Suunto Rely on Luck TRAINING GUIDEBOOK
SUUNTO ON
How Not
to
Rely on Luck
WHEN OPTIMIZING YOUR TRAINING EFFECT.
TRAINING GUIDEBOOK

6417084 110602

TRAINING GUIDEBOOK
3
CONTENTS
5 INTRODUCTION
6 ENSURE EFFECTIVE TRAINING
7 SUUNTO t6 MEASUREMENTS
7 EPOC (EXCESS POST-EXERCISE OXYGEN CONSUMPTION)
8 HOW DOES EPOC ACCUMULATE?
9 HOW DOES EPOC DECREASE?
9 EPOC IN DIFFERENT FORMS OF EXERCISE
10 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT EPOC
11 TRAINING EFFECT
12 TRAINING EFFECT IN DIFFERENT KINDS OF TRAINING
12 OTHER PERFORMANCE PARAMETERS
13 HEART RATE
14 BREATHING PARAMETERS
15 OXYGEN CONSUMPTION
17 ENERGY CONSUMPTION
18 ALTITUDE
19 SUUNTO t6 AS A TRAINING TOOL
19 COMMON TRAINING PRINCIPLES
19 TRAINING EFFECT
20 DIVERSE TRAINING
21 REST AND RECOVERY
23 SUUNTO t6 TIPS FOR BEGINNERS
23 EASY START
24 ESTIMATING YOUR STARTING LEVEL
25 PROGRESSING IN TRAINING
26 SUUNTO t6 IN GOAL-ORIENTED ENDURANCE TRAINING
26 KNOW YOUR OWN TRAINING LEVELS
27 CONTROL TRAINING
30 SUUNTO t6 AND WEIGHT MANAGEMENT
30 SUITABLE TRAINING INTENSITY
32 TIPS FOR THE PC SOFTWARE
35 GLOSSARY
37 REFERENCES
37 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION

4
TRAINING GUIDEBOOK

INTRODUCTION
5
INTRODUCTION
Welcome to the world of Suunto sports instruments! This guide contains basic information about goal-oriented sports training and how the human body functions during
exercise. It also informs you about how the Suunto t6 wristop computer can help you
achieve better results in your training and helps you get the most out of Suunto t6’s
unique features.

6
TRAINING GUIDEBOOK
In addition to heart rate, EPOC and training effect, Suunto Training Manager’s
training analysis tells you your oxygen
uptake, energy consumption, ventilation,
and breathing frequency. The software
also includes versatile diary and planning
functions for monitoring your training.
Suunto t6 is also an excellent tool for
controlling your exertion level during
training. Its easy-to-use heart rate measurement, stopwatch, and alarm functions adapt to different kinds of
training, helping you to perform your
training in accordance with your goals.
Suunto t6 is a new breed of training tool
based on the accurate measurement of
the time between heartbeats. Based on
this time interval and its detected variations, the Suunto Training Manager PC
software can calculate various information about the performance of your
body during training.
The outstanding benefit of Suunto t6’s
physiological analysis is that it is now
possible, for the first time, to measure
the physiological training load to your
body caused by the exercise, known as
EPOC (Excess Post-exercise Oxygen
Consumption). The software relates the
estimated EPOC to your personal performance level, helping you find just the
right level of exertion to give you the
best possible training effect. Suunto t6
helps you make sure that the time you
spend exercising really does improve
your performance and the sweat you
have poured will not have been in vain.
ENSURE EFFECTIVE TRAINING
CORRECT TRAINING LOAD ENSURES OPTIMAL PROGRESS
EPOC
250
225
200
TOO HARD TRAINING
Too hard for current shape
175
Risk of overtraining
Need to adjust training
150
125
100
75
50
25
0
Optimal training
load area
Targeted training
progress
OPTIMAL TRAINING LOAD AREA
Improving training effect
No need to change the training
methods
TOO EASY TRAINING
When getting into better
shape, training load
should increase to create
improving training effect.
Need to adjust training
Training session
Figure 1. Suunto t6 guides you in your training to exercise optimally
for your fitness level.
2220181614121086420
TIME
(weeks)

