Page 1
1
NOTE: DIAGRAMS & ILLUSTRATIONS NOT TO SCALE.
HOMEOWNER'S CARE AND
OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS
38" and 43" Wood Burning Fireplaces
P/N 725,024M REV. N/C 11/2001
BCF-3885 BRF-3875
BCF-4385 BRF-4375
MODELS
RETAIN THESE INSTRUCTIONS
FOR FUTURE REFERENCE
CUSTOM SERIES
The information contained in this manual applies to all model fireplaces
identified on this page. This information will help you obtain safe and
dependable service from your fireplace system. Keep this document in
a safe place for future reference.
Before you start your first fire, read this Care and Operations Manual
carefully to be sure you understand your fireplace system completely.
Failure to follow these suggestions could result in hazardous operation
or fireplace malfunction, creating a serious potential for personal injury
and/or property damage.
If you have any questions regarding the safe use or operation of your
fireplace, contact your local distributor.
U.L. Report No. MH8988
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
General Safety Precautions................ page 2
General Information........................... page 2
Fuels .................................................. page 2
Gas Logs ........................................... page 2
Disposal of Ashes .............................. page 3
Softwood vs Hardwood ..................... page 3
Starting a Fire .................................... page 4
Damper Control ................................. page 4
Glass Door Operating Safety
Precautions and Instructions ........... page 4
Combustion Air ................................. page 5
Refractories ....................................... page 5
Maintenance Guidelines..................... page 6
Twice a Year Check-Up ...................... page 6
Creosote Formation and Removal...... page 6
Troubleshooting ................................ page 6
Warranty............................................ page 7
Product Reference Information ......... page 7
Replacement Parts ............................ page 7
Accessory Components ..................... page 7
Replacement Parts ............................ page 8
GENERAL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
IMPORTANT! READ AND UNDERSTAND BEFORE YOUR FIRST FIRE.
1. Use SOLID WOOD only for fuel. It is best to
use dry and well seasoned hardwood. Soft
woods tend to burn very quickly. Solid scrap
construction lumber produces excessive sparks.
DO NOT use treated wood, artificial wax based
logs, charcoal, coal, trash, driftwood or woods
that have been dipped in tar, pitch, pine tar,
creosote, etc. Wood products made with synthetic binders, such as plywood, produce
abnormally high temperatures and sputtering,
smoking fires.
2. NEVER use gasoline, gasoline-type lantern
fuel, kerosene, charcoal lighter fluid, or similar
liquids to start or “freshen up” a fire in this
fireplace. Keep any flammable liquids a safe
distance from the fireplace.
3. Keep the chimney damper open while any
fire or smoldering embers are present .
4. Never block or restrict the room air intake
grille across the bottom front or the warm air
outlet grille across the top front of the fireplace.
5. Use care when selecting window treatments
for windows located near the fireplace. Avoid
using combustible flowing window treatments
such as curtains on nearby windows that are of
sufficient length to be blown in front of an open
flame when the window is opened.
6. With the fire burning, close the protective
mesh screens to keep sparks and embers INSIDE the firebox.
7. Keep any combustible furniture or decorative pillows at least 36" (914 mm) from the
fireplace opening.
8. Never leave your fireplace unattended while
it is burning.
9. Be careful adding wood fuel to the fire or
handling fireplace tools such as shovels, tongs
or pokers.
10. Never modify or alter your fireplace system
in any way. To do so may create a potential fire
hazard and void the Limited Warranty.
11. The bottom refractory can be cracked by
excessive abuse such as tossing heavy logs onto
the grate or gouging with fireplace tools. Exercise caution when adding wood to your fireplace.
12. DO NOT use a fireplace insert or any other
product not specified by Superior for use with
this fireplace.
13. If you are using your fireplace as a “decorative appliance,” such as with a permanently
installed gas log set, the fireplace damper must
be permanently fixed in the open position.
Listed “vent-free” gas log sets may be used
with the damper closed.
14. Always ensure that an adequate supply of
replacement combustion air from the outside of
the house is accessible to the fire to support
normal combustion. Fireplaces consume large
volumes of air during the normal combustion
process. In the event the home is tightly sealed
with modern energy efficient features, the optional
combustion air kit may not provide all the air
required to support combustion. The manufacturer is not responsible for any smoking or related
problems that may result from the lack of adequate
combustion air. It is the responsibility of the
builder/contractor to ensure that adequate combustion air has been provided for the fireplace.
