Subaru Baja 2005 User Manual
BASIC DIAGNOSTICS PROCEDURE
WIRING SYSTEM
1. Basic Diagnostics Procedure
A: BASIC PROCEDURES
1. GENERAL
The most important purpose of diagnostics is to determine which part is malfunctioning quickly, to
save time and labor.
2. IDENTIFICATION OF TROUBLE SYMPTOM
Determine what the problem is based on symptom.
3. PROBABLE CAUSE OF TROUBLE
Look at the wiring diagram and check system’s circuit. Then check the switch, relay, fuse, ground,
etc.
4. LOCATION AND REPAIR OF TROUBLE
1) Using the diagnostics narrow down the causes.
2) If necessary, use a voltmeter, ohmmeter, etc.
3) Before replacing certain component parts
(switch, relay, etc.), check the power supply,
ground, for open wiring harness, poor connectors,
etc. If no problems are encountered, check the
component parts.
4) With test set-up held as it is, turn the switch ON.
The voltmeter will indicate a voltage and, at the
same time, the light will come on.
5) The circuit is in good order. If a problem such as
a lamp failing to light occurs, use the procedures
outlined above to track down malfunction.
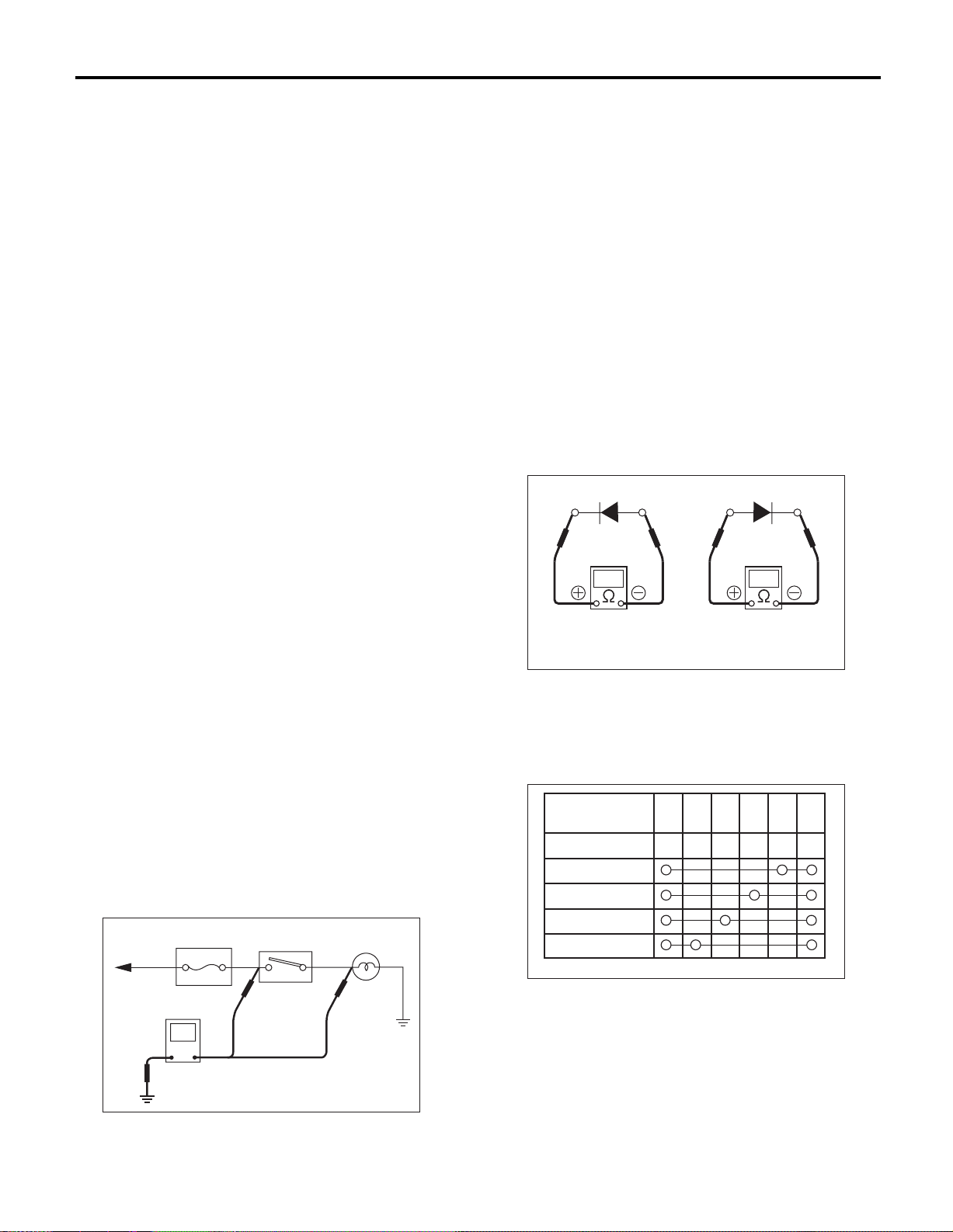
2. CIRCUIT CONTINUITY CHECKS
1) Disconnect the battery cable or connector so
there is no voltage between check points.
Contact the two leads of an ohmmeter to each of
the check points.
If the circuit has diodes, reverse the two leads and
check again.
2) Use an ohmmeter to check for the diode continuity. When contacting the negative lead to diode
positive side and positive lead to negative side,
there should be continuity.
When contacting the two leads in reverse, there
should be no continuity.
5. CONFIRMATION OF SYSTEM OPERATION
After repairing, ensure that the system operates
properly.
B: BASIC INSPECTION
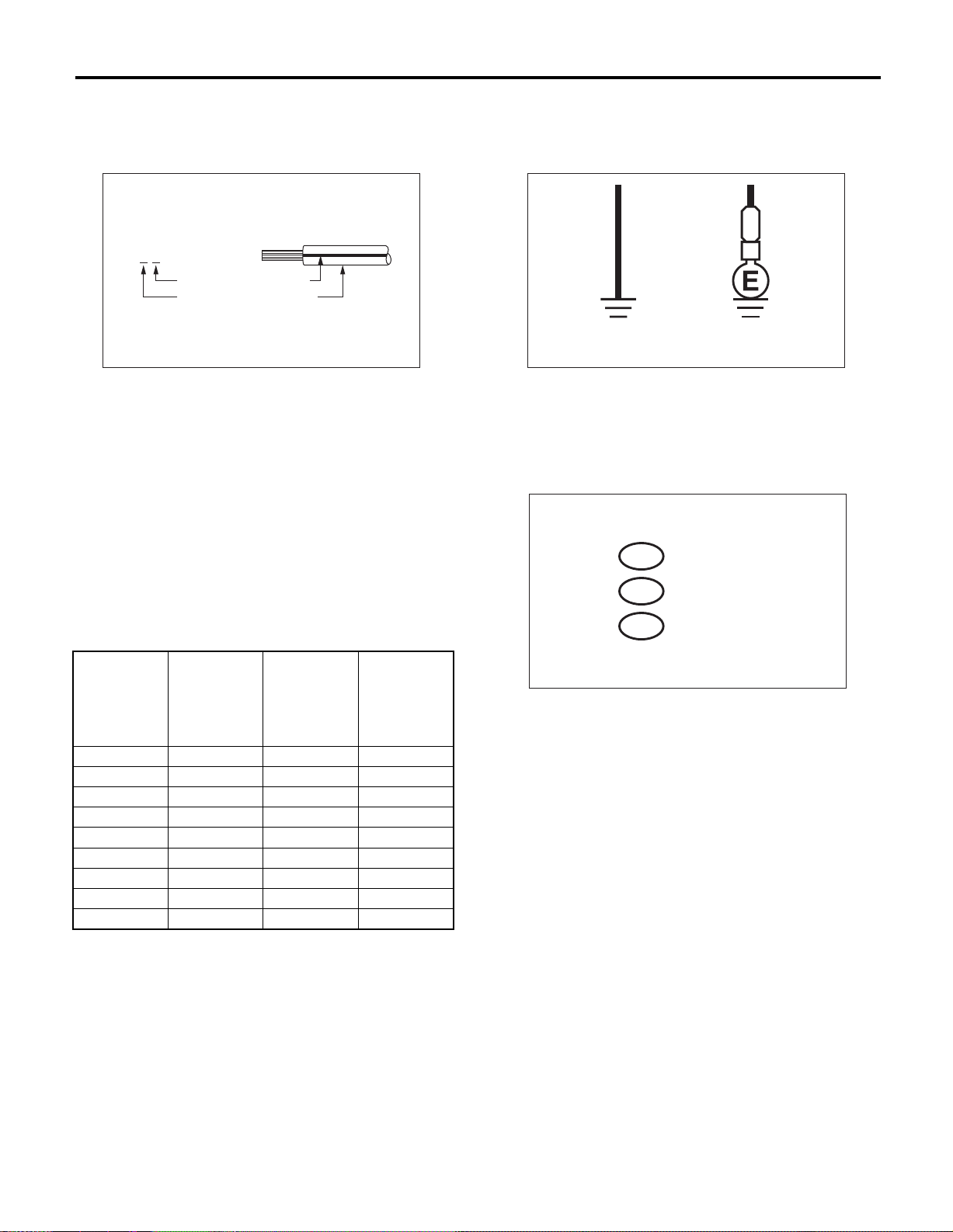
1. VOLTAGE MEASUREMENT
1) Using a voltmeter, connect the negative lead to a
good ground point or negative battery terminal and
the positive lead to the connector or component terminal.
2) Contact the positive probe of the voltmeter on
connector (A).
The voltmeter will indicate a voltage.
3) Shift the positive probe to connector (B). The
voltmeter will indicate no voltage.
To power
supply
FUSE
(A)
Switch
Light
(B)
Continuity No continuity
WI-00095
3) Symbol “❍ — ❍” indicates that continuity exists
between two points or terminals. For example,
when a switch position is “3”, continuity exists
among terminals 1, 3 and 6, as shown in table below.
Terminal
Switch Position
OFF
1
2
3
4
1
234
56
WI-00096
V
WI-00094
WI-3
WIRING SYSTEM
BASIC DIAGNOSTICS PROCEDURE
3. HOW TO DETERMINE AN OPEN CIRCUIT
1) Voltmeter Method:
An open circuit is determined by measuring the
voltage between respective connectors and ground
using a voltmeter, starting with the connector closest to power supply. The power supply must be
turned ON so that current flows in the circuit. If voltage is not present between a particular connector
and ground, the circuit between that connector and
previous connector is open.
Open circuit or wiring
V
No voltage is present
Voltage is present
2) Ohmmeter method:
Disconnect all connectors affected, and check the
continuity in wiring between adjacent connectors.
When the ohmmeter indicates “infinite”, the wiring
is open.
V
WI-00097
Open circuit
4. HOW TO DETERMINE A SHORT CIRCUIT
1) Test lamp method:
Connect a test lamp (rated at approx. 3 watts) in
place of the blown fuse and allow current to flow
through the circuit. Disconnect one connector at a
time from the circuit, starting with the one located
farthest from power supply. If the test lamp goes
out when a connector is disconnected, the wiring
between that connection and next connector (farther from the power supply) is shorted.
Test lamp
Shorted wiring
Fuse holder
WI-00099
2) Ohmmeter method:
Disconnect all affected connectors, and check the
continuity between each connector and ground.
When the ohmmeter indicates continuity between a
particular connector and ground, that the connector
is shorted.
Shorted connector
Continuity does not exist.Continuity exists.
WI-00098
Continuity does not exist.
Continuity exists.
WI-00100
WI-4
BASIC DIAGNOSTICS PROCEDURE
WIRING SYSTEM
C: HOW TO READ WIRING DIA-
GRAMS
1. WIRING DIAGRAM
The wiring diagram of each system is illustrated so
that you can understand the path through which
electric current flows from battery.
Sketches and codes are used in the diagrams.
They should read as follows:
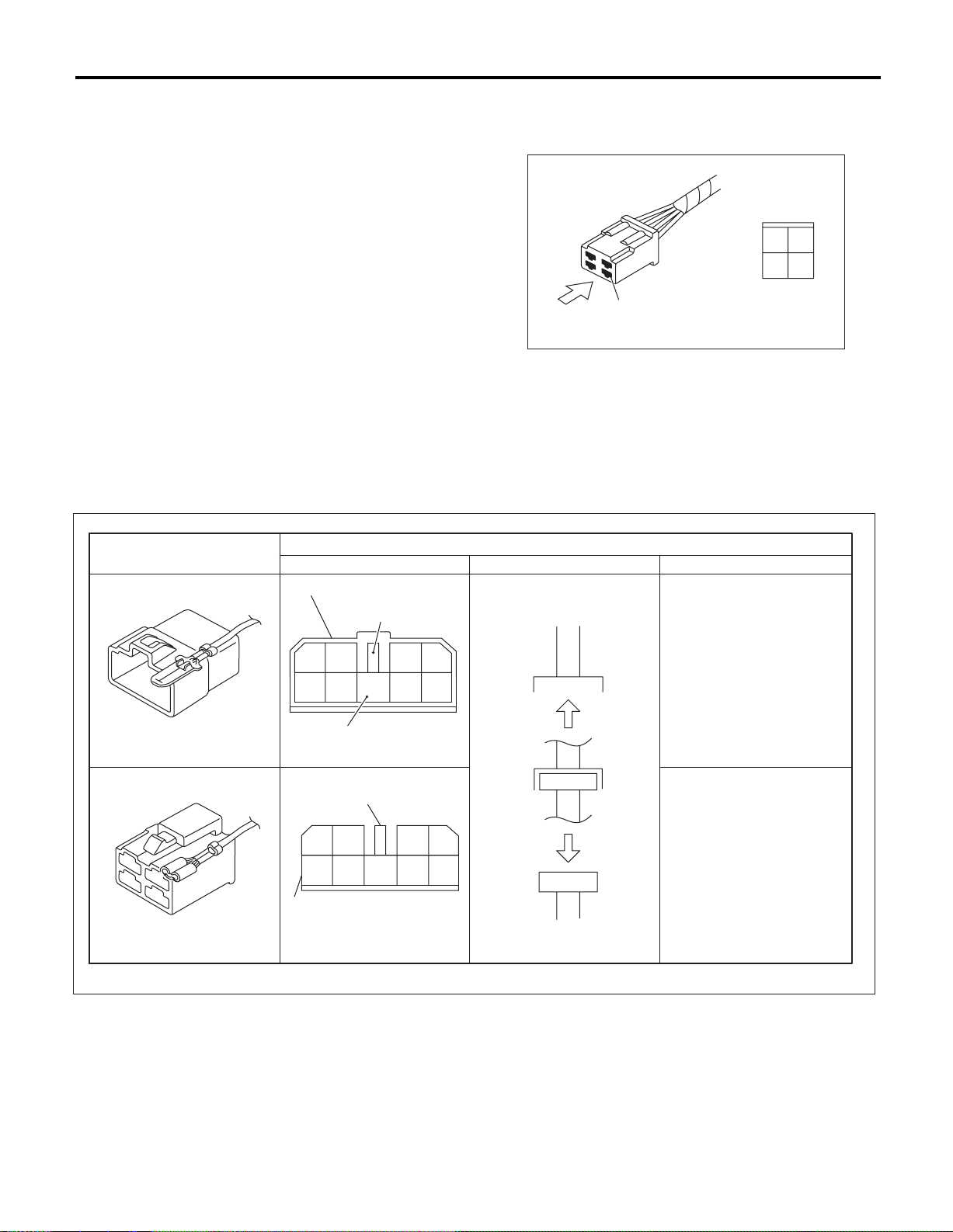
Connector used in vehicle
Double frames
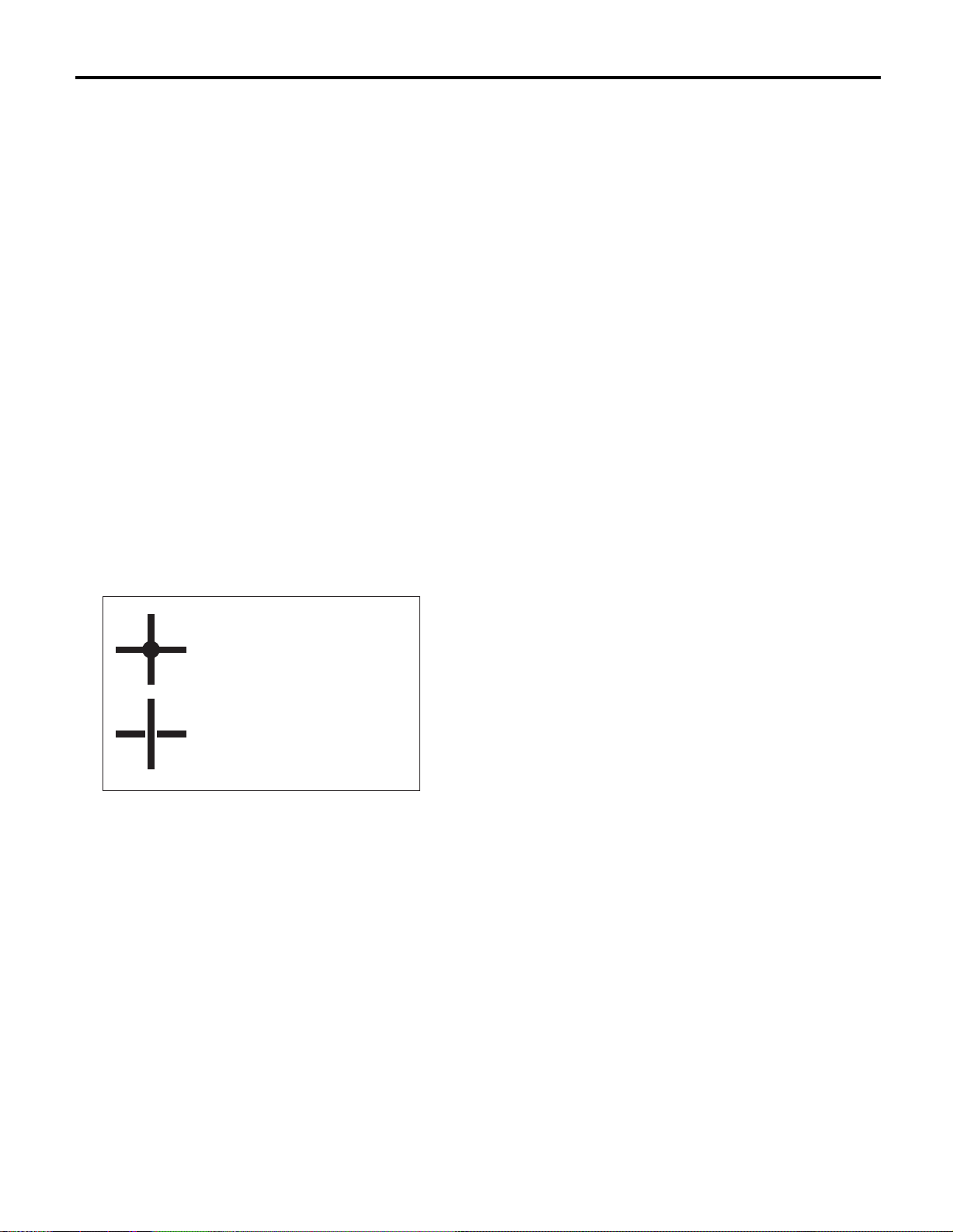
Sketch Symbol Number of poles
Indicates a lock
is included.