TRAINING GUIDEBOOK
7
This chapter introduces the information
related to exercise measured by Suunto
t6, and describes its meaning in terms of
sports.
Suunto t6’s software requires some
background information about the user
for performance analysis. The most
important of these are age, weight,
height, sex, and level of performance
depicting the amount of prior exercise.
Based on this information, the program
calculates assumed values for certain
parameters, such as maximum heart
rate and maximum performance. Actual
maximum heart rate and performance
are, however, very dependent on the
individual, so if you know the exact values of these parameters, we recommend
entering them in the program manually.
This improves the accuracy of the calculation.
SUUNTO t6 MEASUREMENTS
EPOC is short for Excess Post-exercise
Oxygen Consumption and indicates the
amount of extra oxygen your body
needs for recovery after exercise. Due to
the physiological training load caused by
the exercise, your body consumes more
oxygen after exercise than during rest.
The more strenuous the exercise, the
higher this extra consumption of oxygen
(EPOC) is after exercise and the more
your body´s homeostasis is disturbed.
So, EPOC is an indicator of how strenuous the exercise was. It is a numerical
value comprising the duration and inten-
sity of the exercise, as well as other physical and mental factors affecting your
body, such as stress and fatigue.
So far EPOC has only been utilized in
exercise physiology research, because it
was only possible to measure it under
laboratory conditions. Suunto t6 is the
first device that allows the non-invasive
prediction of EPOC already during exercise, which in turn makes it possible to
monitor the exercise load and the training effect.
EPOC (EXCESS POST-EXERCISE
OXYGEN CONSUMPTION)
8
TRAINING GUIDEBOOK
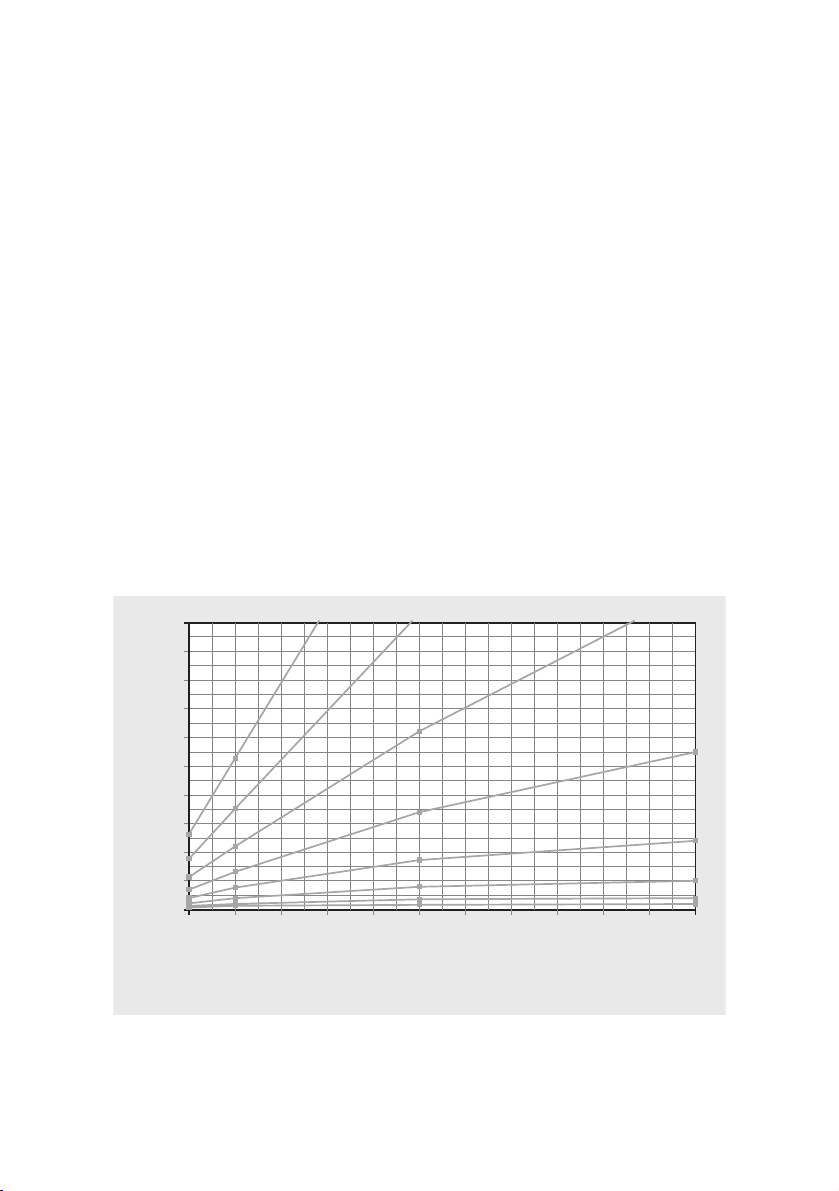
The greater the intensity and the longer
the duration of a training session, the
higher is the EPOC value measured from
the session.
EPOC accumulates faster when the training’s intensity increases than when the
duration increases. This means that low
-intensity training may not necessarily
result in a high EPOC value, even if the
duration of the training is exceptionally
long. With high-intensity training, however, you can reach a high EPOC value
even in a short period of time.
In interval training, periods of high heart
rate and periods of recovery follow each
other. If the recovery periods are short,
EPOC can reach a high value, as it will
not have time to decrease during a short
rest.
The EPOC value attained from similar
exercise can vary from day to day. On a
good day, your body can handle the
training more efficiently, resulting in a
lower EPOC value, but on a bad day, the
physiological training load to your body
and EPOC may be higher. Many factors
affect EPOC during training, such as
your hydration status and the temperature and humidity of the air. If you have
performance anxiety or are nervous,
this may increase the EPOC value.
HOW DOES EPOC ACCUMULATE?
250
225
200
175
150
125
100
EPOC (ml/kg)
75
50
25
0
100% VO
105152025303540455060
2max
90% VO
2max
Time (minutes)
Figure 2. The effect of training duration and intensity (%VO
accumulation.
80% VO
2max
2max
) on EPOC
70% VO
60% VO
50% VO
40% VO
30% VO
55
2max
2max
2max
2max
2max