15. Neither the manufacturer nor the seller warrants “smoke free” operation nor are we
responsible for inadequate system draft caused
by mechanical systems, general construction
conditions, inadequate chimney heights, adverse
wind conditions and/or unusual environmental
factors or conditions beyond our control.
GENERAL INFORMATION
1. The all-steel, multi-wall firebox is the heat
center of the system. It is well insulated for safe
clearance to combustibles.
2. The hearth floor and sidewalls of the firebox
are lined with a brick pattern reinforced refractory for the look of authenticity and to provide
safety.
3. The metal chimney sections extending from
the firebox top to beyond your roof are two
walled and air-cooled. The inner passage, or
flue, provides the exit for smoke and gases.
4. The flue damper is a two position (fully open
or fully closed) mechanism operated by a handle
found at the center top of the fireplace opening.
It must be open when fire is present so smoke
and gases can escape. It should be closed
ONLY when the fire is completely out – keeping
room air from being lost up the flue.
5. Closed screens prevent fire, sparks and
embers from popping out of the firebox while a
fire is burning. Pull screens back when adding
wood to the firebox.
6. Why use a fuel grate? Besides positioning
the firebed properly, it protects the refractory
floor, back and sides of the fireplace. Further, it
ensures a proper flow of combustion air into
and around the firebed. The grate must be used
at all times when burning. Your warranty may
be voided without the use of this grate.
7. Remember, your fireplace is not intended to
heat your entire home.
FUELS
Never Use Coal in Your Fireplace
Your fireplace system is not designed to be
used with coal derivative products. The combustion process of certain types of coal can
deposit corrosive materials in the fireplace and
chimney system which can lead to premature
product failure. Never use coal as a fuel in this
fireplace system.
Gas Logs
If your fireplace system was installed with a gas
line, you may wish to install one of two types of
gas log sets.
This fireplace has been tested and approved for
use with a decorative gas appliance incorporating an automatic shut-off device and complying
with the Standard for Decorative Gas Appliances for installation in vented fireplaces, ANSI
Z21.60 (1991) or American Gas Association
draft requirements for Gas-Fired Log Lighters
for Wood Burning Fireplaces, Draft No. 4 dated
August, 1993. Decorative gas appliances may
be installed in these fireplaces. Installation
must be in accordance with the National Fuel
Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 for compliance with the
revised U.L. 127 Standard.
2
NOTE: DIAGRAMS & ILLUSTRATIONS NOT TO SCALE.
Page 3
CAUTION: WHEN USING A DECORATIVE
GAS APPLIANCE, THE FIREPLACE
DAMPER MUST BE SET TO THE FULLY
OPEN POSITION.
These fireplaces have been tested and approved
to ANSI/IAS/AGA Z21.11.2 for use with an
unvented gas appliance having a maximum rating of 26,000 BTU (for the BRF-3875 and
BCF-3885 models) and 32,000 BTU (for the
BRF-4375 and BCF-4385 models) and complies
with the Standard for Factory-Built Fireplaces,
U.L. 127, when installed with unvented gas log
sets. The limit may be increased to 40,000 BTU
providing that minimum combustible mantle
heights were increased to at least 18 inches
when the fireplace was installed.
Prior to installing any gas log set, (Vented or
Unvented) refer to the fireplace installation
instructions for verification of mantle heights
and placement of combustible materials around
the firebox opening. NEVER INSTALL AN
UNVENTED GAS LOG SET WITH A BTU RATING GREATER THAN 26,000 BTU (BRF-3875
AND BCF-3885 MODELS) AND 32,000 BTU
(BRF-4375 AND BCF-4385 MODELS) IF THE
COMBUSTIBLE MANTLE PROJECTIONS ARE
LOWER THAN 18 INCHES ABOVE THE FIREPLACE OPENING. Vented gas log sets do not
have restrictions placed upon their BTU rating.
Wood Fuel Pointers
Wood is a wonderful renewable fuel source.
Normally it burns clean, leaving only a minimum
of waste ash, provides comforting heat and can
provide a variety of aromas and visual images.
