Page 1

INSTALLATION AND SERVICE MANUAL
J30-05380
OUTDOOR ROOFTOP GAS-FIRED DUCT FURNACE
(NATURAL OR POWER VENTED)
ATTENTION: READ THIS MANUAL AND ALL LABELS ATTACHED TO THE UNIT CAREFULLY BEFORE
ATTEMPTING TO INSTALL, OPERATE OR SERVICE THESE UNITS! CHECK UNIT DATA PLATE FOR
TYPE OF GAS AND ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS AND MAKE CERTAIN THAT THESE AGREE WITH
THOSE AT POINT OF INSTALLATION. RECORD THE UNIT MODEL AND SERIAL No.(s) IN THE SPACE
PROVIDED. RETAIN FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
Unit No. Serial No.
SA VE THIS MANUAL
FOR Y OUR SAFETY
The use and storage of gasoline or other flammable vapors and liquids in open
containers in the vicinity of this appliance is hazardous.
FOR Y OUR SAFETY
If you smell gas:
1. Don’t touch electrical switches.
2. Extinguish any open fl ame.
3. Immediately call your gas supplier.
RISM-14
Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service or maintenance
can cause property damage, injury or death. Read the installation, operating and
maintenance instructions thoroughly before installing or servicing this equipment.
Install, operate and maintain unit in accordance with manufacturer's
instructions to avoid exposure to fuel substances or substances from incomplete
combustion which can cause death or serious illness. The state of California
has determined that these substances may cause cancer, birth defects, or other
reproductive harm.
INSTALLER'S RESPONSIBILITY
Installer Please Note: This equipment has been test fired and inspected. It has been
shipped free from defects from our factor y. However, during shipment and installation,
problems such as loose wires, leaks or loose fasteners may occur. It is the installer's
responsibility to inspect and correct any problems that may be found.
These units are certifi ed by ETL for operation on either natural or propane gas.
Read this manual and all labels attached to the unit carefully before attempting to install, operate or
service the following unit models:*
Outdoor Rooftop Duct Furnaces: QV(RT/PV)- (100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400) (H)(M)
(RT = Natural Vent; PV = Power Vent)
*Look in the direction of the unit air fl ow to determine whether the unit is right or left-hand accessible.
04/13
260 NORTH ELM ST., WESTFIELD, MA 01085
TEL: (413) 568-9571 FAX: (413) 562-8437
www.mestek.com
Page 2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
RECEIVING/PRE-INSTALLATION
INSTRUCTIONS ......................................................2
GENERAL SAFETY INFORMATION ....................2, 3
SPECIFICATIONS
Dimensional Data ..........................................4, 5
Performance and Specifi cation Data .................5
Performance Data Curves .............................6, 7
INSTALLATION
Location/Mounting .....................................2, 3, 8
Clearances ................................................4, 5, 8
Venting ..............................................................9
Duct and Drain Specifi cations .........................10
Gas Connections .................................10, 11, 12
Electrical Connections .....................................12
OPERATION
General Information...................................13, 14
Intermittent Pilot Ignition Parts ........................13
Controls ...........................................................14
Gas Controls ...................................................15
Air Distribution/Throughput .............................16
Lighting ......................................................17, 18
Primary Air Shutter/Pilot Adjustment ...............18
Gas Input Adjustment ......................................18
START-UP ...............................................................19
MAINTENANCE ...............................................20, 21
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE ..........................22-25
REPLACEMENT PARTS ........................................26
WARRANTY ...........................................................26
GAS EQUIPMENT CHECK SHEET .......................28
The following terms are used throughout this manual to
bring attention to the presence of potential hazards or
to important information concerning the product:
on the tracks, and push up into the top lip; swing and
lower the panel in place until it engages with the bottom
panel. Turn the screwhead on each latch clockwise.
The screw must turn freely one quarter turn before
resistance is felt in order for the lock to engage. If the
latch does not hold, turn the screw counter-clockwise
several turns and repeat the above procedure. Also
refer to Figures 8a, 8b and 8c for more specifi cations.
RECEIVING INSTRUCTIONS
Inspect shipment immediately when received to
determine if any damage has occurred to the carton/
crate during shipment.
After the unit has been uncrated, check for any visible
damage to the unit. On power vented units, check
motor position and turn blower wheel by hand to
determine if damage has occurred to these critical
parts.
If any damage is found, the consignee should sign the
bill of lading indicating such damage and immediately
fi le claim for damage with the transportation company.
PRE-INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
When unit is received and uncrated check data plate
on unit for type of gas and electrical specifi cations and
make certain that these agree with those at point of
installation.
Open all disconnect switches
and secure in that position before installing
the unit. Failure to do so may result in personal
injury or death from electrical shock.
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result
in death, serious injury or substantial property
damage.
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result
in death, serious injury or substantial property
damage.
Indicates an imminently hazardous
situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor
injury or property damage.
NOTICE: Used to notify of special instructions on
installation, operation or maintenance which are
important to equipment but not related to personal
injury hazards.
SERVICE ACCESS PANEL REMOVAL
To remove an access panel door, use the following
procedure: remove the two screws and two washers
from the louvered flue discharge area of the service
panel (power vent doors only). Each panel is held
in place with two “Grip” Latches. Using a slotted
head screw driver, tur n the latch screwhead counter
clockwise. Using the handle provided, pull the panel
upwards. Pull the bottom of the panel out and lower
the panel to disengage it from the top lip. To replace
an access door panel, guide the panel door upwards
NOTICE: It is the equipment owner’s responsibility
to provide any scaffolding or other apparatus
required to perform emergency service or annual/
periodic maintenance to this equipment.
RIGGING
Rig the unit using either belt or cable slings. Use spreader
bar to protect the top of the unit when it is lifted.
The furnace units are provided with two holes in the
base rail on each side of the unit. Slide pipes beneath the
unit through these holes and attach rigging to the pipes
for lifting the unit.
LOCATION
Before placing the rooftop unit in its permanent location,
make certain that the roof is capable of carrying the
additional load of this equipment. Check the shipping
weights given in Chart 2.
Refer to Figures 1, 2 and 6 and charts 1 and 2 for
adequate unit dimensions and required clearances.
MOUNTING
The units are mounted on skids and are suitable for use
on combustible fl ooring. It is recommended that the skids
be mounted either on level solid planking or steel
channels, but never on a soft tar roof where the skids
could sink and reduce the clearance between the bottom
panel and the roof.
– 2 –
Page 3
A pilot burner plate is provided for access to the pilot
burner and ignition systems without removing the
burner drawer. Clearances between the external unit
and obstruction must be suffi cient for proper servicing
of pull-out drawer. See Figures 1 and 2 for this
clearance.
The outdoor units are certified for operation on either
natural or propane gas. If a unit is to be installed at an
altitude exceeding 2000 ft. (610 m) above sea level,
derate the input by 4% for each 1000 foot rise (305 m
rise) above sea level. Check all local codes.
Special orifices are required for installations above
2000 ft. (610 m). Check all local codes.
In Canada, if a unit is to be installed at altitudes of
2000 ft. (610 m) to 4500 ft. (1372 m), the unit must be
orifi ced to 90% of the normal altitude rating.
GENERAL SAFETY INFORMATION
Roofcurb kits for rooftop gas heating units are
shipped knocked down. A curb kit contains (insulated)
curb rails, hardware, sealant, self-adhering rubber
gasketing, and installation instructions. Roof insulation,
cant strips, flashing, roof felts, caulking and nails
must be furnished by the installer. See separate curb
specifi cations from manufacturer.
Failure to comply with the general
safety information may result in extensive
property damage, severe personal injury or
death!
This product must be installed by
a licensed plumber or gas fi tter when installed
within the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.
Do not alter the unit heater in
any way or damage to the unit and/or severe
personal injury or death may occur!
Never service any component
without fi rst disconnecting all electrical and gas
supplies to the unit or severe personal injury or
