
4 x 50 W differential quad power amplifier
Features
■ Multipower BCD technology
■ MOSFET output power stage
■ DMOS power output
■ Differential Input
■ New high efficiency (class SB)
■ High output power capability 4x28 W/4 Ω @
14.4 V, 1 kHz, 10% THD, 4x50 W MAX power
■ Max. output power 4x72 W/2 Ω
■ Full I
■ Operates both in I
■ Two selectable I
■ Full fault protection
■ DC offset detection
■ Four independent short circuit protection
■ Clipping detector pin with selectable threshold
■ Standby/mute pin
■ Linear thermal shutdown with multiple thermal
■ ESD protection
Table 1. Device summary
2
C bus driving:
– Standby
– Independent front/rear soft play/mute
– Selectable gain 26 dB /16 dB (for low noise
line output function)
– High efficiency enable/disable
2
–I
C bus digital diagnostics (including DC
and AC load detection)
2
C and non-I2C bus mode
2
C bus addresses
(2 %/10 %)
warning
TDA7567PD
with built-in diagnostics features
PowerSO36
Description
The TDA7567PD is a new BCD technology quad
bridge power amplifier in PowerSO36 package
specially intended for automotive applications.
Thanks to the DMOS output stage the
TDA7567PD has a very low distortion allowing a
clear powerful sound. Among the features, its
superior efficiency performance coming from the
internal exclusive structure, makes it the most
suitable device to simplify the thermal
management in high power sets.
The dissipated output power under average
listening condition is in fact reduced up to 50 %
when compared to the level provided by
conventional class AB solutions.
This device is equipped with a full diagnostics
array that communicates the status of each
speaker through the I
2
The I
C bus can be disabled and the device can
be controlled by standby/mute pin.
2
C bus.
Order code Package Packing
TDA7567PD PowerSO36 Tube
TDA7567PDTR PowerSO36 Tape and reel
December 2009 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 1/30
www.st.com
1

Contents TDA7567PD
Contents
1 Block, application and pins connection diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Electrical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.1 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2 Thermal data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.3 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3 Diagnostics functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.1 Turn-on diagnostic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.2 Permanent diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
3.3 Output DC offset detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.4 AC diagnostic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4 Multiple faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4.1 Faults availability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5 Thermal protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6 Fast muting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
7 Address selection and I2C disable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
8I
2
C bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
8.1 I2C programming/reading sequences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
8.2 I
2
C bus interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
8.2.1 Data validity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
8.2.2 Start and stop conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
8.2.3 Byte format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
8.2.4 Acknowledge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
9 Software specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
10 Examples of bytes sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1

TDA7567PD Contents
11 Package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
12 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 3/30

List of tables TDA7567PD
List of tables
Table 2. Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 3. Thermal Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 4. Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 5. Double fault table for turn-on diagnostic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 6. IB1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 7. IB2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 8. DB1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 9. DB2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 10. DB3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 11. DB4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 12. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1

TDA7567PD List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 2. Application diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 3. Pins connection diagram (top of view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 4. ITU R-ARM frequency response, weighting filter for transient pop. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 5. Turn-on diagnostic: working principle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 6. SVR and output behavior (case 1: without turn-on diagnostic). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 7. SVR and output pin behavior (case 2: with turn-on diagnostic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 8. Short circuit detection thresholds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 9. Load detection thresholds - high gain setting 26 dB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 10. Load detection thresholds - low gain setting 16 dB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 11. Restart timing without diagnostic enable (permanent) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 12. Restart timing with diagnostic enable (permanent). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 13. Current detection high: load impedance |Z| vs. output peak voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 14. Current detection low: load impedance |Z| vs. output peak voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 15. Thermal foldback diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 16. Data validity on the I
Figure 17. Timing diagram on the I
Figure 18. Acknowledge on the I
Figure 19. PowerSO36 (slug up) mechanical data and package dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2
C bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2
C bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2
C bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 5/30
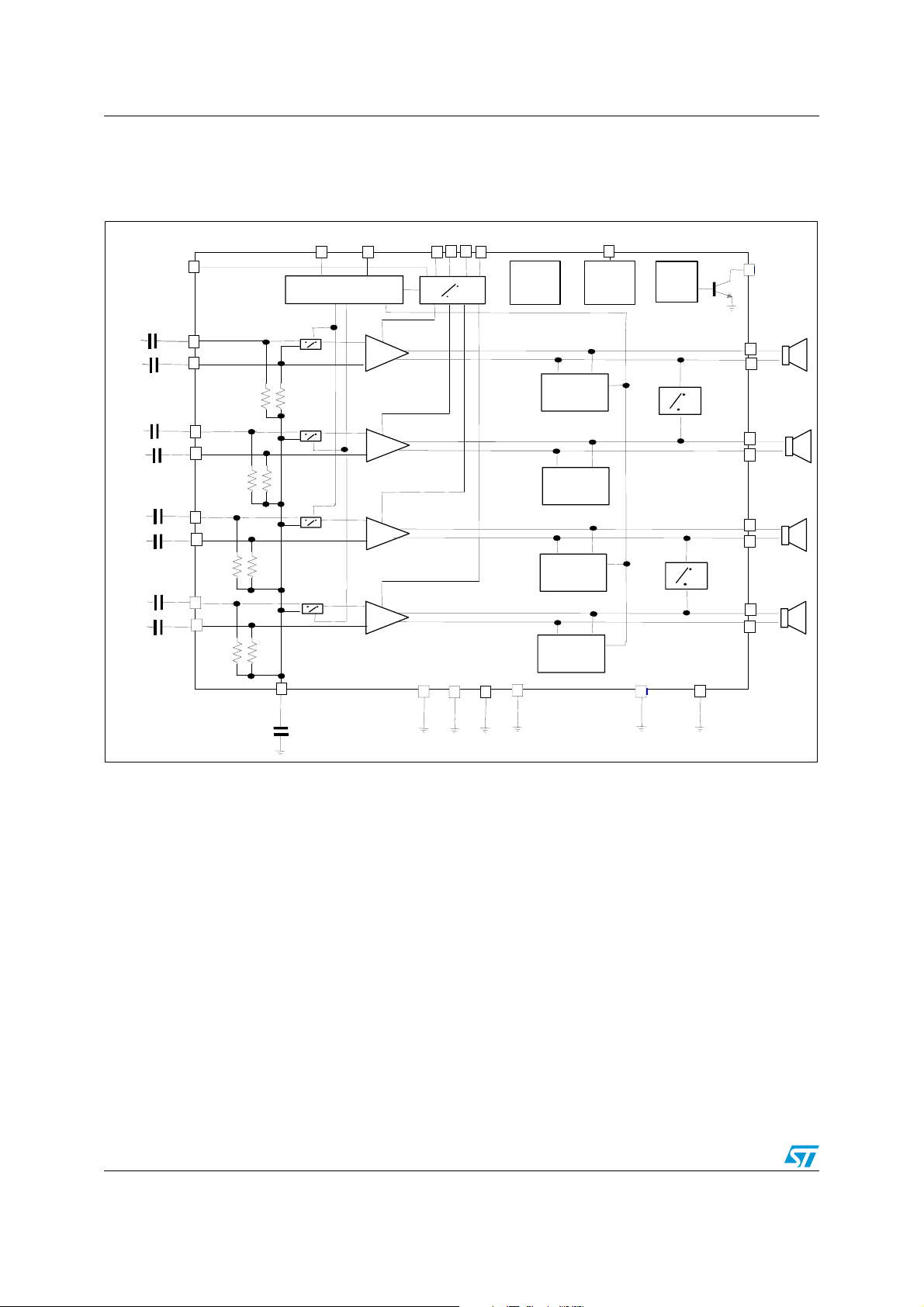
Block, application and pins connection diagrams TDA7567PD
1 Block, application and pins connection diagrams
Figure 1. Block diagram
CLK
DATA
VCC
ADSEL/I2CDIS
IN 3 +
IN 3 -
IN 4 +
IN 4 -
IN 1 +
IN 1 -
IN 2+
IN 2 -
ST-BY/MUTE
SVR
I2CBUS
Mute1 Mute2
16/26dB
16/26dB
16/26dB
16/26dB
Thermal
Protection
& Dump
Short Circuit
Protection &
Diagnostic
Short Circuit
Protection &
Diagnostic
Short Circuit
Protection &
Diagnostic
Short Circuit
Protection &
Diagnostic
ADsel
TAB
Clip
Detector
CD
OUT 3+
OUT 3-
OUT 4+
OUT 4-
OUT 1+
OUT 1-
OUT 2+
OUT 2-
SGND
PWGND
6/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1

