
TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
Rail-to-Rail, Wide-Band, Low-Power Operational Amplifiers
■ 3V, 5V, ±5V specifications
■ 3dB bandwidth: 90MHz
■ Gain bandwidth product: 70MHz
■ Slew rate: 100V/ms
■ Output current: up to 55mA
■ Input single supply voltage
■ Output rail-to-rail
■ Specified for 150Ω loads
■ Low distortion, THD: 0.1%
■ SOT23-5, TSSOP and SO packages
Description
The TSH7x series offers single, dual, triple and
quad operational amplifiers featuring high video
performances with large bandwidth, low distortion
and excellent supply voltage rejection.
Running with a single supply voltage from 3V to
12V, these amplifiers feature a large output
voltage swing and high output current capable of
driving standard 150Ω loads. A low operating
voltage makes TSH7x amplifiers ideal for use in
portable equipment.
The TSH71, TSH73 and TSH75 also feature
standby inputs, each of which allows the op-amp
to be put into a standby mode with low power
consumption and high output impedance. This
function allows power saving or signal
switching/multiplexing for high-speed applications
and video applications.
To economize both board space and weight, the
TSH7x series is proposed in SOT23-5, TSSOP
and SO packages.
Applications
■ Video buffers
■ ADC driver
■ Hi-fi applications
Pin Connections (top view)
TSH70 : SOT23-5/SO8
TSH70 : SOT23-5/SO8
NC
NC
1
1
Output
Output
VCC -
VCC -
Non-Inv. In.
Non-Inv. In.
Non Inverting Input
Non Inverting Input
Inverting Input1 Output2
Inverting Input1 Output2
Non Inverting Input1
Non Inverting Input1
Non Inverting Input1
Non Inverting Input1
Inver ting Input1
Inver ting Input1
Non Inverting Input1
Non Inverting Input1
Non Inverting Input2
Non Inverting Input2
Inver ting Input2
Inver ting Input2
Non Inverting Input1
Non Inverting Input1
Non Inverting Input2
Non Inverting Input2
Inver ting Input2
Inver ting Input2
5
1
5
VCC +
2
2
3
3
Inverting Input
Inverting Input
Inverting Input1
Inverting Input1
Inverting Input1
Inverting Input1
VCC +
+ -
+ -
Inv. In.
Inv. In.
4
4
TSH71 : SO8/TSSOP8
TSH71 : SO8/TSSOP8
NC
NC
1
1
2
2
3
3
VCC -
VCC -
TSH72 : SO8/TSSOP8
TSH72 : SO8/TSSOP8
Output1
Output1
1
1
2
2
_
_
+
+
3
3
VCC -
VCC -
4
4
TSH73 : SO14/TSSOP14
TSH73 : SO14/TSSOP14
STANDB Y1
STANDB Y1
1
1
2
2
STANDB Y2
STANDB Y2
3
STANDB Y3
3
STANDB Y3
VCC + VC C -
VCC + VC C -
4
4
5
5
+
+
_
_
6
6
Output1
7
Output1
7
TSH74 : SO14/TSSOP14
TSH74 : SO14/TSSOP14
1
1
Output1
Output1
2
2
_
_
+
+
3
3
VCC + VC C -
VCC + VC C -
4
4
5
5
+
+
_
_
6
6
7
7
Output2
Output2
TSH75 : SO16/TSSOP16
TSH75 : SO16/TSSOP16
1
1
Output1
Output1
Output2
Output2
STANDBY
STANDBY
_
_
2
2
+
+
3
3
VCC + VC C -
VCC + VC C -
4
4
5
5
+
+
_
_
6
6
7 10
7 10
8 9
8 9
Inv. In .
Inv. In .
Non- Inv. In.
Non- Inv. In.
VCC -
VCC -
_
_
+
+
1
2
2
3
3
STANDBY
STANDBY
8
8
7
7
VCC +
VCC +
6
Output
6
Output
NC
NC
54
54
VCC +
VCC +
8
8
7
7
Inverting Input2
Inverting Input2
_
_
6
6
+
+
Non Inverting Input2
Non Inverting Input2
5
5
14
14
Output3
Output3
Inver ting Input3
Inver ting Input3
13
13
_
_
+
+
Non Inverting Input3
Non Inverting Input3
12
12
11
11
10
10
Non Inverting Input2
Non Inverting Input2
+
+
_
_
Inverting Input2
Inverting Input2
9
9
Output2
Output2
8
8
14
14
Output4
Output4
13
13
Inver ting Input4
Inver ting Input4
_
_
+
+
Non Inverting Input4
Non Inverting Input4
12
12
11
11
10
10
Non Inverting Input3
Non Inverting Input3
+
+
_
_
Inverting Input3
Inverting Input3
9
9
Output3
Output3
8
8
16
16
Output4
Output4
Inver ting Input4
Inver ting Input4
15
15
_
_
+
+
Non Inverting Input4
Non Inverting Input4
14
14
13
13
12
12
Non Inverting Input3
Non Inverting Input3
+
+
_
_
Inverting Input3
Inverting Input3
11
11
Output3
Output3
STANDBY
STANDBY
_
_
+
+
8
8
7
7
6
6
54
54
NC
NC
VCC +
VCC +
Output
Output
NC
NC
May 2006 Rev. 3 1/33
www.st.com
33
Order Codes TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
1 Order Codes
Part Number
TSH70CLT
TSH70CD/CDT SO-8 Tube or Tape & Reel 70C
TSH71CD/CDT SO-8 Tube or Tape & Reel 71C
TSH71CPT TSSOP8 (Thin Shrink Outline Package) Tape & Reel 71C
TSH72CD/CDT SO-8 Tube or Tape & Reel 72C
TSH72CPT TSSOP8 (Thin Shrink Outline Package) Tape & Reel 72C
TSH73CD/CDT SO-14 Tube or Tape & Reel 73C
TSH73CPT TSSOP14 (Thin Shrink Outline Package) Tape & Reel 73C
TSH74CD/CDT SO-14 Tube or Tape & Reel 74C
TSH74CPT TSSOP14 (Thin Shrink Outline Package) Tape & Reel 74C
TSH75CD/CDT SO-16 Tube or Tape & Reel 75C
TSH75CPT TSSOP16 (Thin Shrink Outline Package) Tape & Reel 75C
Temperature
Range
0°C to 70°C
Package Packing Marking
SOT23-5 Tape & Reel K301
2/33
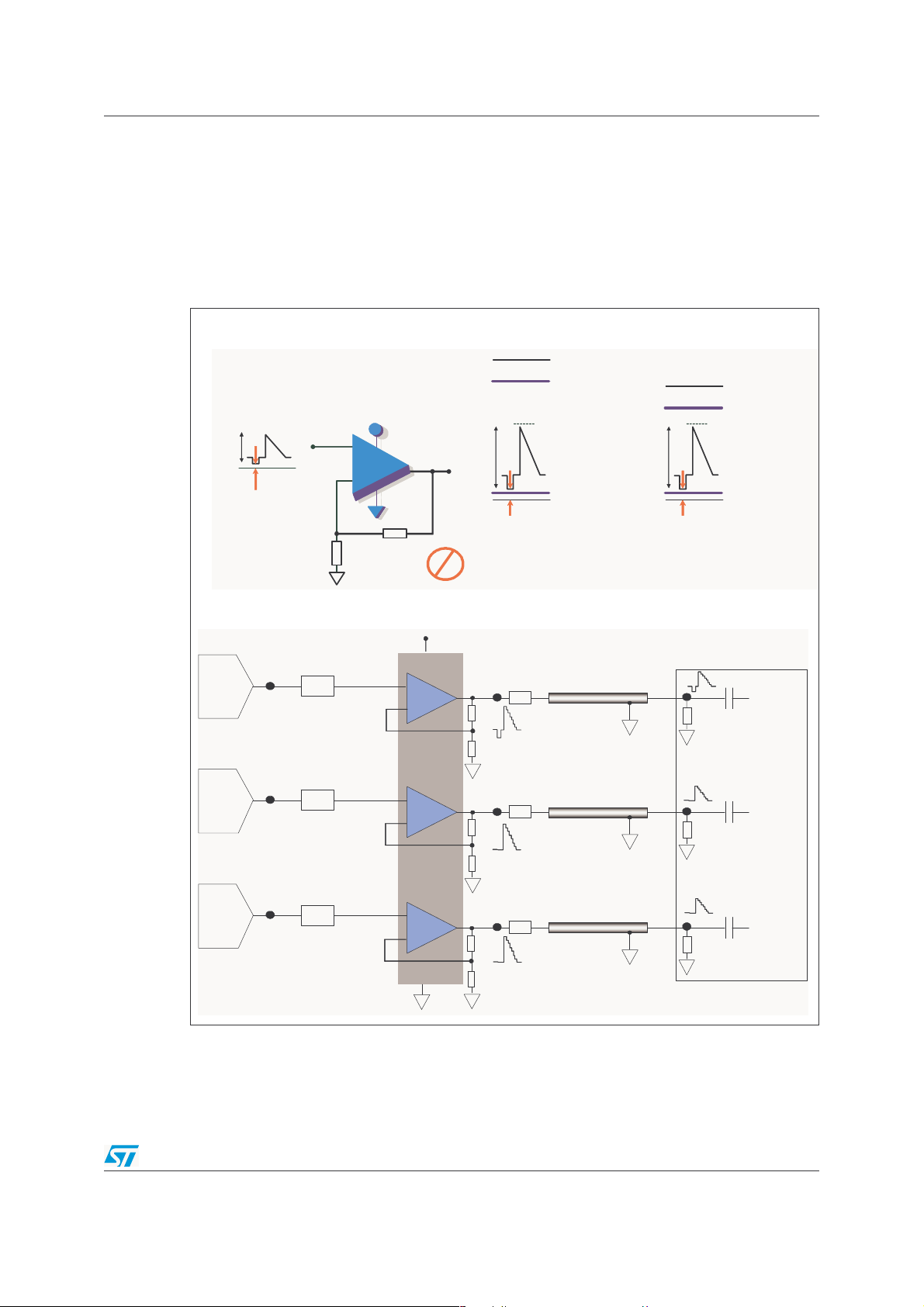
TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Typical Application: Video Driver
2 Typical Application: Video Driver
A typical application for the TSH7x family is that of video driver for driving STi7xxx DAC
outputs on 75-ohm lines.
Figure 1
show the benefits of the TSH7x family as single supply drivers.
Figure 1. Benefits of TSH7x family: +3V or +5V single supply solution
-5V
+5V
+5V
2Vp-p
GND
100mV
75Ω
2Vpp
VOH=4.2Vmin.
(Tested)
2.1V
VOL=40mVmax.
(Tested)
75Ω Cable
+3V
2Vp-p
GND
100mV
1Vpp1Vpp
75Ω
Video DAC’s outputs:
Bottom of
synchronization tip
around 50mV
1Vp-p
GND
50mV
Reconstruction
Y,G
Video
DAC
Filtering
LPF
1kΩ
GND
+
Gain=2
_
Vcc=+5V
Vcc=+3V
GND
1kΩ
+_+
_
VOH=2.45Vmin.
(Tested)
2.1V
VOL=30mVmax.
(Tested)
TV
Video
DAC
Video
DAC
Pb,B
Pr,R
Reconstruction
Filtering
LPF
Reconstruction
Filtering
LPF
GND
+_+
_
+_+
_
TSH73
75Ω
75Ω Cable
0.7Vpp0.7Vpp
75Ω
1.4Vpp1.4Vpp
75Ω
75Ω Cable
0.7Vpp0.7Vpp
75Ω
1.4Vpp1.4Vpp
3/33