• Each connector and its terminal position are indicated by a sketch of the connector in a disconnected state which is viewed from front.
1
3
4
Viewed from this direction
WI-00101
• The number of poles or pins, presence of a lock,
and pin number of each terminal are indicated in
the sketch of each connector. In the sketch, the
highest pole number refers to the number of poles
which connector has. For example, the sketch of
connector shown in the figure indicates the connector has 9 poles.
Connector shown in wiring diagram
2
4
43
98
Indicates the number of poles.
Indicates a lock is included.
12
56
Single frame
7
7
2
65
3
8
1
4
9
Numbered in order from upper
right to lower left.
Numbered in order from upper
left to lower right
WI-00102
WI-5
WIRING SYSTEM
BASIC DIAGNOSTICS PROCEDURE
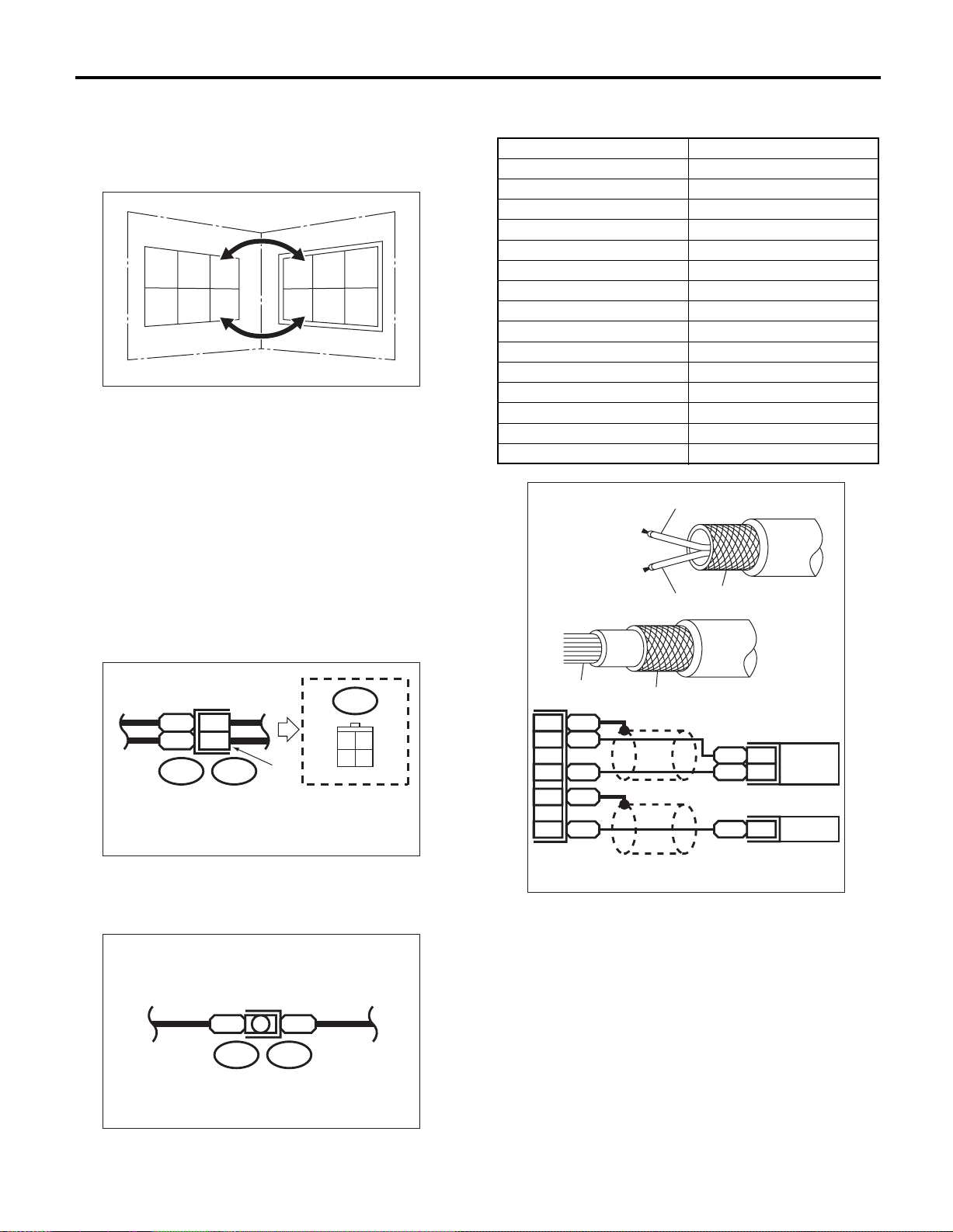
• When one set of connectors is viewed from the
front side, the pole numbers of one connector are
symmetrical to those of other. When these two connectors are connected as a unit, the poles which
have the same number are joined.
1
2
3
6
5
44
3
6
2
5
1
WI-00107
• Electrical wiring harness:
The connectors are numbered along with the number of poles, external colors, and mating connections in accompanying list.
• The sketch of each connector in the wiring diagram usually shows (A) side of the connector. The
relationship between wire color, terminal number
and connector is described in figure.
NOTE:
A wire which runs in one direction from a connector
terminal sometimes may have a different color from
that which runs in the other direction from that terminal.
• The following color codes are used to indicate
the colors of the wires used.
Color code Color
LBlue
BBlack
Y Yellow
GGreen
RRed
WWhite
Br Brown
Lg Light green
Gr Gray
PPink
Or Orange
Lb Light Blue
V Violet
SA Sealed (Inner)
SB Sealed (Outer)
YG
SB
YL
i2
BR
1
RW
3
Wire color :
BR (No. 1 terminal)
RW (No. 3 terminal)
(A)
i2F4
12
34
WI-00108
• In wiring diagram, connectors which have no terminal number refer to one-pole types. Sketches of
these connectors are omitted intentionally.
BB
B15F10
WI-00109
SA
SB10
YL9
YG8
SB22
SA20
SB
YL 2
YG 1
SA 1
WI-00110
WI-6
BASIC DIAGNOSTICS PROCEDURE
WIRING SYSTEM
• The wire color code, which consists of two letters
(or three letters including Br or Lg), indicates the
standard color (base color of the wire covering) by
its first letter and stripe marking by its second letter.
YB
BlackMarking color :
Reference color :
Yellow
WI-00111
• The table lists the nominal sectional areas and
allowable currents of wires.
CAUTION:
When replacing or repairing a wire, be sure to
use the same size and type of wire which was
originally used.
NOTE:
• The allowable current in the table indicates tolerable amperage of each wire at an ambient temperature of 40°C (104°F).
• The allowable current changes with ambient
temperature. Also, it changes if a bundle of more
than two wires is used.
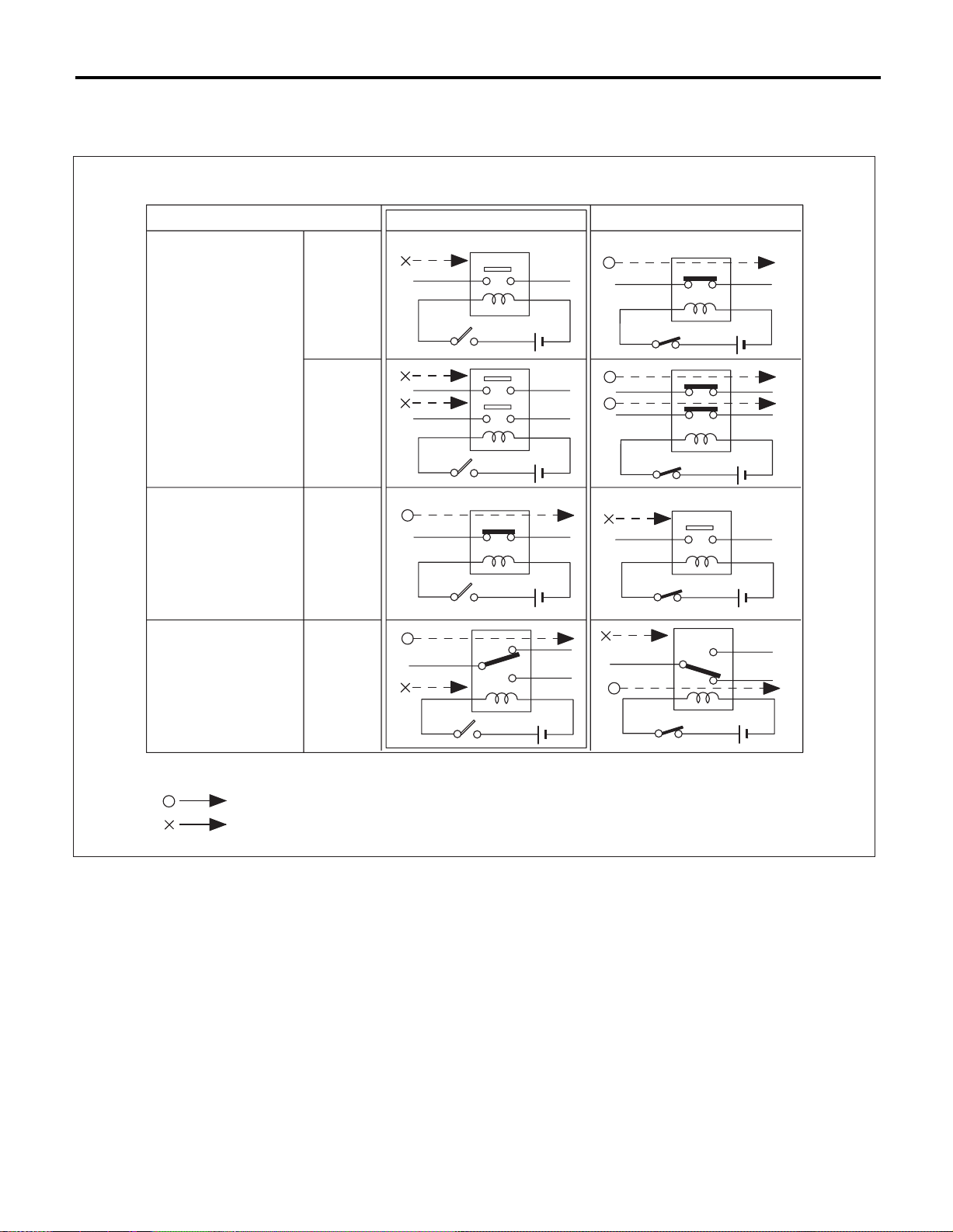
• Each unit is directly grounded to the body or indirectly grounds through a harness ground terminal.
Different symbols are used in the wiring diagram to
identify the two grounding systems.
B
Direct ground Indirect terminal
ground
WI-00112
• The ground points shown in the wiring diagram
refer to the following:
NOTE:
All wiring harnesses are provided with a ground
point which should be securely connected.
: Body ground
GB
: Engine ground
GE
: Radio ground
GR
Nominal sectional area
0.3 7/0.26 1.8 7
0.5 7/0.32 2.2 (or 2.0) 12
0.75 30/0.18 2.6 (or 2.4) 16
0.85 11/0.32 2.4 (or 2.2) 16
1.25 16/0.32 2.7 (or 2.5) 21
2 26/0.32 3.1 (or 2.9) 28
3 41/0.32 3.8 (or 3.6) 38
5 65/0.32 4.6 (or 4.4) 51
8 50/0.45 5.5 67
mm
2
No. of
strands/
strand diameter
Outside
diameter of
finished wiring
mm
Allowable
current
Amps/ 40°C
(104°F)
WI-00113
WI-7
BASIC DIAGNOSTICS PROCEDURE
WIRING SYSTEM
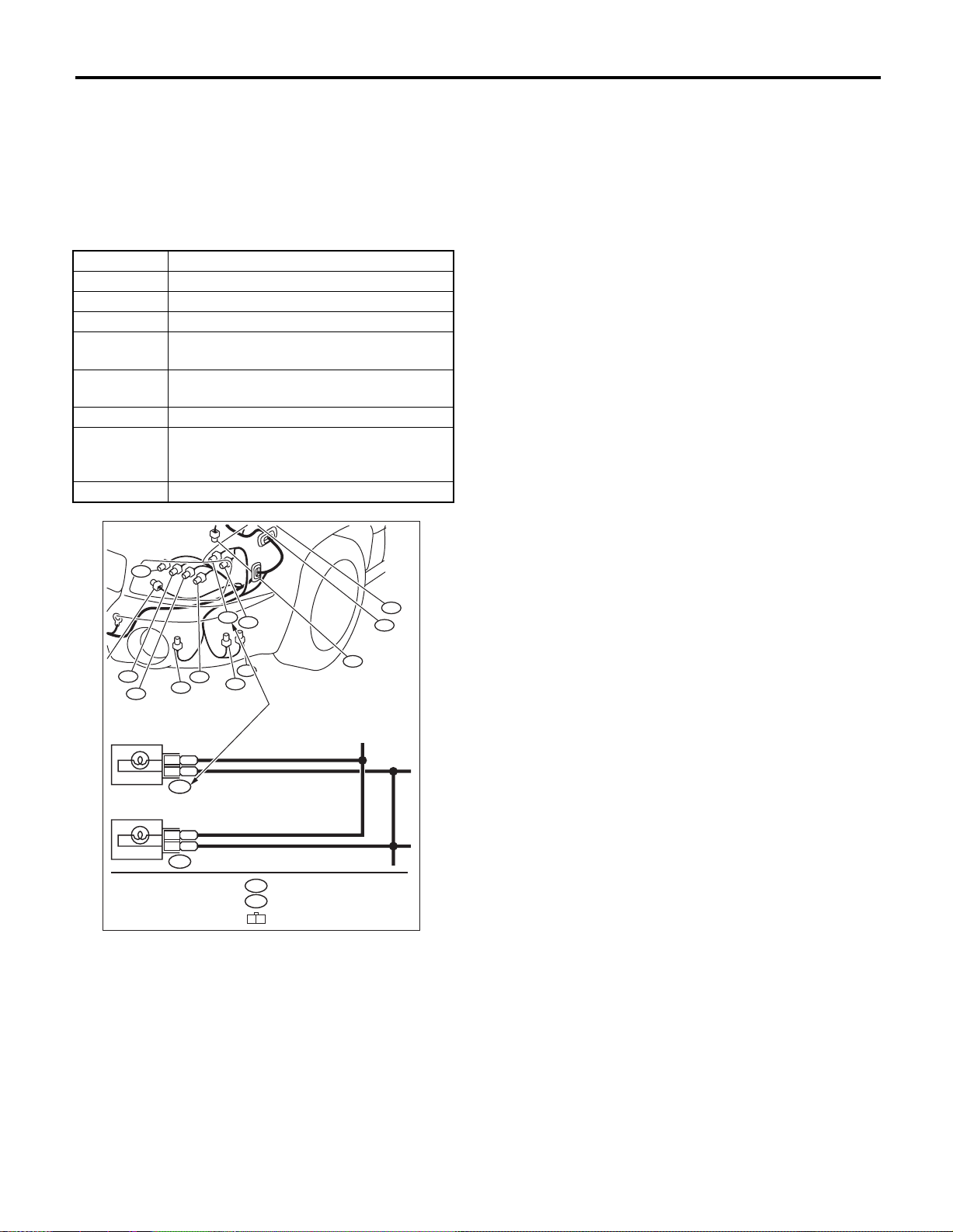
• Relays are classified as normally-open or normally-closed.