TDA7567PD Block, application and pins connection diagrams
r
Figure 2. Application diagram
C8
I2C BUS
I2C BUS
IN 3 +
IN 3 +
IN 4 +
IN 4 +
IN 4 -
IN 4 -
IN 1 +
IN 1 +
IN 1 -
IN 1 -
IN 2 +
IN 2 +
IN 2 -
IN 2 -
V(4V .. V
V(4V .. V
CC)
CC)
DATA
DATA
CLK
CLK
C1 0.22
C1 0.22
C2 0.22
C2 0.22
C3 0.22
C3 0.22
C4 0.22
C4 0.22
C5 0.22
C5 0.22
C6 0.22
C6 0.22
C7 0.22
C7 0.22
C8 0.22
C8 0.22
C8
0.1μF
0.1μF
S
S
μ
μ
μF
μF
μ
μ
μF
μF
μF
μF
μF
μF
SGND
SGND
B
B
T
T
F
F
F
F
μ
μ
F
F
μ
μ
F
F
C7
C7
3300μF
3300μF
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
+
Y
Y
11
11
7
7
2
2
31
31
32IN 3 -
32IN 3 -
30
30
28
28
25
25
23
23
27
27
26
26
29
29
S
S
C6
C6
10μF
10μF
19 36
19 36
24 18
24 18
R
R
V
V
CD
CD
612
612
+
33
33
34
34
35
35
-
-
+
+
3
3
4
4
8
8
-
-
+
+
22
22
21
21
20
20
-
-
+
+
15
15
13
13
10
10
-
-
9 ADSEL/I2CDIS
9 ADSEL/I2CDIS
TAB
TAB
1
1
47K
47K
V
V
OUT 3
OUT 3
OUT 4
OUT 4
OUT 1
OUT 1
OUT 2
OUT 2
Figure 3. Pins connection diagram (top of view)
VCC
OUT3-
PWGND
OUT3+
IN3-
IN3+
IN4+
SGND
IN4-
IN2+ 1027
IN2-
IN1+
SVR 1324
IN1-
OUT1+
PWGND
OUT1-
VCC
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
26
25
23
22
21
20
19
D06AU1641B
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
12
14
15
16
17
18
TAB
CK_HE-selector
OUT4+
PWGND
N.C.
VCC
DATA_Gain-selecto
OUT4-
ADSEL/I2CDIS
OUT2-
STBY
VCC
PWGND
N.C.
OUT2+
N.C.
N.C.
CD
Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 7/30

Electrical specifications TDA7567PD
2 Electrical specifications
2.1 Absolute maximum ratings
Table 2. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
V
T
V
V
peak
V
DATA
I
I
P
stg
Operating supply voltage 18 V
op
DC supply voltage 28 V
S
Peak supply voltage (for t = 50 ms) 50 V
CK pin voltage 6 V
CK
Data pin voltage 6 V
Output peak current (not repetitive t = 100 ms) 8 A
O
Output peak current (repetitive f > 10 Hz) 6 A
O
Power dissipation T
tot
= 70 °C 85 W
case
, TjStorage and junction temperature -55 to 150 °C
2.2 Thermal data
Table 3. Thermal Data
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
R
th j-case
Thermal resistance junction-to-case Max. 1 °C/W
2.3 Electrical characteristics
Refer to the test circuit, VS = 14.4 V; RL = 4 Ω; f = 1 kHz; GV = 26 dB; T
= 25 °C; unless
amb
otherwise specified.
Table 4. Electrical characteristics
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Power amplifier
V
I
P
8/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1
S
d
O
Supply voltage range - 8 - 18 V
Total quiescent drain current - - 180 300 mA
Output power
MAX power (V
wave input (2 Vrms))
THD = 10 %
THD = 1 %
= 2 Ω; THD 10 %
R
L
= 2 Ω; THD 1 %
R
L
R
= 2 Ω; max. power
L
= 15.2 V, square
S
-50-W
25
20
28
22
-
50
-
40
-
75
W
W
W
W
W
TDA7567PD Electrical specifications
Table 4. Electrical characteristics (continued)
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
0.03
-
0.02
0.15
0.1
0.1
0.8
- 0.02 0.05 %
- - 30 µV
THD Total harmonic distortion
Cross talk f = 1 kHz to 10 kHz, Rg = 600 Ω 50 60 - dB
T
Input Impedance - 60 100 130 KΩ
Voltage gain 1 - 25 26 27 dB
Voltage gain match 1 - -1 - 1 dB
V1
Voltage gain 2 - 15 16 17 dB
Voltage gain match 2 - -1 - 1 dB
V2
Output noise voltage 1 Rg = 600 Ω 20 Hz to 22 kHz - - 100 µV
Output noise voltage 2
R
G
ΔG
G
ΔG
E
E
C
IN
V1
V2
IN1
IN2
SVR Supply voltage rejection
PO = 1 W to 10 W; STD MODE
HE MODE; P
HE MODE; P
= 1-10 W, f = 10 kHz - 0.2 0.5 %
P
O
= 16 dB; STD Mode
G
V
= 0.1 to 5 V
V
O
= 1.5 W
O
= 8 W
O
RMS
Rg = 600 Ω; GV = 16 dB
20 Hz to 22 kHz
f = 100 Hz to 10 kHz; V
= 600 Ω
R
g
= 1 Vpk;
r
50 60 - dB
BW Power bandwidth - 100 - - KHz
T
V
CD
CD
A
I
A
V
V
T
V
V
I
SB
SB
M
OS
AM
ON
OFF
SBY
MU
OP
MU
SAT
Standby attenuation - 90 110 - dB
Standby current V
= 0 - 1 10 µA
st-by
Mute attenuation - 80 100 - dB
Offset voltage Mute and play -70 0 70 mV
Min. supply mute threshold - 7 7.5 8 V
Turn ON delay D2/D1 (IB1) 0 to 1 - 15 40 ms
Turn OFF delay D2/D1 (IB1) 1 to 0 - 15 40 ms
Standby/mute pin for standby - 0 - 1.5 V
Standby/mute pin for mute - 3.5 - 5 V
Standby/mute pin for
operating
Standby/mute pin current
Clip det high leakage current CD off / VCD = 6 V - 0 5 μA
LK
-7-V
V
st-by/mute
V
st-by/mute
= 8.5 V - 20 40 μA
< 1.5 V - 0 5 μA
Clip det sat. voltage CD on; ICD = 1 mA - - 300 mV
S
D0 (IB1) = 1 5 10 15 %
CD
THD
Clip det THD level
D0 (IB1) = 0 1 2 3.5 %
%
%
%
V
Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 9/30

