Page 1
DS 6608
Product Reference Guide
Page 2

Page 3

DS 6608
Product Reference Guide
72-67563-02
Revision A
June 2004
Page 4

© 2004 by Symbol Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced or used in any form, or by any electrical or mechanical means, without permission in writing from
Symbol. This includes electronic or mechanical means, such as photocopying, recording, or information storage and retrieval systems. The material
in this manual is subject to change without notice.
The software is provided strictly on an “as is” basis. All software, including firmware, furnished to the user is on a licensed basis. Symbol grants
to the user a non-transferable and non-exclusive license to use each software or firmware program delivered hereunder (licensed program). Except
as noted below, such license may not be assigned, sublicensed, or otherwise transferred by the user without prior written consent of Symbol. No
right to copy a licensed program in whole or in part is granted, except as permitted under copyright law. The user shall not modify, merge, or
incorporate any form or portion of a licensed program with other program material, create a derivative work from a licensed program, or use a
licensed program in a network without written permission from Symbol. The user agrees to maintain Symbol’s copyright notice on the licensed
programs delivered hereunder and to include the same on any authorized copies it makes, in whole or in part. The user agrees not to decompile,
disassemble, decode, or reverse engineer any licensed program delivered to the user or any portion thereof.
Symbol reserves the right to make changes to any software or product to improve reliability, function, or design.
Symbol does not assume any product liability arising out of, or in connection with, the application or use of any product, circuit, or application
described herein.
No license is granted, either expressly or by implication, estoppel, or otherwise under any Symbol Technologies, Inc., intellectual property rights.
An implied license only exists for equipment, circuits and subsystems contained in Symbol products.
Symbol, Spectrum One and Spectrum24 are registered trademarks of Symbol Technologies, Inc. Other product names mentioned in this manual
may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies and are hereby acknowledged.
Symbol Technologies, Inc.
One Symbol Plaza
Holtsville, New York 11742-1300
http://www.symbol.com
Page 5
Contents
About This Guide
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xv
Chapter Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xv
Notational Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xv
Related Publications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
Service Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
Symbol Support Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
Chapter 1. Getting Started
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Unpacking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-3
Setting Up the Digital Scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
Installing the Interface Cable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
Removing the Interface Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
Connecting a Synapse Cable Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-5
Connecting Power (if required) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-5
Configuring the Digital Scanner. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-5
Mounting the Digital Scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
Desk Mount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
Wall Mount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
Chapter 2. Scanning
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Beeper Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-4
Page 6

DS 6608 Product Reference Guideiv
LED Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-5
Scanning in Hand-Held Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-6
Scanning with the Digital Scanner. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-6
Aiming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-7
Scanning in Hands-Free Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-8
Decode Zones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-9
DS 6608 Standard Range Digital Scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-9
DS 6608 High Density Digital Scanner. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-10
Chapter 3. Maintenance and Technical Specifications
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-3
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-3
Technical Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-5
Digital Scanner Signal Descriptions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-6
Chapter 4. User Preferences
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Scanning Sequence Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-3
Errors While Scanning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-3
User Preferences Parameter Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-4
User Preferences. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-5
Set Default Parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-5
Parameter Scanning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-5
Beeper Tone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-6
Beeper Volume . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-7
Power Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-7
Time Delay to Low Power Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-8
Trigger Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-9
Decode Session Timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-10
Timeout Between Decodes, Same Symbol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-10
Beep After Good Decode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-11
Scanstand Session Timeout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-11
Chapter 5. Decoding Preferences
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Scanning Sequence Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-3
Errors While Scanning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-3
Decoding Preferences Parameter Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-4
Decoding Preferences. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-5
Decoding Illumination. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-5
Decode Aiming Pattern. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-5
Chapter 6. Keyboard Wedge Interface
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
Connecting a Keyboard Wedge Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-3
Keyboard Wedge Parameter Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-4
Page 7

Keyboard Wedge Host Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-5
Keyboard Wedge Host Types. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-5
Keyboard Wedge Country Types (Country Codes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-6
Ignore Unknown Characters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-8
Keystroke Delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-8
Intra-Keystroke Delay. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-9
Alternate Numeric Keypad Emulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-9
Caps Lock On . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-10
Caps Lock Override. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-10
Convert Wedge Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-11
Function Key Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-11
FN1 Substitution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-12
Send Make and Break . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-12
Keyboard Maps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-13
ASCII Character Set for Keyboard Wedge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-15
Chapter 7. RS-232 Interface
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
Connecting an RS-232 Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-4
RS-232 Parameter Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-5
RS-232 Host Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-6
RS-232 Host Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-8
Baud Rate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-9
Parity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-11
Stop Bit Select . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-12
Data Bits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-12
Check Receive Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-13
Hardware Handshaking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-14
Hardware Handshaking (continued). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-15
Software Handshaking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-16
Host Serial Response Time-out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-17
RTS Line State . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-18
Beep on <BEL> . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-18
Intercharacter Delay. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-19
Nixdorf Beep/LED Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-20
Ignore Unknown Characters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-20
ASCII Character Set for RS-232 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-21
Contents v
Chapter 8. USB Interface
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-3
Connecting a USB Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-3
USB Parameter Defaults. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-4
USB Host Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-5
USB Device Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-5
USB Country Keyboard Types (Country Codes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-6
USB Keystroke Delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-8
USB CAPS Lock Override . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-8
Page 8

DS 6608 Product Reference Guidevi
USB Ignore Unknown Characters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-9
Emulate Keypad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-9
USB Keyboard FN 1 Substitution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-10
Function Key Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-10
Simulated Caps Lock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-11
Convert Case. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-11
ASCII Character Set for USB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-12
Chapter 9. IBM 468X/469X Interface
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
Connecting to an IBM 468X/469X Host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-3
IBM Parameter Defaults. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-4
IBM 468X/469X Host Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-5
Port Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-5
Convert Unknown to Code 39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-6
Chapter 10. Wand Emulation Interface
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-3
Connecting Using Wand Emulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-3
Wand Emulation Parameter Defaults. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-4
Wand Emulation Host Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-5
Wand Emulation Host Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-5
Leading Margin (Quiet Zone) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-6
Polarity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-6
Ignore Unknown Characters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-8
Convert All Bar Codes to Code 39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-8
Convert Code 39 to Full ASCII . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-9
Chapter 11. Scanner Emulation Interface
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-3
Connecting Using Scanner Emulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-3
Scanner Emulation Parameter Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-4
Scanner Emulation Host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-5
Scanner Emulation Host Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-5
Beep Style. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-5
Parameter Pass-Through . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-6
Convert Newer Code Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-7
Module Width. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-8
Convert All Bar Codes to Code 39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-8
Code 39 Full ASCII Conversion. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-9
Transmission Timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-9
Ignore Unknown Characters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-10
Leading Margin. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-11
Check For Decode LED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-12
Chapter 12. 123 Scan
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-3
Page 9

Communication with 123Scan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12-3
123Scan Parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12-3
Chapter 13. Symbologies
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-5
Scanning Sequence Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-5
Errors While Scanning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-5
Symbology Parameter Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-6
UPC/EAN. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-10
Enable/Disable UPC-A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-10
Enable/Disable UPC-E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-10
Enable/Disable UPC-E1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-11
Enable/Disable EAN-8/JAN-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-11
Enable/Disable EAN-13/JAN-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-12
Enable/Disable Bookland EAN. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-12
Decode UPC/EAN/JAN Supplementals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-13
UPC/EAN/JAN Supplemental Redundancy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-14
Transmit UPC-A Check Digit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-15
Transmit UPC-E Check Digit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-15
Transmit UPC-E1 Check Digit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-16
UPC-A Preamble . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-16
UPC-E Preamble . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-17
UPC-E1 Preamble . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-18
Convert UPC-E to UPC-A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-18
Convert UPC-E1 to UPC-A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-19
EAN-8/JAN-8 Extend . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-19
UCC Coupon Extended Code. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-20
Code 128. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-20
Enable/Disable Code 128. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-20
Enable/Disable UCC/EAN-128 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-21
Enable/Disable ISBT 128 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-21
Code 39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-22
Enable/Disable Trioptic Code 39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-22
Convert Code 39 to Code 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-23
Code 32 Prefix. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-23
Set Lengths for Code 39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-24
Code 39 Check Digit Verification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-25
Transmit Code 39 Check Digit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-26
Code 39 Full ASCII Conversion. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-26
Code 39 Buffering (Scan & Store) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-27
Code 93. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-29
Enable/Disable Code 93. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-29
Set Lengths for Code 93. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-30
Code 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-31
Code 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-31
Set Lengths for Code 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-32
Code 11 Check Digit Verification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-33
Contents vii
Page 10

DS 6608 Product Reference Guideviii
Transmit Code 11 Check Digits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-34
Interleaved 2 of 5 (ITF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-34
Enable/Disable Interleaved 2 of 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-34
Set Lengths for Interleaved 2 of 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-35
I 2 of 5 Check Digit Verification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-36
Transmit I 2 of 5 Check Digit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-37
Convert I 2 of 5 to EAN-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-37
Discrete 2 of 5 (DTF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-38
Enable/Disable Discrete 2 of 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-38
Set Lengths for Discrete 2 of 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-38
Codabar (NW - 7) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-39
Enable/Disable Codabar. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-39
Set Lengths for Codabar. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-40
CLSI Editing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-41
NOTIS Editing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-41
MSI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-42
Enable/Disable MSI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-42
Set Lengths for MSI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-42
MSI Check Digits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-43
Transmit MSI Check Digit(s). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-44
MSI Check Digit Algorithm. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-44
Postal Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-45
US Postnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-45
US Planet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-45
UK Postal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-46
Transmit UK Postal Check Digit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-46
Japan Postal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-47
Australian Postal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-47
Dutch Postal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-48
Transmit US Postal Check Digit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-48
RSS (Reduced Space Symbology). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-49
RSS-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-49
RSS Limited . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-49
RSS Expanded. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-50
Convert RSS to UPC/EAN. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-50
Composite. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-51
Composite CC-C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-51
Composite CC-A/B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-51
Composite TLC-39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-52
UPC Composite Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-53
Composite Beep Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-54
UCC/EAN Code 128 Emulation Mode for UCC/EAN Composite Codes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-54
2D Symbologies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-55
Enable/Disable PDF417 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-55
Enable/Disable MicroPDF417. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-55
Code 128 Emulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-56
Data Matrix. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-57
Maxicode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-57
Page 11

QR Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-58
Redundancy Level. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-59
Security Level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-61
Intercharacter Gap Size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-62
Report Version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-62
Macro PDF Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-63
Flush Macro Buffer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-63
Abort Macro PDF Entry. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13-63
Chapter 14. Miscellaneous Scanner Options
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-3
Scanning Sequence Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-3
Errors While Scanning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-3
Miscellaneous Scanner Parameter Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-4
Miscellaneous Scanner Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-5
Transmit Code ID Character . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-5
Prefix/Suffix Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-6
Scan Data Transmission Format. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-7
FN1 Substitution Values. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-8
Transmit “No Read” Message . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-9
Synapse Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-10
Contents ix
Chapter 15. Advanced Data Formatting
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-3
Rules: Criteria Linked to Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-3
Using ADF Bar Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-4
ADF Bar Code Menu Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-4
Rule 1: The Code 128 Scanning Rule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-5
Rule 2: The UPC Scanning Rule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-5
Alternate Rule Sets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-5
Rules Hierarchy (in Bar Codes). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-6
Default Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-7
Special Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-8
Pause Duration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-8
Begin New Rule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-8
Save Rule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-8
Erase. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-9
Quit Entering Rules. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-9
Disable Rule Set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-10
Criteria . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-11
Code Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-11
Code Lengths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-17
Message Containing A Specific Data String . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-22
Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-27
Send Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-27
Setup Field(s) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-30
Modify Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-36
Page 12

DS 6608 Product Reference Guidex
Pad Data with Spaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-37
Pad Data with Zeros. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-41
Beeps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-46
Send Keystroke (Control Characters and Keyboard Characters) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-46
Send Right Control Key. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-82
Send Graphic User Interface (GUI) Characters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-83
Turn On/Off Rule Sets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-88
Alphanumeric Keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-90
Appendix A. Standard Default Parameters
Appendix B. Programming Reference
Symbol Code Identifiers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-3
AIM Code Identifiers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-4
Appendix C. Sample Bar Codes
Code 39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-3
UPC/EAN. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-3
UPC-A, 100 %. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-3
EAN-13, 100 %. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-3
Code 128. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-3
Interleaved 2 of 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-4
RSS 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-4
PDF417 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-4
Data Matrix. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-4
Maxicode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-5
QR Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-5
US Postnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-5
UK Postal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-5
Appendix D. Numeric Bar Codes
Numeric Bar Codes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-3
Cancel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-4
Appendix E. ASCII Character Sets
Glossary
Index
Page 13
About This Guide
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xv
Chapter Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xv
Notational Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xv
Related Publications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
Service Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
Symbol Support Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
Page 14