death may occur!
Ensure that all power sources
conform to the requirements of the unit heater or
damage to the unit will result!
Installation must be made in accordance with local
codes, or in absence of local codes, with the latest
edition of ANSI Standard Z223.1 (NFPA No. 54)
National Fuel Gas Code. All of the ANSI and NFPA
Standards referred to in these installation instructions
are those that were applicable at the time the design
of the appliance was certified. The ANSI Standards
are available from the American National Standards
Institute, Inc., 11 West 42nd Street, New York, NY,
10036 or www.ansi.org. The NFPA Standards are
available from the National Fire Protection Association,
Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
If installed in Canada, the installation must conform
with local building codes, or in absence of local building
codes, with current CSA-B149.1 “Installation Codes
for Natural Gas Burning Appliance and Equipment”
or CSA-B149.2 “Installation Codes for Propane Gas
Burning Appliances and Equipment”. These outdoor
duct furnaces have been designed for and certifi ed to
comply with CSA 2.8.
These units have been designed and certified for
outdoor use only, and may be located on the roof of
the building or at any convenient location external of
the building to be heated. The input range is 100,000
BTU/HR. (29.3 kW) to 400,000 BTU/HR. (117.1 kW) in
50,000 BTU/HR. (14.6 kW) increments.
The venting is an integral part of the unit and must not
be altered in the field. The Natural Vented units are
equipped with a vent cap which is designed for gravity
venting. Air for combustion enters at the base of the
vent through a protective grille, and the design of the
vent cap is such that the products of combustion are
discharged at the upper section of the cap. This cap
is shipped in a separate carton. It should be fastened
in position as shown in Figure 7 and should not be
altered in any way.
The Power Vented unit has a power venting system
with the inlet and discharge grille located in the upper
section of the side access panel. This balanced flue
design also preforms well under all wind conditions.
All internal parts of the standard unit are fabricated
from aluminized steel. Standard burners are pressed
aluminized steel and have a stainless steel bur ner
port protector and air shutters. All internal and external
jacket parts are fabricated from galvanized steel.
Stainless steel heat exchangers, burners and flue
collectors are optional. An optional 321 or 409 stainless
steel heat exchanger is highly recommended for the
following applications:
1) When the entering air temperature is below
40°F (4.4°C),
2) When the furnace is installed downstream of a
cooling coil section.
A pilot burner plate is provided for access to the pilot
burner and ignition systems without removing the
burner drawer. Clearances between the exter nal unit
and obstruction must be suffi cient for proper servicing
of pull-out drawer. See Figures 1 and 2 for this
clearance.
The outdoor units are certified for operation on either
natural or propane gas. If a unit is to be installed at an
altitude exceeding 2000 ft. (610 m) above sea level,
derate the input by 4% for each 1000 foot rise (305 m
rise) above sea level. Check all local codes.
Special orifices are required for installations above
2000 ft. (610 m). Check all local codes.
In Canada, if a unit is to be installed at altitudes of
2000 ft. (610 m) to 4500 ft. (1372 m), the unit must be
orifi ced to 90% of the normal altitude rating.
Unless otherwise specifi ed, the following conversions
may be used for calculating SI unit measurements:
1 inch = 25.4 mm
1 foot = 0.305 m
1 gallon = 3.785 L
1 pound = 0.454 kg
1 psig = 6.894 kPa
1 cubic foot = 0.028 m
1000 Btu/Cu. Ft. = 37.5 MJ/m
1000 Btu per hour = 0.293 kW
1 inch water column = 0.249 kPa
liter/second = CFM x 0.472
meter/second = FPM ÷ 196.8
3
3
– 3 –
Page 4
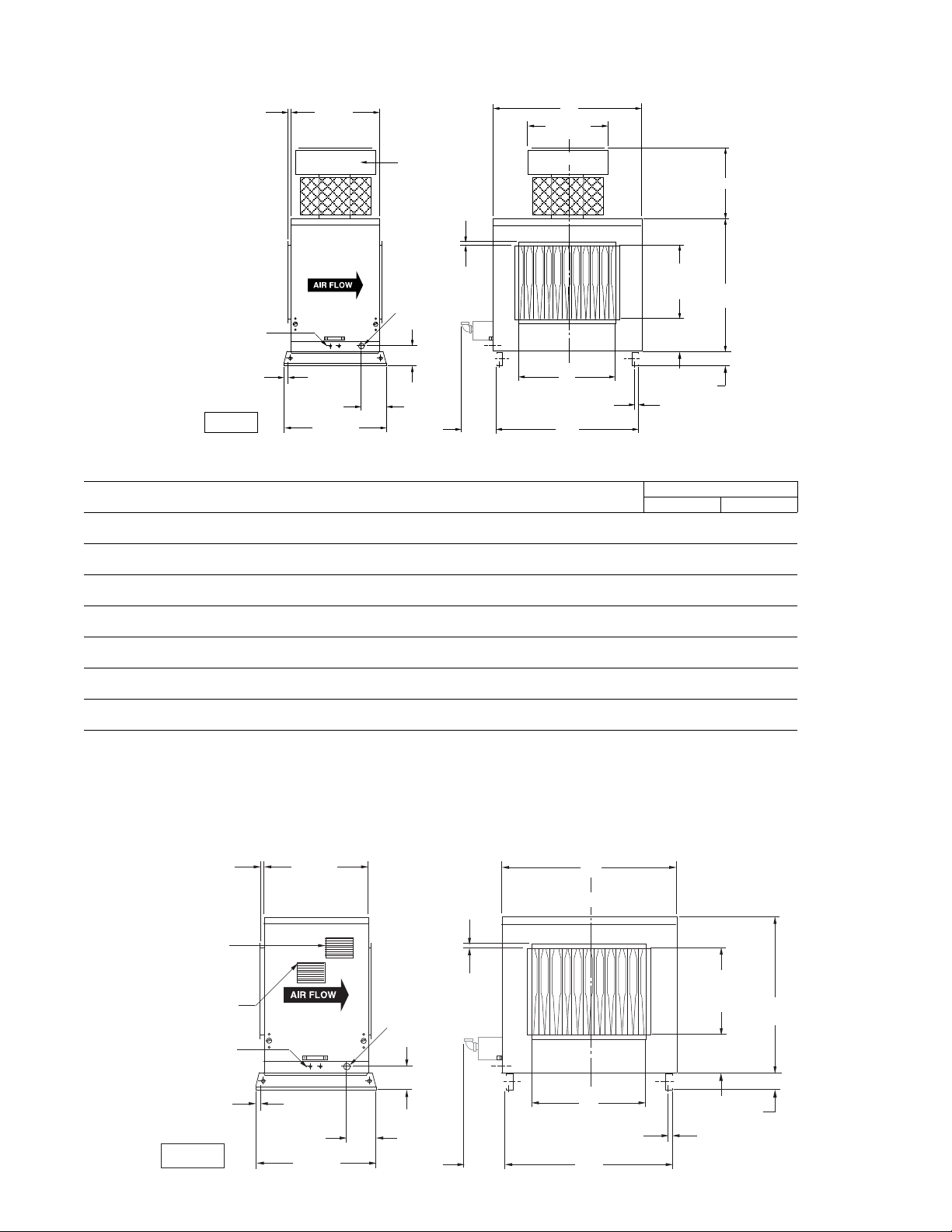
SPECIFICATIONS
DFR3541A
TFR3779 A
4" (102)
1" (25)
Typ.
5-1/16"
(129)
Electrical
Connections
5/8" (16) Typ.
Anchor Hole
Location
A
10-1/8"
(257)
B
Opening Typ.
13/16" (21) Typ.
Anchor Hole
Location
Gas
Connection
8-3/4"
(222)
*
F
26"
(660)
31-1/4"
(794)
C
L
39"
(991)
19"
(483)
Opening
K
1-1/8" (29)
Typ. Duct
Flange
Flue
Product
Outlet
Combustion
Air Inlet
DFR3538A
TFR3779A
4" (102)
1" (25)
Typ.
5-1/16"
(129)
Electrical
Connections
5/8" (16) Typ.
Anchor Hole
Location
Vent Cap
Is Shipped
In Separate
Carton
A
C (Typ.)
10-1/8"
(257)
B
Opening Typ.
13/16" (21) Typ.
Anchor Hole
Location
Gas
Connection
8-3/4"
(222)
*
F
26"
(660)
31-1/4"
(794)
C
L
D
39"
(991)
19"
(483)
Opening
K
1-1/8" (29)
Typ. Duct
Flange
Figure 1 - Standard Natural Vented Outdoor Duct Furnace
Chart 1 - Dimensional/Data
CAPACITY US CANADA GAS INLET
(CA) A B C D D *F K NAT LP
10 32-7/8 15-9/16 12 11 20-11/16 19-3/8 30-3/16 1/2 1/2
(835) (395) (305) (279) (525) (492) (767)
15 32-7/8 18-5/16 21-1/2 16 25-3/16 23-1/2 30-3/16 1/2 1/2
(835) (465) (546) (406) (640) (597) (767)
20 43-7/8 23-13/16 23-1/2 16 25-3/16 26-1/4 41-3/16 1/2 1/2
(1114) (605) (597) (406) (640) (667) (1046)
25 43-7/8 29-5/16 23-1/2 16 25-3/16 34-1/2 41-3/16 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4
(1114) (745) (597) (406) (640) (876) (1046)
30 54-7/8 34-13/16 26 17-1/2 26-11/16 37-1/4 52-3/16 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4
(1394) (884) (660) (445) (678) (946) (1326)
35 54-7/8 40-5/16 26 17-1/2 26-11/16 45-1/2 52-3/16 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4
(1394) (1024) (660) (445) (678) (1156) (1326)
40 60-3/8 45-13/16 26 17-1/2 26-11/16 51 57-11/16 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4
(1534) (1164) (660) (445) (678) (1295) (1465)
NOTE:
DIMENSIONS ARE IN INCHES, DIMENSIONS IN PARENTHESIS ARE IN MILLIMETERS.
* “F” DIMENSION IS THE RECOMMENDED CLEARANCE TO SERVICE THE BURNER DRAWER(S).
REFER TO FIGURE 6 FOR ADDITIONAL CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS.
Figure 2 - Standard Power Vented Outdoor Duct Furnace
– 4 –
Page 5
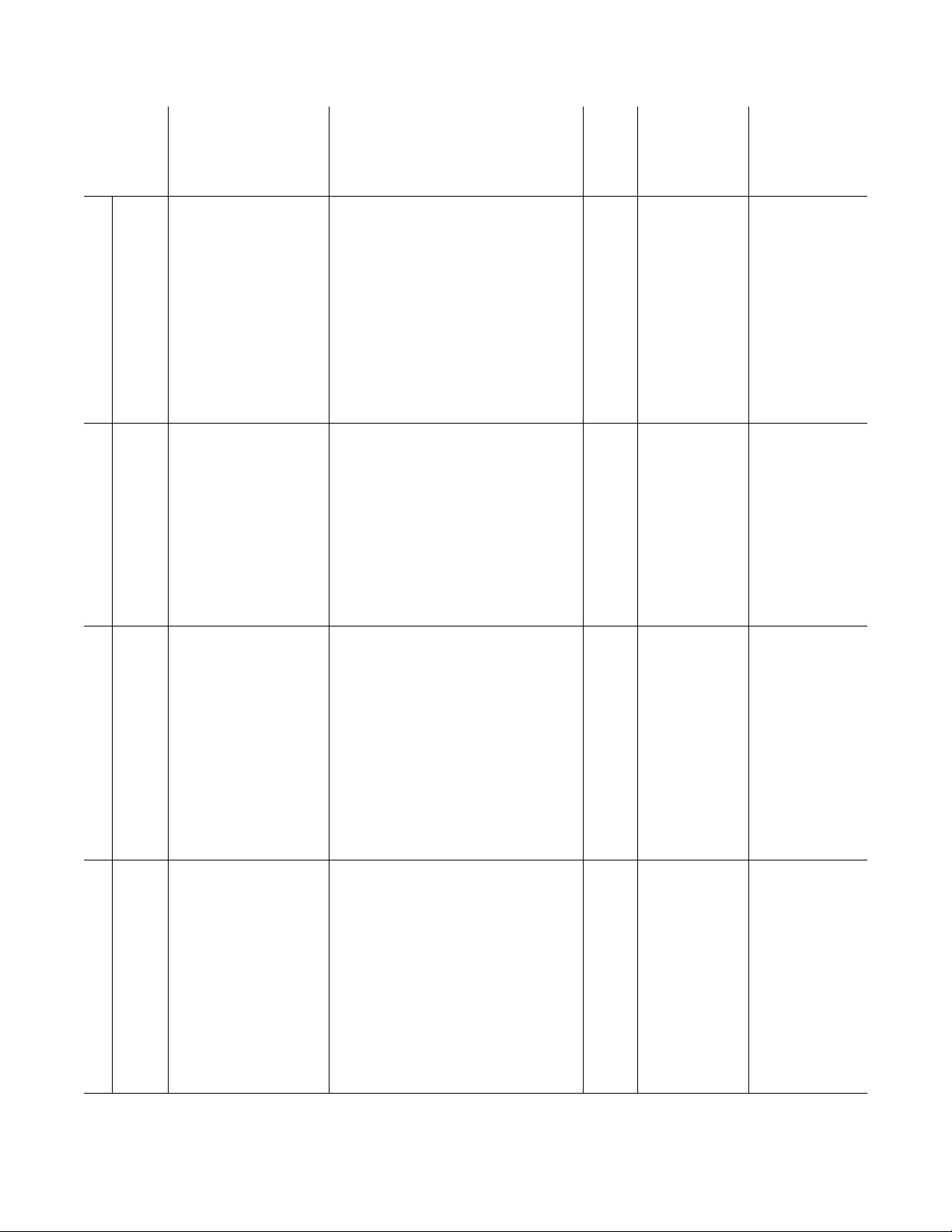
Chart 2 - Performance and Specifi cation Data
F* NG LP
INPUT OUTPUT Temp. Rise Min. Gas Gas Net Shipping
CAPACITY RATING RATING EFF. MIN. MAX. °F Static Clearance Inlet Inlet Weight Weight
MBH BTU/Hr BTU/Hr % CFM CFM (°C) in. of Water in. in. in. lb. lb.
(kW) (kW) (cu. m/s) (cu. m/s) Min. - Max. (KPa) (mm) (kg) (kg)
100 100,000 80,000 80 823 2,469 30 - 90 2 7-1/8 1/2 1/2 256 367
**
(29.3) (23.4) (0.388) (1.165) (17) - (50) (0.50) (181) (116) (166)
150 150,000 120,000 80 1,235 3,704 30 - 90 2 11-1/4 1/2 1/2 307 418
(43.9) (35.1) (0.583) (1.748) (17) - (50) (0.50) (286) (139) (190)
200 200,000 160,000 80 1,646 4,938 30 - 90 2 14 1/2 1/2 365 484
(58.6) (46.9) (0.777) (2.331) (17) - (50) (0.50) (356) (166) (220)
250 250,000 200,000 80 2,058 6,173 30 - 90 2 22-1/4 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 405 524
(73.2) (58.6) (0.971) (2.913) (17) - (50) (0.50) (565) (184) (238)
300 300,000 240,000 80 2,469 7,407 30 - 90 2 34 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 469 596
NA TURAL VENT
(87.8) (70.3) (1.165) (3.496) (17) - (50) (0.50) (864) (213) (270)
350 350,000 280,000 80 2,881 8,642 30 - 90 2 33-1/4 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 510 637
(102.5) (82.0) (1.360) (4.079) (17) - (50) (0.50) (845) (231) (289)
400 400,000 320,000 80 3,292 9,876 30 - 90 2 38 3/4 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 558 690
(117.1) (93.7) (1.554) (4.661) (17) - (50) (0.50) (984) (253) (313)
100 100,000 80,000 80 823 2,469 30 - 90 2 7-1/8 1/2 1/2 262 373
**
(29.3) (23.4) (0.388) (1.165) (17) - (50) (0.50) (181) (119) (169)
150 150,000 120,000 80 1,235 3,704 30 - 90 2 11-1/4 1/2 1/2 298 409
(43.9) (35.1) (0.583) (1.748) (17) - (50) (0.50) (286) (135) (186)
200 200,000 160,000 80 1,646 4,938 30 - 90 2 14 1/2 1/2 356 475
(58.6) (46.9) (0.777) (2.331) (17) - (50) (0.50) (356) (161) (215)
250 250,000 200,000 80 2,058 6,173 30 - 90 2 22-1/4 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 395 514
POWER VENT
(73.2) (58.6) (0.971) (2.913) (17) - (50) (0.50) (565) (179) (233)
350 325,000 260,000 80 2,675 8,025 30 - 90 2 33-1/4 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 495 622
(95.2) (76.2) (1.263) (3.789) (17) - (50) (0.50) (845) (225) (282)
400 400,000 320,000 80 3,292 9,876 30 - 90 2 38-3/4 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 543 675
(117.1) (93.7) (1.554) (4.661) (17) - (50) (0.50) (984) (246) (306)
100 100,000 80,000 80 1,235 3,704 20 - 60 2 7 1/8 1/2 1/2 253 364
***
(29.3) (23.4) (0.583) (1.748) (11) - (33) (0.50) (181) (115) (165)
150 150,000 120,000 80 1,852 5,556 20 - 60 2 11-1/4 1/2 1/2 304 415
(43.9) (35.1) (0.874) (2.622) (11) - (33) (0.50) (286) (138) (188)
200 200,000 160,000 80 2,469 7,407 20 - 60 2 14 1/2 1/2 362 481
(58.6) (46.9) (1.165) (3.496) (11) - (33) (0.50) (356) (164) (218)
250 250,000 200,000 80 3,086 9,259 20 - 60 2 22-1/4 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 402 521
(73.2) (58.6) (1.457) (4.370) (11) - (33) (0.50) (565) (182) (236)
300 300,000 240,000 80 3,704 11,111 20 - 60 2 34 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 466 593
NA TURAL VENT
(87.8) (70.3) (1.748) (5.244) (11) - (33) (0.50) (864) (211) (269)
350 350,000 280,000 80 4,321 12,963 20 - 60 2 33-1/4 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 507 634
(102.5) (82.0) (2.040) (6.119) (11) - (33) (0.50) (845) (230) (288)