Absolute Maximum Ratings & Operating Conditions TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
3 Absolute Maximum Ratings & Operating Conditions
Table 1. Absolute maximum ratings (AMR)
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
(3)
(1)
(2)
(4)
14 V
±2V
±6V
80
28
22
35
°C/W
37
32
35
T
V
R
V
T
CC
id
V
i
oper
stg
T
j
thjc
Supply Voltage
Differential Input Voltage
Input Voltage
Operating Free Air Temperature Range 0 to +70 °C
Storage Temperature -65 to +150 °C
Maximum Junction Temperature 150 °C
Thermal resistance junction to case
SOT23-5
SO-8
SO-14
SO-16
TSSOPO8
TSSOP14
TSSOP16
Thermal resistance junction to ambient area
SOT23-5
SO-8
R
thja
SO-14
SO-16
TSSOPO8
TSSOP14
TSSOP16
250
157
125
110
130
110
110
ESD Human Body Model 2 kV
1. All voltages values, except differential voltage are with respect to network ground terminal
2. Differential voltages are non-inverting input terminal with respect to the inverting terminal
3. The magnitude of input and output must never exceed VCC +0.3V
4. Short-circuits can cause excessive heating
Table 2. Operating conditions
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
CC
V
IC
Standby (V
Supply Voltage 3 to 12 V
Common Mode Input Voltage Range V
CC
-
to (V
CC
-
) to (V
CC
+
-1.1) V
+
)V
CC
°C/W
4/33
TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Electrical Characteristics
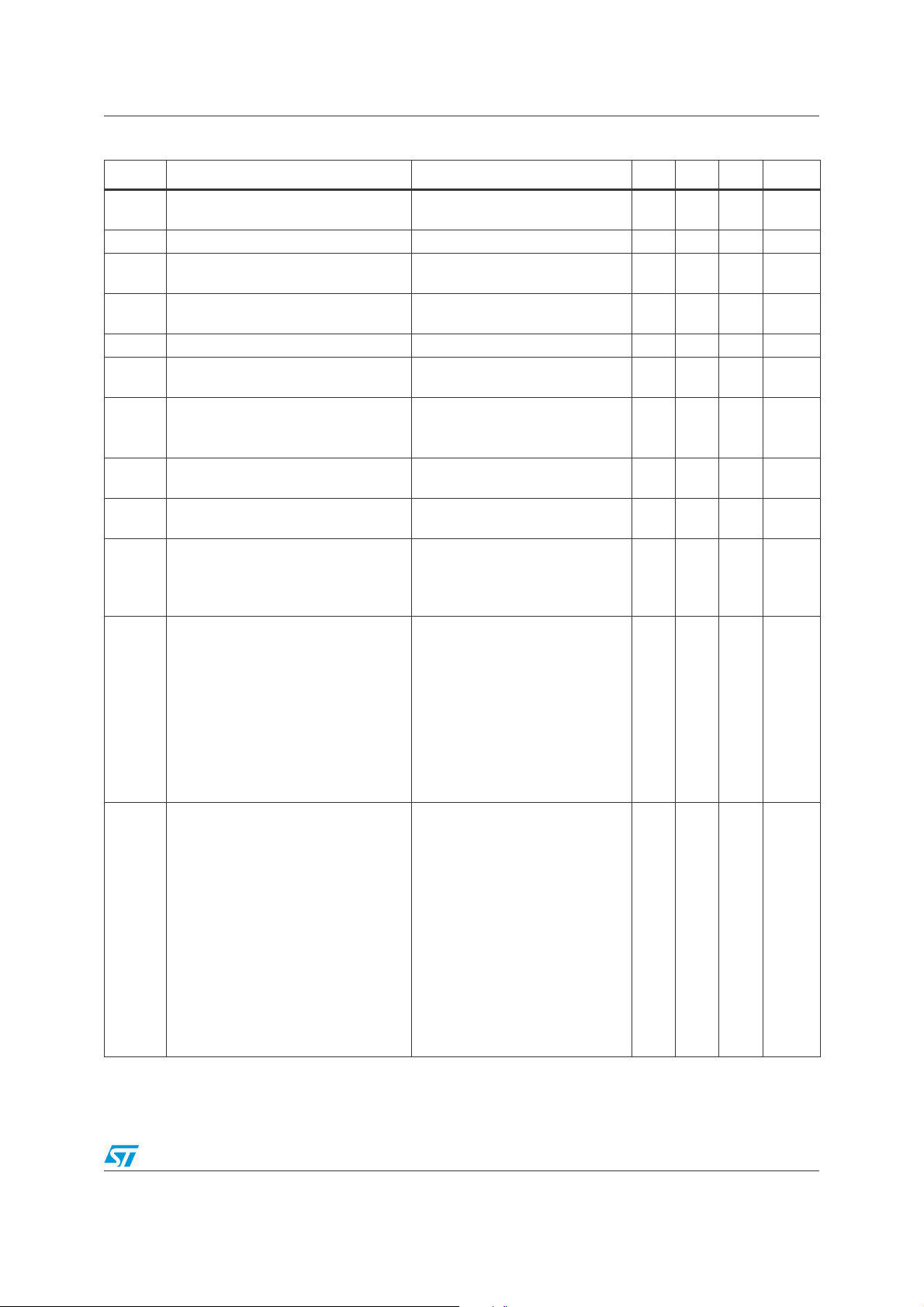
4 Electrical Characteristics
Table 3. V
CC
+
= 3V, V
-
= GND, VIC = 1.5V, T
CC
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
|Vio| Input Offset Voltage
∆V
CMRR
SVRR
PSRR
Input Offset Voltage Drift vs. Temp. T
io
Input Offset Current
I
io
I
Input Bias Current
ib
C
Input Capacitance 0.2 pF
in
Supply Current per Operator
I
CC
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
/δVio)
(δV
IC
Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio
(δVCC/δVio)
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
(δVCC/δV
Large Signal Voltage Gain
A
vd
I
Output Short Circuit Current Source
o
out
)
= 25°C
T
amb
T
< T
amb
< T
amb
= 25°C
< T
amb
= 25°C
< T
amb
= 25°C
< T
amb
<+1.9V & V
IC
= 25°C
< T
= 25°C
< T
amb
< T
< T
< T
< T
< T
amb
< T
< T
max.
max.
max.
max.
max.
max.
max.
out
=1.5V
min.
min.
T
amb
T
min.
T
amb
T
min.
T
amb
T
min.
+0.1<V
T
amb
T
min.
T
amb
T
min.
Positive & Negative Rail 75 dB
=150Ω to 1.5V, V
R
L
= 25°C
T
amb
T
< T
min.
amb
=25°C,
T
amb
V
=+1, V
id
V
=-1, V
id
|
Source
|
Sink
T
min.
Vid=+1, V
V
=-1, V
id
|
Source
|
Sink
T
amb
R
L
R
L
R
L
R
L
to 1.5V,
out
to 1.5V
out
< T
< T
amb
to 1.5V
out
to 1.5V
out
=25°C
= 150Ω to GND
= 600Ω to GND
= 2kΩ to GND
= 10kΩ to GND
< T
max.
max.
=1V to 2V
out
2.45
1.2 10
0.1 3.5
7.2 9.8
656490
666574
706581
43
30
33
20
22
19
2.60
2.87
2.91
2.93
12
mV
4 µV/°C
5
615
20
11
mA
mA
µA
µA
dB
dB
dB
= 150Ω to 1.5V
R
V
High Level Output Voltage
OH
L
R
= 600Ω to 1.5V
L
R
= 2kΩ to 1.5V
L
R
= 10kΩ to 1.5V
L
T
< T
min.
amb
< T
max.
RL = 150Ω to GND
R
= 150Ω to 1.5V
L
2.65
2.4
2.6
2.77
2.90
2.92
2.93
V
5/33
Electrical Characteristics TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
Table 3. V
CC
+
= 3V, V
-
= GND, VIC = 1.5V, T
CC
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
T
=25°C
amb
R
= 150Ω to GND
L
R
= 600Ω to GND
L
R
= 2kΩ to GND
L
R
= 10kΩ to GND
L
= 150Ω to 1.5V
R
V
Low Level Output Voltage
OL
L
R
= 600Ω to 1.5V
L
R
= 2kΩ to 1.5V
L
R
= 10kΩ to 1.5V
L
T
< T
min.
amb
< T
max.
140
RL = 150Ω to GND
R
= 150Ω to 1.5V
L
10
11
11
11
90
68
57
30
300
40
350
mV
F=10MHz
GBP Gain Bandwidth Product
Bw Bandwidth @-3dB A
SR Slew Rate
φm Phase Margin R
A
=+11
VCL
A
=-10
VCL
=+1, RL=150Ω to 1.5V 87 MHz
VCL
=+2, RL=150Ω // CL to 1.5V
A
VCL
= 5pF
C
L
C
= 30pF 458085
L
=150Ω // 30pF to 1.5V 40 °
L
65
55
MHz
V/µs
en Equivalent Input Noise Voltage F=100kHz 11 nV/√Hz
A
=+2, F=4MHz, RL=150Ω //
VCL
THD Total Harmonic Distortion
IM2 Second order intermodulation product
30pF to 1.5V
V
=1Vpp
out
V
=2Vpp
out
A
=+2, V
VCL
R
=150Ω to 1.5V
L
out
=2Vpp
Fin1=180kHz, Fin2=280KHz
-61
-54
-76 dBc
spurious measurements @100kHz
A
IM3 Third order inter modulation product
=+2, V
VCL
R
=150Ω to 1.5V
L
Fin1=180kHz, Fin2=280KHz
out
=2Vpp
-68 dBc
spurious measurements @400kHz
=+2, RL=150Ω to 1.5V
A
∆G Differential gain
Df Differential phase
Gf Gain Flatness F=DC to 6MHz, A
VCL
F=4.5MHz, V
=+2, RL=150Ω to 1.5V
A
VCL
F=4.5MHz, V
out
out
=2Vpp
=2Vpp
=+2 0.2 dB
VCL
0.5 %
0.5 °
Vo1/Vo2 Channel Separation F=1MHz to 10MHz 65 dB
dB
6/33
TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Electrical Characteristics
Table 4. V
CC
+
= 5V, V
-
= GND, VIC = 2.5V, T
CC
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
T
|Vio| Input Offset Voltage
∆V
CMRR
SVRR
PSRR
Input Offset Voltage Drift vs. Temp. T
io
Input Offset Current
I
io
I
Input Bias Current
ib
C
Input Capacitance 0.3 pF
in
Supply Current per Operator
I
CC
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
/δVio)
(δV
IC
Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio
/δVio)
(δV
CC
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
(δV
/δV
out
)
CC
Large Signal Voltage Gain
A
vd
Output Short Circuit Current Source
I
o
= 25°C
amb
T
< T
amb
< T
amb
= 25°C
< T
amb
= 25°C
< T
amb
= 25°C
< T
amb
<3.9V & V
IC
= 25°C
< T
= 25°C
< T
amb
< T
< T
< T
< T
< T
amb
< T
max.
max.
max.
max.
max.
< T
max.
out
max.
=2.5V
min.
min.
T
amb
T
min.
T
amb
T
min.
T
amb
T
min.
+0.1<V
T
amb
T
min.
T
amb
T
min.
Positive & Negative Rail 75 dB
R
=150Ω to 1.5V,
L
V
=1V to 4V
out
= 25°C
T
amb
T
< T
amb
out
out
amb
out
out
< T
to 1.5V,
to 1.5V
< T
max.
to 1.5V
to 1.5V
max.
min.
=25°C,
T
amb
V
=+1, V
id
V
=-1, V
id
|
Source
|
Sink
T
< T
min.
Vid=+1, V
V
=-1, V
id
|
Source
|
Sink
=25°C
T
amb
= 150Ω to GND
R
L
R
= 600Ω to GND
L
R
= 2kΩ to GND
L
R
= 10kΩ to GND
L
1.1 10
0.1 3.5
8.2 10.5
727197
686775
757084
35
33
34
32
4.2
4.36
4.85
4.90
4.93
12
3 µV/°C
5
615
20
11.5
55
55
mV
µA
µA
mA
dB
dB
dB
mA
= 150Ω to 2.5V
R
V
High Level Output Voltage
OH
L
R
= 600Ω to 2.5V
L
R
= 2kΩ to 2.5V
L
R
= 10kΩ to 2.5V
L
T
< T
min.
amb
< T
max.
RL = 150Ω to GND
R
= 150Ω to 2.5V
L
4.5
4.1
4.4
4.66
4.90
4.92
4.93
V
7/33

