions for user group access to different parts of Cisco TMS, the following
choices are available:
Portal
Booking
Monitoring
Systems
Phone Books
Reporting and Administrative Tools
A detailed list of the permissions can be found in the Cisco TMS help system Administrative Tools
section, User Administration > Groups > Setting permissions for groups.
Users
A list of all the registered users is displayed. From here, new users can be created and existing users
can be edited or deleted. Selecting New or Edit/View will open a profile window for that user where
you can add or edit parameters related to that user. The parameters here are more or less selfexplanatory.
Note: The user’s NT login name is important, as this is used for authentication.
When done editing, click Save to store the user’s data.
Note: Users must be members of the Windows Network to be users of Cisco TMS. You cannot delete
your own user representation nor edit your own Windows username while logged on.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 21 of 37
Page 22

User permissions
Default Groups
Default groups define which groups a new user automatically will be assigned to when logging into
Cisco TMS for the first time. By default, all users will be member of the Users group. This cannot be
changed; however, the Cisco TMS administrator may specify more groups that users should be added
to.
To change the default group settings, select the desired groups and click Save.
If you want users to not have access to Cisco TMS by default, there are two options:
1. Change the settings in the Active Directory so that those users don’t have access to log into the
Cisco TMS server.
2. Remove all the permissions from the Users group and set this, and only this, group as the default
group. All new users on the Cisco TMS server will then be denied access to Cisco TMS. If you do
this, you should proceed to create an additional group with the minimum permissions for a trusted
user. These users need to be added into the group after they log into Cisco TMS the first time (so
that the user is created), or you may predefine the users in Cisco TMS and place them in the
group. The next time the user logs in, the username will be matched with the one already
configured.
Default System Access
On this page you can define which permissions should automatically be applied to systems added to
Cisco TMS. These permissions can be adjusted at a later time by going to Systems > Navigator. Five
different access levels are defined for folders and systems. These are:
• Read
• Book
• Edit Settings
• Manage Calls
• Change Permissions
You can set these permissions based on the different access groups in Cisco TMS.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 22 of 37
Page 23

Phone Books
Phone Books
There are three types of phone books available on Cisco endpoints:
Local Directory
The Local Directory is a file stored on the endpoint made by entries inserted through the remote
control on the endpoint. It is not touched by TMS, but can be imported into the Cisco TMS phone
books as an external source.
Global Directory
The Global Directory is a file stored on the codec where the entries cannot be changed via the remote
control. The file is transmitted by HTTP to all endpoints that are subscribing to one or more phone
books in Cisco TMS. Multiple phone books will be merged into one phone book. If containing more
than 400 entries, only the first 400 will be shown on the endpoint. The file will be transmitted to the
endpoint on the intervals set in the Administrative Tools > Configuration > General Settings >
Phone Books Update Frequency field.
Note: This only works on endpoints that support the globdir.prm file.
Corporate Directory
The Corporate Directory is an XML service on the Cisco TMS server that allows the endpoint to
retrieve the phone books directly from the server every time the phone book button on the endpoint is
pressed. It allows for a hierarchy of phonebooks and multiple phone numbers on every entry. The
Corporate Directory is also searchable.
Setting phone books on systems
There is a global setting in Cisco TMS (Administrative Tools > Configuration > General Settings >
General Settings pane > TANDBERG System Phone Books) that allows administrators to select
whether Corporate Directory, Global Directory, or both should be used in their network. Using both is
recommended since this will give the endpoints a failover option. If Cisco TMS is not reachable and
the Corporate Directory cannot be displayed, the Global Directory will show the 400 first entries in a
flat list.
To select which systems should get the different phone books, go to Phone Books in Cisco TMS,
click Set on Systems for a phone book, and select which endpoints should get this phone book.
Endpoints supporting both the Corporate Directory and the Global Directory will have their
Corporate Directory settings adjusted to point to the Cisco TMS server, and have the Global
Directory (the globdir.prm) file transmitted to the endpoint over HTTP at three different events:
• every time adjustments to the Set on system list is made
• at the intervals specified in the Update Frequency dropdown menu
• by a background service that by default will run every four hours if Enforce Management
Settings on Systems is turned on (Administrative Tools > Configuration > Network
Settings > TMS Services pane > Enforce Management Settings on Systems field).
This globdir.prm file will then be available if the Cisco TMS server is offline. The entries will be
showed together with the local entries on the endpoint.
Endpoints such as Cisco TelePresence System MXP and Cisco Classic (E4/B9 or newer). The
Cisco Telepresence System Integrator C Series and Cisco IP Video Phone E20 do not support
the Global Directory.
Endpoints only supporting the Corporate Directory will only have the Corporate Directory settings
set on the system. This will happen every time a change is done to the Set on system list, and at
the intervals specified in the Update Frequency dropdown menu.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 23 of 37
Page 24