The normally-closed relay has one or more contacts.
The wiring diagram shows the relay mode when energizing circuit is OFF.
Relay type
Normally-open type
Normally-closed type
4-pole
6-pole
4-pole
Energizing circuit OFF
Energizing circuit ON
Mixed type
Key to symbols:
6-pole
: Current flows.
: Current does not flow.
WI-00114
WI-8
BASIC DIAGNOSTICS PROCEDURE
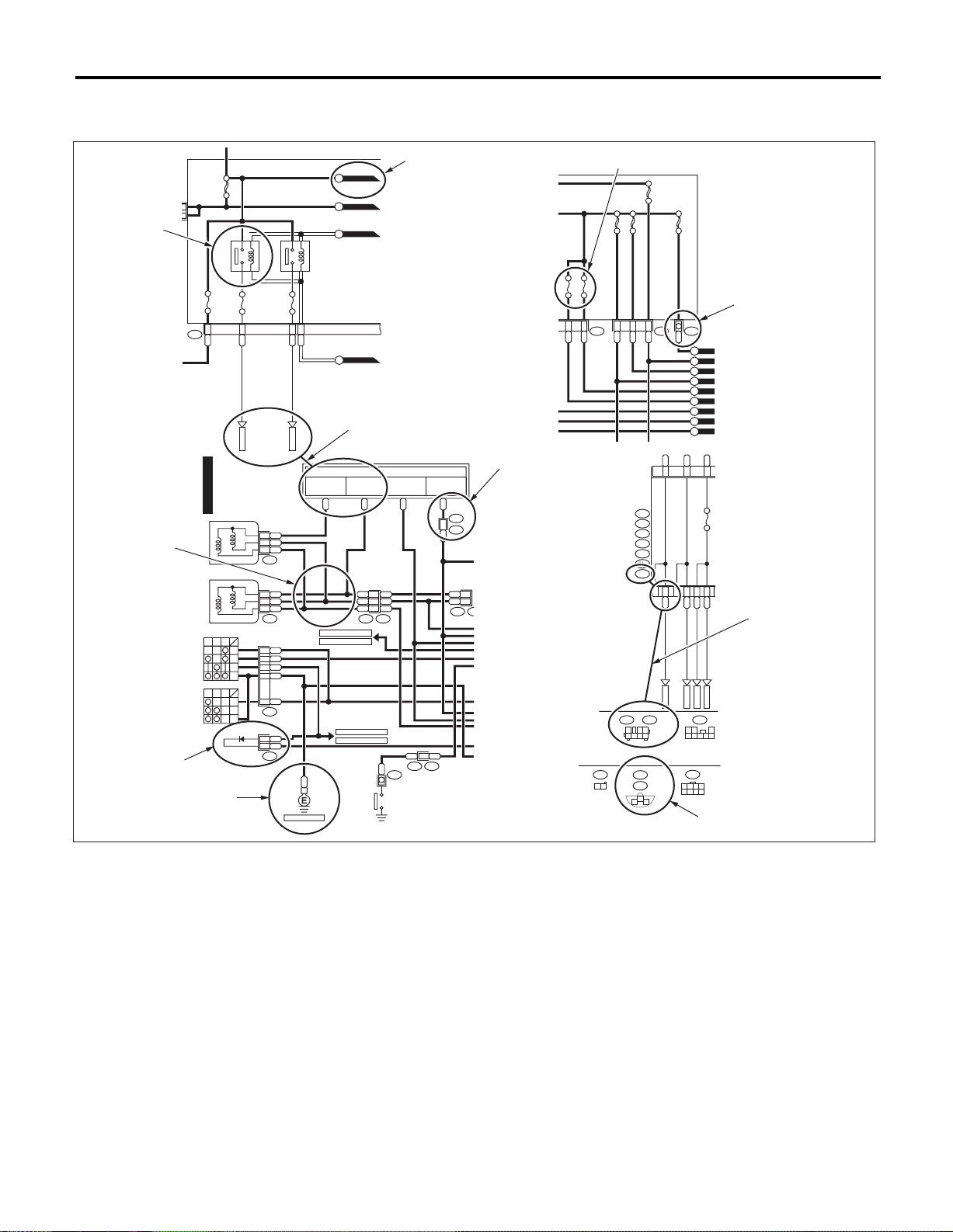
• Each connector number shown in the wiring diagram corresponds to that in wiring harness. The location of each connector in actual vehicle is
determined by reading the first character of the
connector (for example, a “F” for F8, “i” for i16, etc.)
and type of wiring harness.
The first character of each connector number refers
to the area or system of the vehicle.
Symbol Wiring harness and cord
F Front wiring harness
B Bulkhead wiring harness
E Engine wiring harness
T
D
i Instrument panel wiring harness
R
AB Airbag wiring harness
Transmission cord, Rear oxygen sensor
cord
Door cord LH & RH,
Rear door cord LH & RH, Rear gate cord
Rear wiring harness,
Fuel tank cord,
Roof cord, Trunk lid cord
WIRING SYSTEM
F58
F23
F98
FRONT TURN SIGNAL
LIGHT LH (UPPER)
2
1
FRONT TURN SIGNAL
LIGHT LH (LOWER)
3
2
F19
F22
F100
F21
F47
F5
F27
F34
F96
Each connector number
shown in wiring diagram
corresponds to that in
BG
B
F19
BG
B
F22
the vehicle.
(GRAY)
F3
(GRAY)
F19
1 2
WI-00115
WI-9
BASIC DIAGNOSTICS PROCEDURE
WIRING SYSTEM
D: SYMBOLS IN WIRING DIAGRAMS
A number of symbols are used in each wiring diagram to easily identify parts or circuits.
Example
RELAY
SYMBOLS OF
WIRE
CONNECTION
AND CROSSING
DIODE
HEADLIGHT
RELAY
RH
No.3 10A
3
F39
LR
H/L(2L)-01
HEADLIGHT LH
HEADLIGHT RH
DIMMER & PASSING
SWITCH
LOW PASS
UP
LIGHTING SWITCH
12
GROUND
SBF-1 100A
LOW
LOW
HF
HU
HL
E
OFF
HC
TC
EL
DIODE
No.9 15A
7
LW
MB-11
HIGH
HIGH
MAIN FUSE BOX (M/B)
HEADLIGHT
RELAY
LH
No.8 15A
2
RL
MB-10
RL
2
R
1
YL
3
F23
LW2
R
1
YL
3
F7
LY
8
RY
7
YB
17
B
16
LY
13
B71
YB
1
RY2
B112
REF. TO GND-02
5
G
M/B FUSE NO. 8
B
P-SUP-02
A
P-SUP-02
B
P-SUP-02
C
P-SUP-04
D
POWER SUPPLY
ROUTING
TO POWER SUPPLY ROUTING
MB-10
MB-11
M/B FUSE NO. 9
RL
LW
LW 4
R
3
2
YL
F44
REF. TO ST(MT)-01
REF. TO ST(AT)-01
REF. TO FOG(H4)-01
REF. TO FOG(H6)-01
WIRE TRACING
ON EXTENDED
WIRING DIAGRAMS
MB-5
FB-16
HEADLIGHT
F/B FUSE NO. 11
LW
R
YL
B61
P
R4
PARKING BRAKE
SWITCH
(IG)
GR
17
R3 B99
RELAY
LB
F45
B62
LB H1
LW B1
RA1
B36
PP
FUSE No. & RATING
SBF-6 30A
SBF-3 50A
3
R
FUSE &
RELAY
BOX (F/B)
A:
B51
B:
C:
B52
D:
B152
E:
B158
F:
F40
G:
F41
G:
F7
F23
123
SBF-4 50A
CONNECTOR-1
F36 F38F68
W
BW 2
i5
F41
(BLACK)
(BLACK)
A2
(GRAY)
LgB
D4
WR G4
FB-37
A3
123
5 6 7 8
M
L
K
J
I
H
G
F
E
BG
D7
G7
G1
BL
BG
FB-35
FB-36
A:
B51
1 2 3
4 5 6 7 8
F44
P-SUP-04
P-SUP-04
P-SUP-04
P-SUP-04
P-SUP-03
P-SUP-03
P-SUP-04
P-SUP-03
P-SUP-04
Or
D11
No.5 10A
BR D10
FB-34
4
CONNECTOR-2
CONNECTOR
SKETCH
WI-00116
SBF-2 50A
No.1 20A
No.2 15A
1
3
2
LR
L
R
SMJ
SMJ
SMJ
C:
B52
1 2 3
4 5 6 7
B112
1 2
1. RELAY
A symbol used to indicate a relay.
2. CONNECTOR-1
The sketch of the connector indicates one-pole
types.
3. WIRING CONNECTION
Some wiring diagrams are indicated in foldouts for
convenience. Wiring destinations are indicated
where necessary by corresponding symbols (as
when two pages are needed for clear indication).
4. FUSE NO. & RATING
The “FUSE No. & RATING” corresponds with that
used in fuse box (main fuse box, fuse and joint
box).
5. CONNECTOR-2
• Each connector is indicated by a symbol.
• Each terminal number is indicated in the corresponding wiring diagram in an abbreviated form.
• For example, terminal number “G4” refers to No.
4 terminal of connector (G: F41) shown in the connector sketch.
WI-10
BASIC DIAGNOSTICS PROCEDURE
6. CONNECTOR SKETCH
• Each connector sketch clearly identifies the
shape and color of a connector as well as terminal
locations. Non-colored connectors are indicated in
natural color.
• When more than two types of connector number
are indicated in a connector sketch, it means that
the same type connectors are used.
7. GROUND
Each grounding point can be located easily by referring to the corresponding wiring harness.
8. DIODE
A symbol is used to indicate a diode.
9. WIRE TRACING ON EXTENDED WIRING
DIAGRAMS
For a wiring diagram extending over at least two
pages, a symbol (consisting of the same characters
with arrows), facilitates wire tracing from one page
to the next.
A ←→ A, B ←→ B
WIRING SYSTEM
10.SYMBOLS OF WIRE CONNECTION AND
CROSSING
Symbol
Symbol Refers to wires which are
Refers to wires which are
connected and branched
at the dot point.
crossed but not connected.
WI-00117
11.POWER SUPPLY ROUTING
A symbol is used to indicate the power supply in
each wiring diagram.
“MB-5”, “MB-6”, etc., which are used as powersupply symbols throughout the text, correspond
with those shown in POWER SUPPLY ROUTING
in the wiring diagram.
Accordingly, using the POWER SUPPLY ROUTING and wiring diagrams permits service personnel
to understand the entire electrical arrangement of a
system.
12.CLASSIFICATION BY SPECIFICATION
When the wiring diagrams differ according to vehicle specifications, the specification difference is described by using abbreviations.
WI-11
BASIC DIAGNOSTICS PROCEDURE
WIRING SYSTEM
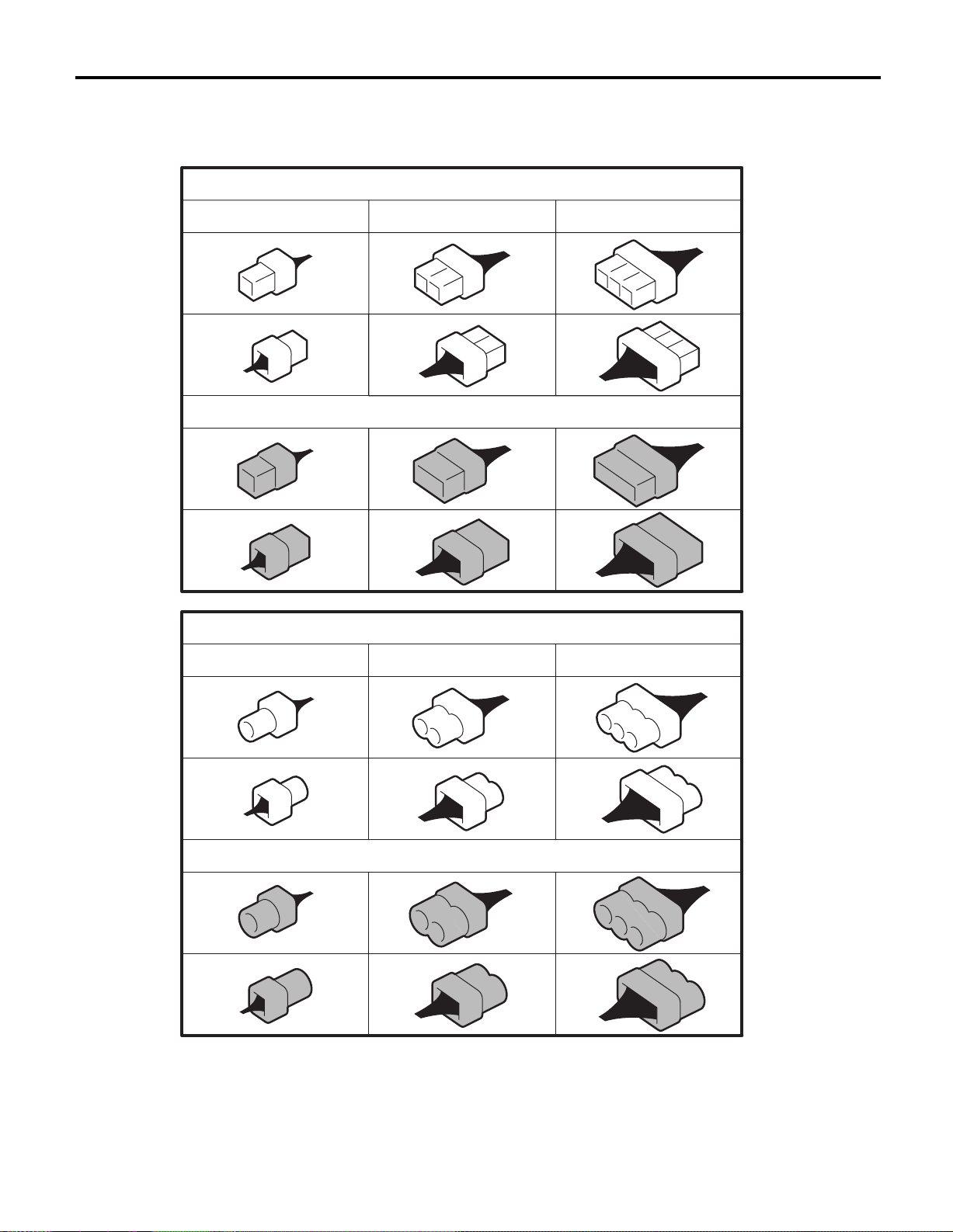
E: CONNECTOR SYMBOL IN WIRING HARNESS
Main symbols of connector (in wiring harness) are indicated in below.
Standard type: Female
Pole: From 1 to 8 Pole: From 9 to 20 Pole: More than 21
Standard type: Male
Water proof type: Female
Pole: From 1 to 8 Pole: From 9 to 20 Pole: More than 21
Water proof type: Male
WI-02445
WI-12
BASIC DIAGNOSTICS PROCEDURE
WIRING SYSTEM
F: ABBREVIATION IN WIRING DIA-
GRAMS
Abbreviation Full name
ABS Antilock Brake System
ACC Accessory
A/C Air Conditioning
AD Auto Down
AT Automatic Transmission
AU Auto Up
A/B Air Bag
A/F Air Fuel
ATF Automatic Transmission Fluid
AVCS Active Valve Control System
AWD All Wheel Drive
BBattery
CPC Canister Purge Control
DDrive Range
DN Down
E Ground
EGR Exhaust Gas Recirculation
ELR Emergency Locking Retractor
ETC Electric Throttle Valve Control
F/B Fuse & Joint Box
FL1.5
FPC Fuel Pump Control
FWD Front Wheel Drive
H/L Head Light
I/F Interface
IG Ignition
Illumi Illumination
INT Intermittent
L/C Low Clutch
LDC Liquid Crystal Display
LH Left Hand
Lo Low
M Motor
M/B Main Fuse Box
MG Magnet
Mi Middle
MT Manual Transmission
N Neutral
OP Optional Parts
P Parking Range
PASS Passing
R Reverse Range
RH Right Hand
SBF Slow Blow Fuse
SMJ Super Multiple Junction
ST Starter
SW Switch
TGV Tumble Generator Valve
Fusible link 1.5 mm
2
Abbreviation Full name
UP Up
WASH Washer
WI-13
WIRING SYSTEM
WORKING PRECAUTIONS
2. Working Precautions
A: PRECAUTIONS WHEN WORKING
WITH THE PARTS MOUNTED ON
THE VEHICLE
1) When working under a vehicle which is jackedup, always be sure to use safety stands.
2) The parking brake must always be applied during working. Also, in automatic transmission models, keep the select lever set to P (Parking) range.
3) Be sure the workshop is properly ventilated
when running the engine. Further, be careful not to
touch the belt or fan while the engine is operating.