400 400,000 320,000 80 4,938 14,815 20 - 60 2 38-3/4 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 555 687
(117.1) (93.7) (2.331) (6.993) (11) - (33) (0.50) (984) (252) (312)
100 100,000 80,000 80 1,235 3,704 20 - 60 2 7-1/8 1/2 1/2 259 370
***
(29.3) (23.4) (0.583) (1.748) (11) - (33) (0.50) (181) (117) (168)
150 150,000 120,000 80 1,852 5,556 20 - 60 2 11-1/4 1/2 1/2 295 406
(43.9) (35.1) (0.874) (2.622) (11) - (33) (0.50) (286) (134) (184)
200 200,000 160,000 80 2,469 7,407 20 - 60 2 14 1/2 1/2 353 472
(58.6) (46.9) (1.165) (3.496) (11) - (33) (0.50) (356) (160) (214)
250 250,000 200,000 80 3,086 9,269 20 - 60 2 22-1/4 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 392 511
(73.2) (58.6) (1.457) (4.375) (11) - (33) (0.50) (565) (178) (232)
300 300,000 240,000 80 3,704 11,111 20 - 60 2 34 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 452 579
POWER VENT
(87.8) (70.3) (1.748) (5.244) (11) - (33) (0.50) (864) (205) (263)
350 350,000 280,000 80 4,321 12,963 20 - 60 2 33-1/4 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 492 619
(102.5) (82.0) (2.040) (6.119) (11) - (33) (0.50) (845) (223) (281)
400 400,000 320,000 80 4,938 14,815 20 - 60 2 38-3/4 3/4 1/2 OR 3/4 540 672
(117.1) (93.7) (2.331) (6.993) (11) - (33) (0.50) (984) (245) (305)
*
See fi gures 1 and 2. ** Indicates high temperature rise furnaces. *** Indicates standard temperature rise furnaces.
The clearances dimensions shown in chart #2 are the absolute minimum clearances for servicing the burner drawer. However, the clearances
shown in chart #1 are the recommended clearances for ease of servicing the unit.
– 5 –
Page 6
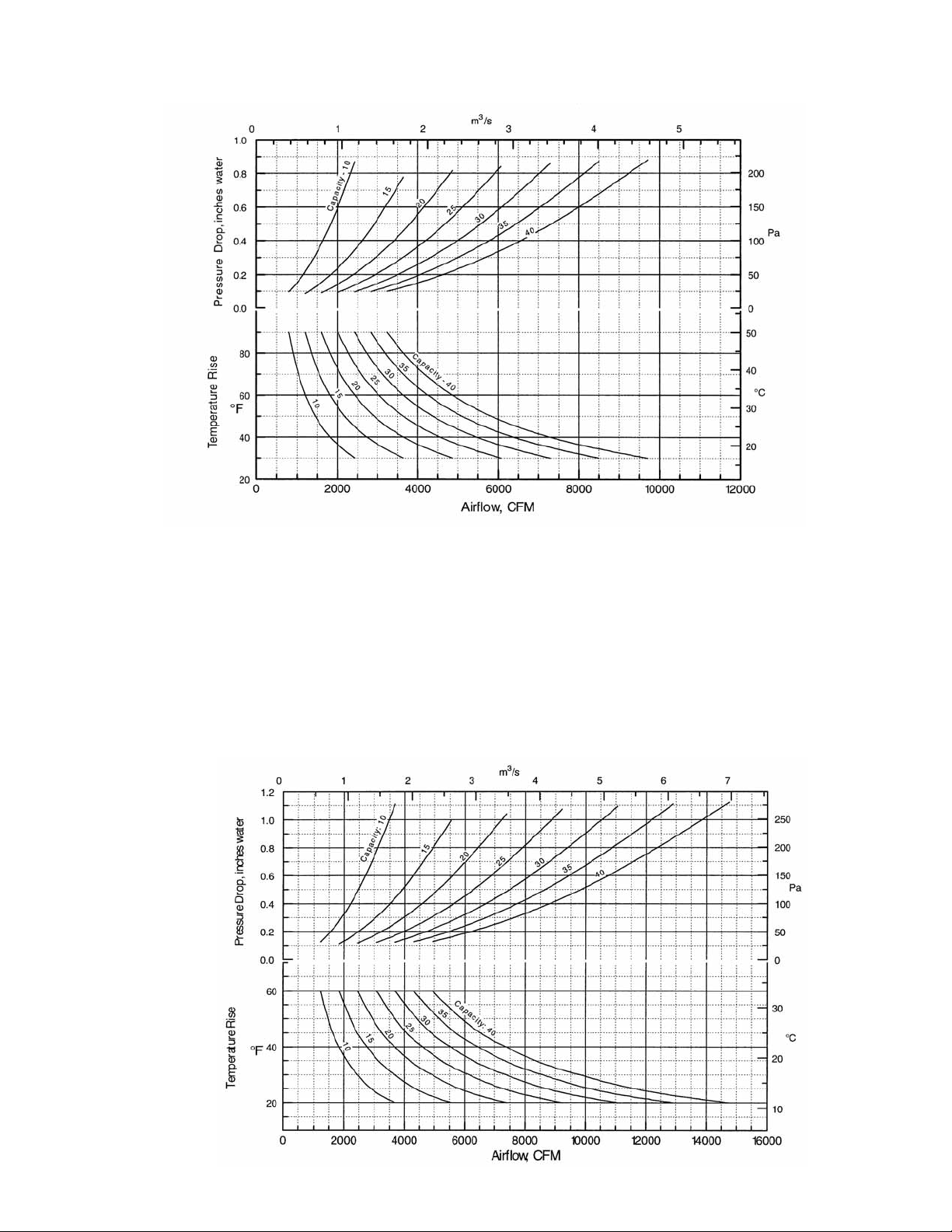
PERFORMANCE DATA CURVES
Figure 3 - High Temperature Rise Duct Furnaces — 30-90°F (17-50°C)
Pressure drop through the heat exchanger is based on
the CFM throughput. The desired data is obtained in
the following manner:
1. Select heater size based on heat loss of the building
to be heated.
2. Select temperature rise desired.
3. Based on temperature rise, the horizontal line intersects heater temperature vs. CFM curve.
Figure 4 - Standard Temperature Rise Duct Furnaces — 20-60°F (11-33°C)
4. Follow vertical line down to select CFM.
5. For pressure drop selection, follow vertical CFM line
until it intersects the selected heater performance
curve vs. pressure drop.
6. Follow the horizontal pressure drop line to the left,
and read pressure drop of the selected heater.
– 6 –
Page 7
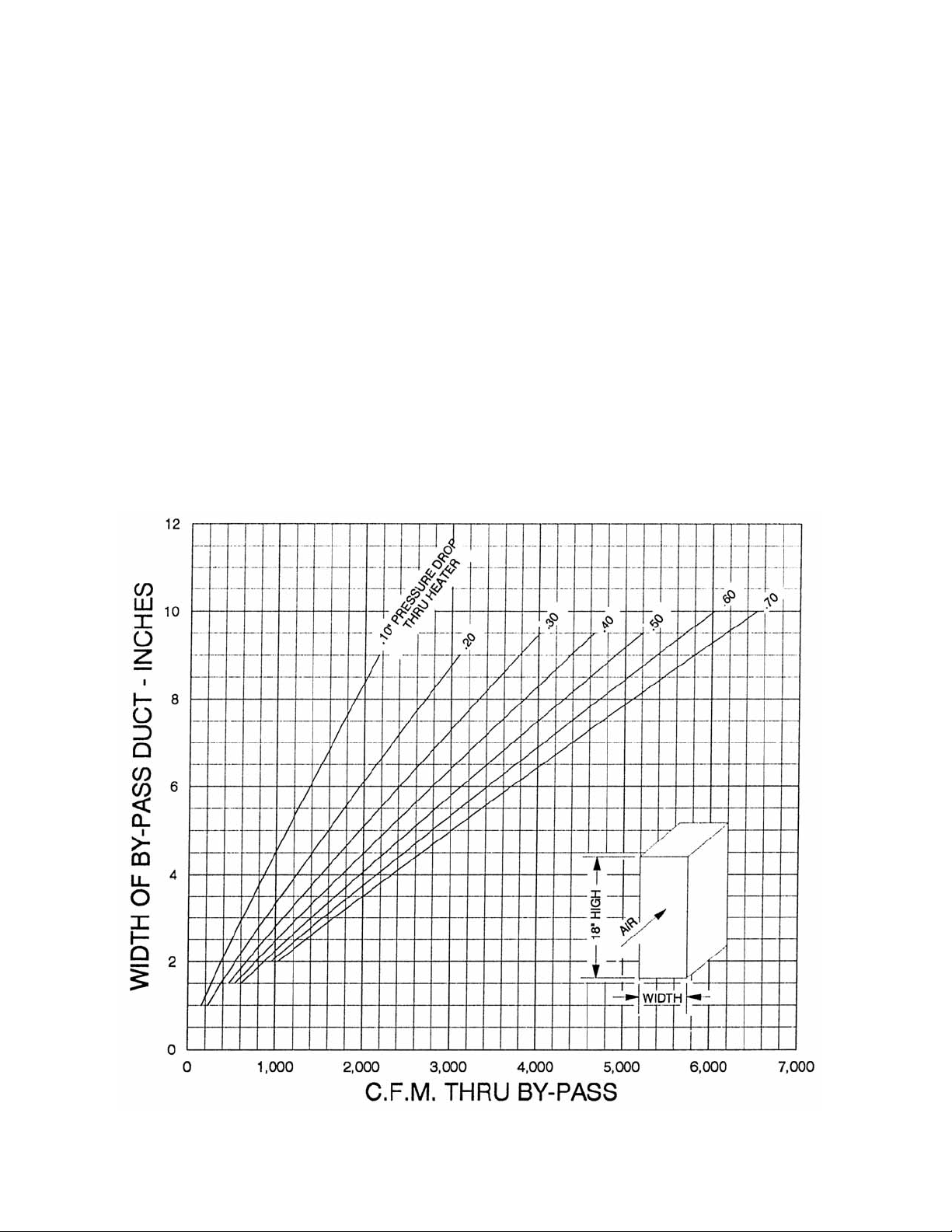
BYPASS SIZING INFORMATION
(BUILT ON THE JOB – NOT FURNISHED BY
FACTORY)
On occassion when a duct furnace is incorporated in an
air handling system, it may be desirable to handle a total
of more CFM than the duct furnace will pass at a given
static pressure drop and temperature rise. Therefore, it
is necessary to arrange to bypass the additional CFM
required. The size of the bypass duct can be determined
by referring to the chart. This permits the static pressure
drop through the bypass to balance off the drop through
the heat exchanger. The bypass duct is not factory
furnished and must be built on the job by the installer and
a damper placed therin if required.
Figure 5 - By-Pass Curve
USE OF BYPASS CURVES
The width of the by-pass for CFM in excess of that
provided through the heater may be found in the
following manner:
1. Determine the CFM and pressure drop through
the heater based on the heating requirement
specifi cations.
2. Determine the additional CFM desired, over and
above the CFM for the heating requirements.
3. Using the pressure drop which was determined from
performance curves above, for the heating load,
locate this pressure drop on the by-pass curves.
Follow this curve until it intersects the vertical CFM
line for the excess CFM desired.
4. Follow horizontal line to left to obtain width of b y-pass
duct.
– 7 –
Page 8
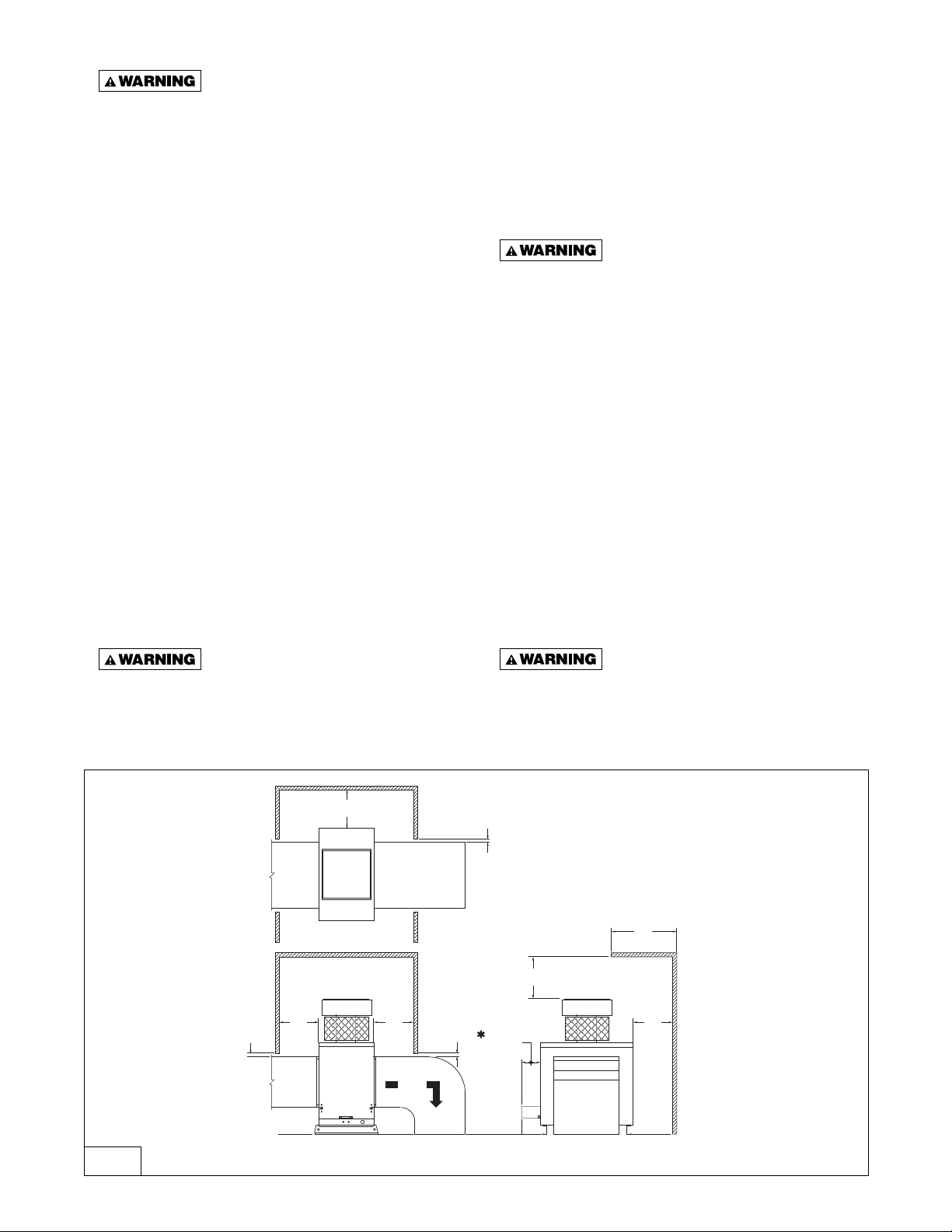
INSTALLATION
D3589A
18"
(457)
5/16"
(8)
Ductwork
Natural
(or Power)
Vent
Furnace
Air Flow
5/16"
(8)
18"
(457)
18"
(457)
36"
(914)
36"
(914)
Clearance
For Drawer
Pul-out
18"
(457)
5/16" (8) Typ.
Open all disconnect switches
and secure in that position before installing
unit. Failure to do so may result in personal
injury or death from electrical shock.
Installation must conform with local building codes,
or in the absence of local codes, with the latest
edition of the National Fuel Gas Code ANSI Z223.1
(NFPA 54).
A heat loss study and a complete layout of the system
should be made fi rst.
When locating the unit in its permanent location, make
certain that the roof is capable of carrying the additional
load of the equipment. Check the net weights from the
engineering data.
Make certain that clearances are provided for service,
minimum clearance to combustible material and to
venting cap. See below for this infor mation. Service
clearance information is given in the engineering data
in Figures 1, 2 and 6. Clearances around secondary air
must be unobstructed.
If the unit is installed downstream of refrigeration coils,
condensate will form and collect in the bottom of the
heater. Drain connections are provided to dispose of
this condensate from the unit. Connect drain pipes to
dispose of this condensate where necessary.
Ducts connected to duct furnaces shall have removable
access panels on both upstream and downstream sides
of the unit. These openings shall be accessible when
the unit is installed in service, and shall be of such size
that smoke or refl ected light may be observed inside the
casing to indicate the presence of leaks in the heating
element. The covers for the openings shall be attached
in such a manner as to prevent leaks.
If a duct furnace is connected
to a return air duct or any other inlet air
restriction, the appliance shall be installed on
the positive pressure side of the air-circulating
blower.
Atmospheres containing solvents or chlorinated
hydrocarbons will produce corrosive acids when
coming in contact with the flames. This will greatly
reduce the life of the gas duct furnace and may void
the warranty. Avoid such areas.
CLEARANCES
Minimum clearances are shown in Figures 1, 2 & 6
and charts 1 & 2. It is important that clearances be
maintained for servicing the unit (refer to Figures 1
& 2 for clearances necessary to pull out the burner
drawer for servicing), and that minimum clearances are
provided from combustible material and from the venting
cap/top of unit. Clearances around the outside air hood
must be unobstructed.
Ducts which are outdoors must
be insulated and sealed to prevent water from
entering either furnace or building through duct
combustibles to prevent injury or death from
fi re.
(see section on duct and drain specifi cations).
Figure 6 - Minimum Clearances to Combustible Material or Obstructions
D3589
*See fi gures 1 & 2 and charts 1 & 2.
– 8 –
Provide adequate clearance from
Power Vent Units required 36"
clearance above top of unit.
Page 9
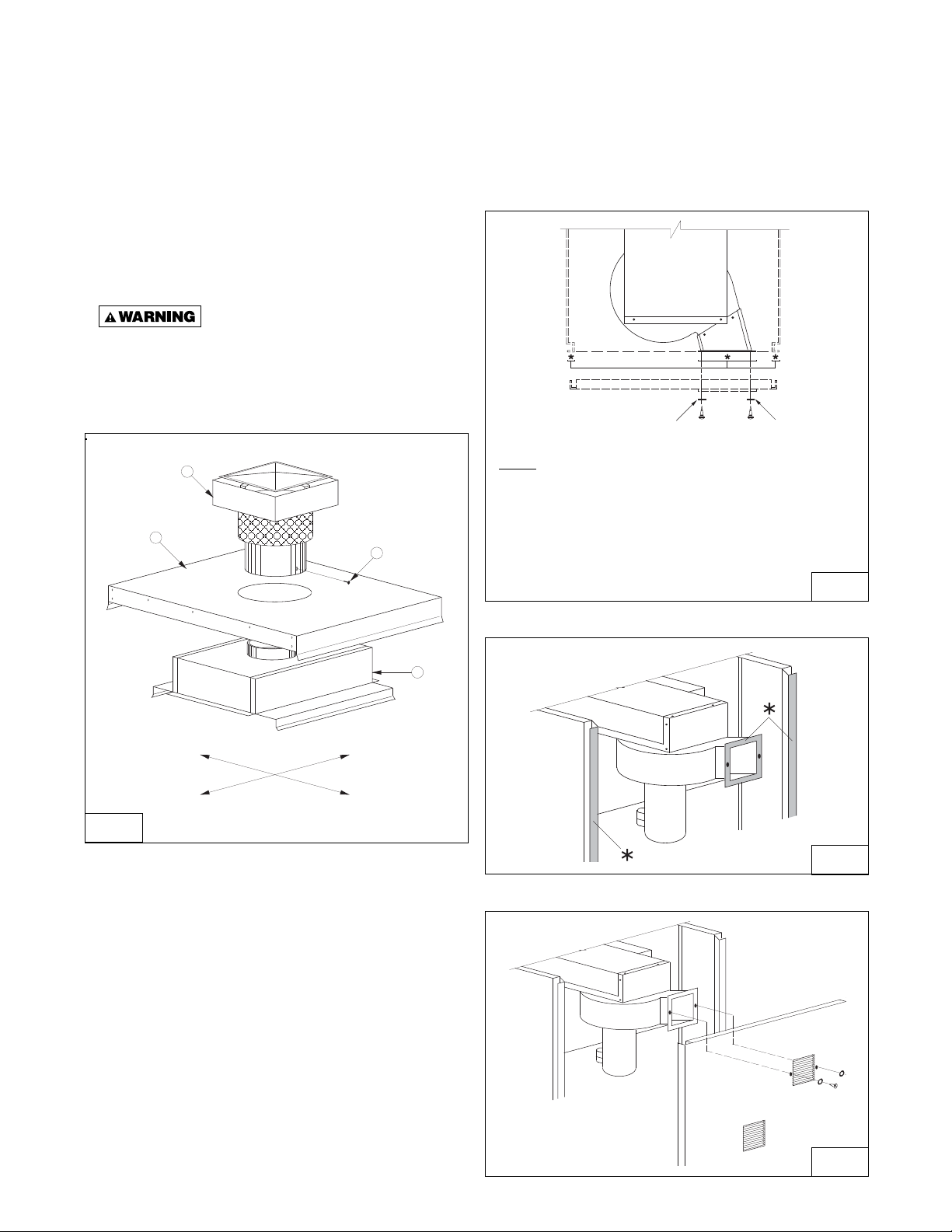
VENTING
2
1
4
3
FRONT
REAR
LEFT
RIGHT
TOP VIEW
Neoprene Washers
Screws
All venting installations shall be in accordance with the
latest edition of “Par t 7, Venting of Equipment of the
National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 (NFPA 54), or
applicable provisions of local building codes”.
Natural venting models are equipped with a vent cap
designed for natural venting. Air for combustion enters
at the base of the vent through a protective grille, and
the design of the vent cap is such that the products of
combustion are discharged at the upper section of the
cap. The cap is shipped in a separate carton. It should
be fastened in position as shown in Figure 7 and
should not be altered in any way.
The venting is an integral part of
the unit and must not be altered in the field. If
altered, excessive carbon monoxide could be
produced.
Figure 7 - Vent Cap Assembly
(Natural Vented Furnaces Only)
Power vented models are designed with combustion
air inlet and fl ue products outlet located in the louvered
side access panel. Never locate these units in an
area where the flue products outlet may be directed
at any fresh air vents.See Figures 8a 8b, and 8c for
installation and servicing requirements.
Figure 8a - Power Venter Discharge Location
*These Surfaces (indicated with an asterisk in fi gures 8a & 8b)
MUST be flush and sealed at all times to ensure the proper
discharge of fl ue products from the unit.
These discharge fl anges are equipped with special gasketing,
which must create an air tight seal connection around the
louvers of the access panel.
Secure in place the access door to the discharge adaptor using
the two screws and neoprene washers, then tighten
the grip latches (see service access panel removal
section).
D3505
D3591
FIELD INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
1. Remove “Side Access Panel”.
2. Insert Vent Sleeve of “Vent Cap Assembly” (Item 1)
thru “Top Panel Assembly” (Item 2), and over Vent
Collar of “Flue Collector Assembly” (Item 3).
3. Align “Vent Cap Assembly” so it is square to “Top
Panel Assembly”.
4. Fasten with “Drill Screw” or “Sheet Metal Scre w” (Item
4) by reaching between “Flue Collector Assembly”
(Item 3) & “Top Panel Assembly” (Item 2), and drilling
through vent sleev e of “Vent Cap Assemb ly” into vent
collar of “Flue Collector Assembly”.
5. Replace “Side Access Panel”.
NOTICE: If your unit is to be equipped with the
optional extended vent cap assembly, see the
special instructions supplied with the vent cap.
Figure 8b
D3725
Figure 8c
D4596
– 9 –
Page 10