Endpoints such as Cisco TelePresence System 150 MXP with L1.x or L2.x software. The Cisco
TelePresence System 150 MXP only supports the Corporate Directory.
Endpoints only supporting the Global Directory (globdir.prm) will have the Global Directory (the
globdir.prm) file transmitted to the endpoint over HTTP every time adjustments to the Set on
system list are made, and at the intervals specified in the Update Frequency dropdown menu.
Endpoints such as Cisco Classic (E3.x/B8.x and older) and Cisco TelePresence MCU (D 3.x or
newer)
Settings that will be set on the endpoints supporting Corporate Directory:
(xconfiguration) corpdir mode on
(xconfiguration) corpdir ipaddr x.x.x.x (server’s IP address)
(xconfiguration) corpdir path TMS/Public/external/phonebook/PhoneBookService.asmx
Phone Books
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 24 of 37
Page 25

Cisco TMS features
Cisco TMS features
Operator conferences
Cisco TMS Conference Control Center supports the concept of Operator Conferences. Operator
Conferences are ad hoc created conferences that can be used by conference operators to work with
individual participants in a conference outside their normally scheduled call.
This means that if a site is having a problem, or has questions, an operator can start a new
conference and add themselves and the problem site(s) to the special conference. When the Operator
is done, the Operator can send the site back to their originally scheduled call. All of this is done with
simple clicks from the Cisco TMS Conference Control Center.
Operator conference features:
• Create Operator conferences on the fly with a single click.
• Click on participants to move to an operator conference without disconnecting the site.
• If no Operator conference exists, a new one can be created automatically.
• Operators can have a default system for themselves that can be automatically added to the
conference when an Operator conference is started.
• Operators can move a participant, or multiple participants in and out of an Operator Conference at
will from the Conference Control Center.
• Multiple Operator conferences can run simultaneously.
• Participants moved to an Operator conference are still shown as participants in the scheduled
meeting, but with special icons to signal that they have been moved.
• Operator conferences will automatically clear themselves out if no longer used by the Operator’s
system.
How to set up an operator conference
Operator conferences can be set up with Cisco TMS and the Cisco TelePresence MCU.
When viewing the conference in Conference Control Center, you can move a participant to an
Operator Conference by first selecting the participant from the participant list and clicking the button
Move to Operator Conference, or right-click on the participant and choose Move to
Operator Conference. A pop-up window will appear asking you to choose an operator
system, and whether the new conference should use encryption. When you have made your selection,
click OK, and the operator conference will be created.
Note: The participant will only be moved out of their original conference when the operator is
successfully connected to the operator conference, eliminating the possibility of the participant being
moved into an empty conference.
To end the operator conference, select the participant from the operator conference and click
the button Move back, or right-click the participant and choose Move back. You may also select the
participant in the original conference and click Get back.
If the Operator Conference is not ended, the operator will still be in the conference, thereby
saving connection time if a new participant is to be pulled into the operator conference.
Provisioning directory
Provisioning was initially introduced in Cisco TelePresence Management Suite version 12.1 and Cisco
VCS version X4.1.
Provisioning allows video conferencing network administrators to create and manage mass deployable
video conferencing solutions. It uses the Cisco TMS Agent to replicate and distribute the Cisco TMS
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 25 of 37
Page 26

Cisco TMS features
Provisioning User Directory and Provisioning information from Cisco TMS via a single or clustered
Cisco VCS to endpoint devices such as the E20 and the Movi software client.
For more information concerning the use and deployment of the Provisioning, see Cisco Provisioning
deployment guide.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 26 of 37
Page 27