4) Be careful not to touch hot metal parts, especially the radiator and exhaust system immediately after the engine has been shut off.
B: PRECAUTIONS IN TROUBLE DI-
AGNOSIS AND REPAIR OF ELECTRIC PARTS
1) The battery cable must be disconnected from
battery’s (−) terminal, and the ignition switch must
be set to OFF position, unless otherwise required
by the diagnostics.
2) Securely fasten the wiring harness with clamps
and slips so that the harness does not interfere with
body end parts or edges and bolts or screws.
3) When installing the parts, be careful not to catch
them on the wiring harness.
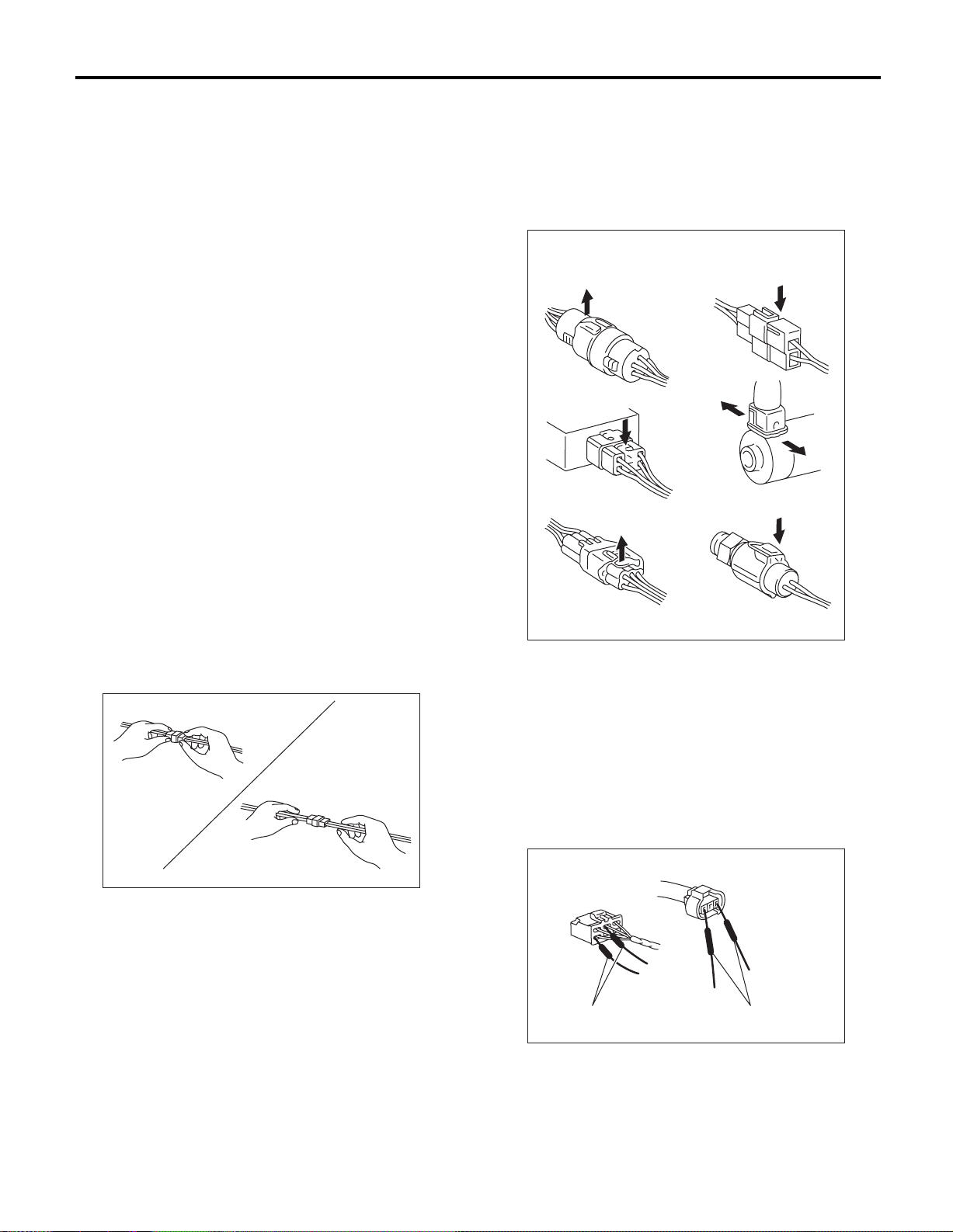
4) When disconnecting a connector, do not pull the
wires, but pull while holding the connector body.
Correct
Wrong
5) Some connectors are provided with a lock. One
type of such a connector is disconnected by pushing the lock, and the other, by moving the lock up.
In either type the lock shape must be identified before attempting to disconnect the connector.
To connect, insert the connector until it snaps and
confirm that it is tightly connected.
Example
LIFT
PUSH
LIFT
PUSH
PUSH
WI-00119
6) When checking continuity between connector
terminals, or measuring the voltage across the terminal and ground, always contact tester probe(s)
on terminals from the wiring connection side. If the
probe is too thick to gain access to the terminal, use
“mini” test leads.
To check water-proof connectors (which are not accessible from the wiring side), contact test probes
on the terminal side being careful not to bend or
damage terminals.
WI-00118
Tester probes "Mini" test leads
WI-00120
7) Sensors, relays, electrical unit, etc., are sensitive to strong impacts.
Handle them with care so that they are not dropped
or mishandled.
WI-14
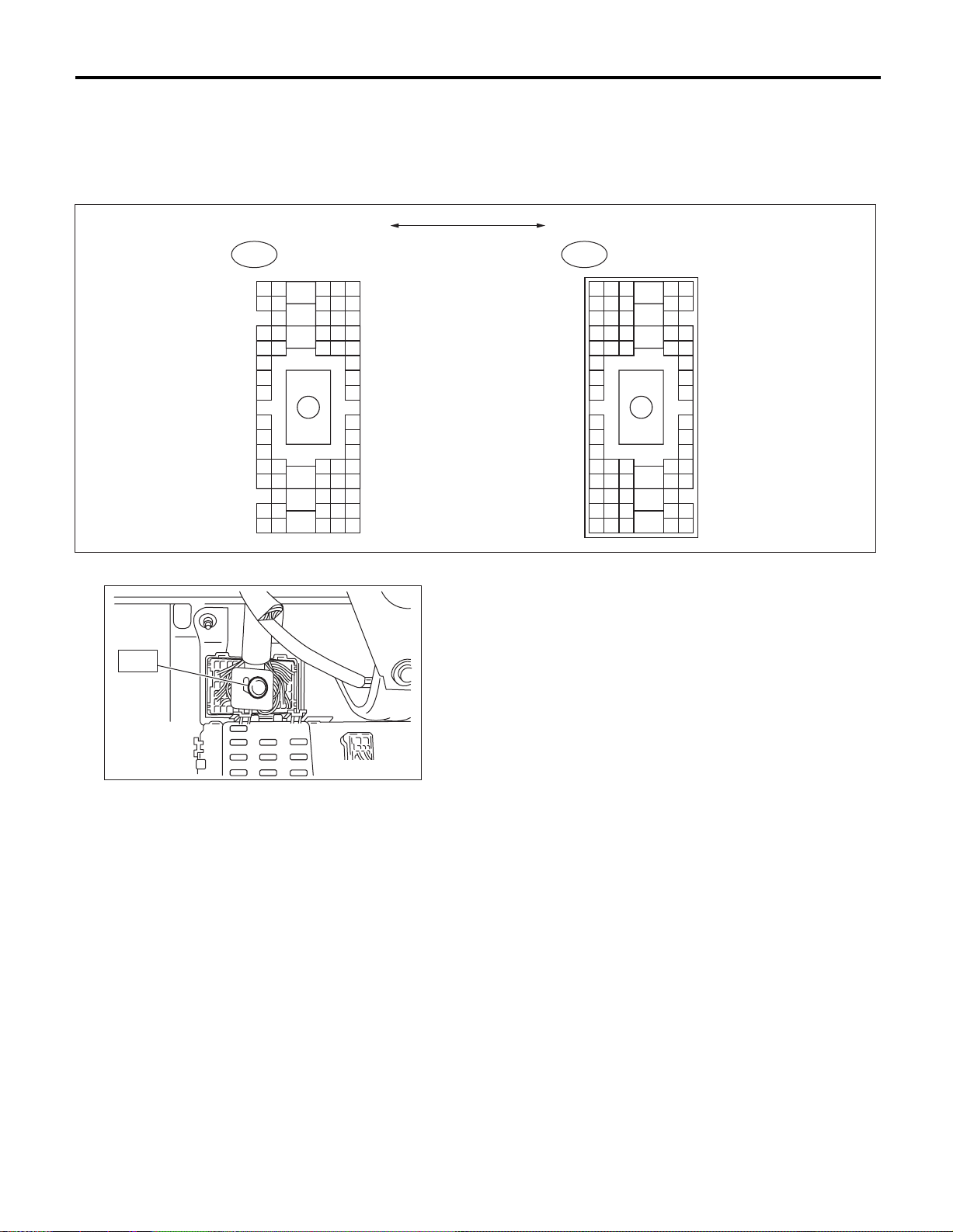
SUPER MULTIPLE JUNCTION (SMJ)
3. Super Multiple Junction (SMJ)
A: HOW TO USE SUPER MULTIPLE JUNCTION (SMJ)
The “SMJ” indicated in wiring diagrams is shown in a simplified form.
B: TERMINAL ARRANGEMENT
WIRING SYSTEM
Bulkhead Wiring Harness
B36
C: INSTALLATION
T
A1 A2
B1 B2
C2
D1 D2
F1
G1
H1
I1
J1
K1
L1
L2
M1 M2
N2
O1 O2
P1 P2
66 Poles
A4 A5 A6
A3
B4 B5 B6
B3
C5 C6
C4
D4 D5 D6
C3
E4 E5 E6E1 E2
L4 L5 L6
N3
M4 M5M6
N5 N6
N4
O3
O4 O5 O6
P3
P4 P5
F6
G6
H6
I6
J6
K6
P6
Instrument Panel Wiring Harness
66 Poles
i1
A4
A5
A6
B6
C6
D6
E6
F6
G6
H6
I6
J6
K6
L6
M6
N6
O6
P6
B5
C5
D5
E5
L5
M5
N5
O5
P5
B4
C4
D4
E4
L4
M4
N4
O4
P4
A3
B3
C3
N3
O3
P3
A2
B2
C2
D2
E2
L2
M2
N2
O2
P2
A1
B1
D1
E1
F1
G1
H1
I1
J1
K1
L1
M1
O1
P1
WI-00706
WI-00707
Tightening torque:
T: 4.4 N·m (0.45 kgf-m, 3.3 ft-lb)
NOTE:
• Align the cutout portion of one connector with
that of other before tightening the connecting bolt.
• Do not tighten the bolt excessively since this may
deform the connectors.
WI-15
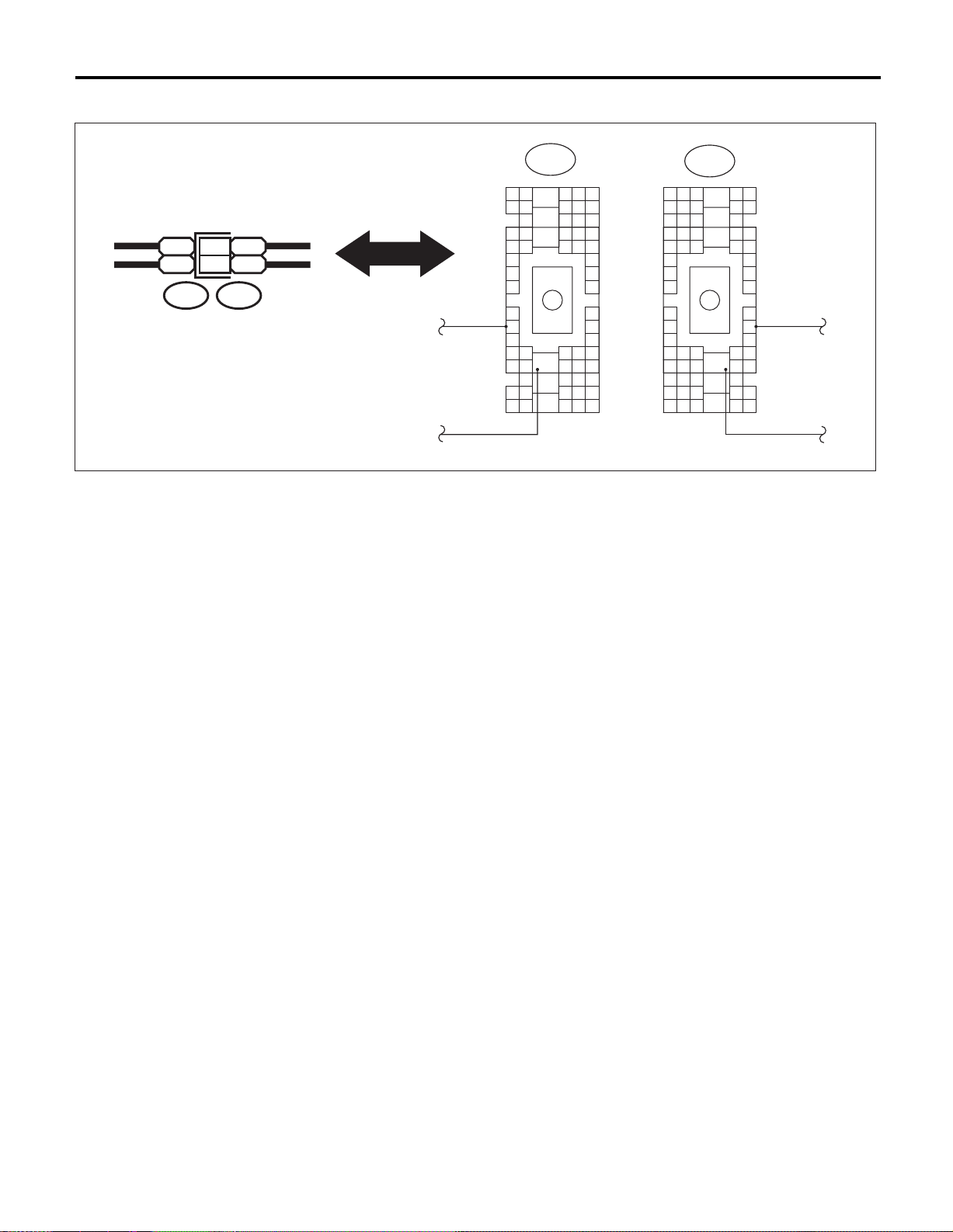
SUPER MULTIPLE JUNCTION (SMJ)
WIRING SYSTEM
D: EXPLANATION OF SMJ SHOWN IN THE WIRING DIRAM
Y
BW
N3
J1
SMJ
B36i1
Y
BW
A1 A2
B1 B2
C2
D1 D2
F1
G1
H1
I1
J1
K1
L1
L2
M1 M2
N2
O1 O2
P1 P2
i1
A3
B3
C3
N3
O3
P3
A4 A5 A6
B4 B5 B6
C5 C6
C4
D4 D5 D6
E4 E5 E6E1 E2
F6
G6
H6
J6
K6
L4 L5 L6
M4 M5M6
N5 N6
N4
O4 O5 O6
P4 P5
P6
I6
A6
B6
C6
D6
E6
F6
G6
H6
J6
K6
L6
M6
N6
O6
P6
B36
A3
B3
C3
N3
O3
P3
A2
B2
C2
D2
E2
L2
M2
N2
O2
P2
A1
B1
D1
E1
F1
G1
H1
I1
J1
K1
L1
M1
O1
P1
BWBW
A5
A4
B5
B4
C5
C4
D5
D4
E5
E4
I6
L5
L4
M5
M4
N5
N4
O5
O4
P5
P4
Y Y
WI-00708
WI-16

MEMO:
SUPER MULTIPLE JUNCTION (SMJ)
WIRING SYSTEM
WI-17
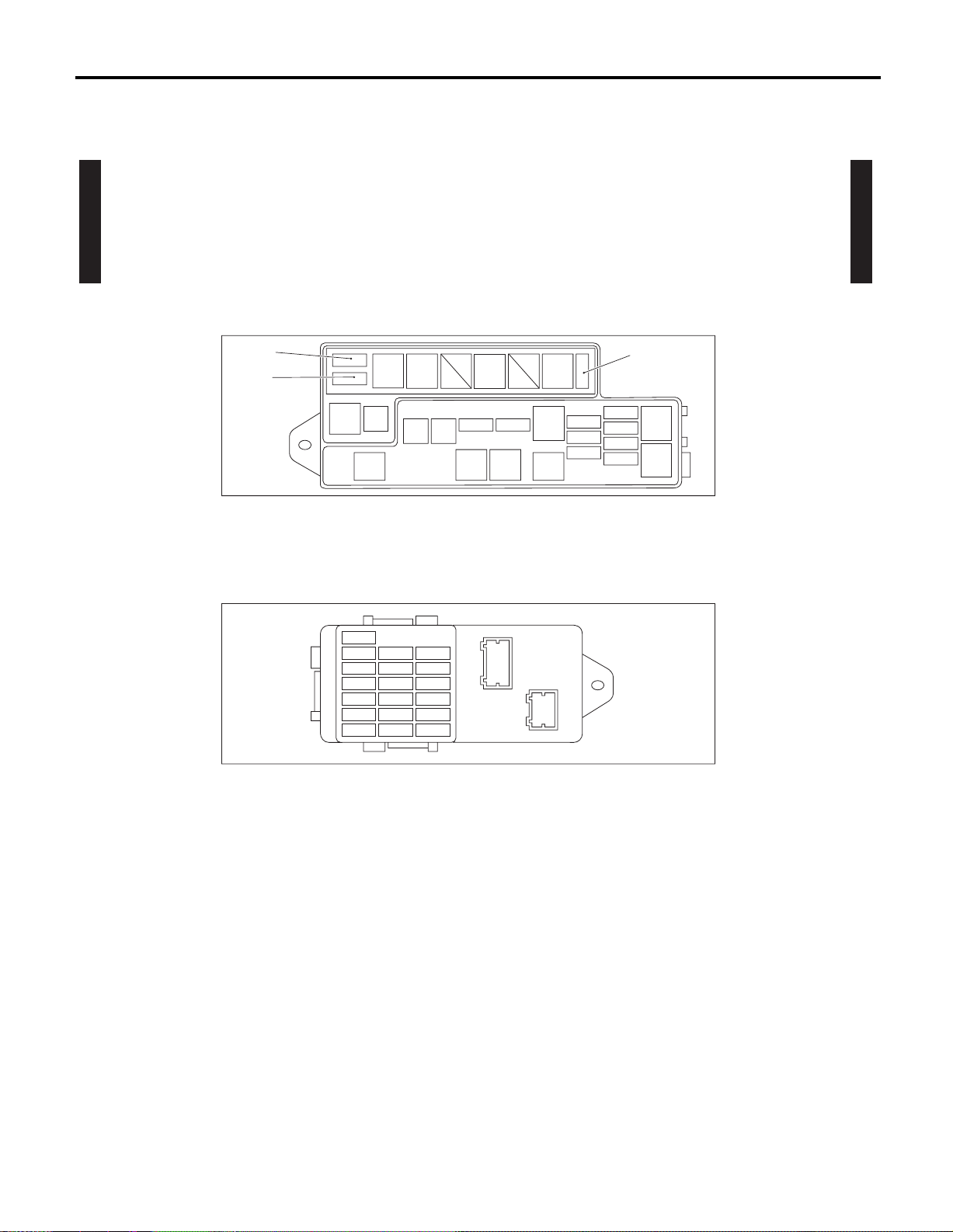