You will want to know which woods are best for
use. Sometimes you may want a quick, short
fire to offset a morning chill. Soft woods are
preferable in this case. Other times you would
want more slow burning and a uniform heat
output. Hardwoods are preferable for this use.
The amount of heat available from the logs will
be about equal on a weight basis. However,
logs are generally not weighed so the amount of
heat will depend on:
1. The type of wood used.
2. How dry it is.
3. How many logs you put in.
4. The size of the logs.
DISPOSAL OF ASHES
Ashes should be placed in a metal container
with a tight fitting lid. The closed container of
ashes should be placed on a noncombustible
floor or on the ground, well away from all
combustible materials, pending final disposal.
If the ashes are to be disposed of by burial in soil
or other wise locally dispersed, they should be
retained in the closed container until all cinders
have thoroughly cooled.
SOFTWOOD VS HARDWOOD
Softwoods contain about 15 percent highly
flammable resin which generates creosote soot
in the chimney flue. Burning softwood exclusively may not be as desirable nor as safe as
burning denser hardwoods. Many experienced
fire-builders use small amounts of softwood
kindling and newspaper in conjunction with
starting a fire with split hardwood logs. Here are
some guidelines to remember:
1. Softwoods produce fast warming and shorter
fires. Hardwoods burn less vigorously, have
shorter flames and produce steady, glowing
coals.
2. As a general rule, denser woods contain
more potential heat per pound. Most softwoods
offer moderate heat value per pound.
3. Different woods vary widely in flame heights,
flame intensities, smoke characteristics and in
sparking. Most hardwoods do not spark.
4. Most freshly cut “green” wood will not burn
well and will smoke. Green wood can be from
10 to 40 percent less efficient than air-dried
seasoned wood.
5. Moisture and resin found inside unseasoned
wood cells will build up pressure under heat
and explode as sparks.
6. Most wood needs to be seasoned 9 to 12
months to reduce the moisture content and
produce good steady fires. When moisture
content is reduced from 60 to 20%, the gain in
heat potential is nearly 7%.
7. Proper storage of wood, especially during
seasoning, is essential. We recommend that
you:
c. Store wood where it will not be excessively
exposed to weather, such as under a tarp or
under a roof.
d. Do not stack wood directly against the walls
of your home.
8. Be a knowledgeable wood buyer. There is a