Electrical Characteristics TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
Table 4. V
CC
+
= 5V, V
-
= GND, VIC = 2.5V, T
CC
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
T
=25°C
amb
R
= 150Ω to GND
L
R
= 600Ω to GND
L
R
= 2kΩ to GND
L
R
= 10kΩ to GND
L
= 150Ω to 2.5V
R
V
Low Level Output Voltage
OL
L
R
= 600Ω to 2.5V
L
R
= 2kΩ to 2.5V
L
R
= 10kΩ to 2.5V
L
T
< T
min.
amb
< T
max.
220
105
RL = 150Ω to GND
R
= 150Ω to 2.5V
L
20
23
23
23
76
61
40
400
60
450
F=10MHz
GBP Gain Bandwidth Product
A
A
Bw Bandwidth @-3dB A
SR Slew Rate
A
R
VCL
VCL
L
C
C
φmPhase Margin R
L
VCL
VCL
=+11
=-10
65
55
=+1, RL=150Ω to 2.5V 87 MHz
=+2,
=150Ω // CL to 2.5V
= 5pF
L
= 30pF 60
L
104
105
=150Ω // 30pF to 2.5V 40 °
MHz
V/µs
en Equivalent Input Noise Voltage F=100kHz 11 nV/√Hz
A
=+2, F=4MHz
VCL
R
=150Ω // 30pF to 2.5V
THD Total Harmonic Distortion
IM2 Second order intermodulation product
L
=1Vpp
V
out
V
=2Vpp
out
A
=+2, V
VCL
R
=150Ω to 2.5V
L
out
=2Vpp
Fin1=180kHz, Fin2=280kHz
-61
-54
-76 dBc
spurious measurements @100kHz
A
IM3 Third order inter modulation product
=+2, V
VCL
R
=150Ω to 2.5V
L
Fin1=180kHz, Fin2=280KHz
out
=2Vpp
-68 dBc
spurious measurements @400kHz
A
=+2, RL=150Ω to 2.5V
∆G Differential gain
Df Differential phase
Gf Gain Flatness F=DC to 6MHz, A
VCL
F=4.5MHz, V
A
=+2, RL=150Ω to 2.5V
VCL
F=4.5MHz, V
out
out
=2Vpp
=2Vpp
=+2 0.2 dB
VCL
0.5 %
0.5 °
Vo1/Vo2 Channel Separation F=1MHz to 10MHz 65 dB
mV
dB
8/33

TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Electrical Characteristics
Table 5. V
CC
+
= 5V, V
-
= -5V, VIC = GND, T
CC
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
T
|Vio| Input Offset Voltage
∆V
CMRR
SVRR
PSRR
V
V
Input Offset Voltage Drift vs. Temp. T
io
Input Offset Current
I
io
I
Input Bias Current
ib
C
Input Capacitance 0.7 pF
in
Supply Current per Operator
I
CC
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
/δVio)
(δV
IC
Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio
/δVio)
(δV
CC
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
(δV
/δV
out
)
CC
Large Signal Voltage Gain
A
vd
Output Short Circuit Current Source
I
o
High Level Output Voltage
OH
Low Level Output Voltage
OL
= 25°C
amb
T
< T
amb
< T
amb
= 25°C
< T
amb
= 25°C
< T
amb
= 25°C
< T
amb
<3.9V & V
IC
= 25°C
< T
= 25°C
< T
amb
< T
< T
< T
< T
< T
amb
< T
< T
max.
max.
max.
max.
max.
max.
out
max.
=GND
min.
min.
T
amb
T
min.
T
amb
T
min.
T
amb
T
min.
-4.9<V
T
amb
T
min.
T
amb
T
min.
Positive & Negative Rail 75 dB
R
=150Ω to GND
L
V
=-4 to +4
out
= 25°C
T
amb
T
< T
amb
out
out
amb
out
out
amb
< T
to 1.5V
to 1.5V
< T
max.
to 1.5V
to 1.5V
< T
max.
max.
min.
=25°C
T
amb
V
=+1, V
id
V
=-1, V
id
|
Source
|
Sink
T
< T
min.
Vid=+1, V
V
=-1, V
id
|
Source
|
Sink
T
=25°C
amb
= 150Ω to GND
R
L
R
= 600Ω to GND
L
R
= 2kΩ to GND
L
R
= 10kΩ to GND
L
< T
T
min.
RL = 150Ω to GND
T
=25°C
amb
= 150Ω to GND
R
L
R
= 600Ω to GND
L
R
= 2kΩ to GND
L
R
= 10kΩ to GND
L
< T
T
min.
amb
< T
max.
RL = 150Ω to GND
0.8 10
0.1 3.5
9.8 12.3
8180106
717077
757086
55
35
55
30
34
29
4.2
4.36
4.85
4.9
4.93
4.1
-4.63
-4.86
-4.9
-4.93
12
2 µV/°C
5
615
20
13.4
-4.4
-4.3
mV
µA
µA
mA
dB
dB
dB
mA
V
V
9/33