DS 6608 Product Reference Guidexiv
Page 15

Introduction
The DS 6608 Product Reference Guide provides general instructions for setting up, operating, maintaining, and troubleshooting the
DS 6608 Standard Range and DS 6608 High Density digital scanners.
Chapter Descriptions
• Chapter 1, Getting Started provides a product overview, unpacking instructions, and cable connection information.
• Chapter 2, Scanning describes parts of the digital scanner, beeper and LED definitions, and how to use the digital scanner
in hand-held and hands-free modes.
• Chapter 3, Maintenance and Technical Specifications provides information on how to care for the digital scanner,
troubleshooting, and technical specifications.
• Chapter 4, User Preferences provides programming bar codes for selecting user preference features for the digital scanner.
• Chapter 5, Decoding Preferences provides programming bar codes for selecting digital scanner preference features.
• Chapter 6, Keyboard Wedge Interface describes how to set up a Keyboard Wedge interface with the digital scanner.
• Chapter 7, RS-232 Interface describes how to set up the digital scanner with an RS-232 host, such as point-of-sale devices,
host computers, or other devices with an available RS-232 port.
• Chapter 8, USB Interface describes how to set up the digital scanner with a USB host.
• Chapter 9, IBM 468X/469X Interface describes how to set up the digital scanner with IBM 468X/469X POS systems.
• Chapter 10, Wand Emulation Interface describes how to set up the digital scanner with a Wand Emulation host when Wand
Emulation communication is needed.
• Chapter 11, Scanner Emulation Interface describes how to set up the digital scanner with an Undecoded Scanner Emulation
host.
• Chapter 12, 123 Scan describes the 123Scan PC-based scanner configuration tool, and provides the bar code to scan to
communicate with the 123Scan program.
• Chapter 13, Symbologies describes all symbology features and provides the programming bar codes necessary for selecting
these features for the digital scanner.
• Chapter 14, Miscellaneous Scanner Options includes commonly used bar codes to customize how data is transmitted to the
host device.
• Chapter 15, Advanced Data Formatting (ADF) describes how to customize scanned data before transmitting to the host.
• Chapter A, Standard Default Parameters provides a table of all host devices and miscellaneous scanner defaults.
• Chapter B, Programming Reference provides a table of AIM code identifiers, ASCII character conversions, and keyboard
maps.
• Chapter C, Sample Bar Codes includes sample bar codes.
• Chapter D, Numeric Bar Codes includes the numeric bar codes to scan for parameters requiring specific numeric values.
• Chapter E, ASCII Character Sets provides ASCII character value tables.
xv
Notational Conventions
The following conventions are used in this document:
• Bullets (•) indicate:
• action items
• lists of alternatives
• lists of required steps that are not necessarily sequential.
• Sequential lists (e.g., those that describe step-by-step procedures) appear as numbered lists.
Page 16

DS 6608 Product Reference Guidexvi
• Throughout the programming bar code menus, asterisks (*) are used to denote default parameter settings.
* Indicates Default
*Baud Rate 9600
Feature/Option
Related Publications
The DS 6608 Quick Start Guide, p/n 72-67311-xx, provides general information for getting started with the digital scanner, and
includes basic set up and operation instructions.
For the latest versions of the DS 6608 Quick Start Guide and Product Reference Guide go to:
http://www.symbol.com/manuals.
Service Information
If you have a problem with your equipment, contact the Symbol Support Center for your region. See page xvi for contact information.
Before calling, have the model number, serial number, and several of your bar code symbols at hand.
Call the Support Center from a phone near the scanning equipment so that the service person can try to talk you through your problem.
If the equipment is found to be working properly and the problem is symbol readability, the Support Center will request samples of
your bar codes for analysis at our plant.
If your problem cannot be solved over the phone, you may need to return your equipment for servicing. If that is necessary, you will
be given specific directions.
Symbol Technologies is not responsible for any damages incurred during shipment if the approved shipping
container is not used. Shipping the units improperly can possibly void the warranty. If the original shipping
Note
container was not kept, contact Symbol to have another sent to you.
Symbol Support Center
For service information, warranty information, or technical assistance contact or call the Symbol Support Center in:
United States
Symbol Technologies, Inc.
One Symbol Plaza
Holtsville, New York 11742-1300
1-800-653-5350
United Kingdom
Symbol Technologies
Symbol Place
Winnersh Triangle, Berkshire RG41 5TP
United Kingdom
0800 328 2424 (Inside UK)
+44 118 945 7529 (Outside UK)
Canada
Symbol Technologies Canada, Inc.
2540 Matheson Boulevard East
Mississauga, Ontario, Canada L4W 4Z2
905-629-7226
Asia/Pacific
Symbol Technologies Asia, Inc (Singapore Branch)
230 Victoria Street #05-07/09
Bugis Junction Office Tower
Singapore 188024
Tel : +65-6796-9600
Fax : +65-6337-6488
Page 17

xvii
Australia
Symbol Technologies Pty. Ltd.
432 St. Kilda Road
Melbourne, Victoria 3004
1-800-672-906 (Inside Australia)
+61-3-9866-6044 (Outside Australia)
Denmark/Danmark
Symbol Technologies AS
Dr. Neergaardsvej 3
2970 Hørsholm
7020-1718 (Inside Denmark)
+45-7020-1718 (Outside Denmark)
Finland/Suomi
Oy Symbol Technologies
Kaupintie 8 A 6
FIN-00440 Helsinki, Finland
9 5407 580 (Inside Finland)
+358 9 5407 580 (Outside Finland)
Germany/Deutchland
Symbol Technologies GmbH
Waldstrasse 66
D-63128 Dietzenbach, Germany
6074-49020 (Inside Germany)
+49-6074-49020 (Outside Germany)
Austria/Österreich
Symbol Technologies Austria GmbH
Prinz-Eugen Strasse 70 / 2.Haus
1040 Vienna, Austria
01-5055794-0 (Inside Austria)
+43-1-5055794-0 (Outside Austria)
Europe/Mid-East Distributor Operations
Contact your local distributor or call
+44 118 945 7360
France
Symbol Technologies France
Centre d'Affaire d'Antony
3 Rue de la Renaissance
92184 Antony Cedex, France
01-40-96-52-21 (Inside France)
+33-1-40-96-52-50 (Outside France)
Italy/Italia
Symbol Technologies Italia S.R.L.
Via Cristoforo Columbo, 49
20090 Trezzano S/N Navigilo
Milano, Italy
2-484441 (Inside Italy)
+39-02-484441 (Outside Italy)
Latin America Sales Support
2730 University Dr.
Coral Springs, FL 33065 USA
1-800-347-0178 (Inside United States)
+1-954-255-2610 (Outside United States)
954-340-9454 (Fax)
Netherlands/Nederland
Symbol Technologies
Kerkplein 2, 7051 CX
Postbus 24 7050 AA
Varsseveld, Netherlands
315-271700 (Inside Netherlands)
+31-315-271700 (Outside Netherlands)
Mexico/México
Symbol Technologies Mexico Ltd.
Torre Picasso
Boulevard Manuel Avila Camacho No 88
Lomas de Chapultepec CP 11000
Mexico City, DF, Mexico
5-520-1835 (Inside Mexico)
+52-5-520-1835 (Outside Mexico)
Norway/Norge
Symbol’s registered and mailing address:
Symbol Technologies Norway
Hoybratenveien 35 C
N-1055 OSLO, Norway
Symbol’s repair depot and shipping address:
Symbol Technologies Norway
Enebakkveien 123
N-0680 OSLO, Norway
+47 2232 4375
Page 18

DS 6608 Product Reference Guidexviii
South Africa
Symbol Technologies Africa Inc.
Block B2
Rutherford Estate
1 Scott Street
Waverly 2090 Johannesburg
Republic of South Africa
11-809 5311 (Inside South Africa)
+27-11-809 5311 (Outside South Africa)
Sweden/Sverige
“Letter” address:
Symbol Technologies AB
Box 1354
S-171 26 SOLNA
Sweden
Visit/shipping address:
Symbol Technologies AB
Solna Strandväg 78
S-171 54 SOLNA
Sweden
Spain/España
Symbol Technologies S.L.
Avenida de Bruselas, 22
Edificio Sauce
Alcobendas, Madrid 28108
Spain
91 324 40 00 (Inside Spain)
+34 91 324 40 00 (Outside Spain)
Fax: +34.91.324.4010
Switchboard: 08 445 29 00 (domestic)
Call Center: +46 8 445 29 29 (international)
Support E-Mail: Sweden.Support@se.symbol.com
If you purchased your Symbol product from a Symbol Business Partner, contact that Business Partner for service.
Page 19
Getting Started
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Unpacking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-3
Setting Up the Digital Scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
Installing the Interface Cable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
Removing the Interface Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
Connecting a Synapse Cable Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-5
Connecting Power (if required) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-5
Configuring the Digital Scanner. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-5
Mounting the Digital Scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
Desk Mount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
Wall Mount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
Page 20