POWER SUPPLY ROUTING
WIRING SYSTEM
4. Power Supply Routing
A: SCHEMATIC
P-SUP-01
MAIN FUSE BOX (M/B)
MAIN FAN
20A
SUB FAN
20A
FUSE & RELAY BOX (F/B)
SBF-7
No. 13
No. 14
No. 15
No. 16
No. 17
No. 18
No. 19
SBF
SBF-1
MAIN
RELAY
-8
FAN
No. 7
No. 8
No. 9
No. 10
No. 11
No. 12
A/C
RELAY
SBF-5SBF
-6
No. 1
No. 2
No. 3
No. 4
No. 5
No. 6
SBF-2
SUB
FAN
RELAY
No. 6No. 1
SBF-3
RELAY
Horn
relay
SBF-4
F-
FOG
No. 5
No. 4
No. 3
FWD SWITCH
No. 9
No. 8
No. 7
No. 2
H/L
relay
RH
H/L
relay
LH
P-SUP-01
WI-18
WI-05686
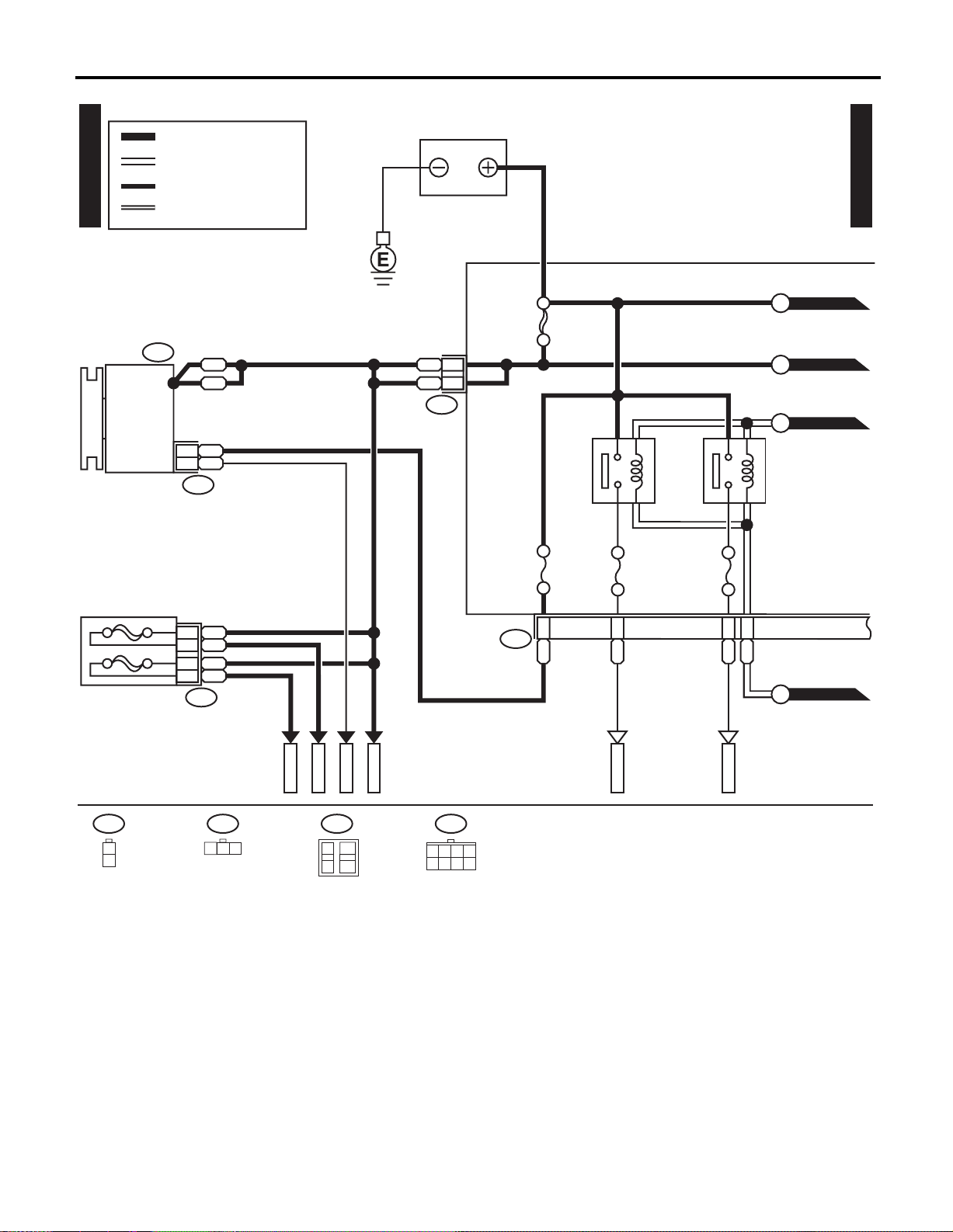
POWER SUPPLY ROUTING
WIRING SYSTEM
BATTERY CURRENT
CURRENT FROM IGNITION
SWITCH “IG” TERMINAL
OTHER CURRENTS
P-SUP-02
GENERATOR
CURRENT FROM IGNITION
SWITCH “ACC” TERMINAL
F25
BATTERY
P-SUP-02
MAIN FUSE BOX (M/B)
P-SUP-03
A
SBF-1 100A
W
W
W
LR
2
1
BY
F26
1
2
W
F35
HEADLIGHT
RELAY
RH
B
C
HEADLIGHT
RELAY
LH
P-SUP-03
P-SUP-03
SBF HOLDER
(BLACK)
F35
1
2
30A
30A
W
1
WR3
W
2
WB4
F34
(GREEN)
F26
1 2 3 12
ALT
SBF-7
SBF-8
(BLACK) (BLACK)
F34 F39
34
MB-12
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
F39
NO. 3 10A
3
LR
NO. 9 15A
7
LW
MB-11
NO. 8 15A
2
RL
MB-10
5
G
P-SUP-05
D
WI-05687
WI-19
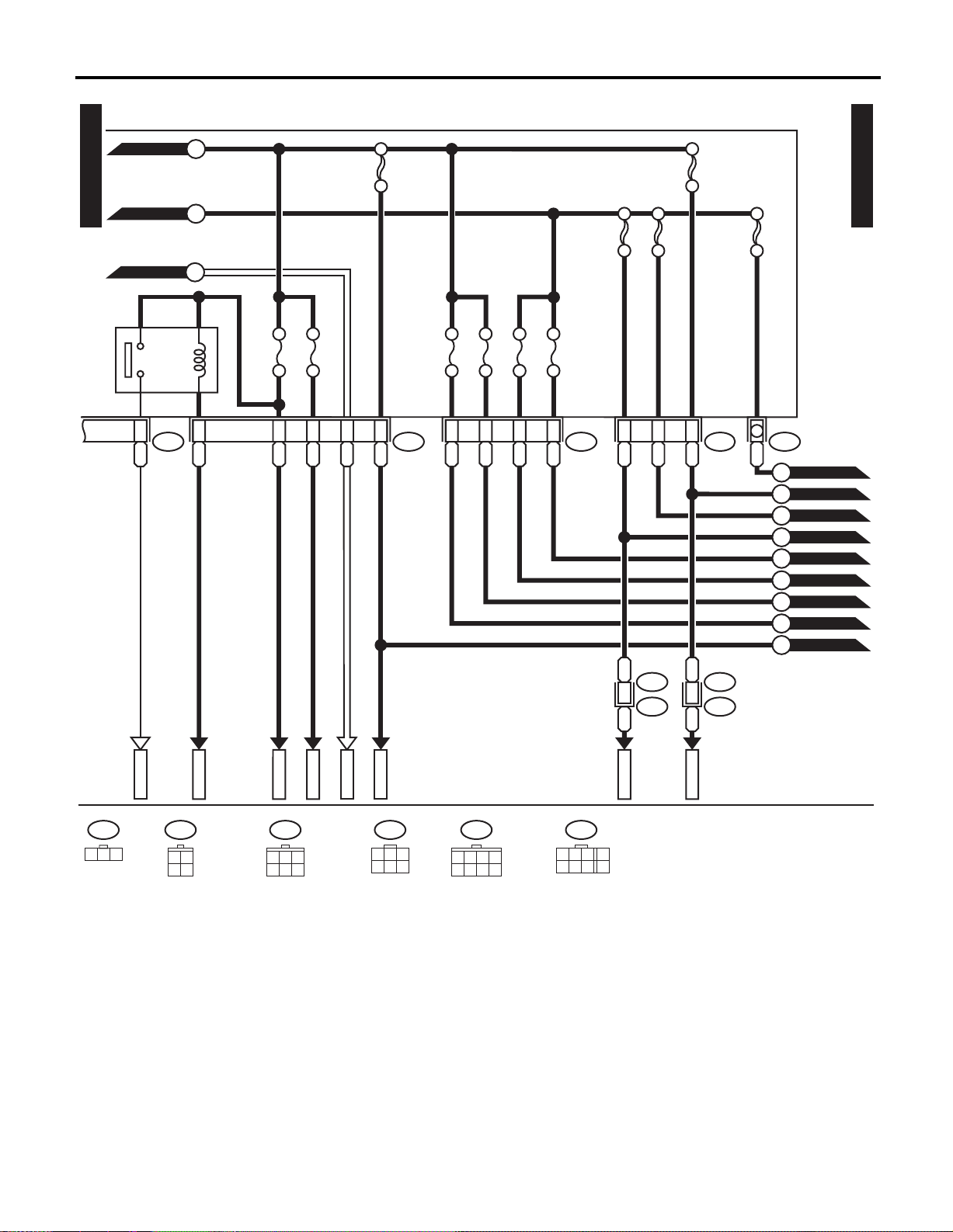
WIRING SYSTEM
P-SUP-02
POWER SUPPLY ROUTING
MAIN FUSE BOX (M/B)
A
P-SUP-03
P-SUP-02
P-SUP-02
HORN
RELAY
SBF-5 30A
B
C
NO. 4 10A
NO. 6 15A
F39 F37
BL 4
RG 4
W2
YR 6
LB 5
SBF-6 30A
SBF-2 50A
SBF-3 50A
NO. 5 15A
NO. 7 20A
BR 1
W4
WL 1
NO. 2 15A
LR 2
NO. 1 20A
R3
F68
L1
L
F46
1
B108
L
3
R
BW 2
BW
1
BW
SBF-4 50A
F36 F38
W
M
L
K
J
H
G
F
E
F44
B61
P-SUP-05
P-SUP-05
P-SUP-05
P-SUP-05
P-SUP-04
I
P-SUP-04
P-SUP-05
P-SUP-04
P-SUP-05
P-SUP-03
F36
1 2 3
MB-9
F68
12
3 4
MB-6
(BLACK)
MB-7
MB-8
(BLACK) (BLACK)
F37
123
4
65
MB-5
MB-4
F46
13
2
456
WI-20
F39
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
F44
123 4
7 8
5 6
(BLACK)
MB-1
MB-2
WI-05688
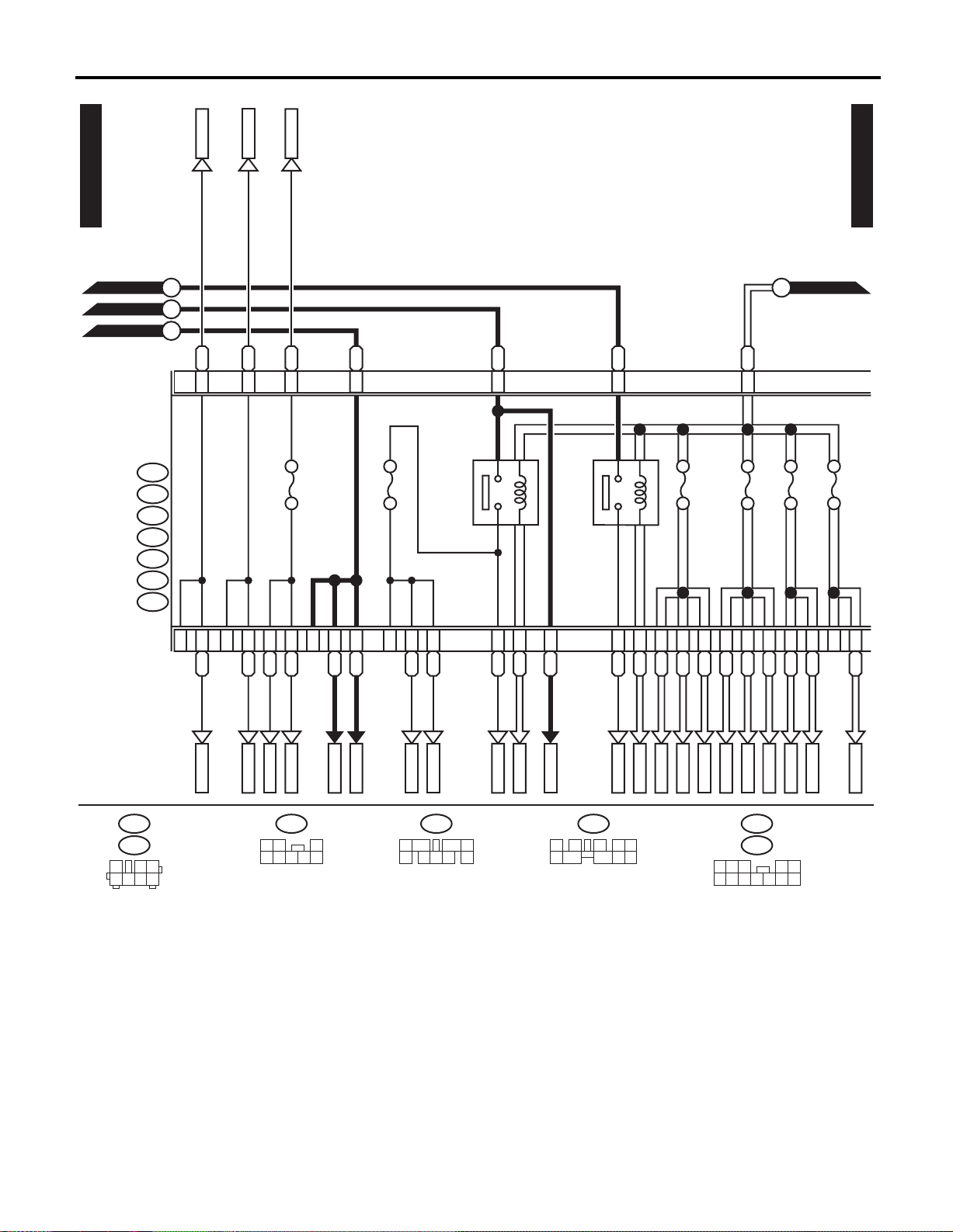
FB-5
FB-4
POWER SUPPLY ROUTING
WIRING SYSTEM
FB-3
P-SUP-04
P-SUP-03
P-SUP-03
P-SUP-03
FUSE &
RELAY
BOX (F/B)
B51A:
i5B:
B52C:
B152D:
B158E:
F40F:
F41G:
F
H
P-SUP-04
G
E8
GL G2
P-SUP-05
N
NO. 11 15A
NO. 6 15A
C4
GR D5
I
D7 BG
G7
BG
BL G1
Or
D11
NO. 5 10A
BR D10
F4 LR
TAIL &
ILLUMI-
NO. 12 10A
A6
B3
LR C6
LR
NATION
RELAY
B2
C7
V
VA1
F9 W
WG D12
D2BW
REAR
DEFOGGER
RELAY
WE5
F8 R
NO. 18 15A
C5
B4VG
RL D1
GB B1
GB
NO. 17 15A
GL B7
LgB
A2
A3
WR G4
B52C:
F41G: (GRAY)
1 2 3
4 5 6 7
FB-37 D4
FB-36
FB-35
1 2 3
4 5 6 7 8
B51A:
FB-34
FB-33
FB-32
FB-27
FB-26
(BROWN) (GRAY)
F40F:
12 3 4
5 6 7 8 9
FB-25
FB-2
FB-24
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9
FB-22
FB-23
B158E:
10
FB-21
FB-1 GB G3
FB-20
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9
FB-19
FB-18
i5B:
B152D:
FB-17 GL C1
(BLUE)
10 11 12
FB-16
FB-15 RA5
FB-14 GY A4
WI-05689
WI-21
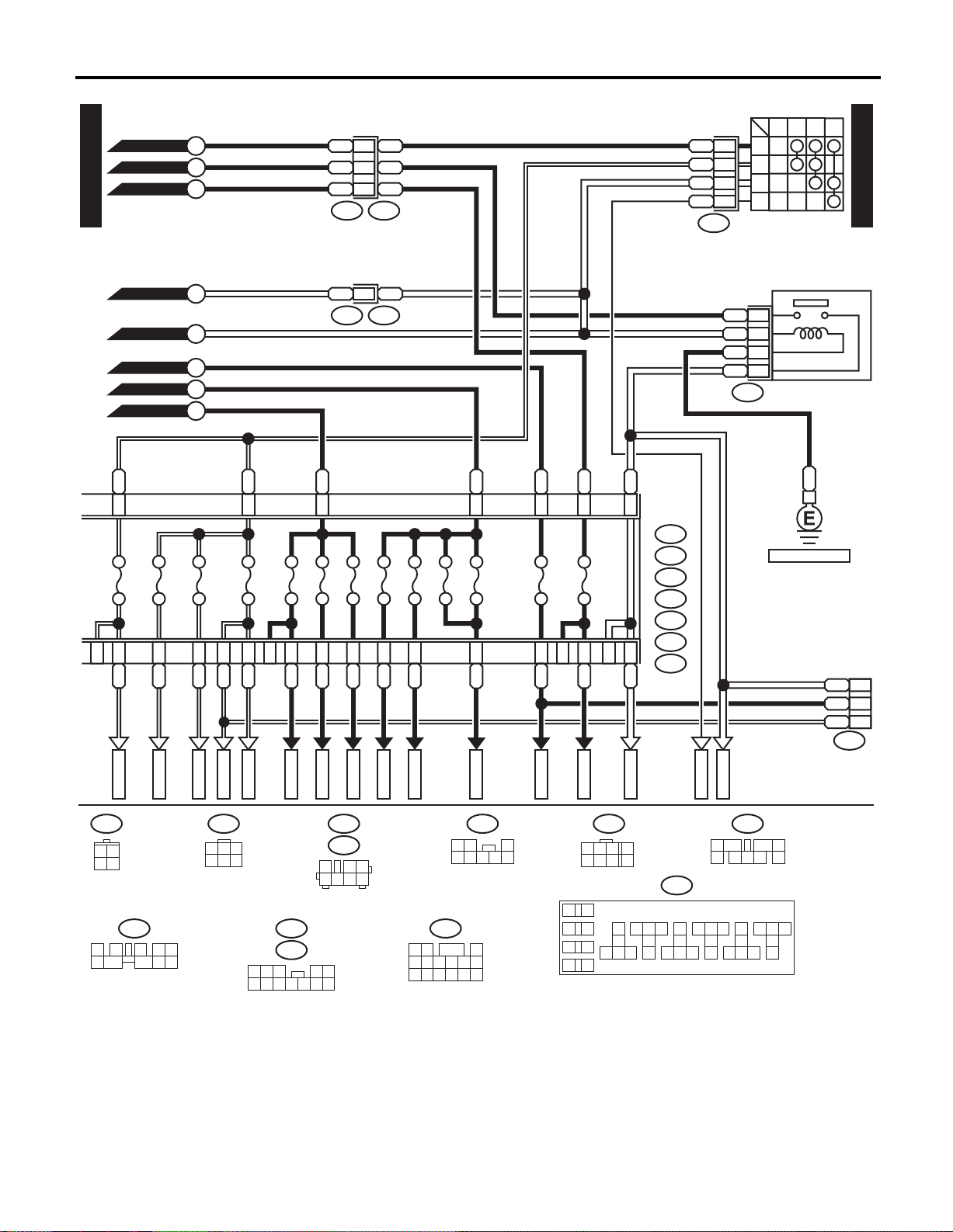
WIRING SYSTEM
P-SUP-03
P-SUP-03
P-SUP-03
P-SUP-05
M
POWER SUPPLY ROUTING
IGNITION SWITCH
OFF
ACC
ON ST
W 5
G
E
WL 7
BR
F44 B61
WL
BR6
W
W
Y
G 4
WB 3
B72
B
1
2
ACC
IG
ST
P-SUP-05
NO. 14 10A
F1
P-SUP-02
P-SUP-04
P-SUP-03
P-SUP-03
P-SUP-03
YE9YG
E4
NO. 15 30A
YB E2
D
N
L
K
J
NO. 9 15A
YG B9
YR C3
YE7
NO. 4 20A
YR B6
NO. 10 15A
B8
BW C2
LF2
NO. 19 20A
LB E10
4 GG
F46 B108
NO. 8 30A
NO. 16 20A
LY E3
G5
RY
NO. 7 15A
RG D9
NO. 2 15A
RF3
NO. 1 15A
D6
RW
BWF6
NO. 3 15A
WR D8
NO. 13 15A
F7
IGNITION RELAY
WL 10
G 11
B 13
GW 9
B225
BRE1
GW
FUSE &
RELAY
D3
BOX (F/B)
B51A:
B:
i5
B52C:
B152D:
E:
B158
F:
GW B11
F40
G:
F41
E6
A8
BL
B
REF. TO GND-02
OP
CONNECTOR
GW 3
WR 1
YR 2