DUCT SPECIFICATIONS
Ductwork which is outdoors must be insulated and
sealed to prevent water from enter ing either furnace
or building through the duct. Do not alter the flange
connection for the duct attachment; air may bypass
and cause combustion problems. Be sure to properly
seal to avoid any air leakage (refer to Figures 1 and 2).
GAS CONNECTIONS
All gas piping should be installed in accordance with
local codes. It is required that a ground union be installed
adjacent to the manifold for easy servicing. On vertical
runs, a drip leg should be provided upstream of the
control manifold (see fi gure 9a). An additional shut-off
must be located externally of the jacket enclosure where
required by local code. The location of this valve must
comply with the local codes. A 1/8 inch NPT plugged
tapping, accessible for test gauge connection, must be
installed immediately upstream of the gas supply
connection to the unit. Field gas piping recommendations
are shown in Figure 9b.
Ductwork connected to duct furnaces should have
removable access panels on both the upstream and
downstream sides of the unit. These openings should
be accessible when the unit is installed, and should be
sized so that smoke or refl ected light can be observed
inside the casing to indicate the presence of leaks in
the heating equipment. The covers of the openings
should be attached in a manner that prevents leaks.
The appliance must be isolated from the gas supply
piping system by closing its individual manual shutoff
valve during any pressure testing of the gas supply
piping system at test pressure equal to or less than
1/2 psig (3.5 kPa).
For additional piping information, refer to the latest
edition of the National Fuel Gas Code ANSI Z233.1
(NFPA 54).
Figure 9a - Drip Leg Installation
It is recommended that the gas piping not be installed
through the bottom of the duct furnace bottom panel. If
piping must penetrate the duct furnace bottom panel, it
must be sealed to prevent water leakage.
To avoid equipment damage or
possible personal injury, do not connect gas
piping to this unit until a supply line pressure/
leak test has been completed. Connecting the
unit before completing the pressure/leak test
may damage the unit gas valve and result in a
fi re hazard.
Do not rely on a shutoff valve to
isolate the unit while conducting gas pressure/leak
tests. These valves may not be completely shut off,
exposing the unit gas valve to excessive pressure
and damage. Do not overtighten the inlet gas piping.
This may cause stresses that would crack the v alve.
Never use an open flame to
detect gas leaks. Explosive conditions may e xist
which would result in personal injury or death.
The gas line should be supported so that no strain is
The gas line should be supported so that no strain
is placed on the unit. Pipe compounds which are not
soluble to liquid petroleum gases should be used on
threaded joints.
D 3 6 31 C
Figure 9b - Field Piping Recommendations
NIPPLE
ELBOW
NIPPLE
UNION
NIPPLE
The appliance and its individual shutoff valve must be
disconnected from the gas supply piping system during
any pressure testing of that system at test pressure in
excess of 1/2 psig (3.5 kPa).
– 10 –
D3726
D3726
ELBOW
NIPPLE
UNION
Page 11