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide1-2
Page 21
Getting Started 1-3
Introduction
The DS 6608 combines superior 1D and 2D omnidirectional bar code scanning and advanced ergonomics to provide the best value in
a digital scanner. Whether in hand-held mode or hands-free mode in a stand, the digital scanner ensures comfort and ease of use for
extended periods of time.
Figure 1-1. DS 6608 Digital Scanner
The digital scanner supports:
• Keyboard Wedge connection to a host. The host interprets scanned data as keystrokes. This interface supports the following
international keyboards (for Windows
Swedish, UK English, Portuguese-Brazilian, and Japanese.
• Standard RS-232 connection to a host. Scan bar code menus to set up proper communication of the digital scanner with the
host.
• USB connection to a host. The digital scanner autodetects a USB host and defaults to the HID keyboard interface type. Select
other USB interface types by scanning programming bar code menus.This interface supports the following international
keyboards (for Windows
English, Portuguese-Brazilian, and Japanese.
• Connection to IBM 468X/469X hosts. Scan bar code menus to set up communication of the digital scanner with the IBM
terminal.
• Wand Emulation connection to a host. The digital scanner is connected to a portable data terminal, a controller, or host
which collects the data as wand data and decodes it.
• Scanner Emulation connection to a host. The digital scanner is connected to a portable data terminal, a controller which
collects the data and interprets it for the host.
• Synapse capability which allows connection to a wide variety of host systems using a Synapse and Synapse adapter cable.
The digital scanner autodetects the host.
• Configuration via 123Scan.
®
environment): North America, German, French, French Canadian, Spanish, Italian, Swedish, UK
®
environment): North America, German, French, French Canadian, Spanish, Italian,
Unpacking
Remove the digital scanner from its packing and inspect it for damage. If the digital scanner was damaged in transit, call the Symbol
Support Center at one of the telephone numbers listed on page xvi. KEEP THE PACKING. It is the approved shipping container; use
this to return the equipment for servicing.
Page 22
DS 6608 Product Reference Guide1-4
Setting Up the Digital Scanner
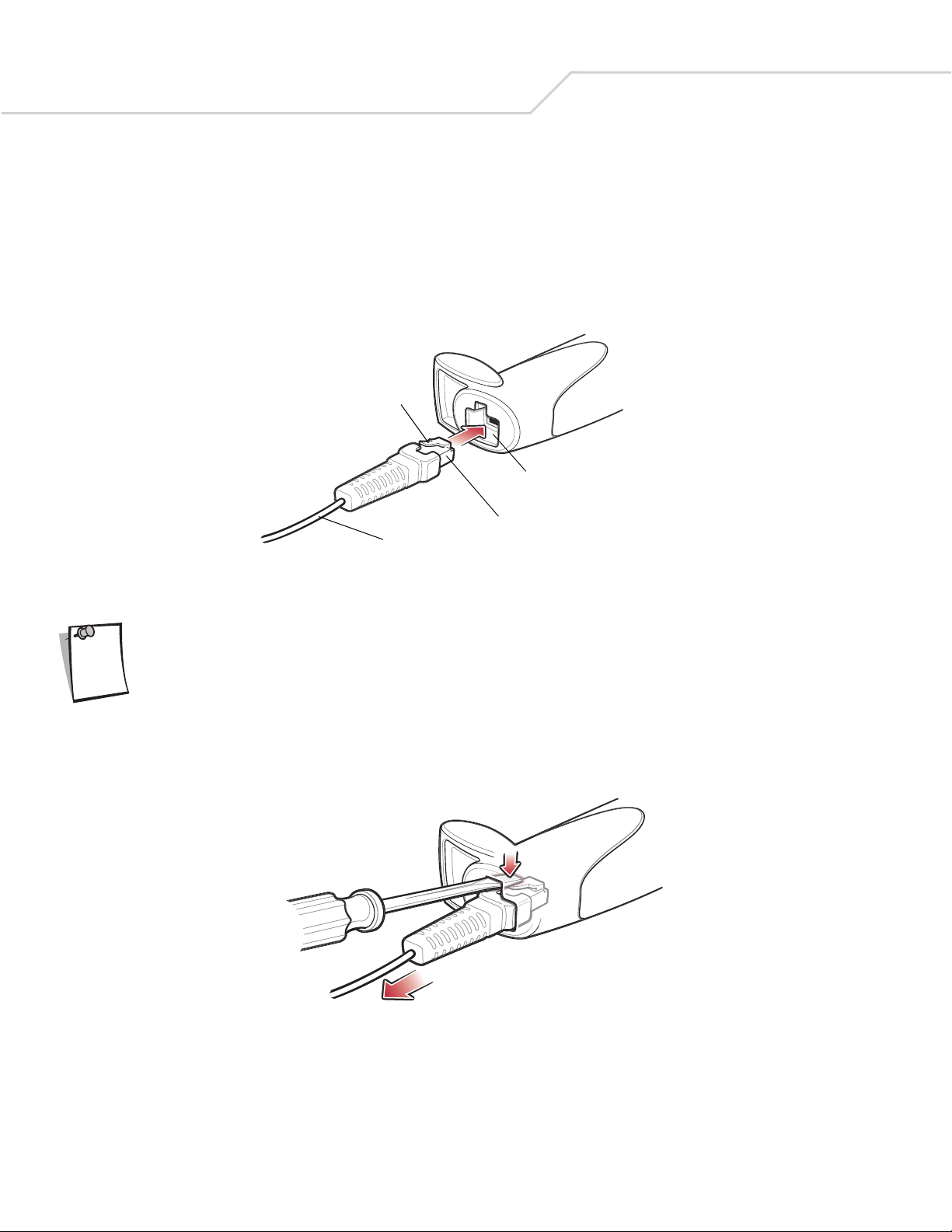
Installing the Interface Cable
1. Plug the interface cable modular connector into the cable interface port on the bottom of the scanner handle. (See Figure 1-
2.)
2. Gently tug the cable to ensure the connector is properly secured.
3. Connect the other end of the interface cable to the host (see the specific host chapter for information on host connections).
Clip
Cable interface port
Interface cable modular connector
To ho st
Figure 1-2. Installing the Cable
Different cables are required for different hosts. The connectors illustrated in each host chapter are
examples only. Connectors vary from those illustrated, but the steps to connect the digital scanner remain
Note
the same.
Removing the Interface Cable
1. Using the tip of a screwdriver, depress the cable’s modular connector clip.
Figure 1-3. Removing the Cable
2. Carefully slide out the cable.
3. Follow the steps for Installing the Interface Cable on page 1-4 to connect a new cable.
Page 23
Getting Started 1-5
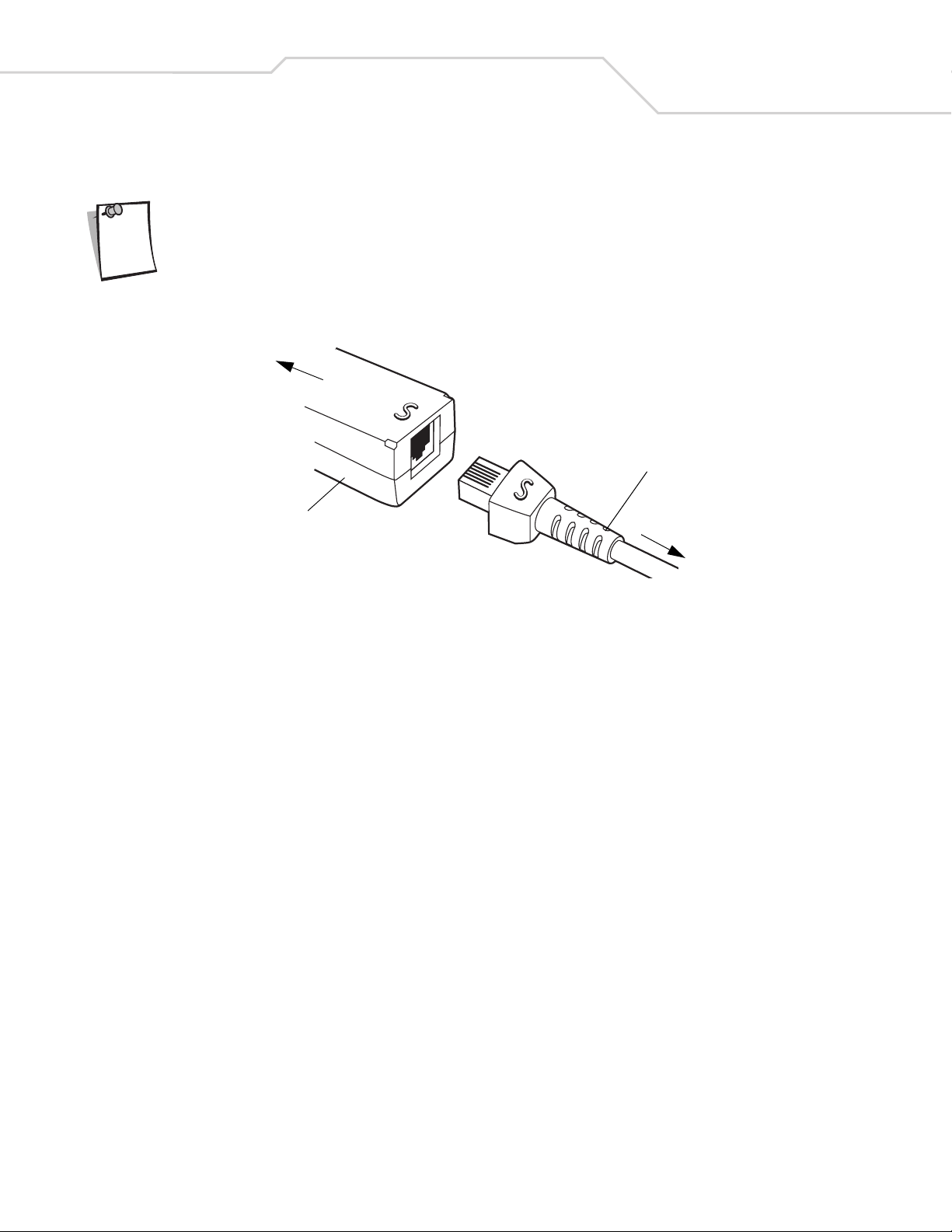
Connecting a Synapse Cable Interface
Refer to the Synapse Interface Guide provided with the Synapse cable for detailed setup instructions.
Note
Symbol’s Synapse Smart Cables enable interfacing to a variety of hosts. The Synapse cable has built-in intelligence to detect that
host.
To ho st
Synapse Adapter Cable
Synapse Smart Cable
To digital scanner
Figure 1-4. Synapse Cable Connection
1. Plug the Synapse adapter cable (p/n 25-32463-xx) into the bottom of the digital scanner, as described in Installing the
Interface Cable on page 1-4.
2. Align the ‘S’ on the Synapse adapter cable with the ‘S’ on the Synapse Smart Cable and plug the cable in.
3. Connect the other end of the Synapse Smart Cable to the host.
Connecting Power (if required)
If the host does not provide power to the digital scanner, connect an external power supply to the digital scanner:
1. Connect the interface cable to the bottom of the digital scanner, as described in Installing the Interface Cable on page 1-4.
2. Connect the other end of the interface cable to the host (refer to the host manual to locate the correct port).
3. Plug the power supply into the power jack on the interface cable. Plug the other end of the power supply into an AC outlet.
Configuring the Digital Scanner
To configure the digital scanner, use the bar codes included in this manual, or the 123Scan configuration program.
See Chapter 4, User Preferences for information about programming the digital scanner using bar code menus. Also see each host-
specific chapter to set up connection to a specific host type.
See Chapter 12, 123 Scan to configure the digital scanner using this configuration program. A help file is available in the program.
Page 24
DS 6608 Product Reference Guide1-6
Mounting the Digital Scanner
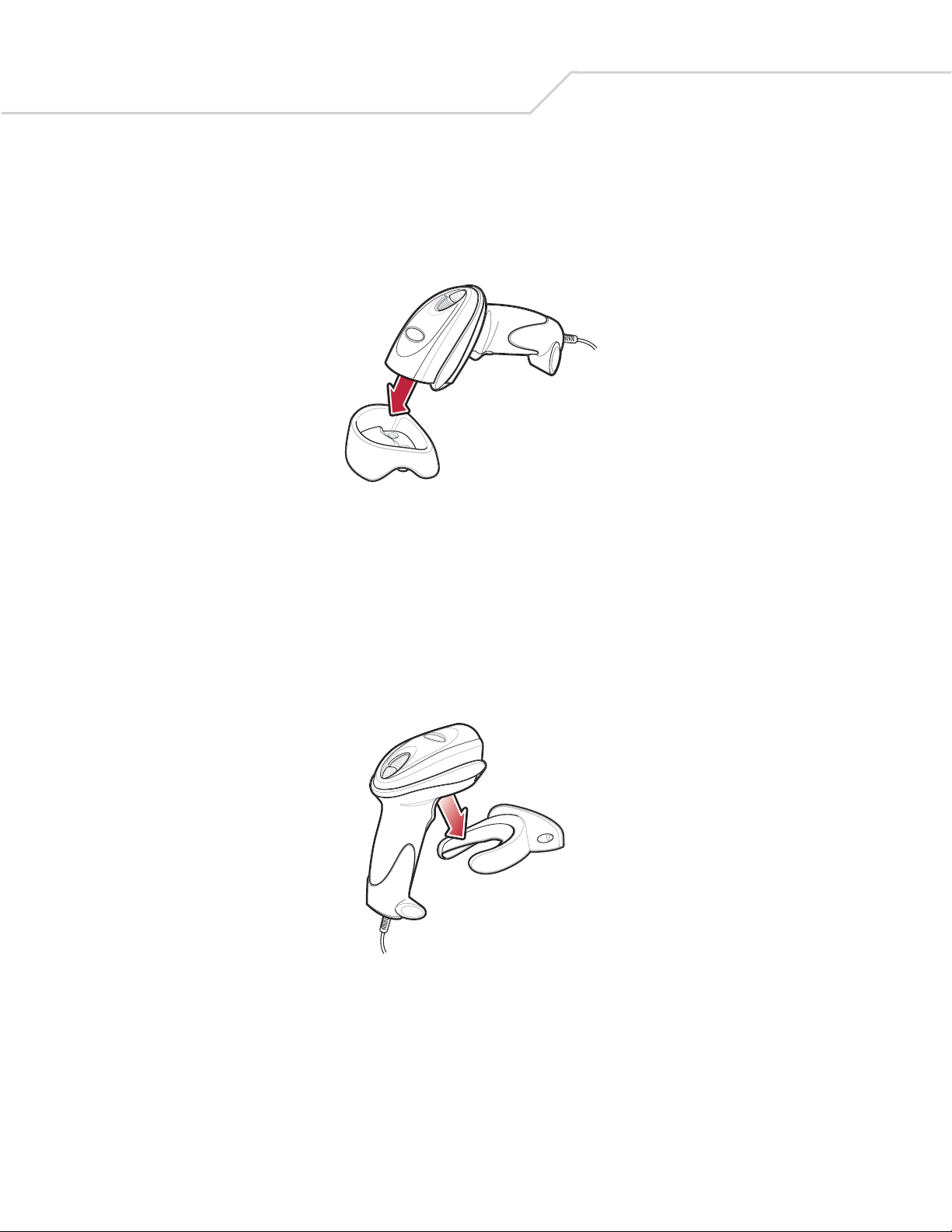
Desk Mount
Use the optional desk mount for convenient and protective placement of the digital scanner on a flat surface. Simply place the mount
on the surface. The rubber feet hold the mount securely in place when inserting and removing the digital scanner.
Figure 1-5. Inserting the Digital Scanner in the Desk Mount
The desk mount can also be secured to a desk surface by inserting two screws* appropriate for the mounting surface through the
screw holes of the desk mount, and into the surface. The desk mount can be screwed onto the surface with or without the rubber feet.
*The recommended screws are two #6 screws (5/8” long).
Wall Mount
To use the optional wall mount to mount the digital scanner on a wall, place the mount in the desired location on the wall and secure
by inserting two screws* appropriate for the mounting surface through the screw holes on the mount, and into the surface. Insert the
digital scanner into the mount as shown.
Figure 1-6. Securing the Wall Mount
*The recommended screws are two #6 screws (1” long) and two #6 washers.
Page 25
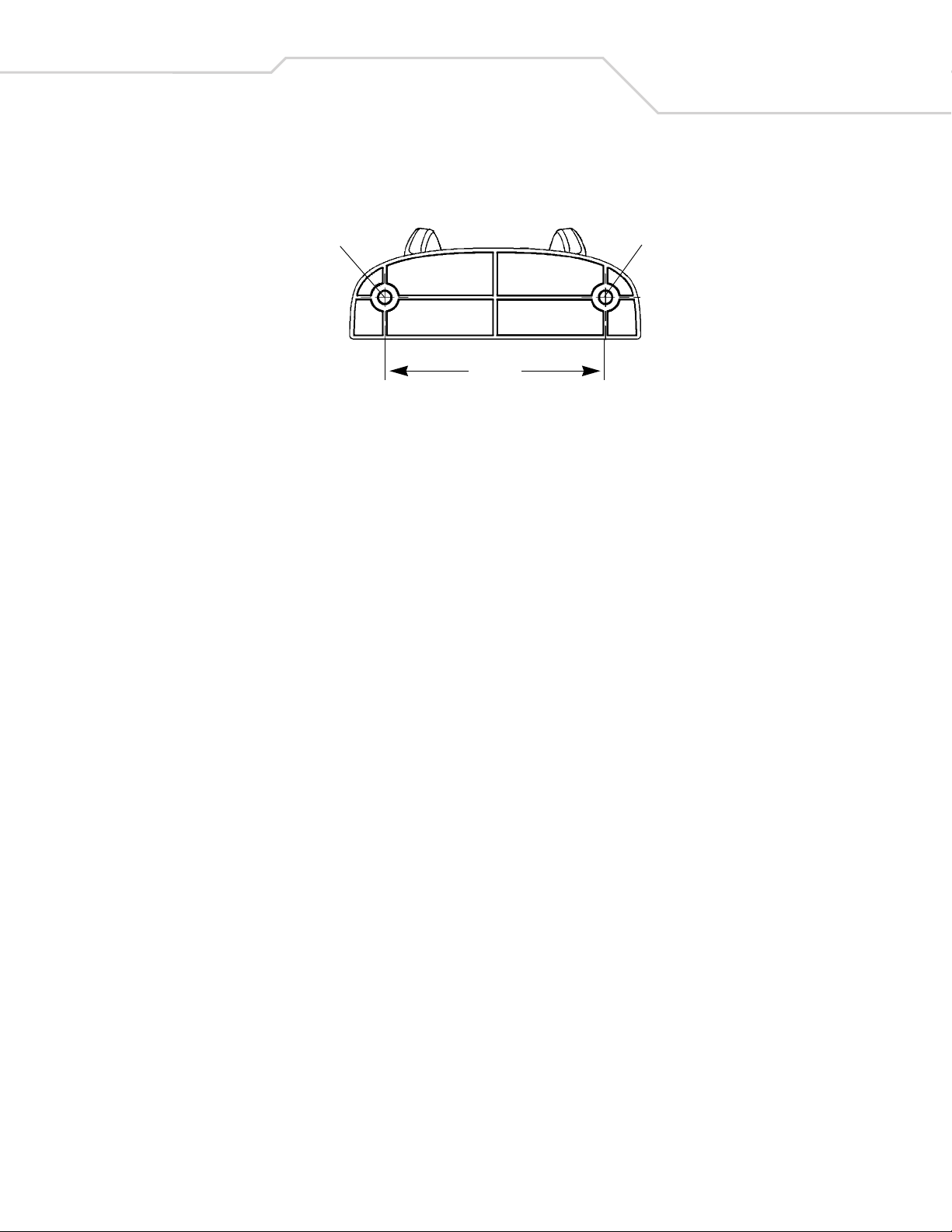
For convenience, print this page and use the template below for mounting hole locations.
Insert mounting screw Insert mounting screw
2.98”
Figure 1-7. Wall Mounting Template
Getting Started 1-7
Page 26