difference in cord sizes. A standard cord stack
of logs is 4 ft. high by 8 ft. long by 4 ft. deep or
the equivalent of this cubic footage, (
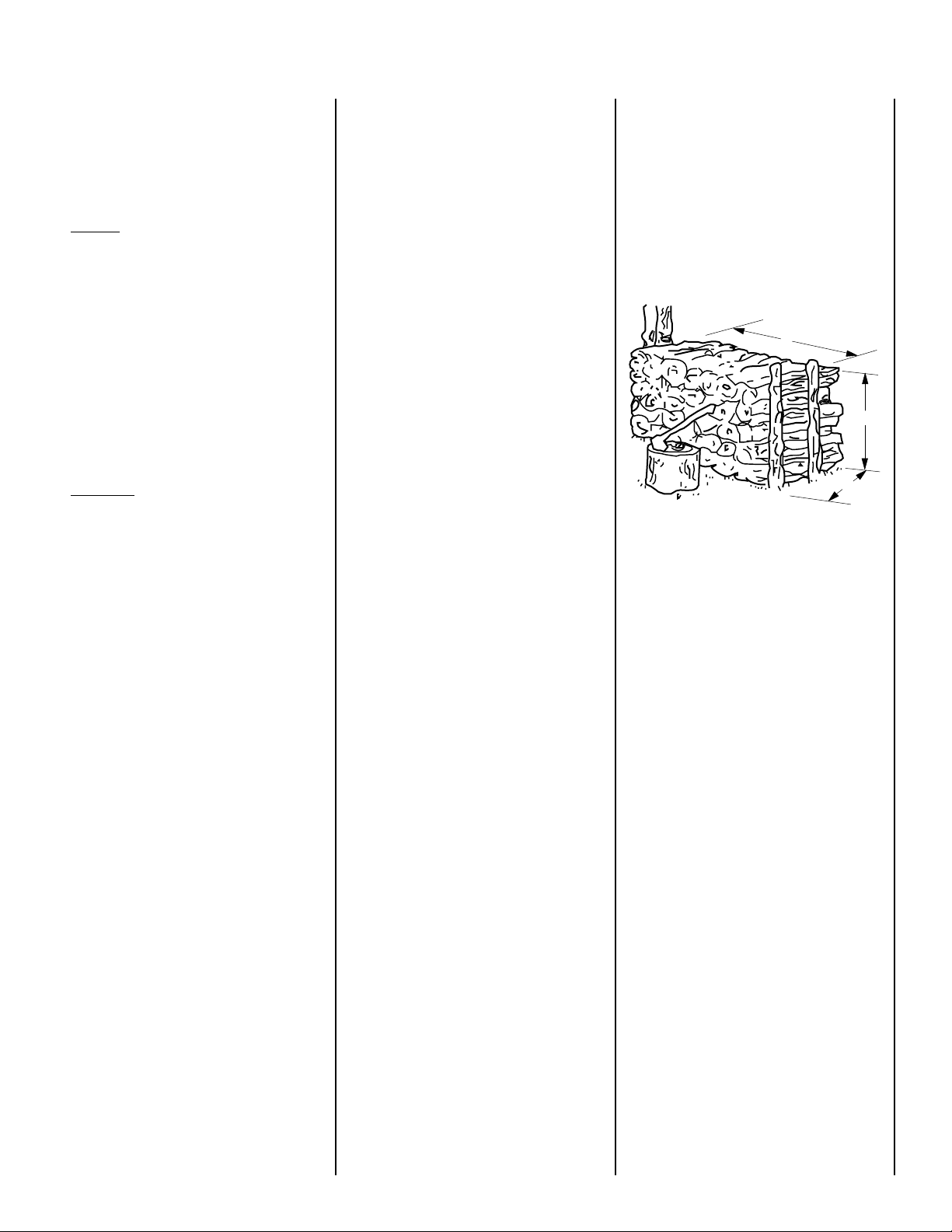
Figure 1
Standard
Cord of
8'
Wood
4'
4'
Figure 1
A face cord is the same height and length as a
standard cord but the depth is only the length
of the logs (12, 18 or 24 inches). A face cord
can contain as little as 25% of the wood found
in a standard cord.
If you buy by the ton, remember that wood
becomes lighter as it dries. When buying green
or wet wood, ask for some extra poundage to
allow for the extra water you will be getting.
9. When comparing woods of the same moisture content and same species, we find most
woods have approximately the same heating
potential per pound.
However, most wood is sold by volume, not by
weight. To determine the best heating source,
look at the density of various wood types.
(Density is the weight for a given size.) The
higher the density, the more potential heat
output. A standard cord has a volume of 128
cubic feet. This figure also includes the air
space between and around the wood. The actual volume in a standard cord is between 60
and 100 cubic feet; depending on how tightly
the wood is packed.
).
The last statement means that one big log
weighing 10 pounds has as much heating potential as 10 pounds of twigs. However, air
cannot get at the solid log to feed the fire so the
solid log will burn slowly. While you would get
the same amount of heat out of either fire, the
smaller the pieces of wood and the more air
space around them, the faster the fire will burn.
a. Never store wood on the ground. This will
cause rotting and insect infiltration. Raise wood
on flat rock or scrap wood.
b. Stack wood loosely to allow air circulation.
NOTE: DIAGRAMS & ILLUSTRATIONS NOT TO SCALE.
Assuming that you are comparing two standard
cords of different species but the same volume
and moisture content, the denser species will
provide more BTU’s. The table of wood species/
densities reveals more helpful guidelines.
3
Page 4

HARDWOODS DENSITY
Alser, Red .41
Ash .49-.60
Aspen .38-.39
Basswood, American .37
Beech, American .64
Birch .55-.65
Butternut .38
Cherry, Black .50
Chestnut, American .43
Cottonwood .34-.40
Elm .60.63
Hackberry .53
Hickory, Pecan .60.66
Hickory, True .69-.75
Honey locust .66 (est.)
Locust, Black .69
Magnolia .48-.50
Maple .48-.63
Oak, Red .59-.67
Oak, White .64-.88
Poplar .42
Sassafras .42
Sweet gum .52
Sycamore, American .49
Tanoak .64 (est.)