GAS CONNECTIONS (continued)
GAS METER
A
20 ft.
6.56 m.
20 ft.
6.56 m.
5 ft.
1.64 m.
5 ft.
1.64 m.
10 ft.
3.48 m.
B
C
D
F
E
10 ft.
3.28 m.
HEATER(S)
200 CFH
HEATER(S)
150 CFH
3588
HEATER(S)
100 CFH
For the most satisfactory piping installation, the follo wing
procedure should be followed. Make piping layout of the
whole installation and calculate the cubic feet of gas that
each supply pipe will carry. See piping example below.
Calculate the cubic feet of gas that each supply pipe
will carry:
Btu/Hr.
1000 Btu Natural Gas/Cu. Ft.
= Cu. Ft. Per Hour of Gas to Unit (cfh)
Unit Kilowatt
37.3 Megajoules Natural Gas/Cu Meter
= Liters per second on Gas to Unit (l/s)
NOTICE: Contact your natural gas supplier for
the Btu/Cu. Ft. content of natural gas in your area.
This may be higher or lower than the nominal
1000 Btu/Cu. Ft. used in this example:
Refering to the piping example in fi gure 10, the length of
pipe from the gas meter (A) to the most remote heater
(E) is 60 feet. This distance should be used for all of the
heaters when determining the pipe size required. Based
on the column marked 60 feet in chart 3, the piping for
this example should be sized as follows:
• 450 cfh is supplied from A to B, requiring
1-1/4 inch pipe.
• 200 cfh is supplied from B to C, requiring
1 inch pipe.
• 250 cfh is supplied from B to D, requiring
1 inch pipe.
• 100 cfh is supplied from D to E, requiring
3/4 inch pipe.
• 150 cfh is supplied from D to F, requiring
1 inch pipe.
For SI calulations, refer to metric conversion chart
in general safety section of this manual.
NOTICE: If more than one gas duct furnace is to be
served by the same piping arrangement, the total cu.
ft./hr. input and length of pipe must be considered.
NOTICE: If the gas duct furnace is to be fired
with LP gas, consult local LP gas dealer for pipe
size information. Heater installation for use with
propane (bottled) gas must be made by a qualifi ed
LP gas dealer or installer. He will insure proper joint
compounds are used for making pipe connections;
that air is purged from lines; that a thorough test is
made for leaks before operating heater; and that it is
properly connected to propane gas supply system.
Before any connection is made to an existing line
supplying other gas appliances, contact the local gas
company to make certain that the existing line is of
adequate size to handle the combined load.
Check all connections with a soap solution before
leaving job.
Figure 10 - Example of Piping Layout for Determining Pipe Size
D3588
– 11 –
Page 12

Chart 3
Maximum Capacity of Pipe in Cubic Feet of Gas per Hour for Gas Pressures of 0.5 psig (3.5 kPa) or Less,
Nominal
Iron
Pipe Size
in. in. 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 125 150 175 200
(mm) (3.0) (6.1) (9.1) (12.2) (15.2) (18.3) (21.3) (24.4) (27.4) (30.5) (38.1) (45.7) (53.3) (61.0)
1/2 0.622 175 120 97 82 73 66 61 57 53 50 44 40 37 35
(16) (4.96) (3.40) (2.75) (2.32) (2.07) (1.87) (1.73) (1.61) (1.50) (1.42) (1.25) (1.13) (1.05) (0.99)
3/4 0.824 360 250 200 170 151 138 125 118 110 103 93 84 77 72
(21) (10.2) (7.08) (5.66) (4.81) (4.28) (3.91) (3.54) (3.34) (3.11) (2.92) (2.63) (2.38) (2.18) (2.04)
1 1.049 680 465 375 320 285 260 240 220 205 195 175 160 145 135
(27) (19.3) (13.2) (10.6) (9.06) (8.07) (7.36) (6.80) (6.23) (5.80) (5.52) (4.96) (4.53) (4.11) (3.82)
1 1/4 1.380 1400 950 770 660 580 530 490 460 430 400 360 325 300 280
(35) (39.6) (26.9) (21.8) (18.7) (16.4) (15.0) (13.9) (13.0) (12.2) (11.3) (10.2) (9.20) (8.50) (7.93)
1 1/2 1.610 2100 1460 1180 990 900 810 750 690 650 620 550 500 460 430
(41) (59.5) (41.3) (33.4) (28.0) (25.5) (22.9) (21.2) (19.5) (18.4) (17.6) (15.6) (14.2) (13.0) (12.2)
2 2.067 3950 2750 2200 1900 1680 1520 1400 1300 1220 1150 1020 950 850 800
(53) (112) (77.9) (62.3) (53.8) (47.6) (43.0) (39.6) (36.8) (34.5) (32.6) (28.9) (26.9) (24.1) (22.7)
2 1/2 2.469 6300 4350 3520 3000 2650 2400 2250 2050 1950 1850 1650 1500 1370 1280
(63) (178) (123) (99.7) (85.0) (75.0) (68.0) (63.7) (58.0) (55.2) (52.4) (46.7) (42.5) (38.8) (36.2)
3 3.068 11000 7700 6250 5300 4750 4300 3900 3700 3450 3250 2950 2650 2450 2280
(78) (311) (218) (177) (150) (135) (122) (110) (105) (97.7) (92.0) (83.5) (75.0) (69.4) (64.6)
4 4.026 23000 15800 12800 10900 9700 8800 8100 7500 7200 6700 6000 5500 5000 4600
(102) (651) (447) (362) (309) (275) (249) (229) (212) (204) (190) (170) (156) (142) (130)
1. *See local codes before installing 1/2" pipe.
Input Rate of Unit
2. FOR NATURAL GAS: cu. ft./hr. =
Btu Value of Gas
3. FOR PROPANE GAS: Multiply the Cu. Ft. / Hr. obtained in note 2 by 0.633 before entering chart.
Internal
Dia.
and a Pressure Drop of 0.5 Inch Water Column (124.4 Pa)
GAS PIPE SIZE
(Based on a 0.60 Specifi c Gravity Gas)
Length of Pipe, ft. (Meters)
ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
HAZARDOUS VOL TA GE!
DISCONNECT ALL ELECTRIC
POWER INCLUDING REMOTE
DISCONNECTS BEFORE
SERVICING. Failure to
disconnect power before
servicing can cause severe
personal injury or death.
The rooftop duct furnace is wired at the factory
and ready to be connected. Actual wiring will differ
according to the options used. Each furnace will be
shipped with its own wiring diagram; refer to this wiring
diagram for all electrical connections to the unit.
All electrical connections must conform to the latest
edition of ANSI/NFPA No. 70 National Electrical Code
and applicable local codes; In Canada, to the Canadian
Electrical Code, Part I CSA Standard C22.1.
Do not use any tools (i.e. screwdriver,
pliers, etc.) across the terminals to check for power.
Use a voltmeter.
The outdoor conduits leading into the unit should be
installed to prevent rain from wetting any high voltage
wire. Locate the ther mostat in accordance with the
instructions packed with each thermostat.
NOTICE: Should any original wire supplied with the
heater have to be replaced, it must be replaced with
wiring material having a temperature rating of at
least 105°C (221°F).
– 12 –
Page 13

OPERATION
O
F
F
8A
O
N
8B
6
C
10
7
GENERAL
All units are equipped with intermittent pilot ignition
systems. This system is 100% pilot burner shut off. See
Figure 11 for burner/gas controls. The pilot is lit and
extinguished during ever y cycle of operation. There is
no burning standing pilot.
NOTICE: Check gas supply pressure (see chart 4).
Gas valves are suitable to a maximum pressure of
0.5 psi (14 inches water column). If the main gas
supply pressure for natural gas is greater than 14
inches WC (3.5 kPa), a stepdown pressure regulator
must be installed ahead of the gas valve. For LP
(propane) gas, the gas pressure supplied should
On natural gas units, the ignitor will spark and pilot gas
not exceed 14 inches WC (3.5 kPa).
will continue to fl ow until the pilot fl ame is proven.
The controls are located inside the compartment on the
LP (propane) gas units are equipped with 100%
lockout. The lockout function shuts off the main and
pilot gas valves if the pilot gas fails to ignite within 30
seconds. In order to initiate a reignition trial, the power
supply must be interrupted for a minimum of 5 minutes
to allow dispertion of unburned gas.
access side of the unit. The input f or single-stage fi ring is
based on full fi re. On two-stage fi re, the unit will fi re 50%
of full fi re on the fi rst stage and full fi re on the second
stage. When electronic modulating is used, the unit will
fi rst fi re at 100% of full fi re and modulate down to 40% of
full fi re.
Figure 11 - Burner Components — Intermittent Pilot Ignition (Natural or Power Vented Duct Furnaces)
BURNER DRAWER COMMON PARTS:
1. MAIN BURNERS
2. BURNER MANIFOLD
3. AIR SHUTTERS
4. BURNER SPRINGS
5. MAIN BURNER ORIFICE
6. TRANSFORMER
7. PILOT TUBING
3
5
1
4
CONTROLS:
8A. MAIN GAS VALVE (HONEYWELL)
8B. MAIN GAS VALVE (WHITE RODGERS)
9. HONEYWELL IGNITOR
10. PILOT BURNER
9
Honeywell
WARNIN
G
S8600M
CONTINUOUS RE-TRY
1
00% SHUTOFF IP
90 SEC. TRIAL
FO
V
M
MV/PV
P
1
2
3
R
D
V
GN
4
IGNITION
)
)
24V
4V
(GND
(BURNER)
2
5
TH-W
(OPT.
6
7
RK
8
SPA
9
– 13 –
Page 14