Troubleshooting the Cisco TMS components
Troubleshooting the Cisco TMS components
This chapter addresses the different components that Cisco TMS consists of: the five services that are
to be running at all times, the Java applet needed to show the monitoring pages, the web server
needed to display Cisco TMS as web-pages and the database were all information is stored.
Phonebook (Corporate Directory) errors
You can get the following errors on the endpoint if corporate directory is not working properly:
Message Explanation or suggested solution
Request timed out, no
response
Warning: directory data not
retrieved: 404
Warning: directory data not
retrieved: 401
TMS: No phonebook(s) set on
this system
Request timed out, no
response
The Cisco TMS server is busy, try again.
The endpoint is configured with the IP address of a different web
server than the Cisco TMS server.
The corporate directory path on the endpoint is wrong.
The “Public” virtual directory on the Cisco TMS server is not
configured to allow Anonymous Access.
The most common problem here is that anonymous access is set,
but the account used has been overwritten by a group policy. The
default IUSR user is a part of the guest account, and typically
group policies disable this account.
No phonebook(s) set on this system in Cisco TMS. Configure the
endpoint to subscribe to phonebooks in Cisco TMS.
Using NAT on the endpoint can lead to Cisco TMS not
recognizing the system and will not allow it to retrieve any phone
books.
The endpoint is configured with the IP address of a non existing web
server.
No contact with server
The IIS is restarting or in a state where corrupted messages are
received.
TMSDatabaseScannerService
The TMSDatabaseScannerService checks the status and configuration of existing systems. The
scanner will check:
The connection status
The call status
The system configuration
If a system is unavailable, the service will get that status until the next scan, or until the endpoint
sends a trap to Cisco TMS.
Note: The scanner pauses for 15 min after scan has finished.
The scanner process is a moderately CPU-intensive process for the server, and should be tuned
according to the need for updated system information in Cisco TMS. To scan one system takes from
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 27 of 37
Page 28

Troubleshooting the Cisco TMS components
two seconds up to approximately 20 seconds (worst case). This means that scanning 100 systems
might take from three minutes up to 30 minutes.
The scanner will read the system connection status and call status on every scan, but will only read
the full system configuration in intervals defined in the field System Force Refresh Interval (in
hours). The scanner will update 20 connection statuses in parallel and read five full system
configurations in parallel.
To improve response time, Cisco TMS runs an extra connection status check each 30 seconds for
systems in these categories:
Cisco TelePresence MCU
gateways
gatekeepers
bordercontrollers
recording devices
supervisors
System types included (in addition to the categories mentioned above):
Cisco TelePresence Server (TS 7010)
Cisco TelePresence System (CTS)
Symptoms
The symptoms are that the system information and system status in Cisco TMS is outdated. Systems
not responding still have the status InCall or Idle.
How to fix
1. Check the logs for symptoms or error messages at c:\Program
Files\TANDBERG\TMS\wwwTMS\Data\Logs\tmsdebug\log-TMSDatabaseScanner.txt on the
server.
2. Restarting the service or the Cisco TMS server will normally fix any problem with this service.
TMSLiveService
This service:
allocates conferences on the Cisco TelePresence MCU
issues the dial commands to the endpoints and the Cisco TelePresence MCU
monitors the activity of the participants during a conference
Symptoms
The call does not start, and the log in the Conference Control Center is almost empty.
You could have only one line that says “Created” in the log. You might have more lines there if the
conference has been changed – but none of them is related to launching the conference.
How to fix
1. Check the logs for symptoms or error messages at c:\Program
Files\TANDBERG\TMS\wwwTMS\Data\Logs\tmsdebug\log-liveservice.txt on the server.
2. Restarting the service or the Cisco TMS server will normally fix any problem with this service.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 28 of 37
Page 29