TRAINING GUIDEBOOK
9
EPOC accumulated during training may
begin to decrease already during the
session, if the training includes sufficiently long rest periods or lower intensity periods.
All substantial physical activity after the
actual training session continues to consume energy delaying the start of full
recovery.
Although EPOC decreases fastest during complete rest, light cool down exercise after hard training will help the
total recovery. Cool down increases the
circulation, flushing the lactic acid from
the muscles faster and speeding up
recovery.
HOW DOES EPOC DECREASE?
EPOC is most useful for describing the
stress caused to your body by forms of
training that especially target the respiratory and cardiovascular system. These
include endurance sports such as running and cycling.
Training involving only small or limited
individual muscle groups (for example,
weight training) will not necessarily
result in an EPOC value as high as training that taxes large muscle groups (for
example running or cross-country skiing). Weight training may feel very
strenuous, because local muscle fatigue
and lactic acid hinder performance even
if your body still has energy for repetitions.
EPOC IN DIFFERENT
FORMS OF EXERCISE
Fast-paced team sports often involve
short but intense bursts of exertion
intermingled with low intensity exertion or rest. During the low-intensity
periods, EPOC increases more slowly
than during high-intensity periods, and
it may even decrease. For this reason,
EPOC is usually lower in team sports
compared to continuous exercise of the
same duration. On the other hand,
breaks in the play enable a high level of
intensity during game time. In some
team sports like basketball or soccer,
where the breaks are short, this allows
EPOC to rise to very high levels.