OPERATION continued
Chart 4 - Gas Supply Pressure
Natural Gas Propane Gas
Heating V alue
Manifold Pressure
Single Stage Application 3.5 inch WC 10.0 inch WC
Two Stage Application - High Fire 3.5 inch WC 10.0 inch WC
Two Stage Application - Low Fire 1.1 inch WC 3.8 inch WC
Modulating Application - High Fire 3.5 inch WC 10.0 inch WC
Modulating Application - Low Fire 0.9 inch WC 3.5 inch WC
Minimum Supply Pressure
Single Stage Application 5.0 inch WC 11.0 inch WC
Two Stage Application 6.5 inch WC 11.5 inch WC
Modulating Application 6.5 inch WC 11.5 inch WC
Maximum Supply Pressure 14.0 inch WC 14.0 inch WC
1075 Btu/Ft3 2500 Btu/Ft
(40.1 MJ/m3) (93.1 MJ/m3)
(0.87 kPa) (2.49 kPa)
(0.87 kPa) (2.49 kPa)
(0.27 kPa) (0.95 kPa)
(0.87 kPa) (2.49 kPa)
(0.22 kPa) (0.87 kPa)
(1.24 kPa) (2.74 kPa)
(1.62 kPa) (2.86 kPa)
(1.62 kPa) (2.86 kPa)
(3.49 kPa) (3.49 kPa)
3
CONTROLS
Electronic modulating gas firing is available from the
factory on natural and propane gas units.
Do not use a thermostatic fan control switch when
either two-stage firing or modulated gas controls are
used. A fan time delay switch can be used, however,
and is available as an option on outdoor duct furnaces.
All controls are located on the access side of the unit.
Chart 5 lists orifi ce sizes for outdoor duct furnaces.
OPERATING HIGH LIMIT CONTROL
The operating limit control is a factory installed
component surface mounted in the inlet air stream end
of the heat exchanger. This surface mounted safety
device must have adequate contact to the rear header
plate of the heat exchanger to insure its function.
When the temperature reaches the limit set point, all
heat is shutoff. The limit control has a built in autoreset that comes on when the equipment is suffi ciently
cooled down. Reference the unit's wiring diagram.
PILOT CONTROL
Intermittent pilot ignition is standard on all outdoor unit
sizes. Intermittent pilot ignition contains a solid state
ignition control system that ignites the pilot by spark for
each cycle of operation. When the pilot fl ame is proven,
the main burner valve opens to allow gas flow to the
burners. Both the pilot and burners are extinguished
during the off cycle.
HIGH GAS LINE PRESSURE REGULATOR
(Natural Gas only)
The pressure regulator is a field installed component
located external of the unit and as close as possible to
where the gas line inlet enters the unit.
The pressure regulator reduces the main gas line
pressure to a minimum of seven inches WC (1.74 kPa).
– 14 –
Page 15

GAS CONTROLS
SINGLE STAGE CONTROL
Gas heating units are factory provided with an automatic
single-stage gas valve. This valve is an on/off type
control, typically activated by a low voltage single-stage
thermostat.
1. The thermostat calls for heat.
2. The pilot valve opens.
3. The ignitor sparks continuously to ignite the pilot.
4. The sensor proves pilot ignition and shuts off the
ignitor.
5. With the pilot lit, the main gas valve opens.
6. Main bur ners are lit at 100 percent of unit's rated
input.
7. The fan time delay relay (optional) allows the heat
exchanger to come up to operating temperature.
At this time, the fan time delay relay closes and
activates the fan controls.
8. The unit continues to fire until the thermostat is
satisfi ed and no longer calls for heat.
9. The main and pilot valves close.
TWO-STAGE CONTROL
Optional two-stage control is provided with a two-stage
gas valve capable of fir ing at 100% and 50% of rated
input. Ignition at a low fi re (50% of the unit's rated input)
and the unit is typically controlled by a voltage two-stage
thermostat.
With power applied to the unit, this system operates in
the following manner:
1. The fi rst stage of the thermostat call for heat.
2. The pilot valve opens.
3. The ignitor sparks continuously to ignite the pilot.
4. The sensor proves pilot ignition and shuts off the
ignitor.
5. With the pilot lit, the main gas valve open to low fi re.
6. Main burners are lit at 50 percent of unit's rated
input.
7. The fan time delay relay (optional) allows the heat
exchanger to come up to operating temperature. At
this time, the fan time dela y closes and activ ates the
fan motor.
8. If additional heat is required, the second stage of the
thermostat calls for heat.
9. The main gas valve opens to full fire. The main
burners are now at full fire. The unit continues a
full fi re until the second stage of the thermostat is
satisfi ed and no longer call for heat.
10. The main valve closes to low fi re. The main burners
are now at low fi re. The unit continues at lo w fi re until
the fi rst stage of the thermostat is satisfi ed and no
longer calls for heat.
11. The main and pilot valves closes.
12. The fan time delay remains closed, keeping the fan
operating to dissipate residual heat from the heat
exchanger. At this time, the fan time delay relay
opens and deactivates the fan motor.
ELECTRONIC MODULATING CONTROL
Units with electronic modulating control are provided
with an electronic modulating valve capab le of fi ring from
100 percent to 40 percent of rated input. Ignition is at
full fi re (100 percent of unit's rated input). The electronic
modulating valve is controlled by a room thermostat or
duct thermostat with remote setpoint adjustment which
modulates the gas input from 100 percent to 40 percent
of rated input.
An optional override room thermostat is available
for use with the duct thermostat. The override room
thermostat allows full fire and overrides the duct
thermostat when the room temperature falls below the
override room thermostat's setpoint.
With power applied to the unit, this system operates in
the following manner:
1. The thermostat calls for heat.
2. The pilot valve opens.
3. The ignitor sparks continuously to ignite the pilot.
4. The sensor proves pilot ignition and shuts off the
ignitor.
5. With the pilot lit, the main gas valve opens.
6. Main burners are lit at 100 percent of unit’s rated
input.
7. The fan time delay relay (optional on duct furnaces)
allows the heat exchanger to come up to operating
temperature. At this time the fan time delay relay
closes and activates the fan motor.
8. The unit is controlled by the electronic thermostat
which modulates the unit from 100 to 40 percent of
unit's rated input. The electronic thermostat can be
a duct sensing device or a room sensing device.
An amplifi er receives an electrical signal from the
thermostat and converts this into a working voltage.
This working voltage determines the position of the
modulating valve. With no voltage applied to the
valve, the valve will be full open and full fire will
occur. As increasing voltage is applied to the valve,
the valve will modulate closed. At approximately
12 volts dc, the valve will be at it's minimum fire
position. As temperature drops, the voltage also
drops causing the relay to reopen the valve. The
unit will continue to cycle in this manner until either
an increase in the unit's fi ring rate is required or the
sensing device is satisfied and no longer calls for
heat. If the voltage continues to increase, indicating
a further reduction in the unit's fi ring is required, the
increased voltage closes a relay which closes the
automatic gas valve.
9. When the sensing device is satisfi ed, the main and
pilot valves close.
10. The fan time delay relay remains closed keeping
the fan motor operating to dissipate residual heat
from the heat exchanger. At this time, the fan time
delay relay opens and deactivates the fan motor.
– 15 –
Page 16

AIR DISTRIBUTION
Two basic air control systems are used to deliver
conditioned air to the occupied space: “constant” fan
operation and “intermittent” fan operation.
INTERMITTENT FAN OPERATION
This air control system is available on duct furnaces
when the fan time delay relay is ordered (optional). The
thermostat turns the gas on whenever the temperature
drops below the thermostat setting. The fan time delay
relay allows the unit to fi re for a period of 60 seconds
before fan operation. It also allows the fan to operate for
120 seconds after burner shutdown.
AIR THROUGHPUT
Static Pressure through the duct furnace should not
exceed 2.0 inches (0.50 kPa) water column. The
standard outdoor duct furnaces are operated at a
temperature rise range of 20° to 60°F (17° to 50°C)
rise. The furnaces are also available at a higher
temperature rise range of 30° - 90°F (17° - 50°C).
NOTICE: It is important that the final temperature
leaving the furnace does not exceed 150°F (66°C).
When final air throughput adjustments are being
made, a quick check of the final temperature can
be made by locating a thermometer approximately
6 to 12 inches (152 to 305 mm) downstream from
the air discharge and approximately 3 to 4 inches
(76 to 102 mm) from the bottom of the duct. The
unit should be operated at least 15 to 20 minutes
before temperature readings are made.
CONSTANT FAN OPERATION
Duct Furnaces: This air control system is standard
on duct furnaces without a fan time delay relay. The
blower operates constantly, circulating air through
the unit, through the discharge, continuously into the
occupied zone, and back to the return. The thermostat
turns the gas valve on or off, raising the temperature of
the air to maintain comfort conditions in the occupied
area.
AIR FILTERS (ON MATED AIR MOVING DEVICE)
It is recommended that air filters be changed or
cleaned at least twice a year. More frequent attention
will be required if the air being handled is unusually
dirty. Air fl ow reduction, caused by clogging air fi lters,
will increase the discharge air temperature and may
cause nuisance tripouts.
Filters (by others) should be serviced regularly and
changed or washed when necessary to maintain the
required throughput. In a dusty environment, fi lters may
clog up in less than one month. A clogged fi lter switch
is recommended to assist with fi lter maintenance.
A unit should never be allowed to
cycle over a prolonged period on the high limit.
The high limit is not an operating control. It is a
safety control to prevent a fire. If cycling on the
high limit is noted, corrective measures should be
taken immediately. Failure to do so could cause unit
damage and possible fi re .
– 16 –
Page 17