Troubleshooting the Cisco TMS components
TMSPLCMDirectoryService
This service is responsible for posting phonebooks to Polycom endpoints. The PLCM endpoint
retrieves the phonebook from this service when requested via the remote control. This is similar to
Corporate Directory in Cisco endpoints.
Symptoms
You don’t get any phonebooks on your Polycom endpoints
How to fix
1. Check the logs for symptoms or error messages at c:\Program
Files\TANDBERG\TMS\wwwTMS\Data\Logs\tmsdebug\log-plcmdir.txt on the server.
2. Restarting the service or the Cisco TMS server will normally fix any problem with this service.
TMSSchedulerService
This service is responsible for launching events at set times. Examples of events are:
System Restore
System Upgrade
Update Phonebooks
This service will also remind the TMSLiveService to start a conference if needed.
Note: TMSLiveService will keep track of all booked conferences, but loose this information if it is
restarted.
Symptoms
Scheduled events do not start.
How to fix
1. Check the logs for symptoms or error messages at c:\Program
Files\TANDBERG\TMS\wwwTMS\Data\Logs\tmsdebug\log-schedulerservice.txt on the server.
2. Restarting the service or the Cisco TMS server will normally fix any problem with this service.
TMSSnmpService (formerly TMSWatchdogServiceStarter.exe)
This service should be turned off if you have Cisco TMS set to HTTPS only. For more information, see
Implementing Secure Management.
The service
collects traps from the endpoints and adds them directly to the database.
is responsible for broadcasting SNMP messages to discover newly added systems.
1. To specify the sub ranges for where TMSSnmpService searches for new endpoints, go to
Administrative Tools > Network Settings > SNMP Broadcast/Multicast Address(es).
2. To specify the SNMP Broadcast Interval, go to Administrative Tools > Network Settings >
SNMP Broadcast Interval (in minutes). Cisco recommends setting SNMP Broadcast Interval
to broadcast 2 times a day depending on video network size. Define multiple scan ranges by
comma separating the ranges. By setting the Broadcast/Multicast Address value to 127.0.0.1,
Cisco TMS will not scan for new systems via SNMP broadcast.
To quickly find which systems are online, you can use the TMSSnmpService and send SNMP Oid
queries to systems that:
3. are known to Cisco TMS
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 29 of 37
Page 30

Troubleshooting the Cisco TMS components
4. supports SNMP
5. do not have status “No Response”, “No SNMP Response” or similar
To enable this feature:
1. Go to Administrative Tools > Network Settings.
2. Turn on the function Scan SNMP capable systems to allow quick discovery of
inaccessibility.
Furthermore, you can specify the interval, and the maximum number of missed SNMP responses
before the system will get the status No SNMP Response. If there is no response to SNMP queries,
Cisco TMS will use an HTTP connection to verify the status of the system. This feature was added in
Cisco TMS12.1.
Symptoms
• The statistics are empty.
• Cisco TMS does not receive system events.
• New systems are not automatically discovered.
How to fix
1. Make sure no other SNMP tool is running on the server, like HP Openview or other server/network
monitoring tools using Microsoft Windows’ SNMP Component.
2. Check the logs for symptoms or error messages at c:\Program
Files\TANDBERG\TMS\wwwTMS\Data\Logs\tmsdebug\log-watchdog.txt on the server.
3. Restarting the service or the Cisco TMS server will normally fix any problem with this service.
TMSServerDiagnosticsService
This service is responsible for checking:
• the server disk space,
• the database size
• that the other services are running
A Cisco TMS ticket is opened if:
• a service is not running
• free disk space is less than 10%
• the database is 90% of max size
Symptoms
Tickets are not opened if:
• the service is not running
• there is less than 10% free disk space
• the database is larger than 90% of its max size
How to fix
1. Check the logs for symptoms or error messages at c:\Program
Files\TANDBERG\TMS\wwwTMS\Data\Logs\tmsdebug\log-TMSServerDiagnosticsService.txt on
the server.
2. Restarting the service or the Cisco TMS server will normally fix any problem with this service.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 30 of 37
Page 31

Troubleshooting the Cisco TMS components
Cisco TMS Database Management Service (optional)
This service is installed by the Cisco TMS backup utility and is responsible for doing scheduled
backups.
Symptoms
If the database is not automatically backed up when scheduled, make sure that this service is installed
and running.
How to fix
Start up the Cisco TMS Database Management Utility and verify the settings in the Automatic
Backup page (Start > All Programs > TANDBERG). To automatically install the service, select the
Enable automatic backup check box.
Note: The Cisco TMS Backup Utility was a separate installation found on the Cisco TMS CD that
installed this service. The Cisco TMS Backup Utility was removed from the Cisco TMS CD in Cisco
TMS 12.1. If this utility was installed prior to this version, and because it was a separate installation,
the Cisco TMS 12.1 (or later) installation will not remove this utility. To remove, go to Add and
Remove Programs, and remove the utility appropriately. Note that when removed, the service will
still remain but be disabled.
TMSAgentService
This service starts the local Cisco TMS Agent. The Cisco TMS Agent is needed for provisioning Movi
clients from version 2.0 and newer, and the E20 endpoint.
Symptoms
You are unable to browse to or create and edit groups or users within Cisco TMS on page Systems >
Provisioning > Directory.
How to fix
• Check the logs for symptoms or error messages at c:\Program
Files\TANDBERG\TMS\wwwTMS\Data\Logs\tmsdebug\ log-tmsagent.txt on the server.
• Restarting the service or the Cisco TMS server will normally fix any problem with this service.
See the Cisco TMS Provisioning deployment guide and the Cisco TMS Provisioning troubleshooting
guide for further specific diagnostics and troubleshooting of the Cisco TMS Agent.
The Web server
Cisco TMS uses Microsoft Internet Information Services to make Cisco TMS available as a webpage.
Since version 9.0, Cisco TMS has been developed with the Microsoft .NET platform and some extra
components are therefore required on the IIS for Cisco TMS to work properly. ASP.NET version 3.5 is
currently in use. These components are installed by Windows during the Cisco TMS installation as
they are required by Cisco TMS, but not Cisco specific. All web-related files will be stored on the
server in the location you specified during the installation. The default location is c:\Program
Files\TANDBERG\TMS\.
In the Internet Information Server Manager you will see that the installation has created five virtual
directories.
TMS
The Application that handles the Cisco TMS web interface.
The virtual directory for this component on the IIS is: http://serverIP/tms.
This component should have the Directory Security set to Windows Integrated Authentication
(default), Basic Authentication or both.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 31 of 37
Page 32