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide1-8
Page 27
Scanning
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Beeper Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-4
LED Definitions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-5
Scanning in Hand-Held Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-6
Scanning with the Digital Scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-6
Aiming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-7
Scanning in Hands-Free Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-8
Decode Zones. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-9
DS 6608 Standard Range Digital Scanner. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-9
DS 6608 High Density Digital Scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-10
Page 28

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide2-2
Page 29
Scanning 2-3
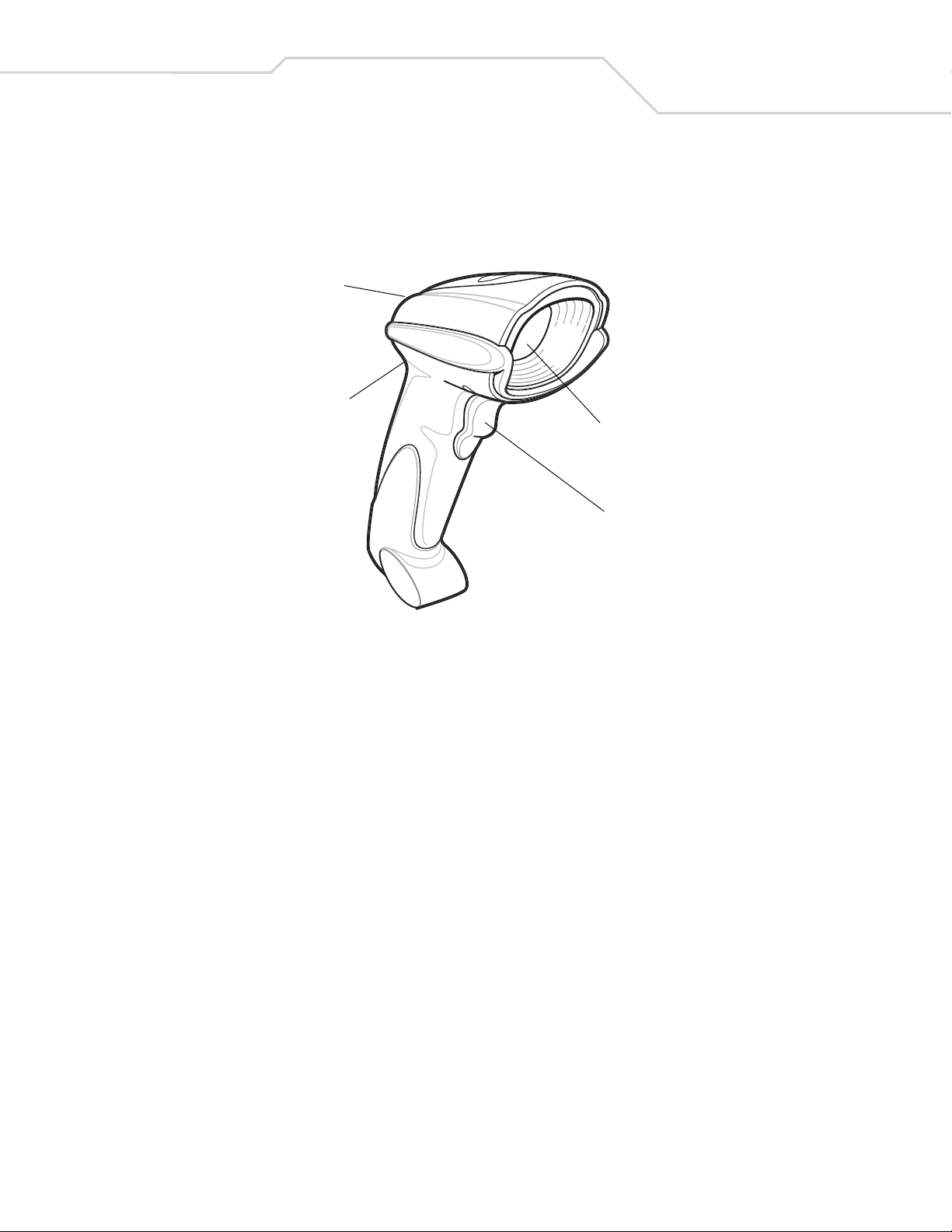
Introduction
This chapter provides beeper and LED definitions, techniques involved in scanning bar codes, general instructions and tips about
scanning, and decode zone diagrams.
LED
Beeper
Scan Window
Tr ig ge r
Figure 2-1. Parts
Page 30

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide2-4
Beeper Definitions
The digital scanner issues different beep sequences and patterns to indicate status. Table 2-1 defines beep sequences that occur
during both normal scanning and while programming the digital scanner.
Table 2-1. Beeper Definitions
Beeper Sequence Indication
Standard Use
Low/medium/high beeps Power up.
Short high beep A bar code symbol was decoded (if decode beeper is enabled).
4 long low beeps A transmission error was detected in a scanned symbol. The data is ignored. This occurs if the digital scanner is not
properly configured. Check option setting.
5 low beeps Conversion or format error.
Lo/hi/lo beeps ADF transmit error. See Chapter 15, Advanced Data Formatting.
Hi/hi/hi/lo beeps RS-232 receive error.
Parameter Menu Scanning
Short high beep Correct entry scanned or correct menu sequence performed.
Lo/hi beeps Input error; incorrect bar code, programming sequence, or Cancel scanned;
remain in ADF program mode.
Hi/lo beeps Keyboard parameter selected. Enter value using numeric bar codes.
Hi/lo/hi/lo beeps Successful program exit with change in parameter setting.
Low/hi/low/hi beeps Out of host parameter storage space. Scan Set Default Parameter on page 4-5.
Code 39 Buffering
Hi/lo beeps New Code 39 data was entered into the buffer.
3 long high beeps Code 39 buffer is full.
Lo/hi/lo beeps The Code 39 buffer was erased or there was an attempt to clear or transmit an empty buffer.
Lo/hi beeps A successful transmission of buffered data.
Macro PDF
2 long low beeps
3 long low beeps Out of memory. There is not enough buffer space to store the current MPDF symbol.
4 long low beeps Bad symbology. Scanned a 1D or 2D bar code in a MPDF sequence, a duplicate MPDF label, a label in an incorrect order,
5 long low beeps Flushing MPDF buffer.
Fast warble beep Aborting MPDF sequence.
Lo/Hi beeps Flushing an already empty MPDF buffer.
ADF Programming: Normal Data Entry. Duration of tones are short.
Hi/Lo beeps Enter another digit. Add leading zeros to the front if necessary.
Lo/Lo beeps Enter another alphabetic character or scan the End of Message bar code.
Hi/Hi beeps Enter another criterion or action, or scan the Save Rule bar code.
File ID error. A bar code not in the current MPDF sequence was scanned.
or trying to transmit an empty or illegal MPDF field.
Hi/Lo/Hi/Lo beeps Rule saved. Rule entry mode exited.
Hi/Lo/Lo beeps All criteria or actions cleared for current rule, continue entering rule.
Page 31

Scanning 2-5
Table 2-1. Beeper Definitions (Continued)
Beeper Sequence Indication
Low beep Delete last saved rule. The current rule is left intact.
Lo/Hi/Hi beeps All rules are deleted.
ADF Programming: Error Indications. Duration of tones are very long.
Lo/Hi/Lo/Hi beeps Out of rule memory. Erase some existing rules, then try to save rule again. (It is not necessary to re-enter the current
rule.)
Lo/Hi/Lo beeps Cancel rule entry. Rule entry mode exited because of an error or the user asked to exit rule entry.
Lo/Hi beeps Entry error, wrong bar code scanned. Re-enter criterion or action. All previously entered criteria and actions are
retained. Criteria or action list is too long for a rule.
Host Specific
USB only
4 short high beeps Digital scannerer has not completed initialization. Wait several seconds and scan again.
Low/medium/high beeps upon
scanning a USB device type
Communication with the bus must be established before the digital scanner can operate at the highest power level.
Low/medium/high beeps occur
more than once.
RS-232 only
1 short high beep A <BEL> character is received and Beep on <BEL> is enabled.
The USB bus can put the digital scanner in a state where power to the digital scanner is cycled on and off more than
once. This is normal and usually happens when the PC cold boots.
LED Definitions
In addition to beep sequences, the digital scanner uses a two-color LED to indicate status. Table 2-2 defines LED colors that display
during scanning.
Table 2-2. Standard LED Definitions
LED Indication
Off No power is applied to the digital scanner, or the digital scanner is on and ready to scan.
Green A bar code was successfully decoded.
Red A data transmission error or digital scanner malfunction occurred.
Page 32

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide2-6
Scanning in Hand-Held Mode
Install and program the digital scanner (see Setting Up the Digital Scanner on page 1-4). For assistance, contact the local supplier or
the local Symbol Support Center.
Scanning with the Digital Scanner
1. Ensure all connections are secure (see the appropriate host chapter.)
2. Aim the digital scanner at the bar code.
3. Press and hold the trigger.
Figure 2-2. Scanning in Hand-Held Mode
4. The digital scanner projects a red laser aiming pattern (shown below) which allows positioning the bar code or object within
the field of view.
Figure 2-3. Laser Aiming Pattern
If necessary, the digital scanner turns on its red LEDs to illuminate the target bar code.
5. Center the symbol in any orientation within the aiming pattern. Be sure the entire symbol is within the rectangular area
formed by the brackets in the pattern.
1D bar code
Linear bar code
Symbol
2D bar code
PDF417 symbol
Aiming Pattern
Figure 2-4. Centering Symbol in Aiming Pattern
Page 33

Scanning 2-7
6. Hold the trigger until the digital scanner beeps, indicating the bar code is successfully decoded. For more information on
beeper and LED definitions, see Table 2-1 and Table 2-2.
This process usually occurs instantaneously. Steps 2 - 4 are repeated on poor quality or difficult bar codes, until the bar code is
decoded, the trigger is released, or the Decode Session Timeout is reached.
Aiming
Hold the digital scanner between two and nine inches (depending on symbol density; see Decode Zones on page 2-9) from the symbol,
centering the aiming pattern cross hairs on the symbol.
The aiming pattern is smaller when the digital scanner is closer to the symbol and larger when it is farther from the symbol. Scan
symbols with smaller bars or elements (mil size) closer to the digital scanner, and those with larger bars or elements (mil size) farther
from the digital scanner.
The digital scanner can also read a bar code presented within the aiming pattern but not centered. The top examples in Figure 2-5
show acceptable aiming options, while the bottom examples can not be decoded.
012345
012345
012345
012345
Figure 2-5. Acceptable and Incorrect Aiming
Page 34

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide2-8
Scanning in Hands-Free Mode
The optional Intellistand adds greater flexibility to scanning operation. When the digital scanner is seated in the stand’s “cup,” the
digital scanner’s built-in sensor places the digital scanner in hands-free mode. When the digital scanner is removed from the stand
it operates in its normal hand-held mode.
Angle Adjustment Knob
Scanner Holder
(Cup)
Height Adjustment Knob
Figure 2-6. Inserting the Digital Scanner in the Intellistand
To operate the digital scanner in the IntelliStand:
1. Ensure the digital scanner is properly connected to the host (see the appropriate host chapter for information on host
connections).
2. Insert the digital scanner in the Intellistand by placing the front of the digital scanner into the stand’s “cup” (see Figure 2-6).
3. Use the Intellistand’s adjustment knobs to adjust the height and angle of the digital scanner.
4. Center the symbol in the aiming pattern. The entire symbol must be within the brackets.
5. Upon successful decode, the digital scanner beeps and the LED turns green. For more information on beeper and LED
definitions, see Table 2-1 and Table 2-2.
Page 35