10
TRAINING GUIDEBOOK
harder on your body on one day, and
easier on another. On a good day, the
same training will have a lower impact
on your body than on a bad day. Factors
increasing EPOC include dehydration,
stress, sleep deprivation, or the start of
flu.
Why is my EPOC sometimes lower
after training while tired than after
an earlier, completely identical training,
I did while well rested?
In certain situations, your body reacts to
training by lowering the heart rate and
maximum heart rate even if your body
is clearly not fully recovered. This may
result in a lower-than-usual EPOC. We
recommend paying attention to such
abnormal behaviour of the EPOC values
and ensure that your training program
includes a sufficient amount of rest,
since continuous training without sufficient recovery leads to overtraining.
Is training more effective
the higher the EPOC?
EPOC is an indicator of how hard the
exercise session was to your body and
how much your physiological homeostasis was disturbed, but the quality of
training always depends on your personal goals and situation. It is important
to have variety in your training program. In order to develop, you need
both high-intensity training where
EPOC rises to high levels, and long-duration, low-intensity training and recovery
exercise where EPOC remains low.
I did short duration, high-intensity
training, after which I was exhausted.
Why was my EPOC value low?
In short-duration, maximal or near-maximal exercise, the cause of exhaustion is
usually an extreme rise in acidity (lactic
acid level) in your body, which makes
you unable to continue training. Longer,
more sustainable workouts may leave
you feeling less exhausted but will cause
more total stress, thus resulting in a
higher EPOC value.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
ABOUT EPOC
Does heart rate influence EPOC?
Yes. The higher the heart rate in relation to the maximum heart rate, the
higher the EPOC.
Why are my EPOC values always
exceptionally high?
If the maximum heart rate used in the
program’s calculations is lower than your
actual maximum heart rate, the program
will overestimate the intensity of the
exercise, resulting in an excessive EPOC
value. Also, too high training intensity
may give exceptionally high EPOC values.
Why are my EPOC values always
exceptionally low?
If the maximum heart rate used in the
program’s calculations is higher than
your actual maximum heart rate, the
program will underestimate the intensity of the exercise, resulting in an EPOC
value which is too low. Also, too low
training intensity may give exceptionally low EPOC values.
Can I speed up the decrease of EPOC?
Yes. Complete rest is the fastest way to
decrease EPOC. However, after high
-intensity training, you should do some
light cool down exercises even if this
slightly delays the start of full recovery.
Why does EPOC only increase at the
start of training, after which it stays
nearly the same or even decreases?
In low-intensity training EPOC will not
increase noticeably after a certain time. In
low-intensity but long-duration training,
EPOC will be lower than in high
-intensity training. However, continuing training even after reaching the EPOC
peak value is worthwhile, because longduration, low-intensity training will develop your body to cope with hard training.
I always run the same distance in the
same time. Why is my EPOC value
sometimes higher, sometimes lower?
Even if training sessions are identical
(same distance, same time), it may be
TRAINING GUIDEBOOK
11
When you practice sports or exercise,
each training session has some kind of
effect on your body. EPOC makes it possible to objectively measure whether
the effect of the session was sufficient
to improve your fitness level. This is
called the Training Effect. The Training
Effect can be determined by comparing
the EPOC value measured from the
training with the athlete’s performance
level.
The Training Effect is an indicator of
how much the training session
improved your aerobic fitness, especially the maximum performance of your
cardiovascular system and the ability to
resist fatigue during endurance training. It does not provide direct information about the effect to, for example,
strength or speed attributes.
The Suunto Training Manager software
divides the Training Effect into five cat-
egories, calculated from your personal
background information. The divisions
between these categories depend on
your fitness level and prior training.
The Training Effect categories are:
1 Minor / recovering effect
2 Maintaining effect
3 Improving effect
4 Highly improving effect
5 Overreaching
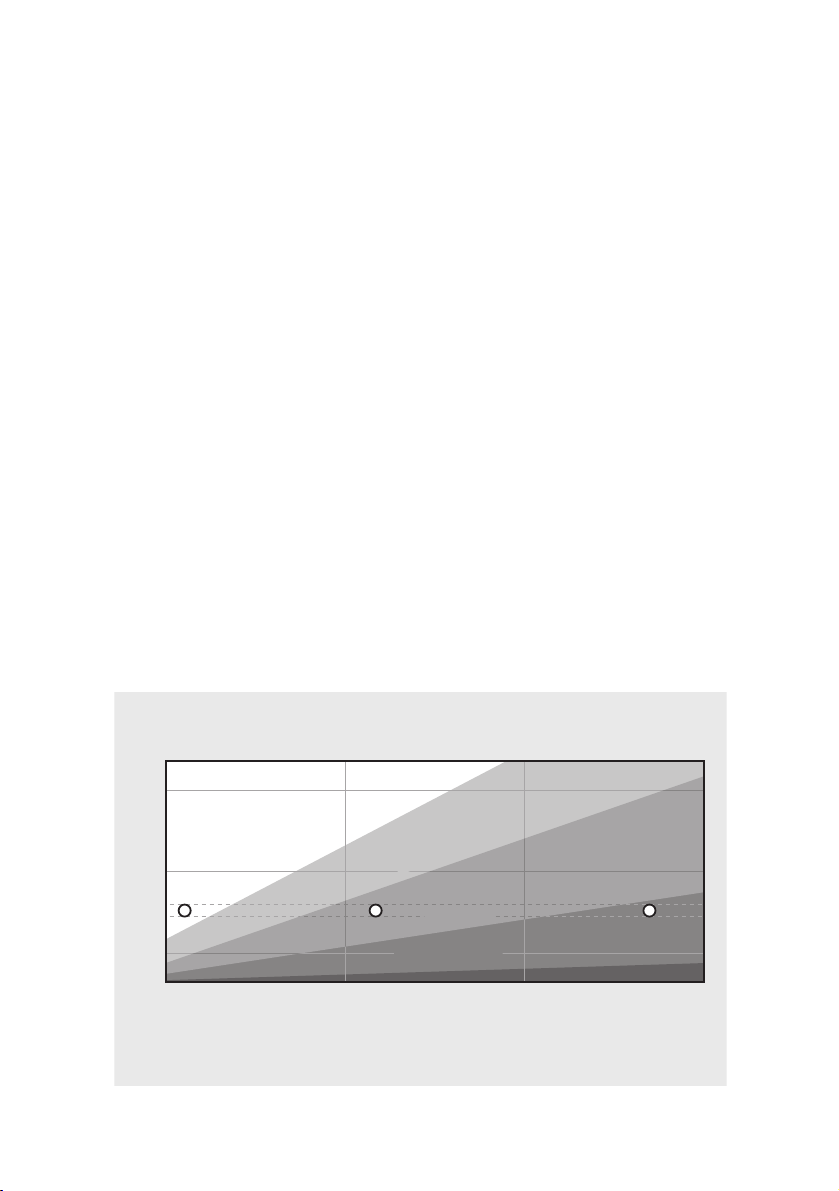
Certain EPOC values correspond with
each category. The better your fitness
level, the more you have to push your
body during the training in order
to improve your performance, and the
higher the EPOC values of the Training
Effect categories. To recap, EPOC is a
general measurement of the physiological load caused by training, used to
determine the individual training value
of each workout.
TRAINING EFFECT
EPOC AND TRAINING EFFECT
EPOC
200
175
150
125
100
75
50
Training
session
25
0
OVERREACHING
HIGHLY IMPROVING EFFECT
PRO
IM
MAINTAINING EFFECT
MINOR EFFECT
INTERMEDIATEBEGINNER
EFFECT
G
IN
V
TOP ATHLETE
Figure 3. The EPOC value required for a certain Training Effect depends on the
fitness level. An EPOC value that indicates highly improving training for a beginner
is merely maintaining for a fit athlete.