Troubleshooting the Cisco TMS components
tms/public
Handles Corporate Directory for Cisco endpoints.
Handles http traps from Cisco TelePresence System MXP and Cisco TelePresence MCU
systems.
The virtual directory for this component on the IIS is: http://serverIP/tms/public.
This component should have the Directory Security set to Anonymous Access.
pwx
Handles HTTP traps from Polycom systems.
Handles phonebooks for Polycom systems.
The virtual directory for this component on the IIS is: http://serverIP/pwx.
This component should have the Directory Security set to Anonymous Access.
This component can be removed if this Cisco TMS installation will not be used with Polycom
endpoints.
XAPSite
Handles communication between Cisco TMS and pre version 7 MGCs.
The virtual directory for this component on the IIS is: http://serverIP/XAPSite.
This component should have the Directory Security set to Anonymous Access.
This component can be removed if this Cisco TMS installation will not be used with a Polycom
MGC with version 6.x or older.
TMSConferenceAPI
This component warns the old Exchange API (Cisco TMS 7 and 8) that it must be upgraded..
The virtual directory for this component on the IIS is: http://serverIP/TMSConferenceAPI.
This component should have the Directory Security set to Anonymous Access.
This component can be removed if this Cisco TMS installation does not have an older Exchange
integration (Cisco TMS 8 or older).
TMSAgent
Handles the proxies for Cisco TMS Agent requests.
The virtual directory for this component on the IIS is : http://serverIP/TMSAgent.
This component should have the Directory Security set to Windows Integrated Authentication
(default), Basic Authentication or both.
AnalyticalExtension (if utilized)
Handles the interface between the Cisco TMS and Analytical Extension application.
The virtual directory for this component on the IIS is: http://serverIP/AnalyticalExtension.
The component should have the Directory Security set to Windows Integrated Authentication
(default).
Symptoms
• You cannot access the Cisco TMS page.
• The corporate directory on the Cisco endpoints does not work and statistics from Cisco
TelePresence System MXP endpoints are empty.
• Statistics from Polycom endpoints are empty.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 32 of 37
Page 33

Troubleshooting the Cisco TMS components
How to fix
• Check that IIS is running.
• Check that you can access the default webpage http://TMSServerName.
• Check that the virtual directories above exist on the Cisco TMS server.
• Check that they are pointing to valid directories on the Cisco TMS server.
• Check that the permission settings are correct according to the list above.
• Check that the IIS allows for running .net extensions.
• Logs are found in c:\Program Files\TANDBERG\TMS\wwwTMS\Data\Logs\tmsdebug\log-web.txt
on the Cisco TMS server.
Java Applet – Monitoring
What it does
The Sun Java applet version is used for displaying dynamic information in Conference Control
Center, Graphical Monitor and Map Monitor. The Java applet adds functionality related to graphics,
clicking, right-clicking and drag-and-drop actions.
Symptoms
• When entering the Conference Control Center, Graphical Monitor or Map Monitor, you are
prompted for a username and password.
• The applet does not load, and there is no Java (coffee cup) icon in the notification area.
• The applet does not load, but Java is installed.
• The applet loads very slowly.
• Conference snapshots are not displayed on some clients.
How to fix
Authentication
The Java Applet will require the users to authenticate themselves if the Cisco TMS server is not part of
the domain (or a trusted domain) the user is logged into. The solution is to make the Cisco TMS server
part of the domain, or insert the username and password when prompted for each session.
Java installation
The Java virtual machine is not installed on the machine, and the client PC does not have direct
access to the Internet to download it automatically. To retrieve:
Install Java from the Cisco TMS CD.
Go to http://www.java.com/ to download and install Java.
Proxy issues
A proxy server might be preventing the Java applet from retrieving the necessary data from the Cisco
TMS server. To open the Java console, right-click the Java icon in the notification area and select
Open Console. Error messages stating Unknown source will be displayed. To solve this problem, try
one or more of the points below:
If using the Cisco TMS server’s IP address when accessing Cisco TMS, try again with the Cisco
TMS server’s host name.
Configure the Java client through the Java Control Panel to use Direct Connection rather than
using the browser’s proxy settings.
The proxy server may have to be configured to allow this kind of traffic from the Cisco TMS server
to the clients.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 33 of 37
Page 34