Electrical specifications TDA7567PD
Table 4. Electrical characteristics (continued)
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
ΔV
OS
During mute ON/OFF output
offset voltage
During standby ON/OFF
output offset voltage
ITU R-ARM weighted (full wave
rectified, standby pin linear
transition = 5.55 V to 6.45 V in 80
ms, @25 °C,
= 14.4V) see Figure 4
V
S
-7.5 - +7.5 mV
-7.5 - +7.5 mV
STD mode selector ADSEL pin floating - - 1.5 V
CK_HE
HE mode selector ADSEL pin floating 2.3 - V
High gain selector ADSEL pin floating - 1.5 V
DATA_gain
Low gain selector ADSEL pin floating 2.3 - - V
Turn on diagnostics 1 (power amplifier mode)
Short to GND det. (Below this
Pgnd
Pvs
Pnop
Lsc Shorted load det. - - 0.5 Ω
Lop Open load det. 85 - Ω
limit, the output is considered
in short circuit to GND)
Short to V
det. (Above this
S
limit, the output is considered
in short circuit to VS)
Normal operation
thresholds.(Within these
limits, the output is
considered without faults).
--1.2V
Vs -1.2 - - V
Power amplifier in standby
1.8 - Vs -1.8 V
Lnop Normal load det. 1.5 - 45 Ω
Turn on diagnostics 2 (line driver mode)
Short to GND det. (Below this
Pgnd
limit, the output is considered
Power amplifier in standby - - 1.2 V
in short circuit to GND)
Short to Vs det. (Above this
Pvs
limit, the output is considered
- Vs -1.2 - - V
in short circuit to VS)
Normal operation thresholds.
Pnop
(Within these limits, the
output is considered without
- 1.8 - Vs -1.8 V
faults).
Lsc Shorted Load det. - - - 1.5 Ω
Lop Open Load det. - 330 - - Ω
Lnop Normal Load det. - 7 - 180 Ω
Permanent diagnostics 2 (Power amplifier mode or line driver mode)
Pgnd
Short to GND det. (Below this
limit, the output is considered
in short circuit to GND)
Power amplifier in mute or play,
one or more short circuits
protection activated
--1.2V
10/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1

TDA7567PD Electrical specifications
Table 4. Electrical characteristics (continued)
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Short to Vs det. (Above this
Pvs
Pnop
limit, the output is considered
in short circuit to VS)
Normal operation thresholds.
(Within these limits, the
output is considered without
faults).
Vs -1.2 - - V
Power amplifier in mute or play,
one or more short circuits
protection activated
1.8 - Vs -1.8 V
L
SC
V
O
I
NLH
I
NLL
I
OLH
I
OLL
2
C bus interface
I
S
CL
V
IL
V
IH
Shorted load det.
Power amplifier mode - - 0.5 Ω
Line driver mode - - 1.5 Ω
Offset detection
Power amplifier in play,
AC Input signals = 0
±1.5 ±2 ±2.5 V
Normal load current detection VO < (VS - 5)pk IB2 (D7) = 0 500 - - mA
Normal load current detection VO < (VS - 5)pk IB2 (D7) = 1 300 - - mA
Open load current detection VO < (VS - 5)pk IB2 (D7) = 0 - - 250 mA
Open load current detection VO < (VS - 5)pk IB2 (D7) =1 - - 125 mA
Clock frequency - - - 400 kHz
Input low voltage - - - 1.5 V
Input high voltage - 2.3 - - V
Figure 4. ITU R-ARM frequency response, weighting filter for transient pop
Output attenuation (dB)
10
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
10 100 1000 10000 100000
Hz
Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 11/30
AC00343

Diagnostics functional description TDA7567PD
3 Diagnostics functional description
3.1 Turn-on diagnostic
It is activated at the turn-on (standby out) under I2C bus request. Detectable output faults
are:
● Short to GND
● Short to Vs
● Short across the speaker
● Open speaker
To verify if any of the above misconnections are in place, a subsonic (inaudible) current
pulse (Figure 5) is internally generated, sent through the speaker(s) and sunk back. The
turn-on diagnostic status is internally stored until a successive diagnostic pulse is requested
(after a I
If the "standby out" and "diagnostic enable" commands are both given through a single
programming step, the pulse takes place first (power stage still in standby mode, low,
outputs= high impedance).
Afterwards, when the amplifier is biased, the PERMANENT diagnostic takes place. The
previous turn-on state is kept until a short appears at the outputs.
2
C reading).
Figure 5. Turn-on diagnostic: working principle
Vs~5V
Isource
CH+
CH-
Isink
I (mA)
Isource
Isink
~100mS
Measure time
t (ms)
Figure 6 and 7 show SVR and output waveforms at the turn-on (standby out) with and
without turn-on diagnostic.
Figure 6. SVR and output behavior (case 1: without turn-on diagnostic)
Vsvr
Out
Permanent diagnostic
acquisition time (100mS Typ)
Bias (power amp turn-on)
Diagnostic Enable
(Permanent)
FAULT
event
Read Data
t
I2CB DATA
12/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1
Permanent Diagnostics data (output)
permitted time