B228
FB-38
B72 (BLUE)
1 2
3 4
(GRAY) (BLUE)
B158E:
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9
FB-31
10
FB-29
FB-30
F46
13
2
456
FB-28
FB-12
B:
i5
D:
B152
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9
10 11 12
FB-11
B52C:
F41G:
1 2 3
4 5 6 7
FB-10
(GRAY)
FB-8
1 2 3
4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12
FB-7
B228
FB-6
B51A:
1 2 3
4 5 6 7 8
13 14 15
WI-22
FB-13
FB-9
123 4
5 6 7 8
1 2
5 6
7 8
FB-39
(BLACK)F44
B225
14 15 16
93 4
10
17
11 12 13
18
21 22 23
RELAY BLOCK (BLACK)
19
20
IG
ST
F:
12 3 4
5 6 7 8 9
24 25 26
27
28
31 32 33
29
30
F40
(BROWN)
34 35 36
37
38
WI-05690
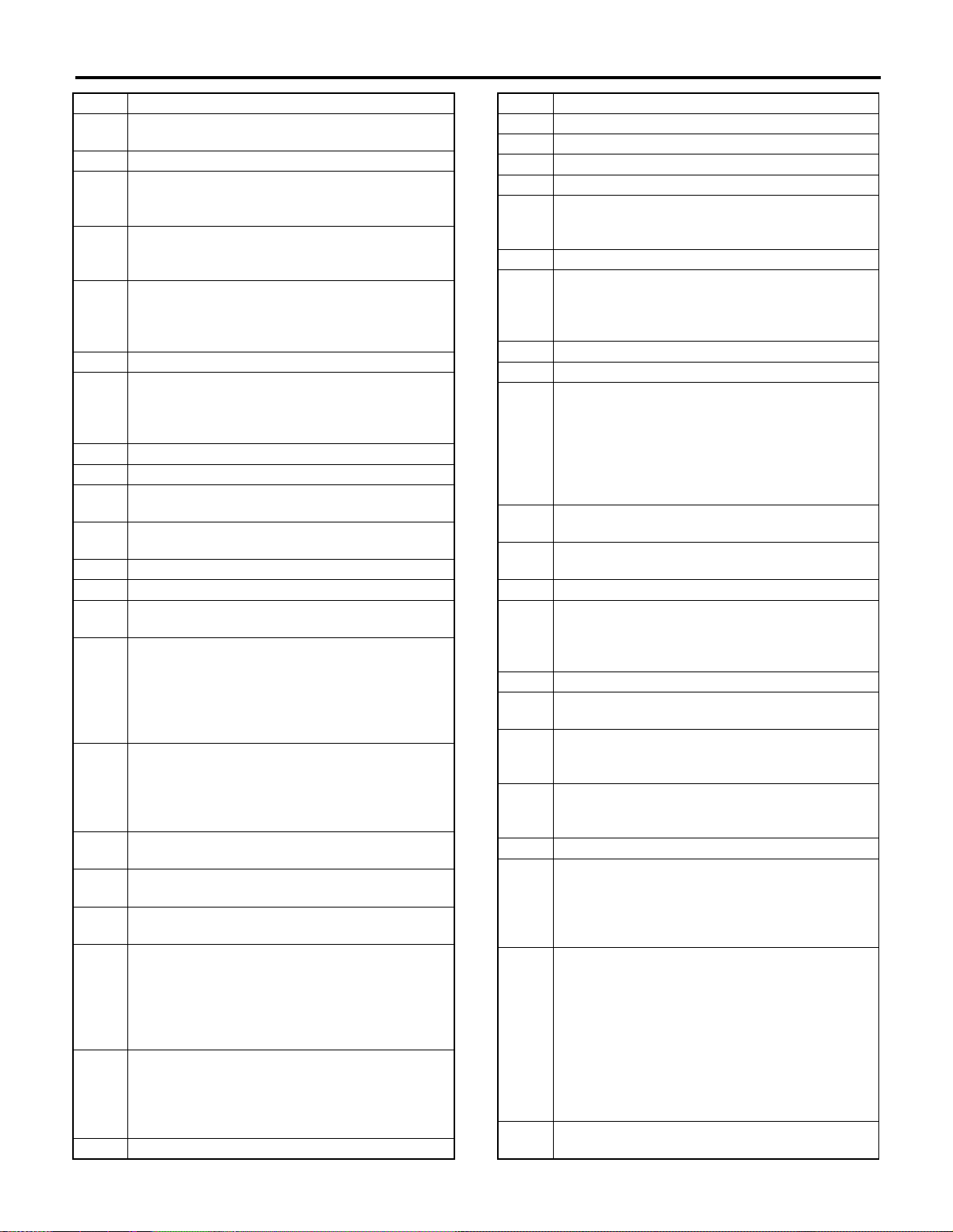
POWER SUPPLY ROUTING
WIRING SYSTEM
No. Load
MB-1
MB-2 Power window circuit breaker
MB-4
MB-5
MB-6
MB-7 Transmission control module (AT)
MB-8
MB-9 Horn
MB-10 Headlight LH
MB-11
MB-12
SBF-7 ABS control module
SBF-8 Oxygen sensor heater relay
ALT
IG
ST
FB-1
FB-2
FB-3
FB-4
FB-5
FB-6 Blower motor relay
Fuse (Seat heater/rear accessory power supply
relay)
Data link connector
Engine control module
Main relay
Cruise control sub switch
Day time running light control module
OP connector
Horn switch
Keyless entry control module
Security horn relay
SPORT shift switch
Hazard switch
Keyless entry control module
Key warning switch
Stop & turn module
Combination meter
Headlight RH
A/C relay holder
SBF holder
Combination meter
OP connector
Check connector
Ignition relay-2
Keyless entry control module
OP connector
Security control module
Vehicle speed sensor (MT)
Cruise control module
Engine control module (AT)
Inhibitor switch (AT)
Interrupt relay
Starter interlock relay
ABS control module
Main fan relay
Parking switch
Security control module
Parking switch
Security control module
Combination meter
Combination switch (Lighting)
Hazard switch
Keyless entry control module
Rear combination light
Stop & turn module
Combination meter
Combination switch (Lighting)
Keyless entry control module
Rear combination light
Stop & turn module
No. Load
FB-7 Front fog light relay
FB-8 ABS control module
FB-9 Fuel pump relay
FB-10 Stop light switch
Cargo Light
FB-11
FB-12 Trailer connector
FB-13
FB-14 Airbag control module
FB-15 Airbag control module
FB-16
FB-17
FB-18
FB-19 Manual A/C control module
FB-20
FB-21 Cruise control main switch
FB-22
FB-23
FB-24
FB-25 Parking switch
FB-26
FB-27
FB-28
SPORT light relay
Wiper deicer relay
Integrated module
Keyless buzzer
Keyless entry control module
OP connector
Daytime running light control module
Daytime running light relay
Engine control module
Fuel pump relay
Ignition coil and ignitor
Integrated module
Transmission control module
A/C pressure switch
Blower motor relay
A/C relay
Sub fan relay
Back-up light switch (MT)
Cruise control module
Inhibitor switch (AT)
Power window relay
Engine control module
Manual A/C control module
Choke coil
Rear defogger
Rear defogger condenser
Combination switch (Lighting)
Engine control module
OP connector
AT select lever illumination light
Integrated module
OP connector
Power window main switch
Seat heater switch
Audio
Ashtray illumination light
SPORT light switch
CD illumination light
Cigar lighter illumination light
Front fog switch
Globe box light
Hazard switch
Manual A/C control module
Wiper deicer switch
Front accessory power supply socket
Multiple power socket relay (Option)
WI-23

WIRING SYSTEM
No. Load
Compass mirror
Integrated module
Mirror heater LH
FB-29
FB-30 Audio
FB-31
FB-32
FB-33
FB-34