Troubleshooting the Cisco TMS components
Slow or incomplete loading
The applet will normally be finished loading within 5 seconds after the Monitoring link is pressed. If you
experience a significantly higher loading time, try the points below:
Turn off Caching in Java and delete the existing temporary files.
1. Open the Java Control Panel,
2. Click the General tab.
3. Click Settings, click View Applets.
4. De-select Enable Caching in the lower left corner.
5. Click Ok.
6. Click Delete Files.
7. Select all check boxes.
8. Click Ok.
9. Click Ok.
10. Click Ok.
Remove old or duplicate Java clients from Internet Explorer.
1. Click Tools in the Internet Explorer menu
2. Click the Programs tab
3. Click Manage Add-ons
4. Disable all old or duplicate Java plug-ins
Remove Google Desktop. We have seen issues where Google Desktop is conflicting with the
Java plug-in and significantly increasing the loading time of Java applets. Other desktop search
engines like MSN Search does not show the same symptoms.
If using Java Runtime Environment (JRE) version 6, update 15 or later, you will need to de-select
Enable the next generation Java plug-in… under Advanced on the Java Control Panel to
make the Graphic and Map Monitor work as expected.
The database
The database is where all information in use by Cisco TMS is stored except software files for system
upgrade and the services’ log files. The database is called tmsng and can run on SQL 2005 servers.
During the installation of Cisco TMS the sa account on the SQL server is automatically chosen to
create and access the database. A different account can be specified by choosing the Custom
installation. The account used to run and upgrade Cisco TMS must have db_owner permissions to the
tmsng database, while a user that also has access to master.mdf is required for creating the tmsng
database the first time.
Symptoms
Cisco TMS does not load and/or you get a stack trace declaring that the SQL server is unavailable:
SQL Server does not exist or access denied is displayed
How to fix
Make sure that the SQL server is running. This can be done by checking the SQL agent of the
server, or going into services and verify that the MSSQLSERVER service is running.
Run an osql script towards the database and see if it returns any data. This script will return the
number of systems in the Cisco TMS database:
• Depending on the SQL configuration, run one of the commands below from the Cisco TMS
server itself.
• osql -E -d tmsng -Q "select count(*) from objsystem"
• osql -E -S .\SQLTMS -d tmsng -Q "select count(*) from objsystem"
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 34 of 37
Page 35

Troubleshooting the Cisco TMS components
Verify that the information Cisco TMS uses to connect to the database is correct. This information
was historically only stored in the registry, but is now also stored encrypted in the web.config file.
It is therefore recommended to use the Cisco TMS Tools application, found under TANDBERG in
the Start menu of the Cisco TMS server, to change and verify this information.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 35 of 37
Page 36

Related documents
Related documents
The following table lists documents and web sites referenced in this document. All product
documentation can be found on our web site.
No. Document reference or location Name
1 D14389.03. Dated May 2010 Cisco TMS Installation Guide
2 D50520.04. December 2010 Cisco TelePresence Implementing Secure Management
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 36 of 37
Page 37

Disclaimers and notices
Disclaimers and notices
THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE
WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO
BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST
TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE
INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS
REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR
CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California,
Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981,
Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE
SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL
WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR
TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING
OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF
THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of
Cisco's trademarks can be found at www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their
respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other
company. (1005R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and
phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the
document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is
unintentional and coincidental.
Cisco TMS Administration Guide Page 37 of 37
 Loading...
Loading...