LIGHTING
NORMAL
(HARD FLAME)
YELLOW TIPPING
(MARGINAL)
YELLOW FLAME
(TOO LITTLE AIR)
LIFTING
(TOO MUCH AIR)
Purge the gas line of air before attempting to light the
pilot in the unit. Wait 5 minutes for unbur ned gas to
vent. Check for gas leaks.
Never use an open flame to
detect gas leaks. Explosive conditions may
exist which could result in personal injury or
death.
The unit is furnished with an intermittent pilot ignition
system. A lighting instruction plate is permanently
attached to the unit for the pilot system supplied with
the unit. To set the intermittent pilot ignition system
in operation, proceed as follows:
1. Turn on the main manual valve and pilot valve.
2. Tur n on electrical power. The unit should now be
under the control of the thermostat.
3. Tur n the thermostat to the high heat reading to see
if the pilot and main burner ignite.
4. Turn the thermostat to the lowest setting to
interrupt power to the ignition system to determine
that both the pilot burner and main burner are
extinguished.
5. Set the ther mostat at the desired setting for normal
operation.
For complete shutdown:
1. Turn the main and pilot valves to the OFF
position.
2. Shut off electric power.
3. Adjust the thermostat to the lowest setting.
Figure 12 - Main Burner Flames
D3652
NOTICE: There may be momentary and spasmodic
orange flashes in the flame. This is caused by the
burning of airborne dust particles, and not to be
confused with the yellow tipping, which is a stable
or permanent situation when there is insufficient
primary air.
Chart 5 - Main Burner Orifi ce Schedule*
STD. TEMP. RISE
FURNACE (20°-60°F)
93
42
42
42
42
42
42
42
42
42
42
42
42
PROPANETYPE OF GAS NATURAL
3
2500 BTU/Ft
(93.1 MJ/m3)
10 inch WC
(2.49 kPA)
3
40
54
50
54
60
54
70
54
80
54
90
54
100
54
120
54
120
54
140
54
140
54
160
54
*
INPUT
IN
1000
BTU
PV/RT
100
PV/RT
125
PV/RT
150
PV/RT
175
PV/RT
200
PV/RT
225
PV/RT
250
PV
300
RT
300
PV
350
RT
350
PV/RT
400
HEA TING V ALUE
MANIFOLD
PRESSURE
FT 3/HR
ORIFICE DRILL
3
FT
/HR
ORIFICE DRILL
3
FT
/HR
ORIFICE DRILL
3
FT
/HR
ORIFICE DRILL
3
FT
/HR
ORIFICE DRILL
3
FT
/HR
ORIFICE DRILL
3
FT
/HR
ORIFICE DRILL
3
FT
/HR
ORIFICE DRILL
3
FT
/HR
ORIFICE DRILL
3
FT
/HR
ORIFICE DRILL
3
FT
/HR
ORIFICE DRILL
3
FT
/HR
ORIFICE DRILL
1075 BTU/Ft
(40.1 MJ/m3)
3.5 inch WC
(0.87kPA)
116
140
163
186
210
233
280
280
326
326
372
NUMBER
OF
BURNER
ORIFICES
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
12
14
14
16
HIGH TEMP. RISE
FURNACE (30°-90°F)
3
1075 BTU/Ft
(40.1 MJ/m3)
3.5 inch WC
(0.87kPA)
2500 BTU/Ft
93
42
116
42
140
42
163
42
186
42
210
42
233
42
NOT AVAILABLE
280
42
302
43
326
42
372
42
PROPANENATURAL
(93.1 MJ/m3)
10 inch WC
(2.49 kPA)
40
54
50
54
60
54
70
54
80
54
90
54
100
54
120
54
130
55
140
54
160
54
* This schedule is for units operating within the U.S.A.
at normal altitudes of 2000 ft. (610m) or less. For
altitudes above 2,000 ft., refer to local codes, or in
absence of local codes, refer to the latest edition of
3
the National Fuel Gas Code ANSI Standard Z223.1
(NFPA no. 54).
When installed in Canada, any references to deration
at altitudes in excess of 2000 feet (610m) are to be
ignored. At altitudes of 2000 to 4500 feet (610 to
1372m), the unit heaters must be orifi ced to 90% of the
normal altitude rating, and be so marked in accordance
with the ETL certifi cation.
– 17 –
Page 18

PRIMARY AIR SHUTTER ADJUSTMENT
After the unit has been operated for at least 15
minutes, adjust the primary air flow to the burners.
Turn the friction-locked, manually-rotated air shutters
clockwise to close, or counterclockwise to open.
PILOT ADJUSTMENT
1. With unit fi ring, remove the pilot adjustment cap.
2. Adjust the pilot screw to provide properly sized
fl ame.
GAS INPUT ADJUSTMENT
When shipped from the factory, all gas fired units are
equipped for the average BTU of the gas stamped on
the rating plate.
Since the BTU content of gases
varies in many localities, the input must be checked
after installation of the unit. If the unit is overfi red,
the overheating will substantially shorten the life of
the heat exchanger. Never exceed the input on the
rating plate.
The input may be checked by either the meter method
or the pressure of the gas in the manifold. A 1/8 inch
pipe tap is available on the body of the gas valve.
Never overfi re the unit heater, as this
may cause unsatisfactory operation or shorten the
life of the heater.
METER METHOD OF CHECKING INPUT:
1. Obtain the heating value of the gas from the
local utility. This should be in BTU per cubic foot
(MJ/m3).
2. Determine the cubic feet per minute of the gas as
shown in the following example. The rating plate
input should be taken from the unit as stamped on
the plate.
EXAMPLE: Assume this is a unit having an input of
250,000 BTU/hr. and the heating value of the gas to
be used in the furnace is 1000 BTU/hr.
For correct air adjustment, close the air shutter until
yellow tips in the flame appear. Then open the air
shutter to the point just beyond the position where
yellow tipping disappears.
3. A proper pilot flame is a soft steady flame that
envelopes 3/8 to 1/2 inch (9.5 to 12.7 mm) of the
fl ame sensor.
4. Replace the pilot adjustment cap.
250,000 BTU/hr.
INPUT=
1000 BTU/cu. ft. x 60 min/hr
= 41.7 cu feet per min.
Before checking the unit input, all other gas
appliances connected to the same meter must be
turned off.
3. Fire the unit according to instructions.
4. Observe on the meter dial the cubic feet of gas for
a period of fi ve minutes. This should be 41.7 cu ft.
per min. x 5 minutes, or 20.8 cu. feet. Minor input
adjustments can be made by moving the regulator
screw clockwise for increased input and counterclockwise for decreased input. Any appreciable
adjustment in input should be made by re-orifi cing.
MANIFOLD PRESSURE METHOD
OF CHECKING INPUT
1. Close the manual gas valve on the unit.
2. Install a 1/8 inch pipe connection in the tapped
hold provided on the valve body and a “U” tube or
manometer by means or a rubber hose.
3. Fire the unit and observe the pressure.
4. Small variations in gas pressure adjustment can
be made by means of the pressure regulator.
Remove the cap from the regulator. Tur ning the
screw clockwise will increase the input, and turning
it counterclockwise will decrease the input. The
adjusted manifold pressure should not vary more
than 10% from the pressures specifi ed in chart 5.
– 18 –
Page 19

START-UP
Before starting the rooftop gas heating unit, use the
“Installation Check Sheet” (found at the end of this
manual) in conjunction with the procedures outlined
below to ensure that the unit is completely and properly
installed and ready for start-up.
1. Inspect all wiring connections; connections should
be clean and tight.
2. Trace circuits to ensure that actual wiring agrees
with the “as wired” diagrams provided with the
unit. Information in the title block of the wiring
diagram(s) should match the data appearing on the
unit nameplate.
3. Verify that the system switch is in the OFF position.
4. Check unit supply voltage to ensure that it is within
the utilization range.
5. Inspect the interior of the unit; remove any debris
or tools which may be present.
STARTING UNIT IN HEATING MODE
1. Close the unit disconnect switch(s) that provide
current to the unit control panel.
High voltage is present in some
areas of the control panel(s) with the unit
disconnect switch closed. Failure to exercise
caution when working around energized
electrical components may result in injury or
death from electrical shock.
2. Set the room thermostat/switching subbase as
indicated below:
a. position the heating system switch at either HEAT
or AUT O;
b. set the fan switch at AUTO; and,
c. adjust the temperature control setting to some
point above room temperature.
3. Place the system switch in the ON position.
With the thermostat calling for heating, unit operation is
automatic.
FINAL CHECKOUT
Run the unit sequentially through its stages of heating.
One proper unit operation is verifi ed, perform these fi nal
steps:
1. Inspect the unit for debris and/or misplaced tools
and hardware.
2. Be sure all gas valves and controls are in the
operating position if the unit will be operating
immediately
3. Secure all exterior panels in place.
– 19 –
Page 20

MAINTENANCE
Open all disconnect switches
and secure in that position before servicing unit.
Failure to do so may result in personal injury or
death from electrical shock.
Gas tightness of the safety shutoff valves must be chec ked on at least an ann ual
basis.
To check gas tightness of the safety shut-off valves,
turn off the manual valve upstream of the appliance
combination control. Remove the 1/8 inch pipe plug on
the inlet side of the combination control and connect a
manometer to that tapping. Turn the manual valve on
to apply pressure to the combination control. Note the
pressure reading on the manometer, then turn the valve
off. A loss of pressure indicates a leak. If a leak is detected,
use a soap solution to check all threaded connections. If
no leak is found, combination control is faulty and must
be replaced before putting appliance back in service.
Rooftop duct furnaces have been developed for
installation. Should maintenance be required,
following inspection and service routine: Inspect area
near the unit to be sure that there is no combustible
material located within minimum clearance requirements
(refer to Figures 1, 2 and 6). Service panels provide easy
access to the burner controls. To remove the service
door, refer to “Access Panel Removal” section (at the
beginning of this manual).
The pilot burner can be serviced by removing the pilot
plate from the main burner assembly.
To remove the main burner drawer assembly for
servicing the burners, proceed as follows:
1. Shut off the main gas valve and electrical power to
the gas duct furnace.
2. To slide out the burner drawer, the following two
procedures (a or b) may be chosen depending on
the complexity of the unit's controls:
a.) Disconnect the pilot burner gas tube. Break the
union between the automatic gas valve and
the burner manifold. Also break the union on
the discharge air end of the furnace (inside the
unit). Loosen the union located directly outside
of the furnace's bottom panel (refer to fi gure 9b).
Swing down this end of the piping to clear the
bottom of the burner drawer. The control and
piping assembly may be tied out of the way of
the pull-out drawer.
b.) Disconnect all wiring to the unit's controls.
Break the union located in the discharge end
of the furnace; loosen the external union, and
swing piping clear of the bottom of the drawer
(same procedure as a).
outdoor
perform the
3. Remove the locking screws holding the burner
drawer in position.
4. Slide the drawer out of the furnace.
5. Bur ners can be removed from the drawer by
raising the front of the burner and pushing it
against the hold-in spring until the front of the
burner comes out of the slot.
6. To clean or replace the main burners, slide out the
pullout drawer, and compress the spring by moving
the burner toward the manifold. Slide the opposite
end of the burner downward from the locating slot
while retaining spring is still compressed. Pull the
burners upward and out.
7. Remove any dirt, dust or other foreign matter from
the burners using a wire brush and/or compressed
air. Ensure that all parts are unobstructed. Inspect
and clean pilot burner if necessary.
8. Reassemble the gas duct furnace by replacing all
parts in order.
9. Complete the appropriate unit start-up procedure
as given in the “Start-Up” section of this manual.
10. Check the burner adjustment. See the “Primary Air
Shutter Adjustment” section of this manual.
11. Check all gas control valves and pipe connections
for leaks.
Under no circumstances should
combustible material be located within the
clearances specified in Figure 6. Failure to
provide proper clearance could result in
personal injury or equipment damage from fi re .
12. Check the operation of the automatic gas valve by
lowering the setting of the thermostat, stopping the
operation of the gas duct furnace. The gas valve
should close tightly, completely extinguishing the
fl ame on the main burners.
13. Check the operation of all safety devices.
14. Inspect and ser vice the blower section of the
system.
The outdoor unit should be thoroughly checked before
the start of the heating season. Check the air throughput as an added precaution to stay within the specifi ed
temperature limits.
If the unit is used with cooling equipment, periodic
maintenance should be scheduled throughout the year.
– 20 –
Page 21

Figure 13 - Natural Vent Duct Furance
Figure 14 - Power Vent Duct Furnace
– 21 –
Page 22

Chart 6 - Troubleshooting
SYMPTOMS
A. Gas odor.
B. Delayed ignition.
C. Pilot will not light, or will not
stay lit.
POSSIBLE CAUSES
1. Shut off gas supply immedi-
ately.
2. Blocked heat exchanger.
3. Drafts around heater.
4. Negative pressure in the
building.
5. Blocked draft hood/fl ue
collector.
1. Excessive primary air.
2. Main burner ports clogged
near pilot.
3. Pressure regulator set too low.
4. Pilot decreases in size when
main burners come on.
5. Pilot fl ame too small.
1. Main gas off.
2. Pilot adjustment screw turned
too low on combination main
gas valve.
3. Air in gas line.
4. Dirt in pilot orifi ce.
5. Extremely high or low gas
pressure.
6. Pilot valve not opening.
a. Faulty wiring.
b. Defective ignition control.
c. Defective valve.
7. No spark.
a. Faulty wiring.
b. Defective pilot.
c. Defective ignition control.
d. Sensor grounded.
CORRECTIVE ACTIONS
1. Inspect all gas piping and
repair.
2. Clean heat exchanger.
3. Eliminate Drafts. Refer to
installation.
4. See installation.
5. Clean draft hood/fl ue collector.
1. Close air shutter. Refer to
operation.
2. Clean main burner ports.
3. Reset manifold pressure.
Refer to operation.
4. Supply piping is inadequately
sized. Refer to installation.
5. Clean pilot orifi ce. Refer to
operation.
1. Open all manual gas valves.
2. Increase size of pilot fl ame.
3. Purge air from gas supply.
4. Remove pilot orifi ce. Clean
with compressed air or solvent.
(Do not ream).
5. Refer to operation.
6.
a. Inspect & correct all wiring.
b. Replace
c. Replace.
7.
a. Inspect & correct all wiring.
b. Replace.
c. Replace.
d. Inspect & correct ignition
system.
D. Main burners will not light.
1. Main gas off.
2. Lack of power at unit.
3. Thermostat not calling for heat.
4. Defective limit switch.
5. Improper thermostat or trans-
former wiring at gas valve.
6. Defective gas valve.
7. Defective thermostat.
– 22 –
1. Open all manual gas valves.
2. Replace fuse or turn on power
supply.
3. Turn up thermostat.
4. Check limit switch with
continuity tester. If open,
replace limit switch.
5. Check wiring per diagrams.
6. Replace gas valve.
7. Check thermostat and replace
if defective.
Page 23