Long-duration, low-intensity endurance
base training (>1h, <50% VO
2max
) improves fat metabolism and increases
capillary density and heart volume over
the long term. This builds a foundation
for better maximum performance and
harder training in the future. Base
endurance training does not usually
have an immediate effect on maximum
performance, so the Training Effect
based on the EPOC value is relatively
low.
High-intensity training (>75% VO
2max
)
directly improves physical properties
that increase maximum endurance performance, such as oxygen transport
from lungs to muscles, energy production and utilization, and nerve/muscle
cooperation. Improving these properties increases the maximum oxygen
intake (VO
2max
) and resistance to
fatigue, thus leading to a better
endurance performance. The effect of
such training depends on its duration.
Depending on individual differences,
athletes’ objectives and training history,
the optimal intensity levels of training
are different. Experienced athletes must
usually train at a higher intensity or for
much longer intervals than beginners in
order to reach a Training Effect that
increases fitness.
TRAINING EFFECT IN DIFFERENT
KINDS OF TRAINING
12
TRAINING GUIDEBOOK
In addition to EPOC and Training Effect,
Suunto t6 also measures other data
about the functioning of your body.
This provides you with more informa-
tion about what happens in your body
during training, and allows you to monitor your development and plan your
training in more detail.
OTHER PERFORMANCE PARAMETERS
 Loading...
Loading...