TDA7567PD Diagnostics functional description
Figure 7. SVR and output pin behavior (case 2: with turn-on diagnostic)
Vsvr
Out
Turn-on diagnostic
acquisition time (100mS Typ)
Permanent diagnostic
acquisition time (100mS Typ)
I2CB DATA
Diagnostic Enable
(Turn-on)
Bias (power amp turn-on)
permitted time
Turn-on Diagnostics data (output)
permitted time
Read Data
Diagnostic Enable
(Permanent)
Permanent Diagnostics data (output)
FAULT
event
permitted time
The information related to the outputs status is read and memorized at the end of the
current pulse top. The acquisition time is 100 ms (typ.). No audible noise is generated in the
process. As for short to GND / Vs the fault-detection thresholds remain unchanged from 26
dB to 16 dB gain setting. They are as follows:
Figure 8. Short circuit detection thresholds
t
S.C. to GND x S.C. to Vs
0V 1.8V VS-1.8V V
1.2V VS-1.2V
xNormal Operation
D01AU1253
S
Concerning short across the speaker / open speaker, the threshold varies from 26 dB to
16 dB gain setting, since different loads are expected (either normal speaker's impedance
or high impedance). The values in case of 26 dB gain are as follows:
Figure 9. Load detection thresholds - high gain setting 26 dB
S.C. across Load x Open Load
0V 1.5Ω
If the line driver mode (G
0.5Ω
= 16 dB and line driver mode diagnostic = 1) is selected, the
v
45Ω
xNormal Operation
85Ω
AC00060
same thresholds will change as follows:
Figure 10. Load detection thresholds - low gain setting 16 dB
S.C. across Load x Open Load
0Ω 7Ω 180Ω infinite
1.5Ω 330Ω
Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 13/30
xNormal Operation
Infinite

Diagnostics functional description TDA7567PD
3.2 Permanent diagnostics
Detectable conventional faults are:
– Short to GND
–Short to Vs
– Short across the speaker
The following additional features are provided:
– Output offset detection
The TDA7567PD has 2 operating status:
1. RESTART mode. The diagnostic is not enabled. Each audio channel operates
independently from each other. If any of the a.m. faults occurs, only the channel(s)
interested is shut down. A check of the output status is made every 1 ms (Figure 11).
Restart takes place when the overload is removed.
2. DIAGNOSTIC mode. It is enabled via I
(such to cause the intervention of the short-circuit protection) occurs to the speakers
outputs. Once activated, the diagnostics procedure develops as follows (Figure 12):
– To avoid momentary re-circulation spikes from giving erroneous diagnostics, a
check of the output status is made after 1ms: if normal situation (no overloads) is
detected, the diagnostic is not performed and the channel returns back active.
– Instead, if an overload is detected during the check after 1 ms, then a diagnostic
cycle having a duration of about 100 ms is started.
– After a diagnostic cycle, the audio channel interested by the fault is switched to
RESTART mode. The relevant data are stored inside the device and can be read
by the microprocessor. When one cycle has terminated, the next one is activated
2
by an I
C reading. This is to ensure continuous diagnostics throughout the car-
radio operating time.
– To check the status of the device a sampling system is needed. The timing is
chosen at microprocessor level (over half a second is recommended).
2
C bus and self activates if an output overload
Figure 11. Restart timing without diagnostic enable (permanent) - Each 1ms time, a
sampling of the fault is done
1-2mS
Overcurrent and short
circuit protection intervention
(i.e. short circuit to GND)
1mS 1mS 1mS
Figure 12. Restart timing with diagnostic enable (permanent)
1-2mS 100/200mS 1mS1mS
Overcurrent and short
circuit protection intervention
(i.e. short circuit to GND)
14/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1
1mS
Out
t
Short circuit removed
t
Short circuit removed

TDA7567PD Diagnostics functional description
3.3 Output DC offset detection
Any DC output offset exceeding ±2 V are signalled out. This inconvenient might occur as a
consequence of initially defective or aged and worn-out input capacitors feeding a DC
component to the inputs, so putting the speakers at risk of overheating.
This diagnostic has to be performed with low-level output AC signal (or V
The test is run with selectable time duration by microprocessor (from a "start" to a "stop"
command):
– START = Last reading operation or setting IB1 - D5 - (OFFSET enable) to 1
– STOP = Actual reading operation
Excess offset is signalled out if persistent throughout the assigned testing time. This feature
is disabled if any overloads leading to activation of the short-circuit protection occurs in the
process.
3.4 AC diagnostic
It is targeted at detecting accidental disconnection of tweeters in 2-way speaker and, more
in general, presence of capacitively (AC) coupled loads.
This diagnostic is based on the notion that the overall speaker's impedance (woofer +
parallel tweeter) will tend to increase towards high frequencies if the tweeter gets
disconnected, because the remaining speaker (woofer) would be out of its operating range
(high impedance). The diagnostic decision is made according to peak output current
thresholds, and it is enabled by setting (IB2-D2) = 1.
Two different detection levels are available:
● High current threshold IB2 (D7) = 0
– Iout > 500 mApk = NORMAL STATUS
– Iout < 300 mApk = OPEN TWEETER
● Low current threshold IB2 (D7) = 1
– Iout > 250 mApk = NORMAL STATUS
– Iout < 125 mApk = OPEN TWEETER
= 0).
in
To correctly implement this feature, it is necessary to briefly provide a signal tone (with the
amplifier in "play") whose frequency and magnitude are such to determine an output current
higher than 500 mApk with IB2(D7)=0 (higher than 250 mApk with IB2(D7)=1) in normal
conditions and lower than 250 mApk with IB2(D7)=0 (lower than 125 mApk with IB2(D7)=1)
should the parallel tweeter be missing.
The test has to last for a minimum number of 3 sine cycles starting from the activation of the
AC diagnostic function IB2<D2>) up to the I
2
C reading of the results (measuring period). To
confirm presence of tweeter, it is necessary to find at least 3 current pulses over the above
thresholds over all the measuring period, else an "open tweeter" message will be issued.
The frequency / magnitude setting of the test tone depends on the impedance
characteristics of each specific speaker being used, with or without the tweeter connected
(to be calculated case by case). High-frequency tones (> 10 kHz) or even ultrasonic signals
are recommended for their negligible acoustic impact and also to maximize the impedance
module's ratio between with tweeter-on and tweeter-off.
Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 15/30