Electrical Characteristics TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
Table 5. V
CC
+
= 5V, V
-
= -5V, VIC = GND, T
CC
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
F=10MHz
GBP Gain Bandwidth Product
Bw Bandwidth @-3dB
SR Slew Rate
φm Phase Margin R
A
=+11
VCL
A
=-10
VCL
=+1
A
VCL
R
=150Ω // 30pF to GND
L
=+2,
A
VCL
R
=150Ω // CL to GND
L
= 5pF
C
L
C
= 30pF 68
L
=150Ω to GND 40 °
L
65
55
100 MHz
117
118
MHz
V/µs
en Equivalent Input Noise Voltage F=100kHz 11 nV/√Hz
=+2, F=4MHz
A
VCL
R
=150Ω // 30pF to GND
THD Total Harmonic Distortion
IM2 Second order intermodulation product
L
=1Vpp
V
out
V
=2Vpp
out
A
=+2, V
VCL
R
=150Ω to GND
L
out
=2Vpp
Fin1=180kHz, Fin2=280KHz
-61
-54
-76 dBc
spurious measurements @100kHz
A
IM3 Third order intermodulation product
=+2, V
VCL
R
=150Ω to GND
L
Fin1=180kHz, Fin2=280KHz
out
=2Vpp
-68 dBc
spurious measurements @400kHz
A
=+2, RL=150Ω to GND
∆G Differential gain
Df Differential phase
Gf Gain Flatness F=DC to 6MHz, A
VCL
F=4.5MHz, V
=+2, RL=150Ω to GND
A
VCL
F=4.5MHz, V
out
out
=2Vpp
=2Vpp
=+2 0.2 dB
VCL
0.5 %
0.5 °
Vo1/Vo2 Channel Separation F=1MHz to 10MHz 65 dB
dB
10/33

TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Electrical Characteristics
4.1 Standby mode
+
Table 6. V
CC
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
V
I
CC STBY
Z
T
Standby Low Level V
low
Standby High Level (V
high
Current Consumption per Operator
when STANDBY is Active
Output Impedance (R
out
Time from Standby Mode to Active
on
Mode
, V
CC
-
, T
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
pin 8 (TSH71) to V
pin 1,2 or 3 (TSH73) to V
pin 8 (TSH75) to V
pin 9 (TSH75) to V
R
out
//C
out
)
out
C
out
CC
CC
CC
-
(V
-
CC
-
+2) (V
CC
-
-
CC
+
-
20 55 µA
10
17
CC
+0.8)
CC
V
+
)V
MΩ
pF
2 µs
T
Time from Active Mode to Standby
off
Mode
Down to I
CC STBY
= 10µA10µs
TSH71 STANDBY CONTROL pin 8 (STBY) OPERATOR STATUS
V
low
V
high
Standby
Active
TSH73 STANDBY CONTROL OPERATOR STATUS
pin 1
OP1)
(STBY
V
low
V
high
xV
xV
pin 2
(STBY OP2)
x x Standby x x
xxActivexx
low
high
xxV
xxV
pin 3
(STBY OP3)
OP1 OP1 OP3
x x Standby x
xActivex
low
high
x x Standby
xxActive
TSH75 STANDBY CONTROL OPERATOR STATUS
pin 8
(STBY OP2)
V
high
V
high
V
low
V
low
pin 9
(STBY
V
V
V
V
OP3)
low
high
low
high
OP1 OP2 OP3 OP4
Active Standby Standby Active
Active Standby Active Active
Active Active Standby Active
Active Active Active Active
11/33

Electrical Characteristics TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
4.2 Characteristic curves for VCC=3V
Figure 2. Closed loop gain and phase vs.
frequency (Gain = +2, V
R
= 150Ω, T
10
5
0
-5
Gain (dB)
-10
-15
-20
1E+4 1E+5 1E+6 1E+7 1E +8 1E+9
L
Gain
Phase
Frequency (Hz)
amb
= 25°C)
= ±1.5V,
CC
200
100
0
Phase (°)
-100
-200
Figure 4. Closed loop gain and phase vs.
200
150
100
50
0
-50
= ±1.5V,
CC
Phase (°)
frequency (Gain = -10, V
R
= 150Ω, T
30
20
10
Gain (dB)
0
L
Gain
amb
Phase
= 25°C)
Figure 3. Overshoot function of output
= ±1.5V,
CC
10
5
Gain (dB)
0
-5
1E+6 1E+7
capacitance (Gain = +2, V
T
= 25°C)
amb
150Ω//33pF
150Ω//22pF
150Ω//10pF
150
Ω
1E+8 1E+9
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 5. Closed loop gain and phase vs.
frequency (Gain = +11, V
R
= 150Ω, T
30
20
10
Gain (dB)
0
L
Gain
amb
Phase
= 25°C)
= ±1.5V,
CC
0
-50
-100
Phase (°)
-10
1E+4 1E+5 1E+6 1E+7 1E+8 1E+9
Frequency (Hz)
-100
Figure 6. Large signal measurement -
positive slew rate (Gain = 2,
V
=±1.5V, ZL=150Ω//5.6pF)
1
0.5
0
Vout (V)
-0.5
-1
0 102030405060
12/33
CC
Time (ns)
-10
1E+4 1E+5 1E+6 1E+7 1E+8 1E+9
Frequency (Hz)
-150
Figure 7. Large signal measurement -
negative slew rate (Gain = 2,
VCC=±1.5V, ZL = 150Ω//5.6pF)
1
0.5
0
Vout (V)
-0.5
-1
0102030
Time (ns)
50
40

TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Electrical Characteristics
Figure 8. Small signal measurement - rise
time (Gain = 2, V
Z
= 150Ω)
0.06
0.04
0.02
0
Vin, Vout (V)
-0.02
-0.04
-0.06
L
Vin
0 102030405060
Vout
Time (ns)
= ±1.5V,
CC
Figure 10. Channel separation (Xtalk) vs.
frequency (measurement
configuration: Xtalk = 20log (V0/V1))
VIN
+
+
49.9Ω
-
49.9
100
Ω
100Ω
-
Ω
1k
Ω
+
-
1kΩ
150Ω
150
V1
VO
Ω
Figure 9. Small signal measurement - fall time
(Gain = 2, V
0.06
0.04
0.02
0
Vin, Vout (V)
-0.02
-0.04
-0.06
0 10 2030405060
Vin
Time (ns)
= ±1.5V, ZL = 150Ω)
CC
Vout
Figure 11. Channel separation (Xtalk) vs.
frequency (Gain = +11, V
Z
= 150Ω//27pF)
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
Xtalk (dB)
-80
-90
-100
-110
1E+4 1E+5 1E+6 1E+7
L
3/1output
2/1output
Frequency (Hz)
4/1output
= 1.5V,
CC
Figure 12. Equivalent noise voltage
(Gain = 100, V
30
+
25
20
Hz)
√
15
en (nV/
10
5
0.1 1 10 100 1000
_
10k
100
Frequency (kHz)
= ±1.5V, No load)
CC
Figure 13. Maximum output swing
(Gain = 11, V
5
4
3
2
1
0
-1
Vin, Vout (V)
-2
-3
-4
-5
0.0E+0 5 .0E-2 1.0E-1 1.5E-1 2.0E-1
13/33
Vout
Vin
Time (ms)
= ±5V, RL = 150Ω)
CC

Electrical Characteristics TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
Figure 14. Standby mode - Ton, T
off
(VCC = ±1.5V, open loop)
2
1
0
Vin, Vout (V)
-1
-2
Vin
Vout
Ton
0 2E-6 4E-6 6E-6 8E-6 1E-5
Standby
Time (s)
Toff
Figure 16. Third order intermodulation
(Gain = 2, VCC = ±1.5V,
=150Ω//27pF, T
Z
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
IM3 (dBc)
-70
-80
-90
-100
L
80kHz
740kHz
640kHz
380kHz
01234
Vout peak(V)
1. Note on intermodulation products:
The IFR2026 synthesizer generates a two tones signal
(F1=180kHz, F2=280kHz); each tone having the same
amplitude level.
The HP3585 spectrum analyzer measures the
intermodulation products function of the output voltage.
The generator and the spectrum analyzer are phase
locked for precision considerations.
amb
= 25°C)
(1)
Figure 15. Group delay gain = 2
= 150Ω//27pF, T
Z
Gain
Group
Delay
L
5.87ns
amb
(VCC = ±1.5V,
= 25°C)
14/33

TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Electrical Characteristics
4.3 Characteristic curves for VCC=5V
Figure 17. Closed loop gain and phase vs.
frequency
= 150Ω, T
R
10
L
(Gain = +2, VCC = ±2.5V,
= 25°C)
amb
200
Figure 18. Overshoot function of output
capacitance
= 25°C)
T
10
amb
(Gain = +2, V
= ±2.5V,
CC
5
0
-5
Gain (dB)
-10
-15
1E+4 1E+5 1E+6 1E+7 1E+8 1E+9
Gain
Phase
Frequency (Hz)
100
0
Phase (°)
-100
-200
Figure 19. Closed loop gain and phase vs.
frequency
= 150Ω, T
R
30
20
10
Gain (dB)
0
L
Gain
(Gain = -10, V
= 25°C)
amb
Phase
200
150
100
50
0
-50
= ±2.5V,
CC
Phase (°)
150Ω//33pF
5
Gain (dB)
0
-5
1E+6 1E+7 1E+8 1E+9
150Ω
Frequency (Hz)
150Ω//22pF
150Ω//10pF
Figure 20. Closed loop gain and phase vs.
frequency
= 150Ω, T
R
30
20
10
Gain (dB )
0
L
Gain
(Gain = +11, V
= 25°C)
amb
Phase
0
-50
-100
= ±2.5V,
CC
Phase (°)
-10
1E+4 1E+5 1E+6 1E+7 1E+8 1E+9
Frequency (Hz)
-100
Figure 21. Large signal measurement - positive
slew rate
= 150Ω//5.6pF)
Z
3
2
1
0
Vout (V)
-1
-2
-3
0 1020304050607080
L
(Gain = 2, V
Time (ns)
= ±2.5V,
CC
-10
1E+4 1E+5 1E+6 1E+7 1E+8 1E+9
Frequency (Hz)
-150
Figure 22. Large signal measurement -
negative slew rate
= ±2.5V, ZL = 150Ω//5.6pF)
V
3
2
1
0
Vout (V)
-1
-2
-3
0 10203040506070
15/33
CC
Time (ns)
(Gain = 2,

Electrical Characteristics TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
Figure 23. Small signal measurement - rise
time
(Gain = 2, VCC = ±2.5V,
= 150Ω)
Z
0.06
0.04
0.02
0
L
Vout
Vin
Vin, Vout (V)
-0.02
-0.04
-0.06
0 102030405060
Time (ns)
Figure 25. Channel separation (Xtalk) vs.
frequency
(measurement
configuration: Xtalk = 20log (V0/V1))
VIN
+
+
Ω
49.9
-
49.9Ω
-
100
+
-
100Ω
1kΩ
Ω
1kΩ
150
150
V1
Ω
VO
Ω
Figure 24. Small signal measurement - fall time
(Gain = 2, V
0.06
0.04
0.02
0
Vin Vout (V)
-0.02
-0.04
-0.06
0 102030405060
Vin
= ±2.5V, ZL= 150Ω)
CC
Vout
Time (ns)
Figure 26. Channel separation (Xtalk) vs.
frequency
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
Xtalk (dB)
-80
-90
-100
-110
1E+4 1E+5 1E+6 1E+7
= 150Ω//27pF)
Z
L
(Gain = +11, V
4/1output
3/1output
2/1output
Frequency (Hz)
= ±2.5V,
CC
Figure 27. Equivalent noise voltage
(Gain = 100, V
30
+
25
20
Hz)
√
15
en (nV/
10
5
0.1 1 10 100 1000
16/33
_
10k
100
Frequency (kHz)
= ±2.5V, no load)
CC
Figure 28. Maximum output swing
(Gain = 11, V
3
2
1
0
Vin, Vout (V)
-1
-2
-3
0.0E+0 5.0E-2 1. 0E-1 1.5E -1 2.0E-1
Vout
Vin
Time (ms)
= ±2.5V, RL = 150Ω)
CC

TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Electrical Characteristics
Figure 29. Standby mode - Ton, T
off
(VCC = ±2.5V, open loop)
3
2
1
0
-1
Vin, Vout (V)
-2
-3
Ton Toff
0 2E-64E-66E-68E-61E-5
Vout
Standby
Time (s)
Vin
Figure 31. Third order intermodulation
(Gain = 2, VCC = ±2.5V,
=150Ω//27pF, T
Z
80kHz
380kHz
L
740kHz
640kHz
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
IM3 (dBc)
-70
-80
-90
-100
01234
Vout peak(V)
1. Note on intermodulation products:
The IFR2026 synthesizer generates a two tones signal
(F1=180kHz, F2=280kHz); each tone having the same
amplitude level.
The HP3585 spectrum analyzer measures the
intermodulation products function of the output voltage.
The generator and the spectrum analyzer are phase
locked for precision considerations.
amb
= 25°C)
(1)
Figure 30. Group delay
= 150Ω//27pF, T
Z
L
Gain
Group
Delay
5.32ns
(Gain = 2, VCC = ±2.5V,
= 25°C)
amb
17/33

Electrical Characteristics TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
)
4.4 Characteristic curves for VCC=10V
Figure 32. Closed loop gain and phase vs.
frequency
= 150Ω, T
R
10
5
0
-5
Gain (dB)
-10
-15
1E+4 1E+5 1E +6 1E+7 1 E+8 1E+9
L
Frequency (Hz)
(Gain = +2, V
= 25°C)
amb
Gain
Phase
200
100
0
-100
-200
CC
= ±5V,
Phase (°)
Figure 34. Closed loop gain and phase vs.
frequency
= 150Ω, T
R
30
20
10
Gain (dB)
0
L
Gain
(Gain = -10, V
= 25°C)
amb
Phase
CC
200
150
100
50
0
= ±5V,
Phase (°)
Figure 33. Overshoot function of output
capacitance
= 25°C)
T
10
5
Gain (dB)
0
-5
1E+6 1E+ 7 1E+8 1E+9
amb
Ω
150
Frequency (Hz)
(Gain = +2, V
150Ω//33pF
150Ω//22pF
150Ω//10p F
CC
= ±5V,
Figure 35. Closed Loop Gain and Phase vs.
Frequency
= 150Ω, T
R
30
20
10
Gain (dB)
0
L
Gain
(Gain = +11, V
= 25°C)
amb
Phase
CC
0
-50
-100
= ±5V,
Phase (°)
-10
1E+4 1E+5 1E+6
1E+7 1E+8
Frequency (Hz)
-50
1E+9
Figure 36. Large signal measurement - positive
slew rate
Z
5
4
3
2
1
0
Vout (V)
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
0 20406080100
18/33
L
(Gain = 2,V
= 150Ω//5.6pF)
Time (ns)
CC
= ±5V,
-10
1E+4 1E+5 1E+6 1E+7 1E+8 1E+9
Frequency (Hz
-150
Figure 37. Large Signal Measurement -
Negative Slew Rate
= ±5V, ZL = 150Ω//5.6pF)
V
5
4
3
2
1
0
Vout (V)
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
0 20406080100
CC
Time (ns)
(Gain = 2

TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Electrical Characteristics
Figure 38. Small signal measurement - rise
time
(Gain = 2, V
0.06
0.04
0.02
0
Vin, Vout (V)
-0.02
-0.04
-0.06
0 102030405060
Vin
Vout
Time (ns)
= ±5V, ZL = 150Ω)
CC
Figure 40. Channel separation (Xtalk) vs.
frequency
(measurement
configuration: Xtalk = 20log(V0/V1))
VIN
+
+
49.9Ω
-
49.9
100
Ω
100
-
Ω
1k
Ω
+
-
Ω
1k
Ω
V1
150Ω
VO
150Ω
Figure 39. Small signal measurement - fall time
(Gain = 2, V
0.06
0.04
0.02
0
Vin, Vout (V)
-0.02
-0.04
-0.06
0 102030405060
Vin
= ±5V, ZL = 150Ω)
CC
Vout
Time (ns)
Figure 41. Channel separation (Xtalk) vs.
frequency
= 150Ω//27pF)
Z
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
Xtalk (dB)
-80
-90
-100
-110
1E+4 1E+5 1E+6
L
(Gain = +11, V
3/1output
Frequency (Hz)
2/1output
CC
4/1output
= ±5V,
1E+7
Figure 42. Equivalent noise voltage
(Gain =100, V
30
25
20
Hz)
√
15
en (nV/
10
5
0.1 1 10 100 1000
+
_
10k
100
Frequency (kHz)
= ±5V, no load)
CC
Figure 43. Maximum output swing
(Gain = 11, V
5
4
3
2
1
0
-1
Vin, Vout (V)
-2
-3
-4
-5
0.0E+0 5.0E-2 1.0E-1 1.5E-1 2.0E-1
19/33
Vout
Vin
Time (ms)
= ±5V, RL = 150Ω)
CC

Electrical Characteristics TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
Figure 44. Standby mode - Ton, T
off
(VCC = ±5V, open loop)
Vin
5
Vout
0
Vin, Vout (V)
-5
Ton Toff
0 2E-6 4E-6 6E-6 8E-6
Standby
Time (s)
Figure 46. Third order intermodulation
(Gain = 2, VCC = ±5V,
= 150Ω//27pF, T
Z
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
IM3 (dBc)
-70
-80
-90
-100
L
740kHz
640kHz
01234
Vout peak(V)
1. Note on intermodulation products:
The IFR2026 synthesizer generates a two tones signal
(F1=180kHz, F2=280kHz); each tone having the same
amplitude level.
The HP3585 spectrum analyzer measures the
intermodulation products function of the output voltage.
The generator and the spectrum analyzer are phase
locked for precision considerations.
.
amb
= 25°C
(1)
80kHz
380kHz
Figure 45. Group Delay
= 150Ω//27pF, T
Z
L
Gain
Group
Delay
5.1ns
(Gain = 2, VCC= ±5V
= 25°C)
amb
20/33

TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Testing Conditions
5 Testing Conditions
5.1 Layout precautions
To use the TSH7X circuits in the best manner at high frequencies, some precautions have to
be taken for power supplies:
– First of all, the implementation of a proper ground plane in both sides of the PCB is
mandatory for high speed circuit applications to provide low inductance and low
resistance common return.
– Power supply bypass capacitors (4.7uF and ceramic 100pF) should be placed as
close as possible to the IC pins in order to improve high frequency bypassing and
reduce harmonic distortion. The power supply capacitors must be incorporated for
both the negative and the positive pins.
● Proper termination of all inputs and outputs must be in accordance with output
termination resistors; in this way, the amplifier load will be resistive only, and the
stability of the amplifier will be improved.
● All leads must be wide and as short as possible (especially for op-amp inputs and
outputs) in order to decrease parasitic capacitance and inductance.
● For lower gain applications, care should be taken to avoid large feedback resistance
Ω) in order to reduce the time constant of parasitic capacitances.
(>1k
● Choose component sizes as small as possible (SMD).
● Finally, on output, the load capacitance must be negligible to maintain good stability.
You can put a serial resistance as close as possible to the output pin to minimize
capacitance.
5.2 Maximum input level
Figure 47. CCIR330 video line
The input level must not exceed the following values:
● negative peak: must be greater than -V
● positive peak value: must be lower than +V
+400mV.
CC
CC
-400mV.
21/33

Testing Conditions TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
The electrical characteristics show the influence of the load on this parameter.
5.3 Video capabilities
To characterize the differential phase and differential gain, a CCIR330 video line is used.
The video line contains 5 (flat) levels of luma on which is superimposed chroma signal. The
first level contains no luma. The luma gives various amplitudes which define the saturation
of the signal. The chrominance gives various phases which define the color of the signal.
Differential phase (respectively differential gain) distortion is present if a signal chrominance
phase (gain) is affected by luminance level. They represent the ability to uniformly process
the high frequency information at all luminance levels.
When differential gain is present, color saturation is not correctly reproduced.
The input generator is the Rohde & Schwarz CCVS. The output measurement was done by
the Rohde and Schwarz VSA.
Figure 48. Measurement on Rohde and Schwarz VSA
Table 7. Video results
Parameter
Lum NL 0.1 0.3 %
Lum NL Step 1 100 100 %
Lum NL Step 2 100 99.9 %
Lum NL Step 3 99.9 99.8 %
Lum NL Step 4 99.9 99.9 %
Lum NL Step 5 99.9 99.7 %
Diff Gain pos 0 0 %
Diff Gain neg -0.7 -0.6 %
Diff Gain pp 0.7 0.6 %
22/33
V
CC
Value
= ±2.5V
V
CC
Value
= ±5V
Unit

TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Testing Conditions
Table 7. Video results
Parameter
Diff Gain Step1 -0.5 -0.3 %
Diff Gain Step2 -0.7 -0.6 %
Diff Gain Step3 -0.3 -0.5 %
Diff Gain Step4 -0.1 -0.3 %
Diff Gain Step5 -0.4 -0.5 %
Diff Phase pos 0 0.1 deg
Diff Phase neg -0.2 -0.4 deg
Diff Phase pp 0.2 0.5 deg
Diff Phase Step1 -0.2 -0.4 deg
Diff Phase Step2 -0.1 -0.4 deg
Diff Phase Step3 -0.1 -0.3 deg
Diff Phase Step4 0 0.1 deg
Diff Phase Step5 -0.2 -0.1 deg
V
CC
Value
= ±2.5V
V
CC
Value
= ±5V
5.4 Precautions when operating on an asymmetrical supply
Unit
The TSH7X can be used with either a dual or a single supply. If a single supply is used, the
inputs are biased to the mid-supply voltage (+V
/2). This bias network must be carefully
CC
designed, in order to reject any noise present on the supply rail.
As the bias current is 15uA, you must carefully choose the resistance R1 so as not to
introduce an offset mismatch at the amplifier inputs.
Figure 49. Schematic of asymmetrical (single) supply
C
IN
in
R1
R2
R3
Vcc+
C1C3C2
+
-
R5
Cf
C
out
OUT
R
L
R4
R1 = 10KΩ is a typical and convenient value. C1, C2, C3 are bypass capacitors that filter
perturbations on V
, as well as for the input and output signals. We choose C1 = 100nF
CC
and C2 = C3 = 100uF.
R2, R3 are such that the current through them must be greater than 100 times the bias
current. Therefore, we set R2 = R3 = 4.7K
Ω.
23/33