Decode Zones
DS 6608 Standard Range Digital Scanner
Scanning 2-9
Note: Typical performance at 68˚F (20˚C)
on high quality symbols.
Top of
scanner
5 mil Code 39
2.8
2.6
0.6
1.0
In.
0
cm
2
0 5.1 10.1 15.2 20.3 25.4 30.5 35.6
5.8
Postnet
100% 13 mil UPC
20 mil Code 39
4
6 8 10 12 14
12.5
14.0
16
40.6
18
45.7
20
50.8
21.0
22
55.9
In. cm
15.2
6
4
10.1
5.1
2
0
0
5.1
2
4
10.1
6
15.2
W
d
h
o
F
e
d
Depth of Field
Figure 2-7. DS 6608 Standard Range Digital Scanner Decode Zone for 1D Bar Codes
Note: Typical performance at 68˚F (20˚C)
on high quality symbols.
Top of
scanner
6.6 mil PDF417
In.
cm
3.4
10 mil QR Code
2.6
2.3 7.5
2.3
2.1
1.5
0
0
2
5.1
10 mil MicroPDF
10 mil Data Matrix
10 mil PDF417
4
10.1
5.7
35 mil Maxicode
6810
15.2 20.3 25.4
Depth of Field
6.8
8.0
8.9
12.8
12
30.5
14
35.6
In. cm
3
7.6
2
5.1
1
2.5
0
1
2.5
2
5.1
3
7.6
W
i
d
t
h
o
f
0
F
i
e
l
d
i
t
f
i
l
Figure 2-8. DS 6608 Standard Range Digital Scanner Decode Zone for 2D Bar Codes
Page 36

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide2-10
DS 6608 High Density Digital Scanner
Note: Typical performance at 68˚F (20˚C)
on high quality symbols.
Top of
scanner
In. cm
2
5.1
1
2.5
W
i
d
t
h
o
0
0
f
F
1
5 mil Code 39
100% 13 mil UPC
10 mil Code 39
2.4
2
34567
4.8
Postnet
1.1
0.5
0.3
In.
0
cm
0 2.5 5.1 7.6 10.1 12.7 15.2 17.8
7.0
122.5
5.1
7.3
7.4
8
20.3
i
e
l
d
Depth of Field
Figure 2-9. DS 6608 High Density Digital Scanner Decode Zone for 1D Bar Codes
Note: Typical performance at 68˚F (20˚C)
on high quality symbols.
Top of
scanner
5 mil PDF417
1.9
6.6 mil PDF417
1.5
10 mil QR Code
1.4
1.1 5.1
1.0
1.1
0.6
In.
0
cm
0 2.5 5.1 7.6 10.1 12.7 15.2 17.8
10 mil MicroPDF
10 mil Data Matrix
2
1
10 mil PDF417
3.6
4.5
5.1
5.1
35 mil Maxicode
34567
Depth of Field
5.3
8
20.3
7.8
In. cm
2
5.1
1
2.5
0
122.5
5.1
W
i
d
t
h
o
f
0
F
i
e
l
d
Figure 2-10. DS 6608 High Density Digital Scanner Decode Zone for 2D Bar Codes
Page 37

Maintenance and Technical
Specifications
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-3
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-3
Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-5
Digital Scanner Signal Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-6
Page 38

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide3-2
Page 39

Maintenance and Technical Specifications 3-3
Introduction
This chapter provides suggested scanner maintenance, troubleshooting, technical specifications, and signal descriptions (pinouts).
Maintenance
Cleaning the scan window is the only maintenance required. A dirty window can affect scanning accuracy.
• Do not allow abrasive material to touch the window.
• Remove any dirt particles with a damp cloth.
• Wipe the window using a tissue moistened with ammonia/water.
• Do not spray water or other cleaning liquids directly into the window.
Troubleshooting
Table 3-1. Troubleshooting
Problem Possible Causes Possible Solutions
The aiming pattern does not appear when pressing
the trigger.
Scanner emits short low/short medium/short high
beep sequence (power-up beep sequence) more than
once.
Digital scanner emits aiming pattern, but does not
decode the bar code.
Digital scanner emits 4 short high beeps during
decode attempt.
No power to the digital scanner. If the configuration requires a power supply,
re-connect the power supply.
Incorrect host interface cable is used. Connect the correct host interface cable.
Interface/power cables are loose. Re-connect cables.
Digital scanner is disabled. For Synapse or IBM 468x mode, enable the digital
scanner via the host interface. Otherwise, see the
technical person in charge of scanning.
If using RS-232 Nixdorf B mode, CTS is not asserted. Assert CTS line.
Aiming pattern is disabled. Enable the aiming pattern. See Decode Aiming
Pattern on page 5-5.
The USB bus may put the digital scanner in a state
where power to the digital scanner is cycled on and
off more than once.
Digital scanner is not programmed for the correct bar
code type.
Bar code symbol is unreadable. Scan test symbols of the same bar code type to
The symbol is not completely inside aiming pattern. Move the symbol completely within the aiming
Digital scanner has not completed USB initialization. Wait several seconds and scan again.
Normal during host reset.
Program the digital scanner to read that type of bar
code. See Chapter 13, Symbologies.
determine if the bar code is defaced.
pattern.
Page 40

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide3-4
Problem Possible Causes Possible Solutions
Digital scanner decodes bar code, but does not
transmit the data to the host.
Table 3-1. Troubleshooting (Continued)
Digital scanner is not programmed for the correct
host type.
Interface cable is loose. Re-connect the cable.
Scan the appropriate host type programming bar
code. See the chapter corresponding to the host
type.
If 4 long low beeps are heard, a transmission error
occurred.
If 5 low beeps are heard, a conversion or format error
occurred.
If lo/hi/lo beeps are heard, an invalid ADF rule is
detected.
If hi/lo beeps are heard, the digital scanner is
buffering Code 39 data.
Host displays scanned data incorrectly. Digital scanner is not programmed to work with the
host.
Digital scanner emits hi/hi/hi/Lo beeps when not in
use.
Digital scanner emits lo/hi beeps during
programming.
RS-232 receive error. Normal during host reset. Otherwise, set the digital
Input error or Cancel bar code was scanned. Scan the correct numeric bar codes within range for
Set the digital scanner's communication parameters
to match the host's setting.
Configure the digital scanner's conversion
parameters properly.
Program the correct ADF rules.
Normal scanning a Code 39 bar code and the Code
39 Buffering option is enabled.
Scan the appropriate host type programming bar
code.
For RS-232, set the digital scanner's communication
parameters to match the host's settings.
For a Keyboard Wedge configuration, program the
system for the correct keyboard type, and turn off the
CAPS LOCK key.
Program the proper editing options (e.g., UPC-E to
UPC-A Conversion).
scanner's RS-232 parity to match the host setting.
the parameter programmed.
Digital scanner emits lo/hi/lo/hi beeps during
programming.
Digital scanner emits lo/hi/lo beeps. Clearing Code 39 buffer. Normal when scanning the Code 39 Buffering Clear
Digital scanner emits a power-up beep after
changing USB host type.
Digital scanner emits one high beep when not in use. In RS-232 mode, a <BEL> character was received
Out of ADF parameter storage space. Erase all rules and re-program with shorter rules.
Out of Synapse parameter storage space. Scan Set Synapse Defaults bar code for cables no
longer in use and re-program the digital scanner for
the current host interface.
Buffer bar code or upon attempt to transmit an
empty Code 39 buffer.
The USB bus re-established power to the digital
scanner.
and Beep on <BEL> option is enabled.
Normal when changing USB host type.
Normal when Beep on <BEL> is enabled and the
digital scanner is in RS-232 mode.
If after performing these checks the digital scanner still experiences problems, contact the distributor or call
the local Symbol Support Center. See page xvi for the telephone numbers.
Note
Page 41

Maintenance and Technical Specifications 3-5
Technical Specifications
Table 3-2. Technical Specifications
Item Description
Power Requirements 5 VDC + / - 10% @ approximately 220 mA RMS (nominal), 500 mA (max)
Depending on host:
Power Source
Decode Capability
Beeper Operation User-selectable: enable, disable
Beeper Volume User-selectable: three levels
Beeper Tone User-selectable: three tones
Yaw Tolerance ± 50° from normal
Pitch Tolerance ± 60° from normal
Roll Tolerance ± 180° from normal
Print Contrast Minimum 25% minimum reflectance differential, measured at 650 nm.
• Host powered
• External power supply, 5.2 V nominal
UPC/EAN, UPC/EAN with supplementals, UCC/EAN, JAN 8 & 13, 128, Code 39, Code 39 Full ASCII, Code 39 Trioptic,
Codabar (NW7), Interleaved 2 of 5, Discrete 2 of 5, IATA 2 of 5, Code 128, Code 93, MSI, Code 11, Code 32, Coupon
Code, Bookland EAN, RSS, US Postnet, US Planet,UK Postal, Japan Postal, Australia Postal, Dutch Postal, Composite
Codes, PDF417, MicroPDF, Maxicode, Data Matrix (ECC 200), QR Code.
Ambient Light Immunity 10,000 Ft Candles (107,600 Lux)
Durability 6 ft (1.8 m) drop to concrete
Operating Temperature 32° to 122° F (0° to 50° C)
Storage Temperature -40° to 158° F (-40° to 70° C)
Humidity 5% to 95% (non-condensing)
Weight (without cable) 6.4 oz. (181.4 g)
Dimensions:
Height
Width
Depth
Laser 650nm laser diode
Laser Classifications IEC 825-1 Class 2
ESD
Minimum Element Width 5 mil (0.127 mm)
Interfaces Supported RS-232, Keyboard Wedge, Wand Emulation, Scanner Emulation, IBM 468X/469X, USB, Synapse
Electrical Safety UL1950, CSA C22.2 No.950. EN60950/IC950
Input Transient Protection IEC 1000-4-(2,3,4,5,6,11)
EMI
6.55 in. (16.64 cm)
2.82 in. (7.16 cm)
4.72 in. (11.99 cm)
15 kV area discharge
8 kV contact discharge
FCC Part 15 Class B, ICES-003 Class B European Union EMC Directive,
Japan VCCI/MITI/Dentori
Page 42

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide3-6
Digital Scanner Signal Descriptions
Bottom of digital scanner
Cable interface port
Pin 10
Interface cable
modular connector
Pin 1
Figure 3-1. Digital Scanner Cable Pinouts
The signal descriptions in Table 3-3 apply to the connector on the digital scanner and are for reference only.
Table 3-3. Digital Scanner Signal Pin-outs
Pin IBM Synapse RS-232 Keyboard Wedge Wand USB
1 Reserved SynClock Reserved Reserved Reserved Jump to Pin 6 DBP
2 Power Power Power Power Power Power Power
Scanner
Emulation
3 Ground Ground Ground Ground Ground Ground Ground
4 IBM_A(+) Reserved TxD KeyClock DBP Reserved SOS
5 Reserved Reserved RxD TermData CTS D + Decode
6 IBM_B(-) SynData RTS KeyData RTS Jump to Pin 1 Trigger
7 Reserved Reserved CTS TermClock Reserved D - Enable
8 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
9 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
10 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
Page 43

User Preferences
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Scanning Sequence Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-3
Errors While Scanning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-3
User Preferences Parameter Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-4
User Preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-5
Set Default Parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-5
Parameter Scanning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-5
Beeper Tone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-6
Beeper Volume. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-7
Power Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-7
Time Delay to Low Power Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-8
Trigger Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-9
Decode Session Timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-10
Timeout Between Decodes, Same Symbol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-10
Beep After Good Decode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-11
Scanstand Session Timeout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-11
Page 44

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide4-2
Page 45

User Preferences 4-3
Introduction
If desired, program the digital scanner to perform various functions, or activate different features. This chapter describes each user
preference feature and provides the programming bar codes necessary for selecting these features.
The digital scanner ships with the settings shown in the Table 4-1 on page 4-4 (also see Appendix A, Standard Default Parameters
for all host device and miscellaneous defaults). If the default values suit requirements, programming is not necessary.
To set feature values, scan a single bar code or a short bar code sequence. The settings are stored in non-volatile memory and are
preserved even when the digital scanner is powered down.
Most computer monitors allow scanning the bar codes directly on the screen. When scanning from the
screen, be sure to set the document magnification to a level where the bar code can be seen clearly, and
Note
power-up beeps sound. This is only necessary upon the first power-up when connected to a new host.
To return all features to default values, scan the *Set All Defaults on page 4-5. Throughout the programming bar code menus, default
values are indicated with asterisks (
bars and/or spaces are not merging.
If not using a Synapse or USB cable, select a host type (see each host chapter for specific host information) after the
*).
* Indicates Default
*High Volume
Feature/Option
Scanning Sequence Examples
In most cases, scanning one bar code sets the parameter value. For example, to set the beeper tone to high, scan the High Frequency
(beeper tone) bar code listed under Beeper Tone on page 4-6. The digital scanner issues a fast warble beep and the LED turns green,
signifying a successful parameter entry.
Other parameters, such as Serial Response Time-Out or Data Transmission Formats, require scanning several bar codes. See
these parameter descriptions for this procedure.
Errors While Scanning
Unless otherwise specified, to correct an error during a scanning sequence, just re-scan the correct parameter.
Page 46