Chart 6 - Troubleshooting continued
SYMPTOMS
D. Main burners will not light.
continued
E. Flame lifting from burner ports.
F. Flame pops back.
POSSIBLE CAUSES
8. Defective transformer.
9. Loose wiring.
10. Defective ignition control.
1. Pressure regulator set too
high.
2. Defective regulator.
3. Burner orifi ce too large.
1. Excessive primary air.
CORRECTIVE ACTION
8. Be sure 115 volts is supplied
to the transformer primary then
check for 24 volts at secondary
terminal before replacing.
9. Check and tighten all wiring
connections.
10. Replace.
1. Reset manifold pressure.
Refer to operation.
2. Replace regulator section of
combination gas valve or
complete valve.
3. Check with local gas supplier
for proper orifi ce size and
replace. Refer to operation.
1. Close air shutter. Refer to
Operation.
2. Check with local gas supplier
for proper orifi ce size and
replace.
G. Noisy fl ame.
H. Yellow tip fl ame (some yellow
tipping on propane gas is
permissible.
1. Too much primary air.
2. Noisy pilot.
3. Irregular orifi ce causing whistle
or resonance.
4. Excessive gas input.
a. Pressure regulator set too
high.
b. Defective regulator.
c. Burner orifi ce too large.
1. Insuffi cient primary air.
2. Clogged main burner ports.
3. Misaligned orifi ces.
4. Air shutter linted.
5. Insuffi cient combustion air.
6. Clogged draft hood/fl ue
collector.
1. Close air shutter. Open all
manual gas valves.
2. Reduce pilot gas. Refer to
operation.
3. Replace orifi ce.
4.
a. Reset manifold pressure
Refer to operation.
b. Replace regulator section of
combination gas valve or
complete valve.
c. Check with local gas
supplier for proper orifi ce
size and replace. Refer to
operation.
1. Open air shutters. Refer to
operation.
2. Clean main burner ports.
3. Replace manifold assembly.
4. Check for dust or lint at air
mixer opening and around the
air shutter.
5. Clean combustion air inlet
openings in bottom panel.
Refer to installation.
6. Clean draft hood/fl ue collecter.
– 23 –
Page 24

Chart 6 - Troubleshooting continued
SYMPTOMS
J. Floating fl ame.
K. Burner won't turn off.
POSSIBLE CAUSES
1. Blocked heat exchanger.
2. Insuffi cient combustion air.
3. Blocked venting.
4. Air leak into combined
chamber, draft hood, or fl ue
collector.
1. Poor thermostat location.
2. Defective thermostat.
3. Improper thermostat or
transformer.
4. Short circuit.
5. Defective or sticking gas valve.
6. Excessive gas supply
pressure.
CORRECTIVE ACTION
1. Clean heat exchanger.
2. Clean combustion air inlet
openings in bottom panel.
Refer to installation.
3. Clean fl ue. Refer to
installation.
4. Determine cause and repair
accordingly. Refer to
installation.
1. Relocate thermostat away
from drafts.
2. Replace thermostat.
3. Check wiring diagrams.
4. Check operation at valve.
Look for short and correct
(such as staples piercing
thermostat wiring).
5. Replace gas valve.
6. Refer to operation.
L. Rapid burner cycling.
M. Not enough heat.
1. Loose electrical connections at
gas valve or thermostat.
2. Excessive thermostat heat
anticipation.
3. Unit cycling on high limit.
4. Poor thermostat location.
1. Incorrect gas input.
2. Heater undersized.
3. Thermostat malfuction.
4. Heater cycling on limit control.
5. Check outside dampers if
used.
1. Tighten all electrical
connections.
2. Adjust thermostat heat
anticipation for longer cycles.
Refer to operation.
3. Check for proper air supply
across heat exchanger.
4. Relocate thermostat. (Do not
mount thermostat on unit).
1. Refer to operation.
2. This is especially true when
the heated space is enlarged.
Have the heat loss calculated
and compare to the heater
output (80% of input). Your
gas supplier or installer can
furnish this information. If
heater is undersized, add
additional heaters.
3. Replace thermostat.
4. Check air movement through
heat exchanger. Check
voltage to power venter motor,
clean power venter wheel and
heat exchanger, and oil power
venter motor. Check fi lters,
replace if necessary.
5. Adjust dampers accordingly.
– 24 –
Page 25

Chart 6 - Troubleshooting continued
SYMPTOMS
N. Too much heat.
*P. Power venter motor will not
start.
*Q. Noisy power venter.
POSSIBLE CAUSES
1. Thermostat malfunction.
2. Heater runs continuously.
a. Improper thermostat or
transformer wiring at gas
valve.
b. Short circuit.
c. Defective or sticking gas
valve.
d. Excessive gas supply
pressure.
1. Lack of power at unit.
2. Defective power venter relay.
3. Defective motor.
4. Thermostat not calling for heat.
5. Defective limit switch.
1. Power venter wheel loose.
2. Bearings dry.
3. Power venter wheel blade
dirty.
4. Power venter wheel rubbing
housing.
CORRECTIVE ACTION
1. Replace thermostat.
2.
a. Check wiring per diagrams.
b. Check operation at valve.
Look for short and correct
(such as staples piercing
thermostat wiring).
c. Replace gas valve.
d. Refer to operation.
1. Replace fuse or turn on power.
2. Replace.
3. Replace.
4. Turn up thermostat.
5. Replace limit switch.
1. Tighten or replace.
2. Oil bearings on power venter
motor.
3. Clean power venter wheel
blade.
4. Realign power venter wheel.
*R. Power venter will not run.
*S. Power venter motor will not
stop.
1. Loose wiring.
2. Defective motor overload
protector or defective motor.
3. Defective power venter relay.
1. Improperly wired fan relay.
2. Defective fan relay.
*Indicates Power Vent Units Only
1. Check and tighten all wiring
connections per diagrams.
2. Replace motor.
3. Check for 24V across 1 & 3
terminals on fan relay. If 24V
is present, jumper terminals
numbered 2 and 4. If motor
runs, relay is defective and
must be replaced. If 24V is not
present check wiring diagrams.
1. Check all wiring.
2. Replace fan relay.
– 25 –
Page 26

How to order Replacement Parts
Please provide the following information to your local representative:
• Unit Number
• Serial Number (if any)
• Part Description and Number as shown in Replacement Parts Literature
If further assistance is needed, please contact the manufacturer's customer service department.
SERVICE NOTE
Due to the many confi gurations, options and voltage
characteristics available on Outdoor Duct Furnaces,
the information provided in their manual is somewhat
general in its context. Should user or service
organization incur a problem, the nature of which is
not herein, we urge you to contact the manufacturer. It
would be of great assistance to the manufacturer if you
can provide the model and serial number and wiring
diagram number, as well as access type.
LIMITED W ARRANTY
Gas–Fired Engineered Products
Natural or Power Vented Outdoor Duct Furnaces
The “Manufacturer” warrants to the original owner at the original installation site that the Gas–Fired Engineered
Products (the “Product”) will be free from defects in material or workmanship for a period not to exceed one (1)
year from the date start up or eighteen (18) months from the date of shipment from the factory, whichever occurs
fi rst. If upon examination by the Manufacturer the Product is shown to have a defect in material or workmanship
during the warranty period, the Manufacturer will repair or replace, at its option, that part of the Product which is
shown to be defective.
This limited warranty does not apply:
(a) if the Product has been subjected to misuse or neglect, has been accidentally or intentionally damaged,
has not been installed, maintained or operated in accordance with the furnished written instructions, or
has been altered or modifi ed in any way.
(b) to any expenses, including labor or material, incurred during removal or reinstallation of the defective
Product or parts thereof.
(c) to any damage due to corrosion by chemicals (including halogenated hydrocarbons) precipitated in the
air.
(d) to any workmanship of the installer of the Product.
This limited warranty is conditional upon:
(a) shipment, to the Manufacturer, of that part of the Product thought to be defective. Goods can only be
returned with prior written approval from the Manufacturer. All returns must be freight prepaid.
(b) determination, in the reasonable opinion, of the Manufacturer that there exists a defect in material or
workmanship.
Repair or replacement of any part under this Limited Warranty shall not extend the duration of the warranty with
respect to such repaired or replaced part beyond the stated warranty period.
THIS LIMITED WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
AND ALL SUCH OTHER WARRANTIES, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, ARE HEREBY DISCLAIMED AND
EXCLUDED FROM THIS LIMITED WARRANTY. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE MANUFACTURER BE LIABLE
IN ANY WAY FOR ANY CONSEQUENTIAL, SPECIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES OF ANY NATURE
WHATSOEVER, OR FOR ANY AMOUNTS IN EXCESS OF THE SELLING PRICE OF THE PRODUCT OR ANY
PARTS THEREOF FOUND TO BE DEFECTIVE. THIS LIMITED WARRANTY GIVES THE ORIGINAL OWNER
OF THE PRODUCT SPECIFIC LEGAL RIGHTS. YOU MAY ALSO HAVE OTHER RIGHTS WHICH MAY VARY
BY EACH JURISDICTION.
In the interest of product improvement, we reserve the right to make changes without notice.
– 26 –
Page 27

NOTES:
– 27 –
Page 28

GAS EQUIPMENT
START-UP
Customer ____________________________________ Job Name & Number _________________________
PRE-INSPECTION INFORMATION
With power and gas off.
Type of Equip: Duct Furnace Rooftop DF
Serial Number _________________________ Model Number __________________________
Name Plate Voltage: _____________ Name Plate Amperage: _____________
Type of Gas: Natural LP Tank Capacity _______ lbs. Rating: _ _____ BTU @ ____ °F
_______ kg _ _____ kw @ ____ °C
❐ Are all panels, doors, vent caps in place?
❐ Has the unit suffered any external damage? Damage ______________________________
❐ Does the gas piping and electric wiring appear to be installed in a professional manner?
❐ Has the gas and electric been inspected by the local authority having jurisdiction?
❐ Is the gas supply properly sized for the equipment?
❐ Were the installation instructions followed when the equipment was installed?
❐ Have all fi eld installed controls been installed?
❐ Do you understand all the controls on this equipment? If not, contact your wholesaler or rep.
(DO NOT START this equipment unless you fully understand the controls.)
GENERAL
With power and gas off.
❐ Make certain all packing has been removed.
❐ Tighten all electrical terminals and connections.
❐ Check damper linkages for tightness.
❐ Check all fans & blowers for free movement.
❐ Check all controls for proper settings.
❐ Check all set screws on blowers and bearings.
❐ Check belt tightness.
❐ Inlet gas pressure. ____ in. WC or ____ kPa
❐ Pilot & main burner ignition.
❐ Manifold gas pressure. ____ in. WC or ____ kPa
❐ Cycle fi restat and/or freezestat.
❐ Check electronic modulation. Set at: __________
❐ Cycle and check all other controls not listed.
❐ Check operation of remote panel.
❐ Entering air temp. ____ °F or ____ °C
GAS HEATING
With power and gas on.
❐ Discharge air temp. (high fi re) ____ °F ____ °C
❐ External static pressure ____ in. WC or ____ kPa
❐ Cycle by thermostat or operating control.
❐ Combustion Reading
Carbon Monoxide ____ PPM
Carbon Dioxide ____ %
Remarks: _____________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
 Loading...
Loading...