Diagnostics functional description TDA7567PD
Figure 13 shows the load impedance as a function of the peak output voltage and the
relevant diagnostic fields.
This feature is disabled if any overloads leading to activation of the short-circuit protection
occurs in the process.
Figure 13. Current detection high: load impedance |Z| vs. output peak voltage
Load |z| (Ohm)
50
Low current detection area
30
D5 = 1 of the DBx byres
20
(Open load)
Iout (peak) <250mA
Iout (peak) >500mA
10
IB2(D7) = 0
5
3
2
1
12345678
High current detection area
(Normal load)
D5 = 0 of the DBx bytes
Vout (Peak)
Figure 14. Current detection low: load impedance |Z| vs. output peak voltage
Load |z| (Ohm)
50
Low current dete ction area
30
D5 = 1 of the DBx byres
20
10
5
3
2
1
0.5
(Open load)
1
1.5
High current detection area
(Normal load)
D5 = 0 of the DBx bytes
2
Vout (Peak)
2.5
3
3.5 4
Iout (peak) <125mA
Iout (peak) >250mA
IB2(D7) = 1
16/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1
TDA7567PD Multiple faults
4 Multiple faults
When more misconnections are simultaneously in place at the audio outputs, it is
guaranteed that at least one of them is initially read out. The others are notified after
successive cycles of I
This is true for both kinds of diagnostic (Turn-on and Permanent).
The table below shows all the couples of double-fault possible. It should be taken into
account that a short circuit with the 4 ohm speaker unconnected is considered as double
fault.
Table 5. Double fault table for turn-on diagnostic
2
C reading and faults removal, provided that the diagnostic is enabled.
S. GND (so) S. GND (sk) S. Vs S. Across L. Open L.
S. GND (so) S. GND S. GND
S. GND (sk) / S. GND S. Vs S. GND Open L. (*)
S. Vs / / S. Vs S. Vs S. Vs
S. Across L. / / / S. Across L. N.A.
Open L. / / / / Open L. (*)
S. GND (so) / S. GND (sk) in the above table make a distinction according to which of the 2
outputs is shorted to ground (test-current source side= so, test-current sink side = sk). More
precisely, in Channels CH3 and CH2, so = CH+, sk = CH-; in Channels CH4 and CH1, so =
CH-, sk = CH+.
In Permanent Diagnostic the table is the same, with only a difference concerning Open
Load(*), which is not among the recognizable faults. Should an Open Load be present
during the device's normal working, it would be detected at a subsequent Turn on Diagnostic
cycle (i.e. at the successive Car Radio Turn on).
4.1 Faults availability
All the results coming from I2Cb us, by read operations, are the consequence of
measurements inside a defined period of time. If the fault is stable throughout the whole
period, it will be sent out.
S. Vs + S.
GND
S. GND S. GND
To guarantee always resident functions, every kind of diagnostic cycles (Turn on,
Permanent, Offset) will be reactivate after any I
reads the I
2
C, a new cycle will be able to start, but the read data will come from the previous
2
C reading operation. So, when the micro
diag. cycle (i.e. The device is in turn-on state, with a short to GND, then the short is removed
and micro reads I
previous cycle. If another I
general to observe a change in Diagnostic bytes, two I
2
C. The short to GND is still present in bytes, because it is the result of the
2
C reading operation occurs, the bytes do not show the short). In
Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 17/30
2
C reading operations are necessary.

Thermal protection TDA7567PD
5 Thermal protection
Thermal protection is implemented through thermal foldback (Figure 15).
Thermal foldback begins limiting the audio input to the amplifier stage as the junction
temperatures rise above the normal operating range. This effectively limits the output power
capability of the device thus reducing the temperature to acceptable levels without totally
interrupting the operation of the device.
The output power will decrease to the point at which thermal equilibrium is reached.
Thermal equilibrium will be reached when the reduction in output power reduces the
dissipated power such that the die temperature falls below the thermal foldback threshold.
Should the device cool, the audio level will increase until a new thermal equilibrium is
reached or the amplifier reaches full power. Thermal foldback will reduce the audio output
level in a linear manner.
Three Thermal warning are available through the I
Figure 15. Thermal foldback diagram
2
C bus data.
Vout
Vout
CD out
TH. WARN.
< T
SD
ON
TH. SH.
START
> TSD(with same input
signal)
TH. SH.
END
°C)
Tj (
Tj ( °C)
Tj ( °C)
18/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1

TDA7567PD Fast muting
6 Fast muting
The muting time can be shortened to less than 1.5 ms by setting (IB2) D5 = 1. This option
can be useful in transient battery situations (i.e. during car engine cranking) to quickly
turnoff the amplifier for avoiding any audible effects caused by noise/transients being
injected by preamp stages. The bit must be set back to “0” shortly after the mute transition.
Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 19/30

Address selection and I2C disable TDA7567PD
7 Address selection and I2C disable
When the ADSEL/I2CDIS pin is left open the I2C bus is disabled and the device can be
controlled by the STBY/MUTE pin.
In this status (no - I
MODE; 1 = HE MODE) and the DATA pin sets the gain (0 = 26 dB; 1 = 16 dB).
When the ADSEL/I2CDIS pin is connected to GND the I
<1101100-1>.
To select the other I
following:
0<R<~10kΩ: I
~25k<R< 35kΩ: I
R>60k: Legacy mode only
(x: read/write bit selector)
2
C bus) the CK pin enables the HIGH-EFFICIENCY MODE (0 = STD
2
C bus is active with address
2
C address a resistor must be connected to ADSEL/I2CDIS pin as
2
C bus active with address <1101100x>
2
C bus active with address <1101101x>
20/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1

TDA7567PD I2C bus
8 I2C bus
8.1 I2C programming/reading sequences
A correct turn on/off sequence respectful of the diagnostic timings and producing no audible
noises could be as follows (after battery connection):
● Turn-on: Pin2 > 7V --- 10 ms --- (STANDBY OUT + DIAG ENABLE) --- 500 ms (min) ---
MUTING OUT
●
Turn-off: MUTING IN --- 20 ms --- (DIAG DISABLE + STANDBY IN) --- 10 ms --- PIN2 = 0
● Car radio installation: Pin2 > 7V --- 10ms DIAG ENABLE (write) --- 200 ms --- I
(repeat until All faults disappear).
● Offset test: Device in Play (no signal) -- OFFSET ENABLE - 30 ms - I
2
I
C reading until high-offset message disappears).
8.2 I2C bus interface
2
C reading (repeat
2
C read
Data transmission from microprocessor to the TDA7567PD and viceversa takes place
through the 2 wires I
resistors to positive supply voltage must be connected).
2
C bus interface, consisting of the two lines SDA and SCL (pull-up
8.2.1 Data validity
As shown by Figure 16, the data on the SDA line must be stable during the high period of
the clock. The HIGH and LOW state of the data line can only change when the clock signal
on the SCL line is LOW.
8.2.2 Start and stop conditions
As shown by Figure 17 a start condition is a HIGH to LOW transition of the SDA line while
SCL is HIGH. The stop condition is a LOW to HIGH transition of the SDA line while SCL is
HIGH.
8.2.3 Byte format
Every byte transferred to the SDA line must contain 8 bits. Each byte must be followed by an
acknowledge bit. The MSB is transferred first.
Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 21/30