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide4-4
User Preferences Parameter Defaults
Table 4-1 lists defaults for user preferences parameters. To change any option, scan the appropriate bar code(s) provided in the User
Preferences section beginning on page 4-5.
See Appendix A, Standard Default Parameters for all user preferences, hosts, symbologies, and
miscellaneous default parameters.
Note
Table 4-1. User Preferences Default Table
Parameter
Parameter
User Preferences
Set Default Parameter All Defaults 4-5
Parameter Scanning ECh Enable 4-5
Beeper Tone 91h Medium 4-6
Beeper Volume 8Ch High 4-7
Power Mode 80h Continuous On 4-7
Time Delay to Low Power Mode 92h 5 Minutes 4-8
Trigger Mode 8Ah Level 4-9
Decode Session Timeout 88h 9.9 Sec 4-10
Timeout Between Decodes, Same Symbol 89h 0.6 Sec 4-10
Beep After Good Decode 38h Enable 4-11
Scanstand Session Timeout F0h, 90h 2 Seconds 4-11
Number Default
Number
Page
Page 47

User Preferences 4-5
User Preferences
Set Default Parameter
Scan this bar code to return all parameters to the default values listed in Table A-1 on page A-3.
*Set All Defaults
Parameter Scanning
Parameter # ECh
To disable decoding of parameter bar codes, scan the Disable Parameter Scanning bar code below. Note that the Set Defaults
parameter bar code can still be decoded. To enable decoding of parameter bar codes, either scan Enable Parameter Scanning or
Set All Defaults.
*Enable Parameter Scanning
(01h)
Disable Parameter Scanning
(00h)
Page 48

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide4-6
Beeper Tone
Parameter # 91h
To select a decode beep frequency (tone), scan the Low Frequency, Medium Frequency, or High Frequency bar code.
Low Frequency
(02h)
*Medium Frequency
(Optimum Setting)
(01h)
High Frequency
(00h)
Page 49

Beeper Volume
Parameter # 8Ch
To select a beeper volume, scan the Low Volume, Medium Volume, or High Volume bar code.
Low Volume
(02h)
Medium Volume
User Preferences 4-7
(01h)
*High Volume
(00h)
Power Mode
Parameter # 80h
This parameter determines whether or not power remains on after a decode attempt. In reduced power mode, the digital scanner
enters into a low power consumption mode to preserve battery life after each decode attempt. In continuous power mode, power
remains on after each decode attempt.
*Continuous On
(00h)
Reduced Power Mode
(01h)
Page 50

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide4-8
Time Delay to Low Power Mode
Parameter # 92h
This parameter only applies when Power Mode is set to Reduced Power.
Note
This parameter sets the time the digital scanner remains active after decoding. The digital scanner wakes upon trigger pull or when
the host attempts to communicate with the digital scanner.
1 Second
(11h)
1 Minute
(21h)
5 Seconds
(15h)
*5 Minutes
(25h)
Page 51

Time Delay to Low Power Mode (continued)
15 Minutes
(2Bh)
Trigger Mode
Parameter # 8Ah
Select one of the following trigger modes for the digital scanner:
User Preferences 4-9
1 Hour
(31h)
• Level - A trigger pull activates decode processing. Decode processing continues until the bar code is decoded, the trigger
is released, or the Decode Session Timeout is reached.
• Blink - This trigger mode is used in hands-free (Intellistand) mode. The digital scanner activates decode processing when
it detects a bar code in its field of view. Decoding range is reduced in this mode.
• Host - A host command issues the triggering signal. The digital scanner interprets an actual trigger pull as a Level triggering
.
option
*Level
(00h)
Blink
(07h)
Host
(08h)
Page 52

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide4-10
Decode Session Timeout
Parameter # 88h
This parameter sets the maximum time decode processing continues during a scan attempt. It is programmable in 0.1 second
increments from 0.5 to 9.9 seconds. The default timeout is 9.9 seconds.
To set a Decode Session Timeout, scan the bar code below. Next, scan two numeric bar codes from Appendix D, Numeric Bar Codes
that correspond to the desired on time. Single digit numbers must have a leading zero. For example, to set a Decode Session Timeout
of 0.5 seconds, scan the bar code below, then scan the 0 and 5 bar codes. To correct an error or change the selection, scan Cancel
on page D-4.
Decode Session Timeout
Timeout Between Decodes, Same Symbol
Parameter # 89h
This option is used in hands-free (Intellistand) mode to prevent the beeper from continuously beeping when a symbol is left in the
digital scanner’s field of view. It is programmable in 0.1 second increments from 0.0 to 9.9 seconds. The default interval is 0.6 seconds.
To select the timeout between decodes for the same symbol, scan the bar code below, then scan two numeric bar codes from
Appendix D, Numeric Bar Codes that correspond to the desired interval, in 0.1 second increments.
Timeout Between Decodes, Same Symbol
Page 53

User Preferences 4-11
Beep After Good Decode
Parameter # 38h
Scan a bar code below to select whether or not the digital scanner beeps after a good decode. If selecting Do Not Beep After Good
Decode, the beeper still operates during parameter menu scanning and to indicate error conditions.
*Beep After Good Decode
(Enable)
(01h)
Do Not Beep After Good Decode
(Disable)
(00h)
Scanstand Session Timeout
Parameter # F0h, 90h
To set the amount of time the digital scanner attempts to decode a bar code in hands-free mode (blink mode), scan the bar code below.
Next, scan three numeric bar codes from Appendix D, Numeric Bar Codes to select a value between 1 and 255 that represents tenths
of a second. Single digit numbers must have a leading zero. For example, to set 0.5 seconds, scan the bar code below, then scan the
0, 0, 5 bar codes. To correct an error or change the selection, scan Cancel on page D-4. The default value is 2 seconds.
Scanstand Session Timeout
Page 54

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide4-12
Page 55

Decoding Preferences
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Scanning Sequence Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-3
Errors While Scanning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-3
Decoding Preferences Parameter Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-4
Decoding Preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-5
Decoding Illumination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-5
Decode Aiming Pattern . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-5
Page 56

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide5-2
Page 57

Decoding Preferences 5-3
Introduction
If desired, program the digital scanner to perform various functions, or activate different features. This chapter describes digital
scanner preference features and provides the programming bar codes for selecting these features.
The digital scanner ships with the settings shown in the Decoding Preferences Default Table on page 5-4 (also see Appendix A,
Standard Default Parameters for all host device and miscellaneous defaults). If the default values suit requirements, programming is
not necessary.
To set feature values, scan a single bar code or a short bar code sequence. The settings are stored in non-volatile memory and are
preserved even when the digital scanner is powered down.
Most computer monitors allow scanning the bar codes directly on the screen. When scanning from the
screen, be sure to set the document magnification to a level where the bar code can be seen clearly, and
Note
If not using a Synapse or USB cable, select a host type (see each host chapter for specific host information) after the power-up beeps
sound. This is only necessary upon the first power-up when connected to a new host.
bars and/or spaces are not merging.
To return all features to default values, scan the Set Default Parameter bar code on page 4-5. Throughout the programming bar code
menus, default values are indicated with asterisks (
* Indicates Default
*).
*Enable Decode Aiming Pattern
(02h)
Feature/Option
Hex Value
Scanning Sequence Examples
In most cases scanning one bar code sets the parameter value. For example, to disable the decode aiming pattern, scan the Disable
Decode Aiming Pattern bar code listed under Decode Aiming Pattern on page 5-5. The digital scanner issues a fast warble beep
and the LED turns green, signifying a successful parameter entry.
Other parameters require scanning several bar codes. See these parameter descriptions for this procedure.
Errors While Scanning
Unless otherwise specified, to correct an error during a scanning sequence, just re-scan the correct parameter.
Page 58

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide5-4
Decoding Preferences Parameter Defaults
Table 5-1 lists defaults for digital scanner preferences parameters. To change any option, scan the appropriate bar code(s) provided
in Decoding Preferences on page 5-5.
See Appendix A, Standard Default Parameters for all user preferences, hosts, symbologies, and
miscellaneous default parameters.
Note
Table 5-1. Decoding Preferences Default Table
Parameter
Decoding Options
Decoding Illumination F0h 2Ah Enable 5-5
Decode Aiming Pattern F0h 32h Enable 5-5
Parameter
Number
Default
Page
Number
Page 59

Decoding Preferences 5-5
Decoding Preferences
The parameters in this chapter control bar code decoding characteristics.
Decoding Illumination
Parameter # F0h, 2Ah
Selecting Enable Illumination causes the digital scanner to flash illumination to aid decoding. Select Disable Illumination to prevent
the digital scanner from using decoding illumination.
Enabling illumination usually results in superior images. The effectiveness of the illumination decreases as the distance to the target
increases.
*Enable Decoding Illumination
(01h)
Disable Decoding Illumination
(00h)
Decode Aiming Pattern
Parameter # F0h, 32h
This parameter only applies when in Decode Mode. Select Enable Decode Aiming Pattern to project the aiming pattern during bar
code capture, or Disable Decode Aiming Pattern to turn the aiming pattern off.
*Enable Decode Aiming Pattern
(02h)
Disable Decode Aiming Pattern
(00h)
Page 60

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide5-6
Page 61

Keyboard Wedge Interface
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
Connecting a Keyboard Wedge Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-3
Keyboard Wedge Parameter Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-4
Keyboard Wedge Host Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-5
Keyboard Wedge Host Types. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-5
Keyboard Wedge Country Types (Country Codes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-6
Ignore Unknown Characters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-8
Keystroke Delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-8
Intra-Keystroke Delay. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-9
Alternate Numeric Keypad Emulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-9
Caps Lock On . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-10
Caps Lock Override. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-10
Convert Wedge Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-11
Function Key Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-11
FN1 Substitution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-12
Send Make and Break . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-12
Keyboard Maps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-13
ASCII Character Set for Keyboard Wedge. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-15
Page 62

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide6-2
Page 63

Keyboard Wedge Interface
6-3
Introduction
This chapter describes how to set up a Keyboard Wedge interface with the digital scanner. With this interface, the digital scanner is
connected between the keyboard and host computer, and translates bar code data into keystrokes. The host computer accepts the
keystrokes as if they originated from the keyboard. This mode adds bar code reading functionality to a system designed for manual
keyboard input. Keyboard keystrokes are simply passed through.
Throughout the programming bar code menus, default values are indicated with asterisks (
Note
* Indicates Default
Most computer monitors allow scanning the bar codes directly on the screen. When scanning from the screen, be sure
to set the document magnification to a level where the bar code can be seen clearly, and bars and/or spaces are not
merging.
*North American
Feature/Option
Connecting a Keyboard Wedge Interface
Male DIN Connector
*).
Keyboard Connector
Female DIN Connector
Figure 6-1. Keyboard Wedge Connection with Y-cable
To connect the Keyboard Wedge interface Y-cable:
Interface cables vary depending on configuration. The connectors illustrated in Figure 6-1 are examples only.
The connectors may be different than those illustrated, but the steps to connect the scanner remain the
Note
1. Turn off the host and unplug the keyboard connector.
2. Attach the modular connector of the Y-cable to the cable interface port on the digital scanner. (See Installing the Interface
same.
Cable on page 1-4.)
Page 64

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide6-4
3. Connect the round male DIN host connector of the Y-cable to the keyboard port on the host device.
4. Connect the round female DIN keyboard connector of the Y-cable to the keyboard connector.
5. If needed, attach the optional power supply to the connector in the middle of the Y-cable.
6. Ensure that all connections are secure.
7. Turn on the host system.
8. Select the Keyboard Wedge host type by scanning the appropriate bar code from Keyboard Wedge Host Types on page 6-5.
9. To modify any other parameter options, scan the appropriate bar codes in this chapter.
Keyboard Wedge Parameter Defaults
Table 6-1 lists the defaults for Keyboard Wedge host parameters. To change any option, scan the appropriate bar code(s) in the
Keyboard Wedge Host Parameters section beginning on page 6-5.
See Appendix A, Standard Default Parameters for all user preferences, hosts, symbologies, and
miscellaneous default parameters.
Note
Table 6-1. Keyboard Wedge Host Default Table
Parameter Default Page Number
Keyboard Wedge Host Parameters
Keyboard Wedge Host Type IBM PC/AT& IBM PC Compatibles 6-5
Country Types (Country Codes) North American 6-6
Ignore Unknown Characters Transmit 6-8
Keystroke Delay No Delay 6-8
Intra-Keystroke Delay Disable 6-9
Alternate Numeric Keypad Emulation Disable 6-9
Caps Lock On Disable 6-10
Caps Lock Override Disable 6-10
Convert Wedge Data No Convert 6-11
Function Key Mapping Disable 6-11
FN1 Substitution Disable 6-12
Send and Make Break Send 6-12
Page 65

Keyboard Wedge Host Parameters
Keyboard Wedge Host Types
Select the Keyboard Wedge host by scanning one of the bar codes below.
IBM PC/AT & IBM PC Compatibles
Keyboard Wedge Interface
IBM PS/2 (Model 30)
6-5
IBM AT Notebook
NCR 7052
IBM XT
Page 66

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide6-6
Keyboard Wedge Country Types (Country Codes)
Scan the bar code corresponding to the keyboard type. If the keyboard type is not listed, see Alternate Numeric Keypad Emulation on
page 6-9.
*North American
German Windows
French Windows
French Canadian Windows XP/2000
French Canadian Windows 95/98
Spanish Windows
Page 67