FB-35
FB-36 Front turn signal light LH (Up, Lo)
FB-37 Front turn signal light RH (Up, Lo)
FB-39
Mirror heater RH
OP connector
Rear accessory power supply relay
Remote control rearview mirror switch
Vanity mirror illumination light
Combination switch (Washer)
Front washer motor
Front wiper motor
Combination meter
Integrated module
Key illumination light
Key warning and step light diode
Room light
Security control module
Security horn relay
Stop light
Step light
Audio
Combination meter
License plate light LH
License plate light RH
Rear combination light LH
Rear combination light RH
Rear finisher light LH
Rear finisher light RH
Trailer connector
Front clearance light LH
Front clearance light RH
Combination meter
Hazard switch
POWER SUPPLY ROUTING
WI-24

MEMO:
POWER SUPPLY ROUTING
WIRING SYSTEM
WI-25
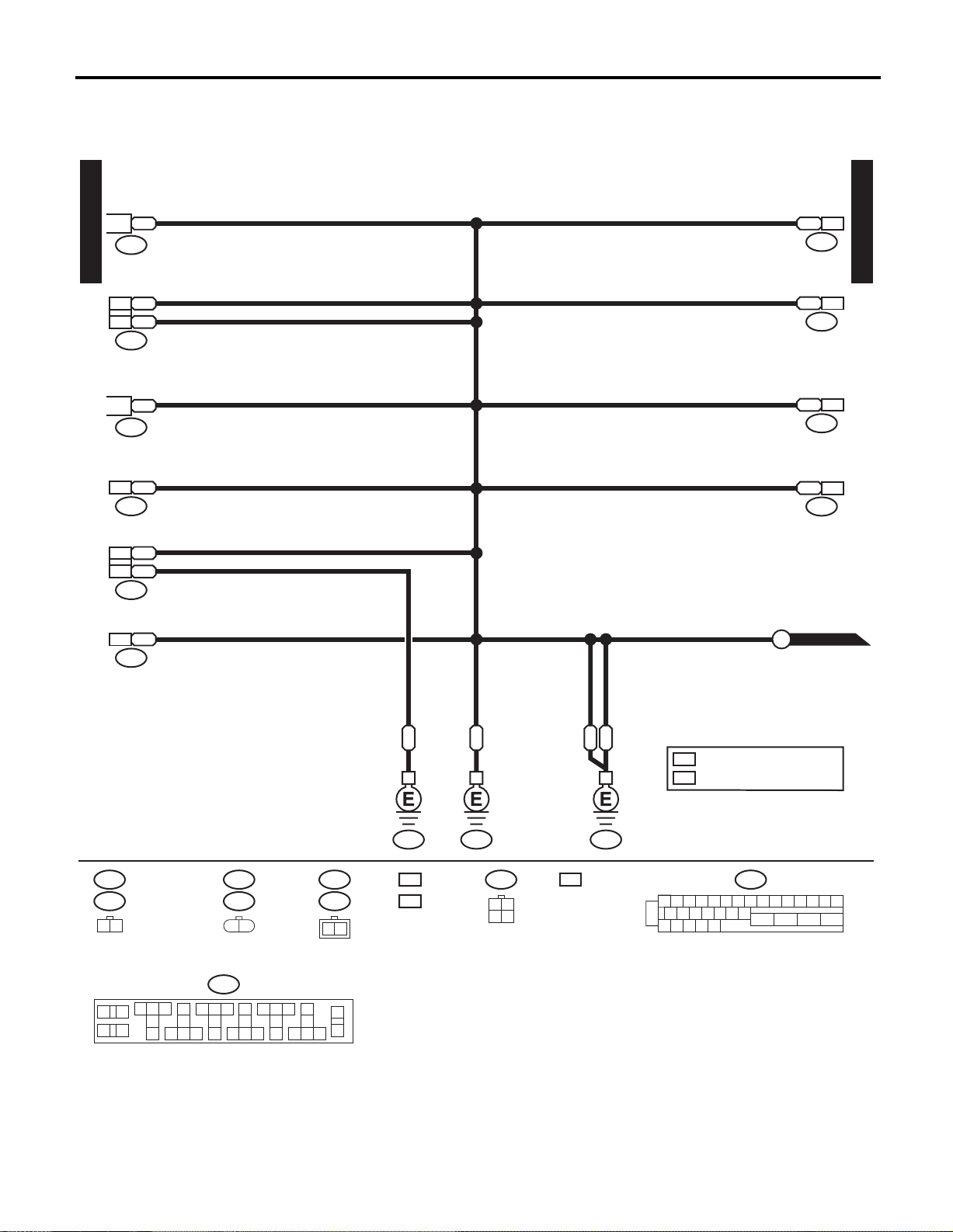
WIRING SYSTEM
5. Ground Distribution
A: SCHEMATIC
GROUND DISTRIBUTION
MAIN FAN MOTOR
B
1
F17
GND-01
SUB FAN MOTOR
(TURBO ENGINE MODEL)
B3
B4
F16
SUB FAN MOTOR
(NON-TURBO ENGINE MODEL)
1
B
F16
FAN MODE RELAY
(TURBO ENGINE MODEL)
B31
F27
ABS CONTROL MODULE
B
23
B26
F49
FWD SWITCH
35
B
F27
FRONT FOG LIGHT LH
FRONT FOG LIGHT RH
FRONT TURN SIGNAL
LIGHT LH (UPPER)
FRONT TURN SIGNAL
LIGHT RH (UPPER)
A
B 2
F21
B 2
F6
B 1
F19
B 1
F3
GND-02
GND-01
F3
F19
1 2
1 2
3 4
HR
(GRAY)
HR
(GRAY)
57
6
8
9
F27
15 1716
10
11
18
19
1312
14
RELAY HOLDER
F6
F21
12
20
21
2322
24
25 2726
GB-2
B
F16
(GRAY) (BLACK) (BLACK) :
12
34
B
F73
F16
F17 (BLACK) :
2 1
30
35
31
28
29
36
34
3332
NA
NA
B
B
: NON-TURBO ENGINE MODEL
NA
: TURBO ENGINE MODEL
TB
GB-1
:
TB
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
16 17 18 19 20 21 22
27 28 29 30 31
F49
10 11 12 13 14 15
23 24 25 26
WI-06751
WI-26
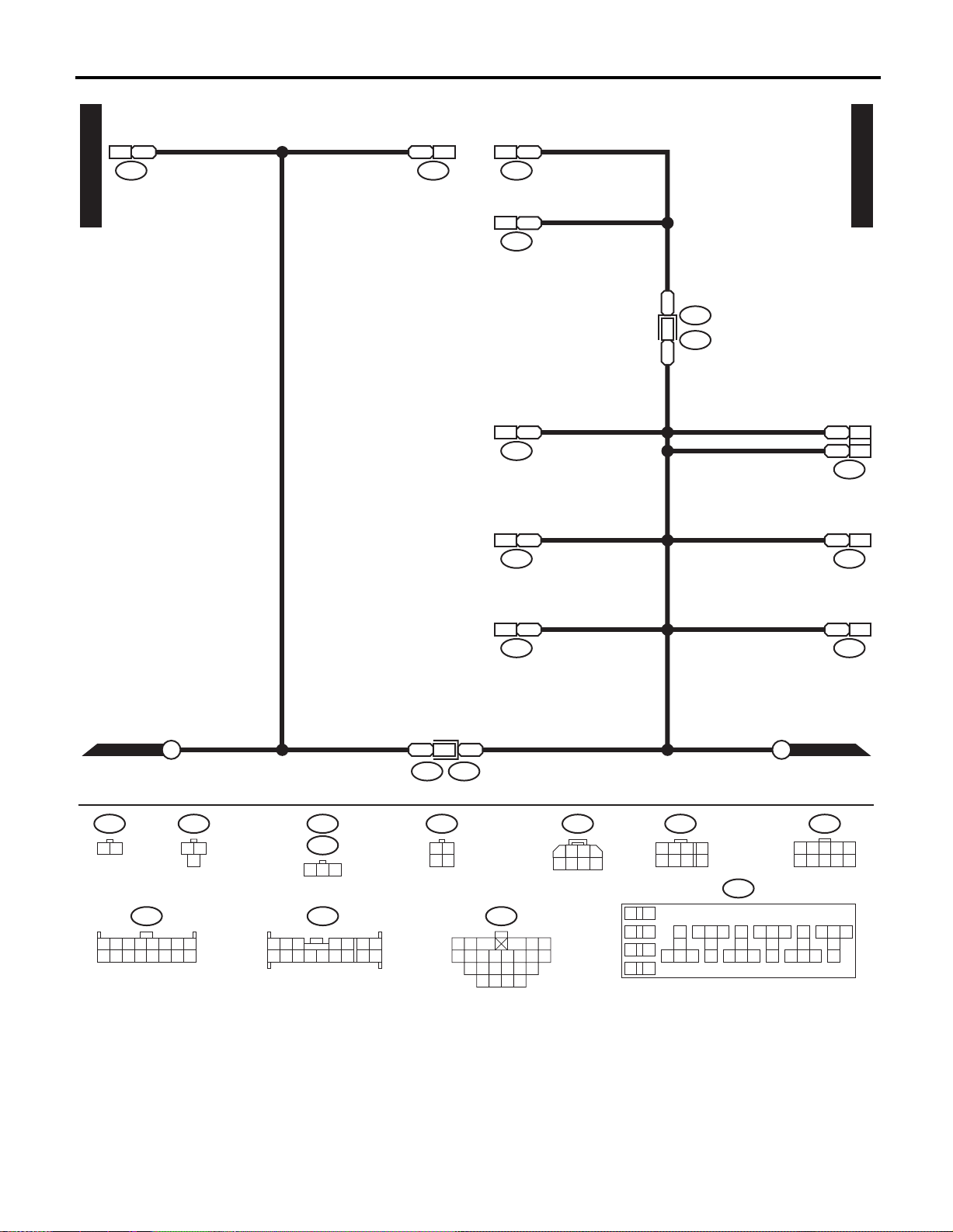
GROUND DISTRIBUTION
WIRING SYSTEM
FRONT CLEARANCE
LIGHT LH AND FRONT TURN
SIGNAL LIGHT LH (LOWER)
B2
F22
GND-02
FRONT CLEARANCE
LIGHT RH AND FRONT TURN
SIGNAL LIGHT RH (LOWER)
2
B
F4
POWER WINDOW
MAIN SWITCH
B1
D7
REMOTE CONTROLLED
REARVIEW MIRROR SWITCH
B2
D61
TURN & HAZARD
MODULE
B1
B32
POWER WINDOW RELAY
B16
B225
GND-02
D1
3 B
B30
B
INTEGRATED
MODULE
B 4
B 13
B:
B281
FUEL PUMP RELAY
(TURBO ENGINE MODEL)
B 3
B46
GND-01
B73
1 2
12345678
9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16
B281
A
1 2
(BLUE)B:
KEY LOCK SOLENOID
(AT MODEL)
B1
B73
B
8 B
B61F44
HR
(GRAY)
(BLACK)B32
3
1 2 3
8 9
F4
HR
(GRAY)
F22
1 2 3
D7
10411 12 13 14 15 16
5 6
7
B46
12
3
4
7
(GREEN)
B30
3412
89
10 11 12 13 14
15 16 17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24
56
B333
1 2 3 4
7 8
5 6
1 2
5 6
7 8
(BLACK)
F44
123 4
7 8
5 6
14 15 16
93 4
10
17
11 12 13
18
RELAY BLOCK (BLACK)
STOP & TURN MODULE
C
B225
19
24 25 26
20
27
21 22 23
28
GND-03
D61
1234
6 7 8 9510
29
34 35 36
30
31 32 33
B 7
B333
37
38
WI-06752
WI-27
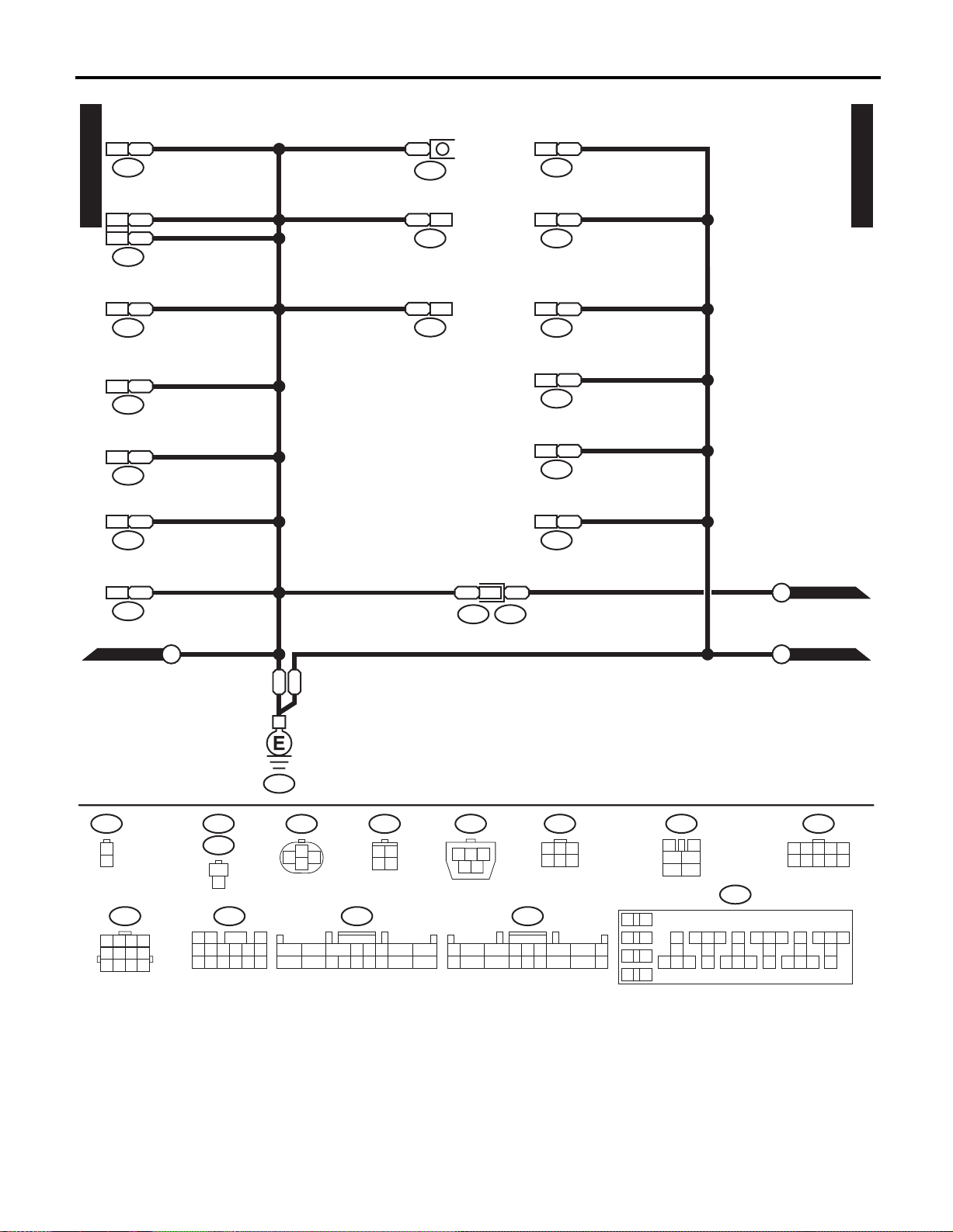
WIRING SYSTEM
GROUND DISTRIBUTION
COMBINATION SWITCH
(WIPER)
B
2
B70
GND-03
COMBINATION SWITCH (LIGHTING)
B
16
B
10
B71
DAYTIME RUNNING LIGHT RELAY
B38
B225
SEAT HEATER/REAR ACCESSORY
POWER SUPPLY RELAY
B
3
B104
CLUTCH SWITCH (MT)
B1
B106
IGNITION RELAY
B13
B225
KEYLESS REGISTRATION
CONNECTOR
B
B184
DAYTIME RUNNING
LIGHT CONTROL MODULE
B 10
B242
OP CONNECTOR
B 7
B228
CRUISE CONTROL
ACTUATOR
B6
B7
FRONT WIPER MOTOR
B2
B8
A/C PRESSURE SWITCH
(TURBO ENGINE MODEL)
B3
B10
INHIBITOR SWITCH (AT)
B4
B12
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
B2
B16
MAIN RELAY (NON-TURBO
ENGINE MODEL)
B1
B47
GND-03
WIPER DEICER
1