I2C bus TDA7567PD
8.2.4 Acknowledge
The transmitter puts a resistive high level on the SDA line during the acknowledge clock
pulse (see Figure 18). The receiver the acknowledges has to pull-down (low) the SDA line
during the acknowledge clock pulse, so that the SDA line is stable low during this clock
pulse.
Transmitter:
● master (µP) when it writes an address to the TDA7567PD
● slave (TDA7567PD) when the µP reads a data byte from TDA7567PD
Receiver:
● slave (TDA7567PD) when the µP writes an address to the TDA7567PD
● master (µP) when it reads a data byte from TDA7567PD
Figure 16. Data validity on the I
SDA
SCL
STABLE, DATA
2
DATA LINE
VALID
C bus
Figure 17. Timing diagram on the I
SCL
SDA
START
Figure 18. Acknowledge on the I
SCL
1
2
23789
2
C bus
C bus
CHANGE
DATA
ALLOWED
D99AU1032
D99AU1031
2
I
STOP
CBUS
SDA
START
MSB
D99AU1033
22/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
FROM RECEIVER
TDA7567PD Software specifications
9 Software specifications
All the functions of the TDA7567PD are activated by I2C interface.
The bit 0 of the "Address Byte" defines if the next bytes are write instruction (from µP to
TDA7567PD) or read instruction (from TDA7567PD to µP).
Chip address
D7 D0
110110
1. Address selector bit, please refer to address selection description on Chapter 7.
X = 0 Write to device
X = 1 Read from device
If R/W = 0, the µP sends 2 "Instruction Bytes": IB1 and IB2.
Table 6. IB1
Bit Instruction decoding bit
(1)
XD8 Hex
D7 0
D6
D5
Diagnostic enable (D6 = 1)
Diagnostic defeat (D6 = 0)
Offset detection enable (D5 = 1)
Offset detection defeat (D5 = 0)
Front channel
D4
Gain = 26 dB (D4 = 0)
Gain = 16 dB (D4 = 1)
Rear channel
D3
Gain = 26dB (D3 = 0)
Gain = 16dB (D3 = 1)
D2
D1
D0
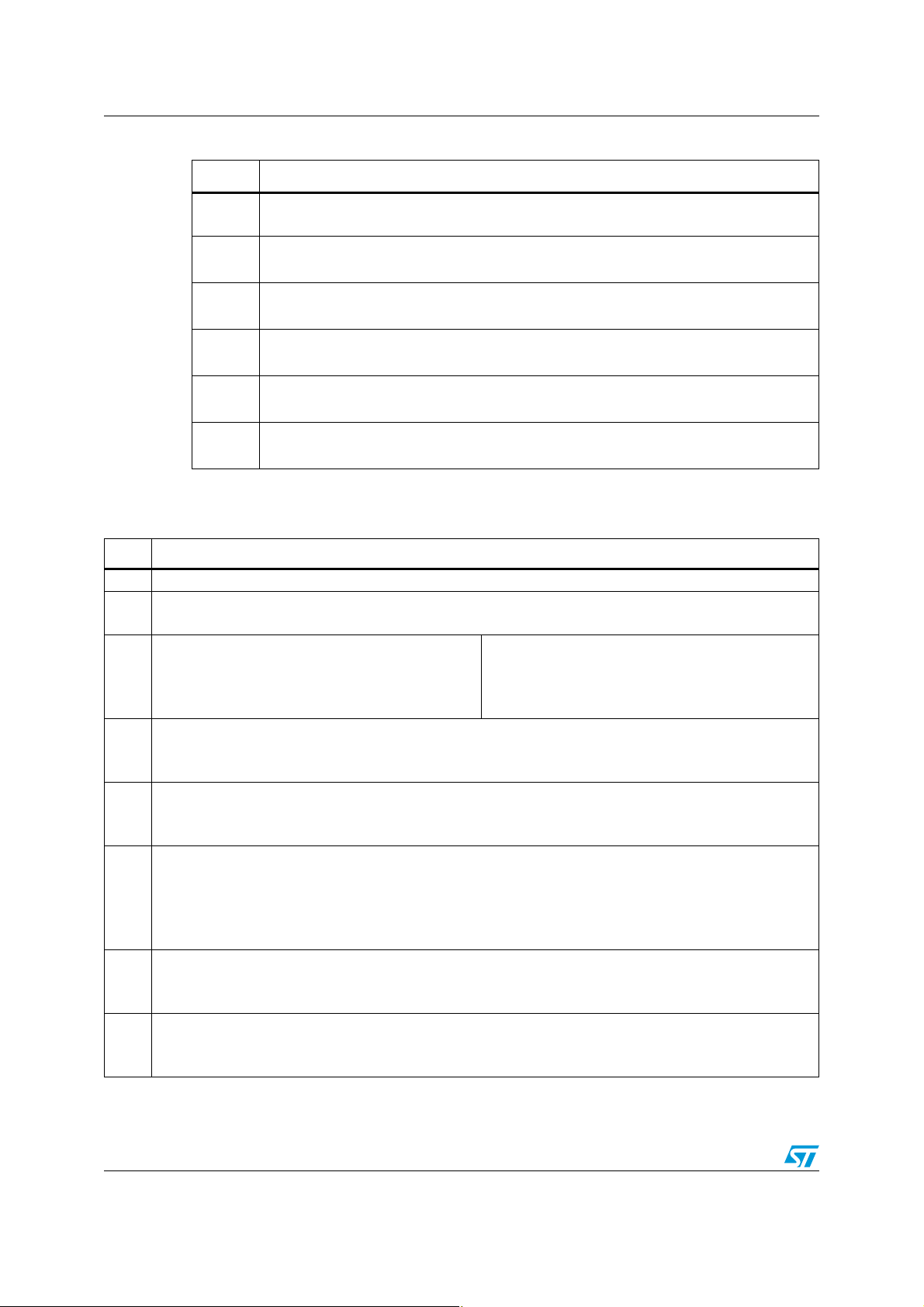
Table 7. IB2
Mute front channels (D2 = 0)
Unmute front channels (D2 = 1)
Mute rear channels (D1 = 0)
Unmute rear channels (D1 = 1)
CD 2% (D0 = 0)
CD 10% (D0 = 1)
Bit Instruction decoding bit
D7
D6 0
Current detection threshold
High th (D7 = 0)
Low th (D7 =1)
Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 23/30
Software specifications TDA7567PD
Table 7. IB2 (continued)
Bit Instruction decoding bit
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
Normal muting time (D5 = 0)
Fast muting time (D5 = 1)
Standby on - Amplifier not working - (D4 = 0)
Standby off - Amplifier working - (D4 = 1)
Power amplifier mode diagnostic (D3 = 0)
Line driver mode diagnostic (D3 = 1)
Current detection diagnostic enabled (D2 =1)
Current detection diagnostic defeat (D2 =0)
Right channel power amplifier working in standard mode (D1 = 0)
Power amplifier working in high efficiency mode (D1 = 1)
Left channel power amplifier working in standard mode (D0 = 0)
Power amplifier working in high efficiency mode (D0 = 1)
If R/W = 1, the TDA7567PD sends 4 "Diagnostics Bytes" to µP: DB1, DB2, DB3 and DB4.
Table 8. DB1
Bit Instruction decoding bit
D7 Thermal warning 1 active (D7 = 1) T = 140 °C
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
Diag. cycle not activated or not terminated (D6 = 0)
Diag. cycle terminated (D6 = 1)
Channel CH3
current detection IB2 (D7) = 0
Output peak current < 300 mA - Open load (D5 = 1)
Output peak current > 500 mA - Normal load (D5 = 0)
Channel CH3
Turn-on diagnostic (D4 = 0)
Permanent diagnostic (D4 = 1)
Channel CH3
Normal load (D3 = 0)
Short load (D3 = 1)
Channel CH3
Turn-on diag.: No open load (D2 = 0)
Open load detection (D2 = 1)
Offset diag.: No output offset (D2 = 0)
Output offset detection (D2 = 1)
Channel CH3
No short to Vcc (D1 = 0)
Short to Vcc (D1 = 1)
Channel CH3
No short to GND (D1 = 0)
Short to GND (D1 = 1)
Channel CH3
current detection IB2 (D7) = 1
Output peak current < 125 mA - Open load (D5 = 1)
Output peak current > 250 mA - Normal load (D5 = 0)
24/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1
TDA7567PD Software specifications
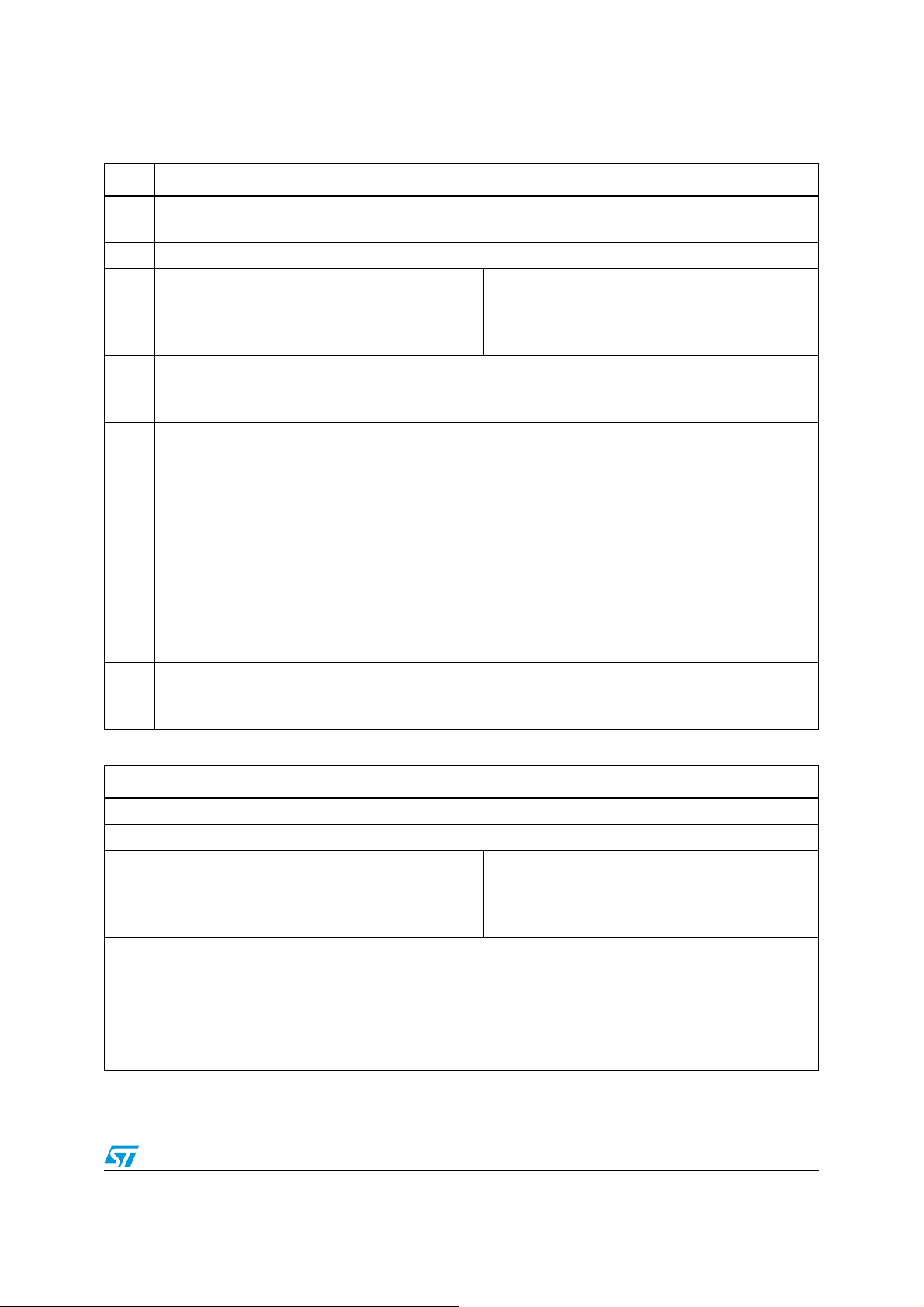
Table 9. DB2
Bit Instruction decoding bit
Offset detection not activated (D7 = 0)
D7
Offset detection activated (D7 = 1)
D6 X
Channel CH4
current detection IB2 (D7) = 0
D5
Output peak current < 300 mA - Open load (D5 = 1)
Output peak current > 500 mA - Normal load (D5 = 0)
Channel CH4
current detection IB2 (D7) = 1
Output peak current < 125 mA - Open load (D5 = 1)
Output peak current > 250 mA - Normal load (D5 = 0)
Channel CH4
D4
Turn-on diagnostic (D4 = 0)
Permanent diagnostic (D4 = 1)
Channel CH4
D3
Normal load (D3 = 0)
Short load (D3 = 1)
Channel CH4
Turn-on diag.: No open load (D2 = 0)
D2
Open load detection (D2 = 1)
Permanent diag.: No output offset (D2 = 0)
Output offset detection (D2 = 1)
Channel CH4
D1
No short to Vcc (D1 = 0)
Short to Vcc (D1 = 1)
Channel CH4
D0
No short to GND (D1 = 0)
Short to GND (D1 = 1)
Table 10. DB3
Bit Instruction decoding bit
D7 Standby status (= IB1 - D4)
D6 Diagnostic status (= IB1 - D6)
Channel CH1
current detection IB2 (D7) = 0
D5
Output peak current < 300 mA - Open load (D5 = 1)
Output peak current > 500 mA - Normal load (D5 = 0)
Channel CH1
current detection IB2 (D7) = 1
Output peak current < 125 mA - Open load (D5 = 1)
Output peak current > 250 mA - Normal load (D5 = 0)
Channel CH1
D4
Turn-on diagnostic (D4 = 0)
Permanent diagnostic (D4 = 1)
Channel CH1
D3
Normal load (D3 = 0)
Short load (D3 = 1)
Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 25/30