Keyboard Wedge Country Types (continued)
Italian Windows
Keyboard Wedge Interface
Swedish Windows
6-7
UK English Windows
Portuguese-Brazilian Windows
Japanese Windows
Page 68

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide6-8
Ignore Unknown Characters
Unknown characters are characters the host does not recognize. When Send Bar Codes With Unknown Characters is selected,
all bar code data is sent except for unknown characters, and no error beeps sound on the digital scanner. When Do Not Send Bar
Codes With Unknown Characters is selected, bar code data is sent up to the first unknown character, then the digital scanner
issues an error beep.
*Send Bar Codes with Unknown Characters
(Transmit)
Do Not Send Bar Codes with Unknown Characters
Keystroke Delay
This is the delay in milliseconds between emulated keystrokes. Scan a bar code below to increase the delay when hosts require a
slower transmission of data.
*No Delay
Medium Delay (20 msec)
Long Delay (40 msec)
Page 69

Keyboard Wedge Interface
Intra-Keystroke Delay
When enabled, an additional delay is inserted between each emulated key depression and release. This sets the Keystroke Delay
parameter to a minimum of 5 msec as well.
Enable
*Disable
6-9
Alternate Numeric Keypad Emulation
This allows emulation of most other country keyboard types not listed in Keyboard Wedge Country Types (Country Codes) on page 6-
6 in a Microsoft
®
operating system environment.
Enable Alternate Numeric Keypad
*Disable Alternate Numeric Keypad
Page 70

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide6-10
Caps Lock On
When enabled, the digital scanner emulates keystrokes as if the Caps Lock key is always pressed.
Enable Caps Lock On
*Disable Caps Lock On
Caps Lock Override
When enabled, on AT or AT Notebook hosts, the keyboard ignores the state of the Caps Lock key. Therefore, an ‘A’ in the bar code is
sent as an ‘A’ no matter what the state of the keyboard’s Caps Lock key.
Note
Enable Caps Lock Override
*Disable Caps Lock Override
If both Caps Lock On and Caps Lock Override are enabled, Caps Lock Override takes precedence.
Page 71

Convert Wedge Data
When enabled, the digital scanner converts all bar code data to the selected case.
Convert to Upper Case
Keyboard Wedge Interface
Convert to Lower Case
6-11
*No Convert
Function Key Mapping
ASCII values under 32 are normally sent as control key sequences (see Table 6-2 on page 6-15). When this parameter is enabled, the
keys in bold are sent in place of the standard key mapping. Table entries that do not have a bold entry remain the same whether or
not this parameter is enabled.
Enable
*Disable
Page 72

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide6-12
FN1 Substitution
When this is enabled, the digital scanner replaces FN1 characters in an EAN128 bar code with a keystroke chosen by the user (see
FN1 Substitution Values on page 14-8).
Enable
*Disable
Send Make and Break
When enabled, the scan codes for releasing a key are not sent.
*Send Make and Break Scan Codes
Send Make Scan Code Only
Page 73

Keyboard Wedge Interface
Keyboard Maps
The following keyboard maps are provided for prefix/suffix keystroke parameters. To program the prefix/suffix values, see the bar
codes on page 14-6.
6-13
7014 5001 5002 5003 5004 5005 5006 5007 5008 5009 5010
7009
Figure 6-2. IBM PS2 Type Keyboard
5001
5003
5005
5007
5009
5002
5004
5006
5008
5010
7014
7009
5011
7008
7013
7013
5012
7010 7007
7012
7011
7002 7004 7005
7015
7017 7016
7006
7001
7008
7003
7018
7013
7012
7004
7011 7002
7003
7006
5001
5003
5005
5007
5009
5002
5004
5006
5008
5010
7009
Figure 6-3. IBM PC/XT
Figure 6-4. IBM PC/AT
7008
7013
7014
7012
7004
7011
7003
7002
Page 74

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide6-14
5001
5003
5005 5006
5007
5009
1066
1065
1072
1073
1079 1080
5002
5001
5003
5004
5002
5011
5004
5008
5010
1048
5012
1046
(1048 if double key)
Figure 6-5. NCR 7052 32-KEY
1067
1074
1081
5011
1068
1075
1082
1045
5014
1043
5017
7013
(7013 if double key)
1070
1069
1076
1077
1083 1084
1045
5013
5014
5015
5013
5015
5016
5018
5019
1071
1078
1085
1086
1087
5005 5006
5007
5008
5009
5010
1043
5017
5012
1048
(1048 if double key)
1046
7013
(1043 if double key)
Figure 6-6. NCR 7052 58-KEY
5016
5018
5019
1088
1089
1090
Page 75

ASCII Character Set for Keyboard Wedge
Code 39 Full ASCII interprets the bar code special character ($ + % /) preceding a Code 39 character and
assigns an ASCII character value to the pair. For example, when Code 39 Full ASCII is enabled and +B is
Note
scanned, it is interpreted as b, %J as ?, and %V as @. Scanning ABC%I outputs the keystroke equivalent
of ABC >.
Table 6-2. Keyboard Wedge ASCII Character Set
Full ASCII
Code 39
ASCII Value
1001 $A CTRL A
1002 $B CTRL B
1003 $C CTRL C
1004 $D CTRL D
1005 $E CTRL E
1006 $F CTRL F
Encode Char.acter Keystroke
Keyboard Wedge Interface
6-15
1007 $G CTRL G
1008 $H CTRL H/BACKSPACE
1009 $I CTRL I/HORIZONTAL
1010 $J CTRL J
1011 $K CTRL K
1012 $L CTRL L
1013 $M CTRL M/ENTER
1014 $N CTRL N
1015 $O CTRL O
1016 $P CTRL P
1017 $Q CTRL Q
1018 $R CTRL R
1019 $S CTRL S
1020 $T CTRL T
1021 $U CTRL U
1022 $V CTRL V
1023 $W CTRL W
TAB
1
1
1
1024 $X CTRL X
1025 $Y CTRL Y
1026 $Z CTRL Z
1027 %A CTRL [ /ESC
1
The keystroke in bold is sent only if the “Function Key Mapping” is enabled. Otherwise,
the unbolded keystroke is sent.
1
Page 76

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide6-16
Table 6-2. Keyboard Wedge ASCII Character Set (Continued)
Full ASCII
Code 39
ASCII Value
1028 %B CTRL \
1029 %C CTRL ]
1030 %D CTRL 6
1031 %E CTRL 1032 Space Space
1033 /A !
1034 /B “
1035 /C #
1036 /D $
1037 /E %
1038 /F &
Encode Char.acter Keystroke
1039 /G ‘
1040 /H (
1041 /I )
1042 /J *
1043 /K +
1044 /L ,
1045 - 1046 . .
1047 /O /
1048 0 0
1049 1 1
1050 2 2
1051 3 3
1052 4 4
1053 5 5
1054 6 6
1055 7 7
1056 8 8
1057 9 9
1058 /Z :
1059 %F ;
1060 %G <
1
The keystroke in bold is sent only if the “Function Key Mapping” is enabled. Otherwise,
the unbolded keystroke is sent.
Page 77

Table 6-2. Keyboard Wedge ASCII Character Set (Continued)
Full ASCII
Code 39
ASCII Value
1061 %H =
1062 %I >
1063 %J ?
1064 %V @
1065 A A
1066 B B
1067 C C
1068 D D
1069 E E
1070 F F
1071 G G
Encode Char.acter Keystroke
Keyboard Wedge Interface
6-17
1072 H H
1073 I I
1074 J J
1075 K K
1076 L L
1077 M M
1078 N N
1079 O O
1080 P P
1081 Q Q
1082 R R
1083 S S
1084 T T
1085 U U
1086 V V
1087 W W
1088 X X
1089 Y Y
1090 Z Z
1091 %K [
1092 %L \
1093 %M ]
1
The keystroke in bold is sent only if the “Function Key Mapping” is enabled. Otherwise,
the unbolded keystroke is sent.
Page 78

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide6-18
Table 6-2. Keyboard Wedge ASCII Character Set (Continued)
Full ASCII
Code 39
ASCII Value
1094 %N ^
1095 %O _
1096 %W ‘
1097 +A a
1098 +B b
1099 +C c
1100 +D d
1101 +E e
1102 +F f
1103 +G g
1104 +H h
Encode Char.acter Keystroke
1105 +I i
1106 +J j
1107 +K k
1108 +L l
1109 +M m
1110 +N n
1111 +O o
1112 +P p
1113 +Q q
1114 +R r
1115 +S s
1116 +T t
1117 +U u
1118 +V v
1119 +W w
1120 +X x
1121 +Y y
1122 +Z z
1123 %P {
1124 %Q |
1125 %R }
1126 %S ~
1
The keystroke in bold is sent only if the “Function Key Mapping” is enabled. Otherwise,
the unbolded keystroke is sent.
Page 79

Table 6-3. Keyboard Wedge ALT Key Character Set
ALT Keys Keystroke
2065 ALT A
2066 ALT B
2067 ALT C
2068 ALT D
2069 ALT E
2070 ALT F
2071 ALT G
2072 ALT H
2073 ALT I
2074 ALT J
2075 ALT K
2076 ALT L
2077 ALT M
Keyboard Wedge Interface
6-19
2078 ALT N
2079 ALT O
2080 ALT P
2081 ALT Q
2082 ALT R
2083 ALT S
2084 ALT T
2085 ALT U
2086 ALT V
2087 ALT W
2088 ALT X
2089 ALT Y
2090 ALT Z
Table 6-4. Keyboard Wedge GUI Key Character Set
GUI Keys Keystrokes
3000 Right Control Key
3048 GUI 0
3049 GUI 1
3050 GUI 2
3051 GUI 3
3052 GUI 4
Page 80

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide6-20
Table 6-4. Keyboard Wedge GUI Key Character Set (Continued)
GUI Keys Keystrokes
3053 GUI 5
3054 GUI 6
3055 GUI 7
3056 GUI 8
3057 GUI 9
3065 GUI A
3066 GUI B
3067 GUI C
3068 GUI D
3069 GUI E
3070 GUI F
3071 GUI G
3072 GUI H
3073 GUI I
3074 GUI J
3075 GUI K
3076 GUI L
3077 GUI M
3078 GUI N
3079 GUI O
3080 GUI P
3081 GUI Q
3082 GUI R
3083 GUI S
3084 GUI T
3085 GUI U
3086 GUI V
3087 GUI W
3088 GUI X
3089 GUI Y
3090 GUI Z
Page 81

Table 6-5. Keyboard Wedge F Key Character Set
F Keys Keystroke
5001 F1
5002 F2
5003 F3
5004 F4
5005 F5
5006 F6
5007 F7
5008 F8
5009 F9
5010 F10
5011 F11
5012 F12
5013 F13
Keyboard Wedge Interface
6-21
5014 F14
5015 F15
5016 F16
5017 F17
5018 F18
5019 F19
5020 F20
5021 F21
5022 F22
5023 F23
5024 F24
Table 6-6. Keyboard Wedge Numeric Keypad Character Set
Numeric Keypad Keystroke
6042 *
6043 +
6044 undefined
6045 6046 .
6047 /
6048 0
6049 1
Page 82

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide6-22
Table 6-6. Keyboard Wedge Numeric Keypad Character Set (Continued)
Numeric Keypad Keystroke
6050 2
6051 3
6052 4
6053 5
6054 6
6055 7
6056 8
6057 9
6058 Enter
6059 Num Lock
Table 6-7. Keyboard Wedge Extended Keypad Character Set
Extended Keypad Keystroke
7001 Break
7002 Delete
7003 Pg Up
7004 End
7005 Pg Dn
7006 Pause
7007 Scroll Lock
7008 Backspace
7009 Tab
7010 Print Screen
7011 Insert
7012 Home
7013 Enter
7014 Escape
7015 Up Arrow
7016 Dn Arrow
7017 Left Arrow
7018 Right Arrow
Page 83

RS-232 Interface
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
Connecting an RS-232 Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-4
RS-232 Parameter Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-5
RS-232 Host Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-6
RS-232 Host Types. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-8
Baud Rate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-9
Parity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-11
Stop Bit Select . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-12
Data Bits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-12
Check Receive Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-13
Hardware Handshaking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-14
Hardware Handshaking (continued). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-15
Software Handshaking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-16
Host Serial Response Time-out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-17
RTS Line State . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-18
Beep on <BEL> . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-18
Intercharacter Delay. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-19
Nixdorf Beep/LED Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-20
Ignore Unknown Characters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-20
ASCII Character Set for RS-232 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-21
Page 84

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide7-2
Page 85

RS-232 Interface 7-3
Introduction
This chapter describes how to set up the digital scanner with an RS-232 host. The RS-232 interface is used to connect the digital
scanner to point-of-sale devices, host computers, or other devices with an available RS-232 port (e.g., com port).
If the host is not listed in Table 7-2, refer to the documentation for the host device to set communication parameters to match the host.
The digital scanner uses TTL RS-232 signal levels, which interface with most system architectures. For
system architectures requiring RS-232C signal levels, Symbol offers different cables providing TTL-to-RS-
Note
232C conversion. Contact the Symbol Support Center for more information.
Note
Throughout the programming bar code menus, default values are indicated with asterisks (
* Indicates Default
Most computer monitors allow scanning the bar codes directly on the screen. When scanning from the screen, be sure
to set the document magnification to a level where the bar code can be seen clearly, and bars and/or spaces are not
merging.
*Baud Rate 57,600
Feature/Option
*).
Page 86