Tupelo .50
Walnut, Black .55
Willow, Black .39
SOFTWOODS DENSITY
Bald cypress .46
Cedar .31-.47
Douglas Fir .46-.50
Fir .32-.43
Hemlock .40-.45
Larch, Western .52
Pine .39-.59
Redwood .35-.40
Spruce .35-.41
Tamarack .53
STARTING A FIRE
1. To start a fire in a the fireplace properly, first
check the operation of the flue damper.
2. To prevent smoking at start-up, close any
window located near the fireplace when first
lighting a fire. The closed windows may be
reopened once a chimney draft is drawn in the
fireplace.
DAMPER CONTROL
This fireplace is fitted with a manually controlled chimney damper. The chimney damper
should be closed when the fireplace is not in
use to prevent cold air from entering the home
through the chimney system.
The damper is controlled through the use of a
control lever located within the firebox opening at the top center just behind the firebox
lintel (
Figure 2
). The control lever snaps into
place at the extreme range of motion, up and
back in the closed position. When pulled
forward and down, the damper is open.
Damper
Closed
Lintel
Damper
Open
Figure 2
The appliance flue damper must always remain open when operating.
2. The grate in the firebox should be centered
on or over the bottom hearth so your fire can
breath properly. Crumble and twist plenty of
newspapers UNDER the grate and criss-cross
some small dry kindling sticks on top of the
paper or on the bottom of the grate.
3. Build a pyramid of three split logs (split will
start much faster). Arrange the uneven wood
to provide plenty of air space between.
4. Now, light the paper at both sides of the
firebox.
5. Close the screens to prevent the escape of
sparks and embers.
6. Close the damper only when your fire is
completely out and ashes are cold. Keep closed
when fireplace is not in use to prevent unnecessary loss of heated or cooled air.
GLASS DOOR OPERATING SAFETY
PRECAUTIONS AND INSTRUCTIONS
These fireplaces may be equipped with glass
doors. Refer to the end of this document for a
listing of the glass doors approved for use with
these fireplaces.
WARNING: IF YOUR FIREPLACE IS
EQUIPPED WITH GLASS DOORS, IT
SHOULD BE OPERATED WITH THE
DOORS FULLY OPEN OR FULLY CLOSED.
IF THE DOORS ARE LEFT PARTIALLY
OPEN, GAS AND FLAMES MAY BE DRAWN
OUT OF THE OPENING, CREATING RISKS
OF BOTH FIRE AND SMOKE. REFER TO
FIGURES 3 AND 4
FOR PROPER OPER-
ATING CONDITIONS.
Glass Doors
Fully Open or
Fully Closed
(Bi-Fold Doors)
Figure 3
Glass Doors
Fully Open or
Fully Closed
(Twin-Pane Doors)
Figure 4
CAUTION: IF A SMOKING CONDITION EXISTS, GLASS DOORS SHOULD BE CLOSED
DURING FIREPLACE OPERATION.
Care and Cleaning of Your Glass Doors
Never clean the glass when the doors are hot.
Do not use ammonia or ammonia based glass
or household cleaner to clean the glass or the
door frame. An ammonia based cleaner will
damage the finish of the glass door.
Clean the glass doors by wiping with a damp
towel followed by a clean dry towel to remove
streaks.
Remove stubborn stains from the glass with a
mild soap solution and a towel dampened with
clean water. Dry with a clean dry towel.
4
NOTE: DIAGRAMS & ILLUSTRATIONS NOT TO SCALE.
Page 5

• The fire must always be confined within the
boundaries of the fuel grate.
• The fireplace screens must always be closed
whenever the fireplace is being used.
• Never slam the glass door since it could cause
the glass to break.
• Do not build excessively large or hot fires —
scorching or discoloring of the plated brass
trim may occur.
• Extreme temperature changes can cause glass
breakage — do not build a hot fire and close the
glass doors if the doors are cold.
• If the tempered glass pane becomes scratched
or chipped, it creates a weakness in the glass
which can cause the glass to break when
heated. Replace the pane of glass by contacting your nearest dealer.
CAUTION: GLASS AND METAL FRAMES
GET HOT — ALWAYS USE HANDLES TO
OPEN AND CLOSE THE DOORS.