Software specifications TDA7567PD
Table 10. DB3 (continued)
Bit Instruction decoding bit
Channel CH1
Turn-on diag.: No open load (D2 = 0)
D2
Open load detection (D2 = 1)
Permanent diag.: No output offset (D2 = 0)
Output offset detection (D2 = 1)
Channel CH1
D1
No short to Vcc (D1 = 0)
Short to Vcc (D1 = 1)
Channel CH1
D0
No short to GND (D1 = 0)
Short to GND (D1 = 1)
Table 11. DB4
Bit Instruction decoding bit
D7 Thermal warning 2 active (D7 =1) T
D6 Thermal warning 3 active (D6 =1) T
Channel CH2
current detection IB2 (D7) = 0
D5
Output peak current < 300 mA - Open load (D5 = 1)
Output peak current > 500 mA - Normal load (D5 = 0)
=133°C
j
=118°C
j
Channel CH2
current detection IB2 (D7) = 1
Output peak current < 125mA - Open load (D5 = 1)
Output peak current > 250 mA - Normal load (D5 = 0)
Channel CH2
D4
Turn-on diagnostic (D4 = 0)
Permanent diagnostic (D4 = 1)
Channel CH2
D3
Normal load (D3 = 0)
Short load (D3 = 1)
Channel CH2
Turn-on diag.: No open load (D2 = 0)
D2
Open load detection (D2 = 1)
Permanent diag.: No output offset (D2 = 0)
Output offset detection (D2 = 1)
Channel CH2
D1
No short to Vcc (D1 = 0)
Short to Vcc (D1 = 1)
Channel CH2
D0
No short to GND (D1 = 0)
Short to GND (D1 = 1)
26/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1