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide7-4
Connecting an RS-232 Interface
This connection is made directly from the digital scanner to the host computer.
Serial Port Connector to Host
Power Supply Cable
Interface Cable
Figure 7-1. RS-232 Direct Connection
Interface cables vary depending on configuration. The connectors illustrated in Figure 7-1 are examples only.
The connectors may be different than those illustrated, but the steps to connect the scanner remain the
Note
1. Attach the modular connector of the RS-232 interface cable to the cable interface port on the digital scanner (see Installing
2. Connect the other end of the RS-232 interface cable to the serial port on the host.
3. Connect the power supply to the serial connector end of the RS-232 interface cable. Plug the power supply into an
4. Select the RS-232 host type by scanning the appropriate bar code from RS-232 Host Types on page 7-8.
5. To modify any other parameter options, scan the appropriate bar codes in this chapter.
same.
the Interface Cable on page 1-4).
appropriate outlet.
Page 87

RS-232 Interface 7-5
RS-232 Parameter Defaults
Table 7-1 lists the defaults for RS-232 host parameters. To change any option, scan the appropriate bar code(s) provided in the RS-
232 Host Parameters section beginning on page 7-6.
See Appendix A, Standard Default Parameters for all user preferences, hosts, symbologies, and
miscellaneous default parameters.
Note
Table 7-1. RS-232 Host Default Table
Parameter Default Page Number
RS-232 Host Parameters
RS-232 Host Types Standard 7-8
Baud Rate 9600 7-9
Parity Type None 7-11
Stop Bit Select 1 Stop Bit 7-12
Data Bits 8-Bit 7-12
Check Receive Errors Enable 7-13
Hardware Handshaking None 7-14
Software Handshaking None 7-16
Host Serial Response Time-out 2 Sec 7-17
RTS Line State Low RTS 7-18
Beep on <BEL> Disable 7-18
Intercharacter Delay 0 msec 7-19
Nixdorf Beep/LED Options Normal Operation 7-20
Ignore Unknown Characters Send Bar Code 7-20
Page 88

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide7-6
RS-232 Host Parameters
Various RS-232 hosts are set up with their own parameter default settings (Table 7-2). Selecting standard, ICL, Fujitsu, Wincor-
Nixdorf Mode A, Wincor-Nixdorf Mode B, OPOS/JPOS, Olivetti, or Omron sets the defaults listed below.
Table 7-2. Terminal Specific RS-232
Parameter
Transmit Code ID No YesYesYesYes YesYes
Data Transmission Format
Suffix CR/LF (7013) CR (1013) CR (1013) CR (1013) CR (1013) ETX (1002) CR (1013)
Baud Rate 9600 9600 9600 9600 9600 9600 9600
Parity None Even None Odd Odd Even None
Hardware Handshaking
Software Handshaking None None None None None Ack/Nak None
Serial Response Time-out 2 Sec. 9.9 Sec. 2 Sec. 9.9 Sec. 9.9 Sec. 9.9 Sec. 9.9 Sec.
Stop Bit Select One One One One One One One
ASCII Format 8-Bit 8-Bit 8-Bit 8-Bit 8-Bit 7-Bit 8-Bit
Beep On <BEL> Disable Disable Disable Disable Disable Disable Disable
RTS Line State
Prefix None None None None None STX (1003) None
Standard
(Default)
Data as is Data/Suffix Data/Suffix Data/Suffix Data/Suffix Prefix/Data/
None RTS/CTS
Low High Low Low Low = No data to
ICL Fujitsu
None RTS/CTS
Option 3
Wincor-
Nixdorf
Mode A
Option 3
Wincor-Nixdorf
Mode B/OPOS/
JPOS
RTS/CTS Option 3 None None
send
Olivetti Omron
Data/Suffix
Suffix
Low High
*In the Nixdorf Mode B, if CTS is Low, scanning is disabled. When CTS is High, the user can scan bar codes.
**If Nixdorf Mode B is scanned without the digital scanner connected to the proper host, it may appear unable to scan. If this happens, scan a different RS-232
host type within 5 seconds of cycling power to the digital scanner.
Page 89

RS-232 Interface 7-7
RS-232 Host Parameters (continued)
Selecting ICL, Fujitsu, Wincor-Nixdorf Mode A, Wincor-Nixdorf Mode B, OPOS/JPOS, Olivetti, or Omron enables the transmission of
code ID characters listed in Table 7-3. These code ID characters are not programmable and are separate from the Transmit Code ID
feature. Do not enable the Transmit Code ID feature for these terminals.
Table 7-3. Terminal Specific Code ID Characters
Wincor-
ICL Fujitsu
UPC-A AAAAAA
UPC-E EECCCE
EAN-8/JAN-8 FFFFBBBFF
EAN-13/JAN-13 FF AAAF
Code 39 C <len> None M M M <len> C <len>
Codabar N <len> None N N N <len> N <len>
Code 128 L <len> None K K K <len> L <len>
I 2 of 5 I <len> None I I I <len> I <len>
Code 93 None None L L L <len> None
D 2 of 5 H <len> None H H H <len> H <len>
UCC/EAN 128 L <len> None P P P <len> L <len>
MSI None None O O O <len> None
Bookland EAN F F AAAF
Trioptic None None None None None None
Code 11 None None None None None None
Nixdorf
Mode A
Wincor-
Nixdorf
Mode B/
OPOS/JPOS
Olivetti Omron
IATA H<len> None H H None None
Code 32 None None None None None None
Page 90

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide7-8
RS-232 Host Types
To select an RS-232 host interface, scan one of the following bar codes.
Standard RS-232
ICL RS-232
Wincor-Nixdorf RS-232 Mode A
Olivetti ORS4500
Wincor-Nixdorf RS-232 Mode B
Omron
Page 91

RS-232 Interface 7-9
RS-232 Host Types (continued)
OPOS/JPOS
Fujitsu RS-232
Baud Rate
Baud rate is the number of bits of data transmitted per second. Set the digital scanner's baud rate to match the baud rate setting of
the host device. Otherwise, data may not reach the host device or may reach it in distorted form.
Baud Rate 600
Baud Rate 2400
Baud Rate 1200
Baud Rate 4800
Page 92

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide7-10
Baud Rate (continued)
*Baud Rate 9600
Baud Rate 19,200
Baud Rate 38,400
Baud Rate 57,600
Page 93

RS-232 Interface 7-11
Parity
A parity check bit is the most significant bit of each ASCII coded character. Select the parity type according to host device
requirements.
• Select Odd parity and the parity bit value is set to 0 or 1, based on data, to ensure that an odd number of 1 bits are contained
in the coded character.
• Select Even parity and the parity bit value is set to 0 or 1, based on data, to ensure that an even number of 1 bits are
contained in the coded character.
• Select Mark parity and the parity bit is always 1.
• Select Space parity and the parity bit is always 0.
• Select None when no parity bit is required.
Odd
Mark
*None
Even
Space
Page 94

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide7-12
Stop Bit Select
The stop bit(s) at the end of each transmitted character marks the end of transmission of one character and prepares the receiving
device for the next character in the serial data stream. The number of stop bits selected (one or two) depends on the number the
receiving terminal is programmed to accommodate. Set the number of stop bits to match host device requirements.
*1 Stop Bit
2 Stop Bits
Data Bits
This parameter allows the digital scanner to interface with devices requiring a 7-bit or 8-bit ASCII protocol.
7-Bit
*8-Bit
Page 95

RS-232 Interface 7-13
Check Receive Errors
Select whether or not the parity, framing, and overrun of received characters are checked. The parity value of received characters is
verified against the parity parameter selected above.
*Check For Received Errors
Do Not Check For Received Errors
Page 96

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide7-14
Hardware Handshaking
The data interface consists of an RS-232 port designed to operate either with or without the hardware handshaking lines, Request to
Send (RTS), and Clear to Send (CTS).
If Standard RTS/CTS handshaking is not selected, scan data is transmitted as it becomes available. If Standard RTS/CTS handshaking
is selected, scan data is transmitted according to the following sequence:
• The digital scanner reads the CTS line for activity. If CTS is asserted, the digital scanner waits up to Host Serial Response
Time-out for the host to de-assert the CTS line. If, after Host Serial Response Time-out (default), the CTS line is still asserted,
the digital scanner sounds a transmit error, and any scanned data is lost.
• When the CTS line is de-asserted, the digital scanner asserts the RTS line and waits up to Host Serial Response Time-out
for the host to assert CTS. When the host asserts CTS, data is transmitted. If, after Host Serial Response Time-out (default),
the CTS line is not asserted, the digital scanner sounds a transmit error, and discards the data.
• When data transmission is complete, the digital scanner de-asserts RTS 10 msec after sending the last character.
• The host should respond by negating CTS. The digital scanner checks for a de-asserted CTS upon the next transmission of
data.
During the transmission of data, the CTS line should be asserted. If CTS is deasserted for more than 50 ms between characters, the
transmission is aborted, the digital scanner sounds a transmission error, and the data is discarded.
If the above communication sequence fails, the digital scanner issues an error indication. In this case, the data is lost and must be
rescanned.
If Hardware Handshaking and Software Handshaking are both enabled, Hardware Handshaking takes precedence.
The DTR signal is jumpered to the active state.
Note
• None: Scan the bar code below if no Hardware Handshaking is desired.
• Standard RTS/CTS: Scan the bar code below to select Standard RTS/CTS Hardware Handshaking.
• RTS/CTS Option 1: When RTS/CTS Option 1 is selected, the digital scanner asserts RTS before transmitting and ignores
the state of CTS. The digital scanner de-asserts RTS when the transmission is complete.
• RTS/CTS Option 2: When Option 2 is selected, RTS is always high or low (user-programmed logic level). However, the
digital scanner waits for CTS to be asserted before transmitting data. If CTS is not asserted within Host Serial Response
Time-out (default), the digital scanner issues an error indication and discards the data.
• RTS/CTS Option 3: When Option 3 is selected, the digital scanner asserts RTS prior to any data transmission, regardless
of the state of CTS. The digital scanner waits up to Host Serial Response Time-out (default) for CTS to be asserted. If CTS
is not asserted during this time, the digital scanner issues an error indication and discards the data. The digital scanner deasserts RTS when transmission is complete.
Page 97

Hardware Handshaking (continued)
None
*
RS-232 Interface 7-15
Standard RTS/CTS
RTS/CTS Option 1
RTS/CTS Option 3
RTS/CTS Option 2
Page 98

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide7-16
Software Handshaking
This parameter offers control of the data transmission process in addition to, or instead of, that offered by hardware handshaking.
There are five options.
If Software Handshaking and Hardware Handshaking are both enabled, Hardware Handshaking takes precedence.
• None: When this option is selected, data is transmitted immediately. No response is expected from host.
• ACK/NAK: When this option is selected, after transmitting data, the digital scanner expects either an ACK or NAK response
from the host. When a NAK is received, the digital scanner transmits the same data again and waits for either an ACK or
NAK. After three unsuccessful attempts to send data when NAKs are received, the digital scanner issues an error indication
and discards the data.
The digital scanner waits up to the programmable Host Serial Response Time-out to receive an ACK or NAK. If the digital
scanner does not get a response in this time, it issues an error indication and discards the data. There are no retries when
a time-out occurs.
• ENQ: hen this option is selected, the digital scanner waits for an ENQ character from the host before transmitting data. If
an ENQ is not received within the Host Serial Response Time-out, the digital scanner issues an error indication and discards
the data. The host must transmit an ENQ character at least every Host Serial Response Time-out to prevent transmission
errors.
• ACK/NAK with ENQ: This combines the two previous options. For re-transmissions of data, due to a NAK from the host,
an additional ENQ is not required.
• XON/XOFF: An XOFF character turns the digital scanner transmission off until the digital scanner receives an XON character.
There are two situations for XON/XOFF:
• XOFF is received before the digital scanner has data to send. When the digital scanner has data to send, it waits up to
Host Serial Response Time-out for an XON character before transmission. If the XON is not received within this time, the
digital scanner issues an error indication and discards the data.
• XOFF is received during a transmission. Data transmission then stops after sending the current byte. When the digital
scanner receives an XON character, it sends the rest of the data message. The digital scanner waits up to 30 seconds
for the XON.
*None
ENQ
ACK/NAK
Page 99

RS-232 Interface 7-17
Software Handshaking (continued)
ACK/NAK with ENQ
XON/XOFF
Host Serial Response Time-out
This parameter specifies how long the digital scanner waits for an ACK, NAK, or CTS before determining that a transmission error
has occurred. This only applies when in one of the ACK/NAK Software Handshaking modes, or RTS/CTS Hardware Handshaking
option.
*Minimum: 2 Sec
Medium: 5 Sec
Low: 2.5 Sec
High: 7.5 Sec
Page 100

DS 6608 Product Reference Guide7-18
Host Serial Response Time-out (continued)
Maximum: 9.9 Sec
RTS Line State
This parameter sets the idle state of the Serial Host RTS line. Scan a bar code below to select Low RTS or High RTS line state.
*Host: Low RTS
Host: High RTS
Beep on <BEL>
When this parameter is enabled, the digital scanner issues a beep when a <BEL> character is detected on the RS-232 serial line.
<BEL> is issued to gain a user's attention to an illegal entry or other important event.
Beep On <BEL> Character
(Enable)
*Do Not Beep On <BEL> Character
(Disable)
 Loading...
Loading...