B
B177
GND-02
B16 (GRAY)
1
2
HR
B12
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9
10 11 12
C
(BLACK)
B106
B177
121
2
B228
1 2 3
4 5 6 7 8 9
13 14 15
10 11 12
B
B
GB-3
B71
B104
12
34
132
B10
1
3
4
2
23456718
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
9
BA3B
B36
i1
SMJ
HR
B8
4 5
2 3 64 571 8 9
11 12 1513 14 1610 17 18
B70
B7
(BLACK)
13
2
456
1 2
5 6
7 8
B47 (BROWN)
12
34
56
B225
14 15 16
93 4
10
17
11 12 13
18
21 22 23
RELAY BLOCK (BLACK)
19
20
D
24 25 26
27
28
GND-05
GND-04
E
B242
1234
6 7 8 9510
29
30
31 32 33
34 35 36
37
38
WI-06753
WI-28
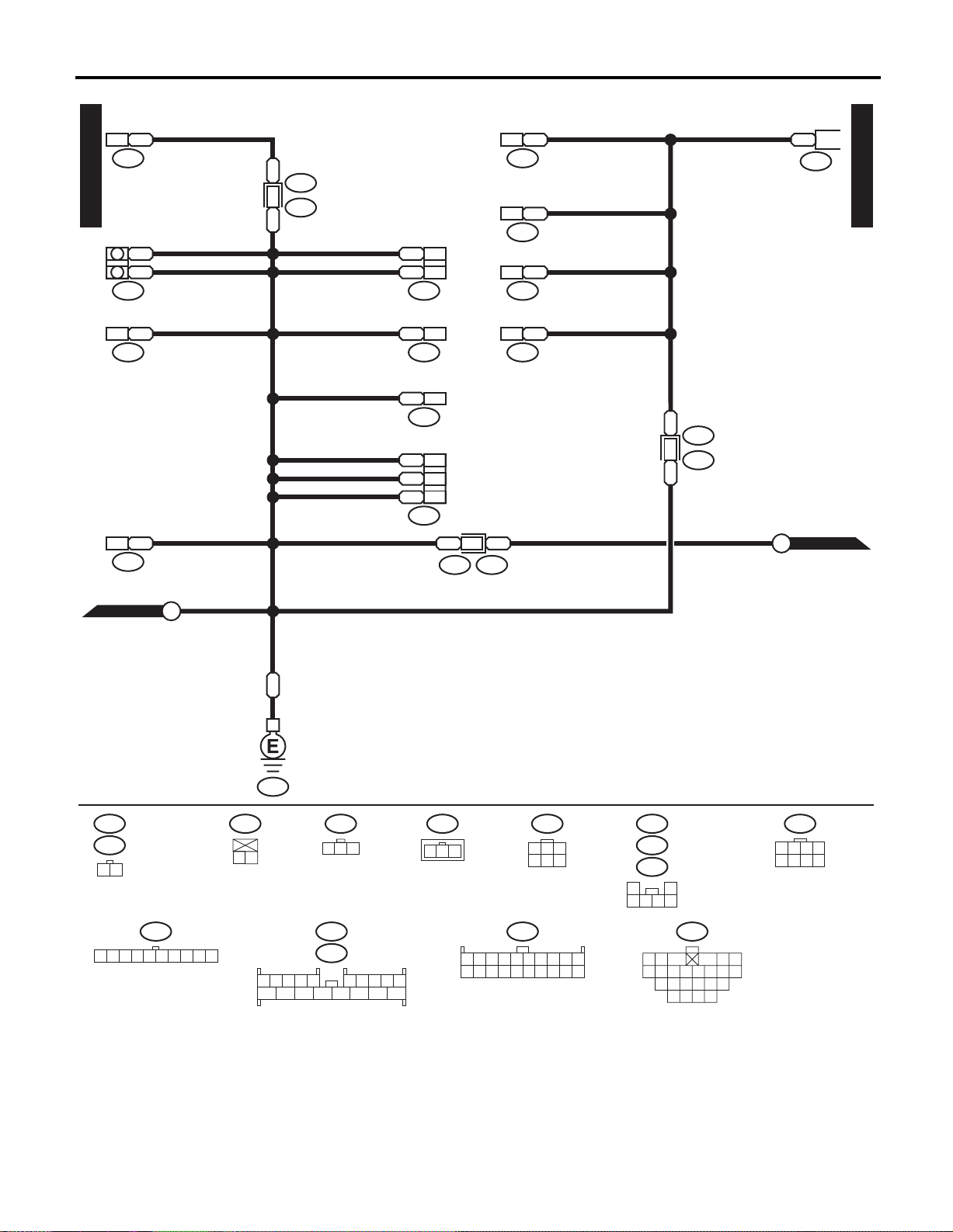
GROUND DISTRIBUTION
WIRING SYSTEM
MANUAL DOOR LOCK SWITCH
B5
D62
GND-04
DIAGNOSIS TERMINAL
B
B
B81
MODE ACTUATOR
B10
B77
SECURITY CONTROL
MODULE
B14
B93
B3B
D11
B101
AT SELECT LEVER
ILLUMINATION LIGHT
CRUISE CONTROL
MODULE
KEYLESS ENTRY
CONTROL MODULE
SPORT SHIFT SWITCH
(TURBO ENGINE AT MODEL)
B 5
B 6
B116
B 6
B94
B 11
B176
B 3
B 4
B 6
B237
B
5
B97 R1
VANITY MIRROR
ILLUMINATION LIGHT LH
B2
R54
VANITY MIRROR
ILLLUMINATION LIGHT RH
B2
R51
ROOM LIGHT
B3
R52
SPOT LIGHT
B2
R56
B
COMPASS MIRROR
B
2
R139
GND-04
B3B
R50
B90
GND-06
F
GND-03
R51
R54
1 2
123456789
(BLACK)
(BLACK)
B77
E
(BROWN)
B
GB-5
B94
B90
13
2
456
(BLACK)
10
R56
21
10
2 3 4 5 671 8 9
11
12 13 14 15 16 17 18
R52
1 2 3
B93
B176
R139
123
123456789
10
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
B116
(BLACK)B237
(BROWN)
D62
12
3456
B101
3412
89
7
10 11 12 13 14
15 16 17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24
56
B97
1234
5 6 7 8
WI-05800
WI-29
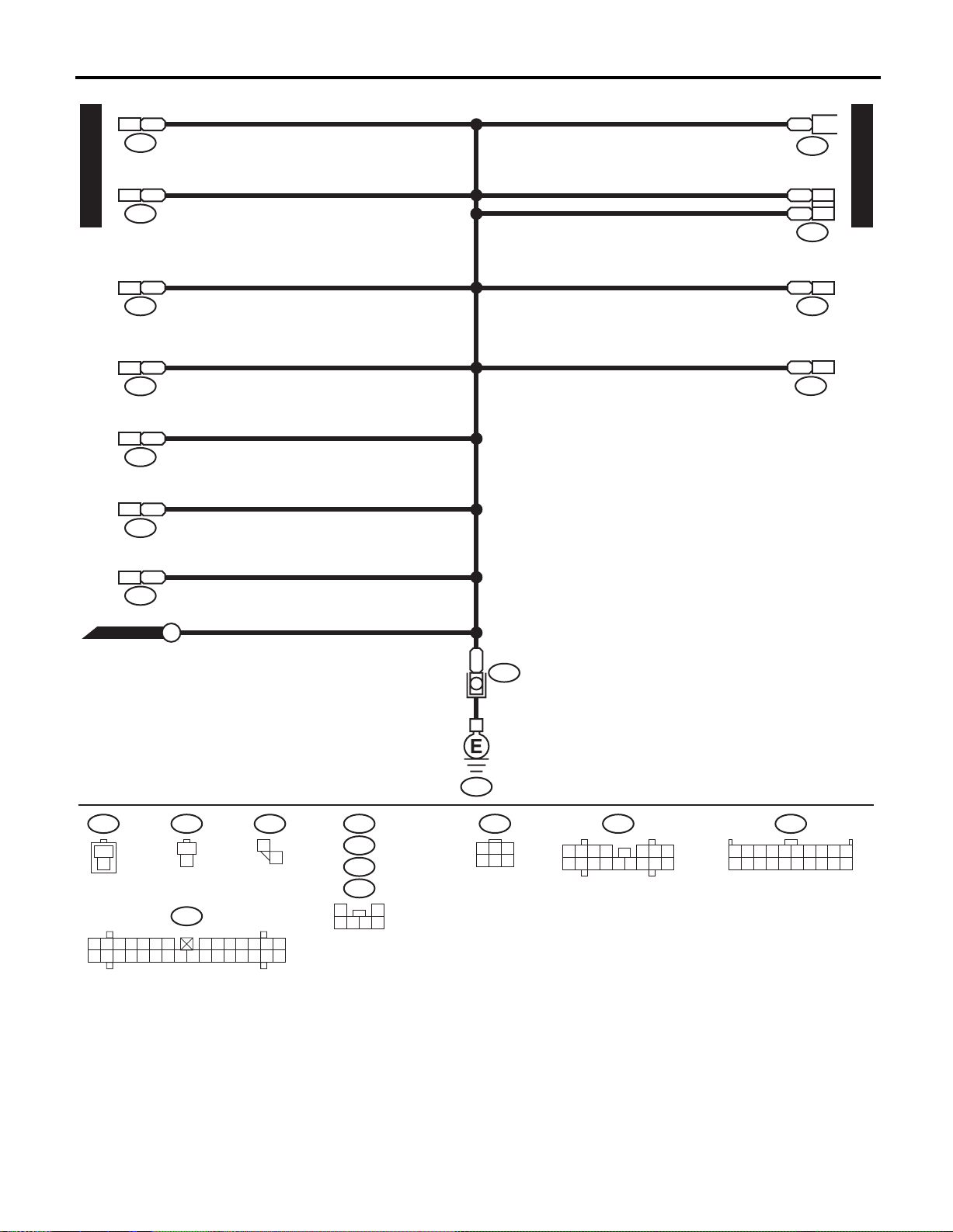
WIRING SYSTEM
GROUND DISTRIBUTION
FRONT FOG LIGHT SWITCH
B6
i7
COMBINATION METER
B
A20
GND-05
A:
i10
B
B16
B:
i11
MODE CONTROL PANEL
(MANUAL-A/C)
B
2
i15
MODE CONTROL PANEL
(MANUAL-A/C)
B10
i17
GLOVE BOX
ILLUMINATION LIGHT
B1
i23
FRONT ACCESSORY
POWER SUPPLY SOCKET
1
B
i24
ASHTRAY ILLUMINATION LIGHT
B
1
i21
WIPER DEICER SWITCH
WORKING LIGHT SWITCHCOMBINATION METER
SPORT LIGHT SWITCH
B 5
B
i43
B 5
i67
B
i68
6
6
GND-05
GND-03
i21
1
2
1 2 3 4
15 16 17 18
D
i23
1
2
(GREEN)A:
i10
7
5 6
21 22 232425 2627282930
19 20
9
8
i24
1
1011121314
B
i28
GB-7
(YELLOW)
i7
2
i43
(GRAY)
i67
(GRAY)i68
12
3456
i15
13
2
456
123
10411 12 13 14 15 16
89
i11
(GREEN)B:
567
(GRAY)
i17
123456789
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
10
WI-05695
WI-30
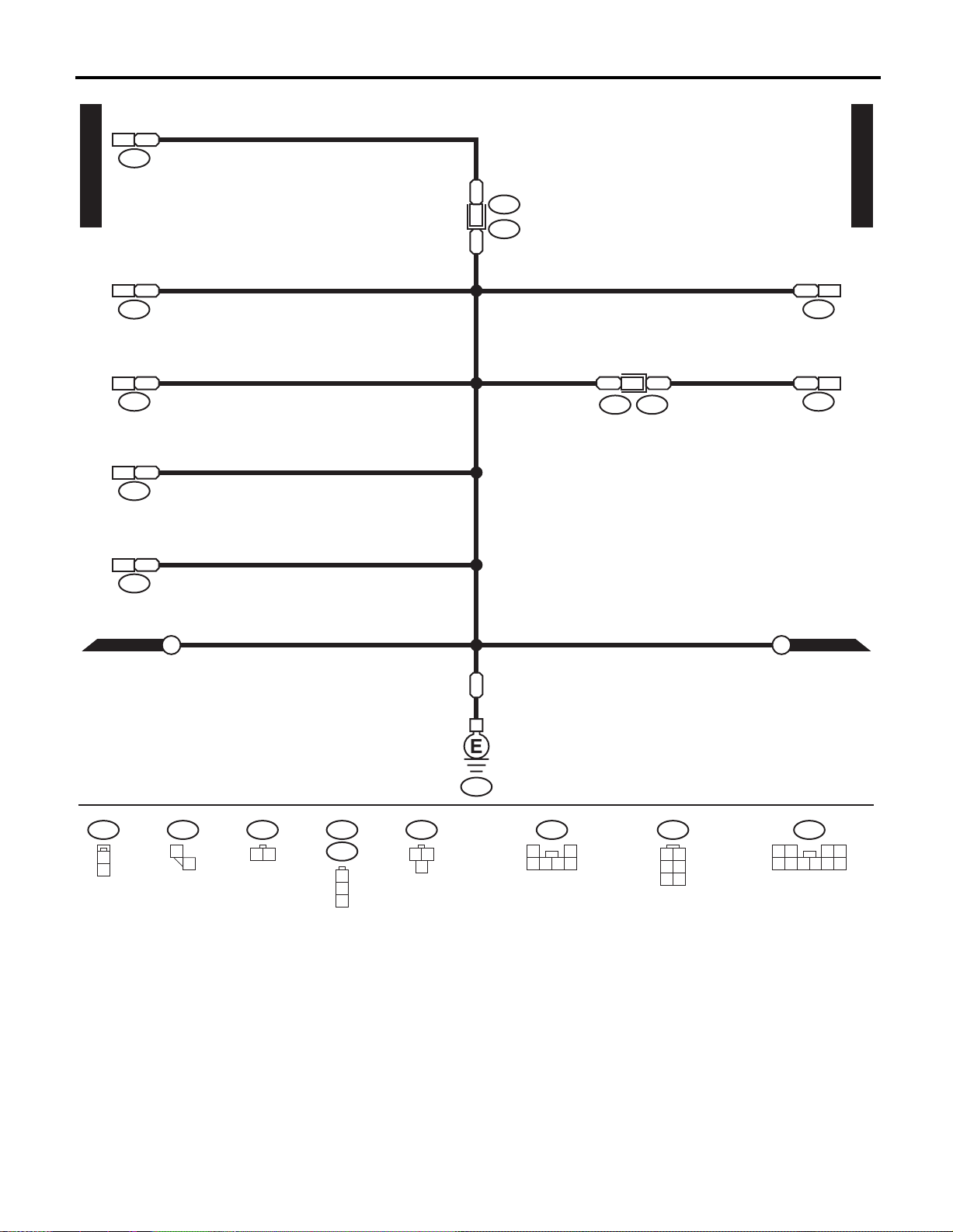
FUEL PUMP ASSEMBLY (WITHOUT FPC)
B1
R58
GROUND DISTRIBUTION
WIRING SYSTEM
GND-06
SEAT BELT SWITCH
B
2
R8
FRONT DOOR SWITCH LH
B3
R9
FRONT DOOR SWITCH RH
B3
R12
REAR DOOR SWITCH RH
B3
R16
B
R57
2B
R15
FUEL PUMP CONTROL MODULE
B
2
R194 R195
(WITH FPC)
REAR ACCESSORY POWER
B
SUPPLY SOCKET
B
R122
B
R32
GND-06
5
1
R8
1
2
GND-04
GND-07
F
B
GB-8
R32
1
(BLACK)
R194
2
1 2
R9
R12
1
2
3
R16
1 2
3
(BLACK)
R57
12
3456
R58
12
34
56
(GRAY)
G
1
2
6 7 8 9
5
R122
HRHR
3 4
10
WI-06754
WI-31
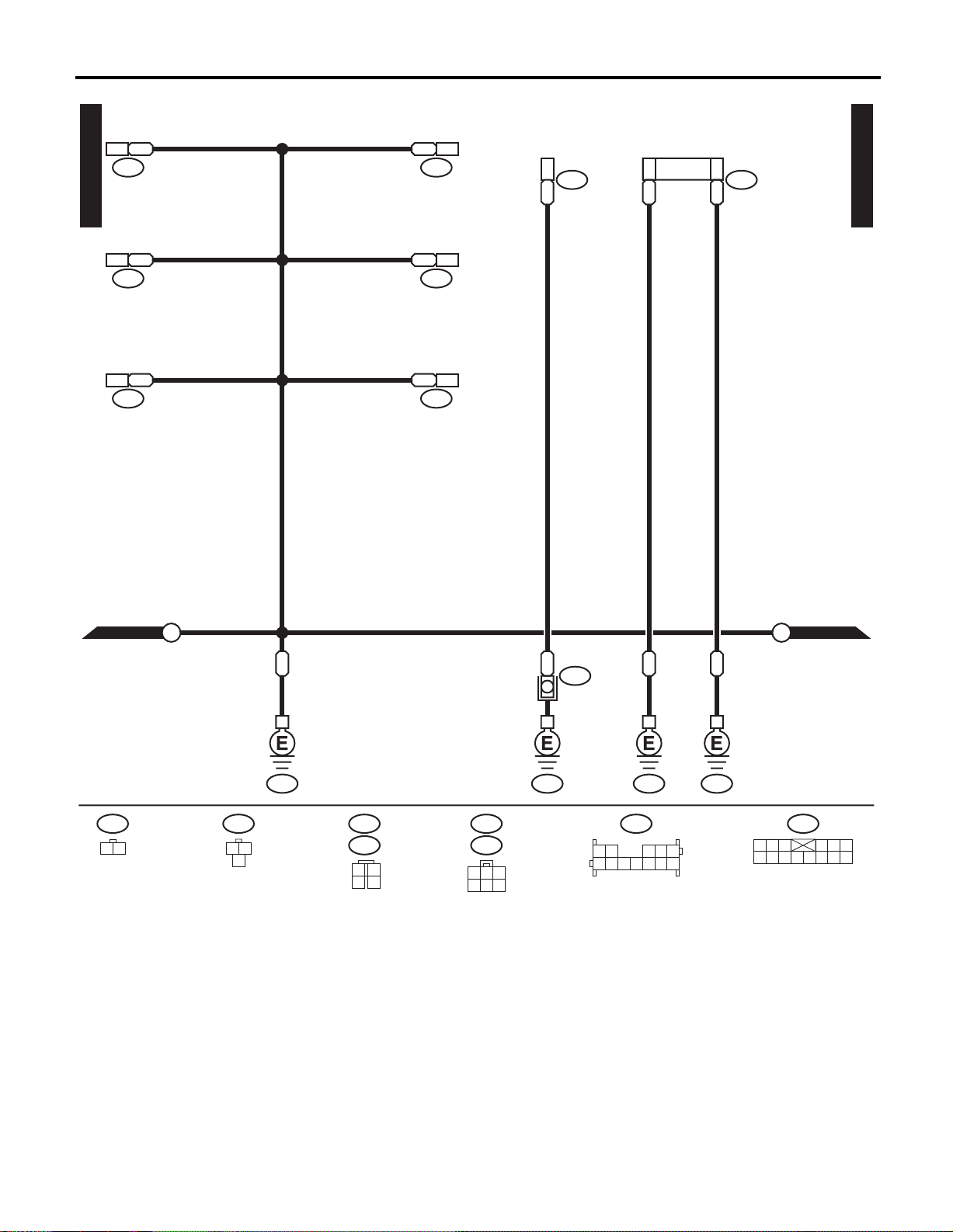
WIRING SYSTEM
GROUND DISTRIBUTION
REAR DOOR SWITCH LH
B3
R22
SEAT HEATER SWITCH LH
B
R43
GND-07
SEAT HEATER RH SEAT HEATER LH
BB1
R41
SEAT HEATER SWITCH RH
3
R42
B 1
R44
POWER SEAT
B 1
R109
3
RADIO SRS HARNESS
11B
i26
5
B
4
B31
B
GND-07
GND-06
R109 (BLACK)
1 2
G
GR
B
i29
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9
B
GB-9
(BLACK)R22
1
2
3
R41
R44
1 2
3 4
(BLUE)
(BLUE)
R42
(BLUE)
R43
13
2
456
GB-4
10 11 12
B
(YELLOW)B31
B
GB-6
GND-08
H
i26
1 2 3 4 5 6
7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14
WI-05802
WI-32
 Loading...
Loading...