TDA7567PD Examples of bytes sequence
10 Examples of bytes sequence
1 - Turn-on diagnostic - Write operation
Start Address byte with D0 = 0 ACK IB1 with D6 = 1 ACK IB2 ACK STOP
2 - Turn-on diagnostic - Read operation
Start Address byte with D0 = 1 ACK DB1 ACK DB2 ACK DB3 ACK DB4 ACK STOP
The delay from 1 to 2 can be selected by software, starting from 200 ms
3a - Turn-on of the power amplifier with 26 dB gain, mute on, diagnostic defeat, CD = 2 %
.
Start Address byte with D0 = 0 ACK IB1 ACK IB2 ACK STOP
X0000000 XXX1XX11
3b - Turn-off of the power amplifier
Start Address byte with D0 = 0 ACK IB1 ACK IB2 ACK STOP
X0XXXXXX XXX0XXXX
4 - Offset detection procedure enable
Start Address byte with D0 = 0 ACK IB1 ACK IB2 ACK STOP
XX1XX11X XXX1XXXX
5 - Offset detection procedure stop and reading operation (the results are valid only for the
offset detection bits (D2 of the bytes DB1, DB2, DB3, DB4)
.
Start Address byte with D0 = 1 ACK DB1 ACK DB2 ACK DB3 ACK DB4 ACK STOP
● The purpose of this test is to check if a D.C. offset (2 V typ.) is present on the outputs,
produced by input capacitor with anomalous leakage current or humidity between pins.
● The delay from 4 to 5 can be selected by software, starting from 30 ms
Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 27/30

Package information TDA7567PD
11 Package information
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of
ECOPACK
®
packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK
®
specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at: www.st.com.
ECOPACK
®
is an ST trademark.
Figure 19. PowerSO36 (slug up) mechanical data and package dimensions
DIM.
A 3.270 - 3.410 0.1287 - 0.1343
A2 3.100 - 3.180 0.1220 - 0.1252
A4 0.800 - 1.000 0.0315 - 0.0394
A5 - 0.200 - - 0.0079 a1 0.030 -
b 0.220 - 0.380 0.0087 - 0.0150
c 0.230 - 0.320 0.0091 - 0.0126
D 15.800 - 16.000 0.6220 - 0.6299
D1 9.400 - 9.800 0.3701 - 0.3858
D2 - 1.000 - - 0.0394 -
E 13.900 - 14.500 0.5472 - 0.5709
E1 10.900 - 11.100 0.4291 - 0.4370
E2 - - 2.900 - - 0.1142
E3 5.800 - 6.200 0.2283 - 0.2441
E4 2.900 - 3.200 0.1142 - 0.1260
e - 0.650 - - 0.0256 -
e3 - 11.050 - - 0.4350 -
G 0 - 0.075 0 - 0.0031
H 15.500 - 15.900 0.6102 - 0.6260
h - - 1.100 - - 0.0433
L 0.800 - 1.100 0.0315 - 0.0433
N - - 10˚ - - 10˚
s - -8˚- -8˚
(1) “D and E1” do not include mold flash or protusions.
Mold flash or protusions shall not exceed 0.15mm (0.006”).
(2) No intrusion allowed inwards the leads.
mm inch
MIN. TYP. MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
-0.040
0.0012 - -0.0016
OUTLINE AND
MECHANICAL DATA
PowerSO36 (SLUG UP)
28/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1
7183931 G

TDA7567PD Revision history
12 Revision history
Table 12. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
11-Dec-2009 1 Initial release.
Doc ID 16903 Rev 1 29/30

TDA7567PD
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2009 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
30/30 Doc ID 16903 Rev 1
 Loading...
Loading...