WARNING: BE AWARE THAT SAFETY
GLASS IS UNPREDICTABLE WHEN HOT
AND MAY BREAK, EXPELLING HOT GLASS
INTO THE ROOM. ADVISE ALL FAMILY
MEMBERS TO REMAIN WELL AWAY
FROM THE FIREPLACE WHEN OPERATING WITH DOORS CLOSED TO AVOID
ANY POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
IMPORTANT: Plated polished brass glass
doors may have a plastic covering over all
brass pieces for protection during shipping
and handling. The plastic covering should be
removed before installation of the glass doors.
Under the plastic covering is a protective
lacquer coating which should not be removed.
In some instances, if it is removed, irreversible damage to the brass finish could occur.
Refer to the following for specific information
on plated polished brass.
IMPORTANT: The lacquer coating on the polished brass glass doors and trim pieces can
be damaged or removed causing corrosion
and/or tarnish. Do not remove the protective
lacquer coating from plated polished doors
and trim. To help protect the finish; use a
non-acidic wax and avoid the over-spray of
acidic/alkali based glass cleaners on the
brass pieces. Please understand that the
heat of the fire will cause the protective
lacquer finish to slightly change to a light
caramel color. Do not be alarmed as this is
a normal occurrence.
COMBUSTION AIR
A proper amount of combustion air is important
for your fireplace. Fireplaces consume large
amounts of oxygen. It is important to allow an
adequate supply of air.
If the fireplace is not equipped with an outside
air kit, it may not obtain sufficient amounts of
combustion air from inside the house or structure in which it is installed. Therefore, the fire
may draw from an outside air source and pull
air in through the chimney. This may cause
smoke spillage into the room.
Smoke spillage often occurs when a fire is first
started, until the fireplace and the chimney has
had the opportunity to “come up to temperature” and to begin to function normally. If
smoke spillage problems persist, a window
may be opened just a crack to allow the proper
flow of combustion air to the fireplace.
If your fireplace is equipped with an outside
combustion air kit, keep it open at all times
when fire is burning and close when fire is out
to prevent cold air intrusion.
Combustion Air Control
If your BCF/BRF Series fireplace is equipped
with the optional combustion air kit, the combustion air control lever is located on the left
side of the fireplace opening behind the screen
panel. To open the air damper, pull the lever all
the way out. To close, push the lever all the
way in (
Figure 5
).
Closed
Open
Figure 5
The outside air damper should be kept closed
on all fireplaces except when the fireplace is in
operation. If there is no heat present in the
firebox, the air damper should be closed at
night before retiring to prevent intrusion of
outside air into the home.
WARNING: DO NOT OPERATE THE COMBUSTION AIR ACTUATOR UNLESS A
COMPLETE OUTSIDE COMBUSTION AIR
VENT SYSTEM HAS BEEN INSTALLED
WITH YOUR FIREPLACE.
REFRACTORIES
All fireboxes contain a furnace refractory floor,
sides and back. These refractories are reinforced with steel, but can be broken by improper
use. Dropping logs on the bottom refractory
and building fires directly against the refractories can cause premature burnout of these
components. It may easily be repaired or replaced at costs far below repair and maintenance
for masonry fireplaces.
Proper care and “burn-in” of the firebox will
prolong the period of enjoyment without extensive maintenance. For the first few uses, build
small fires – not roaring infernos. The materials
used in the refractories contain and absorb moisture. It is important to “cure” the refractories by
building only modest fires. Under normal usage,
it is expected that hairline cracks will appear in
the refractory surface. These hairline cracks do
not affect the safe operation of the fireplace.
Refractories should be replaced when:
1. The crack opens more than ¹⁄₄" (19 mm).
2. Pitting in the surface is extensive and pits
become deeper than ³⁄₁₆" (4.76 mm).
3. Any piece of refractory larger than 2" (51 mm)
in radius and ³⁄₁₆" deep becomes dislodged.
If conditions 1, 2 or 3 occur, the refractory
should be replaced.
MAINTENANCE GUIDELINES
Your fireplace is designed to operate troublefree with minimum maintenance. However, like
any fine appliance, it deserves and requires
some housekeeping attention.