Testing Conditions TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
Cin, as C
By taking R1 = 10K
, is chosen to filter the DC signal by the low-pass filters (R1,Cin and R
out
Ω, R
= 150Ω, and Cin= 2uF, C
L
=220uF we provide a cut-off frequency
out
below 10Hz.
Figure 50. Use of the TSH7x in gain = -1 configuration
C
f
1k
C
IN
in
R1
R2
1k
Vcc+
-
+
C
out
OUT
R
L
R3 C1C3C2
Some precautions must be taken, especially for low-power supply applications.
A feedback capacitance, C
impact of the capacitance C
, should be added for better stability.
f
on the phase margin of the circuit.
f
Table 8
summarizes the
out
, C
out
).
Table 8. Impact capacitance C
Parameter Cf (pF) V
Phase Margin
0
f-3dB 40 39.3 38.3 MHz
Phase Margin
5.6
f-3dB 40 39.3 38.3 MHz
Phase Margin
22
f-3dB 37 34 32 MHz
Phase Margin
33
f-3dB 33.7 30.7 27.6 MHz
f
= ±1.5V VCC = ±2.5V VCC = ±5V Unit
CC
28 43 56 deg
30 43 56 deg
37 52 67 deg
48 65 78 deg
24/33

TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Package Mechanical Data
6 Package Mechanical Data
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in ECOPACK®
packages. These packages have a Lead-free second level interconnect. The category of
second level interconnect is marked on the package and on the inner box label, in
compliance with JEDEC Standard JESD97. The maximum ratings related to soldering
conditions are also marked on the inner box label. ECOPACK is an ST trademark.
ECOPACK specifications are available at: www.st.com
6.1 SO-8 Package
SO-8 MECHANICAL DATA
.
DIM.
A 1.35 1.75 0.053 0.069
A1 0.10 0.25 0.04 0.010
A2 1.10 1.65 0.043 0.065
B 0.33 0.51 0.013 0.020
C 0.19 0.25 0.007 0.010
D 4.80 5.00 0.189 0.197
E 3.80 4.00 0.150 0.157
e 1.27 0.050
H 5.80 6.20 0.228 0.244
h 0.25 0.50 0.010 0.020
L 0.40 1.27 0.016 0.050
k ˚ (max.)
ddd 0.1 0.04
MIN. TYP MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
mm. inch
8
0016023/C
25/33

Package Mechanical Data TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
6.2 TSSOP8 Package
TSSOP8 MECHANICAL DATA
DIM.
A 1.2 0.047
A1 0.05 0.15 0.002 0.00 6
A2 0.80 1.00 1.05 0.031 0 .039 0.041
b 0.19 0.30 0.007 0.01 2
c 0.09 0.20 0.004 0.008
D 2.90 3.00 3.10 0.11 4 0 .118 0.122
E 6 .20 6.40 6.60 0.244 0.252 0.260
E1 4.30 4.40 4.50 0.169 0 .173 0.177
e 0.65 0.0256
K0˚ 8˚0˚ 8˚
L 0.45 0.60 0.75 0.01 8 0 .024 0.030
L1 1 0.039
MIN. TYP MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
mm. inch
26/33
0079397/D

TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Package Mechanical Data
6.3 SO-14 Package
SO-14 MECHANICAL DATA
DIM.
A 1.75 0.068
a1 0.1 0.2 0.003 0.007
a2 1.65 0.064
b 0.35 0.46 0.013 0.018
b1 0.19 0.25 0.007 0.010
C 0.5 0.019
c1 45˚ (typ.)
D 8.55 8.75 0.336 0.344
E 5.8 6.2 0.228 0.244
e 1.27 0.050
e3 7.62 0.300
F 3.8 4.0 0.149 0.157
G 4.6 5. 3 0.181 0.208
L 0.5 1.27 0.019 0.050
M 0.68 0.026
S˚ (max.)
MIN. TYP MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
mm. inch
8
PO13G
27/33

Package Mechanical Data TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
6.4 TSSOP14 Package
TSSOP14 MECHANICAL DATA
DIM.
A 1.2 0.047
A1 0.05 0.15 0.002 0.004 0.006
A2 0.8 1 1.05 0.031 0.039 0.041
b 0.19 0.30 0.007 0.012
c 0.09 0.20 0.004 0.0089
D 4.9 5 5.1 0.193 0.197 0.201
E 6.2 6.4 6.6 0.244 0.252 0.260
E1 4.3 4.4 4.48 0.169 0.173 0. 176
e 0.65 BSC 0.0256 BSC
K0˚ 8˚0˚ 8˚
L 0.45 0.60 0.75 0.018 0.024 0.030
MIN. TYP MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
A2
A
A1
mm. inch
b
e
c
K
L
E
PIN 1 IDENTIFICATION
D
E1
1
0080337D
28/33

TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Package Mechanical Data
6.5 SO-16 Package
SO-16 MECHANICAL DATA
DIM.
A 1.75 0.068
a1 0.1 0.2 0.004 0.008
a2 1.65 0.064
b 0.35 0.46 0.013 0.018
b1 0.19 0.25 0.007 0.010
C 0.5 0.019
c1 45˚ (typ.)
D 9.8 10 0.385 0.393
E 5.8 6.2 0.228 0.244
e 1.27 0.050
e3 8.89 0.350
F 3.8 4.0 0.149 0.157
G 4.6 5. 3 0.181 0.208
L 0.5 1.27 0.019 0.050
M 0.62 0.024
S8 ˚ (max.)
MIN. TYP MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
mm. inch
PO13H
29/33

Package Mechanical Data TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
6.6 TSSOP16 Package
TSSOP16 MECHANICAL DATA
DIM.
A 1.2 0.047
A1 0.05 0.15 0.002 0.004 0.006
A2 0.8 1 1.05 0.031 0.039 0.041
b 0.19 0.30 0.007 0.012
c 0.09 0.20 0.004 0.0079
D 4.9 5 5.1 0.193 0.197 0.201
E 6.2 6.4 6.6 0.244 0.252 0.260
E1 4.3 4.4 4.48 0.169 0.173 0. 176
e 0.65 BSC 0.0256 BSC
K0˚ 8˚0˚ 8˚
L 0.45 0.60 0.75 0.018 0.024 0.030
MIN. TYP MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
A2
A
A1
mm. inch
b
e
c
K
L
E
PIN 1 IDENTIFICATION
D
E1
1
0080338D
30/33

TSH70,71,72,73,74,75 Package Mechanical Data
6.7 SOT23-5 Package
SOT23-5L MECHANICAL DATA
DIM.
MIN. TYP MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
A 0.90 1.45 35.4 57.1
A1 0.00 0.15 0.0 5.9
A2 0.90 1.30 35.4 51.2
b 0.35 0.50 13.7 19.7
C 0.09 0.20 3.5 7.8
D 2.80 3.00 110.2 118.1
E 2.60 3.00 102.3 118.1
E1 1.50 1.75 59.0 68.8
e.95 37.4
e1 1.9 74.8
L 0.35 0.55 13.7 21.6
mm. mils
0
31/33

Revision History TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
7 Revision History
Table 9. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
Nov. 2000 1 First Release.
Aug. 2002 2
May 2006 3
Limit min. of I
from 24mA to 20mA (only on 3V power
sink
supply).
Reason: yield improvement.
Improvement of VOL max. at 3V and 5V power supply on 150ohm load connected to GND (pages 6 and 8).
Reason: TSH7x can drive video signals from DACs to lines in
single supply (3V or 5V) without any DC level change of the
video signals.
Grammatical and typographical changes throughout.
Package mechanical data updated.
32/33

TSH70,71,72,73,74,75
y
y
Please Read Carefully:
Informatio n in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at an
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZE REPRESENTATIVE OF ST, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED,
AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING APPLICATIONS,
NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS, WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY, DEATH, OR
SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, an
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2006 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
33/33
 Loading...
Loading...