Your fireplace will perform better – and certainly look more attractive to family and friends
– if it is cleaned before each use. Before the first
seasonal use in Autumn and after the last fire in
Spring, it is important to inspect the fireplace
system carefully. We recommend at least two
complete fireplace inspections a year.
NOTE: DIAGRAMS & ILLUSTRATIONS NOT TO SCALE.
5
Page 6

6
NOTE: DIAGRAMS & ILLUSTRATIONS NOT TO SCALE.
Before Each Use
1. Clean the firebox of excessive ashes. Some
owners prefer to leave a small layer to insulate
the cold refractory below the grate which helps
fire starting.
This fireplace has a factory supplied grate attached, it is permissible to remove the grate for
cleaning; however, the grate must be re-attached to the fireplace before the next burn.
2. Keep the fireplace screens clean so combustion air flows freely.
3. Spot check the brick-like refractory for small
cracks. Heat from the fire expands it slightly.
When it cools, it contracts.
TWICE A YEAR CHECK-UP
Normally, twice a year, you should inspect your
fireplace following this list:
1. Inspect the opening in your chimney top and
remove any debris that could clog it. The cap is
usually held in place by four (4) screws, which
remove easily for checking or cleaning the full
length of the flue from above. Remove the
chimney top while wearing gloves to guard
against any sharp metal edges.
2. Inspect the entire flue from the top down for
obstructions such as birds nests, leaves, etc.
This may be done by using a flexible handled
chimney cleaning brush. If the chimney contains offset/return elbows; a soft brush cleaning
from the top down to any elbow and then from
the firebox up to the offset/return section is the
proper method. The beam from a powerful
flashlight will help in this inspection.
3. Look up from inside the fireplace (damper
open) to see any obstructions in the lower flue
area. If present, shut the damper and glass doors
(if installed) to seal the firebox and contain any
soot that might fall. If your do not have glass
doors installed, a damp sheet covering the fireplace opening and sealed with masking tape will
do. Then clean the flue from the top down (if an
offset system, clean per Step 2) using a proper
size chimney brush with flexible pole sections.
Don’t open the doors or remove the sheet until all
soot has settled. Vacuum, don’t sweep.
4. Check the metal flashing and seals around
your chimney. Seal any cracks or loose nailhead openings to prevent roof leaks.
1. Remember – always check to ensure your
flue damper is in the open position before
lighting a fire!
2. When lighting your fire, a little smoke may
escape into the room – more likely if the
chimney is cold. To correct this, hold a lighted
newspaper up inside the firebox near the open
flue damper. This will turn around any downdraft and clear the flue of cold air. As your log
fire burns below, the updraft will improve as
the chimney heats up.
3. Is your fire too far forward? Move it toward
the back with your poker. Keep the fire well
within the confines of your fuel grate.
4. Keep your fire up on the grate and the
refractory below free of excessive ashes. The
fire needs plenty of air movement around the
logs.
5. If smoking occurs an hour or two after
lighting the fire, perhaps your well-insulated
house is too airtight and there is scarcely any
way for replacement air to enter and feed the
fire. Check to see if your outside combustion
air kit (if installed) is open. Check outside to
ensure no obstructions are in front of exterior
air entry. Open a window slightly, open doors
to one or two rooms and see if this stops the
smoking.
6. Is a vent fan, exhaust hood or central
heating/cooling system stealing combustion
air from your fireplace? If their volume is high
enough, this can cause negative pressure and
an unwanted downdraft – and smoking.
7. Is your wood fuel too wet or unseasoned?
Or does it contain some chemical substance
that causes sputtering, smoking and toxic
fumes?
8.
Figure 6
illustrates the correct height of
your chimney top. It is unlikely that your installation does not adhere to the installation
instructions. However, if not correct, you could
experience an unusual downdraft. Usually,
the best solution is to increase the chimney
height. This may also be necessary if nearby
trees, adjoining roof lines or a hill is causing a
downdraft condition.
9. Remember, your fireplace has been designed as a supplemental heating device only,
it is not intended to heat your entire home.
CREOSOTE FORMATION AND REMOVAL
When wood is burned slowly, it produces tar
and other organic vapors, which combine with
expelled moisture to form creosote. The creosote vapors condense in the relatively cool
chimney flue of a slow-burning fire. As a result,
creosote residue accumulates on the flue lining. When ignited, this creosote makes an
extremely hot fire.
The chimney should be inspected at least twice
yearly during the heating season to determine
if a creosote build-up has occurred.
If creosote has accumulated, it should be removed to reduce the risk of a chimney fire.
If creosote build-up is found, do not use chemical chimney cleaners that are poured on a hot
fire. The chemical cleaners can be dangerous
and generally only work on the flue section
nearest the fire, leaving the rest of the flue
unaffected. It is best to take the time to clean the
flue as previously described or have the chimney professionally cleaned by a qualified
chimney sweep.
TROUBLESHOOTING
No Smoking Allowed
Your new fireplace is designed not to smoke if
properly installed and operated per our instructions. If you do experience a problem,
following are several things to check:
WARNING: CONTINUED OVERFIRING
CAN PERMANENTLY DAMAGE YOUR
FIREPLACE SYSTEM. SOME EXAMPLES
OF OVERFIRING ARE:
• BURNING QUANTITIES OF SCRAP
LUMBER, PINE BRANCHES, PAPER OR
CARDBOARD BOXES WHICH EXCEED
THE VOLUME OF THE NORMAL LOG
FIRE.
• USE OF ARTIFICIAL WAX BASE LOGS,
TRASH OR OTHER CHEMICALS OR
CHEMICALLY TREATED COMBUSTIBLES.
5. Clean the firebox thoroughly by using a soft
brush or equivalent.
Page 7

Less Than 10'
ACCESSORY COMPONENTS
2' Min.
3' Min.
10'
2' Min.
3' Min.
Figure 6
WARRANTY
This fireplace is covered by a limited warranty detailed separately from this document.
Retain this manual. File it with your other documents for future reference.
PRODUCT REFERENCE INFORMATION
We recommend that you record the following important information about your fireplace. Please
contact your dealer for any questions or concerns.
Your Fireplace's Model Number _______________________________________
Your Fireplace's Serial Number ________________________________________
12M09 43 ABF
12M07 38 ABF
12M10 43 ABF-BB
Bi-Fold Doors 12M08 38 ABF-BB
Bi-Fold Doors
Your fireplace can be fitted with beautiful bifold doors. Model ABF doors are available for
use with these fireplace. Doors are easily fitted
to the fireplace opening. Use Model 38 doors
with 38 inch fireplaces and Model 43 doors with
43 inch fireplaces. Model ABF doors come with
standard black finish. Model ABF-BB doors
have a beautiful bright brass finish.
The Date On Which Your Fireplace Was Installed __________________________
Your Dealer's Name_________________________________________________
REPLACEMENT PARTS
A complete parts list is found at the end of this
manual. Use only parts supplied from the
manufacturer.
Normally, all parts should be ordered through
your distributor or dealer. Parts will be shipped
at prevailing prices at time of order.
When ordering repair parts, always give the
following information:
1. The model number of the appliance.
2. The serial number of the appliance.
3. The part number.
4. The description of the part.
5. The quantity required.
6. The installation date of the appliance.
Forced Air Blower Kit 011781 FAK-1500
Blower Kit
The FAK-1500 blower provides for a constant
velocity forced air circulation feature for your
appliance.
NOTE: DIAGRAMS & ILLUSTRATIONS NOT TO SCALE.
7
Page 8

REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST
DESCRIPTION Part No. Qty. Part No. Qty.
Fireplace Assembly – – – –
Firescreen 090674 2 090675 2
Rod, Screen 011382 2 010234 2
Refractory, Side, Right (Standard) 026042 1 026042 1
Refractory, Side, Left (Standard) 026041 1 026041 1
Refractory, Rear (Standard) 026021 1 026022 1
Refractory Base (Standard) 044991 1 044992 1
Grate 12M79 1 12M79 1
Models 38 Models 43
The manufacturer reserves the right to make changes at any time, without notice, in design,
materials, specifications, prices and also to discontinue colors, styles and products.
Consult your local distributor for fireplace code information.
Printed in U.S.A. © 2001 by LHP
P/N 700,024M REV. N/C 11/2001
1110 West Taft Avenue
Orange, CA 92865
 Loading...
Loading...